Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

How to Write a Research Question: Types and Examples

The first step in any research project is framing the research question. It can be considered the core of any systematic investigation as the research outcomes are tied to asking the right questions. Thus, this primary interrogation point sets the pace for your research as it helps collect relevant and insightful information that ultimately influences your work.
Typically, the research question guides the stages of inquiry, analysis, and reporting. Depending on the use of quantifiable or quantitative data, research questions are broadly categorized into quantitative or qualitative research questions. Both types of research questions can be used independently or together, considering the overall focus and objectives of your research.
What is a research question?
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, and arguable question on which your research and writing are centered. 1 It states various aspects of the study, including the population and variables to be studied and the problem the study addresses. These questions also set the boundaries of the study, ensuring cohesion.
Designing the research question is a dynamic process where the researcher can change or refine the research question as they review related literature and develop a framework for the study. Depending on the scale of your research, the study can include single or multiple research questions.
A good research question has the following features:
- It is relevant to the chosen field of study.
- The question posed is arguable and open for debate, requiring synthesizing and analysis of ideas.
- It is focused and concisely framed.
- A feasible solution is possible within the given practical constraint and timeframe.
A poorly formulated research question poses several risks. 1
- Researchers can adopt an erroneous design.
- It can create confusion and hinder the thought process, including developing a clear protocol.
- It can jeopardize publication efforts.
- It causes difficulty in determining the relevance of the study findings.
- It causes difficulty in whether the study fulfils the inclusion criteria for systematic review and meta-analysis. This creates challenges in determining whether additional studies or data collection is needed to answer the question.
- Readers may fail to understand the objective of the study. This reduces the likelihood of the study being cited by others.
Now that you know “What is a research question?”, let’s look at the different types of research questions.
Types of research questions
Depending on the type of research to be done, research questions can be classified broadly into quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods studies. Knowing the type of research helps determine the best type of research question that reflects the direction and epistemological underpinnings of your research.
The structure and wording of quantitative 2 and qualitative research 3 questions differ significantly. The quantitative study looks at causal relationships, whereas the qualitative study aims at exploring a phenomenon.
- Quantitative research questions:
- Seeks to investigate social, familial, or educational experiences or processes in a particular context and/or location.
- Answers ‘how,’ ‘what,’ or ‘why’ questions.
- Investigates connections, relations, or comparisons between independent and dependent variables.
Quantitative research questions can be further categorized into descriptive, comparative, and relationship, as explained in the Table below.
- Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional, and more flexible. It concerns broad areas of research or more specific areas of study to discover, explain, or explore a phenomenon. These are further classified as follows:
- Mixed-methods studies
Mixed-methods studies use both quantitative and qualitative research questions to answer your research question. Mixed methods provide a complete picture than standalone quantitative or qualitative research, as it integrates the benefits of both methods. Mixed methods research is often used in multidisciplinary settings and complex situational or societal research, especially in the behavioral, health, and social science fields.
What makes a good research question
A good research question should be clear and focused to guide your research. It should synthesize multiple sources to present your unique argument, and should ideally be something that you are interested in. But avoid questions that can be answered in a few factual statements. The following are the main attributes of a good research question.
- Specific: The research question should not be a fishing expedition performed in the hopes that some new information will be found that will benefit the researcher. The central research question should work with your research problem to keep your work focused. If using multiple questions, they should all tie back to the central aim.
- Measurable: The research question must be answerable using quantitative and/or qualitative data or from scholarly sources to develop your research question. If such data is impossible to access, it is better to rethink your question.
- Attainable: Ensure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific.
- You have the expertise
- You have the equipment and resources
- Realistic: Developing your research question should be based on initial reading about your topic. It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline.
- Based on some sort of rational physics
- Can be done in a reasonable time frame
- Timely: The research question should contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on.
- Novel
- Based on current technologies.
- Important to answer current problems or concerns.
- Lead to new directions.
- Important: Your question should have some aspect of originality. Incremental research is as important as exploring disruptive technologies. For example, you can focus on a specific location or explore a new angle.
- Meaningful whether the answer is “Yes” or “No.” Closed-ended, yes/no questions are too simple to work as good research questions. Such questions do not provide enough scope for robust investigation and discussion. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation before providing an answer.
Steps for developing a good research question
The importance of research questions cannot be understated. When drafting a research question, use the following frameworks to guide the components of your question to ease the process. 4
- Determine the requirements: Before constructing a good research question, set your research requirements. What is the purpose? Is it descriptive, comparative, or explorative research? Determining the research aim will help you choose the most appropriate topic and word your question appropriately.
- Select a broad research topic: Identify a broader subject area of interest that requires investigation. Techniques such as brainstorming or concept mapping can help identify relevant connections and themes within a broad research topic. For example, how to learn and help students learn.
- Perform preliminary investigation: Preliminary research is needed to obtain up-to-date and relevant knowledge on your topic. It also helps identify issues currently being discussed from which information gaps can be identified.
- Narrow your focus: Narrow the scope and focus of your research to a specific niche. This involves focusing on gaps in existing knowledge or recent literature or extending or complementing the findings of existing literature. Another approach involves constructing strong research questions that challenge your views or knowledge of the area of study (Example: Is learning consistent with the existing learning theory and research).
- Identify the research problem: Once the research question has been framed, one should evaluate it. This is to realize the importance of the research questions and if there is a need for more revising (Example: How do your beliefs on learning theory and research impact your instructional practices).
How to write a research question
Those struggling to understand how to write a research question, these simple steps can help you simplify the process of writing a research question.
Sample Research Questions
The following are some bad and good research question examples
- Example 1
- Example 2
References:
- Thabane, L., Thomas, T., Ye, C., & Paul, J. (2009). Posing the research question: not so simple. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia/Journal canadien d’anesthésie , 56 (1), 71-79.
- Rutberg, S., & Bouikidis, C. D. (2018). Focusing on the fundamentals: A simplistic differentiation between qualitative and quantitative research. Nephrology Nursing Journal , 45 (2), 209-213.
- Kyngäs, H. (2020). Qualitative research and content analysis. The application of content analysis in nursing science research , 3-11.
- Mattick, K., Johnston, J., & de la Croix, A. (2018). How to… write a good research question. The clinical teacher , 15 (2), 104-108.
- Fandino, W. (2019). Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia , 63 (8), 611.
- Richardson, W. S., Wilson, M. C., Nishikawa, J., & Hayward, R. S. (1995). The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP journal club , 123 (3), A12-A13
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
- 6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs in the World of Research
Language and grammar rules for academic writing, you may also like, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , 9 steps to publish a research paper, what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging, 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., presenting research data effectively through tables and figures, ethics in science: importance, principles & guidelines , jenni ai review: top features, pricing, and alternatives.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write a Research Question

Academic writing and research require a distinct focus and direction. A well-designed research question gives purpose and clarity to your research. In addition, it helps your readers understand the issue you are trying to address and explore.
Every time you want to know more about a subject, you will pose a question. The same idea is used in research as well. You must pose a question in order to effectively address a research problem. That's why the research question is an integral part of the research process. Additionally, it offers the author writing and reading guidelines, be it qualitative research or quantitative research.
In your research paper , you must single out just one issue or problem. The specific issue or claim you wish to address should be included in your thesis statement in order to clarify your main argument.
A good research question must have the following characteristics.

- Should include only one problem in the research question
- Should be able to find the answer using primary data and secondary data sources
- Should be possible to resolve within the given time and other constraints
- Detailed and in-depth results should be achievable
- Should be relevant and realistic.
- It should relate to your chosen area of research
While a larger project, like a thesis, might have several research questions to address, each one should be directed at your main area of study. Of course, you can use different research designs and research methods (qualitative research or quantitative research) to address various research questions. However, they must all be pertinent to the study's objectives.
What is a Research Question?

A research question is an inquiry that the research attempts to answer. It is the heart of the systematic investigation. Research questions are the most important step in any research project. In essence, it initiates the research project and establishes the pace for the specific research A research question is:
- Clear : It provides enough detail that the audience understands its purpose without any additional explanation.
- Focused : It is so specific that it can be addressed within the time constraints of the writing task.
- Succinct: It is written in the shortest possible words.
- Complex : It is not possible to answer it with a "yes" or "no", but requires analysis and synthesis of ideas before somebody can create a solution.
- Argumental : Its potential answers are open for debate rather than accepted facts.
A good research question usually focuses on the research and determines the research design, methodology, and hypothesis. It guides all phases of inquiry, data collection, analysis, and reporting. You should gather valuable information by asking the right questions.
Why are Research Questions so important?
Regardless of whether it is a qualitative research or quantitative research project, research questions provide writers and their audience with a way to navigate the writing and research process. Writers can avoid "all-about" papers by asking straightforward and specific research questions that help them focus on their research and support a specific thesis.
Types of Research Questions

There are two types of research: Qualitative research and Quantitative research . There must be research questions for every type of research. Your research question will be based on the type of research you want to conduct and the type of data collection.
The first step in designing research involves identifying a gap and creating a focused research question.
Below is a list of common research questions that can be used in a dissertation. Keep in mind that these are merely illustrations of typical research questions used in dissertation projects. The real research questions themselves might be more difficult.
Example Research Questions

The following are a few examples of research questions and research problems to help you understand how research questions can be created for a particular research problem.
Steps to Write Research Questions

You can focus on the issue or research gaps you're attempting to solve by using the research questions as a direction.
If you're unsure how to go about writing a good research question, these are the steps to follow in the process:
- Select an interesting topic Always choose a topic that interests you. Because if your curiosity isn’t aroused by a subject, you’ll have a hard time conducting research around it. Alos, it’s better that you pick something that’s neither too narrow or too broad.
- Do preliminary research on the topic Search for relevant literature to gauge what problems have already been tackled by scholars. You can do that conveniently through repositories like Scispace , where you’ll find millions of papers in one place. Once you do find the papers you’re looking for, try our reading assistant, SciSpace Copilot to get simple explanations for the paper . You’ll be able to quickly understand the abstract, find the key takeaways, and the main arguments presented in the paper. This will give you a more contextual understanding of your subject and you’ll have an easier time identifying knowledge gaps in your discipline.
Also: ChatPDF vs. SciSpace Copilot: Unveiling the best tool for your research
- Consider your audience It is essential to understand your audience to develop focused research questions for essays or dissertations. When narrowing down your topic, you can identify aspects that might interest your audience.
- Ask questions Asking questions will give you a deeper understanding of the topic. Evaluate your question through the What, Why, When, How, and other open-ended questions assessment.
- Assess your question Once you have created a research question, assess its effectiveness to determine if it is useful for the purpose. Refine and revise the dissertation research question multiple times.
Additionally, use this list of questions as a guide when formulating your research question.
Are you able to answer a specific research question? After identifying a gap in research, it would be helpful to formulate the research question. And this will allow the research to solve a part of the problem. Is your research question clear and centered on the main topic? It is important that your research question should be specific and related to your central goal. Are you tackling a difficult research question? It is not possible to answer the research question with a simple yes or no. The problem requires in-depth analysis. It is often started with "How" and "Why."
Start your research Once you have completed your dissertation research questions, it is time to review the literature on similar topics to discover different perspectives.
Strong Research Question Samples
Uncertain: How should social networking sites work on the hatred that flows through their platform?
Certain: What should social media sites like Twitter or Facebook do to address the harm they are causing?
This unclear question does not specify the social networking sites that are being used or what harm they might be causing. In addition, this question assumes that the "harm" has been proven and/or accepted. This version is more specific and identifies the sites (Twitter, Facebook), the type and extent of harm (privacy concerns), and who might be suffering from that harm (users). Effective research questions should not be ambiguous or interpreted.
Unfocused: What are the effects of global warming on the environment?
Focused: What are the most important effects of glacial melting in Antarctica on penguins' lives?
This broad research question cannot be addressed in a book, let alone a college-level paper. Focused research targets a specific effect of global heating (glacial melting), an area (Antarctica), or a specific animal (penguins). The writer must also decide which effect will have the greatest impact on the animals affected. If in doubt, narrow down your research question to the most specific possible.
Too Simple: What are the U.S. doctors doing to treat diabetes?
Appropriately complex: Which factors, if any, are most likely to predict a person's risk of developing diabetes?
This simple version can be found online. It is easy to answer with a few facts. The second, more complicated version of this question is divided into two parts. It is thought-provoking and requires extensive investigation as well as evaluation by the author. So, ensure that a quick Google search should not answer your research question.
How to write a strong Research Question?

The foundation of all research is the research question. You should therefore spend as much time as necessary to refine your research question based on various data.
You can conduct your research more efficiently and analyze your results better if you have great research questions for your dissertation, research paper , or essay .
The following criteria can help you evaluate the strength and importance of your research question and can be used to determine the strength of your research question:
- Researchable
- It should only cover one issue.
- A subjective judgment should not be included in the question.
- It can be answered with data analysis and research.
- Specific and Practical
- It should not contain a plan of action, policy, or solution.
- It should be clearly defined
- Within research limits
- Complex and Arguable
- It shouldn't be difficult to answer.
- To find the truth, you need in-depth knowledge
- Allows for discussion and deliberation
- Original and Relevant
- It should be in your area of study
- Its results should be measurable
- It should be original
Conclusion - How to write Research Questions?
Research questions provide a clear guideline for research. One research question may be part of a larger project, such as a dissertation. However, each question should only focus on one topic.
Research questions must be answerable, practical, specific, and applicable to your field. The research type that you use to base your research questions on will determine the research topic. You can start by selecting an interesting topic and doing preliminary research. Then, you can begin asking questions, evaluating your questions, and start your research.
Now it's easier than ever to streamline your research workflow with SciSpace ResearchGPT . Its integrated, comprehensive end-to-end platform for research allows scholars to easily discover, read, write and publish their research and fosters collaboration.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
- (855) 776-7763
Training Maker
All Products
Qualaroo Insights
ProProfs.com
- Sign Up Free
Do you want a free Survey Software?
We have the #1 Online Survey Maker Software to get actionable user insights.
How To Write a Good Research Question: Guide with Definition, Tips & Examples

Sameer Bhatia
Founder and CEO - ProProfs
Review Board Member
Sameer Bhatia is the Founder and Chief Executive Officer of ProProfs.com. He believes that software should make you happy and is driven to create a 100-year company that delivers delightfully ... Read more
Sameer Bhatia is the Founder and Chief Executive Officer of ProProfs.com. He believes that software should make you happy and is driven to create a 100-year company that delivers delightfully smart software with awesome support. His favorite word is 'delight,' and he dislikes the term 'customer satisfaction,' as he believes that 'satisfaction' is a low bar and users must get nothing less than a delightful experience at ProProfs. Sameer holds a Masters in Computer Science from the University of Southern California (USC). He lives in Santa Monica with his wife & two daughters. Read less

Market Research Specialist
Emma David, a seasoned market research professional, specializes in employee engagement, survey administration, and data management. Her expertise in leveraging data for informed decisions has positively impacted several brands, enhancing their market position.

Research questions form the backbone of any study, guiding researchers in their search for knowledge and understanding. Framing relevant research questions is the first essential step for ensuring the research is effective and produces valuable insights.
In this blog, we’ll explore what research questions are, tips for crafting them, and a variety of research question examples across different fields to help you formulate a well-balanced research questionnaire.
Let’s begin.
What Is a Research Question?
A research question is a specific inquiry or problem statement guiding a research study, outlining the researcher’s intention to investigate. Think of it as a roadmap for your paper or thesis – it tells you exactly what you want to explore, giving your work a clear purpose.
A good research question not only helps you focus your writing but also guides your readers. It gives them a clear idea of what your research is about and what you aim to achieve. Before you start drafting your paper and even before you conduct your study, it’s important to write a concise statement of what you want to accomplish or discover.
This sets the stage for your research and ensures your work is focused and purposeful.
Why Are Research Questions Important?
Research questions are the cornerstone of any academic or scientific inquiry. They serve as a guide for the research process, helping to focus the study, define its goals, and structure its methodology.
Below are some of its most significant impacts, along with hypothetical examples to help you understand them better:
1. Guidance and Focus
Research questions provide a clear direction for the study, enabling researchers to narrow down the scope of their investigation to a manageable size. Research efforts can become scattered and unfocused without a well-defined question without a well-defined question, leading to wasted time and resources.
For example, consider a researcher interested in studying the effects of technology on education. A broad interest in technology and education could lead to an overwhelming range of topics to cover. However, by formulating a specific research question such as, “ How does the use of interactive digital textbooks in high school science classes affect students’ learning outcomes?” the researcher can focus their study on a specific aspect of technology in education, making the research more manageable and directed.
2. Defining the Research Objectives
A well-crafted research question helps to clearly define what the researcher aims to discover, examine, or analyze. This clarity is crucial for determining the study’s objectives and ensures that every step of the research process contributes toward achieving these goals.
For example, in a study aimed at understanding the impact of remote work on employee productivity, a research question such as “ Does remote work increase productivity among information technology professionals? ” directly sets the objective of the study to measure productivity levels among a specific group when working remotely.
3. Determining the Research Methodology
The research question influences the choice of methodology, including the design, data collection methods, and analysis techniques. It dictates whether the study should be qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods and guides the selection of tools and procedures for conducting the research.
For example, in a research question like “ What are the lived experiences of first-generation college students? ” a qualitative approach using interviews or focus groups might be chosen to gather deep, nuanced insights into students’ experiences. In contrast, a question such as “ What percentage of first-generation college students graduate within four years?” would require a quantitative approach, possibly utilizing existing educational data sets for analysis.
4. Enhancing Relevance and Contribution
A well-thought-out research question ensures that the study addresses a gap in the existing literature or solves a real-world problem. This relevance is crucial for the contribution of the research to the field, as it helps to advance knowledge, inform policy, or offer practical solutions.
For example, in a scenario where existing research has largely overlooked the environmental impacts of single-use plastics in urban waterways, a question like “ What are the effects of single-use plastic pollution on the biodiversity of urban waterways?” can fill this gap, contributing valuable new insights to environmental science and potentially influencing urban environmental policies.
5. Facilitating Data Interpretation and Analysis
Clear research questions help in structuring the analysis, guiding the interpretation of data, and framing the discussion of results. They ensure that the data collected is directly relevant to the questions posed, making it easier to draw meaningful conclusions.
For example, in a study asking, “ How do social media algorithms influence political polarization among users? ” the data analysis would specifically focus on the mechanisms of algorithmic content delivery and its effects on user behavior and political views. This focus makes it straightforward to interpret how algorithm-induced echo chambers might contribute to polarization.
Types of Research Questions
Understanding the different types of research questions is essential for researchers to effectively design and conduct studies that align with their research objectives and methodologies
These questions can be broadly categorized into three main types: quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-method research questions.
Let’s explore each type in-depth, along with some examples.
Type A: Quantitative Research Questions
Quantitative research involves the collection and analysis of numerical data to answer specific research questions or hypotheses. It focuses on quantifying relationships, patterns, and phenomena, often using statistical methods for analysis. Quantitative research questions are typically structured and aim to explore relationships between variables or assess the impact of interventions.
Quantitative research questions can again be subcategorized into three distinct types:
1. Descriptive Questions :
Descriptive questions aim to describe characteristics, behaviors, or phenomena within a population. These questions often start with words like “ how much ,” “ how many ,” or “ what is the frequency of .” They provide a snapshot of a particular situation or phenomenon.
Example: “ What is the average age of first-time homebuyers in the United States?”
2. Comparative Questions :
Comparative questions seek to compare two or more groups, conditions, or variables to identify differences or similarities. They often involve the use of statistical tests to determine the significance of observed differences or associations.
Example: “Is there a significant difference in academic performance between students who receive tutoring and those who do not?”
3. Relationship Questions:
Relationship questions explore the associations or correlations between variables. They aim to determine the strength and direction of relationships, allowing researchers to assess the predictive power of one variable on another.
Example: “What is the relationship between exercise frequency and levels of anxiety among adults?”
Type B: Qualitative Research Questions
Qualitative research involves the exploring and understanding of complex phenomena through an in-depth examination of individuals’ experiences, behaviors, and perspectives. It aims to uncover meaning, patterns, and underlying processes within a specific context, often through techniques such as interviews, observations, and content analysis.
Types of qualitative research questions:
1. Exploratory Questions:
Exploratory questions seek to understand a particular phenomenon or issue in depth. They aim to uncover new insights, perspectives, or dimensions that may not have been previously considered.
Example: “What are the experiences of LGBTQ+ individuals in accessing healthcare services in rural communities?”
2. Descriptive Questions:
Descriptive questions aim to provide a detailed description or portrayal of a phenomenon or social context. They focus on capturing the intricacies and nuances of a particular situation or setting.
Example: “What are the communication patterns within multicultural teams in a corporate setting?”
3. Explanatory Questions:
Explanatory questions delve into the underlying reasons, mechanisms, or processes that influence a phenomenon or behavior. They aim to uncover the ‘why’ behind observed patterns or relationships.
Example: “What factors contribute to employee turnover in the hospitality industry?”
Type C: Mixed-Methods Research Questions
Mixed-methods research integrates both quantitative and qualitative approaches within a single study, allowing researchers to gain a comprehensive understanding of a research problem. Mixed-method research questions are designed to address complex phenomena from multiple perspectives, combining the strengths of both quantitative and qualitative methodologies.
Types of Mixed-Methods Research Questions:
1. Sequential Questions:
Sequential questions involve the collection and analysis of quantitative and qualitative data in separate phases or stages. The findings from one phase inform the design and implementation of the subsequent phase.
Example: “Quantitatively, what are the prevalence rates of mental health disorders among adolescents? Qualitatively, what are the factors influencing help-seeking behaviors among adolescents with mental health concerns?”
2. Concurrent Questions:
Concurrent questions involve the simultaneous collection and analysis of quantitative and qualitative data. Researchers triangulate findings from both methods to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the research problem.
Example: “How do students’ academic performance (quantitative) correlate with their perceptions of school climate (qualitative)?”
3. Transformative Questions:
Transformative questions aim to use mixed-methods research to bring about social change or inform policy decisions. They seek to address complex societal issues by combining quantitative data on prevalence rates or trends with qualitative insights into lived experiences and perspectives.
Example: “What are the barriers to accessing healthcare services for underserved communities, and how can healthcare policies be redesigned to address these barriers effectively?”
Steps to Developing a Good Research Question
Developing a good research question is a crucial first step in any research endeavor. A well-crafted research question serves as the foundation for the entire study, guiding the researcher in formulating hypotheses, selecting appropriate methodologies, and conducting meaningful analyses.
Here are the steps to developing a good research question:
Identify a Broad Topic
Begin by identifying a broad area of interest or a topic that you would like to explore. This could stem from your academic discipline, professional interests, or personal curiosity. However, make sure to choose a topic that is both relevant and feasible for research within the constraints of your resources and expertise.
Conduct Preliminary Research
Before refining your research question, conduct preliminary research to familiarize yourself with existing literature and identify gaps, controversies, or unanswered questions within your chosen topic. This step will help you narrow down your focus and ensure that your research question contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
Narrow Down Your Focus
Based on your preliminary research, narrow down your focus to a specific aspect, problem, or issue within your chosen topic. Consider the scope of your study, the availability of resources, and the feasibility of addressing your research question within a reasonable timeframe. Narrowing down your focus will help you formulate a more precise and manageable research question.
Define Key Concepts and Variables
Clearly define the key concepts, variables, or constructs that are central to your research question. This includes identifying the main variables you will be investigating, as well as any relevant theoretical or conceptual frameworks that will guide your study. Clarifying these aspects will ensure that your research question is clear, specific, and focused.
Formulate Your Research Question
Based on your narrowed focus and defined key concepts, formulate your research question. A good research question is concise, specific, and clearly articulated. It should be phrased in a way that is open-ended and leads to further inquiry. Avoid vague or overly broad questions that are difficult to answer or lack clarity.
Consider the Type of Research
Consider whether your research question is best suited for quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods research. The type of research question will influence your choice of methodologies, data collection techniques, and analytical approaches. Tailor your research question to align with the goals and requirements of your chosen research paradigm.
Evaluate the Significance and Relevance
Evaluate the significance and relevance of your research question within the context of your academic discipline, field of study, or practical implications. Consider how your research question fills gaps in knowledge, addresses practical problems, or advances theoretical understanding. A good research question should be meaningful and contribute to the broader scholarly conversation.
Refine and Revise
Finally, refine and revise your research question based on feedback from colleagues, advisors, or peers. Consider whether the question is clear, feasible, and likely to yield meaningful results. Be open to making revisions as needed to ensure that your research question is well-constructed and aligned with the goals of your study.
Examples of Research Questions
Below are some example research questions from various fields to provide a glimpse into the diverse array of inquiries within each field.
1. Psychology Research Questions:
- How does childhood trauma influence the development of personality disorders in adulthood?
- What are the effects of mindfulness meditation on reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression?
- How does social media usage impact self-esteem among adolescents?
- What factors contribute to the formation and maintenance of romantic relationships in young adults?
- What are the cognitive mechanisms underlying decision-making processes in individuals with addiction?
- How does parenting style affect the development of resilience in children?
- What are the long-term effects of early childhood attachment patterns on adult romantic relationships?
- What role does genetics play in the predisposition to mental health disorders such as schizophrenia?
- How does exposure to violent media influence aggressive behavior in children?
- What are the psychological effects of social isolation on mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic?
2. Business Research Questions:
- What are the key factors influencing consumer purchasing behavior in the e-commerce industry?
- How does organizational culture impact employee job satisfaction and retention?
- What are the strategies for successful international market entry for small businesses?
- What are the effects of corporate social responsibility initiatives on brand reputation and consumer loyalty?
- How do leadership styles influence organizational innovation and performance?
- What are the challenges and opportunities for implementing sustainable business practices in emerging markets?
- What factors contribute to the success of startups in the technology sector?
- How do economic fluctuations affect consumer confidence and spending behavior?
- What are the impacts of globalization on supply chain management practices?
- What are the determinants of successful mergers and acquisitions in the corporate sector?
3. Education Research Questions:
- What teaching strategies are most effective for promoting student engagement in online learning environments?
- How does socioeconomic status impact academic achievement and educational attainment?
- What are the barriers to inclusive education for students with disabilities?
- What factors influence teacher job satisfaction and retention in urban schools?
- How does parental involvement affect student academic performance and school outcomes?
- What are the effects of early childhood education programs on later academic success?
- How do culturally responsive teaching practices impact student learning outcomes in diverse classrooms?
- What are the best practices for implementing technology integration in K-12 education?
- How do school leadership practices influence school climate and student outcomes?
- What interventions are most effective for addressing the achievement gap in STEM education?
4. Healthcare Research Questions:
- What are the factors influencing healthcare-seeking behavior among underserved populations?
- How does patient-provider communication affect patient satisfaction and treatment adherence?
- What are the barriers to implementing telemedicine services in rural communities?
- What interventions are effective for reducing hospital readmissions among elderly patients?
- How does access to healthcare services impact health disparities among marginalized communities?
- What are the effects of nurse staffing levels on patient outcomes in acute care settings?
- How do socioeconomic factors influence access to mental healthcare services?
- What are the best practices for managing chronic disease patients in primary care settings?
- What are the impacts of healthcare reform policies on healthcare delivery and patient outcomes?
- How does cultural competence training for healthcare providers affect patient trust and satisfaction?
5. Computer Science Research Questions:
- What are the security vulnerabilities of blockchain technology, and how can they be mitigated?
- How can machine learning algorithms be used to detect and prevent cyber-attacks?
- What are the privacy implications of data mining techniques in social media platforms?
- How can artificial intelligence be used to improve medical diagnosis and treatment?
- What are the challenges and opportunities for implementing edge computing in IoT systems?
- How can natural language processing techniques be applied to improve human-computer interaction?
- What are the impacts of algorithmic bias on fairness and equity in decision-making systems?
- How can quantum computing algorithms be optimized for solving complex computational problems?
- What are the ethical considerations surrounding the use of autonomous vehicles in transportation systems?
- How does the design of user interfaces influence user experience and usability in mobile applications?
Create a Compelling Research Question With the Given Examples
Understanding research questions is essential for any successful research endeavor. We’ve explored the various research questions – quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-methods – each with unique characteristics and purposes.
Through various examples, tips, and strategies, we’ve seen how research questions can be tailored to specific fields of study.
By following these guidelines, we are confident that your research questions will be well-designed, focused, and capable of yielding valuable insights.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some good research question examples.
Good research questions are clear, specific, relevant, and feasible. For example, “How does childhood trauma influence the development of personality disorders in adulthood?”
What are some examples of good and bad research questions?
Good research questions are focused and relevant, such as “What factors influence employee job satisfaction in the hospitality industry?” Bad research questions are vague or trivial, like “What is the favorite color of employees in the hospitality industry?”
Watch: How to Create a Survey Using ProProfs Survey Maker

About the author
Emma David is a seasoned market research professional with 8+ years of experience. Having kick-started her journey in research, she has developed rich expertise in employee engagement, survey creation and administration, and data management. Emma believes in the power of data to shape business performance positively. She continues to help brands and businesses make strategic decisions and improve their market standing through her understanding of research methodologies.
Popular Posts in This Category

Measuring Service Quality- Your Guide to Customer Service Metrics

10 Best Exit Interview Software to Look for in 2024
20 Best Net Promoter Score Survey (NPS) Tools & Software in 2024

A Comprehensive Guide to Quantitative Research: Types, Characteristics, Methods & Examples

Net Promoter Score: The Ultimate NPS Survey Guide for Growth

How to Embed a Survey on Your Website
- How it works
How to Write the Research Questions – Tips & Examples
Published by Owen Ingram at August 13th, 2021 , Revised On October 3, 2023
Conducting research and writing an academic paper requires a clear direction and focus.
A good research question provides purpose to your research and clarifies the direction. It further helps your readers to understand what issue your research aims to explore and address.
If you are unsure about how to write research questions, here is a list of the attributes of a good research question;
- The research question should contain only a single problem
- You should be able to find the answer to it using primary and secondary data sources
- You should be able to address it within the time limit and other constraints
- Can attain in-depth and detailed results
- Relevant and applicable
- Should relate to your chosen field of research
Whenever you want to discover something new about a topic , you will ask a question about it. Therefore, the research question is important in the overall research process and provides the author with the reading and writing guidelines.
In a research paper or an essay, you will need to create a single research question that highlights just one problem or issue. The thesis statement should include the specific problem you aim to investigate to establish your argument’s central position or claim.
A larger project such as a dissertation or thesis , on the other hand, can have multiple research questions, but every question should focus on your main research problem . Different types of research will help you answer different research questions, but they should all be relevant to the research scope.
How to Write a Research Question
Steps to develop your research question.
- Choose a topic with a wide range of published literature
- Read and skim relevant articles to find out different problems and issues
- Specify a theoretical or practical research problem that your research question will address
- Narrow down the focus of your selected core niche

Example Research Question (s)
Here are examples of research problems and research questions to help you understand how to create a research question for a given research problem.
Types of Research Questions
There are two main types of research; quantitative and qualitative research . Both types of research require research questions. What research question you will answer is dependent on the type of research you wish to employ.
The first part of designing research is to find a gap and create a fully focused research question.
The following table shows common research questions for a dissertation project. However, it is important to note that these examples of dissertation research questions are straightforward, and the actual research questions may be more complicated than these examples.
What data collection method best suits your research?
- Find out by hiring an expert from ResearchProspect today!
- Despite how challenging the subject may be, we are here to help you.
Steps to Write Research Questions
The research question provides you with a path and focuses on the real problem and the research gap you aim to fill. These are steps you need to take if you are unsure about how to write a research question:
Choose an Interesting Topic
Choose a topic of research according to your interest. The selected topic should be neither too broad nor too narrow.
Do Preliminary Research on the Topic
Find articles, books, journals, and theses relevant to your chosen topic. Understand what research problem each scholar addressed as part of their research project.
Consider your Audience
It is necessary to know your audience to develop focused research questions for your essay or dissertation. You can find aspects of your topic that could be interesting to your audience when narrowing your topic.
Start Asking Questions
What, why, when, how, and other open-ended questions will provide in-depth knowledge about the topic.
Evaluate your Question
After formulating a research question, evaluate to check its effectiveness and how it can serve the purpose. Revise and refine the dissertation research question.
- Do you have a clear research question?
It would help if you formed the research question after finding a research gap. This approach will enable the research to solve part of the problem.
- Do you have a focused research question?
It is necessary that the research question is specific and relating to the central aim of your research.
- Do you have a complex research question?
The research question cannot be answered by yes or no but requires in-depth analysis. It often begins with “How” or “Why.”
Begin your Research
After you have prepared dissertation research questions, you should research the existing literature on similar topics to find various perspectives.
Also See: Formulation of Research Question
If you have been struggling to devise research questions for your dissertation or are unsure about which topic would be suitable for your needs, then you might be interested in taking advantage of our dissertation topic and outline service, which includes several topic ideas in your preferred area of study and a 500/1000 words plan on your chosen topic. Our topic and outline service will help you jump-start your dissertation project.
Find out How Our Topics & Outline Service Can Help You!
Tips on How to Write a Strong Research Question
A research question is the foundation of the entire research. Therefore, you should spend as much time as required to refine the research question.
If you have good research questions for the dissertation, research paper , or essay, you can perform the research and analyse your results more effectively. You can evaluate the strength of the research question with the help of the following criteria. Your research question should be;
Intensive and Researchable
- It should cover a single issue
- The question shouldn’t include a subjective judgment
- It can be answerable with the data analysis or research=
Practical and Specific
- It should not include a course of action, policy, or solution
- It should be well-defined
- Answerable within research limits
Complicated and Arguable
- It should not be simple to answer
- Need in-depth knowledge to find facts
- Provides scope for debate and deliberation
Unique and Relevant
- It should lie in your field of study
- Its results should be contributable
- It should be unique
Conclusion – How to Write Research Questions
A research question provides a clear direction for research work. A bigger project, such as a dissertation, may have more than one research question, but every question should focus on one issue only.
Your research questions should be researchable, feasible to answer, specific to find results, complex (for Masters and PhD projects), and relevant to your field of study. Dissertation research questions depend upon the research type you are basing your paper on.
Start creating a research question by choosing an interesting topic, do some preliminary research, consider your audience, start asking questions, evaluating your question, and begin your research.
At ResearchProspect, we have dissertation experts for all academic subjects. Whether you need help with the individual chapters or the whole dissertation paper, you can be confident that your paper competed to the highest academic standard. There is a reason why our clients keep returning to us over and over. You can also look at our essay services if you are struggling to draft a first-class academic paper.
At ResearchProspect, we have dissertation experts for all academic subjects. Whether you need help with the individual chapters or the whole dissertation paper, you can be confident that your paper competed to the highest academic standard. There is a reason why our clients keep returning to us over and over.
You can also look at our essay services if you are struggling to draft a first-class academic paper.
Place Order
Frequently Asked Questions
How are research questions written.
Research questions are written by:
- Identifying your topic.
- Considering what you want to explore.
- Making questions clear and concise.
- Ensuring they’re researchable.
- Avoiding bias or leading language.
- Focusing on one main idea per question.
What are examples of research questions?
- Does regular exercise improve mental well-being in adults over 50?
- How do online courses impact student engagement compared to traditional classes?
- What are the economic effects of prolonged pandemic lockdowns?
- How does early childhood nutrition influence academic performance in later life?
- Does urban green space reduce stress levels?
How to write a research question?
- Identify a specific topic or issue of interest.
- Conduct preliminary research to understand existing knowledge.
- Narrow the focus to address gaps or unresolved issues.
- Phrase the question to be clear, concise, and researchable.
- Ensure it is specific enough for systematic investigation.
How to formulate my research questions for my geography dissertation?
- Identify a geographical topic or phenomenon of interest.
- Review existing literature to find gaps.
- Consider spatial, temporal, environmental, or societal aspects.
- Ensure questions are specific, feasible, and significant.
- Frame questions to guide methodology: quantitative, qualitative, or mixed.
- Seek feedback from peers/advisors.
You May Also Like
Penning your dissertation proposal can be a rather daunting task. Here are comprehensive guidelines on how to write a dissertation proposal.
This article is a step-by-step guide to how to write statement of a problem in research. The research problem will be half-solved by defining it correctly.
Make sure that your selected topic is intriguing, manageable, and relevant. Here are some guidelines to help understand how to find a good dissertation topic.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Questions
Definition:
Research questions are the specific questions that guide a research study or inquiry. These questions help to define the scope of the research and provide a clear focus for the study. Research questions are usually developed at the beginning of a research project and are designed to address a particular research problem or objective.
Types of Research Questions
Types of Research Questions are as follows:
Descriptive Research Questions
These aim to describe a particular phenomenon, group, or situation. For example:
- What are the characteristics of the target population?
- What is the prevalence of a particular disease in a specific region?
Exploratory Research Questions
These aim to explore a new area of research or generate new ideas or hypotheses. For example:
- What are the potential causes of a particular phenomenon?
- What are the possible outcomes of a specific intervention?
Explanatory Research Questions
These aim to understand the relationship between two or more variables or to explain why a particular phenomenon occurs. For example:
- What is the effect of a specific drug on the symptoms of a particular disease?
- What are the factors that contribute to employee turnover in a particular industry?
Predictive Research Questions
These aim to predict a future outcome or trend based on existing data or trends. For example :
- What will be the future demand for a particular product or service?
- What will be the future prevalence of a particular disease?
Evaluative Research Questions
These aim to evaluate the effectiveness of a particular intervention or program. For example:
- What is the impact of a specific educational program on student learning outcomes?
- What is the effectiveness of a particular policy or program in achieving its intended goals?
How to Choose Research Questions
Choosing research questions is an essential part of the research process and involves careful consideration of the research problem, objectives, and design. Here are some steps to consider when choosing research questions:
- Identify the research problem: Start by identifying the problem or issue that you want to study. This could be a gap in the literature, a social or economic issue, or a practical problem that needs to be addressed.
- Conduct a literature review: Conducting a literature review can help you identify existing research in your area of interest and can help you formulate research questions that address gaps or limitations in the existing literature.
- Define the research objectives : Clearly define the objectives of your research. What do you want to achieve with your study? What specific questions do you want to answer?
- Consider the research design : Consider the research design that you plan to use. This will help you determine the appropriate types of research questions to ask. For example, if you plan to use a qualitative approach, you may want to focus on exploratory or descriptive research questions.
- Ensure that the research questions are clear and answerable: Your research questions should be clear and specific, and should be answerable with the data that you plan to collect. Avoid asking questions that are too broad or vague.
- Get feedback : Get feedback from your supervisor, colleagues, or peers to ensure that your research questions are relevant, feasible, and meaningful.
How to Write Research Questions
Guide for Writing Research Questions:
- Start with a clear statement of the research problem: Begin by stating the problem or issue that your research aims to address. This will help you to formulate focused research questions.
- Use clear language : Write your research questions in clear and concise language that is easy to understand. Avoid using jargon or technical terms that may be unfamiliar to your readers.
- Be specific: Your research questions should be specific and focused. Avoid broad questions that are difficult to answer. For example, instead of asking “What is the impact of climate change on the environment?” ask “What are the effects of rising sea levels on coastal ecosystems?”
- Use appropriate question types: Choose the appropriate question types based on the research design and objectives. For example, if you are conducting a qualitative study, you may want to use open-ended questions that allow participants to provide detailed responses.
- Consider the feasibility of your questions : Ensure that your research questions are feasible and can be answered with the resources available. Consider the data sources and methods of data collection when writing your questions.
- Seek feedback: Get feedback from your supervisor, colleagues, or peers to ensure that your research questions are relevant, appropriate, and meaningful.
Examples of Research Questions
Some Examples of Research Questions with Research Titles:
Research Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
- Research Question : What is the relationship between social media use and mental health, and how does this impact individuals’ well-being?
Research Title: Factors Influencing Academic Success in High School
- Research Question: What are the primary factors that influence academic success in high school, and how do they contribute to student achievement?
Research Title: The Effects of Exercise on Physical and Mental Health
- Research Question: What is the relationship between exercise and physical and mental health, and how can exercise be used as a tool to improve overall well-being?
Research Title: Understanding the Factors that Influence Consumer Purchasing Decisions
- Research Question : What are the key factors that influence consumer purchasing decisions, and how do these factors vary across different demographics and products?
Research Title: The Impact of Technology on Communication
- Research Question : How has technology impacted communication patterns, and what are the effects of these changes on interpersonal relationships and society as a whole?
Research Title: Investigating the Relationship between Parenting Styles and Child Development
- Research Question: What is the relationship between different parenting styles and child development outcomes, and how do these outcomes vary across different ages and developmental stages?
Research Title: The Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy in Treating Anxiety Disorders
- Research Question: How effective is cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating anxiety disorders, and what factors contribute to its success or failure in different patients?
Research Title: The Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity
- Research Question : How is climate change affecting global biodiversity, and what can be done to mitigate the negative effects on natural ecosystems?
Research Title: Exploring the Relationship between Cultural Diversity and Workplace Productivity
- Research Question : How does cultural diversity impact workplace productivity, and what strategies can be employed to maximize the benefits of a diverse workforce?
Research Title: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
- Research Question: How can artificial intelligence be leveraged to improve healthcare outcomes, and what are the potential risks and ethical concerns associated with its use?
Applications of Research Questions
Here are some of the key applications of research questions:
- Defining the scope of the study : Research questions help researchers to narrow down the scope of their study and identify the specific issues they want to investigate.
- Developing hypotheses: Research questions often lead to the development of hypotheses, which are testable predictions about the relationship between variables. Hypotheses provide a clear and focused direction for the study.
- Designing the study : Research questions guide the design of the study, including the selection of participants, the collection of data, and the analysis of results.
- Collecting data : Research questions inform the selection of appropriate methods for collecting data, such as surveys, interviews, or experiments.
- Analyzing data : Research questions guide the analysis of data, including the selection of appropriate statistical tests and the interpretation of results.
- Communicating results : Research questions help researchers to communicate the results of their study in a clear and concise manner. The research questions provide a framework for discussing the findings and drawing conclusions.
Characteristics of Research Questions
Characteristics of Research Questions are as follows:
- Clear and Specific : A good research question should be clear and specific. It should clearly state what the research is trying to investigate and what kind of data is required.
- Relevant : The research question should be relevant to the study and should address a current issue or problem in the field of research.
- Testable : The research question should be testable through empirical evidence. It should be possible to collect data to answer the research question.
- Concise : The research question should be concise and focused. It should not be too broad or too narrow.
- Feasible : The research question should be feasible to answer within the constraints of the research design, time frame, and available resources.
- Original : The research question should be original and should contribute to the existing knowledge in the field of research.
- Significant : The research question should have significance and importance to the field of research. It should have the potential to provide new insights and knowledge to the field.
- Ethical : The research question should be ethical and should not cause harm to any individuals or groups involved in the study.
Purpose of Research Questions
Research questions are the foundation of any research study as they guide the research process and provide a clear direction to the researcher. The purpose of research questions is to identify the scope and boundaries of the study, and to establish the goals and objectives of the research.
The main purpose of research questions is to help the researcher to focus on the specific area or problem that needs to be investigated. They enable the researcher to develop a research design, select the appropriate methods and tools for data collection and analysis, and to organize the results in a meaningful way.
Research questions also help to establish the relevance and significance of the study. They define the research problem, and determine the research methodology that will be used to address the problem. Research questions also help to determine the type of data that will be collected, and how it will be analyzed and interpreted.
Finally, research questions provide a framework for evaluating the results of the research. They help to establish the validity and reliability of the data, and provide a basis for drawing conclusions and making recommendations based on the findings of the study.
Advantages of Research Questions
There are several advantages of research questions in the research process, including:
- Focus : Research questions help to focus the research by providing a clear direction for the study. They define the specific area of investigation and provide a framework for the research design.
- Clarity : Research questions help to clarify the purpose and objectives of the study, which can make it easier for the researcher to communicate the research aims to others.
- Relevance : Research questions help to ensure that the study is relevant and meaningful. By asking relevant and important questions, the researcher can ensure that the study will contribute to the existing body of knowledge and address important issues.
- Consistency : Research questions help to ensure consistency in the research process by providing a framework for the development of the research design, data collection, and analysis.
- Measurability : Research questions help to ensure that the study is measurable by defining the specific variables and outcomes that will be measured.
- Replication : Research questions help to ensure that the study can be replicated by providing a clear and detailed description of the research aims, methods, and outcomes. This makes it easier for other researchers to replicate the study and verify the results.
Limitations of Research Questions
Limitations of Research Questions are as follows:
- Subjectivity : Research questions are often subjective and can be influenced by personal biases and perspectives of the researcher. This can lead to a limited understanding of the research problem and may affect the validity and reliability of the study.
- Inadequate scope : Research questions that are too narrow in scope may limit the breadth of the study, while questions that are too broad may make it difficult to focus on specific research objectives.
- Unanswerable questions : Some research questions may not be answerable due to the lack of available data or limitations in research methods. In such cases, the research question may need to be rephrased or modified to make it more answerable.
- Lack of clarity : Research questions that are poorly worded or ambiguous can lead to confusion and misinterpretation. This can result in incomplete or inaccurate data, which may compromise the validity of the study.
- Difficulty in measuring variables : Some research questions may involve variables that are difficult to measure or quantify, making it challenging to draw meaningful conclusions from the data.
- Lack of generalizability: Research questions that are too specific or limited in scope may not be generalizable to other contexts or populations. This can limit the applicability of the study’s findings and restrict its broader implications.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...

How to Develop a Good Research Question? — Types & Examples
Cecilia is living through a tough situation in her research life. Figuring out where to begin, how to start her research study, and how to pose the right question for her research quest, is driving her insane. Well, questions, if not asked correctly, have a tendency to spiral us!
Image Source: https://phdcomics.com/
Questions lead everyone to answers. Research is a quest to find answers. Not the vague questions that Cecilia means to answer, but definitely more focused questions that define your research. Therefore, asking appropriate question becomes an important matter of discussion.
A well begun research process requires a strong research question. It directs the research investigation and provides a clear goal to focus on. Understanding the characteristics of comprising a good research question will generate new ideas and help you discover new methods in research.
In this article, we are aiming to help researchers understand what is a research question and how to write one with examples.
Table of Contents
What Is a Research Question?
A good research question defines your study and helps you seek an answer to your research. Moreover, a clear research question guides the research paper or thesis to define exactly what you want to find out, giving your work its objective. Learning to write a research question is the beginning to any thesis, dissertation , or research paper. Furthermore, the question addresses issues or problems which is answered through analysis and interpretation of data.
Why Is a Research Question Important?
A strong research question guides the design of a study. Moreover, it helps determine the type of research and identify specific objectives. Research questions state the specific issue you are addressing and focus on outcomes of the research for individuals to learn. Therefore, it helps break up the study into easy steps to complete the objectives and answer the initial question.
Types of Research Questions
Research questions can be categorized into different types, depending on the type of research you want to undergo. Furthermore, knowing the type of research will help a researcher determine the best type of research question to use.
1. Qualitative Research Question
Qualitative questions concern broad areas or more specific areas of research. However, unlike quantitative questions, qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional and more flexible. Qualitative research question focus on discovering, explaining, elucidating, and exploring.
i. Exploratory Questions
This form of question looks to understand something without influencing the results. The objective of exploratory questions is to learn more about a topic without attributing bias or preconceived notions to it.
Research Question Example: Asking how a chemical is used or perceptions around a certain topic.
ii. Predictive Questions
Predictive research questions are defined as survey questions that automatically predict the best possible response options based on text of the question. Moreover, these questions seek to understand the intent or future outcome surrounding a topic.
Research Question Example: Asking why a consumer behaves in a certain way or chooses a certain option over other.
iii. Interpretive Questions
This type of research question allows the study of people in the natural setting. The questions help understand how a group makes sense of shared experiences with regards to various phenomena. These studies gather feedback on a group’s behavior without affecting the outcome.
Research Question Example: How do you feel about AI assisting publishing process in your research?
2. Quantitative Research Question
Quantitative questions prove or disprove a researcher’s hypothesis through descriptions, comparisons, and relationships. These questions are beneficial when choosing a research topic or when posing follow-up questions that garner more information.
i. Descriptive Questions
It is the most basic type of quantitative research question and it seeks to explain when, where, why, or how something occurred. Moreover, they use data and statistics to describe an event or phenomenon.
Research Question Example: How many generations of genes influence a future generation?
ii. Comparative Questions
Sometimes it’s beneficial to compare one occurrence with another. Therefore, comparative questions are helpful when studying groups with dependent variables.
Example: Do men and women have comparable metabolisms?
iii. Relationship-Based Questions
This type of research question answers influence of one variable on another. Therefore, experimental studies use this type of research questions are majorly.
Example: How is drought condition affect a region’s probability for wildfires.
How to Write a Good Research Question?

1. Select a Topic
The first step towards writing a good research question is to choose a broad topic of research. You could choose a research topic that interests you, because the complete research will progress further from the research question. Therefore, make sure to choose a topic that you are passionate about, to make your research study more enjoyable.
2. Conduct Preliminary Research
After finalizing the topic, read and know about what research studies are conducted in the field so far. Furthermore, this will help you find articles that talk about the topics that are yet to be explored. You could explore the topics that the earlier research has not studied.

3. Consider Your Audience
The most important aspect of writing a good research question is to find out if there is audience interested to know the answer to the question you are proposing. Moreover, determining your audience will assist you in refining your research question, and focus on aspects that relate to defined groups.
4. Generate Potential Questions
The best way to generate potential questions is to ask open ended questions. Questioning broader topics will allow you to narrow down to specific questions. Identifying the gaps in literature could also give you topics to write the research question. Moreover, you could also challenge the existing assumptions or use personal experiences to redefine issues in research.
5. Review Your Questions
Once you have listed few of your questions, evaluate them to find out if they are effective research questions. Moreover while reviewing, go through the finer details of the question and its probable outcome, and find out if the question meets the research question criteria.
6. Construct Your Research Question
There are two frameworks to construct your research question. The first one being PICOT framework , which stands for:
- Population or problem
- Intervention or indicator being studied
- Comparison group
- Outcome of interest
- Time frame of the study.
The second framework is PEO , which stands for:
- Population being studied
- Exposure to preexisting conditions
- Outcome of interest.
Research Question Examples
- How might the discovery of a genetic basis for alcoholism impact triage processes in medical facilities?
- How do ecological systems respond to chronic anthropological disturbance?
- What are demographic consequences of ecological interactions?
- What roles do fungi play in wildfire recovery?
- How do feedbacks reinforce patterns of genetic divergence on the landscape?
- What educational strategies help encourage safe driving in young adults?
- What makes a grocery store easy for shoppers to navigate?
- What genetic factors predict if someone will develop hypothyroidism?
- Does contemporary evolution along the gradients of global change alter ecosystems function?
How did you write your first research question ? What were the steps you followed to create a strong research question? Do write to us or comment below.
Frequently Asked Questions
Research questions guide the focus and direction of a research study. Here are common types of research questions: 1. Qualitative research question: Qualitative questions concern broad areas or more specific areas of research. However, unlike quantitative questions, qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional and more flexible. Different types of qualitative research questions are: i. Exploratory questions ii. Predictive questions iii. Interpretive questions 2. Quantitative Research Question: Quantitative questions prove or disprove a researcher’s hypothesis through descriptions, comparisons, and relationships. These questions are beneficial when choosing a research topic or when posing follow-up questions that garner more information. Different types of quantitative research questions are: i. Descriptive questions ii. Comparative questions iii. Relationship-based questions
Qualitative research questions aim to explore the richness and depth of participants' experiences and perspectives. They should guide your research and allow for in-depth exploration of the phenomenon under investigation. After identifying the research topic and the purpose of your research: • Begin with Broad Inquiry: Start with a general research question that captures the main focus of your study. This question should be open-ended and allow for exploration. • Break Down the Main Question: Identify specific aspects or dimensions related to the main research question that you want to investigate. • Formulate Sub-questions: Create sub-questions that delve deeper into each specific aspect or dimension identified in the previous step. • Ensure Open-endedness: Make sure your research questions are open-ended and allow for varied responses and perspectives. Avoid questions that can be answered with a simple "yes" or "no." Encourage participants to share their experiences, opinions, and perceptions in their own words. • Refine and Review: Review your research questions to ensure they align with your research purpose, topic, and objectives. Seek feedback from your research advisor or peers to refine and improve your research questions.
Developing research questions requires careful consideration of the research topic, objectives, and the type of study you intend to conduct. Here are the steps to help you develop effective research questions: 1. Select a Topic 2. Conduct Preliminary Research 3. Consider Your Audience 4. Generate Potential Questions 5. Review Your Questions 6. Construct Your Research Question Based on PICOT or PEO Framework
There are two frameworks to construct your research question. The first one being PICOT framework, which stands for: • Population or problem • Intervention or indicator being studied • Comparison group • Outcome of interest • Time frame of the study The second framework is PEO, which stands for: • Population being studied • Exposure to preexisting conditions • Outcome of interest
A tad helpful
Had trouble coming up with a good research question for my MSc proposal. This is very much helpful.
This is a well elaborated writing on research questions development. I found it very helpful.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Industry News
- Trending Now
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Diversity and Inclusion
The Silent Struggle: Confronting gender bias in science funding
In the 1990s, Dr. Katalin Kariko’s pioneering mRNA research seemed destined for obscurity, doomed by…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…
Setting Rationale in Research: Cracking the code for excelling at research
Research Problem Statement — Find out how to write an impactful one!
Experimental Research Design — 6 mistakes you should never make!

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
Research Aims, Objectives & Questions
The “Golden Thread” Explained Simply (+ Examples)
By: David Phair (PhD) and Alexandra Shaeffer (PhD) | June 2022
The research aims , objectives and research questions (collectively called the “golden thread”) are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you’re crafting a research proposal , dissertation or thesis . We receive questions almost every day about this “holy trinity” of research and there’s certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we’ve crafted this post to help you navigate your way through the fog.
Overview: The Golden Thread
- What is the golden thread
- What are research aims ( examples )
- What are research objectives ( examples )
- What are research questions ( examples )
- The importance of alignment in the golden thread
What is the “golden thread”?
The golden thread simply refers to the collective research aims , research objectives , and research questions for any given project (i.e., a dissertation, thesis, or research paper ). These three elements are bundled together because it’s extremely important that they align with each other, and that the entire research project aligns with them.
Importantly, the golden thread needs to weave its way through the entirety of any research project , from start to end. In other words, it needs to be very clearly defined right at the beginning of the project (the topic ideation and proposal stage) and it needs to inform almost every decision throughout the rest of the project. For example, your research design and methodology will be heavily influenced by the golden thread (we’ll explain this in more detail later), as well as your literature review.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread) define the focus and scope ( the delimitations ) of your research project. In other words, they help ringfence your dissertation or thesis to a relatively narrow domain, so that you can “go deep” and really dig into a specific problem or opportunity. They also help keep you on track , as they act as a litmus test for relevance. In other words, if you’re ever unsure whether to include something in your document, simply ask yourself the question, “does this contribute toward my research aims, objectives or questions?”. If it doesn’t, chances are you can drop it.
Alright, enough of the fluffy, conceptual stuff. Let’s get down to business and look at what exactly the research aims, objectives and questions are and outline a few examples to bring these concepts to life.

Research Aims: What are they?
Simply put, the research aim(s) is a statement that reflects the broad overarching goal (s) of the research project. Research aims are fairly high-level (low resolution) as they outline the general direction of the research and what it’s trying to achieve .
Research Aims: Examples
True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording “this research aims to…”, “this research seeks to…”, and so on. For example:
“This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.” “This study sets out to assess the interaction between student support and self-care on well-being in engineering graduate students”
As you can see, these research aims provide a high-level description of what the study is about and what it seeks to achieve. They’re not hyper-specific or action-oriented, but they’re clear about what the study’s focus is and what is being investigated.
Need a helping hand?
Research Objectives: What are they?
The research objectives take the research aims and make them more practical and actionable . In other words, the research objectives showcase the steps that the researcher will take to achieve the research aims.
The research objectives need to be far more specific (higher resolution) and actionable than the research aims. In fact, it’s always a good idea to craft your research objectives using the “SMART” criteria. In other words, they should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound”.
Research Objectives: Examples
Let’s look at two examples of research objectives. We’ll stick with the topic and research aims we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic:
To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation. To assess employee perceptions of digital transformation in retail HR. To identify the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR.
And for the student wellness topic:
To determine whether student self-care predicts the well-being score of engineering graduate students. To determine whether student support predicts the well-being score of engineering students. To assess the interaction between student self-care and student support when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students.
As you can see, these research objectives clearly align with the previously mentioned research aims and effectively translate the low-resolution aims into (comparatively) higher-resolution objectives and action points . They give the research project a clear focus and present something that resembles a research-based “to-do” list.

Research Questions: What are they?
Finally, we arrive at the all-important research questions. The research questions are, as the name suggests, the key questions that your study will seek to answer . Simply put, they are the core purpose of your dissertation, thesis, or research project. You’ll present them at the beginning of your document (either in the introduction chapter or literature review chapter) and you’ll answer them at the end of your document (typically in the discussion and conclusion chapters).
The research questions will be the driving force throughout the research process. For example, in the literature review chapter, you’ll assess the relevance of any given resource based on whether it helps you move towards answering your research questions. Similarly, your methodology and research design will be heavily influenced by the nature of your research questions. For instance, research questions that are exploratory in nature will usually make use of a qualitative approach, whereas questions that relate to measurement or relationship testing will make use of a quantitative approach.
Let’s look at some examples of research questions to make this more tangible.
Research Questions: Examples
Again, we’ll stick with the research aims and research objectives we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic (which would be qualitative in nature):
How do employees perceive digital transformation in retail HR? What are the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR?
And for the student wellness topic (which would be quantitative in nature):
Does student self-care predict the well-being scores of engineering graduate students? Does student support predict the well-being scores of engineering students? Do student self-care and student support interact when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students?
You’ll probably notice that there’s quite a formulaic approach to this. In other words, the research questions are basically the research objectives “converted” into question format. While that is true most of the time, it’s not always the case. For example, the first research objective for the digital transformation topic was more or less a step on the path toward the other objectives, and as such, it didn’t warrant its own research question.
So, don’t rush your research questions and sloppily reword your objectives as questions. Carefully think about what exactly you’re trying to achieve (i.e. your research aim) and the objectives you’ve set out, then craft a set of well-aligned research questions . Also, keep in mind that this can be a somewhat iterative process , where you go back and tweak research objectives and aims to ensure tight alignment throughout the golden thread.
The importance of strong alignment
Alignment is the keyword here and we have to stress its importance . Simply put, you need to make sure that there is a very tight alignment between all three pieces of the golden thread. If your research aims and research questions don’t align, for example, your project will be pulling in different directions and will lack focus . This is a common problem students face and can cause many headaches (and tears), so be warned.
Take the time to carefully craft your research aims, objectives and research questions before you run off down the research path. Ideally, get your research supervisor/advisor to review and comment on your golden thread before you invest significant time into your project, and certainly before you start collecting data .
Recap: The golden thread
In this post, we unpacked the golden thread of research, consisting of the research aims , research objectives and research questions . You can jump back to any section using the links below.
As always, feel free to leave a comment below – we always love to hear from you. Also, if you’re interested in 1-on-1 support, take a look at our private coaching service here.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

39 Comments
Thank you very much for your great effort put. As an Undergraduate taking Demographic Research & Methodology, I’ve been trying so hard to understand clearly what is a Research Question, Research Aim and the Objectives in a research and the relationship between them etc. But as for now I’m thankful that you’ve solved my problem.
Well appreciated. This has helped me greatly in doing my dissertation.
An so delighted with this wonderful information thank you a lot.
so impressive i have benefited a lot looking forward to learn more on research.
I am very happy to have carefully gone through this well researched article.
Infact,I used to be phobia about anything research, because of my poor understanding of the concepts.
Now,I get to know that my research question is the same as my research objective(s) rephrased in question format.
I please I would need a follow up on the subject,as I intends to join the team of researchers. Thanks once again.
Thanks so much. This was really helpful.
I know you pepole have tried to break things into more understandable and easy format. And God bless you. Keep it up
i found this document so useful towards my study in research methods. thanks so much.
This is my 2nd read topic in your course and I should commend the simplified explanations of each part. I’m beginning to understand and absorb the use of each part of a dissertation/thesis. I’ll keep on reading your free course and might be able to avail the training course! Kudos!
Thank you! Better put that my lecture and helped to easily understand the basics which I feel often get brushed over when beginning dissertation work.
This is quite helpful. I like how the Golden thread has been explained and the needed alignment.
This is quite helpful. I really appreciate!
The article made it simple for researcher students to differentiate between three concepts.
Very innovative and educational in approach to conducting research.
I am very impressed with all these terminology, as I am a fresh student for post graduate, I am highly guided and I promised to continue making consultation when the need arise. Thanks a lot.
A very helpful piece. thanks, I really appreciate it .
Very well explained, and it might be helpful to many people like me.
Wish i had found this (and other) resource(s) at the beginning of my PhD journey… not in my writing up year… 😩 Anyways… just a quick question as i’m having some issues ordering my “golden thread”…. does it matter in what order you mention them? i.e., is it always first aims, then objectives, and finally the questions? or can you first mention the research questions and then the aims and objectives?
Thank you for a very simple explanation that builds upon the concepts in a very logical manner. Just prior to this, I read the research hypothesis article, which was equally very good. This met my primary objective.
My secondary objective was to understand the difference between research questions and research hypothesis, and in which context to use which one. However, I am still not clear on this. Can you kindly please guide?
In research, a research question is a clear and specific inquiry that the researcher wants to answer, while a research hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction about the relationship between variables or the expected outcome of the study. Research questions are broader and guide the overall study, while hypotheses are specific and testable statements used in quantitative research. Research questions identify the problem, while hypotheses provide a focus for testing in the study.
Exactly what I need in this research journey, I look forward to more of your coaching videos.
This helped a lot. Thanks so much for the effort put into explaining it.
What data source in writing dissertation/Thesis requires?
What is data source covers when writing dessertation/thesis
This is quite useful thanks
I’m excited and thankful. I got so much value which will help me progress in my thesis.
where are the locations of the reserch statement, research objective and research question in a reserach paper? Can you write an ouline that defines their places in the researh paper?
Very helpful and important tips on Aims, Objectives and Questions.
Thank you so much for making research aim, research objectives and research question so clear. This will be helpful to me as i continue with my thesis.
Thanks much for this content. I learned a lot. And I am inspired to learn more. I am still struggling with my preparation for dissertation outline/proposal. But I consistently follow contents and tutorials and the new FB of GRAD Coach. Hope to really become confident in writing my dissertation and successfully defend it.
As a researcher and lecturer, I find splitting research goals into research aims, objectives, and questions is unnecessarily bureaucratic and confusing for students. For most biomedical research projects, including ‘real research’, 1-3 research questions will suffice (numbers may differ by discipline).
Awesome! Very important resources and presented in an informative way to easily understand the golden thread. Indeed, thank you so much.
Well explained
The blog article on research aims, objectives, and questions by Grad Coach is a clear and insightful guide that aligns with my experiences in academic research. The article effectively breaks down the often complex concepts of research aims and objectives, providing a straightforward and accessible explanation. Drawing from my own research endeavors, I appreciate the practical tips offered, such as the need for specificity and clarity when formulating research questions. The article serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers, offering a concise roadmap for crafting well-defined research goals and objectives. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced researcher, this article provides practical insights that contribute to the foundational aspects of a successful research endeavor.
A great thanks for you. it is really amazing explanation. I grasp a lot and one step up to research knowledge.
I really found these tips helpful. Thank you very much Grad Coach.
I found this article helpful. Thanks for sharing this.
thank you so much, the explanation and examples are really helpful
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Research Paper Guides
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- How to Write a Research Question: Types & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
How to Write a Research Question: Types & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A research question is the main query that researchers seek to answer in their study. It serves as the basis for a scholarly project such as research paper, thesis or dissertation. A good research question should be clear, relevant and specific enough to guide the research process. It should also be open-ended, meaning that it allows for multiple possible answers or interpretations.
If you have located your general subject and main sources but still aren’t quite sure about the exact research questions for your paper, this guide will help you out. First, we will explore the concept of it together, so you could answer it in your work. Then some simple steps on composing your inquiry will be suggested. In the end, we will draw your attention to some specific details which can make your work good or bad. Sometimes it’s just easier to delegate all challenging tasks to a reliable research paper service . StudyCrumb is a trustable network of qualified writers ready to efficiently solve students’ challenges.
What Is a Good Research Question: Full Definition
Good research questions provide a concise definition of a problem. As a scholar, your main goal at the beginning is to select the main focus. It should be narrow enough so you could examine it within your deadline. Your work should be focused on something specific. Otherwise, it will require too much work and might not produce clear answers. At the same time your answer should be arguable and supported by data you’ve collected. Take a look at this example:

How to Write a Research Question: Step-By-Step Guide
In this section we will examine the process of developing a research question. We will guide you through it, step by step. Keep in mind that your subject should be important for your audience. So it requires some preliminary study and brainstorming. Let’s take a closer look at the main steps.
Step 1. Choose a Broad Topic for Your Research Paper Question
First, you need to decide on your general direction. When trying to identify your research paper questions, it is better to choose an area you are really interested in. You should be able to obtain enough data to write something about this topic. Therefore, do not choose something out of your reach. At the same time, your broad topic should not be too simple. Research paper questions that can be answered without any study would hardly make any sense for your project.
Step 2. Do Preliminary Reading Before Starting Your Research Question
Next, it is time we explore the context of the selected topic. You wouldn’t want to choose research questions that have already been examined and answered in detail. On the other hand, choosing a topic that is a complete ‘terra incognita’ might be a bridge too far for your project. Browse through available sources that are related to this topic. You should try and find out what has been discovered about it before. Do you see a gap that you can fill with your study? You can proceed with developing your exact inquiry! Have no time for in-depth topic exploration? Leave this task to professionals. Entrust your “ write my research paper ” order to StudyCrumb and get a top-notch work.
Step 3. Consider an Audience for Your Research Question
It is good to know your reader well to be able to convey your ideas and results to them in the best possible way. Before writing research questions for your projects, you might need to perform a brief analysis of your audience. That's how you'll be able to understand what is interesting for them and what is not. This will allow you to make better decisions when narrowing your broad topic down. Select a topic that is interesting for your reader! This would contribute much to the success for writing a research paper .
Step 4. Start Asking a Good Research Question
After you have considered your options, go ahead and compose the primary subject of your paper. What makes a good research question? It should highlight some problematic and relevant aspects of the general topic. So, after it is answered, you should have obtained some new valuable knowledge about the subject. Typically scholars start narrowing down their general topic by asking ‘how’, ‘why’ or ‘what’s next’ questions. This approach might help you come up with a great idea quickly.
Step 5. Evaluate Your Research Question
Finally, after you have composed a research paper question, you should take a second look at it and see if it is good enough for your paper. It would be useful to analyze it from the following sides:
- Is it clear for your audience?
- Is it complex enough to require significant study?
- Is it focused on a certain aspect of your general topic?
You might use the help of your peers or your friends at this step. You can also show it to your tutor and ask for their opinion.
Types of Research Questions: Which to Choose
A number of research questions types are available for use in a paper. They are divided into two main groups:
Qualitative questions:
- Explanatory
- Ethnographic
Quantitative questions:
- Descriptive
- Comparative
- Relationship based.
Selecting a certain type would impact the course of your study. We suggest you think about it carefully. Below you can find a few words about each type. Also, you can seek proficient help from academic experts. Buy a research paper from real pros and forget about stress once and for all.
Qualitative Research Questions: Definition With Example
When doing qualitative research, you are expected to aim to understand the different aspects and qualities of your target problem. Therefore, your thesis should focus on analyzing people’s experience, ideas and reflections rather than on obtaining some statistical data and calculating trends. Thus, this inquiry typically requires observing people’s behavior, interacting with them and learning how they interpret your target problem. Let’s illustrate this with an example:

What Is Contextual Research Questions
Contextual research revolves around examining your subject in its natural, everyday environment. It may be watching animals living in their usual habitats or people doing their normal activities in their familiar surroundings (at home, at school or at office). This academic approach helps to understand the role of the context. You'll be able to better explain connections between your problem, its environment and outcomes. This type of inquiry ought to be narrow enough. You shouldn’t have to examine each and every aspect of the selected problem in your paper. Consider this example:

Definition and Sample of Evaluative Research Questions
Evaluative research is performed in order to carefully assess the qualities of a selected object, individual, group, system or concept. It typically serves the purpose of collecting evidence that supports or contradicts solutions for a problem. This type of inquiry should focus on how useful a certain quality is for solving the problem. To conduct such study, you need to examine selected qualities in detail. Then, you should assume whether they match necessary criteria. It might include some quantitative methods such as collecting statistics. Although, the most important part is analyzing the qualities. If you need some examples, here’s one for you:

Explanatory Research Questions: Definition With Example
Your paper can be dedicated to explaining a certain phenomenon, finding its reasons and important relationships between it and other important things. Your explanatory research question should aim to highlight issues, uncertainties and problematic aspects of your subject. So, your study should bring clarity about these qualities. It should show how and why they have developed this way. An explanation may include showing causes and effects of issues in question, comparing the selected phenomenon to other similar types and showing whether the selected qualities match some predefined criteria. If you need some examples, check this one:

Generative Research Questions
This type of research is conducted in order to better understand the subject. With its help, you can find some new solutions or opportunities for improvement. Therefore, its main purpose is to develop a theoretical basis for further actions. You need to compose your generative research questions in a way that facilitates obtaining new ideas. It would help to begin with asking ‘why’, ‘what is the relationship between the subject and the problems X, Y, and Z’, ‘what can be improved here’, ‘how we can prevent it’ and so on. Need relevant examples? We’ve got one for you:

Ethnographic Research Question
Ethnography research is focused on a particular group of people. The aim is to study their behavior, typical reactions to certain events or information, needs, preferences or habits. Important parameters of this group which are most relevant to your general subject are taken into consideration. These are age, sex, language, religion, ethnicity, social status and so on. Main method in this case is first-hand observation of people from the selected group during an extended period of time. If you need strong examples, here’s one:

Quantitative Research Questions: Full Definition With Examples
Quantitative research deals with data – first of all, it is numeric data. It involves mathematical calculations and statistical analysis. It helps to obtain knowledge which is mostly expressed in numbers, graphs and tables. Unlike the qualitative type, the purpose of quantitative research is finding patterns, calculating probabilities, testing causal relationships and making predictions. It is focused on testing theories and hypotheses. (We have the whole blog on what is a hypothesis .) It is mostly used in natural and social sciences. These are: chemistry, biology, psychology, economics, sociology, marketing, etc. Here are a couple of examples:

Descriptive Research Questions: Definition With Example
This is probably the most widespread type of quantitative research question. Such inquiries seek to explain when, where, why, or how something occurred. They describe it accurately and systematically. These inquiries typically start with ‘what’. You are expected to use various methods to investigate one or more variables and determine their dependencies. Note, however, that you cannot control or manipulate any of these variables. You can only observe and measure them. Looking for some interesting examples? Here is one:

Definition of Comparative Research Questions
Comparative research question is used to highlight different variables and provide numerical evidence. This type is based on comparing one object, parameter or issue with another one of a similar kind. It can help to discover the differences between two or more groups by examining their outcome variables. Take a look at these two examples:

Relationship Research Questions
We conduct this type of research when we need to make it clear whether one parameter of a selected object causes another one. A relationship based quantitative research question should help us to explore and define trends and interactions between two or more variables. Are these two things mutually dependent? What kind of dependence is it? How has it developed? And what are possible outcomes of this connection? Here is an example of relationship-based quantitative research questions:

Research Questions Examples: Free
This section contains a number of helpful examples of research questions. Feel free to use them as inspiration to create your own questions and conduct productive study. Let’s start with two simple ones:

Are you interested in well written and inspiring questions? Do you want to learn what to avoid in your study? Just stay with us – there will be more of them below.
Examples of Good and Bad Research Questions
Everyone is interested in getting the best possible appraisal for their study. Choosing a topic which doesn't suit your specific situation may be discouraging. Thus, the quality of your paper might get affected by a poor choice. We have put together some good and bad examples so that you could avoid such mistakes.
Good Research Questions Examples
It is important to include clear terms into your questions. Otherwise, it would be difficult for you to plan your investigation properly. Also, they must be focused on a certain subject, not multiple ones. And finally, it should be possible to answer them. Let’s review several good examples:

Examples of Bad Research Questions
It is difficult to evaluate qualities of objects, individuals or groups if your purpose is not clear. This is why you shouldn’t create unclear research questions or try to focus on many problems at once. Some preliminary study might help to understand what you should focus on. Here are several bad examples:

In case you may need some information about the discussion section of a research paper example , find it in our blog.
Final Thoughts on Research Questions
In this article we have made a detailed review of the most popular types of research questions. We described peculiarities. We also provided some tips on conducting various kinds of study. Besides, a number of useful examples have been given for each category of questions.
Feel free to check out essay writing services. We have experienced writers who can help you compose your paper in time. They will absolutely ensure the high quality of your text.
Frequently Asked Questions About Research Questions
1. what is an example of a weak research question.
Here is an example of the weakest research question:
An answer would be simply making a list of species that inhabit the country. This subject does not require any actual study to be conducted. There is nothing to calculate or analyze here.
2. What is the most effective type of research question?
Most effective type of research question is the one that doesn't have a single correct answer. However, you should also pay close attention to your audience. If you need to create a strong effect, better choose a topic which is relevant for them.
3. What is a good nursing research question?
If you need an idea for a nursing research question, here are a few helpful examples you could use as a reference:
4. What are some sociological research questions?
Sociological questions are the ones that examine the social patterns or a meaning of a social phenomenon. They could be qualitative or quantitative. They should target groups of people with certain parameters, such as age or income level. Keep in mind that type of study usually requires collecting numerous data about your target groups.

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
You may also like

- Research Questions: Definitions, Types + [Examples]

Research questions lie at the core of systematic investigation and this is because recording accurate research outcomes is tied to asking the right questions. Asking the right questions when conducting research can help you collect relevant and insightful information that ultimately influences your work, positively.
The right research questions are typically easy to understand, straight to the point, and engaging. In this article, we will share tips on how to create the right research questions and also show you how to create and administer an online questionnaire with Formplus .
What is a Research Question?
A research question is a specific inquiry which the research seeks to provide a response to. It resides at the core of systematic investigation and it helps you to clearly define a path for the research process.
A research question is usually the first step in any research project. Basically, it is the primary interrogation point of your research and it sets the pace for your work.
Typically, a research question focuses on the research, determines the methodology and hypothesis, and guides all stages of inquiry, analysis, and reporting. With the right research questions, you will be able to gather useful information for your investigation.
Types of Research Questions
Research questions are broadly categorized into 2; that is, qualitative research questions and quantitative research questions. Qualitative and quantitative research questions can be used independently and co-dependently in line with the overall focus and objectives of your research.
If your research aims at collecting quantifiable data , you will need to make use of quantitative research questions. On the other hand, qualitative questions help you to gather qualitative data bothering on the perceptions and observations of your research subjects.
Qualitative Research Questions
A qualitative research question is a type of systematic inquiry that aims at collecting qualitative data from research subjects. The aim of qualitative research questions is to gather non-statistical information pertaining to the experiences, observations, and perceptions of the research subjects in line with the objectives of the investigation.
Types of Qualitative Research Questions
- Ethnographic Research Questions
As the name clearly suggests, ethnographic research questions are inquiries presented in ethnographic research. Ethnographic research is a qualitative research approach that involves observing variables in their natural environments or habitats in order to arrive at objective research outcomes.
These research questions help the researcher to gather insights into the habits, dispositions, perceptions, and behaviors of research subjects as they interact in specific environments.
Ethnographic research questions can be used in education, business, medicine, and other fields of study, and they are very useful in contexts aimed at collecting in-depth and specific information that are peculiar to research variables. For instance, asking educational ethnographic research questions can help you understand how pedagogy affects classroom relations and behaviors.
This type of research question can be administered physically through one-on-one interviews, naturalism (live and work), and participant observation methods. Alternatively, the researcher can ask ethnographic research questions via online surveys and questionnaires created with Formplus.
Examples of Ethnographic Research Questions
- Why do you use this product?
- Have you noticed any side effects since you started using this drug?
- Does this product meet your needs?
- Case Studies
A case study is a qualitative research approach that involves carrying out a detailed investigation into a research subject(s) or variable(s). In the course of a case study, the researcher gathers a range of data from multiple sources of information via different data collection methods, and over a period of time.
The aim of a case study is to analyze specific issues within definite contexts and arrive at detailed research subject analyses by asking the right questions. This research method can be explanatory, descriptive , or exploratory depending on the focus of your systematic investigation or research.
An explanatory case study is one that seeks to gather information on the causes of real-life occurrences. This type of case study uses “how” and “why” questions in order to gather valid information about the causative factors of an event.
Descriptive case studies are typically used in business researches, and they aim at analyzing the impact of changing market dynamics on businesses. On the other hand, exploratory case studies aim at providing answers to “who” and “what” questions using data collection tools like interviews and questionnaires.
Some questions you can include in your case studies are:
- Why did you choose our services?
- How has this policy affected your business output?
- What benefits have you recorded since you started using our product?
An interview is a qualitative research method that involves asking respondents a series of questions in order to gather information about a research subject. Interview questions can be close-ended or open-ended , and they prompt participants to provide valid information that is useful to the research.
An interview may also be structured, semi-structured , or unstructured , and this further influences the types of questions they include. Structured interviews are made up of more close-ended questions because they aim at gathering quantitative data while unstructured interviews consist, primarily, of open-ended questions that allow the researcher to collect qualitative information from respondents.
You can conduct interview research by scheduling a physical meeting with respondents, through a telephone conversation, and via digital media and video conferencing platforms like Skype and Zoom. Alternatively, you can use Formplus surveys and questionnaires for your interview.
Examples of interview questions include:
- What challenges did you face while using our product?
- What specific needs did our product meet?
- What would you like us to improve our service delivery?
Quantitative Research Questions
Quantitative research questions are questions that are used to gather quantifiable data from research subjects. These types of research questions are usually more specific and direct because they aim at collecting information that can be measured; that is, statistical information.
Types of Quantitative Research Questions
- Descriptive Research Questions
Descriptive research questions are inquiries that researchers use to gather quantifiable data about the attributes and characteristics of research subjects. These types of questions primarily seek responses that reveal existing patterns in the nature of the research subjects.
It is important to note that descriptive research questions are not concerned with the causative factors of the discovered attributes and characteristics. Rather, they focus on the “what”; that is, describing the subject of the research without paying attention to the reasons for its occurrence.
Descriptive research questions are typically closed-ended because they aim at gathering definite and specific responses from research participants. Also, they can be used in customer experience surveys and market research to collect information about target markets and consumer behaviors.
Descriptive Research Question Examples
- How often do you make use of our fitness application?
- How much would you be willing to pay for this product?
- Comparative Research Questions
A comparative research question is a type of quantitative research question that is used to gather information about the differences between two or more research subjects across different variables. These types of questions help the researcher to identify distinct features that mark one research subject from the other while highlighting existing similarities.
Asking comparative research questions in market research surveys can provide insights on how your product or service matches its competitors. In addition, it can help you to identify the strengths and weaknesses of your product for a better competitive advantage.
The 5 steps involved in the framing of comparative research questions are:
- Choose your starting phrase
- Identify and name the dependent variable
- Identify the groups you are interested in
- Identify the appropriate adjoining text
- Write out the comparative research question
Comparative Research Question Samples
- What are the differences between a landline telephone and a smartphone?
- What are the differences between work-from-home and on-site operations?
- Relationship-based Research Questions
Just like the name suggests, a relationship-based research question is one that inquires into the nature of the association between two research subjects within the same demographic. These types of research questions help you to gather information pertaining to the nature of the association between two research variables.
Relationship-based research questions are also known as correlational research questions because they seek to clearly identify the link between 2 variables.
Read: Correlational Research Designs: Types, Examples & Methods
Examples of relationship-based research questions include:
- What is the relationship between purchasing power and the business site?
- What is the relationship between the work environment and workforce turnover?
Examples of a Good Research Question
Since research questions lie at the core of any systematic investigations, it is important to know how to frame a good research question. The right research questions will help you to gather the most objective responses that are useful to your systematic investigation.
A good research question is one that requires impartial responses and can be answered via existing sources of information. Also, a good research question seeks answers that actively contribute to a body of knowledge; hence, it is a question that is yet to be answered in your specific research context.
- Open-Ended Questions
An open-ended question is a type of research question that does not restrict respondents to a set of premeditated answer options. In other words, it is a question that allows the respondent to freely express his or her perceptions and feelings towards the research subject.
Examples of Open-ended Questions
- How do you deal with stress in the workplace?
- What is a typical day at work like for you?
- Close-ended Questions
A close-ended question is a type of survey question that restricts respondents to a set of predetermined answers such as multiple-choice questions . Close-ended questions typically require yes or no answers and are commonly used in quantitative research to gather numerical data from research participants.
Examples of Close-ended Questions
- Did you enjoy this event?
- How likely are you to recommend our services?
- Very Likely
- Somewhat Likely
- Likert Scale Questions
A Likert scale question is a type of close-ended question that is structured as a 3-point, 5-point, or 7-point psychometric scale . This type of question is used to measure the survey respondent’s disposition towards multiple variables and it can be unipolar or bipolar in nature.
Example of Likert Scale Questions
- How satisfied are you with our service delivery?
- Very dissatisfied
- Not satisfied
- Very satisfied
- Rating Scale Questions
A rating scale question is a type of close-ended question that seeks to associate a specific qualitative measure (rating) with the different variables in research. It is commonly used in customer experience surveys, market research surveys, employee reviews, and product evaluations.
Example of Rating Questions
- How would you rate our service delivery?
Examples of a Bad Research Question
Knowing what bad research questions are would help you avoid them in the course of your systematic investigation. These types of questions are usually unfocused and often result in research biases that can negatively impact the outcomes of your systematic investigation.
- Loaded Questions
A loaded question is a question that subtly presupposes one or more unverified assumptions about the research subject or participant. This type of question typically boxes the respondent in a corner because it suggests implicit and explicit biases that prevent objective responses.
Example of Loaded Questions
- Have you stopped smoking?
- Where did you hide the money?
- Negative Questions
A negative question is a type of question that is structured with an implicit or explicit negator. Negative questions can be misleading because they upturn the typical yes/no response order by requiring a negative answer for affirmation and an affirmative answer for negation.
Examples of Negative Questions
- Would you mind dropping by my office later today?
- Didn’t you visit last week?
- Leading Questions
A l eading question is a type of survey question that nudges the respondent towards an already-determined answer. It is highly suggestive in nature and typically consists of biases and unverified assumptions that point toward its premeditated responses.
Examples of Leading Questions
- If you enjoyed this service, would you be willing to try out our other packages?
- Our product met your needs, didn’t it?
Read More: Leading Questions: Definition, Types, and Examples
How to Use Formplus as Online Research Questionnaire Tool
With Formplus, you can create and administer your online research questionnaire easily. In the form builder, you can add different form fields to your questionnaire and edit these fields to reflect specific research questions for your systematic investigation.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to create an online research questionnaire with Formplus:
- Sign in to your Formplus accoun t, then click on the “create new form” button in your dashboard to access the Form builder.
- In the form builder, add preferred form fields to your online research questionnaire by dragging and dropping them into the form. Add a title to your form in the title block. You can edit form fields by clicking on the “pencil” icon on the right corner of each form field.
- Save the form to access the customization section of the builder. Here, you can tweak the appearance of your online research questionnaire by adding background images, changing the form font, and adding your organization’s logo.
- Finally, copy your form link and share it with respondents. You can also use any of the multiple sharing options available.
Conclusion
The success of your research starts with framing the right questions to help you collect the most valid and objective responses. Be sure to avoid bad research questions like loaded and negative questions that can be misleading and adversely affect your research data and outcomes.
Your research questions should clearly reflect the aims and objectives of your systematic investigation while laying emphasis on specific contexts. To help you seamlessly gather responses for your research questions, you can create an online research questionnaire on Formplus.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- abstract in research papers
- bad research questions
- examples of research questions
- types of research questions
- busayo.longe

You may also like:
How to Write a Problem Statement for your Research
Learn how to write problem statements before commencing any research effort. Learn about its structure and explore examples

How to do a Meta Analysis: Methodology, Pros & Cons
In this article, we’ll go through the concept of meta-analysis, what it can be used for, and how you can use it to improve how you...
Research Summary: What Is It & How To Write One
Introduction A research summary is a requirement during academic research and sometimes you might need to prepare a research summary...
How to Write An Abstract For Research Papers: Tips & Examples
In this article, we will share some tips for writing an effective abstract, plus samples you can learn from.
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..

9 9. Writing your research question
Chapter outline.
- Empirical vs. ethical questions (4 minute read)
- Characteristics of a good research question (4 minute read)
- Quantitative research questions (7 minute read)
- Qualitative research questions (3 minute read)
- Evaluating and updating your research questions (4 minute read)
Content warning: examples in this chapter include references to sexual violence, sexism, substance use disorders, homelessness, domestic violence, the child welfare system, cissexism and heterosexism, and truancy and school discipline.
9.1 Empirical vs. ethical questions
Learning objectives.
Learners will be able to…
- Define empirical questions and provide an example
- Define ethical questions and provide an example
Writing a good research question is an art and a science. It is a science because you have to make sure it is clear, concise, and well-developed. It is an art because often your language needs “wordsmithing” to perfect and clarify the meaning. This is an exciting part of the research process; however, it can also be one of the most stressful.
Creating a good research question begins by identifying a topic you are interested in studying. At this point, you already have a working question. You’ve been applying it to the exercises in each chapter, and after reading more about your topic in the scholarly literature, you’ve probably gone back and revised your working question a few times. We’re going to continue that process in more detail in this chapter. Keep in mind that writing research questions is an iterative process, with revisions happening week after week until you are ready to start your project.
Empirical vs. ethical questions
When it comes to research questions, social science is best equipped to answer empirical questions —those that can be answered by real experience in the real world—as opposed to ethical questions —questions about which people have moral opinions and that may not be answerable in reference to the real world. While social workers have explicit ethical obligations (e.g., service, social justice), research projects ask empirical questions to help actualize and support the work of upholding those ethical principles.

In order to help you better understand the difference between ethical and empirical questions, let’s consider a topic about which people have moral opinions. How about SpongeBob SquarePants? [1] In early 2005, members of the conservative Christian group Focus on the Family (2005) [2] denounced this seemingly innocuous cartoon character as “morally offensive” because they perceived his character to be one that promotes a “pro-gay agenda.” Focus on the Family supported their claim that SpongeBob is immoral by citing his appearance in a children’s video designed to promote tolerance of all family forms (BBC News, 2005). [3] They also cited SpongeBob’s regular hand-holding with his male sidekick Patrick as further evidence of his immorality.
So, can we now conclude that SpongeBob SquarePants is immoral? Not so fast. While your mother or a newspaper or television reporter may provide an answer, a social science researcher cannot. Questions of morality are ethical, not empirical. Of course, this doesn’t mean that social science researchers cannot study opinions about or social meanings surrounding SpongeBob SquarePants (Carter, 2010). [4] We study humans after all, and as you will discover in the following chapters of this textbook, we are trained to utilize a variety of scientific data-collection techniques to understand patterns of human beliefs and behaviors. Using these techniques, we could find out how many people in the United States find SpongeBob morally reprehensible, but we could never learn, empirically, whether SpongeBob is in fact morally reprehensible.
Let’s consider an example from a recent MSW research class I taught. A student group wanted to research the penalties for sexual assault. Their original research question was: “How can prison sentences for sexual assault be so much lower than the penalty for drug possession?” Outside of the research context, that is a darn good question! It speaks to how the War on Drugs and the patriarchy have distorted the criminal justice system towards policing of drug crimes over gender-based violence.
Unfortunately, it is an ethical question, not an empirical one. To answer that question, you would have to draw on philosophy and morality, answering what it is about human nature and society that allows such unjust outcomes. However, you could not answer that question by gathering data about people in the real world. If I asked people that question, they would likely give me their opinions about drugs, gender-based violence, and the criminal justice system. But I wouldn’t get the real answer about why our society tolerates such an imbalance in punishment.
As the students worked on the project through the semester, they continued to focus on the topic of sexual assault in the criminal justice system. Their research question became more empirical because they read more empirical articles about their topic. One option that they considered was to evaluate intervention programs for perpetrators of sexual assault to see if they reduced the likelihood of committing sexual assault again. Another option they considered was seeing if counties or states with higher than average jail sentences for sexual assault perpetrators had lower rates of re-offense for sexual assault. These projects addressed the ethical question of punishing perpetrators of sexual violence but did so in a way that gathered and analyzed empirical real-world data. Our job as social work researchers is to gather social facts about social work issues, not to judge or determine morality.
Key Takeaways
- Empirical questions are distinct from ethical questions.
- There are usually a number of ethical questions and a number of empirical questions that could be asked about any single topic.
- While social workers may research topics about which people have moral opinions, a researcher’s job is to gather and analyze empirical data.
- Take a look at your working question. Make sure you have an empirical question, not an ethical one. To perform this check, describe how you could find an answer to your question by conducting a study, like a survey or focus group, with real people.
9.2 Characteristics of a good research question
- Identify and explain the key features of a good research question
- Explain why it is important for social workers to be focused and clear with the language they use in their research questions
Now that you’ve made sure your working question is empirical, you need to revise that working question into a formal research question. So, what makes a good research question? First, it is generally written in the form of a question. To say that your research question is “the opioid epidemic” or “animal assisted therapy” or “oppression” would not be correct. You need to frame your topic as a question, not a statement. A good research question is also one that is well-focused. A well-focused question helps you tune out irrelevant information and not try to answer everything about the world all at once. You could be the most eloquent writer in your class, or even in the world, but if the research question about which you are writing is unclear, your work will ultimately lack direction.
In addition to being written in the form of a question and being well-focused, a good research question is one that cannot be answered with a simple yes or no. For example, if your interest is in gender norms, you could ask, “Does gender affect a person’s performance of household tasks?” but you will have nothing left to say once you discover your yes or no answer. Instead, why not ask, about the relationship between gender and household tasks. Alternatively, maybe we are interested in how or to what extent gender affects a person’s contributions to housework in a marriage? By tweaking your question in this small way, you suddenly have a much more fascinating question and more to say as you attempt to answer it.
A good research question should also have more than one plausible answer. In the example above, the student who studied the relationship between gender and household tasks had a specific interest in the impact of gender, but she also knew that preferences might be impacted by other factors. For example, she knew from her own experience that her more traditional and socially conservative friends were more likely to see household tasks as part of the female domain, and were less likely to expect their male partners to contribute to those tasks. Thinking through the possible relationships between gender, culture, and household tasks led that student to realize that there were many plausible answers to her questions about how gender affects a person’s contribution to household tasks. Because gender doesn’t exist in a vacuum, she wisely felt that she needed to consider other characteristics that work together with gender to shape people’s behaviors, likes, and dislikes. By doing this, the student considered the third feature of a good research question–she thought about relationships between several concepts. While she began with an interest in a single concept—household tasks—by asking herself what other concepts (such as gender or political orientation) might be related to her original interest, she was able to form a question that considered the relationships among those concepts.
This student had one final component to consider. Social work research questions must contain a target population. Her study would be very different if she were to conduct it on older adults or immigrants who just arrived in a new country. The target population is the group of people whose needs your study addresses. Maybe the student noticed issues with household tasks as part of her social work practice with first-generation immigrants, and so she made it her target population. Maybe she wants to address the needs of another community. Whatever the case, the target population should be chosen while keeping in mind social work’s responsibility to work on behalf of marginalized and oppressed groups.
In sum, a good research question generally has the following features:
- It is written in the form of a question
- It is clearly written
- It cannot be answered with “yes” or “no”
- It has more than one plausible answer
- It considers relationships among multiple variables
- It is specific and clear about the concepts it addresses
- It includes a target population
- A poorly focused research question can lead to the demise of an otherwise well-executed study.
- Research questions should be clearly worded, consider relationships between multiple variables, have more than one plausible answer, and address the needs of a target population.
Okay, it’s time to write out your first draft of a research question.
- Once you’ve done so, take a look at the checklist in this chapter and see if your research question meets the criteria to be a good one.
Brainstorm whether your research question might be better suited to quantitative or qualitative methods.
- Describe why your question fits better with quantitative or qualitative methods.
- Provide an alternative research question that fits with the other type of research method.
9.3 Quantitative research questions
- Describe how research questions for exploratory, descriptive, and explanatory quantitative questions differ and how to phrase them
- Identify the differences between and provide examples of strong and weak explanatory research questions
Quantitative descriptive questions
The type of research you are conducting will impact the research question that you ask. Probably the easiest questions to think of are quantitative descriptive questions. For example, “What is the average student debt load of MSW students?” is a descriptive question—and an important one. We aren’t trying to build a causal relationship here. We’re simply trying to describe how much debt MSW students carry. Quantitative descriptive questions like this one are helpful in social work practice as part of community scans, in which human service agencies survey the various needs of the community they serve. If the scan reveals that the community requires more services related to housing, child care, or day treatment for people with disabilities, a nonprofit office can use the community scan to create new programs that meet a defined community need.
Quantitative descriptive questions will often ask for percentage, count the number of instances of a phenomenon, or determine an average. Descriptive questions may only include one variable, such as ours about student debt load, or they may include multiple variables. Because these are descriptive questions, our purpose is not to investigate causal relationships between variables. To do that, we need to use a quantitative explanatory question.

Quantitative explanatory questions
Most studies you read in the academic literature will be quantitative and explanatory. Why is that? If you recall from Chapter 2 , explanatory research tries to build nomothetic causal relationships. They are generalizable across space and time, so they are applicable to a wide audience. The editorial board of a journal wants to make sure their content will be useful to as many people as possible, so it’s not surprising that quantitative research dominates the academic literature.
Structurally, quantitative explanatory questions must contain an independent variable and dependent variable. Questions should ask about the relationship between these variables. The standard format I was taught in graduate school for an explanatory quantitative research question is: “What is the relationship between [independent variable] and [dependent variable] for [target population]?” You should play with the wording for your research question, revising that standard format to match what you really want to know about your topic.
Let’s take a look at a few more examples of possible research questions and consider the relative strengths and weaknesses of each. Table 9.1 does just that. While reading the table, keep in mind that I have only noted what I view to be the most relevant strengths and weaknesses of each question. Certainly each question may have additional strengths and weaknesses not noted in the table. Each of these questions is drawn from student projects in my research methods classes and reflects the work of many students on their research question over many weeks.
Making it more specific
A good research question should also be specific and clear about the concepts it addresses. A student investigating gender and household tasks knows what they mean by “household tasks.” You likely also have an impression of what “household tasks” means. But are your definition and the student’s definition the same? A participant in their study may think that managing finances and performing home maintenance are household tasks, but the researcher may be interested in other tasks like childcare or cleaning. The only way to ensure your study stays focused and clear is to be specific about what you mean by a concept. The student in our example could pick a specific household task that was interesting to them or that the literature indicated was important—for example, childcare. Or, the student could have a broader view of household tasks, one that encompasses childcare, food preparation, financial management, home repair, and care for relatives. Any option is probably okay, as long as the researcher is clear on what they mean by “household tasks.” Clarifying these distinctions is important as we look ahead to specifying how your variables will be measured in Chapter 11 .
Table 9.2 contains some “watch words” that indicate you may need to be more specific about the concepts in your research question.
It can be challenging to be this specific in social work research, particularly when you are just starting out your project and still reading the literature. If you’ve only read one or two articles on your topic, it can be hard to know what you are interested in studying. Broad questions like “What are the causes of chronic homelessness, and what can be done to prevent it?” are common at the beginning stages of a research project as working questions. However, moving from working questions to research questions in your research proposal requires that you examine the literature on the topic and refine your question over time to be more specific and clear. Perhaps you want to study the effect of a specific anti-homelessness program that you found in the literature. Maybe there is a particular model to fighting homelessness, like Housing First or transitional housing, that you want to investigate further. You may want to focus on a potential cause of homelessness such as LGBTQ+ discrimination that you find interesting or relevant to your practice. As you can see, the possibilities for making your question more specific are almost infinite.
Quantitative exploratory questions
In exploratory research, the researcher doesn’t quite know the lay of the land yet. If someone is proposing to conduct an exploratory quantitative project, the watch words highlighted in Table 9.2 are not problematic at all. In fact, questions such as “What factors influence the removal of children in child welfare cases?” are good because they will explore a variety of factors or causes. In this question, the independent variable is less clearly written, but the dependent variable, family preservation outcomes, is quite clearly written. The inverse can also be true. If we were to ask, “What outcomes are associated with family preservation services in child welfare?”, we would have a clear independent variable, family preservation services, but an unclear dependent variable, outcomes. Because we are only conducting exploratory research on a topic, we may not have an idea of what concepts may comprise our “outcomes” or “factors.” Only after interacting with our participants will we be able to understand which concepts are important.
Remember that exploratory research is appropriate only when the researcher does not know much about topic because there is very little scholarly research. In our examples above, there is extensive literature on the outcomes in family reunification programs and risk factors for child removal in child welfare. Make sure you’ve done a thorough literature review to ensure there is little relevant research to guide you towards a more explanatory question.
- Descriptive quantitative research questions are helpful for community scans but cannot investigate causal relationships between variables.
- Explanatory quantitative research questions must include an independent and dependent variable.
- Exploratory quantitative research questions should only be considered when there is very little previous research on your topic.
- Identify the type of research you are engaged in (descriptive, explanatory, or exploratory).
- Create a quantitative research question for your project that matches with the type of research you are engaged in.
Preferably, you should be creating an explanatory research question for quantitative research.
9.4 Qualitative research questions
- List the key terms associated with qualitative research questions
- Distinguish between qualitative and quantitative research questions
Qualitative research questions differ from quantitative research questions. Because qualitative research questions seek to explore or describe phenomena, not provide a neat nomothetic explanation, they are often more general and openly worded. They may include only one concept, though many include more than one. Instead of asking how one variable causes changes in another, we are instead trying to understand the experiences , understandings , and meanings that people have about the concepts in our research question. These keywords often make an appearance in qualitative research questions.
Let’s work through an example from our last section. In Table 9.1, a student asked, “What is the relationship between sexual orientation or gender identity and homelessness for late adolescents in foster care?” In this question, it is pretty clear that the student believes that adolescents in foster care who identify as LGBTQ+ may be at greater risk for homelessness. This is a nomothetic causal relationship—LGBTQ+ status causes changes in homelessness.
However, what if the student were less interested in predicting homelessness based on LGBTQ+ status and more interested in understanding the stories of foster care youth who identify as LGBTQ+ and may be at risk for homelessness? In that case, the researcher would be building an idiographic causal explanation . The youths whom the researcher interviews may share stories of how their foster families, caseworkers, and others treated them. They may share stories about how they thought of their own sexuality or gender identity and how it changed over time. They may have different ideas about what it means to transition out of foster care.

Because qualitative questions usually center on idiographic causal relationships, they look different than quantitative questions. Table 9.3 below takes the final research questions from Table 9.1 and adapts them for qualitative research. The guidelines for research questions previously described in this chapter still apply, but there are some new elements to qualitative research questions that are not present in quantitative questions.
- Qualitative research questions often ask about lived experience, personal experience, understanding, meaning, and stories.
- Qualitative research questions may be more general and less specific.
- Qualitative research questions may also contain only one variable, rather than asking about relationships between multiple variables.
Qualitative research questions have one final feature that distinguishes them from quantitative research questions: they can change over the course of a study. Qualitative research is a reflexive process, one in which the researcher adapts their approach based on what participants say and do. The researcher must constantly evaluate whether their question is important and relevant to the participants. As the researcher gains information from participants, it is normal for the focus of the inquiry to shift.
For example, a qualitative researcher may want to study how a new truancy rule impacts youth at risk of expulsion. However, after interviewing some of the youth in their community, a researcher might find that the rule is actually irrelevant to their behavior and thoughts. Instead, their participants will direct the discussion to their frustration with the school administrators or the lack of job opportunities in the area. This is a natural part of qualitative research, and it is normal for research questions and hypothesis to evolve based on information gleaned from participants.
However, this reflexivity and openness unacceptable in quantitative research for good reasons. Researchers using quantitative methods are testing a hypothesis, and if they could revise that hypothesis to match what they found, they could never be wrong! Indeed, an important component of open science and reproducability is the preregistration of a researcher’s hypotheses and data analysis plan in a central repository that can be verified and replicated by reviewers and other researchers. This interactive graphic from 538 shows how an unscrupulous research could come up with a hypothesis and theoretical explanation after collecting data by hunting for a combination of factors that results in a statistically significant relationship. This is an excellent example of how the positivist assumptions behind quantitative research and intepretivist assumptions behind qualitative research result in different approaches to social science.
- Qualitative research questions often contain words or phrases like “lived experience,” “personal experience,” “understanding,” “meaning,” and “stories.”
- Qualitative research questions can change and evolve over the course of the study.
- Using the guidance in this chapter, write a qualitative research question. You may want to use some of the keywords mentioned above.
9.5 Evaluating and updating your research questions
- Evaluate the feasibility and importance of your research questions
- Begin to match your research questions to specific designs that determine what the participants in your study will do
Feasibility and importance
As you are getting ready to finalize your research question and move into designing your research study, it is important to check whether your research question is feasible for you to answer and what importance your results will have in the community, among your participants, and in the scientific literature
Key questions to consider when evaluating your question’s feasibility include:
- Do you have access to the data you need?
- Will you be able to get consent from stakeholders, gatekeepers, and others?
- Does your project pose risk to individuals through direct harm, dual relationships, or breaches in confidentiality? (see Chapter 6 for more ethical considerations)
- Are you competent enough to complete the study?
- Do you have the resources and time needed to carry out the project?
Key questions to consider when evaluating the importance of your question include:
- Can we answer your research question simply by looking at the literature on your topic?
- How does your question add something new to the scholarly literature? (raises a new issue, addresses a controversy, studies a new population, etc.)
- How will your target population benefit, once you answer your research question?
- How will the community, social work practice, and the broader social world benefit, once you answer your research question?
- Using the questions above, check whether you think your project is feasible for you to complete, given the constrains that student projects face.
- Realistically, explore the potential impact of your project on the community and in the scientific literature. Make sure your question cannot be answered by simply reading more about your topic.
Matching your research question and study design
This chapter described how to create a good quantitative and qualitative research question. In Parts 3 and 4 of this textbook, we will detail some of the basic designs like surveys and interviews that social scientists use to answer their research questions. But which design should you choose?
As with most things, it all depends on your research question. If your research question involves, for example, testing a new intervention, you will likely want to use an experimental design. On the other hand, if you want to know the lived experience of people in a public housing building, you probably want to use an interview or focus group design.
We will learn more about each one of these designs in the remainder of this textbook. We will also learn about using data that already exists, studying an individual client inside clinical practice, and evaluating programs, which are other examples of designs. Below is a list of designs we will cover in this textbook:
- Surveys: online, phone, mail, in-person
- Experiments: classic, pre-experiments, quasi-experiments
- Interviews: in-person or via phone or videoconference
- Focus groups: in-person or via videoconference
- Content analysis of existing data
- Secondary data analysis of another researcher’s data
- Program evaluation
The design of your research study determines what you and your participants will do. In an experiment, for example, the researcher will introduce a stimulus or treatment to participants and measure their responses. In contrast, a content analysis may not have participants at all, and the researcher may simply read the marketing materials for a corporation or look at a politician’s speeches to conduct the data analysis for the study.
I imagine that a content analysis probably seems easier to accomplish than an experiment. However, as a researcher, you have to choose a research design that makes sense for your question and that is feasible to complete with the resources you have. All research projects require some resources to accomplish. Make sure your design is one you can carry out with the resources (time, money, staff, etc.) that you have.
There are so many different designs that exist in the social science literature that it would be impossible to include them all in this textbook. The purpose of the subsequent chapters is to help you understand the basic designs upon which these more advanced designs are built. As you learn more about research design, you will likely find yourself revising your research question to make sure it fits with the design. At the same time, your research question as it exists now should influence the design you end up choosing. There is no set order in which these should happen. Instead, your research project should be guided by whether you can feasibly carry it out and contribute new and important knowledge to the world.
- Research questions must be feasible and important.
- Research questions must match study design.
- Based on what you know about designs like surveys, experiments, and interviews, describe how you might use one of them to answer your research question.
- You may want to refer back to Chapter 2 which discusses how to get raw data about your topic and the common designs used in student research projects.
- Not familiar with SpongeBob SquarePants? You can learn more about him on Nickelodeon’s site dedicated to all things SpongeBob: http://www.nick.com/spongebob-squarepants/ ↵
- Focus on the Family. (2005, January 26). Focus on SpongeBob. Christianity Today . Retrieved from http://www.christianitytoday.com/ct/2005/januaryweb-only/34.0c.html ↵
- BBC News. (2005, January 20). US right attacks SpongeBob video. Retrieved from: http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/americas/4190699.stm ↵
- In fact, an MA thesis examines representations of gender and relationships in the cartoon: Carter, A. C. (2010). Constructing gender and relationships in “SpongeBob SquarePants”: Who lives in a pineapple under the sea . MA thesis, Department of Communication, University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL. ↵
research questions that can be answered by systematically observing the real world
unsuitable research questions which are not answerable by systematic observation of the real world but instead rely on moral or philosophical opinions
the group of people whose needs your study addresses
attempts to explain or describe your phenomenon exhaustively, based on the subjective understandings of your participants
"Assuming that the null hypothesis is true and the study is repeated an infinite number times by drawing random samples from the same populations(s), less than 5% of these results will be more extreme than the current result" (Cassidy et al., 2019, p. 233).
whether you can practically and ethically complete the research project you propose
the impact your study will have on participants, communities, scientific knowledge, and social justice
Graduate research methods in social work Copyright © 2021 by Matthew DeCarlo, Cory Cummings, Kate Agnelli is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg
- v.24(1); Jan-Mar 2019
Formulation of Research Question – Stepwise Approach
Simmi k. ratan.
Department of Pediatric Surgery, Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, India
1 Department of Community Medicine, North Delhi Municipal Corporation Medical College, New Delhi, India
2 Department of Pediatric Surgery, Batra Hospital and Research Centre, New Delhi, India
Formulation of research question (RQ) is an essentiality before starting any research. It aims to explore an existing uncertainty in an area of concern and points to a need for deliberate investigation. It is, therefore, pertinent to formulate a good RQ. The present paper aims to discuss the process of formulation of RQ with stepwise approach. The characteristics of good RQ are expressed by acronym “FINERMAPS” expanded as feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, relevant, manageable, appropriate, potential value, publishability, and systematic. A RQ can address different formats depending on the aspect to be evaluated. Based on this, there can be different types of RQ such as based on the existence of the phenomenon, description and classification, composition, relationship, comparative, and causality. To develop a RQ, one needs to begin by identifying the subject of interest and then do preliminary research on that subject. The researcher then defines what still needs to be known in that particular subject and assesses the implied questions. After narrowing the focus and scope of the research subject, researcher frames a RQ and then evaluates it. Thus, conception to formulation of RQ is very systematic process and has to be performed meticulously as research guided by such question can have wider impact in the field of social and health research by leading to formulation of policies for the benefit of larger population.
I NTRODUCTION
A good research question (RQ) forms backbone of a good research, which in turn is vital in unraveling mysteries of nature and giving insight into a problem.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ] RQ identifies the problem to be studied and guides to the methodology. It leads to building up of an appropriate hypothesis (Hs). Hence, RQ aims to explore an existing uncertainty in an area of concern and points to a need for deliberate investigation. A good RQ helps support a focused arguable thesis and construction of a logical argument. Hence, formulation of a good RQ is undoubtedly one of the first critical steps in the research process, especially in the field of social and health research, where the systematic generation of knowledge that can be used to promote, restore, maintain, and/or protect health of individuals and populations.[ 1 , 3 , 4 ] Basically, the research can be classified as action, applied, basic, clinical, empirical, administrative, theoretical, or qualitative or quantitative research, depending on its purpose.[ 2 ]
Research plays an important role in developing clinical practices and instituting new health policies. Hence, there is a need for a logical scientific approach as research has an important goal of generating new claims.[ 1 ]
C HARACTERISTICS OF G OOD R ESEARCH Q UESTION
“The most successful research topics are narrowly focused and carefully defined but are important parts of a broad-ranging, complex problem.”
A good RQ is an asset as it:
- Details the problem statement
- Further describes and refines the issue under study
- Adds focus to the problem statement
- Guides data collection and analysis
- Sets context of research.
Hence, while writing RQ, it is important to see if it is relevant to the existing time frame and conditions. For example, the impact of “odd-even” vehicle formula in decreasing the level of air particulate pollution in various districts of Delhi.
A good research is represented by acronym FINERMAPS[ 5 ]
Interesting.
- Appropriate
- Potential value and publishability
- Systematic.
Feasibility means that it is within the ability of the investigator to carry out. It should be backed by an appropriate number of subjects and methodology as well as time and funds to reach the conclusions. One needs to be realistic about the scope and scale of the project. One has to have access to the people, gadgets, documents, statistics, etc. One should be able to relate the concepts of the RQ to the observations, phenomena, indicators, or variables that one can access. One should be clear that the collection of data and the proceedings of project can be completed within the limited time and resources available to the investigator. Sometimes, a RQ appears feasible, but when fieldwork or study gets started, it proves otherwise. In this situation, it is important to write up the problems honestly and to reflect on what has been learned. One should try to discuss with more experienced colleagues or the supervisor so as to develop a contingency plan to anticipate possible problems while working on a RQ and find possible solutions in such situations.
This is essential that one has a real grounded interest in one's RQ and one can explore this and back it up with academic and intellectual debate. This interest will motivate one to keep going with RQ.
The question should not simply copy questions investigated by other workers but should have scope to be investigated. It may aim at confirming or refuting the already established findings, establish new facts, or find new aspects of the established facts. It should show imagination of the researcher. Above all, the question has to be simple and clear. The complexity of a question can frequently hide unclear thoughts and lead to a confused research process. A very elaborate RQ, or a question which is not differentiated into different parts, may hide concepts that are contradictory or not relevant. This needs to be clear and thought-through. Having one key question with several subcomponents will guide your research.
This is the foremost requirement of any RQ and is mandatory to get clearance from appropriate authorities before stating research on the question. Further, the RQ should be such that it minimizes the risk of harm to the participants in the research, protect the privacy and maintain their confidentiality, and provide the participants right to withdraw from research. It should also guide in avoiding deceptive practices in research.
The question should of academic and intellectual interest to people in the field you have chosen to study. The question preferably should arise from issues raised in the current situation, literature, or in practice. It should establish a clear purpose for the research in relation to the chosen field. For example, filling a gap in knowledge, analyzing academic assumptions or professional practice, monitoring a development in practice, comparing different approaches, or testing theories within a specific population are some of the relevant RQs.
Manageable (M): It has the similar essence as of feasibility but mainly means that the following research can be managed by the researcher.
Appropriate (A): RQ should be appropriate logically and scientifically for the community and institution.
Potential value and publishability (P): The study can make significant health impact in clinical and community practices. Therefore, research should aim for significant economic impact to reduce unnecessary or excessive costs. Furthermore, the proposed study should exist within a clinical, consumer, or policy-making context that is amenable to evidence-based change. Above all, a good RQ must address a topic that has clear implications for resolving important dilemmas in health and health-care decisions made by one or more stakeholder groups.
Systematic (S): Research is structured with specified steps to be taken in a specified sequence in accordance with the well-defined set of rules though it does not rule out creative thinking.
Example of RQ: Would the topical skin application of oil as a skin barrier reduces hypothermia in preterm infants? This question fulfills the criteria of a good RQ, that is, feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, and relevant.
Types of research question
A RQ can address different formats depending on the aspect to be evaluated.[ 6 ] For example:
- Existence: This is designed to uphold the existence of a particular phenomenon or to rule out rival explanation, for example, can neonates perceive pain?
- Description and classification: This type of question encompasses statement of uniqueness, for example, what are characteristics and types of neuropathic bladders?
- Composition: It calls for breakdown of whole into components, for example, what are stages of reflux nephropathy?
- Relationship: Evaluate relation between variables, for example, association between tumor rupture and recurrence rates in Wilm's tumor
- Descriptive—comparative: Expected that researcher will ensure that all is same between groups except issue in question, for example, Are germ cell tumors occurring in gonads more aggressive than those occurring in extragonadal sites?
- Causality: Does deletion of p53 leads to worse outcome in patients with neuroblastoma?
- Causality—comparative: Such questions frequently aim to see effect of two rival treatments, for example, does adding surgical resection improves survival rate outcome in children with neuroblastoma than with chemotherapy alone?
- Causality–Comparative interactions: Does immunotherapy leads to better survival outcome in neuroblastoma Stage IV S than with chemotherapy in the setting of adverse genetic profile than without it? (Does X cause more changes in Y than those caused by Z under certain condition and not under other conditions).
How to develop a research question
- Begin by identifying a broader subject of interest that lends itself to investigate, for example, hormone levels among hypospadias
- Do preliminary research on the general topic to find out what research has already been done and what literature already exists.[ 7 ] Therefore, one should begin with “information gaps” (What do you already know about the problem? For example, studies with results on testosterone levels among hypospadias
- What do you still need to know? (e.g., levels of other reproductive hormones among hypospadias)
- What are the implied questions: The need to know about a problem will lead to few implied questions. Each general question should lead to more specific questions (e.g., how hormone levels differ among isolated hypospadias with respect to that in normal population)
- Narrow the scope and focus of research (e.g., assessment of reproductive hormone levels among isolated hypospadias and hypospadias those with associated anomalies)
- Is RQ clear? With so much research available on any given topic, RQs must be as clear as possible in order to be effective in helping the writer direct his or her research
- Is the RQ focused? RQs must be specific enough to be well covered in the space available
- Is the RQ complex? RQs should not be answerable with a simple “yes” or “no” or by easily found facts. They should, instead, require both research and analysis on the part of the writer
- Is the RQ one that is of interest to the researcher and potentially useful to others? Is it a new issue or problem that needs to be solved or is it attempting to shed light on previously researched topic
- Is the RQ researchable? Consider the available time frame and the required resources. Is the methodology to conduct the research feasible?
- Is the RQ measurable and will the process produce data that can be supported or contradicted?
- Is the RQ too broad or too narrow?
- Create Hs: After formulating RQ, think where research is likely to be progressing? What kind of argument is likely to be made/supported? What would it mean if the research disputed the planned argument? At this step, one can well be on the way to have a focus for the research and construction of a thesis. Hs consists of more specific predictions about the nature and direction of the relationship between two variables. It is a predictive statement about the outcome of the research, dictate the method, and design of the research[ 1 ]
- Understand implications of your research: This is important for application: whether one achieves to fill gap in knowledge and how the results of the research have practical implications, for example, to develop health policies or improve educational policies.[ 1 , 8 ]
Brainstorm/Concept map for formulating research question
- First, identify what types of studies have been done in the past?
- Is there a unique area that is yet to be investigated or is there a particular question that may be worth replicating?
- Begin to narrow the topic by asking open-ended “how” and “why” questions
- Evaluate the question
- Develop a Hypothesis (Hs)
- Write down the RQ.
Writing down the research question
- State the question in your own words
- Write down the RQ as completely as possible.
For example, Evaluation of reproductive hormonal profile in children presenting with isolated hypospadias)
- Divide your question into concepts. Narrow to two or three concepts (reproductive hormonal profile, isolated hypospadias, compare with normal/not isolated hypospadias–implied)
- Specify the population to be studied (children with isolated hypospadias)
- Refer to the exposure or intervention to be investigated, if any
- Reflect the outcome of interest (hormonal profile).
Another example of a research question
Would the topical skin application of oil as a skin barrier reduces hypothermia in preterm infants? Apart from fulfilling the criteria of a good RQ, that is, feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, and relevant, it also details about the intervention done (topical skin application of oil), rationale of intervention (as a skin barrier), population to be studied (preterm infants), and outcome (reduces hypothermia).
Other important points to be heeded to while framing research question
- Make reference to a population when a relationship is expected among a certain type of subjects
- RQs and Hs should be made as specific as possible
- Avoid words or terms that do not add to the meaning of RQs and Hs
- Stick to what will be studied, not implications
- Name the variables in the order in which they occur/will be measured
- Avoid the words significant/”prove”
- Avoid using two different terms to refer to the same variable.
Some of the other problems and their possible solutions have been discussed in Table 1 .
Potential problems and solutions while making research question

G OING B EYOND F ORMULATION OF R ESEARCH Q UESTION–THE P ATH A HEAD
Once RQ is formulated, a Hs can be developed. Hs means transformation of a RQ into an operational analog.[ 1 ] It means a statement as to what prediction one makes about the phenomenon to be examined.[ 4 ] More often, for case–control trial, null Hs is generated which is later accepted or refuted.
A strong Hs should have following characteristics:
- Give insight into a RQ
- Are testable and measurable by the proposed experiments
- Have logical basis
- Follows the most likely outcome, not the exceptional outcome.
E XAMPLES OF R ESEARCH Q UESTION AND H YPOTHESIS
Research question-1.
- Does reduced gap between the two segments of the esophagus in patients of esophageal atresia reduces the mortality and morbidity of such patients?
Hypothesis-1
- Reduced gap between the two segments of the esophagus in patients of esophageal atresia reduces the mortality and morbidity of such patients
- In pediatric patients with esophageal atresia, gap of <2 cm between two segments of the esophagus and proper mobilization of proximal pouch reduces the morbidity and mortality among such patients.
Research question-2
- Does application of mitomycin C improves the outcome in patient of corrosive esophageal strictures?
Hypothesis-2
In patients aged 2–9 years with corrosive esophageal strictures, 34 applications of mitomycin C in dosage of 0.4 mg/ml for 5 min over a period of 6 months improve the outcome in terms of symptomatic and radiological relief. Some other examples of good and bad RQs have been shown in Table 2 .
Examples of few bad (left-hand side column) and few good (right-hand side) research questions

R ESEARCH Q UESTION AND S TUDY D ESIGN
RQ determines study design, for example, the question aimed to find the incidence of a disease in population will lead to conducting a survey; to find risk factors for a disease will need case–control study or a cohort study. RQ may also culminate into clinical trial.[ 9 , 10 ] For example, effect of administration of folic acid tablet in the perinatal period in decreasing incidence of neural tube defect. Accordingly, Hs is framed.
Appropriate statistical calculations are instituted to generate sample size. The subject inclusion, exclusion criteria and time frame of research are carefully defined. The detailed subject information sheet and pro forma are carefully defined. Moreover, research is set off few examples of research methodology guided by RQ:
- Incidence of anorectal malformations among adolescent females (hospital-based survey)
- Risk factors for the development of spontaneous pneumoperitoneum in pediatric patients (case–control design and cohort study)
- Effect of technique of extramucosal ureteric reimplantation without the creation of submucosal tunnel for the preservation of upper tract in bladder exstrophy (clinical trial).
The results of the research are then be available for wider applications for health and social life
C ONCLUSION
A good RQ needs thorough literature search and deep insight into the specific area/problem to be investigated. A RQ has to be focused yet simple. Research guided by such question can have wider impact in the field of social and health research by leading to formulation of policies for the benefit of larger population.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
R EFERENCES

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Research Questions – How to-Guide | Definition & Examples
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Definition: Research Question
The research question states the aim of a paper in form of a question. The purpose of writing the paper is to provide an answer to the research questions No article/paper can cover all aspects of a broad topic.
You must select a more specific aspect that has the potential to yield significant results as part of the topic and then find a connection to your Thesis Statement .
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 What is a Research Question?
- 4 Dos and Don’ts
- 5 Finding the right words
- 6 Sample research questions
- 7 Research question vs. title
- 8 The research question: Where it belongs
- 9 In summary
- 10 References
What is a Research Question?
The research question lies at the heart of every piece of academic writing . The research question determines the sources to be quoted, how to structure the argument, and what a paper aims at.
The research question narrows down the topic and makes sure that the paper has a common thread. Moreover, the research question gives the reader a clear idea of what to expect from the paper.
You cannot start writing without having a research question in mind. It is easiest to think of a research question as a Wh-question . Finding an answer to the research question you formulate is your personal contribution. You must state your research question right at the beginning, as part of the introduction.
Also useful: What is plagiarism?
How do you write a research question?
- Choose an interesting research topic . Something you’re interested in.
- Conduct some exploratory research.
- Begin formulating questions around areas of your topic that you think need more research.
- Conduct further research and narrow in on a few of your preliminary research questions.
- Pick your final research question and refine it.
What makes a good research question?
It’s important that your research question is focused on one single research topic , or a few interdependent topics. If your research question is too vague, then you will find it difficult to stay on topic whilst writing. It’s a good idea to focus on an unresolved problem- a problem that you never found a solution/many solutions for in your research. Your goal will be to resolve this problem in your paper.
How is the research question different from the hypothesis?
The hypothesis states your educated prediction regarding what you will find during your research. A hypothesis is used mostly in experimental or correlational research. It is your preliminary answer to your research question.
On the other hand, your research question states the aim of your paper and it is connected to your thesis statement . Throughout your paper, the hypothesis will be supported or contradicted with the collection and analysis of data.
What are the types of research questions?
There are many different types of research questions. However, the most common types are:
- Descriptive questions
- Relationship-based questions (explanation)
- criticism/improvement-based questions
Already refined your research question? Then you’re ready to begin writing your research proposal . It’s a long process, but stick with it and your paper will be done before you know it!
How do I write a research question for a thesis?
The process for writing a research question for a bachelor’s thesis or a master’s thesis stays the same. You begin with your inital research before narrowing in further on a few specific topics. The only difference is that your thesis will be significantly larger than a mid-semester paper so you will need more time to conduct some very intensive research before you begin writing.
The aim of a research question
“The research question is also the question why you should delight the world with another pile of printed paper” (cf. Winter 2004: 28).
A bachelor’s or master’s thesis is not something you write just for the sake of writing something. The aim is to create new scientific knowledge or to test and newly interpret existing theories. To achieve this aim, a thorough literature research is necessary to find an under-researched topic having new aspects you can focus on – a gap in scientific literature, so to speak.
To be even more precise: you can pose a very specific research question that nobody has asked before.
Esselborn-Krumbiegel says it is essential to understand what is required of every academic piece of writing, namely finding an answer to an open question (cf. 2002: 60). First, you have to find a topic and then formulate a research question derived from said topic . The topic as such will only be dealt with in terms of your specific research question (cf. Franck & Stary 2009: 167).
General example for creating a research question
The following diagram depicts how to proceed from a broad topic to a precise research question.
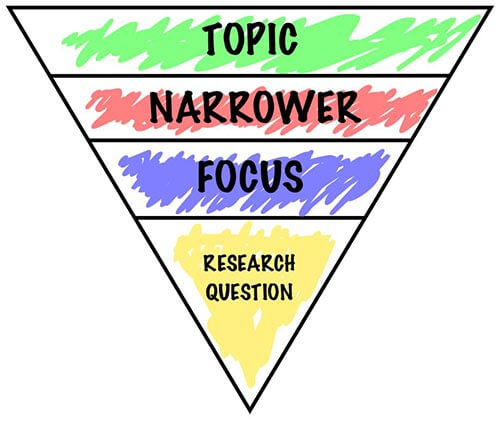
Concrete example using the topic of media violence
The following example shows how to derive a detailed research question from the topic “Media Violence”:
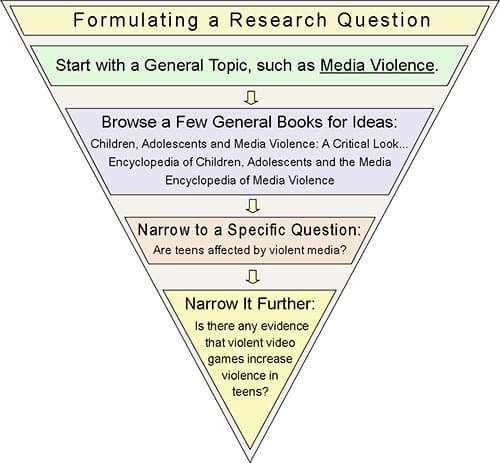
Example: How the topic, problem, research question, and aim of the paper are interrelated
Examples: deriving a research question from a topic.
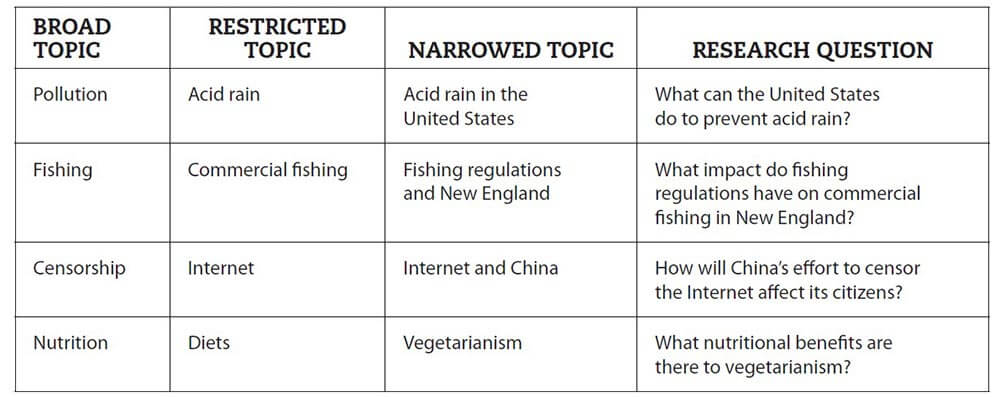
Dos and Don’ts
Take your time when formulating your research question – it will definitely pay off! Be careful not to pose a research question that is ambiguous. People might wonder if you actually know what you want to work on and which research question you are setting out to answer (cf. Kornmeier 2013: 71).
The following list details Dos and Don’ts of writing a good research question to make sure you know what to include and what to avoid when formulating your research question (cf. Karmasin & Ribing 2014: 24; Samac, Prenner & Schwetz 2009: 47).
Examples of good and bad research questions
The Center for Innovation in Research and Teaching (CIRT) suggests how to transform a bad research question into a good research questions using the following examples:
(cf. CIRT, n.d., https://cirt.gcu.edu/research/developmentresources/tutorials/question . Last accessed 19 th Feb 2019)
Finding the right words
The easiest way to formulate a research question is to turn your whole bachelor’s thesis into one question . This will help to define the aim of your bachelor’s thesis (cf. Samac, Prenner & Schwetz 2009: 46). You can make choices concerning the literature, the structure and the content, as well as the study design, only if you have a very clear idea of what you want to write about (cf. Kornmeier 2013: 56).
The research question can also be formulated as an interrogative sentence, e.g. “The question this paper sets out to answer is…” or “This paper deals with the following question:…” (cf. Kruse 2010: 80). A question mark signals to the reader that there is an unresolved problem and your work offers a solution.
A good research question is precise and narrow . Andermann, Drees & Grätz say it is a cardinal error if an author thinks that everything that s/he has read about a topic must go into the paper. In a figurative sense, starting with Adam and Eve and the original sin, as well as trying to reinvent the wheel, are major mistakes for prospective scientists (cf. 2006: 33).
Sample research questions
In addition to developing the main research question, you have to be clear about the connection of your sub-research questions. Moreover, you have to figure out what type of research question you want to deal with. Otherwise, you run the risk of including everything you find out about a term or a statement during your literature research even if the latter play only a minor role in your research question (cf. Bänsch & Alewell 2013: 3-4).
Research question vs. title
(cf. Kruse 2007: 128)
The research question: Where it belongs
The research question determines the contents and the methods used in your bachelor’s and master’s thesis. Therefore, the research question must be introduced at the very beginning of your work. Moreover, the sole purpose of your paper is to answer the research question, so it is essential that the reader understands your research question. So you need to know: How to write an introduction
In your introduction, you should briefly introduce the topic and its relevance. Right after this, you have to pose your research question and highlight how it is part of a larger topic (cf. Oertner, St. John, & Thelen 2014: 31). You can split the research question into sub research questions, which should reflect in the structure of your paper. This means you are answering a bigger research question successively (cf. Karmasin & Ribing 2014: 24; Esselborn-Krumbiegel 2002: 64).
After all, longer papers like a master’s thesis do not consist of one big chapter only. Rather, several chapters building on each other are needed to adequately answer the research question (state of research, methods, empirical data collection, data analysis, etc.). Don’t forget to answer the research question in your thesis statement .
- The research question is central to every bachelor’s and master’s thesis. It determines the content, the structure, and the aim of an academic paper — i.e., finding an answer to the research question.
- The research question is closely related to the topic and the title of the paper. You will never be able to deal with all aspects of a topic. The research question is the narrowed down version that shows which particular aspect you want to focus on in your thesis/paper.
- The research question is best phrased as a Wh-question and must address a problem/an aspect that is new (no other paper has dealt with this issue/looked at this issue from the same angle).
- It is not your task to reinvent the wheel. The research question narrows down the topic and, thus, excludes aspects that are not essential to the research question.
- Answering your research question is your personal contribution to science and represents newly generated knowledge.
- The research question is part of the introduction , right after a brief introduction of the topic.
- There are different types of research questions: descriptive, explanatory, creative, critical/evaluative, and utopic.
- It is important to ensure that a research question is never vague or biased. It pays off to take enough time to formulate a research question properly. Moreover, a research question must be researchable and relevant for the field of study.
Andermann, Ulrich, Martin Drees & Frank Götz. 2006. Wie verfasst man wissenschaftliche Arbeiten? 3 rd Ed. Mannheim: Dudenverlag.
Bänsch, Axel & Dorothea Alewell. 2013. Wissenschaftliches Arbeiten . 11 th Ed. Munich: Oldenbourg Verlag.
CIRT. “Writing a Good Research Question”, in: CIRT. https://cirt.gcu.edu/research/developmentresources/tutorials/question . Last accessed 26 th Mar 2019.
Esselborn-Krumbiegel, Helga. 2002. Von der Idee zum Text – Eine Anleitung zum wissenschaftlichen Schreiben . Paderborn: Ferdinand Schöningh.
Flinn, Chad. “What makes a good research question”, in: Chad Flinn. https://malat-webspace.royalroads.ca/rru0054/what-makes-a-good-research-question/ . Last accessed 26 th Mar 2019.
Franck, Norbert & Joachim Stary. 2009. Die Technik des wissenschaftlichen Arbeitens . 15 th Ed. Paderborn: Ferdinand Schöningh.
Karmasin, Matthias & Rainer Ribing. 2014. Die Gestaltung wissenschaftlicher Arbeiten. 8 th Ed. Vienna: Facultas.
Kruse, Otto. 2007. Keine Angst vor dem leeren Blatt – Ohne Schreibblockaden durchs Studium . 12 th Ed. Frankfurt: Campus.
Kruse, Otto. 2010. Lesen und Schreiben – Der richtige Umgang mit Texten im Studium. Konstanz: UVK Verlagsgesellschaft.
Kornmeier, Martin. 2013. Wissenschaftlich schreiben leicht gemacht – für Bachelor, Master und Dissertation . 6 th Ed. Bern: Haupt.
Lamar Memorial Library. “Creating a Research Question”, in: Lamar Memorial Library. https://library.maryvillecollege.edu/c.php?g=616334&p=4320157 . Last accessed 26 th Mar 2019.
Lewis A. Jackson Library. “Forming a Research Question”, in: Lewis A. Jackson Library. http://indwes.libguides.com/c.php?g=71141&p=458447 . Last accessed 26 th Mar 2019.
Oertner, Monika, Illona St. John & Gabriele Thelen. 2014. Wissenschaftlich Schreiben – Ein Praxisbuch für Schreibtrainer und Studierende . Paderborn: Wilhelm Fink.
Rossig, Wolfram E. & Joachim Prätsch. 2005. Wissenschaftliche Arbeiten . 5 th Ed. Weyhe: PRINT-TEC.
Samac, Klaus, Monika Prenner & Herbert Schwetz. 2009. Die Bachelorarbeit an Universität und Fachhochschule . Vienna: Facultas.
Winter, Wolfgang. 2005. Wissenschaftliche Arbeiten schreiben . 2 nd Ed. Frankfurt: Redline Wirtschaft.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Consider This from NPR

- LISTEN & FOLLOW
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
- Amazon Music
Your support helps make our show possible and unlocks access to our sponsor-free feed.
Is this fictitious civil war closer to reality than we think?
You're reading the Consider This newsletter, which unpacks one major news story each day. Subscribe here to get it delivered to your inbox, and listen to more from the Consider This podcast .

(L-R) Kirsten Dunst, Cailee Spaeny Murray Close/A24 hide caption
(L-R) Kirsten Dunst, Cailee Spaeny
1. A civil war for the silver screen
Civil War, the new A24 film from British director Alex Garland, imagines a scenario that might not seem so far-fetched to some; a contemporary civil war breaking out in the United States.
In this world, the U.S. has split into various factions. The president, played by Nick Offerman – has given himself a third term, and he's hoping to fend off an assault from one of the more powerful groups.
In what might seem like the most unbelievable narrative twist, California and Texas form an alliance to become the "Western Forces" and fight against Offerman's regime. Sure, I guess!

Some independent candidates start their own political parties to ease ballot access
2. how far are we from reality.
NPR movie critic Bob Mondello says the movie doesn't do a lot of explaining to help us understand how the U.S. got to this moment. But he says that makes it stronger.
"What became much more interesting in the moment was what it looks like to transpose things that we've always associated with other countries – the bombed out helicopters and things like that – to place that in a J.C. Penney parking lot."
And while the film has taken heat for little mention of politics, the question of an actual civil war has everything to do with it.
Polling has shown a significant minority thinks a civil war is at least somewhat likely in the next 10 years. So what do the experts say?

Movie Reviews
'civil war' is a doomsday thought experiment — that could have used more thinking, 3. division in the u.s..
Amy Cooter is a director of research at the Center on Terrorism, Extremism, and Counterterrorism at the Middlebury Institute of International Studies. Her work has led her to the question that Garland's movie has put in the minds of both moviegoers and political pundits: Could a second civil war really happen here?
Cooter wants to make one thing clear: "I don't think that civil war is imminent, but I think there are some people who wish we would have one, and wish that they could be effectively culture soldiers to re-enact a civil order that they see as better for them and their families."
In her studies of militias and political extremists, Cooter has observed a movement of groups similar to those who joined in on the January 6th riots who feel disconnected from the current political moment, or perhaps want to return to a previous version of society, that they feel served them better.
And while Cooter doesn't think a civil war will be happening anytime soon, she does say this:
"I think we are at a moment of extreme political division that may get worse before it gets better."
This episode was produced by Marc Rivers. It was edited by Jeanette Woods, Jonaki Mehta and Courtney Dorning. Our executive producer is Sami Yenigun.
- far-right extremism
- political divide
Poll: Election interest hits new low in tight Biden-Trump race
The share of voters who say they have high interest in the 2024 election has hit a nearly 20-year low at this point in a presidential race, according to the latest national NBC News poll , with majorities holding negative views of both President Joe Biden and former President Donald Trump.
The poll also shows Biden trimming Trump’s previous lead to just 2 points in a head-to-head contest, an improvement within the margin of error compared to the previous survey, as Biden bests Trump on the issues of abortion and uniting the country, while Trump is ahead on competency and dealing with inflation.
And it finds inflation and immigration topping the list of most important issues facing the country, as just one-third of voters give Biden credit for an improving economy.
But what also stands out in the survey is how the low voter interest and the independent candidacy of Robert F. Kennedy Jr. could scramble what has been a stable presidential contest with more than six months until Election Day. While Trump holds a 2-point edge over Biden head to head, Biden leads Trump by 2 points in a five-way ballot test including Kennedy and other third-party candidates.
“I don’t think Biden has done much as a president. And if Trump gets elected, I just feel like it’s going to be the same thing as it was before Biden got elected,” said poll respondent Devin Fletcher, 37, of Wayne, Michigan, a Democrat who said he’s still voting for Biden.
“I just don’t feel like I have a candidate that I’m excited to vote for,” Fletcher added.
Another poll respondent from New Jersey, who declined to provide her name and voted for Biden in 2020, said she wouldn’t be voting in November.
“Our candidates are horrible. I have no interest in voting for Biden. He did nothing. And I absolutely will not vote for Trump,” she said.
Democratic pollster Jeff Horwitt of Hart Research Associates, who conducted the survey with Republican pollster Bill McInturff of Public Opinion Strategies, said, “Americans don’t agree on much these days, but nothing unites the country more than voters’ desire to tune this election out.”
The poll was conducted April 12-16, during yet another turbulent time in American politics, including the beginning of Trump’s criminal trial in New York and new attacks and heightened tensions in the Middle East.
According to the poll, 64% of registered voters say they have high levels of interest in November’s election — registering either a “9” or a 10” on a 10-point scale of interest.
That’s lower than what the NBC News poll showed at this time in the 2008 (74%), 2012 (67%), 2016 (69%) and 2020 (77%) presidential contests.
The question dates to the 2008 election cycle. The lowest level of high election interest in the poll during a presidential cycle was in March 2012 — at 59%. But it quickly ticked up in the next survey.
This election cycle, high interest has been both low and relatively flat for months, according to the poll.
McInturff, the Republican pollster, says the high level of interest in the poll has “always been a signal for the level of turnout” for a presidential contest.
“It makes it very hard for us to predict turnout this far in advance of November, but every signal is turnout will be a lower percentage of eligible voters than in 2020,” he said.
By party, the current poll shows 70% of self-identified Republicans saying they have high interest in the coming election, compared with 65% of Democrats who say so.
Independents are at 48%, while only 36% of voters ages 18 to 34 rate themselves as highly interested in the election.
“They just aren’t low interest,” McInturff said of young voters. “They are off-the-charts low.”
NBC News poll: Frequently asked questions
Professional pollsters at a Democratic polling firm (Hart Research Associates) and a Republican firm (Public Opinion Strategies) have worked together to conduct and operate this poll since 1989. (Coldwater Corporation served as the Republican firm from 1989-2004.)
The polling firms employ a call center, where live interviewers speak by cell phone and telephone with a cross section of (usually) 1,000 respondents. The respondents are randomly selected from national lists of households and cell numbers. Respondents are asked for by name, starting with the youngest male adult or female adult in the household.
One of the common questions that critics ask of polls is, "I wasn't interviewed, so why should this poll matter?” By interviewing 1,000 respondents and applying minimal weights based on race, ethnicity, age, gender, education and the 2020 presidential vote, the poll achieves a representative sample of the nation at large – with a margin of error at a 95% confidence level.
NBC News editors and reporters — along with the pollsters at Hart Research and Public Opinion Strategies — all work to formulate the questions to try to capture the news and current events NBC is trying to gauge. Both Hart Research and Public Opinion Strategies work to ensure the language and placement of the questions are as neutral as possible.
Biden trims Trump’s lead
The poll also finds Trump narrowly ahead of Biden by 2 points among registered voters in a head-to-head matchup, 46% to 44% — down from Trump’s 5-point advantage in January, 47% to 42%.
The movement, which is within the poll’s margin of error of plus or minus 3.1 percentage points, is consistent with what other national polls have found in the Trump-Biden race.
Trump’s biggest advantages are among men (53% to 37%), white voters (54% to 37%) and white voters without college degrees (65% to 25%).
Biden’s top advantages are among Black voters (71% to 13%), women (50% to 39%) and Latinos (49% to 39%).
The poll shows the two candidates are essentially tied among independents (Biden 36%, Trump 34%) and voters ages 18-34 (Biden 44%, Trump 43%). One of the big polling mysteries this cycle is whether young voters have defected from Biden (as the NBC News poll has found over multiple surveys) or whether Democrats have maintained their advantage among that demographic.
When the ballot is expanded to five named candidates, Biden takes a 2-point lead over Trump: Biden 39%, Trump 37%, Kennedy 13%, Jill Stein 3% and Cornel West 2%.
Again, the result between Biden and Trump is within the poll’s margin of error.
Notably, the poll finds a greater share of Trump voters from the head-to-head matchup supporting Kennedy in the expanded ballot compared with Biden voters, different from the results of some other surveys.
(Read more here about how Kennedy's candidacy affe cts the 2024 race, according to the poll.)
The president’s approval rating ticks up to 42%
In addition, the poll found 42% of registered voters approving of Biden’s overall job performance — up 5 points since January’s NBC News poll, which found Biden at the lowest point of his presidency.
Fifty-six percent of voters say they disapprove of the job he has done, which is down 4 points from January.
Biden’s gains over the past few months have come from key parts of his 2020 base, especially among Democrats and Black voters. But he continues to hold low ratings among Latinos (40% approval), young voters (37%) and independents (36%).
“The data across this poll show that Joe Biden has begun to gain some ground in rebuilding his coalition from 2020,” said Horwitt, the Democratic pollster. “The question is whether he can build upon this momentum and make inroads with the groups of voters that still are holding back support.”
But McInturff, the GOP pollster, points out that the only recent presidents who lost re-election had approval ratings higher than Biden’s at this point in the election cycle: George H.W. Bush (43%) and Trump (46%).
“President Biden has a precarious hold on the presidency and is in a difficult position as it relates to his re-election,” McInturff said.
On the issues, 39% of voters say they approve of Biden’s handling of the economy (up from 36% in January), 28% approve of his handling of border security and immigration, and just 27% approve of his handling of the Israel-Hamas war (down from 29% in January).
Voters gave Biden his highest issue rating on addressing student loan debt, with 44% approving of his handling of the issue, compared with 51% who say they disapprove.
Biden leads on abortion and unity; Trump leads on inflation and competency
The NBC News poll asked voters to determine which candidate they thought is better on several different issues and attributes.
Biden holds a 15-point advantage over Trump on dealing with the issue of abortion, and he is ahead by 9 points on having the ability to bring the country together — though that is down from his 24-point advantage on that issue in the September 2020 NBC News poll.
Trump, meanwhile, leads in having the ability to handle a crisis (by 4 points), in having a strong record of accomplishments (by 7 points), in being competent and effective (by 11 points), in having the necessary mental and physical health to be president (by 19 points) and in dealing with inflation and the cost of living (by 22 points).
Inflation, immigration are the top 2024 issues
Inflation and the cost of living top the list of issues in the poll, with 23% of voters saying they’re the most important issue facing the country.
The other top voters is immigration and the situation at the border (22%) — followed by threats to democracy (16%), jobs and the economy (11%), abortion (6%) and health care (6%).
In addition, 63% of voters say their families’ incomes are falling behind the cost of living — essentially unchanged from what the poll found in 2022 and 2023.
And 53% of voters say the country’s economy hasn’t improved, compared with 33% who say that it has improved and that Biden deserves some credit for it and another 8% who agree the economy has improved but don’t give him credit for it.
“If I look back to when I had all three of my children in the house — we only have one child left in the house now, and we’re spending more now than what we did when we had a family of five,” said poll respondent Art Fales, 45, of Florida, who says he’s most likely voting for Trump.
But on a separate question — is there an issue so important that you’ll vote for or against a candidate solely on that basis? — the top responses are protecting democracy and constitutional rights (28%), immigration and border security (20%) and abortion (19%).
Indeed, 30% of Democrats, 29% of young voters and 27% of women say they are single-issue voters on abortion.
“I have a right to what I do with my body,” said poll respondent Amanda Willis, 28, of Louisiana, who said she’s voting for Biden. “And I don’t believe that other people should have the ability to determine that.”
Other poll findings
- With Trump’s first criminal trial underway, 50% of voters say he is being held to the same standard as anyone else when it comes to his multiple legal challenges. That compares with 43% who believe he’s being unfairly targeted in the trials.
- 52% of voters have unfavorable views of Biden, while 53% share the same views of Trump.
- And Democrats and Republicans are essentially tied in congressional preference, with 47% of voters preferring Republicans to control Congress and 46% wanting Democrats in charge. Republicans held a 4-point lead on this question in January.
The NBC News poll of 1,000 registered voters nationwide — 891 contacted via cellphone — was conducted April 12-16, and it has an overall margin of error of plus or minus 3.1 percentage points.
Mark Murray is a senior political editor at NBC News.
Sarah Dean is a 2024 NBC News campaign embed.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
1. Start with a broad topic. A broad topic provides writers with plenty of avenues to explore in their search for a viable research question. Techniques to help you develop a topic into subtopics and potential research questions include brainstorming and concept mapping.
Designing the research question is a dynamic process where the researcher can change or refine the research question as they review related literature and develop a framework for the study. Depending on the scale of your research, the study can include single or multiple research questions. A good research question has the following features:
The research question should be realistic in time, scope, and budget. There are two main constraints to the research process: timeframe and budget. A proper research question will include study or experimental procedures that can be executed within a feasible time frame, typically by a graduate doctoral or master's student or lab technician.
Most professional researchers focus on topics they are genuinely interested in studying. Writers should choose a broad topic about which they genuinely would like to know more. An example of a general topic might be "Slavery in the American South" or "Films of the 1930s.". Do some preliminary research on your general topic.
There are two types of research: Qualitative research and Quantitative research. There must be research questions for every type of research. Your research question will be based on the type of research you want to conduct and the type of data collection. The first step in designing research involves identifying a gap and creating a focused ...
5. Facilitating Data Interpretation and Analysis. Clear research questions help in structuring the analysis, guiding the interpretation of data, and framing the discussion of results. They ensure that the data collected is directly relevant to the questions posed, making it easier to draw meaningful conclusions.
As the name suggests, these types of research questions seek to explore the relationships between variables. Here, an example could be something like "What is the relationship between X and Y" or "Does A have an impact on B". As you can see, these types of research questions are interested in understanding how constructs or variables ...
Example Research Question (s) Here are examples of research problems and research questions to help you understand how to create a research question for a given research problem. Example Research Problem. Example Research Question (s) A small-scale company, 'A' in the UK, cannot allocate a marketing budget for next year due to their poor ...
How to write research questions. Follow these steps when writing a research question: 1. Select a general topic. The first step to writing a research question is to choose a broad topic for your question. This can be something like "1920s novels" or "effects of technology." It's helpful to select something you are interested in and want to know ...
Definition: Research questions are the specific questions that guide a research study or inquiry. These questions help to define the scope of the research and provide a clear focus for the study. Research questions are usually developed at the beginning of a research project and are designed to address a particular research problem or objective.
This form of question looks to understand something without influencing the results. The objective of exploratory questions is to learn more about a topic without attributing bias or preconceived notions to it. Research Question Example: Asking how a chemical is used or perceptions around a certain topic. ii.
Hannah, a writer and editor since 2017, specializes in clear and concise academic and business writing. She has mentored countless scholars and companies in writing authoritative and engaging content. A research question is a question that a research project seeks to answer. Learn how to craft an effective research question with our step-by ...
Be sure to expand your literature search to include any new concepts you may identify along the way. Your research question should be clear, focused, and complex enough to allow for adequate research and analysis. Most importantly, your research question should be interesting to you - you will be spending a great deal of time researching and ...
Research Aims: Examples. True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording "this research aims to…", "this research seeks to…", and so on. For example: "This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.". "This study sets out to assess the interaction between student ...
Check for free. A research question is the main query that researchers seek to answer in their study. It serves as the basis for a scholarly project such as research paper, thesis or dissertation. A good research question should be clear, relevant and specific enough to guide the research process.
A qualitative research question is a type of systematic inquiry that aims at collecting qualitative data from research subjects. The aim of qualitative research questions is to gather non-statistical information pertaining to the experiences, observations, and perceptions of the research subjects in line with the objectives of the investigation.
Writing a good research question is an art and a science. It is a science because you have to make sure it is clear, concise, and well-developed. It is an art because often your language needs "wordsmithing" to perfect and clarify the meaning. This is an exciting part of the research process; however, it can also be one of the most stressful.
Abstract. Formulation of research question (RQ) is an essentiality before starting any research. It aims to explore an existing uncertainty in an area of concern and points to a need for deliberate investigation. It is, therefore, pertinent to formulate a good RQ. The present paper aims to discuss the process of formulation of RQ with stepwise ...
Good writing begins with clearly stating your research question (or hypothesis) in the Introduction section —the focal point on which your entire paper builds and unfolds in the subsequent Methods, Results, and Discussion sections. This research question or hypothesis that goes into the first section of your research manuscript, the ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
The research question lies at the heart of every piece of academic writing. The research question determines the sources to be quoted, how to structure the argument, and what a paper aims at. The research question narrows down the topic and makes sure that the paper has a common thread. Moreover, the research question gives the reader a clear ...
Writing Survey Questions. Perhaps the most important part of the survey process is the creation of questions that accurately measure the opinions, experiences and behaviors of the public. Accurate random sampling will be wasted if the information gathered is built on a shaky foundation of ambiguous or biased questions.
3. Division in the U.S. Amy Cooter is a director of research at the Center on Terrorism, Extremism, and Counterterrorism at the Middlebury Institute of International Studies.
Join us as we listen to Dr. Naomi Zimmerman, Asst. Prof at University of British Columbia and the Canada Research Chair in Sustainability, at the upcoming CE-CERT Research Seminar Series. Dr. Zimmerman's expertise lies at the intersection of air quality research, technological innovation, and sustainability. Event Details: Date: Thursday, May 2nd, 2024 Time: 2:00 - 3:00 PM Location: CE-CERT ...
The question dates to the 2008 election cycle. The lowest level of high election interest in the poll during a presidential cycle was in March 2012 — at 59%. But it quickly ticked up in the next ...
Change Healthcare Cybersecurity Incident Frequently Asked Questions. (i) In the case in which there is insufficient or out-of-date contact information for fewer than 10 individuals, then such substitute notice may be provided by an alternative form of written notice, telephone, or other means. (ii) In the case in which there is insufficient or out-of-date contact information for 10 or more ...
Job Summary: The Researcher I will provide technical expertise to fundamental scientific research in the Drummond-Barbosa Lab in the Department of Genetics. Specifically, the Researcher I will be responsible for working long-term on independent, discovery-based research projects investigating the physiological and metabolic regulation of stem cell lineages in the ovaries of the fruit fly ...
Here is a cover letter template you can use to create your own. [Your Full Name] [Company Name] Dear [Recipient's Name], I am writing in response to your recently advertised research fellowship position at [institution name]. As a highly motivated research professional with a [your degree] in [your field of study] and [number of years] of ...