- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Teaching Expertise
- Classroom Ideas
- Teacher’s Life
- Deals & Shopping
- Privacy Policy

20 Superb Sociology Activities
February 28, 2023 // by Kaitlyn Townsend
Here are 20 awesome activities to help students explore sociology. Sociology is the study of culture and includes everything from social justice movements to race to manners. These activities are appropriate for a wide variety of ages and contexts and sure to help you devise creative and engaging lessons!
1. Nature vs. Nurture
This is a great way to check for understanding of a previously studied unit. Students take 30 traits and categorize them on a Venn diagram. The packet also includes an answer key.
Learn More: Teachers Pay Teachers
2. Family Life Cycle
This packet walks students through the various aspects of life in a family’s social construction. Students examine graphs and facts and complete a fill-in-the-blank worksheet. Finally, students complete a graphic organizer which can be updated after a class discussion.
3. Identity Lesson

American society is built on diversity. In this lesson, students identify important parts of their identity. They reflect on how differences are important and how learners can stand up to injustice. Use this activity at the beginning of the year to build a healthy classroom community.
Learn More: The Responsive Counselor
4. Sociology Games

This is a great list of sociology activities to expand on or wrap up a unit. Topics include human rights, longevity, and inequality amongst others. These games are most appropriate for middle school and early high school students.
Learn More: Mr. Don
5. Community Events
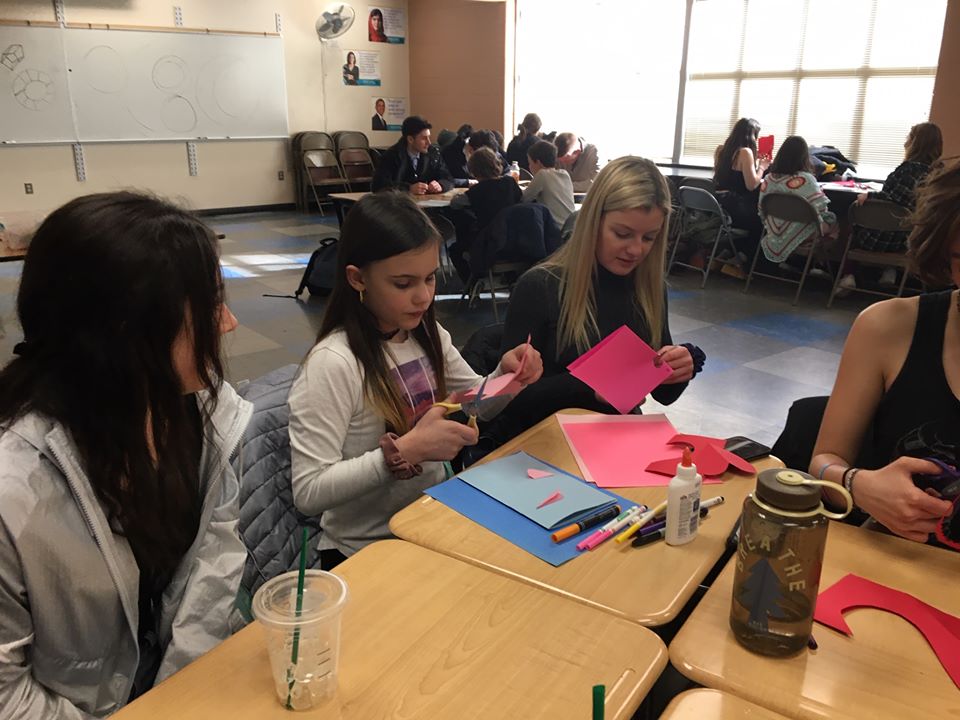

This sociology class really thought outside the box. This teacher provides a brief but meaningful list of activities for students to learn about sociology by helping the community. Activities include volunteering at a women’s shelter, collaborating with elementary school students, and more.
Learn More: Not Another History Teacher
6. Sociology Projects
This list of activities is flexible enough to easily adapt to current events. Each project also corresponds to specific units; making lesson planning a breeze. Activities include discussing the meaning behind a song or researching the biggest problems facing public schools.
7. Sociology Jobs

What can you do with a sociology degree? Here is a breakdown of 12 jobs you can do with a sociology degree. Turn this into an activity by asking students to write their own job description for one of these jobs or by identifying which particular sociology skills are used in each job.
Learn More: The University Network
8. I’m More Than…

When class starts, students write about how they want to be perceived by their peers vs how they think they are perceived. After students watch a specific Ted Talk, they can complete a prompt about how they are more than “a single camera perspective”. This is a great way to help students have increased empathy for themselves and their peers.
Learn More: The Daring English Teacher
9. Create a Meme
Students explore social construction in real time with this meme activity. Students poke fun at various aspects of life by creating their own memes. Use the finished product to kick the class off with a laugh.
Learn More: Tracee Orman
10. Compliments
Compliments are an important part of social life. During this lesson, students learn how to appropriately give and receive compliments from their peers. This is an uplifting and important teaching activity for February.
Learn More: Badger State
11. Culture of Kindness
Lots of social factors are constantly in play inside a school. This book is a great resource full of activities, lessons, and more to create a culture of kindness in your middle schooler’s daily life.
Learn More: National School Products
12. My Heart Full of All
Tolerating diversity and having empathy for others are important aspects of society. This beautifully illustrated book also helps students learn about other cultures. This is a great teaching activity for all schools; regardless of their demographic.
Learn More: Amazon
13. Poverty and Hunger
This is a great teaching activity to explain poverty and hunger in an age-appropriate way. Start class by asking students to think about a difficult time in their own lives. Finish storytime by brainstorming ways that the class can combat hunger in their community.
14. I Love My Hair
Ask children to look in the mirror and describe their hair. Then, show them pictures of people around the world with various hairstyles. Finish the activity by watching this Sesame Street song about different natural hairstyles.
Learn More: Sesame Street
15. Color of Me
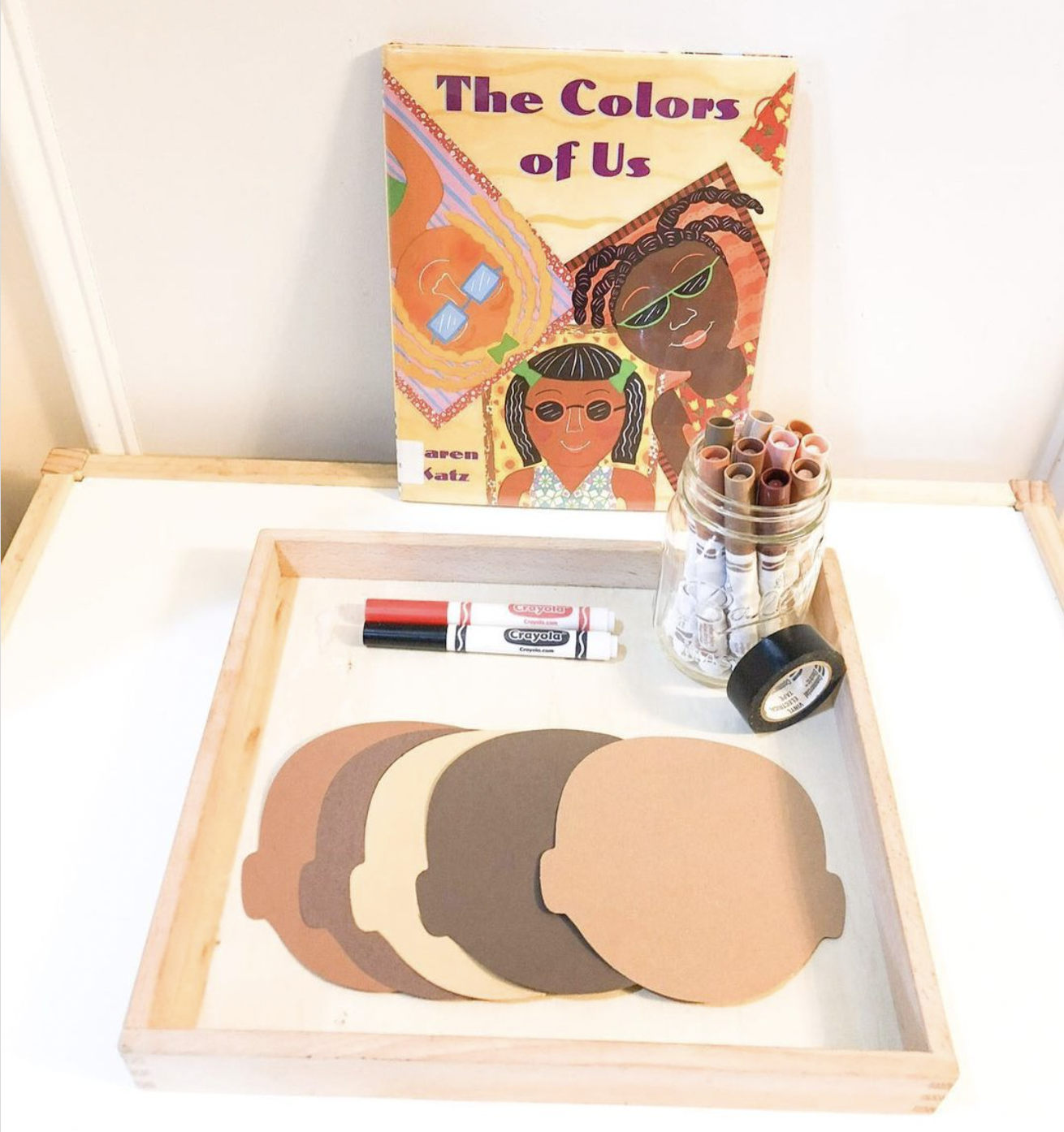

Read The Color of Me. Afterward, layout head templates in a variety of skin tones and ask students to complete a self-portrait. It’s important to provide as many options as possible so that everyone feels included.
Learn More: Happy Toddler
16. Be Who You Are
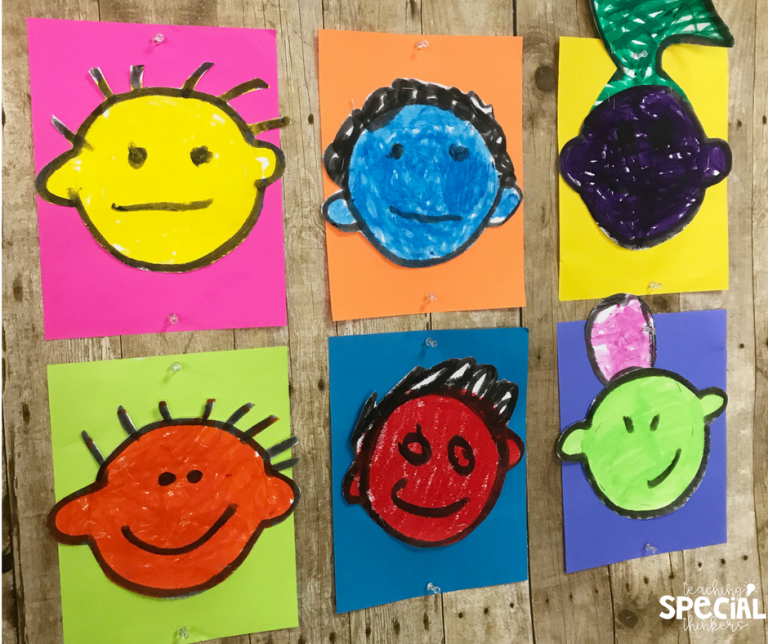

This is a great teaching activity for the special education classroom. While these self-portraits are less literal than others, self-perception is equally important. Reading Be Who You Are is a great way to enforce this message.
Learn More: Teaching Special Thinkers
17. Birdsong
Katherena and Agnes have so much in common, but Agnes’ health is failing. What will happen to their friendship? This is a beautiful book about interacting with elderly individuals. Follow-up class activities could include visiting a nursing home.
Learn More: Bookshop
18. Multicultural Food

This matching activity helps children discover new foods and new flags from across the globe. Some students might even recognize their home flag in this activity. Finish up this class activity by having students try a selection of the pictured foods.
Learn More: Pre-K Printable Fun
19. It’s Ok
Pick a book about diversity to read to the class. Then, pose various discussion questions like, “How are you different than others?” and “Why are differences important?” Then, ask students to write about a difference they are proud of.
Learn More: Jodi Durgin
20. Teaching Diversity
Teaching children about diversity in a middle-class “single camera perspective” demographic can be difficult. Open students’ eyes to a new version of reality through field trips, attending festivals, or writing to penpals. This website also includes a list of helpful online resources and books.
Learn More: Multicultural Kid Blogs
Faculty Resources
In-class activities.

Suggestions for in-class activities, as well as additional essay and discussion questions are included below. Suggested in-class activities and additional essay and discussion questions can also be downloaded as a document here . This was originally created by Kathy Dolan and Jennie Law from Georgia State University.
Module 1 Foundations of Sociology
Short answers:.
- How would you define sociology to someone who knows nothing about it?
- What is the sociological imagination? Illustrate your definition with an example.
- What are the benefits of studying sociology?
- Describe the differences between micro-level and macro-level theories. Illustrate your point with examples.
- Describe the history of sociology, naming and describing the contributions of three different sociological theorists.
- Should we raise the minimum wage? Present arguments for and against raising the minimum wage. Identify which of the three sociological theories would best match arguments for and against raising the minimum wage.
Online Discussion Question:
- Do some online research on locavores and one specific locavore group. Describe the group using the symbolic interactionist perspective. Include web links and other relevant sources.
Class Activities:
- Create an infographic (using an infographic creator tool or website tool) showcasing the main parts of each of the three major sociological theories, Functionalism, Conflict Theory, and Symbolic Interactionism.
- Create a simulation of a social media conversation between two different sociological theorists on the nature of society.
Module 2 Sociological Research
- What are the advantages of using surveys in research?
- Define reliability and validity.
- Devise a hypothesis about some aspect of society. Identify your dependent and independent variables.
- What is interpretive research? Give an example of a research question that would be best answered using an interpretive framework.
- Outline and define the steps of the sociological research process.
- Describe at least three ethical concerns in sociological research and how the profession addresses those concerns. Make up original examples to illustrate your points.
- If you had a million-dollar research grant to study anything about society, what would you study? Why would you choose this topic? Remember to develop a sociological question with sociological reasoning. Try to be value free. Which research method would you use and why?
Class Activity:
- As a class or in groups, identify a sociological research topic. Ask a question about this topic. Formulate a hypothesis. Create 10 closed-ended survey questions addressing your hypothesis. Use a program like Plickers or an electronic polling tool to have students in class answer the questions. Create infographics, charts, etc. to display the results to the class. Have each group discuss the results for their questions and their conclusions about their hypothesis. Explain to students why these results pertain just to this class and cannot be generalized.
Module 3 Culture
- Describe at item of material culture that is important to you. What symbolic significance does it hold for you?
- How is social control functional for society?
- Describe the difference between folkways and mores. Give an original example for each.
- Technology does not just meet modern technology. Describe two original examples of technological developments that had an impact on group living.
- Describe how the media can have a life-changing function. Illustrate with an original example.
- Define ideal and real culture. Explain the concepts with an original example.
- Describe high culture and popular culture. Provide original examples for each, explaining why they fit the description.
- What is the digital divide? How is this concept related to social class and inequality? Who suffers from the digital divide?
- What is media consolidation, and what impact does it have on society?
- Have you ever experienced culture shock? Describe a time you experienced culture shock. What was surprising to you? How did you react to the surprise? How did you overcome your culture shock?
- Have you ever thought about inventing something, or that someone else should invent something to solve a specific problem? What would you invent if you could? Explain how your invention would be functional for society.
- Imagine knowing nothing about human life in the United States. Pick an aspect of life that seems mundane and normal to you, and explain it to someone who is experiencing culture shock.
- The Breaching Experiment, as described on P. 58 of your text, is a classic sociological experiment. For this assignment, students should break a social norm at the folkway level. Be sure students understand that they should not do anything dangerous or illegal or that would put them at risk in any way. Often students will choose to do this assignment with a family member or friend. Have students report to the class on what they did and how people reacted. Discuss sanctions and social control.
- As individuals, small groups or a whole class, create a new norm for society. Decide what the norm is, how it will be enforced, and what the sanctions will be for following or breaking the norm. Then describe how you would effectively socialize people into this norm. Discuss.
Module 4 Socialization
- How do sociologists and psychologists view the world differently? Give an original example to illustrate your point.
- What is resocialization? Illustrate your definition with an original example.
- How important are peer groups to socialization? In what ways do they influence individuals throughout the life course?
- Describe the concept of the social construction of reality. Illustrate your essay with an original example.
- Describe Erving Goffman’s theory of the presentation of self in everyday life through role performance. Illustrate the theory with original examples.
- Have you ever observed someone experiencing a self-fulfilling prophecy? Explain. If you have not personally observed this, use an example from the media, books, movies, or TV.
- Have you ever experienced role strain or role conflict? Describe the different roles and how they were strained or conflicted. How did you resolve this?
- Since socialization is often so unconscious, we sometimes take for granted what we know without thinking too much about how we came to know it. For this discussion, think about an aspect of life you take for granted, and describe what you can remember about being socialized or taught specific norms.
Module 5 Society and Groups
- How did the Industrial Revolution lead to urbanization?
- Describe Karl Marx’s theory of alienation.
- What is the difference between social group and institutional agents of socialization? Explain your answer with original examples from both social group and institutional agents.
- Define the concept of the McDonaldization of society, including the 4 characteristics Ritzer describes in his book.
- Choose two of the four characteristics of the McDonaldization of Society and show how these concepts can be applied to other aspects of our lives.
- Define and describe two different leadership styles. Give original examples of both from your own life or in society and explain why they are good examples of the style.
- What would life be like if the Internet just stopped working? Describe how this event would impact two different social institutions.
- Briefly describe the concept of Mcdonaldization.
- Describe your example.
- Apply the four characteristics of McDonaldization to your example.
- Include inserted photos, links, and resources to help illustrate your example.
- How does advertising play on the ideas of in-groups and out-groups to sell products and services?
- Are you a part of any voluntary groups? Describe them and why you joined them. What do you get out of them? What do you contribute to them?
- How are sociological theorists relevant to today’s world? As individuals or as a class, do a hashtag search for Karl Marx on a social media platform that uses hashtags. Do a brief content analysis of the posts that you find to describe their relevance.
- You can use this activity in class with magazines and glue sticks, using old file folders as the base, or you can have students create their image boards using online tools and programs. Have students make an image/text board or infographic using images and text that illustrate the McDonaldization of Society. These can be posted online and discussed or discussed in the classroom.
Module 6 Deviance, Crime, and Social Control
- How can deviance be positive? Explain your answer using an original example.
- What are the two main ways we get statistics on crime in the United States? Name the reports and describe how their data is collected.
- Describe 2 of the 4 types of social bonds in control theory. Give original examples of each.
- According to Functionalist theory, deviance can be functional for society. Give 4 specific, original examples of how deviance can be functional for society.
- Sanctions, or reactions to behavior, can be positive or negative and formal or informal. Define the 4 combinations and give original examples to illustrate your descriptions.
Online Discussion Questions:
- What do you think about C. Wright Mills’ notion of the Power Elite? Who do you think makes up the power elite? Give two specific original examples, and show how their decisions can impact society as a whole.
- What is panoptic surveillance? Besides prison, where else do we find this? Why does it exist? Describe two original examples.
- Make a list of common law-breaking activities or actions that most people do not consider serious, and the legal penalty in your area for each. Using Plickers or another classroom survey tool in an anonymous way, ask students who has broken each law. Have them tally up how much they would owe in fines and jail time had they been caught and convicted of these offenses. Discuss perceptions of crime and why different law-breaking activities are treated differently.
Module 7 Stratification and Inequality
- What is meritocracy? To what extent do you think the United States is a meritocracy? Give two original examples to justify your response.
- Why do most Americans self-identify as middle class?
- Why are conflict theorists deeply critical of social stratification?
- Briefly describe Wallerstein’s world systems approach to global inequality.
- Differentiate between extreme and relative poverty, and give original examples for both.
- Social mobility can take many forms. List and describe three types of social mobility. Give original examples of each to illustrate your answer.
- Compare and contrast how conspicuous consumption would be explained by a symbolic interactionist theorist and a functionalist theorist.
- What is meant by the cycle of poverty? How does it operate? How is poverty feminized? How does the feminization of poverty impact the cycle of poverty?
- How would you describe your standard of living? What factors are you basing your description on? Has your standard of living changed over time or by circumstances? What are some indicators of that change?
- Discuss conspicuous consumption. Insert photos from the Internet or original photos of your own of 3 examples of conspicuous consumption. What are these items supposed to signify? What are some other social meanings that might be assigned to these items if viewed from a different perspective?
- Do you think you purchase goods made in sweat shops? Look up where some of your clothes and goods are made. Look up the records on working conditions of the workers in companies that make your products. Who actually made them? If they were made in sweatshops, does that matter? Why or why not?
- Are there any forms of cultural capital that can be acquired without economic capital? That is, can one cultivate habits of speech and appearance that suggest higher social status but which do not cost money? (or at least very much money?) What symbolic values are at work here?
- If prestigious brand-name products, such as the Louis Vuitton handbag we started with, confer some sort of high status on those who possess and display them, then how does the “branding” of the self function in our 21st-Century economy? When individuals brand themselves through social media and other public platforms, whether as employees or “influencers” and such, what status or characteristics are they trying to claim? What do they hope to gain?
- The sociologist Charles Horton Cooley introduced the concept of the “looking glass self,” which says we develop our sense of self according to how we believe others perceive us. Can this idea help us understand how social status and economic class are related? To what extent are status and class a matter of self-conscious performance for the benefit of an imagined audience?
- Have students go to Playspent.org and play through the game at least twice. Or, you can do this in the classroom and make choices as a group. Each choice opens up the conversation to discussions of inequality and structural and personal factors that impact those living in poverty. Discuss how poverty is linked to so many other social problems.
- As individuals, groups, or a class, list several indicators of global stratification. Choose three countries you think will rank differently on these indicators and find data on the chosen indicators for each country. Compare and discuss results and how stratification manifests in your examples.
Module 8 Race and Ethnicity
- How are stereotypes both functional and dysfunctional for society?
- What is racial steering? In what ways do things like this exist today?
- What is intersection theory? How can we use it to help understand the experiences of those around us? Illustrate your answer with an original example.
- What do you do when you hear someone tell a racist joke? What social responsibility do you think we have to speak up or stand up when we see or hear racist behavior or talk?
- Have you ever been incorrectly stereotyped? Describe the situation and why you think you were stereotyped. Why was the stereotype wrong?
- Have students go to Implicit Association Test Website and take an Implicit Association Test related to race and ethnicity. In advance, explain to them how the test works and what the results will and will not mean. The website has a great explanation and answers to questions. Discuss results and why students think they got the results they did (go beyond the mechanics of the test).
Module 9 Gender, Sex, and Sexuality
- What is gender identity? How does society contribute to our understanding of what it means to identify ourselves and others by gender categories?
- How did the work of Alfred Kinsey impact the field of sexuality studies?
- How does the concept of heteronormativity manifest in society? Describe three original examples.
- How does inequality based on gender impact society? Compare and contrast the functionalist and conflict views on gender inequality.
- It is easier to see examples of gender role socialization in children than it is in adults. Think of some examples of how adults are socialized into gender roles over the life course. What does society expect of people based on gender at different ages?
- In small groups, create Public Service Announcements (PSAs) targeted at teaching boys and men not to sexually assault girls and women. Use some class time to prepare, and the rest for the students to act out or demonstrate their PSAs. As a class, discuss the perceived pros and cons of the PSAs.
Module 10 Marriage and Family
- How does the U.S. Census definition of family compare to the sociological definition of family?
- How do changes in one social institution or structure impact another? Give an original example using the institution of the family.
- How does symbolic interactionism describe how we develop an understanding of what constitutes a family? How does this differ from a functionalist explanation?
- Describe intimate partner violence in the United States using an intersectional approach.
- Who do you consider to be family? Do you consider only relatives, or do other people or creatures fit that description for you? How do you decide who you consider family?
- As a class, list the functions of the family. Divide the class into small groups and have them imagine a society where the institution of the family does not exist. In their society, how would the functions the class listed be filled? Groups should be creative and inventive. After about half of the class period is over, ask groups to describe their societies and how the functions that would be met by the institution of the family are met in their imagined society. Students should be thinking in terms of social structure.
Module 11 Religion
- How does a religious movement move from being a sect to a denomination?
- Explain 3 functions of religion that are positive for society.
- What is liberation theology? Give an original example from current events.
- How does the social structure of religion impact other institutions in a society? Illustrate your description with two original examples.
- How is the Protestant Work Ethic related to capitalism? How might it be used to justify inequality?
- Megachurches are a relatively recent phenomenon described in your text. What is a megachurch? Find an example of a megachurch and do some research on it. Using functionalist theory, explain how the megachurch meets various needs for its members and for society. Give concrete examples.
- Individually or in small groups, have students investigate death rituals from a culture other than mainstream U.S. culture. What are the functions of the death rituals for the group? As a class, discuss similarities and differences in death rituals across cultures.
Module 12 Education
- How is education related to life expectancy?
- In what ways is the U.S. education system unequal?
- What is social promotion? How can it be both functional and dysfunctional?
- How does cultural transmission work through the institution of education? Give three original examples.
- How is the importance of credentialism in today’s society explained by labeling theory? Illustrate your explanation with original examples.
- You read about grade inflation in this chapter. What do you think about it? How do you think grades in your college classes should be calculated and distributed? Give some examples related to grades that you have experienced that you thought were either helpful or harmful and discuss why you feel the way you do.
- In small groups, have students design a sex ed curriculum for 5th, 8th, and 11th grade public school students. What topics would they cover at each grade level and why? What topics would they exclude and why? What is the overall goal of their curriculum? Discuss as a class, and have each student group add to a written chart on the board.
Module 13 Health and Medicine
- Define and describe the stigmatization of illness. Illustrate your description with an original example.
- How does socioeconomic status influence health?
- How does health and wellness differ between high and low income nations? Give at least 3 examples.
- What is socialized medicine? Describe 2 benefits and 2 drawbacks.
- What are your thoughts on the medicalization of deviance? How might this view be beneficial for society? For the deviant individual? How might it be detrimental? Do a little online research and describe an example of a deviant behavior being medicalized.
- Look up and examine historical changes in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual. You may want to assign topics to small groups in class. Discuss how the changes in the conceptions of mental illness are related to other things happening in society. Discuss how social views and the social construction of reality impact the definition of mental illness.
Module 14 Aging and the Elderly
- Why do we distinguish between three different stages of seniors? What is the basis of the distinction between stages?
- How is ageism institutionalized? Illustrate your explanation with an original example.
- What makes the Baby Boomers an important generation? Describe three ways they are impacting how society deals with aging.
- Compare disengagement theory with modernization theory. Which theory do you think better applies to today’s seniors? Explain and give an original example.
- How much do you think we value the elderly in American society? How are our ideas about what and who is considered “old” changing? What is driving the change in our conceptions of age?
- Have students ask elder members of their family to describe their impressions of their own grandparents, great-grandparents or other family elders when they were a child. Ask how their own senior years are comparing to those of their ancestors. Discuss these changes as a class, and connect them to historical and social structural factors in society.
Module 15 Government and Politics
- Describe the three types of authority, and give original examples for each.
- How would a symbolic interactionist theorist study government? Illustrate with an example.
- Describe two social factors that impact voter participation in the United States.
- Compare and contrast two different forms of government.
- How is voting impacted by race, class, and gender issues?
- Using functionalist theory, describe the four main functions of the government. Give an original example for each function.
- Why do you think some Americans have such a fascination with royal families and monarchies? How do you think views on royalty have changed since an American actress recently married into the British royal family?
- Have students create and administer a short interview guide concerning voter participation and attitudes toward voting. They should interview 3 people and discuss their findings with the class.
Module 16 Work and the Economy
- What are the main differences between capitalism and socialism?
- What impact have women had on the modern workforce?
- How do developed countries protect their citizens from extreme poverty?
- How is the information age changing the institution of work?
- How has globalization impacted the nature of work? Include discussion of global assembly lines and global commodity chains.
- You read in your text about the woman who lives without money. Find another example of a group that lives without money. Describe the group’s philosophy on money and how they replace money in their economic system. Provide links to sources where possible, and insert relevant pictures and video clips into your post.
- Have students write their description of their ideal job. What would it be? What would the working conditions be like? Responsibilities? Compensation? Then have them search Indeed.com for the job they have described. Students should report back to the class how their ideal job compared to the actual jobs available.
Module 17 Population, Urbanization, and the Environment
- What is fertility rate and mortality rate? What do these measures tell us about a population?
- How does the Cornucopia theory address the idea that the human population may become unsustainable?
- Compare and contrast two demographic theories with regard to how societies develop.
- What is gentrification? What are some functions and dysfunctions of gentrification? How does it impact different groups?
- Investigate an organization that is working to ease some aspect of the trash problem somewhere in the world. Check the discussion board before you post to be sure you are posting about an organization that has not already been discussed. Describe the specific trash problem the organization is addressing, the mission of the organization and the impact of their work on the trash problem. Include links, pictures, and video clips when you can.
- As individuals or in small groups, think of some items that are generally considered trash and easily thrown away, and come up with a reasonable way to reuse the item. Be inventive and creative as well as practical. Leave time for each group to describe their ideas to the class and for the class to discuss the merits of each idea.
Module 18 Social Movements and Social Change
- Give an example of each of the three types of framing using frame analysis.
- The Internet serves many positive functions for society. What are three ways it has been dysfunctional?
- Describe the four different types of crowds, and give original examples for each.
- There are 5 types of social movements, each with different goals. Define and describe them, and give an original example for each.
- Fads are a type of collective behavior. Investigate a fad, from now or the past, and describe what the fad is, how it became popular and how it declined. Which groups were the first to adopt the fad? Who was influential in the spread of the fad? Was the fad related to other things happening in society? Include links, pictures and video clips where you can.
- In small groups, have students develop a plan to start a social movement. What social problem are they addressing? Have students restate the claim using three different framing techniques. As a class, discuss each group’s ideas and which of the three framing techniques might be most successful in attaining attention and resources for their social movement.
- There has been years of debate over the question of whether violence in media and video games causes young people to be violent. Discuss arguments on both side.
- Advertisers have had to become more innovative and clever in order to get their message to a public that may not watch traditional TV ads or see them in print magazines. Discuss two original examples of how advertisers are getting their message to consumers in new ways. Try to give examples classmates have not already given. Include links when you can.
- Have students keep notes on everything they see in one day that is advertising a brand, product, or service. A lot of these things fly under our radar and we often do not pay close attention to things like company logos on someone’s tee shirt, product placement in movies, or an ad on a social media page. Ask students to jot down notes throughout the day because it will be harder to remember them all later. Discuss their examples and the pervasive nature of advertising
Contribute!
Improve this page Learn More
- In-Class Activities modification, adaptation, and original content. Authored by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Classroom. Authored by : Prosymbols. Provided by : Noun Project. Located at : https://thenounproject.com/term/classroom/520781/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Resources for Instructors, Openstax Sociology 2E. Authored by : Kathy Dolan and Jennie Law. Provided by : Georgia State University. Located at : https://oer.galileo.usg.edu/psychology-ancillary/11/?fbclid=IwAR0w1n8jecFiy49h_hKpaZ5bqd43keKhxGxKtpYUs6_eNatlYVhpYadleIA . Project : Affordable Learning Georgia Grant. License : CC BY: Attribution

- Privacy and Cookie Policy
- Ancient History
- Our Free Lesson Plans and Classroom Activities
- Archaeology
- Early Humans
- Mesopotamia
- Free Use Clipart
- American History
- Native Americans
- New World Explorers
- 13 Colonies
- Revolutionary War
- Creating a New Nation and US Constitution
- Western Expansion
- The Civil War
- Industrial Revolution
- Roaring 20s
- Great Depression
- World History
- African Kingdoms
- Middle Ages
- Renaissance Reformation and More
- Age of Exploration
- Holidays Around the World
- FAQ, About Us, Contact
- Show More Show Less
Sociology Lesson Plans, Games, Activities
What is sociology?
Covers several topics in sociology, lesson plans and activities
Founding Fathers of Sociology
Culture, Status, Roles
Social Stratification
Social Class Stereotypes
Social Inequalities
Social Interaction
Social Groups, Institutions, Formal Organizations, Bureaucracies
Social Change & Population
Socialization
Types of Human Societies Pre-Industrial & Industrial Societies
Collective Behavior - Fads, Fashions, Panic, Mass Hysteria
Propaganda Lesson Plans
Family Relationships
Bullying, Bullying Prevention
Gangs & School Violence
Lesson Plans & Games on Aging
Human Rights
More Lesson Plan for Sociology - Overviews
Sociology Research Lessons & Topic Suggestions
Sociology Games & Quizzes for Kids
Interaction Classroom Games for Sociology
Dr. kelly s. meier.

Students fascinated with how people interact are drawn to sociology as an academic discipline. You can help students think more deeply about sociology by getting them involved in fun activities that explore individual and group behavior. Even the way your class responds to the activities is a sociological lesson. Prepare students with reading assignments in advance of your planned activity, and follow up with discussion or written reflection to enhance the learning experience.
Explore this article
- A Puzzle as Metaphor for Sociology
- How Jobs Are Valued: Follow the Money
- A Walk on the Outside of Social Norms
- Looking Backward: See How Society Changes
1 A Puzzle as Metaphor for Sociology
Help students understand the framework of sociological theory by bringing a puzzle to class. Have your students begin assembling a 500-piece puzzle. After the border is assembled and pieces have been sorted, stop the activity and have a large-group discussion. Explain that working a puzzle is a lot like the study of sociology. Sociologists find meaning by gathering individual pieces of data and putting them together to find broader meaning. The puzzle serves as a metaphor for this, and helps beginning students understand basic principles of sociology.
2 How Jobs Are Valued: Follow the Money
After teaching about sociological theories related to socioeconomic values, engage your students in an exercise that explores how various jobs are valued. Divide the class into small groups and give each group a list of job titles. Include a wide range of occupations including physician, garbage collector, plumber, bank teller, teacher, housekeeper and corporate executive officer. Next, give each group a sum of money and ask them to determine a salary for each occupation. They can only use the money you give them for the salaries. Determine the amount of money based upon the jobs you select. Have the groups come back together and share their work. Discuss societal values related to income and how the theories provides an explanation for these standards.
3 A Walk on the Outside of Social Norms
Observation is a powerful tool when teaching students about societal influence. Ask your students to bring a homemade costume to class. Suggest men’s clothes for women, women’s clothes for men, winter clothes if it’s warm or an outfit from a different time period. Have students spend 30 to 40 minutes walking around campus, wearing these out-of-the-ordinary clothes. Ask them to check out a book from the library, buy a cup of coffee or ask someone for directions. When students return to class, have them jot down notes about their experience and share with the class. In a large group, ask what it was like to go against social norms. To further the assignment, have each student write a reflection paper that discusses their experience and relates it to sociological theories.
4 Looking Backward: See How Society Changes
Expose your students to organizational change by studying the history of the college. Divide your class into small groups and give them a copy of the current college organizational chart and one from 25 years ago. Ask them to identify the structural differences and how they may be related to societal issues of the same time period. Each group should discuss the reasons for differences in the charts and what the evolution indicates about societal change. Provide an opportunity for large group discussion and ask each group to report their findings.
- 1 Sage Publications: Sociology Through Active Learning
- 2 American Sociological Association: Breaking a Social Norm
- 3 American Sociological Association: Using Puzzle Construction to Understand the Role of Theory in Sociology
About the Author
Dr. Kelly Meier earned her doctorate from Minnesota State Mankato in Educational Leadership. She is the author and co-author of 12 books and serves as a consultant in K-12 and higher education. Dr. Meier is is a regular contributor for The Equity Network and has worked in education for more than 30 years. She has numerous publications with Talico, Inc., DynaTEAM Consulting, Inc. and Kinect Education Group.
Related Articles

How to Teach an Introduction to Sociology

Classes to Take for Criminology

Sociological Hypothesis Ideas

What Are the Stages of Communism?

Microeconomics Research Paper Topics

Classroom Exercises for Introduction to Sociology

What Kind of Math Classes Do You Have to Take to Become...

Definition of Micro & Macro Economics


How to Write an Ethnography

How to Promote Diversity in the Classroom

Research Paper Topics on Organizational Behavior

Independent vs. Dependent Variables in Sociology

Are Communism & Marxism the Same Thing?

How to Write an Ethnographic Case Study

What Does Sociopolitical Mean?

How to Celebrate Diversity

Tools for Economic Analysis

The Scientific Methods in the Study of Economics

Fun Activities for Team Building for Teens to Get to...

Types of Intercultural Relationships
Regardless of how old we are, we never stop learning. Classroom is the educational resource for people of all ages. Whether you’re studying times tables or applying to college, Classroom has the answers.
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy
- Manage Preferences
© 2020 Leaf Group Ltd. / Leaf Group Media, All Rights Reserved. Based on the Word Net lexical database for the English Language. See disclaimer .
- Technical Support
- Find My Rep
You are here
Sociology in action free activities.

Try these free Sociology in Action activities in your class
Sociology in action, third edition , edited by: kathleen odell korgen and maxine p. atkinson, includes everything you need to get students doing sociology through real-world activities designed to increase learning, retention, and engagement. each chapter is contributed by an expert and experienced teacher in that area who uses active learning in their courses., below, we have selected a few exercises for you to try with your students. we hope you enjoy teaching with these , activity 1: conflict theory and student athletes.
Doing Sociology 2.2 Conflict Theory and Student Athletes
In this activity, you will apply conflict theory to analyze pay for student athletes.NCAA regulations have traditionally limited the ways student athletes can profit from their participation in sports at their colleges and universities—even if they belong to one of the programs that collects millions of dollars in television fees and other revenues. In 2021, the NCAA changed some of these regulations... more .
Activity 2: Identifying Deviance Neutralizations
Doing Sociology 6.4 Identifying Deviance Neutralizations
In this exercise, you will examine respondent quotes from Alexander and Opsal’s (2021) research on hazing among college students, identify the techniques of neutralization they use, and consider why they attempt to neutralize the deviance of hazing... more .
Activity 3: Media and Gender and Sexual Identities
Doing Sociology 8.3 Media and Gender and Sexual Identities
In this activity, you will consider how we create our gender and sexual identities amid the media we consume.Write answers to the following questions... more .
Learn more about the Sociology in Action Series:
Race and Ethnicity
Sociology in Action
Social Problems
Social Research Methods
- Conflict Theory and Student Athletes
- Identifying Deviance Neutralizations
- Media and Gender and Sexual Identities
- New Titles and Best Sellers
- Vantage Courseware Offerings
- Sociology in Action Series

- Communities
- Toggle navigation
SOC 100 | Intro to Sociology | OER Course Hub
A collection of open teaching and learning materials curated by BMCC faculty
Category: Assignments
Children’s books as agents of socialization activity.
This is a fun in-class activity in which small groups of students analyze children’s books as agents of socialization. You can do this by bringing books into class or possibly by having students visit the library and find a children’s book there.
Sociological Methods Exercise
This is a useful low-stakes small group exercise that can help students learn how to formulate research questions and how different sociological research methods might be used. You can give students any manageable research “topic” but I find something related to college/higher education to work well.
Sinking Ship Exercise
This is a fun, low-stakes exercise that helps students understand Moore and Davis’s functionalist theory of social stratification. For in-person classes, I put students into groups of 3-5 and ask them to together “save” 6 people; for online synchronous classes, I create a Google Form and ask students to individually select their 6 people and then we look together at who the class has “saved.”
Rich and Poor (low-stakes writing assignment)
Faculty: This is a quick writing exercise that can get students thinking about social class divisions. I like to use this as a way into discussing sociological theories of social class division (Marx, Weber, and Moore and Davis’s functionalist theory). For in person classes, students can free write on paper; for online synchronous classes students can put their responses into a Google Doc or Google form.
Instructions for students: Free write for five minutes a response to this question.
Why are some people rich and some people poor?
Sociological Imagination Essay
This is an essay that I assign early in the semester to encourage students to start to use their sociological imagination by thinking about how a daily activity they do is influenced by society and history. The questions/prompts below the assignment can also be adapted for an in-class exercise for students to do in small groups.
Ice Breaker Bingo
This is a fun ice breaker I do with all my SOC 100 students on the first day of class. Each student must try to complete the bingo sheet by speaking to people in class. Students should find someone who fits the category, introduce themselves, and write their name in the square. They have to fill the whole board. The professor also plays the game. The first student to fill in the entire board wins a KitKat bar. I insist that all the students get up from their chairs and walk around the room to interact with their classmates.
The bingo game gently touches on many of the key themes of the course, such as race, class, gender, religion, the media, politics, economics, culture, family, criminal justice, and the environment. I have found that this bingo game is terrific in breaking the ice and helps establish a sense of connection and fun in the class on the very first day.
PhotoVoice Assignment
Welcome to the bmcc openlab.
BMCC’s OpenLab is an online platform where the College’s students, faculty and staff can come together to learn, work, play and share ideas.
Powered by:

‘what is deviance?’ in-class activity
- What Is Deviance – Handout
The handout posted here has a great in-class activity designed and used by sociology professor Ann Meier at the University of Minnesota . The activity encourages student to identify and categorize deviant acts (such as breaking a window) or deviant attributes (such as working as a prostitute) using the following scale:
Not deviant at all = 1 Not so deviant = 2 Neutral = 3 Somewhat deviant = 4 Very deviant = 5
Then, students are encouraged to discuss why they chose to label certain acts and attributes the way that they did. This exercise is a great way to get students thinking about sociological concepts of deviance, conformity, social control, folkways and mores, as well as crime… plus it can get them up out of their chairs!
Roger — October 19, 2010
Great site - thanks for the insights, ideas, and the many tips. Roger
Neil — March 13, 2011
I like the idea. It's a great activity to hook the kids into the unit.
accessibility
- No categories
climate change
Research on teaching.
- tech & media in the classroom
service learning
Teaching contest.
- 2018 winners
- 2019 winners
Teaching Resources
- assessments, evaluations, & rubrics
- classroom warm-ups & ice breakers
- in-class exercises/activities
- lesson plans
- teaching tips
- worksheets & printables
- writing in the classroom
white privilege
CC Attribution Non-Commercial Share Alike

Thursday, February 23: The Clark Library is closed today.
SOC 101: Introduction to Sociology: Class Activities
- Class Activities
- Where to Look
- Increase Your Search Success
- Scholarly Articles
- Track Down the Full Text
- Cite Sources: ASA
Online Worksheets
- Link to Article Anatomy & Reference Review Worksheet
Articles for In-Class Activity
- Table 1: The confidence delusion: A sociological exploration of participants’ confidence in sport-for-development
- Table 2: Ecological disruptions and well-being among children in foster care
- Table 3: Exploring a social work lead mindfulness-based intervention to address burnout among inpatient psychiatric nurses: A pilot study
- Table 4: Has There Been a Transgender Tipping Point? Gender Identification Differences in U.S. Cohorts Born between 1935 and 2001
- Table 5: Inclusion Work: Children of Immigrants Claiming Membership in Everyday Life
- Table 6: Rumors and factitious informational blends: The role of the web in speculative politics
- Table 7: The sleep and technology use of Americans: findings from the National Sleep Foundation's 2011 Sleep in America poll
- Table 8: Creating Sacred Spaces: Buddhist, Hindu, Jewish, and Muslim Student Groups at U.S. Colleges and Universities
- Table 9: Ethnic-racial socialization among Black, Latinx, and White parents of elementary school-age children
- Table 10: #BlackGirlMagic: Using multiple data sources to learn about Black adolescent girls’ identities, intersectionality, and media socialization
Discussion Questions for Article Anatomy
How can an abstract help you decide if an article will be useful?
What sorts of graphics are typically included in a research article?
How long do you imagine it took for the author(s) to perform the research described in their Methods section?
Which section other than the abstract would you read first, to get a sense of the usefulness of the article?
Discussion Questions for Review of References
What types of sources seem to be most commonly cited by scholars in sociology?
Why do you think these types of sources are most commonly cited?
Are these types of sources more authoritative or trustworthy? Why? Are there other reasons why these types of sources might be more cited than others?
Are there any types of sources that rarely seem to be cited in the field?
What did you learn in this activity that may be relevant to you while working on your sociology assignment? Both in terms of the sources you will incorporate into your own research, and in how you might share your own research with others?
- << Previous: Welcome!
- Next: Where to Look >>
- Last Updated: Oct 17, 2023 3:14 PM
- URL: https://libguides.up.edu/soc101
Want a daily email of lesson plans that span all subjects and age groups?
Subjects all subjects all subjects the arts all the arts visual arts performing arts value of the arts back business & economics all business & economics global economics macroeconomics microeconomics personal finance business back design, engineering & technology all design, engineering & technology design engineering technology back health all health growth & development medical conditions consumer health public health nutrition physical fitness emotional health sex education back literature & language all literature & language literature linguistics writing/composition speaking back mathematics all mathematics algebra data analysis & probability geometry measurement numbers & operations back philosophy & religion all philosophy & religion philosophy religion back psychology all psychology history, approaches and methods biological bases of behavior consciousness, sensation and perception cognition and learning motivation and emotion developmental psychology personality psychological disorders and treatment social psychology back science & technology all science & technology earth and space science life sciences physical science environmental science nature of science back social studies all social studies anthropology area studies civics geography history media and journalism sociology back teaching & education all teaching & education education leadership education policy structure and function of schools teaching strategies back thinking & learning all thinking & learning attention and engagement memory critical thinking problem solving creativity collaboration information literacy organization and time management back, filter by none.
- Elementary/Primary
- Middle School/Lower Secondary
- High School/Upper Secondary
- College/University
- TED-Ed Animations
- TED Talk Lessons
- TED-Ed Best of Web
- Under 3 minutes
- Under 6 minutes
- Under 9 minutes
- Under 12 minutes
- Under 18 minutes
- Over 18 minutes
- Algerian Arabic
- Azerbaijani
- Cantonese (Hong Kong)
- Chinese (Hong Kong)
- Chinese (Singapore)
- Chinese (Taiwan)
- Chinese Simplified
- Chinese Traditional
- Chinese Traditional (Taiwan)
- Dutch (Belgium)
- Dutch (Netherlands)
- French (Canada)
- French (France)
- French (Switzerland)
- Kurdish (Central)
- Luxembourgish
- Persian (Afghanistan)
- Persian (Iran)
- Portuguese (Brazil)
- Portuguese (Portugal)
- Spanish (Argentina)
- Spanish (Latin America)
- Spanish (Mexico)
- Spanish (Spain)
- Spanish (United States)
- Western Frisian
sort by none
- Longest video
- Shortest video
- Most video views
- Least video views
- Most questions answered
- Least questions answered

The true cost of gold
Lesson duration 04:57
441,998 Views

3 myths about racism that keep the US from progress - Candis Watts Smith
Lesson duration 10:26
85,666 Views

The dark history of zombies
Lesson duration 05:10
893,491 Views

The movement that inspired the Holocaust
1,286,273 Views

Why are US cities still so segregated?
Lesson duration 06:04
421,239 Views

What is “normal” and what is “different”?
Lesson duration 05:08
804,532 Views

How one person saved over 2,000 children from the Nazis
Lesson duration 05:57
1,815,478 Views

What few people know about the program that "saved" America
Lesson duration 05:04
472,738 Views

How compassion could save your strained relationships - Betty Hart
Lesson duration 11:08
91,008 Views

What it takes to be racially literate - Priya Vulchi and Winona Guo
Lesson duration 12:23
153,247 Views

A brief history of divorce
Lesson duration 05:39
720,274 Views

10 ways to have a better conversation - Celeste Headlee
Lesson duration 11:45
13,914,467 Views

How we can face the future without fear, together - Rabbi Lord Jonathan Sacks
Lesson duration 12:37
263,365 Views

Can you outsmart a troll (by thinking like one)?
Lesson duration 05:01
761,133 Views

Why fascism is so tempting— and how your data could power it - Yuval Noah Harari
Lesson duration 18:23
758,599 Views

The rise of modern populism
Lesson duration 06:22
603,082 Views

Prohibition: Banning alcohol was a bad idea...
Lesson duration 05:13
663,449 Views

Which voting system is the best?
Lesson duration 05:33
1,140,954 Views

What can DNA tests really tell us about our ancestry?
Lesson duration 06:45
1,125,164 Views

When is a pandemic over?
Lesson duration 05:53
4,909,012 Views

The dark history of IQ tests
Lesson duration 06:10
2,236,489 Views

I grew up in the Westboro Baptist Church. Here's why I left - Megan Phelps-Roper
Lesson duration 15:18
6,650,615 Views

How to build your confidence— and spark it in others - Brittany Packnett
Lesson duration 13:31
1,789,074 Views

Empathy is not endorsement - Dylan Marron
Lesson duration 10:53
305,862 Views

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Sociology is the study of culture and includes everything from social justice movements to race to manners. These activities are appropriate for a wide variety of ages and contexts and sure to help you devise creative and engaging lessons! 1. Nature vs. Nurture. This is a great way to check for understanding of a previously studied unit.
Class Activity: As a class or in groups, identify a sociological research topic. Ask a question about this topic. Formulate a hypothesis. Create 10 closed-ended survey questions addressing your hypothesis. Use a program like Plickers or an electronic polling tool to have students in class answer the questions.
What is sociology? Covers several topics in sociology, lesson plans and activities. Founding Fathers of Sociology. Culture, Status, Roles. Social Stratification. Social Class Stereotypes. Social Inequalities. Social Interaction. Social Groups, Institutions, Formal Organizations, Bureaucracies. Social Change & Population. Socialization. Types of ...
Students fascinated with how people interact are drawn to sociology as an academic discipline. You can help students think more deeply about sociology by getting them involved in fun activities that explore individual and group behavior.
Sociology in Action. Kristin Kenneavy Catherine E. Harnois Maxine P. Atkinson Kathleen Odell Korgen. $56.00. Review copy available. Student Study Site. Try these free Sociology in Action activities in your class Sociology in Action, Third Edition, edited by: Kathleen Odell Korgen and Maxine P. Atkinson, includes everything you need to get ...
This assignment (group and individual) offers systematic practice in the recognition and analysis of norms in everyday life situations. The Symbolic Basis of Culture: The Cultural Cocktail Party 31 Andrea Malkin Brenner, American University Welcome to the cultural cocktail party—a fun group exercise involving role playing that will enable you
This is a fun, low-stakes exercise that helps students understand Moore and Davis’s functionalist theory of social stratification. For in-person classes, I put students into groups of 3-5 and ask them to together “save” 6 people; for online synchronous classes, I create a Google Form and ask students to individually select their 6 people and then we look together at who the class has ...
What Is Deviance – Handout. The handout posted here has a great in-class activity designed and used by sociology professor Ann Meier at the University of Minnesota. The activity encourages student to identify and categorize deviant acts (such as breaking a window) or deviant attributes (such as working as a prostitute) using the following ...
Table 1: The confidence delusion: A sociological exploration of participants’ confidence in sport-for-development. Table 2: Ecological disruptions and well-being among children in foster care. Table 3: Exploring a social work lead mindfulness-based intervention to address burnout among inpatient psychiatric nurses: A pilot study.
305,854 Views. 1. 2. 3. TED-Ed lessons on the subject Sociology. TED-Ed celebrates the ideas of teachers and students around the world. Discover hundreds of animated lessons, create customized lessons, and share your big ideas.