

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that he or she will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove her point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, he or she still has to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and she already knows everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality she or he expects.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

Definition of 'assignment'

Video: pronunciation of assignment

assignment in American English
Assignment in british english, examples of 'assignment' in a sentence assignment, related word partners assignment, trends of assignment.
View usage over: Since Exist Last 10 years Last 50 years Last 100 years Last 300 years
Browse alphabetically assignment
- assigned randomly
- assigned risk
- assimilability
- assimilable
- All ENGLISH words that begin with 'A'
Related terms of assignment
- seat assignment
- tough assignment
- writing assignment
- challenging assignment
- difficult assignment
- View more related words
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

Wordle Helper

Scrabble Tools
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of assignment noun from the Oxford Advanced American Dictionary
Take your English to the next level
The Oxford Learner’s Thesaurus explains the difference between groups of similar words. Try it for free as part of the Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary app

Communications from the Library: Please note all communications from the library, concerning renewal of books, overdue books and reservations will be sent to your NCI student email account.
- << Previous: The Writing Process
- Next: Brainstorming Techniques >>
- Last Updated: Dec 15, 2023 10:00 AM
- URL: https://libguides.ncirl.ie/academic_writing_skills
Assignments usually ask you to demonstrate that you have immersed yourself in the course material and that you've done some thinking on your own; questions not treated at length in class often serve as assignments. Fortunately, if you've put the time into getting to know the material, then you've almost certainly begun thinking independently. In responding to assignments, keep in mind the following advice.
- Beware of straying. Especially in the draft stage, "discussion" and "analysis" can lead you from one intrinsically interesting problem to another, then another, and then ... You may wind up following a garden of forking paths and lose your way. To prevent this, stop periodically while drafting your essay and reread the assignment. Its purposes are likely to become clearer.
- Consider the assignment in relation to previous and upcoming assignments. Ask yourself what is new about the task you're setting out to do. Instructors often design assignments to build in complexity. Knowing where an assignment falls in this progression can help you concentrate on the specific, fresh challenges at hand.
Understanding some key words commonly used in assignments also may simplify your task. Toward this end, let's take a look at two seemingly impenetrable instructions: "discuss" and "analyze."
1. Discuss the role of gender in bringing about the French Revolution.
- "Discuss" is easy to misunderstand because the word calls to mind the oral/spoken dimension of communication. "Discuss" suggests conversation, which often is casual and undirected. In the context of an assignment, however, discussion entails fulfilling a defined and organized task: to construct an argument that considers and responds to an ample range of materials. To "discuss," in assignment language, means to make a broad argument about a set of arguments you have studied. In the case above, you can do this by
- pointing to consistencies and inconsistencies in the evidence of gendered causes of the Revolution;
- raising the implications of these consistencies and/or inconsistencies (perhaps they suggest a limited role for gender as catalyst);
- evaluating different claims about the role of gender; and
- asking what is gained and what is lost by focusing on gendered symbols, icons and events.
A weak discussion essay in response to the question above might simply list a few aspects of the Revolution—the image of Liberty, the executions of the King and Marie Antoinette, the cry "Liberte, Egalite, Fraternite!" —and make separate comments about how each, being "gendered," is therefore a powerful political force. Such an essay would offer no original thesis, but instead restate the question asked in the assignment (i.e., "The role of gender was very important in the French Revolution" or "Gender did not play a large role in the French Revolution").
In a strong discussion essay, the thesis would go beyond a basic restatement of the assignment question. You might test the similarities and differences of the revolutionary aspects being discussed. You might draw on fresh or unexpected evidence, perhaps using as a source an intriguing reading that was only briefly touched upon in lecture.
2. Analyze two of Chaucer's Canterbury Tales, including one not discussed in class, as literary works and in terms of sources/analogues.
The words "analyze" and "analysis" may seem to denote highly advanced, even arcane skills, possessed in virtual monopoly by mathematicians and scientists. Happily, the terms refer to mental activity we all perform regularly; the terms just need decoding. "Analyze" means two things in this specific assignment prompt.
- First, you need to divide the two tales into parts, elements, or features. You might start with a basic approach: looking at the beginning, middle, and end. These structural features of literary works—and of historical events and many other subjects of academic study—may seem simple or even simplistic, but they can yield surprising insights when examined closely.
- Alternatively, you might begin at a more complex level of analysis. For example, you might search for and distinguish between kinds of humor in the two tales and their sources in Boccaccio or the Roman de la Rose: banter, wordplay, bawdy jokes, pranks, burlesque, satire, etc.
Second, you need to consider the two tales critically to arrive at some reward for having observed how the tales are made and where they came from (their sources/analogues). In the course of your essay, you might work your way to investigating Chaucer's broader attitude toward his sources, which alternates between playful variation and strict adherence. Your complex analysis of kinds of humor might reveal differing conceptions of masculine and feminine between Chaucer and his literary sources, or some other important cultural distinction.
Analysis involves both a set of observations about the composition or workings of your subject and a critical approach that keeps you from noticing just anything—from excessive listing or summarizing—and instead leads you to construct an interpretation, using textual evidence to support your ideas.
Some Final Advice
If, having read the assignment carefully, you're still confused by it, don't hesitate to ask for clarification from your instructor. He or she may be able to elucidate the question or to furnish some sample responses to the assignment. Knowing the expectations of an assignment can help when you're feeling puzzled. Conversely, knowing the boundaries can head off trouble if you're contemplating an unorthodox approach. In either case, before you go to your instructor, it's a good idea to list, underline or circle the specific places in the assignment where the language makes you feel uncertain.
William C. Rice, for the Writing Center at Harvard University
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Assignment is a task given to students by a teacher or professor, usually as a means of assessing their understanding and application of course material. Assignments can take various forms, including essays, research papers, presentations, problem sets, lab reports, and more.
Assignments are typically designed to be completed outside of class time and may require independent research, critical thinking, and analysis. They are often graded and used as a significant component of a student’s overall course grade. The instructions for an assignment usually specify the goals, requirements, and deadlines for completion, and students are expected to meet these criteria to earn a good grade.
History of Assignment
The use of assignments as a tool for teaching and learning has been a part of education for centuries. Following is a brief history of the Assignment.
- Ancient Times: Assignments such as writing exercises, recitations, and memorization tasks were used to reinforce learning.
- Medieval Period : Universities began to develop the concept of the assignment, with students completing essays, commentaries, and translations to demonstrate their knowledge and understanding of the subject matter.
- 19th Century : With the growth of schools and universities, assignments became more widespread and were used to assess student progress and achievement.
- 20th Century: The rise of distance education and online learning led to the further development of assignments as an integral part of the educational process.
- Present Day: Assignments continue to be used in a variety of educational settings and are seen as an effective way to promote student learning and assess student achievement. The nature and format of assignments continue to evolve in response to changing educational needs and technological innovations.
Types of Assignment
Here are some of the most common types of assignments:
An essay is a piece of writing that presents an argument, analysis, or interpretation of a topic or question. It usually consists of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Essay structure:
- Introduction : introduces the topic and thesis statement
- Body paragraphs : each paragraph presents a different argument or idea, with evidence and analysis to support it
- Conclusion : summarizes the key points and reiterates the thesis statement
Research paper
A research paper involves gathering and analyzing information on a particular topic, and presenting the findings in a well-structured, documented paper. It usually involves conducting original research, collecting data, and presenting it in a clear, organized manner.
Research paper structure:
- Title page : includes the title of the paper, author’s name, date, and institution
- Abstract : summarizes the paper’s main points and conclusions
- Introduction : provides background information on the topic and research question
- Literature review: summarizes previous research on the topic
- Methodology : explains how the research was conducted
- Results : presents the findings of the research
- Discussion : interprets the results and draws conclusions
- Conclusion : summarizes the key findings and implications
A case study involves analyzing a real-life situation, problem or issue, and presenting a solution or recommendations based on the analysis. It often involves extensive research, data analysis, and critical thinking.
Case study structure:
- Introduction : introduces the case study and its purpose
- Background : provides context and background information on the case
- Analysis : examines the key issues and problems in the case
- Solution/recommendations: proposes solutions or recommendations based on the analysis
- Conclusion: Summarize the key points and implications
A lab report is a scientific document that summarizes the results of a laboratory experiment or research project. It typically includes an introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
Lab report structure:
- Title page : includes the title of the experiment, author’s name, date, and institution
- Abstract : summarizes the purpose, methodology, and results of the experiment
- Methods : explains how the experiment was conducted
- Results : presents the findings of the experiment
Presentation
A presentation involves delivering information, data or findings to an audience, often with the use of visual aids such as slides, charts, or diagrams. It requires clear communication skills, good organization, and effective use of technology.
Presentation structure:
- Introduction : introduces the topic and purpose of the presentation
- Body : presents the main points, findings, or data, with the help of visual aids
- Conclusion : summarizes the key points and provides a closing statement
Creative Project
A creative project is an assignment that requires students to produce something original, such as a painting, sculpture, video, or creative writing piece. It allows students to demonstrate their creativity and artistic skills.
Creative project structure:
- Introduction : introduces the project and its purpose
- Body : presents the creative work, with explanations or descriptions as needed
- Conclusion : summarizes the key elements and reflects on the creative process.
Examples of Assignments
Following are Examples of Assignment templates samples:
Essay template:
I. Introduction
- Hook: Grab the reader’s attention with a catchy opening sentence.
- Background: Provide some context or background information on the topic.
- Thesis statement: State the main argument or point of your essay.
II. Body paragraphs
- Topic sentence: Introduce the main idea or argument of the paragraph.
- Evidence: Provide evidence or examples to support your point.
- Analysis: Explain how the evidence supports your argument.
- Transition: Use a transition sentence to lead into the next paragraph.
III. Conclusion
- Restate thesis: Summarize your main argument or point.
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your essay.
- Concluding thoughts: End with a final thought or call to action.
Research paper template:
I. Title page
- Title: Give your paper a descriptive title.
- Author: Include your name and institutional affiliation.
- Date: Provide the date the paper was submitted.
II. Abstract
- Background: Summarize the background and purpose of your research.
- Methodology: Describe the methods you used to conduct your research.
- Results: Summarize the main findings of your research.
- Conclusion: Provide a brief summary of the implications and conclusions of your research.
III. Introduction
- Background: Provide some background information on the topic.
- Research question: State your research question or hypothesis.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of your research.
IV. Literature review
- Background: Summarize previous research on the topic.
- Gaps in research: Identify gaps or areas that need further research.
V. Methodology
- Participants: Describe the participants in your study.
- Procedure: Explain the procedure you used to conduct your research.
- Measures: Describe the measures you used to collect data.
VI. Results
- Quantitative results: Summarize the quantitative data you collected.
- Qualitative results: Summarize the qualitative data you collected.
VII. Discussion
- Interpretation: Interpret the results and explain what they mean.
- Implications: Discuss the implications of your research.
- Limitations: Identify any limitations or weaknesses of your research.
VIII. Conclusion
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your paper.
Case study template:
- Background: Provide background information on the case.
- Research question: State the research question or problem you are examining.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of the case study.
II. Analysis
- Problem: Identify the main problem or issue in the case.
- Factors: Describe the factors that contributed to the problem.
- Alternative solutions: Describe potential solutions to the problem.
III. Solution/recommendations
- Proposed solution: Describe the solution you are proposing.
- Rationale: Explain why this solution is the best one.
- Implementation: Describe how the solution can be implemented.
IV. Conclusion
- Summary: Summarize the main points of your case study.
Lab report template:
- Title: Give your report a descriptive title.
- Date: Provide the date the report was submitted.
- Background: Summarize the background and purpose of the experiment.
- Methodology: Describe the methods you used to conduct the experiment.
- Results: Summarize the main findings of the experiment.
- Conclusion: Provide a brief summary of the implications and conclusions
- Background: Provide some background information on the experiment.
- Hypothesis: State your hypothesis or research question.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of the experiment.
IV. Materials and methods
- Materials: List the materials and equipment used in the experiment.
- Procedure: Describe the procedure you followed to conduct the experiment.
- Data: Present the data you collected in tables or graphs.
- Analysis: Analyze the data and describe the patterns or trends you observed.
VI. Discussion
- Implications: Discuss the implications of your findings.
- Limitations: Identify any limitations or weaknesses of the experiment.
VII. Conclusion
- Restate hypothesis: Summarize your hypothesis or research question.
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your report.
Presentation template:
- Attention grabber: Grab the audience’s attention with a catchy opening.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of your presentation.
- Overview: Provide an overview of what you will cover in your presentation.
II. Main points
- Main point 1: Present the first main point of your presentation.
- Supporting details: Provide supporting details or evidence to support your point.
- Main point 2: Present the second main point of your presentation.
- Main point 3: Present the third main point of your presentation.
- Summary: Summarize the main points of your presentation.
- Call to action: End with a final thought or call to action.
Creative writing template:
- Setting: Describe the setting of your story.
- Characters: Introduce the main characters of your story.
- Rising action: Introduce the conflict or problem in your story.
- Climax: Present the most intense moment of the story.
- Falling action: Resolve the conflict or problem in your story.
- Resolution: Describe how the conflict or problem was resolved.
- Final thoughts: End with a final thought or reflection on the story.
How to Write Assignment
Here is a general guide on how to write an assignment:
- Understand the assignment prompt: Before you begin writing, make sure you understand what the assignment requires. Read the prompt carefully and make note of any specific requirements or guidelines.
- Research and gather information: Depending on the type of assignment, you may need to do research to gather information to support your argument or points. Use credible sources such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites.
- Organize your ideas : Once you have gathered all the necessary information, organize your ideas into a clear and logical structure. Consider creating an outline or diagram to help you visualize your ideas.
- Write a draft: Begin writing your assignment using your organized ideas and research. Don’t worry too much about grammar or sentence structure at this point; the goal is to get your thoughts down on paper.
- Revise and edit: After you have written a draft, revise and edit your work. Make sure your ideas are presented in a clear and concise manner, and that your sentences and paragraphs flow smoothly.
- Proofread: Finally, proofread your work for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors. It’s a good idea to have someone else read over your assignment as well to catch any mistakes you may have missed.
- Submit your assignment : Once you are satisfied with your work, submit your assignment according to the instructions provided by your instructor or professor.
Applications of Assignment
Assignments have many applications across different fields and industries. Here are a few examples:
- Education : Assignments are a common tool used in education to help students learn and demonstrate their knowledge. They can be used to assess a student’s understanding of a particular topic, to develop critical thinking skills, and to improve writing and research abilities.
- Business : Assignments can be used in the business world to assess employee skills, to evaluate job performance, and to provide training opportunities. They can also be used to develop business plans, marketing strategies, and financial projections.
- Journalism : Assignments are often used in journalism to produce news articles, features, and investigative reports. Journalists may be assigned to cover a particular event or topic, or to research and write a story on a specific subject.
- Research : Assignments can be used in research to collect and analyze data, to conduct experiments, and to present findings in written or oral form. Researchers may be assigned to conduct research on a specific topic, to write a research paper, or to present their findings at a conference or seminar.
- Government : Assignments can be used in government to develop policy proposals, to conduct research, and to analyze data. Government officials may be assigned to work on a specific project or to conduct research on a particular topic.
- Non-profit organizations: Assignments can be used in non-profit organizations to develop fundraising strategies, to plan events, and to conduct research. Volunteers may be assigned to work on a specific project or to help with a particular task.
Purpose of Assignment
The purpose of an assignment varies depending on the context in which it is given. However, some common purposes of assignments include:
- Assessing learning: Assignments are often used to assess a student’s understanding of a particular topic or concept. This allows educators to determine if a student has mastered the material or if they need additional support.
- Developing skills: Assignments can be used to develop a wide range of skills, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, research, and communication. Assignments that require students to analyze and synthesize information can help to build these skills.
- Encouraging creativity: Assignments can be designed to encourage students to be creative and think outside the box. This can help to foster innovation and original thinking.
- Providing feedback : Assignments provide an opportunity for teachers to provide feedback to students on their progress and performance. Feedback can help students to understand where they need to improve and to develop a growth mindset.
- Meeting learning objectives : Assignments can be designed to help students meet specific learning objectives or outcomes. For example, a writing assignment may be designed to help students improve their writing skills, while a research assignment may be designed to help students develop their research skills.
When to write Assignment
Assignments are typically given by instructors or professors as part of a course or academic program. The timing of when to write an assignment will depend on the specific requirements of the course or program, but in general, assignments should be completed within the timeframe specified by the instructor or program guidelines.
It is important to begin working on assignments as soon as possible to ensure enough time for research, writing, and revisions. Waiting until the last minute can result in rushed work and lower quality output.
It is also important to prioritize assignments based on their due dates and the amount of work required. This will help to manage time effectively and ensure that all assignments are completed on time.
In addition to assignments given by instructors or professors, there may be other situations where writing an assignment is necessary. For example, in the workplace, assignments may be given to complete a specific project or task. In these situations, it is important to establish clear deadlines and expectations to ensure that the assignment is completed on time and to a high standard.
Characteristics of Assignment
Here are some common characteristics of assignments:
- Purpose : Assignments have a specific purpose, such as assessing knowledge or developing skills. They are designed to help students learn and achieve specific learning objectives.
- Requirements: Assignments have specific requirements that must be met, such as a word count, format, or specific content. These requirements are usually provided by the instructor or professor.
- Deadline: Assignments have a specific deadline for completion, which is usually set by the instructor or professor. It is important to meet the deadline to avoid penalties or lower grades.
- Individual or group work: Assignments can be completed individually or as part of a group. Group assignments may require collaboration and communication with other group members.
- Feedback : Assignments provide an opportunity for feedback from the instructor or professor. This feedback can help students to identify areas of improvement and to develop their skills.
- Academic integrity: Assignments require academic integrity, which means that students must submit original work and avoid plagiarism. This includes citing sources properly and following ethical guidelines.
- Learning outcomes : Assignments are designed to help students achieve specific learning outcomes. These outcomes are usually related to the course objectives and may include developing critical thinking skills, writing abilities, or subject-specific knowledge.
Advantages of Assignment
There are several advantages of assignment, including:
- Helps in learning: Assignments help students to reinforce their learning and understanding of a particular topic. By completing assignments, students get to apply the concepts learned in class, which helps them to better understand and retain the information.
- Develops critical thinking skills: Assignments often require students to think critically and analyze information in order to come up with a solution or answer. This helps to develop their critical thinking skills, which are important for success in many areas of life.
- Encourages creativity: Assignments that require students to create something, such as a piece of writing or a project, can encourage creativity and innovation. This can help students to develop new ideas and perspectives, which can be beneficial in many areas of life.
- Builds time-management skills: Assignments often come with deadlines, which can help students to develop time-management skills. Learning how to manage time effectively is an important skill that can help students to succeed in many areas of life.
- Provides feedback: Assignments provide an opportunity for students to receive feedback on their work. This feedback can help students to identify areas where they need to improve and can help them to grow and develop.
Limitations of Assignment
There are also some limitations of assignments that should be considered, including:
- Limited scope: Assignments are often limited in scope, and may not provide a comprehensive understanding of a particular topic. They may only cover a specific aspect of a topic, and may not provide a full picture of the subject matter.
- Lack of engagement: Some assignments may not engage students in the learning process, particularly if they are repetitive or not challenging enough. This can lead to a lack of motivation and interest in the subject matter.
- Time-consuming: Assignments can be time-consuming, particularly if they require a lot of research or writing. This can be a disadvantage for students who have other commitments, such as work or extracurricular activities.
- Unreliable assessment: The assessment of assignments can be subjective and may not always accurately reflect a student’s understanding or abilities. The grading may be influenced by factors such as the instructor’s personal biases or the student’s writing style.
- Lack of feedback : Although assignments can provide feedback, this feedback may not always be detailed or useful. Instructors may not have the time or resources to provide detailed feedback on every assignment, which can limit the value of the feedback that students receive.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 2: Understanding Assignment Outlines and Instructions
Understanding assignment outlines and instructions, writing for whom writing for what.
The first principle of good communication is knowing your audience . Often when you write for an audience of one, you might write a text or email. But college papers aren’t written like emails; they’re written like articles for a hypothetical group of readers that you don’t actually know much about. There’s a fundamental mismatch between the real-life audience and the form your writing takes.
Unless there is a particular audience specified in the assignment, you would do well to imagine yourself writing for a group of peers who have some introductory knowledge of the field but are unfamiliar with the specific topic you’re discussing. Imagine them being interested in your topic but also busy; try to write something that is well worth your readers’ time. Keeping an audience like this in mind will help you distinguish common knowledge in the field from that which must be defined and explained in your paper.
Another basic tenet of good communication is clarifying the purpose of the communication and letting that purpose shape your decisions. Your professor wants to see you work through complex ideas and demonstrate your learning through the process of producing the paper. Each assignment—be it an argumentative paper, reaction paper, reflective paper, lab report, discussion question, blog post, essay exam, project proposal, or what have you—is ultimately about your learning. To succeed with writing assignments (and benefit from them) you first have to understand their learning-related purposes. As you write for your audience, you’re demonstrating to your professor how far you’ve gotten in analyzing your topic.
Professors don’t assign writing lightly. Grading student writing is generally the hardest, most intensive work instructors do. You would do well to approach every assignment by putting yourself in the shoes of your instructor and asking yourself, “Why did she give me this assignment? How does it fit into the learning goals of the course? Why is this question/topic/problem so important to my professor that he is willing to spend time reading and commenting on several dozen papers on it?”
Professors certainly vary in the quantity and specificity of the guidelines and suggestions they distribute with each writing assignment. Some professors make a point to give very few parameters about an assignment—perhaps just a topic and a length requirement—and they likely have some good reasons for doing so. Here are some possible reasons:
- They figured it out themselves when they were students . Many instructors will teach how they were taught in school. The emphasis on student-centered instruction is relatively recent; your instructors more often had professors who adhered to the classic model of college instruction: they went to lectures and/or labs and wrote papers. Students were often ‘on their own’ to learn the lingo and conventions of each field, to identify the key concepts and ideas within readings and lectures, and to sleuth out instructors’ expectations for written work. Learning goals, rubrics, quizzes, and preparatory assignments were generally rare.
- They think figuring it out yourself is good for you . Because your professors often succeeded in a much less supportive environment , they appreciate how learning to thrive in those conditions gave them life-long problem-solving and critical thinking skills. Many think you should be able to figure it out yourself and that it would be good practice for you to do so. Even those who do include a lot of guidance with writing assignments sometimes worry that they’re depriving you of an important personal and intellectual challenge. Figuring out unspoken expectations is a valuable skill in itself. They may also want to give you the freedom to explore and produce new and interesting ideas and feel that instructions that are too specific may limit you. There’s a balancing act to creating a good assignment outline, so sometimes you might need to ask for clarification.
- They think you already know the skills/concepts : Some professors assume that students come with a fully developed set of academic skills and knowledge. You may need to ask your professor for clarification or help and it’s good to learn what additional resources are out there to assist you (the Library, Writing Guides, etc).
It is understandably frustrating when you feel you don’t know how to direct your efforts to succeed with an assignment. The transparency that you get from some professors—along with books like this one—will be a big help to you in situations where you have to be scrappier and more pro-active, piecing together the clues you get from your professors, the readings, and other course documents.
The assignment prompt: what does “analyze” mean anyway?
Often, the handout or other written text explaining the assignment—what professors call the assignment prompt or outline—will explain the purpose of the assignment, the required parameters (length, number and type of sources, referencing style, etc.), and the criteria for evaluation.
Sometimes, though—especially when you are new to a field—you will encounter the baffling situation in which you comprehend every single sentence in the prompt but still have absolutely no idea how to approach the assignment. No one is doing anything wrong in a situation like that. It just means that further discussion of the assignment is in order. Here are some tips:
Video source: https://youtu.be/JZ175MLpOmE
- Try to brainstorm or do a free-write . A free-write is when you just write, without stopping, for a set period of time. That doesn’t sound very “free;” it actually sounds kind of coerced. The “free” part is what you write—it can be whatever comes to mind. Professional writers use free-writing to get started on a challenging (or distasteful) writing task or to overcome writers block or a powerful urge to procrastinate. The idea is that if you just make yourself write, you can’t help but produce some kind of useful nugget. Thus, even if the first eight sentences of your free write are all variations on “I don’t understand this” or “I’d really rather be doing something else,” eventually you’ll write something like “I guess the main point of this is …” and—booyah!—you’re off and running. If your instructor doesn’t make time for that in class, a quick free-write on your own will quickly reveal whether you need clarification about the assignment and, often, what questions to ask.
Rubrics as road maps
Not all professors use rubrics : some mark “holistically” (which means that they evaluate the paper as a whole), versus “analytically” (where they break down the marks by criteria). If the professor took the trouble to prepare and distribute a rubric, you can be sure that they will use it to grade your paper. A rubric is the clearest possible statement of what the professor is looking for in the paper. If it’s wordy, it may seem like those online “terms and conditions” that we routinely accept without reading. But you really should read it over carefully before you begin and again as your work progresses. A lot of rubrics do have some useful specifics. Even less specific criteria (such as “incorporates course concepts” and “considers counter-arguments”) will tell you how you should be spending your writing time.
Even the best rubrics aren’t completely transparent because they simply can’t be. For example, what is the real difference between “demonstrating a thorough understanding of context, audience, and purpose” and “demonstrating adequate consideration” of the same? It depends on the specific context. So how can you know whether you’ve done that? A big part of what you’re learning, through feedback from your professors, is to judge the quality of your writing for yourself. Your future employers are counting on that. At this point, it is better to think of rubrics as roadmaps, displaying your destination, rather than a GPS system directing every move you make.
Video source: https://youtu.be/mXRzyZAE8Y4
What’s critical about critical thinking?
Critical thinking is one of those terms that has been used so often and in so many different ways that if often seems meaningless. It also makes one wonder, is there such a thing as uncritical thinking? If you aren’t thinking critically, then are you even thinking?
Despite the prevalent ambiguities, critical thinking actually does mean something. The Association of American Colleges and Universities usefully defines it as “a habit of mind characterized by the comprehensive exploration of issues, ideas, artifacts, and events before accepting or formulating an opinion or conclusion.” [1]
The critical thinking rubric produced by the AAC&U describes the relevant activities of critical thinking in more detail. To think critically, one must …
(a) “clearly state and comprehensively describe the issue or problem”,
(b) “independently interpret and evaluate sources”,
(c) “thoroughly analyze assumptions behind and context of your own or others’ ideas”,
(d) “argue a complex position and one that takes counter-arguments into account,” and
(e) “arrive at logical and well informed conclusions”. [2]
While you are probably used to providing some evidence for your claims, you can see that college-level expectations go quite a bit further. When professors assign an analytical paper, they don’t just want you to formulate a plausible-sounding argument. They want you to dig into the evidence, think hard about unspoken assumptions and the influence of context, and then explain what you really think and why.
Thinking critically—thoroughly questioning your immediate intuitive responses—is difficult work, but every organization and business in the world needs people who can do that effectively. The ability to think critically also entails being able to hear and appreciate multiple perspectives on an issue, even if we don’t agree with them. While writing time is often solitary, it’s meant to plug you into a vibrant academic community. What your professors want, overall, is for you to join them in asking and pursuing important questions about the natural, social, and creative worlds.
- Terrel Rhodes, ed., Assessing Outcomes and Improving Achievement: Tips and Tools for Using Rubrics (Washington, DC: Association of American Colleges and Universities, 2010). ↵
- Ibid ↵
Writing for Academic and Professional Contexts: An Introduction Copyright © 2023 by Sheridan College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
📬 Sign Up for Our Amazing Newsletter!
Get our latest updates, including live webinars, give aways and exclusive content right into your inbox!
.png)
What Is My Assignment From God?
hat is my assignment from God? This is a question that many resonate with because God has given each one of us a direct assignment. When many in the body of Christ think of their God-given assignment, they make the mistake to understand it on a broad level that feels unreachable. As we will unpack today, an assignment is something that God uses to start us on the path of our destiny.
After Jesus had risen from the dead, and spent 40 days walking with his disciples, He gave them disciples an amazing assignment.
“Then the eleven disciples went to Galilee, to the mountain where Jesus had told them to go. When they saw him, they worshiped him; but some doubted. Then Jesus came to them and said, “All authority in heaven and on earth has been given to me. Therefore go and make disciples of all nations, baptizing them in the name of the Father and of the Son and of the Holy Spirit, and teaching them to obey everything I have commanded you. And surely I am with you always, to the very end of the age.” (Matthew 28:16-20)
The disciples were given a direct assignment from Jesus to go and to “make disciples of all nations.” How were they to go about accomplishing this assignment? By “teaching them to obey everything” Jesus had taught them. This assignment is known today as the great commission. Why did Jesus give them this assignment?
It is in the Father’s heart for His children to partner with Him. In the beginning, Adam co-labored with God in stewarding the garden of Eden (see Genesis 2:15 ). This assignment was given so that Adam could discover God’s heart and love for the earth. Today, in the same way, God gives His children unique assignments to carry out so that they can release the love of God on the earth.
Jesus Modeled The Perfect Assignment
When Jesus walked the earth, he modeled the perfect assignment. As one reads the Gospels, they understand Jesus had a clear mission - to usher the kingdom of heaven into the earth. This mission released various assignments from God to destroy the works of the devil. 1 John 3:8 makes this assignment clear. “For this purpose the Son of God was manifested, that He might destroy the works of the devil.”
As Jesus modeled the perfect assignment, he invited others to share in this responsibility. Many times, after healing the sick or performing a sign to inaugurate the kingdom of God, he would release the recipients with a direct assignment.
“Jesus stood up and said to her, “Woman, where are they? Has no one condemned you?” She said, “No one, Lord.” And Jesus said, “Neither do I condemn you; go, and from now on sin no more.” (John 8:10-11)
When the woman who was caught in adultery was brought to Jesus, she discovered something she never expected. In the aftermath of being forgiven and unjudged by the Son of God, he gave her a direct command, “Go and sin no more.”
In order to release her into her God-given destiny, Jesus commanded her to walk away from her former life and to follow the direction of Jesus. By her sinning no more and obeying the word of God, she would be released to walk in a manner that she had never once walked in before.
Assignments Fulfill Our Purpose
When we discover our assignments from God, we partner with Him into his divine plans for our lives. The book of Jeremiah speaks to the intentions of God’s plans over us.
“For I know the plans I have for you, declares the Lord, plans for welfare and not for evil, to give you a future and a hope.” (Jeremiah 29:11)
God has a plan for our lives. These divine plans are rooted in our welfare and give us a wonderful hope and a future. Although this is an amazing promise in scripture, when many read this verse they forget that it is a conditional promise, according to the preceding verses.
“Then you will call upon me and come and pray to me, and I will hear you. You will seek me and find me, when you seek me with all your heart.” (Jeremiah 29:12-13)
After God reveals to us His divine plans, He gives us a direct assignment. Those that embark upon His plans of welfare must take on the assignment to seek Him with all of their heart. By obeying this command, one embarks upon the road of their own destiny.
This passage of scripture makes it clear, the path of our purpose is found by saying yes to our God-given assignments. Saying yes to God’s assignment allows His purpose to begin working in your life. When Jesus called his first disciples, he gave them clear assignments to propel them into their future.
“And he said to them, “Follow me, and I will make you fishers of men.” (Matthew 4:19)
Jesus could of stop after his initial calling of “follow me”, but he didn’t. Why? Because Jesus wasn’t looking for followers alone, he was looking for co-labors in the kingdom of heaven. Just as God gave Adam tasks to steward the garden, so Jesus gave his disciples tasks to steward the kingdom of God.
Jesus didn’t ask the first disciples to just simply follow him, he gave them an assignment, “to become fishers of men.” This assignment set them on the path of their destiny. Years later, the disciples would produce the first fruits of the great commission by spreading the gospel around the modern world. Imagine if Jesus would have never given them an assignment, could they have taken on their destiny?
God gives us assignments to steward His divine purpose for our life. Sometimes, His assignments make no sense to us at first (think of Noah), but we must obey them. Obedience releases a grace of faith that unlocks our destiny and fulfills our assignment.
Today, know this - God has called you and has a plan for your life. The Lord has assigned an amazing purpose for you. It can only be unlocked through your response to His assignments and developed over the course of your own spiritual life. One thing is certain, His assignments are meant to fulfill the words of Jesus in the Lord’s Prayer ,
“Your kingdom come, your will be done on earth as it is in heaven.” (Matthew 6:10)
Kyle Echols
The christian work ethic: unlocking the power of diligence, finding redemption: will god forgive me for watching bad things, is baptism a one-time event or can you get baptized twice, conditional love: exploring its meaning from a christian perspective, join our newsletter and get the latest posts to your inbox, walking on water with jesus: unveiling the identity of the brave disciple, unveiling the deeper significance of pentecost: a divine encounter, guarding the gates: bible verses to keep evil spirits away, sponsored song.

There is More Posts
Understanding affliction in the christian context: a biblical exploration, unveiling theophilus: exploring the enigmatic figure in the bible, decoding the taboo: why 'hell' is more than a four-letter word, heavenly creatures: do animals go to heaven, exploring muslim beliefs: do muslims believe in jesus christ.

Featured Posts
Copied URL to clipboard!
Understood the Assignment
“Understood the assignment" is a phrase that is used to acknowledge someone who has done an exceptional job or exceeded expectations.
What does "Understood the Assignment" mean on social media?
The phrase has become popular on social media and in popular culture and is often used to praise someone who is giving it their all whether that’s with their achievements, what they’re wearing or what they’re doing more generally.
For example, if someone shows up to the party in a great outfit in this context, saying they “Understood the assignment” means that the person is at the top of their game and pulled up in a great look.
The phrase can also be used sarcastically to criticize someone who has failed to meet expectations or has done a poor job. Overall, "Understood the assignment" is a phrase that is used to acknowledge someone's efforts or accomplishments and has become a popular way to express praise or criticism in slang.
The future of social delivered to your inbox
Sign up for Later’s newsletter & be the first to access news, expert tips, and free resources.
Email Address
By entering your email, you're accepting Later's Terms of Service and Privacy Policy .
- The Top TikTok Trends to Try This Week
- The Top Instagram Reels Trends to Try This Week

Stay in the know & grow your business
Create & manage all of your social media content in one app.

What Does Understood The Assignment Mean? – Meaning, Uses and More

What Does Understood The Assignment Mean?
The slang phrase understood the assignment is used to praise someone who goes above and beyond or consistently performs well. It can be applied in various situations, such as complimenting someone’s work, outfit, or performance. The phrase gained popularity in 2021, particularly on social media platforms like TikTok and Twitter. The origins of “understood the assignment” are unclear, but it became more widely known after American rapper Tay Money released a song titled “The Assignment” in October 2021. The phrase went viral on Twitter, with users using it to pay tribute to their favorite actors and actresses who excel in their roles. Here are some examples of how to use the phrase “understood the assignment”:
- “Your presentation was amazing! You really understood the assignment.”
- “That outfit is fire! You totally understood the assignment.”
- “I told my son to clean his room, and he really understood the assignment. It’s spotless!”
- “That new employee really understood the assignment. She’s already making a big impact on the team.”
- “I’m not sure if I understood the assignment for this project. Can you give me some more guidance?”
The phrase “understood the assignment” is a fun and playful way to praise someone for their exceptional work or effort. It can be used sincerely or sarcastically, depending on the context.
What Does Understood The Assignment Mean From a Girl?
When a girl uses the phrase “understood the assignment,” she typically means the same thing as everyone else. It is a way to praise someone for going above and beyond or consistently performing well. Girls use it in various situations, such as complimenting someone’s work, outfit, or performance.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Specific meaning from a girl : Girls use the phrase “understood the assignment” to acknowledge and praise someone’s exceptional work or effort.
- How girls use it : Girls may use the phrase in conversations with their friends, colleagues, or online communities to show appreciation for someone’s achievements.
- How to reply : If someone says “understood the assignment” to you, you can reply with a simple “thank you” or express your gratitude for their recognition.
Girls use the phrase similarly to everyone else. It is a lighthearted and positive way to acknowledge someone’s accomplishments. So, if a girl says “understood the assignment” to you, take it as a compliment and feel proud of your achievements!
- Girl A: I just finished my final project for school!
- Girl B: Nice job! You totally understood the assignment !
- Girl: I saw your artwork on Instagram. It’s amazing!
- Artist: Thank you so much! I’m glad you think I understood the assignment .
- Girl A: Check out this outfit I put together for the party tonight.
- Girl B: Wow, you look stunning! You definitely understood the assignment .
- Girl: I just aced my math test!
- Friend: That’s awesome! You really understood the assignment .
- Girl A: I finally finished writing my novel.
- Girl B: That’s incredible! You truly understood the assignment and brought your story to life.
What Does Understood The Assignment Mean From a Guy?
When a guy uses the phrase “understood the assignment,” it can have similar meanings as when a girl uses it. However, there may be some slight differences in how guys use and interpret the slang. Here’s what you need to know:
Complimenting appearance or performance : Like girls, guys may use “understood the assignment” to compliment someone’s appearance or performance. They might use it to acknowledge someone’s stylish outfit, impressive skills, or exceptional work.
Acknowledging achievements : Guys may also use “understood the assignment” to recognize someone’s achievements or efforts. Whether it’s in sports, academics, or any other area, they use it to show appreciation for someone who has gone above and beyond.
Flirting or expressing interest : In some cases, guys may use “understood the assignment” as a flirty hint or a way to express their interest in someone. It can be a playful way of showing admiration and attraction.
Different tone or delivery : While the overall meaning is similar, guys may have a different tone or delivery when using “understood the assignment.” They might use it in a more casual or laid-back manner compared to girls.
If a guy says “understood the assignment” to you, here are a few things to consider:
Context of the conversation : Pay attention to the context in which he used the phrase. Was it in response to something specific you did or said? Understanding the context can give you clues about his intentions.
Your relationship with him : Consider your relationship with this guy. Are you friends, dating, or just acquaintances? The meaning behind his use of “understood the assignment” can vary depending on your relationship dynamics.
Body language and tone : Take note of his body language and tone of voice when he says it. Does he seem serious, playful, or flirtatious? These non-verbal cues can provide additional context to help you understand his intentions.
Of course, it’s important to remember that not every guy will use “understood the assignment” in the same way. Some may use it casually without any specific meaning, while others may use it as a genuine compliment or flirtation. If you’re unsure about his intentions, don’t hesitate to ask for clarification or simply take it as a positive acknowledgment of your achievements.
- Guy 1: Dude, did you see that new video game trailer? It looks insane!
- Guy 2: Yeah, the graphics are next level. The developers really understood the assignment .
- Guy 1: Check out this painting I just finished. What do you think?
- Guy 2: Wow, man! You really understood the assignment . It’s so detailed and vibrant.
- Guy 1: I aced my math test today!
- Guy 2: Nice job, dude! You definitely understood the assignment . Math can be tough, but you nailed it.
- Guy 1: I just finished renovating my apartment. Take a look!
- Guy 2: Whoa, it looks amazing! You totally understood the assignment . The design is on point.
- Guy: I saw your dance performance last night. You killed it!
- Girl: Thanks! I practiced so hard. I’m glad it paid off.
- Guy: It definitely did. You absolutely understood the assignment on that stage!
What Does Understood The Assignment Mean Sexually?
No, “understood the assignment” does not have a sexual or NSFW meaning. It is a slang phrase used to praise someone who goes above and beyond or consistently performs well in various situations.
Origin of Understood The Assignment
The origins of the phrase “understood the assignment” are unclear. It gained popularity in 2021, particularly on social media platforms like TikTok and Twitter. It is possible that the phrase originated from the common understanding of assignments in school or the workplace, where individuals who excel or consistently perform well are said to have understood the assignment. However, it is also possible that the phrase emerged organically as a catchy and expressive way to praise someone’s exceptional work or effort. Without further information, it is difficult to determine if it is a derived word or a popular typo.
Frequently Asked Questions
Slangs similar to understood the assignment.
The slang phrase “understood the assignment” is similar to the words “outdated,” “trying too hard,” “conformist,” “on trend,” “generic,” and “out of touch” because they all describe someone or something that is not keeping up with trends, not standing out, or lacking originality or uniqueness. These terms are used to criticize or describe someone or something that is not meeting expectations or societal norms.
Is Understood The Assignment A Bad Word?
No, “understood the assignment” is not a bad word or vulgar word. It is a phrase used to praise someone who goes above and beyond to do a good job or who is always on point. It gained popularity in 2021 and is often used on social media platforms like TikTok and Twitter to remark about fantastic and on point things.
Is Understood The Assignment a Typo or Misspelling?
The term “dyat” could be a misspelling or typo, as it is not a recognized word and may have been mistyped due to its similarity to the word “dat” or “diet.”
You may also like

What Does Oy Mean? – Meaning, Uses and More

What Does Pud Mean? – Meaning, Uses and More

What Does Wapo Mean? – Meaning, Uses and More

What Does Cus Mean? – Meaning, Uses and More

Assignment Dream Meaning: What Your Mind Is Trying to Tell You
Written by:
Have you ever woken up feeling stressed and overwhelmed after having a dream about an assignment? You’re not alone. Assignment dreams are more common than you might think and can leave you feeling anxious and uneasy throughout the day. These dreams can take on many different forms and scenarios, leaving you perplexed and wondering what they might mean. In this article, we’ll explore the different types of assignment dreams and the possible reasons why you might be having them. We’ll also examine the various interpretations and what they could be telling you about your life. So, put your thinking cap on and let’s dive into the world of assignment dream meanings.
What is an Assignment Dream?

Assignment Dream Definition
An assignment dream is a dream where an individual is assigned a task or project to complete. This type of dream typically involves a specific deadline, a set of instructions, and a desired outcome. In the dream, the individual may or may not feel prepared to accomplish the task, and there may be obstacles or distractions in the way.
In these dreams, the location and nature of the assignment can vary greatly. For example, it could take place in a classroom setting where the dreamer is given a difficult test to complete or it could be a work-related project that must be finished by a certain date. The assignment might even be a personal task, such as cleaning the house or cooking a meal for guests.
What makes an assignment dream unique is the sense of pressure and responsibility that the dreamer feels. Even though it is just a dream, the individual may experience anxiety and stress related to completing the task. Despite the fact that the consequences of the assignment are not real, the emotions felt during the dream can be just as intense as if they were.
Common Scenarios
One’s own life experiences and current circumstances can play a significant role in shaping the content of one’s assignment dreams. Below are common scenarios that people have reported experiencing in their assignment dreams:
Although these scenarios may differ in specifics, they all share the underlying theme of academic stress and anxiety. It’s important to remember that these dreams can serve as useful indicators of one’s current emotional state and can be addressed accordingly.

Why Do You Have an Assignment Dream?
As you wake up from an assignment dream, you might wonder why you keep having them. There can be various reasons for these types of dreams, and it can be perplexing to figure out which one applies to you. From stress and anxiety to a fear of failure or perfectionism, the reasons can vary greatly. Understanding the root of your assignment dream can give you insight into your subconscious and help you work through any underlying issues that may be causing these dreams. In this section, we will explore some common reasons why you might be having an assignment dream. So, grab a cup of coffee and let’s dive in, unless you are reading about the smelling coffee dream meaning .
Stress and Anxiety
One of the most common reasons for having an assignment dream is due to stress and anxiety in your waking life. This is especially true if you have a looming deadline or unfinished work that needs to be completed. Often, these dreams are a reflection of the pressure you feel to stay on top of your obligations.
According to a study published in Sleep Medicine Journal, people who reported high stress levels during the day were more likely to experience stressful dreams at night. These dreams can be intense and emotionally disturbing, leaving you feeling drained and overwhelmed in the morning.
If you frequently have assignment dreams that leave you feeling stressed and anxious, it may be helpful to explore different stress-management techniques like exercise, meditation, or talk therapy.
By incorporating stress-management techniques into your daily routine, you may find that your assignment dreams become less frequent or less intense over time.
Click here to learn about how dreams of being unable to run may also be related to stress and anxiety.
Fear of Failure
Having a fear of failure is one of the most common reasons why people have an assignment dream. The fear of failure is a normal and understandable anxiety that people feel in many different areas of their lives. It is a feeling of not feeling competent enough or not being able to meet the expectations of others or themselves. When it comes to assignment dreams, the fear of failure often focuses on the idea of not being able to complete a task or meet a deadline, and the potential consequences that may come with that failure.
The fear of failure can be overwhelming and can affect the quality of life. It can result in not taking risks or avoiding tasks that could lead to failure altogether. Unfortunately, avoiding tasks that could lead to failure can also mean missing out on important opportunities for personal growth and development.
Instead of avoiding failure, it is important to embrace it as an opportunity to learn and grow. When it comes to assignment dreams, it is important to recognize that the dream is not a prediction of the future, but rather a reflection of our current fears and anxieties. By identifying the root cause of our fear of failure, we can address it and take proactive steps to overcome it.
One strategy for overcoming the fear of failure is to set realistic goals. By breaking larger tasks into smaller, more manageable pieces, the overall goal can seem less daunting. Another strategy for dealing with the fear of failure is to seek support and guidance from others. Talking to friends, family, or even a therapist can provide valuable insight, encouragement, and perspective.
It is important to remember that failure is a natural part of life and growth, and it is a necessary component of achieving success. It is through failing that we learn, grow, and develop the skills and abilities required to succeed.
If you want to read about more dream meanings, check out our article on dreams of drinking alcohol , lettuce dream meaning, being chased by skunk dream meaning , mercy dream meaning , I of you dream meaning , hallway dream meaning , someone is searching through my purse dream meaning , and shiny tools dream meaning .
Perfectionism
One possible reason why you might have an assignment dream is perfectionism. This is a personality trait characterized by a high need for achievement, a tendency to set particularly high standards, and a strong inclination towards self-criticism. Individuals who struggle with perfectionism often feel that nothing they do is ever good enough, which can lead to chronic feelings of dissatisfaction, frustration, and anxiety.
Some signs of perfectionism may include:
- Difficulty delegating tasks to others.
- An obsession with details and order.
- An excessive self-focus and self-criticism.
- A fear of making mistakes and being judged critically by others.
- A tendency to procrastinate and delay tasks due to the fear of failing.
Perfectionism can also be a root cause of assignment dreams. A dream in which you are struggling to complete a perfect assignment that meets all requirements and expectations may be a reflection of your own internal pressure to achieve an idealistic goal. Additionally, dreams in which a teacher or authority figure is very critical of your work may be a manifestation of your fear of being judged and evaluated by others.
It is important to remember that: striving for high standards and self-improvement is healthy and motivating, but placing unrealistic expectations on oneself or living in constant fear of criticism can be detrimental to mental health and well-being. It is essential to find a healthy balance between seeking excellence and kindness towards oneself. Additionally, exploring and addressing the root causes of perfectionism with a mental health professional can be helpful for managing these tendencies and finding more balance and satisfaction in life.
What Does an Assignment Dream Mean?

Reminder of Responsibilities
One possible way to write in detail about the “Reminder of Responsibilities” aspect of assignment dreams is:
Research suggests that one of the possible meanings of assignment dreams is a reminder of responsibilities that you have in your waking life. These dreams may occur when you feel overwhelmed with tasks or obligations, and your subconscious mind tries to process them during sleep.
To understand this aspect of assignment dreams, you can consider the following points:
- Work or school-related tasks: If you frequently dream about assignments that resemble the ones you have in your work or school environment, it’s possible that your dream symbolizes your diligence and commitment to fulfill your obligations. For example, if you have a deadline approaching for a project, your subconscious mind may create an assignment dream where you are struggling to complete it, or where you excel at it. These dream scenarios may reflect your attitude towards your work or academic responsibilities and how you perceive your performance and progress.
- Personal or household tasks: Assignment dreams don’t have to be limited to work or school contexts. You may dream about house chores, errands, or personal goals that you have set for yourself. These dreams can indicate a sense of duty or accountability that you feel towards yourself, your family, or your community. For instance, if you dream about cleaning your house or doing laundry, it may reflect your desire to maintain order and cleanliness in your life. Similarly, if you dream about exercising or dieting, it may signify your efforts to improve your health and well-being.
- Unfulfilled tasks: Another possible interpretation of assignment dreams is that they represent unfulfilled tasks or unmet expectations that you have in your life. These dreams may emerge when you feel dissatisfied with your progress or when you sense that you have missed out on opportunities. For example, if you dream about failing an assignment from the past, it may reflect your regret or disappointment about not doing your best or not achieving your goals. Alternatively, if you dream about getting an assignment that you never received in reality, it may symbolize your desire for new challenges or experiences.
The “Reminder of Responsibilities” aspect of assignment dreams can reveal your sense of duty, diligence, and accountability, as well as your aspirations and regrets. By analyzing your dream scenarios and identifying the tasks or obligations they represent, you can gain insight into your priorities, goals, and challenges, and find ways to improve your productivity, motivation, and satisfaction.
Inadequacy and Fear of Judgement
For some people, an assignment dream might signify a deeper feeling of inadequacy and fear of judgement . These dreams often involve scenarios where the dreamer is being evaluated or graded harshly on their performance.
The fear of judgement can stem from a variety of sources. Perhaps the dreamer had strict or critical parents who were never satisfied with their efforts, leading to a lifetime of feeling like they are never good enough. It could also be a result of societal pressure to constantly achieve and be successful.
Regardless of the cause, this fear of judgement can lead to feelings of anxiety and stress in the waking life. It’s important to address these feelings and find ways to cope with them.
One way to address these feelings is to consider the source of the judgement. Is it coming from an external source, such as a boss or teacher, or is it self-imposed? If it’s an external source, try to understand their expectations and communicate with them about your concerns. If it’s self-imposed, it can be helpful to reframe your thoughts and focus on your achievements and progress.
Another way to cope with these feelings is to seek support from trusted friends or a therapist. Talking about your fears and receiving validation and encouragement can be helpful in combating the negative thoughts and emotions associated with an assignment dream.
Ultimately, it’s important to remember that a single assignment or task does not define your worth as a person. You are capable and deserving of success, regardless of any past failures or setbacks. Taking steps to address your fears and seek support can help turn a negative dream into a positive learning opportunity.
Moving Forward
After understanding the possible meanings of your assignment dream, it’s time to take action and move forward. Here are some steps you can take to deal with your assignment dreams.
Remember that dreams are a natural way for our minds to process our emotions and experiences. While assignment dreams can be overwhelming and stressful, they can also help you identify areas in your life that need improvement. By taking action and moving forward, you can turn your assignment dreams into opportunities for growth and self-improvement.
How to Deal With Your Assignment Dreams
Navigating through assignment dreams can be a daunting task, especially if you’re constantly experiencing them. However, it’s important to remember that these dreams are a manifestation of your emotions and psyche. As such, you shouldn’t ignore them because they could be an indication of a deeper issue. In this section, we’ll explore practical tips on how to deal with your assignment dreams and turn them into a powerful tool for growth and self-awareness.
Recognize Your Emotions
One of the first steps in dealing with assignment dreams is to recognize the emotions you are experiencing. These dreams can evoke a range of feelings such as stress, pressure, or even fear, and it’s important to acknowledge them in order to better understand what your subconscious is trying to tell you.
Below is a table that highlights some of the common emotions that may be associated with an assignment dream and their potential meanings:
By recognizing the emotions present in your assignment dream, you can start to explore the root cause of the dream and what it means for you in your waking life. It’s important to note that these dreams are not necessarily negative, and can serve as powerful messages if we take the time to interpret and understand them.
Find the Root Cause
To effectively address your assignment dreams, you need to identify the root cause of your anxiety. A common culprit is stress and anxiety from your daily life. It could be work-related stress, personal issues or academic pressure. However, there are other deeper reasons why you could be having recurring assignment dreams. An unrealistic need for perfectionism can also lead to such dreams. The need to excel in everything you do can cause you to constantly worry about your performance, leading to dreams of being assigned more tasks than you can handle.
Another reason that could be the cause of your assignment dreams is a fear of failure . Such dreams might signify that you have a deep-seated fear of not succeeding in your personal and professional life. You could be harboring feelings of inadequacy and are concerned about being judged by others. This concern about what others think of you could be taking a toll on your mental health and causing you to have recurrent assignment dreams.
To find the root cause of your assignment dreams, try to identify what triggers them. Start with keeping a dream journal where you document your dreams every night. Note any similarities and patterns that you notice. This could offer you insight into what could be causing your dreams. Also, try to reflect on your waking life and identify any stressors that could be causing your anxiety.
You could also speak to a therapist or counselor who can help you to explore the underlying reasons for your recurring assignment dreams. The therapist can offer you tools and techniques to help you manage your anxiety and stress levels.
Identifying the root cause of your assignment dreams is an essential step towards overcoming them. Once you know what the underlying cause of your anxiety is, you can take practical steps to address it and manage your stress levels effectively.
Take Action
Once you have recognized and identified the root cause of your assignment dreams, it’s time to take action towards resolving the underlying issue. The following table provides some actionable steps you can take to overcome some of the common causes of assignment dreams.
Remember, taking action may require some effort and discomfort, but it’s important for your mental well-being and personal growth. Don’t be afraid to seek support from friends, family, or a mental health professional as needed. With time and effort, you can overcome the underlying issues that lead to assignment dreams and find more peace and confidence in your waking life.
In conclusion, assignment dreams can be quite common and may indicate deeper emotions and stress within us. It is important to recognize and address these emotions and take necessary action to prevent them from affecting our mental health and performance.
By acknowledging the potential causes of these dreams such as stress, fear of failure, and perfectionism, we can better understand our own tendencies and work to overcome them.
If you find yourself experiencing assignment dreams frequently, it may be helpful to speak with a therapist or counselor who can assist in identifying and addressing any underlying issues. Additionally, finding healthy coping mechanisms such as exercise, meditation, or writing can aid in managing stress and anxiety.
Remember that while assignment dreams may be unsettling, they can also serve as a wake-up call to address our emotional and mental health. By taking the steps to understand and manage our emotions, we can move forward with greater confidence and ease.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do assignment dreams occur.
Assignment dreams can occur due to stress, anxiety, fear of failure, or perfectionism.
Are assignment dreams common?
Yes, assignment dreams are common, especially among students and those with demanding jobs.
What do assignment dreams typically involve?
Assignment dreams typically involve a task or deadline that needs to be completed.
Can assignment dreams be beneficial?
Yes, assignment dreams can be beneficial as they serve as reminders of responsibilities and can motivate individuals to take action.
How can I deal with my assignment dreams?
You can deal with your assignment dreams by recognizing your emotions, finding the root cause, and taking action.
What is the meaning behind assignment dreams?
The meaning behind assignment dreams can include a reminder of responsibilities, inadequacy and fear of judgement, and the need to take action to move forward.
Can assignment dreams be a sign of burnout?
Yes, assignment dreams can be a sign of burnout and should be taken as a warning to take a break and practice self-care.
What can I do to prevent assignment dreams?
To prevent assignment dreams, try to manage stress levels, set realistic goals and deadlines, and practice self-care.
Are assignment dreams a sign of procrastination?
Not necessarily. Assignment dreams can occur even when there is no procrastination involved.
Can assignment dreams be a sign of a deeper issue?
Yes, assignment dreams can be a sign of underlying issues such as anxiety, stress, or a fear of failure that may require professional attention.
Related Posts:

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Privacy Overview
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Gender pay gap in U.S. hasn’t changed much in two decades
The gender gap in pay has remained relatively stable in the United States over the past 20 years or so. In 2022, women earned an average of 82% of what men earned, according to a new Pew Research Center analysis of median hourly earnings of both full- and part-time workers. These results are similar to where the pay gap stood in 2002, when women earned 80% as much as men.
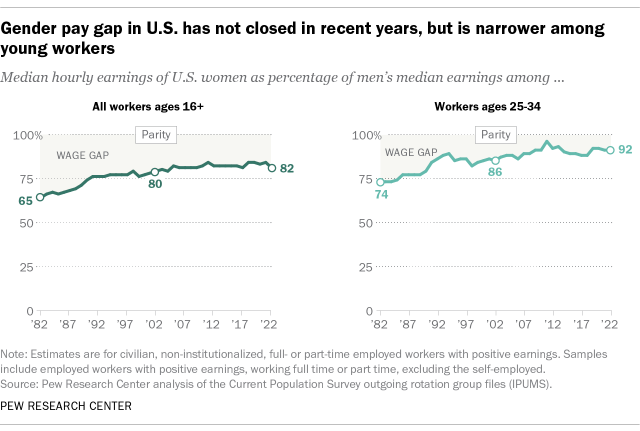
As has long been the case, the wage gap is smaller for workers ages 25 to 34 than for all workers 16 and older. In 2022, women ages 25 to 34 earned an average of 92 cents for every dollar earned by a man in the same age group – an 8-cent gap. By comparison, the gender pay gap among workers of all ages that year was 18 cents.
While the gender pay gap has not changed much in the last two decades, it has narrowed considerably when looking at the longer term, both among all workers ages 16 and older and among those ages 25 to 34. The estimated 18-cent gender pay gap among all workers in 2022 was down from 35 cents in 1982. And the 8-cent gap among workers ages 25 to 34 in 2022 was down from a 26-cent gap four decades earlier.
The gender pay gap measures the difference in median hourly earnings between men and women who work full or part time in the United States. Pew Research Center’s estimate of the pay gap is based on an analysis of Current Population Survey (CPS) monthly outgoing rotation group files ( IPUMS ) from January 1982 to December 2022, combined to create annual files. To understand how we calculate the gender pay gap, read our 2013 post, “How Pew Research Center measured the gender pay gap.”
The COVID-19 outbreak affected data collection efforts by the U.S. government in its surveys, especially in 2020 and 2021, limiting in-person data collection and affecting response rates. It is possible that some measures of economic outcomes and how they vary across demographic groups are affected by these changes in data collection.
In addition to findings about the gender wage gap, this analysis includes information from a Pew Research Center survey about the perceived reasons for the pay gap, as well as the pressures and career goals of U.S. men and women. The survey was conducted among 5,098 adults and includes a subset of questions asked only for 2,048 adults who are employed part time or full time, from Oct. 10-16, 2022. Everyone who took part is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used in this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology .
The U.S. Census Bureau has also analyzed the gender pay gap, though its analysis looks only at full-time workers (as opposed to full- and part-time workers). In 2021, full-time, year-round working women earned 84% of what their male counterparts earned, on average, according to the Census Bureau’s most recent analysis.
Much of the gender pay gap has been explained by measurable factors such as educational attainment, occupational segregation and work experience. The narrowing of the gap over the long term is attributable in large part to gains women have made in each of these dimensions.
Related: The Enduring Grip of the Gender Pay Gap
Even though women have increased their presence in higher-paying jobs traditionally dominated by men, such as professional and managerial positions, women as a whole continue to be overrepresented in lower-paying occupations relative to their share of the workforce. This may contribute to gender differences in pay.
Other factors that are difficult to measure, including gender discrimination, may also contribute to the ongoing wage discrepancy.
Perceived reasons for the gender wage gap
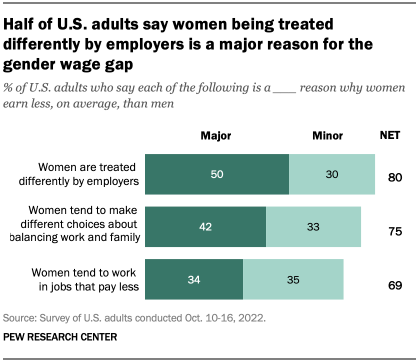
When asked about the factors that may play a role in the gender wage gap, half of U.S. adults point to women being treated differently by employers as a major reason, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted in October 2022. Smaller shares point to women making different choices about how to balance work and family (42%) and working in jobs that pay less (34%).
There are some notable differences between men and women in views of what’s behind the gender wage gap. Women are much more likely than men (61% vs. 37%) to say a major reason for the gap is that employers treat women differently. And while 45% of women say a major factor is that women make different choices about how to balance work and family, men are slightly less likely to hold that view (40% say this).
Parents with children younger than 18 in the household are more likely than those who don’t have young kids at home (48% vs. 40%) to say a major reason for the pay gap is the choices that women make about how to balance family and work. On this question, differences by parental status are evident among both men and women.
Views about reasons for the gender wage gap also differ by party. About two-thirds of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents (68%) say a major factor behind wage differences is that employers treat women differently, but far fewer Republicans and Republican leaners (30%) say the same. Conversely, Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say women’s choices about how to balance family and work (50% vs. 36%) and their tendency to work in jobs that pay less (39% vs. 30%) are major reasons why women earn less than men.
Democratic and Republican women are more likely than their male counterparts in the same party to say a major reason for the gender wage gap is that employers treat women differently. About three-quarters of Democratic women (76%) say this, compared with 59% of Democratic men. And while 43% of Republican women say unequal treatment by employers is a major reason for the gender wage gap, just 18% of GOP men share that view.
Pressures facing working women and men
Family caregiving responsibilities bring different pressures for working women and men, and research has shown that being a mother can reduce women’s earnings , while fatherhood can increase men’s earnings .
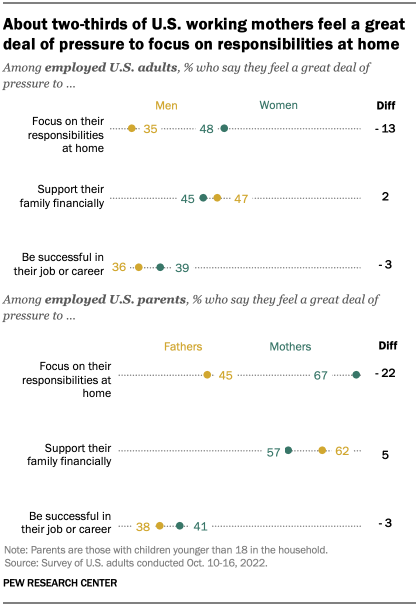
Employed women and men are about equally likely to say they feel a great deal of pressure to support their family financially and to be successful in their jobs and careers, according to the Center’s October survey. But women, and particularly working mothers, are more likely than men to say they feel a great deal of pressure to focus on responsibilities at home.
About half of employed women (48%) report feeling a great deal of pressure to focus on their responsibilities at home, compared with 35% of employed men. Among working mothers with children younger than 18 in the household, two-thirds (67%) say the same, compared with 45% of working dads.
When it comes to supporting their family financially, similar shares of working moms and dads (57% vs. 62%) report they feel a great deal of pressure, but this is driven mainly by the large share of unmarried working mothers who say they feel a great deal of pressure in this regard (77%). Among those who are married, working dads are far more likely than working moms (60% vs. 43%) to say they feel a great deal of pressure to support their family financially. (There were not enough unmarried working fathers in the sample to analyze separately.)
About four-in-ten working parents say they feel a great deal of pressure to be successful at their job or career. These findings don’t differ by gender.
Gender differences in job roles, aspirations
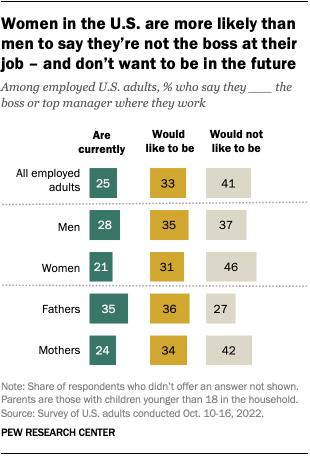
Overall, a quarter of employed U.S. adults say they are currently the boss or one of the top managers where they work, according to the Center’s survey. Another 33% say they are not currently the boss but would like to be in the future, while 41% are not and do not aspire to be the boss or one of the top managers.
Men are more likely than women to be a boss or a top manager where they work (28% vs. 21%). This is especially the case among employed fathers, 35% of whom say they are the boss or one of the top managers where they work. (The varying attitudes between fathers and men without children at least partly reflect differences in marital status and educational attainment between the two groups.)
In addition to being less likely than men to say they are currently the boss or a top manager at work, women are also more likely to say they wouldn’t want to be in this type of position in the future. More than four-in-ten employed women (46%) say this, compared with 37% of men. Similar shares of men (35%) and women (31%) say they are not currently the boss but would like to be one day. These patterns are similar among parents.
Note: This is an update of a post originally published on March 22, 2019. Anna Brown and former Pew Research Center writer/editor Amanda Barroso contributed to an earlier version of this analysis. Here are the questions used in this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology .
What is the gender wage gap in your metropolitan area? Find out with our pay gap calculator
- Gender & Work
- Gender Equality & Discrimination
- Gender Pay Gap
- Gender Roles

Women have gained ground in the nation’s highest-paying occupations, but still lag behind men
Diversity, equity and inclusion in the workplace, the enduring grip of the gender pay gap, more than twice as many americans support than oppose the #metoo movement, women now outnumber men in the u.s. college-educated labor force, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
My job is classified as salaried, nonexempt: What does that mean? Ask HR

Johnny C. Taylor Jr. tackles your human resources questions as part of a series for USA TODAY. Taylor is president and CEO of the Society for Human Resource Management, the world's largest HR professional society and author of "Reset: A Leader’s Guide to Work in an Age of Upheaval.”
Have a question? Submit it here .
Question: My job is classified as ‘salaried, nonexempt.’ Though I’ve seen the term many times before, I’ve never understood what exactly it meant. What does that mean? How does it affect my pay? – Marlene
Most people are either salaried or nonexempt, but some assume you can’t be both. Well, that’s wrong. “Salaried” means you are paid a weekly rate and “nonexempt” means you are still entitled to overtime pay for any hours worked over 40 in a week. So, let’s say you make $52,000 per year (or $1000 per week) and you work 50 hours one week. That week, you would earn a $1000 salary plus $375 overtime pay (10 hours at $37.50 per hour) as both a salaried and nonexempt employee.
These salary, hourly, exempt, and nonexempt classifications are regulated at the federal level. However, some states may have different overtime pay requirements, such as daily overtime calculations.
While the term “nonexempt” is often associated with hourly employees, your employer is not necessarily required to pay you on an hourly basis. Instead, nonexempt employees can receive compensation through various methods, including salary, piece rate, commission, etc., provided their total weekly pay meets the minimum wage requirements and overtime is appropriately compensated for any hours worked beyond 40 in a workweek.
Despite being paid a salary, as a salaried, nonexempt employee, your employer is still obligated to track and record your work hours. If you work overtime, your employer must calculate your regular hourly rate based on your salary and pay you accordingly for all overtime hours worked. This ensures compliance with federal and state labor laws regarding compensation for nonexempt employees.
Again, thanks for asking, and I hope this makes your job designation clearer.
I’m considering putting in for a transfer to another department. What is the best way to inquire about a transfer without burning bridges with my current team and manager? – Dean
Navigating an internal transfer while maintaining positive relationships with your current team and manager requires careful consideration and communication. Here’s how you can approach the process without burning bridges:
- Review company policies: Start by familiarizing yourself with your company's internal transfer policy and process. Ensure that you meet the eligibility requirements for a transfer and carefully assess the qualifications and skills required for the position you’re interested in.
- Initiate a candid discussion: Transparency is vital in this situation. Schedule a meeting with your manager to have an open and honest conversation about your intention to apply for a transfer. Clearly communicate your reasons for seeking the transfer, such as a desire for career growth or a better alignment with your career goals. Emphasize that your decision does not reflect any issues with your current team or manager, but rather a personal career choice.
- Involve human resources: Once you’ve discussed with your manager your intent to transfer, contact your HR department to kickstart the internal transfer process. They can provide guidance on the necessary paperwork and steps to formalize your request.
- Exercise discretion with co-workers: While being transparent with your manager is essential, consider keeping your intention to transfer confidential from your co-workers until your move is confirmed. This can help minimize any disruptions within your team, especially if you’re not ultimately selected for the transfer. However, if you are chosen for the new position, offer your assistance in training your replacement and supporting your team during the transition period.
Following these steps and maintaining open communication allows you to conduct the internal transfer process smoothly while preserving the valued relationships with your current team and manager. Good luck as you pursue this new opportunity!
A Guide to Taylor Swift’s The Tortured Poets Department

What Taylor’s ‘Cassandra’ Lyrics Mean

‘I Can Fix Him (No Really I Can),’ Explained

Taylor Explores Breakup in ‘How Did It End?’

Taylor Asks: ‘Who’s Afraid of Little Old Me?’

What Taylor Swift’s ‘The Black Dog’ Is About

Taylor Swift’s ‘imgonnagetyouback,’ Explained

Read Taylor Swift’s ‘Guilty as Sin?’ Lyrics

'Chloe or Sam or Sophia or Marcus,' Explained

Taylor Sings About Travis on ‘So High School’

How Taylor’s Ex Feels About Her New Album
Where Clara Bow Ends and Taylor Swift Begins
What is Taylor Swift's 'Florida!!!' song about? Here's what Swift said about the Sunshine State
According to Taylor Swift, “Florida!!!” is “one hell of a drug.”
Swift released her highly anticipated album "The Tortured Poets Department" at midnight on Friday, April 19, with some extra special nods to the Sunshine State.
"Welcome to New York," from Taylor's "1989" album might have a run for its money with her new Florida-centric song. The former may be the anthem blasting in the mind of every 20-something girl that moves to New York City, but "Florida!!!" has the makings of a new unofficial Sunshine State anthem.
And fans are theorizing that the song could be about Swift and Joe Alwyn's breakup, which happened while she was touring in Florida on the first leg of her record-breaking "Eras Tour" in 2023.
What do we know about 'The Tortured Poets Department?'
As USA Today's Taylor Swift reporter Bryan West says, the track titles are brutal .
Swift announced the album at the Grammys, when she won her 13th career Grammy for pop album of the year. Post Malone and Florence and The Machine are both featured on the album.
Fans speculated the album is mostly about Swift’s six-year relationship with English actor Joe Alwyn and their breakup. Both stars kept the relationship out of the public eye, but this album gives fans more leverage to guess at what happened between the two.
But there's also songs that are seemingly aimed at other figures in Swift's life, good and bad. From giddy love songs to boyfriend Travis Kelce, to relatable anthems about awful "situationships" aimed at Matty Healy . Even a few songs that seem to throw shade at her long-time adversary Kim Kardashian.
Here's the entire tracklist:
- "Fortnight (feat. Post Malone)"
- "The Tortured Poets Department"
- "My Boy Only Breaks His Favorite Toys"
- "So Long, London"
- "But Daddy I Love Him"
- "Fresh Out the Slammer"
- "Florida!!!" (feat. Florence + The Machine)
- "Guilty as Sin?"
- "Who's Afraid of Little Old Me?"
- "I Can Fix Him (No Really I Can)"
- "I Can Do It With a Broken Heart"
- "The Smallest Man Who Ever Lived"
- "The Alchemy"
- "Clara Bow"
Here are the 15 bonus tracks:
- "The Black Dog"
- "imgonnagetyouback"
- "The Albatross"
- "Chloe or Sam or Sophia or Marcus"
- "How Did It End?"
- "So High School"
- "I Hate It Here"
- "thanK you aIMee"
- "I Look in People’s Windows"
- "The Prophecy"
- "Cassandra"
- "The Bolter"
- "The Manuscript"
Who is 'Florence and the Machine' featuring on 'Florida!!!' track?
Florence Welch is the powerhouse lead vocalist for the English indie rock band "Florence + the Machine." Welch is known for several hits over the past decade, such as 2009's "Dog Days are Over," 2011's "Shake it Out" and 2015's "Sweet Nothings" collaboration with Calvin Harris.
"Florida!!!" is the first time Swift and Welch have collaborated on a song together.
What is Taylor Swift's 'Florida!!!' about?
“Florida!!!” is a pretty grungy, dark song about trying to separate yourself from a bad or painful situation and going to Florida to forget about it. You be the judge of if it’s reflective of the Sunshine State or not.
Swift told iHeart Radio that after getting inspiration from crime shows, she thought of where she'd go if she needed to reinvent herself.
"I think I was coming up with this idea of 'what happens when your life doesn't fit' or 'the choices you've made catch up with you' and you're surrounded by these harsh consequences and judgement," Swift said. "And circumstances did not lead you to where you thought you'd be."
The opening line is “You can beat the heat, if you beat the charges, too. They said I was a cheat, I guess it must be true.”
Building up to the chorus, Swift sings a line that no-doubt has Florida’s tourism industry cooking up ideas:
“Little did you know your home’s really only a town you’re just a guest in. So you work your life away just to pay for a timeshare down in Destin .”
If all of your Swiftie friends are googling "Destin, Florida" and "Timeshares in Destin," now you know why.
In the chorus, Swift and Florence Welch, who is featured on the song, both sing "Florida! Is one hell of a drug. Florida! Can I use you up?"
One of the most instantly iconic lines from the song comes after the chorus, when Taylor sings "I need to forget, so take me to Florida."
Which other song did Taylor Swift mention Florida in?
"Florida!!!" isn't the only song where the state got a shoutout. In the first song on the album, titled "Fortnight," both Swift and Post Malone sing:
"'Nother fortnight lost in America. Move to Florida, buy the car you want . But it won't start up 'til you touch, touch, touch me. Thought of calling ya, but you won't pick up"
Where can I buy 'The Tortured Poets Department?'
You can purchase it on her website . There are several versions of the album available, including a CD, cassette, vinyl and digital album.
These retailers will sell the album:
- Francesca's
- Barnes and Noble
- Local record stores (Record Store Day is tomorrow!)
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Manage Your Subscription
- Give a Gift Subscription
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
- Human Interest
What Is Your Moon Sign? How Your Lunar Sign Affects Your Emotions, According to An Astrologer
Your moon sign plays a big part in your emotional life. Here is what it means, according to astrologer Lisa Stardust
The moon is a captivating celestial object that exerts a powerful influence . Its energy sustains life and fosters connections with nature and others. By regulating the water on our planet, the moon plays a vital role in our existence, as we are mostly made up of water. Consequently, it also impacts us as we interact with others.
Moon (or lunar) signs hold significant importance as not all individuals resonate with their sun sign. For instance, there are many Pisces who are not very imaginative and concentrate more on facts due to their moon sign being in Aquarius which is an air sign focused on truth. Understanding moon signs provides a comprehensive insight into the multifaceted nature of our personalities.
The birth chart provides a glimpse into the astrological conditions during our birth. Our lunar sign, which represents the moon’s position at the time of birth, plays a crucial role in understanding our personality as it reflects our deep emotions and desires. It indicates our tendencies towards nurturing, caring and seeking comfort, as well as our attitudes toward ourselves, others and the world in general.
What is a moon sign?
Among the various components of a birth chart, the moon is one of the most influential as it defines our emotional makeup and reactions to situations. It also reveals how we connect with others and what makes us sentimental. Additionally, the moon represents our relationship with our mothers or other maternal figures in our lives and how we express our feelings towards them. Hence, comprehending the moon’s importance is crucial for anyone intrigued by the cosmos.
How does your moon sign differ from your sun sign?
The is a symbol of our emotions and intuition and it plays a significant role in shaping our experiences and relationships with others. Unlike our sun signs , which represent our egos, our moon signs represent the parts of ourselves that we keep hidden and don't express as openly.
Your lunar sign represents the parts of yourself that you might not express easily — secrets, memories, sense of security, how you connect with people, the things you hold dear, etc. The moon also represents how we heal, so it's vital in moving forward past setbacks.
Not only that, but the moon encompasses a romantic and imaginative nature. It's about how we want to feel within and how we bring that out into the world. However, we often handle these things with care because our feelings can be tender and we don't want to get hurt.
Because the moon sign changes every 2.5 days, it's possible that people who share the same sun sign — which changes every 30 days — have different ways of processing their life experiences.
What does my moon sign mean?
You can find your moon sign by visiting sites such as USA Astrology and Cafe Astrology . Below is a breakdown of what each moon sign means.
With a fire sign moon, those with this lunar placement may experience intense emotional passion and impulsiveness. They tend to be argumentative and competitive with loved ones to make sure they are treated equally. On the bright side, Aries moons are fiercely protective of those they love and will fight diligently to protect others.
When one’s moon falls in the dependable sign Taurus, they will find comfort in indulging in earthly pleasures while also maintaining a sense of stability and security. Similarly, being loyal makes for a dependable friend, lover and partner who’ll always remain faithful and reliable in times of need. Also, creativity allows their talents to shine.
Gemini moons possess a dual nature: On one hand, they tend to speak in circles. And on the other, they find it challenging to put their thoughts into action. Nevertheless, they always strive to convey their emotions to others, especially regarding the way they express their feelings — which always has some wit and playfulness.
Individuals who have a Cancer moon in their birth chart tend to be emotionally intelligent and maternal. Their feelings are private and only shared with those they trust. As the moon’s phases and signs change, so do their emotions, making it difficult to predict their next move and keep up with their ever-changing sentiments.
Leo moons come across as boisterous, proud and a bit dramatic at times. Nevertheless, they have an entertaining personality and are never hesitant to speak their minds or help others. Leo moons have a good sense of humor and tend to approach life with a romantic outlook as long as they’re given respect and some TLC.
Virgo moons over-analyze their emotions, often coming up with solutions in their minds. They have a cerebral approach to life, treating people with fairness, compassion and giving them the benefit of the doubt. However, they are also about reciprocity and Virgo moons need to ensure they receive the same amount of kindness they give to others.
When the moon is in airy Libra, the focus is on creating long-term partnerships. They strive to find a balance and work together with others, even if it means avoiding conflict through passive-aggressive behavior. Despite this, those born under this moon sign are always willing to negotiate and compromise to maintain good relationships with others.
Scorpio moons have a reputation for being intense, due to their tendency to delve deeply into situations and relationships. When they choose to open up to others, they do so with great dedication, but if they’re hurt, they may lash out with their stingers in an attempt to retaliate. Be nice or pay the price!
Sagittarius
The lunar Sagittarius brings a wistful desire for independence and a constant search for excitement. They tend to admire individuals who possess unique qualities that set them apart from the norm. When provoked, they may assert their emotions with harsh language or aggression, but ultimately they strive to progress rather than dwell on the past.
Capricorn moons need to align themselves with others who are just as serious and hard-working as they are for them to feel as though their efforts are paying off. They do not mince words and are serious when expressing how they feel. , are down-to-earth and serious when expressing how they feel. Meaning, they only open their hearts to people they definitely care about.
Individuals with an Aquarius moon tend to be forward-thinking and express their innermost feelings in a unique way. They prefer to be around like-minded individuals and often devote their time to humanitarian causes. However, they may come across as aloof when faced with emotional situations because they have their own distinctive way of expressing themselves.
The Pisces moon is tender, intuitive and imaginative. Sometimes, they like to run away from their emotions and escape. They have so many feelings because they can take on the burdens of others due to their empathetic sentiments. They often use dreams, spirituality and idealism to develop relationships that speak to their loving nature.
Related Articles
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of on assignment in English
On assignment, on assignment | intermediate english, translations of on assignment.
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
have irons in the fire
to be involved with many activities or jobs at the same time or to make certain that there are always several possibilities available

Binding, nailing, and gluing: talking about fastening things together

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Phrase
- Intermediate Idiom
- Translations
- All translations
Add on assignment to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The meaning of ASSIGNMENT is the act of assigning something. How to use assignment in a sentence. Synonym Discussion of Assignment.
What this handout is about. The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms ...
ASSIGNMENT definition: 1. a piece of work given to someone, typically as part of their studies or job: 2. a job that…. Learn more.
14 Understanding Your Assignment Before you begin working on an essay, don't forget to spend some time reading and analyzing the assignment sheet, making note of key words, and asking clarifying questions. ... effectively, and ethically. With that last point, you must ensure you retain the accurate meaning of the subject/source/text and do ...
assignment in American English. (əˈsainmənt) noun. 1. something assigned, as a particular task or duty. She completed the assignment and went on to other jobs. 2. a position of responsibility, post of duty, or the like, to which one is appointed. He left for his assignment in the Middle East.
1 [countable, uncountable] a task or piece of work that someone is given to do, usually as part of their job or studies You will need to complete three written assignments per semester. She is in Greece on an assignment for one of the Sunday newspapers. one of our reporters on assignment in China I had given myself a tough assignment. a business/special assignment
Assignment definition: something assigned, as a particular task or duty. See examples of ASSIGNMENT used in a sentence.
assignment meaning: a piece of work or job that you are given to do: . Learn more.
Understanding the question is the first and most important step when starting your assignments and helps to ensure that your research and writing is more focused and relevant. This means understanding both the individual words, and also the general scope of the question. A common mistake students make with their assignments is to misinterpret ...
How to Read an Assignment. Assignments usually ask you to demonstrate that you have immersed yourself in the course material and that you've done some thinking on your own; questions not treated at length in class often serve as assignments. Fortunately, if you've put the time into getting to know the material, then you've almost certainly ...
assignment: 1 n an undertaking that you have been assigned to do (as by an instructor) Types: show 6 types... hide 6 types... school assignment , schoolwork a school task performed by a student to satisfy the teacher writing assignment , written assignment an assignment to write something classroom project a school task requiring considerable ...
1. : a job or duty that is given to someone : a task someone is required to do. [count] My assignment was to clean the equipment. = They gave me the assignment of cleaning the equipment. The students were given a homework assignment. The reporter's assignment is to interview the candidate. The reporter is here on an assignment.
Definition: Assignment is a task given to students by a teacher or professor, usually as a means of assessing their understanding and application of course material. Assignments can take various forms, including essays, research papers, presentations, problem sets, lab reports, and more. Assignments are typically designed to be completed ...
Work assignments are most common in creative and technical fields of work. For example, writers may need to complete a trial piece before being hired, and marketing professionals may have to create a campaign pitch and outline as part of their interview process. For more technical work, like information technology or computer science, the ...
The assignment prompt: what does "analyze" mean anyway? Often, the handout or other written text explaining the assignment—what professors call the assignment prompt or outline—will explain the purpose of the assignment, the required parameters (length, number and type of sources, referencing style, etc.), and the criteria for evaluation.
When many in the body of Christ think of their God-given assignment, they make the mistake to understand it on a broad level that feels unreachable. As we will unpack today, an assignment is something that God uses to start us on the path of our destiny. After Jesus had risen from the dead, and spent 40 days walking with his disciples, He gave ...
Overall, "Understood the assignment" is a phrase that is used to acknowledge someone's efforts or accomplishments and has become a popular way to express praise or criticism in slang. Saying someone "Understood the assignment" indicates that someone has successfully completed a task or achieved a goal; read more about this slang term here.
ASSIGNMENT meaning: 1. a piece of work given to someone, typically as part of their studies or job: 2. a job that…. Learn more.
First, for many law-related purposes, the temp agency and its client many be considered joint employers. Second, "terminated" in the dictionary-definition sense means "ended." It is neutral in that it does not indicate who the moving party was. However, these days, many people interpret the word "terminated" to mean "fired."
Flirting or expressing interest: In some cases, guys may use "understood the assignment" as a flirty hint or a way to express their interest in someone. It can be a playful way of showing admiration and attraction. Different tone or delivery: While the overall meaning is similar, guys may have a different tone or delivery when using ...
ASSIGNMENT definition: a piece of work or job that you are given to do: . Learn more.
What Does an Assignment Dream Mean? As you wake up from a dream about an assignment, you may feel perplexed and unsure about what it could mean. However, these dreams can hold valuable insights into your subconscious thoughts and emotions. By exploring the possible interpretations of assignment dreams, you can gain a better understanding of ...
I love you, it's ruining my life. I love you, it's ruining my life. I touched you for only a fortnight. I touched you, I touched you. I call you up but you won't pick up. Another fortnight ...
The gender gap in pay has remained relatively stable in the United States over the past 20 years or so. In 2022, women earned an average of 82% of what men earned, according to a new Pew Research Center analysis of median hourly earnings of both full- and part-time workers. These results are similar to where the pay gap stood in 2002, when ...
Well, that's wrong. "Salaried" means you are paid a weekly rate and "nonexempt" means you are still entitled to overtime pay for any hours worked over 40 in a week. So, let's say you ...
I wrote a thousand songs that you find uncool. I built a legacy which you can't undo. But when I count the scars, there's a moment of truth. That there wouldn't be this, if there hadn't ...
What is Taylor Swift's 'Florida!!!' about? "Florida!!!" is a pretty grungy, dark song about trying to separate yourself from a bad or painful situation and going to Florida to forget about it.
Your moon sign plays a big part in your emotional life. Here is what it means, according to astrologer Lisa Stardust Getty The moon is a captivating celestial object that exerts a powerful ...
April 15 is the last call for 2023 federal tax returns for most taxpayers. While many people have already been granted extensions to file, they were not necessarily granted an extension to pay ...
ON ASSIGNMENT meaning: 1. Someone who is on assignment is doing a particular job or piece of work, usually in a particular…. Learn more.