

Trigonometry Practice Questions
Click here for questions, click here for answers.
Answers – Version 1
Answers – Version 2
GCSE Revision Cards

5-a-day Workbooks

Primary Study Cards

Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Corbettmaths © 2012 – 2024

Trigonometry Worksheets
Free worksheets with answer keys.
Enjoy these free sheets. Each one has model problems worked out step by step, practice problems, as well as challenge questions at the sheets end. Plus each one comes with an answer key.
(This sheet is a summative worksheet that focuses on deciding when to use the law of sines or cosines as well as on using both formulas to solve for a single triangle's side or angle)
- Law of Sines
- Ambiguous Case of the Law of Sines
- Law Of Cosines
- Sine, Cosine, Tangent, to Find Side Length
- Sine, Cosine, Tangent Chart
- Inverse Trig Functions
- Real World Applications of SOHCATOA
- Mixed Review
- Vector Worksheet
- Unit Circle Worksheet
- Graphing Sine and Cosine Worksheet
Ultimate Math Solver (Free) Free Algebra Solver ... type anything in there!
Popular pages @ mathwarehouse.com.
Trigonometry Questions
Trigonometry questions given here involve finding the missing sides of a triangle with the help of trigonometric ratios and proving trigonometry identities. We know that trigonometry is one of the most important chapters of Class 10 Maths. Hence, solving these questions will help you to improve your problem-solving skills.
What is Trigonometry?
The word ‘trigonometry’ is derived from the Greek words ‘tri’ (meaning three), ‘gon’ (meaning sides) and ‘metron’ (meaning measure). Trigonometry is the study of relationships between the sides and angles of a triangle.
The basic trigonometric ratios are defined as follows.
sine of ∠A = sin A = Side opposite to ∠A/ Hypotenuse
cosine of ∠A = cos A = Side adjacent to ∠A/ Hypotenuse
tangent of ∠A = tan A = (Side opposite to ∠A)/ (Side adjacent to ∠A)
cosecant of ∠A = cosec A = 1/sin A = Hypotenuse/ Side opposite to ∠A
secant of ∠A = sec A = 1/cos A = Hypotenuse/ Side adjacent to ∠A
cotangent of ∠A = cot A = 1/tan A = (Side adjacent to ∠A)/ (Side opposite to ∠A)
Also, tan A = sin A/cos A
cot A = cos A/sin A
Also, read: Trigonometry
Trigonometry Questions and Answers
1. From the given figure, find tan P – cot R.

From the given,
In the right triangle PQR, Q is right angle.
By Pythagoras theorem,
PR 2 = PQ 2 + QR 2
QR 2 = (13) 2 – (12) 2
= 169 – 144
tan P = QR/PQ = 5/12
cot R = QR/PQ = 5/12
So, tan P – cot R = (5/12) – (5/12) = 0
2. Prove that (sin 4 θ – cos 4 θ +1) cosec 2 θ = 2
L.H.S. = (sin 4 θ – cos 4 θ +1) cosec 2 θ
= [(sin 2 θ – cos 2 θ) (sin 2 θ + cos 2 θ) + 1] cosec 2 θ
Using the identity sin 2 A + cos 2 A = 1,
= (sin 2 θ – cos 2 θ + 1) cosec 2 θ
= [sin 2 θ – (1 – sin 2 θ) + 1] cosec 2 θ
= 2 sin 2 θ cosec 2 θ
= 2 sin 2 θ (1/sin 2 θ)
3. Prove that (√3 + 1) (3 – cot 30°) = tan 3 60° – 2 sin 60°.
LHS = (√3 + 1)(3 – cot 30°)
= (√3 + 1)(3 – √3)
= 3√3 – √3.√3 + 3 – √3
= 2√3 – 3 + 3
RHS = tan 3 60° – 2 sin 60°
= (√3) 3 – 2(√3/2)
= 3√3 – √3
Therefore, (√3 + 1) (3 – cot 30°) = tan 3 60° – 2 sin 60°.
Hence proved.
4. If tan(A + B) = √3 and tan(A – B) = 1/√3 ; 0° < A + B ≤ 90°; A > B, find A and B.
tan(A + B) = √3
tan(A + B) = tan 60°
A + B = 60°….(i)
tan(A – B) = 1/√3
tan(A – B) = tan 30°
A – B = 30°….(ii)
Adding (i) and (ii),
A + B + A – B = 60° + 30°
Substituting A = 45° in (i),
45° + B = 60°
B = 60° – 45° = 15°
Therefore, A = 45° and B = 15°.
5. If sin 3A = cos (A – 26°), where 3A is an acute angle, find the value of A.
sin 3A = cos(A – 26°); 3A is an acute angle
cos(90° – 3A) = cos(A – 26°) {since cos(90° – A) = sin A}
⇒ 90° – 3A = A – 26
⇒ 3A + A = 90° + 26°
⇒ 4A = 116°
⇒ A = 116°/4
6. If A, B and C are interior angles of a triangle ABC, show that sin (B + C/2) = cos A/2.
We know that, for a given triangle, the sum of all the interior angles of a triangle is equal to 180°
A + B + C = 180° ….(1)
B + C = 180° – A
Dividing both sides of this equation by 2, we get;
⇒ (B + C)/2 = (180° – A)/2
⇒ (B + C)/2 = 90° – A/2
Take sin on both sides,
sin (B + C)/2 = sin (90° – A/2)
⇒ sin (B + C)/2 = cos A/2 {since sin(90° – x) = cos x}
7. If tan θ + sec θ = l, prove that sec θ = (l 2 + 1)/2l.
tan θ + sec θ = l….(i)
We know that,
sec 2 θ – tan 2 θ = 1
(sec θ – tan θ)(sec θ + tan θ) = 1
(sec θ – tan θ) l = 1 {from (i)}
sec θ – tan θ = 1/l….(ii)
tan θ + sec θ + sec θ – tan θ = l + (1/l)
2 sec θ = (l 2 + 1)l
sec θ = (l 2 + 1)/2l
8. Prove that (cos A – sin A + 1)/ (cos A + sin A – 1) = cosec A + cot A, using the identity cosec 2 A = 1 + cot 2 A.
LHS = (cos A – sin A + 1)/ (cos A + sin A – 1)
Dividing the numerator and denominator by sin A, we get;
= (cot A – 1 + cosec A)/(cot A + 1 – cosec A)
Using the identity cosec 2 A = 1 + cot 2 A ⇒ cosec 2 A – cot 2 A = 1,
= [cot A – (cosec 2 A – cot 2 A) + cosec A]/ (cot A + 1 – cosec A)
= [(cosec A + cot A) – (cosec A – cot A)(cosec A + cot A)] / (cot A + 1 – cosec A)
= cosec A + cot A
9. Prove that: (cosec A – sin A)(sec A – cos A) = 1/(tan A + cot A)
[Hint: Simplify LHS and RHS separately]
LHS = (cosec A – sin A)(sec A – cos A)
= (cos 2 A/sin A) (sin 2 A/cos A)
= cos A sin A….(i)
RHS = 1/(tan A + cot A)
= (sin A cos A)/ (sin 2 A + cos 2 A)
= (sin A cos A)/1
= sin A cos A….(ii)
From (i) and (ii),
i.e. (cosec A – sin A)(sec A – cos A) = 1/(tan A + cot A)
10. If a sin θ + b cos θ = c, prove that a cosθ – b sinθ = √(a 2 + b 2 – c 2 ).
a sin θ + b cos θ = c
Squaring on both sides,
(a sin θ + b cos θ) 2 = c 2
a 2 sin 2 θ + b 2 cos 2 θ + 2ab sin θ cos θ = c 2
a 2 (1 – cos 2 θ) + b 2 (1 – sin 2 θ) + 2ab sin θ cos θ = c 2
a 2 – a 2 cos 2 θ + b 2 – b 2 sin 2 θ + 2ab sin θ cos θ = c 2
a 2 + b 2 – c 2 = a 2 cos 2 θ + b 2 sin 2 θ – 2ab sin θ cos θ
a 2 + b 2 – c 2 = (a cos θ – b sin θ ) 2
⇒ a cos θ – b sin θ = √(a 2 + b 2 – c 2 )
Video Lesson on Trigonometry
Practice Questions on Trigonometry
Solve the following trigonometry problems.
- Prove that (sin α + cos α) (tan α + cot α) = sec α + cosec α.
- If ∠A and ∠B are acute angles such that cos A = cos B, then show that ∠A = ∠B.
- If sin θ + cos θ = √3, prove that tan θ + cot θ = 1.
- Evaluate: 2 tan 2 45° + cos 2 30° – sin 2 60°
- Express cot 85° + cos 75° in terms of trigonometric ratios of angles between 0° and 45°.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


Child Login
- Number Sense and Operations
- Measurement
- Statistics and Data Analysis
- Pre-Algebra
- Trigonometry
Trigonometry Charts
Quadrants and Angles
- Degrees and Radians
Degrees, Minutes and Seconds
Reference and Coterminal Angles
- Trigonometric Ratios
Trigonometric Identities
- Unit Circle
- Trig Ratios of Allied Angles
- Evaluating Trig Expressions
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- Law of Sines
- Law of Cosines
- Solving Triangles
- Principal Solutions - Trig Equations
- General Solutions - Trig Equations
- Math Workbooks
- English Language Arts
- Social Studies
- Holidays and Events
- Worksheets >
Trigonometry Worksheets for High School
Explore the surplus collection of trigonometry worksheets that cover key skills in quadrants and angles, measuring angles in degrees and radians, conversion between degrees, minutes and radians, understanding the six trigonometric ratios, unit circles, frequently used trigonometric identities, evaluating, proving and verifying trigonometric expressions and the list go on...
List of Trigonometry Worksheets
Explore the trigonometry worksheets in detail.
Grasp and retain trigonometric concepts with ease employing these visually appealing charts for quadrants and angles, right triangle trigonometric ratio chart, trigonometric ratio tables, allied angles and unit circle charts to mention a few.
Identify the quadrant encompassing the terminal side of the angle with this set of quadrants and angles worksheets. Draw the indicated angle on the coordinate plane, measure the angles in the quadrant and represent as degrees and radians and a lot more.
Conversion of Degrees and Radians
Introduce the two ways to measure an angle, namely degrees and radians with this set of worksheets. Adequate worksheets are provided to assist in practicing prompt conversions of degrees to radians and vice-versa.
To specifically and accurately measure the size of an angle in degrees, it is further broken down into degrees, minutes and seconds. This worksheet stack consists of ample exercises to practice conversion between degrees, minutes and seconds.
Determine the reference angles in degrees and radians, find the coterminal angles for the indicated angles, and positive and negative coterminal angles with this assemblage of reference and coterminal angles worksheets.
Trigonometric Ratios | Right Triangle Trigonometry
Kick start your learning with these trig ratio worksheets. Identify the legs, side and angles, introduce the six trigonometric ratios both primary trig ratios and reciprocal trig ratios and much more with these trigonometric ratio worksheets.
Included here are fundamental identities like quotient, reciprocal, cofunction and Pythagorean identities, sum and difference identities, sum-to-product, product-to-sum, double angle and half angle identities and ample trig expression to be simplified, proved and verified using the trigonometric formulas.
Unit Circle Worksheets
Packed in these unit circle worksheets are exercises to find the coordinates of a point on the unit circle, determine the corresponding angle measure, use the unit circle to find the six trigonometric ratios and a lot more.
Trigonometric Ratios of Allied Angles
Allied angle worksheets here enclose exercises like finding the exact value of the trigonometric ratio offering angle measures in degrees or radians, evaluating trig ratios of allied angles and proving the trigonometric statements to mention just a few.
Evaluating Trigonometric Expressions
These worksheets outline the concept of evaluating trigonometric expressions involving primary, reciprocal and fundamental trigonometric ratios, evaluating expressions using a calculator, evaluate using allied angles and more!
Evaluating Trigonometric Functions Worksheets
With this set of evaluating trigonometric functions worksheets at your disposal, you have no dearth of practice exercises. Begin with substituting the specified x-values in trigonometric functions and solve for f(x).
Inverse Trigonometric Function Worksheets
Utilize this adequate supply of inverse trigonometric ratio worksheets to find the exact value of inverse trig ratios using charts and calculators, find the measure of angles, solve the equations, learn to evaluate inverse and the composition of trigonometric functions and a lot more.
Law of Sines Worksheets
Navigate through this law of sines worksheets that encompass an array of topics like finding the missing side and the unknown angles, solving triangles, an ambiguous case in a triangle, finding the area of SAS triangle and more.
Law of Cosines Worksheets
Incorporate the law of cosines worksheets to elevate your understanding of the concept and practice to find the missing sides of a triangle, finding the unknown angles (SAS & SSS), solving triangles and much more.
Solving Triangles Worksheets
Access this huge collection of solving triangles worksheets to comprehend the topics like solving triangles, finding the area of the triangle, solving the triangle using the given area and much more worksheets are included.
Principal Solutions of Trig Equations Worksheets
Reinforce the concept of principal solutions of trigonometric equations with this adequate supply of worksheets like solving linear trigonometric equations, solving trigonometric equations in quadratic form and much more.
General Solutions of Trig Equations Worksheets
Employ this assortment of general solutions of trigonometric equations worksheets that feature ample of exercises to hone your skills in solving different types of trigonometric equations to obtain the general solutions.
Sample Worksheets

Become a Member
Membership Information
Privacy Policy
What's New?
Printing Help
Testimonial
Copyright © 2024 - Math Worksheets 4 Kids
One to one maths interventions built for KS4 success
Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons now available
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
This topic is relevant for:

Trigonometry
Here we will learn about trigonometry including how to use SOHCAHTOA, inverse trigonometric functions, exact trigonometric values and the hypotenuse. We’ll also learn about the sine rule, the cosine rule, how to find the area of a triangle using ½abSinC , 3 D trigonometry and how to use the sine, cosine and tangent graphs.
There are also trigonometry worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What is trigonometry?
Trigonometry is the relationship between angles and side lengths within triangles; it is derived from the greek words “trigōnon” meaning triangle and “metron” meaning measure.
Trigonometry was originally used by the Babylonians, over 1500 years before the Greek form that we use today. It is used widely in science and engineering and product design.
The higher GCSE curriculum expands the use of trigonometric functions for non right-angle triangles, developing from the fundamental knowledge of the three trigonometric ratios (expressed as the mnemonic SOHCAHTOA) and exact trigonometric values in right angle triangles.
See also: 15 Trigonometry questions
What is trigonometry
Trigonometry worksheet
Get your free trigonometry worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
What is SOHCAHTOA?
SOHCAHTOA is the abbreviation used to describe the three trigonometric ratios for the sine , cosine and tangent functions.
To determine which trigonometric function you need to use to answer a question, it depends on the location of the angle and the sides of the triangle that will be used. The trigonometric functions apply to right-angle triangles.
- If you know the hypotenuse and the opposite side of the angle, you would use the sine function.
- If you know the hypotenuse and the adjacent side (next to) the angle, you would use the cosine function.
- If you know the opposite and adjacent sides to the angle, you use the tangent function.
We can use SOHCAHTOA to calculate lengths and angles in 2D and 3D shapes by recognising right-angle triangles. E.g. We can find the length A C of a parallelogram or the length A H in the cuboid below.
Step-by-step guide: SOHCAHTOA
What is the hypotenuse?
The hypotenuse is the longest side of a right angle triangle. It is the side opposite the right angle.
The hypotenuse does not occur for other types of triangles unless we know more information (such as an isosceles triangle can be made from 2 identical right angle triangles, back-to-back).
Labelling the other sides of the triangle
Once we know which angle we are using, we can label the sides opposite (O) , adjacent ( A ) and hypotenuse (H) . We know the hypotenuse is opposite the right angle. The opposite side is opposite the angle we are using. The adjacent side is next to the angle we are using. The triangle below is labelled based on using the angle θ .
Step-by-step guide: Hypotenuse
Example 1: find a side given the angle and the hypotenuse
ABC is a right angle triangle. The size of angle ACB = 60º and the length BC = 16cm .
Calculate the value of x .
Labelling the sides OAH in relation to the angle 60º , we can use the hypotenuse, and we need to find the adjacent side. We therefore need to use the cosine function.
Inverse trigonometric functions
What are inverse trigonometric functions.
Inverse trigonometric functions allow us to calculate the size of angle θ for a right-angle triangle.
The inverse trigonometric functions look like this:
Step-by-step guide: Trigonometric functions
Example 2: find the angle using inverse trigonometric functions
Calculate the size of angle θ correct to 2 decimal places.
The two sides that can be used to calculate the value of θ are the opposite and the hypotenuse and so we apply the sine function to θ to get
In order to calculate θ , we rearrange the equation by using the inverse sine function.
We therefore have:
Exact trigonometric values
What are exact trigonometric values.
Exact trigonometric values are found when the relationship between the sides and the angles in a triangle have a specific relationship. Summarising these values, we obtain the exact trigonometric values for sine, cosine and tangent for 0 ≤ θ ≤ 90º .
Example 3: using exact trigonometric values
ABC is an equilateral triangle. M is the midpoint of AC . Calculate the exact size of the angle θ .
AC = 6cm so MC = 3cm
We therefore have the triangle:
Using the table above,
Pythagoras or trigonometry?
We need to be able to interpret problems and recognise whether we need to use Pythagoras’ Theorem in 2 D, 3 D, or one of the three trigonometric ratios.
This flow chart describes the information you need to know about a shape in order to solve the problem.
It is important to recognise that with most of these problems, you may need to use the Pythagorean Theorem, or trigonometry, or both within the same question so you must be confident with these topics individually to access this topic fully.
Below is a summary of methods that can be used for right angled triangles:
Example 4: find the hypotenuse using trigonometry
Calculate the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle, x , to 1 decimal place.
The two important sides in this question are the opposite side ( O ) to the angle and the hypotenuse ( H ) so we need to use the sine function to calculate the value of x .
Solving non right angle triangles
Sine rule (the law of sines), what is the sine rule.
The sine rule (or the law of sines) is a relationship between the size of an angle in a triangle and the opposite side. There are three relationships in a triangle as there are 3 angles with their opposing sides but you will only need to use two.
Pythagoras’ Theorem cannot be used to find the third side of a non-right angled triangle. Instead we can use the sine rule or the cosine rule, depending on the information we know about the triangle.
To find a missing angle: \frac{\sin (A)}{a}=\frac{\sin (B)}{b}
To find a missing side: \frac{a}{\sin (A)}=\frac{b}{\sin (B)}
Step-by-step guide: Sine rule
Example 5: Finding a missing side of a triangle using the sine rule
Calculate the length AB . Write your answer to 2 decimal places.
Label each angle A, B and C and each side a, b and c:
Here we know side a and we want to find the length of c , therefore we can state:
Here, the length AB = 7.00cm (2dp) .
Cosine rule (the law of cosines)
What is the cosine rule.
The cosine rule (or the law of cosines) is a formula which can be used to calculate the missing sides of a triangle or to find a missing angle. To do this we need to know the two arrangements of the formula and what each variable represents.
To find a missing side: a^{2}=b^{2}+c^{2}-2bc\cos(A)
To find a missing angle: A=\cos^{-1}(\frac{b^2+c^2-a^2}{2bc})
Step-by-step guide: Cosine rule
Example 6: find the missing side using the cosine rule
Find the length of x for triangle ABC , correct to 2 decimal places.
The vertices are already labelled with A located on the angle we are using so we only need to label the opposite sides of a, b, and c .
Here, we need to find the missing side a , therefore we need to state the cosine rule with a 2 as the subject:
1/2abSin(C) (area of a triangle)
What is 1/2absin(c) .
\frac{1}{2}abSin(C) is a formula to calculate the area of any triangle.
Step-by-step guide: Area of a triangle trig
Example 7: area using A=1/2ab S in(C)
Calculate the area of the triangle ABC . Write your answer to 2 decimal places.
Here, we label each side a, b, and c .
3D trigonometry
What is 3d trigonometry.
3 D trigonometry is the application of the trigonometric skills developed for 2 dimensional triangles.
To find missing sides or angles in 3 dimensional shapes, we need to be very clear with the rules and formulae to find these different angles and side lengths. The flowchart below can help determine which function you need to use:
Once you can justify which rule or formulae you need to use, you may need to carry out this process again for another triangle in the question.
Top tip: Look out for common angles or common sides.
Step-by-step guide: 3D trigonometry

Example 8: find the missing angle in a triangular prism
Calculate the size of the angle in the triangular prism ABCDEF.
We can see that triangle ABF and triangle ACF share the side AF . We can use triangle ACF to calculate the length of AF , which will then help us calculate the size of angle θ .
This triangle contains no information about the angles so we need to use Pythagoras Theorem.
This is a right angled triangle involving angles so we need to use SOHCAHTOA.
Since we know O and A , we need to use tan.
Trigonometric graphs
The trigonometric functions sine, cosine and tangent can be represented by graphs.
For example, as the angle changes, so does the value of sine. This can be plotted on a graph.
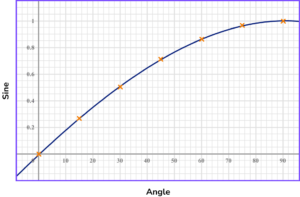
Let’s look at this in more detail below.
Sine, cosine and tangent graphs
What are sine, cosine, and tangent graphs.
Trigonometric graphs are a visual representation of the sine, cosine and tangent functions. The horizontal axis represents the angle, usually written as θ , and the vertical axis is the trig function.
See below for all three trigonometric graphs for all angles of θ between -360º and 360º (-360 < θ < 360).
The graph of y = sin(θ)
Step-by-step guide: Sin graph
The graph of y = cos(θ)
Step-by-step guide: Cos graph
The graph of y = tan(θ)
Step-by-step guide: Tan graph
Example 9: state the value of tan(θ) with θ known
Use the graph of y = tan(θ) to estimate the value of y when θ = 120º .
Here we draw the vertical line at 120º until it reaches the tangent curve and then a horizontal line towards the y -axis.
As the scale for each mark on the y- axis is 0.25 , the value for tan(120) is approximately equal to -1.7 (1dp) .
Common misconceptions
- Labelling a triangle incorrectly
E.g. This triangle has been incorrectly labelled with the side next to the angle.
This will have an impact on the formula for the sine rule, the cosine rule, and the area of the triangle.
- Using the incorrect trigonometric function
If the triangle is incorrectly labelled it can lead to the use of the incorrect standard or inverse trigonometric function.
- Rounding the decimal too early
This can lose accuracy marks. Always use as many decimal places as possible throughout the calculation, then round the solution.
- Pythagoras’ Theorem or trigonometry?
Use the flowchart to help you to recognise when to use Pythagoras’ Theorem and when to use trigonometry. Remember, you may need to use both.
- Using the sine rule instead of cosine rule
In order to use the sine rule we need to have pairs of opposite angles and sides.
- Not using the included angle
For the cosine rule and the area of a triangle using A=1/2absin(C) , the angle is included between the two sides. Using any other angle will result in an incorrect solution.
- Using A = b × h ÷ 2
If the vertical height of a triangle is not available then we cannot calculate the area by halving the base times the height.
- Using the inverse trig function instead, inducing a mathematical error
If the inverse trig function is used instead of the standard trig function, the calculator may return a maths error as the solution does not exist.
- Sine and cosine graphs switched
The sine and cosine graphs are very similar and can easily be confused with one another. A tip to remember is that you “sine up” from 0 for the sine graph so the line is increasing whereas you “cosine down” from 1 so the line is decreasing for the cosine graph.
- Asymptotes are drawn incorrectly for the graph of the tangent function
The tangent function has an asymptote at 90º because this value is undefined. As the curve repeats every 180º , the next asymptote is at 270º and so on.
- The graphs are sketched using a ruler
Each trigonometric graph is a curve and therefore the only time you are required to use a ruler is to draw a set of axes. Practice sketching each curve freehand and label important values on each axis.
Practice trigonometry questions
1. Calculate the length of the side BC:

This is a right angled triangle involving angles so use SOHCAHTOA.
First we need to label the sides O, A and H.
We know A and we want to find H so we need to use cos.
2. Using your knowledge of exact trigonometric values, work out the size of the angle marked . \theta
Using the exact trigonometric values,
3. Work out the size of angle \theta .
This is not a right angled triangle and we know an angle and its opposite side so we need to use the sine rule.
4. Calculate the area of the following triangle:
We do not know the base or the height so we need to use:
5. Calculate the length of AE.
The triangles AGH and AEH share the line AH . Using the triangle AGH we can calculate the length of the line AH.
Using the triangle AEH we can calculate the length of AE .
6. Write down the coordinates of a minimum point on the graph of y=cos(\theta) for 0^{\circ} \leqslant \theta \leqslant 360^{\circ}
The minimum point occurs at (180, -1)
Trigonometry GCSE questions
1. Below is a sketch of a football pitch ABCD .
(a) Player F is standing exactly 60m perpendicular to Player E on the goal line and 75m from the corner where Player A is standing.
Player A kicks the football directly to Player F . Calculate the bearing of F from A . Write your answer correct to 2 decimal places.
(b) Player F then passes the ball to Player G (the goal keeper). Player G is standing at the midpoint of BC at a bearing of 060^{\circ} from F .
How far is Player G from Player F ? Write your answer to 2 decimal places.
Bearing of F from A = 180 – angle EAF
Angle AEF = \sin^{-1}(\frac{60}{75})
Angle AEF = 53.13^{\circ}
Bearing of F from A = 180 – 53.13 =126.87^{\circ}
FG = \frac{45}{sin(60)}
FG = 51.96m
2. Triangle ABE and ACD are similar with AB:BC = 1:3. Using the information on the diagram, calculate the area of the shaded region BCDE .
State the units in your answer.
Area (ABE) = ½ × a × b × sin(C) = ½ × 4 × 6 × sin(30)
Sin(30) = ½
Area (ABE) = 6cm^2
As AB:BC=1:3, BC= 4 × 3 = 12cm and DE = 6 × 3 = 18cm
AC = 12+4 = 16cm and AD = 6+18 = 24cm
Area (ACD) = ½ × a × b × sin(C) = ½ × 16 × 24 × sin(30)
Area (ACD) = 96cm^2
Area BCDE = 96 – 6 = 90cm^2
3. (a) The cuboid ABCDEFGH is shown below. ADEF is a square face with the side length of 2m , and the length AB = 8cm.
Calculate the length of the line AE. Write your answer as a surd in its simplest form.
(b) Given that the point X lies on the line EH so that XH = 3EX and angle XAB = 54.7^{\circ} , calculate the length of the line BX .
AE^2 = AF^2 + EF^2
AE^2 = 2^2 + 2^2 = 8
AE = \sqrt{8} = 2\sqrt{2}
EX = 8 / 4 = 2m
AX = \sqrt{2^{2}+2\sqrt{2}^{2}}
AX = 2\sqrt{3}
Cosine rule stated to find BX :
BX^{2}=AX^{2}+AB^{2}-2\times{AX}\times{AB}\times\cos(A)
BX^{2}=(2\sqrt{3})^{2}+8^{2}-2\times{2\sqrt{3}}\times{8}\times\cos(54.7)
BX^{2}=43.97m
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- use trigonometric ratios in similar triangles to solve problems involving right-angled triangles
- recognise, sketch and interpret graphs of trigonometric functions (with arguments in degrees) y = sin x, y = cos x and y = tan x for angles of any size
- apply trigonometric ratios to find angles and lengths in right-angled triangles and, where possible, general triangles in 2 and 3 dimensional figures
- know the exact values of sin θ and cos θ for θ = 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90° ; know the exact value of tan θ for θ = 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°
- know and apply the sine rule, and cosine rule, to find unknown lengths and angles
- know and apply area = \frac{1}{2}abSinC to calculate the area, sides or angles of any triangle
The next lessons are
- Pythagoras theorem
- Circle theorems
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.
Privacy Overview

Chapter 4: Trig Functions
Exercises: 4.2 Graphs of Trigonometric Functions
skills.
Practice each skill in the Homework Problems listed:
- Find coordinates
- Use bearings to determine position
- Sketch graphs of the sine and cosine functions
- Find the coordinates of points on a sine or cosine graph
- Use function notation
- Find reference angles
- Solve equations graphically
- Graph the tangent function
- Find and use the angle of inclination of a line
Suggested Problems
Homework 4.2
Exercise group.
For Problems 1–6, find exact values for the coordinates of the point.
For Problems 7–12, find the coordinates of the point, rounded to hundredths.
For Problems 13–18, a ship sails from the seaport on the given bearing for the given distance.
- Make a sketch showing the ship’s current location relative to the seaport.
- How far east or west of the seaport is the ship’s present location? How far north or south?
[latex]36°{,}[/latex] 26 miles
[latex]124°{,}[/latex] 80 km
[latex]230°{,}[/latex] 120 km
[latex]318°{,}[/latex] 75 miles
[latex]285°{,}[/latex] 32 km
[latex]192°{,}[/latex] 260 miles
- Draw vertical line segments from the unit circle to the [latex]x[/latex]-axis to illustrate the [latex]y[/latex]-coordinate of each point designated by the angles, [latex]0°[/latex] to [latex]90°{,}[/latex] shown on the figure below.
- Transfer your vertical line segments to the appropriate position on the grid below.
- Repeat parts (a) and (b) for the other three quadrants.
- Connect the tops of the segments to sketch a graph of [latex]y = \sin \theta{.}[/latex]
- Draw horizontal line segments from the unit circle to the [latex]y[/latex]-axis to illustrate the [latex]x[/latex]-coordinate of each point designated by the angles, [latex]0°[/latex] to [latex]90°{,}[/latex] shown on the figure below.
- Transfer your horizontal line segments into vertical line segments at the appropriate position on the grid below.
- Connect the tops of the segments to sketch a graph of [latex]y = \cos \theta{.}[/latex]
- Prepare a graph with the horizontal axis scaled from [latex]0°[/latex] to [latex]360°[/latex] in multiples of [latex]45°{.}[/latex]
- Sketch a graph of [latex]f(\theta) = \sin \theta[/latex] by plotting points for multiples of [latex]45°{.}[/latex]
- Sketch a graph of [latex]f(\theta) = \cos \theta[/latex] by plotting points for multiples of [latex]45°{.}[/latex]
- Prepare a graph with the horizontal axis scaled from [latex]0°[/latex] to [latex]360°[/latex] in multiples of [latex]30°{.}[/latex]
- Sketch a graph of [latex]f(\theta) = \cos \theta[/latex] by plotting points for multiples of [latex]30°{.}[/latex]
- Sketch a graph of [latex]f(\theta) = \sin \theta[/latex] by plotting points for multiples of [latex]30°{.}[/latex]
For Problems 27–30, give the coordinates of each point on the graph of [latex]f(\theta) = \sin \theta[/latex] or [latex]f(\theta) = \cos \theta -27.[/latex]
Make a short table of values like the one shown and sketch the function by hand. Be sure to label the [latex]x[/latex]-axis and [latex]y[/latex]-axis appropriately.
- [latex]\displaystyle f(\theta) = \sin \theta[/latex]
- [latex]\displaystyle f(\theta) = \cos \theta[/latex]
For Problems 33–40, evaluate the expression for [latex]f(\theta) = \sin \theta[/latex] and [latex]g(\theta) = \cos \theta{.}[/latex]
[latex]3 + f(30°)[/latex]
[latex]3 f(30°)[/latex]
[latex]4g(225°) - 1[/latex]
[latex]-4 + 2g(225°) - 1[/latex]
[latex]-2f(3\theta){,}[/latex] for [latex]\theta = 90°[/latex]
[latex]6f(\dfrac{\theta}{2}){,}[/latex] for [latex]\theta = 90°[/latex]
[latex]8 - 5g(\dfrac{\theta}{3}){,}[/latex] for [latex]\theta = 360°[/latex]
[latex]1 - 4g(4\theta){,}[/latex] for [latex]\theta = 135°[/latex]
Draw two different angles [latex]\alpha[/latex] and [latex]\beta[/latex] in standard position whose sine is [latex]0.6{.}[/latex]
- Use a protractor to measure [latex]\alpha[/latex] and [latex]\beta{.}[/latex]
- Find the reference angles for both [latex]\alpha[/latex] and [latex]\beta{.}[/latex] Draw in the reference triangles.
Draw two different angles [latex]\theta[/latex] and [latex]\phi[/latex] in standard position whose sine is [latex]-0.8{.}[/latex]
- Use a protractor to measure [latex]\theta[/latex] and [latex]\phi{.}[/latex]
- Find the reference angles for both [latex]\theta[/latex] and [latex]\phi{.}[/latex] Draw in the reference triangles.
Draw two different angles [latex]\alpha[/latex] and [latex]\beta[/latex] in standard position whose cosine is [latex]0.3{.}[/latex]
Draw two different angles [latex]\theta[/latex] and [latex]\phi[/latex] in standard position whose cosine is [latex]-0.4{.}[/latex]
[latex]\sin \theta = 0.6[/latex]
[latex]\sin \theta = -0.8[/latex]
[latex]\cos \theta = 0.3[/latex]
[latex]\cos \theta = -0.4[/latex]
[latex]\sin \theta = -0.2[/latex]
[latex]\sin \theta = 1.2[/latex]
[latex]\cos \theta = -0.9[/latex]
[latex]\cos \theta = -1.1[/latex]
- What happens to [latex]\tan \theta[/latex] as [latex]\theta[/latex] increases toward [latex]90°{?}[/latex]
- What happens to [latex]\tan \theta[/latex] as [latex]\theta[/latex] decreases toward [latex]90°{?}[/latex]
- What value does your calculator give for [latex]\tan 90°{?}[/latex] Why?
- Sketch by hand a graph of [latex]y = \tan \theta[/latex] for [latex]-180° \le \theta \le 180°{.}[/latex]
- Use your calculator to graph [latex]y = \tan \theta[/latex] in the ZTrig window (press ZOOM 7). Sketch the result. On your sketch, mark scales on the axes and include dotted lines for the vertical asymptotes.
For Problems 61–64, find the angle of inclination of the line.
[latex]y = \dfrac{5}{4}x - 3[/latex]
[latex]y = 6 + \dfrac{2}{9}x[/latex]
[latex]y = -2 - \dfrac{3}{8}x[/latex]
[latex]y = \dfrac{-7}{2}x + 1[/latex]
For Problems 65–68, find an equation for the line passing through the given point with angle of inclination [latex]\alpha{.}[/latex]
[latex](3,-5), ~\alpha = 28°[/latex]
[latex](-2,6), ~\alpha = 67°[/latex]
[latex](-8,12), ~\alpha = 112°[/latex]
[latex](-4,-1), ~\alpha = 154°[/latex]
The slope of a line is a function of its angle of inclination, [latex]m = f(\alpha){.}[/latex] Complete the table and sketch a graph of the function.
- What happens to the slope of the line as [latex]\alpha[/latex] increases toward [latex]90°{?}[/latex]
- What happens to the slope of the line as [latex]\alpha[/latex] decreases toward [latex]90°{?}[/latex]
The angle of inclination of a line is a function of its slope, [latex]\alpha = g(m){.}[/latex] Complete the table and sketch a graph of the function.
- What happens to the angle of inclination as the slope increases toward infinity?
- What happens to the angle of inclination as the slope decreases toward negative infinity?
Trigonometry Copyright © 2024 by Bimal Kunwor; Donna Densmore; Jared Eusea; and Yi Zhen. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search
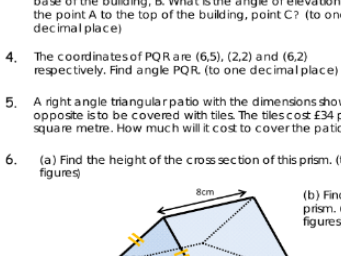
Trigonometry mixed homework including problem solving
Subject: Mathematics
Age range: 14-16
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
26 April 2018
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

Trigonometry questions designed to test students ability to apply their knowledge of basic trigonometry using the sine, cosine and tangent ratios. Includes problem solving questions. Solutions provided!
If you like the resource please rate or review - thank you :-)
Creative Commons "Sharealike"
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
Thank you, this is perfect for a summary HW with extension.<br /> Even better with answers!
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
OreoBiscuit
Londonteachsec, londonsecondary.
Thank you for the positive feedback :-)
Great mixture of questions, thank you!
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
Trigonometry Calculators
- Pythagorean Theorem Calculator
- Triangle Calculator
- Privacy Policy--New
- Terms ( Premium )
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
- Mathway © 2024
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&
Want Better Math Grades?
✅ Unlimited Solutions
✅ Step-by-Step Answers
✅ Available 24/7
➕ Free Bonuses ($1085 value!)
On this page
- Search IntMath
- Math interactives
- About (site info)
- Uses of Trignometry
- ASCIIMath input, KaTeX output
- ASCIIMath input, LaTeX and KaTeX output
- Send Math in emails
- Syntax for ASCIIMathML
- Math Display Experiments
- Scientific Notebook
- Math Problem Solver
Related Sections
Math Tutoring
Need help? Chat with a tutor anytime, 24/7.
Trigonometry Problem Solver

This tool combines the power of mathematical computation engine that excels at solving mathematical formulas with the power of artificial intelligence large language models to parse and generate natural language answers. This creates a math problem solver that's more accurate than ChatGPT, more flexible than a math calculator, and provides answers faster than a human tutor.
Sign up for free here .
Problem Solver Subjects
Our math problem solver that lets you input a wide variety of trigonometry math problems and it will provide a step by step answer. This math solver excels at math word problems as well as a wide range of math subjects.
- Math Word Problems
- Pre-Algebra
- Geometry Graphing
- Trigonometry
- Precalculus
- Finite Math
- Linear Algebra
Here are example math problems within each subject that can be input into the calculator and solved. This list is constanstly growing as functionality is added to the calculator.
Basic Math Solutions
Below are examples of basic math problems that can be solved.
- Long Arithmetic
- Rational Numbers
- Operations with Fractions
- Ratios, Proportions, Percents
- Measurement, Area, and Volume
- Factors, Fractions, and Exponents
- Unit Conversions
- Data Measurement and Statistics
- Points and Line Segments
Math Word Problem Solutions
Math word problems require interpreting what is being asked and simplifying that into a basic math equation. Once you have the equation you can then enter that into the problem solver as a basic math or algebra question to be correctly solved. Below are math word problem examples and their simplified forms.
Word Problem: Rachel has 17 apples. She gives some to Sarah. Sarah now has 8 apples. How many apples did Rachel give her?
Simplified Equation: 17 - x = 8
Word Problem: Rhonda has 12 marbles more than Douglas. Douglas has 6 marbles more than Bertha. Rhonda has twice as many marbles as Bertha has. How many marbles does Douglas have?
Variables: Rhonda's marbles is represented by (r), Douglas' marbles is represented by (d) and Bertha's marbles is represented by (b)
Simplified Equation: {r = d + 12, d = b + 6, r = 2 �� b}
Word Problem: if there are 40 cookies all together and Angela takes 10 and Brett takes 5 how many are left?
Simplified: 40 - 10 - 5
Pre-Algebra Solutions
Below are examples of Pre-Algebra math problems that can be solved.
- Variables, Expressions, and Integers
- Simplifying and Evaluating Expressions
- Solving Equations
- Multi-Step Equations and Inequalities
- Ratios, Proportions, and Percents
- Linear Equations and Inequalities
Algebra Solutions
Below are examples of Algebra math problems that can be solved.
- Algebra Concepts and Expressions
- Points, Lines, and Line Segments
- Simplifying Polynomials
- Factoring Polynomials
- Linear Equations
- Absolute Value Expressions and Equations
- Radical Expressions and Equations
- Systems of Equations
- Quadratic Equations
- Inequalities
- Complex Numbers and Vector Analysis
- Logarithmic Expressions and Equations
- Exponential Expressions and Equations
- Conic Sections
- Vector Spaces
- 3d Coordinate System
- Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
- Linear Transformations
- Number Sets
- Analytic Geometry
Trigonometry Solutions
Below are examples of Trigonometry math problems that can be solved.
- Algebra Concepts and Expressions Review
- Right Triangle Trigonometry
- Radian Measure and Circular Functions
- Graphing Trigonometric Functions
- Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions
- Verifying Trigonometric Identities
- Solving Trigonometric Equations
- Complex Numbers
- Analytic Geometry in Polar Coordinates
- Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
- Vector Arithmetic
Precalculus Solutions
Below are examples of Precalculus math problems that can be solved.
- Operations on Functions
- Rational Expressions and Equations
- Polynomial and Rational Functions
- Analytic Trigonometry
- Sequences and Series
- Analytic Geometry in Rectangular Coordinates
- Limits and an Introduction to Calculus
Calculus Solutions
Below are examples of Calculus math problems that can be solved.
- Evaluating Limits
- Derivatives
- Applications of Differentiation
- Applications of Integration
- Techniques of Integration
- Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates
- Differential Equations
Statistics Solutions
Below are examples of Statistics problems that can be solved.
- Algebra Review
- Average Descriptive Statistics
- Dispersion Statistics
- Probability
- Probability Distributions
- Frequency Distribution
- Normal Distributions
- t-Distributions
- Hypothesis Testing
- Estimation and Sample Size
- Correlation and Regression
Finite Math Solutions
Below are examples of Finite Math problems that can be solved.
- Polynomials and Expressions
- Equations and Inequalities
- Linear Functions and Points
- Systems of Linear Equations
- Mathematics of Finance
- Statistical Distributions
Linear Algebra Solutions
Below are examples of Linear Algebra math problems that can be solved.
- Introduction to Matrices
- Linear Independence and Combinations
Chemistry Solutions
Below are examples of Chemistry problems that can be solved.
- Unit Conversion
- Atomic Structure
- Molecules and Compounds
- Chemical Equations and Reactions
- Behavior of Gases
- Solutions and Concentrations
Physics Solutions
Below are examples of Physics math problems that can be solved.
- Static Equilibrium
- Dynamic Equilibrium
- Kinematics Equations
- Electricity
- Thermodymanics
Geometry Graphing Solutions
Below are examples of Geometry and graphing math problems that can be solved.
- Step By Step Graphing
- Linear Equations and Functions
- Polar Equations
Looking for the old Mathway Calculator? We've moved it to here .
Tips, tricks, lessons, and tutoring to help reduce test anxiety and move to the top of the class.
Email Address Sign Up

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn trigonometry—right triangles, the unit circle, graphs, identities, and more. ... Community questions. Our mission is to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere. Khan Academy is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization. Donate or volunteer today! Site Navigation.
Click here for Answers. . Answers - Version 1. Trigonometry Answers Version 1 - Corbettmaths. Watch on. Answers - Version 2. Trigonometry Answers Version 2 - Corbettmaths. Watch on. Practice Questions.
Free math problem solver answers your trigonometry homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app ... Download free in Windows Store. get Go. Trigonometry. Basic Math. Pre-Algebra. Algebra. Trigonometry. Precalculus. Calculus. Statistics. Finite Math. Linear Algebra ...
Trigonometry Worksheets Free worksheets with answer keys. ... Each one has model problems worked out step by step, practice problems, as well as challenge questions at the sheets end. Plus each one comes with an answer key. Law of Sines and Cosines Worksheet (This sheet is a summative worksheet that focuses on deciding when to use the law of ...
Trigonometry questions: missing side. 1. A zip wire runs between two posts, 25m 25m apart. The zip wire is at an angle of 10^ {\circ} 10∘ to the horizontal. Calculate the length of the zip wire. 2.
Practice Questions on Trigonometry. Solve the following trigonometry problems. Prove that (sin α + cos α) (tan α + cot α) = sec α + cosec α. If ∠A and ∠B are acute angles such that cos A = cos B, then show that ∠A = ∠B. If sin θ + cos θ = √3, prove that tan θ + cot θ = 1. Evaluate: 2 tan 2 45° + cos 2 30° - sin 2 60°.
Yearly. Trigonometry 4 units · 36 skills. Unit 1 Right triangles & trigonometry. Unit 2 Trigonometric functions. Unit 3 Non-right triangles & trigonometry. Unit 4 Trigonometric equations and identities. Course challenge. Test your knowledge of the skills in this course. Start Course challenge.
Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 1,700 Mastery points! Start Unit test. Let's extend trigonometric ratios sine, cosine, and tangent into functions that are defined for all real numbers. You might be surprised at how we can use the behavior of those functions to model real-world situations involving carnival rides and ...
Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Start 7-day free trial on the app.
Consider the trigonometric ratio tan (theta) = 12/5. a. State the reference angle to the nearest hundredth of a radian. b. Determine all other values for theta, where -pi le theta le 2pi. c. Determi... View Answer. Evaluate the expression cot^2 135 - sin 30 + 4 tan 45.
Trigonometry Worksheets for High School. Explore the surplus collection of trigonometry worksheets that cover key skills in quadrants and angles, measuring angles in degrees and radians, conversion between degrees, minutes and radians, understanding the six trigonometric ratios, unit circles, frequently used trigonometric identities, evaluating ...
Example 1: find a side given the angle and the hypotenuse. ABC is a right angle triangle. The size of angle ACB = 60º and the length BC = 16cm. Calculate the value of x. Labelling the sides OAH in relation to the angle 60º, we can use the hypotenuse, and we need to find the adjacent side. We therefore need to use the cosine function.
Transfer your horizontal line segments into vertical line segments at the appropriate position on the grid below. Repeat parts (a) and (b) for the other three quadrants. Connect the tops of the segments to sketch a graph of [latex]y = \cos \theta {.} [/latex] 23.
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Trigonometry - 9781305652224, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Now, with expert-verified solutions from Trigonometry 8th Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for Trigonometry includes answers to chapter ...
Unit test. Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 600 Mastery points! Start Unit test. This unit tackles the medium-difficulty geometry and trigonometry questions on the SAT Math test. Work through each skill, taking quizzes and the unit test to level up your mastery progress.
Browse Recent Trigonometry Expert Q&A. Browse our recently answered Trigonometry homework questions. Q: 1. Evaluate the following integrals. (a) (sin 8) (cse³ # - csc² 0 - tan 0 sec 6) dº 78 (2³+3) 3-r…. Q: Find an angle with 0° < 0 < 360° that has the same: Sine as 260°: 0= Cosine as 260°: 0 = degrees….
Trigonometry Homework Help. Triangulate a path to better grades on your trig homework! Study smarter with bartleby's step-by-step trigonometry textbook solutions, a searchable library of homework questions (asked and answered) from your fellow students, and subject matter experts on standby 24/7 to provide homework help when you need it.
Exercise 113. Exercise 114. Exercise 115. Exercise 116. Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Trigonometry - 9780321839855, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence.
Free lessons, worksheets, and video tutorials for students and teachers. Topics in this unit include: similar triangles, sohcahtoa, right triangle trigonometry, solving for sides and angles using sine cosine and tangent, sine law, cosine law, applications. This follows chapter 7 and 8 of the principles of math grade 10 McGraw Hill textbook.
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Trigonometry - 9780134217437, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Now, with expert-verified solutions from Trigonometry 11th Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for Trigonometry includes answers to chapter ...
Subject: Mathematics. Age range: 14-16. Resource type: Worksheet/Activity. File previews. pdf, 59.72 KB. pdf, 58.84 KB. Trigonometry questions designed to test students ability to apply their knowledge of basic trigonometry using the sine, cosine and tangent ratios. Includes problem solving questions. Solutions provided!
Trigonometry Calculators. Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor.
Problem Solver Subjects. Our math problem solver that lets you input a wide variety of trigonometry math problems and it will provide a step by step answer. This math solver excels at math word problems as well as a wide range of math subjects. Here are example math problems within each subject that can be input into the calculator and solved.
Integrated math 3 13 units · 110 skills. Unit 1 Polynomial arithmetic. Unit 2 Polynomial factorization. Unit 3 Polynomial division. Unit 4 Polynomial graphs. Unit 5 Logarithms. Unit 6 Transformations of functions. Unit 7 Equations. Unit 8 Trigonometry.