- Utility Menu
- ARC Scheduler
- Student Employment
- Senior Theses
Doing a senior thesis is an exciting enterprise. It’s often the first time students are engaging in truly original research and trying to develop a significant contribution to a field of inquiry. But as joyful as an independent research process can be, you don’t have to go it alone. It’s important to have support as you navigate such a large endeavor, and the ARC is here to offer one of those layers of support.
Whether or not to write a senior thesis is just the first in a long line of questions thesis writers need to consider. In addition to questions about the topic and scope of your thesis, there are questions about timing, schedule, and support. For example, if you are collecting data, when should data collection start and when should it be completed? What kind of schedule will you write on? How will you work with your adviser? Do you want to meet with your adviser about your progress once a month? Once a week? What other resources can you turn to for information, feedback, and support?
Even though there is a lot to think about and a lot to do, doing a thesis really can be an enjoyable experience! Keep reminding yourself why you chose this topic and why you care about it.
Tips for Tackling Big Projects:

Break the process down into manageable chunks.
- When you’re approaching a big project, it can seem overwhelming to look at the whole thing at once, so it’s essential to identify the smaller steps that will move you towards the completed project.
- Your adviser is best suited to help you break down the thesis process with field-specific advice.
- If you need to refine the breakdown further so it makes sense for you, schedule an appointment with an Academic Coach . An academic coach can help you think through the steps in a way that works for you.
Schedule brief writing sessions at regular times.
- Pre-determine the time, place, and duration.
- Keep it short (15 to 60 minutes).
- Have a clear and reasonable goal for each writing session.
- Make it a regular event (every day, every other day, MWF).
- time is not wasted deciding to write if it’s already in your calendar;
- keeping sessions short reduces the competition from other tasks that are not getting done;
- having an achievable goal for each session provides a sense of accomplishment (a reward for your work);
- writing regularly can turn into a productive habit.
Create accountability structures.
- In addition to having a clear goal for each writing session, it's important to have clear goals for each week and to find someone to communicate these goals to, such as your adviser, a “thesis buddy,” your roommate, etc. Communicating your goals and progress to someone else creates a useful sense of accountability.
- If your adviser is not the person you are communicating your progress to on a weekly basis, then request to set up a structure with your adviser that requires you to check in at less frequent but regular intervals.
- Commit to attending Accountability Hours at the ARC on the same day every week. Making that commitment will add both social support and structure to your week. Use the ARC Scheduler to register for Accountability Hours.
- Set up an accountability group in your department or with thesis writers from different departments.
Create feedback structures.
- It’s important to have a means for getting consistent feedback on your work and to get that feedback early. Work on large projects often lacks the feeling of completeness, so don’t wait for a whole section (and certainly not the whole thesis) to feel “done” before you get feedback on it!
- Your thesis adviser is typically the person best positioned to give you feedback on your research and writing, so communicate with your adviser about how and how often you would like to get feedback.
- If your adviser isn’t able to give you feedback with the frequency you’d like, then fill in the gaps by creating a thesis writing group or exploring if there is already a writing group in your department or lab.
- The Harvard College Writing Center is a great resource for thesis feedback. Writing Center Senior Thesis Tutors can provide feedback on the structure, argument, and clarity of your writing and help with mapping out your writing plan. Visit the Writing Center website to schedule an appointment with a thesis tutor .
Accept that there will be some anxious moments.
- To reduce this source of anxiety, try keeping a separate document where you jot down ideas on how your research questions or central argument might be clarifying or changing as you research and write. Doing this will enable you to stay focused on the section you are working on and to stop worrying about forgetting the new ideas that are emerging.
- You might feel anxious when you realize that you need to update your argument in response to the evidence you have gathered or the new thinking your writing has unleashed. Know that that is OK. Research and writing are iterative processes – new ideas and new ways of thinking are what makes progress possible.
- Breaking down big projects into manageable chunks and mapping out a schedule for working through each chunk is one way to reduce this source of anxiety. It’s reassuring to know you are working towards the end even if you cannot quite see how it will turn out.
- It may be that your thesis or dissertation never truly feels “done” to you, but that’s okay. Academic inquiry is an ongoing endeavor.
Focus on what works for you.
- Just because your roommate wrote 10 pages in a day doesn’t mean that’s the right pace or strategy for you.
- If you are having trouble figuring out what works for you, use the ARC Scheduler to make an appointment with an Academic Coach , who can help you come up with daily, weekly, and semester-long plans.
Use your resources.
- There’s a lot of the thesis writing process that has to be done independently, but there are also a lot of free resources at Harvard to help you do the work.
- If you’re having trouble finding a source, email your question or set up a research consult via Ask a Librarian .
- If you’re looking for additional feedback or help with any aspect of writing, contact the Harvard College Writing Center . The Writing Center has Senior Thesis Tutors who will read drafts of your thesis (more typically, parts of your thesis) in advance and meet with you individually to talk about structure, argument, clear writing, and mapping out your writing plan.
- If you need help with breaking down your project or setting up a schedule for the week, the semester, or until the deadline, use the ARC Scheduler to make an appointment with an Academic Coach .
- If you would like an accountability structure for social support and to keep yourself on track, come to Accountability Hours at the ARC.
Accordion style
- Assessing Your Understanding
- Building Your Academic Support System
- Common Class Norms
- Effective Learning Practices
- First-Year Students
- How to Prepare for Class
- Interacting with Instructors
- Know and Honor Your Priorities
- Memory and Attention
- Minimizing Zoom Fatigue
- Note-taking
- Office Hours
- Perfectionism
- Scheduling Time
- Study Groups
- Tackling STEM Courses
- Test Anxiety

Honors Theses
What this handout is about.
Writing a senior honors thesis, or any major research essay, can seem daunting at first. A thesis requires a reflective, multi-stage writing process. This handout will walk you through those stages. It is targeted at students in the humanities and social sciences, since their theses tend to involve more writing than projects in the hard sciences. Yet all thesis writers may find the organizational strategies helpful.
Introduction
What is an honors thesis.
That depends quite a bit on your field of study. However, all honors theses have at least two things in common:
- They are based on students’ original research.
- They take the form of a written manuscript, which presents the findings of that research. In the humanities, theses average 50-75 pages in length and consist of two or more chapters. In the social sciences, the manuscript may be shorter, depending on whether the project involves more quantitative than qualitative research. In the hard sciences, the manuscript may be shorter still, often taking the form of a sophisticated laboratory report.
Who can write an honors thesis?
In general, students who are at the end of their junior year, have an overall 3.2 GPA, and meet their departmental requirements can write a senior thesis. For information about your eligibility, contact:
- UNC Honors Program
- Your departmental administrators of undergraduate studies/honors
Why write an honors thesis?
Satisfy your intellectual curiosity This is the most compelling reason to write a thesis. Whether it’s the short stories of Flannery O’Connor or the challenges of urban poverty, you’ve studied topics in college that really piqued your interest. Now’s your chance to follow your passions, explore further, and contribute some original ideas and research in your field.
Develop transferable skills Whether you choose to stay in your field of study or not, the process of developing and crafting a feasible research project will hone skills that will serve you well in almost any future job. After all, most jobs require some form of problem solving and oral and written communication. Writing an honors thesis requires that you:
- ask smart questions
- acquire the investigative instincts needed to find answers
- navigate libraries, laboratories, archives, databases, and other research venues
- develop the flexibility to redirect your research if your initial plan flops
- master the art of time management
- hone your argumentation skills
- organize a lengthy piece of writing
- polish your oral communication skills by presenting and defending your project to faculty and peers
Work closely with faculty mentors At large research universities like Carolina, you’ve likely taken classes where you barely got to know your instructor. Writing a thesis offers the opportunity to work one-on-one with a with faculty adviser. Such mentors can enrich your intellectual development and later serve as invaluable references for graduate school and employment.
Open windows into future professions An honors thesis will give you a taste of what it’s like to do research in your field. Even if you’re a sociology major, you may not really know what it’s like to be a sociologist. Writing a sociology thesis would open a window into that world. It also might help you decide whether to pursue that field in graduate school or in your future career.
How do you write an honors thesis?
Get an idea of what’s expected.
It’s a good idea to review some of the honors theses other students have submitted to get a sense of what an honors thesis might look like and what kinds of things might be appropriate topics. Look for examples from the previous year in the Carolina Digital Repository. You may also be able to find past theses collected in your major department or at the North Carolina Collection in Wilson Library. Pay special attention to theses written by students who share your major.
Choose a topic
Ideally, you should start thinking about topics early in your junior year, so you can begin your research and writing quickly during your senior year. (Many departments require that you submit a proposal for an honors thesis project during the spring of your junior year.)
How should you choose a topic?
- Read widely in the fields that interest you. Make a habit of browsing professional journals to survey the “hot” areas of research and to familiarize yourself with your field’s stylistic conventions. (You’ll find the most recent issues of the major professional journals in the periodicals reading room on the first floor of Davis Library).
- Set up appointments to talk with faculty in your field. This is a good idea, since you’ll eventually need to select an advisor and a second reader. Faculty also can help you start narrowing down potential topics.
- Look at honors theses from the past. The North Carolina Collection in Wilson Library holds UNC honors theses. To get a sense of the typical scope of a thesis, take a look at a sampling from your field.
What makes a good topic?
- It’s fascinating. Above all, choose something that grips your imagination. If you don’t, the chances are good that you’ll struggle to finish.
- It’s doable. Even if a topic interests you, it won’t work out unless you have access to the materials you need to research it. Also be sure that your topic is narrow enough. Let’s take an example: Say you’re interested in the efforts to ratify the Equal Rights Amendment in the 1970s and early 1980s. That’s a big topic that probably can’t be adequately covered in a single thesis. You need to find a case study within that larger topic. For example, maybe you’re particularly interested in the states that did not ratify the ERA. Of those states, perhaps you’ll select North Carolina, since you’ll have ready access to local research materials. And maybe you want to focus primarily on the ERA’s opponents. Beyond that, maybe you’re particularly interested in female opponents of the ERA. Now you’ve got a much more manageable topic: Women in North Carolina Who Opposed the ERA in the 1970s and 1980s.
- It contains a question. There’s a big difference between having a topic and having a guiding research question. Taking the above topic, perhaps your main question is: Why did some women in North Carolina oppose the ERA? You will, of course, generate other questions: Who were the most outspoken opponents? White women? Middle-class women? How did they oppose the ERA? Public protests? Legislative petitions? etc. etc. Yet it’s good to start with a guiding question that will focus your research.
Goal-setting and time management
The senior year is an exceptionally busy time for college students. In addition to the usual load of courses and jobs, seniors have the daunting task of applying for jobs and/or graduate school. These demands are angst producing and time consuming If that scenario sounds familiar, don’t panic! Do start strategizing about how to make a time for your thesis. You may need to take a lighter course load or eliminate extracurricular activities. Even if the thesis is the only thing on your plate, you still need to make a systematic schedule for yourself. Most departments require that you take a class that guides you through the honors project, so deadlines likely will be set for you. Still, you should set your own goals for meeting those deadlines. Here are a few suggestions for goal setting and time management:
Start early. Keep in mind that many departments will require that you turn in your thesis sometime in early April, so don’t count on having the entire spring semester to finish your work. Ideally, you’ll start the research process the semester or summer before your senior year so that the writing process can begin early in the fall. Some goal-setting will be done for you if you are taking a required class that guides you through the honors project. But any substantive research project requires a clear timetable.
Set clear goals in making a timetable. Find out the final deadline for turning in your project to your department. Working backwards from that deadline, figure out how much time you can allow for the various stages of production.
Here is a sample timetable. Use it, however, with two caveats in mind:
- The timetable for your thesis might look very different depending on your departmental requirements.
- You may not wish to proceed through these stages in a linear fashion. You may want to revise chapter one before you write chapter two. Or you might want to write your introduction last, not first. This sample is designed simply to help you start thinking about how to customize your own schedule.
Sample timetable
Avoid falling into the trap of procrastination. Once you’ve set goals for yourself, stick to them! For some tips on how to do this, see our handout on procrastination .
Consistent production
It’s a good idea to try to squeeze in a bit of thesis work every day—even if it’s just fifteen minutes of journaling or brainstorming about your topic. Or maybe you’ll spend that fifteen minutes taking notes on a book. The important thing is to accomplish a bit of active production (i.e., putting words on paper) for your thesis every day. That way, you develop good writing habits that will help you keep your project moving forward.
Make yourself accountable to someone other than yourself
Since most of you will be taking a required thesis seminar, you will have deadlines. Yet you might want to form a writing group or enlist a peer reader, some person or people who can help you stick to your goals. Moreover, if your advisor encourages you to work mostly independently, don’t be afraid to ask them to set up periodic meetings at which you’ll turn in installments of your project.
Brainstorming and freewriting
One of the biggest challenges of a lengthy writing project is keeping the creative juices flowing. Here’s where freewriting can help. Try keeping a small notebook handy where you jot down stray ideas that pop into your head. Or schedule time to freewrite. You may find that such exercises “free” you up to articulate your argument and generate new ideas. Here are some questions to stimulate freewriting.
Questions for basic brainstorming at the beginning of your project:
- What do I already know about this topic?
- Why do I care about this topic?
- Why is this topic important to people other than myself
- What more do I want to learn about this topic?
- What is the main question that I am trying to answer?
- Where can I look for additional information?
- Who is my audience and how can I reach them?
- How will my work inform my larger field of study?
- What’s the main goal of my research project?
Questions for reflection throughout your project:
- What’s my main argument? How has it changed since I began the project?
- What’s the most important evidence that I have in support of my “big point”?
- What questions do my sources not answer?
- How does my case study inform or challenge my field writ large?
- Does my project reinforce or contradict noted scholars in my field? How?
- What is the most surprising finding of my research?
- What is the most frustrating part of this project?
- What is the most rewarding part of this project?
- What will be my work’s most important contribution?
Research and note-taking
In conducting research, you will need to find both primary sources (“firsthand” sources that come directly from the period/events/people you are studying) and secondary sources (“secondhand” sources that are filtered through the interpretations of experts in your field.) The nature of your research will vary tremendously, depending on what field you’re in. For some general suggestions on finding sources, consult the UNC Libraries tutorials . Whatever the exact nature of the research you’re conducting, you’ll be taking lots of notes and should reflect critically on how you do that. Too often it’s assumed that the research phase of a project involves very little substantive writing (i.e., writing that involves thinking). We sit down with our research materials and plunder them for basic facts and useful quotations. That mechanical type of information-recording is important. But a more thoughtful type of writing and analytical thinking is also essential at this stage. Some general guidelines for note-taking:
First of all, develop a research system. There are lots of ways to take and organize your notes. Whether you choose to use note cards, computer databases, or notebooks, follow two cardinal rules:
- Make careful distinctions between direct quotations and your paraphrasing! This is critical if you want to be sure to avoid accidentally plagiarizing someone else’s work. For more on this, see our handout on plagiarism .
- Record full citations for each source. Don’t get lazy here! It will be far more difficult to find the proper citation later than to write it down now.
Keeping those rules in mind, here’s a template for the types of information that your note cards/legal pad sheets/computer files should include for each of your sources:
Abbreviated subject heading: Include two or three words to remind you of what this sources is about (this shorthand categorization is essential for the later sorting of your sources).
Complete bibliographic citation:
- author, title, publisher, copyright date, and page numbers for published works
- box and folder numbers and document descriptions for archival sources
- complete web page title, author, address, and date accessed for online sources
Notes on facts, quotations, and arguments: Depending on the type of source you’re using, the content of your notes will vary. If, for example, you’re using US Census data, then you’ll mainly be writing down statistics and numbers. If you’re looking at someone else’s diary, you might jot down a number of quotations that illustrate the subject’s feelings and perspectives. If you’re looking at a secondary source, you’ll want to make note not just of factual information provided by the author but also of their key arguments.
Your interpretation of the source: This is the most important part of note-taking. Don’t just record facts. Go ahead and take a stab at interpreting them. As historians Jacques Barzun and Henry F. Graff insist, “A note is a thought.” So what do these thoughts entail? Ask yourself questions about the context and significance of each source.
Interpreting the context of a source:
- Who wrote/created the source?
- When, and under what circumstances, was it written/created?
- Why was it written/created? What was the agenda behind the source?
- How was it written/created?
- If using a secondary source: How does it speak to other scholarship in the field?
Interpreting the significance of a source:
- How does this source answer (or complicate) my guiding research questions?
- Does it pose new questions for my project? What are they?
- Does it challenge my fundamental argument? If so, how?
- Given the source’s context, how reliable is it?
You don’t need to answer all of these questions for each source, but you should set a goal of engaging in at least one or two sentences of thoughtful, interpretative writing for each source. If you do so, you’ll make much easier the next task that awaits you: drafting.
The dread of drafting
Why do we often dread drafting? We dread drafting because it requires synthesis, one of the more difficult forms of thinking and interpretation. If you’ve been free-writing and taking thoughtful notes during the research phase of your project, then the drafting should be far less painful. Here are some tips on how to get started:
Sort your “evidence” or research into analytical categories:
- Some people file note cards into categories.
- The technologically-oriented among us take notes using computer database programs that have built-in sorting mechanisms.
- Others cut and paste evidence into detailed outlines on their computer.
- Still others stack books, notes, and photocopies into topically-arranged piles.There is not a single right way, but this step—in some form or fashion—is essential!
If you’ve been forcing yourself to put subject headings on your notes as you go along, you’ll have generated a number of important analytical categories. Now, you need to refine those categories and sort your evidence. Everyone has a different “sorting style.”
Formulate working arguments for your entire thesis and individual chapters. Once you’ve sorted your evidence, you need to spend some time thinking about your project’s “big picture.” You need to be able to answer two questions in specific terms:
- What is the overall argument of my thesis?
- What are the sub-arguments of each chapter and how do they relate to my main argument?
Keep in mind that “working arguments” may change after you start writing. But a senior thesis is big and potentially unwieldy. If you leave this business of argument to chance, you may end up with a tangle of ideas. See our handout on arguments and handout on thesis statements for some general advice on formulating arguments.
Divide your thesis into manageable chunks. The surest road to frustration at this stage is getting obsessed with the big picture. What? Didn’t we just say that you needed to focus on the big picture? Yes, by all means, yes. You do need to focus on the big picture in order to get a conceptual handle on your project, but you also need to break your thesis down into manageable chunks of writing. For example, take a small stack of note cards and flesh them out on paper. Or write through one point on a chapter outline. Those small bits of prose will add up quickly.
Just start! Even if it’s not at the beginning. Are you having trouble writing those first few pages of your chapter? Sometimes the introduction is the toughest place to start. You should have a rough idea of your overall argument before you begin writing one of the main chapters, but you might find it easier to start writing in the middle of a chapter of somewhere other than word one. Grab hold where you evidence is strongest and your ideas are clearest.
Keep up the momentum! Assuming the first draft won’t be your last draft, try to get your thoughts on paper without spending too much time fussing over minor stylistic concerns. At the drafting stage, it’s all about getting those ideas on paper. Once that task is done, you can turn your attention to revising.
Peter Elbow, in Writing With Power, suggests that writing is difficult because it requires two conflicting tasks: creating and criticizing. While these two tasks are intimately intertwined, the drafting stage focuses on creating, while revising requires criticizing. If you leave your revising to the last minute, then you’ve left out a crucial stage of the writing process. See our handout for some general tips on revising . The challenges of revising an honors thesis may include:
Juggling feedback from multiple readers
A senior thesis may mark the first time that you have had to juggle feedback from a wide range of readers:
- your adviser
- a second (and sometimes third) faculty reader
- the professor and students in your honors thesis seminar
You may feel overwhelmed by the prospect of incorporating all this advice. Keep in mind that some advice is better than others. You will probably want to take most seriously the advice of your adviser since they carry the most weight in giving your project a stamp of approval. But sometimes your adviser may give you more advice than you can digest. If so, don’t be afraid to approach them—in a polite and cooperative spirit, of course—and ask for some help in prioritizing that advice. See our handout for some tips on getting and receiving feedback .
Refining your argument
It’s especially easy in writing a lengthy work to lose sight of your main ideas. So spend some time after you’ve drafted to go back and clarify your overall argument and the individual chapter arguments and make sure they match the evidence you present.
Organizing and reorganizing
Again, in writing a 50-75 page thesis, things can get jumbled. You may find it particularly helpful to make a “reverse outline” of each of your chapters. That will help you to see the big sections in your work and move things around so there’s a logical flow of ideas. See our handout on organization for more organizational suggestions and tips on making a reverse outline
Plugging in holes in your evidence
It’s unlikely that you anticipated everything you needed to look up before you drafted your thesis. Save some time at the revising stage to plug in the holes in your research. Make sure that you have both primary and secondary evidence to support and contextualize your main ideas.
Saving time for the small stuff
Even though your argument, evidence, and organization are most important, leave plenty of time to polish your prose. At this point, you’ve spent a very long time on your thesis. Don’t let minor blemishes (misspellings and incorrect grammar) distract your readers!
Formatting and final touches
You’re almost done! You’ve researched, drafted, and revised your thesis; now you need to take care of those pesky little formatting matters. An honors thesis should replicate—on a smaller scale—the appearance of a dissertation or master’s thesis. So, you need to include the “trappings” of a formal piece of academic work. For specific questions on formatting matters, check with your department to see if it has a style guide that you should use. For general formatting guidelines, consult the Graduate School’s Guide to Dissertations and Theses . Keeping in mind the caveat that you should always check with your department first about its stylistic guidelines, here’s a brief overview of the final “finishing touches” that you’ll need to put on your honors thesis:
- Honors Thesis
- Name of Department
- University of North Carolina
- These parts of the thesis will vary in format depending on whether your discipline uses MLA, APA, CBE, or Chicago (also known in its shortened version as Turabian) style. Whichever style you’re using, stick to the rules and be consistent. It might be helpful to buy an appropriate style guide. Or consult the UNC LibrariesYear Citations/footnotes and works cited/reference pages citation tutorial
- In addition, in the bottom left corner, you need to leave space for your adviser and faculty readers to sign their names. For example:
Approved by: _____________________
Adviser: Prof. Jane Doe
- This is not a required component of an honors thesis. However, if you want to thank particular librarians, archivists, interviewees, and advisers, here’s the place to do it. You should include an acknowledgments page if you received a grant from the university or an outside agency that supported your research. It’s a good idea to acknowledge folks who helped you with a major project, but do not feel the need to go overboard with copious and flowery expressions of gratitude. You can—and should—always write additional thank-you notes to people who gave you assistance.
- Formatted much like the table of contents.
- You’ll need to save this until the end, because it needs to reflect your final pagination. Once you’ve made all changes to the body of the thesis, then type up your table of contents with the titles of each section aligned on the left and the page numbers on which those sections begin flush right.
- Each page of your thesis needs a number, although not all page numbers are displayed. All pages that precede the first page of the main text (i.e., your introduction or chapter one) are numbered with small roman numerals (i, ii, iii, iv, v, etc.). All pages thereafter use Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, etc.).
- Your text should be double spaced (except, in some cases, long excerpts of quoted material), in a 12 point font and a standard font style (e.g., Times New Roman). An honors thesis isn’t the place to experiment with funky fonts—they won’t enhance your work, they’ll only distract your readers.
- In general, leave a one-inch inch margin on all sides. However, for the copy of your thesis that will be bound by the library, you need to leave a 1.25-inch margin on the left.
How do I defend my honors thesis?
Graciously, enthusiastically, and confidently. The term defense is scary and misleading—it conjures up images of a military exercise or an athletic maneuver. An academic defense ideally shouldn’t be a combative scene but a congenial conversation about the work’s merits and weaknesses. That said, the defense probably won’t be like the average conversation that you have with your friends. You’ll be the center of attention. And you may get some challenging questions. Thus, it’s a good idea to spend some time preparing yourself. First of all, you’ll want to prepare 5-10 minutes of opening comments. Here’s a good time to preempt some criticisms by frankly acknowledging what you think your work’s greatest strengths and weaknesses are. Then you may be asked some typical questions:
- What is the main argument of your thesis?
- How does it fit in with the work of Ms. Famous Scholar?
- Have you read the work of Mr. Important Author?
NOTE: Don’t get too flustered if you haven’t! Most scholars have their favorite authors and books and may bring one or more of them up, even if the person or book is only tangentially related to the topic at hand. Should you get this question, answer honestly and simply jot down the title or the author’s name for future reference. No one expects you to have read everything that’s out there.
- Why did you choose this particular case study to explore your topic?
- If you were to expand this project in graduate school, how would you do so?
Should you get some biting criticism of your work, try not to get defensive. Yes, this is a defense, but you’ll probably only fan the flames if you lose your cool. Keep in mind that all academic work has flaws or weaknesses, and you can be sure that your professors have received criticisms of their own work. It’s part of the academic enterprise. Accept criticism graciously and learn from it. If you receive criticism that is unfair, stand up for yourself confidently, but in a good spirit. Above all, try to have fun! A defense is a rare opportunity to have eminent scholars in your field focus on YOU and your ideas and work. And the defense marks the end of a long and arduous journey. You have every right to be proud of your accomplishments!
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Atchity, Kenneth. 1986. A Writer’s Time: A Guide to the Creative Process from Vision Through Revision . New York: W.W. Norton.
Barzun, Jacques, and Henry F. Graff. 2012. The Modern Researcher , 6th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage Learning.
Elbow, Peter. 1998. Writing With Power: Techniques for Mastering the Writing Process . New York: Oxford University Press.
Graff, Gerald, and Cathy Birkenstein. 2014. “They Say/I Say”: The Moves That Matter in Academic Writing , 3rd ed. New York: W.W. Norton and Company.
Lamott, Anne. 1994. Bird by Bird: Some Instructions on Writing and Life . New York: Pantheon.
Lasch, Christopher. 2002. Plain Style: A Guide to Written English. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press.
Turabian, Kate. 2018. A Manual for Writers of Term Papers, Theses, Dissertations , 9th ed. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications. If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- How to write a research paper
Last updated
11 January 2024
Reviewed by
With proper planning, knowledge, and framework, completing a research paper can be a fulfilling and exciting experience.
Though it might initially sound slightly intimidating, this guide will help you embrace the challenge.
By documenting your findings, you can inspire others and make a difference in your field. Here's how you can make your research paper unique and comprehensive.
- What is a research paper?
Research papers allow you to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of a particular topic. These papers are usually lengthier and more detailed than typical essays, requiring deeper insight into the chosen topic.
To write a research paper, you must first choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to the field of study. Once you’ve selected your topic, gathering as many relevant resources as possible, including books, scholarly articles, credible websites, and other academic materials, is essential. You must then read and analyze these sources, summarizing their key points and identifying gaps in the current research.
You can formulate your ideas and opinions once you thoroughly understand the existing research. To get there might involve conducting original research, gathering data, or analyzing existing data sets. It could also involve presenting an original argument or interpretation of the existing research.
Writing a successful research paper involves presenting your findings clearly and engagingly, which might involve using charts, graphs, or other visual aids to present your data and using concise language to explain your findings. You must also ensure your paper adheres to relevant academic formatting guidelines, including proper citations and references.
Overall, writing a research paper requires a significant amount of time, effort, and attention to detail. However, it is also an enriching experience that allows you to delve deeply into a subject that interests you and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your chosen field.
- How long should a research paper be?
Research papers are deep dives into a topic. Therefore, they tend to be longer pieces of work than essays or opinion pieces.
However, a suitable length depends on the complexity of the topic and your level of expertise. For instance, are you a first-year college student or an experienced professional?
Also, remember that the best research papers provide valuable information for the benefit of others. Therefore, the quality of information matters most, not necessarily the length. Being concise is valuable.
Following these best practice steps will help keep your process simple and productive:
1. Gaining a deep understanding of any expectations
Before diving into your intended topic or beginning the research phase, take some time to orient yourself. Suppose there’s a specific topic assigned to you. In that case, it’s essential to deeply understand the question and organize your planning and approach in response. Pay attention to the key requirements and ensure you align your writing accordingly.
This preparation step entails
Deeply understanding the task or assignment
Being clear about the expected format and length
Familiarizing yourself with the citation and referencing requirements
Understanding any defined limits for your research contribution
Where applicable, speaking to your professor or research supervisor for further clarification
2. Choose your research topic
Select a research topic that aligns with both your interests and available resources. Ideally, focus on a field where you possess significant experience and analytical skills. In crafting your research paper, it's crucial to go beyond summarizing existing data and contribute fresh insights to the chosen area.
Consider narrowing your focus to a specific aspect of the topic. For example, if exploring the link between technology and mental health, delve into how social media use during the pandemic impacts the well-being of college students. Conducting interviews and surveys with students could provide firsthand data and unique perspectives, adding substantial value to the existing knowledge.
When finalizing your topic, adhere to legal and ethical norms in the relevant area (this ensures the integrity of your research, protects participants' rights, upholds intellectual property standards, and ensures transparency and accountability). Following these principles not only maintains the credibility of your work but also builds trust within your academic or professional community.
For instance, in writing about medical research, consider legal and ethical norms , including patient confidentiality laws and informed consent requirements. Similarly, if analyzing user data on social media platforms, be mindful of data privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with laws governing personal information collection and use. Aligning with legal and ethical standards not only avoids potential issues but also underscores the responsible conduct of your research.
3. Gather preliminary research
Once you’ve landed on your topic, it’s time to explore it further. You’ll want to discover more about available resources and existing research relevant to your assignment at this stage.
This exploratory phase is vital as you may discover issues with your original idea or realize you have insufficient resources to explore the topic effectively. This key bit of groundwork allows you to redirect your research topic in a different, more feasible, or more relevant direction if necessary.
Spending ample time at this stage ensures you gather everything you need, learn as much as you can about the topic, and discover gaps where the topic has yet to be sufficiently covered, offering an opportunity to research it further.
4. Define your research question
To produce a well-structured and focused paper, it is imperative to formulate a clear and precise research question that will guide your work. Your research question must be informed by the existing literature and tailored to the scope and objectives of your project. By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers.
5. Write a thesis statement
A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction. It serves as an overall guide to summarize the overall intent of the research paper for you and anyone wanting to know more about the research.
A strong thesis statement is:
Concise and clear: Explain your case in simple sentences (avoid covering multiple ideas). It might help to think of this section as an elevator pitch.
Specific: Ensure that there is no ambiguity in your statement and that your summary covers the points argued in the paper.
Debatable: A thesis statement puts forward a specific argument––it is not merely a statement but a debatable point that can be analyzed and discussed.
Here are three thesis statement examples from different disciplines:
Psychology thesis example: "We're studying adults aged 25-40 to see if taking short breaks for mindfulness can help with stress. Our goal is to find practical ways to manage anxiety better."
Environmental science thesis example: "This research paper looks into how having more city parks might make the air cleaner and keep people healthier. I want to find out if more green spaces means breathing fewer carcinogens in big cities."
UX research thesis example: "This study focuses on improving mobile banking for older adults using ethnographic research, eye-tracking analysis, and interactive prototyping. We investigate the usefulness of eye-tracking analysis with older individuals, aiming to spark debate and offer fresh perspectives on UX design and digital inclusivity for the aging population."
6. Conduct in-depth research
A research paper doesn’t just include research that you’ve uncovered from other papers and studies but your fresh insights, too. You will seek to become an expert on your topic––understanding the nuances in the current leading theories. You will analyze existing research and add your thinking and discoveries. It's crucial to conduct well-designed research that is rigorous, robust, and based on reliable sources. Suppose a research paper lacks evidence or is biased. In that case, it won't benefit the academic community or the general public. Therefore, examining the topic thoroughly and furthering its understanding through high-quality research is essential. That usually means conducting new research. Depending on the area under investigation, you may conduct surveys, interviews, diary studies , or observational research to uncover new insights or bolster current claims.
7. Determine supporting evidence
Not every piece of research you’ve discovered will be relevant to your research paper. It’s important to categorize the most meaningful evidence to include alongside your discoveries. It's important to include evidence that doesn't support your claims to avoid exclusion bias and ensure a fair research paper.
8. Write a research paper outline
Before diving in and writing the whole paper, start with an outline. It will help you to see if more research is needed, and it will provide a framework by which to write a more compelling paper. Your supervisor may even request an outline to approve before beginning to write the first draft of the full paper. An outline will include your topic, thesis statement, key headings, short summaries of the research, and your arguments.
9. Write your first draft
Once you feel confident about your outline and sources, it’s time to write your first draft. While penning a long piece of content can be intimidating, if you’ve laid the groundwork, you will have a structure to help you move steadily through each section. To keep up motivation and inspiration, it’s often best to keep the pace quick. Stopping for long periods can interrupt your flow and make jumping back in harder than writing when things are fresh in your mind.
10. Cite your sources correctly
It's always a good practice to give credit where it's due, and the same goes for citing any works that have influenced your paper. Building your arguments on credible references adds value and authenticity to your research. In the formatting guidelines section, you’ll find an overview of different citation styles (MLA, CMOS, or APA), which will help you meet any publishing or academic requirements and strengthen your paper's credibility. It is essential to follow the guidelines provided by your school or the publication you are submitting to ensure the accuracy and relevance of your citations.
11. Ensure your work is original
It is crucial to ensure the originality of your paper, as plagiarism can lead to serious consequences. To avoid plagiarism, you should use proper paraphrasing and quoting techniques. Paraphrasing is rewriting a text in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. Quoting involves directly citing the source. Giving credit to the original author or source is essential whenever you borrow their ideas or words. You can also use plagiarism detection tools such as Scribbr or Grammarly to check the originality of your paper. These tools compare your draft writing to a vast database of online sources. If you find any accidental plagiarism, you should correct it immediately by rephrasing or citing the source.
12. Revise, edit, and proofread
One of the essential qualities of excellent writers is their ability to understand the importance of editing and proofreading. Even though it's tempting to call it a day once you've finished your writing, editing your work can significantly improve its quality. It's natural to overlook the weaker areas when you've just finished writing a paper. Therefore, it's best to take a break of a day or two, or even up to a week, to refresh your mind. This way, you can return to your work with a new perspective. After some breathing room, you can spot any inconsistencies, spelling and grammar errors, typos, or missing citations and correct them.
- The best research paper format
The format of your research paper should align with the requirements set forth by your college, school, or target publication.
There is no one “best” format, per se. Depending on the stated requirements, you may need to include the following elements:
Title page: The title page of a research paper typically includes the title, author's name, and institutional affiliation and may include additional information such as a course name or instructor's name.
Table of contents: Include a table of contents to make it easy for readers to find specific sections of your paper.
Abstract: The abstract is a summary of the purpose of the paper.
Methods : In this section, describe the research methods used. This may include collecting data , conducting interviews, or doing field research .
Results: Summarize the conclusions you drew from your research in this section.
Discussion: In this section, discuss the implications of your research . Be sure to mention any significant limitations to your approach and suggest areas for further research.
Tables, charts, and illustrations: Use tables, charts, and illustrations to help convey your research findings and make them easier to understand.
Works cited or reference page: Include a works cited or reference page to give credit to the sources that you used to conduct your research.
Bibliography: Provide a list of all the sources you consulted while conducting your research.
Dedication and acknowledgments : Optionally, you may include a dedication and acknowledgments section to thank individuals who helped you with your research.
- General style and formatting guidelines
Formatting your research paper means you can submit it to your college, journal, or other publications in compliance with their criteria.
Research papers tend to follow the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), or Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) guidelines.
Here’s how each style guide is typically used:
Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS):
CMOS is a versatile style guide used for various types of writing. It's known for its flexibility and use in the humanities. CMOS provides guidelines for citations, formatting, and overall writing style. It allows for both footnotes and in-text citations, giving writers options based on their preferences or publication requirements.
American Psychological Association (APA):
APA is common in the social sciences. It’s hailed for its clarity and emphasis on precision. It has specific rules for citing sources, creating references, and formatting papers. APA style uses in-text citations with an accompanying reference list. It's designed to convey information efficiently and is widely used in academic and scientific writing.
Modern Language Association (MLA):
MLA is widely used in the humanities, especially literature and language studies. It emphasizes the author-page format for in-text citations and provides guidelines for creating a "Works Cited" page. MLA is known for its focus on the author's name and the literary works cited. It’s frequently used in disciplines that prioritize literary analysis and critical thinking.
To confirm you're using the latest style guide, check the official website or publisher's site for updates, consult academic resources, and verify the guide's publication date. Online platforms and educational resources may also provide summaries and alerts about any revisions or additions to the style guide.
Citing sources
When working on your research paper, it's important to cite the sources you used properly. Your citation style will guide you through this process. Generally, there are three parts to citing sources in your research paper:
First, provide a brief citation in the body of your essay. This is also known as a parenthetical or in-text citation.
Second, include a full citation in the Reference list at the end of your paper. Different types of citations include in-text citations, footnotes, and reference lists.
In-text citations include the author's surname and the date of the citation.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of each page of your research paper. They may also be summarized within a reference list at the end of the paper.
A reference list includes all of the research used within the paper at the end of the document. It should include the author, date, paper title, and publisher listed in the order that aligns with your citation style.
10 research paper writing tips:
Following some best practices is essential to writing a research paper that contributes to your field of study and creates a positive impact.
These tactics will help you structure your argument effectively and ensure your work benefits others:
Clear and precise language: Ensure your language is unambiguous. Use academic language appropriately, but keep it simple. Also, provide clear takeaways for your audience.
Effective idea separation: Organize the vast amount of information and sources in your paper with paragraphs and titles. Create easily digestible sections for your readers to navigate through.
Compelling intro: Craft an engaging introduction that captures your reader's interest. Hook your audience and motivate them to continue reading.
Thorough revision and editing: Take the time to review and edit your paper comprehensively. Use tools like Grammarly to detect and correct small, overlooked errors.
Thesis precision: Develop a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your paper. Ensure that your thesis aligns with your research's overall purpose and contribution.
Logical flow of ideas: Maintain a logical progression throughout the paper. Use transitions effectively to connect different sections and maintain coherence.
Critical evaluation of sources: Evaluate and critically assess the relevance and reliability of your sources. Ensure that your research is based on credible and up-to-date information.
Thematic consistency: Maintain a consistent theme throughout the paper. Ensure that all sections contribute cohesively to the overall argument.
Relevant supporting evidence: Provide concise and relevant evidence to support your arguments. Avoid unnecessary details that may distract from the main points.
Embrace counterarguments: Acknowledge and address opposing views to strengthen your position. Show that you have considered alternative arguments in your field.
7 research tips
If you want your paper to not only be well-written but also contribute to the progress of human knowledge, consider these tips to take your paper to the next level:
Selecting the appropriate topic: The topic you select should align with your area of expertise, comply with the requirements of your project, and have sufficient resources for a comprehensive investigation.
Use academic databases: Academic databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and JSTOR offer a wealth of research papers that can help you discover everything you need to know about your chosen topic.
Critically evaluate sources: It is important not to accept research findings at face value. Instead, it is crucial to critically analyze the information to avoid jumping to conclusions or overlooking important details. A well-written research paper requires a critical analysis with thorough reasoning to support claims.
Diversify your sources: Expand your research horizons by exploring a variety of sources beyond the standard databases. Utilize books, conference proceedings, and interviews to gather diverse perspectives and enrich your understanding of the topic.
Take detailed notes: Detailed note-taking is crucial during research and can help you form the outline and body of your paper.
Stay up on trends: Keep abreast of the latest developments in your field by regularly checking for recent publications. Subscribe to newsletters, follow relevant journals, and attend conferences to stay informed about emerging trends and advancements.
Engage in peer review: Seek feedback from peers or mentors to ensure the rigor and validity of your research . Peer review helps identify potential weaknesses in your methodology and strengthens the overall credibility of your findings.
- The real-world impact of research papers
Writing a research paper is more than an academic or business exercise. The experience provides an opportunity to explore a subject in-depth, broaden one's understanding, and arrive at meaningful conclusions. With careful planning, dedication, and hard work, writing a research paper can be a fulfilling and enriching experience contributing to advancing knowledge.
How do I publish my research paper?
Many academics wish to publish their research papers. While challenging, your paper might get traction if it covers new and well-written information. To publish your research paper, find a target publication, thoroughly read their guidelines, format your paper accordingly, and send it to them per their instructions. You may need to include a cover letter, too. After submission, your paper may be peer-reviewed by experts to assess its legitimacy, quality, originality, and methodology. Following review, you will be informed by the publication whether they have accepted or rejected your paper.
What is a good opening sentence for a research paper?
Beginning your research paper with a compelling introduction can ensure readers are interested in going further. A relevant quote, a compelling statistic, or a bold argument can start the paper and hook your reader. Remember, though, that the most important aspect of a research paper is the quality of the information––not necessarily your ability to storytell, so ensure anything you write aligns with your goals.
Research paper vs. a research proposal—what’s the difference?
While some may confuse research papers and proposals, they are different documents.
A research proposal comes before a research paper. It is a detailed document that outlines an intended area of exploration. It includes the research topic, methodology, timeline, sources, and potential conclusions. Research proposals are often required when seeking approval to conduct research.
A research paper is a summary of research findings. A research paper follows a structured format to present those findings and construct an argument or conclusion.

Editor’s picks
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
- 10 research paper
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Presentations
How to Write a Seminar Paper
Last Updated: October 17, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 16 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 623,058 times.
A seminar paper is a work of original research that presents a specific thesis and is presented to a group of interested peers, usually in an academic setting. For example, it might serve as your cumulative assignment in a university course. Although seminar papers have specific purposes and guidelines in some places, such as law school, the general process and format is the same. The steps below will guide you through the research and writing process of how to write a seminar paper and provide tips for developing a well-received paper.
Getting Started

- an argument that makes an original contribution to the existing scholarship on your subject
- extensive research that supports your argument
- extensive footnotes or endnotes (depending on the documentation style you are using)

- Make sure that you understand how to cite your sources for the paper and how to use the documentation style your professor prefers, such as APA , MLA , or Chicago Style .
- Don’t feel bad if you have questions. It is better to ask and make sure that you understand than to do the assignment wrong and get a bad grade.

- Since it's best to break down a seminar paper into individual steps, creating a schedule is a good idea. You can adjust your schedule as needed.
- Do not attempt to research and write a seminar in just a few days. This type of paper requires extensive research, so you will need to plan ahead. Get started as early as possible. [3] X Research source

- Listing List all of the ideas that you have for your essay (good or bad) and then look over the list you have made and group similar ideas together. Expand those lists by adding more ideas or by using another prewriting activity. [5] X Research source
- Freewriting Write nonstop for about 10 minutes. Write whatever comes to mind and don’t edit yourself. When you are done, review what you have written and highlight or underline the most useful information. Repeat the freewriting exercise using the passages you underlined as a starting point. You can repeat this exercise multiple times to continue to refine and develop your ideas. [6] X Research source
- Clustering Write a brief explanation (phrase or short sentence) of the subject of your seminar paper on the center of a piece of paper and circle it. Then draw three or more lines extending from the circle. Write a corresponding idea at the end of each of these lines. Continue developing your cluster until you have explored as many connections as you can. [7] X Research source
- Questioning On a piece of paper, write out “Who? What? When? Where? Why? How?” Space the questions about two or three lines apart on the paper so that you can write your answers on these lines. Respond to each question in as much detail as you can. [8] X Research source

- For example, if you wanted to know more about the uses of religious relics in medieval England, you might start with something like “How were relics used in medieval England?” The information that you gather on this subject might lead you to develop a thesis about the role or importance of relics in medieval England.
- Keep your research question simple and focused. Use your research question to narrow your research. Once you start to gather information, it's okay to revise or tweak your research question to match the information you find. Similarly, you can always narrow your question a bit if you are turning up too much information.
Conducting Research

- Use your library’s databases, such as EBSCO or JSTOR, rather than a general internet search. University libraries subscribe to many databases. These databases provide you with free access to articles and other resources that you cannot usually gain access to by using a search engine. If you don't have access to these databases, you can try Google Scholar.

- Publication's credentials Consider the type of source, such as a peer-reviewed journal or book. Look for sources that are academically based and accepted by the research community. Additionally, your sources should be unbiased.
- Author's credentials Choose sources that include an author’s name and that provide credentials for that author. The credentials should indicate something about why this person is qualified to speak as an authority on the subject. For example, an article about a medical condition will be more trustworthy if the author is a medical doctor. If you find a source where no author is listed or the author does not have any credentials, then this source may not be trustworthy. [12] X Research source
- Citations Think about whether or not this author has adequately researched the topic. Check the author’s bibliography or works cited page. If the author has provided few or no sources, then this source may not be trustworthy. [13] X Research source
- Bias Think about whether or not this author has presented an objective, well-reasoned account of the topic. How often does the tone indicate a strong preference for one side of the argument? How often does the argument dismiss or disregard the opposition’s concerns or valid arguments? If these are regular occurrences in the source, then it may not be a good choice. [14] X Research source
- Publication date Think about whether or not this source presents the most up to date information on the subject. Noting the publication date is especially important for scientific subjects, since new technologies and techniques have made some earlier findings irrelevant. [15] X Research source
- Information provided in the source If you are still questioning the trustworthiness of this source, cross check some of the information provided against a trustworthy source. If the information that this author presents contradicts one of your trustworthy sources, then it might not be a good source to use in your paper.

- Give yourself plenty of time to read your sources and work to understand what they are saying. Ask your professor for clarification if something is unclear to you.
- Consider if it's easier for you to read and annotate your sources digitally or if you'd prefer to print them out and annotate by hand.

- Be careful to properly cite your sources when taking notes. Even accidental plagiarism may result in a failing grade on a paper.
Drafting Your Paper

- Make sure that your thesis presents an original point of view. Since seminar papers are advanced writing projects, be certain that your thesis presents a perspective that is advanced and original. [18] X Research source
- For example, if you conducted your research on the uses of relics in medieval England, your thesis might be, “Medieval English religious relics were often used in ways that are more pagan than Christian.”

- Organize your outline by essay part and then break those parts into subsections. For example, part 1 might be your introduction, which could then be broken into three sub-parts: a)opening sentence, b)context/background information c)thesis statement.

- For example, in a paper about medieval relics, you might open with a surprising example of how relics were used or a vivid description of an unusual relic.
- Keep in mind that your introduction should identify the main idea of your seminar paper and act as a preview to the rest of your paper.

- For example, in a paper about relics in medieval England, you might want to offer your readers examples of the types of relics and how they were used. What purpose did they serve? Where were they kept? Who was allowed to have relics? Why did people value relics?
- Keep in mind that your background information should be used to help your readers understand your point of view.

- Remember to use topic sentences to structure your paragraphs. Provide a claim at the beginning of each paragraph. Then, support your claim with at least one example from one of your sources. Remember to discuss each piece of evidence in detail so that your readers will understand the point that you are trying to make.

- For example, in a paper on medieval relics, you might include a heading titled “Uses of Relics” and subheadings titled “Religious Uses”, “Domestic Uses”, “Medical Uses”, etc.

- Synthesize what you have discussed . Put everything together for your readers and explain what other lessons might be gained from your argument. How might this discussion change the way others view your subject?
- Explain why your topic matters . Help your readers to see why this topic deserve their attention. How does this topic affect your readers? What are the broader implications of this topic? Why does your topic matter?
- Return to your opening discussion. If you offered an anecdote or a quote early in your paper, it might be helpful to revisit that opening discussion and explore how the information you have gathered implicates that discussion.

- Ask your professor what documentation style he or she prefers that you use if you are not sure.
- Visit your school’s writing center for additional help with your works cited page and in-text citations.
Revising Your Paper

- What is your main point? How might you clarify your main point?
- Who is your audience? Have you considered their needs and expectations?
- What is your purpose? Have you accomplished your purpose with this paper?
- How effective is your evidence? How might your strengthen your evidence?
- Does every part of your paper relate back to your thesis? How might you improve these connections?
- Is anything confusing about your language or organization? How might your clarify your language or organization?
- Have you made any errors with grammar, punctuation, or spelling? How can you correct these errors?
- What might someone who disagrees with you say about your paper? How can you address these opposing arguments in your paper? [26] X Research source

Features of Seminar Papers and Sample Thesis Statements

Community Q&A
- Keep in mind that seminar papers differ by discipline. Although most seminar papers share certain features, your discipline may have some requirements or features that are unique. For example, a seminar paper written for a Chemistry course may require you to include original data from your experiments, whereas a seminar paper for an English course may require you to include a literature review. Check with your student handbook or check with your advisor to find out about special features for seminar papers in your program. Make sure that you ask your professor about his/her expectations before you get started as well. [27] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- When coming up with a specific thesis, begin by arguing something broad and then gradually grow more specific in the points you want to argue. Thanks Helpful 23 Not Helpful 11
- Choose a topic that interests you, rather than something that seems like it will interest others. It is much easier and more enjoyable to write about something you care about. Thanks Helpful 6 Not Helpful 1

- Do not be afraid to admit any shortcomings or difficulties with your argument. Your thesis will be made stronger if you openly identify unresolved or problematic areas rather than glossing over them. Thanks Helpful 13 Not Helpful 6
- Plagiarism is a serious offense in the academic world. If you plagiarize your paper you may fail the assignment and even the course altogether. Make sure that you fully understand what is and is not considered plagiarism before you write your paper. Ask your teacher if you have any concerns or questions about your school’s plagiarism policy. Thanks Helpful 7 Not Helpful 2
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://umweltoekonomie.uni-hohenheim.de/fileadmin/einrichtungen/umweltoekonomie/1-Studium_Lehre/Materialien_und_Informationen/Guidelines_Seminar_Paper_NEW_14.10.15.pdf
- ↑ https://www.bestcolleges.com/blog/how-to-ask-professor-feedback/
- ↑ http://www.law.georgetown.edu/library/research/guides/seminar_papers.cfm
- ↑ https://www.stcloudstate.edu/writeplace/_files/documents/writing%20process/choosing-and-narrowing-an-essay-topic.pdf
- ↑ http://writing.ku.edu/prewriting-strategies
- ↑ http://www.kuwi.europa-uni.de/en/lehrstuhl/vs/politik3/Hinweise_Seminararbeiten/haenglish.html
- ↑ https://guides.lib.uw.edu/research/faq/reliable
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/673/1/
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/thesis-statements/
- ↑ https://www.irsc.edu/students/academicsupportcenter/researchpaper/researchpaper.aspx?id=4294967433
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/engagement/2/2/58/
- ↑ http://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/beginning-academic-essay
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/589/02/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/561/05/
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/Handbook/ReverseOutlines.html
About This Article

To write a seminar paper, start by writing a clear and specific thesis that expresses your original point of view. Then, work on your introduction, which should give your readers relevant context about your topic and present your argument in a logical way. As you write, break up the body of your paper with headings and sub-headings that categorize each section of your paper. This will help readers follow your argument. Conclude your paper by synthesizing your argument and explaining why this topic matters. Be sure to cite all the sources you used in a bibliography. For advice on getting started on your seminar paper, keep reading. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Mehammed A.
Dec 28, 2023
Did this article help you?
Patrick Topf
Jul 4, 2017
Flora Ballot
Oct 10, 2016
Igwe Uchenna
Jul 19, 2017
Saudiya Kassim Aliyu
Oct 11, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
How to Write a Research Paper as a High School Student

By Carly Taylor
Senior at Stanford University
6 minute read
Read our guide to learn why you should write a research paper and how to do so, from choosing the right topic to outlining and structuring your argument.
What is a research paper?
A research paper poses an answer to a specific question and defends that answer using academic sources, data, and critical reasoning. Writing a research paper is an excellent way to hone your focus during a research project , synthesize what you’re learning, and explain why your work matters to a broader audience of scholars in your field.
The types of sources and evidence you’ll see used in a research paper can vary widely based on its field of study. A history research paper might examine primary sources like journals and newspaper articles to draw conclusions about the culture of a specific time and place, whereas a biology research paper might analyze data from different published experiments and use textbook explanations of cellular pathways to identify a potential marker for breast cancer.
However, researchers across disciplines must identify and analyze credible sources, formulate a specific research question, generate a clear thesis statement, and organize their ideas in a cohesive manner to support their argument. Read on to learn how this process works and how to get started writing your own research paper.
Choosing your topic
Tap into your passions.
A research paper is your chance to explore what genuinely interests you and combine ideas in novel ways. So don’t choose a subject that simply sounds impressive or blindly follow what someone else wants you to do – choose something you’re really passionate about! You should be able to enjoy reading for hours and hours about your topic and feel enthusiastic about synthesizing and sharing what you learn.
We've created these helpful resources to inspire you to think about your own passion project . Polygence also offers a passion exploration experience where you can dive deep into three potential areas of study with expert mentors from those fields.
Ask a difficult question
In the traditional classroom, top students are expected to always know the answers to the questions the teacher asks. But a research paper is YOUR chance to pose a big question that no one has answered yet, and figure out how to make a contribution to answering that question. So don’t be afraid if you have no idea how to answer your question at the start of the research process — this will help you maintain a motivational sense of discovery as you dive deeper into your research. If you need inspiration, explore our database of research project ideas .
Be as specific as possible
It’s essential to be reasonable about what you can accomplish in one paper and narrow your focus down to an issue you can thoroughly address. For example, if you’re interested in the effects of invasive species on ecosystems, it’s best to focus on one invasive species and one ecosystem, such as iguanas in South Florida , or one survival mechanism, such as supercolonies in invasive ant species . If you can, get hands on with your project.
You should approach your paper with the mindset of becoming an expert in this topic. Narrowing your focus will help you achieve this goal without getting lost in the weeds and overwhelming yourself.
Would you like to write your own research paper?
Polygence mentors can help you every step of the way in writing and showcasing your research paper
Preparing to write
Conduct preliminary research.
Before you dive into writing your research paper, conduct a literature review to see what’s already known about your topic. This can help you find your niche within the existing body of research and formulate your question. For example, Polygence student Jasmita found that researchers had studied the effects of background music on student test performance, but they had not taken into account the effect of a student’s familiarity with the music being played, so she decided to pose this new question in her research paper.
Pro tip: It’s a good idea to skim articles in order to decide whether they’re relevant enough to your research interest before committing to reading them in full. This can help you spend as much time as possible with the sources you’ll actually cite in your paper.
Skimming articles will help you gain a broad-strokes view of the different pockets of existing knowledge in your field and identify the most potentially useful sources. Reading articles in full will allow you to accumulate specific evidence related to your research question and begin to formulate an answer to it.
Draft a thesis statement
Your thesis statement is your succinctly-stated answer to the question you’re posing, which you’ll make your case for in the body of the paper. For example, if you’re studying the effect of K-pop on eating disorders and body image in teenagers of different races, your thesis may be that Asian teenagers who are exposed to K-pop videos experience more negative effects on their body image than Caucasian teenagers.
Pro Tip: It’s okay to refine your thesis as you continue to learn more throughout your research and writing process! A preliminary thesis will help you come up with a structure for presenting your argument, but you should absolutely change your thesis if new information you uncover changes your perspective or adds nuance to it.
Create an outline
An outline is a tool for sketching out the structure of your paper by organizing your points broadly into subheadings and more finely into individual paragraphs. Try putting your thesis at the top of your outline, then brainstorm all the points you need to convey in order to support your thesis.
Pro Tip : Your outline is just a jumping-off point – it will evolve as you gain greater clarity on your argument through your writing and continued research. Sometimes, it takes several iterations of outlining, then writing, then re-outlining, then rewriting in order to find the best structure for your paper.
Writing your paper
Introduction.
Your introduction should move the reader from your broad area of interest into your specific area of focus for the paper. It generally takes the form of one to two paragraphs that build to your thesis statement and give the reader an idea of the broad argumentative structure of your paper. After reading your introduction, your reader should know what claim you’re going to present and what kinds of evidence you’ll analyze to support it.
Topic sentences
Writing crystal clear topic sentences is a crucial aspect of a successful research paper. A topic sentence is like the thesis statement of a particular paragraph – it should clearly state the point that the paragraph will make. Writing focused topic sentences will help you remain focused while writing your paragraphs and will ensure that the reader can clearly grasp the function of each paragraph in the paper’s overall structure.
Transitions
Sophisticated research papers move beyond tacking on simple transitional phrases such as “Secondly” or “Moreover” to the start of each new paragraph. Instead, each paragraph flows naturally into the next one, with the connection between each idea made very clear. Try using specifically-crafted transitional phrases rather than stock phrases to move from one point to the next that will make your paper as cohesive as possible.
In her research paper on Pakistani youth in the U.S. , Polygence student Iba used the following specifically-crafted transition to move between two paragraphs: “Although the struggles of digital ethnography limited some data collection, there are also many advantages of digital data collection.” This sentence provides the logical link between the discussion of the limitations of digital ethnography from the prior paragraph and the upcoming discussion of this techniques’ advantages in this paragraph.
Your conclusion can have several functions:
To drive home your thesis and summarize your argument
To emphasize the broader significance of your findings and answer the “so what” question
To point out some questions raised by your thesis and/or opportunities for further research
Your conclusion can take on all three of these tasks or just one, depending on what you feel your paper is still lacking up to this point.
Citing sources
Last but not least, giving credit to your sources is extremely important. There are many different citation formats such as MLA, APA, and Chicago style. Make sure you know which one is standard in your field of interest by researching online or consulting an expert.
You have several options for keeping track of your bibliography:
Use a notebook to record the relevant information from each of your sources: title, author, date of publication, journal name, page numbers, etc.
Create a folder on your computer where you can store your electronic sources
Use an online bibliography creator such as Zotero, Easybib, or Noodletools to track sources and generate citations
You can read research papers by Polygence students under our Projects tab. You can also explore other opportunities for high school research .
If you’re interested in finding an expert mentor to guide you through the process of writing your own independent research paper, consider applying to be a Polygence scholar today!
Your research paper help even you to earn college credit , get published in an academic journal , contribute to your application for college , improve your college admissions chances !
Feeling Inspired?
Interested in doing an exciting research project? Click below to get matched with one of our expert mentors!
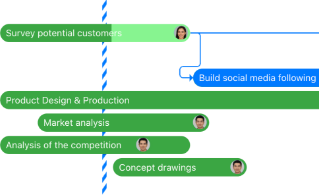
Finally see how to stop getting stuck in a project management tool
20 min. personalized consultation with a project management expert
Smart Note-Taking for Research Paper Writing
How to organize research notes using the Zettelkasten Method when writing academic papers

With plenty of note-taking tips and apps available, online and in paper form, it’s become extremely easy to take note of information, ideas, or thoughts. As simple as it is to write down an idea or jot down a quote, the skill of academic research and writing for a thesis paper is on another level entirely. And keeping a record or an archive of all of the information you need can quickly require a very organized system.

The use of index cards seems old-fashioned considering that note-taking apps (psst! Hypernotes ) offer better functionality and are arguably more user-friendly. However, software is only there to help aid our individual workflow and thinking process. That’s why understanding and learning how to properly research, take notes and write academic papers is still a highly valuable skill.
Let’s Start Writing! But Where to Start…
Writing academic papers is a vital skill most students need to learn and practice. Academic papers are usually time-intensive pieces of written content that are a requirement throughout school or at University. Whether a topic is assigned or you have to choose your own, there’s little room for variation in how to begin.
Popular and purposeful in analyzing and evaluating the knowledge of the author as well as assessing if the learning objectives were met, research papers serve as information-packed content. Most of us may not end up working jobs in academic professions or be researchers at institutions, where writing research papers is also part of the job, but we often read such papers.
Despite the fact that most research papers or dissertations aren’t often read in full, journalists, academics, and other professionals regularly use academic papers as a basis for further literary publications or blog articles. The standard of academic papers ensures the validity of the information and gives the content authority.
There’s no-nonsense in research papers. To make sure to write convincing and correct content, the research stage is extremely important. And, naturally, when doing any kind of research, we take notes.
Why Take Notes?
There are particular standards defined for writing academic papers . In order to meet these standards, a specific amount of background information and researched literature is required. Taking notes helps keep track of read/consumed literary material as well as keeps a file of any information that may be of importance to the topic.
The aim of writing isn’t merely to advertise fully formed opinions, but also serves the purpose of developing opinions worth sharing in the first place.
What is Note-Taking?

Note-taking (sometimes written as notetaking or note-taking ) is the practice of recording information from different sources and platforms. For academic writing, note-taking is the process of obtaining and compiling information that answers and supports the research paper’s questions and topic. Notes can be in one of three forms: summary, paraphrase, or direct quotation.
Note-taking is an excellent process useful for anyone to turn individual thoughts and information into organized ideas ready to be communicated through writing. Notes are, however, only as valuable as the context. Since notes are also a byproduct of the information we consume daily, it’s important to categorize information, develop connections, and establish relationships between pieces of information.
What Type of Notes Can I Take?
- Explanation of complex theories
- Background information on events or persons of interest
- Definitions of terms
- Quotations of significant value
- Illustrations or graphics
Note-Taking 101

Taking notes or doing research for academic papers shouldn’t be that difficult, considering we take notes all the time. Wrong. Note-taking for research papers isn’t the same as quickly noting down an interesting slogan or cool quote from a video, putting it on a sticky note, and slapping it onto your bedroom or office wall.
Note-taking for research papers requires focus and careful deliberation of which information is important to note down, keep on file, or use and reference in your own writing. Depending on the topic and requirements of your research paper from your University or institution, your notes might include explanations of complex theories, definitions, quotations, and graphics.
Stages of Research Paper Writing
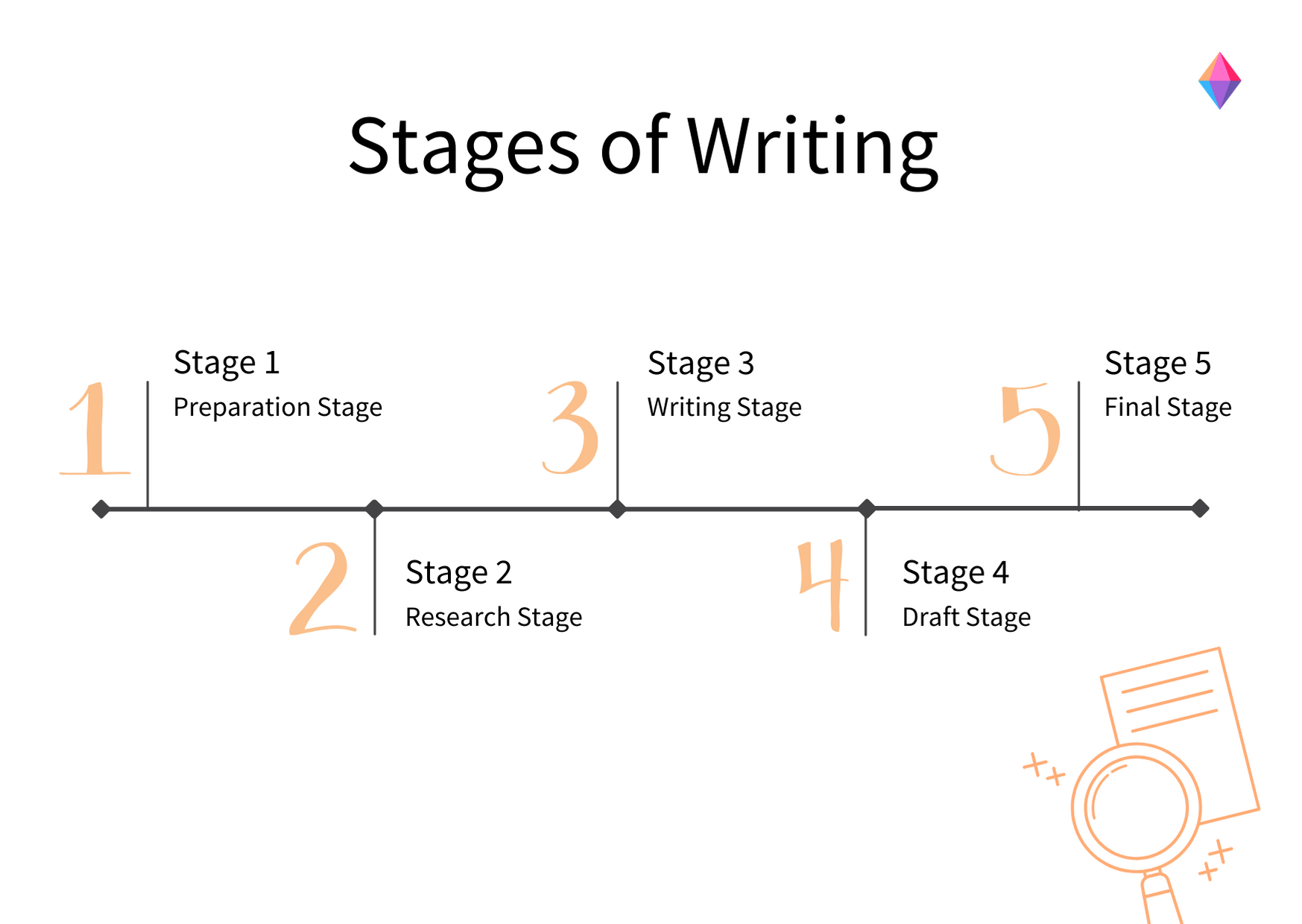
1. Preparation Stage
Before you start, it’s recommended to draft a plan or an outline of how you wish to begin preparing to write your research paper. Make note of the topic you will be writing on, as well as the stylistic and literary requirements for your paper.
2. Research Stage
In the research stage, finding good and useful literary material for background knowledge is vital. To find particular publications on a topic, you can use Google Scholar or access literary databases and institutions made available to you through your school, university, or institution.
Make sure to write down the source location of the literary material you find. Always include the reference title, author, page number, and source destination. This saves you time when formatting your paper in the later stages and helps keep the information you collect organized and referenceable.

In the worst-case scenario, you’ll have to do a backward search to find the source of a quote you wrote down without reference to the original literary material.
3. Writing Stage
When writing, an outline or paper structure is helpful to visually break up the piece into sections. Once you have defined the sections, you can begin writing and referencing the information you have collected in the research stage.
Clearly mark which text pieces and information where you relied on background knowledge, which texts are directly sourced, and which information you summarized or have written in your own words. This is where your paper starts to take shape.
4. Draft Stage
After organizing all of your collected notes and starting to write your paper, you are already in the draft stage. In the draft stage, the background information collected and the text written in your own words come together. Every piece of information is structured by the subtopics and sections you defined in the previous stages.
5. Final Stage
Success! Well… almost! In the final stage, you look over your whole paper and check for consistency and any irrelevancies. Read through the entire paper for clarity, grammatical errors , and peace of mind that you have included everything important.
Make sure you use the correct formatting and referencing method requested by your University or institution for research papers. Don’t forget to save it and then send the paper on its way.
Best Practice Note-Taking Tips
- Find relevant and authoritative literary material through the search bar of literary databases and institutions.
- Practice citation repeatedly! Always keep a record of the reference book title, author, page number, and source location. At best, format the citation in the necessary format from the beginning.
- Organize your notes according to topic or reference to easily find the information again when in the writing stage. Work invested in the early stages eases the writing and editing process of the later stages.
- Summarize research notes and write in your own words as much as possible. Cite direct quotes and clearly mark copied text in your notes to avoid plagiarism.
Take Smart Notes

Taking smart notes isn’t as difficult as it seems. It’s simply a matter of principle, defined structure, and consistency. Whether you opt for a paper-based system or use a digital tool to write and organize your notes depends solely on your individual personality, needs, and workflow.
With various productivity apps promoting diverse techniques, a good note-taking system to take smart notes is the Zettelkasten Method . Invented by Niklas Luhmann, a german sociologist and researcher, the Zettelkasten Method is known as the smart note-taking method that popularized personalized knowledge management.
As a strategic process for thinking and writing, the Zettelkasten Method helps you organize your knowledge while working, studying, or researching. Directly translated as a ‘note box’, Zettelkasten is simply a framework to help organize your ideas, thoughts, and information by relating pieces of knowledge and connecting pieces of information to each other.
Hypernotes is a note-taking app that can be used as a software-based Zettelkasten, with integrated features to make smart note-taking so much easier, such as auto-connecting related notes, and syncing to multiple devices. In each notebook, you can create an archive of your thoughts, ideas, and information.
Using the tag system to connect like-minded ideas and information to one another and letting Hypernotes do its thing with bi-directional linking, you’ll soon create a web of knowledge about anything you’ve ever taken note of. This feature is extremely helpful to navigate through the enormous amounts of information you’ve written down. Another benefit is that it assists you in categorizing and making connections between your ideas, thoughts, and saved information in a single notebook. Navigate through your notes, ideas, and knowledge easily.
Ready, Set, Go!
Writing academic papers is no simple task. Depending on the requirements, resources available, and your personal research and writing style, techniques, apps, or practice help keep you organized and increase your productivity.
Whether you use a particular note-taking app like Hypernotes for your research paper writing or opt for a paper-based system, make sure you follow a particular structure. Repeat the steps that help you find the information you need quicker and allow you to reproduce or create knowledge naturally.
Images from NeONBRAND , hana_k and Surface via Unsplash
A well-written piece is made up of authoritative sources and uses the art of connecting ideas, thoughts, and information together. Good luck to all students and professionals working on research paper writing! We hope these tips help you in organizing the information and aid your workflow in your writing process.
Cheers, Jessica and the Zenkit Team

FREE 20 MIN. CONSULTATION WITH A PROJECT MANAGEMENT EXPERT
Wanna see how to simplify your workflow with Zenkit in less than a day?
- digital note app
- how to smart notes
- how to take notes
- hypernotes note app
- hypernotes take notes
- note archive software
- note taking app for students
- note taking tips
- note-taking
- note-taking app
- organize research paper
- reading notes
- research note taking
- research notes
- research paper writing
- smart notes
- taking notes zettelkasten method
- thesis writing
- writing a research paper
- writing a thesis paper
- zettelkasten method
More from Karen Bradford
10 Ways to Remember What You Study
More from Kelly Moser
How Hot Desking Elevates the Office Environment in 2024
More from Chris Harley
8 Productivity Tools for Successful Content Marketing
2 thoughts on “ Smart Note-Taking for Research Paper Writing ”
Thanks for sending really an exquisite text.
Great article thank you for sharing!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Zenkit Comment Policy
At Zenkit, we strive to post helpful, informative, and timely content. We want you to feel welcome to comment with your own thoughts, feedback, and critiques, however we do not welcome inappropriate or rude comments. We reserve the right to delete comments or ban users from commenting as needed to keep our comments section relevant and respectful.
What we encourage:
- Smart, informed, and helpful comments that contribute to the topic. Funny commentary is also thoroughly encouraged.
- Constructive criticism, either of the article itself or the ideas contained in it.
- Found technical issues with the site? Send an email to [email protected] and specify the issue and what kind of device, operating system, and OS version you are using.
- Noticed spam or inappropriate behaviour that we haven’t yet sorted out? Flag the comment or report the offending post to [email protected] .
What we’d rather you avoid:
Rude or inappropriate comments.
We welcome heated discourse, and we’re aware that some topics cover things people feel passionately about. We encourage you to voice your opinions, however in order for discussions to remain constructive, we ask that you remember to criticize ideas, not people.
Please avoid:
- name-calling
- ad hominem attacks
- responding to a post’s tone instead of its actual content
- knee-jerk contradiction
Comments that we find to be hateful, inflammatory, threatening, or harassing may be removed. This includes racist, gendered, ableist, ageist, homophobic, and transphobic slurs and language of any sort. If you don’t have something nice to say about another user, don't say it. Treat others the way you’d like to be treated.
Trolling or generally unkind behaviour
If you’re just here to wreak havoc and have some fun, and you’re not contributing meaningfully to the discussions, we will take actions to remove you from the conversation. Please also avoid flagging or downvoting other users’ comments just because you disagree with them.
Every interpretation of spamming is prohibited. This means no unauthorized promotion of your own brand, product, or blog, unauthorized advertisements, links to any kind of online gambling, malicious sites, or otherwise inappropriate material.
Comments that are irrelevant or that show you haven’t read the article
We know that some comments can veer into different topics at times, but remain related to the original topic. Be polite, and please avoid promoting off-topic commentary. Ditto avoid complaining we failed to mention certain topics when they were clearly covered in the piece. Make sure you read through the whole piece before saying your piece!
Breaches of privacy
This should really go without saying, but please do not post personal information that may be used by others for malicious purposes. Please also do not impersonate authors of this blog, or other commenters (that’s just weird).

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The writing guides below aim to introduce students both to the specific methods and conventions of writing original research in their area of concentration and to effective writing process. ... See also The Brief Guide to Writing the History Paper. A Guide to Writing a Senior Thesis in Sociology. Author: Department of Sociology, Harvard University.
• A senior thesis must be an original research project of no fewer than 10,000 words and no more than 20,000 words, not counting notes and bibliography. Students may petition the Director of Studies to write a thesis that exceeds 20,000 words. Typical theses run somewhere in the range of 15,000-20,000 words.
2 Q: Why should I write a Senior Thesis? A: While writing a thesis is one way to become eligible for honors, and the only way to become eligible for the summa cum laude level of honors, the best motivations are a love of research and/or a burning question. You should not consider a Senior Thesis if your primary motivations are not intellectually based, but are instead more practical—i.e ...
crafting your research question, compiling an annotated bibliography, and writing as a "process"—just to name a few of the topics covered here—are key issues of concern for ALL thesis writers, no matter what question you plan to investigate.
A senior thesis in literature, on the other hand, will likely involve studying a movement, trope, author, or theme, and your sources will involve a combination of fiction, historical context, literary criticism, and literary theory. At many schools, a thesis ranges from 80 to 125 pages. At other universities, as few as 25 pages might fill the ...
The Writing Center has Senior Thesis Tutors who will read drafts of your thesis (more typically, parts of your thesis) in advance and meet with you individually to talk about structure, argument, clear writing, and mapping out your writing plan. If you need help with breaking down your project or setting up a schedule for the week, the semester ...
What this handout is about. Writing a senior honors thesis, or any major research essay, can seem daunting at first. A thesis requires a reflective, multi-stage writing process. This handout will walk you through those stages. It is targeted at students in the humanities and social sciences, since their theses tend to involve more writing than ...
usually require students to write reading responses, complete exercises, and, very often, turn in a final research paper . We recommend that you write down the questions and sub-topics that interest you while taking tutorials, so that you can think about the possi-bilities of turning these questions into a research project .
senior thesis is not simply a much longer term paper. It is not simply an independent project carried out under the general guidance of an advisor. It does not simply require more research, more evidence, and more writing. Rather, your thesis requires more methodology. In a nutshell, that is what this handbook is meant to provide.
Whether writing a JP or a senior thesis, your question should be complex enough to warrant serious treatment in a lengthy paper, but focused enough that you can do a thorough job with your analysis. (For a discussion of suggested length and format of a JP and senior thesis, see Chapter 9, "Other Helpful Information.")
We've covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are: To choose a research question and review the literature. To plan your paper structure and draft an outline. To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing.
Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist.
Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers. 5. Write a thesis statement. A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction.
Sub-point of sub-point 1. Essentially the same as the alphanumeric outline, but with the text written in full sentences rather than short points. Example: First body paragraph of the research paper. First point of evidence to support the main argument. Sub-point discussing evidence outlined in point A.
The research project demonstrates a student's skills to carry out independent research. 4. While composing the senior project's manuscri pt, the student has to follow the
After you get enough feedback and decide on the journal you will submit to, the process of real writing begins. Copy your outline into a separate file and expand on each of the points, adding data and elaborating on the details. When you create the first draft, do not succumb to the temptation of editing.
eight weeks summer senior thesis research in sub-Saharan Africa (consultation with CAS recommended). Davis Center for Russian and Eurasian Studies Summer Travel Grants (Goldman Grant) for summer senior thesis research Russia, Eastern Europe, or Central Asia on a topic related to Russian or Eurasian studies.
X Research source. Clustering Write a brief explanation (phrase or short sentence) of the subject of your seminar paper on the center of a piece of paper and circle it. Then draw three or more lines extending from the circle. Write a corresponding idea at the end of each of these lines.
Create a folder on your computer where you can store your electronic sources. Use an online bibliography creator such as Zotero, Easybib, or Noodletools to track sources and generate citations. You can read research papers by Polygence students under our Projects tab. You can also explore other opportunities for high school research.
Step 2: Methods. Next, indicate the research methods that you used to answer your question. This part should be a straightforward description of what you did in one or two sentences. It is usually written in the past simple tense, as it refers to completed actions.
Use strong action verbs to describe the effect of your research, such as "transforms," "enables," "revolutionizes," or "underscores.". 5. Keep it concise. Focus on writing within the word limit and keeping the information that is required to be showcased or highlighted. After drafting your abstract, review it specifically for ...
For academic writing, note-taking is the process of obtaining and compiling information that answers and supports the research paper's questions and topic. Notes can be in one of three forms: summary, paraphrase, or direct quotation. Note-taking is an excellent process useful for anyone to turn individual thoughts and information into ...
Appendix B: Research and Writing ... Studies to withdraw from candidacy for honors and must submit two twenty-page papers (one each semester) or one forty-page paper (in early May) to receive credit for History and ... Williams as a junior, it's fineto write about him again as a senior. But you must ask a new question