Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top

Scientific Method
Science is an enormously successful human enterprise. The study of scientific method is the attempt to discern the activities by which that success is achieved. Among the activities often identified as characteristic of science are systematic observation and experimentation, inductive and deductive reasoning, and the formation and testing of hypotheses and theories. How these are carried out in detail can vary greatly, but characteristics like these have been looked to as a way of demarcating scientific activity from non-science, where only enterprises which employ some canonical form of scientific method or methods should be considered science (see also the entry on science and pseudo-science ). Others have questioned whether there is anything like a fixed toolkit of methods which is common across science and only science. Some reject privileging one view of method as part of rejecting broader views about the nature of science, such as naturalism (Dupré 2004); some reject any restriction in principle (pluralism).
Scientific method should be distinguished from the aims and products of science, such as knowledge, predictions, or control. Methods are the means by which those goals are achieved. Scientific method should also be distinguished from meta-methodology, which includes the values and justifications behind a particular characterization of scientific method (i.e., a methodology) — values such as objectivity, reproducibility, simplicity, or past successes. Methodological rules are proposed to govern method and it is a meta-methodological question whether methods obeying those rules satisfy given values. Finally, method is distinct, to some degree, from the detailed and contextual practices through which methods are implemented. The latter might range over: specific laboratory techniques; mathematical formalisms or other specialized languages used in descriptions and reasoning; technological or other material means; ways of communicating and sharing results, whether with other scientists or with the public at large; or the conventions, habits, enforced customs, and institutional controls over how and what science is carried out.
While it is important to recognize these distinctions, their boundaries are fuzzy. Hence, accounts of method cannot be entirely divorced from their methodological and meta-methodological motivations or justifications, Moreover, each aspect plays a crucial role in identifying methods. Disputes about method have therefore played out at the detail, rule, and meta-rule levels. Changes in beliefs about the certainty or fallibility of scientific knowledge, for instance (which is a meta-methodological consideration of what we can hope for methods to deliver), have meant different emphases on deductive and inductive reasoning, or on the relative importance attached to reasoning over observation (i.e., differences over particular methods.) Beliefs about the role of science in society will affect the place one gives to values in scientific method.
The issue which has shaped debates over scientific method the most in the last half century is the question of how pluralist do we need to be about method? Unificationists continue to hold out for one method essential to science; nihilism is a form of radical pluralism, which considers the effectiveness of any methodological prescription to be so context sensitive as to render it not explanatory on its own. Some middle degree of pluralism regarding the methods embodied in scientific practice seems appropriate. But the details of scientific practice vary with time and place, from institution to institution, across scientists and their subjects of investigation. How significant are the variations for understanding science and its success? How much can method be abstracted from practice? This entry describes some of the attempts to characterize scientific method or methods, as well as arguments for a more context-sensitive approach to methods embedded in actual scientific practices.
1. Overview and organizing themes
2. historical review: aristotle to mill, 3.1 logical constructionism and operationalism, 3.2. h-d as a logic of confirmation, 3.3. popper and falsificationism, 3.4 meta-methodology and the end of method, 4. statistical methods for hypothesis testing, 5.1 creative and exploratory practices.
- 5.2 Computer methods and the ‘new ways’ of doing science
6.1 “The scientific method” in science education and as seen by scientists
6.2 privileged methods and ‘gold standards’, 6.3 scientific method in the court room, 6.4 deviating practices, 7. conclusion, other internet resources, related entries.
This entry could have been given the title Scientific Methods and gone on to fill volumes, or it could have been extremely short, consisting of a brief summary rejection of the idea that there is any such thing as a unique Scientific Method at all. Both unhappy prospects are due to the fact that scientific activity varies so much across disciplines, times, places, and scientists that any account which manages to unify it all will either consist of overwhelming descriptive detail, or trivial generalizations.
The choice of scope for the present entry is more optimistic, taking a cue from the recent movement in philosophy of science toward a greater attention to practice: to what scientists actually do. This “turn to practice” can be seen as the latest form of studies of methods in science, insofar as it represents an attempt at understanding scientific activity, but through accounts that are neither meant to be universal and unified, nor singular and narrowly descriptive. To some extent, different scientists at different times and places can be said to be using the same method even though, in practice, the details are different.
Whether the context in which methods are carried out is relevant, or to what extent, will depend largely on what one takes the aims of science to be and what one’s own aims are. For most of the history of scientific methodology the assumption has been that the most important output of science is knowledge and so the aim of methodology should be to discover those methods by which scientific knowledge is generated.
Science was seen to embody the most successful form of reasoning (but which form?) to the most certain knowledge claims (but how certain?) on the basis of systematically collected evidence (but what counts as evidence, and should the evidence of the senses take precedence, or rational insight?) Section 2 surveys some of the history, pointing to two major themes. One theme is seeking the right balance between observation and reasoning (and the attendant forms of reasoning which employ them); the other is how certain scientific knowledge is or can be.
Section 3 turns to 20 th century debates on scientific method. In the second half of the 20 th century the epistemic privilege of science faced several challenges and many philosophers of science abandoned the reconstruction of the logic of scientific method. Views changed significantly regarding which functions of science ought to be captured and why. For some, the success of science was better identified with social or cultural features. Historical and sociological turns in the philosophy of science were made, with a demand that greater attention be paid to the non-epistemic aspects of science, such as sociological, institutional, material, and political factors. Even outside of those movements there was an increased specialization in the philosophy of science, with more and more focus on specific fields within science. The combined upshot was very few philosophers arguing any longer for a grand unified methodology of science. Sections 3 and 4 surveys the main positions on scientific method in 20 th century philosophy of science, focusing on where they differ in their preference for confirmation or falsification or for waiving the idea of a special scientific method altogether.
In recent decades, attention has primarily been paid to scientific activities traditionally falling under the rubric of method, such as experimental design and general laboratory practice, the use of statistics, the construction and use of models and diagrams, interdisciplinary collaboration, and science communication. Sections 4–6 attempt to construct a map of the current domains of the study of methods in science.
As these sections illustrate, the question of method is still central to the discourse about science. Scientific method remains a topic for education, for science policy, and for scientists. It arises in the public domain where the demarcation or status of science is at issue. Some philosophers have recently returned, therefore, to the question of what it is that makes science a unique cultural product. This entry will close with some of these recent attempts at discerning and encapsulating the activities by which scientific knowledge is achieved.
Attempting a history of scientific method compounds the vast scope of the topic. This section briefly surveys the background to modern methodological debates. What can be called the classical view goes back to antiquity, and represents a point of departure for later divergences. [ 1 ]
We begin with a point made by Laudan (1968) in his historical survey of scientific method:
Perhaps the most serious inhibition to the emergence of the history of theories of scientific method as a respectable area of study has been the tendency to conflate it with the general history of epistemology, thereby assuming that the narrative categories and classificatory pigeon-holes applied to the latter are also basic to the former. (1968: 5)
To see knowledge about the natural world as falling under knowledge more generally is an understandable conflation. Histories of theories of method would naturally employ the same narrative categories and classificatory pigeon holes. An important theme of the history of epistemology, for example, is the unification of knowledge, a theme reflected in the question of the unification of method in science. Those who have identified differences in kinds of knowledge have often likewise identified different methods for achieving that kind of knowledge (see the entry on the unity of science ).
Different views on what is known, how it is known, and what can be known are connected. Plato distinguished the realms of things into the visible and the intelligible ( The Republic , 510a, in Cooper 1997). Only the latter, the Forms, could be objects of knowledge. The intelligible truths could be known with the certainty of geometry and deductive reasoning. What could be observed of the material world, however, was by definition imperfect and deceptive, not ideal. The Platonic way of knowledge therefore emphasized reasoning as a method, downplaying the importance of observation. Aristotle disagreed, locating the Forms in the natural world as the fundamental principles to be discovered through the inquiry into nature ( Metaphysics Z , in Barnes 1984).
Aristotle is recognized as giving the earliest systematic treatise on the nature of scientific inquiry in the western tradition, one which embraced observation and reasoning about the natural world. In the Prior and Posterior Analytics , Aristotle reflects first on the aims and then the methods of inquiry into nature. A number of features can be found which are still considered by most to be essential to science. For Aristotle, empiricism, careful observation (but passive observation, not controlled experiment), is the starting point. The aim is not merely recording of facts, though. For Aristotle, science ( epistêmê ) is a body of properly arranged knowledge or learning—the empirical facts, but also their ordering and display are of crucial importance. The aims of discovery, ordering, and display of facts partly determine the methods required of successful scientific inquiry. Also determinant is the nature of the knowledge being sought, and the explanatory causes proper to that kind of knowledge (see the discussion of the four causes in the entry on Aristotle on causality ).
In addition to careful observation, then, scientific method requires a logic as a system of reasoning for properly arranging, but also inferring beyond, what is known by observation. Methods of reasoning may include induction, prediction, or analogy, among others. Aristotle’s system (along with his catalogue of fallacious reasoning) was collected under the title the Organon . This title would be echoed in later works on scientific reasoning, such as Novum Organon by Francis Bacon, and Novum Organon Restorum by William Whewell (see below). In Aristotle’s Organon reasoning is divided primarily into two forms, a rough division which persists into modern times. The division, known most commonly today as deductive versus inductive method, appears in other eras and methodologies as analysis/synthesis, non-ampliative/ampliative, or even confirmation/verification. The basic idea is there are two “directions” to proceed in our methods of inquiry: one away from what is observed, to the more fundamental, general, and encompassing principles; the other, from the fundamental and general to instances or implications of principles.
The basic aim and method of inquiry identified here can be seen as a theme running throughout the next two millennia of reflection on the correct way to seek after knowledge: carefully observe nature and then seek rules or principles which explain or predict its operation. The Aristotelian corpus provided the framework for a commentary tradition on scientific method independent of science itself (cosmos versus physics.) During the medieval period, figures such as Albertus Magnus (1206–1280), Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274), Robert Grosseteste (1175–1253), Roger Bacon (1214/1220–1292), William of Ockham (1287–1347), Andreas Vesalius (1514–1546), Giacomo Zabarella (1533–1589) all worked to clarify the kind of knowledge obtainable by observation and induction, the source of justification of induction, and best rules for its application. [ 2 ] Many of their contributions we now think of as essential to science (see also Laudan 1968). As Aristotle and Plato had employed a framework of reasoning either “to the forms” or “away from the forms”, medieval thinkers employed directions away from the phenomena or back to the phenomena. In analysis, a phenomena was examined to discover its basic explanatory principles; in synthesis, explanations of a phenomena were constructed from first principles.
During the Scientific Revolution these various strands of argument, experiment, and reason were forged into a dominant epistemic authority. The 16 th –18 th centuries were a period of not only dramatic advance in knowledge about the operation of the natural world—advances in mechanical, medical, biological, political, economic explanations—but also of self-awareness of the revolutionary changes taking place, and intense reflection on the source and legitimation of the method by which the advances were made. The struggle to establish the new authority included methodological moves. The Book of Nature, according to the metaphor of Galileo Galilei (1564–1642) or Francis Bacon (1561–1626), was written in the language of mathematics, of geometry and number. This motivated an emphasis on mathematical description and mechanical explanation as important aspects of scientific method. Through figures such as Henry More and Ralph Cudworth, a neo-Platonic emphasis on the importance of metaphysical reflection on nature behind appearances, particularly regarding the spiritual as a complement to the purely mechanical, remained an important methodological thread of the Scientific Revolution (see the entries on Cambridge platonists ; Boyle ; Henry More ; Galileo ).
In Novum Organum (1620), Bacon was critical of the Aristotelian method for leaping from particulars to universals too quickly. The syllogistic form of reasoning readily mixed those two types of propositions. Bacon aimed at the invention of new arts, principles, and directions. His method would be grounded in methodical collection of observations, coupled with correction of our senses (and particularly, directions for the avoidance of the Idols, as he called them, kinds of systematic errors to which naïve observers are prone.) The community of scientists could then climb, by a careful, gradual and unbroken ascent, to reliable general claims.
Bacon’s method has been criticized as impractical and too inflexible for the practicing scientist. Whewell would later criticize Bacon in his System of Logic for paying too little attention to the practices of scientists. It is hard to find convincing examples of Bacon’s method being put in to practice in the history of science, but there are a few who have been held up as real examples of 16 th century scientific, inductive method, even if not in the rigid Baconian mold: figures such as Robert Boyle (1627–1691) and William Harvey (1578–1657) (see the entry on Bacon ).
It is to Isaac Newton (1642–1727), however, that historians of science and methodologists have paid greatest attention. Given the enormous success of his Principia Mathematica and Opticks , this is understandable. The study of Newton’s method has had two main thrusts: the implicit method of the experiments and reasoning presented in the Opticks, and the explicit methodological rules given as the Rules for Philosophising (the Regulae) in Book III of the Principia . [ 3 ] Newton’s law of gravitation, the linchpin of his new cosmology, broke with explanatory conventions of natural philosophy, first for apparently proposing action at a distance, but more generally for not providing “true”, physical causes. The argument for his System of the World ( Principia , Book III) was based on phenomena, not reasoned first principles. This was viewed (mainly on the continent) as insufficient for proper natural philosophy. The Regulae counter this objection, re-defining the aims of natural philosophy by re-defining the method natural philosophers should follow. (See the entry on Newton’s philosophy .)
To his list of methodological prescriptions should be added Newton’s famous phrase “ hypotheses non fingo ” (commonly translated as “I frame no hypotheses”.) The scientist was not to invent systems but infer explanations from observations, as Bacon had advocated. This would come to be known as inductivism. In the century after Newton, significant clarifications of the Newtonian method were made. Colin Maclaurin (1698–1746), for instance, reconstructed the essential structure of the method as having complementary analysis and synthesis phases, one proceeding away from the phenomena in generalization, the other from the general propositions to derive explanations of new phenomena. Denis Diderot (1713–1784) and editors of the Encyclopédie did much to consolidate and popularize Newtonianism, as did Francesco Algarotti (1721–1764). The emphasis was often the same, as much on the character of the scientist as on their process, a character which is still commonly assumed. The scientist is humble in the face of nature, not beholden to dogma, obeys only his eyes, and follows the truth wherever it leads. It was certainly Voltaire (1694–1778) and du Chatelet (1706–1749) who were most influential in propagating the latter vision of the scientist and their craft, with Newton as hero. Scientific method became a revolutionary force of the Enlightenment. (See also the entries on Newton , Leibniz , Descartes , Boyle , Hume , enlightenment , as well as Shank 2008 for a historical overview.)
Not all 18 th century reflections on scientific method were so celebratory. Famous also are George Berkeley’s (1685–1753) attack on the mathematics of the new science, as well as the over-emphasis of Newtonians on observation; and David Hume’s (1711–1776) undermining of the warrant offered for scientific claims by inductive justification (see the entries on: George Berkeley ; David Hume ; Hume’s Newtonianism and Anti-Newtonianism ). Hume’s problem of induction motivated Immanuel Kant (1724–1804) to seek new foundations for empirical method, though as an epistemic reconstruction, not as any set of practical guidelines for scientists. Both Hume and Kant influenced the methodological reflections of the next century, such as the debate between Mill and Whewell over the certainty of inductive inferences in science.
The debate between John Stuart Mill (1806–1873) and William Whewell (1794–1866) has become the canonical methodological debate of the 19 th century. Although often characterized as a debate between inductivism and hypothetico-deductivism, the role of the two methods on each side is actually more complex. On the hypothetico-deductive account, scientists work to come up with hypotheses from which true observational consequences can be deduced—hence, hypothetico-deductive. Because Whewell emphasizes both hypotheses and deduction in his account of method, he can be seen as a convenient foil to the inductivism of Mill. However, equally if not more important to Whewell’s portrayal of scientific method is what he calls the “fundamental antithesis”. Knowledge is a product of the objective (what we see in the world around us) and subjective (the contributions of our mind to how we perceive and understand what we experience, which he called the Fundamental Ideas). Both elements are essential according to Whewell, and he was therefore critical of Kant for too much focus on the subjective, and John Locke (1632–1704) and Mill for too much focus on the senses. Whewell’s fundamental ideas can be discipline relative. An idea can be fundamental even if it is necessary for knowledge only within a given scientific discipline (e.g., chemical affinity for chemistry). This distinguishes fundamental ideas from the forms and categories of intuition of Kant. (See the entry on Whewell .)
Clarifying fundamental ideas would therefore be an essential part of scientific method and scientific progress. Whewell called this process “Discoverer’s Induction”. It was induction, following Bacon or Newton, but Whewell sought to revive Bacon’s account by emphasising the role of ideas in the clear and careful formulation of inductive hypotheses. Whewell’s induction is not merely the collecting of objective facts. The subjective plays a role through what Whewell calls the Colligation of Facts, a creative act of the scientist, the invention of a theory. A theory is then confirmed by testing, where more facts are brought under the theory, called the Consilience of Inductions. Whewell felt that this was the method by which the true laws of nature could be discovered: clarification of fundamental concepts, clever invention of explanations, and careful testing. Mill, in his critique of Whewell, and others who have cast Whewell as a fore-runner of the hypothetico-deductivist view, seem to have under-estimated the importance of this discovery phase in Whewell’s understanding of method (Snyder 1997a,b, 1999). Down-playing the discovery phase would come to characterize methodology of the early 20 th century (see section 3 ).
Mill, in his System of Logic , put forward a narrower view of induction as the essence of scientific method. For Mill, induction is the search first for regularities among events. Among those regularities, some will continue to hold for further observations, eventually gaining the status of laws. One can also look for regularities among the laws discovered in a domain, i.e., for a law of laws. Which “law law” will hold is time and discipline dependent and open to revision. One example is the Law of Universal Causation, and Mill put forward specific methods for identifying causes—now commonly known as Mill’s methods. These five methods look for circumstances which are common among the phenomena of interest, those which are absent when the phenomena are, or those for which both vary together. Mill’s methods are still seen as capturing basic intuitions about experimental methods for finding the relevant explanatory factors ( System of Logic (1843), see Mill entry). The methods advocated by Whewell and Mill, in the end, look similar. Both involve inductive generalization to covering laws. They differ dramatically, however, with respect to the necessity of the knowledge arrived at; that is, at the meta-methodological level (see the entries on Whewell and Mill entries).
3. Logic of method and critical responses
The quantum and relativistic revolutions in physics in the early 20 th century had a profound effect on methodology. Conceptual foundations of both theories were taken to show the defeasibility of even the most seemingly secure intuitions about space, time and bodies. Certainty of knowledge about the natural world was therefore recognized as unattainable. Instead a renewed empiricism was sought which rendered science fallible but still rationally justifiable.
Analyses of the reasoning of scientists emerged, according to which the aspects of scientific method which were of primary importance were the means of testing and confirming of theories. A distinction in methodology was made between the contexts of discovery and justification. The distinction could be used as a wedge between the particularities of where and how theories or hypotheses are arrived at, on the one hand, and the underlying reasoning scientists use (whether or not they are aware of it) when assessing theories and judging their adequacy on the basis of the available evidence. By and large, for most of the 20 th century, philosophy of science focused on the second context, although philosophers differed on whether to focus on confirmation or refutation as well as on the many details of how confirmation or refutation could or could not be brought about. By the mid-20 th century these attempts at defining the method of justification and the context distinction itself came under pressure. During the same period, philosophy of science developed rapidly, and from section 4 this entry will therefore shift from a primarily historical treatment of the scientific method towards a primarily thematic one.
Advances in logic and probability held out promise of the possibility of elaborate reconstructions of scientific theories and empirical method, the best example being Rudolf Carnap’s The Logical Structure of the World (1928). Carnap attempted to show that a scientific theory could be reconstructed as a formal axiomatic system—that is, a logic. That system could refer to the world because some of its basic sentences could be interpreted as observations or operations which one could perform to test them. The rest of the theoretical system, including sentences using theoretical or unobservable terms (like electron or force) would then either be meaningful because they could be reduced to observations, or they had purely logical meanings (called analytic, like mathematical identities). This has been referred to as the verifiability criterion of meaning. According to the criterion, any statement not either analytic or verifiable was strictly meaningless. Although the view was endorsed by Carnap in 1928, he would later come to see it as too restrictive (Carnap 1956). Another familiar version of this idea is operationalism of Percy William Bridgman. In The Logic of Modern Physics (1927) Bridgman asserted that every physical concept could be defined in terms of the operations one would perform to verify the application of that concept. Making good on the operationalisation of a concept even as simple as length, however, can easily become enormously complex (for measuring very small lengths, for instance) or impractical (measuring large distances like light years.)
Carl Hempel’s (1950, 1951) criticisms of the verifiability criterion of meaning had enormous influence. He pointed out that universal generalizations, such as most scientific laws, were not strictly meaningful on the criterion. Verifiability and operationalism both seemed too restrictive to capture standard scientific aims and practice. The tenuous connection between these reconstructions and actual scientific practice was criticized in another way. In both approaches, scientific methods are instead recast in methodological roles. Measurements, for example, were looked to as ways of giving meanings to terms. The aim of the philosopher of science was not to understand the methods per se , but to use them to reconstruct theories, their meanings, and their relation to the world. When scientists perform these operations, however, they will not report that they are doing them to give meaning to terms in a formal axiomatic system. This disconnect between methodology and the details of actual scientific practice would seem to violate the empiricism the Logical Positivists and Bridgman were committed to. The view that methodology should correspond to practice (to some extent) has been called historicism, or intuitionism. We turn to these criticisms and responses in section 3.4 . [ 4 ]
Positivism also had to contend with the recognition that a purely inductivist approach, along the lines of Bacon-Newton-Mill, was untenable. There was no pure observation, for starters. All observation was theory laden. Theory is required to make any observation, therefore not all theory can be derived from observation alone. (See the entry on theory and observation in science .) Even granting an observational basis, Hume had already pointed out that one could not deductively justify inductive conclusions without begging the question by presuming the success of the inductive method. Likewise, positivist attempts at analyzing how a generalization can be confirmed by observations of its instances were subject to a number of criticisms. Goodman (1965) and Hempel (1965) both point to paradoxes inherent in standard accounts of confirmation. Recent attempts at explaining how observations can serve to confirm a scientific theory are discussed in section 4 below.
The standard starting point for a non-inductive analysis of the logic of confirmation is known as the Hypothetico-Deductive (H-D) method. In its simplest form, a sentence of a theory which expresses some hypothesis is confirmed by its true consequences. As noted in section 2 , this method had been advanced by Whewell in the 19 th century, as well as Nicod (1924) and others in the 20 th century. Often, Hempel’s (1966) description of the H-D method, illustrated by the case of Semmelweiss’ inferential procedures in establishing the cause of childbed fever, has been presented as a key account of H-D as well as a foil for criticism of the H-D account of confirmation (see, for example, Lipton’s (2004) discussion of inference to the best explanation; also the entry on confirmation ). Hempel described Semmelsweiss’ procedure as examining various hypotheses explaining the cause of childbed fever. Some hypotheses conflicted with observable facts and could be rejected as false immediately. Others needed to be tested experimentally by deducing which observable events should follow if the hypothesis were true (what Hempel called the test implications of the hypothesis), then conducting an experiment and observing whether or not the test implications occurred. If the experiment showed the test implication to be false, the hypothesis could be rejected. If the experiment showed the test implications to be true, however, this did not prove the hypothesis true. The confirmation of a test implication does not verify a hypothesis, though Hempel did allow that “it provides at least some support, some corroboration or confirmation for it” (Hempel 1966: 8). The degree of this support then depends on the quantity, variety and precision of the supporting evidence.
Another approach that took off from the difficulties with inductive inference was Karl Popper’s critical rationalism or falsificationism (Popper 1959, 1963). Falsification is deductive and similar to H-D in that it involves scientists deducing observational consequences from the hypothesis under test. For Popper, however, the important point was not the degree of confirmation that successful prediction offered to a hypothesis. The crucial thing was the logical asymmetry between confirmation, based on inductive inference, and falsification, which can be based on a deductive inference. (This simple opposition was later questioned, by Lakatos, among others. See the entry on historicist theories of scientific rationality. )
Popper stressed that, regardless of the amount of confirming evidence, we can never be certain that a hypothesis is true without committing the fallacy of affirming the consequent. Instead, Popper introduced the notion of corroboration as a measure for how well a theory or hypothesis has survived previous testing—but without implying that this is also a measure for the probability that it is true.
Popper was also motivated by his doubts about the scientific status of theories like the Marxist theory of history or psycho-analysis, and so wanted to demarcate between science and pseudo-science. Popper saw this as an importantly different distinction than demarcating science from metaphysics. The latter demarcation was the primary concern of many logical empiricists. Popper used the idea of falsification to draw a line instead between pseudo and proper science. Science was science because its method involved subjecting theories to rigorous tests which offered a high probability of failing and thus refuting the theory.
A commitment to the risk of failure was important. Avoiding falsification could be done all too easily. If a consequence of a theory is inconsistent with observations, an exception can be added by introducing auxiliary hypotheses designed explicitly to save the theory, so-called ad hoc modifications. This Popper saw done in pseudo-science where ad hoc theories appeared capable of explaining anything in their field of application. In contrast, science is risky. If observations showed the predictions from a theory to be wrong, the theory would be refuted. Hence, scientific hypotheses must be falsifiable. Not only must there exist some possible observation statement which could falsify the hypothesis or theory, were it observed, (Popper called these the hypothesis’ potential falsifiers) it is crucial to the Popperian scientific method that such falsifications be sincerely attempted on a regular basis.
The more potential falsifiers of a hypothesis, the more falsifiable it would be, and the more the hypothesis claimed. Conversely, hypotheses without falsifiers claimed very little or nothing at all. Originally, Popper thought that this meant the introduction of ad hoc hypotheses only to save a theory should not be countenanced as good scientific method. These would undermine the falsifiabililty of a theory. However, Popper later came to recognize that the introduction of modifications (immunizations, he called them) was often an important part of scientific development. Responding to surprising or apparently falsifying observations often generated important new scientific insights. Popper’s own example was the observed motion of Uranus which originally did not agree with Newtonian predictions. The ad hoc hypothesis of an outer planet explained the disagreement and led to further falsifiable predictions. Popper sought to reconcile the view by blurring the distinction between falsifiable and not falsifiable, and speaking instead of degrees of testability (Popper 1985: 41f.).
From the 1960s on, sustained meta-methodological criticism emerged that drove philosophical focus away from scientific method. A brief look at those criticisms follows, with recommendations for further reading at the end of the entry.
Thomas Kuhn’s The Structure of Scientific Revolutions (1962) begins with a well-known shot across the bow for philosophers of science:
History, if viewed as a repository for more than anecdote or chronology, could produce a decisive transformation in the image of science by which we are now possessed. (1962: 1)
The image Kuhn thought needed transforming was the a-historical, rational reconstruction sought by many of the Logical Positivists, though Carnap and other positivists were actually quite sympathetic to Kuhn’s views. (See the entry on the Vienna Circle .) Kuhn shares with other of his contemporaries, such as Feyerabend and Lakatos, a commitment to a more empirical approach to philosophy of science. Namely, the history of science provides important data, and necessary checks, for philosophy of science, including any theory of scientific method.
The history of science reveals, according to Kuhn, that scientific development occurs in alternating phases. During normal science, the members of the scientific community adhere to the paradigm in place. Their commitment to the paradigm means a commitment to the puzzles to be solved and the acceptable ways of solving them. Confidence in the paradigm remains so long as steady progress is made in solving the shared puzzles. Method in this normal phase operates within a disciplinary matrix (Kuhn’s later concept of a paradigm) which includes standards for problem solving, and defines the range of problems to which the method should be applied. An important part of a disciplinary matrix is the set of values which provide the norms and aims for scientific method. The main values that Kuhn identifies are prediction, problem solving, simplicity, consistency, and plausibility.
An important by-product of normal science is the accumulation of puzzles which cannot be solved with resources of the current paradigm. Once accumulation of these anomalies has reached some critical mass, it can trigger a communal shift to a new paradigm and a new phase of normal science. Importantly, the values that provide the norms and aims for scientific method may have transformed in the meantime. Method may therefore be relative to discipline, time or place
Feyerabend also identified the aims of science as progress, but argued that any methodological prescription would only stifle that progress (Feyerabend 1988). His arguments are grounded in re-examining accepted “myths” about the history of science. Heroes of science, like Galileo, are shown to be just as reliant on rhetoric and persuasion as they are on reason and demonstration. Others, like Aristotle, are shown to be far more reasonable and far-reaching in their outlooks then they are given credit for. As a consequence, the only rule that could provide what he took to be sufficient freedom was the vacuous “anything goes”. More generally, even the methodological restriction that science is the best way to pursue knowledge, and to increase knowledge, is too restrictive. Feyerabend suggested instead that science might, in fact, be a threat to a free society, because it and its myth had become so dominant (Feyerabend 1978).
An even more fundamental kind of criticism was offered by several sociologists of science from the 1970s onwards who rejected the methodology of providing philosophical accounts for the rational development of science and sociological accounts of the irrational mistakes. Instead, they adhered to a symmetry thesis on which any causal explanation of how scientific knowledge is established needs to be symmetrical in explaining truth and falsity, rationality and irrationality, success and mistakes, by the same causal factors (see, e.g., Barnes and Bloor 1982, Bloor 1991). Movements in the Sociology of Science, like the Strong Programme, or in the social dimensions and causes of knowledge more generally led to extended and close examination of detailed case studies in contemporary science and its history. (See the entries on the social dimensions of scientific knowledge and social epistemology .) Well-known examinations by Latour and Woolgar (1979/1986), Knorr-Cetina (1981), Pickering (1984), Shapin and Schaffer (1985) seem to bear out that it was social ideologies (on a macro-scale) or individual interactions and circumstances (on a micro-scale) which were the primary causal factors in determining which beliefs gained the status of scientific knowledge. As they saw it therefore, explanatory appeals to scientific method were not empirically grounded.
A late, and largely unexpected, criticism of scientific method came from within science itself. Beginning in the early 2000s, a number of scientists attempting to replicate the results of published experiments could not do so. There may be close conceptual connection between reproducibility and method. For example, if reproducibility means that the same scientific methods ought to produce the same result, and all scientific results ought to be reproducible, then whatever it takes to reproduce a scientific result ought to be called scientific method. Space limits us to the observation that, insofar as reproducibility is a desired outcome of proper scientific method, it is not strictly a part of scientific method. (See the entry on reproducibility of scientific results .)
By the close of the 20 th century the search for the scientific method was flagging. Nola and Sankey (2000b) could introduce their volume on method by remarking that “For some, the whole idea of a theory of scientific method is yester-year’s debate …”.
Despite the many difficulties that philosophers encountered in trying to providing a clear methodology of conformation (or refutation), still important progress has been made on understanding how observation can provide evidence for a given theory. Work in statistics has been crucial for understanding how theories can be tested empirically, and in recent decades a huge literature has developed that attempts to recast confirmation in Bayesian terms. Here these developments can be covered only briefly, and we refer to the entry on confirmation for further details and references.
Statistics has come to play an increasingly important role in the methodology of the experimental sciences from the 19 th century onwards. At that time, statistics and probability theory took on a methodological role as an analysis of inductive inference, and attempts to ground the rationality of induction in the axioms of probability theory have continued throughout the 20 th century and in to the present. Developments in the theory of statistics itself, meanwhile, have had a direct and immense influence on the experimental method, including methods for measuring the uncertainty of observations such as the Method of Least Squares developed by Legendre and Gauss in the early 19 th century, criteria for the rejection of outliers proposed by Peirce by the mid-19 th century, and the significance tests developed by Gosset (a.k.a. “Student”), Fisher, Neyman & Pearson and others in the 1920s and 1930s (see, e.g., Swijtink 1987 for a brief historical overview; and also the entry on C.S. Peirce ).
These developments within statistics then in turn led to a reflective discussion among both statisticians and philosophers of science on how to perceive the process of hypothesis testing: whether it was a rigorous statistical inference that could provide a numerical expression of the degree of confidence in the tested hypothesis, or if it should be seen as a decision between different courses of actions that also involved a value component. This led to a major controversy among Fisher on the one side and Neyman and Pearson on the other (see especially Fisher 1955, Neyman 1956 and Pearson 1955, and for analyses of the controversy, e.g., Howie 2002, Marks 2000, Lenhard 2006). On Fisher’s view, hypothesis testing was a methodology for when to accept or reject a statistical hypothesis, namely that a hypothesis should be rejected by evidence if this evidence would be unlikely relative to other possible outcomes, given the hypothesis were true. In contrast, on Neyman and Pearson’s view, the consequence of error also had to play a role when deciding between hypotheses. Introducing the distinction between the error of rejecting a true hypothesis (type I error) and accepting a false hypothesis (type II error), they argued that it depends on the consequences of the error to decide whether it is more important to avoid rejecting a true hypothesis or accepting a false one. Hence, Fisher aimed for a theory of inductive inference that enabled a numerical expression of confidence in a hypothesis. To him, the important point was the search for truth, not utility. In contrast, the Neyman-Pearson approach provided a strategy of inductive behaviour for deciding between different courses of action. Here, the important point was not whether a hypothesis was true, but whether one should act as if it was.
Similar discussions are found in the philosophical literature. On the one side, Churchman (1948) and Rudner (1953) argued that because scientific hypotheses can never be completely verified, a complete analysis of the methods of scientific inference includes ethical judgments in which the scientists must decide whether the evidence is sufficiently strong or that the probability is sufficiently high to warrant the acceptance of the hypothesis, which again will depend on the importance of making a mistake in accepting or rejecting the hypothesis. Others, such as Jeffrey (1956) and Levi (1960) disagreed and instead defended a value-neutral view of science on which scientists should bracket their attitudes, preferences, temperament, and values when assessing the correctness of their inferences. For more details on this value-free ideal in the philosophy of science and its historical development, see Douglas (2009) and Howard (2003). For a broad set of case studies examining the role of values in science, see e.g. Elliott & Richards 2017.
In recent decades, philosophical discussions of the evaluation of probabilistic hypotheses by statistical inference have largely focused on Bayesianism that understands probability as a measure of a person’s degree of belief in an event, given the available information, and frequentism that instead understands probability as a long-run frequency of a repeatable event. Hence, for Bayesians probabilities refer to a state of knowledge, whereas for frequentists probabilities refer to frequencies of events (see, e.g., Sober 2008, chapter 1 for a detailed introduction to Bayesianism and frequentism as well as to likelihoodism). Bayesianism aims at providing a quantifiable, algorithmic representation of belief revision, where belief revision is a function of prior beliefs (i.e., background knowledge) and incoming evidence. Bayesianism employs a rule based on Bayes’ theorem, a theorem of the probability calculus which relates conditional probabilities. The probability that a particular hypothesis is true is interpreted as a degree of belief, or credence, of the scientist. There will also be a probability and a degree of belief that a hypothesis will be true conditional on a piece of evidence (an observation, say) being true. Bayesianism proscribes that it is rational for the scientist to update their belief in the hypothesis to that conditional probability should it turn out that the evidence is, in fact, observed (see, e.g., Sprenger & Hartmann 2019 for a comprehensive treatment of Bayesian philosophy of science). Originating in the work of Neyman and Person, frequentism aims at providing the tools for reducing long-run error rates, such as the error-statistical approach developed by Mayo (1996) that focuses on how experimenters can avoid both type I and type II errors by building up a repertoire of procedures that detect errors if and only if they are present. Both Bayesianism and frequentism have developed over time, they are interpreted in different ways by its various proponents, and their relations to previous criticism to attempts at defining scientific method are seen differently by proponents and critics. The literature, surveys, reviews and criticism in this area are vast and the reader is referred to the entries on Bayesian epistemology and confirmation .
5. Method in Practice
Attention to scientific practice, as we have seen, is not itself new. However, the turn to practice in the philosophy of science of late can be seen as a correction to the pessimism with respect to method in philosophy of science in later parts of the 20 th century, and as an attempted reconciliation between sociological and rationalist explanations of scientific knowledge. Much of this work sees method as detailed and context specific problem-solving procedures, and methodological analyses to be at the same time descriptive, critical and advisory (see Nickles 1987 for an exposition of this view). The following section contains a survey of some of the practice focuses. In this section we turn fully to topics rather than chronology.
A problem with the distinction between the contexts of discovery and justification that figured so prominently in philosophy of science in the first half of the 20 th century (see section 2 ) is that no such distinction can be clearly seen in scientific activity (see Arabatzis 2006). Thus, in recent decades, it has been recognized that study of conceptual innovation and change should not be confined to psychology and sociology of science, but are also important aspects of scientific practice which philosophy of science should address (see also the entry on scientific discovery ). Looking for the practices that drive conceptual innovation has led philosophers to examine both the reasoning practices of scientists and the wide realm of experimental practices that are not directed narrowly at testing hypotheses, that is, exploratory experimentation.
Examining the reasoning practices of historical and contemporary scientists, Nersessian (2008) has argued that new scientific concepts are constructed as solutions to specific problems by systematic reasoning, and that of analogy, visual representation and thought-experimentation are among the important reasoning practices employed. These ubiquitous forms of reasoning are reliable—but also fallible—methods of conceptual development and change. On her account, model-based reasoning consists of cycles of construction, simulation, evaluation and adaption of models that serve as interim interpretations of the target problem to be solved. Often, this process will lead to modifications or extensions, and a new cycle of simulation and evaluation. However, Nersessian also emphasizes that
creative model-based reasoning cannot be applied as a simple recipe, is not always productive of solutions, and even its most exemplary usages can lead to incorrect solutions. (Nersessian 2008: 11)
Thus, while on the one hand she agrees with many previous philosophers that there is no logic of discovery, discoveries can derive from reasoned processes, such that a large and integral part of scientific practice is
the creation of concepts through which to comprehend, structure, and communicate about physical phenomena …. (Nersessian 1987: 11)
Similarly, work on heuristics for discovery and theory construction by scholars such as Darden (1991) and Bechtel & Richardson (1993) present science as problem solving and investigate scientific problem solving as a special case of problem-solving in general. Drawing largely on cases from the biological sciences, much of their focus has been on reasoning strategies for the generation, evaluation, and revision of mechanistic explanations of complex systems.
Addressing another aspect of the context distinction, namely the traditional view that the primary role of experiments is to test theoretical hypotheses according to the H-D model, other philosophers of science have argued for additional roles that experiments can play. The notion of exploratory experimentation was introduced to describe experiments driven by the desire to obtain empirical regularities and to develop concepts and classifications in which these regularities can be described (Steinle 1997, 2002; Burian 1997; Waters 2007)). However the difference between theory driven experimentation and exploratory experimentation should not be seen as a sharp distinction. Theory driven experiments are not always directed at testing hypothesis, but may also be directed at various kinds of fact-gathering, such as determining numerical parameters. Vice versa , exploratory experiments are usually informed by theory in various ways and are therefore not theory-free. Instead, in exploratory experiments phenomena are investigated without first limiting the possible outcomes of the experiment on the basis of extant theory about the phenomena.
The development of high throughput instrumentation in molecular biology and neighbouring fields has given rise to a special type of exploratory experimentation that collects and analyses very large amounts of data, and these new ‘omics’ disciplines are often said to represent a break with the ideal of hypothesis-driven science (Burian 2007; Elliott 2007; Waters 2007; O’Malley 2007) and instead described as data-driven research (Leonelli 2012; Strasser 2012) or as a special kind of “convenience experimentation” in which many experiments are done simply because they are extraordinarily convenient to perform (Krohs 2012).
5.2 Computer methods and ‘new ways’ of doing science
The field of omics just described is possible because of the ability of computers to process, in a reasonable amount of time, the huge quantities of data required. Computers allow for more elaborate experimentation (higher speed, better filtering, more variables, sophisticated coordination and control), but also, through modelling and simulations, might constitute a form of experimentation themselves. Here, too, we can pose a version of the general question of method versus practice: does the practice of using computers fundamentally change scientific method, or merely provide a more efficient means of implementing standard methods?
Because computers can be used to automate measurements, quantifications, calculations, and statistical analyses where, for practical reasons, these operations cannot be otherwise carried out, many of the steps involved in reaching a conclusion on the basis of an experiment are now made inside a “black box”, without the direct involvement or awareness of a human. This has epistemological implications, regarding what we can know, and how we can know it. To have confidence in the results, computer methods are therefore subjected to tests of verification and validation.
The distinction between verification and validation is easiest to characterize in the case of computer simulations. In a typical computer simulation scenario computers are used to numerically integrate differential equations for which no analytic solution is available. The equations are part of the model the scientist uses to represent a phenomenon or system under investigation. Verifying a computer simulation means checking that the equations of the model are being correctly approximated. Validating a simulation means checking that the equations of the model are adequate for the inferences one wants to make on the basis of that model.
A number of issues related to computer simulations have been raised. The identification of validity and verification as the testing methods has been criticized. Oreskes et al. (1994) raise concerns that “validiation”, because it suggests deductive inference, might lead to over-confidence in the results of simulations. The distinction itself is probably too clean, since actual practice in the testing of simulations mixes and moves back and forth between the two (Weissart 1997; Parker 2008a; Winsberg 2010). Computer simulations do seem to have a non-inductive character, given that the principles by which they operate are built in by the programmers, and any results of the simulation follow from those in-built principles in such a way that those results could, in principle, be deduced from the program code and its inputs. The status of simulations as experiments has therefore been examined (Kaufmann and Smarr 1993; Humphreys 1995; Hughes 1999; Norton and Suppe 2001). This literature considers the epistemology of these experiments: what we can learn by simulation, and also the kinds of justifications which can be given in applying that knowledge to the “real” world. (Mayo 1996; Parker 2008b). As pointed out, part of the advantage of computer simulation derives from the fact that huge numbers of calculations can be carried out without requiring direct observation by the experimenter/simulator. At the same time, many of these calculations are approximations to the calculations which would be performed first-hand in an ideal situation. Both factors introduce uncertainties into the inferences drawn from what is observed in the simulation.
For many of the reasons described above, computer simulations do not seem to belong clearly to either the experimental or theoretical domain. Rather, they seem to crucially involve aspects of both. This has led some authors, such as Fox Keller (2003: 200) to argue that we ought to consider computer simulation a “qualitatively different way of doing science”. The literature in general tends to follow Kaufmann and Smarr (1993) in referring to computer simulation as a “third way” for scientific methodology (theoretical reasoning and experimental practice are the first two ways.). It should also be noted that the debates around these issues have tended to focus on the form of computer simulation typical in the physical sciences, where models are based on dynamical equations. Other forms of simulation might not have the same problems, or have problems of their own (see the entry on computer simulations in science ).
In recent years, the rapid development of machine learning techniques has prompted some scholars to suggest that the scientific method has become “obsolete” (Anderson 2008, Carrol and Goodstein 2009). This has resulted in an intense debate on the relative merit of data-driven and hypothesis-driven research (for samples, see e.g. Mazzocchi 2015 or Succi and Coveney 2018). For a detailed treatment of this topic, we refer to the entry scientific research and big data .
6. Discourse on scientific method
Despite philosophical disagreements, the idea of the scientific method still figures prominently in contemporary discourse on many different topics, both within science and in society at large. Often, reference to scientific method is used in ways that convey either the legend of a single, universal method characteristic of all science, or grants to a particular method or set of methods privilege as a special ‘gold standard’, often with reference to particular philosophers to vindicate the claims. Discourse on scientific method also typically arises when there is a need to distinguish between science and other activities, or for justifying the special status conveyed to science. In these areas, the philosophical attempts at identifying a set of methods characteristic for scientific endeavors are closely related to the philosophy of science’s classical problem of demarcation (see the entry on science and pseudo-science ) and to the philosophical analysis of the social dimension of scientific knowledge and the role of science in democratic society.
One of the settings in which the legend of a single, universal scientific method has been particularly strong is science education (see, e.g., Bauer 1992; McComas 1996; Wivagg & Allchin 2002). [ 5 ] Often, ‘the scientific method’ is presented in textbooks and educational web pages as a fixed four or five step procedure starting from observations and description of a phenomenon and progressing over formulation of a hypothesis which explains the phenomenon, designing and conducting experiments to test the hypothesis, analyzing the results, and ending with drawing a conclusion. Such references to a universal scientific method can be found in educational material at all levels of science education (Blachowicz 2009), and numerous studies have shown that the idea of a general and universal scientific method often form part of both students’ and teachers’ conception of science (see, e.g., Aikenhead 1987; Osborne et al. 2003). In response, it has been argued that science education need to focus more on teaching about the nature of science, although views have differed on whether this is best done through student-led investigations, contemporary cases, or historical cases (Allchin, Andersen & Nielsen 2014)
Although occasionally phrased with reference to the H-D method, important historical roots of the legend in science education of a single, universal scientific method are the American philosopher and psychologist Dewey’s account of inquiry in How We Think (1910) and the British mathematician Karl Pearson’s account of science in Grammar of Science (1892). On Dewey’s account, inquiry is divided into the five steps of
(i) a felt difficulty, (ii) its location and definition, (iii) suggestion of a possible solution, (iv) development by reasoning of the bearing of the suggestions, (v) further observation and experiment leading to its acceptance or rejection. (Dewey 1910: 72)
Similarly, on Pearson’s account, scientific investigations start with measurement of data and observation of their correction and sequence from which scientific laws can be discovered with the aid of creative imagination. These laws have to be subject to criticism, and their final acceptance will have equal validity for “all normally constituted minds”. Both Dewey’s and Pearson’s accounts should be seen as generalized abstractions of inquiry and not restricted to the realm of science—although both Dewey and Pearson referred to their respective accounts as ‘the scientific method’.
Occasionally, scientists make sweeping statements about a simple and distinct scientific method, as exemplified by Feynman’s simplified version of a conjectures and refutations method presented, for example, in the last of his 1964 Cornell Messenger lectures. [ 6 ] However, just as often scientists have come to the same conclusion as recent philosophy of science that there is not any unique, easily described scientific method. For example, the physicist and Nobel Laureate Weinberg described in the paper “The Methods of Science … And Those By Which We Live” (1995) how
The fact that the standards of scientific success shift with time does not only make the philosophy of science difficult; it also raises problems for the public understanding of science. We do not have a fixed scientific method to rally around and defend. (1995: 8)
Interview studies with scientists on their conception of method shows that scientists often find it hard to figure out whether available evidence confirms their hypothesis, and that there are no direct translations between general ideas about method and specific strategies to guide how research is conducted (Schickore & Hangel 2019, Hangel & Schickore 2017)
Reference to the scientific method has also often been used to argue for the scientific nature or special status of a particular activity. Philosophical positions that argue for a simple and unique scientific method as a criterion of demarcation, such as Popperian falsification, have often attracted practitioners who felt that they had a need to defend their domain of practice. For example, references to conjectures and refutation as the scientific method are abundant in much of the literature on complementary and alternative medicine (CAM)—alongside the competing position that CAM, as an alternative to conventional biomedicine, needs to develop its own methodology different from that of science.
Also within mainstream science, reference to the scientific method is used in arguments regarding the internal hierarchy of disciplines and domains. A frequently seen argument is that research based on the H-D method is superior to research based on induction from observations because in deductive inferences the conclusion follows necessarily from the premises. (See, e.g., Parascandola 1998 for an analysis of how this argument has been made to downgrade epidemiology compared to the laboratory sciences.) Similarly, based on an examination of the practices of major funding institutions such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Biomedical Sciences Research Practices (BBSRC) in the UK, O’Malley et al. (2009) have argued that funding agencies seem to have a tendency to adhere to the view that the primary activity of science is to test hypotheses, while descriptive and exploratory research is seen as merely preparatory activities that are valuable only insofar as they fuel hypothesis-driven research.
In some areas of science, scholarly publications are structured in a way that may convey the impression of a neat and linear process of inquiry from stating a question, devising the methods by which to answer it, collecting the data, to drawing a conclusion from the analysis of data. For example, the codified format of publications in most biomedical journals known as the IMRAD format (Introduction, Method, Results, Analysis, Discussion) is explicitly described by the journal editors as “not an arbitrary publication format but rather a direct reflection of the process of scientific discovery” (see the so-called “Vancouver Recommendations”, ICMJE 2013: 11). However, scientific publications do not in general reflect the process by which the reported scientific results were produced. For example, under the provocative title “Is the scientific paper a fraud?”, Medawar argued that scientific papers generally misrepresent how the results have been produced (Medawar 1963/1996). Similar views have been advanced by philosophers, historians and sociologists of science (Gilbert 1976; Holmes 1987; Knorr-Cetina 1981; Schickore 2008; Suppe 1998) who have argued that scientists’ experimental practices are messy and often do not follow any recognizable pattern. Publications of research results, they argue, are retrospective reconstructions of these activities that often do not preserve the temporal order or the logic of these activities, but are instead often constructed in order to screen off potential criticism (see Schickore 2008 for a review of this work).
Philosophical positions on the scientific method have also made it into the court room, especially in the US where judges have drawn on philosophy of science in deciding when to confer special status to scientific expert testimony. A key case is Daubert vs Merrell Dow Pharmaceuticals (92–102, 509 U.S. 579, 1993). In this case, the Supreme Court argued in its 1993 ruling that trial judges must ensure that expert testimony is reliable, and that in doing this the court must look at the expert’s methodology to determine whether the proffered evidence is actually scientific knowledge. Further, referring to works of Popper and Hempel the court stated that
ordinarily, a key question to be answered in determining whether a theory or technique is scientific knowledge … is whether it can be (and has been) tested. (Justice Blackmun, Daubert v. Merrell Dow Pharmaceuticals; see Other Internet Resources for a link to the opinion)
But as argued by Haack (2005a,b, 2010) and by Foster & Hubner (1999), by equating the question of whether a piece of testimony is reliable with the question whether it is scientific as indicated by a special methodology, the court was producing an inconsistent mixture of Popper’s and Hempel’s philosophies, and this has later led to considerable confusion in subsequent case rulings that drew on the Daubert case (see Haack 2010 for a detailed exposition).
The difficulties around identifying the methods of science are also reflected in the difficulties of identifying scientific misconduct in the form of improper application of the method or methods of science. One of the first and most influential attempts at defining misconduct in science was the US definition from 1989 that defined misconduct as
fabrication, falsification, plagiarism, or other practices that seriously deviate from those that are commonly accepted within the scientific community . (Code of Federal Regulations, part 50, subpart A., August 8, 1989, italics added)
However, the “other practices that seriously deviate” clause was heavily criticized because it could be used to suppress creative or novel science. For example, the National Academy of Science stated in their report Responsible Science (1992) that it
wishes to discourage the possibility that a misconduct complaint could be lodged against scientists based solely on their use of novel or unorthodox research methods. (NAS: 27)
This clause was therefore later removed from the definition. For an entry into the key philosophical literature on conduct in science, see Shamoo & Resnick (2009).
The question of the source of the success of science has been at the core of philosophy since the beginning of modern science. If viewed as a matter of epistemology more generally, scientific method is a part of the entire history of philosophy. Over that time, science and whatever methods its practitioners may employ have changed dramatically. Today, many philosophers have taken up the banners of pluralism or of practice to focus on what are, in effect, fine-grained and contextually limited examinations of scientific method. Others hope to shift perspectives in order to provide a renewed general account of what characterizes the activity we call science.
One such perspective has been offered recently by Hoyningen-Huene (2008, 2013), who argues from the history of philosophy of science that after three lengthy phases of characterizing science by its method, we are now in a phase where the belief in the existence of a positive scientific method has eroded and what has been left to characterize science is only its fallibility. First was a phase from Plato and Aristotle up until the 17 th century where the specificity of scientific knowledge was seen in its absolute certainty established by proof from evident axioms; next was a phase up to the mid-19 th century in which the means to establish the certainty of scientific knowledge had been generalized to include inductive procedures as well. In the third phase, which lasted until the last decades of the 20 th century, it was recognized that empirical knowledge was fallible, but it was still granted a special status due to its distinctive mode of production. But now in the fourth phase, according to Hoyningen-Huene, historical and philosophical studies have shown how “scientific methods with the characteristics as posited in the second and third phase do not exist” (2008: 168) and there is no longer any consensus among philosophers and historians of science about the nature of science. For Hoyningen-Huene, this is too negative a stance, and he therefore urges the question about the nature of science anew. His own answer to this question is that “scientific knowledge differs from other kinds of knowledge, especially everyday knowledge, primarily by being more systematic” (Hoyningen-Huene 2013: 14). Systematicity can have several different dimensions: among them are more systematic descriptions, explanations, predictions, defense of knowledge claims, epistemic connectedness, ideal of completeness, knowledge generation, representation of knowledge and critical discourse. Hence, what characterizes science is the greater care in excluding possible alternative explanations, the more detailed elaboration with respect to data on which predictions are based, the greater care in detecting and eliminating sources of error, the more articulate connections to other pieces of knowledge, etc. On this position, what characterizes science is not that the methods employed are unique to science, but that the methods are more carefully employed.
Another, similar approach has been offered by Haack (2003). She sets off, similar to Hoyningen-Huene, from a dissatisfaction with the recent clash between what she calls Old Deferentialism and New Cynicism. The Old Deferentialist position is that science progressed inductively by accumulating true theories confirmed by empirical evidence or deductively by testing conjectures against basic statements; while the New Cynics position is that science has no epistemic authority and no uniquely rational method and is merely just politics. Haack insists that contrary to the views of the New Cynics, there are objective epistemic standards, and there is something epistemologically special about science, even though the Old Deferentialists pictured this in a wrong way. Instead, she offers a new Critical Commonsensist account on which standards of good, strong, supportive evidence and well-conducted, honest, thorough and imaginative inquiry are not exclusive to the sciences, but the standards by which we judge all inquirers. In this sense, science does not differ in kind from other kinds of inquiry, but it may differ in the degree to which it requires broad and detailed background knowledge and a familiarity with a technical vocabulary that only specialists may possess.
- Aikenhead, G.S., 1987, “High-school graduates’ beliefs about science-technology-society. III. Characteristics and limitations of scientific knowledge”, Science Education , 71(4): 459–487.
- Allchin, D., H.M. Andersen and K. Nielsen, 2014, “Complementary Approaches to Teaching Nature of Science: Integrating Student Inquiry, Historical Cases, and Contemporary Cases in Classroom Practice”, Science Education , 98: 461–486.
- Anderson, C., 2008, “The end of theory: The data deluge makes the scientific method obsolete”, Wired magazine , 16(7): 16–07
- Arabatzis, T., 2006, “On the inextricability of the context of discovery and the context of justification”, in Revisiting Discovery and Justification , J. Schickore and F. Steinle (eds.), Dordrecht: Springer, pp. 215–230.
- Barnes, J. (ed.), 1984, The Complete Works of Aristotle, Vols I and II , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Barnes, B. and D. Bloor, 1982, “Relativism, Rationalism, and the Sociology of Knowledge”, in Rationality and Relativism , M. Hollis and S. Lukes (eds.), Cambridge: MIT Press, pp. 1–20.
- Bauer, H.H., 1992, Scientific Literacy and the Myth of the Scientific Method , Urbana: University of Illinois Press.
- Bechtel, W. and R.C. Richardson, 1993, Discovering complexity , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Berkeley, G., 1734, The Analyst in De Motu and The Analyst: A Modern Edition with Introductions and Commentary , D. Jesseph (trans. and ed.), Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1992.
- Blachowicz, J., 2009, “How science textbooks treat scientific method: A philosopher’s perspective”, The British Journal for the Philosophy of Science , 60(2): 303–344.
- Bloor, D., 1991, Knowledge and Social Imagery , Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2 nd edition.
- Boyle, R., 1682, New experiments physico-mechanical, touching the air , Printed by Miles Flesher for Richard Davis, bookseller in Oxford.
- Bridgman, P.W., 1927, The Logic of Modern Physics , New York: Macmillan.
- –––, 1956, “The Methodological Character of Theoretical Concepts”, in The Foundations of Science and the Concepts of Science and Psychology , Herbert Feigl and Michael Scriven (eds.), Minnesota: University of Minneapolis Press, pp. 38–76.
- Burian, R., 1997, “Exploratory Experimentation and the Role of Histochemical Techniques in the Work of Jean Brachet, 1938–1952”, History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences , 19(1): 27–45.
- –––, 2007, “On microRNA and the need for exploratory experimentation in post-genomic molecular biology”, History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences , 29(3): 285–311.
- Carnap, R., 1928, Der logische Aufbau der Welt , Berlin: Bernary, transl. by R.A. George, The Logical Structure of the World , Berkeley: University of California Press, 1967.
- –––, 1956, “The methodological character of theoretical concepts”, Minnesota studies in the philosophy of science , 1: 38–76.
- Carrol, S., and D. Goodstein, 2009, “Defining the scientific method”, Nature Methods , 6: 237.
- Churchman, C.W., 1948, “Science, Pragmatics, Induction”, Philosophy of Science , 15(3): 249–268.
- Cooper, J. (ed.), 1997, Plato: Complete Works , Indianapolis: Hackett.
- Darden, L., 1991, Theory Change in Science: Strategies from Mendelian Genetics , Oxford: Oxford University Press
- Dewey, J., 1910, How we think , New York: Dover Publications (reprinted 1997).
- Douglas, H., 2009, Science, Policy, and the Value-Free Ideal , Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh Press.
- Dupré, J., 2004, “Miracle of Monism ”, in Naturalism in Question , Mario De Caro and David Macarthur (eds.), Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, pp. 36–58.
- Elliott, K.C., 2007, “Varieties of exploratory experimentation in nanotoxicology”, History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences , 29(3): 311–334.
- Elliott, K. C., and T. Richards (eds.), 2017, Exploring inductive risk: Case studies of values in science , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Falcon, Andrea, 2005, Aristotle and the science of nature: Unity without uniformity , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Feyerabend, P., 1978, Science in a Free Society , London: New Left Books
- –––, 1988, Against Method , London: Verso, 2 nd edition.
- Fisher, R.A., 1955, “Statistical Methods and Scientific Induction”, Journal of The Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological) , 17(1): 69–78.
- Foster, K. and P.W. Huber, 1999, Judging Science. Scientific Knowledge and the Federal Courts , Cambridge: MIT Press.
- Fox Keller, E., 2003, “Models, Simulation, and ‘computer experiments’”, in The Philosophy of Scientific Experimentation , H. Radder (ed.), Pittsburgh: Pittsburgh University Press, 198–215.
- Gilbert, G., 1976, “The transformation of research findings into scientific knowledge”, Social Studies of Science , 6: 281–306.
- Gimbel, S., 2011, Exploring the Scientific Method , Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Goodman, N., 1965, Fact , Fiction, and Forecast , Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill.
- Haack, S., 1995, “Science is neither sacred nor a confidence trick”, Foundations of Science , 1(3): 323–335.
- –––, 2003, Defending science—within reason , Amherst: Prometheus.
- –––, 2005a, “Disentangling Daubert: an epistemological study in theory and practice”, Journal of Philosophy, Science and Law , 5, Haack 2005a available online . doi:10.5840/jpsl2005513
- –––, 2005b, “Trial and error: The Supreme Court’s philosophy of science”, American Journal of Public Health , 95: S66-S73.
- –––, 2010, “Federal Philosophy of Science: A Deconstruction-and a Reconstruction”, NYUJL & Liberty , 5: 394.
- Hangel, N. and J. Schickore, 2017, “Scientists’ conceptions of good research practice”, Perspectives on Science , 25(6): 766–791
- Harper, W.L., 2011, Isaac Newton’s Scientific Method: Turning Data into Evidence about Gravity and Cosmology , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Hempel, C., 1950, “Problems and Changes in the Empiricist Criterion of Meaning”, Revue Internationale de Philosophie , 41(11): 41–63.
- –––, 1951, “The Concept of Cognitive Significance: A Reconsideration”, Proceedings of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences , 80(1): 61–77.
- –––, 1965, Aspects of scientific explanation and other essays in the philosophy of science , New York–London: Free Press.
- –––, 1966, Philosophy of Natural Science , Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
- Holmes, F.L., 1987, “Scientific writing and scientific discovery”, Isis , 78(2): 220–235.
- Howard, D., 2003, “Two left turns make a right: On the curious political career of North American philosophy of science at midcentury”, in Logical Empiricism in North America , G.L. Hardcastle & A.W. Richardson (eds.), Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, pp. 25–93.
- Hoyningen-Huene, P., 2008, “Systematicity: The nature of science”, Philosophia , 36(2): 167–180.
- –––, 2013, Systematicity. The Nature of Science , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Howie, D., 2002, Interpreting probability: Controversies and developments in the early twentieth century , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Hughes, R., 1999, “The Ising Model, Computer Simulation, and Universal Physics”, in Models as Mediators , M. Morgan and M. Morrison (eds.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 97–145
- Hume, D., 1739, A Treatise of Human Nature , D. Fate Norton and M.J. Norton (eds.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2000.
- Humphreys, P., 1995, “Computational science and scientific method”, Minds and Machines , 5(1): 499–512.
- ICMJE, 2013, “Recommendations for the Conduct, Reporting, Editing, and Publication of Scholarly Work in Medical Journals”, International Committee of Medical Journal Editors, available online , accessed August 13 2014
- Jeffrey, R.C., 1956, “Valuation and Acceptance of Scientific Hypotheses”, Philosophy of Science , 23(3): 237–246.
- Kaufmann, W.J., and L.L. Smarr, 1993, Supercomputing and the Transformation of Science , New York: Scientific American Library.
- Knorr-Cetina, K., 1981, The Manufacture of Knowledge , Oxford: Pergamon Press.
- Krohs, U., 2012, “Convenience experimentation”, Studies in History and Philosophy of Biological and BiomedicalSciences , 43: 52–57.
- Kuhn, T.S., 1962, The Structure of Scientific Revolutions , Chicago: University of Chicago Press
- Latour, B. and S. Woolgar, 1986, Laboratory Life: The Construction of Scientific Facts , Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2 nd edition.
- Laudan, L., 1968, “Theories of scientific method from Plato to Mach”, History of Science , 7(1): 1–63.
- Lenhard, J., 2006, “Models and statistical inference: The controversy between Fisher and Neyman-Pearson”, The British Journal for the Philosophy of Science , 57(1): 69–91.
- Leonelli, S., 2012, “Making Sense of Data-Driven Research in the Biological and the Biomedical Sciences”, Studies in the History and Philosophy of the Biological and Biomedical Sciences , 43(1): 1–3.
- Levi, I., 1960, “Must the scientist make value judgments?”, Philosophy of Science , 57(11): 345–357
- Lindley, D., 1991, Theory Change in Science: Strategies from Mendelian Genetics , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Lipton, P., 2004, Inference to the Best Explanation , London: Routledge, 2 nd edition.
- Marks, H.M., 2000, The progress of experiment: science and therapeutic reform in the United States, 1900–1990 , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Mazzochi, F., 2015, “Could Big Data be the end of theory in science?”, EMBO reports , 16: 1250–1255.
- Mayo, D.G., 1996, Error and the Growth of Experimental Knowledge , Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- McComas, W.F., 1996, “Ten myths of science: Reexamining what we think we know about the nature of science”, School Science and Mathematics , 96(1): 10–16.
- Medawar, P.B., 1963/1996, “Is the scientific paper a fraud”, in The Strange Case of the Spotted Mouse and Other Classic Essays on Science , Oxford: Oxford University Press, 33–39.
- Mill, J.S., 1963, Collected Works of John Stuart Mill , J. M. Robson (ed.), Toronto: University of Toronto Press
- NAS, 1992, Responsible Science: Ensuring the integrity of the research process , Washington DC: National Academy Press.
- Nersessian, N.J., 1987, “A cognitive-historical approach to meaning in scientific theories”, in The process of science , N. Nersessian (ed.), Berlin: Springer, pp. 161–177.
- –––, 2008, Creating Scientific Concepts , Cambridge: MIT Press.
- Newton, I., 1726, Philosophiae naturalis Principia Mathematica (3 rd edition), in The Principia: Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy: A New Translation , I.B. Cohen and A. Whitman (trans.), Berkeley: University of California Press, 1999.
- –––, 1704, Opticks or A Treatise of the Reflections, Refractions, Inflections & Colors of Light , New York: Dover Publications, 1952.
- Neyman, J., 1956, “Note on an Article by Sir Ronald Fisher”, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological) , 18: 288–294.
- Nickles, T., 1987, “Methodology, heuristics, and rationality”, in Rational changes in science: Essays on Scientific Reasoning , J.C. Pitt (ed.), Berlin: Springer, pp. 103–132.
- Nicod, J., 1924, Le problème logique de l’induction , Paris: Alcan. (Engl. transl. “The Logical Problem of Induction”, in Foundations of Geometry and Induction , London: Routledge, 2000.)
- Nola, R. and H. Sankey, 2000a, “A selective survey of theories of scientific method”, in Nola and Sankey 2000b: 1–65.
- –––, 2000b, After Popper, Kuhn and Feyerabend. Recent Issues in Theories of Scientific Method , London: Springer.
- –––, 2007, Theories of Scientific Method , Stocksfield: Acumen.
- Norton, S., and F. Suppe, 2001, “Why atmospheric modeling is good science”, in Changing the Atmosphere: Expert Knowledge and Environmental Governance , C. Miller and P. Edwards (eds.), Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 88–133.
- O’Malley, M., 2007, “Exploratory experimentation and scientific practice: Metagenomics and the proteorhodopsin case”, History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences , 29(3): 337–360.
- O’Malley, M., C. Haufe, K. Elliot, and R. Burian, 2009, “Philosophies of Funding”, Cell , 138: 611–615.
- Oreskes, N., K. Shrader-Frechette, and K. Belitz, 1994, “Verification, Validation and Confirmation of Numerical Models in the Earth Sciences”, Science , 263(5147): 641–646.
- Osborne, J., S. Simon, and S. Collins, 2003, “Attitudes towards science: a review of the literature and its implications”, International Journal of Science Education , 25(9): 1049–1079.
- Parascandola, M., 1998, “Epidemiology—2 nd -Rate Science”, Public Health Reports , 113(4): 312–320.
- Parker, W., 2008a, “Franklin, Holmes and the Epistemology of Computer Simulation”, International Studies in the Philosophy of Science , 22(2): 165–83.
- –––, 2008b, “Computer Simulation through an Error-Statistical Lens”, Synthese , 163(3): 371–84.
- Pearson, K. 1892, The Grammar of Science , London: J.M. Dents and Sons, 1951
- Pearson, E.S., 1955, “Statistical Concepts in Their Relation to Reality”, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society , B, 17: 204–207.
- Pickering, A., 1984, Constructing Quarks: A Sociological History of Particle Physics , Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press.
- Popper, K.R., 1959, The Logic of Scientific Discovery , London: Routledge, 2002
- –––, 1963, Conjectures and Refutations , London: Routledge, 2002.
- –––, 1985, Unended Quest: An Intellectual Autobiography , La Salle: Open Court Publishing Co..
- Rudner, R., 1953, “The Scientist Qua Scientist Making Value Judgments”, Philosophy of Science , 20(1): 1–6.
- Rudolph, J.L., 2005, “Epistemology for the masses: The origin of ‘The Scientific Method’ in American Schools”, History of Education Quarterly , 45(3): 341–376
- Schickore, J., 2008, “Doing science, writing science”, Philosophy of Science , 75: 323–343.
- Schickore, J. and N. Hangel, 2019, “‘It might be this, it should be that…’ uncertainty and doubt in day-to-day science practice”, European Journal for Philosophy of Science , 9(2): 31. doi:10.1007/s13194-019-0253-9
- Shamoo, A.E. and D.B. Resnik, 2009, Responsible Conduct of Research , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Shank, J.B., 2008, The Newton Wars and the Beginning of the French Enlightenment , Chicago: The University of Chicago Press.
- Shapin, S. and S. Schaffer, 1985, Leviathan and the air-pump , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Smith, G.E., 2002, “The Methodology of the Principia”, in The Cambridge Companion to Newton , I.B. Cohen and G.E. Smith (eds.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 138–173.
- Snyder, L.J., 1997a, “Discoverers’ Induction”, Philosophy of Science , 64: 580–604.
- –––, 1997b, “The Mill-Whewell Debate: Much Ado About Induction”, Perspectives on Science , 5: 159–198.
- –––, 1999, “Renovating the Novum Organum: Bacon, Whewell and Induction”, Studies in History and Philosophy of Science , 30: 531–557.
- Sober, E., 2008, Evidence and Evolution. The logic behind the science , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
- Sprenger, J. and S. Hartmann, 2019, Bayesian philosophy of science , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Steinle, F., 1997, “Entering New Fields: Exploratory Uses of Experimentation”, Philosophy of Science (Proceedings), 64: S65–S74.
- –––, 2002, “Experiments in History and Philosophy of Science”, Perspectives on Science , 10(4): 408–432.
- Strasser, B.J., 2012, “Data-driven sciences: From wonder cabinets to electronic databases”, Studies in History and Philosophy of Science Part C: Studies in History and Philosophy of Biological and Biomedical Sciences , 43(1): 85–87.
- Succi, S. and P.V. Coveney, 2018, “Big data: the end of the scientific method?”, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A , 377: 20180145. doi:10.1098/rsta.2018.0145
- Suppe, F., 1998, “The Structure of a Scientific Paper”, Philosophy of Science , 65(3): 381–405.
- Swijtink, Z.G., 1987, “The objectification of observation: Measurement and statistical methods in the nineteenth century”, in The probabilistic revolution. Ideas in History, Vol. 1 , L. Kruger (ed.), Cambridge MA: MIT Press, pp. 261–285.
- Waters, C.K., 2007, “The nature and context of exploratory experimentation: An introduction to three case studies of exploratory research”, History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences , 29(3): 275–284.
- Weinberg, S., 1995, “The methods of science… and those by which we live”, Academic Questions , 8(2): 7–13.
- Weissert, T., 1997, The Genesis of Simulation in Dynamics: Pursuing the Fermi-Pasta-Ulam Problem , New York: Springer Verlag.
- William H., 1628, Exercitatio Anatomica de Motu Cordis et Sanguinis in Animalibus , in On the Motion of the Heart and Blood in Animals , R. Willis (trans.), Buffalo: Prometheus Books, 1993.
- Winsberg, E., 2010, Science in the Age of Computer Simulation , Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Wivagg, D. & D. Allchin, 2002, “The Dogma of the Scientific Method”, The American Biology Teacher , 64(9): 645–646
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- Blackmun opinion , in Daubert v. Merrell Dow Pharmaceuticals (92–102), 509 U.S. 579 (1993).
- Scientific Method at philpapers. Darrell Rowbottom (ed.).
- Recent Articles | Scientific Method | The Scientist Magazine
al-Kindi | Albert the Great [= Albertus magnus] | Aquinas, Thomas | Arabic and Islamic Philosophy, disciplines in: natural philosophy and natural science | Arabic and Islamic Philosophy, historical and methodological topics in: Greek sources | Arabic and Islamic Philosophy, historical and methodological topics in: influence of Arabic and Islamic Philosophy on the Latin West | Aristotle | Bacon, Francis | Bacon, Roger | Berkeley, George | biology: experiment in | Boyle, Robert | Cambridge Platonists | confirmation | Descartes, René | Enlightenment | epistemology | epistemology: Bayesian | epistemology: social | Feyerabend, Paul | Galileo Galilei | Grosseteste, Robert | Hempel, Carl | Hume, David | Hume, David: Newtonianism and Anti-Newtonianism | induction: problem of | Kant, Immanuel | Kuhn, Thomas | Leibniz, Gottfried Wilhelm | Locke, John | Mill, John Stuart | More, Henry | Neurath, Otto | Newton, Isaac | Newton, Isaac: philosophy | Ockham [Occam], William | operationalism | Peirce, Charles Sanders | Plato | Popper, Karl | rationality: historicist theories of | Reichenbach, Hans | reproducibility, scientific | Schlick, Moritz | science: and pseudo-science | science: theory and observation in | science: unity of | scientific discovery | scientific knowledge: social dimensions of | simulations in science | skepticism: medieval | space and time: absolute and relational space and motion, post-Newtonian theories | Vienna Circle | Whewell, William | Zabarella, Giacomo
Copyright © 2021 by Brian Hepburn < brian . hepburn @ wichita . edu > Hanne Andersen < hanne . andersen @ ind . ku . dk >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2023 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
What is the Scientific Method: How does it work and why is it important?
The scientific method is a systematic process involving steps like defining questions, forming hypotheses, conducting experiments, and analyzing data. It minimizes biases and enables replicable research, leading to groundbreaking discoveries like Einstein's theory of relativity, penicillin, and the structure of DNA. This ongoing approach promotes reason, evidence, and the pursuit of truth in science.
Updated on November 18, 2023

Beginning in elementary school, we are exposed to the scientific method and taught how to put it into practice. As a tool for learning, it prepares children to think logically and use reasoning when seeking answers to questions.
Rather than jumping to conclusions, the scientific method gives us a recipe for exploring the world through observation and trial and error. We use it regularly, sometimes knowingly in academics or research, and sometimes subconsciously in our daily lives.
In this article we will refresh our memories on the particulars of the scientific method, discussing where it comes from, which elements comprise it, and how it is put into practice. Then, we will consider the importance of the scientific method, who uses it and under what circumstances.
What is the scientific method?
The scientific method is a dynamic process that involves objectively investigating questions through observation and experimentation . Applicable to all scientific disciplines, this systematic approach to answering questions is more accurately described as a flexible set of principles than as a fixed series of steps.
The following representations of the scientific method illustrate how it can be both condensed into broad categories and also expanded to reveal more and more details of the process. These graphics capture the adaptability that makes this concept universally valuable as it is relevant and accessible not only across age groups and educational levels but also within various contexts.

Steps in the scientific method
While the scientific method is versatile in form and function, it encompasses a collection of principles that create a logical progression to the process of problem solving:
- Define a question : Constructing a clear and precise problem statement that identifies the main question or goal of the investigation is the first step. The wording must lend itself to experimentation by posing a question that is both testable and measurable.
- Gather information and resources : Researching the topic in question to find out what is already known and what types of related questions others are asking is the next step in this process. This background information is vital to gaining a full understanding of the subject and in determining the best design for experiments.
- Form a hypothesis : Composing a concise statement that identifies specific variables and potential results, which can then be tested, is a crucial step that must be completed before any experimentation. An imperfection in the composition of a hypothesis can result in weaknesses to the entire design of an experiment.
- Perform the experiments : Testing the hypothesis by performing replicable experiments and collecting resultant data is another fundamental step of the scientific method. By controlling some elements of an experiment while purposely manipulating others, cause and effect relationships are established.
- Analyze the data : Interpreting the experimental process and results by recognizing trends in the data is a necessary step for comprehending its meaning and supporting the conclusions. Drawing inferences through this systematic process lends substantive evidence for either supporting or rejecting the hypothesis.
- Report the results : Sharing the outcomes of an experiment, through an essay, presentation, graphic, or journal article, is often regarded as a final step in this process. Detailing the project's design, methods, and results not only promotes transparency and replicability but also adds to the body of knowledge for future research.
- Retest the hypothesis : Repeating experiments to see if a hypothesis holds up in all cases is a step that is manifested through varying scenarios. Sometimes a researcher immediately checks their own work or replicates it at a future time, or another researcher will repeat the experiments to further test the hypothesis.

Where did the scientific method come from?
Oftentimes, ancient peoples attempted to answer questions about the unknown by:
- Making simple observations
- Discussing the possibilities with others deemed worthy of a debate
- Drawing conclusions based on dominant opinions and preexisting beliefs
For example, take Greek and Roman mythology. Myths were used to explain everything from the seasons and stars to the sun and death itself.
However, as societies began to grow through advancements in agriculture and language, ancient civilizations like Egypt and Babylonia shifted to a more rational analysis for understanding the natural world. They increasingly employed empirical methods of observation and experimentation that would one day evolve into the scientific method .
In the 4th century, Aristotle, considered the Father of Science by many, suggested these elements , which closely resemble the contemporary scientific method, as part of his approach for conducting science:
- Study what others have written about the subject.
- Look for the general consensus about the subject.
- Perform a systematic study of everything even partially related to the topic.

By continuing to emphasize systematic observation and controlled experiments, scholars such as Al-Kindi and Ibn al-Haytham helped expand this concept throughout the Islamic Golden Age .
In his 1620 treatise, Novum Organum , Sir Francis Bacon codified the scientific method, arguing not only that hypotheses must be tested through experiments but also that the results must be replicated to establish a truth. Coming at the height of the Scientific Revolution, this text made the scientific method accessible to European thinkers like Galileo and Isaac Newton who then put the method into practice.
As science modernized in the 19th century, the scientific method became more formalized, leading to significant breakthroughs in fields such as evolution and germ theory. Today, it continues to evolve, underpinning scientific progress in diverse areas like quantum mechanics, genetics, and artificial intelligence.
Why is the scientific method important?
The history of the scientific method illustrates how the concept developed out of a need to find objective answers to scientific questions by overcoming biases based on fear, religion, power, and cultural norms. This still holds true today.
By implementing this standardized approach to conducting experiments, the impacts of researchers’ personal opinions and preconceived notions are minimized. The organized manner of the scientific method prevents these and other mistakes while promoting the replicability and transparency necessary for solid scientific research.
The importance of the scientific method is best observed through its successes, for example:
- “ Albert Einstein stands out among modern physicists as the scientist who not only formulated a theory of revolutionary significance but also had the genius to reflect in a conscious and technical way on the scientific method he was using.” Devising a hypothesis based on the prevailing understanding of Newtonian physics eventually led Einstein to devise the theory of general relativity .
- Howard Florey “Perhaps the most useful lesson which has come out of the work on penicillin has been the demonstration that success in this field depends on the development and coordinated use of technical methods.” After discovering a mold that prevented the growth of Staphylococcus bacteria, Dr. Alexander Flemimg designed experiments to identify and reproduce it in the lab, thus leading to the development of penicillin .
- James D. Watson “Every time you understand something, religion becomes less likely. Only with the discovery of the double helix and the ensuing genetic revolution have we had grounds for thinking that the powers held traditionally to be the exclusive property of the gods might one day be ours. . . .” By using wire models to conceive a structure for DNA, Watson and Crick crafted a hypothesis for testing combinations of amino acids, X-ray diffraction images, and the current research in atomic physics, resulting in the discovery of DNA’s double helix structure .
Final thoughts
As the cases exemplify, the scientific method is never truly completed, but rather started and restarted. It gave these researchers a structured process that was easily replicated, modified, and built upon.
While the scientific method may “end” in one context, it never literally ends. When a hypothesis, design, methods, and experiments are revisited, the scientific method simply picks up where it left off. Each time a researcher builds upon previous knowledge, the scientific method is restored with the pieces of past efforts.
By guiding researchers towards objective results based on transparency and reproducibility, the scientific method acts as a defense against bias, superstition, and preconceived notions. As we embrace the scientific method's enduring principles, we ensure that our quest for knowledge remains firmly rooted in reason, evidence, and the pursuit of truth.

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Scientific Method Steps in Psychology Research
Steps, Uses, and Key Terms
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Verywell / Theresa Chiechi
How do researchers investigate psychological phenomena? They utilize a process known as the scientific method to study different aspects of how people think and behave.
When conducting research, the scientific method steps to follow are:
- Observe what you want to investigate
- Ask a research question and make predictions
- Test the hypothesis and collect data
- Examine the results and draw conclusions
- Report and share the results
This process not only allows scientists to investigate and understand different psychological phenomena but also provides researchers and others a way to share and discuss the results of their studies.
Generally, there are five main steps in the scientific method, although some may break down this process into six or seven steps. An additional step in the process can also include developing new research questions based on your findings.
What Is the Scientific Method?
What is the scientific method and how is it used in psychology?
The scientific method consists of five steps. It is essentially a step-by-step process that researchers can follow to determine if there is some type of relationship between two or more variables.
By knowing the steps of the scientific method, you can better understand the process researchers go through to arrive at conclusions about human behavior.
Scientific Method Steps
While research studies can vary, these are the basic steps that psychologists and scientists use when investigating human behavior.
The following are the scientific method steps:
Step 1. Make an Observation
Before a researcher can begin, they must choose a topic to study. Once an area of interest has been chosen, the researchers must then conduct a thorough review of the existing literature on the subject. This review will provide valuable information about what has already been learned about the topic and what questions remain to be answered.
A literature review might involve looking at a considerable amount of written material from both books and academic journals dating back decades.
The relevant information collected by the researcher will be presented in the introduction section of the final published study results. This background material will also help the researcher with the first major step in conducting a psychology study: formulating a hypothesis.
Step 2. Ask a Question
Once a researcher has observed something and gained some background information on the topic, the next step is to ask a question. The researcher will form a hypothesis, which is an educated guess about the relationship between two or more variables
For example, a researcher might ask a question about the relationship between sleep and academic performance: Do students who get more sleep perform better on tests at school?
In order to formulate a good hypothesis, it is important to think about different questions you might have about a particular topic.
You should also consider how you could investigate the causes. Falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In other words, if a hypothesis was false, there needs to be a way for scientists to demonstrate that it is false.
Step 3. Test Your Hypothesis and Collect Data
Once you have a solid hypothesis, the next step of the scientific method is to put this hunch to the test by collecting data. The exact methods used to investigate a hypothesis depend on exactly what is being studied. There are two basic forms of research that a psychologist might utilize: descriptive research or experimental research.
Descriptive research is typically used when it would be difficult or even impossible to manipulate the variables in question. Examples of descriptive research include case studies, naturalistic observation , and correlation studies. Phone surveys that are often used by marketers are one example of descriptive research.
Correlational studies are quite common in psychology research. While they do not allow researchers to determine cause-and-effect, they do make it possible to spot relationships between different variables and to measure the strength of those relationships.
Experimental research is used to explore cause-and-effect relationships between two or more variables. This type of research involves systematically manipulating an independent variable and then measuring the effect that it has on a defined dependent variable .
One of the major advantages of this method is that it allows researchers to actually determine if changes in one variable actually cause changes in another.
While psychology experiments are often quite complex, a simple experiment is fairly basic but does allow researchers to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. Most simple experiments use a control group (those who do not receive the treatment) and an experimental group (those who do receive the treatment).
Step 4. Examine the Results and Draw Conclusions
Once a researcher has designed the study and collected the data, it is time to examine this information and draw conclusions about what has been found. Using statistics , researchers can summarize the data, analyze the results, and draw conclusions based on this evidence.
So how does a researcher decide what the results of a study mean? Not only can statistical analysis support (or refute) the researcher’s hypothesis; it can also be used to determine if the findings are statistically significant.
When results are said to be statistically significant, it means that it is unlikely that these results are due to chance.
Based on these observations, researchers must then determine what the results mean. In some cases, an experiment will support a hypothesis, but in other cases, it will fail to support the hypothesis.
So what happens if the results of a psychology experiment do not support the researcher's hypothesis? Does this mean that the study was worthless?
Just because the findings fail to support the hypothesis does not mean that the research is not useful or informative. In fact, such research plays an important role in helping scientists develop new questions and hypotheses to explore in the future.
After conclusions have been drawn, the next step is to share the results with the rest of the scientific community. This is an important part of the process because it contributes to the overall knowledge base and can help other scientists find new research avenues to explore.
Step 5. Report the Results
The final step in a psychology study is to report the findings. This is often done by writing up a description of the study and publishing the article in an academic or professional journal. The results of psychological studies can be seen in peer-reviewed journals such as Psychological Bulletin , the Journal of Social Psychology , Developmental Psychology , and many others.
The structure of a journal article follows a specified format that has been outlined by the American Psychological Association (APA) . In these articles, researchers:
- Provide a brief history and background on previous research
- Present their hypothesis
- Identify who participated in the study and how they were selected
- Provide operational definitions for each variable
- Describe the measures and procedures that were used to collect data
- Explain how the information collected was analyzed
- Discuss what the results mean
Why is such a detailed record of a psychological study so important? By clearly explaining the steps and procedures used throughout the study, other researchers can then replicate the results. The editorial process employed by academic and professional journals ensures that each article that is submitted undergoes a thorough peer review, which helps ensure that the study is scientifically sound.
Once published, the study becomes another piece of the existing puzzle of our knowledge base on that topic.
Before you begin exploring the scientific method steps, here's a review of some key terms and definitions that you should be familiar with:
- Falsifiable : The variables can be measured so that if a hypothesis is false, it can be proven false
- Hypothesis : An educated guess about the possible relationship between two or more variables
- Variable : A factor or element that can change in observable and measurable ways
- Operational definition : A full description of exactly how variables are defined, how they will be manipulated, and how they will be measured
Uses for the Scientific Method
The goals of psychological studies are to describe, explain, predict and perhaps influence mental processes or behaviors. In order to do this, psychologists utilize the scientific method to conduct psychological research. The scientific method is a set of principles and procedures that are used by researchers to develop questions, collect data, and reach conclusions.
Goals of Scientific Research in Psychology
Researchers seek not only to describe behaviors and explain why these behaviors occur; they also strive to create research that can be used to predict and even change human behavior.
Psychologists and other social scientists regularly propose explanations for human behavior. On a more informal level, people make judgments about the intentions, motivations , and actions of others on a daily basis.
While the everyday judgments we make about human behavior are subjective and anecdotal, researchers use the scientific method to study psychology in an objective and systematic way. The results of these studies are often reported in popular media, which leads many to wonder just how or why researchers arrived at the conclusions they did.
Examples of the Scientific Method
Now that you're familiar with the scientific method steps, it's useful to see how each step could work with a real-life example.
Say, for instance, that researchers set out to discover what the relationship is between psychotherapy and anxiety .
- Step 1. Make an observation : The researchers choose to focus their study on adults ages 25 to 40 with generalized anxiety disorder.
- Step 2. Ask a question : The question they want to answer in their study is: Do weekly psychotherapy sessions reduce symptoms in adults ages 25 to 40 with generalized anxiety disorder?
- Step 3. Test your hypothesis : Researchers collect data on participants' anxiety symptoms . They work with therapists to create a consistent program that all participants undergo. Group 1 may attend therapy once per week, whereas group 2 does not attend therapy.
- Step 4. Examine the results : Participants record their symptoms and any changes over a period of three months. After this period, people in group 1 report significant improvements in their anxiety symptoms, whereas those in group 2 report no significant changes.
- Step 5. Report the results : Researchers write a report that includes their hypothesis, information on participants, variables, procedure, and conclusions drawn from the study. In this case, they say that "Weekly therapy sessions are shown to reduce anxiety symptoms in adults ages 25 to 40."
Of course, there are many details that go into planning and executing a study such as this. But this general outline gives you an idea of how an idea is formulated and tested, and how researchers arrive at results using the scientific method.
Erol A. How to conduct scientific research ? Noro Psikiyatr Ars . 2017;54(2):97-98. doi:10.5152/npa.2017.0120102
University of Minnesota. Psychologists use the scientific method to guide their research .
Shaughnessy, JJ, Zechmeister, EB, & Zechmeister, JS. Research Methods In Psychology . New York: McGraw Hill Education; 2015.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1: The Scientific Method
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 24832

- Laci M. Gerhart-Barley
- College of Biological Sciences - UC Davis
Biologists, and other scientists, study the world using a formal process referred to as the scientific method . The scientific method was first documented by Sir Francis Bacon (1561–1626) of England, and can be applied to almost all fields of study. The scientific method is founded upon observation, which then leads to a question and the development of a hypothesis which answers that question. The scientist can then design an experiment to test the proposed hypothesis, and makes a prediction for the outcome of the experiment, if the proposed hypothesis is true. In the following sections, we will use a simple example of the scientific method, based on a simple observation of the classroom being too warm.
Proposing a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is one possible answer to the question that arises from observations. In our example, the observation is that the classroom is too warm, and the question taht arises from that observation is why the classroom is too warm. One (of many) hypotheses is “The classroom is warm because no one turned on the air conditioning.” Another hypothesis could be “The classroom is warm because the heating is set too high."
Once a hypothesis has been developed, the scientist then makes a prediction, which is similar to a hypothesis, but generally follows the format of “If . . . then . . . .” In our example, a prediction arising from the first hypothesis might be, “ If the air-conditioning is turned on, then the classroom will no longer be too warm.” The initial steps of the scientific method (observation to prediction) are outlined in Figure 1.1.1.
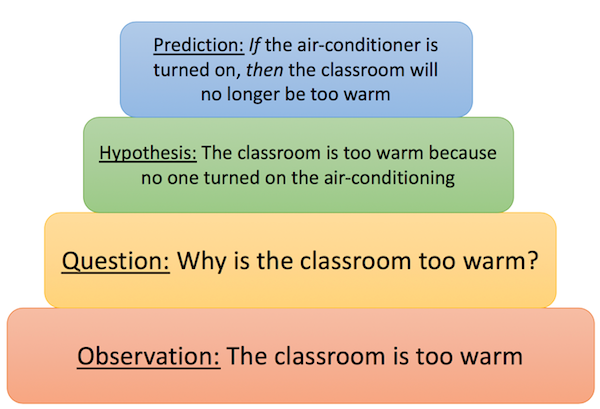
Testing a Hypothesis
A valid hypothesis must be testable. It should also be falsifiable, meaning that it can be disproven by experimental results. Importantly, science does not claim to “prove” anything because scientific understandings are always subject to modification with further information. To test a hypothesis, a researcher will conduct one or more experiments designed to eliminate one or more of the hypotheses. Each experiment will have one or more variables and one or more controls. A variable is any part of the experiment that can vary or change during the experiment. The control group contains every feature of the experimental group except it is not given the manipulation that tests the hypothesis. Therefore, if the results of the experimental group differ from the control group, the difference must be due to the hypothesized manipulation, rather than some outside factor. Look for the variables and controls in the examples that follow. To test the first hypothesis, the student would find out if the air conditioning is on. If the air conditioning is turned on but does not work, then the hypothesis that the air conditioning was not turned on should be rejected. To test the second hypothesis, the student could check the settings of the classroom heating unit. If the heating unit is set at an appropriate temperature, then this hypothesis should also be rejected. Each hypothesis should be tested by carrying out appropriate experiments. Be aware that rejecting one hypothesis does not determine whether or not the other hypotheses can be accepted; it simply eliminates one hypothesis that is not valid. Using the scientific method, the hypotheses that are inconsistent with experimental data are rejected.
While this “warm classroom” example is based on observational results, other hypotheses and experiments might have clearer controls. For instance, a student might attend class on Monday and realize they had difficulty concentrating on the lecture. One observation to explain this occurrence might be, “When I eat breakfast before class, I am better able to pay attention.” The student could then design an experiment with a control to test this hypothesis.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
In the example below, the scientific method is used to solve an everyday problem. Order the scientific method steps (numbered items) with the process of solving the everyday problem (lettered items). Based on the results of the experiment, is the hypothesis correct? If it is incorrect, propose some alternative hypotheses.
- Observation
- Hypothesis (answer)
- The car battery is dead.
- If the battery is dead, then the headlights also will not turn on.
- My car won't start.
- I turn on the headlights.
- The headlights work.
- Why does the car not start?
C, F, A, B, D, E
The scientific method may seem overly rigid and structured; however, there is flexibility. Often, the process of science is not as linear as the scientific method suggests and experimental results frequently inspire a new approach, highlight patterns or themes in the study system, or generate entirely new and different observations and questions. In our warm classroom example, testing the air conditioning hypothesis could, for example, unearth evidence of faulty wiring in the classroom. This observation could then inspire additional questions related to other classroom electrical concerns such as inconsistent wireless internet access, faulty audio/visual equipment functioning, non-functional power outlets, flickering lighting, etc. Notice, too, that the scientific method can be applied to solving problems that aren’t necessarily scientific in nature.
This section was adapted from OpenStax Chapter 1:2 The Process of Science

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.3: The Scientific Method - How Chemists Think
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 47444
Learning Objectives
- Identify the components of the scientific method.
Scientists search for answers to questions and solutions to problems by using a procedure called the scientific method. This procedure consists of making observations, formulating hypotheses, and designing experiments; which leads to additional observations, hypotheses, and experiments in repeated cycles (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)).
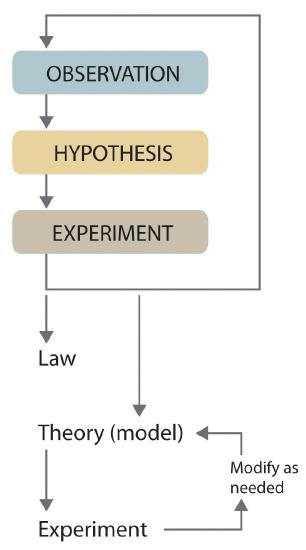
Step 1: Make observations
Observations can be qualitative or quantitative. Qualitative observations describe properties or occurrences in ways that do not rely on numbers. Examples of qualitative observations include the following: "the outside air temperature is cooler during the winter season," "table salt is a crystalline solid," "sulfur crystals are yellow," and "dissolving a penny in dilute nitric acid forms a blue solution and a brown gas." Quantitative observations are measurements, which by definition consist of both a number and a unit. Examples of quantitative observations include the following: "the melting point of crystalline sulfur is 115.21° Celsius," and "35.9 grams of table salt—the chemical name of which is sodium chloride—dissolve in 100 grams of water at 20° Celsius." For the question of the dinosaurs’ extinction, the initial observation was quantitative: iridium concentrations in sediments dating to 66 million years ago were 20–160 times higher than normal.
Step 2: Formulate a hypothesis
After deciding to learn more about an observation or a set of observations, scientists generally begin an investigation by forming a hypothesis, a tentative explanation for the observation(s). The hypothesis may not be correct, but it puts the scientist’s understanding of the system being studied into a form that can be tested. For example, the observation that we experience alternating periods of light and darkness corresponding to observed movements of the sun, moon, clouds, and shadows is consistent with either one of two hypotheses:
- Earth rotates on its axis every 24 hours, alternately exposing one side to the sun.
- The sun revolves around Earth every 24 hours.
Suitable experiments can be designed to choose between these two alternatives. For the disappearance of the dinosaurs, the hypothesis was that the impact of a large extraterrestrial object caused their extinction. Unfortunately (or perhaps fortunately), this hypothesis does not lend itself to direct testing by any obvious experiment, but scientists can collect additional data that either support or refute it.
Step 3: Design and perform experiments
After a hypothesis has been formed, scientists conduct experiments to test its validity. Experiments are systematic observations or measurements, preferably made under controlled conditions—that is—under conditions in which a single variable changes.
Step 4: Accept or modify the hypothesis
A properly designed and executed experiment enables a scientist to determine whether or not the original hypothesis is valid. If the hypothesis is valid, the scientist can proceed to step 5. In other cases, experiments often demonstrate that the hypothesis is incorrect or that it must be modified and requires further experimentation.
Step 5: Development into a law and/or theory
More experimental data are then collected and analyzed, at which point a scientist may begin to think that the results are sufficiently reproducible (i.e., dependable) to merit being summarized in a law, a verbal or mathematical description of a phenomenon that allows for general predictions. A law simply states what happens; it does not address the question of why.
One example of a law, the law of definite proportions , which was discovered by the French scientist Joseph Proust (1754–1826), states that a chemical substance always contains the same proportions of elements by mass. Thus, sodium chloride (table salt) always contains the same proportion by mass of sodium to chlorine, in this case 39.34% sodium and 60.66% chlorine by mass, and sucrose (table sugar) is always 42.11% carbon, 6.48% hydrogen, and 51.41% oxygen by mass.
Whereas a law states only what happens, a theory attempts to explain why nature behaves as it does. Laws are unlikely to change greatly over time unless a major experimental error is discovered. In contrast, a theory, by definition, is incomplete and imperfect, evolving with time to explain new facts as they are discovered.
Because scientists can enter the cycle shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) at any point, the actual application of the scientific method to different topics can take many different forms. For example, a scientist may start with a hypothesis formed by reading about work done by others in the field, rather than by making direct observations.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Classify each statement as a law, a theory, an experiment, a hypothesis, an observation.
- Ice always floats on liquid water.
- Birds evolved from dinosaurs.
- Hot air is less dense than cold air, probably because the components of hot air are moving more rapidly.
- When 10 g of ice were added to 100 mL of water at 25°C, the temperature of the water decreased to 15.5°C after the ice melted.
- The ingredients of Ivory soap were analyzed to see whether it really is 99.44% pure, as advertised.
- This is a general statement of a relationship between the properties of liquid and solid water, so it is a law.
- This is a possible explanation for the origin of birds, so it is a hypothesis.
- This is a statement that tries to explain the relationship between the temperature and the density of air based on fundamental principles, so it is a theory.
- The temperature is measured before and after a change is made in a system, so these are observations.
- This is an analysis designed to test a hypothesis (in this case, the manufacturer’s claim of purity), so it is an experiment.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Classify each statement as a law, a theory, an experiment, a hypothesis, a qualitative observation, or a quantitative observation.
- Measured amounts of acid were added to a Rolaids tablet to see whether it really “consumes 47 times its weight in excess stomach acid.”
- Heat always flows from hot objects to cooler ones, not in the opposite direction.
- The universe was formed by a massive explosion that propelled matter into a vacuum.
- Michael Jordan is the greatest pure shooter to ever play professional basketball.
- Limestone is relatively insoluble in water, but dissolves readily in dilute acid with the evolution of a gas.
The scientific method is a method of investigation involving experimentation and observation to acquire new knowledge, solve problems, and answer questions. The key steps in the scientific method include the following:
- Step 1: Make observations.
- Step 2: Formulate a hypothesis.
- Step 3: Test the hypothesis through experimentation.
- Step 4: Accept or modify the hypothesis.
- Step 5: Develop into a law and/or a theory.
Contributions & Attributions
Scientific Method
Illustration by J.R. Bee. ThoughtCo.
- Cell Biology
- Weather & Climate
- B.A., Biology, Emory University
- A.S., Nursing, Chattahoochee Technical College
The scientific method is a series of steps followed by scientific investigators to answer specific questions about the natural world. It involves making observations, formulating a hypothesis , and conducting scientific experiments . Scientific inquiry starts with an observation followed by the formulation of a question about what has been observed. The steps of the scientific method are as follows:
Observation
The first step of the scientific method involves making an observation about something that interests you. This is very important if you are doing a science project because you want your project to be focused on something that will hold your attention. Your observation can be on anything from plant movement to animal behavior, as long as it is something you really want to know more about. This is where you come up with the idea for your science project.
Once you've made your observation, you must formulate a question about what you have observed. Your question should tell what it is that you are trying to discover or accomplish in your experiment. When stating your question you should be as specific as possible. For example, if you are doing a project on plants , you may want to know how plants interact with microbes. Your question may be: Do plant spices inhibit bacterial growth ?
The hypothesis is a key component of the scientific process. A hypothesis is an idea that is suggested as an explanation for a natural event, a particular experience, or a specific condition that can be tested through definable experimentation. It states the purpose of your experiment, the variables used, and the predicted outcome of your experiment. It is important to note that a hypothesis must be testable. That means that you should be able to test your hypothesis through experimentation . Your hypothesis must either be supported or falsified by your experiment. An example of a good hypothesis is: If there is a relation between listening to music and heart rate, then listening to music will cause a person's resting heart rate to either increase or decrease.
Once you've developed a hypothesis, you must design and conduct an experiment that will test it. You should develop a procedure that states very clearly how you plan to conduct your experiment. It is important that you include and identify a controlled variable or dependent variable in your procedure. Controls allow us to test a single variable in an experiment because they are unchanged. We can then make observations and comparisons between our controls and our independent variables (things that change in the experiment) to develop an accurate conclusion.
The results are where you report what happened in the experiment. That includes detailing all observations and data made during your experiment. Most people find it easier to visualize the data by charting or graphing the information.
The final step of the scientific method is developing a conclusion. This is where all of the results from the experiment are analyzed and a determination is reached about the hypothesis. Did the experiment support or reject your hypothesis? If your hypothesis was supported, great. If not, repeat the experiment or think of ways to improve your procedure.
- Six Steps of the Scientific Method
- What Is an Experiment? Definition and Design
- Scientific Method Flow Chart
- Scientific Method Lesson Plan
- How To Design a Science Fair Experiment
- How to Do a Science Fair Project
- What Are the Elements of a Good Hypothesis?
- How to Write a Lab Report
- Biology Science Fair Project Ideas
- What Is a Hypothesis? (Science)
- Understanding Simple vs Controlled Experiments
- Null Hypothesis Definition and Examples
- Stove Top Frozen Pizza Science Experiment
- Dependent Variable Definition and Examples
- Kindergarten Science Projects
- What Are Examples of a Hypothesis?
Writers' Center
Eastern Washington University
Scientific Writing
Thinking and writing like a scientist, writing clearly, citation help.
[ Back to resource home ]

[email protected] 509.359.2779
Cheney Campus JFK Library Learning Commons
Spokane Campus Catalyst Building C451 and C452
Stay Connected! Instagram Facebook
Helpful Links
For more information on writing your scientific papers, here are some good resources:
http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/scientific-reports/
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1559667/
The Scientific Method
When writing or reading about science, it is useful to keep the scientific method in mind. The scientific method is used as a model to construct writing that can be shared with others in a logical and informative way. Any piece of scientific writing is informative and persuasive: informative because the author is telling the audience how he or she conducted their research and what new information they learned, and persuasive because science papers demonstrate how that new information was obtained and what conclusions can be drawn from the data collected. The format of most journal articles follows the steps of the scientific method, with Introduction, Methods, and Results sections at a minimum.

Evidence and Argumentation
Science writing has a persuasive element to it. Researchers need to convince others that they have done their experiments properly and that they have answered their central research questions. Therefore, all science papers, even theoretical ones, make use of evidence to support their points. Remember that statistical measures, while extremely useful, are not the only source of evidence. Observations of even a single event can be useful in the right context. Remember to use logic to link your evidence and claims together!
Tips for writing a persuasive paper: http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/awolaver/term1.htm
Relating evidence and ideas: http://undsci.berkeley.edu/article/coreofscience_01
Clarity and Reader Expectations
Many people complain that scientific literature is difficult to understand because of the complicated language and the use of jargon. However, scientific literature can be difficult to understand even if one is familiar with the concepts being discussed.
To avoid confusing the reader, writers should focus on writing clearly and keeping the reader’s expectations in mind. In a scientific paper, it is important that most readers will agree with the information being presented. Writing in a clear and concise way helps the writer accomplish this. Use the paper as a story-telling medium. Concentrate on showing the reader that your experiments show definite conclusion, and how this contribution changes the state of knowledge in the field.
Gopen and Swan (1990) offer the following seven easy ways to make your writing more clear and to say what you want the reader to hear.
- Follow a grammatical subject as soon as possible with its verb.
- Place in the stress position the "new information" you want the reader to emphasize.
- Place the person or thing whose "story" a sentence is telling at the beginning of the sentence, in the topic position.
- Place appropriate "old information" (material already stated in the discourse) in the topic position for linkage backward and contextualization forward.
- Articulate the action of every clause or sentence in its verb.
- In general, provide context for your reader before asking that reader to consider anything new.
- In general, try to ensure that the relative emphases of the substance coincide with the relative expectations for emphasis raised by the structure.
[Gopen, G. and Swan, J. 1990. The Science of Scientific Writing. American Scientist. Available here: https://www.americanscientist.org/blog/the-long-view/the-science-of-scientific-writing ]
One major problem many students have when they start writing papers is using so called “running jumps.” This is the placement of unnecessary words at the beginning of a sentence. For example:
RUNNING JUMP: According to the researchers, the control group showed more change in chlorophyll production (Smith et. al., 2014).
NO RUNNING JUMP: The control group showed more change in chlorophyll production (Smith et. al., 2014).
We’ve already cited a study, so it’s clear that we are referring to researchers and their findings. So the first part of the sentence is unnecessary.
Try to limit the number of ideas expressed in a single sentence. If a sentence seems like it is trying to say more than two things at once, split it into two sentences. If a sentence is long and tangled and just doesn't make sense, don't try to perform "surgery" to fix the sentence. Instead, "kill" the sentence and start over, using short, direct sentences to express what you mean.
If you can make a noun phrase into a verb, do it! For example, made note of = noted, provided a similar opinion = agreed with, conducted an experiment = experimented, etc.

Avoid the Passive Voice Where You Can
If a sentence is written in the passive voice, the subject of the sentence (person/thing doing the action) does not come first; rather, the object of the sentence (person/thing not doing the action) is the first noun in the sentence.
PASSIVE: Radiation was the mechanism by which the samples were sterilized.
MORE ACTIVE: The samples were sterilized using radiation.
ACTIVE: We sterilized the samples using radiation.
Professors (and scientific journals) have differing opinions on the use of passive voice. Some consider it unacceptable, but many are more lenient. And in fact, often it will make more sense to write in the passive voice in certain sections (i.e. Methods) and when you can't use first-person pronouns like "I." In any case, reducing overuse of passive voice in your writing makes it more concise and easier to understand.
Here's a useful link for clear scientific writing style: http://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/effective-writing-13815989
Posters are often used as an accompaniment to a talk or presentation, or as a substitute. You’ve probably seen posters hanging up around campus, showcasing students' research. The idea of a poster is to simplify a study and present it in a visual way, so it can be understood by a wide audience. The most important thing to remember when designing a poster (or completing any kind of published work) is to follow the guidelines given. If your instructor, or the conference you’re presenting at, wants a certain format, adhere to that format. These three rules are especially important to follow:
- Shorter is better: make sure that your poster does not contain too much text! Packing text onto the poster makes it difficult to read and understand.
- Bigger is better. No, this is not a contradiction of rule 1! Make sure your text is large enough to read, and readable against the background of the poster.
- Use images. The key aspect of a poster is that it is a visual medium. Include graphs, photos, and illustrations of your work.
Here are some excellent tips and templates for research posters:
1. http://colinpurrington.com/tips/academic/posterdesign
2. http://www.waspacegrant.org
3. http://www.personal.psu.edu/drs18/postershow/ : Poster tips from Penn State
Most scientific citation styles are based on APA format. It’s totally okay to use a resource to look up how to format a paper in APA style! As you become more familiar with the format, you will become less reliant on these resources, but for now, here are some sites that may be useful .
Our APA guide
APA Style Official Website
- Last Updated: Jul 21, 2021 3:01 PM
- URL: https://research.ewu.edu/writers_center_sci_writing

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the 6 scientific method steps and how to use them.
General Education

When you’re faced with a scientific problem, solving it can seem like an impossible prospect. There are so many possible explanations for everything we see and experience—how can you possibly make sense of them all? Science has a simple answer: the scientific method.
The scientific method is a method of asking and answering questions about the world. These guiding principles give scientists a model to work through when trying to understand the world, but where did that model come from, and how does it work?
In this article, we’ll define the scientific method, discuss its long history, and cover each of the scientific method steps in detail.
What Is the Scientific Method?
At its most basic, the scientific method is a procedure for conducting scientific experiments. It’s a set model that scientists in a variety of fields can follow, going from initial observation to conclusion in a loose but concrete format.
The number of steps varies, but the process begins with an observation, progresses through an experiment, and concludes with analysis and sharing data. One of the most important pieces to the scientific method is skepticism —the goal is to find truth, not to confirm a particular thought. That requires reevaluation and repeated experimentation, as well as examining your thinking through rigorous study.
There are in fact multiple scientific methods, as the basic structure can be easily modified. The one we typically learn about in school is the basic method, based in logic and problem solving, typically used in “hard” science fields like biology, chemistry, and physics. It may vary in other fields, such as psychology, but the basic premise of making observations, testing, and continuing to improve a theory from the results remain the same.

The History of the Scientific Method
The scientific method as we know it today is based on thousands of years of scientific study. Its development goes all the way back to ancient Mesopotamia, Greece, and India.
The Ancient World
In ancient Greece, Aristotle devised an inductive-deductive process , which weighs broad generalizations from data against conclusions reached by narrowing down possibilities from a general statement. However, he favored deductive reasoning, as it identifies causes, which he saw as more important.
Aristotle wrote a great deal about logic and many of his ideas about reasoning echo those found in the modern scientific method, such as ignoring circular evidence and limiting the number of middle terms between the beginning of an experiment and the end. Though his model isn’t the one that we use today, the reliance on logic and thorough testing are still key parts of science today.
The Middle Ages
The next big step toward the development of the modern scientific method came in the Middle Ages, particularly in the Islamic world. Ibn al-Haytham, a physicist from what we now know as Iraq, developed a method of testing, observing, and deducing for his research on vision. al-Haytham was critical of Aristotle’s lack of inductive reasoning, which played an important role in his own research.
Other scientists, including Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī, Ibn Sina, and Robert Grosseteste also developed models of scientific reasoning to test their own theories. Though they frequently disagreed with one another and Aristotle, those disagreements and refinements of their methods led to the scientific method we have today.
Following those major developments, particularly Grosseteste’s work, Roger Bacon developed his own cycle of observation (seeing that something occurs), hypothesis (making a guess about why that thing occurs), experimentation (testing that the thing occurs), and verification (an outside person ensuring that the result of the experiment is consistent).
After joining the Franciscan Order, Bacon was granted a special commission to write about science; typically, Friars were not allowed to write books or pamphlets. With this commission, Bacon outlined important tenets of the scientific method, including causes of error, methods of knowledge, and the differences between speculative and experimental science. He also used his own principles to investigate the causes of a rainbow, demonstrating the method’s effectiveness.
Scientific Revolution
Throughout the Renaissance, more great thinkers became involved in devising a thorough, rigorous method of scientific study. Francis Bacon brought inductive reasoning further into the method, whereas Descartes argued that the laws of the universe meant that deductive reasoning was sufficient. Galileo’s research was also inductive reasoning-heavy, as he believed that researchers could not account for every possible variable; therefore, repetition was necessary to eliminate faulty hypotheses and experiments.
All of this led to the birth of the Scientific Revolution , which took place during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. In 1660, a group of philosophers and physicians joined together to work on scientific advancement. After approval from England’s crown , the group became known as the Royal Society, which helped create a thriving scientific community and an early academic journal to help introduce rigorous study and peer review.
Previous generations of scientists had touched on the importance of induction and deduction, but Sir Isaac Newton proposed that both were equally important. This contribution helped establish the importance of multiple kinds of reasoning, leading to more rigorous study.
As science began to splinter into separate areas of study, it became necessary to define different methods for different fields. Karl Popper was a leader in this area—he established that science could be subject to error, sometimes intentionally. This was particularly tricky for “soft” sciences like psychology and social sciences, which require different methods. Popper’s theories furthered the divide between sciences like psychology and “hard” sciences like chemistry or physics.
Paul Feyerabend argued that Popper’s methods were too restrictive for certain fields, and followed a less restrictive method hinged on “anything goes,” as great scientists had made discoveries without the Scientific Method. Feyerabend suggested that throughout history scientists had adapted their methods as necessary, and that sometimes it would be necessary to break the rules. This approach suited social and behavioral scientists particularly well, leading to a more diverse range of models for scientists in multiple fields to use.

The Scientific Method Steps
Though different fields may have variations on the model, the basic scientific method is as follows:
#1: Make Observations
Notice something, such as the air temperature during the winter, what happens when ice cream melts, or how your plants behave when you forget to water them.
#2: Ask a Question
Turn your observation into a question. Why is the temperature lower during the winter? Why does my ice cream melt? Why does my toast always fall butter-side down?
This step can also include doing some research. You may be able to find answers to these questions already, but you can still test them!
#3: Make a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is an educated guess of the answer to your question. Why does your toast always fall butter-side down? Maybe it’s because the butter makes that side of the bread heavier.
A good hypothesis leads to a prediction that you can test, phrased as an if/then statement. In this case, we can pick something like, “If toast is buttered, then it will hit the ground butter-first.”
#4: Experiment
Your experiment is designed to test whether your predication about what will happen is true. A good experiment will test one variable at a time —for example, we’re trying to test whether butter weighs down one side of toast, making it more likely to hit the ground first.
The unbuttered toast is our control variable. If we determine the chance that a slice of unbuttered toast, marked with a dot, will hit the ground on a particular side, we can compare those results to our buttered toast to see if there’s a correlation between the presence of butter and which way the toast falls.
If we decided not to toast the bread, that would be introducing a new question—whether or not toasting the bread has any impact on how it falls. Since that’s not part of our test, we’ll stick with determining whether the presence of butter has any impact on which side hits the ground first.
#5: Analyze Data
After our experiment, we discover that both buttered toast and unbuttered toast have a 50/50 chance of hitting the ground on the buttered or marked side when dropped from a consistent height, straight down. It looks like our hypothesis was incorrect—it’s not the butter that makes the toast hit the ground in a particular way, so it must be something else.
Since we didn’t get the desired result, it’s back to the drawing board. Our hypothesis wasn’t correct, so we’ll need to start fresh. Now that you think about it, your toast seems to hit the ground butter-first when it slides off your plate, not when you drop it from a consistent height. That can be the basis for your new experiment.
#6: Communicate Your Results
Good science needs verification. Your experiment should be replicable by other people, so you can put together a report about how you ran your experiment to see if other peoples’ findings are consistent with yours.
This may be useful for class or a science fair. Professional scientists may publish their findings in scientific journals, where other scientists can read and attempt their own versions of the same experiments. Being part of a scientific community helps your experiments be stronger because other people can see if there are flaws in your approach—such as if you tested with different kinds of bread, or sometimes used peanut butter instead of butter—that can lead you closer to a good answer.

A Scientific Method Example: Falling Toast
We’ve run through a quick recap of the scientific method steps, but let’s look a little deeper by trying again to figure out why toast so often falls butter side down.
#1: Make Observations
At the end of our last experiment, where we learned that butter doesn’t actually make toast more likely to hit the ground on that side, we remembered that the times when our toast hits the ground butter side first are usually when it’s falling off a plate.
The easiest question we can ask is, “Why is that?”
We can actually search this online and find a pretty detailed answer as to why this is true. But we’re budding scientists—we want to see it in action and verify it for ourselves! After all, good science should be replicable, and we have all the tools we need to test out what’s really going on.
Why do we think that buttered toast hits the ground butter-first? We know it’s not because it’s heavier, so we can strike that out. Maybe it’s because of the shape of our plate?
That’s something we can test. We’ll phrase our hypothesis as, “If my toast slides off my plate, then it will fall butter-side down.”
Just seeing that toast falls off a plate butter-side down isn’t enough for us. We want to know why, so we’re going to take things a step further—we’ll set up a slow-motion camera to capture what happens as the toast slides off the plate.
We’ll run the test ten times, each time tilting the same plate until the toast slides off. We’ll make note of each time the butter side lands first and see what’s happening on the video so we can see what’s going on.
When we review the footage, we’ll likely notice that the bread starts to flip when it slides off the edge, changing how it falls in a way that didn’t happen when we dropped it ourselves.
That answers our question, but it’s not the complete picture —how do other plates affect how often toast hits the ground butter-first? What if the toast is already butter-side down when it falls? These are things we can test in further experiments with new hypotheses!
Now that we have results, we can share them with others who can verify our results. As mentioned above, being part of the scientific community can lead to better results. If your results were wildly different from the established thinking about buttered toast, that might be cause for reevaluation. If they’re the same, they might lead others to make new discoveries about buttered toast. At the very least, you have a cool experiment you can share with your friends!
Key Scientific Method Tips
Though science can be complex, the benefit of the scientific method is that it gives you an easy-to-follow means of thinking about why and how things happen. To use it effectively, keep these things in mind!
Don’t Worry About Proving Your Hypothesis
One of the important things to remember about the scientific method is that it’s not necessarily meant to prove your hypothesis right. It’s great if you do manage to guess the reason for something right the first time, but the ultimate goal of an experiment is to find the true reason for your observation to occur, not to prove your hypothesis right.
Good science sometimes means that you’re wrong. That’s not a bad thing—a well-designed experiment with an unanticipated result can be just as revealing, if not more, than an experiment that confirms your hypothesis.
Be Prepared to Try Again
If the data from your experiment doesn’t match your hypothesis, that’s not a bad thing. You’ve eliminated one possible explanation, which brings you one step closer to discovering the truth.
The scientific method isn’t something you’re meant to do exactly once to prove a point. It’s meant to be repeated and adapted to bring you closer to a solution. Even if you can demonstrate truth in your hypothesis, a good scientist will run an experiment again to be sure that the results are replicable. You can even tweak a successful hypothesis to test another factor, such as if we redid our buttered toast experiment to find out whether different kinds of plates affect whether or not the toast falls butter-first. The more we test our hypothesis, the stronger it becomes!
What’s Next?
Want to learn more about the scientific method? These important high school science classes will no doubt cover it in a variety of different contexts.
Test your ability to follow the scientific method using these at-home science experiments for kids !
Need some proof that science is fun? Try making slime

Melissa Brinks graduated from the University of Washington in 2014 with a Bachelor's in English with a creative writing emphasis. She has spent several years tutoring K-12 students in many subjects, including in SAT prep, to help them prepare for their college education.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Science
Essay Samples on Scientific Method
Understanding the seven steps of the scientific method.
What is the scientific method? A procedural method that has been characterized by natural sciences since the seventeenth century, including systematic observation, measurement, and experimentation, as well as the formulation, testing, and modification of hypotheses. 'Criticism is the backbone of the scientific method' The scientific...
- Scientific Method
The Importance of the Scientific Method in Psychology Experiments
The scientific method is “ the tactic of a process that has characterized physical discipline since the seventeenth century, consisting in systematic observation, measurement, and experiment, and therefore the formulation, testing, and altar of hypothesis”. The scientific method is used throughout the world that provides...
Learning to Think Scientifically: A Look at the Scientific Method
Students, and now and again even teachers, commonly anticipate scientists solely use the scientific approach to reply to science-related questions. In fact, you can comply with the scientific technique to nearly any problem. The key is to use the factors (steps) to restrict bias and...
Scientific Method: Its Role in Advancing Science and Technology
Since the human been appear, use the logic and arise different questions, begins the scientific method, after years this practice evolve to what we know this age. Even when we were kids, we use this method not for scientific reasons, just to know something like...
Experimentation & Innovation: The Importance of the Scientific Method
Our life without the scientific method would be unrecognizable. Most individuals don’t realize how our daily life and routine has been improved because of experimentation. Without the scientific method, we would not be so technologically advanced. We would not have all the latest cell phones,...
Stressed out with your paper?
Consider using writing assistance:
- 100% unique papers
- 3 hrs deadline option
The Role of Reasoning in Science: Inductive and Deductive Approaches
Introduction This essay will focus on the principles of the scientific method, considering Francis Bacon’s method of induction contrasted with Karl Poppers’ Hypothetico-Deductive approach as a means of defining what is scientifically accurate. Both approaches are used in modern-day science, where experiment and observation are...
The Common Themes and Diverse Practices of Scientific Methods
Introduction Science in some form or another has been practiced for millennia, to varying degrees of success, and throughout this time, people have argued about which is the way to practice science. The study of the scientific method can be described as the attempt to...
Best topics on Scientific Method
1. Understanding the Seven Steps of the Scientific Method
2. The Importance of the Scientific Method in Psychology Experiments
3. Learning to Think Scientifically: A Look at the Scientific Method
4. Scientific Method: Its Role in Advancing Science and Technology
5. Experimentation & Innovation: The Importance of the Scientific Method
6. The Role of Reasoning in Science: Inductive and Deductive Approaches
7. The Common Themes and Diverse Practices of Scientific Methods
- Space Exploration
- Hermit Crab
- Applied Sciences
- Ethnography
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
Scientific Methods
What is scientific method.
The Scientific method is a process with the help of which scientists try to investigate, verify, or construct an accurate and reliable version of any natural phenomena. They are done by creating an objective framework for the purpose of scientific inquiry and analysing the results scientifically to come to a conclusion that either supports or contradicts the observation made at the beginning.
Scientific Method Steps
The aim of all scientific methods is the same, that is, to analyse the observation made at the beginning. Still, various steps are adopted per the requirement of any given observation. However, there is a generally accepted sequence of steps in scientific methods.
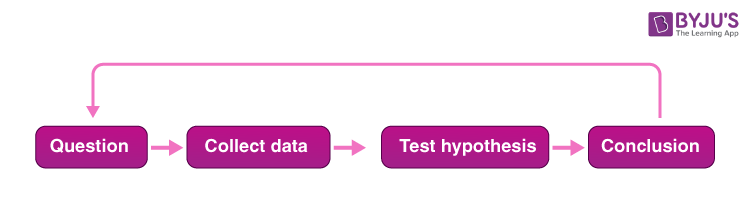
- Observation and formulation of a question: This is the first step of a scientific method. To start one, an observation has to be made into any observable aspect or phenomena of the universe, and a question needs to be asked about that aspect. For example, you can ask, “Why is the sky black at night? or “Why is air invisible?”
- Data Collection and Hypothesis: The next step involved in the scientific method is to collect all related data and formulate a hypothesis based on the observation. The hypothesis could be the cause of the phenomena, its effect, or its relation to any other phenomena.
- Testing the hypothesis: After the hypothesis is made, it needs to be tested scientifically. Scientists do this by conducting experiments. The aim of these experiments is to determine whether the hypothesis agrees with or contradicts the observations made in the real world. The confidence in the hypothesis increases or decreases based on the result of the experiments.
- Analysis and Conclusion: This step involves the use of proper mathematical and other scientific procedures to determine the results of the experiment. Based on the analysis, the future course of action can be determined. If the data found in the analysis is consistent with the hypothesis, it is accepted. If not, then it is rejected or modified and analysed again.
It must be remembered that a hypothesis cannot be proved or disproved by doing one experiment. It needs to be done repeatedly until there are no discrepancies in the data and the result. When there are no discrepancies and the hypothesis is proved, it is accepted as a ‘theory’.
Scientific Method Examples
Following is an example of the scientific method:
Growing bean plants:
- What is the purpose: The main purpose of this experiment is to know where the bean plant should be kept inside or outside to check the growth rate and also set the time frame as four weeks.
- Construction of hypothesis: The hypothesis used is that the bean plant can grow anywhere if the scientific methods are used.
- Executing the hypothesis and collecting the data: Four bean plants are planted in identical pots using the same soil. Two are placed inside, and the other two are placed outside. Parameters like the amount of exposure to sunlight, and amount of water all are the same. After the completion of four weeks, all four plant sizes are measured.
- Analyse the data: While analysing the data, the average height of plants should be taken into account from both places to determine which environment is more suitable for growing the bean plants.
- Conclusion: The conclusion is drawn after analyzing the data.
- Results: Results can be reported in the form of a tabular form.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is scientific method, what is hypothesis, give an example of a simple hypothesis., define complex hypothesis., what are the steps of the scientific method, what is the aim of scientific methods, state true or false: observation and formulation of a question is the third step of scientific method, explain the step: analysis and conclusion., leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

1.2 The Scientific Methods
Section learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
- Explain how the methods of science are used to make scientific discoveries
- Define a scientific model and describe examples of physical and mathematical models used in physics
- Compare and contrast hypothesis, theory, and law
Teacher Support
The learning objectives in this section will help your students master the following standards:
- (A) know the definition of science and understand that it has limitations, as specified in subsection (b)(2) of this section;
- (B) know that scientific hypotheses are tentative and testable statements that must be capable of being supported or not supported by observational evidence. Hypotheses of durable explanatory power which have been tested over a wide variety of conditions are incorporated into theories;
- (C) know that scientific theories are based on natural and physical phenomena and are capable of being tested by multiple independent researchers. Unlike hypotheses, scientific theories are well-established and highly-reliable explanations, but may be subject to change as new areas of science and new technologies are developed;
- (D) distinguish between scientific hypotheses and scientific theories.
Section Key Terms
[OL] Pre-assessment for this section could involve students sharing or writing down an anecdote about when they used the methods of science. Then, students could label their thought processes in their anecdote with the appropriate scientific methods. The class could also discuss their definitions of theory and law, both outside and within the context of science.
[OL] It should be noted and possibly mentioned that a scientist , as mentioned in this section, does not necessarily mean a trained scientist. It could be anyone using methods of science.
Scientific Methods
Scientists often plan and carry out investigations to answer questions about the universe around us. These investigations may lead to natural laws. Such laws are intrinsic to the universe, meaning that humans did not create them and cannot change them. We can only discover and understand them. Their discovery is a very human endeavor, with all the elements of mystery, imagination, struggle, triumph, and disappointment inherent in any creative effort. The cornerstone of discovering natural laws is observation. Science must describe the universe as it is, not as we imagine or wish it to be.
We all are curious to some extent. We look around, make generalizations, and try to understand what we see. For example, we look up and wonder whether one type of cloud signals an oncoming storm. As we become serious about exploring nature, we become more organized and formal in collecting and analyzing data. We attempt greater precision, perform controlled experiments (if we can), and write down ideas about how data may be organized. We then formulate models, theories, and laws based on the data we have collected, and communicate those results with others. This, in a nutshell, describes the scientific method that scientists employ to decide scientific issues on the basis of evidence from observation and experiment.
An investigation often begins with a scientist making an observation . The scientist observes a pattern or trend within the natural world. Observation may generate questions that the scientist wishes to answer. Next, the scientist may perform some research about the topic and devise a hypothesis . A hypothesis is a testable statement that describes how something in the natural world works. In essence, a hypothesis is an educated guess that explains something about an observation.
[OL] An educated guess is used throughout this section in describing a hypothesis to combat the tendency to think of a theory as an educated guess.
Scientists may test the hypothesis by performing an experiment . During an experiment, the scientist collects data that will help them learn about the phenomenon they are studying. Then the scientists analyze the results of the experiment (that is, the data), often using statistical, mathematical, and/or graphical methods. From the data analysis, they draw conclusions. They may conclude that their experiment either supports or rejects their hypothesis. If the hypothesis is supported, the scientist usually goes on to test another hypothesis related to the first. If their hypothesis is rejected, they will often then test a new and different hypothesis in their effort to learn more about whatever they are studying.
Scientific processes can be applied to many situations. Let’s say that you try to turn on your car, but it will not start. You have just made an observation! You ask yourself, "Why won’t my car start?" You can now use scientific processes to answer this question. First, you generate a hypothesis such as, "The car won’t start because it has no gasoline in the gas tank." To test this hypothesis, you put gasoline in the car and try to start it again. If the car starts, then your hypothesis is supported by the experiment. If the car does not start, then your hypothesis is rejected. You will then need to think up a new hypothesis to test such as, "My car won’t start because the fuel pump is broken." Hopefully, your investigations lead you to discover why the car won’t start and enable you to fix it.
A model is a representation of something that is often too difficult (or impossible) to study directly. Models can take the form of physical models, equations, computer programs, or simulations—computer graphics/animations. Models are tools that are especially useful in modern physics because they let us visualize phenomena that we normally cannot observe with our senses, such as very small objects or objects that move at high speeds. For example, we can understand the structure of an atom using models, without seeing an atom with our own eyes. Although images of single atoms are now possible, these images are extremely difficult to achieve and are only possible due to the success of our models. The existence of these images is a consequence rather than a source of our understanding of atoms. Models are always approximate, so they are simpler to consider than the real situation; the more complete a model is, the more complicated it must be. Models put the intangible or the extremely complex into human terms that we can visualize, discuss, and hypothesize about.
Scientific models are constructed based on the results of previous experiments. Even still, models often only describe a phenomenon partially or in a few limited situations. Some phenomena are so complex that they may be impossible to model them in their entirety, even using computers. An example is the electron cloud model of the atom in which electrons are moving around the atom’s center in distinct clouds ( Figure 1.12 ), that represent the likelihood of finding an electron in different places. This model helps us to visualize the structure of an atom. However, it does not show us exactly where an electron will be within its cloud at any one particular time.
As mentioned previously, physicists use a variety of models including equations, physical models, computer simulations, etc. For example, three-dimensional models are often commonly used in chemistry and physics to model molecules. Properties other than appearance or location are usually modelled using mathematics, where functions are used to show how these properties relate to one another. Processes such as the formation of a star or the planets, can also be modelled using computer simulations. Once a simulation is correctly programmed based on actual experimental data, the simulation can allow us to view processes that happened in the past or happen too quickly or slowly for us to observe directly. In addition, scientists can also run virtual experiments using computer-based models. In a model of planet formation, for example, the scientist could alter the amount or type of rocks present in space and see how it affects planet formation.
Scientists use models and experimental results to construct explanations of observations or design solutions to problems. For example, one way to make a car more fuel efficient is to reduce the friction or drag caused by air flowing around the moving car. This can be done by designing the body shape of the car to be more aerodynamic, such as by using rounded corners instead of sharp ones. Engineers can then construct physical models of the car body, place them in a wind tunnel, and examine the flow of air around the model. This can also be done mathematically in a computer simulation. The air flow pattern can be analyzed for regions smooth air flow and for eddies that indicate drag. The model of the car body may have to be altered slightly to produce the smoothest pattern of air flow (i.e., the least drag). The pattern with the least drag may be the solution to increasing fuel efficiency of the car. This solution might then be incorporated into the car design.
Using Models and the Scientific Processes
Be sure to secure loose items before opening the window or door.
In this activity, you will learn about scientific models by making a model of how air flows through your classroom or a room in your house.
- One room with at least one window or door that can be opened
- Work with a group of four, as directed by your teacher. Close all of the windows and doors in the room you are working in. Your teacher may assign you a specific window or door to study.
- Before opening any windows or doors, draw a to-scale diagram of your room. First, measure the length and width of your room using the tape measure. Then, transform the measurement using a scale that could fit on your paper, such as 5 centimeters = 1 meter.
- Your teacher will assign you a specific window or door to study air flow. On your diagram, add arrows showing your hypothesis (before opening any windows or doors) of how air will flow through the room when your assigned window or door is opened. Use pencil so that you can easily make changes to your diagram.
- On your diagram, mark four locations where you would like to test air flow in your room. To test for airflow, hold a strip of single ply tissue paper between the thumb and index finger. Note the direction that the paper moves when exposed to the airflow. Then, for each location, predict which way the paper will move if your air flow diagram is correct.
- Now, each member of your group will stand in one of the four selected areas. Each member will test the airflow Agree upon an approximate height at which everyone will hold their papers.
- When you teacher tells you to, open your assigned window and/or door. Each person should note the direction that their paper points immediately after the window or door was opened. Record your results on your diagram.
- Did the airflow test data support or refute the hypothetical model of air flow shown in your diagram? Why or why not? Correct your model based on your experimental evidence.
- With your group, discuss how accurate your model is. What limitations did it have? Write down the limitations that your group agreed upon.
- Yes, you could use your model to predict air flow through a new window. The earlier experiment of air flow would help you model the system more accurately.
- Yes, you could use your model to predict air flow through a new window. The earlier experiment of air flow is not useful for modeling the new system.
- No, you cannot model a system to predict the air flow through a new window. The earlier experiment of air flow would help you model the system more accurately.
- No, you cannot model a system to predict the air flow through a new window. The earlier experiment of air flow is not useful for modeling the new system.
This Snap Lab! has students construct a model of how air flows in their classroom. Each group of four students will create a model of air flow in their classroom using a scale drawing of the room. Then, the groups will test the validity of their model by placing weathervanes that they have constructed around the room and opening a window or door. By observing the weather vanes, students will see how air actually flows through the room from a specific window or door. Students will then correct their model based on their experimental evidence. The following material list is given per group:
- One room with at least one window or door that can be opened (An optimal configuration would be one window or door per group.)
- Several pieces of construction paper (at least four per group)
- Strips of single ply tissue paper
- One tape measure (long enough to measure the dimensions of the room)
- Group size can vary depending on the number of windows/doors available and the number of students in the class.
- The room dimensions could be provided by the teacher. Also, students may need a brief introduction in how to make a drawing to scale.
- This is another opportunity to discuss controlled experiments in terms of why the students should hold the strips of tissue paper at the same height and in the same way. One student could also serve as a control and stand far away from the window/door or in another area that will not receive air flow from the window/door.
- You will probably need to coordinate this when multiple windows or doors are used. Only one window or door should be opened at a time for best results. Between openings, allow a short period (5 minutes) when all windows and doors are closed, if possible.
Answers to the Grasp Check will vary, but the air flow in the new window or door should be based on what the students observed in their experiment.
Scientific Laws and Theories
A scientific law is a description of a pattern in nature that is true in all circumstances that have been studied. That is, physical laws are meant to be universal , meaning that they apply throughout the known universe. Laws are often also concise, whereas theories are more complicated. A law can be expressed in the form of a single sentence or mathematical equation. For example, Newton’s second law of motion , which relates the motion of an object to the force applied ( F ), the mass of the object ( m ), and the object’s acceleration ( a ), is simply stated using the equation
Scientific ideas and explanations that are true in many, but not all situations in the universe are usually called principles . An example is Pascal’s principle , which explains properties of liquids, but not solids or gases. However, the distinction between laws and principles is sometimes not carefully made in science.
A theory is an explanation for patterns in nature that is supported by much scientific evidence and verified multiple times by multiple researchers. While many people confuse theories with educated guesses or hypotheses, theories have withstood more rigorous testing and verification than hypotheses.
[OL] Explain to students that in informal, everyday English the word theory can be used to describe an idea that is possibly true but that has not been proven to be true. This use of the word theory often leads people to think that scientific theories are nothing more than educated guesses. This is not just a misconception among students, but among the general public as well.
As a closing idea about scientific processes, we want to point out that scientific laws and theories, even those that have been supported by experiments for centuries, can still be changed by new discoveries. This is especially true when new technologies emerge that allow us to observe things that were formerly unobservable. Imagine how viewing previously invisible objects with a microscope or viewing Earth for the first time from space may have instantly changed our scientific theories and laws! What discoveries still await us in the future? The constant retesting and perfecting of our scientific laws and theories allows our knowledge of nature to progress. For this reason, many scientists are reluctant to say that their studies prove anything. By saying support instead of prove , it keeps the door open for future discoveries, even if they won’t occur for centuries or even millennia.
[OL] With regard to scientists avoiding using the word prove , the general public knows that science has proven certain things such as that the heart pumps blood and the Earth is round. However, scientists should shy away from using prove because it is impossible to test every single instance and every set of conditions in a system to absolutely prove anything. Using support or similar terminology leaves the door open for further discovery.
Check Your Understanding
- Models are simpler to analyze.
- Models give more accurate results.
- Models provide more reliable predictions.
- Models do not require any computer calculations.
- They are the same.
- A hypothesis has been thoroughly tested and found to be true.
- A hypothesis is a tentative assumption based on what is already known.
- A hypothesis is a broad explanation firmly supported by evidence.
- A scientific model is a representation of something that can be easily studied directly. It is useful for studying things that can be easily analyzed by humans.
- A scientific model is a representation of something that is often too difficult to study directly. It is useful for studying a complex system or systems that humans cannot observe directly.
- A scientific model is a representation of scientific equipment. It is useful for studying working principles of scientific equipment.
- A scientific model is a representation of a laboratory where experiments are performed. It is useful for studying requirements needed inside the laboratory.
- The hypothesis must be validated by scientific experiments.
- The hypothesis must not include any physical quantity.
- The hypothesis must be a short and concise statement.
- The hypothesis must apply to all the situations in the universe.
- A scientific theory is an explanation of natural phenomena that is supported by evidence.
- A scientific theory is an explanation of natural phenomena without the support of evidence.
- A scientific theory is an educated guess about the natural phenomena occurring in nature.
- A scientific theory is an uneducated guess about natural phenomena occurring in nature.
- A hypothesis is an explanation of the natural world with experimental support, while a scientific theory is an educated guess about a natural phenomenon.
- A hypothesis is an educated guess about natural phenomenon, while a scientific theory is an explanation of natural world with experimental support.
- A hypothesis is experimental evidence of a natural phenomenon, while a scientific theory is an explanation of the natural world with experimental support.
- A hypothesis is an explanation of the natural world with experimental support, while a scientific theory is experimental evidence of a natural phenomenon.
Use the Check Your Understanding questions to assess students’ achievement of the section’s learning objectives. If students are struggling with a specific objective, the Check Your Understanding will help identify which objective and direct students to the relevant content.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute Texas Education Agency (TEA). The original material is available at: https://www.texasgateway.org/book/tea-physics . Changes were made to the original material, including updates to art, structure, and other content updates.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/physics/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Physics
- Publication date: Mar 26, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/physics/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/physics/pages/1-2-the-scientific-methods
© Jan 19, 2024 Texas Education Agency (TEA). The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Scientific Method: Role and Importance Essay. The scientific method is a problem-solving strategy that is at the heart of biology and other sciences. There are five steps included in the scientific method that is making an observation, asking a question, forming a hypothesis or an explanation that could be tested, and predicting the test.
The scientific method. At the core of biology and other sciences lies a problem-solving approach called the scientific method. The scientific method has five basic steps, plus one feedback step: Make an observation. Ask a question. Form a hypothesis, or testable explanation. Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
The six steps of the scientific method include: 1) asking a question about something you observe, 2) doing background research to learn what is already known about the topic, 3) constructing a hypothesis, 4) experimenting to test the hypothesis, 5) analyzing the data from the experiment and drawing conclusions, and 6) communicating the results ...
The study of scientific method is the attempt to discern the activities by which that success is achieved. ... , many of the steps involved in reaching a conclusion on the basis of an experiment are now made inside a "black box", without the direct involvement or awareness of a human. ... , Medawar argued that scientific papers generally ...
The scientific method is critical to the development of scientific theories, which explain empirical (experiential) laws in a scientifically rational manner. In a typical application of the scientific method, a researcher develops a hypothesis, tests it through various means, and then modifies the hypothesis on the basis of the outcome of the ...
Article. Research Process. The scientific method is a systematic process involving steps like defining questions, forming hypotheses, conducting experiments, and analyzing data. It minimizes biases and enables replicable research, leading to groundbreaking discoveries like Einstein's theory of relativity, penicillin, and the structure of DNA.
When conducting research, the scientific method steps to follow are: Observe what you want to investigate. Ask a research question and make predictions. Test the hypothesis and collect data. Examine the results and draw conclusions. Report and share the results. This process not only allows scientists to investigate and understand different ...
The before steps. The scientific writing process can be a daunting and often procrastinated "last step" in the scientific process, leading to cursory attempts to get scientific arguments and results down on paper. However, scientific writing is not an afterthought and should begin well before drafting the first outline.
The scientific method was first documented by Sir Francis Bacon (1561-1626) of England, and can be applied to almost all fields of study. The scientific method is founded upon observation, which then leads to a question and the development of a hypothesis which answers that question. The scientist can then design an experiment to test the ...
The scientific method is a method of investigation involving experimentation and observation to acquire new knowledge, solve problems, and answer questions. The key steps in the scientific method include the following: Step 1: Make observations. Step 2: Formulate a hypothesis. Step 3: Test the hypothesis through experimentation.
The scientific method is a series of steps followed by scientific investigators to answer specific questions about the natural world. It involves making observations, formulating a hypothesis, and conducting scientific experiments. Scientific inquiry starts with an observation followed by the formulation of a question about what has been ...
The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since ... Later stances include physicist Lee Smolin's 2013 essay "There Is No Scientific Method", in which he espouses two ethical ... The iterative cycle inherent in this step-by-step method goes from point 3 to 6 and back to ...
The Scientific Method. When writing or reading about science, it is useful to keep the scientific method in mind. The scientific method is used as a model to construct writing that can be shared with others in a logical and informative way. Any piece of scientific writing is informative and persuasive: informative because the author is telling ...
The scientific method is guidelines/steps which scientists follow to solve a problem. There are several steps in the scientific method depends on the problem at hand. Amongst these steps include 1) observation, 2) hypothesis, 3) research, 4) experiment 5) data analysis 6) conclusion of that question 7) communicate results.
The number of steps varies, but the process begins with an observation, progresses through an experiment, and concludes with analysis and sharing data. One of the most important pieces to the scientific method is skepticism —the goal is to find truth, not to confirm a particular thought. That requires reevaluation and repeated experimentation ...
The Scientific Method Essay. The Scientific Method is the standardized procedure that scientists are supposed to follow when conducting experiments, in order to try to construct a reliable, consistent, and non-arbitrary representation of our surroundings. To follow the Scientific Method is to stick very tightly to a order of experimentation.
Understanding the Seven Steps of the Scientific Method. 2. The Importance of the Scientific Method in Psychology Experiments. 3. Learning to Think Scientifically: A Look at the Scientific Method. 4. Scientific Method: Its Role in Advancing Science and Technology. 5. Experimentation & Innovation: The Importance of the Scientific Method. 6.
Scientific Method Examples. Following is an example of the scientific method: Growing bean plants: What is the purpose: The main purpose of this experiment is to know where the bean plant should be kept inside or outside to check the growth rate and also set the time frame as four weeks. Construction of hypothesis: The hypothesis used is that ...
The scientific method contains seven steps: asking a question, researching the problem, forming a hypothesis, experimentation, observing and recording the experiment results, drawing a conclusion, and sharing the results. These steps are most commonly thought to be used strictly for scientific research in labs but they can also be used in a ...
Here are the seven steps of the scientific method illustrated by an example scientific hypothesis: 1. Ask a question. The first step in the scientific method is asking a question you want to answer. This question will include one of the key starters: how, what, when, why, where, who or which. The question you ask should also be measurable and ...
In our textbook, the Scientific Method is addressed along with different designs in research. The steps in the scientific method include: 1) Identify a question of scientific interest, 2) Form a hypothesis, 3) Choose a research method and research design, 4) Collect data to test the hypothesis and 5)Draw conclusions and form new questions and hypothesis.
A) scientific process: The scientific process, also known as the scientific method is an organized way to help answer a question or to a hypothesis. The method includes six steps; make a conclusion, form a question, construct a hypothesis, test the hypothesis, analyze the data, and finally draw a conclusion, these steps can be modified once the ...
Teacher Support [OL] Pre-assessment for this section could involve students sharing or writing down an anecdote about when they used the methods of science. Then, students could label their thought processes in their anecdote with the appropriate scientific methods. The class could also discuss their definitions of theory and law, both outside and within the context of science.