

[Solved] Boeing 7E7 Case Study Solution: WACC Calculations and Answers to 7 Questions
![[Solved] Boeing 7E7 Case Study Solution: WACC Calculations and Answers to 7 Questions 3 Boeing 7E7 Case Study Solution, 7E7 Case Study, Boeing WACC Calculation](https://www.simplimba.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Blue-aircraft-Travel-Postcard-1200-%C3%97-700-px-1024x597.jpg)
Boeing 7E7 Case Study Solution
The Boeing 7E7 Case Study is a case study from HBR . The Case be analyzed from the perspective of new product introduction, financial estimations for Weighted Average cost of accounting (WACC), IRR (internal rates of Return), and NPV (Net Present Value). The case presents an opportunity to undertake a financial analysis and project viability document for New Product Introduction.
For Solutions to more cases like Boeing 7E7 Case Study, follow our case studies archive
Boeing 7E7 Case Study: Introduction
In 2003, Boeing announced their intention to create a new “super-efficient” commercial jet codenamed “7E7” or “Dreamliner.” Similar to when it first developed the 747 and 777, Boeing effectively “bet the farm” on this venture. The new airframe is technologically superior, and it will be sold in a rapidly expanding market, so the project should be greenlit. However, the demand for commercial planes dropped as a result of global travel warnings issued in response to the spread of the highly contagious SARS virus.
The board of directors at Boeing would have to consider all of these factors before giving the project final approval. The Critical task is to determine how the 7E7 project stacks up against a financial benchmark, such as the rate of return sought by potential backers. Internal rates of return (IRR) for the 7E7 project are displayed in the case, both for the baseline scenario and for alternative scenarios. The value of these internal rates of return (IRRs) is determined by students’ estimates of Boeing’s commercial-aircraft business segment’s weighted-average cost of capital (WACC). Students will be able to differentiate between qualitative risks that Boeing is taking and identify “key value drivers” after completing this analysis.
Learning how to calculate the weighted average cost of capital and the cost of equity is the primary focus of this case. The ability to compare beta estimates and use the levered-beta formulas is essential for students attempting to calculate the WACC of a segment. Boeing faces competition in both the civilian and military aircraft markets. The commercial aircraft division of Boeing’s overall corporate WACC must be isolated to determine an appropriate benchmark WACC for the 7E7 project. In this way, the concept of adding value to something is introduced to the students.
Boeing 7E7 Case Study Solution: Why is Boeing contemplating the launch of the 7E7 project? Is this a good time to do so?
As a result of the available technology, Boeing is considering beginning the 7E7 project. Boeing’s main rivals claimed that the 7E7 was an engineer’s nightmare but a salesperson’s paradise. Carbon-reinforced materials, which are stronger than regular aluminum, will be used extensively in the construction of this project, making it the first commercial aircraft of its kind.
However, the threat of rivalry must also be considered. When a brand-new airplane hits the market, it’s bound to sell like hotcakes at first, but competitors taking the plunge to try to replicate 7E7’s success would be foolish. Both Boeing’s asking price and the number of 7E7 planes it could sell were constrained by the lack of information about the plane’s specifications and the threat of competition.
Although Boeing must take chances to maintain its standing in the aircraft industry, now is not the time to launch its project 7E7, in my opinion.
Boeing 7E7 Case Study Solution: Should Boeing’s Board approve the 7E7?
Board members at Boeing should vote to green-light the 7E7 so that the company can continue to compete with Airbus and regain market share in the commercial aircraft sector. There is a scope for undertaking a financial analysis in the Boeing 7E& Case Study, which we will see later.
Boeing 7E7 Case Study Solution: How would we know if the 7E7 project will create value?
In capital budgeting, NPV is used to evaluate a project’s or investment’s profitability. It does this by looking at the future value of a dollar and comparing it to its value right now. According to the case and Boeing’s Market Outlook, NPV is a short-term metric, making Project 7E7 unfavorable. The negative cash flows are another reason why this project should be rejected.
Examine the details of how to estimate the WACC :
WACC = (Wdebt)(rd)(1-tc) + (Wequity)(re)
- Wdebt = proportion of debt in a market- value capital structure
- rd = pretax cost of debt capital
- tc = marginal effective corporate tax rate
- Wequity = proportion of equity in a market-value capital structure
- re = cost of equity capital
- From Exhibit 10 : Debt / Equity ratio= 0.525
Tc = 0.35 (From page 237)
- From Exhibit 2, Wdebt = 44646 / 129686 = 0.344
Wequity = 85040/129686 = 0.656
- From Exhibit 11, Rd is calculated as below which is 5.335%
The cost of equity capital (re ) will be calculated using CAPM. re = Rf + β*E(Rm)
BetaAsset = BetaEquity / [1+(1-tc)D/E]
Beta Equity Boeing =1.62Market-value debt/equity ratio = 0.525BetaAsset = 1.62/[1+(1-0.35)0.525] = 1.21
- Exhibit 10 indicates the percentage of revenues derived from government for Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman is 93% and 91%, which will help to estimate beta asset of defense.
- Debt /equity ratio for Lockheed Martin = 0.410
- Betaasset defense = 0.37/[1+(1-0.35)0.41] = 0.29
- S&P500 60 trading day BetaEquityNG for Northrop Grumman=0.30
- Debt/equity ratio for Northrop Grumman = 0.640
- Exhibit 10, Boeing Rev from Defense (Wdefense) = 0.46
- Boeing Rev from Commercial Sales (Wcommercial) = 0.54
- βBoeing= βcommercial* Wcommercial + βdefense*Wdefense
- 1.21= βcommercial *0.54+0.25*0.46
- β asset commercial =1.095/0.54= 2.03
- β equity commercial =2.031+(1-0.35)0.525=2.72
- re = Rf + β*E(Rm)- Rf]
=0.85%+2.72(8.4%)
WACC= % debt (rd)(1-tc)+ % equity(re)
=0.344*0.05335*(1-0.35)+0.656*0.2370
WACC=16.74%
Boeing 7E7 Case Study Solution: Is there anything else the board of directors should consider in assessing the financial appeal of this project?
There are a few different approaches to calculating the economic viability of the Boeing 7E7 project before making a decision about whether or not to move forward with it. These include the Payback period (which does not account for the time value of money, but is simple to calculate and is based on projects with higher liquidity), as well as the Discount Payback period (which is based on projects with higher liquidity) ( it consider the time value of money).
The Boeing 7E7 was a long-term project that required a significant investment to get off the ground. This is yet another reason why it was delayed. Therefore, more time will be required to accumulate the most wealth and settle all financial obligations. In the event that this is not the case, the money that has already been invested in the project by the board of directors will be wasted.
Boeing 7E7 Case Study Solution: What should the board do?
As the first plane to use carbon body construction and employ wingtip extenders, both of which will add to the level of risk because they have never been used on large-scale projects before, the board should approve the launch of the Boeing 7E7 Project despite the high level of risk associated with the project due to its design. Not mentioning that Airbus is about to introduce their brand new A380 would be negligent of us. Boeing should go ahead with the launch of the 7E7 because it will have a lower fuel requirement and will be able to carry a larger number of passengers.
If you have any questions, reach out to the author
Follow us on Quora
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page
The marketplace for case solutions.
The Boeing 7E7 – Case Solution
The Boeing Company was planning to build an efficient commercial plane that will be called the "7e7" or the "Dreamliner." With a rapidly-growing market segment, the approval for the Boeing 7E7 project needed approval, taking into consideration the current market for commercial airplanes. This case study provides the opportunity for students to assess the feasibility of the said project.
Robert F. Bruner and James Tompkins Harvard Business Review ( UV0281-PDF-ENG ) July 29, 2004
Case questions answered:
- In assigning a cost of debt from which to construct the project’s WACC, which benchmark debt did you use?
- At the end of the day, should the project be undertaken, matching WACC against IRR?
- Construct a CAPM for Boeing. What estimation period? What Equity Risk Premium (arithmetic or geometric)
- Construct a corporate cost of capital for Boeing. What cost of debt should be used?
- Construct a CAPM for the Commercial Airframe Segment. How do we allocate between Defense and Commercial Airframes? What estimation period? What Equity Risk Premium (arithmetic or geometric)?
- Construct a divisional cost of capital for Commercial Airframe. What cost of debt should be used?
- Match Commercial Airframe WACC against IRR. Create sensitivity analyses against R&D; Price; Overhead; Revenue estimates
- Construct a Sensitivity Analysis around Beta Estimation Periods to defend your contention.
- Identify contingent/qualitative options for undertaking the project.
Not the questions you were looking for? Submit your own questions & get answers .
The Boeing 7E7 Case Answers
This case solution includes an Excel file with calculations.
Date: March 13, 2022 To: The Boeing Company Subject: New Project – The Boeing 7E7
Background – the boeing company.
The Boeing Company is currently reviewing the feasibility and profitability of investing in a new project, The Boeing 7E7, a new product line in Boeing’s commercial plane family.
The project aims to make the 7E7 cover more flight ranges with less operating and manufacturing costs and more safety.
However, the project faces many obstacles, such as technical issues, financial awareness from the Board, and competition from its competitor.
Therefore, this financial analysis provides more information and advice on whether the company needs to invest in this new project.
The primary part of this analysis is to calculate the WACC for the commercial segment of Boeing. The analysis starts with calculating the unlevered beta for the defense segment of Boeing.
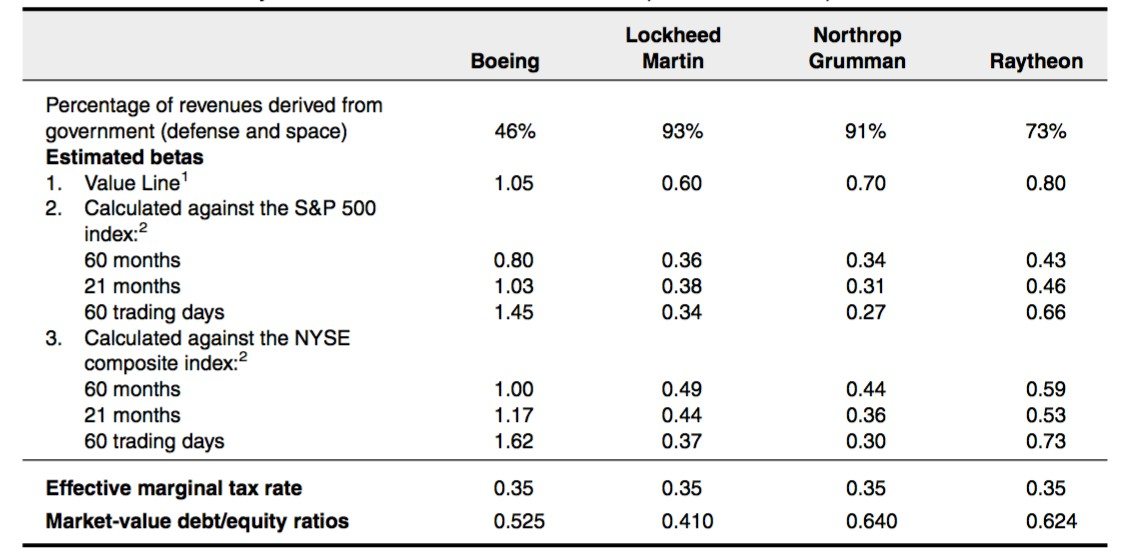
The financial data of Lockheed and Northrop are applied as proxies. Raytheon is not included as a proxy because only 73% of its revenues are derived from the defense segment. However, over 90% of the revenues are from the defense segment for the other two companies.
The S&P 500 index is applied in the estimation because the S&P 500 is Boeing’s index membership. The timeframe is from June 16, 1998, to June 16, 2003.
The unlevered betas for Lockheed and Northrop are 0.284 and 0.240, respectively, based on the D/E ratio. The unlevered beta for the defense segment of Boeing is estimated to be 0.262, which is the average of the unlevered betas for the proxies.
The beta of the entire company needs to be considered to calculate the unlevered beta for the commercial segment. The beta against the S&P 500 in the timeframe from June 16, 1998, to June 16, 2003, is applied to be consistent with the proxies. The unlevered beta for the entire company is 0.596.
The allocations of defense and commercial segments are 46% and 54%. The unlevered beta for the commercial segment is estimated to be 0.881, which is calculated based on the weights of the commercial and defense segments.
After levering the beta, the levered beta for the commercial segment is 1.182. The risk-free rate and risk premia are 4.56% and 5%, respectively.
According to CAPM, the cost of equity is estimated to be 10.47%. The cost of debt is expected to be 5.31%, which is the ratio of total interest to total debt. WACC for the project is 8.05%.
For the entire company, the levered beta is 0.8. The cost of equity is 8.56% based on CAPM. The WACC of Boeing is 6.80%.
The projected IRR for The Boeing 7E7 project is…
Unlock Case Solution Now!
Get instant access to this case solution with a simple, one-time payment ($24.90).
After purchase:
- You'll be redirected to the full case solution.
- You will receive an access link to the solution via email.
Best decision to get my homework done faster! Michael MBA student, Boston
How do I get access?
Upon purchase, you are forwarded to the full solution and also receive access via email.
Is it safe to pay?
Yes! We use Paypal and Stripe as our secure payment providers of choice.
What is Casehero?
We are the marketplace for case solutions - created by students, for students.
The Boeing 7E7 Project Management Case Study
Executive summary.
This case study entails the examination of various data and information and decision-making recommendations for the Boeing Company’s board. The impacts of the 9/11 terror attack and America’s economic trend are some worrying issues for the board to approve the 7E7 project. The analysis examines the project’s profitability and attractiveness. The project’s WACC remains consistent compared with that of the commercial division, which resulted in the determination of beta using unlevered industrial average and Boing’s leverage, and division beta using WACC of two different departments. This produces the project’s WACC to be 10.33%. The analysis also uses IRR to measure the project’s profitability, since its comparison with the WACC determines if the board should approve the project or stop it. Moreover, sensitivity analysis is conducted to give the board a comprehensive perspective of the project regarding internal and external environmental forces such as costs and returns. It is therefore concluded that the board should accept the project due to its opportunities and benefits to the company.
Introduction
Boeing had planned to initiate a project known as 7E7 in 2003. Starting such a project in the manufacture of airplanes is considered one of the most daring moves a company can make. Mr. Bair must show evidence that Boeing 7E7 is profitable based on his valuation of the project and sectoral analysis for the board to accept it. Therefore, this analysis considers the project’s strengths and weaknesses, its major competition, calculations of costs and capital, and scenario scrutiny.
The Boeing 7E7 Project
The Boeing 7E7 entailed a design of an airplane that was meant for short and long distances and various cargo and passenger capacities. At the same time, the jet was supposed to consume 80% of fuel compared to its predecessor and would cost customers 10% cheaper. The aircraft was thus designed to make more profits and save Boeing from its lost customers in the commercial air carrier sales.
Strength and Weaknesses of the Project
Boing 7E7 project was flexible in handling short domestic travel and long international ones. The aircraft would be 10% cheaper thus attracting more customers in addition to consuming less fuel than other aircraft of the same size. Moreover, its production cost would be less because of composites and carbon-reinforced matter. However, the project’s downside was its choice of Snap-On wing extensions, which would cost a lot more due to the limits of technology.
Competition
Boeing faced and still faces aggressive competition from its main rival Airbus. Boeing would reduce this competition by lowering its operational costs and fuel consumption. This can help the manufacturer get more aircraft buyers, thus gaining its market share. Moreover, it should implement its expandable wing, to give the airline owners options to cover more cargo and passenger routes. Enabling carrier companies to access more routes means more customers and more revenue, which would attract airline buyers to purchase from Boeing.
Cost of Capital
Since Boeing mainly builds its aircrafts for defense and commercial use, it shows the commercial division of the manufacturer faces more risk, thus higher Beta compared to the defense division. The cost of equity rises with the level of Beta, showing that the commercial division must have a higher weighted average cost of capital (WACC) (Vitolla et al. 525). The comparison of the commercial division’s WACC and the project’s rate of return can help be the board decide whether to accept or reject the Boeing E7E. Consequently, this analysis utilizes the 21-month S&P 500 Beta, which eliminates the impact of 9/11.
This analysis uses the pure-play technique to identify companies that operate as the defense division of Boeing and determine their unlevered Beta. The analysis then calculates the average of the individual company Betas and uses that for Boeing (Santos). This analysis uses the information presented in Exhibit 1, particularly using Raytheon and Northrop Grumman, which relate closely to Boeing.

The calculations above are presented in Exhibit 2.
Boeing’s defense division unlevered Beta can be re-levered to determines its financial position as follows:
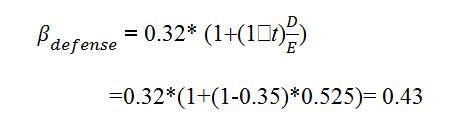
The above values can then be used to determine the company’s commercial division Beta as follows:

There the commercial division’s WACC is calculated as follows:
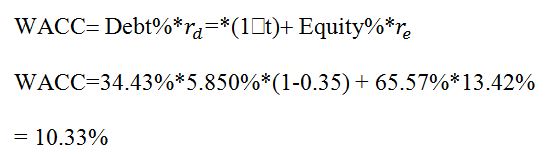
Evaluation of Boeing E7E
The project’s sensitivity analysis gives optimistic and pessimistic estimates for the variables affecting sales’ costs and volume as shown in Exhibit 3. Using the determined WACC and information presented in Exhibit 3, it is revealed that the internal rate of return (IRR) tends to equal WACC in most pessimistic scenarios (Radiant and Ahmad 137). This indicates it is not possible to disregard the project due to the above analysis conducted above. Moreover, it is also revealed that the project can be discarded in cases where the cost exceeds 8 million dollars, and the cost of goods rises above 84 %. Consequently, this requires scenario analysis since both IRR and WACC are affected by costs and economic conditions surrounding the business. The environment affects the firm’s market premium, cost of debt, and Beta. An optimistic economy implies a reduced cost of capital, which Exhibit 4 reveals would translate to a reduction of cost of debt by 5%, which reduces WACC from 10.33% to 9.92%.
Overstating the risk reduces WACC further to 9.71% since the actual Beta for Boeing’s commercial division is 1.5. Since the market return is also crucial in estimating WACC, then the underperformance of the market will result in reduced market return, which in turn will further reduce the company’s market premium, thus lowering WACC. Contrarily, a pessimistic economy results in higher WACC due to the increased cost of debt resulting in higher risk and market underperformance as shown in Exhibit 4.
Boeing must build its 7E7 aircraft to counter the forces of such rivals. The risk to developing Boeing E7E means it will develop its expandable wing, which will increase its versatility. This means the airplane will be open to new routes and serve more customers, while at the same time, utilizing fuel efficiently. The company can increase the wealth of its shareholders by ensuring that its IRR is equal to or greater than its WACC. This indicates that Boeing must strive and sell a minimum of 1500 of its E7E aircrafts within 20 years. It must ensure that its cost of developing the planes remains below $8 billion and that the cost of goods is below 84%. Amidst its risks, the project can result in better outcomes for Boeing’s shareholders, hence a desirable understanding. The board should therefore accept E7E because its benefits outweigh its risks.
Works Cited
Radiant, Joseph and Prasetyo, Ahmad Danu. “Investment Analysis of Integration Project (Case Study: Pt Bandung XYZ).” International Journal of Accounting, Finance and Business . vol. 6, no. 32, 2021: pp. 128-139.
Santos, Ricardo Sérgio Gomes. Equity Valuation: Netflix, Inc ., 2021. Doctoral Dissertation.
Vitolla, Filippo et al. “The Impact on The Cost of Equity Capital In the Effects of Integrated Reporting Quality.” Business Strategy and the Environment. vol. 29, no. 2, 2020: pp. 519-529.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, February 25). The Boeing 7E7 Project Management. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-boeing-7e7-project-management/
"The Boeing 7E7 Project Management." IvyPanda , 25 Feb. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/the-boeing-7e7-project-management/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'The Boeing 7E7 Project Management'. 25 February.
IvyPanda . 2023. "The Boeing 7E7 Project Management." February 25, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-boeing-7e7-project-management/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Boeing 7E7 Project Management." February 25, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-boeing-7e7-project-management/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Boeing 7E7 Project Management." February 25, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-boeing-7e7-project-management/.
- Returning to the Aviation Market: The Boeing Company
- Global Business: Airbus and Boeing Companies
- Starbucks and McDonald's Companies' Profitability
- Case Analysis on Capital Budgeting
- Corporate Finance: Weighted Average Cost of Capital
- Airbus Company: Calculation of Cost of Capital
- The Weighted Average Cost of Capital
- The ExxonMobil Company's Capital Cost Analysis
- Tesco Company's Capital Structure and Finance
- Alternatives or Other Complexities in Adjusting Discount Rates
- Implications of Cultural Differences in International Projects
- Quality Assurance and Quality Control – Is There a Difference?
- The PwC India Project Management and Maturity Model
- Farcargo’s System Implementation Document
- A Web-Based Information Project Feasibility Analysis
The Boeing 7E7

Related documents

Study collections
Add this document to collection(s).
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer
Brought to you by:

The Boeing 7E7
By: Robert F. Bruner, James Tompkins
In 2003 The Boeing Company announced plans to build a new "super-efficient" commercial jet called the "7E7" or "Dreamliner." This was a "bet the farm" gamble by Boeing, similar in magnitude to its…
- Length: 23 page(s)
- Publication Date: Jul 29, 2004
- Discipline: Finance
- Product #: UV0281-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Teaching Note
- Educator Copy
- Supplements
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
In 2003 The Boeing Company announced plans to build a new "super-efficient" commercial jet called the "7E7" or "Dreamliner." This was a "bet the farm" gamble by Boeing, similar in magnitude to its earlier introductions of the 747 and 777 airliners. The technological superiority of the new airframe and the fact that it would penetrate a rapidly growing market segment argued for approval of the project. On the other hand, the current market for commercial airplanes was depressed, reflecting terrorism risk, war, and SARS, a contagious illness resulting in global travel warnings. Boeing's board of directors would need to weigh these considerations in granting final approval to proceed with the project The task for students is to evaluate the 7E7 project against a financial standard, the investors' required returns. The case gives internal rates of return (IRR) for the 7E7 project under base case and alternative forecasts. The students must estimate a weighted-average cost of capital (WACC) for Boeing's commercial-aircraft business segment in order to evaluate these IRRs. As a result of this analysis the students identify the "key value drivers" and distinguish, on a qualitative basis, the key gambles Boeing is making. The general objective of this case is to exercise students' skills in estimating a weighted average cost of capital and cost of equity. The need for students to estimate a segment WACC draws out their abilities to critique different estimates of beta and to manipulate the levered-beta formulas. Boeing competes in both the commercial aircraft and defense business; thus, deriving the appropriate benchmark WACC for the 7E7 project requires isolating the commercial aircraft component from Boeing's overall corporate WACC. In doing so, students engage the concept of value additivity.
Learning Objectives
The general objective of this case is to exercise students' skills in estimating a weighted-average cost of capital and cost of equity. The task for students is to evaluate the 7E7 project against a financial standard, the investors' required returns. The students must estimate a weighted-average cost of capital (WACC) for Boeing's commercial-aircraft business segment in order to evaluate the IRRs.
Jul 29, 2004 (Revised: Apr 12, 2023)
Discipline:
Darden School of Business
UV0281-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Don't have an account? Sign up now
Already have an account login, get 10% off on your next order.
Subscribe now to get your discount coupon *Only correct email will be accepted
(Approximately ~ 0.0 Page)
Total Price
Thank you for your email subscription. Check your email to get Coupon Code.
The Boeing 7E7 Case Analysis and Case Solution
Posted by Peter Williams on Aug-09-2018
Introduction of The Boeing 7E7 Case Solution
The The Boeing 7E7 case study is a Harvard Business Review case study, which presents a simulated practical experience to the reader allowing them to learn about real life problems in the business world. The The Boeing 7E7 case consisted of a central issue to the organization, which had to be identified, analysed and creative solutions had to be drawn to tackle the issue. This paper presents the solved The Boeing 7E7 case analysis and case solution. The method through which the analysis is done is mentioned, followed by the relevant tools used in finding the solution.
The case solution first identifies the central issue to the The Boeing 7E7 case study, and the relevant stakeholders affected by this issue. This is known as the problem identification stage. After this, the relevant tools and models are used, which help in the case study analysis and case study solution. The tools used in identifying the solution consist of the SWOT Analysis, Porter Five Forces Analysis, PESTEL Analysis, VRIO analysis, Value Chain Analysis, BCG Matrix analysis, Ansoff Matrix analysis, and the Marketing Mix analysis. The solution consists of recommended strategies to overcome this central issue. It is a good idea to also propose alternative case study solutions, because if the main solution is not found feasible, then the alternative solutions could be implemented. Lastly, a good case study solution also includes an implementation plan for the recommendation strategies. This shows how through a step-by-step procedure as to how the central issue can be resolved.
Problem Identification of The Boeing 7E7 Case Solution
Harvard Business Review cases involve a central problem that is being faced by the organization and these problems affect a number of stakeholders. In the problem identification stage, the problem faced by The Boeing 7E7 is identified through reading of the case. This could be mentioned at the start of the reading, the middle or the end. At times in a case analysis, the problem may be clearly evident in the reading of the HBR case. At other times, finding the issue is the job of the person analysing the case. It is also important to understand what stakeholders are affected by the problem and how. The goals of the stakeholders and are the organization are also identified to ensure that the case study analysis are consistent with these.

Analysis of the The Boeing 7E7 HBR Case Study
The objective of the case should be focused on. This is doing the The Boeing 7E7 Case Solution. This analysis can be proceeded in a step-by-step procedure to ensure that effective solutions are found.
- In the first step, a growth path of the company can be formulated that lays down its vision, mission and strategic aims. These can usually be developed using the company history is provided in the case. Company history is helpful in a Business Case study as it helps one understand what the scope of the solutions will be for the case study.
- The next step is of understanding the company; its people, their priorities and the overall culture. This can be done by using company history. It can also be done by looking at anecdotal instances of managers or employees that are usually included in an HBR case study description to give the reader a real feel of the situation.
- Lastly, a timeline of the issues and events in the case needs to be made. Arranging events in a timeline allows one to predict the next few events that are likely to take place. It also helps one in developing the case study solutions. The timeline also helps in understanding the continuous challenges that are being faced by the organisation.
SWOT analysis of The Boeing 7E7
An important tool that helps in addressing the central issue of the case and coming up with The Boeing 7E7 HBR case solution is the SWOT analysis.
- The SWOT analysis is a strategic management tool that lists down in the form of a matrix, an organisation's internal strengths and weaknesses, and external opportunities and threats. It helps in the strategic analysis of The Boeing 7E7.
- Once this listing has been done, a clearer picture can be developed in regards to how strategies will be formed to address the main problem. For example, strengths will be used as an advantage in solving the issue.
Therefore, the SWOT analysis is a helpful tool in coming up with the The Boeing 7E7 Case Study answers. One does not need to remain restricted to using the traditional SWOT analysis, but the advanced TOWS matrix or weighted average SWOT analysis can also be used.
Porter Five Forces Analysis for The Boeing 7E7
Another helpful tool in finding the case solutions is of Porter's Five Forces analysis. This is also a strategic tool that is used to analyse the competitive environment of the industry in which The Boeing 7E7 operates in. Analysis of the industry is important as businesses do not work in isolation in real life, but are affected by the business environment of the industry that they operate in. Harvard Business case studies represent real-life situations, and therefore, an analysis of the industry's competitive environment needs to be carried out to come up with more holistic case study solutions. In Porter's Five Forces analysis, the industry is analysed along 5 dimensions.
- These are the threats that the industry faces due to new entrants.
- It includes the threat of substitute products.
- It includes the bargaining power of buyers in the industry.
- It includes the bargaining power of suppliers in an industry.
- Lastly, the overall rivalry or competition within the industry is analysed.
This tool helps one understand the relative powers of the major players in the industry and its overall competitive dynamics. Actionable and practical solutions can then be developed by keeping these factors into perspective.
PESTEL Analysis of The Boeing 7E7
Another helpful tool that should be used in finding the case study solutions is the PESTEL analysis. This also looks at the external business environment of the organisation helps in finding case study Analysis to real-life business issues as in HBR cases.
- The PESTEL analysis particularly looks at the macro environmental factors that affect the industry. These are the political, environmental, social, technological, environmental and legal (regulatory) factors affecting the industry.
- Factors within each of these 6 should be listed down, and analysis should be made as to how these affect the organisation under question.
- These factors are also responsible for the future growth and challenges within the industry. Hence, they should be taken into consideration when coming up with the The Boeing 7E7 case solution.
VRIO Analysis of The Boeing 7E7
This is an analysis carried out to know about the internal strengths and capabilities of The Boeing 7E7. Under the VRIO analysis, the following steps are carried out:
- The internal resources of The Boeing 7E7 are listed down.
- Each of these resources are assessed in terms of the value it brings to the organization.
- Each resource is assessed in terms of how rare it is. A rare resource is one that is not commonly used by competitors.
- Each resource is assessed whether it could be imitated by competition easily or not.
- Lastly, each resource is assessed in terms of whether the organization can use it to an advantage or not.
The analysis done on the 4 dimensions; Value, Rareness, Imitability, and Organization. If a resource is high on all of these 4, then it brings long-term competitive advantage. If a resource is high on Value, Rareness, and Imitability, then it brings an unused competitive advantage. If a resource is high on Value and Rareness, then it only brings temporary competitive advantage. If a resource is only valuable, then it’s a competitive parity. If it’s none, then it can be regarded as a competitive disadvantage.
Value Chain Analysis of The Boeing 7E7
The Value chain analysis of The Boeing 7E7 helps in identifying the activities of an organization, and how these add value in terms of cost reduction and differentiation. This tool is used in the case study analysis as follows:
- The firm’s primary and support activities are listed down.
- Identifying the importance of these activities in the cost of the product and the differentiation they produce.
- Lastly, differentiation or cost reduction strategies are to be used for each of these activities to increase the overall value provided by these activities.
Recognizing value creating activities and enhancing the value that they create allow The Boeing 7E7 to increase its competitive advantage.
BCG Matrix of The Boeing 7E7
The BCG Matrix is an important tool in deciding whether an organization should invest or divest in its strategic business units. The matrix involves placing the strategic business units of a business in one of four categories; question marks, stars, dogs and cash cows. The placement in these categories depends on the relative market share of the organization and the market growth of these strategic business units. The steps to be followed in this analysis is as follows:
- Identify the relative market share of each strategic business unit.
- Identify the market growth of each strategic business unit.
- Place these strategic business units in one of four categories. Question Marks are those strategic business units with high market share and low market growth rate. Stars are those strategic business units with high market share and high market growth rate. Cash Cows are those strategic business units with high market share and low market growth rate. Dogs are those strategic business units with low market share and low growth rate.
- Relevant strategies should be implemented for each strategic business unit depending on its position in the matrix.
The strategies identified from the The Boeing 7E7 BCG matrix and included in the case pdf. These are either to further develop the product, penetrate the market, develop the market, diversification, investing or divesting.
Ansoff Matrix of The Boeing 7E7
Ansoff Matrix is an important strategic tool to come up with future strategies for The Boeing 7E7 in the case solution. It helps decide whether an organization should pursue future expansion in new markets and products or should it focus on existing markets and products.
- The organization can penetrate into existing markets with its existing products. This is known as market penetration strategy.
- The organization can develop new products for the existing market. This is known as product development strategy.
- The organization can enter new markets with its existing products. This is known as market development strategy.
- The organization can enter into new markets with new products. This is known as a diversification strategy.
The choice of strategy depends on the analysis of the previous tools used and the level of risk the organization is willing to take.
Marketing Mix of The Boeing 7E7
The Boeing 7E7 needs to bring out certain responses from the market that it targets. To do so, it will need to use the marketing mix, which serves as a tool in helping bring out responses from the market. The 4 elements of the marketing mix are Product, Price, Place and Promotions. The following steps are required to carry out a marketing mix analysis and include this in the case study analysis.
- Analyse the company’s products and devise strategies to improve the product offering of the company.
- Analyse the company’s price points and devise strategies that could be based on competition, value or cost.
- Analyse the company’s promotion mix. This includes the advertisement, public relations, personal selling, sales promotion, and direct marketing. Strategies will be devised which makes use of a few or all of these elements.
- Analyse the company’s distribution and reach. Strategies can be devised to improve the availability of the company’s products.
The Boeing 7E7 Blue Ocean Strategy
The strategies devised and included in the The Boeing 7E7 case memo should have a blue ocean strategy. A blue ocean strategy is a strategy that involves firms seeking uncontested market spaces, which makes the competition of the company irrelevant. It involves coming up with new and unique products or ideas through innovation. This gives the organization a competitive advantage over other firms, unlike a red ocean strategy.
Competitors analysis of The Boeing 7E7
The PESTEL analysis discussed previously looked at the macro environmental factors affecting business, but not the microenvironmental factors. One of the microenvironmental factors are competitors, which are addressed by a competitor analysis. The Competitors analysis of The Boeing 7E7 looks at the direct and indirect competitors within the industry that it operates in.
- This involves a detailed analysis of their actions and how these would affect the future strategies of The Boeing 7E7.
- It involves looking at the current market share of the company and its competitors.
- It should compare the marketing mix elements of competitors, their supply chain, human resources, financial strength etc.
- It also should look at the potential opportunities and threats that these competitors pose on the company.
Organisation of the Analysis into The Boeing 7E7 Case Study Solution
Once various tools have been used to analyse the case, the findings of this analysis need to be incorporated into practical and actionable solutions. These solutions will also be the The Boeing 7E7 case answers. These are usually in the form of strategies that the organisation can adopt. The following step-by-step procedure can be used to organise the Harvard Business case solution and recommendations:
- The first step of the solution is to come up with a corporate level strategy for the organisation. This part consists of solutions that address issues faced by the organisation on a strategic level. This could include suggestions, changes or recommendations to the company's vision, mission and its strategic objectives. It can include recommendations on how the organisation can work towards achieving these strategic objectives. Furthermore, it needs to be explained how the stated recommendations will help in solving the main issue mentioned in the case and where the company will stand in the future as a result of these.
- The second step of the solution is to come up with a business level strategy. The HBR case studies may present issues faced by a part of the organisation. For example, the issues may be stated for marketing and the role of a marketing manager needs to be assumed. So, recommendations and suggestions need to address the strategy of the marketing department in this case. Therefore, the strategic objectives of this business unit (Marketing) will be laid down in the solutions and recommendations will be made as to how to achieve these objectives. Similar would be the case for any other business unit or department such as human resources, finance, IT etc. The important thing to note here is that the business level strategy needs to be aligned with the overall corporate strategy of the organisation. For example, if one suggests the organisation to focus on differentiation for competitive advantage as a corporate level strategy, then it can't be recommended for the The Boeing 7E7 Case Study Solution that the business unit should focus on costs.
- The third step is not compulsory but depends from case to case. In some HBR case studies, one may be required to analyse an issue at a department. This issue may be analysed for a manager or employee as well. In these cases, recommendations need to be made for these people. The solution may state that objectives that these people need to achieve and how these objectives would be achieved.
The case study analysis and solution, and The Boeing 7E7 case answers should be written down in the The Boeing 7E7 case memo, clearly identifying which part shows what. The The Boeing 7E7 case should be in a professional format, presenting points clearly that are well understood by the reader.
Alternate solution to the The Boeing 7E7 HBR case study
It is important to have more than one solution to the case study. This is the alternate solution that would be implemented if the original proposed solution is found infeasible or impossible due to a change in circumstances. The alternate solution for The Boeing 7E7 is presented in the same way as the original solution, where it consists of a corporate level strategy, business level strategy and other recommendations.
Implementation of The Boeing 7E7 Case Solution
The case study does not end at just providing recommendations to the issues at hand. One is also required to provide how these recommendations would be implemented. This is shown through a proper implementation framework. A detailed implementation framework helps in distinguishing between an average and an above average case study answer. A good implementation framework shows the proposed plan and how the organisations' resources would be used to achieve the objectives. It also lays down the changes needed to be made as well as the assumptions in the process.
- A proper implementation framework shows that one has clearly understood the case study and the main issue within it.
- It shows that one has been clarified with the HBR fundamentals on the topic.
- It shows that the details provided in the case have been properly analysed.
- It shows that one has developed an ability to prioritise recommendations and how these could be successfully implemented.
- The implementation framework also helps by removing out any recommendations that are not practical or actionable as these could not be implemented. Therefore, the implementation framework ensures that the solution to the The Boeing 7E7 Harvard case is complete and properly answered.
Recommendations and Action Plan for The Boeing 7E7 case analysis
For The Boeing 7E7, based on the SWOT Analysis, Porter Five Forces Analysis, PESTEL Analysis, VRIO analysis, Value Chain Analysis, BCG Matrix analysis, Ansoff Matrix analysis, and the Marketing Mix analysis, the recommendations and action plan are as follows:
- The Boeing 7E7 should focus on making use of its strengths identified from the VRIO analysis to make the most of the opportunities identified from the PESTEL.
- The Boeing 7E7 should enhance the value creating activities within its value chain.
- The Boeing 7E7 should invest in its stars and cash cows, while getting rid of the dogs identified from the BCG Matrix analysis.
- To achieve its overall corporate and business level objectives, it should make use of the marketing mix tools to obtain desired results from its target market.
Baron, E. (2015). How They Teach the Case Method At Harvard Business School. Retrieved from https://poetsandquants.com/2015/09/29/how-they-teach-the-case-method-at-harvard-business-school/
Bartol. K, & Martin, D. (1998). Management, 3rd edition. Boston: Irwin McGrawHill.
Free Management E-Books. (2013a). PESTLE Analysis. Retrieved from http://www.free-management-ebooks.com/dldebk-pdf/fme-pestle-analysis.pdf
Gupta, A. (2013). Environment & PEST analysis: an approach to the external business environment. International Journal of Modern Social Sciences, 2(1), 34-43.
Hambrick, D. C., MacMillan, I. C., & Day, D. L. (1982). Strategic attributes and performance in the BCG matrix—A PIMS-based analysis of industrial product businesses. Academy of Management Journal, 25(3), 510-531.
Hill, C., & Jones, G. (2010). Strategic Management Theory: An Integrated Approach, Ninth Ed. Mason, OH: South-Western, Cengage Learning.
Hussain, S., Khattak, J., Rizwan, A., & Latif, M. A. (2013). ANSOFF matrix, environment, and growth-an interactive triangle. Management and Administrative Sciences Review, 2(2), 196-206.
IIBMS. (2015). 7 Effective Steps to Solve Case Study. Retrieved from http://www.iibms.org/c-7-effective-steps-to-solve-case-study/
Kim, W. C., & Mauborgne, R. (2004). Blue ocean strategy. If you read nothing else on strategy, read thesebest-selling articles., 71.
Kotler, P., & Armstrong, G. (2010). Principles of marketing. Pearson education.
Kulkarni, N. (2018). 8 Tips to Help You Prepare for the Case Method. Retrieved from https://www.hbs.edu/mba/blog/post/8-tips-to-help-you-prepare-for-the-case-method
Lin, C., Tsai, H. L., Wu, Y. J., & Kiang, M. (2012). A fuzzy quantitative VRIO-based framework for evaluating organizational activities. Management Decision, 50(8), 1396-1411.
Nixon, J., & Helms, M. M. (2010). Exploring SWOT analysis – where are we now?: A review of academic research from the last decade. Journal of Strategy and Management, 3(3), 215-251.
Panagiotou, G. (2003). Bringing SWOT into Focus. Business Strategy Review, 14(2), 8-10.
Pickton, D. W., & Wright, S. (1998). What's swot in strategic analysis? Strategic Change, 7(2), 101-109.
Porter, M. E. (2001). The value chain and competitive advantage. Understanding Business Processes, 50-66.
Porter, M. E. (1985). Competitive advantage: creating and sustaining superior performance (Vol. 2). New York: Free Press.
Porter, M.E. (1979, March). Harvard Business Review: Strategic Planning, How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy. Retrieved July 7, 2016, from https://hbr.org/1979/03/how-competitive-forces-shape-strategy
Rastogi, N., & Trivedi, M. K. (2016). PESTLE Technique–a Tool to Identify External Risks in Construction Projects. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), 3(1), 384-388.
Rauch, P. (2007). SWOT analyses and SWOT strategy formulation for forest owner cooperations in Austria. European Journal of Forest Research, 126(3), 413-420.
Warning! This article is only an example and cannot be used for research or reference purposes. If you need help with something similar, please submit your details here .
9413 Students can’t be wrong
PhD Experts
Nataliya Pavlovich
This time the quality of the assignment was really good. An excellent term paper’’’’. Carry on guys!
These guys absolutely make documents in keeping with students' requirements. Very good and just a perfect assignment!
Petra Rahel
The writer did what he said to me. I asked for the revision and it is still an outstanding service. Thanks a lot!
Claire Kieran
I honestly recommend this paper writing service to those who want to get outstanding results with affordable prices. Today, my teacher praised my paper a lot that was supplied by this custom writing help. Thanks a lot!
Calculate the Price
(approx ~ 0.0 page), total price $0, next articles.
- Zeus Asset Management, Inc. Case Analysis
- The Corporation's Cost Of Capital (Abridged) Case Analysis
- The Weighted Average Cost Of Capital Case Analysis
- MCI Communications Corp.: Capital Structure Theory (A) Case Analysis
- Phon Tech Corporation, 1996 Case Analysis
- The Boeing 777 Case Analysis
- Superior Industries International Case Analysis
- Blue Cross And Blue Shield Of Virginia: Cost Of Capital Case Analysis
- Introduction To The Cost Of Equity Case Analysis
- Housing Investment Case Analysis
Previous Articles
- Applying The Capital Asset Pricing Model Case Analysis
- Geo Tech Case Analysis
- MCI Communications Corp.: Capital Structure Theory (SPANISH) Case Analysis
- The Investment Detective Case Analysis
- Rhone Poulenc S.A. Case Analysis
- United Telecommunications, Inc. Case Analysis
- General Motors: Valuation Of Class E Contingent Notes Case Analysis
- Adams, Inc.: Fur Industry Merger Exercise Case Analysis
- Jindo Corporation: Fur Industry Merger Exercise Case Analysis
- Battle For Value: Federal Express Corporation Vs. United Parcel Service Of America, Inc. Case Analysis
Be a great writer or hire a greater one!
Academic writing has no room for errors and mistakes. If you have BIG dreams to score BIG, think out of the box and hire Case48 with BIG enough reputation.

Our Guarantees
Zero plagiarism, best quality, qualified writers, absolute privacy, timely delivery.
Interesting Fact
Most recent surveys suggest that around 76 % students try professional academic writing services at least once in their lifetime!
Allow Our Skilled Essay Writers to Proficiently Finish Your Paper.
We are here to help. Chat with us on WhatsApp for any queries.
Customer Representative

- Order Status
- Testimonials
- What Makes Us Different
The Boeing 7E7 Harvard Case Solution & Analysis
Home >> Harvard Case Study Analysis Solutions >> The Boeing 7E7
The Boeing 7E7 Case Solution
QUESTION NO 1:
The calculated IRR for the project is 15.7%.This rate of return is calculated by taking the effect of forecaster free cash flows of the project. The assumption taken in account was that ‘Dream line’ aircraft would provide 16% return i.e. the IRR to the investors. The forecaster values for IRR which is streamlined with the assumed figure is 15.7%. It means that project would be feasible if it would fetch above 15.7% return from the investor prospect, and maintaining the units sold over and above 2500. Thus by getting 5% premium above the minimum assumed price project would be feasible.
But IRR analysis shows risks as well, if different variations are considered for the project i.e. cost of construction, development costs, design cost and production costs as well. Some other factors might also hinder the performance of the Airbus.If the travel demand gets worsened or any other company enters the market with the new competitive product.
By considering all the above factors, the IRR should be 15.7 % or above for the prospective years, and by this the project’s viability increases.
QUESTION NO 2:
The beta used in the analysis (refer excel sheet), is the beta given in the case study in exhibit no. 10. The choices available to use beta factor to evaluate the risk in the project comprises of:
The beta for 60 months, 21 months and 60 trading days. The beta used in the analysis is for 60 months. The reason for using it in the analysis is the fact that airline industry invests in manufacturing new jets on long term basis. The pros and cons of investing the venture must be evaluated in long-term. The betas for the lesser time duration are volatile, and cannot epics the truer risk which company might face after investing into this venture.
The selection is made from S&P 500 index values, because the values by them are more authentic and reliable. Analyst mostly considers their values for determining the financial viability of the projects. The figures from the financial data of the companies under the same industry are not considered,because most of the revenues of such companies are driven from government. Hence BOEING is earning only 46% of the revenue from government sectors. To make the analysis clear and uniform. The averages of the comparable figures are not considered. Correspondent market risk premium and other variables are used from the available sources in the light of beta determined.
QUESTION NO. 3:
The cost of debt is determined by using the figures extracted from the financial data of the company is given in the excel sheets.
The Boeing 7E7 Harvard Case Solution & Analysis
QUESTION NO 4:
The weighted average cost of capital is calculated (refer Excel sheet).
The composition of debt and equity i.e. the relative weights used in the calculation are extracted from the financial data given in the case study under the heading of exhibit 10. The proportions of debt and equity are also calculated with their relative percentages from the balance sheet of the company as well. The percentage used in the analysis is taken from the exhibit 10 as calculated under special considerations.Which shows the market value of debt/equity ratio for Boeing, thus for the financial evaluation, this percentage is considered for calculating WACC In our analysis.................
This is just a sample partial case solution. Please place the order on the website to order your own originally done case solution.
Related Case Solutions & Analyses:

Hire us for Originally Written Case Solution/ Analysis
Like us and get updates:.
Harvard Case Solutions
Search Case Solutions
- Accounting Case Solutions
- Auditing Case Studies
- Business Case Studies
- Economics Case Solutions
- Finance Case Studies Analysis
- Harvard Case Study Analysis Solutions
- Human Resource Cases
- Ivey Case Solutions
- Management Case Studies
- Marketing HBS Case Solutions
- Operations Management Case Studies
- Supply Chain Management Cases
- Taxation Case Studies
More From Harvard Case Study Analysis Solutions
- Abby Hamilton
- The Squeaky Horn
- Cherie Blair: Inventing Herself
- Strategic Formulation
- Shanghai Property Market and Hong Kong Developers
- Q and Sessions with Akhil Gupta Deputy Group CEO and Managing Director of Bharti Enterprises Video Supplement
- Samsung Electronics in 2004: Conquering the Wireless Digital World
Contact us:

Check Order Status

How Does it Work?
Why TheCaseSolutions.com?

You have no items in your shopping cart.

- Accounting & Control
- Business & Government
- Case Method
- Decision Analysis
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Leadership & Organizational Behavior
- Management Communications
- Operations Management
- Darden Course Pack
- Forio Simulation
- Multimedia Case
- Technical Note
- Video Playlist
Share This Product
The boeing 7e7, product overview.
In 2003, The Boeing Company announced plans to build a new "super-efficient" commercial jet called the "7E7" or "Dreamliner." This was a "bet the farm" gamble by Boeing, similar in magnitude to its earlier introductions of the 747 and 777 airliners. The technological superiority of the new airframe and the fact that it would penetrate a rapidly growing market segment argued for approval of the project. On the other hand, the current market for commercial airplanes was depressed; reflecting terrorism risk, war, and SARS, a contagious illness resulting in global travel warnings. Boeing's board of directors would need to weigh these considerations in granting final approval to proceed with the project. The task for students is to evaluate the 7E7 project against a financial standard, the investors' required returns. The case gives internal rates of return (IRR) for the 7E7 project under base-case and alternative forecasts. The students must estimate a weighted-average cost of capital (WACC) for Boeing's commercial-aircraft business segment in order to evaluate these IRRs. As a result of this analysis, the students identify the "key value drivers" and distinguish, on a qualitative basis, the key gambles Boeing is making. The general objective of this case is to exercise students' skills in estimating a weighted average cost of capital and cost of equity. The need for students to estimate a segment WACC draws out their abilities to critique different estimates of beta and to manipulate the levered-beta formulas. Boeing competes in both the commercial aircraft and defense business; thus, deriving the appropriate benchmark WACC for the 7E7 project requires isolating the commercial aircraft component from Boeing's overall corporate WACC. In doing so, students engage the concept of value additivity.
- Add to Cart
- Save to Library
- Learning Objectives
Related Products
- Teletech Corporation, 2005 Bruner, Robert F.; Carr, Sean Case
- Nike, Inc.: Cost of Capital Bruner, Robert F.; Chan, Jessica; Carr, Sean Case
Customers Also Bought
- Carded Graphics, LLC: Sheeter Replacement Decision Lipson, Marc L.; Mastelli, Irene Case
- California Pizza Kitchen Schill, Michael J.; Shumadine, Elizabeth Case

COMMENTS
Boeing 7E7 Case Study: Introduction . In 2003, Boeing announced their intention to create a new "super-efficient" commercial jet codenamed "7E7" or "Dreamliner." Similar to when it first developed the 747 and 777, Boeing effectively "bet the farm" on this venture.
With a rapidly-growing market segment, the approval for the Boeing 7E7 project needed approval, taking into consideration the current market for commercial airplanes. This case study provides the opportunity for students to assess the feasibility of the said project. Robert F. Bruner and James Tompkins Harvard Business Review (UV0281-PDF-ENG)
This made Boeing decide to come up with an all-new aircraft featuring the more advanced technologies which is Boeing 7E7 to replace the 757, 767, A300 and even the successful A330 aircraft in early 2003. With almost every U. major airline operating a large fleet of 757/767 aircraft, this will be the main target market for Boeing 7E7.
The Boeing 7E7 Project. The Boeing 7E7 entailed a design of an airplane that was meant for short and long distances and various cargo and passenger capacities. At the same time, the jet was supposed to consume 80% of fuel compared to its predecessor and would cost customers 10% cheaper. The aircraft was thus designed to make more profits and ...
The Boeing 7E7 Case Solution,The Boeing 7E7 Case Analysis, The Boeing 7E7 Case Study Solution, PROBLEM STATEMENT: In the case, Bair was concerned about the board of directors and members that now it is the right time to design and launch a new. ... NPV< 0 or negative NPV - pretty obvious answer - no, don't pursue it, unless the goal is not the ...
in the case study of Boeing 7E7, how to calculate market return which is Rm. There are 2 steps to solve this one.
The Boeing 7E7 Project. The Boeing 7E7 entailed a design of an airplane that was meant for short and long distances and various cargo and passenger capacities. At the same time, the jet was supposed to consume 80% of fuel compared to its predecessor and would cost customers 10% cheaper.
Accounting questions and answers. The Boeing 7E7 case illustrates the concept and estimation process of the weighted average cost of capital (WACC). Boeing has two divisions: commercial and defense. The defense division generated $20 million in revenue last year while the commercial division generated $80 million.
The 7E7 Project is a risky project. With a beta of 2.540738, which is substantially. higher than the stock market average company, volatility is expected in this investment. However, with risk comes a reward. The 7E7 project would need to provide returns of. 22.7009% in order to be considered a sound investment.
In 2003 The Boeing Company announced plans to build a new "super-efficient" commercial jet called the "7E7" or "Dreamliner." This was a "bet the farm" gamble by Boeing, similar in magnitude to its earlier introductions of the 747 and 777 airliners. The technological superiority of the new airframe and the fact that it would penetrate a rapidly growing market segment argued for approval of the ...
Boeing case study case 17 the boeing 7e7 we still have lot to get done as we move toward authority to offer the 7e7 to our customers. the team is making great. Skip to document. ... Chapter 2 Answers. Corporate Finance 100% (2) 3. S1 Tutorial - Corp fin. Corporate Finance 100% (1) 35. Corp Fin Notes.
The The Boeing 7E7 case study consists of the history of the company given at the start. Reading it thoroughly will provide you with an understanding of the company's aims and objectives. You will keep these in mind as any Harvard Business Case Solutions you provide will need to be aligned with these. 2.
The case study analysis and solution, and The Boeing 7E7 case answers should be written down in the The Boeing 7E7 case memo, clearly identifying which part shows what. The The Boeing 7E7 case should be in a professional format, presenting points clearly that are well understood by the reader.
Step 1. To calculate the market return for the Boeing 7E7 case study, you typically use historical data and ... View the full answer. Step 2. Unlock. Unlock. Answer. Unlock. Unlock.
The Boeing 7E7 Harvard Case Solution & Analysis . QUESTION NO 4: The weighted average cost of capital is calculated (refer Excel sheet). The composition of debt and equity i.e. the relative weights used in the calculation are extracted from the financial data given in the case study under the heading of exhibit 10.
Using this methodology, without any premium for the promised lower operating costs, the minimum price for the 7E7 and 7E7 Stretch was estimated to be $114.5 million and $144.5 million, respectively, in 2002. The forecast assumed that customers would be willing to pay a 5% price premium for the lower operating costs.
The case gives the internal rates of return (IRR) if the 7E7 project under base case and alternative forecasts. Students must estimate the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) for Boeing's' commercial aircraft business segment in order to evaluate the IRR's. as a result of that analysis, students will identify the key value drivers and ...
Case - The Boeing 7E7 Executive summary Since the beginning of 2000, successive the events of 911, technology bubbles, the Iraq war, and the SARS have had an unprecedented impact on global airlines. Under the dual pressure of being overtaken by competitors and the sluggish market, Boeing proposed the 7E7 project in 2003. The aircraft has the characteristics of the short production cycle, fuel ...
Yes Positive NPV IRR Stay Competitive IRR 15.66% 30 Year Note WACC 12.49% 7E7 Project Analysis 30 Year Note NPV 30 Year Note 4.56% Objectives Background Calculations Sensitivity Analysis Recommendations Sensitivity Analysis WACC 12.49% Risk Free Rate & Market Return Background
View 84630520-Boeing-7E7-Case-Study-Solution.docx from FIN 4311 at West Texas A&M University. BACKGROUND As the worlds largest aerospace company and leading manufacturer of commercial jetliners ... Getting to the Answer Start by checking the answers against paragraph 1 where. The Galaxy School. SG 33. document. results 9 Proceed to Lesson 5 ...
Transcribed image text: 7. The Boeing 7E7 case illustrates the concept and estimation process of the weighted average cost of capital (WACC). Boeing has two divisions: commercial and defense. The defense division generated $20 million in revenue last year while the commercial division generated $80 million. Boeing is considering the 7E7 project ...
Case. In 2003, The Boeing Company announced plans to build a new "super-efficient" commercial jet called the "7E7" or "Dreamliner." This was a "bet the farm" gamble by Boeing, similar in magnitude to its earlier introductions of the 747 and 777 airliners. The technological superiority of the new airframe and the fact that it would penetrate a ...
At the date of the case, the 74-year equity market risk premium (EMRP) was estimated to be 8.4% over. The Boeing 7E7: Case Study. Advance Assignment Questions: What is an appropriate required rate of return against which to evaluate the prospective IRRs from the Boeing 7E7? 2. Please use the Capital Asset Pricing Model to estimate the cost of ...