
- How it Works
- Professional Advisors
- Companies & Individuals
- Advanced Knowledge Base
- Lite Knowledge Base
- Samples & Publications
- User Support

The Most Common Business Plan Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them

Recent Posts
- Tips for Small Businesses to Conquer Challenges of Remote Work
- Mastering the Art of Marketing: An Introduction to Marketing Plans
- How Can SMEs Leverage Artificial Intelligence (AI) to Drive Growth?
- 6 Cost-Effective Marketing Hacks
- How Small Businesses Can Stay the Course on the Road to Success
Every company benefits from an updated business plan. While it seems necessary for start-ups, it applies to established firms, too. An efficiently written business plan keeps the whole business on track in the process of execution of the company’s strategy and reaching its business goals. Business plan mistakes can result in anything ranging from small oversights to fatal errors for your business. It is even more important for the business who are at the funds raising stage, so the information they provide is accurate and none of your ideas are misleading and are in tune with the current market. To help you avoid your business plan from being discarded, here are some of the critical business plan mistakes to be careful with:
- Long and bulky Executive Summary The readers of business plan such as investors, bank institutions and key vendors start considering your business idea from reading the executive summary. Executive summary is a highlight of the most important items of your business plan in a concise but informative way. It should succinctly describe your compelling story on how a highly skilled team will deliver products or services to precisely defined target markets based on a consistent strategy. Besides, it should state the company’s value proposition on how their products or services will change the life of its customers for the better in a profitable way. In fact, many executive summaries are boring and state some business idea whose execution remains vague. Often, it is presented as just cut and paste of some sections from the introduction and some other parts of business plan. Therefore, there are high chances of the busy investor to move on to the next proposal, if executive summary does not provide a clear, convincing, and persuasive overview of the business.
- Attaching your value proposition to dated technology or dwindling markets When formulating in your business plan the opportunity you see for a product or service, you need to question it and can’t just assume that the idea has automatic demand in the real world. A professionally written business plan will assure you are setting up your business for success. This implies that you must develop a value proposition of your product or service that will change an emerging or existing market. Those markets that are shrinking or are being replaced by new industries will make it incredibly challenging for you to get funding. For instance, what would your reaction be if someone developed waterproof ink for typewriter ribbons? You wouldn’t necessarily be amazed, because the number of people looking to buy something like that is miniscule.
- Not knowing the target audience and segments A product or service that is everything to everyone does not exist. If that were so, we would all be using the same phone. In fact, your product or service is specific and advantageous to an ideal type of customer. Without defining your target market, you cannot reason how you will handle the fierce competition. There are competitors who are providing the same product and service. Investors trust their funds to companies that have completed and gained a complete knowledge of primary and secondary market. You must define your target market and outline how you will target this audience.
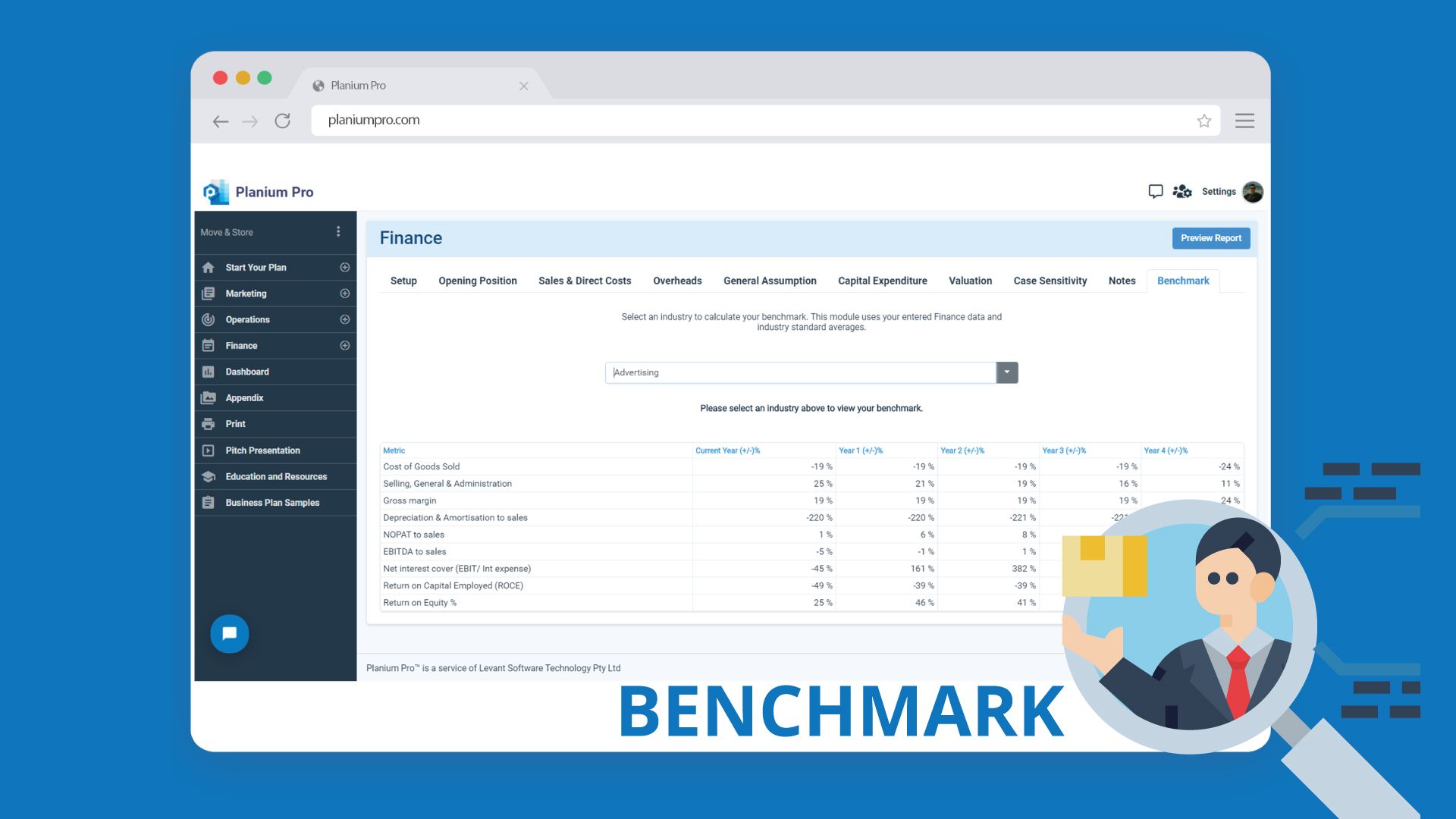
- Having unrealistic and aggressive growth projections Having read the executive summary, many investors jump straight to the financial section of the business plan. It is important that the assumptions and projections in this section to be realistic. Plans that show sales forecast, operating margin and revenues that are poorly reasoned, internally inconsistent or simply unrealistic significantly damage the credibility of the entire business plan. In opposite, sober, well-supported financial assumptions and projections communicate operational maturity and credibility. Benchmarking is an especially useful tool to use in your financial analysis. By comparing and basing your projections on the financial performance of public companies within your marketplace, you can prove that your assumptions and projections are achievable. Planium Pro makes your life easier in that regard. Finance section of the Planium Pro’s software provides an easy and quick benchmarking tool for a variety of industries so you can efficiently measure your projections and key ratios against your market averages.
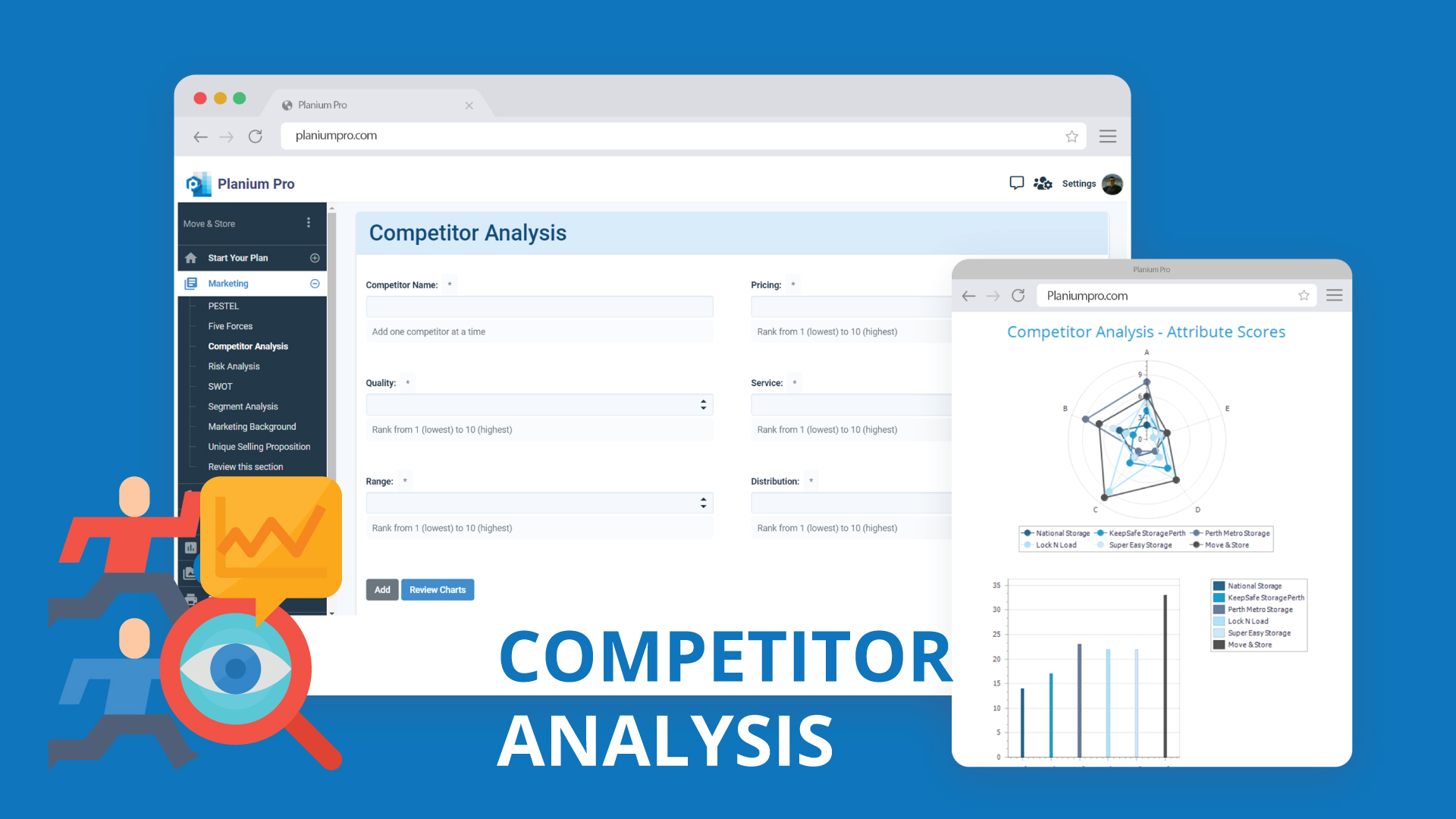
- Acknowledging your competitors, but not researching them Many new businesses are too much inward-focused. Being confident about your product or service is certainly a good attitude. But there is risk that this could twist your idea of how it correlates with products and services of competitors who have been in the market for some time. Besides, quite often entrepreneurs also miss or underestimate the possibility of new entrants who could increase competitive pressure. Our recommendation is to learn as much as you can about the people you’re going up against and perform Competitor Analysis, based on their pricing, quality, service and distribution channels. Knowing this information helps you prepare your own strategy to differentiate your business from theirs.
Next Steps • Keep these critical mistakes in mind when writing your business plan. • If you have already started writing your plan, use Planium Pro software to ease your preparation and streamline the process. Join our Planium Pro to see all the benefits yourself. Read More We would be interested to receive comments from small-business owners on what mistakes you have made in business plan writing and how you fixed them.
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Planium Pro
For professional & advanced users

Planium Pro Lite
For startup entrepreneur or small business users
Available at the following online bookstores:

Plan Smarter, Grow Faster:
25% Off Annual Plans! Save Now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
17 Key Business Plan Mistakes to Avoid in 2024
Posted december 6, 2023 by noah parsons.

If you’re like most people and you’re writing a business plan for the first time, you want to make sure you get it right. Even if you follow the instructions in one of the popular business plan templates out there, you can still make mistakes.
After having spent countless hours reading thousands of business plans and having judged hundreds of business plan competitions, I’ve assembled a list of the biggest business plan mistakes that I’ve seen.
What is the biggest mistake when preparing a business plan?
The absolute biggest business plan mistake you can make is to not plan at all.
That doesn’t mean everyone must write a detailed business plan. While you should do some planning to figure out what direction you want to take your business—your plan could be as simple as a one-page business plan, or even a pitch presentation that highlights your current strategy.
Your strategy and ideas will certainly evolve as you go, but taking a little time to figure out how your business works will pay dividends over time.
17 common business plan mistakes to avoid
Assuming you’ve at least decided that you should do some business planning, here are the top business plan mistakes to avoid:
1. Not taking the planning process seriously
Writing a business plan just to “tick the box” and have a pile of paper to hand to a loan officer at the bank is the wrong way to approach business planning.
If you don’t take the business planning process seriously, it’s going to show that you don’t really care about your business and haven’t really thought through how your business is going to be successful.
Instead, take the time and use the planning process to strengthen your understanding of how your business will be successful. It will improve your chances with lenders and investors and help you run a better business in the long run.
2. Not having a defined purpose for your business plan
Why are you writing a business plan?
Is it to raise money? Are you just trying to get your team on the same page as you so they understand your strategy? Or are you planning a new period of growth?
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will help you stay focused on what matters to help you achieve your goals, while not wasting time on areas of the plan that don’t matter for what you’re doing.
For example, if you’re writing an internal business plan, you can probably skip the sections that describe your team.
3. Not writing for the right audience
When you’re putting together your business plan, make sure to consider who your readers are. This is especially important for businesses that are in the technology and medical industries .
If your audience isn’t going to understand the specialized vocabulary that you use to describe your business and what you do, they aren’t going to be able to understand your business.
On the other hand, if your audience is going to be all industry insiders, make sure to write in the language that they understand.
4. Writing a business plan that’s too long
Don’t write a book when you’re putting together your plan. Your audience doesn’t have time to spend reading countless pages about your business. Instead, focus on getting straight to the point and make your business plan as short as possible.
Start with a one-page plan to keep things concise. You can always include additional details in an appendix or in follow-up documents if your reader needs more information.
5. Not doing enough research
You don’t need to spend endless time researching, but your business plan should demonstrate that you truly understand your industry, your target market, and your competitors. If you don’t have this core knowledge, it’s going to show that you’re not prepared to launch your business.
To keep things simple, start with this four-step process to make sure you cover your bases with an initial market analysis.
6. Not defining your target market
Don’t assume your products are for “everyone.”
Even a company like Facebook that now truly does target “everyone” started out with a focus on college students. Make sure you take some time to understand your target market and who your customers really are.
Investors will want to see that you understand who you are marketing to and that you’re building your product or service for a specific market.
7. Failing to establish a sound business model
Every business needs to eventually have a way to make money. Your business plan needs to clearly explain who your customers are, what they pay you, and have financial projections that show your path to profitability.
Without a real business model , where income covers your expenses, it will be difficult to show that you have a viable path to success.
8. Failing to showcase current traction and milestones
Great business plans are more than just a collection of ideas. They also demonstrate that you have early traction — a fancy way of saying that you have some initial success.
This could come in the form of pre-orders from a Kickstarter campaign or initial contracts that you’ve signed with your first customers. Traction can be as little as expressed interest from potential customers, but the more commitment you have, the better. The companion to traction is milestones. Milestones are simply your roadmap for the future — your next steps with details of what you’re going to do and when you’re going to do it. Make sure to include your best guess at your future timeline as part of your business plan.
9. Having unrealistic financial projections
Everyone dreams of sales that start from zero and then just skyrocket off the charts. Unfortunately, this rarely happens. So, if you have financial projections that look too good to be true, it’s worth a second look.
Investors don’t want you to be overly conservative either. You just need to have a financial forecast that’s based in reality and that you can easily explain.
Keep in mind that when first starting out, you may not have exact numbers to work with. That’s perfectly fine. You can work with general assumptions and compare against competitive benchmarks to set a baseline for your business.
The key here is to develop reasonable projections that you and any external parties can reference and see as viable.
10. Ignoring your competitors
Not knowing who your competitors are , or pretending that you have no competition, is a common mistake. It’s easy to say that you have “no competition,” but that’s just taking the easy way out. Every business has competition, even if it’s a completely different way of solving the same problem.
For example, Henry Ford’s early competition to the automobile wasn’t other cars — it was horses.
11. Missing organizational or team information
When you’re starting a business, it’s likely that you haven’t hired everyone that you’re going to need. That’s OK. The mistake people make in their business plan is not acknowledging that there are key positions yet to be filled.
A successful plan will highlight the key roles that you plan to hire for in the future and the types of people you’ll be looking for. This is especially vital when pitching to investors to showcase that you’re already thinking ahead.
12. Inconsistent information and mistakes
This almost goes without saying, but make sure to proofread your plan before you send it out. Beyond ensuring that you use proper grammar and spelling, make sure that any numbers that you mention in your plan are the same ones that you have in your financial projections.
You don’t want to write that you’re aiming for $2 million in sales, while your sales forecast shows $3 million.
13. Including incomplete financial information
You may have a great idea, but a business plan isn’t complete without a full financial forecast. Too many business plans neglect this area, probably because it seems like it’s the most challenging. But, if you use a good forecasting tool like LivePlan , the process is easy.
Make sure to include forecasts for Profit and Loss, Cash Flow, and Balance Sheet. You may also want to include additional detail related to your sales forecast.
For example, if you run a subscription business , you should include information about your churn rate and customer retention.
14. Adding too much information
Don’t fall into the trap of adding everything you know about your business, your industry, and your target market into your business plan. Your business plan should just cover the highlights so that it’s short enough that people will read it.
A simple and concise plan will engage your reader and could prompt follow-up requests for additional information.
Focus on writing an engaging executive summary and push non-critical, detailed information into your appendix — or leave it out altogether and leave the details for those that ask.
Remember, your business plan is there to serve a purpose. If you’re raising money, you want to get that next meeting with your investors. If you’re sharing your strategy with your team, you want your team to actually read what you wrote.
Keep your plan short and simple to help achieve these goals.
What should not be included in a business plan?
Here are a few things to leave out of your plan:
- Full resumes of each team member. Just hit the highlights.
- Detailed technical explanations or schematics of how your product works. Put these in the appendix or just leave them out completely.
- A long history of your industry. A few sentences should be enough.
- Detailed market research. Yes, you want market research but just include the summary of your findings, not all the data.
Make sure to include:
- Executive summary.
- Financial projections.
- Market research (just a summary)
- Competition overview
- Funding needs (if you’re raising money)
15. Having no one review your plan
As with any work that you do, it’s always helpful to have a few other people take a look at your work as you go. You don’t have to please everyone and you don’t have to implement every comment, but you should listen for themes in your feedback and make adjustments as you go.
A fresh pair of eyes will always help spot pesky typos as well as highlight areas of your plan that may not make sense. You can even explore having a plan writing expert review your plan for a more in-depth analysis.
16. Never revisiting your business plan
Business plans are never 100% accurate and things never go exactly as planned. Just like when you set out on a road trip, you have a plan to reach your final destination and an idea of how you will get there.
But, things can change as you go and you may want to adjust your route.
Planning for your business is often the same as that road trip and your plans will change as you grow your business. Keeping your plan updated will help you set new goals for you and your team and, most importantly, set financial goals and budgets that will help your business thrive.
Incorporate your plan into regular review meetings to be sure you’re consistently revisiting it and integrating the time spent reviewing into your current workflow.
17. Not using your business plan to manage your business
Revisiting and revising your business plan is how you use your plan to manage your business. If you aren’t updating your goals and following a budget, you’re flying blind. Your plan is your ultimate tool to help you manage your business to success. You can use it to set sales goals and figure out when and how you should expand.
You’ll use your plan to ensure that you have healthy cash flow and enough money in the bank to handle your growth. Without managing your plan, you’re left to guess and live with a level of uncertainty about where your business is headed.
How a business planning and management tool helps you avoid mistakes
Writing a business plan can seem like a daunting task. Sure, you can do it yourself with free templates and advice like you find on this website . But, doing it on your own can just slow the process down, lead to mistakes, and keep you from actually working on building your business.
Instead, consider using a planning tool, like LivePlan, which features step-by-step guidance and financial forecasting tools that propel you through the process.
LivePlan will help you include only what you need in your plan and reduce the time you spend on formatting and presenting. You’ll also get help building solid financial models that you can trust, without having to worry about getting everything right in a spreadsheet.
Finally, it will transform your plan into a management tool that will help you easily compare your forecasts to your actual results. This makes it easy to track your progress and make adjustments as you go.
So, whether you’re writing a plan to explore a new business idea, looking to raise money from investors, seeking a loan, or just trying to run your business better—a solid business plan built with LivePlan will help get you there.
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Noah Parsons
Posted in business plan writing, join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

10 Common Business Plan Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
There is plenty of information available via books and seminars on how to write a good business plan. And yet, many companies, especially start-ups, make serious mistakes in business plan writing that could have been avoided with more knowledge and effort.
As a business plan contest reviewer, I see a number of typical mistakes coming up again and again. Here are 10 of the most common business plan mistakes I have come across:
1. Boring Executive Summary
Investors, bankers, and other business plan readers usually start looking at the executive summary. It should highlight the most important points of the business plan in a pithy way. The business plan should provide a convincing story on how a a highly competent team will provide products or services to precisely defined target markets based on a consistent strategy. Moreover, it should share the company’s vision on how their products or services will make the world of their customers better in a profitable way.
In reality, many executive summaries are lackluster and incomplete summaries of a business idea whose implementation remains unclear. Sometimes, it is just cut and paste of some sections from the introduction and some other parts.
Losing the busy reader already in this part could mean that investors never care to go through the whole document. They may be missing some hidden gems. However, it is the job of the business plan writer to present these gems convincingly in the executive summary.
2. Lack of Focus
Many business plans are lacking a clear focus in defining their target markets and how the envisage products and services are competitive in serving the market needs better than others. Especially for innovative start-ups there is a risk of not focusing enough on a clearly define product/service segment and target market.
The result are often business plans describing a ‘me too’ business whose reason for existence does not become clear, not to speak of electrifying potential investors or customers.
3. Superficial Definition of Target Customers
Understanding who your target customers are and how your product adds value for them is crucial. That includes a granular segmentation of target customers and how the company’s products and services will satisfy the different needs of these different customer groups.
Many business plans, however, keep the definition of target customers very general. For example, saying that your travel app is aimed for everyone who is traveling may sound great first, because this is a very large number of people. However, different groups of travelers have different needs. Without clearly defining these needs in a differentiated way, the result will either be an app with the lowest common denominator of functionality needed by most, or it may be at risk of becoming overly complex, as it tries to please everyone.
4. Overly Optimistic Evaluation of Market Size and Opportunities
Entrepreneurs need to be optimistic to start a business in the first place. However, there is fine line between being upbeat about your business prospects and presenting a distorted view of the market size which is more driven by dreams than data. It can be related to a superficial definition of the target customers. If you think, for example, that 20% of all travelers worldwide will use your app, you would need to have a lot of supporting evidence to credibly convey how you will achieve that. It is not bad for an entrepreneur to think big. However, if you, for example, overestimate the readiness of people to buy your product, you may end up with dream figures you cannot achieve.
5. Underestimating the Competition
Many start-ups are too much self-centered. Being convinced of your product or service is certainly a good attitude. However, there is risk that this could distort your view of how it matches up against products and services of competitors who have been in the market for some time. In addition, some entrepreneurs also overlook or underestimate the possibility of new entrants who could increase competitive pressure.
6. Underestimating Business Risks
Understandably, entrepreneurs focus on exploiting opportunities. Some, however, underestimate or even neglect serious business risks that could endanger the existence of the company. Ignoring the risks will not make them disappear. Instead, it will leave the company unprepared, if a risk materializes. Apart from risk caused by changing demand trends, increasing competition, or unexpected increase of production there are also political and regulatory risks to be considered. If you have, for example, an export-oriented business, you need to take into account global trends like increasing protectionism and regulatory barriers in your target markets.
7. Too Detailed Description of the Product or Service
Especially innovative technology start-ups, often led by engineers, are really excited about the technical details of their product or service. It is part of a credible story to provide enough details so the reader understands that the product or service is well designed. However, if it drifts into jargon and technical details not relevant for understanding the business impact or innovative edge of a product, then details can become a distraction or even barrier, putting off the reader.
8. Unrealistic Financial Projections
This mistake is related to false assumptions on, for example, market size, competitive pressure, and financial risks. Nobody knows the future, and projections can, thus, not be exact. However, they can be based on real data related to general market trends and past revenue and cost development.
9. Unconvincing Presentation of the Executive Team
Quite often, there are just a couple of portrait photos and CVs pasted into the business plan without explaining to the reader, why exactly this team is complementary in their competencies specifically for running the particular business presented in the plan. Investors can get very critical, if they see that important competencies in an executive team are lacking. For example, if a group of engineers without business experience is launching a start-up, there will be questions on how competence gaps in areas like financial management and marketing will be covered.
10. Lack of Review
A team working enthusiastically on a business plan is at risk of false, overly optimistic assumptions and other mistakes that can easily be overlooked, if you are immersed in the process. Thus, not having a review of the business plan by an experienced consultant or a friendly business partner who has been there can lead to mistakes with detrimental effects. A review can help find flaws in the overall business rationale, market and customer definition, or the financial projections. Even if you are not looking for external funding, not having your business plan reviewed is a serious omission.
How to Avoid Business Plan Mistakes
The simple answer would be to be aware of these mistakes and make sure not to do them. However, it is not that easy. Even if you are aware of potential mistakes, it does not automatically mean you are capable of avoiding them. It is like with people who have bad eating habits. They know all about healthy eating and are fully aware of their mistakes. And yet the still continue making these mistakes.
This is where coaching comes in. You can either try self-coaching in the executive team, which requires a high level of awareness, openness and self-distance. Or you can hire an external coach to help you discover your blind spots, become aware of unproductive habits and attitudes like, e.g., over-optimism, and change them.
I would be interested to receive comments from entrepreneurs on what mistakes they have made in business plan writing and how they fixed them.
Why do business plans fail?
Table of Contents
Bad product ideas
Poor partnerships , a lack of detail , unrealistic financial planning , how a simple app can help improve your business plan.
Unfortunately, not every business will be a success. The failure of businesses is usually due to some issue in their business plan, and there are hundreds of different issues a business plan could have.
This article will describe some of the most common reasons a business plan might fail and how you can avoid them. We’ll look at common pitfalls such as:
- Poor partnerships
- A lack of detail
- Unrealistic financial planning
Sometimes, a business plan fails simply because it focuses on bad product ideas. A bad product idea means that the product or service your business specialises in does not sell well, and the lack of sales leads to an income problem for your business.
Business plans containing bad product ideas usually come about due to a misunderstanding of the term ‘ unique selling point ’. A unique selling point is what makes your product stand out from the products of the competition. It’s a feature that makes the product better as well as being unique.
Many bad product ideas come from individuals that focus too much on the ‘unique’ part of the term unique selling point. While it is important to have a different product from anything else on the market, make sure you also know what your customers want from a product .
While it’s nice to have help running your business, it’s important to find the right person for the job before you write a contract for a business partnership . If you create a business plan as a partnership and your partner fails to fulfil their responsibilities, your business will struggle to succeed.
There are three things you may want to consider if you’re trying to avoid poor partnerships. The first is your partner’s skill set: look for someone with talents related to your business idea as well as talents you don’t possess. It’s helpful to have a diverse collection of skills within your business.
Secondly, make sure your potential partner is as passionate about the business as you are. If they aren’t, you may find that you end up doing most of the work or that they leave the business as soon as things become difficult. While measuring passion and emotional investment is challenging, finding a business partner that matches your feelings regarding your business plan is vital.
Finally, create an exit strategy. While you may have found a perfect business partner, you never know what difficulties you’ll encounter in the future. So make sure you know what to do if there is an internal conflict in your company that you can’t resolve peacefully.
When you write a business plan , you need to make sure that you plan for almost anything. One of the biggest reasons business plans fail is because they don’t account for certain situations.
It’s impossible to plan for truly unexpected problems, but a detailed business plan will account for most situations by listing off your company’s weaknesses during a SWOT analysis . SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, and it’s a standard part of most business plans.
By using SWOT to list weaknesses in your business plan and potential threats to your success, you can start planning ways to deal with problems. For instance, you might identify a lack of sales as a potential threat. To account for this, you could invest in marketing or reduce your prices. If your business plan doesn’t account for these sorts of situations, it increases its chances of failure.
Another reason for lack of detail in a business plan is low-quality research or not performing research at all. Without researching the market and industry you operate in, you’ll struggle to learn about your competitors or understand your customers’ needs. Thorough research is an essential part of avoiding business plan failure.
Financial planning is essential in business. You might not know the future of your business, but with a decent financial plan, you’ll be able to avoid most obstacles to success. If your financial plan is poorly thought-out or unrealistic, though, it might not be as valuable.
Financial plans are all about mapping out your company’s growth. If you’re too optimistic about this growth, it can cause serious problems. Unrealistic expectations can cause unprepared businesses to go bankrupt very quickly.
For example, say you expect to be making £1,000 a week in sales revenue by your second week of business. Your financial plan relies on this for you to pay rent and buy supplies. If it gets to that week and you’re only making £500, you’ll not be able to pay the bills that allow your business to operate.
To avoid these problems, try lowering your expectations. Even if you think you have a fantastic product idea, it’s better to prepare for the worst than plan for the best and run into trouble. If you create a conservative financial plan that expects some success but accounts for things like low sales, your business plan is much less likely to fail.
One of the biggest parts of your business plan is the financial aspect. To create a business plan that’s unlikely to fail, you’ll need to make sure you have a good understanding of accounting and a way to track how you’re spending your money.
The Countingup app offers built-in accounting software with its business account so that you can manage all your financial data in one place.
With additional features like automatic expense categorisation, invoicing on the go, receipt capture tools, tax estimates, and cash flow insights, you can confidently keep on top of your business finances wherever you are.
You can also share your bookkeeping with your accountant instantly without worrying about duplication errors, data lags or inaccuracies. Seamless, simple, and straightforward!
Find out more here .

- Counting Up on Facebook
- Counting Up on Twitter
- Counting Up on LinkedIn
Related Resources
What insurance does a self-employed hairdresser need.
As a self-employed hairdresser, you’re open to risks in your everyday work. Whether
What are assets and liabilities in a business?
Anyone going into business needs to be familiar with assets and liabilities. They
Personal car for business use: How does it work?
Access to a car is a must for most businesses, meaning that travel
Advantages and disadvantages of using personal savings in business
Have you got a new business idea? And are you considering using your
How to pay Corporation Tax
Corporation Tax is the main tax your limited company has to pay every
How long do CHAPS & BACS payments take?
If you are making transfers frequently between banks in the UK, you have
11 common costs of running a business
When running a business, the various costs can quickly add up. If you
How to buy a vehicle through a limited company
Buying a vehicle through a limited company works similarly to how you may
What is a sales strategy? (with example)
When you run a small business, it’s important to consider how you’ll optimise
Preparing business packages for distribution
You may think shipping your product is as easy as popping it in
How to use cloud services for a business
The development of cloud computing is a game changer for businesses big and
How do EU imports and exports work?
In January 2022, the UK introduced new EU imports and exports regulations. If

Business Plan Development
Masterplans experts will help you create business plans for investor funding, bank/SBA lending and strategic direction
Investor Materials
A professionally designed pitch deck, lean plan, and cash burn overview will assist you in securing Pre-Seed and Seed Round funding
Immigration Business Plans
A USCIS-compliant business plan serves as the foundation for your E-2, L-1A, EB-5 or E-2 visa application
Customized consulting tailored to your startup's unique challenges and goals
Our team-based approach supports your project with personal communication and technical expertise.
Pricing that is competitive and scalable for early-stage business services regardless of industry or stage.
Client testimonials from just a few of the 18,000+ entrepreneurs we've worked with over the last 20 years
Free tools, research, and templates to help with business plans & pitch decks
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Business Plan
Crafting a business plan is a delicate balancing act. It demands a deep understanding of your market, a clear value proposition, realistic financial projections, a competent team, and the flexibility to adapt to changing circumstances.
All too frequently, an entrepreneur or business owner may lean on a business plan template or outsourced freelancer, bypassing the essential strategic work that needs to go behind it. This often results in a business plan that is generic and lacks the specific details and insights that make the business unique.
Remember, a good business plan is not just a document; it's a reflection of your business idea and strategy. It's an opportunity to delve deep into your business idea, understand your market, define your value proposition, and plan for your business's future.
So, whether you're a first-time entrepreneur with a new business idea or a small business owner looking to expand, here are some common mistakes made during the business planning process.
Insufficient Market Research
Market research is the foundation of business planning. It's the key to unlocking a profound understanding of your target audience, offering invaluable insights that can steer your business decisions. Without comprehensive market research, you risk basing your strategies on assumptions about your customers' needs and preferences, a misstep that can lead to expensive errors and overlooked opportunities.
In the rapidly evolving business landscape, the freshness of your data is paramount. Markets are in a constant state of flux, and data that was accurate a year ago may not hold true today. This is particularly relevant in the wake of the recent pandemic, which has caused seismic shifts across every industry.
Therefore, it's crucial to not only use the most recent data but also understand the context behind the numbers. This involves analyzing the data in relation to your business goals, industry trends, and market dynamics. It's about asking the right questions: What do these numbers mean for your business? How do they impact your target audience? What opportunities do they present, and what challenges do they pose?
The real value of market research lies in your ability to interpret the data, identify gaps and opportunities, and apply these insights to your business strategy. It's about turning raw data into actionable intelligence that can inform your business decisions.
There's a wide array of tools at your disposal for conducting market research , from free resources to premium platforms. Government resources such as the U.S. Census Bureau can offer a wealth of insights into consumer behavior and market trends. However, for more granular and industry-specific data, you might need to turn to premium sources like IBISWorld or paid industry reports.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a potent tool for market research. However, it's important to exercise caution when using AI for data collection. Even advanced AI tools like ChatGPT-4, with the aid of browser plugins, can sometimes provide inaccurate data. Therefore, always cross-verify the sources and accuracy of the data obtained from AI. Remember, a single oversight in your market research can undermine the credibility of your entire business plan.
Where AI truly shines is in its ability to analyze vast amounts of data swiftly and accurately, revealing patterns and trends that might be challenging to discern manually.
Beyond online research, don't underestimate the power of direct interaction with potential customers. Conducting surveys or simply engaging in conversations can offer firsthand insights into your customers' needs and preferences, often revealing valuable information that isn't readily available in online data.
Ignoring Your Target Customer
Your target audience is the lifeblood of your business. They are the people who will use your product or service, advocate for your brand, and ultimately drive your revenue. Therefore, it's crucial to understand who they are, what they need, and what they value.
Start by creating customer personas . These are detailed profiles of your ideal customers, including demographic information, interests, pain points, and buying behavior. This will help you understand your customers' needs and preferences, allowing you to tailor your business plan to meet these needs .
However, understanding your customer is only half the battle. The other half is communicating how your product or service meets their needs and adds value to their lives. This is where understanding your unique value proposition comes into play.
Your value proposition is what sets you apart from your competitors and persuades customers to choose your product or service. Highlight the unique benefits that you offer, such as superior quality, convenience, or affordability. Use clear, concise language that resonates with your target audience. Your value proposition should be the cornerstone of all your marketing efforts, from your website copy to your social media posts.
Neglecting Competitive Analysis
In the realm of business, being unaware of your competitors is a recipe for disaster. Overlooking your competitors can leave you unprepared and unable to counter their strategies effectively. As such, a comprehensive competitive analysis should be a fundamental part of your business plan.
Begin by pinpointing your primary competitors. Scrutinize their products or services, pricing strategies, marketing approaches, and customer feedback. This analysis will help you comprehend their strengths and weaknesses, and identify opportunities for differentiation.
Digital tools can be a great help in this regard. For instance, you can use AI tools like ChatGPT-4 to analyze a competitor's website and summarize its products, services, and unique value proposition. This can give you a clear idea of how your competitors position themselves in the market.
Next, delve into what customers are saying about your competitors. Online reviews on platforms like Yelp! or Google Reviews can provide invaluable insights into what customers like and dislike about your competitors' offerings. This can help you identify gaps in their products or services that you can fill.
If the competitor has a brick-and-mortar location, pay it a visit. Use your powers of observation and take note of their customer service, the arrangement of their store, their product presentations, and any other aspects that could provide insights into their operations. If your business offers a service, consider reaching out to competitors as a potential customer. This can provide valuable information about their pricing structure and sales approach.
Numerous entrepreneurs succumb to the misconception that they have no competitors because their idea is genuinely innovative. Even if your offering is revolutionary, your potential customers are currently allocating their resources elsewhere. This concept aligns with the "Jobs to Be Done" theory, which posits that customers "hire" products or services to perform specific "jobs" or fulfill certain needs. Therefore, you're competing with whatever your potential customers are currently "hiring" to do the job your product or service aims to do, whether it's a similar product, a different solution to the same problem, or even an entirely different product that accomplishes the same job. These constitute your indirect competitors, and comprehending them is just as vital as understanding your direct competitors.
By meticulously examining your direct and indirect competitors, you can start to identify areas where you can distinguish yourself. Your competitive edge lies in the unique traits or abilities that make your business outshine others in your market. This advantage could be derived from your groundbreaking technology, exclusive processes, exceptional team, or a strong brand reputation.
To convey your competitive advantage, your business plan must express how you plan to capitalize on it. This could involve showcasing your innovative technology, underscoring your team's expertise, or demonstrating your brand's solid reputation. Remember, business is a competition, and your goal is to win by convincing customers to choose you over your competitors.
Forgetting The Goal
Different stakeholders have different expectations and requirements from a business plan. For instance, a bank looking at your business plan for a loan application will have different criteria than a potential investor considering an equity investment.
A bank is primarily concerned with your ability to repay the loan. They will focus on your financial projections, cash flow, and collateral. They want to see that your business is stable and has a reliable source of income to service the debt. Therefore, when writing a business plan for a bank , you should emphasize your financial stability and risk management strategies.
On the other hand, an investor is looking for growth potential and a return on their investment. They are interested in your business model, market opportunity, competitive advantage, and exit strategy. They want to see that your business has the potential to scale and deliver a significant return. Therefore, when writing a business plan for an investor , you should highlight your growth strategy and potential return on investment.
Your internal strategic plan, however, serves a different purpose. It's a tool for setting your business goals, defining your strategies for achieving them, and identifying metrics for measuring your progress. It's more detailed and operational than a business plan for external stakeholders. It includes specific tasks, responsibilities, and timelines. Therefore, when writing an internal strategic plan, you should focus on your operational plans and key performance indicators (KPIs).
The language and tone of your business plan should also be adapted to your audience. A business plan intended for a bank or potential investors should be formally written and highly professional, while an internal strategic plan can be more straightforward, using bullet points and an iterative approach that allows for adjustments as needed.
Finally, consider how you'll present your business plan. Banks may not require a highly visual presentation and might prefer a more traditional, text-heavy document. Investors, on the other hand, value more impact, such as a pitch deck or a well-designed executive summary that can help them quickly understand your business model and growth potential.
Being Unrealistic About Your Financial Projections
When it comes to financial projections, achieving a balance between optimism and realism is key. It's crucial to demonstrate to investors that your business has the potential for success, but it's equally important to show that you have a clear understanding of the market and your financials. Overly optimistic projections can raise red flags for investors, leading them to question your financial management skills and decision-making abilities. Conversely, overly conservative projections may make your business appear less appealing and unlikely to yield substantial returns.
Thorough research, market trend analysis, and expert consultation are crucial to creating realistic and achievable financial projections that align with your business goals. By doing so, you gain confidence from lenders and investors and increase the likelihood of securing funding for your business.
To estimate your revenue, consider factors like your pricing strategy, sales volume, and market size. It's important to be conservative in your estimates and consider a sensitivity analysis with best-case and worst-case scenarios.
When forecasting your revenue, consider whether to a bottom-up or a top-down approach . A bottom-up approach starts with the unit sales (like a single product sale) and scales up, while a top-down approach starts with the total market size and estimates what portion of that market you can capture. Both approaches have their merits and can provide valuable insights when used together.
Fixed expenses, such as rent and salaries, remain constant regardless of your business activity, while variable costs, like raw materials and shipping, fluctuate depending on your business activity. By accurately estimating your revenue and expenses , you can create a realistic budget that helps you avoid financial pitfalls.
Don't stop with just the financial forecast, because that alone is only part of your financial health. Your cash flow projection should include your expected cash inflows from sales and other sources, and your expected cash outflows for expenses and investments. This will help you anticipate periods of negative cash flow and plan for contingencies.
In your financial planning, be sure to assess the company's break-even point, which is when your total revenue equals your total costs, and demonstrates the point at which your business becomes profitable.
Neglecting the Importance of Your Team
Your team members are more than just employees; they are the catalysts propelling your business's growth and development. When investors, lenders, and other stakeholders scrutinize your business plan, they are looking for a team that is not only skilled and experienced but also cohesive and committed.
Begin by introducing each key team member. Include their name, role, and a brief biography that highlights their relevant skills and experience. The qualifications of your team should extend beyond their educational background and work history. Emphasize their unique "soft skills" and other talents that make them indispensable to your business. Consider their history of success and how their past experiences can contribute to the growth of your business.
Moreover, the cohesion of your team is equally significant. Illustrate how your team members' skills complement each other and how they work collectively to achieve your business goals.
If you haven't assembled your team yet, discuss your plans for recruitment and training. Outline the qualities and skills you're looking for in potential team members, and explain how you plan to attract and retain top talent. Discuss your strategies for fostering a positive and productive work environment, and how you plan to train your team to ensure they have the skills and knowledge needed to succeed.
Thinking Your Business Plan is Done
Your business plan is a dynamic document that should mirror your evolving business reality and market conditions. It's not a one-off task, but an ongoing process that demands regular review and revision.
To ensure your business plan remains pertinent and effective, it should be reviewed and updated regularly. Establish a review schedule, such as quarterly or annually, and adhere to it. During each review, evaluate your progress towards your goals, identify any shifts in your market or industry, and adjust your strategies accordingly.
Market trends fluctuate, new technologies surface (looking at you AI), and customer preferences change. Keep your finger on the pulse of market trends and disruptions, and be prepared to seize new opportunities as they emerge. This could involve embracing new technologies, penetrating new markets, or pivoting your product or service. By being proactive and adaptable, you can convert market changes and opportunities into a competitive edge.
If your current strategy isn't working, or if new opportunities arise, your business plan should guide you in knowing how and when you need to pivot . This might involve changing your target market, adjusting your product or service, or adopting a new business model. By being flexible and responsive, you can ensure your business remains competitive and resilient in the face of change.
By steering clear of these common mistakes, you can craft a business plan that is comprehensive, compelling, and convincing to your stakeholders. A well-constructed business plan not only aids in attracting funding and customers but also serves as a roadmap for your business's success. Invest the time to do it right, and your business will reap the rewards.

How to Write a Management Summary for Your Business Plan
Entrepreneurs are often celebrated for their uncanny ability to understand others – their customers, the market, and the ever-evolving global...

Understanding Venture Debt vs Venture Capital
Despite growth in sectors like artificial intelligence, venture capital funding has seen better days. After peaking at $347.5 billion in 2021, there...

Going Beyond Writing: The Multifaceted Role of Business Plan Consultants
Most people think of a professional business plan company primarily as a "business plan writer." However, here at Masterplans, we choose to approach...
A business journal from the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania
Knowledge at Wharton Podcast
Why creating a business plan is a ‘waste of time’, may 24, 2018 • 23 min listen.
What entrepreneurs need is flexibility and innovation -- not a traditional business plan -- says economist and author Carl Schramm.

Economist and author Carl Schramm discusses his new book, 'Burn the Business Plan.'

The following is an edited transcript of the conversation.
Knowledge at Wharton: Why is a business plan unnecessary?
Carl Schramm: It’s the basis of much of the teaching about how to start a business, and so much of what’s taught is basically conjecture. My book is developed off 10 years of research that we did at the Kauffman Foundation. If you look at all our older major corporations — U.S. Steel, General Electric, IBM, American Airlines — and then you look at our newer companies like Amazon, Apple, Facebook, Microsoft, none of these companies ever had a business plan before they got started. Empirically, it appears as if you don’t need a business plan.
Second, the business planning process is largely generated as a preview for venture capital. As I show in my book, from empirical studies, much less than 1% of all new startups ever see a venture capitalist. Much less than 1% of all new companies every year have venture backing of any kind. So, I largely view the creation of a business plan as something of a waste of time.
The third problem is that it seems to make starting a business somewhat like a cookbook. If you do this, and then you do this, and then you do this, the cake will come out okay. And that’s really not how it happens.
“Empirically, it appears as if you don’t need a business plan.”
Knowledge at Wharton: Let’s talk about age because many entrepreneurs are in their late 30s or 40s. These are people who made a shift in their career paths.
Schramm: Precisely. It goes to this question of, “What are we doing when we’re trying to teach high school kids?” Even grammar school children get courses and exposure to entrepreneurship. At the university level, it’s now a major in probably 3,000 colleges and universities. And the whole schema, including the notion of a business plan as the formal way to teach how to start a business in a college classroom, is geared to 20-year-olds.
Much of our mythology is that unicorn companies are started by people, like Mark Zuckerberg, who are in their 20s. But the reality is, the vast majority of people who start businesses are middle-career people who have been surprised by the fact that they actually had an idea, and their idea was good enough to build a business around.
Another thing wrong with how we write about entrepreneurship, how it’s taught, is that somehow people set out to be entrepreneurs as if they set out to be a dentist or an accountant. The vast majority of entrepreneurs were really amazed to find out that they became an entrepreneur. In my case, I was a professor at Johns Hopkins for 15 years, and then one day my research sort of slapped me in the face. I said, “Holy smokes, if I want to really make this work and actually change the world, I can’t do it by writing an academic paper. I have to start a business.”
Knowledge at Wharton: How should we teach our kids about entrepreneurship?
Schramm: I don’t think [the current curriculum] can be tweaked. I think it should be abandoned. I think it should be overthrown. Because if you look empirically at where entrepreneurs come from, if they have formal training, it’s not in entrepreneurship. It’s in engineering or the STEM subjects, the technical subjects.
Many, many more entrepreneurs come out of MIT because it’s an engineering and a technical school. Same thing for Caltech. Caltech doesn’t even teach entrepreneurship. At MIT, there’s one professor in the business program there who teaches entrepreneurship. But it doesn’t matter because if they didn’t teach it at all, these schools would be producing many, many new businesses all the time.
Knowledge at Wharton: You said not much funding comes from venture capitalists or angel investors. How are entrepreneurs getting the money they need to execute their ideas?
Schramm: One reason people can become entrepreneurs at midlife is they turn to their own savings, their own assets, to friends and families for loans. By the time you’re 40, which is the average age at which people start businesses, you’ve settled your student debt. You’ve got a house. You’re likely to have a spouse who has a job, which is a huge protection if you start a new company because she or he has health insurance and other benefits. So, most companies are self-funded.
Knowledge at Wharton: In the book, you also talk about the incubator. But you think the incubator isn’t having the desired effect that a lot of people are hoping for. Can you explain?
Schramm: Again, empirically, very few companies come out of these incubators. I was trained as a labor economist. I’m in the middle of writing an essay about incubators, and the premise is that as we turn towards 3% and 4% GDP, and much lower rates of unemployment and much higher demand for well-trained people, no one is going to want to spend time in an incubator. They can get a job. And that’s a really important part of the drama of becoming an entrepreneur.
In the book, I make the case that the most effective place to learn how to be entrepreneurial is to go into a big company. That’s where you see innovation happen. More innovation happens in big companies than, for example, university laboratories. It’s also where you learn all the skills that make a business work, where you’re exposed to what scale looks like in a business. This is critical and this is experiential knowledge. You can’t teach scale in a classroom. It has to be felt. You have to see it, to experience it.
“The vast majority of people who start businesses are middle-career people.”
Knowledge at Wharton: You give real-world examples in the book, including the story about vacuum cleaning company Dyson.
Schramm: Yes, Dyson is a fantastic story. James Dyson was an industrial designer by background, and he came to the view that vacuum cleaners had been a technology that hadn’t moved very far. He was using a vacuum cleaner and noticed that the more you used it, and the dirtier the dustbin got, the less power it had. This became the question that triggered his search.
Dyson built over 1,000 prototypes. He quit his job. His wife was a teacher, and he lived off a much more modest income. His wife did all the money-earning in the family. When he began to push his product out, no companies in the United States or England wanted any part of it. They resisted it because they were making a lot of money on selling paper bags for conventional, old-fashioned vacuum cleaners. He had to take it to Japan. When it became successful in Japan, American and British companies tried to steal his design. He successfully defended against that.
The best part of Dyson’s story is he never had outside investors. [Dyson] never wanted to be a public company. It’s a huge company now. He’s like most entrepreneurs. If your idea clicks and you can make it work, and you haven’t taken your company public — that is, you still control it — you’re going to work there for the rest of your life. They become places where your own creativity works, and you can keep at it. You can keep designing. Really, it becomes your life.
It’s an important point, particularly for people who are in higher education. Students in universities are programmed to think that somehow people who work in the government or in nonprofit or NGOs are somehow more creative. They’re like the people who take art and art history and design in college, or people who write music. They’re a different breed, and they’re really geniuses.
The reality is that 95% of kids graduating from college this year are going to work in companies. They’re not not creative. Look at our huge economy. That all happens because of people who are creative and gifted in business and the invention of things that help other people. And [taking] these things to market [requires] very, very creative skills.
Knowledge at Wharton: Would you say that passion and determination are two of the great qualities that a lot of entrepreneurs have?
Schramm: Yes, it’s true. Students in college are told to follow your passion and start a company. But a lot of times, the passion doesn’t make any sense. I’ve seen students who are passionate about having a web app for frying pans. I sort of make fun of it in the book. I’ve judged business plan competitions at the college level and seen the same idea come up five times. Invent a sensor for a frying pan, and it tells you on your phone when your eggs are cooked. Kids are passionate about that, but it’s not an idea that’s ever going to work. They’re making the simplicity of cooking an egg into a complex technical project.
Passion really clicks when you’ve got an idea and it starts to have market feedback. The thrill of it is when other people are saying, “What you came up with is valuable.” What they’re telling you is, “You created something out of your head that makes my life easier, and I value it. So, I’ll give my money to you for your idea.”
Knowledge at Wharton: Is Yeti one of those great ideas?
Schramm: Yeti is a fabulous story. It’s one of those things where those guys didn’t expect to be entrepreneurs. The idea snuck up on then. They love to go fishing, and they fell through regular Igloo boxes because they’re not all that well made. One of the two brothers said, “You know, what we ought to do is make a cooler that’s so sturdy, you could stand on it.” Yeti cooler came out of something just that simple.
Knowledge at Wharton: What are 20-somethings missing to be able to build that great company?
Schramm: They’re missing experience. If you really want to be an entrepreneur and you don’t have a really great idea when you’re 21, getting out of school, don’t fret. Just wait. What shall you do while you wait? Go learn stuff. The stuff you should learn is easiest learned in big businesses because you’ll go out there and watch the innovation process work.
I consult at several companies, and what I’m watching all time is these companies constantly trying to renew themselves with new, better products. They spend a lot of money on research and development. Anybody who’s working in one of these companies can see the constant iterative change that’s taking place. You actually get innovation into your normal daily routine. I think that’s one of the greatest things that you can learn.
The book points to the fact that many new companies come out of old companies. The entrepreneurs see stuff, and two routes are the way this happens. The companies decide that they’re going to stick to their core competency and reject a brand new idea. They often say to people, “if you love this idea so much, go do it with our blessing. You can have the intellectual property.” In some cases, like IBM, they actually finance the startups. That was the case with Cerner, the health care data company.
“More innovation happens in big companies than, for example, university laboratories.”
The other thing is a much more difficult problem. That is, people who go to management and say, “This is the better way to do it,” or “Here’s a new application or a new market, and we have all the technology. If we configure it differently, we can own and capture this market.” MBA-type managers often say, “no, we’re going to stick to our core competency. We don’t know how to do that. It’s not our karma, it’s not our destiny.” And frustrated employees walk out. I interview people like that in the book. They say again and again, “I could have made all this money for my old employer, but they just wouldn’t listen to me.”
Knowledge at Wharton: Are companies wasting their human capital?
Schramm: It’s happening in every single company. You’ve got creative people in there. They might be running a machine. They might be on the production line. They could be any place in your company. They could be at the loading dock. They see things, and they could do things differently.
One of my favorite examples that’s not in the book is container boxes. It’s one of the great logistics revolutions that permits all of our prices for consumer goods to be much, much lower than they would have been. The boxes on the back of a trailer that come off the trailer, go right on a ship.
That was developed by a truck driver in Newark, N.J., In the old days, when trailer trucks were inflexible, they were fixed. Every time you went into a yard or a loading dock, people had to go on the dock, take the stuff off and reload it. He said, “You know, it’s a big steel box. Why don’t you just take the whole box, the whole back end of the truck, and put it on a ship?” This is a truck driver who saw that. He gave us the container revolution that made a world revolution in logistics.
Knowledge at Wharton: There are some very well-known companies like Microsoft and Apple and Facebook that didn’t have a plan at the outset. But now they are working through a variety of plans.
Schramm: That’s right. They went and tried it. We have this drive in our society. I think it’s in human nature. We don’t think that important things happen by chaotic means. If you look around, there are academics and experts who are struggling constantly to make the process of starting a business somehow logical, planned, orderly. These are sort of cookbook approaches.
You don’t have the right answer at the beginning. You never have the right answer. The market changes, technology changes. Your customers’ tastes are changing. Price points change. Your competitors change. You’ve got to be at this all the time. And a lot of times, that’s a hidden assumption in all the advice that’s given to entrepreneurs. If you crack it once, you can go right to the bank. You buy a jet. You’re over with. You do a public offering, and you’re rich and out by 30.
That’s not the case at all. You start a business, that’s only the beginning. And it’s the beginning of trying to make it big because growth is what’s important. Scale is the critical issue. The only way you can get there is constantly reacting to the market and all the signals it’s sending as to what it needs.
More From Knowledge at Wharton


How Financial Frictions Hinder Innovation

How Early Adopters of Gen AI Are Gaining Efficiencies

How Is AI Affecting Innovation Management?
Looking for more insights.
Sign up to stay informed about our latest article releases.
Small Business BC
Resources for entrepreneurs to start and grow successful businesses.
Accédez la page d'accueil dédiée aux ressources en française de SBBC
Utilisez notre outil de traduction pour le site entier
10 Common Business Plan Mistakes
Are you thinking about getting your business plan underway? Many elements go into a good business plan. And it often takes time, patience, and many revisions before you get it right. Set yourself up for success by learning how to avoid these ten common business plan mistakes.
1. Unrealistic Financial Projections
Lenders and investors expect to see a realistic picture of where your business is now and where you hope it goes. One of the most common business plan mistakes is overestimating the value of your company. Ensure your plan is pragmatic and explain your projections. This way, lenders and investors are much more likely to accept your plan, knowing you’re thinking logically.
2. Not Defining a Target Audience
You must define your specific target market, present how you’ve made these assumptions, and outline how you’ll target them. No business will appeal to everyone, so think carefully about who your audience is.
Need help defining your target market and learning about market research? We offer resources such as a Market Research Resources Guide , seminars on market research and one-on-one consultations with in-house experts.
3. Too Much Hype
It’s essential to believe in your business idea. But, to truly showcase its potential, you should focus on providing backup for this belief. Instead of relying on superlatives like “hottest” and “greatest,” wow them with your well-researched business plan. Let your good ideas and preparation speak for themselves.
4. Poor Research
Don’t let your hard work go to waste. Remember to double-check and substantiate all your research. Using incorrect or out-of-date information would discredit your business idea and plan. If you need clarification, get a colleague, friend, or family member to help you review it.
5. No Focus on Your Competition
Even if your business is one-of-a-kind, there’s no such thing as no competition. It’s important to highlight your competition, but not so much that the investor worries the business won’t survive. Focus on your niche and what separates you from other companies. Highlight how you plan to compete in the marketplace and paint an accurate picture of what the industry is like now and where you see it going.
6. Hiding Your Weaknesses
Every business has weaknesses, but you could risk deterring the investor if you hide or highlight them too much. The best way to address them is to include a detailed strategy for solving them. Ensure you’re being realistic and tackle these weaknesses head-on.
7. Not Knowing Your Distribution Channels
Consider how you will provide your service or distribute your product and create a secure plan. Include all possible channels and explain why they’re correct for reaching your target market. Your ability to articulate your strategy for how your product or service will reach clients is vital.
8. Including Too Much Information
Most investors have a mental checklist of 10 to 12 points they’re looking for in a business plan. The purpose of your plan is not to show the depth of your knowledge but to focus on the key elements of your business. Strive for clear and concise writing. If you have more information you want to include, create an appendix.
9. Being Inconsistent
Take time to review each section of your business plan and ensure it’s consistent. Double-check your highlighted target markets, statistics, and strategies to show investors you’re well-prepared and knowledgeable.
10. One Writer, One Reader
Remember to ask several people to review your plan before submitting it. Since you’re familiar with the information, it’s easy to miss spelling and grammatical errors. Another set of eyes will help your plan look more professional and ensure it reads correctly.
Need Help with your Business Plan?
Get started on your business plan by downloading our Business Plan Template and Cashflow Forecasting Tool.
Small Business BC’s advisors will help review your business plan and provide you with feedback with our Business Plan Review Advisory Service .
How Small Business BC Can Help Your Business
SBBC is a non-profit resource centre for BC-based small businesses. Whatever your idea of success is, we’re here to provide holistic support and resources at every step of the journey. Check out our range of business webinars , on-demand E-Learning Education , our Talk to an Expert Advisories , or browse our business articles .
Share this Story

About Small Business BC
When you find yourself asking "How do I...?" Give us a call. We'd be happy to help.
- Sign up for eNews to get the latest SBBC updates:
- Your Name * First Last
Note: you can withdraw your consent at any time - for more information see our Privacy Policy or Contact Us for more details.
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
We respectfully acknowledge our place of work is within the ancestral, traditional and unceded territories of the Xʷməθkʷəy̓əm (Musqueam), Sḵwx̱wú7mesh (Squamish) and səl̓ilwətaʔɬ/sel̓ílwitulh (Tsleil-Waututh) and that we serve the Peoples of the many Nations throughout British Columbia.
Avoid these 5 common business plan mistakes
A good business plan requires significant research and effort. To make the best impression, be sure to take the extra time to fine-tune your plan, so your audience will find it easy to read and understand.
Ready to start your business? Plans start at $0 + filing fees.

by Jane Haskins, Esq.
Jane has written hundreds of articles aimed at educating the public about the legal system, especially the legal aspe...
Read more...
Updated on: March 21, 2023 · 3 min read
1. Poor grammar, spelling, and punctuation
2. too much information, 3. not enough information about risks and competition, 4. unclear or unfocused writing, 5. formatting issues.
You've worked hard to put together a business plan for your new venture. You've followed expert advice and included sections that address your business and industry, your strategy for reaching your goals, your products and competitors, your marketing plan, your management team, and the money you'll need.
And now you're ready to share your business plan with banks and potential investors.
Before you present your plan , watch out for these common mistakes that can destroy your chances for funding, even if you've got a great idea that should be destined for success.

Investors and bankers tend to notice misspellings, typos, and punctuation errors right away. These mistakes can signal that you are careless, do shoddy work, or pay attention to details. They create a bad first impression that can quickly land your plan in the rejection pile. Have someone skilled at proofreading look over your plan before you present it.
You wouldn't be an entrepreneur if you weren't eager to talk about your business idea, and yet it's easy to get carried away with irrelevant information or technical details. This is especially true if you're in a tech-related business.
Investors need specific information about your products and services, but they may lose interest if your business plan wanders off into your life story or reads more like a technical handbook.
A typical business plan runs from 15 to 25 pages and should include an executive summary that provides a quick overview of your plan as a whole. If your plan needs to be much longer, consider putting some details into an appendix or supplementing your full plan with a shorter version you can use for making presentations.
Simultaneously, hardly anyone likes to talk about the competition or the risks involved in a new venture. A surprising number of business plans claim there's no competition at all.
Resist the temptation to gloss over the downsides—assess your competition realistically and explain how your product or service is different and why people want it.
Also, include detailed financial projections and industry information that is grounded in facts. Provide a basis for any assumptions you make. Take the time to do the research and assemble a full picture of your business and the reasons it is poised for success.
When you're close to a project, it can be surprisingly difficult to describe it in a way that outsiders can understand. You may neglect to say what your product is or what it's used for without realizing it.
Or you may use acronyms and industry jargon without explaining what the terms mean. A related problem is rambling, or sections that bounce from one thought to another, making it difficult for readers to follow.
Investors see lots of business plans, and, if yours isn't easy to understand, they'll quickly move on to the next one. Show your business plan to someone who isn't involved in your project and who isn't in your industry. Ask them for an honest assessment—if they find it hard to follow, make revisions, so your plan is crystal clear.
It sounds like a picky point, but details like fonts, headings, and formatting make a difference. Your goal is for your readers to believe in your business and give you money.
Make things easier for them by using an easy-to-read font, large enough type, and tables of contents and headings to guide them through the document.
Make sure your fonts and formatting are consistent throughout your business plan. Inconsistency looks sloppy, and that reflects badly on you. If your computer skills are lacking, hire someone to clean up the document and make it look neat and orderly.
You may also like

What does 'inc.' mean in a company name?
'Inc.' in a company name means the business is incorporated, but what does that entail, exactly? Here's everything you need to know about incorporating your business.
October 9, 2023 · 10min read

Why do I need to conduct a trademark search?
By knowing what other trademarks are out there, you will understand if there is room for the mark that you want to protect. It is better to find out early, so you can find a mark that will be easier to protect.
October 4, 2023 · 4min read

How to start an LLC in 7 easy steps
2024 is one of the best years ever to start an LLC, and you can create yours in only a few steps.
May 6, 2024 · 22min read
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
No Plan, No Problem? Though formal business plans have been getting some flack, you still can't skip the planning process.
By Tim Berry • Mar 15, 2007
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
In January, I really enjoyed the fuss surrounding Kelly Spors' column in The Wall Street Journal , " Do Startups Really Need Formal Business Plans? " But I'm also worried about it and the misunderstanding it may create.
The column cites research that questions the need for formal business plans for all startups. It tells stories of would-be entrepreneurs who failed despite their seemingly impeccable business plans and stories of successful startups without business plans. It mentions investors who invest in businesses, not plans. And it concludes that business plans are overrated.
The concept that a plan itself means very little isn't a new idea. Who would think spending a year doing a business plan is a good thing? Or that investors buy plans, not people? Or that formal business plans spell success?
Business plans are sometimes overdone and misused, but the planning process is critical. All businesses, not just startups, need planning. About 60 years ago, Dwight D. Eisenhower said, "The plan is useless; it's the planning that's important." That's still true today.
In fact, all business plans are wrong. They're the work of humans guessing the future, dealing with uncertainty and making assumptions. Still, the planning process is absolutely essential. A startup entrepreneur's planning process should start with a plan and continue with a plan vs. reality review, progress tracking and course correction. The planning process is as vital to business as steering is to driving; it takes near constant correction to stay on track.
Planning is about controlling your destiny. Establish your business goals and outline the steps needed to achieve them--don't just react to events. While your plan will be wrong, of course, how would you track what is going wrong without it? You can't have a route without a starting point and a destination, but even the most well-planned route may require some detours.
For the best results, planning should be concrete and specific. For each step in your plan, create dates, deadlines and clearly assigned responsibilities. You can't track your progress and steer your company efficiently with vague generalities.
Now here's the tricky part: As with so many good things, plans can be overdone. It can be easy to obsess about future details, wasting valuable time and resources. But most startup entrepreneurs will quickly realize the value of moving forward and getting going. All you need to do is focus on priorities, play to your strengths, and work on core competencies, positioning and differentiation. You don't need a 100-page document to do that, but you certainly need to do it.
In real-world planning, form follows function. When new businesses seek investors they usually need formal plans. Investors who say they don't need formal plans still need to see your strategy, focus, priorities, commitments, dates and deadlines. The content has to be there, regardless of the format.
If you're not showing your plan to outsiders, don't bother writing more than bullet points. Keep it short. If it fits on the back of an envelope, great; nobody really suggests measuring the value of planning in pounds or pages. If you can fit strategy, milestones, dates, deadlines and cash flow on the back of an envelope, use the envelope. If you would rather put it in PowerPoint slides, do that.
Although you may not need a formal plan, all businesses need to go through the planning process. There will always be examples of businesses with great plans that fail and businesses with no plans that succeed, but I feel it's very dangerous to tell startup entrepreneurs they don't need a plan. The truth of the matter is most of us need more planning, not more rationalizations for not doing it.
Entrepreneur, Business Planner and Angel Investor
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- This Mother and Daughter Were 'Kind of Fringe Weirdos' When They Started an Uncommon Business in Their Garage. Now They're in Major Retailers — and Victoria Beckham Is a Fan.
- Lock A Leadership Shortage Is Coming. Here's What Needs to Happen to Prevent It.
- Lock The Author of 'Million Dollar Weekend' Says This Is the Only Difference Between You and the Many 'Very, Very Dumb People' Making a Lot of Money
- What the NLRB Appeal of the Expanded Joint Employer Rule Judgment Means for Your Business
- Lock 12 Books That Self-Made Millionaires Swear By
- The Sweet Side Hustle She Started in an Old CVS Made $800,000 in One Year. Now She's Repeating the Success With Her Daughter — and They've Already Exceeded 8 Figures.
Most Popular Red Arrow
63 small business ideas to start in 2024.
We put together a list of the best, most profitable small business ideas for entrepreneurs to pursue in 2024.
Protect Your Business Computer From Hackers and Trackers with This $70 VPN Deal
Windscribe VPN supports unlimited devices, a global VPN network, and more.
7 Tips for Empowering Mothers in the Workplace
Moms make up an important and large segment of the workforce, yet too often have been overlooked in the development of company culture. In this article, we explore seven ways that companies can empower mothers in the workplace, through the lens of my own experience as a mom and CEO.
Keep Learning with Rosetta Stone and More During Limited-Time Price Drop
Open up a world of business opportunities with a new language and other growth courses.
Get Microsoft Office Plus Windows 11 Pro for $70 This Week Only
Use Microsoft Office to streamline productivity and Windows 11 Pro for security, collaboration, and more.
Warren Buffett Had to Work From His iPhone After Telephone Lines Went Down at Berkshire Hathaway: 'I'm Glad We Didn't Sell All of Our Apple'
Berkshire sold around $20 billion worth of Apple recently.
Successfully copied link
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for May 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
What is a Business Plan? Definition and Resources

9 min. read
Updated May 10, 2024
If you’ve ever jotted down a business idea on a napkin with a few tasks you need to accomplish, you’ve written a business plan — or at least the very basic components of one.
The origin of formal business plans is murky. But they certainly go back centuries. And when you consider that 20% of new businesses fail in year 1 , and half fail within 5 years, the importance of thorough planning and research should be clear.
But just what is a business plan? And what’s required to move from a series of ideas to a formal plan? Here we’ll answer that question and explain why you need one to be a successful business owner.
- What is a business plan?

A business plan lays out a strategic roadmap for any new or growing business.
Any entrepreneur with a great idea for a business needs to conduct market research , analyze their competitors , validate their idea by talking to potential customers, and define their unique value proposition .
The business plan captures that opportunity you see for your company: it describes your product or service and business model , and the target market you’ll serve.
It also includes details on how you’ll execute your plan: how you’ll price and market your solution and your financial projections .
Reasons for writing a business plan
If you’re asking yourself, ‘Do I really need to write a business plan?’ consider this fact:
Companies that commit to planning grow 30% faster than those that don’t.
Creating a business plan is crucial for businesses of any size or stage. It helps you develop a working business and avoid consequences that could stop you before you ever start.
If you plan to raise funds for your business through a traditional bank loan or SBA loan , none of them will want to move forward without seeing your business plan. Venture capital firms may or may not ask for one, but you’ll still need to do thorough planning to create a pitch that makes them want to invest.
But it’s more than just a means of getting your business funded . The plan is also your roadmap to identify and address potential risks.
It’s not a one-time document. Your business plan is a living guide to ensure your business stays on course.
Related: 14 of the top reasons why you need a business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
What research shows about business plans
Numerous studies have established that planning improves business performance:
- 71% of fast-growing companies have business plans that include budgets, sales goals, and marketing and sales strategies.
- Companies that clearly define their value proposition are more successful than those that can’t.
- Companies or startups with a business plan are more likely to get funding than those without one.
- Starting the business planning process before investing in marketing reduces the likelihood of business failure.
The planning process significantly impacts business growth for existing companies and startups alike.
Read More: Research-backed reasons why writing a business plan matters
When should you write a business plan?
No two business plans are alike.
Yet there are similar questions for anyone considering writing a plan to answer. One basic but important question is when to start writing it.
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business.
But the reality can be more nuanced – it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written.
Ideal times to write a business plan include:
- When you have an idea for a business
- When you’re starting a business
- When you’re preparing to buy (or sell)
- When you’re trying to get funding
- When business conditions change
- When you’re growing or scaling your business
Read More: The best times to write or update your business plan
How often should you update your business plan?
As is often the case, how often a business plan should be updated depends on your circumstances.
A business plan isn’t a homework assignment to complete and forget about. At the same time, no one wants to get so bogged down in the details that they lose sight of day-to-day goals.
But it should cover new opportunities and threats that a business owner surfaces, and incorporate feedback they get from customers. So it can’t be a static document.
Related Reading: 5 fundamental principles of business planning
For an entrepreneur at the ideation stage, writing and checking back on their business plan will help them determine if they can turn that idea into a profitable business .
And for owners of up-and-running businesses, updating the plan (or rewriting it) will help them respond to market shifts they wouldn’t be prepared for otherwise.
It also lets them compare their forecasts and budgets to actual financial results. This invaluable process surfaces where a business might be out-performing expectations and where weak performance may require a prompt strategy change.
The planning process is what uncovers those insights.
Related Reading: 10 prompts to help you write a business plan with AI
- How long should your business plan be?
Thinking about a business plan strictly in terms of page length can risk overlooking more important factors, like the level of detail or clarity in the plan.
Not all of the plan consists of writing – there are also financial tables, graphs, and product illustrations to include.
But there are a few general rules to consider about a plan’s length:
- Your business plan shouldn’t take more than 15 minutes to skim.
- Business plans for internal use (not for a bank loan or outside investment) can be as short as 5 to 10 pages.
A good practice is to write your business plan to match the expectations of your audience.
If you’re walking into a bank looking for a loan, your plan should match the formal, professional style that a loan officer would expect . But if you’re writing it for stakeholders on your own team—shorter and less formal (even just a few pages) could be the better way to go.
The length of your plan may also depend on the stage your business is in.
For instance, a startup plan won’t have nearly as much financial information to include as a plan written for an established company will.
Read More: How long should your business plan be?
What information is included in a business plan?
The contents of a plan business plan will vary depending on the industry the business is in.
After all, someone opening a new restaurant will have different customers, inventory needs, and marketing tactics to consider than someone bringing a new medical device to the market.
But there are some common elements that most business plans include:
- Executive summary: An overview of the business operation, strategy, and goals. The executive summary should be written last, despite being the first thing anyone will read.
- Products and services: A description of the solution that a business is bringing to the market, emphasizing how it solves the problem customers are facing.
- Market analysis: An examination of the demographic and psychographic attributes of likely customers, resulting in the profile of an ideal customer for the business.
- Competitive analysis: Documenting the competitors a business will face in the market, and their strengths and weaknesses relative to those competitors.
- Marketing and sales plan: Summarizing a business’s tactics to position their product or service favorably in the market, attract customers, and generate revenue.
- Operational plan: Detailing the requirements to run the business day-to-day, including staffing, equipment, inventory, and facility needs.
- Organization and management structure: A listing of the departments and position breakdown of the business, as well as descriptions of the backgrounds and qualifications of the leadership team.
- Key milestones: Laying out the key dates that a business is projected to reach certain milestones , such as revenue, break-even, or customer acquisition goals.
- Financial plan: Balance sheets, cash flow forecast , and sales and expense forecasts with forward-looking financial projections, listing assumptions and potential risks that could affect the accuracy of the plan.
- Appendix: All of the supporting information that doesn’t fit into specific sections of the business plan, such as data and charts.
Read More: Use this business plan outline to organize your plan
- Different types of business plans
A business plan isn’t a one-size-fits-all document. There are numerous ways to create an effective business plan that fits entrepreneurs’ or established business owners’ needs.
Here are a few of the most common types of business plans for small businesses:
- One-page plan : Outlining all of the most important information about a business into an adaptable one-page plan.
- Growth plan : An ongoing business management plan that ensures business tactics and strategies are aligned as a business scales up.
- Internal plan : A shorter version of a full business plan to be shared with internal stakeholders – ideal for established companies considering strategic shifts.
Business plan vs. operational plan vs. strategic plan
- What questions are you trying to answer?
- Are you trying to lay out a plan for the actual running of your business?
- Is your focus on how you will meet short or long-term goals?
Since your objective will ultimately inform your plan, you need to know what you’re trying to accomplish before you start writing.
While a business plan provides the foundation for a business, other types of plans support this guiding document.
An operational plan sets short-term goals for the business by laying out where it plans to focus energy and investments and when it plans to hit key milestones.
Then there is the strategic plan , which examines longer-range opportunities for the business, and how to meet those larger goals over time.
Read More: How to use a business plan for strategic development and operations
- Business plan vs. business model
If a business plan describes the tactics an entrepreneur will use to succeed in the market, then the business model represents how they will make money.
The difference may seem subtle, but it’s important.
Think of a business plan as the roadmap for how to exploit market opportunities and reach a state of sustainable growth. By contrast, the business model lays out how a business will operate and what it will look like once it has reached that growth phase.
Learn More: The differences between a business model and business plan
- Moving from idea to business plan
Now that you understand what a business plan is, the next step is to start writing your business plan .
The best way to start is by reviewing examples and downloading a business plan template. These resources will provide you with guidance and inspiration to help you write a plan.
We recommend starting with a simple one-page plan ; it streamlines the planning process and helps you organize your ideas. However, if one page doesn’t fit your needs, there are plenty of other great templates available that will put you well on your way to writing a useful business plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.
.png?format=auto)
Table of Contents
- Reasons to write a business plan
- Business planning research
- When to write a business plan
- When to update a business plan
- Information to include
- Business vs. operational vs. strategic plans
Related Articles

16 Min. Read
How to Write a Mission Statement + 10 Great Examples

7 Min. Read
How to Write an Assisted Living Business Plan + Free Sample Plan PDF

6 Min. Read
How to Write a Law Firm Business Plan + Free Sample Plan PDF

How to Write a Real Estate Business Plan + Example Templates
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
7 Examples of Data Misuse in the Modern World
Every time we use social media, sign up for a mailing list, or download a free app onto our phones, we agree to the provider’s terms of use.
While many of these agreements are unnecessarily dense and challenging to process, they do serve one very specific role for everyday people like you and me—they set the terms for how a company can use the personal data they collect from us. Typically, that data gets used in one of three ways:
- Personal data is aggregated and analyzed to provide us with more personalized advertisements.
- Personal data is logged and assessed for research and development.
- Personal data is sold to a data brokerage.
In all three of these scenarios, there are specific parameters for how companies handle, store, and distribute your personal data. Yet, in a work-from-home world, it’s becoming more and more difficult for companies to enforce protections against sensitive data to prevent both internal and external data breaches.
What is Data Misuse?
Data misuse occurs when individuals or organizations use personal data beyond those stated intentions. Often, data misuse isn’t the result of direct company action but rather the missteps of an individual or even a third-party partner. For example, a bank employee might access private accounts to view a friend’s current balance, or a marketer using one client’s data to inform another customer’s campaign.
What Are The Types of Misuse of Personal Information?
In broad strokes, there are 3 different types of data misuse:
- Commingling
- Personal Benefit
1. Commingling
Commingling happens when an organization captures data from a specific audience from a specific stated purpose, then reuses that same personal data for a separate task in the future. Reusing data submitted for academic research for marketing purposes or sharing client data between sister organizations without consent are some of the most common commingling scenarios. Commingling often occurs out of ease of access—marketers and business owners already have the data and assume that, since they collected it, they are entitled to use it at their own discretion.
2. Personal Benefit
Data misuse for personal benefit occurs when someone with access to personal data abuses that power for their own gain. Whether simple curiosity or as a competitive advantage, this type of misuse is rarely done with malicious intent. Personal gain cases regularly involve company employees moving data to personal devices for easy access, often with disastrous results.
3. Ambiguity
Ambiguity occurs when organizations fail to explicitly disclose how user data is collected and what that data will be used for in a concise and accessible manner. Traditionally, organizations use this strategy because they were unsure how they wanted to use customer data but still wanted to collect it. However, ambiguity leaves the terms of use wide open to vague interpretation, giving the organization a blank check to use customer personal data as they wish.
Is Data Misuse Illegal?
To be clear, data misuse isn’t necessarily theft—theft occurs when a bad actor takes personal data without permission—data misuse is when legitimately collected information is applied in a way beyond its original purpose. Typically, these instances are less malicious than an insider threat selling company data to a third party and instead take a more negligent approach.
While the intention may be simple, the stakes can be incredibly high. The cost of data misuse can range from thousands to billions of dollars in fines, not including ransomware or settlements resulting from the misuse. We’ve seen data misuse cases take center stage multiple times in recent years, and in every instance, there have been significant ramifications for the company and its customers.
6 Examples of Data Misuse in the Modern World
- Facebook and Cambridge Analytica
- Morgan Stanley
- Leave.EU and Eldon Insurance
1. Facebook and Cambridge Analytica Election Influencing
Perhaps the most infamous example of data misuse, in 2018, news outlets revealed that the UK political consulting firm acquired and used personal data from Facebook users that was initially collected from a third party for academic research. In total, Cambridge Analytica had unauthorized access to the data of nearly 87 million Facebook users—many of whom had not given any explicit permission for the company to use or even access their information. Within two months of the scandal, Cambridge Analytica was bankrupt and defunct, while Facebook was left with a $5 billion fine by the Federal Trade Commission.
2. Twitter Targeted Advertising
In September 2019, Twitter admitted to letting advertisers access its users’; personal data to improve the targeting of marketing campaigns. Cited by the company as an internal error, the bug allowed Twitter’s Tailored Audiences advertisers access to user email addresses and phone numbers. Twitter’s ad buyers could then cross-reference their marketing database with Twitters to identify shared customers and serve them targeted ads—all without our permission.
Not to be outdone, preliminary investigations in a European Union competition watchdog effort found the online retailer “appears to use competitively sensitive information – about marketplace sellers, their products and transactions on the marketplace.” The EU went on to open a second investigation in 2020 concerning the retailer’s use of non-public independent seller data. The outcomes of both are still pending.
3. Google Location Tracking for Advertisers
Google was fined nearly $57 million in 2020 by the French data protection authority for failing to acknowledge how it used users’ personal data. During that same time, Ireland’s Data Protection Commission notified the global juggernaut of their intentions to investigate the company’s use of and transparency around user location data—its second notification since the GDPR was made policy in 2018.
4. Uber “God View” Rider Tracking
Getting in on data misuse before it was cool, Uber was fined $20,000 by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) for its “God View” tool in 2014. “God View” let Uber employees access and track the location and movements of Uber riders without their permission. As a result of their settlement with the FTC, Uber paid their fine and agreed to hire an outside firm to audit their privacy practices every two years from 2014 through 2034.
5. Morgan Stanley Data Breach
And it’s not just tech firms! In 2015, a Morgan Stanley financial advisor pleaded guilty to taking the data for roughly 730,000 accounts—roughly 10% of the wealth management firm’s user base—and attempting to take that information with him to a competitor. In the security breach, the personal data of nearly 900 users was accessed and posted online by hackers that accessed the former employee’s home computer.
6. Leave.EU and Eldon Insurance Data Commingling
While the pro-Brexit group Leave.EU and UK insurance provider Eldon Insurance have very little in common on the surface, both organizations were co-founded by businessman Aaron Banks. In 2019, the UK’s Information Commissioner’s Office fined both organizations roughly $83,000 apiece for commingling customer data—political data for insurance and insurance data for politics.
What Are The Risks of Data Misuse?
While the financial impact of data misuse shouldn’t be understated, perhaps the greatest business impact comes in the loss of trust between the company and its audience.
It is entirely reasonable to expect the companies that handle our data to do so securely and under the agreed terms. Anything sort of that agreement is a massive violation of trust between the people and the service provider—trust that is not easily rebuilt. Cambridge Analytica folded in less than three months, Google is still facing constant criticism, and Uber will be audited for the better part of the next two decades.
While these actions may lack the malice of a traditional black hat cyberattack, data misuse increases the opportunities for these criminals to access private data. Many instances of data misuse start with employees or third-party vendors with legitimate access transferring company data from a secure server onto a personal device with less stringent data security features. Even the most robust network security provisions are irrelevant once data leaves the secure perimeter. Once that personal data—or access to it—is controlled by a more susceptible device, cybercriminals have a much easier path to accessing the personal data they desire.
In 2020, hackers accessed 5.2 million Marriott guest records, including customer contact information, personal preferences, birthdays, and more. This attack succeeded because the attackers compromised employee credentials to access a third-party application. It was two months before anyone realized something was wrong.
How Can Misuse of Data Be Prevented?
Often, data misuse boils down to ignorance and negligence. However, as our digital footprints continue to grow and evolve, the necessity for responsible digital hygiene extends to every citizen of the internet—not just IT professionals.
That starts with improving our general online practices so that we as users are more selective about the companies we trust with our data and that we, as professionals, are treating our customers’ data with the same care we would our own.
1. Leave work at work
Don’t mix professional and personal devices. Never download workplace data to your personal laptop, smartphone, desktop, home server, or whatever device you choose, no matter how fancy your home firewall, encryption, or VPN may be. This mixture of circumstances only invites further scrutiny and additional opportunities for cyber-attacks.
2. Practice conscious digital hygiene
Phishing instances have skyrocketed in recent years, and while many users are more and more confident in their ability to sniff out bad actors, there’s always one person on our social media feeds trying to sell knock-off Ray-Bans. Don’t fall for the cheap tactics of bad actors. Confirm URLs before submitting personal data, don’t click links from email addresses you don’t recognize, and use complex passwords.
3. Be selective
For organizations and individuals alike, putting your faith in the wrong partner can have disastrous results. As we saw on Facebook and Marriott, poor practices by a third-party vendor can not only compromise entire organizational networks but can sully the trust between brands and their customers in an instant. Likewise, we ought to carefully measure the quality of the places where we share our personal data.
While we can refine and perfect our online habits to prevent our own potential misuse, we rarely get to set data policies for the companies we frequent. We as users and customers and contributors must hold the brands we trust accountable for maintaining those expectations. Change never happens out of complacency; whether it’s Big Tech or Wall Street, the only way organizations create serious policy around data misuse is when their customers demand it. Organizations should have basic security structures like behavior alerts and access management tools complemented by need-to-know access and zero-trust architectures. Likewise, we as consumers have a right to clear data collection policies and transparent use cases.
As governing policies like the EU’s GDPR or California’s CCPA continue to shape the future of data regulation, it is only a matter of time before global expectations around data ownership and data misuse become more explicit expectations in every region.
How is Invisibly Combatting Data Misuse?
If you bank online, use social media, or send emails through any large tech platform, then your data is already being shared and sold for profit. It’s time to reclaim its worth and use it to unlock premium rewards instead of giving it away for free.
Invisibly is a platform that allows you to maximize the value of your data and earn brand rewards for it. The data collected is the data you decide to share – putting you in direct control, always. Connect your bank or credit card account(s), take surveys, and earn points to unlock your rewards from brand partners including Target, Ulta Beauty, Best Buy, and many more.

See your data work for you.
Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- 4 Ways Statistics Can Be Misused – and How to Avoid Them

In a quote that is widely attributed to George Bernard Shaw, Bertrand Russell once said that an ideal character might “go so far as to enable a man to be moved emotionally by statistics.”
You should also read…
- 35 Terms to Enhance Your Business English Vocabulary
- 10 Oxford Donors and How They Made Their Money
It’s easy to see why this degree of sympathy might not be accessible by most of us. Another famous quotation runs, “a single death is a tragedy; a million deaths is a statistic”; it’s usually attributed to Stalin but is probably apocryphal. Wherever it comes from, it gets requoted endlessly because it is both shocking – a million deaths certainly ought to be viewed as a tragedy – and it has a core of truth. Humans evolved in small groups; past a certain size, the difference between large numbers is very hard for us to conceptualise. A million is a thousand times smaller than a billion, but as every newspaper subeditor knows, we get them confused all the time. It’s easy enough to find shocking statistics – even heartbreaking ones. 80% of those dying of malaria in Africa are children. 10 million children die before their 5th birthday. More refugees have died at sea trying to make it to Europe in January 2016 as in the two preceding Januaries put together. But would it alter your perception significantly if you were told that it was 8 million children who die before their 5th birthday, or 15 million? Many statistics, no matter how affecting, don’t engage us closely with the issue at hand. That’s why they’re so easily misused or just plain made up. Here’s our guide to using statistics more wisely, and the errors to avoid.
1. “He uses statistics as a drunken man uses a lamppost – for support, not illumination.”
Another quote of dubious origin demonstrates the biggest sin in use of statistics. You have a point to make but not much by way of reasons to back it up? No problem; use some statistics.

The TV series Yes, Prime Minister demonstrated how this can be done beautifully after a poll is released showing that a majority of the public favour reintroducing conscription. Sir Humphrey (a senior civil servant) asks his colleague, Bernard, to commission a poll showing the opposite – and then shows how this is done. He asks Bernard a series of questions (“Are you worried about the rise in crime among teenagers?”; “Do you think young people welcome some authority and leadership in their lives?” and so on) to get Bernard to agree that conscription should be reintroduced, and then another series (“Do you think there is a danger in giving young people guns and teaching them how to kill?”; “Do you think it is wrong to force people to take up arms against their will?”) to get him to agree to the exact opposite. Bernard, he concludes, is “the perfect balanced sample.” It can be tricky to know how to support a point otherwise. After all, you’ve probably heard that the plural of anecdote is not data (or in other words, a collection of anecdotes doesn’t add up to a consensus). And while it’s fun to argue on the basis of thought experiments and deduction, at some point you will probably want some concrete evidence. And so you turn to statistics. Make sure the statistics you choose don’t break any of the other rules on this list and you’ll be off to a good start.
2. Sample sizes matter
100% of people writing this article are hungry. There is, however, only one person writing this article, so this is not a useful statistical guide to the general hunger levels of Oxford Royale Summer Schools writers. This much seems obvious. But it doesn’t stop people from coming up with statistics based on all kinds of absurd sample sizes. For instance, it was gleefully pointed out on Twitter that of all the trolls imprisoned for the harassment of feminist campaigner Caroline Criado-Perez, 50% were female. Evidence, then, that Criado-Perez’s views were opposed by women just as much as by men; that the harassment she faced couldn’t really be down to sexism; that in fact, it was probably altogether justified. The only problem? A grand total of two people were imprisoned for harassing Criado-Perez. One of them was female.

The Criado-Perez example is an extreme one, but this crops up repeatedly. Think about the shampoo adverts where of 50 women surveyed, 70% reported that their hair had increased volume and shine. That is not very many! Not just the size but the type of sample matters; polling companies failed utterly to predict a Conservative majority in the 2015 British General Election, which has been put down partly to finding Labour-dominated samples. Conservative voters are likely to be busier (so not at home to answer the door for door-to-door polling) and less likely to be active online (so not responding to online polls). Not accounting for that difference when weighting scores can have pretty extreme consequences. Unweighted polling currently shows Labour and the Conservatives neck-and-neck. Allow for the need to weight the data, and the Conservatives end up with a lead of seven or eight percentage points. One of the worst offenders here are psychology statistics. Psychology students are required for their university courses to carry out a lot of research, and they also get credit for taking part in research. This can result in research that consists of psychology undergraduates studying other psychology undergraduates; which is an excellent way of learning about the psychology of psychology undergraduates, but terrible when applied to the wider population. It’s worth noting that this is not the fault of the undergraduates themselves, but of anyone who comes across this data and decides to report it as if it applied to the world as a whole.
3. Bells and degenerates
These are types of distributions, not an album title (sadly). A bell curve usually refers to a normal distribution, which is the easiest kind for most non-statisticians to imagine. Think of a class of students of roughly similar ability. They take a test and the average score out of ten is five. Most of them get 5 out of 10, some get 4 or 6 out of 10, and a couple get 3 or 7 out of 10. If you were to plot their scores on a graph and draw a line through it, the line would form the shape of a bell. Hence, bell curve.

One of the problems that you might encounter is that when you say – for instance – “the class average was five out of ten”, the natural assumption is a bell curve with results like the ones described above. But that could also be the case if about half the class scored 0 or 1 out of 10, and the other half got 9 out of 10 or full marks – an inverted bell that would probably not be what you originally pictured. Similarly, if you were told that you were going to be giving a speech to a group of people with an average age of 60, you might assume you’d be addressing a group of older people and tailor your speech accordingly. You might then be surprised to see a group of people with ages ranging from toddlers to very elderly people, with, say, a large contingent of teenagers. The average age could still be 60, while the range could be much greater than you’d expect. It’s also worth thinking about the different types of average. Normally, when we say “average”, we mean the mean – all the numbers added together, divided by the total number of numbers. So we might have a group of people at a knitting circle who are aged 55, 67, 82, 89, 13, 13, 13, 56 and 0.5. The mean of their ages would be 43 – an age in a decade that no one represents. The modal average age – the most common age – is 13, which doesn’t seem right either. The median average is worked out by putting all the numbers in order and finding the middle one, so here it would be 0.5, 13, 13, 13, 55, 56, 67, 82 and 89 – and the middle age is 55, which does feel more appropriately representative of the group as a whole. But ultimately, if you were going to describe the knitting group, you’d probably say something like, “it’s mostly older people, a few teenagers, and one person sometimes brings a baby” – an arrangement that refuses to fit into a bell curve and that statistics struggle to describe.
4. Statistics are like a red, red rose
The stock market has been turbulent lately and you might well have seen headline like “Dow Jones plunges 276 points”. If you’re a regular reader of the business news and you know how much variation there usually is in the number of points up or down that the Dow Jones closes, then this is a useful figure for you – at least, it enables you to know just how much you need to worry. However, for many of us this kind of statistic is utterly useless because we have no baseline to compare it to. You end up second guessing what sounds like a big number and can end up in a considerable muddle. Think about a tabloid headline – unemployment at such-and-such a percentage, literacy rates at such-and-such a percentage, this number of violent crimes per year – all of which could sound very alarming and make you conclude that everything is going downhill and the apocalypse is nigh.

This is unless you know that unemployment is at a 10-year low, literacy is higher than ever and the rise in violent crime is not because more crimes are being committed but because far more violent crimes are being reported; in other words, there are some crimes that people previously hadn’t been reporting to the police – perhaps because they thought that no action would be taken or because they didn’t think it was serious enough to bother – that they now are telling the police about. That doesn’t seem like a country in chaos. But you have to have some context, some point of comparison, to be able to tell. Worse than no comparison, however, is a bad comparison; at least having no comparison might encourage the reader to seek out their own. You can witness this any time comparisons between countries are made that are not on a per capita basis. So for instance, Germany has been lauded for its promise to take in 1.5 million refugees. Lebanon has taken in about 1 million refugees. On that basis, Germany’s commitment looks more impressive; however, Germany has a population of 80 million to Lebanon’s 5 million, and a GDP of $3.7 trillion to Lebanon’s $44 billion. Or take Richard Dawkins’ controversial tweet that Trinity College, Cambridge has won more Nobel prizes than “all the world’s Muslims”. He defended himself by saying he was just pointing out a fact. But Trinity College, Cambridge graduates and academic staff have also won more Nobel prizes than Japan, Russia or the continent of Oceania – it is not that the world’s Muslims are punching significantly below their weight in terms of Nobel prizes, but that Trinity College is peerless in its success. On the topic of Nobel prizes, there’s a strong positive correlation between the number of Nobel prizes the people of a country have earned and the quantity of chocolate that the people of that country eat annually. It’s an obvious point, but one that cannot be made often enough: this does not show that eating more chocolate will earn you a Nobel prize, nor that being surrounded by a greater number of Nobel prize winners give you more of a hankering for chocolate. Correlation does not imply causation. Here it’s the case that the countries that eat the most chocolate are either the ones near where the Nobel committee is based (Sweden, Denmark, Norway), wealthier countries where chocolate is inexpensive and easy to get hold of, and Western countries generally where chocolate is a favourite treat, which tend to be wealthier and therefore have more money to invest in education and research – resulting in more Nobel prizes. But this tenuous connection between chocolate-eating and Nobel prizes is greater than the connection between some correlated values. This page has a selection of statistics that show a correlation entirely by chance. Have you come across any hilarious example of the misuse of statistics? Let us know in the comments! image credits: laptop and desk , giraffes , dog and man , bell curve , dwarves .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The top 8 reasons business plans fail. 1. Bad business ideas. Nobody likes to talk about it, but the main reason why business plans fail is bad ideas. Most ideas look great on paper—but all too often, companies realize they have invested in a bad idea once it is too late. To avoid this, smart businesses are using "user-driven development ...
Business plans can be different things: they are sometimes just sales documents to explain a new business. They can also be flexible Lean Plans, detailed action plans, financial plans, marketing plans, and even personnel plans. They can be used to start a business, or just run a business better. Develop the plan that best suits your business ...
Every company benefits from an updated business plan. While it seems necessary for start-ups, it applies to established firms, too. An efficiently written business plan keeps the whole business on track in the process of execution of the company's strategy and reaching its business goals. Business plan mistakes can result in anything ranging from small […]
12. Inconsistent information and mistakes. This almost goes without saying, but make sure to proofread your plan before you send it out. Beyond ensuring that you use proper grammar and spelling, make sure that any numbers that you mention in your plan are the same ones that you have in your financial projections.
Here are 10 of the most common business plan mistakes I have come across: 1. Boring Executive Summary. Investors, bankers, and other business plan readers usually start looking at the executive summary. It should highlight the most important points of the business plan in a pithy way. The business plan should provide a convincing story on how a ...
4. Failing To Research The Target Market. One business plan mistake that new entrepreneurs often make is failing to research their target market properly. They may have a great product or service ...
Sometimes, a business plan fails simply because it focuses on bad product ideas. A bad product idea means that the product or service your business specialises in does not sell well, and the lack of sales leads to an income problem for your business. Business plans containing bad product ideas usually come about due to a misunderstanding of the ...
Crafting a business plan is a delicate balancing act. It demands a deep understanding of your market, a clear value proposition, realistic financial projections, a competent team, and the flexibility to adapt to changing circumstances. All too frequently, an entrepreneur or business owner may lean on a business plan template or outsourced ...
So if they start paging through your plan and can't find the section on "Management," they may decide to move on to the next, more organized plan in the stack. 3. The plan is incomplete. Every ...
It's okay to be wrong, but you have to be specific if you want measurable, actionable targets. 4. Your models aren't realistic. That being said, specific goals often aren't enough to make your ...
Entrepreneurs will typically need to make assumptions about three key areas when writing a business plan: Sales, variable costs and fixed costs. "In the simplest form, you're projecting what sales you'll need to cover fixed and variable costs," LaBossière says. "Entrepreneurs often fail to include detailed assumptions that are clearly broken down.
His new book, Burn the Business Plan: What Great Entrepreneurs Really Do, says the true blueprint for success requires innovative ideas, real-world experience and keen judgment. Schramm joined the ...
Set yourself up for success by learning how to avoid these ten common business plan mistakes. 1. Unrealistic Financial Projections. Lenders and investors expect to see a realistic picture of where your business is now and where you hope it goes. One of the most common business plan mistakes is overestimating the value of your company.
Too much information. 3. Not enough information about risks and competition. 4. Unclear or unfocused writing. 5. Formatting issues. You've worked hard to put together a business plan for your new venture. You've followed expert advice and included sections that address your business and industry, your strategy for reaching your goals, your ...
Business plans are sometimes overdone and misused, but the planning process is critical. All businesses, not just startups, need planning. About 60 years ago, Dwight D. Eisenhower said, "The plan ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business. But the reality can be more nuanced - it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written. Ideal times to write a business plan include: When you have an idea for a ...
Describe your company, its mission, and vision. Identifying the "why" of your business is a crucial step in learning how to write a business plan. There are two ways of articulating that "why.". One is your company's mission statement — a brief explanation of what you hope to achieve by starting or growing your business.
4. Uber "God View" Rider Tracking. Getting in on data misuse before it was cool, Uber was fined $20,000 by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) for its "God View" tool in 2014. "God View" let Uber employees access and track the location and movements of Uber riders without their permission. As a result of their settlement with the FTC ...
A business code of ethics is a set of rules that outline the ethical values a business implements in its policies and expects its staff to adhere to. The principles outline the mission and values of an organisation and can aid in guiding a business's decision-making and distinguishing right from wrong. In some industries, such as finance, law ...
Many statistics, no matter how affecting, don't engage us closely with the issue at hand. That's why they're so easily misused or just plain made up. Here's our guide to using statistics more wisely, and the errors to avoid. 1. "He uses statistics as a drunken man uses a lamppost - for support, not illumination.".
Data misuse is the use of information in ways it wasn't intended for. User agreements, corporate policies, data privacy laws, and industry regulations all set conditions for how data can be collected and used. Data misuse violates these requirements. Unlike data theft, data misuse doesn't necessarily happen as a result of a cyberattack or ...