Appendix B: Geometry
Using the properties of triangles to solve problems, learning outcomes.
- Given the measures of two angles of a triangle, find the third
- Use properties of similar triangles to find unknown lengths of triangles
What do you already know about triangles? Triangle have three sides and three angles. Triangles are named by their vertices. The triangle below is called [latex]\Delta ABC[/latex], read ‘triangle [latex]\text{ABC}[/latex] ’. We label each side with a lower case letter to match the upper case letter of the opposite vertex.
[latex]\Delta ABC[/latex] has vertices [latex]A,B,\text{ and }C[/latex] and sides [latex]a,b,\text{ and }c\text{.}[/latex]
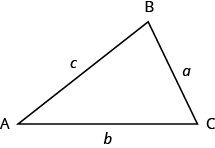
[latex]m\angle A+m\angle B+m\angle C=\text{180}^ \circ[/latex]

Sum of the Measures of the Angles of a Triangle
For any [latex]\Delta ABC[/latex], the sum of the measures of the angles is [latex]\text{180}^ \circ[/latex].
The measures of two angles of a triangle are [latex]55^\circ [/latex] and [latex]82^\circ [/latex]. Find the measure of the third angle.
In the following video we show an example of how to find the measure of an unknown angle in a triangle. In this example, we have two triangles who share a common side, and find two unknown interior angles.
Right Triangles
Some triangles have special names. We will look first at the right triangle. A right triangle has one [latex]90^\circ[/latex] angle, which is often marked with the symbol shown in the triangle below.
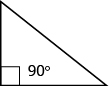
One angle of a right triangle measures [latex]28^\circ [/latex]. What is the measure of the third angle?
In the examples so far, we could draw a figure and label it directly after reading the problem. In the next example, we will have to define one angle in terms of another. So we will wait to draw the figure until we write expressions for all the angles we are looking for.
The measure of one angle of a right triangle is [latex]20^\circ [/latex] more than the measure of the smallest angle. Find the measures of all three angles.

Similar Triangles
When we use a map to plan a trip, a sketch to build a bookcase, or a pattern to sew a dress, we are working with similar figures. In geometry, if two figures have exactly the same shape but different sizes, we say they are similar figures. One is a scale model of the other. The corresponding sides of the two figures have the same ratio, and all their corresponding angles are have the same measures.
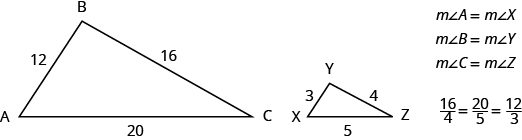
The two triangles below are similar. Each side of [latex]\Delta ABC[/latex] is four times the length of the corresponding side of [latex]\Delta XYZ[/latex] and their corresponding angles have equal measures.
[latex]\Delta ABC[/latex] and [latex]\Delta XYZ[/latex] are similar triangles. Their corresponding sides have the same ratio and the corresponding angles have the same measure.
Properties of Similar Triangles
If two triangles are similar, then their corresponding angle measures are equal and their corresponding side lengths are in the same ratio.
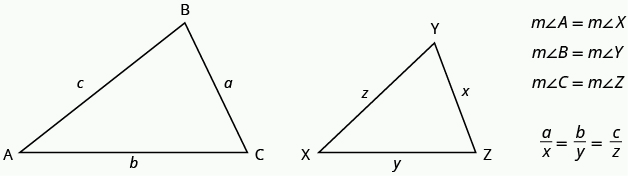
The length of a side of a triangle may be referred to by its endpoints, two vertices of the triangle. For example, in [latex]\Delta ABC\text{:}[/latex]
[latex]\begin{array}{c}\text{the length }a\text{can also be written}BC\hfill \\ \text{the length}b\text{ can also be written }AC\hfill \\ \text{the length }c\text{ can also be written }AB\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
We will often use this notation when we solve similar triangles because it will help us match up the corresponding side lengths.
[latex]\Delta ABC[/latex] and [latex]\Delta XYZ[/latex] are similar triangles. The lengths of two sides of each triangle are shown. Find the lengths of the third side of each triangle.
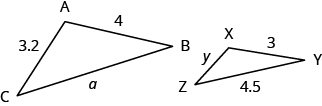
In the video below we show an example of how to find the missing sides of two triangles that are similar. Note that the measures of the sides in this example are whole numbers, and we use a cross product to solve the resulting proportions.
- Question ID 146912, 146498, 146499, 146500. Authored by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Ex 2B: Find the Measure of an Interior Angle of a Triangle. Authored by : James Sousa (mathispower4u.com). Located at : https://youtu.be/3kRLkbU6-cI . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Prealgebra. Provided by : OpenStax. License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Triangles are 2D shapes with three straight sides and three vertices. These are the only two key properties of triangles. To solve problems involving triangles, we need to be able to gather information about its side lengths and/or its interior angles and apply these to the problem. The sum of interior angles of a triangle is \bf{180°}. For ...
The measures of two angles of a triangle are 55∘ 55 ∘ and 82∘ 82 ∘. Find the measure of the third angle. Solution. Step 1. Read the problem. Draw the figure and label it with the given information. Step 2. Identify what you are looking for. The measure of the third angle in the triangle.