

42 Writing Prompts About The Constitution
Although it was written in the 18th century, the U.S. Constitution is the principle by which our country lives.
This means that it is very important for students to read, learn about, and understand the Constitution and how it affects their lives—even in ways that they’d never realized.
As you study American History and the Constitution, it is important to give students a chance to write about and reflect on what they’ve learned so they can really understand the material.
Below, you’ll find a list of writing prompts—which can be changed depending on grade level—to help students think more deeply about the Constitution and what they’ve learned.
How to use these prompts:
Use this writing guide in tandem with your curriculum about American History and the U.S. Constitution. Here are some ways you can use this list of prompts in your classroom:
- Divide your classroom into groups and have each group work on a certain number of prompts.
- Challenge your students to write using one prompt in their journal each day for a week.
- Use these prompts to help students gain a further understanding if they seem to be struggling with the topic.
Life, Liberty, and the Pursuit of Writing Prompts
- Who are some prominent people who were at the creation of the Constitution?
- Why is the Constitution important?
- What is the Bill of Rights?
- Why is the Bill of Rights so important today?
- Make a list of 5 things that are considered a right.
- Make a list of 5 things that are not considered a right.
- Copy the preamble to the Constitution in your best handwriting.
- Pretend to be a reporter and write an article about the creation of the Constitution.
- How does the system of checks and balances work?
- What is the role of the legislative branch of the government?
- What is the role of the executive branch of the government?
- What is the role of the judicial branch of the government?
- What is an amendment?
- Why was it important to create amendments to the Constitution?
- Paparazzi are protected by freedom of the press. Do you think they overuse this right in order to get the best pictures and stories, or are they within their rights to do what they want?
- If you could write an amendment to the Constitution today, what would it be?
- Write your own Bill of Rights for your classroom.
- How did the Constitution create a division in the U.S.?
- Why did the U.S. abandon the Articles of Confederation in exchange for the Constitution?
- Do you think the Constitution applies to today, or should it be changed because times have changed?
- Which amendment in the Bill of Rights do you think is the most important? Why?
- Do you agree that all U.S. citizens should read and understand the Constitution? Explain your answer.
- How did the Revolutionary War influence the Constitution?
- Do you think the Constitution could be changed in the future?
- Write 2-5 paragraphs discussing what you know about the creation of the U.S. Constitution.
- Are students able to influence a change in school rules and policies? Explain with examples.
- Have you ever signed a petition for change? Explain?
- What does it mean to be accountable to the law?
- What happens when groups of people stop abiding by the law?
- Give an example of someone following a law even when it’s inconvenient for them to do so.
- Give at least five examples of how the rule of law affects your daily life.
- How does the Constitution guarantee that citizens are to be treated fairly by the government?
- Summarize the Preamble of the Constitution.
- What does the first amendment of the Bill of Rights guarantee? Give a few examples throughout U.S. history where this right proved to be important.
- Compare and contrast two amendments in the Bill of Rights.
- Why do you think Congress is so unpopular among the American people?
- Why do states have their own constitutions? Do they vary by state?
- Which U.S. state’s name is spelled wrong in the Constitution? How do you think this happened?
- Does the Constitution mention women’s rights? Explain your answer.
- Is slavery mentioned in the Constitution? Explain your answer.
- Compare and contrast the U.S. Constitution with state constitutions.
- What are the seven main purposes of the U.S. Constitution? Do you think any one is more important than the others? Explain.
Looking For More Teaching Resources?
Our site is home to many different resources for teachers, educators, and parents to help students succeed in an abundance of subjects.
If you are looking for something specific, reach out and let us know!

25 Essay Topics for American Government Classes
Writing Ideas That Will Make Students Think
- Teaching Resources
- An Introduction to Teaching
- Tips & Strategies
- Policies & Discipline
- Community Involvement
- School Administration
- Technology in the Classroom
- Teaching Adult Learners
- Issues In Education
- Becoming A Teacher
- Assessments & Tests
- Elementary Education
- Secondary Education
- Special Education
- Homeschooling
- M.Ed., Curriculum and Instruction, University of Florida
- B.A., History, University of Florida
If you are a teacher searching for essay topics to assign to your U.S. government or civics class or looking for ideas, do not fret. It is easy to integrate debates and discussions into the classroom environment. These topic suggestions provide a wealth of ideas for written assignments such as position papers , compare-and-contrast essays , and argumentative essays . Scan the following 25 question topics and ideas to find just the right one. You'll soon be reading interesting papers from your students after they grapple with these challenging and important issues.
- Compare and contrast what is a direct democracy versus representative democracy.
- React to the following statement: Democratic decision-making should be extended to all areas of life including schools, the workplace, and the government.
- Compare and contrast the Virginia and New Jersey plans. Explain how these led to the Great Compromise .
- Pick one thing about the U.S. Constitution including its amendments that you think should be changed. What modifications would you make? Explain your reasons for making this change.
- What did Thomas Jefferson mean when he said, "The tree of liberty must be refreshed from time to time with the blood of patriots and tyrants?" Do you think that this statement still applies to today's world?
- Compare and contrast mandates and conditions of aid regarding the federal government's relationship with states. For example, how has the Federal Emergency Management Agency delivered support to states and commonwealths that have experienced natural disasters?
- Should individual states have more or less power compared to the federal government when implementing laws dealing with topics such as the legalization of marijuana and abortion ?
- Outline a program that would get more people to vote in presidential elections or local elections.
- What are the dangers of gerrymandering when it comes to voting and presidential elections?
- Compare and contrast the major political parties in the United States. What policies are they preparing for upcoming elections?
- Why would voters choose to vote for a third party, even though they know that their candidate has virtually no chance of winning?
- Describe the major sources of money that are donated to political campaigns. Check out the Federal Election Regulatory Commission's website for information.
- Should corporations be treated as individuals regarding being allowed to donate to political campaigns? Look at the 2010 Citizens United v. FEC ruling on the issue. Defend your answer.
- Explain the role of social media in connecting interest groups that have grown stronger as the major political parties have grown weaker.
- Explain why the media has been called the fourth branch of government. Include your opinion on whether this is an accurate portrayal.
- Compare and contrast the campaigns of U.S. Senate and House of Representatives candidates.
- Should term limits be instituted for members of Congress? Explain your answer.
- Should members of Congress vote their conscience or follow the will of the people who elected them into office? Explain your answer.
- Explain how executive orders have been used by presidents throughout the history of the U.S. What is the number of executive orders issued by the current president?
- In your opinion, which of the three branches of the federal government has the most power? Defend your answer.
- Which of the rights guaranteed by the First Amendment do you consider the most important? Explain your answer.
- Should a school be required to get a warrant before searching a student's property? Defend your answer.
- Why did the Equal Rights Amendment fail? What kind of campaign could be run to see it passed?
- Explain how the 14th Amendment has affected civil liberties in the United States from the time of its passage at the end of the Civil War.
- Do you think that the federal government has enough, too much or just the right amount of power? Defend your answer.
- January Writing Prompts
- Key Election Terms for Students
- Voting Rights Background for Students
- Presidential Elections: ESL Lesson
- 501 Topic Suggestions for Writing Essays and Speeches
- Expository Essay Genre With Suggested Prompts
- Current Political Campaign Contribution Limits
- 50 Argumentative Essay Topics
- American Government Journal Topics
- Campaign Finance Laws: Definition and Examples
- 12 Interesting Ethical Topics for Essay Papers
- What Is Political Participation? Definition and Examples
- Fun March Writing Prompts for Journaling
- The Important Role of US Third Parties
- Why Puerto Rico Matters in the US Presidential Election
- What Is a Caucus? Definition and Examples
Constitution of United States of America

45 pages • 1 hour read
A modern alternative to SparkNotes and CliffsNotes, SuperSummary offers high-quality Study Guides with detailed chapter summaries and analysis of major themes, characters, and more.
Chapter Summaries & Analyses
Preamble-Article 1, Section 10
Article 2, Sections 1-4
Article 3, Section 1-Article 4, Section 4
Articles 6-7
Key Figures
Index of Terms
Important Quotes
Essay Topics
Discussion Questions
Identify and explain three to four ambiguous passages in the Constitution. Why might the Framers have deliberately included these ambiguities?
The Constitution enshrines some protections for those accused of crimes. Why is it important for the Constitution to do so?
How does the Constitution approach the existence of Indigenous Americans, enslaved peoples, and indentured servants at the time of its writing? Provide examples from the text in support of your response.

Don't Miss Out!
Access Study Guide Now
Featured Collections
Books on U.S. History
View Collection
Nation & Nationalism
Political Science Texts
Politics & Government
True Crime & Legal
Background Essay: “A Glorious Liberty Document:” The U.S. Constitution and Its Principles

Guiding Questions: How are republican principles of limited government, separation of powers, and checks and balances reflected in the U.S. Constitution?
- I can identify the ways the Founders tried to limit the power of the government.
- I can explain how the principles of government in the Constitution limit the power of the government.
- I can explain how the Constitution protects liberty.
Essential Vocabulary
Introduction.
In 1852, abolitionist Frederick Douglass gave a speech on the meaning of the Fourth of July. He addressed the inequalities and injustices for Black Americans that made them feel they did not belong and had no reason to celebrate the holiday. However, he also stated his belief that the Constitution was “a glorious liberty document.” Douglass believed that the document created a constitutional government with the central purpose of protecting liberty and a free society for all Americans.

The Founders of the Constitution wanted to build a new and enduring representative government based on the authority of the people. Important constitutional principles guided their work at the Constitutional Convention during the summer of 1787. The balancing act of including these principles was difficult but necessary to protect the liberties of the people. Given their assumptions about human nature, and always keeping in mind the ideals of the Declaration of Independence, the Founders created a Constitution rooted in sound principles of government.
Human Nature and Limited Government
The Founders’ understanding of human nature determined the kind of government they created. In Federalist No. 51, James Madison asked, “What is government itself, but the greatest of all reflections on human nature?” The Founders believed that humans were flawed but capable of virtue. Therefore, humans must be allowed to govern themselves, but that government had to be limited and controlled by the people, or liberty would be lost.
The Constitution defines the powers of the national government. Some powers are enumerated powers , or specifically listed. Others are implied powers or not explicitly listed. These are powers that relate to other powers and are therefore implied. For example, the power to raise an army for defense implicitly includes the power to raise an air force. The Founders wanted to strengthen the national government over what existed under the Articles of Confederation, but they also wanted to limit the powers of that government.
Republican Government and Popular Sovereignty
Based upon the Enlightenment ideas of John Locke, the Declaration asserted that just governments derive their powers from the consent of the governed and thus laid the basis for American self-government. This is the principle of popular sovereignty , which means the people hold ultimate authority. The authority of the people themselves is the greatest limit on the power of the government. In Federalist No. 39 , Madison defined a republic as a government that derives its powers from the people and is governed by representatives elected by the people to serve for a defined period.
The republican principle of self-government guided the Founders in creating the new constitutional government. The Preamble begins, “We the People,” and lists the guiding principles of government. The Constitution also provides for defined terms of office, including two years for the House of Representatives, four years for the president, and six years for the Senate. The most republican feature of the Constitution is the predominance of the legislative branch, which is closest to the people.
Separation of Powers
The Founders trusted the people and their representatives in the new government but created additional tools to prevent government from amassing too much power. Madison made it clear in Federalist No. 48 that the people cannot rely on mere “parchment barriers,” limits written on paper, to control government. Government is most effectively limited through well-founded institutions. The Founders chose to divide power as the best way to avoid tyranny and to ensure the rights of the people are protected. The Constitution contains many examples of the separation of powers . Each division of government exercises distinct powers to carry out its functions and to prevent the accumulation of power. The Congress is divided into two houses—a House of Representatives and a Senate—in a principle called bicameralism. The national government is divided into three branches with different powers and functions to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful. A legislature makes the law, an executive enforces the law, and a judiciary interprets the law. Some specific constitutional examples are Congress’s power to declare war, the president’s power to make treaties, and the courts’ power to hear cases resulting from legal disputes. The government is also divided into different levels—national, state, and local—to separate power and limit government. This principle of different levels of government having their respective powers is called federalism .
Checks and Balances
Another central device limiting the power of the national government is the provision for the three branches to check and balance each other’s powers. The Constitution contains many such examples of checks and balances . Congress may pass a law, but the president has to sign or veto it. The president can make treaties, but the Senate has to ratify them. The Supreme Court can review a congressional law or an executive order. Another example is that the House can impeach a president and the Senate can remove a president from office if found guilty in a trial presided over by the chief justice of the Supreme Court. There are numerous other examples that would make a very long list.
The division of power among different levels of government is called federalism. As Madison described in Federalist No. 39 , the Constitution is a mixture of the national and the federal principles. In other words, sometimes the national government has exclusive power, and at other times, the national government shares power with the states. Some examples of federalism from the Constitution include the ratification process for the document itself. The people and their representatives had to decide whether to ratify, or approve, the Constitution in popular ratifying [approving] conventions in the states. The amendment process includes ratification by three-quarters of state legislatures or state conventions. Structuring these processes through the states ensures that approval of and changes to the national government are balanced among the states. Similarly, the Senate equally comprises two senators per state, who were originally elected by state legislatures. The Electoral College gives the states a voice in presidential elections through electors the states choose. These provisions also ensure that though the federal government is supreme, the states have a meaningful role in the system.
In the American federal system, both the national and state governments have sovereignty. In general, the national government is sovereign over national matters, such as national defense, foreign trade, and immigration, while states are sovereign over local matters, including basic rules of public order. As Madison noted in Federalist No. 45 , “The powers delegated by the proposed Constitution to the federal government are few and defined. Those which are to remain in the State governments are numerous and indefinite.” In the federal system, the ultimate power to make decisions for the entire nation rests exclusively with the national government, which, when operating under its proper jurisdiction,is supreme in its enumerated powers. Article VI of the Constitution states that the Constitution, all constitutional laws, and all treaties are the supreme law of the land. More generally, the Constitution empowers the national government to govern for the entire nation. It makes the laws for the country. It makes decisions related to war and peace and conducts relations with foreign nations. It regulates trade between the states and settles disputes among them.
Constitutional Government
American constitutional government is rooted in the ideas of limited government, popular sovereignty, separation of powers, checks and balances, and federalism. These ideas protect the liberties of the people and their right to govern themselves. The Constitution contains words and principles that have the flexibility to respond to centuries of social, economic, and technological change. While the text of the Constitution has words that should be adhered to closely, they are hardly etched in marble. Besides the amendment process that offers a constitutional means of change over time, the American people and their representatives breathe life into the meaning of their Founding documents. They have done so for more than two centuries, through civil dialogue, debate, and deliberation, to reason through the often contested meaning of the Constitution.
Related Content

Background Essay Graphic Organizer: “A Glorious Liberty Document”: The U.S. Constitution and Its Principles

“A Glorious Liberty Document”: The U.S. Constitution and Its Principles
How are the republican principles of limited government, separation of powers, and checks and balances reflected in the U.S. Constitution?

James Madison and Federalist No. 51

The Battle of the Branches: Madison’s “Auxiliary Precautions”
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Constitution
By: History.com Editors
Updated: March 28, 2023 | Original: October 27, 2009

The Constitution of the United States established America’s national government and fundamental laws, and guaranteed certain basic rights for its citizens.
It was signed on September 17, 1787, by delegates to the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia. Under America’s first governing document, the Articles of Confederation, the national government was weak and states operated like independent countries. At the 1787 convention, delegates devised a plan for a stronger federal government with three branches—executive, legislative and judicial—along with a system of checks and balances to ensure no single branch would have too much power.
The Preamble to the U.S. Constitution
The Preamble outlines the Constitution's purpose and guiding principles. It reads:
The Bill of Rights were 10 amendments guaranteeing basic individual protections, such as freedom of speech and religion, that became part of the Constitution in 1791. To date, there are 27 constitutional amendments.
Articles of Confederation
America’s first constitution, the Articles of Confederation , was ratified in 1781, a time when the nation was a loose confederation of states, each operating like independent countries. The national government was comprised of a single legislature, the Congress of the Confederation; there was no president or judicial branch.
The Articles of Confederation gave Congress the power to govern foreign affairs, conduct war and regulate currency; however, in reality these powers were sharply limited because Congress had no authority to enforce its requests to the states for money or troops.
Did you know? George Washington was initially reluctant to attend the Constitutional Convention. Although he saw the need for a stronger national government, he was busy managing his estate at Mount Vernon, suffering from rheumatism and worried that the convention wouldn't be successful in achieving its goals.
Soon after America won its independence from Great Britain with its 1783 victory in the American Revolution , it became increasingly evident that the young republic needed a stronger central government in order to remain stable.
In 1786, Alexander Hamilton , a lawyer and politician from New York , called for a constitutional convention to discuss the matter. The Confederation Congress, which in February 1787 endorsed the idea, invited all 13 states to send delegates to a meeting in Philadelphia.
Forming a More Perfect Union
On May 25, 1787, the Constitutional Convention opened in Philadelphia at the Pennsylvania State House, now known as Independence Hall, where the Declaration of Independence had been adopted 11 years earlier. There were 55 delegates in attendance, representing all 13 states except Rhode Island , which refused to send representatives because it did not want a powerful central government interfering in its economic business. George Washington , who’d become a national hero after leading the Continental Army to victory during the American Revolution, was selected as president of the convention by unanimous vote.
The delegates (who also became known as the “framers” of the Constitution) were a well-educated group that included merchants, farmers, bankers and lawyers. Many had served in the Continental Army, colonial legislatures or the Continental Congress (known as the Congress of the Confederation as of 1781). In terms of religious affiliation, most were Protestants. Eight delegates were signers of the Declaration of Independence, while six had signed the Articles of Confederation.
At age 81, Pennsylvania’s Benjamin Franklin (1706-90) was the oldest delegate, while the majority of the delegates were in their 30s and 40s. Political leaders not in attendance at the convention included Thomas Jefferson (1743-1826) and John Adams (1735-1826), who were serving as U.S. ambassadors in Europe. John Jay (1745-1829), Samuel Adams (1722-1803) and John Hancock (1737-93) were also absent from the convention. Virginia’s Patrick Henry (1736-99) was chosen to be a delegate but refused to attend the convention because he didn’t want to give the central government more power, fearing it would endanger the rights of states and individuals.
Reporters and other visitors were barred from the convention sessions, which were held in secret to avoid outside pressures. However, Virginia’s James Madison (1751-1836) kept a detailed account of what transpired behind closed doors. (In 1837, Madison’s widow Dolley sold some of his papers, including his notes from the convention debates, to the federal government for $30,000.)
Debating the Constitution
The delegates had been tasked by Congress with amending the Articles of Confederation; however, they soon began deliberating proposals for an entirely new form of government. After intensive debate, which continued throughout the summer of 1787 and at times threatened to derail the proceedings, they developed a plan that established three branches of national government–executive, legislative and judicial. A system of checks and balances was put into place so that no single branch would have too much authority. The specific powers and responsibilities of each branch were also laid out.
Among the more contentious issues was the question of state representation in the national legislature. Delegates from larger states wanted population to determine how many representatives a state could send to Congress, while small states called for equal representation. The issue was resolved by the Connecticut Compromise, which proposed a bicameral legislature with proportional representation of the states in the lower house ( House of Representatives ) and equal representation in the upper house (Senate).
Another controversial topic was slavery. Although some northern states had already started to outlaw the practice, they went along with the southern states’ insistence that slavery was an issue for individual states to decide and should be kept out of the Constitution. Many northern delegates believed that without agreeing to this, the South wouldn’t join the Union. For the purposes of taxation and determining how many representatives a state could send to Congress, it was decided that enslaved people would be counted as three-fifths of a person. Additionally, it was agreed that Congress wouldn’t be allowed to prohibit the slave trade before 1808, and states were required to return fugitive enslaved people to their owners.
Ratifying the Constitution
By September 1787, the convention’s five-member Committee of Style (Hamilton, Madison, William Samuel Johnson of Connecticut, Gouverneur Morris of New York, Rufus King of Massachusetts ) had drafted the final text of the Constitution, which consisted of some 4,200 words. On September 17, George Washington was the first to sign the document. Of the 55 delegates, a total of 39 signed; some had already left Philadelphia, and three–George Mason (1725-92) and Edmund Randolph (1753-1813) of Virginia , and Elbridge Gerry (1744-1813) of Massachusetts–refused to approve the document. In order for the Constitution to become law, it then had to be ratified by nine of the 13 states.
James Madison and Alexander Hamilton, with assistance from John Jay, wrote a series of essays to persuade people to ratify the Constitution. The 85 essays, known collectively as “The Federalist” (or “The Federalist Papers”), detailed how the new government would work, and were published under the pseudonym Publius (Latin for “public”) in newspapers across the states starting in the fall of 1787. (People who supported the Constitution became known as Federalists, while those opposed it because they thought it gave too much power to the national government were called Anti-Federalists.)
Beginning on December 7, 1787, five states– Delaware , Pennsylvania, New Jersey , Georgia and Connecticut–ratified the Constitution in quick succession. However, other states, especially Massachusetts, opposed the document, as it failed to reserve un-delegated powers to the states and lacked constitutional protection of basic political rights, such as freedom of speech, religion and the press.
In February 1788, a compromise was reached under which Massachusetts and other states would agree to ratify the document with the assurance that amendments would be immediately proposed. The Constitution was thus narrowly ratified in Massachusetts, followed by Maryland and South Carolina . On June 21, 1788, New Hampshire became the ninth state to ratify the document, and it was subsequently agreed that government under the U.S. Constitution would begin on March 4, 1789. George Washington was inaugurated as America’s first president on April 30, 1789. In June of that same year, Virginia ratified the Constitution, and New York followed in July. On February 2, 1790, the U.S. Supreme Court held its first session, marking the date when the government was fully operative.
Rhode Island, the last holdout of the original 13 states, finally ratified the Constitution on May 29, 1790.
The Bill of Rights
In 1789, Madison, then a member of the newly established U.S. House of Representatives , introduced 19 amendments to the Constitution. On September 25, 1789, Congress adopted 12 of the amendments and sent them to the states for ratification. Ten of these amendments, known collectively as the Bill of Rights , were ratified and became part of the Constitution on December 10, 1791. The Bill of Rights guarantees individuals certain basic protections as citizens, including freedom of speech, religion and the press; the right to bear and keep arms; the right to peaceably assemble; protection from unreasonable search and seizure; and the right to a speedy and public trial by an impartial jury. For his contributions to the drafting of the Constitution, as well as its ratification, Madison became known as “Father of the Constitution.”
To date, there have been thousands of proposed amendments to the Constitution. However, only 17 amendments have been ratified in addition to the Bill of Rights because the process isn’t easy–after a proposed amendment makes it through Congress, it must be ratified by three-fourths of the states. The most recent amendment to the Constitution, Article XXVII, which deals with congressional pay raises, was proposed in 1789 and ratified in 1992.
The Constitution Today
In the more than 200 years since the Constitution was created, America has stretched across an entire continent and its population and economy have expanded more than the document’s framers likely ever could have envisioned. Through all the changes, the Constitution has endured and adapted.
The framers knew it wasn’t a perfect document. However, as Benjamin Franklin said on the closing day of the convention in 1787: “I agree to this Constitution with all its faults, if they are such, because I think a central government is necessary for us… I doubt too whether any other Convention we can obtain may be able to make a better Constitution.” Today, the original Constitution is on display at the National Archives in Washington, D.C. Constitution Day is observed on September 17, to commemorate the date the document was signed.

HISTORY Vault
Stream thousands of hours of acclaimed series, probing documentaries and captivating specials commercial-free in HISTORY Vault

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
182 Constitution Essay Topics & Examples for Students
Searching for perfect constitution essay topics can take a while. We did this job for you, so now you can check our compilation of 89 constitutional issues topics in this article
🏆 Best Constitution Essay Topics
👍 good constitution essay topics for students, 💡 most interesting constitutional issues topics, 🎓 good research topics about constitution, ❓ essay questions about the constitution.
- Similarities and Differences between Articles of Confederation and Constitution – Compare and Contrast Essay In both, the laws are made by the legislature, whereby the articles of confederation have only one house which is referred to as Congress, and the constitution has got two houses.
- The Framing of the US Constitution In addition, the UK put these ideas to enhance the fusion of powers, unlike the USA, which framed the constitution to enhance the strict system of separation of powers.
- The Efforts and Activities of the Paparazzi are Protected by the Freedom of the Press Clause of the Constitution The First Amendment of the American constitution protects the paparazzi individually as American citizens through the protection of their freedom of speech and expression and professionally through the freedom of the press clause.
- Why Is the Bill of Rights Important Today Essay The bill of rights is one of the basic provisions of a given constitution and it spells out the rights and freedoms of all the citizens of a given nation.
- Aspects of Arizona Constitution Below the attorney general is the treasurer, while the superintendent of public instruction is at the bottom of the ladder. I believe that the current qualifications for members of the plural executive in Arizona are […]
- Democratic and Undemocratic Elements of the Constitution The judicial arm, also known as the Supreme Court, functioned to establish the jurisdiction of particular cases under the US judicial system; the disposition of convicted prisoners; and the production of evidence and testimonies as […]
- The Border Security Tax and Violation of the U.S. Constitution One of them is known as “taxation without representation,” and its applicability to the case is conditional upon the attempts of the president to make Mexico pay for the prospective wall construction.
- Notwithstanding Clause in the Canadian Constitution In such a case, a legislator might refer to the notwithstanding clause and justify the priority of the collective majority’s rights over individual rights and freedoms of the citizens.
- Democratic Principle: The Constitution of the US The two major democratic principles are closely interrelated and the parties involved into them can actually change places from time to time: the minority has the right to become the majority, thus the latter becomes […]
- Uncodified Constitution of the United Kingdom According to Oxford Dictionary of law, “constitution” is defined as “the rules and practices that determine the composition and functions of the organs of central and local government in a state and regulate the relationship […]
- Double Jeopardy: The Fifth Amendment to the Constitution This therefore means that punishment will only be done ones and in case the offender is tried again, it will be considered as double jeopardy.
- Canada’s Constitution and Its Surprising Aspects The peculiarity of the Canadian Constitution is that it includes two parts, namely: written, which consists of separate judicial precedents and legislative acts, and unwritten in the form of agreements and established legal customs.
- Purpose of Government and Preamble of Constitution The Preamble distilled the objective of the Constitution. Under the Constitution’s Preamble, the government establishes the laws of the land.
- The US Constitution Ratification Dispute Moreover, the anti-federalists argued that the citizens would not be able to participate in administration because of the undemocratic nature of the Constitution.
- Should the Texas Constitution Be Reformed? The structure of the Texas Constitution is quite intricate, and its text is one of the longest in the United States.
- US Constitution and International Law & Policy In international law, popular sovereignty takes on the concept of state sovereignty, which is the ability, power, and immunity of a state or territory to make autonomous choice.
- Aspects of the U.N. Charter and the US Constitution As well-established, the US Constitution is the document that defines the national frame of government in the United States and serves as the supreme “law of the land” being the foundation of US legislation and […]
- Constitution Changes After Pandemic He is a writer who has authored books on legal representation of the low-standard people, the politics of Texas, and the election of judges, among others. Therefore, the issues of vaccination and the related constitutional […]
- The Conception of the American Constitution In the years following America’s victory for independence in 1776, the country was ruled by a small Confederate government consisting of a Congress bound by the Articles of Confederation.
- The Articles of Confederation and the Road to the Constitution The question of the abolition of slavery only received the beginnings of discussion thanks to the representatives of the North, but for the most part, the aspect of taxation and the counting of servants in […]
- Constitution of Trusts and Gifts The law defines capacity as the capability to understand and retain information relating to the decision and to weigh it in balance when making a decision.
- The New Jersey Constitution: The Protection of the Rights of Citizens The constitution of each state enshrined provision for the protection of individual rights of citizens, which also applies to New Jersey.
- The 13th and 15th Amendments to the U.S. Constitution The abolition of slavery across the state has impacted U.S.history and the life of every American citizen, as this process initiated the restoration of individual freedom and nationwide democracy.
- Alan Westin and the US Constitution on Privacy The position of the Supreme Court in this regard is roughly consistent with this in the sense that it does not focus on privacy per se.
- The US Constitution: Creation Process The independence of the United States after the Revolutionary War began with the establishment of the Articles of Confederation. The Constitution that corrected the inefficiencies of the Articles of Confederation was created and established in […]
- Provisions of the Constitution of the United States and the State of Illinois It is also essential to mention Article Three of the Illinois Constitution, which established the suffrage of citizens and the right to elections.
- The Bill of Rights and the Florida Constitution The Constitution of the state of Florida is similar to the bill of rights, yet distinct in a variety of freedoms and protections it offers.
- Neil Gorsuch and the Constitution In the video, the main topic is the discussion of constitutional issues and the organization of state power. The executive branch monitors compliance with the correct execution of the law, while the judiciary relies on […]
- Ratification Process of the Constitution of 1787 The anti-federalists believed that the legal status of the states should remain high and that the states had every right to self-government.
- Shotoku Taishi’s Seventeen Article Constitution of Japan In that, just as the Lord, who is Heaven commands its subject, should obey, the people of Japan should pay heed to their imperial powers and submit to avoid harsh consequences, which are otherwise termed […]
- Personal Jurisdiction: The United States Constitution In reality, the court may reject a case for lack of subject-matter jurisdiction on the spot if the contents of the case transpire the limits of the court’s jurisdiction.
- US Constitution Changes Regarding Electoral College The first lens is the political lens, which is the understanding of the power relationship between those who possess the power and those who lack it.
- The Amendment of the Missouri Constitution However, the addition of the number of women seats according to the demographic sizes directly affects and influences almost every member of the community.
- Happy Coffee Shop: Draft Corporate Constitution Happy Coffee Shop has all legal capacity and power as provided in the Corporations Act (CA). This is the constitution of Happy Coffee Shop Propriety Limited.
- Cell Phone Privacy and the Constitution In this chapter, the authors investigate the concept of privacy and whether government employers’ warrantless searches may be considered reasonable and justified.
- Alexander Stephens on Slavery and Confederate Constitution The speaker remarks that the persistent lack of consensus over the subordination and slavery of the “Negro” between the South and North was the immediate reason why the Confederates decided to secede and establish their […]
- Resolving Disputes and the Constitution Yona Shamir outlines the positive aspects of mediation which include: 1) mediation largely helps in bringing to the forefront the main and contentious issues of the dispute due to the fact that it has the […]
- How Relevant Is the Constitution to Our Government Today? The original text of the Constitution was not perfect, and not even all delegates were ready to sign this document due to the lack of a bill of rights.
- U.S. Constitution, 17 September 1787 The Constitution is the supreme law of the US. It spells out the relationship between the ruled and the ruler.
- Ratifying the New American Constitution James Madison is believed to be one of the most influential people that the US has ever had, his Father was a plantation owner and he studied in the state of Virginia in the US.
- United Sates and Arizona Constitution Final Action: subsequent to both the House and Senate accepting a bill in the same shape, it is propelled to the president.
- Evaluation of the Constitution of the United States of America The Constitution of the United States of America is deemed as the supreme law. The Constitution grants rights to the nation of the United States.
- The Federalist Papers to Understand the United States Constitution The purpose of the federalist papers was to convince the people of New York to ratify the proposed constitution because most of the other states had already done so.
- Double Jeopardy Clause of the U.S. Constitution In as much as the constitution provides for a strict verdict pertaining to continuation of cases, Double Jeopardy Clause is not at all violated in this scenario.”Under the certain circumstances two state trials in two […]
- Analysis of the Constitution of the United States It is also the right of the accused to be informed of the right to call witnesses to support his case.
- National Security Within the Constitution On the other hand, the legislature has the mandate to formulate laws for the sake of citizens because they are representatives of the people; thus, judicial review of laws, which are passed by the legislature, […]
- Zoning Ordinance in Georgian Constitution, US The local government in Atlanta can be compelled by the court to justify the zoning ordinance if Irene Lopez can demonstrate that it has caused financial losses and contradicts public interest.
- Warrantless Search: The 4th Amendment to the US Constitution That is why it is now illegal for the officers to conduct a warrantless search if they are convinced that any time wastage would jeopardize their ability to succeed in making an arrest.
- The Australian Constitution and Council of Australian Governments The first requirement that should be met in the initialization of the process that sets the stage for the amendment of the constitution is prior notice.
- Appeal of Quebec Concerning the Constitution of Canada The appeal was directed at considering the veto set on the First Reference, by the Quebec Court of Appeal. 3 The answer of the Court of Appeal to the question was negative.
- Correctional Law: Amendments in the US Constitution In an incident in which the prisoner was searched by a female officer in the absence of a male officer while in prison, the Fourth Amendment of the prisoner was not violated, because the female […]
- US Constitution and Ruling of Loving vs. Virginia Such examples of the Main Law of the country and the Declaration of Peoples’ Rights violation as in the case of Dr.
- Constitution of the State of Georgia, USA In this regard, below, there is a proposition of a hypothetical modification of the Georgia constitution by the current situation in the United States and the world – for example, it is possible to propose […]
- What the Declaration and the Constitution Mean to Me For me, the Constitution is, first and foremost, the necessary complement to the core values of the Declaration: the notions of equality and irrevocable rights.
- Beard’s Interpretation of the Constitution The primary aim of the Constitution was to unite the nation and create a number of regulations suitable for all kinds of people, which is why the framers tried to reach compromises in every question.
- Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution Review In the current board post, the question on what the 13th Amendment is and how it relates to ongoing free “slave” labor in U.S.prisons will be considered and discussed. The 13th Amendment to the United […]
- The Us Constitution: The Concept of the Lifetime Appointment The main motive for creating Article III was the desire to protect the judges of the Supreme Court from the need to participate in political events, which excludes their bias.
- Creation of Constitution and Bill of Rights The Articles of Confederation failed to unify the nation because in this document, the empowerment of the government of the United States was utterly limited.
- American Government Congress. Referring to Constitution Congress men and women therefore make every effort to attune business on the floor of the house to the perspective of their constituents.
- Courts Seeking the “Original Meaning” of the Constitution As a solution to any misinterpretation of the law, basically because of the probable fact that times have changed and that the original meaning may not make sense, there is usually room for amendments that […]
- Should Courts Seek Original Meaning of Constitution? It is therefore not in the interest of the people that the courts search for the original meaning of the constitution and apply it in deciding the cases involving the people.
- Is the Constitution Supportive of Today’s Democracy? Additionally, one of the dominant elements in most constitutions is the principle of democracy which refers to the government by the people for the people themselves.
- Origin and History of the Democratic Party and the Federal Constitution The acknowledgement of the USA independence by the Great Britain and the ratification of the treaty of peace of the 1783 at once led to the formation of schemes and the organization of factions, having […]
- 1910-1940 Mexican Political Development In this essay, I will discuss the causes of the Mexican revolutions, the major stages in the revolution, immediate and long term effects of the revolution, the constitution and the Presidents who served Mexico from […]
- Justice in America: Constitution, Laws and Reality The metaphysical essence of notions of justice, freedom and intellectual excellence in this country, directly derives out of European mentality and out of European sense of religiosity; therefore, these notions can hardly be thought of […]
- The American Constitution: Short History This makes the US constitution the oldest in the world, where 159 countries of the world had a constitution by the end of the 20th century.
- Britain’s Unwritten Constitution The issue of democracy in many states has led to a lot of criticism of the unwritten constitution in Britain because the disadvantages accompanying it are viewed to make it look bad.
- The Problem of the New Constitution: Eric Foner’s “Give Me Liberty! An American History” The ratification of the Constitution made the representatives of Antifederalists create the list of commentaries related to the new document adoption.
- US Political Science: Constitution Establishing justice is surely also the consequence of injustice that dominated the human and legal relations in the USA in the times of the British reign.
- South Africa: Human Rights in the Constitution The Bill of Rights serves as the foundation upon which the democratic character of the Republic of South Africa is built.
- The Progressive and California’s Changing Constitution According to the author of the aforementioned book, the issue lies with the lack of a proper leadership which would seek to revolutionize the current form of constitutional order by indulging in some of the […]
- Constitution and James Madison’s Influence on It Though, “the natural liberty” of an individual is argued in the work so that to find out the truth in evaluating the concept of freedom in the state supported by the Constitution in our case.
- US Constitution in the E-Commerce Context If we are speaking about E-commerce, one of the most stressful issues is the problem of privacy and confidentiality, because many people who prefer to operate in Web environment, try to make sure that their […]
- The U.S Constitution and National Security The rights of U.S.citizens to non invasion of privacy, unreasonable search and seizures, which are protected by the fourth and ninth amendments of the U.S.
- Formation of the U.S. Constitution Not only did the states have to approve, but also congress did not have the power to take appropriate measures to any state that failed to adhere to the stipulations of the treaty thus making […]
- James Madison and the United States Constitution The formation of the U.S.constitution was faced by challenges due to the existence of the federalists, who supported the constitution and the anti-federalists, who were against the constitution.
- The Constitution of the French Fifth Republic The standard process of constitutional amendment is as follows: the amendment must be accepted in equal periods by both houses of Parliament, they must be either accepted by a simple mainstream in a referendum, or […]
- Drug Testing and 4th Amendment of the US Constitution S Constitution on the drug prevention in the nation and it tries to judge whether legalization, decriminalizing drug use and drug treatment could offer a better solution to the issue of drug use and drug […]
- Montesquieu and the US Constitution The constitution of the United States says that, the power of legislation is vested upon a congress of United States, which consists of a senate and House of Representatives, the executive power is vested on […]
- Canadian Constitution Reform and Charlottetown Accord It was by the intervention of the supreme court of Canada which gave the ruling that the British parliament should pass the Canada act 1982 into law because the constitution applied to all the provinces […]
- Constitution According to Dworkin’s Theory We can observe the consequences of the accident, which appeared to be fatal for its victims; the involvement in the case where the emotional injuries are awarded is regarded from the theory of Dworkin.
- Government Amending the American Constitution The first reference to the use of a convention requested by the States is found in drafts of the Constitution kept by the Committee of Detail.
- Most Significant Amendments to the Constitution At the end of the 19th century, there was very little opportunity at the Constitutional Convention for Madison to support a bill of rights of the conventional sort.
- Texas Government and State Constitution With the thoughts of the civilian revolution still in mind, there arose a need to re-write the constitution that witnessed the creation of a constitution that devolved the powers of the government to the local […]
- Majority Rule in US Constitution and Policies The same document ensures that the majority is not able to infringe on the rights of the minority. The majority rule is the basic principle of U.S.democratic government, which rests on the assumption that policies […]
- Federal Constitution Pros and Cons He also opposed Brutus idea of a small state with absolute liberty and said that it was to be replaced by the bigger state under the confederation.
- The President’s Czars: Undermining Congress and the Constitution Rozell “The President’s Czars: Undermining Congress and the Constitution,” which elaborates a comprehensive definition of a czar, offers a history of the phenomenon, and provides analysis of the matter. The major part of the book […]
- The Preamble to the U.S. Constitution The Preamble is imperative to the constitutional development of the country because it establishes a certain set of goals that the Constitution is aiming to reach: “We the people of the United States, in Order […]
- American Constitution, Its Strengths and Gaps On the one hand, the primary goal of the document was achieved, as it defined the scope of the power of the new state.
- Why Blacks Are Not Mentioned in the Constitution? The fight for supremacy in the congress room was also one of the factors that led to the lack of inclusion of the blacks in the constitution.
- US Constitution as a Source of Contradictions It has to be mentioned that by the time when the Articles of Confederation appeared slavery on the territory of the United States was very popular and the majority of the most outstanding politicians such […]
- Social Inequality, Constitution, and Revolution Rousseau argued that in the past people had no hunger for individual ownership of the property until one person fenced a piece of land and claimed that the land belonged to him; after this, people […]
- Justifying the Bill of Rights: the US Constitution The constitution depends upon the process of amendment to guarantee personal freedom and the nature of the adaptability of the constitution.
- Intrastate Commerce Law and the US Constitution Due to the fact that the interest of the state is higher than that of the country, the statute is thus regarded as unconstitutional since it affects the commerce of the states.
- Articles of Confederation and Constitution of the US Drafted in 1776 and ratified on 1 March 1781, the Articles of Confederation was the first constitution for the government of the colonies.
- United States Constitution and Criminal Procedure The view of the role of the judiciary and the rule of law in society is also provided in the paper.
- Affirmative Action and South African Constitution The police service argued that the National Commissioner had been justified in his decision because he was following the Employment Equity Plan and that since making appointments was his prerogative, he was not bound by […]
- Flag Desecration: US Constitution Amendement 21: “A joint resolution proposing an amendment to the Constitution of the United States authorizing the Congress to prohibit the physical desecration of the flag of the United States”.
- The Sixth Amendment to the United States Constitution The original document contained all the provisions of the current legislation except the right of a defendant to get the services of a lawyer.
- Court System vs. the United States Constitution This meant that the judicial districts were matched to the state borders and supported the exploitation of the particular state’s legislation for the majority of court proceedings in the area.
- The United States Constitution and Criminal Justice The legal principle called the Exclusionary Rule is the result of the Supreme Court interpretation of the constitutional right of the United States citizens to be free from unreasonable searches and seizures.
- Reasons Why Britain needs a Written Constitution According to Thompson, Britain is a prominent country in the European region, and in the whole world. A written constitution would, however, ensure the influence of lawmakers is kept in check and that avenues of […]
- The Rise of American Democracy: Influences of the Constitution The American constitution shares similar concepts of the importance of written documents, limited government and the citizen’s rights to modify government forms, should the government fail to act as the citizens recommend.
- U.S. Constitution Law’s Impact on Tanya’s Company For this reason, the state of confusion statue is unconstitutional and therefore, Tanya needs to find the court that has jurisdiction over this case and proceed to file a suit.
- The Constitution of China: the Shaanxi Province Position Thus, in spite of the fact Shaanxi Province was discussed during a long period of time as the centre of the conservative and revolutionary communistic forces in the country, today the governmental representatives of Shaanxi […]
- The Georgia State Constitution and Systems The two branches are the executive branch, which is composed of the governor, the plural executive, and constitutional boards and commissions, and the judicial branch composed of trial courts, appellate courts, and district attorneys and […]
- The Constitution and the African Slave Trade (1787) First of all, the document stresses the need to unite all the states with the purpose of unity of the people.
- The U.S. Constitution: Protection of Rights and Vagueness The premises for the provision of rights to every single denizen of the U.S.population can be viewed as the key asset of the Constitution.
- Confederation Articles and 1787 Constitution The article created slack independent states giving limited powers to the overall central government, the major weakness with this part of the article was that each state possessed a single vote in the house of […]
- The US Constitution Overview and Its Aspects In the constitution a lot of individual rights are mentioned and seem to be the top agenda in the composition of its text. The interpretation of the constitution should not be left to the politically […]
- US Constitution: Amendments, Agreements, Compromises The major agreement and compromises that were mainly discussed in the US constitution were the issue of slavery, and the content of the legislature.
- Government and Constitution of the United States of America The sharing of power is essential in the process of governance because government services are taken closer to the citizens and the citizens’ views are considered by leaders.
- The Constitution, Social Rights, and Liberal Political Justification Also, the critique investigates research designs and conceptualized results, which are quantifiable and assess the same in terms of relevance in the present application of the law.
- The Equal Rights in the U.S. Constitution In the first part of the article, the authors present the history of the debates on the topic, highlighting the main ideas expressed in favor and against of the ERA ratification in the U.S.
- The U.S. Constitution: Fifth Amendment While the Fifth Amendment applies to the rights of the accused to an attorney during interrogation, the Sixth Amendment is applicable after the indictment.
- Comparing the Articles of Confederation with the Federal Constitution The Articles of Confederation and the Federal Constitution agreed on the title of “The United States of America” as the official name of the newly united colonies.
- Title VII of the Constitution In the organization, article VII requires that the religious beliefs and practices of employees should be given priority over the interests of the company.
- Attorney General in Charter of Rights and Freedoms Cases Edwards argued that in an event that the attorney general represented the government in the Charter of Rights litigation, he had a constitutional duty to protect the interests of the public.
- The Constitution of Medina The constitution of Medina outlines a series of agreements that were drawn up in the first three years after the Hirja to end the differences between the people of Yatrib and the Muhajirun.
- Components of the American Constitution that reflect pluralis These intentions include the successful distribution of powers between the three arms of the government, which are the judiciary, the executive and the legislature, establishing a system of checks and balances and limiting the control […]
- Leadership and Constitution According to the United States constitution, the President is the Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces. Article 1, section 2 of the US constitution stipulates that the president has the power to appoint and dismiss high-ranking […]
- Objections to the U.S. Constitution of 1787 It is also observed that it was not representative a huge percentage of the populace was not guaranteed of representation of its views. The constitution even threatened the very existence of the states.
- Gay Marriages and US Constitution 37 % of voters in the United States of America are of the opinion that gays and lesbians should be allowed to marry legally.
- National Security and the Constitution The major causes of these contradictions include: The 1996 Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act [HIPAA], the Financial Services Modernization Act [FSMA] enacted in 1999, the Homeland Security Act enacted in 2002, information-sharing, national security, […]
- American Revolution and the Crisis of the Constitution of the USA In whole, the American people paving the way to independence have to face challenges in the form of restricted provisions of Constitution, wrong interpretation and understanding of the American Revolution, and false representation of conservative […]
- O’Connor and Sabato: “The Constitution” Chapter The authors of the book believe that the issue of slavery was one of the most important issues in the US legislature.
- History of Slavery Constitution in US The framers of the constitution did not tackle clearly the issue of slavery and they were compelled to make a temporary compromise in order to unite the states in the country.
- Thomas Jefferson and the Writing of the Bill of Rights and the US Constitution The important nature of the Declaration of Independence cannot be overstated; it was through the statement that the 13 colonies in America declared their independence from the British Empire.
- The Constitution in Public Administration: A Report on Education The constitution should be the overall law that governs issues and management of public institutions; in some instances, the constitution may have some bureaucracy that hinders efficiency among public administrators however it is normative that […]
- Presidential Powers in the United States Constitution The establishment of the senate, congress, electoral system, and limitation of the presidential term to four years is some of the systems that control presidential powers.
- Differences Between State of Nature, State of War and United States Constitution The state of the nature allows people the state of liberty to dispose of themselves or their possession in nobler instances. The nature of the state accords the jurisdiction to take law in the hands […]
- American Constitution as a Critical Component of American Government The American constitution is also a critical component of American government.[1] The constitution is used as the supreme law of the land since all other statutes operate below it.
- The Constitution of the US : Issues and Amendments The constitution of the US is the absolute law of the nation, which acts as a guide to the political culture of the Americans and the law.
- New Constitution of USA in 1787 Contrary to the Virginia plan, the New Jersey plan called for equal state representation in the congress regardless of the size of the state.
- Concept of Living Constitution in “Essential of American Government: Root and Reforms” a Book by O’Connor, Yanus and Sabato Therefore, the constitution had to be made in such a way as to allow its evolution in order to accommodate the needs of the society.
- Political Concepts: the New Kenyan Constitution In the article, the author suggests that the former president is the winner in the recently concluded elections because his political students made it to power.
- The Specifics of Society Genetic Constitution In other words, in order for a particular rich individual to be admitted to the ‘club’, he or she would have to prove the sincereness of its commitment to the existential values, shared by the […]
- Robert A. Dahl’s book – “How Democratic is the American Constitution” In this book, Dahl reminds the American society of the missing link in their constitution; a flaw that makes the sacred draft unqualified as a basis for the country’s democratic system.
- Killing Someone Without Going Against the Constitution Elder and Terkel illustrate that “if the death penalty is not abolished, the population of death row inmates in the US will exceed 4,000 by the end of the decade”. This confirms the fact that […]
- Does the Constitution represent a fulfillment or a betrayal? The term federalists in American history mainly referred to two instances and in the first case the term is used to refer to the public figures or statesmen who made the ratification of the proposed […]
- The Constitution and Civil Liberties It grants rights and freedoms namely, freedom of religion, freedom of press, and freedom of speech, among others. It also provides rights to equal protection, freedom of conscience, opinion and religion, as well as speech […]
- The United States Constitution The United States’ constitution is a legal framework that anchors several amendments and provisions in view of evolving legal issues of governance in the modern world.
- The Fourteenth Amendment to the US Constitution Therefore, we hold that the plaintiffs and others.are, by reason of the segregation complained of, deprived of the equal protection of the laws guaranteed by the Fourteenth Amendment”.
- Declaration of Independence – Constitution Thirteen to 22 abuses describe in detail the use of parliament by the King to destroy the colonies’ right to independence.
- Role of the American Constitution in America’s Political Process In analysing the power of the constitution when defining the American political landscape, this study will evaluate the role of the constitution in establishing checks and balances in government from an analysis of the senate, […]
- On the First Amendment to the U.S. Constitution The freedom that Americans experience comes at a price because there are conflicts and problems that arise from the interpretation and implementation of the First Amendment, however, many legal experts are saying that it is […]
- Constitution and Government System Federalism is the embryonic rapport “between the states and the federal government of the United Stases”. The powers of federal administration are officiated in the constitution and the rest belong to regional governments.
- Constitution Ethical Issues However, the United States constitution has put checks and balances in place in order to ensure that in maintaining law and order, the police officers respect the rights of the populace.
- The Right to Bear Arms in the US Constitution The research paper seeks to explore the Right to bear arms and the Right of search and seizure as stipulated in the US constitution.
- How the Constitution Applies to Being a Military Leader/Officer On the other hand, it must be mentioned that though it is the duty of the military to protect the Constitution it is only through the Constitution itself and its various amendments that the military […]
- The Relevance of the US Constitution The principles which are presented in the Constitution of the USA are the significant components of the Americans’ national identity. These associations are the results of the country’s policy which is based on the principles […]
- US Constitution Reflections on the First Amendment Paper The first amendments made on the constitution of the United States of America in the year 1789 concerned the bill of rights.
- How Did the Constitution Attempt to Correct the Flaws of the Articles of Confederation?
- Does the Constitution Forbid Religious Displays on Public Property?
- How Did Abraham Lincoln Shed the Constitution to Become the Greatest President the Nation Has Seen?
- Did the Constitution Intend for a Multi-Party Political System?
- How Does Constitution Affect Arizona?
- Does the Constitution Guarantee the Right to Clone?
- How Did the Constitution Cause Our Nation?
- Should Courts Seek the Original Meaning of the Constitution?
- How Did the Constitution Guard Against Tyranny?
- Does the Constitution’s Fourth Amendment Protect Information Contained in a Paging Device?
- How Did the Constitution Set the Precedent for the Civil War?
- Did the Constitution Guard Against Tyranny?
- How Did the Framers Create the Constitution?
- Does the U.S. Constitution Need an Equal Rights Amendment?
- How Did the Nineteenth Amendment Come To Be Part of Our Constitution and Why Was It Significant?
- What Is the Role of the US Constitution and the US Legal System in Business Regulation?
- How Did the U.S. Constitution Cause Separation?
- Does the U.S. Constitution Stand the Test of Time?
- How Does Digital Evidence Affect the Digital Constitution Act?
- Did the Constitution Contribute to the Failure of the Union It Created?
- How Does the Australian Constitution Empower the Commonwealth Parliament to Make the Most of the Country’s Laws?
- Does the Constitution Define Marriage?
- How Are Abortion, Freedom, and Corruption Depicted in the Constitution’s Fifth and Fourteenth Amendments?
- Should Banning Same-Sex Marriages Be in the US Constitution?
- How Does the Constitution Affect Governance Today?
- Should Terrorists Have Miranda Rights Based on the Constitution?
- How Does the Constitution Effectively Protect Freedom?
- Should the UK’s Constitution Remain Uncodified?
- Why Did the United States Dump the Articles of Confederation for the Constitution of 1787?
- What Were the Most Important Weaknesses of the Weimar Constitution?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, September 18). 182 Constitution Essay Topics & Examples for Students. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/constitution-essay-topics/
"182 Constitution Essay Topics & Examples for Students." IvyPanda , 18 Sept. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/constitution-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2023) '182 Constitution Essay Topics & Examples for Students'. 18 September.
IvyPanda . 2023. "182 Constitution Essay Topics & Examples for Students." September 18, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/constitution-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "182 Constitution Essay Topics & Examples for Students." September 18, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/constitution-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "182 Constitution Essay Topics & Examples for Students." September 18, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/constitution-essay-topics/.
- Criminal Justice Essay Topics
- Supreme Court Essay Topics
- Civil Law Paper Topics
- Human Rights Essay Ideas
- Women’s Rights Titles
- Civil Rights Movement Questions
- Freedom Topics
- Bill of Rights Research Ideas
- Declaration of Independence Paper Topics
- Children’s Rights Research Ideas
- Fourth Amendment Essay Topics
- Electoral College Research Topics
- First Amendment Research Topics
- Sixth Amendment Topics
- Fifth Amendment Essay Ideas

- Teacher Opportunities
- AP U.S. Government Key Terms
- Bureaucracy & Regulation
- Campaigns & Elections
- Civil Rights & Civil Liberties
- Comparative Government
- Constitutional Foundation
- Criminal Law & Justice
- Economics & Financial Literacy
- English & Literature
- Environmental Policy & Land Use
- Executive Branch
- Federalism and State Issues
- Foreign Policy
- Gun Rights & Firearm Legislation
- Immigration
- Interest Groups & Lobbying
- Judicial Branch
- Legislative Branch
- Political Parties
- Science & Technology
- Social Services
- State History
- Supreme Court Cases
- U.S. History
- World History
Log-in to bookmark & organize content - it's free!
- Bell Ringers
- Lesson Plans
- Featured Resources

Lesson Plan: AP Government: Argumentative Essay Practice
The Federalist Papers
Boston College professor Mary Sarah Bilder gives a brief overview backgrounding the Federalist Papers
Description
This is intended as an end-of-course review activity for practice with the argumentative essay format included on the AP United States Government and Politics exam since the 2018 redesign. Eleven practice prompts are provided, reflecting content from Units 1-3.
ARGUMENTATIVE ESSAY PROMPT ANALYSIS
- Review the provided Argumentative Essay Prompts in either an individual or jigsaw format.
- Write a thesis statement for your selected prompt(s) and identify the selection you would make from the provided list and the second piece of evidence you would choose.
- If there are prompts for which you struggle to develop a thesis, or items on the bulleted lists with which you are not conversant, use the hyperlinked C-SPAN Classroom resources to extend your understanding of the required founding documents and SCOTUS cases that you found challenging.
ARGUMENTATIVE ESSAY
- Chose one or more of the provided Argumentative Essay Prompts , as assigned, and use the planning and exploration you did above to write a full essay in response to your designated prompt(s) in 25 or fewer minutes , since that's the time limit you'll face on the AP Exam!
- Exchange essays with a classmate and evaluate each others' work.
- 1st Amendment
- Branches Of Government
- Constitution
- House Of Representatives
- Separation Of Powers
- Supreme Court
- Call to +1 (844) 889-9952
95 Constitution Research Topics & Essay Examples
📝 constitution research papers examples, 💡 essay ideas on constitution, ❓ constitution research questions.
- Citizens and Citizenship Rights Law essay sample: This paper will explore the history of citizenship and citizens’ rights. The paper will focus on the history of the issue, the constitution, and the controversies arising from the issue.
- The First Amendment and Privacy Rights in the US Law essay sample: As illustrated by the first amendment notable cases, the United States supreme court can only interpret the constitution, or decide how the amendments are to be applied.
- The US Constitution's Influence on the Criminal Justice System Law essay sample: The U.S. Constitution is the supreme law of the land and the guide for all criminal law processes within the judicial system.
- The United States Constitution Law essay sample: This work examines what types of powers are given to the national government by the Constitution and studies the issue of The Equal Protection Clause, part of the US Constitution.
- Is the Bill of Rights Necessary or Not Law essay sample: Why do we have a Bill of Rights? The Founding Fathers argued over its necessity. Explanation of the personal view on whether the Bill of Rights is necessary or not.
- Supreme Court and the Federal Court System Law essay sample: The US Supreme Court is the highest court on the land charged with the responsibility of interpreting important questions about the constitution.
- The Bill of Rights in the United States Law essay sample: This paper defines what is bill of rights as the fundamental rights and freedoms which should be provided to everyone to preserve human dignity.
- Rights and Freedoms in US Law essay sample: The U.S. Constitution is the supreme law of the land and the guide for all criminal law processes within the judicial system. The article specifies the points of human rights and freedoms.
- Constitution and System of Separation of Powers Law essay sample: The Constitution has three main articles that show the power the three branches have: Congress, the executive, the judiciary.
- Why Britain Needs a Written Constitution? Law essay sample: In this paper, there are a lot of persuasive arguments for creating and implementing a written constitution in The United Kingdom of Great Britain.
- Constitutional Interpretation and Judicial Review Law essay sample: Judicial Review is a power conferred to a court to review a section of regulation, statute, or constitution in a bid to check if it is constitutionality.
- Issues Surrounding the Ratification of the New Constitution Law essay sample: A number of different factors contributed to the formation of the classical model of federalism; however, the adoption of a Constitution was accompanied by acute debates.
- Rights Protected by the Second Amendment Law essay sample: The Second Amendment right hence gives individuals the right to privately possess as well as carry firearms peacefully.
- Should Same-Sex Couples Receive Constitutional Protection? Law essay sample: The constitutional rights and principles set social order and relations inside society so that legal same-sex marriage will hurt most people's social morals and ethical values.
- Is Healthcare a Civil or Human Right? Law essay sample: This paper seeks to argue out that like any other fundamental human right like food and shelter, health care is a human right and should not be considered a legal right.
- Stop-and-Frisk Is Not Constitutional Law essay sample: Stop-and-frisk is a policy that is common in many nations across the world. In some countries, the act is constitutional, while in others, it is unconstitutional.
- The Role of the Appellate Court System in the USA Law essay sample: The U.S. appellate court system is important to protect defendants’ rights and correct errors made in courts. The U.S. Supreme Court plays the main role.
- Bill of Rights in US and South Africa Constitutions Law essay sample: This paper compares the Bill of Rights found in the United States Constitution to the Bill of Rights found in the Republic of South Africa’s Constitution.
- First Amendment and the Concept of Free Government Law essay sample: The first amendment forms part of the bill of rights of America’s constitution, and it is one of the changes that have reinforced US democracy.
- Traffic Stops, Searches, and Seizures Law essay sample: A traffic stop, search, and seizure refer to the legal act of stopping an automobile, searching it, and seizing contraband or any material that is considered evidence.
- The First, Fourth and Sixth Constitutional Amendments Law essay sample: The bill of rights plays a crucial role in the lives of American citizens. As discussed above, the first amendment prohibits Congress from establishing a religion.
- Bill of Rights and Florida Legislature Law essay sample: The Bill of Rights has set the foundation for ensuring every citizen’s safety, agency, and dignity. The constitution of each state shares principal ideas with the Bill of Rights.
- The Florida Constitution and the Bill of Rights to the U.S. Constitution Law essay sample: This work compares the Bill of Rights to the US Constitution, and the Constitution of the State of Florida, which declares the rights of a citizen of the State.
- State Powers: The Bill of Rights of the United States Law essay sample: This paper analyzes the commonality and differences between the Bill of Rights of the United States of America with the Constitution of the State of California for similarities.
- Access to Healthcare in the Context of the U.S. Constitution Law essay sample: This paper examines the issue of equitable access to healthcare in the context of the U.S. Constitution, and the steps that have been taken at the policy level.
- America’s Constitution and the Views of the Anti Federalists
- British Political System: Analyzing the Constitution to Understand the Concept
- Constitution, Declaration and Address of the American Anti-slavery Society
- Drafting, Ratification and Implementation of the USA Constitution
- United States Constitution and Health Insurance
- Christian Religious Holidays and the Constitution of the United States
- Controversies Surrounding the Ratification of the Constitution
- Democratic Republicans and Federalists’ Interpretation of the Constitution
- Differences Between the State and the Federal Constitution
- Explaining Constitution-Makers’ Preferences: The Cases of Estonia and the United States
- The Primary Purpose of the Constitution and Identify
- Advantages and Disadvantages of the Process of Amending the Constitution
- Formal and Informal Institutions Under Codecision: Continuous Constitution Building in Europe
- Forming Laws and Application of the Constitution in the United States
- Human Rights and the Constitution : Property Rights
- Protection for the Rights of the Individual in the U.S. Constitution
- Freedom From Religion: Perversion of the U.S. Constitution
- Constitutional Agreement during the Drafting of the Constitution: A New Interpretation
- Impressive and Historic Documents of the Constitution
- Jefferson’s Attitudes and Contributions to the Constitution of the United States
- Political Polarization and the French Rejection of the European Constitution
- Slavery Compromises and the Constitution of the United States
- The Constitution and the Issues Surrounding the Rights to Privacy in the United States
- The Advantages and Disadvantages of an Unwritten Constitution in the UK
- Embodiment, Enaction, and Culture: Investigating the Constitution of the Shared World
- The American Revolution and the Modeling of the Constitution
- The Confederate Constitution, Tariffs, and the Laffer Relationship
- Women and the 1991 Colombian Constitution
- The Conflicts That Arose in the Debates Over the U.S. Constitution
- The Constitution and the Declaration of Independence of the United States of America
- The Role and Importance of the First Amendment of the Constitution
- Comparing the United States Constitution with Local State Constitutions
- British Politics and Constitution According to Hippolyte Taine
- The Major Reasons of the U.S. Constitution Being an Economic Document
- The Enshrinement of Federalism in the Constitution
- The Texas Immigration Policies That Challenge the Constitution
- Arguments for and Against Adopting a Codified Constitution in the UK
- The Separation and Balance of Powers in the UK Constitution
- Analyzing Originalism and Pragmatism as Depicted in the United States Constitution
- The Need for Clarification of the First Amendment of the United States Constitution
- Does the Constitution Guarantee the Right to Clone?
- How Did the Constitution Guard Against Tyranny?
- How Effectively the Constitution Protects Freedom?
- How Much Power and Liberty Did the Constitution Give to the People?
- How the Constitution Defines the Roles of Government?
- How Long Did It Take to Create the Constitution?
- How Many Delegates Were There During the Signing of the Constitution?
- Are Taxes Specifically Mentioned in the Constitution?
- What Is Most Important in the Constitution?
- Who Wrote the Bill of Rights and When Was It Added to the Constitution?
- What Power Does the Constitution Deny?
- Who Made the Constitution?
- Can the Supreme Court Overrule the Constitution?
- Who Can Override the Constitution?
- What Are the Principles of the Constitution?
- Why Was the Constitution Written?
- Does the Constitution Limit Power?
- What Are the Individual Rights in the Constitution?
- What Are the 10 Articles of the Constitution?
- What Are the Rules of the Constitution?
- Who Is the Father of the Constitution?
- How Many Constitutions Does the United States Have?
- Who Signed the Constitution First?
- How Many People Wrote the Constitution?
- Who Has the Biggest Constitution?
- Can the Constitution Be Changed?
- What Are the Basic of the Constitution?
- Which Is the Oldest Constitution in the World?
- What Is the Difference Between the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence?
- What Is the Highest Power in the Constitution?
Cite this paper
Select style
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
LawBirdie. (2024, January 25). 95 Constitution Research Topics & Essay Examples. https://lawbirdie.com/topics/constitution-research-topics/
"95 Constitution Research Topics & Essay Examples." LawBirdie , 25 Jan. 2024, lawbirdie.com/topics/constitution-research-topics/.
LawBirdie . (2024) '95 Constitution Research Topics & Essay Examples'. 25 January.
LawBirdie . 2024. "95 Constitution Research Topics & Essay Examples." January 25, 2024. https://lawbirdie.com/topics/constitution-research-topics/.
1. LawBirdie . "95 Constitution Research Topics & Essay Examples." January 25, 2024. https://lawbirdie.com/topics/constitution-research-topics/.
Bibliography
LawBirdie . "95 Constitution Research Topics & Essay Examples." January 25, 2024. https://lawbirdie.com/topics/constitution-research-topics/.
- Serial Killer
- Crime Investigation
- Juvenile Delinquency
- Contract Law
- Criminal Justice
Home » Resources » Constitution Day Writing Prompts – Middle and High School
Constitution Day Writing Prompts – Middle and High School

Three writing prompts for Constitution Day are provided for middle school and high school. The prompts can be used as a formal essay, at writing stations, or as a “discuss and write.”

Resource Types
Teaching strategies, constitution articles, more resources like this.
- Perspectives
- Back-to-School Playbook: Five Practices to Foster Constructive Dialogue in Your Classroom
- Co-Equal Leader: The Role of the Chief Justice of the United States
Help For Teaching
News & events.
- Ham4Progress Award for Educational Advancement
- Help Find the Next Street Law Classroom Champion
- Summer Residential Programs at Mount Vernon
- Nominate a Student for Mount Vernon Prize
- Registration Open for Gilder Lehrman Summer 2023 PD
Find what you need to study
AP Gov Free Response Questions (FRQ) – Past Prompts
12 min read • may 12, 2023
Fatima Raja
We’ve compiled a sortable list of a bunch of the AP US Government & Politics past prompts! The AP Gov essays (or all written portions) are 50% of the exam including short-answer questions (SAQs) and an Argument Essay. It’s important that you understand the rubrics and question styles going into the exam. Use this list to practice!
By practicing with previously released free response questions (FRQs), you’ll build critical-thinking and analytical skills that will prepare you for the exam. These past prompts have been designed to help you connect concepts and ideas to each other while applying your knowledge to real-life scenarios.
The AP Gov curriculum was updated in 2018 to focus more on primary documents and have more specific course content outlines, but the past prompts are still a good resource to practice with!
If you need more support with AP Gov, join us live for reviews, concept explanations, practice FRQs, and more!
All credit to College Board.
👉 2019 AP Gov FRQs
Qualitative Analysis
Interactions among branches of government (congress, policy-making, interest groups).
Since 2008 the Alliance Defending Freedom, a conservative Christian interest group, has promoted an annual event known as Pulpit Freedom Sunday. On this occasion, pastors are encouraged to challenge a provision of the tax law known as the Johnson Amendment, which prohibits political activity by certain nonprofit organizations, including religious organizations. While the Johnson Amendment does not restrict religious leaders from speaking out regarding social issues, it does prohibit them from contributing money to political campaigns or speaking out in favor or against candidates running for political office.
On Pulpit Freedom Sunday, as an act of civil disobedience, pastors and religious leaders preach openly about the moral qualifications of candidates seeking office.
Describe an action Congress could take to address the concerns of the interest group in the scenario.
In the context of the scenario, explain how partisan divisions could prevent the action described in part A.
Explain why the Alliance Defending Freedom might argue that their constitutional rights are threatened by the Johnson Amendment.
What are they actually asking?
To carefully read the provided passage and then use the information provided to describe responses that Congress could take, potential partisan obstacles, and how an interest group could argue their rights are being threatened by the scenario.
Quantitative Analysis
American political ideologies and belief (political parties, polls).
Identify the political affiliation of people who are most likely to believe elected officials should compromise.
Describe the difference between Democrats and Republicans on their attitudes of whether government officials should stick to their principles, based on the data in the bar graph.
Explain how the data in the bar graph could influence how a Republican candidate would shift his or her campaign positions after securing the Republican nomination for president.
Explain how the data in the bar graph could affect policy making interactions between the president and Congress.
Using the graphic provided and your knowledge of the AP Gov course, analyze the data provided and apply it to the situations provided.
Supreme Court Case
Civil liberties and civil rights (civil rights, fourteenth amendment).
In the 1950s, Pete Hernandez, a Mexican American agricultural worker, was found guilty of murder and sentenced to life in prison by an all-white jury in Jackson County, Texas. Hernandez’s defense claimed that people of Mexican ancestry had been discriminated against in Jackson County. They pointed to the fact that no person of Mexican ancestry had served on a jury in 25 years and that the Jackson County Courthouse itself practiced segregation in its facilities. The five jury commissioners, who selected the members of the grand jury, testified under oath that they selected jurors based only on their qualifications and did not consider race or national origin in their decisions.
In the ensuing case, Hernandez v. Texas (1954), the Supreme Court unanimously ruled in favor of Hernandez, deciding that evidence of discrimination against Mexican Americans existed in Jackson County and that the Constitution prohibits such discrimination.
Identify the clause in the Fourte enth Amendment that was used as the basis for the decision in both Brown v. Board of Education (1954) and Hernandez v. Texas (1954).
Explain how the facts in both Brown v. Board of Education and Hernandez v. Texas led to a similar decision in both cases.
Explain how an interest group could use the decision in Hernandez v. Texas to advance its agenda.
Using your knowledge of the 14th Amendment and Brown v. Board of Education , explain the decision and explain how you would apply it to Hernandez v. Texas .
Argument Essay
Foundations of american democracy (federalism).
The United States Constitution establishes a federal system of government. Under federalism, policy making is shared between national and state governments. Over time, the powers of the national government have increased relative to those of the state governments.
Develop an argument about whether the expanded powers of the national government benefits or hinders policy making.
Use at least one piece of evidence from one of the following foundational documents:
The Articles of Confederation
The Federalist 10
Using one of the documents listed and additional outside evidence, argue whether or not the expanded powers of the federal government is good or bad for policy-making.
👉 2018 AP Gov FRQs
Political Participation (political parties, third-parties)
Political parties seek to win elections to control government
Identify two activities that political parties do to win elections.
Describe one way third parties can affect elections.
Explain how single-member districts make it difficult for third parties to win elections.
Explain how electoral competition is affected by gerrymandering.
What are they actually asking for?
Demonstrate your understanding of how electoral competition affects third-parties and is affected by gerrymandering.
Political Participation (polls)
Public opinion polls are commonly used by politicians and the media.
Identify two characteristics of a reliable scientific public opinion poll.
Describe two ways polling results are used by politicians.
Explain how frequent public opinion polls impact media coverage of political campaigns.
Demonstrate your understanding of polling by explaining what makes a poll reliable and how they are used.
Quantitative Reasoning
Interactions between branches (vetos).
The United States Constitution gave Congress and the president specific legislative powers. As a result, the interactions between the two are dynamic and complex.
Describe the constitutional principle of checks and balances.
Describe EACH of the following presidential powers in the legislative process:
State of the Union address
Using the data in the chart, describe the relationship between the number of presidential vetoes and the number of congressional overrides.
Explain how Congress can reduce the likelihood of a presidential veto.
Demonstrate your understanding of checks and balances by explaining the relationships between vetos, the State of the Union Address, and congressional overrides.
Interactions Between Branches (republicanism)
In a democracy, what the majority wants should influence public policy. The opinion of the majority is sometimes, but not always, reflected in policy change.
Explain how interest groups reduce the influence of public opinion on policy.
Explain how EACH of the following increases the likelihood of policy change.
Newly elected president
National crisis
Describe the role of EACH of the following institutions in the policy process.
Demonstrate your understanding of the policy-making process by explaining the influence of interest groups, the media, and public opinion and explain how different situations can affect it.
👉 2017 AP Gov FRQs
Foundations of Democracy (Supreme Court)
The framers of the Constitution intended the Supreme Court to be politically insulated. Despite this intent, the Supreme Court is not completely insulated from political influences.
Describe one constitutional provision that seeks to insulate the Supreme Court from public opinion.
Identify a power exercised by the Supreme Court that acts as a check on another branch of the federal government.
Explain how each of the following can limit the independence of the Supreme Court.
Explain how the Supreme Court protects its political independence.
Explain how the Supreme Court maintains its independence from public opinion and how Congress and the President can limit it.
Political Participation (Interest Groups)
Interest groups play an important role in the political process.
Identify the primary goal of interest groups.
Describe EACH of the following strategies used by interest groups.
Amicus curiae
Explain how EACH of the following hinders the success of interest groups in obtaining their primary goal.
Separation of powers
Bureaucratic discretion
To describe the functions and goals of interest groups in policy-making.
Interactions Among Branches of Government (Federal Spending)
Social Security, Medicaid, and Medicare are all mandatory spending programs, also known as entitlement programs.
Identify a change in federal spending between 1970 and 2023 (projected) based on the chart above.
Describe the difference between entitlement programs and discretionary programs.
Describe one demographic trend that has contributed to changes in entitlement spending.
Explain why changes in entitlement spending make balancing the federal budget difficult.
Explain how deficit spending affects the projected trend in net interest.
To describe how federal spending, including entitlement and discretionary programs, functions and is affected by different factors.
Interactions Between Branches of Government (federalism)
The balance of power between the United States national government and state governments is shaped by the Constitution and Supreme Court rulings.
Describe EACH of the following constitutional provisions.
Supremacy clause
Tenth Amendment
Explain how ONE of the following court rulings changed the balance of power between the national government and state governments.
United States v. Lopez
Obergefell v. Hodges
Describe TWO advantages of federalism for the creation of public policy in the United States.
To explain how the relationship between the state and federal governments is shaped by constitutional clauses and has changed over the years.
👉 2016 AP Gov FRQs
Political Participation (linkage institutions)
Linkage Institutions - such as political parties, the media, and interest groups - connect citizens to the government and play significant roles in the electoral process.
Describe one important function of political parties as a linkage institution in elections.
Describe the influence of the media on the electoral process in each of the following roles.
Gatekeeping/agenda setting
Scorekeeping/horse race journalism
Describe two strategies interest groups use to influence the electoral process.
Explain how, according to critics, interest groups may limit representative democracy.
Describe the relationships between interest groups, political parties, and the media as linkage institutions and the federal government and how they affect elections and policy-making.
Political Participation (Demographics and Elections)
The United States is experiencing a dramatic change in the makeup of its population. These changes have political consequences for political institutions.
Identify a trend depicted in the chart.
Assuming that recent voting patterns continue, explain how the trend identified in (a) is likely to affect the electoral success of either the Democratic Party or the Republican Party.
Explain how the demographic changes shown in the chart above are likely to affect the way in which parties operate in Congress.
Describe two specific actions that presidents can take to respond to the demographic changes in the chart above.
Describe how demographic changes will affect political parties and the electoral process.
Interactions Between Branches of Government (policy-making)
The public policy process involves interactions between Congress and the bureaucracy.
Identify the primary role of Congress in the policy process.
Explain how divided party control of Congress can make the policy process difficult.
Identify the primary role of the bureaucracy in the policy process.
Explain how one of the following increases the power of the bureaucracy in the policy process.
Rule making
Explain how each of the following enables Congress to limit the power of the bureaucracy.
Oversight hearings
Power of the purse
Describe the policy-making process, its challenges, the bureaucracy's role within it, and how Congress conducts oversight over the bureaucracy.
Interactions Between Branches, Political Participation (federalism, voting)
The Constitution limited the power of the national government and restricted popular control; however, citizen participation has changed over time.
Explain how each of the following constitutional features protects against the concentration of power in the national government.
Checks and balances
Explain how one of the following features of the Constitution limited the people’s ability to influence the national government.
Electoral college
Selection of senators before the Seventeenth Amendment
Describe a constitutional amendment that increased suffrage.
Describe the effect of one of the following laws on citizen participation in elections.
Voting Rights Act of 1965
National Voter Registration Act of 1993 (Motor Voter Act)
Explain how the power of the federal government is limited, how people's influence on the federal government was limited, how suffrage increased, and how the passage of certain legislation affected voter participation.
👉 2015 AP Gov FRQs
Interactions Among Branches of Government (presidential roles)
American politics has often been called an "invitation to struggle." Although in recent years the president has been thought to have an advantage in policy making, there are still constraints on the power of the president.
Describe a power of the president in each of the following roles.
Chief legislator
Chief bureaucrat or chief administrator
Explain how each of the following limits the president’s influence in policy making.
Civil service employees
The Supreme Court
Describe the influence of divided government on the policy-making process.
Explain how the president can influence policy-making as well as the limits that the Supreme Court, civil service, and a divided government could place on. them.
The framers of the Constitution devised a federal system of government that affected the relationship between the national and state governments.
Compare state sovereignty under the Articles of Confederation and under the Constitution.
Explain how each of the following has been used to expand the power of the federal government over the states.
Commerce clause
Explain how each of the following has played a role in the devolution of power from the national government to the states.
Block grants
Supreme Court decisions
Describe how the relationship between the federal and state governments has changed and how different branches have played a role in that change.
Qualitative/Visual Analysis
Political participation (electoral college).
The framers created the electoral college to elect the president of the United States. This system influences the campaign strategies of presidential candidates.
Describe one reason that the framers chose to use the electoral college as the method to elect the president.
Describe the message the cartoon above conveys about presidential elections.
Explain why California, Texas, and New York do not appear prominently in the cartoon above.
Describe two campaign tactics presidential candidates use to win the key states identified in the cartoon above.
Explain the electoral college, how it functions, and how it affects presidential campaigns.
Civil Liberties and Civil Rights (civil rights and liberties)
The Fourteenth Amendment protects civil rights and civil liberties.
Describe the difference between civil rights and civil liberties.
Identify the primary clause of the Fourteenth Amendment that is used to extend civil rights.
Describe a specific legislative action that extended civil rights to each of the following.
Persons with disabilities
Identify the primary clause of the Fourteenth Amendment that is used to extend civil liberties.
Explain how civil liberties were incorporated by the Supreme Court in two of the following cases.
Gideon v. Wainwright
Mapp v. Ohio
Miranda v. Arizona
Demonstrate your understanding of civil rights and liberties, the Fourteenth Amendment, and Supreme Court cases affected by it.

Stay Connected
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website.
165 Constitution Essay Topics & Research Questions
🏆 best constitution essay topics, ✍️ constitution essay topics for college, 👍 good constitution research paper topics, 🌶️ hot constitutional law research paper topics, 🎓 most interesting constitution essay examples, ❓ research questions about the constitution, ⚖️ constitutional law essay questions, 🦅 us constitution essay questions.
- The Constitution as the Fundamental Law
- The Articles of Confederation and the US Constitution Comparison
- Performative Acts and Gender Constitution
- How the U.S. Constitution and the Bill of Rights Were Influenced by the Classical School of Criminology?
- Minnesota Constitutions and the US Constitution
- Compare and Contrast Louisiana with US Constitution
- The Russian Federation Constitution’s Features
- The United Kingdom’s Constitution: Does It Exist? It has been a debatable question for a while whether the United Kingdom has a constitution or it does not. It is still been widely discussed by politicians and political theorists.
- “We The People”: Preamble of the Constitution The first three words of the Preamble of the Constitution were incredibly significant since they indicated the beginning of a new nation and new country.
- Confederate Constitution and “Cornerstone” Speech Both the Confederate Constitution and the speech demonstrate the eagerness to secure slavery and incorporate its ideological justifications into the political fabric of the law.
- The Judicial Review Process and the UK Constitution The process of judicial review is a necessary procedure to ensure the fairness of justice. The judicial review process consists of seven basic steps.
- How Democratic Is the American Constitution? This essay paper discuss deeply the American constitution, how democratic and anti-democratic it has been, and how it should be improved to be more democratic.
- The Formation of the American Constitution The American constitution was crafted from four main sources. They included the constitutional, statutory, administrative regulations and the common laws.
- Checks and Balances in the U.S. Constitution The US government comprises three branches: legislative, executive and judicial. With checks and balances, any decisions made by one branch have to be confirmed by the rest.
- The United States Legal System and Constitution US legal system relies much on the common laws in administering justice from cases arising from societal norms and values which are not in the constitution.
- “How Democratic Is the American Constitution?” by Robert A. Dahl The book How Democratic is the American Constitution? by Robert A. Dahl is a provocative examination of the American constitution.
- Robert A. Dahl’s Analysis of the American Constitution Although some people believe that the American Constitution framers were inspired, wise, and philosophical, many scholars still question their original intentions.
- Amending the Constitution of the U.S. The Constitution of the U.S. is its supreme law, as it controls the whole country through its government. The Constitution is amended to include some improvements and corrections regarding the needs.
- Constitution, Declaration of Independence, and Letter to Danbury Baptists The Constitution and the Declaration of Independence are the key documents in US history. The Letter to the Danbury Baptists serves as a corroboration for American values.
- The Constitution: United States Citizen’s Rights The Constitution of the United States contains rights for both citizens and noncitizens. Certain rights are granted and legitimately apply to U.S. citizens.
- Declaration of Independence and Constitution The Declaration of Independence is a list of grievances against the English king, and it broke the political ties between Great Britain and the American colonies.
- Magna Carta and the U.S. Constitution A group of insurgent medieval lords persuaded King John of England to accept a long list of demands in 1215, which became known as the Great Charter, or Magna Carta in Latin.
- How to Read the Constitution and Why In Wehle’s How to Read the Constitution and Why, the author provides both a practical and metaphorical approach to interpreting the most important legal document of the United States.
- “The Constitution Was Made for Us…” by Bouie The American Constitution has many political and legislative restrictions for making the necessary changes. This is also connected with the topic of direct democracy.
- The Framers of the Constitution and the Bicameral Legislature The writers of the Constitution believed that having a bicameral legislature gave them a powerful tool for preventing any violations of the authority.
- The US Constitution: Morality, Knowledge, and Religion The values of religion, morality, and knowledge combined in the US Constitution allowed people to be free to hold any beliefs and practice any religion.
- The Declaration, The Constitution, and The Bill of Rights The Declaration, the Constitution, and the Bill of Rights are melded together in the imaginations of Americans because they embody what is best about America.
- Natural Rights and Their Protection in the Constitution A primary goal of the U.S. Constitution, as stated in the Declaration of Independence, is to protect people’s natural rights.
- The Constitution and Its Application to Business The United States Constitution is the supreme law through which Americans abide, and apart from affording rights to citizens, it provides rights to businesses.
- The Supreme Court and the American Constitution The paper looks upon Constitutional provisions and Supreme Court’s rulings and discusses the impact they had on American life.
- Connections between the Quotations: The Constitution of the United States The analysis of the resources considered shows that they are all united by the theme of territorial integration, which is essential to adhere to counter external threats.
- The United States Constitution Review The US Constitution is the supreme law of the U.S., designed to protect and preserve the rights of state citizens. The Constitution has been changed majorly through Amendments.
- The Constitution of the United Kingdom Great Britain differs from other countries because it does not have a single document called a Constitution. The absence of such a document impacts the state system.
- Researching the Constitution of the Russian Federation The Constitution of the Russian Federation is a suitable example of how the fundamental law can be misused, bringing benefits to government authorities.
- The US Constitution and the Bill of Rights The Constitution of the US is the greatest law in the US because incorporated elements like Natural Rights Philosophy, Classical Republicanism and Bill of Rights of England.
- The Articles of Confederation and the Constitution The Articles of Confederation (further referred to as the Articles) were developed due to wartime necessity and are now considered the first Constitution of America.
- American Constitution and Articles of Confederation The need to develop or form a government after winning the Revolutionary War triggered the creation of the Articles of Confederation.
- How to Reform the U.S Constitution to Function Correctly The essay presents a proposal for reforming the U.S Constitution to function correctly to reflect the societal change in the 230 years since its ratification.
- Representation of the Environment of the Time in Constitution The stability of the American constitutional order, and the inviolability of its fundamental principles, have remained relevant for three centuries and to this day.
- Gil’s Idea of the Paradoxical Body and Gender Constitution and Concerning Black Identity The idea of being black is an identity that colonizers constructed, and identity should never be based on race. The universal identity that everyone should recognize is being human.
- Federalist, Anti-Federalist Governments, and the U.S. Constitution At the end of the 18th century, Federalists and Anti-Federalists, who were against the ratification of the US Constitution, initiated the dispute over the state’s future.
- The Articles of Confederation and the Constitution The American Revolution brought a number of changes that people demanded, and they are noted in two important documents known as the Articles of Confederation and the Constitution.
- English Elite Colonists’ Goals and Constitution Many representatives of the elite colonists perceived the new Constitution as a serious limitation of their actions and refused to sign it.
- The US Constitution and Fears of Antifederalists The division and separation of powers by the Constitution of the US may be regarded as a powerful mechanism for the preservation of democracy, order, and citizens’ freedoms.
- Hypothetical Amendment to the U.S. Constitution Proposing amendments to the U.S. Constitution is a complex process, but there are crucial opportunities for improving the country’s supreme law.
- Anti-Federalist Position of the US Constitution The US Constitution rather vaguely limits the power of the new unified Government, which hardly represents the core interests of the free inhabitants of the USA.
- The 13th-15th Amendments of the US Constitution The thirteenth, fourteenth, and fifteenth amendments of the US constitution are the most important ones that brought equality to American society.
- Drafting of the U.S. Constitution The drafting of the U.S. Constitution is one of the most critical events in the country’s history. This paper explains the causes that led to the drafting of the U.S. Constitution.
- US Constitution Draft in Historical Context The research aims to consider the drafting of the U.S. Constitution and the historical context within which it was created and enacted.
- Free Expression for Businesses under the US Constitution The US Constitution’s First Amendment Clause embodies was adopted in 1791, together with the other amendments that constitute the Bill of Rights.
- The Constitution Day in the USA On September 17, 2015, the USA is celebrating a very prominent day in American history. It is the day of the signing of one of the most important documents – the Constitution.
- Woody Holton’s “Unruly Americans and the Origins of the Constitution” Woody Holton’s book Unruly Americans and the Origins of the Constitution discusses the historic events that played a central role in the development of the Constitution.
- The United States Constitution in the Historical Context the historical context and the Electoral College establishment have a direct link, as this institution served as the last barrier to preventing undesirable consequences.
- 1st and 14th Amendments of Constitution in Historical Context The Fourteenth Amendment of the Constitution stated that no state could deprive a person of life, liberty, or property without due process of law.
- The Creation of the Constitution of the USA The Articles of Confederation introduced a great number of various debates about the main laws of the country. Due to these debates, the USA obtained its Constitution and nationhood.
- European Community Laws: Law of the Constitution European Community (EC) is a union of three communities. the European Coal and Steel Community the European Economic Community and the European Atomic Energy Committee.
- The Fourth Amendment to the United States Constitution The Fourth Amendment to the United States Constitution protects American citizens against illegal evidence collections methods that are against their rights.
- U.S. Legislation: First Amendment to the Constitution The article examines the first amendment to the Constitution of the United States of America, as well as situations in which it can be limited, using the example of Harry Heckler.
- Representing Democracy: Reference to American Constitution Controversies surrounded the 2018 senate election in the state of Florida, which occasioned recounting of the votes cast.
- Approaches to Understanding the Constitution The purpose is to discuss whether the document should be interpreted literally or the changes that have occurred over time shall be taken into consideration while interpreting.
- Constitution of 1876 Analysis The Constitution of 1876 is the sixth Constitution under which Texas had been governed since the point when the state acquired independence from Mexico in 1838.
- How Is the Texas Constitution Changed? The changes to the Texas Constitution are being implemented rather often. A majority vote can only approve them in a statewide election.
- The Book “A Brilliant Solution: Inventing the American Constitution” by Carol Berkin The book “A Brilliant Solution: Inventing the American Constitution” by Carol Berkin can be described as an efficient work on the history of creation of the American Constitution.
- The United States Constitution and Its Principles The US Constitution is based on the principles of equality, independence, and democracy that have been key concepts for the US.
- US Constitution Revision: Secession Procedure The essence of my proposal: the Constitution should unequivocally state that the secession of any state of the collection can only be possible with the ratification by all the states.
- The U.S. Constitution, the Federalist Papers and the Bill of Rights The need for the U.S. Constitution arose from the fact that the Articles of Confederation were not effective enough in the governance of the country.
- Confederation and the Constitution: Principal Differences The Articles of Confederation adopted approximately by the end of the eighteenth century functioned as the first corpus of fundamental principles for governing the United States.
- Confederation and Constitution in the United States The Formation and the Advantages of the New Constitution The federal convention of the United States formed the Constitution in Philadelphia in 1787.
- Articles of Confederation vs. Constitution The Constitution and the Articles of Confederation both marked the path towards the beginning of the democratic tradition in the United States.
- The Role of the Courts Under the U.S. Constitution The judicial branch of the US system of government sees its core role in protecting the supremacy of law and civil liberties.
- Difference Between Articles of Confederation and Constitution The Constitution was built as a firm union of people with the national government. This contrasts harshly with the loose connection of states under the Articles of Confederation.
- Arizona Constitution and How It Affects Counties Arizona’s constitution, just like any other constitution, sets laws that affect all the other laws that are set by a different government system of the government.
- Governing the Nation: Constitution for Slaveholders Considering the Constitution and the Articles of Confederation, the major arguments for and against the ratification of these laws will be discussed.
- Arizona Statehood and Constitution In Arizona, judges were not elected but they were selected by a system called Merit Selection; the residents of the state never felt that this way of selecting the judges was good.
- Article of Federation and the New Constitution: Various Views of Critics and Supporters The Articles of Confederation were a combination of guidelines that was adopted as the constitution of America immediately after the Revolutionary War in 1777.
- Business, the Constitution and Administrative Agencies Laws that govern business play an important part in lawmaking and granting equal rights and obligations. Such leverage is represented by the Constitution and Administrative Agencies.
- Framers of the Constitution: Alexander Hamilton The essay describes the historical significance of Alexander Hamilton as one of the Framers of the Constitution.
- Right to a Free Press in the Australian Constitution The negative connotations of the Bill of Rights are: The rights of Australians are already well protected; high courts are already protecting rights by interpreting the constitution and the common law.
- Constructing and Ratifying the United States Constitution The events which led to the ratification of the constitution were the end of the revelation and opposition between the states, peace with Great Britain, and economic depression that affected all states.
- Constitution and Contract: Is the Spirit of Barbara Jordan Dead in Progressive Politics? Barbara Jordan’s views are associated with the focus on long-term benefits and the ability to seize opportunities to develop an equal society where all groups have equal access to resources.
- The US Constitution: Abduction & Causal Mechanisms This paper explores the two current perspectives on the relevance of the US Constitution, including abductive theory and causal mechanisms.
- Constitution of the United States: Digital Field Trip The document under consideration is the Constitution of the United States. It consists of four pages that are permanently displayed at the National Archives.
- The History of United States Constitution The United States Constitution is one of the most well-known government documents in history and modern politics.
- American Confederation and Constitution To understand the essence of American political theory, the process which the Constitution underwent to compromise and establish the principles of Democracy must be carefully examined.
- The U.S. Constitution Place in the Debate on Gun Rights For the purpose of this exploration and reflection, it was chosen to examine the Constitution of the United States as one of the pillars upon which America was built.
- The Bill of Rights in United States Constitution The Bill of Rights establishes the freedom to own and use lethal weaponry, and any efforts to overturn the trend would have to involve further amendments to the Constitution.
- The Constitution of the United States This paper considers the Constitution of the USA, highlighting its strength and weakness, and describing options to maintain its strength and correct the weakness.
- Early American History: Ratifying the Constitution The Constitution remains one of the most complex and fundamental political documents that has survived centuries of historical turmoil and social evolution.
- American Constitution Development and Challenges The US Constitution became one of the building blocks of the new nation that secured the rights of states while facilitating their fruitful collaboration.
- US Constitution 1787 and Articles of Confederation America in the 1780s was in a state of political volatility, with the country’s system of government undergoing reevaluation and amendment.
- Articles of Confederation and Constitution of 1787: Comparison and Analysis The Articles of Confederations were replaced by the new Constitution of 1787, which was a new period in the development of American society.
- From Articles of Confederation to the US Constitution This paper aims to investigate the principal differences and contrasts between the Articles and the Constitution.
- Articles of Confederation vs. New Constitution The purpose of this paper is to compare and contrast the Articles of Confederation and the new Constitution of 1787 in terms of the strengths and weaknesses of each.
- The US Constitution: First Amendment Paper The ancestors ratified the first amendment of the US constitution in 1791, which formed the basis of the Bill of Rights. It is imperative to assert that this amendment contains five provisions.
- US Constitution: Right to the Second Amendment The right to the Second Amendment is one of the most controversial issues of the contemporary legal system because it is closely related to personal and collective safety.
- The Articles of Confederation and the New Constitution The constitution is one of the symbols of national unity. However, the development process was not that peaceful. It involved a lot of bargaining and compromise.
- American Constitution and Its Influencing Factors The paper presents information on documents, philosophers, and selected patriots that contributed to the formation of the United States Constitution.
- US Constitution of 1787: Formation and Ratification The Articles of Confederation, drafted during the independence movement in 1776-1777, became the first official regulation that increased the power of the states.
- Judicial Review and the American Constitution Judicial review refers to “a process under which executive or legislative actions are subject to review by the judiciary”. The executive may issue orders that may go against the constitution.
- The Creation of the US Constitution in the 1780s After the independence of the thirteen American colonies was declared in 1776, the need to lay the foundation for the future existence of the states together arose.
- The Need to Draft a New Constitution The leaders of the newly independent states decided to create a legal framework that prevented the emergence of an extremely powerful central government.
- United States Constitution Ratification in 1787 The current paper describes three research articles related to Constitution, institutional design, and ratification debates in 1787 in the United States.
- The Roman Constitution: Augustus and Polybius Comparison This paper compares the significance of the Roman Constitution and the people’s role in it at Augustus’s “The Deeds of the Divine Augustus” and Polybius’s “The Histories.”
- Articles of Confederation Improved in Constitution The Articles of Confederation was drafted and adopted in 1777 by the Second Continental Congress, bringing to an end the strife for a new government system.
- American Confederation and Constitution History In the paper, the articles of Confederation and new a Constitution of 1748 are compared, and weaknesses and strengths are determined.
- The Ratification of the Constitution Although the present-day Constitution seems indispensable to the US government, the ratification of its first version was a complex and controversial procedure.
- Constitution of the United States and Its Context The Constitution of the United States consists of four handwritten pages. It comprises seven articles, which united the citizens of the country in their desire to become a nation.
- The Articles of Confederation vs. the New Constitution The Articles of the Confederation (1781-1789) preceded the New Constitution of the US ratified in 1789. Although the two documents have some commonalities, they differ in many respects.
- The Articles of Confederation and the Constitution of 1789: Two Basic American Legislative Acts The essay reveals the essence of two American legislative acts that regulated the both the internal relations between the U.S. states and the establishment of external contacts.
- American Articles of Confederation vs. Constitution The goal of this essay is to compare and contrast the content of the Articles of Confederation and the U.S. Constitution by presenting the weaknesses and threats of documents.
- American Confederation and First Constitution After independence, the US went through multiple constitutional reformations. Polishing the authority system, the United States government developed its first Constitution.
- First US Constitution vs. New Constitution of 1787 Prior to the ratification of the US Constitution created in 1787, the state-operated under another document known as the Articles of Confederation, which became effective in 1781.
- New American Constitution’s Establishment The main goal of this paper is to discuss the most important aspects of the establishment of the Constitution of the United States.
- American Constitution: Creation and Ratification The American Constitution had a long way to its ratification, but it has been used for centuries which is the proof of the correct choice in 1787.
- New Constitution of 1787 Ratification Debates The Constitution would initially ensure powerful central government, while the added Bill of Rights guaranteed that the government would not overstep its authority.
- Rethinking the Texas Constitution of 1876 “Of Rutabagas and Redeemers” proved that the ideals enforced in the Texas constitution are not solely the effort of the Grange Democrats, but also non-grange Democratic members.
- American Constitution’s Creation Controversy The creation of the Constitution was associated with major controversy, which revolved primarily around the degree of centralization of the country’s governance.
- American Constitution of 1787 and Related Debates The paper compares the Articles of Confederation with the Constitution of 1787, as well as analyzes the drafting of the Constitution and debates over it.
- Confederation and Constitution’ Comparison This paper compares and contrasts the Articles of Confederation with the new Constitution of 1787. It discusses what were the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles vis-à-vis the Constitution.
- The Constitution of 1787: Compromises and Debates This paper will compare the old Articles of Confederation and the new Constitution, as well as examine the compromises that occurred during its drafting process.
- The First US Constitution vs. Constitution of 1787 This paper analyzes the strengths and weaknesses of the old Articles of Confederation and the new Constitution and analyzes the process of drafting the Constitution.
- The US Constitution’s Foundation History The Constitution was formed through many political challenges and compromises. It stands as the foundation and governing document of the United States democratic republic.
- American Constitution Drafting and Ratification The Constitution is one of the crucial documents because many critical aspects were taken into account, which helped address some of the problems that were present.
- The 1787 Constitution and the Great Debate The crisis of the 1780’s was due in large part to the government structure of the United States in the aftermath of the American Revolution.
- The Transition From the Articles of Confederation to the New Constitution: Drafting and Ratification The problems that evolved from the Articles of Confederation affected the way the country was being managed and the ways authorities could execute their power.
- Articles of Confederation vs. Constitution of 1787 This paper focuses on the features of the Constitution and the Articles of Confederation as well as the factors that played an important role in the ratification of the former.
- Analysis of the Constitution of Texas This paper is aimed at examining the systems of checks and balances included in the Constitution of Texas. These provisions are supposed to limit the authority of the government.
- Article of Confederation and the New Constitution This paper explores the similarities and differences between the two sets of supreme laws: Articles of Confederation and the new constitution based on the Bill of Rights.
- Criminal Procedure: the Fourth Amendment to the Constitution The Fourth Amendment to the United States Constitution is included in the Bill of Rights. It protects people against unreasonable searches and seizures and generally requires to obtain a warrant.
- Inventing the American Constitution In her book A Brilliant Solution: Inventing the American Constitution, Carol Berkin describes the process of deciding the Constitution and portrays the Founding Fathers as experienced politicians.
- How Does the U.S. Constitution Compare to State Constitutions?
- Are State Constitutions Different in the Different States?
- What Is the Main Purpose of a State Constitution?
- How Do Constitutions Differ Across the States?
- What Is One Thing That All State Constitutions Have?
- How Does the Constitution Resolve Conflicts Between State and Federal Laws?
- What Was the First Constitution of the United States and Why Did It Fail?
- How Did the Failure of the Articles of Confederation Influence the Constitution?
- Why Did the US Constitution Replace the Articles of Confederation?
- Did the Equal Rights Amendment Become Part of the Constitution?
- What Is the Difference Between Codified and Uncodified Constitutions?
- Which Countries Have an Uncodified Constitution?
- Does the US Constitution Live Up to Its Principles?
- What Was Wrong With the Original Constitution?
- Why Does the UK Have No Written Constitution?
- Does the Constitution Have Mistakes?
- What State Is Spelled Wrong in the Constitution?
- Is Slavery Mentioned in the Constitution?
- Why Was Slavery Allowed in the Constitution?
- What Does the Constitution Say About Women’s Rights?
- Is There Any Country Without Constitution?
- What Is the Oldest Constitution in the World?
- Which Country Has the Smallest Constitution?
- How Many Times Is Slavery Mentioned in the Constitution?
- Which Country Has the Oldest Written Constitution in the World?
- How Does the Bill of Rights Limit the Government Power?
- Why Is the Process of Amending the Constitution Made Difficult Intentionally?
- How Does the US Constitution Address the Issue of Federalism?
- How Is “Due Process” Protected by the US Constitution?
- What Is the Role of the Supreme Court in Interpreting the Constitution?
- Why Is the Commerce Clause Significant in Regulating Economic Activities?
- How Does the Constitution Protect the Rights of Minorities?
- How Does the Supreme Court Interpret the Second Amendment?
- What Is the Role of the Electoral College in Presidential Elections as per the Constitution?
- How Does the US Constitution protect the freedom of speech, assembly, and religion?
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, September 9). 165 Constitution Essay Topics & Research Questions. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/constitution-essay-topics/
"165 Constitution Essay Topics & Research Questions." StudyCorgi , 9 Sept. 2021, studycorgi.com/ideas/constitution-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) '165 Constitution Essay Topics & Research Questions'. 9 September.
1. StudyCorgi . "165 Constitution Essay Topics & Research Questions." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/constitution-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "165 Constitution Essay Topics & Research Questions." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/constitution-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "165 Constitution Essay Topics & Research Questions." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/constitution-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Constitution were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 5, 2024 .
Home — Essay Samples — Law, Crime & Punishment — Constitution — The Constitution of the United States
The Constitution of The United States
- Categories: Constitution
About this sample

Words: 613 |
Published: Jan 4, 2019
Words: 613 | Page: 1 | 4 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Law, Crime & Punishment

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 634 words
1 pages / 606 words
4 pages / 2030 words
3 pages / 1466 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Constitution
The United States Constitution, written over 200 years ago, is often revered as a groundbreaking document that established the framework for a functional and democratic government. However, as time has passed, there is a growing [...]
The United States Constitution, often regarded as the cornerstone of American democracy, was adopted in 1787. Over two centuries later, it remains the supreme law of the land. However, the longevity and enduring relevance of the [...]
The United States Constitution stands as a foundational document that shapes the legal landscape of the nation. Its significance cannot be overstated, as it serves as the bedrock of American law, guiding the principles and [...]
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the land, providing the framework for the government and the rights and freedoms of its citizens. Since its ratification in 1787, there has been ongoing debate about [...]
IntroductionThe ratification of the Constitution in 1787 marked a pivotal moment in American history. It was a significant step towards establishing a strong federal government and ensuring the stability of the young nation. [...]
Tyranny is exhibited in many ways. In 1787 our founding fathers met in Philadelphia to discuss a problem, The Articles of Confederation were not working. So after a long debate, they made a decision, to throw out the old and in [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
About 1 in 5 U.S. teens who’ve heard of ChatGPT have used it for schoolwork

Roughly one-in-five teenagers who have heard of ChatGPT say they have used it to help them do their schoolwork, according to a new Pew Research Center survey of U.S. teens ages 13 to 17. With a majority of teens having heard of ChatGPT, that amounts to 13% of all U.S. teens who have used the generative artificial intelligence (AI) chatbot in their schoolwork.
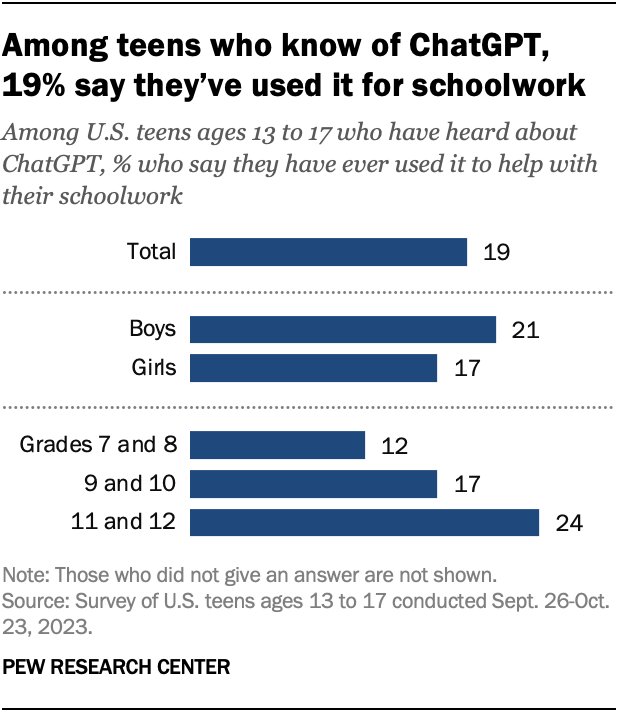
Teens in higher grade levels are particularly likely to have used the chatbot to help them with schoolwork. About one-quarter of 11th and 12th graders who have heard of ChatGPT say they have done this. This share drops to 17% among 9th and 10th graders and 12% among 7th and 8th graders.
There is no significant difference between teen boys and girls who have used ChatGPT in this way.
The introduction of ChatGPT last year has led to much discussion about its role in schools , especially whether schools should integrate the new technology into the classroom or ban it .
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to understand American teens’ use and understanding of ChatGPT in the school setting.
The Center conducted an online survey of 1,453 U.S. teens from Sept. 26 to Oct. 23, 2023, via Ipsos. Ipsos recruited the teens via their parents, who were part of its KnowledgePanel . The KnowledgePanel is a probability-based web panel recruited primarily through national, random sampling of residential addresses. The survey was weighted to be representative of U.S. teens ages 13 to 17 who live with their parents by age, gender, race and ethnicity, household income, and other categories.
This research was reviewed and approved by an external institutional review board (IRB), Advarra, an independent committee of experts specializing in helping to protect the rights of research participants.
Here are the questions used for this analysis , along with responses, and its methodology .
Teens’ awareness of ChatGPT
Overall, two-thirds of U.S. teens say they have heard of ChatGPT, including 23% who have heard a lot about it. But awareness varies by race and ethnicity, as well as by household income:
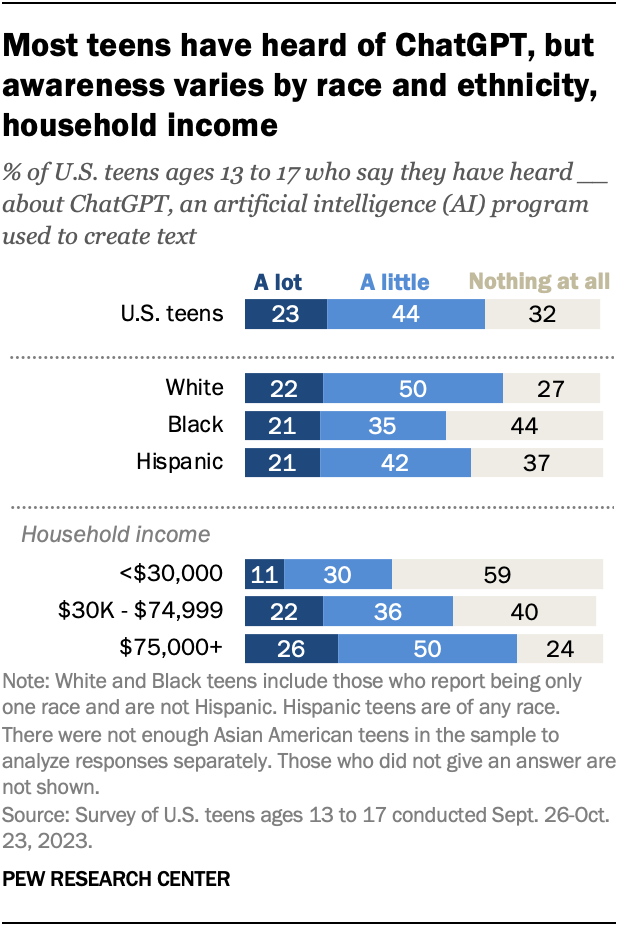
- 72% of White teens say they’ve heard at least a little about ChatGPT, compared with 63% of Hispanic teens and 56% of Black teens.
- 75% of teens living in households that make $75,000 or more annually have heard of ChatGPT. Much smaller shares in households with incomes between $30,000 and $74,999 (58%) and less than $30,000 (41%) say the same.
Teens who are more aware of ChatGPT are more likely to use it for schoolwork. Roughly a third of teens who have heard a lot about ChatGPT (36%) have used it for schoolwork, far higher than the 10% among those who have heard a little about it.
When do teens think it’s OK for students to use ChatGPT?
For teens, whether it is – or is not – acceptable for students to use ChatGPT depends on what it is being used for.
There is a fair amount of support for using the chatbot to explore a topic. Roughly seven-in-ten teens who have heard of ChatGPT say it’s acceptable to use when they are researching something new, while 13% say it is not acceptable.
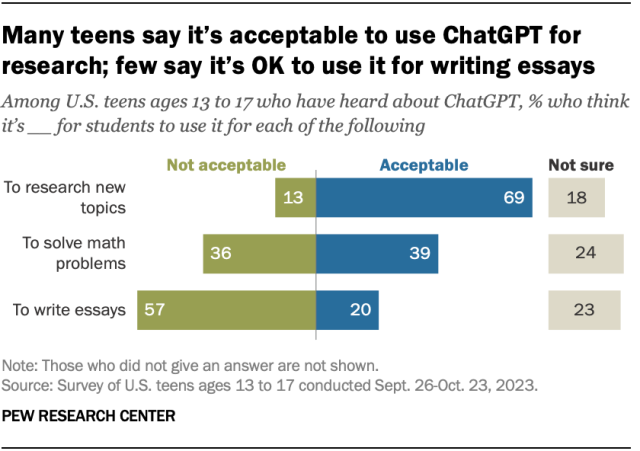
However, there is much less support for using ChatGPT to do the work itself. Just one-in-five teens who have heard of ChatGPT say it’s acceptable to use it to write essays, while 57% say it is not acceptable. And 39% say it’s acceptable to use ChatGPT to solve math problems, while a similar share of teens (36%) say it’s not acceptable.
Some teens are uncertain about whether it’s acceptable to use ChatGPT for these tasks. Between 18% and 24% say they aren’t sure whether these are acceptable use cases for ChatGPT.
Those who have heard a lot about ChatGPT are more likely than those who have only heard a little about it to say it’s acceptable to use the chatbot to research topics, solve math problems and write essays. For instance, 54% of teens who have heard a lot about ChatGPT say it’s acceptable to use it to solve math problems, compared with 32% among those who have heard a little about it.
Note: Here are the questions used for this analysis , along with responses, and its methodology .
- Artificial Intelligence
- Technology Adoption
- Teens & Tech

Many Americans think generative AI programs should credit the sources they rely on
Americans’ use of chatgpt is ticking up, but few trust its election information, q&a: how we used large language models to identify guests on popular podcasts, striking findings from 2023, what the data says about americans’ views of artificial intelligence, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
42 Writing Prompts About The Constitution. Although it was written in the 18th century, the U.S. Constitution is the principle by which our country lives. This means that it is very important for students to read, learn about, and understand the Constitution and how it affects their lives—even in ways that they'd never realized.
25 Topics. Compare and contrast what is a direct democracy versus representative democracy. React to the following statement: Democratic decision-making should be extended to all areas of life including schools, the workplace, and the government. Compare and contrast the Virginia and New Jersey plans. Explain how these led to the Great Compromise.
To write an essay about the U.S. Constitution, you first need to read and understand the text. Complete the guided reading worksheet . Understanding the U.S. Constitution which will give you a foundation upon which to build your essay. You will write an argumentative essay in which you will make a reasoned case for your opinion on one of the ...
Why use Essays to Teach about the U.S. Constitution. Students often have a hard time engaging with a document that was written hundreds of years in the past. By allowing students the time and ...
This part of the Constitution Annotated includes broad introductory essays covering historical background, providing authorization information, addressing ratification and overarching constitutional issues, and more. A few key introductory essays are summarized below: Historical Note on the Adoption of the Constitution.This essay 1 Footnote Intro.6.1 Continental Congress and Adoption of the ...
Intro.1 The 2022 Edition. As the keystone of the United States, the Constitution informs federal and state law; delineates the distinct roles of the Executive, Legislative, and Judicial Branches of the U.S. Government; and demarcates the powers of the United States from those of the states. Supreme Court Justice Hugo Black memorably remarked ...
Thanks for exploring this SuperSummary Study Guide of "Constitution of United States of America" by Constitutional Convention. A modern alternative to SparkNotes and CliffsNotes, SuperSummary offers high-quality Study Guides with detailed chapter summaries and analysis of major themes, characters, and more.
Footnotes Jump to essay-1 See Stephen Gardbaum, The Myth and the Reality of American Constitutional Exceptionalism, 107 Mich. L. Rev. 391, 399 (2008) (Overall, the U.S. Constitution is exceptional among written constitutions both in its age and its brevity. It is the oldest currently in effect and . . . is among the shortest at 7591 words including amendments . . . .
These ideas protect the liberties of the people and their right to govern themselves. The Constitution contains words and principles that have the flexibility to respond to centuries of social, economic, and technological change. While the text of the Constitution has words that should be adhered to closely, they are hardly etched in marble.
The Bill of Rights. In 1789, Madison, then a member of the newly established U.S. House of Representatives, introduced 19 amendments to the Constitution. On September 25, 1789, Congress adopted 12 ...
The constitution of the US is the absolute law of the nation, which acts as a guide to the political culture of the Americans and the law. New Constitution of USA in 1787. Contrary to the Virginia plan, the New Jersey plan called for equal state representation in the congress regardless of the size of the state.
Chose one or more of the provided Argumentative Essay Prompts, as assigned, and use the planning and exploration you did above to write a full essay in response to your designated prompt (s) in 25 ...
2006- #2: Evaluate the extent to which the ratification of the US Constitution was a turning point for the traditional American political elite. 2005 - #1: Evaluate the extent to which the American Revolution changed the political, economic, and social aspects of American society from 1775 to 1800.
Bill of Rights and Florida Legislature. Law essay sample: The Bill of Rights has set the foundation for ensuring every citizen's safety, agency, and dignity. The constitution of each state shares principal ideas with the Bill of Rights. The Florida Constitution and the Bill of Rights to the U.S. Constitution.
Three writing prompts for Constitution Day are provided for middle school and high school. The prompts can be used as a formal essay, at writing stations, or as a "discuss and write." ... Co-Equal Leader: The Role of the Chief Justice of the United States; Help For Teaching . News & Events.
establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America. The revised draft with its changed Preamble was largely the work of Gouverneur Morris.
Footnotes Jump to essay-1 C. Stephenson & F. Marcham, Sources of English Constitutional History 125 (1937). Jump to essay-2 12 Encyclopedia of the Social Sciences 98 (1934). Jump to essay-3 United States v. Cruikshank, 92 U.S. 542, 551 (1876). Jump to essay-4 Edward S. Corwin, The Constitution and What It Means Today 293-94 (Harold W. Chase & Craig R. Ducat eds., 1973) (citations omitted).
Overview. We've compiled a sortable list of a bunch of the AP US Government & Politics past prompts! The AP Gov essays (or all written portions) are 50% of the exam including short-answer questions (SAQs) and an Argument Essay. It's important that you understand the rubrics and question styles going into the exam. Use this list to practice!
Step 1: Analyze the Prompt. The Argument Essay question format is relatively straightforward, and the language will largely be the same for all Argument Essay prompts except for two parts: the topic and the short list of relevant foundational documents. With this in mind, analyzing the prompt for this question type is easy!
This essay paper discuss deeply the American constitution, how democratic and anti-democratic it has been, and how it should be improved to be more democratic. The American constitution was crafted from four main sources. They included the constitutional, statutory, administrative regulations and the common laws.
The 1st amendment of the constitution is, "Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof; or abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press; or the right of the people peaceably to assemble, and to petition the Government for a redress of grievances"., this states that our ...
1204 Words. 5 Pages. 3 Works Cited. Open Document. A constitution is a written document that sets forth the fundamental rules by which a society is governed. Throughout the course of history the United States has lived under two Constitutions since the British-American colonies declared their independence from Great Britain in 1776. First in ...
Footnotes Jump to essay-1 Certain provisions of the Constitution may not lend themselves to full essays on each provision. In such instances, the constitutional provision may contain a single Constitution Annotated essay that provides an overview, historical background, and the doctrine collapsed in one. Jump to essay-2 See Black's Law Dictionary 585 (10th ed. 2014) (defining doctrine ...
United States Constitution -- 10th. PAGES 3 WORDS 870. Filburn harvested nearly 12 acres of wheat above his allotment. He claimed that he wanted the wheat for use on his farm, including feed for his poultry and livestock. Fiburn was penalized. He argued that the excess wheat was unrelated to commerce since he grew it for his own use.
However, there is much less support for using ChatGPT to do the work itself. Just one-in-five teens who have heard of ChatGPT say it's acceptable to use it to write essays, while 57% say it is not acceptable. And 39% say it's acceptable to use ChatGPT to solve math problems, while a similar share of teens (36%) say it's not acceptable.
Jump to essay-4 Joseph Story, Commentaries on the Constitution of the United States § 814 (1833). Jump to essay-5 The Federalist No. 59 (Alexander Hamilton). Jump to essay-6 Id. Jump to essay-7 See Joseph Story, Commentaries on the Constitution of the United States § 818 (1833) (Who are to pass the laws for regulating elections? The congress ...
Footnotes Jump to essay-1 469 U.S. 528 (1985). Jump to essay-2 See New York v. United States, 505 U.S. 144, 157-58 (1992) (finding protection for state sovereignty against commandeering was not derived from the text of the Tenth Amendment itself but in how it confirms that the power of the Federal Government is subject to limits); accord Murphy v. NCAA, No. 16-476, slip op. at 15-16 (U.S ...