The road to entrepreneurial success: business plans, lean startup, or both?
New England Journal of Entrepreneurship
ISSN : 2574-8904
Article publication date: 19 February 2021
Issue publication date: 18 June 2021
The goal of this research is to investigate the relationship between two different sets of practices, lean startup and business planning, and their relation to entrepreneurial performance.

Design/methodology/approach
The authors collected data from 120 entrepreneurs across the US about a variety of new venture formation activities within the categories of lean startup or business planning. They use hierarchical regression to examine the relationship between these activities and new venture performance using both a subjective and objective measure of performance.
The results show that talking to customers, collecting preorders and pivoting based on customer feedback are lean startup activities correlated with performance; writing a business plan is the sole business planning activity correlated with performance.
Research limitations/implications
This research lays the foundation for understanding the components of both lean startup and business planning. Moreover, these results demonstrate that the separation of lean startup and business planning represents a false dichotomy.
Practical implications
These findings suggest that entrepreneurs should engage in some lean startup activities and still write a business plan.
Originality/value
This article offers the first quantitative, empirical comparison of lean startup activities and business planning. Furthermore, it provides support for the relationship between specific lean startup activities and firm performance.
Business planning
- Entrepreneurship
Lean Startup
Welter, C. , Scrimpshire, A. , Tolonen, D. and Obrimah, E. (2021), "The road to entrepreneurial success: business plans, lean startup, or both?", New England Journal of Entrepreneurship , Vol. 24 No. 1, pp. 21-42. https://doi.org/10.1108/NEJE-08-2020-0031
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2021, Chris Welter, Alex Scrimpshire, Dawn Tolonen and Eseoghene Obrimah
Published in New England Journal of Entrepreneurship . Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) license. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this license may be seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
Introduction
No business plan survives first contact with a customer – Steve Blank
This quote represents the differing perspectives on the value of business planning relative to the value of lean startup methods proposed by Blank and others ( Blank and Dorf, 2012 ). Much of traditional entrepreneurial training centers on the business plan ( Honig, 2004 ). Collective research on business planning's antecedents ( Brinckmann et al. , 2019 ) and its performance outcomes have found nuanced results ( Brinckmann et al. , 2010 ), but there seem to be at least some instances where business planning reliably increases performance ( Welter and Kim, 2018 ). Studies suggest that the majority of prominent business schools offer business planning courses ( Honig, 2004 ; Katz et al. , 2016 ), and bookstores are filled with books detailing how to write a business plan ( Karlsson and Honig, 2007 ). Nonetheless, the research is fragmented at best, and often results in equivocal findings with regard to its relationship with firm performance ( Brinckmann et al. , 2010 , Delmar and Shane, 2003 ; Gruber, 2007 ). This lack of clear indication from researchers opens the door for critique of business planning from proponents of the lean startup ( Ghezzi et al. , 2015 ).
Lean startup methods have drawn increasing attention in entrepreneurial communities ( Ries, 2011 ). In accelerators, incubators and other spaces within startup ecosystems the wisdom of Eric Ries (2011) and Steve Blank ( Blank and Dorf, 2012 ) can be heard in training sessions and everyday conversations. Some entrepreneurial programs have adopted lean startup methods as well ( Bliemel, 2014 ). On one hand, conceptual articles have described how lean startup fits adjacent to current and past academic conversations ( Contigiani and Levinthal, 2019 ). On the other hand, practitioner articles have discussed the benefits and limitations of the models ( Ladd, 2016 ). In both cases, existing literature describes how these processes aim to avoid the pitfall of launching products that no one actually wants ( Blank, 2013 ).
Despite all the popular attention given to lean startup methods, little empirical research has been completed (see Trimi and Berbegal-Mirabent (2012) , Ghezzi et al. (2015) , and Ghezzi (2019) for exceptions). Some researchers (e.g. Frederickson and Brem, 2017 ) have drawn the parallels between lean startup methods and effectuation ( Sarasvathy, 2001 ), but these parallels do not sufficiently support the use of lean startup methods. While practitioners seem to embrace lean startup methods, academics have offered little in terms of direct investigation into those methods ( Shepherd and Gruber, 2020 ). Most of the research on lean startup methods focuses on cognitive processes ( Yang et al. , 2018 ; York and Danes, 2014 ). Recent critique ( Felin et al. , 2019 ) coupled with the dearth of empirical research calls into question the efficacy of lean startup methods. To that end, more research is needed to see how lean startup methods relate to new venture success especially in comparison to business planning. This is particularly important as new venture formation activities are the practices that can legitimize the firm ( De Clercq and Voronov, 2009 ).
As such, we propose the following question: which individual aspects of business planning and lean startup methods are related to success? We study the components of both business planning and lean startup methods as there is some academic support for aspects of lean startup such as experimentation ( Carmuffo et al. , 2019 ), but limited empirical investigation into lean startup more broadly. We specifically focus on the underlying activities that make up the processes of lean startup and business planning since our initial surveying showed that entrepreneurs often employ aspects of each. To examine this question, we created a survey that captured the various activities – both from lean startup and business planning – that entrepreneurs used in pursuing their new venture and compared those with measures of success.
Our findings suggest that certain lean startup activities and the act of writing a business plan are correlated with success. These findings help to undo a false dichotomy of either lean startup or business planning by suggesting that some activities from each side can lead to success. We contribute to business planning research by offering a possible explanation for the existing equivocal findings. Namely, that the act of writing a business plan may be important, but that the uses of a business plan for feedback or financing are not necessarily associated with success. We contribute to research on lean startup by offering the first quantitative support for specific lean startup activities. Taken together, this research lays the foundation for a more nuanced understanding of the value of business planning and lean startup methods.
Theoretical framework and hypotheses
The literature on business planning is vast focusing on both antecedents to business planning ( Brinckmann et al. , 2019 ) and outcomes of it ( Brinckmann et al. , 2010 ). Honig and colleagues have driven much of the research into business planning since the turn of the century ( Honig, 2004 ; Honig and Karlsson, 2004 ; Honig and Samuelsson, 2012 , 2014 ; Karlsson and Honig, 2009 ). They have challenged prior planning-performance paradigms that suggested planning would naturally increase performance ( Ajzen, 1985 ; Mintzberg and Waters, 1985 ; Ansoff, 1991 ). This debate about the value of planning has underscored the recent research into selection effects associated with business planning ( Burke et al. , 2010 ; Greene and Hopp, 2017 ).
Brinckmann et al. (2010) address this debate directly. Their meta-analytic review of business planning literature suggests that three contingencies need to be considered in terms of the effectiveness of business planning: uncertainty, limited prior information, and the lack of business planning structures. The presence of these three suggest that business planning may be less effective. We look at each of these three contingencies in more depth next.
For uncertainty, planning scholars (e.g. Priem et al. , 1995 ) suggest that unstable and uncertain environments would benefit most from planning as planning can reduce uncertainty through facilitating faster decision-making ( Dean and Sharfman, 1996 ). However, emergent strategies seem to be more effective at controlling uncertainty ( Mintzberg, 1994 ; Sarasvathy, 2001 ). Brinckmann et al. (2010) confirms the latter intuition suggesting that uncertainty makes planning efforts less effective. This logic falls in line with research on effectuation ( Sarasvathy, 2001 ), where planning is described as the appropriate strategy for risky environments and effectuation, in contrast, is appropriate for uncertain environments. Recent work has confirmed this logic depending on how accurate the entrepreneur can be when predicting the future ( Welter and Kim, 2018 ).
Turning to the concept of limited prior information, planning proponents suggest that the shorter feedback cycles in new and small firms combined with the positive motivational effects of planning will make it more effective ( Delmar and Shane, 2003 ). In essence, despite the lack of history for de novo firms, short cycle times create history quickly and planning itself serves to motivate these fledgling organizations. However, Brinckmann et al. (2010) find that these firms lack the information necessary to make such plans effective. As firms pursue novel strategies, planning seems to be less effective or firms abandon plans all together as they move forward ( Karlsson and Honig, 2009 ).
Finally, for plans to be effective firms need to have the structures in place to both plan and make use of those plans ( Brinckmann et al. , 2010 ). New firms tend to lack the organizational structures relevant to create and use plans ( Forbes, 2007 ). While Karlsson and Honig (2009) found that firms typically ignore or abandon plans after they have been made, often due to insufficient support structures, Honig and Samuelsson (2012) show that even when firms change their plans over time there is little impact on firm performance. In general, the literature on business planning suggests that planning has more benefits for established firms with data and history to support both the plan and the planning process.
Business planning activities improve the likelihood of success for new ventures.
Typically, business planning has been analyzed as the single act of writing a business plan (e.g. Honig and Karlsson, 2004 ). However, business planning is made up of a variety of activities ( Gruber, 2007 ), which entrepreneurs may utilize as a whole, or simply choose parts of the business planning process. It is worth noting that these specific activities are not mutually exclusive with lean startup activities that we will detail later. One source of the gap between the prevalence of business planning use and research supporting the efficacy of business plans may be this holistic perspective. The constituent parts of business planning may be executed as a whole, or may be chosen a la carte. Examining the various activities that make up business planning offers insight into which aspects of the process are related to firm performance.
Arguably the first step in the business planning process is the work that precedes the actual writing of a business plan. First, entrepreneurs must collect data – typically external data ( Brinckmann et al. , 2010 ). This data collection process may or may not result in an actual business plan being written and, therefore, can be treated as a separate step itself.
Beyond the data collection and writing, the planning process can play a role in routinizing the initial practices of entrepreneurs. While entrepreneurs may engage in social resourcing ( Keating et al. , 2014 ) and collective sense-making ( Wood and McKinley, 2010 ), the act of codifying the results of these activities can objectify these practices. Entrepreneurs engage socially on a number of dimensions in the pursuit of a venture, but physically writing down a business plan that can be shared externally can serve as a commitment mechanism. Entrepreneurs may share this plan with external stakeholders simply for feedback ( Wood and McKinley, 2010 ) or they may use it to seek funding ( Richbell et al. , 2006 ).
Writing a business plan improves the likelihood of success for new ventures.
Gathering secondary data improves the likelihood of success for new ventures.
Sharing a business plan with potential stakeholders in order to get feedback improves the likelihood of success for new ventures.
Sharing a business plan with potential financiers in order to obtain funding improves the likelihood of success for new ventures.
Lean startup
The concept and the phrase “Lean Startup” stem from Eric Ries (2011) and his popular press book by the same name. The phrase borrows from the idea of lean manufacturing in the sense of eliminating waste and pushing production and supply as late in the process as possible to delay purchasing until the last moment. The book draws primarily on Ries's personal experience in founding a company along with some consulting work. Further development of the ideas around lean startup methods comes from Steve Blank ( Blank and Dorf, 2012 ). Blank (2013) described three principles of lean startup: hypothesis creation, customer development, and agile development. Hypothesis creation represents the belief that founders begin with little more than untested hypotheses. Customer development represents the approach of interviewing and interacting with customers in order to verify or discard the aforementioned hypotheses. Finally, agile development conceptualizes that minimally viable products (MVPs) are deployed quickly to verify the hypotheses that are believed to be true.
These concepts are often practiced by entrepreneurs and taught at incubators and accelerators ( Ladd, 2016 ), but there is little academic research to support these practices. Ghezzi et al. (2015) offer one of the only comparative empirical studies between lean startup and business planning. Their findings from a four-case study suggest that lean startup methods lead to superior outcomes. The majority of other papers are conceptual explorations of lean startup methods focusing on the decision-making of entrepreneurs ( Frederickson and Brem, 2017 ; Yang et al. , 2018 ; York and Danes, 2014 ). These conceptual pieces draw parallels between lean startup and effectuation ( Sarasvathy, 2001 ).
The literature on effectuation is much larger than that of lean startup (see recent reviews and retrospectives by Arend et al. (2015) and Reymen et al. (2015) ). Effectuation has been defined as entrepreneurial expertise that utilizes heuristics to make decisions focused on the means available rather than on desired ends ( Sarasvathy, 2001 ). One heuristic, in particular, has driven the comparison between lean startup and effectuation: experimentation ( Camuffo et al. , 2019 ). However, the comparisons may stem from the lack of clear boundaries in effectuation (see Welter et al. , 2016 ). While some researchers might argue that effectuation is a more robust articulation of lean startup ( Frederickson and Brem, 2017 ), there are significant departures. Effectuation makes no mention of MVPs or agile development, but instead focuses on the means at hand ( Sarasvathy and Dew, 2008 ). These means direct the venture as opposed to a focus on a specific end in mind ( Sarasvathy, 2001 ). This is in contrast to lean startup methods that create specific tests in order to verify a predetermined path ( Blank, 2013 ). Thus, researchers have suggested that lean startup intersects with effectuation, as well as other research streams ( Contigiani and Levinthal, 2019 ; Ghezzi, 2019 ).
Utilizing lean startup methods improves the likelihood of success for new business ventures.
Similar to business planning, lean startup is a process with several component parts from which an entrepreneur may select without needing to accomplish each task. Moreover, these component parts may be used in conjunction with business planning activities. Since lean startup has been developed more by practitioners than academics, there is not a clearly-defined, comprehensive list of activities that constitutes lean startup. Bortolini et al. (2018) review the academic and popular press literature on lean startup and describe the process at a more theoretical level than the work of Blank (2013) and Ries (2011) . Between these two perspectives, a specific list of six lean startup activities can be derived.
The lean startup process begins with customer discovery ( Blank and Dorf, 2012 ). In its most basic sense, the process of customer discovery begins with interviewing potential customers to surface their problems. Blank (2013) describes how lean startups “get out of the building” throughout the process to validate customer assumptions regarding all aspects of a potential business model. This validation process involves a variety of different forms of potential customer interviews.
From there, entrepreneurs craft hypotheses and build experiments as Bortolini et al. (2018) describe. This part of the process can be deconstructed into developing prototypes, showing those prototypes to customers, and running experiments. These sub-processes are discrete steps that may depend on each other, but may also occur independently. For instance, entrepreneurs may develop prototypes in their own quest to improve the product without actually showing a given prototype to potential customers. Alternatively, entrepreneurs may run experiments that do not necessarily involve the use of a prototype. These experiments may include observing customers in their daily routine to better understand customer problems. Each of these processes, however, align with the practitioner perspectives and the theoretical perspectives ( Blank and Dorf, 2012 ; Bortolini et al. , 2018) .
Beyond these specific activities, we examine two other activities within lean startup: collecting preorders and pivoting. Collecting preorders for new products has been suggested by Ries (2011) , but also aligns with research on enrolling external stakeholders ( Burns et al. , 2016 ) and the principles of effectuation ( Sarasvathy, 2001 ). By seeking out early stakeholders to make commitments like preorders or input on prototypes, entrepreneurs seek social resources to enable and direct their progress ( Keating et al. , 2014 ).
Interviewing potential customers improves the likelihood of success for new business ventures.
Developing a prototype improves the likelihood of success for new business ventures.
Showing a prototype to potential customers improves the likelihood of success for new business ventures.
Experimenting to test business model assumptions improves the likelihood of success for new business ventures.
Collecting preorders improves the likelihood of success for new business ventures.
Pivoting based on customer feedback improves the likelihood of success for new business ventures.
We began our study by conducting semi-structured interviews with five entrepreneurs to guide the construction of the survey. These entrepreneurs were selected from the authors' personal networks to represent a variety of perspectives and experiences. The group included two female founders and three male founders; two of the founders created high-tech scalable businesses and three represented small businesses. The interviews lasted 75 min on average.
All interviewees were familiar with business plans. All interviewees had heard of “lean startup” but only one entrepreneur had any education on the subject – they had read Eric Ries's book ( Ries, 2011 ). Nonetheless, none of the entrepreneurs could articulate specific aspects of lean startup or how it would be different from or related to writing a business plan.
The data collected from these interviews was used to develop a survey for distribution to a wider group of entrepreneurs. Within the qualitative data we noted how both business planning and lean startup represented groups of activities to the entrepreneurs. In discussing business planning, all of the entrepreneurs discussed more than simply producing a formal business plan. While four of the five entrepreneurs created formal business plans, each discussed a slightly different process. Some included financial planning while others mentioned secondary research. On the lean startup approach, the entrepreneurs did not specifically state which activities they pursued that were in line with lean startup, but multiple entrepreneurs mentioned each of the aspects of lean startup that we included in the survey.
This qualitative investigation altered our survey design to focus more on the activities that entrepreneurs completed rather than focusing on their understanding of the different approaches. Before distributing the survey, we tested it with two entrepreneurs to obtain feedback on its understandability – one from the original interviewees and one unfamiliar with the research project. Based on these tests, minor modifications to word choice were made.
We reached out to the startup ecosystem in a major Midwestern city. The online survey was emailed to incubators, accelerators, individual entrepreneurs, and organizations that reach outside the Midwest. Participation in the study was voluntary. Participants received a $1 USD donation to a non-profit organization of their choice for completing the survey. A total of 41 entrepreneurs responded to the initial survey request. We excluded seven of these cases because they did not adequately describe their business.
To bolster the sample size, we enlisted the Qualtrics panel development team to collect approximately 100 additional survey responses from entrepreneurs. Qualtrics, in addition to providing online survey tools, is a research panel aggregator with the ability to recruit hard-to-reach demographics. Qualtrics utilizes specialized recruitment campaigns to assemble niche survey panels based on pre-specified criteria. To fit in this group, entrepreneurs must own a business that they have started within the last ten years. Respondents in this group were compensated with $25 USD for their participation and were not offered any donation option. A total of 106 completed surveys were returned from this group. We excluded 20 of these cases because they were unable to adequately describe their business. See the Appendix for the complete survey instrument.
Participants and procedures
The participants completed an online questionnaire with thirty-two questions on the details of how they started their business, the success of the business, activities they conducted while starting the business, and demographic variables. The sample was recruited via a snowball sample method as well as through a Qualtrics panel as described above.
The majority of our sample is comprised of Caucasians (81.7%), followed by Black/African Americans (11.7%), then Hispanics (3.3%), then Asians (1.7%). The median age of our sample was 46.5 years old and the sample was 49.2% female. The majority of our dataset is currently married (61.7%) with 55.8% having at least a bachelor's degree. Table 1 shows the means and standard deviations for each of the variables as well as the correlations between them.
Dependent variables
There are various difficulties in obtaining concrete objective measures of success from entrepreneurs. Reasons stem from factors such as small business owners not always running their businesses to maximize financial performance ( Jacobs et al. , 2016 ) or running a business because it allows for a preferred lifestyle ( Jennings and Beaver, 1997 ; Walker and Brown, 2004 ). Because of this, there are a few ways researchers can gain acceptable insight into the success of an entrepreneurial venture. One approach is to use subjective measures when other types of information are unavailable ( Dawes, 1999 ). Thus, following previous research ( Besser, 1999 ; Jacobs et al. , 2016 ) which has noted that entrepreneurial success may not always mean optimal financial measures and instead may be more along the lines of maintaining an acceptable level of income for themselves and their employees ( Beaver, 2002 ) or sustaining a lifestyle more aimed at being part of a creative output than being financially successful ( Chaston, 2008 ), we first analyzed the entrepreneurs' perceived organizational success. A second approach is to ask about objective success measures. We strengthened our study by asking entrepreneurs about objective measures of their firm's success via focusing on their firm's growth, specifically, asking about objective growth indicators in terms of increased number of employees, increased number of customers, or increased revenue as previous research has used these measures to indicate success ( Walker and Brown, 2004 ). Therefore, we analyzed the full model for both the subjective and objective dependent variables.
Given that entrepreneurial motivations can vary widely ( Shane et al. , 2003 ), defining success can vary based on the individual. To address this, studies have surveyed entrepreneurs for their subjective perception of their venture's success ( Fisher et al. , 2014 ; Keith et al. , 2016 ). Walker and Brown (2004 , p. 585) find that “Personal satisfaction, pride and a flexible lifestyle were the most important considerations for these business owners.” They argue that objective, financial measures that are often used in research offer objectivity and accessibility, but may not capture the true value of success for many entrepreneurs. These alternative motivations make success difficult to quantify objectively, leading researchers to utilize more subjective measures. Therefore, in line with prior research on entrepreneurial success perceptions ( Jacobs et al. , 2016 ; Besser, 1999 ), we asked respondents “How strongly do you agree or disagree with the following statement? My business is a success.” Respondents rated their agreement on a five-point Likert scale (1 = Strongly Agree, 5 = Strongly Disagree).
Firm Growth:
To strengthen the findings from our subjective measure of success we also asked respondents about objective measures of firm growth. By asking respondents about obvious measures of growth we can offer a more objective view on the success of the firm. We asked respondents if their firm had grown by any of the following three metrics: number of employees, number of customers, or total revenue (cf. Jacobs et al. , 2016 ). Given the variety of motivations of entrepreneurs, we chose not to limit the type of growth that would reflect success. In some cases, an entrepreneur may seek to increase the impact of the business by providing services to a greater number of customers, while maintaining a lean staff to control pricing. Alternatively, an entrepreneur may be seeking autonomy, and therefore choose not to hire in order to create greater autonomy. However, it is likely that some firm growth – in revenue, employees, or customers – is likely to occur in successful firms. Therefore, we combined these three types of growth as a dichotomous variable, wherein growth in any one or more of these areas would be coded as a “1” for growth and an answer of no growth in all of these areas would be coded as a “0” for no growth.
Independent variables
Business planning.
We defined business planning using four activities. We asked respondents if they (1) wrote a business plan [ Write BPlan ]; (2) gathered secondary data on industry statistics or trends [ Secondary Data ]; (3) shared your business plan with people outside the company for feedback [ BPlan Feedback ]; and (4) shared your business plan with people outside the company for funding [ BPlan Funding ]. These were not loaded as a factor as these do not represent an underlying factor, but rather are individual activities that all represent a variety of activities pertaining to the use of business plans.
We defined lean startup using six activities. We asked respondents if they (1) interviewed potential customers [ Interview ]; (2) created a prototype [ Prototype ]; (3) showed a prototype to potential customers for feedback [ Show Proto ]; (4) conducted an experiment to better understand some portion of your business [ Experiment ]; (5) used customer feedback to alter the direction of your business (“pivoted”) [ Pivot ]; and (6) accepted money for preorders [ Preorders ]. Similar to business planning activities, these were not loaded as a factor, as these activities do not represent an underlying factor, but rather a collection of potential activities.
For each of the IVs, respondents were first asked which of the above activities they engaged in during their venture startup process. The order of the activities was randomized. For each activity that was selected, respondents were asked to rate “how much did each of those activities positively impact the performance of this venture?” Respondents were given a five-point Likert scale (1 = “Not at all” to 5 = “A great deal”) and if the respondent did not do the activity, the response was coded as a 0. To calculate the IVs, each response was weighted by the level of impact. For example, if the respondent rated Experiment as a 5 for a great deal of impact, then it would be coded 5. If it was rated 3, then it would be coded 3. Any activity not completed was not rated (or effectively coded a 0).
We used the ratings to allow for variance in the impact of any activity. In our preliminary interviews, we heard that entrepreneurs may have performed the same activity, such as interviewing customers, but some placed a greater emphasis on this activity whereas others performed it only cursorily. We also performed a robustness check on the data using non-weighted values for the IVs and found similar results (these are available from the corresponding author upon request).
Control variables
We controlled for the following variables: (1) the firm's age in years [Firm Age] ; (2) the entrepreneur's prior startup experience [Ent XP] ; (3) the entrepreneur's age in years [Age] ; (4) the entrepreneur's education level [Education] ; (5) the case sample [case Sample]; and (6) if the firm was a high-tech growth firm [Hi-tech growth firms] . Firm age is likely related to perceptions of success in the minds of entrepreneurs. If an entrepreneur perceives themselves as unsuccessful, they are likely to quit pursuing their venture. Thus, entrepreneurs with older businesses are more likely to have higher perceptions of their own success. Ent XP, Age , and Education have all been investigated in the past for their relationship to entrepreneurial firm performance (e.g. Hechavarría and Welter, 2015 ). We also control for the case sample since our sample was collected in two different processes. Finally, we control for Hi-tech growth firms since some firms in our sample are oriented toward accelerated growth and others may be content with stable returns, which may impact the use and effectiveness of business planning ( Brinckmann et al. , 2010 ).
Regression results for success DV
We tested our hypotheses using hierarchical regression [ 3 ]. In Step 1, we entered Firm Age (in years), the entrepreneur's prior startup experience, the entrepreneur's age, the entrepreneur's education level, the case source, and whether the firm was a hi-tech growth firm as controls ( Van Dyne and LePine, 1998 ). In Step 2, we entered our independent variables that relate to the business plan approach: writing a business plan, gathering secondary data on the industry, sharing the business plan to receive feedback, and sharing the business plan to obtain funding. We also included the variables related to the lean startup approach: interviewing potential customers, creating prototypes, showing prototypes to potential customers for feedback, conducting an experiment to better understand a portion of the business, pivoting based on customer feedback, and accepting money for preorders.
Table 1 reports descriptive statistics and correlations, whereas Table 2 presents the hierarchical regression results for the success dependent variable. As can be seen in Table 2 , consistent with H1a , writing a business plan was related to success ( β = 0.09, p = 0.09). However, we do not find support for our other hypotheses: gathering secondary data on the industry, sharing the business plan to receive feedback, and sharing the business plan to obtain funding were all not significantly related to success.
When we looked at the activities that contribute to lean startup methods, we found that interviewing potential customers ( β = 0.09, p = 0.08) and accepting money for preorders ( β = 0.15, p = 0.03) supported H2a and H2e respectively, suggesting these are correlated with success. Similar to the business plan approach there was not sufficient support for all our hypotheses: creating prototypes, showing prototypes to potential customers for feedback, conducting an experiment to better understand a portion of the business, and pivoting were not supported. The findings with regard to each hypothesis are summarized in Table 3 .
Regression results for growth DV
Similar to the subjective success dependent variable, we tested our hypotheses using logistic regression for our objective growth dependent variable [ 4 ]. A logistic regression was performed for each of our approaches, the business plan and lean startup since our growth DV is dichotomous ( Mason et al. , 2018 ).
Table 1 reports descriptive statistics and correlations, whereas Table 4 presents the logistic regression results for the effects of writing a business plan, gathering secondary data on the industry, sharing the business plan to receive feedback, and sharing the business plan to obtain funding had on our growth dependent variable. The logistic regression model was statistically significant, χ 2 (10) = 39.16, p < 0.005. The model explained 39.2% (Nagelkerke R 2 ) of the variance in business growth and correctly classified 69.2% of cases. As can be seen in Table 4 , consistent with H1a , writing a business plan was related to success ( β = 0.30, p = 0.036). As before we did not find support for our other hypotheses: gathering secondary data on the industry, sharing the business plan to receive feedback, and sharing the business plan to obtain funding.
Next, we looked at the actions that constitute lean startup, interviewing potential customers, creating prototypes, showing prototypes to potential customers for feedback, conducting an experiment to better understand a portion of the business, and pivoting based on customer feedback had on our growth dependent variable. The logistic regression model was statistically significant, χ 2 (12) = 53.82, p < 0.005. The model explained 51.0% (Nagelkerke R 2 ) of the variance in business growth and correctly classified 85% of cases. Our logistic regression results found that interviewing potential customers ( β = 0.25, p = 0.08), accepting money for preorders ( β = 0.89, p = 0.04), and pivoting based on customer feedback ( β = 0.34, p = 0.03), provided support for H2a , H2e , and H2f respectively, suggesting these are correlated with success in terms of growth. We did not find support for our other hypotheses about lean startup activities. These were, creating prototypes, showing prototypes to potential customers for feedback, conducting an experiment to better understand a portion of the business, and pivoting. The findings with regard to each hypothesis are summarized in Table 5 .
In this paper, we sought to understand the relationship between lean startup activities and success as well as the relationship between business planning activities and success. To answer this question, we began by gathering qualitative data from entrepreneurs to better understand their perspective and language regarding these two approaches. From there, we created a survey and collected responses from 120 entrepreneurs about their activities and their perception of success and the growth of their firms. Controlling for common influencers of success, we found that the act of writing a business plan ( H1a ), interviewing potential customers ( H2a ), and taking preorders ( H2e ) were all correlated with subjective perceptions of success. For the firm growth dependent variable, we found that the act of writing a business plan ( H1a ), taking preorders ( H2e ), and pivoting based on customer feedback ( H2f ) were all correlated with objective measures of firm growth. Interestingly, these results represent a combination of lean startup and business planning activities. What is more, the two activities that are supported by both dependent variables, represent the most well-researched activities. As mentioned, the literature on business planning is well developed ( Honig and Karlsson, 2004 ), and the use of preorders is most directly tied to research on enrolling stakeholders ( Burns et al. , 2016 ) as well as effectuation ( Sarasvathy, 2001 ).
Our results give some understanding to the prior equivocal findings on business planning ( Brinkmann et al. , 2010 ). The qualitative data we gathered suggests that entrepreneurs complete different activities in their business planning process. In the past, there has not been much discussion about separate aspects of business planning or the impact they may have. Our findings suggest that the act of writing a business plan is related to success, but the other business planning activities – gathering secondary data, sharing the business plan for feedback or funding – are not related. This suggests that the planning process itself may mean more than the uses of a business plan. Even if a business plan is not revised or revisited as an entrepreneur pursues their venture ( Karlsson and Honig, 2009 ), the act of writing the plan is still connected with success. Entrepreneurs going through the exercise of planning are likely to gain a better understanding of the entire endeavor of launching a new business. This would give entrepreneurs a better grasp of what the range of possible outcomes would be and likely temper any overly optimistic and unfounded hopes. Therefore, it is likely that simply writing the business plan helps calibrate entrepreneur expectations, which, in turn, helps entrepreneurs achieve success.
Rather than viewing lean startup as a cohesive whole, our qualitative data suggests that entrepreneurs make use of differing combinations of lean startup activities. This discovery informed our survey which offers some of the first direct quantitative evidence of the efficacy of lean startup methods. What we find, however, is that not all activities are linked to success. Perhaps the most straightforward finding is that taking preorders is correlated with both subjective and objective measures of success. If entrepreneurs are able to complete their first sales prior to actually creating their products or services, then success seems much more likely. Venture success, in this case, is agnostic toward the level of innovation in the firm. As such, the critique of lean startup from Felin et al. (2019) as a method that helps orient entrepreneurs to ideas that can be quickly and transparently tested still requires further investigation.
The other relevant activities are those most aligned with customers. Interviewing customers ensures that entrepreneurs design businesses that serve customers rather than building something that no one wants ( Blank and Dorf, 2012 ). However, it is worth noting that interviewing customers must be done with an awareness of the entrepreneur's own cognitive biases ( Chen et al. , 2015 ). Furthermore, pivoting as a result of these discussions with customers also shows a response to customers' desires.
The most interesting aspect of our findings is likely the combination of activities across business planning and lean startup. While lean startup proponents might argue that “no business plan survives its first contact with customers” ( Blank and Dorf, 2012 , p. 53), the act of writing a business plan is correlated with success. It is worth noting that the separation between lean startup and business planning may be a false dichotomy. The underlying activities are not mutually exclusive and do not seem to be detrimental to each other. It is entirely possible, and based on these results advisable, that an entrepreneur would interview customers throughout the process of creating a business plan and use customer feedback to alter both the plan and the business itself. Furthermore, taking customer preorders serves to solidify the relationship between customers and the firm which would only improve that communication.
Limitations
In order to create one of the first quantitative, empirical investigations of business planning and lean startup practices, some tradeoffs needed to be made. We believe that while these limitations may restrict the strength of some of our findings, the direct nature of our approach offers a contribution to the ongoing conversations among scholars and practitioners.
Our sample size is 120. Obviously, a larger sample may lead to more robust and generalizable results. Furthermore, we gathered the sample using two different methods and controlling for the sample method was a significant predictor. We leave it to further research to expand upon our findings and investigate various entrepreneurial samples for differences that may arise.
One of our dependent variables was a subjective measure of success, which may be considered a weakness. We used this measure given the variety of preferred outcomes an entrepreneur may be pursuing – financial objectives, personal objectives, or mission-based objectives. Our other dependent variable was an objective measure of growth across three categories and serves to bolster confidence in the subjective measure.
Another area of concern may be common method variance given that we collected both independent variables and dependent variables from the same instrument. To address this concern, we collected data from individual entrepreneurs that all represented different companies and utilized two different samples so as to minimize the issues that may arise from common method variance ( Chang et al. , 2010 ). Lastly, our independent variables are more objective. For example, writing a business plan is a discrete event as is creating a prototype. For these reasons, we do not believe the common method variance is a major concern for this study.
One other potential weakness is the degree to which entrepreneurs actually utilized the activities of lean startup or business planning. The weighting scheme we employed aims to address this issue by weighting the degree to which entrepreneurs found each activity useful. However, we cannot be sure whether or not an entrepreneur executed the given activity well and this variability goes uncaptured in our study. Quantitative studies like this one will typically suffer from this limitation but case studies may be able to overcome these weaknesses (see Ghezzi et al. , 2015 ).
Finally, our design is cross sectional and does not allow us to make causal inferences. We can only imply the relationship between our independent and dependent variables. Our hope is this is a first step to future research which may be better able to test the causality of the various aspects of business planning and lean startup as they relate to entrepreneurial success.
Implications for research and practice
This manuscript has important implications for research and practice. With respect to research, we have demonstrated that aspects of business planning and lean startup both are associated with success. Furthermore, entrepreneurs seem unlikely to enact either business planning or lean startup wholesale but are likely to pursue individual aspects of these concepts. Future research can investigate how entrepreneurs select between activities as well as how training and education regarding these practices impact the entrepreneurs' choice. The training and education surrounding the entrepreneur represent aspects of the organizing context ( Johannisson, 2011 ), which influence how entrepreneurs construct their firms. Therefore, future research could add further institutional aspects or conduct randomized controlled trials to see the impact of these practices in the organizing context.
In terms of implications for practice, this research highlights the use of a variety of activities when it comes to entrepreneurial success. Some of the activities from both lean startup and business planning are useful for entrepreneurs. This also offers insight for educators as they seek to equip the next generation of entrepreneurs. Educators can offer potential entrepreneurs a wide range of activities without prognosticating one aspect of the false dichotomy between lean startup and business planning.
In this paper, we provide one of the first quantitative empirical studies investigating lean startup methods and business planning. In breaking down these areas, we undermine the false dichotomy between these two startup tools. Our findings demonstrate that truly understanding customers through preorders and interviews can lead to better business plans and better pivots. Ultimately, this results in firms with a greater chance of success. Understanding the variety of activities that entrepreneurs can pursue helps entrepreneurs and educators increase the chances of success for new businesses.
Correlations
Summary regression results for the growth DV
We do not believe that business planning exists as a latent construct necessarily comprised of these activities, but rather each of these activities are potential components of the concept referred to as “business planning” in prior research.
Similar to business planning activities, we believe that lean startup is not a latent construct but rather these activities in some combination is what is meant when practitioners and scholars refer to lean startup. As such we test each of the activities individually rather than as a construct.
Following the extant guidelines on regression assumptions ( Osborne and Waters, 2002 ), we tested our model to ensure the regression assumptions were met. First, to check if our error terms ( Flatt and Jacobs, 2019 ) are normally distributed, the P - P plot suggests normality as the plot is largely linear. Second, to check for a linear relationship between the independent and dependent variable, our residual plot showed a linear relationship. Third, as our variables were not latent, there is no concern for measurement error for this approach. However, we did follow best practices suggested by Flatt and Jacobs (2019) and tested the Durbin–Watson statistic. Our value for this measure is 1.5 and their guidelines are that this statistic should be close to 2. Values between 1.2 and 1.6 represent only a minor violation of the statistical independence of error terms. Finally, to address the assumption of homoscedasticity, inspection of our standardized residuals showed our residuals scattered around the 0 (horizontal line). Therefore, for our dependent variable of success, we can feel comfortable our data meets the assumptions of linear regression.
As this dependent variable was analyzed using logistic regression, we analyzed our data following best practices from Garson (2012) . First, our dependent variable is dichotomous. Second our scatterplot showed no outliers in our data. Third, the correlation table showed no evidence for multicollinearity as no correlations were above 0.9 ( Tabachnick et al. , 2007 ). Hence, we feel our data meets the assumptions for logistic regression.
Appendix Qualtrics Survey
[Business Background]
Started (or am starting it) myself
When you first started pursuing the business, how many people were on the founding team (including yourself)?
High Tech Startup (External/Venture funded)
Steady Growth Business (Internally/Self-funded)
Lifestyle Business
Business Idea
Decision to Start a Business
Occurred Together
Month (1–12)
Year (YYYY)
[Lean Start Up, Business Planning Practices]
Interviewed potential customers
Created a prototype
Showed a prototype to potential customers for feedback
Conducted an experiment to better understand some portion of your business
Wrote a business plan
Accepted money for pre-orders
Used customer feedback to alter the direction of your business ("pivoted")
Gathered secondary data on industry statistics or trends
Shared your business plan with people outside the company for feedback
Shared your business plan with people outside the company for funding
[Demographics]
How old are you? 0.5
Prefer not to answer
Black or African American
American Indian or Alaska Native
Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander
Living with a partner
Never married
Up to 8th grade
Some High School
High School Diploma
Some College
Associate's Degree
Bachelor's Degree
Some Graduate School
Master's Degree
More than 1
[Success Criteria]
My business is a success
Increased Annual Revenue
Increased Annual Customers
Increased Number of Employees
Thank you for completing the survey!
Ajzen , I. ( 1985 ), “ From intentions to actions: a theory of planned behavior ”, Action Control , Springer , Berlin, Heidelberg , pp. 11 - 39 .
Ansoff , H.I. ( 1991 ), “ Critique of Henry Mintzberg's ‘The design school: reconsidering the basic premises of strategic management’ ”, Strategic Management Journal , Vol. 12 No. 6 , pp. 449 - 461 .
Arend , R. , Sarooghi , H. and Burkemper , A. ( 2015 ), “ Effectuation as ineffectual? Applying the 3E theory-assessment framework to a proposed new theory of entrepreneurship ”, Academy of Management , Vol. 40 No. 4 , pp. 630 - 651 .
Beaver , G. ( 2002 ), Small Business, Entrepreneurship and Enterprise Development , Pearson Education , Harlow .
Besser , T.L. ( 1999 ), “ Community involvement and the perception of success among small business operators in small towns ”, Journal of Small Business Management , Vol. 37 No. 4 , pp. 16 - 29 .
Blank , S. ( 2013 ), “ Why the lean start-up changes everything ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 91 No. 5 , pp. 64 - 72 .
Blank , S. and Dorf , B. ( 2012 ), “ The startup owner's manual ”, The Step-by-step Guide for Building a Great Company , Vol. 1 .
Bliemel , M. ( 2014 ), “ Getting entrepreneurship education out of the classroom and into students’ heads ”, Entrepreneurship Research Journal , Vol. 4 No. 2 , pp. 237 - 260 .
Bortolini , R.F. , Nogueira Cortimiglia , M. , Danilevicz , A.D.M.F. and Ghezzi , A. ( 2018 ), “ Lean startup: a comprehensive historical review ”, Management Decision . doi: 10.1108/MD-07-2017-0663 .
Brinckmann , J. , Grichnik , D. and Kapsa , D. ( 2010 ), “ Should entrepreneurs plan or just storm the castle? A meta-analysis on contextual factors impacting the business planning–performance relationship in small firms ”, Journal of Business Venturing , Vol. 25 No. 1 , pp. 24 - 40 .
Brinckmann , J. , Dew , N. , Read , S. , Mayer-Haug , K. and Grichnik , D. ( 2019 ), “ Of those who plan: a meta-analysis of the relationship between human capital and business planning ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 52 No. 2 , pp. 173 - 188 .
Burke , A. , Fraser , S. and Greene , F. ( 2010 ), “ The multiple effects of business planning on new venture performance ”, Journal of Management Studies , Vol. 47 No. 3 , pp. 391 - 415 .
Burns , B.L. , Barney , J.B. , Angus , R.W. and Herrick , H.N. ( 2016 ), “ Enrolling stakeholders under conditions of risk and uncertainty ”, Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal , Vol. 10 No. 1 , pp. 97 - 106 .
Camuffo , A. , Cordova , A. , Gambardella , A. and Spina , C. ( 2019 ), “ A scientific approach to entrepreneurial decision making: evidence from a randomized control trial ”, Management Science . doi: 10.1287/mnsc.2018.3249 .
Chang , S.J. , Van Witteloostuijn , A. and Eden , L. ( 2010 ), “ From the editors: common method variance in international business research ”, Journal of International Business Studies , Vol. 41 No. 2 , pp. 178 - 184 .
Chaston , I. ( 2008 ), “ Small creative industry firms: a development dilemma? ”, Management Decision , Vol. 46 No. 6 , pp. 819 - 831 .
Chen , T. , Simon , M. , Kim , J. and Poploskie , B. ( 2015 ), “ Out of the building, into the fire: an analysis of cognitive biases during entrepreneurial interviews ”, New England Journal of Entrepreneurship , Vol. 18 No. 1 , pp. 59 - 70 .
Contigiani , A. and Levinthal , D. ( 2019 ), “ Situating the construct of lean startup: adjacent ‘Conversations’ and possible future directions ”, Industrial and Corporate Change , Vol. 28 No. 3 , pp. 551 - 564 .
Dawes , J. ( 1999 ), “ The relationship between subjective and objective company performance measures in market orientation research: further empirical evidence ”, Marketing Bulletin - Department of Marketing Massey University , Vol. 10 , pp. 66 - 75 .
De Clercq , D. and Voronov , M. ( 2009 ), “ Toward a practice perspective of entrepreneurship entrepreneurial legitimacy as habitus ”, International Small Business Journal , Vol. 27 No. 4 , pp. 395 - 419 .
Dean , J. and Sharfman , M. ( 1996 ), “ Does decision process matter? A study of strategic decision-making effectiveness ”, Academy of Management Journal , Vol. 39 No. 2 , pp. 368 - 392 .
Delmar , F. and Shane , S. ( 2003 ), “ Does business planning facilitate the development of new ventures? ”, Strategic Management Journal , Vol. 24 No. 12 , pp. 1165 - 1185 .
Felin , T. , Gambardella , A. , Stern , S. and Zenger , T. ( 2019 ), “ Lean startup and the business model: experimentation revisited ”, Forthcoming in Long Range Planning (Open Access), available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3427084 (accessed 29 June 2019) .
Fisher , R. , Maritz , A. and Lobo , A. ( 2014 ), “ Evaluating entrepreneurs' perception of success: development of a measurement scale ”, International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior and Research , Vol. 20 No. 5 , pp. 478 - 492 .
Flatt , C. and Jacobs , R.L. ( 2019 ), “ Principle assumptions of regression analysis: testing, techniques, and statistical reporting of imperfect data sets ”, Advances in Developing Human Resources , Vol. 21 No. 4 , pp. 484 - 502 .
Forbes , D.P. ( 2007 ), “ Reconsidering the strategic implications of decision comprehensiveness ”, Academy of Management Review , Vol. 32 No. 2 , pp. 361 - 376 .
Frederiksen , D. and Brem , A. ( 2017 ), “ How do entrepreneurs think they create value? A scientific reflection of Eric Ries' lean startup approach ”, International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal , Vol. 13 No. 1 , pp. 169 - 189 .
Garson , G.D. ( 2012 ), Logistic Regression: Binomial and Multinomial , Statistical Associates Publishers , Asheboro, NC .
Ghezzi , A. ( 2019 ), “ Digital Startups and the adoption and implementation of Lean Startup approaches: effectuation, bricolage and opportunity creation in practice ”, Technological Forecasting and Social Change , Vol. 146 , pp. 945 - 960 , doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2018.09.017 .
Ghezzi , A. , Cavallaro , A. , Rangone , A. and Balocco , R. ( 2015 ), “ On business models, resources and exogenous (dis) continuous innovation: evidences from the mobile applications industry ”, International Journal of Technology Management , Vol. 68 Nos 1-2 , pp. 21 - 48 .
Greene , F. and Hopp , C. ( 2017 ), “ Are formal planners more likely to achieve new venture viability? A counterfactual model and analysis ”, Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal , Vol. 11 No. 1 , pp. 36 - 60 .
Gruber , M. ( 2007 ), “ Uncovering the value of planning in new venture creation: a process and contingency perspective ”, Journal of Business Venturing , Vol. 22 No. 6 , pp. 782 - 807 .
Hechavarría , D.M. and Welter , C. ( 2015 ), “ Opportunity types, social entrepreneurship and innovation: evidence from the panel study of entrepreneurial dynamics ”, The International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Innovation , Vol. 16 No. 4 , pp. 237 - 251 .
Honig , B. ( 2004 ), “ Entrepreneurship education: toward a model of contingency-based business planning ”, The Academy of Management Learning and Education , Vol. 3 No. 3 , pp. 258 - 273 .
Honig , B. and Karlsson , T. ( 2004 ), “ Institutional forces and the written business plan ”, Journal of Management , Vol. 30 No. 1 , pp. 29 - 48 .
Honig , B. and Samuelsson , M. ( 2012 ), “ Planning and the entrepreneur: a longitudinal examination of nascent entrepreneurs in Sweden ”, Journal of Small Business Management , Vol. 50 No. 3 , pp. 365 - 388 .
Honig , B. and Samuelsson , M. ( 2014 ), “ Data replication and extension: a study of business planning and venture-level performance ”, Journal of Business Venturing Insights , Vols 1-2 Nos 1-2 , pp. 18 - 25 .
Jacobs , S. , Cambre , B. , Huysentruyt , M. and Schramme , A. ( 2016 ), “ Multiple pathways to success in small creative businesses: the case of Belgian furniture designers ”, Journal of Business Research , Vol. 69 No. 11 , pp. 5461 - 5466 .
Jennings , P. and Beaver , G. ( 1997 ), “ The performance and competitive advantage of small firms: a management perspective ”, International Small Business Journal , Vol. 15 No. 2 , pp. 63 - 75 .
Johannisson , B. ( 2011 ), “ Towards a practice theory of entrepreneuring ”, Small Business Economics , Vol. 36 No. 2 , pp. 135 - 150 .
Karlsson , T. and Honig , B. ( 2007 ), “ Norms surrounding business plans and their effect on entrepreneurial behavior ”, Frontier of Entrepreneurship Research , Vol. 27 No. 22 , pp. 1 - 22 .
Karlsson , T. and Honig , B. ( 2009 ), “ Judging a business by its cover: an institutional perspective on new ventures and the business plan ”, Journal of Business Venturing , Vol. 24 No. 1 , pp. 27 - 45 .
Katz , J.A. , Hanke , R. , Maidment , F. , Weaver , K.M. and Alpi , S. ( 2016 ), “ Proposal for two model undergraduate curricula in entrepreneurship ”, International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal , Vol. 12 No. 2 , pp. 487 - 506 .
Keating , A. , Geiger , S. and McLoughlin , D. ( 2014 ), “ Riding the practice waves: social resourcing practices during new venture development ”, Entrepreneurship: Theory and Practice , Vol. 38 , pp. 1207 - 1235 .
Keith , N. , Unger , J.M. , Rauch , A. and Frese , M. ( 2016 ), “ Informal learning and entrepreneurial success: a longitudinal study of deliberate practice among small business owners ”, Applied Psychology , Vol. 65 No. 3 , pp. 515 - 540 .
Ladd , T. ( 2016 ), “ The limits of the lean startup method ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 94 No. 3 , pp. 2 - 3 .
Mason , C. , Twomey , J. , Wright , D. and Whitman , L. ( 2018 ), “ Predicting engineering student attrition risk using a probabilistic neural network and comparing results with a backpropagation neural network and logistic regression ”, Research in Higher Education , Vol. 59 No. 3 , pp. 382 - 400 .
Mintzberg , H. ( 1994 ), “ The fall and rise of strategic planning ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 72 No. 1 , pp. 107 - 114 .
Mintzberg , H. and Waters , J.A. ( 1985 ), “ Of strategies, deliberate and emergent ”, Strategic Management Journal , Vol. 6 No. 3 , pp. 257 - 272 .
Osborne , J.W. and Waters , E. ( 2002 ), “ Four assumptions of multiple regression that researchers should always test ”, Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation , Vol. 8 No. 1 , pp. 1 - 5, 2 , doi: 10.7275/r222-hv23 .
Priem , R.L. , Rasheed , A.M.A. and Kotulic , A.G. ( 1995 ), “ Rationality in strategic decision processes, environmental dynamism and firm performance ”, Journal of Management , Vol. 21 No. 5 , pp. 913 - 929 .
Reymen , I.M.M.J. , Andries , P. , Berends , H. , Mauer , R. , Stephan , U. and Burg , E. ( 2015 ), “ Understanding dynamics of strategic decision making in venture creation: a process study of effectuation and causation ”, Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal , Vol. 9 No. 4 , pp. 351 - 379 .
Richbell , S.M. , Watts , H.D. and Wardle , P. ( 2006 ), “ Owner-managers and business planning in the small firm ”, International Small Business Journal , Vol. 24 No. 5 , pp. 496 - 514 .
Ries , E. ( 2011 ), The Lean Startup: How Today's Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses , Crown Business , New York: New York .
Sarasvathy , S.D. ( 2001 ), “ Causation and effectuation: toward a theoretical shift from economic inevitability to entrepreneurial contingency ”, The Academy of Management Review , Vol. 26 No. 2 , pp. 243 - 263 .
Sarasvathy , S.D. and Dew , N. ( 2008 ), “ Effectuation and over-trust: debating goel and karri ”, Entrepreneurship: Theory and Practice , Vol. 32 No. 4 , pp. 727 - 737 .
Shane , S. , Locke , E.A. and Collins , C.J. ( 2003 ), “ Entrepreneurial motivation ”, Human Resource Management Review , Vol. 13 No. 2 , pp. 257 - 279 .
Shepherd , D. and Gruber , M. ( 2020 ), “ The lean startup framework: closing the academic-practitioner divide ”, Entrepreneurship: Theory and Practice . doi: 10.1177/1042258719899415 .
Tabachnick , B.G. , Fidell , L.S. and Ullman , J.B. ( 2007 ), Using Multivariate Statistics , Pearson , Boston, MA , Vol. 5 , pp. 481 - 498 .
Trimi , S. and Berbegal-Mirabent , J. ( 2012 ), “ Business model innovation in entrepreneurship ”, International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal , Vol. 8 No. 4 , pp. 449 - 465 .
Van Dyne , L. and LePine , J.A. ( 1998 ), “ Helping and voice extra-role behaviors: evidence of construct and predictive validity ”, Academy of Management Journal , Vol. 41 No. 1 , pp. 108 - 119 .
Walker , E. and Brown , A. ( 2004 ), “ What success factors are important to small business owners? ”, International Small Business Journal , Vol. 22 No. 6 , pp. 577 - 594 .
Welter , C. and Kim , S. ( 2018 ), “ Effectuation under risk and uncertainty: a simulation model ”, Journal of Business Venturing , Vol. 33 No. 1 , pp. 100 - 116 .
Welter , C. , Mauer , R. and Wuebker , R.J. ( 2016 ), “ Bridging behavioral models and theoretical concepts: effectuation and bricolage in the opportunity creation framework ”, Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal , Vol. 10 No. 1 , pp. 5 - 20 .
Wood , M.S. and McKinley , W. ( 2010 ), “ The production of entrepreneurial opportunity: a constructivist perspective ”, Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal , Vol. 4 No. 1 , pp. 66 - 84 .
Wood , M.S. , Palich , L.E. and Browder , R.E. ( 2018 ), “ Full steam ahead or abandon ship? An empirical investigation of complete pivot decisions ”, Journal of Small Business Management , Vol. 17 No. 4 , pp. 351 - 24 .
Yang , X. , Sun , S.L. and Zhao , X. ( 2018 ), “ Search and execution: examining the entrepreneurial cognitions behind the lean startup model ”, Small Business Economics , pp. 1 - 13 .
York , J. and Danes , J. ( 2014 ), “ Customer development, innovation, and decision-making biases in the lean startup ”, Journal of Small Business Strategy , Vol. 24 No. 2 , pp. 21 - 39 .
Acknowledgements
A portion of this research was funded by the Downing Scholars research grant at Xavier University.
Corresponding author
Related articles, we’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
The Value of Business Plans for New Ventures: Company and Entrepreneur Outcomes
- Richard C. Becherer University of Tennessee at Chatanooga
- Marilyn M. Helms Dalton State College
Allred, Anthony T. and Addams, H. Lon (2006). After Receiving Financing, Do Inc. 500 Companies Continue To Utilize Their Business Plan? Journal of Small Business Strategy. 17(1), 17-26.
Armstrong, J.S. and Overton, T.S. (1977). Estimating Nonresponse Bias in Mail Surveys. Journal of Marketing Research, 16(August), 396-492.
Bartlett, Sarah (2002). "Seat of their Pants," Inc. Magazine, October. Accessed May 14, 2009 at http://www.inc.com/magazine/20021015 /24772.html.
Bowers, Brent (2009) "In the Hunt: Investors Pay Business Plans Little Heed, Study Finds," New York Times, May 14, Small Business, p. 1
Delmar, Frederic and Shane, Scott (2003) "Does Business Planning Facilitate the Development of New Ventures?" Strategic Management Journal, 24, 1165-1185.
Fiet, James O. and Patel, Pankaj C. (2006). Evaluating the Wealth-Creating Potential of Business Plans. The Journal of Private Equity. 10(1), 18-32.
Fletcher, Margaret and Harris, Simon. (2002). Sever Aspects of Strategy Formation," International Small Business Journal, 20(3), 297-314.
Goldfarb, Kirsch, and Gera (2009) "Form or Substance? The Role of Business Plans in
Venture Capital Decision Making," Strategic Management Journal, May. Hand, H. W.; Sineath, P. and Howle, W. E. (1987) "Small Business Concepts and their Relationship to Performance: A Field Study of Retail Service Stations," Journal of Small Business Management, 25(2), 55-63.
Hannon, P. D. and Atherton, A. (1998) "Small Firm Success and the Art of Orienteering: The Value of Plans, Planning, and Strategic Awareness in the Competitive Small firm," Journal of Small Business and Enterprise, 5(2), 102-119.
Heriot, Kirk C.; Campbell, Noel D.; and Finney, R. Zachary (2004). "Omitted Variable Biases in the Link Between Planning and Performance," New England Journal of Entrepreneurship, 7(2), 27-31.
Hormozi, Amir M.; Sutton, Gail S.; McMinn, Robert D.; and Lucio, Wendy (2002). "Business Plans for New or Small Businesses: Paving the Path to Success," Management Decision, 40(7/8), 755-763.
Karlsson, Tomas and Honig, Benson. (2009). Judging A Business By Its Cover: An Institutional Perspective On New Ventures And The Business Plan. Journal Of Business Venturing. 24(1), 27-47.
Koh, Inkon; Kim, Dae Ho; and Lee, Sang Suk. (2008). A Study On The Relationship Between Business Plan Components And Corporate Performance. International Journal Of Entrepreneurship And Innovation Management. 8(4), 359-379.
Liao, Jianwen (Jon), and Gartner, William B. (2008). The Influence of Pre- Venture Planning on New Venture Creation. Journal Of Small Business Strategy. Fall/Winter, 18(2), 1-21.
Parks, Bill; Olson, Philip D. and Bokor, Donald W. (1991). "Don't Mistake Business Plans for Planning (It May Be Dangerous to Your Financial Health)," Journal of Small Business Strategy, 1(2), 15-24.
Perry, Stephan C. (2001). The Relationship between Written Business Plans and the Failure of Small Businesses in the U.S., Journal of Small Business Management, 39(3), 201-208.
Peters, T.J., and Waterman, R.H. (1982). In Search of Excellence: Lessons From America's Best Run Companies, New York, NY: Harper and Row.
Sharma, S., Netemeyer, R. G., and Mahajan, V. (1990). In Search of Excellence Revisited: an Empirical Evaluation of Peters and Waterman's Attributes of Excellence. In W. O. B. a. A. Parasuraman (Ed.), Enhancing Knowledge Development in Marketing (Vol. 1, pp. 322-328).
Rue, L. W. and Ibrahim, N. A. (1998) The Relationship Between Planning Sophistication and Performance in Small Businesses, Journal of Small Business Management, 36(4), 24-33.
Sahlman, W. A. (1997) "How to Write a Great Business Plan." Harvard Business Review 75(4), 99-110.
Shane, S. and Delmar, F. (2004) "Planning for the Market: Business Planning Before Marketing and the Continuation of Organizing Efforts," Journal of Business Venturing, 19, 767- 785.
Singhvi, S. S. (2000). Business Planning Practices In Small Size Companies: Survey Results. The Journal Of Business Forecasting Methods & Systems. 19(2), 3- 8.
Struebing, L. (1997). Recipe For Success: Prepare A Business Plan. Quality Progress. 30(8), 20.
Upton, N.; Teal, E. J.; and Felan, J. T. (2001). Strategic And Business Planning Practices Of Fast Growth Family Firms. Journal of Small Business Management, 29(1), 60-72.
How to Cite
- Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Richard C. Becherer, J. Howard Finch, Marilyn M. Helms, The Influences of Entrepreneurial Motivation and New Business Acquisition on Strategic Decision Making , Journal of Small Business Strategy (archive only): Vol. 16 No. 2 (2005)
- Richard C. Becherer, Marilyn M. Helms, Green Goals in Organizations: Do Small Businesses Engage in Environmentally Friendly Strategies? , Journal of Small Business Strategy (archive only): Vol. 24 No. 1 (2014)
- Richard C. Becherer, Diane Halstead, John Maurer, Antecedents of Job Burnout Among Small Company Presidents , Journal of Small Business Strategy (archive only): Vol. 11 No. 1 (2000)
Information
- For Readers
- For Authors
- For Librarians
Developed By
Submissions.
JSBS is now accepting submissions through our new site. Please click the following button to be directed to the new submission site.

Digital Scholarship Initaitives , Walker Library , Middle Tennessee State University

Table of Contents
What is a business plan, the advantages of having a business plan, the types of business plans, the key elements of a business plan, best business plan software, common challenges of writing a business plan, become an expert business planner, business planning: it’s importance, types and key elements.

Every year, thousands of new businesses see the light of the day. One look at the World Bank's Entrepreneurship Survey and database shows the mind-boggling rate of new business registrations. However, sadly, only a tiny percentage of them have a chance of survival.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, about 20% of small businesses fail in their first year, about 50% in their fifth year.
Research from the University of Tennessee found that 44% of businesses fail within the first three years. Among those that operate within specific sectors, like information (which includes most tech firms), 63% shut shop within three years.
Several other statistics expose the abysmal rates of business failure. But why are so many businesses bound to fail? Most studies mention "lack of business planning" as one of the reasons.
This isn’t surprising at all.
Running a business without a plan is like riding a motorcycle up a craggy cliff blindfolded. Yet, way too many firms ( a whopping 67%) don't have a formal business plan in place.
It doesn't matter if you're a startup with a great idea or a business with an excellent product. You can only go so far without a roadmap — a business plan. Only, a business plan is so much more than just a roadmap. A solid plan allows a business to weather market challenges and pivot quickly in the face of crisis, like the one global businesses are struggling with right now, in the post-pandemic world.
But before you can go ahead and develop a great business plan, you need to know the basics. In this article, we'll discuss the fundamentals of business planning to help you plan effectively for 2021.
Now before we begin with the details of business planning, let us understand what it is.
No two businesses have an identical business plan, even if they operate within the same industry. So one business plan can look entirely different from another one. Still, for the sake of simplicity, a business plan can be defined as a guide for a company to operate and achieve its goals.
More specifically, it's a document in writing that outlines the goals, objectives, and purpose of a business while laying out the blueprint for its day-to-day operations and key functions such as marketing, finance, and expansion.
A good business plan can be a game-changer for startups that are looking to raise funds to grow and scale. It convinces prospective investors that the venture will be profitable and provides a realistic outlook on how much profit is on the cards and by when it will be attained.
However, it's not only new businesses that greatly benefit from a business plan. Well-established companies and large conglomerates also need to tweak their business plans to adapt to new business environments and unpredictable market changes.
Before getting into learning more about business planning, let us learn the advantages of having one.
Since a detailed business plan offers a birds-eye view of the entire framework of an establishment, it has several benefits that make it an important part of any organization. Here are few ways a business plan can offer significant competitive edge.
- Sets objectives and benchmarks: Proper planning helps a business set realistic objectives and assign stipulated time for those goals to be met. This results in long-term profitability. It also lets a company set benchmarks and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) necessary to reach its goals.
- Maximizes resource allocation: A good business plan helps to effectively organize and allocate the company’s resources. It provides an understanding of the result of actions, such as, opening new offices, recruiting fresh staff, change in production, and so on. It also helps the business estimate the financial impact of such actions.
- Enhances viability: A plan greatly contributes towards turning concepts into reality. Though business plans vary from company to company, the blueprints of successful companies often serve as an excellent guide for nascent-stage start-ups and new entrepreneurs. It also helps existing firms to market, advertise, and promote new products and services into the market.
- Aids in decision making: Running a business involves a lot of decision making: where to pitch, where to locate, what to sell, what to charge — the list goes on. A well thought-out business plan provides an organization the ability to anticipate the curveballs that the future could throw at them. It allows them to come up with answers and solutions to these issues well in advance.
- Fix past mistakes: When businesses create plans keeping in mind the flaws and failures of the past and what worked for them and what didn’t, it can help them save time, money, and resources. Such plans that reflects the lessons learnt from the past offers businesses an opportunity to avoid future pitfalls.
- Attracts investors: A business plan gives investors an in-depth idea about the objectives, structure, and validity of a firm. It helps to secure their confidence and encourages them to invest.
Now let's look at the various types involved in business planning.
Become a Business and Leadership Professional
- Top 10 skills in demand Business Analysis As A Skill In 2020
- 14% Growth in Jobs Of Business Analysis Profile By 2028
Business Analyst
- Industry-recognized certifications from IBM and Simplilearn
- Masterclasses from IBM experts
Post Graduate Program in Business Analysis
- Certificate from Simplilearn in collaboration with Purdue University
- Become eligible to be part of the Purdue University Alumni Association
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Assistant Consultant at Tata Consultancy Services , Tata Consultancy Services
My experience with Simplilearn has been great till now. They have good materials to start with, and a wide range of courses. I have signed up for two courses with Simplilearn over the past 6 months, Data Scientist and Agile and Scrum. My experience with both is good. One unique feature I liked about Simplilearn is that they give pre-requisites that you should complete, before a live class, so that you go there fully prepared. Secondly, there support staff is superb. I believe there are two teams, to cater to the Indian and US time zones. Simplilearn gives you the most methodical and easy way to up-skill yourself. Also, when you compare the data analytics courses across the market that offer web-based tutorials, Simplilearn, scores over the rest in my opinion. Great job, Simplilearn!
I was keenly looking for a change in my domain from business consultancy to IT(Business Analytics). This Post Graduate Program in Business Analysis course helped me achieve the same. I am proficient in business analysis now and am looking for job profiles that suit my skill set.
Business plans are formulated according to the needs of a business. It can be a simple one-page document or an elaborate 40-page affair, or anything in between. While there’s no rule set in stone as to what exactly a business plan can or can’t contain, there are a few common types of business plan that nearly all businesses in existence use.
Here’s an overview of a few fundamental types of business plans.
- Start-up plan: As the name suggests, this is a documentation of the plans, structure, and objections of a new business establishments. It describes the products and services that are to be produced by the firm, the staff management, and market analysis of their production. Often, a detailed finance spreadsheet is also attached to this document for investors to determine the viability of the new business set-up.
- Feasibility plan: A feasibility plan evaluates the prospective customers of the products or services that are to be produced by a company. It also estimates the possibility of a profit or a loss of a venture. It helps to forecast how well a product will sell at the market, the duration it will require to yield results, and the profit margin that it will secure on investments.
- Expansion Plan: This kind of plan is primarily framed when a company decided to expand in terms of production or structure. It lays down the fundamental steps and guidelines with regards to internal or external growth. It helps the firm to analyze the activities like resource allocation for increased production, financial investments, employment of extra staff, and much more.
- Operations Plan: An operational plan is also called an annual plan. This details the day-to-day activities and strategies that a business needs to follow in order to materialize its targets. It outlines the roles and responsibilities of the managing body, the various departments, and the company’s employees for the holistic success of the firm.
- Strategic Plan: This document caters to the internal strategies of the company and is a part of the foundational grounds of the establishments. It can be accurately drafted with the help of a SWOT analysis through which the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats can be categorized and evaluated so that to develop means for optimizing profits.
There is some preliminary work that’s required before you actually sit down to write a plan for your business. Knowing what goes into a business plan is one of them.
Here are the key elements of a good business plan:
- Executive Summary: An executive summary gives a clear picture of the strategies and goals of your business right at the outset. Though its value is often understated, it can be extremely helpful in creating the readers’ first impression of your business. As such, it could define the opinions of customers and investors from the get-go.
- Business Description: A thorough business description removes room for any ambiguity from your processes. An excellent business description will explain the size and structure of the firm as well as its position in the market. It also describes the kind of products and services that the company offers. It even states as to whether the company is old and established or new and aspiring. Most importantly, it highlights the USP of the products or services as compared to your competitors in the market.
- Market Analysis: A systematic market analysis helps to determine the current position of a business and analyzes its scope for future expansions. This can help in evaluating investments, promotions, marketing, and distribution of products. In-depth market understanding also helps a business combat competition and make plans for long-term success.
- Operations and Management: Much like a statement of purpose, this allows an enterprise to explain its uniqueness to its readers and customers. It showcases the ways in which the firm can deliver greater and superior products at cheaper rates and in relatively less time.
- Financial Plan: This is the most important element of a business plan and is primarily addressed to investors and sponsors. It requires a firm to reveal its financial policies and market analysis. At times, a 5-year financial report is also required to be included to show past performances and profits. The financial plan draws out the current business strategies, future projections, and the total estimated worth of the firm.
The importance of business planning is it simplifies the planning of your company's finances to present this information to a bank or investors. Here are the best business plan software providers available right now:
- Business Sorter
The importance of business planning cannot be emphasized enough, but it can be challenging to write a business plan. Here are a few issues to consider before you start your business planning:
- Create a business plan to determine your company's direction, obtain financing, and attract investors.
- Identifying financial, demographic, and achievable goals is a common challenge when writing a business plan.
- Some entrepreneurs struggle to write a business plan that is concise, interesting, and informative enough to demonstrate the viability of their business idea.
- You can streamline your business planning process by conducting research, speaking with experts and peers, and working with a business consultant.
Whether you’re running your own business or in-charge of ensuring strategic performance and growth for your employer or clients, knowing the ins and outs of business planning can set you up for success.
Be it the launch of a new and exciting product or an expansion of operations, business planning is the necessity of all large and small companies. Which is why the need for professionals with superior business planning skills will never die out. In fact, their demand is on the rise with global firms putting emphasis on business analysis and planning to cope with cut-throat competition and market uncertainties.
While some are natural-born planners, most people have to work to develop this important skill. Plus, business planning requires you to understand the fundamentals of business management and be familiar with business analysis techniques . It also requires you to have a working knowledge of data visualization, project management, and monitoring tools commonly used by businesses today.
Simpliearn’s Executive Certificate Program in General Management will help you develop and hone the required skills to become an extraordinary business planner. This comprehensive general management program by IIM Indore can serve as a career catalyst, equipping professionals with a competitive edge in the ever-evolving business environment.
What Is Meant by Business Planning?
Business planning is developing a company's mission or goals and defining the strategies you will use to achieve those goals or tasks. The process can be extensive, encompassing all aspects of the operation, or it can be concrete, focusing on specific functions within the overall corporate structure.
What Are the 4 Types of Business Plans?
The following are the four types of business plans:
Operational Planning
This type of planning typically describes the company's day-to-day operations. Single-use plans are developed for events and activities that occur only once (such as a single marketing campaign). Ongoing plans include problem-solving policies, rules for specific regulations, and procedures for a step-by-step process for achieving particular goals.
Strategic Planning
Strategic plans are all about why things must occur. A high-level overview of the entire business is included in strategic planning. It is the organization's foundation and will dictate long-term decisions.
Tactical Planning
Tactical plans are about what will happen. Strategic planning is aided by tactical planning. It outlines the tactics the organization intends to employ to achieve the goals outlined in the strategic plan.
Contingency Planning
When something unexpected occurs or something needs to be changed, contingency plans are created. In situations where a change is required, contingency planning can be beneficial.
What Are the 7 Steps of a Business Plan?
The following are the seven steps required for a business plan:
Conduct Research
If your company is to run a viable business plan and attract investors, your information must be of the highest quality.
Have a Goal
The goal must be unambiguous. You will waste your time if you don't know why you're writing a business plan. Knowing also implies having a target audience for when the plan is expected to get completed.
Create a Company Profile
Some refer to it as a company profile, while others refer to it as a snapshot. It's designed to be mentally quick and digestible because it needs to stick in the reader's mind quickly since more information is provided later in the plan.
Describe the Company in Detail
Explain the company's current situation, both good and bad. Details should also include patents, licenses, copyrights, and unique strengths that no one else has.
Create a marketing plan ahead of time.
A strategic marketing plan is required because it outlines how your product or service will be communicated, delivered, and sold to customers.
Be Willing to Change Your Plan for the Sake of Your Audience
Another standard error is that people only write one business plan. Startups have several versions, just as candidates have numerous resumes for various potential employers.
Incorporate Your Motivation
Your motivation must be a compelling reason for people to believe your company will succeed in all circumstances. A mission should drive a business, not just selling, to make money. That mission is defined by your motivation as specified in your business plan.
What Are the Basic Steps in Business Planning?
These are the basic steps in business planning:
Summary and Objectives
Briefly describe your company, its objectives, and your plan to keep it running.
Services and Products
Add specifics to your detailed description of the product or service you intend to offer. Where, why, and how much you plan to sell your product or service and any special offers.
Conduct research on your industry and the ideal customers to whom you want to sell. Identify the issues you want to solve for your customers.
Operations are the process of running your business, including the people, skills, and experience required to make it successful.
How are you going to reach your target audience? How you intend to sell to them may include positioning, pricing, promotion, and distribution.
Consider funding costs, operating expenses, and projected income. Include your financial objectives and a breakdown of what it takes to make your company profitable. With proper business planning through the help of support, system, and mentorship, it is easy to start a business.
Our Business And Leadership Courses Duration And Fees
Business And Leadership Courses typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
Get Free Certifications with free video courses
Business and Leadership
Business Analysis Basics
Data Science & Business Analytics
Business Intelligence Fundamentals
Learn from Industry Experts with free Masterclasses
Product Manager Role Breakdown: Skills, Career Paths, and Salaries
How to Build Your UI/UX Portfolio with the Caltech UI/UX Bootcamp
Career Information Session: Find Out How to Become a Business Analyst with IIT Roorkee
Recommended Reads
Business Intelligence Career Guide: Your Complete Guide to Becoming a Business Analyst
Corporate Succession Planning: How to Create Leaders According to the Business Need
Top Business Analyst Skills
Business Analytics Basics: A Beginner’s Guide
Financial Planning for Businesses Across the Globe
How to Become a Business Analyst
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Reimagining marketing strategy: driving the debate on grand challenges
Ko de ruyter.
1 King’s College, London, London, UK
Debbie Isobel Keeling
2 University of Sussex, Brighton, UK
Kirk Plangger
Matteo montecchi, maura l. scott.
3 Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL USA
Darren W. Dahl
4 University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada
Associated Data
A little less conversation….
A little more action, please. There is no record of Elvis Presley's views on responsible marketing, but his 1968 song, “A Little Less Conversation,” could have been written as a reflection on the global marketing community’s current progress in transforming our field. At the United Nations (UN) General Assembly in 2015, the leaders of 193 nations adopted an ambitious set of 17 global Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) combatting poverty, inequality, and discrimination. Since then, it has been an imperative for organizations to reimagine their marketing strategy with an eye towards global impact. This is not only a matter of international policy; important shifts in stakeholder views on responsible marketing are also starting to emerge. For example, supply chain partners and end-customers across many industries are increasingly interested in end-of-life cycle initiatives, product-emission rates, product provenance, and transparency of production. These stakeholders are steadily demanding more environmentally-friendly packaging and lower carbon footprints. Further, stakeholders expect human dignity to be respected along this process. Consequently, long-term supply chain strategies are being redefined to acknowledge climate change and human rights issues in strategy formulation and execution.
In turn, marketing scholars have increasingly become concerned with responsible marketing, and although these issues have not always been the focus of our scholarship, it is evident from current work that they are now. There is a growing, rich conversation involving notions of responsibility within marketing in the current scholarship base. The past decade has witnessed an expansion of concepts and empirical evidence regarding the challenges of environmental sustainability, social responsibility, (mental) health and social care, wealth disparities and poverty, nationalism and its impact on global trade, identity loss, and a wide array of unintended consequences of digitization (Hensen et al., 2016 ). As an academic marketing community we are well-placed to lead on relevant change across the social, economic, environmental, and political landscapes; doing so will provide further opportunities for novel contributions to marketing strategy knowledge. Moreover, there is a wider call for societal and political action through purposeful engagement with the world’s grand challenges, thereby inspiring scholars and industry to work together as partners to reimagine the very definition of effective marketing strategy.
Key to successfully transforming marketing strategy is the creation of forward-looking intellectual frameworks, which can serve as springboards for future research that can inform creative and critical scholarship and practice. At this point, marketing scholars are primed to develop sustainable solutions by aligning the interests of principal stakeholders, not just shareholders, and by balancing longer-term and shorter-term benefits. The conversation about reimagining marketing strategy started with a fundamental and paradigmatic shift away from the discipline’s earlier focus on agency and transaction costs. A fruitful lens through which to continue this conversation is the emerging theorizing on stewardship (c.f., Mick et al., 2012 ), which can simultaneously be aligned with sustaining contributions to (or even reimagining) the bottom-line. Furthermore, and in the spirit of stewardship thinking, we recognize that the strength of extant marketing scholarship lies in its knowledge exchange and co-creation with stakeholders. This collaborative approach during the various stages of research design and execution can, and does, bring about meaningful change. It also involves consideration of the interplay between customers/consumers, firms, governmental policies, and society.
We begin by introducing the notion of stewardship as a basis for identifying three complementary principles to guide the continued transformation of marketing strategy (i.e., becoming responsible, respectful, and resilient), which we discuss and integrate with the 17 UN SDGs ( https://sdgs.un.org/goals ). Importantly, we argue that the application of these principles to the grand challenges faced by society today will be an effective way to frame marketing investigations and achieve substantive contributions that meet these challenges. Subsequently, we take stock of the current marketing scholarship through the lens of these three principles by applying them directly to the results of a bibliometric analysis of the marketing literature. We conclude by reflecting on the opportunities for academic practice in marketing with respect to meeting the grand challenges that the world faces.
Responsible, resilient, and respectful principles
Central to stewardship theory is recognizing the importance of balancing personal goals with goals of a larger entity (Hernandez, 2008 ). We feel that stewardship provides a robust basis for reimagining marketing strategy for three reasons. First, if individuals are to assume responsibility to support the greater good, they do so based on the development of an ideological and relational commitment. There is an opportunity for marketing scholars to both identify business practices that can promote collective solutions that benefit both society and the firm, and also quantify benefits to firms and customers of taking a broader collective focus in business practices. This may encourage managers and decision-makers to strive for equilibrium between personal and collective interests. For example, how a store manager values collective welfare (e.g., environmental responsibility) can inspire sales associates to engage in selling green products while managing their sales targets, or can shape how novel product attributes, such as recyclability, biodegradability, and ethical sourcing, can best be promoted. Second, the notion of stewardship implies that people may not fully realize the longer-term consequences of near-term actions. Marketing research on self-control and self-regulation can offer insights into the trade-offs between near-term actions and longer-term consequences of such decisions. This underlines marketing’s unique capacity to conceive solutions that are both resilient and sustainable to collective interests across time; this could involve intergenerational product positioning, and potentially influence environmentally-friendly behaviors across different stakeholders. Third, stewardship affords an equitable distribution of rewards, which indicates the integrity and respect of a shared value approach to contributors to economic and social activity. Marketing’s deep understanding of value can inform facilitation of shared value(s) between stakeholders in multiple domains. This is, perhaps, particularly the case in complex services, which are often characterized by complex power, knowledge, and experiential asymmetries (Keeling et al., 2021 ). Based on this foundation from the stewardship literature, we identify three principles to guide the transformation of marketing strategy in becoming increasingly responsible , resilient, and respectful .
The Responsible principle requires giving voice to all marketing stakeholders for a shared vision of what constitutes a well-balanced and sustainable offering. This principle can be advanced by being approached in a manner that is mutually beneficial to other long-term organizational goals, especially when these offerings challenge conventional thinking or center on short-term benefits. For example, marketing scholars can collaborate with organizations to understand how service firms can adapt to support refugees, and how novel approaches can also strengthen relationships with existing customers. This approach requires extending the focus of scholarly marketing research to include themes that are traditionally not considered to be ‘marketing’, as well as articulating social benefits alongside economic ones. For example, marketing scholarship can make a substantive contribution to public health policy by addressing such issues as how to combat stigmatization in mental health campaigns and how to heighten engagement in health communities among stigmatized patients. Conversely, it also involves taking a fresh look at traditional topics of academic inquiry and revisiting them with a responsibility perspective, in which balancing the needs of individuals and societal concerns are in fact key priorities of the organization. For example, the Responsible Research in Business and Management network encourages research that aligns with this principle ( www.rrbm.network ). Thus, marketing scholarship can help to advance UN SDGs, such as promoting good health and wellbeing (SDG 3), and responsible consumption and production (SDG 12).
The Resilient principle is based on continuous improvement through self and group reflections. Here, the focus is on ensuring and enculturating operational effectiveness and sustainability. This is achieved through establishing world class infrastructure and supply chains, and appropriately harnessing innovation and entrepreneurship. The Covid-19 crisis has exposed the vulnerability of international supply chains, as well as cash and information flows; firms need to develop resilience strategies to deal with this moving forward. Firms are currently revisiting their (ethical) sourcing and procuring (e.g., support of local suppliers), and manufacturing and contactless delivering systems (e.g., Amazon’s last mile concept) to fulfil the changing needs of channel partners and end-consumers. Furthermore, the pandemic-driven surge in peer-to-peer home delivery services (e.g., Instacart, UberEats) has introduced novel dilemmas for firms in terms of product safety, brand management and uniformity, and developing a sustainable workforce. Resilience could also be viewed in terms of marketing’s contribution to alleviating poverty and addressing potential issues associated with climate change, natural resource sustainability, and social instability.
The Respectful principle focuses on enabling different levels of aspiration within a fair society. Equality, diversity, and social inclusion underpin this principle to ensure that vulnerable, disadvantaged, and previously marginalized communities are empowered to make their own meaningful contributions in marketplaces. Mars (a manufacturer of confectionery, pet food, and other food products) revised its advertising code based on the principle of respect, pledging to facilitate casting that ‘ reflects the true diversity of the consumer base that we sell to, as determined by gender, race, sexuality, age, ability, class’ and to portray people as ‘empowered actors and full personalities, rather than using stereotypes ’ (Whiteside, 2021 ). There is a plethora of research themes stemming from the respectful principle, such as implicit gender bias in conversational AI-agents, and rebranding and advertising in times of increased social-political movements (e.g., MeToo, Black Lives Matter). Conversely, uncovering research themes from cases like The Wine Noire, an African American women-owned wine collective organized around an equitable and sustainable supply chain and logistic services for female winemakers and winemakers of color, might inform an agenda of research action.
Mapping the conversation
To further the discussion of the Responsible, Resilient, and Respectful principles, we illustrate current scholarly conversations using a bibliometric approach. This approach organizes the literature by identifying important contributors, contributions, and knowledge structures (Zupic & Čater, 2015 ). Informed by past JAMS editorials, four authors debated and selected keywords relevant to the three principles. 1 We used this curated set of keywords to identify and select articles published in the six leading marketing journals listed in the FT 50 journal ranking. 2 An initial search and article extraction performed on Scopus ( www.scopus.com ) resulted in a sample of 536 articles. We examined each article’s title, keywords, and abstract to determine its relevance to the three principles and retained a final sample of 254 articles.
Annual scientific production (in terms of publications) in our sample has increased substantially over the period considered (1973 to May 2021), exhibiting a compound annual growth of 6.12%. The first production peak is in 1997 with nine articles that broadly examine pro-environmental and pro-social marketing strategies, as well as the impact of these strategies on consumers’ perceptions of firms. The annual scholarly outputs have grown steadily every year since 2011, as evidenced by the 18 articles already published by May 2021. Among the six leading marketing journals we selected, the Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science dominates this literature domain (86 articles), followed by the Journal of Marketing (57 articles) and the Journal of Consumer Psychology (51 articles). We assessed authors’ influence by examining the total number of articles published and citations accumulated by each author. Julie Irwin (McCombs School, University of Texas) is the most prolific author in our sample with a total of seven articles, whereas CB Bhattacharya (Katz Graduate School of Business, University of Pittsburg) leads the citations ranking with 5012 total citations across five publications.
To identify the intellectual structure of this literature domain, we constructed a bibliometric network with VOS Viewer using bibliographic coupling (Fig. 1 3 ). Bibliographic coupling examines similarities between articles in a collection by considering the number of cited references that the articles share (Zupic & Čater, 2015 ). This analysis revealed seven clusters of articles representing distinctive lines of inquiry. We named these clusters to reflect the substantive focus of the scholarly contributions included therein, and then grouped them according to the principles (Table (Table1 1 ).

Bibliometric visualization of the literature according to the Responsible, Resilient, and Respectful principles
Responsible, Respectful, and Resilient principles literature clusters
Notes: a The table includes the top three articles in each cluster by normalized number of citations. The normalization takes into consideration that more recent articles had less time to accumulate citations. The formula is as follows: N o r m a l i z e d - c i t a t i o n s - f o r - a n - a r t i c l e = T o t a l - c i t a t i o n s - o f - a n - a r t i c l e A v e . - c i t a t i o n s - f o r - a l l - a r t i c l e s - p u b l i s h e d - i n - t h e - s a m e - y e a r - i n c l . - i n - s a m p l e
b Key: JM = Journal of Marketing; JCP = Journal of Consumer Psychology; JCR = Journal of Consumer Research; JMR = Journal of Marketing Research; JAMS = Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science
The conceptual building blocks of the Responsible principle are reflected in Clusters A, B, and C. Articles in the largest cluster (A – Green consumption) examine factors leading to consumer preferences for environmentally-friendly and ethically sourced products, as well as associated persuasion strategies. Taking a broader perspective, contributions in the second largest cluster (B – Responses to Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) strategies) examine how consumers’ react to firms’ CSR associations. The articles within these clusters are closely connected with the research in Cluster C (Stakeholder relationships) that explores how CSR contributes to corporate reputation among external firm’s stakeholders. In short, despite the extensive conversations regarding corporate responsibility issues, further research needs to focus on how marketing approaches the CSR agenda to encourage even more sustainable behaviors that appeal to a wider range of stakeholders.
The Resilience principle is well represented by Clusters D and E. Cluster D’s (Sustainable marketing strategies) research revolves around green approaches that inoculate marketing from environmental challenges, including enviropreneurialism, corporate environmentalism, and organizational capabilities for resilience. Articles in Cluster E (CSR strategies and firm performance) examine strategic outcomes of CSR investments, including firm market value, firm idiosyncratic risk, and customers’ product and brand evaluations. In sum, the Resilience principle incorporates seminal conceptualizations of sustainability and CSR marketing strategies as drivers of firms’ competitive advantage. However, recent external challenges (e.g., the COVID pandemic) call for a re-examination of these ideas to re-imagine marketing capabilities that will increase the resilience of firms.
The Respectful principle is represented by Clusters F and G. Cluster F’s (Ethical consumption) research concentrates on ethical consumer choices in the context of environmental sustainability, cause-related initiatives, stakeholder collaborations, and other ethical initiatives. Articles in Cluster G (Ethical marketing strategies) includes contributions elucidating the relationship between marketing strategy and CSR initiatives to achieve organizational effectiveness and ethical managerial decision making. As depicted in Fig. 1 , research on the Respectful principle is somewhat more dispersed and often disparate from other conversations. However, research inspired by the Respectful principle has the potential for many substantive future contributions that will shape how organizations interact with diverse, vulnerable, and underrepresented stakeholder groups.
A little more impact please …
Current societal expectations set within the broader context of the UN SDGs, recognition of the individual value of research endeavors (San Francisco Declaration on Research Assessment, DORA, https://sfdora.org/ ), and the move towards wide-scale Open Access of research, mean that the position, nature, and value of academic research in society is being reexamined. This is also the case for business research. For instance, the Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business (AACSB, www.aacsb.edu/ ) has expanded its accreditation standards to include ‘engagement and social impact’, a change which is directly tied to the UN SDGs. In parallel, the traditional academic role is changing within Higher Education, as distinct career pathways develop that recognize differing, yet complementary, expertise in research, education, and enterprise. Together, these drivers offer opportunities for further innovation in the field of marketing, integral to which is a change in how marketing scholars and practitioners understand, discuss, and measure research ‘impact’ and how changes in our academic environment offer further channels for development.
With respect to research impact, marketing, as an applied discipline, has consistently examined the ‘fitness’ of research as defined by its relevance and robustness in today’s dynamic environment. The Responsible, Resilient, and Respectful principles that we outline can provide a guide toward articulating impactful contributions to knowledge and practice. As a discipline, marketing is well-placed to develop the opportunities within each of these principles with respect to marketing strategy. We offer Table Table2, 2 , which identifies example research questions that connect each of the stewardship principles to the UN SDGs, as an initial template in framing research impact for marketing strategy moving forward.
Examples of future marketing research questions at the intersection of stewardship principles and United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs)
With respect to the changing academic environment, like many other disciplines, the marketing discipline’s application of impact metrics is in flux and will continue to change in the coming years. The current assessment of output impact based on output levels (typically published journal articles) and using mainly numerical indicators is being challenged (e.g., through institutions committing to the San Francisco Declaration on Research Assessment). Instead, applying the Responsible principle, there is now a demand for broader (e.g., AltMetrics) and more qualitative evaluations of research impact. This demand will drive change in the types of output that articulate how marketing scholars undertake research that generates value for multiple stakeholders. In developing a cohesive narrative of the impact value of scholarly marketing research, there is an opportunity to broaden the definition of impact to include impactful outcomes , in addition to impactful outputs . For example, impactful outcomes due to changes in the marketing strategies that promote electric vehicle adoption will bring a corresponding positive change in the quality of life of consumers by improving air quality. Or consider the example of altering marketing strategies to combat youth obesity by restricting when and where sugary drinks and other junk food can be advertised. At the same time, marketing scholars can also examine the thresholds and timeframes for reasonable expectations about the impact that marketing strategy can achieve.
Furthermore, researchers often navigate the tension between generating research that addresses the need for academic relevance and robustness alongside the need for societal relevance and robustness. Academic relevance (in how contributions and implications are framed) and robustness (in how methodological approaches are framed) are familiar building blocks in the literature. However, due to a broad scope, the marketing discipline has less clarity and consensus on societal relevance and societal robustness . Societal relevance directly asks: ‘What societal challenge does this research contribute to?’ Societal robustness demands not only value for money, but also, more fundamentally, research accessibility and usefulness. An impact framework that integrates outcomes valued by multiple stakeholders can help guide the marketing discipline’s pursuit of high impact research with a societal focus. Such a framework can readily be devised in directly linking the reimagining of marketing strategy to the UN SDGs (such as in Table Table2) 2 ) to enable researchers to articulate the value of their research in terms of mutual relevance, robustness and value.
The Resilient principle calls into question the longevity of what marketing research and practice offers, and how this contributes to sustainable solutions for society. The nature of published content undoubtedly needs to be more diversified to effectively meet the demands of differing audiences. Journal articles are an important means of mobilizing knowledge in academia and for other ‘users’ of research who are able to access such sources. However, journal articles are one part of a wider portfolio of content and services that could fulfil the different needs and purposes of society. Many universities and academics are already diversifying their research portfolios, both in terms of the content produced and services offered (e.g., professional development opportunities directly extending from research), alongside the approaches to communication of outcomes (e.g., podcasts, open access toolkits). This trend will help develop sustainable solutions, especially with respect to the UN SDGs. For example, creating health communications in collaboration with the intended audiences can result in tools that are readily accepted by those audiences, in terms of language, format and content, to bring about the intended impact.
The existing tension is often a simple one: How might we best develop and share proven methods or tools to embed them in practice, and in such a way that this effort is also recognized as a valuable scholarly activity? Companies and communities want to work with academics, but the outcomes they value are not always easily aligned with the outputs valued by academia. This is by no means a new challenge, but the conversation about impact potentially changes the perspective of said challenge. One promising development, in our view, to meet this challenge is the current change in emergent specialist career pathways. These pathways will broaden the way in which academic work is conducted and delivered, thus, impacting traditional research portfolios (i.e., in terms of outputs and outcomes). That is, marketing academics specializing in education are updating pedagogical approaches for future academics and practitioners to aid marketing strategy in coping with global challenges. Those specializing in knowledge exchange are innovating how knowledge about developing marketing strategy is mobilized in multiple formats to reach wider and more diverse user groups. Finally, those specializing in relevant enterprise are driving practical changes in marketing strategy through the commercialization of academic research into valuable products to society. The emergence of these new pathways provides opportunities to not only better address the questions laid out in Table Table2, 2 , but also presents exciting opportunities for academics to further develop new capabilities, for example, their entrepreneurial skills, that complement existing academic skillsets.
More fundamentally, the move towards embracing representatives of a broader society as both co-creators and drivers of the research process is completely changing the conversation between marketing and society. The Respectful principle assumes co-creation. A distinctive strength that marketing strategy scholars bring to the literature is their experience and expertise in working with stakeholders in the field (e.g., consumer groups, nonprofits, companies, governmental agencies). Thus, marketing strategy can leverage these insights to support the development of rigorous research focused on pursuing the grand challenges that are more directly linked to those who are most impacted. The concept here is that outputs and outcomes are not delivered to ‘users’, but rather co-created with stakeholders in society. There are multiple emerging co-creation processes across disciplines and sectors. In healthcare, for example, the principle of respect is embedded within the process of co-production (e.g., https://www.nihr.ac.uk/documents/co-production-in-action-number-three/26382 ). Engaging non-academic partners as co-creators means being respectful of their lived experiences and how it shapes their active creator roles, as well as rebalancing power structures to allow multiple voices to be heard.
At the same time, it is important to respectfully acknowledge and accommodate individual or group heterogeneity in terms of motivation, knowledge and ability to co-create. New approaches (that are to be celebrated in our estimation) involve training non-academic co-creators in research methods. Conversely, in the future, non-academic co-creators can also train academics in this manner. As marketing scholars are aware, the integration of resources in the form of knowledge, skills, experience, enterprise, and networks creates connections and builds awareness between stakeholders to heighten impact. This connectivity is especially valuable where stakeholders have not had an opportunity to meet, discuss, and share ideas previously. Using the UN SDGs, it is possible to identify situations in which stakeholder groups have not had this opportunity, especially groups who are perceived as more vulnerable. An additional benefit of building co-creation opportunities with vulnerable groups is increased transparency and trust between the academic and wider communities. Conflicts can emerge during such collaboration, especially where there has been little previous interaction, but facilitating resolution of this conflict is impactful in its own right. Marketing, with its keen understanding of stakeholder perspectives, can empower groups of stakeholders to move away from normalized or entrenched expert knowledge and solutions. In doing so, groups of co-creation partners can truly deliver outcomes that are very much ‘fit for purpose’ (e.g., in relation to innovative solutions to address aspects of the UN SDGs). We see marketing as a discipline that is well-positioned to take the lead in developing and fostering diverse multi-disciplinary groups to bring about this shift.
Embracing the broader changes in academia, the outcome we seek here is a renewed call for the facilitation of better marketing strategy that will boldly address society’s grand challenges, and contribute to tackling the UN SDGs through responsible, resilient, and respectful research collaborations with stakeholders.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
1 Our selection of keywords included: societal, corporate social responsibility, social responsibility, CSR, sustainability, sustainable, ethics, ethical, cause-related, environmental, stewardship, vulnerable, disenfranchise, equality, diversity, inclusivity, morality, empowerment . This set of keywords allowed us to extract a comprehensive literature sample that delineates the core themes in marketing strategy relevant to the three principles. We acknowledge that this set of keywords is not comprehensively conclusive. Within the context of this editorial, our analysis is intended as a conversation and action starter.
2 Journals included: Journal of Consumer Psychology, Journal of Consumer Research, Journal of Marketing, Journal of Marketing Research, Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, Marketing Science .
3 To reduce visual complexity and aid interpretation, we set the minimum number of article citations to five and excluded articles without links in the collection. This resulted in a total of 196 articles that were visualized in the figure by normalized number of citations.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- Hensen N, Keeling DI, de Ruyter K, Wetzels M, de Jong A. Making SENS: Exploring the antecedents and impact of store environmental stewardship climate. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science. 2016; 44 (4):497–515. doi: 10.1007/s11747-015-0446-5. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hernandez M. Promoting stewardship behavior in organizations: A leadership model. Journal of Business Ethics. 2008; 80 :121–128. doi: 10.1007/s10551-007-9440-2. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Keeling DI, Keeling K, de Ruyter K, Laing A. How value co-creation and co-destruction unfolds: A longitudinal perspective on dialogic engagement in health services interactions. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science. 2021; 49 (2):236–257. doi: 10.1007/s11747-020-00737-z. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mick, D. G., Pettigrew, S., Pechmann, C. (Connie)., & Ozanne, J. L. (Eds.). (2012). Transformative consumer research for personal and collective well-being . Routledge.
- Whiteside, S. (2021), Mars makes the case of more responsible marketing, WARC paper accessed on June 7 th , 2021, https://www.warc.com/content/paywall/article/event-reports/mars-makes-the-case-for-responsible-marketing/127027
- Zupic I, Čater T. Bibliometric Methods in Management and Organization. Organizational Research Methods. 2015; 18 (3):429–472. doi: 10.1177/1094428114562629. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Advertisement

Business plan competitions and nascent entrepreneurs: a systematic literature review and research agenda
- Open access
- Published: 28 February 2023
- Volume 19 , pages 863–895, ( 2023 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Léo-Paul Dana ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0806-1911 1 , 2 ,
- Edoardo Crocco ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9797-3962 3 ,
- Francesca Culasso ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8357-1914 3 &
- Elisa Giacosa ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0445-3176 3
3684 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Business plan competitions (BPCs) are opportunities for nascent entrepreneurs to showcase their business ideas and obtain resources to fund their entrepreneurial future. They are also an important tool for policymakers and higher education institutions to stimulate entrepreneurial activity and support new entrepreneurial ventures from conceptual and financial standpoints. Academic research has kept pace with the rising interest in BPCs over the past decades, especially regarding their implications for entrepreneurial education. Literature on BPCs has grown slowly but steadily over the years, offering important insights that entrepreneurship scholars must collectively evaluate to inform theory and practice. Yet, no attempt has been made to perform a systematic review and synthesis of BPC literature. Therefore, to highlight emerging trends and draw pathways to future research, the authors adopted a systematic approach to synthesize the literature on BPCs. The authors performed a systematic literature review on 58 articles on BPCs. Several themes emerge from the BPC literature, including BPCs investigated as prime opportunities to develop entrepreneurial education, the effects of BPC participation on future entrepreneurial activity, and several attempts to frame an ideal BPC blueprint for future contests. However, several research gaps emerge, especially regarding the lack of theoretical underpinnings in the literature stream and the predominance of exploratory research. This paper provides guidance for practice by presenting a roadmap for future research on BPCs drawing from the sample reviewed. From a theoretical perspective, the study offers several prompts for further research on the topic through a concept map and a structured research agenda.
Similar content being viewed by others

Trends and patterns in entrepreneurial action research: a bibliometric overview and research agenda

Lancaster University
Re-thinking university spin-off: a critical literature review and a research agenda.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Business plan competitions (BPCs) give nascent entrepreneurs the chance to present their business ideas to an industry and investment peer group tasked with judging each project and picking the most viable one (Overall et al., 2018 ). Winners are awarded various prizes (McGowan & Cooper, 2008 ). The purpose of BPCs is to stimulate new entrepreneurial activity and support novel entrepreneurial ideas (Kwong et al., 2012 ). In return, BPC organizers emphasize the benefits of participating, such as cash prizes and financing (McGowan & Cooper, 2008 ), visibility and reputational benefits (Parente et al., 2015 ), networking with other aspiring entrepreneurs (Thomas et al., 2014 ), and meeting potential stakeholders, including customers and investors (Passaro et al., 2020 ).
BPCs have been used by new entrepreneurs to kickstart their business ideas (Cant, 2018 ). They have been popular throughout the years, especially during the global recession in the first decade of the 2000s. BPCs have become widely popular across both developed (Licha & Brem, 2018 ) and developing countries (Efobi & Orkoh, 2018 ; McKenzie & Sansone, 2019 ), as poor economic conditions have driven young entrepreneurs toward any opportunity they can find (Cant, 2018 ). Since the origin of BPCs in the USA in the 1980s (Buono, 2000 ), several universities have implemented them in their educational ecosystem to foster practical learning. From there, BPCs have rapidly spread in Europe (Riviezzo et al., 2012 ) and within developing nations in Asia (Wong, 2011 ) and Africa (House-Soremenkun & Falola, 2011 ). Despite contextual peculiarities, the significance of BPCs is equally pertinent for developed and emerging economies (Tipu, 2018 ), as they contribute to shaping a lively local entrepreneurial fabric (Barbini et al., 2021 ).
Opportunities arising from BPC participation come in various forms, including knowledge (Barbini et al., 2021 ), networking, and promotion (Cant, 2016a ); however, finding economic resources to finance entrepreneurial ventures has proven to be the main concern (Kwong et al., 2012 ; McGowan & Cooper, 2008 ). BPCs are attractive to entrepreneurs, as they can be prime opportunities not only to receive feedback on their ideas, but also to get the monetary funds needed to realize them (Mosey et al., 2012 ). In addition, a successful BPC does not merely identify the most intriguing business idea but also supports entrepreneurs during the early stages of their new ventures, whether or not they win the competition (Watson et al., 2015 ).
Several research streams have emerged around the topic of BPCs (Cant, 2018 ). For example, entrepreneurial education has been investigated in several studies (Licha & Brem, 2018 ; Olokundun et al., 2017 ) as a way to effectively provide learning support to nascent entrepreneurs and boost their chances of success. Moreover, university-based BPCs are being explored in terms of their potential as learning experiences and how specific lessons learned during these competitions may affect future entrepreneurial orientations (Overall et al., 2018 ). For example, some argue that promoting sustainable production during BPCs has a tangible impact on the integration of sustainability practices into future business activities (Fichter & Tiemann, 2020 ).
Start-up competitions have gained global prominence since the 1980s (Kraus & Schwarz, 2007 ; Ross & Byrd, 2011 ). Today, they are a popular form of support for nascent entrepreneurs (Dee et al., 2015 ), featuring steady growth in numbers over recent years (Fichter & Tiemann, 2020 ). Consistent with BPCs’ importance, the literature examining them is growing, with an increasing number of empirical studies published each year. However, despite the attention from policymakers and academics, no attempts have been made thus far to review the literature on BPCs systematically. Additionally, there is a need for a structured research agenda that could shed light on currently unexplored topics in entrepreneurship research, such as the role of institutions in emergent entrepreneurial intentions (Audretsch et al., 2022 ; Barbini et al., 2021 ), contextual factors stimulating nascent entrepreneurial intentions (Zhu et al., 2022 ), and the development of richer theory about practical entrepreneurial training (Clingingsmith et al., 2022 ).
To the best of our knowledge, the only previous attempt at synthesizing BPC literature was performed by Tipu ( 2018 ). While their contribution is of absolute importance, its scope was limited to 22 papers published in the early 2000s and late 90 s, thus leaving a consistent portion of recent academic literature unexplored. Consequently, we believe that a systematic review of the BPC literature could be of interest to both practitioners and academics. Building on previous systematic literature reviews (SLRs) from the entrepreneurship field, we aim to provide a detailed analysis of the relevant literature on BPCs. We focus on several key aspects of BPCs that emerged from the analysis, starting with the ways in which they are currently implemented, the benefits they provide to new entrepreneurs, and the role played by BPC promotion in the early stages of the entrepreneurial life cycle (Cant, 2016a ). Our analysis reveals several factors that influence the successful implementation of BPCs as ways to boost the effectiveness of novel entrepreneurial ventures, including entrepreneurial education for individuals who take part in the program (McGowan & Cooper, 2008 ) and entrepreneurs’ personal traits and dispositions (Kwong et al., 2012 ). Therefore, our study is not limited to a synthesis of the existing literature on the topic; rather, it develops a comprehensive framework for both professionals and academic researchers to guide future projects on BPCs. This study is guided by four main research questions (RQs):
RQ1: What is the current research profile of BPC literature?
RQ2: What are the key emerging topics to be found in BPC literature?
RQ3: What research gaps are currently present in the BPC literature and what future research agenda can be set according to said gaps?
RQ4: Can a comprehensive conceptual framework be synthesized from the literature to help academics, practitioners, and other relevant stakeholders?
Drawing on previous SLR research on entrepreneurship (Kraus et al., 2020 ), we synthesized the literature to reach our research goal and answer the questions listed above. RQ1 was addressed by gathering all the available literature that satisfied the inclusion criteria in terms of research scope, relevance, and keywords. The research profile was then obtained by conducting several descriptive observations meant to understand the volume of annual scientific production, the most cited sources, the geographical focus, the theoretical frameworks used by the authors, and the emerging themes across the sample. RQ2 was addressed by reviewing the literature presented in the sample through in-depth content analysis techniques. From the analysis, the following themes emerged across the sample: (1) BPCs as opportunities for entrepreneurial education, (2) the role of BPCs in the promotion and visibility of nascent entrepreneurs, (3) the contexts surrounding BPCs, and (4) methodological choices and research design in BPC publications. Regarding RQ3, we manually reviewed each document to identify relevant research gaps in the BPC literature. This allowed us to suggest several research questions that could serve as a foundation for future studies. Finally, RQ4 was addressed by developing a framework that synthesized the thematic findings of our SLR.
The present SLR can contribute significantly to both theory and practice. Overall, SLRs critically assess and synthesize extant research, developing a comprehensive theoretical framework that can guide scholars and practitioners. In other words, a systematic review highlights the different thematic areas of prior research, delineates the research profile of the existing literature, identifies research gaps, projects possible avenues for future research, and develops a synthesized research framework on the topic (Dhir et al., 2020 ). Thus, from a theoretical perspective, our study should interest a broad range of researchers, as it links back to the ongoing global conversation regarding BPCs. It does so by synthesizing the knowledge on the topic and formulating a structured research agenda that could serve as a reference for researchers to conduct future studies and address issues of topical interest that have yet to receive sufficient attention from authors. The research agenda is built upon extant gaps found in our in-depth analysis of the sample. Similarly, practitioners can use the findings to recognize the drivers and outcomes of BPC programs and shed light on their core characteristics when designing one. Likewise, policymakers should use the present work as a blueprint for BPC planning, as the findings presented in this paper summarize how to set up a BPC effectively.
The article begins by outlining the scope of the research and explaining what types of studies will be included in the SLR in terms of content. We then explain the methodology used to gather the research sample and provide a descriptive overview of the data. Next, we provide a thematic review of the studies featured in the SLR. We identify gaps in the literature and avenues for further research before finally discussing the study’s limitations, as well as its theoretical and practical implications.
Scope of the review
Specifying the scope of the SLR and outlining its conceptual boundaries enhance the search protocol's transparency and academic rigor (Dhir et al., 2020 ). We achieved the above by clearly defining the theoretical background of the phenomenon under investigation, thus establishing the definition of the term BPC and employing it as the conceptual boundary of the review.
The BPC literature is part of a broader stream of competition-based learning in higher education institutions (Connell, 2013 ; Olssen & Peters, 2005 ). The peculiarities of BPCs consist in the presence of rewards for participation (Brentnall et al., 2018 ), the development of core entrepreneurial competencies (Arranz et al., 2017 ; Florin et al., 2007 ), and the overall effectiveness in terms of entrepreneurial survival (Jones & Jones, 2011 ; Russell et al., 2008 ). Previous research has focused on the core elements of BPC programs, such as mentoring, feedback, and networking; the way they affect future entrepreneurial lives (McGowan & Cooper, 2008 ; Watson et al., 2015 ; Watson & McGowan, 2019 ); and the rewards from BPC participation (Russell et al., 2008 ).
From a geographical perspective, the significance of BPCs is equally pertinent for developed and emerging economies (Tipu, 2018 ), albeit nascent entrepreneurs face unique challenges in developing countries, such as the lack of educational support (Hyder & Lussier, 2016 ) and institutional instability (Farashahi & Hafsi, 2009 ). We find the most significant levels of literary production in the USA (Buono, 2000 ), where BPCs originated back in the 1980s, and Europe (Riviezzo et al., 2012 ). BPC programs are also gaining traction in developing countries, especially in Asia (Wong, 2011 ) and Africa (House-Soremenkun & Falola, 2011 ). In China, for instance, BPCs are recognized as a reasonable means to obtain practical entrepreneurial knowledge (Fayolle, 2013 ). Similarly, in Kenya, there is an unprecedented level of interest in BPCs, especially from stakeholders involved in entrepreneurial education (Mboha, 2018 ). Finally, in Australia, Lu et al. ( 2018 ) noted the importance of funding from the federal government, such as the New Colombo Plan or the Endeavour Mobility funding schemes, in terms of support and promotion of BPC programs.
Despite the broad geographical scope of BPC literature, there is still a considerable paucity of research on the impact of BPCs on local entrepreneurship and enterprise development. Additionally, the few published studies feature mixed results. For instance, the study by Russell et al. ( 2008 ) reported a positive impact of the MI50K Entrepreneurship Competition in terms of job creation and overall funding obtained. However, the results of the study by Fayolle and Klandt ( 2006 ) are contradictory, as they note how entrepreneurial training via BPC participation does not always equate to a successful future venture. In this regard, BPC literature echoes decades-old controversial stances in entrepreneurship research, such as the perceived usefulness of business plans (Gumpert, 2003 ; Leadbeater & Oakley, 2001 ).
At this juncture, we also consider it prudent to formulate the definition of BPC that will be used as a conceptual boundary for the present study. While BPCs worldwide share a core definition and essence, they come in various forms (McKenzie, 2017 ). We adopted Passaro et al.'s ( 2017 ) definition of BPC, highlighting three essential structural and procedural features. The first is the presence of an organizing committee overseeing the competition and sponsors willing to invest in the most promising entries (Bell, 2010 ). Second, the participants are required to submit business plans to participate in the competition, and participants often consist of teams, as knowledge sharing across multiple people is deemed a crucial component of entrepreneurial success (Weisz et al., 2010 ). Third, after an initial screening, only participants with the most promising ideas are asked to further develop their business plans in the final stages of the competition (Burton, 2020 ). Thus, with the above conceptual scope in mind, our study includes contributions that have examined BPCs, their core characteristics, their implications for entrepreneurship education, and both the antecedents and consequences of BPC participation. However, we do not include studies investigating entrepreneurship education, universities' incubators, and generic entrepreneurial themes. Such studies have already been discussed at length by previous researchers.
The SLR approach was undertaken in an attempt to present the current literature in a comprehensive and extensive way. SLRs have been widely used in entrepreneurship research, and we use previously published SLRs as a methodological reference to guide our study (Mary George et al., 2016 ; Paek & Lee, 2018 ; Tabares et al., 2021 ). In accordance with previous work (Hu & Hughes, 2020 ), we performed a systematic review of BPC literature divided into two distinct steps. We first extracted the dataset required to perform the study, in what we will refer to as the data extraction phase. We later profiled the sample obtained in terms of descriptive statistics, such as annual scientific production, most cited countries, authors’ networks, and collaborations. Additional analyses were conducted by using the VOSviewer software tool (version 1.6.10., Leiden University, Leiden, the Netherlands) and Microsoft Excel (Dhir et al., 2020 ). The tools make use of bibliographic data to determine the frequencies of the published materials, design relevant charts and graphs, construct and visualize the bibliometric networks, and calculate the citation metrics.
Data extraction
The three central databases utilized for the present study are Web of Science (WoS), Scopus, and Google Scholar, as per the suggestions by Mariani et al. ( 2018 ). The first step in order to conduct the extraction of data was to identify the appropriate set of keywords. Based on the conceptual boundaries of the SLR, we determined an initial set of keywords. The keywords included ‘business plan competitions', ‘business plan contests’, and ‘business creation competitions’. The above keywords were used to perform an initial search on Google Scholar to examine if our keywords were sufficient. The first 50 results were taken into consideration (Dhir et al., 2020 ). We also searched the exact keywords in top journals, such as Entrepreneurship, Theory and Practice ; Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal ; International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal ; and Entrepreneurship Research Journal . Subsequently, we updated the list with keywords from the above sources. We consulted the panel to finalize the set of keywords, which ultimately resulted in the following: business plan competition*, business creation competition*, social business plan competition*, business plan contest*, business creation competition*, pitch competition*, pitch contest*. Data were collected from two databases, Scopus and WoS, which are generally well renowned in previous SLR studies on entrepreneurship (Hu & Hughes, 2020 ). Then, a rigorous set of inclusion and exclusion criteria was established. As for the inclusion criterion, we wanted to include only peer-reviewed works. This decision was made to strengthen the validity of the findings. Consequently, all forms of literature that may not have been subjected to a rigorous review process were excluded. This exclusion criterion thus filtered out conference proceedings, book chapters, editorials, websites, and magazine articles from the sample. The English language was used as an additional inclusion criterion to avoid language bias (Dhir et al., 2020 ). A complete list of the inclusion/exclusion criteria can be found in Table 1 .
Data collection and screening of literature
The search for keywords, abstract, and title was done in selected databases using the search string featured in Table 2 . An initial search in Scopus attained 195 distinct records, including full-length articles, book chapters, conferences proceedings, review articles, and research notes. We filtered out three publications written in languages other than English. Further, after manually reviewing each record, we excluded 36 publications that were not related to BPCs and 29 publications other than peer-reviewed journal articles. This step allowed us to reduce the overall number to 76 unique records. The same research protocol was performed on the WoS database and provided an initial total of 68 records, all of which were published in English. We filtered out 24 records as they were conference proceedings, review articles, book chapters, or meeting abstracts. Subsequently, we merged the two collections and removed any duplicate records we found in the process. As a final step, we performed chain referencing to identify further relevant studies that were not found in the previous steps. We then reviewed each publication title to identify and exclude journals that could be referred to as gray literature. This brought the total number of publications to 58, which we agreed to as the definitive number to be considered for the SLR. While somewhat limited, the final sample size is in line with the standards set for management studies (Hiebl, 2021 ) and previously published SLRs in entrepreneurship research (Paek & Lee, 2018 ; Poggesi et al., 2020 ).
Research profiling
Research profiling allowed us to review the sample in terms of several descriptive statistics meant to give us a comprehensive understanding of the current state of the art of BPC research (Dhir et al., 2020 ). Starting with Fig. 1 , we address the annual scientific production of papers included in the sample. Data suggest how BPC literature has been steady over the past two decades, with a sharp increase in recent years. The year 2018 features a significant spike in publications, with 11 distinct records to consider. These trends are in line with the consistent growth in broader entrepreneurship literature, as policymakers have shown increasing levels of interest in BPCs as effective means to create new jobs, foster innovation, and recover from economic crisis (Barbini et al., 2021 ).
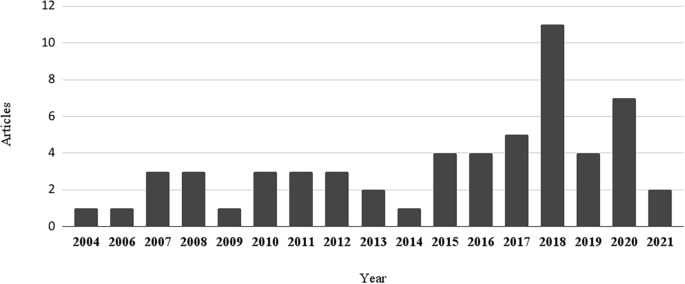
Year of publication of the selected studies
Figure 2 shows the distribution of articles throughout the various sources included in the sample. The International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal , International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior and Research , Journal of Entrepreneurship Education , and International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Small Business rank at the top.

Journals publishing the selected studies
In terms of publishing outlets, the variety of journals publishing relevant research on BPC further highlights the increasing attention scholars have devoted to this domain. Through a closer analysis, we note how leading entrepreneurship journals feature most of research articles on BPCs, thus testifying the intersection between the BPC stream and entrepreneurial education literature.
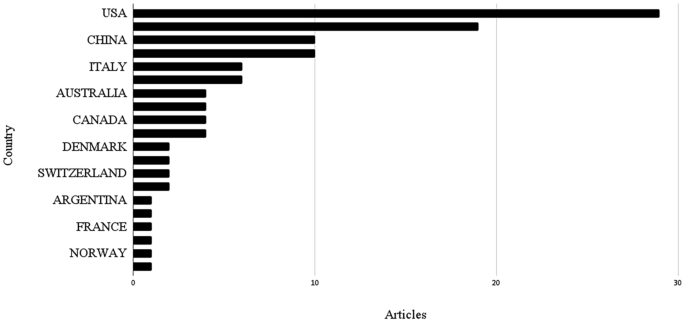
Establishments examined by the selected studies
The examination of the geographic scope of the prior studies is featured in Fig. 3 and it suggests that the majority focused on a single country, with most conducted in the United States. The United Kingdom, China, and Germany also feature a significant number of publications in terms of corresponding authors’ nationality. Other countries include South Africa, Australia, Canada, Italy, Switzerland, Argentina, Brazil, France, Nigeria, and Venezuela. The above results corroborate extant research, as it sees the USA as predominant due to them being where BPC first originated (Buono, 2000 ), thus having a more prosperous and profound history. Consistently with previous research, we also find a solid scientific presence in Europe (Riviezzo et al., 2012 ; Waldmann et al., 2010 ) and China (Fayolle, 2013 ). However, developing countries are lagging, possibly because BPCs have only recently become popular there (House-Soremenkun & Falola, 2011 ).
Figure 4 illustrates the top 10 most cited publications. The three most cited papers were published over a decade ago, thus acting as a theoretical foundation for development of the literature stream. More specifically, the work of Liñán et al. ( 2011 ) on factors affecting entrepreneurial intention levels and education is the most cited. In their work, Liñán et al. ( 2011 ) consider and establish empathy as a necessary precursor to social entrepreneurial intentions. At the time of publication, their findings were exploratory in nature, thus prompting several additional studies to expand upon their results and further develop their conclusions.
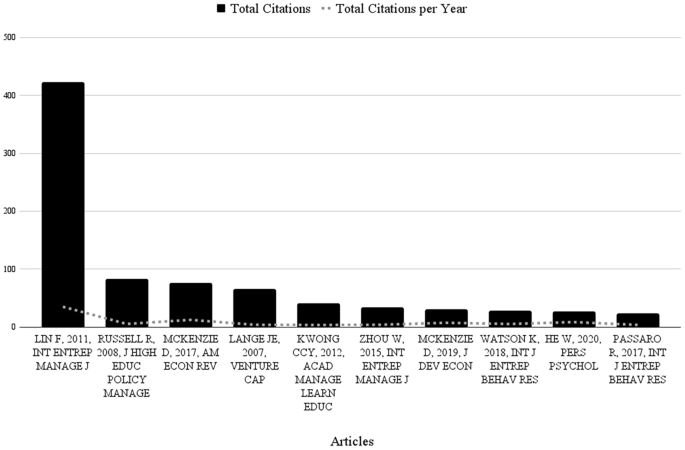
Most cited global documents
Furthermore, the study by Russell et al. ( 2008 ) on the development of entrepreneurial skills and knowledge by higher education institutions ranks at second place. Russell et al. ( 2008 ) noted that BPCs provide fertile ground for new business start-ups and for encouraging entrepreneurial ideas. Russell et al. ( 2008 ) were among the first to suggest a positive correlation between BPCs and entrepreneurial development, thus becoming a theoretical cornerstone for studies willing to further explore the benefits of BPCs for nascent entrepreneurs (Passaro et al., 2017 ).
The study by Lange et al. ( 2007 ) is the third most cited work. Lange et al. ( 2007 ) supported the hypothesis that new ventures created with a written business plan do not outperform new ventures that did not have a written business plan. Their work is often cited among BPC literature when discussing theoretical assumptions against the effectiveness of business plans and, consequently, BPCs (Watson & McGowan, 2019 ).
Several research methods have been adopted in the sample, both qualitative and quantitative. Figure 5 illustrates the methodological choices found within the sample, distinguished as qualitative, quantitative, mixed, and experimental research designs. The amounts shown in Fig. 5 are in absolute value and equal to n = 33 for qualitative research studies, n = 19 for quantitative research, n = 2 for mixed research, and n = 4 for experimental research. The most common choice in research design is the use of a specific BPC as a single empirical case study (Barbini et al., 2021 ; Efobi & Orkoh, 2018 ; Li et al., 2019 ). For instance, Jiang et al. ( 2018 ) investigated the “Challenge Cup” BPC to subsequently develop a longitudinal analysis on creative interaction networks and team creativity evolution. Similarly, Barbini et al. ( 2021 ) investigated data from a BPC in Rimini through the use of a mixed-method analysis. On the other hand, studies that focus on the educational implications of BPCs tend to use students as respondents, instead of BPC participants (Licha & Brem, 2018 ; Olokundun et al., 2017 ).
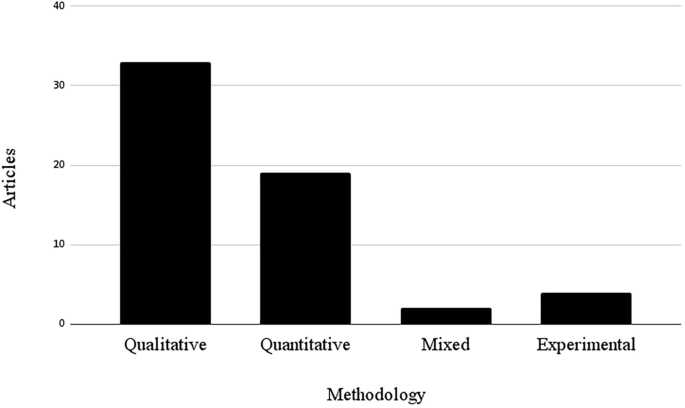
The research designs used in the selected studies
In terms of methodological choices, qualitative research on BPCs is dominated by semi-structured interviews and surveys (Burton, 2020 ; Watson & McGowan, 2019 ; Watson et al., 2018 ). The above is due to how in-depth, open-ended interviews fit a case study research design, thus explaining their popularity in BPC literature (Watson et al., 2015 ). Additionally, amid qualitative research, we find focus groups (Lu et al., 2018 ), fuzzy-set (Lewellyn & Muller-Kahle, 2016 ), content analysis, and cross-sectional research (Passaro et al., 2017 ). Moreover, quantitative studies include partial least squares models (Fichter & Tiemann, 2020 ; Overall et al., 2018 ), regression analysis, longitudinal studies (Jiang et al., 2018 ; Watson et al., 2018 ), and descriptive empirical research based on surveys. Partial least squares regression models are the most popular choice in regards to quantitative BPC research (Fichter & Tiemann, 2020 ; Overall et al., 2018 ), as they have allowed authors to, among other research, test the impacts of several variables on the entrepreneurial activity of BPC participants (Fichter & Tiemann, 2020 ) and to measure the effectiveness of universities’ promotion of entrepreneurship through events, BPCs, and incubators (Overall et al., 2018 ).
Figure 6 was made with the VOSviewer tool and shows the interactions between the most prolific countries in BPC literature. It showcases the co-citation network between the authors in the sample, sorted by their country of origin. In other words, countries appearing near within the diagram have closer collaboration. The size of each bubble indicates the relevance of each country within the network in terms of overall citations. Several main collaboration groups were found, each highlighted in a distinct color. Consistently with the geographical scope of the sample illustrated in Fig. 3 , the UK and the USA play a predominant role in the collaboration network.
The cross-country co-citation network
VOSviewer can also analyze the co-occurrence year between keywords. Through the co-occurrence chronology of keywords, the first co-occurrence time between keywords can be clearly displayed, which helps to understand the research in the field of BPC and how it has evolved over time. The co-occurrence chronology view is shown in Fig. 7 . The color of the line between the keywords in the figure indicates the first co-occurrence time of the two. The thicker the line, the greater the intensity of the two co-occurrences and the greater the number of co-occurrences between the two keywords. We notice how the field initially started around the topic of entrepreneurial education, as highlighted by the purple and blue clusters. Progressively, the focus has shifted towards social media, business development, innovation, and marketing, most likely due to the growing relevance of digital transformation throughout the past decade.
The co-occurrence chronology view of keywords
To provide readers with a comprehensive and in-depth overview of the BPC literature, we analyzed and synthesized the sample using qualitative content analysis. This technique allows researchers to identify key emerging themes from a sample and to group the records depending on their similarities (Baregheh et al., 2009 ). Three researchers conducted the content analysis independently to uncover the thematic structure of the sample. Later, we shared our findings and discussed divergent thoughts and interpretations. The discussion was aided by a senior researcher with relevant expertise in entrepreneurship research. After much debate, we agreed to arrange the results according to four themes: (1) BPCs as opportunities for entrepreneurial education, (2) benefits of BPC participation, (3) the ideal BPC blueprint, and (4) methodological choices and research design in BPC publications. This classification allowed for a more structured overview of the sample that also afforded enough space and detail to adequately review each literature stream. The research questions that emerged from each theme are presented in Table 3 , and they could act as the backbone for future studies on the topic.
BPCs and entrepreneurial education
While entrepreneurship education existed prior to the 1960s, it only became more significant in the second half of the 20th century. Entrepreneurship education was also much more popular in the USA than in the rest of the world, due to a much greater variety of courses at both the undergraduate and postgraduate levels (Dana, 1992 ). Greater academic interest in entrepreneurship was sparked at the beginning of the 21st century, however, and it has increased rapidly over the past two decades, in terms of both scientific publications and courses available to nascent entrepreneurs (Liñán et al., 2011 ).
Overall et al. ( 2018 ) emphasize the importance of universities in entrepreneurial education and BPCs. Oftentimes, universities combine traditional lectures with more practical activities, such as BPCs, to provide students with a more practically oriented schedule. Similarly, Licha and Brem ( 2018 ) highlight the tools and services available to nascent entrepreneurs via universities, including incubators, accelerators, and entrepreneurship-specific teaching methods. The findings of Licha and Brem ( 2018 ) also suggest that universities tend to give their own spin to entrepreneurial programs and that different cultures lead to different results for BPC participants and nascent entrepreneurs in general. While differences may emerge across programs based in different countries (Lewellyn & Muller-Kahle, 2016 ; Zhou et al., 2015 ), the core elements of such competitions remain stable (Parente et al., 2015 ).
Entrepreneurial programs have steadily increased in popularity over the past decade, thus prompting a newly found interest in BPCs as core components of said programs (Laud et al., 2015 ). Raveendra et al. ( 2018 ) identified several skills that universities can transfer to BPC participants, such as time management, problem solving, communication skills, and brainstorming. Although the development of these skills is not, strictly speaking, universities’ prerogative, both governments and employers want skilled entrepreneurs in society (Russell et al., 2008 ). Indeed, BPCs are a prime opportunity for novel entrepreneurs to develop entrepreneurial skills thanks to the potential for networking with peers and a practice-focused competitive environment. Such an opportunity appears to be tied to the historical appeal of BPCs, as they have attracted students from a plethora of disciplines and sectors throughout the decades (Russell et al., 2008 ).
When BPCs are approached with positive attitudes and open minds, participants can actively benefit from what they learn during their entrepreneurial journeys (McGowan & Cooper, 2008 ). The results of their learning experiences tend to emerge during their entrepreneurial careers, as entrepreneurial skills are held in high regard by various stakeholders and shareholders alike, including investors and business angels (Olokundun et al., 2017 ). Several empirical case studies strengthen these findings, illustrating the importance of BPCs as learning opportunities and their importance in terms of future entrepreneurial life (Cervilla, 2008 ; Li et al., 2019 ; Mancuso et al., 2010 ). It is worth mentioning that some studies in the sample had contradictory results, as universities are not always able to promote entrepreneurship with satisfactory results (Wegner et al., 2019 ).
However, the conversation around entrepreneurial education is still developing. For example, not much has been said about interdisciplinary personalized training and self-learning activities (Li et al., 2019 ). Cervilla ( 2008 ) echoes the same necessity in terms of creating and nurturing an interconnected environment around universities and spin-offs. A first set of exploratory findings suggests that the intervention of external professionals could benefit the entrepreneurial education of students; however, much remains to be said about which skills are valued the most by nascent entrepreneurs (Raveendra et al., 2018 ), incentives and returns for universities that host BPCs (Parente et al., 2015 ), and BPCs as a means to instill proactive entrepreneurial intentions in students (Olokundun et al., 2017 ).
Additionally, the debate surrounding the role of higher education institutions in entrepreneurial education remains very active. While universities’ support for BPCs has been proven to benefit participants in the past (Saeed et al., 2014 ), the findings of Wegner et al. ( 2019 ) suggest that the actions of universities have little to no impact on students’ entrepreneurial intentions. Contradicting results can also be found in other studies (e.g., Coduras et al., 2016 ; Shahid et al., 2017 ), which suggests that additional research is needed to expand this literature stream further. Authors have stressed the importance of intangible benefits gained from BPCs, as participants view them as valuable learning experiences and hold the competencies gained from them in high regard, albeit not entirely useful in day-to-day routines (Watson et al., 2018 ). Still, on the topic of competence development, studies have highlighted that stressing the importance of specific skills during BPCs can seriously impact future entrepreneurial ventures (Overall et al., 2018 ).
Finally, several points of contention emerge when discussing the educational outcomes of BPCs. The literature suggests that nascent entrepreneurs rely on BPCs to refine their business ideas and get feedback (Grichnik et al., 2014 ; Tata & Niedworok, 2018 ); however, empirical and theoretical contributions to BPCs as learning experiences are limited and unclear (Schwartz et al., 2013 ). To address this issue, Watson et al. ( 2018 ) claim that researchers need to understand how participation in university-based BPCs affects entrepreneurial learning outcomes among nascent entrepreneurs. So far, the results have been contradictory. Fafchamps et al. ( 2014 ) found little to no impact on the growth of such entrepreneurial ventures.
Non-educational benefits of BPC participation
It goes without saying that winning a BPC implies a significant increase in visibility, which could lead to finding new stakeholders who could prove useful to the project (Parente et al., 2015 ). However, gray areas still exist. As Parente et al. ( 2015 ) suggest, the role of media coverage could be further improved by involving experts specialized in business and entrepreneurship, instead of generalist media alone. Competition promoters should also invest considerably more time and resources into social media promotion, as social media platforms have become more and more prominent over the years for both entrepreneurs and their potential market (Cant, 2016b ; Palacios-Marqués et al., 2015 ). This is especially relevant for tech-savvy entrepreneurs who are active on social media platforms and could benefit from social media exposure, but they need institutions to act accordingly in this regard (Botha & Robertson, 2014 ). Cant ( 2016b ) found that participants in BPCs were satisfied with the exposure they received from the event, noting that it was worth the effort. However, the author also stressed the importance of event promoters being savvy with social media promotion, which was not always the case.
More broadly speaking, BPC winners have been shown to possess a greater survival rate in entrepreneurial life due to a number of factors, including financial aid, attractiveness in the eyes of stakeholders, and a positive impact on investors (McKenzie, 2017 ). Additionally, McKenzie ( 2017 ) analyzed the YouWiN! competition and noted its impact on the survival rates of established firms and start-ups. The main effect of the competition was to enable firms to buy more capital, innovate more, and hire more workers, hence making the BPC an effective tool for long-term growth. The above results add to a pre-existing debate that has characterized entrepreneurship research in the past, as authors do not seem to reach a universal consensus on the perceived usefulness of business plans (Gumpert, 2003 ; Leadbeater & Oakley, 2001 ). Still, on the topic of firm survival, the results of the study conducted by Simón-Moya and Revuelto-Taboada ( 2016 ) are especially interesting for policymakers responsible for aid programs aiming to foster entrepreneurship, as they show how the quality of a business plan alone can be a necessary condition but not a sufficient condition to explain firm survival. Hence, there is a need for policymakers and institutions to foster entrepreneurship via institutional aid and programs, BPCs included.
Moreover, Fichter and Tiemann ( 2020 ) found that the promotion of sustainability in competitions leads to the integration of sustainability practices into future entrepreneurial activities. However, they warn that policymakers need to effectively plan the integration of sustainability with the entrepreneurial mindset of BPC participants, as generic sustainability orientations do not automatically lead to the integration of sustainability goals into future business activities (Cornelissen & Werner, 2014 ). This sentiment has been echoed in more recent research (Daub et al., 2020 ). The debate on the importance of BPC participation still features a few areas that have yet to be fully explored and discussed. For example, Tata and Niedworok ( 2018 ) claim that the evaluation of business plans changes throughout the phases the idea undergoes, which leads to a more prominent role of subjective feedback in the very early stages of their development. Much like business plan evaluators, nascent entrepreneurs change the way they value their competencies over time (Watson et al., 2018 ): what appeared most useful during their time spent educating themselves might not coincide with what is deemed most relevant during their actual entrepreneurial life; however, more evidence is required to get a proper understanding of this phenomenon.
The ideal BPC blueprint
Several studies have been conducted to explore the contexts in which BPCs thrive and the traits they need to possess to successfully shape future entrepreneurs. Cant ( 2018 ) was one of the first authors to provide a tentative blueprint for future competitions, which included a call for a more structured approach and better planning via a set of universal traits that a BPC should possess regardless of the country or culture in which it is set. Drawing on Bell ( 2010 ), Cant ( 2018 ) also stresses the importance of a go-to model as a means for inexperienced institutions to organize and manage a BPC properly without the need for previous experience.
Additionally, several common trends have emerged that could help determine a generalized BPC blueprint as accurately as possible. First, it is important to ensure that the BPC is embedded in an entrepreneur-friendly ecosystem in which both nascent entrepreneurs and professionals, such as venture capitalists, business angels, and generic investors, can interact and network with each other in a seamless way (Passaro et al., 2017 ). The formulation and development of a business plan is an extremely important yet delicate step for new entrepreneurs, and being able to effectively assess their opportunities and make use of feedback from established professionals is crucial (Botha & Robertson, 2014 ). This two-way feedback mechanism can be implemented both in the early stages of competitions via workshops and lectures and after the winner is picked so that everyone has the chance to understand their results and improve (Cant, 2018 ).
Cant’s ( 2018 ) blueprint stresses the importance of industry specialists aiding participants with their submissions. This finding is supported by a case study by Moultry ( 2011 ), in which industry professionals effectively participated in lectures, provided panel discussions, and helped conduct a BPC for pharmacy students. The vast majority of students who took part in the experiment claimed that the help of industry professionals significantly increased their understanding of business plans and consequently increased their chances of future entrepreneurial success. Moreover, establishing a collaboration network that ties BPC participants to industry professionals greatly increases the chances of survival for university spin-offs (Cervilla, 2008 ).
Finally, an effective BPC should provide winners and, when possible, participants in general with enough resources to fund the early stages of their entrepreneurial journeys (Feldman & Oden, 2007 ; Kolb, 2006 ). Funding nascent entrepreneurs through BPCs could provide several benefits that significantly increase their chances of survival, while also providing them with new opportunities, such as access to debt and equity capital (Burton, 2020 ). However, nascent entrepreneurs themselves need to be able to convince investors that their business ideas are worthy of their funding and resources, and in that regard, opportunity templates vary among people who occupy different professional roles (Tata & Niedworok, 2018 ). While expressing their concerns about founders speculating on financial rewards in the business-idea phase and proposing their own BPC evaluation framework, Tata and Niedworok ( 2018 ) call for a balanced number of jurors from each professional domain to mitigate unfair rating biases. However, much about BPC blueprints remains to be determined. Cant ( 2018 ) explains that there are no set rules applicable to all competitions and that, given the increase in popularity of BPCs all over the world, evaluating similar competitions in Europe and Asia would be a natural progression for this specific literature stream.
Methodological choices and research design in BPC publications
The BPC literature features several research design choices, with both qualitative and quantitative approaches to data collection. Generally speaking, there is a noticeable predominance of empirical research based on case studies and descriptive analysis of BPC scenarios (Efobi & Orkoh, 2018 ; Li et al., 2019 ), with little emphasis on theoretical underpinnings or theory development. Multiple longitudinal studies were identified in the sample (Mosey et al., 2012 ; Watson et al., 2018 ; Jiang et al., 2018 ). We were not able to find SLRs on the topic of BPCs, other than the one performed by Tipu ( 2018 ).
From a qualitative perspective, there were several case studies from both developed (Licha & Brem, 2018 ) and developing countries (Efobi & Orkoh, 2018 ; McKenzie & Sansone, 2019 ). A few qualitative studies have also taken an experimental approach (Fafchamps & Quinn, 2017 ; Fafchamps & Woodruff, 2017 ), which was made possible by the availability of students and higher education institution facilities at the authors’ disposal. Semi-structured interviews were conducted in a few studies, mostly with exploratory intentions (Burton, 2020 ; Watson & McGowan, 2019 ).
Only one study can be labeled as mixed methods research (Barbini et al., 2021 ), whereas the remaining studies were quantitative. Methodological approaches using partial least squares regression are prevalent in BPC research (Overall et al., 2018 ; Wegner et al., 2019 ; Fichter & Tiemann, 2020 ) in which authors attempted to test the impacts of several variables on the entrepreneurial future of BPC participants. For example, Fichter and Tiemann ( 2020 ) used structural equation modeling to test whether the integration of sustainability goals into BPC programs affects the future business outcomes of nascent entrepreneurs, especially in terms of the inclusion of sustainability topics. Moreover, Wegner et al. ( 2019 ) applied a similar research design to determine whether universities’ role in promoting entrepreneurship contests such as BPCs positively affects students’ entrepreneurial intentions. Finally, Overall et al. ( 2018 ) used the theory of planned behavior (TPB) as a theoretical framework to measure the effectiveness of universities’ promotion of entrepreneurship through events, BPCs, and incubators.
Additionally, the topic of BPCs is multi-theoretical in nature, allowing scholars to use various theoretical underpinnings to investigate their nature. The sample features several theoretical frameworks used by authors, including screening and signaling theory for the analysis of early-stage venture-investor communication (Wales, et al., 2019 ); the Fishbein–Ajzen framework to predict planned behavior based on four components of reasoned action (Overall et al., 2018 ); institutional theory as a means to explain variation in entrepreneurial intention (Lewellyn & Muller-Kahle, 2016 ); and variations of the psychological model of “planned behavior” (Liñán et al., 2011 ). It is worth noting that while theoretical perspectives are plenty, records featured in the sample do not use multiple theoretical lenses in the same study. Finally, we find a few studies synthesize and develop their unique theoretical frameworks based on extant theory and empirical observations (Wen & Chen, 2007 ; McGowan & Cooper, 2008 ), even though a considerable portion of the sample features purely empirical results (McKenzie, 2017 ; Moultry, 2011 ).
Research gaps
Several research gaps were identified in the sample. To give a more thought-out structure to the presentation of these results, we classified the gaps into two categories: gaps related to the data and gaps related to the analysis.
Data-related gaps
A few studies had generalizability problems. The exploratory nature of some case studies presented intrinsic limitations to generalizability, as the findings were sometimes not applicable to different contexts (Cervilla, 2008 ; Li et al., 2019 ). For example, Licha and Brem’s ( 2018 ) study features two universities located in Germany and Denmark. Future research could expand upon their findings by investigating several other universities in different countries to strengthen and confirm their results.
Several studies have employed qualitative research methods using exploratory (Parente et al., 2015 ) or experimental approaches (Efobi & Orkoh, 2018 ; McKenzie, 2017 ). There are inherent weaknesses in such research, as self-reported surveys cannot guarantee unbiased responses (Efobi & Orkoh, 2018 ). Similarly, semi-structured interviews feature the same bias; however, their results can be verified with follow-up quantitative research on a larger scale (Licha & Brem, 2018 ; Watson et al., 2015 , 2018 ).
Some studies were also limited due to their sample sizes. Small-scale studies are valuable for exploratory research, as they allow for an initial step into a novel investigation, but they lack in terms of representativeness (Tornikoski & Puhakka, 2009 ; Watson et al., 2018 ; Barbini et al., 2021 ). For example, Wegner et al. ( 2019 ) warn readers of the intrinsic limitations of small sample sizes and ask for larger-scale surveys that could potentially test and expand the results of their initial exploratory research. Moreover, Watson et al. ( 2018 ) claim that it is important to investigate other types of competitions and not limit the scope of BPC research to university-based competitions. In doing so, future research could yield new insights and even adopt comparative perspectives to determine the differences between the two worlds (Watson et al., 2018 ).
Gaps related to analysis
Several main gaps were identified related to analysis, including a narrow focus of prior research, limited geographic scope, and a lack of theoretical underpinnings. A few studies were conducted with very narrow foci, effectively leaving the door open for future studies to bridge the gaps they highlighted. For example, Barbini et al. ( 2021 ) focused on the educational backgrounds of nascent entrepreneurs without considering the implications of their work experience. This gap could be addressed in some capacity by future research. Furthermore, Wegner et al. ( 2019 ) point out that their research shared the same limitation, as they focused on comparing individual students’ entrepreneurial intentions rather than comparing the same individual’s intentions over time. They suggest that future research could explore the influence of universities and BPCs on students’ entrepreneurial intentions (Liñán et al., 2011 ).
Another issue related to the analysis was the limited geographic scope of the sample. While the BPC literature includes contributions from both developed and developing countries (Olafsen & Cook, 2016 ), contextual empirical evidence from both sides of the spectrum is limited. Cross-cultural analysis from different countries could lead to new findings and a more comprehensive look at the BPC phenomenon, especially in developing countries, as thus far only one study exists.
Finally, another gap identified in the sample was the lack of theoretical underpinnings in many of the studies. Most of the selected manuscripts featured qualitative case studies or empirical survey-based data (Cervilla, 2008 ; Li et al., 2019 ). Although their findings were insightful, the authors themselves note that the exploratory nature of most of the studies reflects the need for more theory-building studies on BPCs or the implementation of behavioral theories to strengthen the hypotheses developed by researchers.
Potential research areas
We identified several research areas that could be explored in the future by entrepreneurship researchers. Our selection was based on a combination of our manual review of the content included in the sample and the need for further research expressed by the authors themselves. The suggestions refer primarily to the replication of exploratory research, the need for further longitudinal research, and the testing of hypotheses and measures developed by the authors, each of which is discussed below.
Replication of exploratory studies
The lack of representativeness in the studies was the most evident and recurrent gap highlighted in the sample. Scholars could start from the preliminary research findings provided by current BPC research and replicate studies in different geographical contexts. Although BPCs share several similarities in the way they function and are managed, differences in their efficacy and the survival rate of winners and participants in general can arise. However, replicability is useful for demystifying not only the entrepreneurial lives of winners, but also BPC designs themselves. For example, the blueprint developed by Cant ( 2018 ) can be replicated and tested in several contexts to validate its effectiveness and to provide novel insights into it. Future research is required to explore this ongoing debate and to find as much information as possible on how to plan the support of professionals from outside of universities accordingly (Burton, 2020 ) and how they affect BPC participants’ attitudes and entrepreneurship intentions (He et al., 2020 ).
Longitudinal studies on BPC participants’ entrepreneurial survival
Multiple authors have called for longitudinal studies designed to follow the lives of BPC participants both prior to and after the contests take place. A few longitudinal studies already exist; however, they have also called for more studies with similar research designs. For example, Watson et al. ( 2018 ) call for longitudinal research to test the notion of competition competency they introduced in their study. Similarly, Jiang et al. ( 2018 ) claim that their longitudinal approach was severely limited by being narrowly focused on a single competition. Therefore, they call for further longitudinal studies to strengthen the validity of their findings.
Collecting longitudinal data seems to be a fitting way to contribute to BPC research, specifically, and to entrepreneurial research, more broadly, as metrics could help researchers understand the development of nascent entrepreneurial ventures over time while highlighting the effects of factors such as entrepreneurial education or institutional support for BPC participants at the beginning of their journeys (Wegner et al., 2019 ). Currently, little research has been conducted on a longitudinal basis; thus, there is still a severe lack of understanding of BPCs’ impacts on the entrepreneurial teams and businesses that emerge from them (McGowan & Cooper, 2008 ).
Utilization of diverse research methods
Scholars could make use of a more diverse set of research methods in future BPC studies to overcome the paucity of theoretical contributions and quantitative research in general. While several exploratory studies serve as a strong starting point for BPC research (Burton, 2020 ; Parente et al., 2015 ), it is important to approach the topic in a more multidisciplinary manner, for instance, by including more mixed-method studies in the future (Barbini et al., 2021 ). This could lead to more comprehensive results and a more holistic understanding of the BPC literature among academics and practitioners (Efobi & Orkoh, 2018 ).
Diverse theoretical perspectives
Little theory is currently available on BPCs (Cant, 2018 ). Although multi-theoretical in nature, BPC literature draws on a limited number of existing theories, such as the quadruple-helix model (Parente et al., 2015 ) and the TPB (Overall et al., 2018 ). While the results from exploratory research are interesting and valuable, most of these studies are not underpinned by theory or theoretical frameworks of any kind. Furthermore, the paucity of theoretical underpinnings in our sample can be used as a prompt for future research. To date, only a few studies have grounded their research in established theories (Lv et al., 2021 ; Overall et al., 2018 ). Future research could try to bridge this gap, especially with behavior-centered theories and frameworks, which could be used to address several research questions in terms of BPCs’ impacts on future entrepreneurial lives and the way nascent entrepreneurs incorporate what they learn during competitions into their everyday professional practice (Watson & McGowan, 2019 ).
Theoretical framework
After reviewing the theoretical underpinnings found within the sample, we find a predominance of the conceptual framework developed by Fishbein and Ajzen ( 1975 ), namely the theory of reasoned action (TRA), which allows for a systematic theoretical orientation on beliefs and attitudes to perform a certain behavior. By using the TRA as a base reference, we synthesized extant theoretical research found in the BPC literature. We listed several independent and dependent variables depicted in previous work, reviewed the connections found between them, and illustrated the role played by moderating variables. The framework also serves as a reference to determine the impact each factor has on BPC participants in their entrepreneurial futures. The framework is illustrated in Fig. 8 .
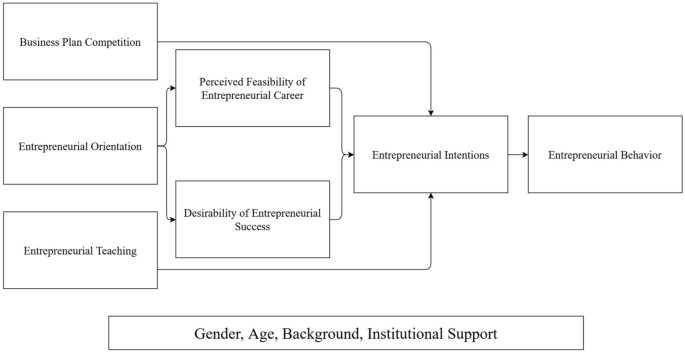
BPC theoretical framework
In the context of BPC, several antecedents can be identified as determinants of future entrepreneurial behavior. Our framework draws on previously published theoretical underpinnings to define both the antecedents of entrepreneurial activity and the multiple intrinsic factors that contribute to its multifaceted nature. We start by identifying entrepreneurial intention and entrepreneurial competence, which have been investigated in the literature through the theoretical lens of the TPB (Ajzen, 1991 ). Then, drawing on the theoretical model Lv et al. ( 2021 ) developed, we expect entrepreneurial teaching and practice support to positively impact future entrepreneurial intention and the development of entrepreneurial competencies. This theoretical assumption is backed by a few studies (Liñán et al., 2011 ) and deemed worthy of further attention. For example, future research could adopt a hierarchical multiple regression to determine the impact of entrepreneurial teaching on future entrepreneurial intention (Olokundun et al., 2017 ). Alternatively, the impact could be investigated through multiple regression models by developing a set of factors tailored to the entrepreneurial education programs and extracted via questionnaires (Liñán et al., 2011 ).
Drawing on entrepreneurial research, we find the perceived desirability of entrepreneurship and the perceived feasibility of entrepreneurship (Schlaegel & Koenig, 2014 ) as the two main attitudes toward entrepreneurial intentions (Ajzen, 1991 ; Fishbein & Ajzen, 1975 ). In other words, per the theoretical model proposed by Overall et al. ( 2018 ), entrepreneurial orientation leads students and nascent entrepreneurs to the desirability of an entrepreneurial career and the perceived feasibility of said career, which subsequently influence their entrepreneurial intentions. Then, drawing on the TRA and TPB frameworks, we propose that when individuals possess strong desirability toward an entrepreneurial career and perceive said career as feasible, they will most likely form entrepreneurial intentions (Overall et al., 2018 ).
We define entrepreneurial teaching as the essential aspect of entrepreneurship education. Research suggests that educational support affects nascent entrepreneurs by providing them with adequate skills to tackle better entrepreneurial life (Grichnik et al., 2014 ; Tata & Niedworok, 2018 ). In other words, entrepreneurial education programs actively contribute to entrepreneurial development (Škare et al., 2022 ). The positive effects of educational support on entrepreneurial success and intention can be found in empirical studies (Thomas et al., 2014 ; Passaro et al., 2020 ). More specifically, we note entrepreneurial education as a key factor in influencing innovation and development. The entrepreneur’s competencies are seen as an individual and organizational resource that needs to be properly developed through educational programs in order to bring out its potential for the entrepreneurial future (Salmony & Kanbach, 2022 ). Overall, drawing on the theoretical framework of Lv et al. ( 2021 ), we find both entrepreneurial teaching and entrepreneurial practice, intended as BPC participation, to affect their entrepreneurial intention significantly.
A set of moderating control variables can be used to provide a more comprehensive overview of the influence played by the stakeholders mentioned above. Wegner et al. ( 2019 ) suggest that future research could specify how age moderates the relationship between entrepreneurial support variables and the outcomes of BPC participants. Other studies have also supported the use of age as a moderator of the effectiveness of BPC support on entrepreneurial intention (Cant, 2018 ; Passaro et al., 2020 ). Furthermore, McGowan and Cooper ( 2008 ) claim that entrepreneurs’ levels of knowledge could be tested as moderating variables of entrepreneurial intention and behavior, as BPC participants might have different backgrounds and levels of expertise, which could influence the outcomes of their entrepreneurship activities. Additionally, Lewellyn and Muller-Kahle ( 2016 ) propose using gender as a moderator of entrepreneurial activity. Finally, Terán-Yépez et al. ( 2022 ) discuss the use of affective dispositions as variables influencing entrepreneurial activity. Future research could expand upon their findings and use hope, courage, fear and regret as moderating variables of entrepreneurial intentions.
Entrepreneurial intention as a variable that affects entrepreneurial behavior is backed by a theoretical study conducted by Overall et al. ( 2018 ), underpinned by the TPB (Ajzen, 1991 ). A positive correlation between the two was deemed consistent and statistically significant. In conclusion, the above framework could help explore the connection between BPC participation and the development of entrepreneurial activity, which thus far has received little empirical attention in research. Future research could delve further into the impact of BPC participation and institutional support on entrepreneurial activity to give proper closure to a long-lasting debate on the usefulness of BPC as a stimulant for entrepreneurial practice (Fayolle & Klandt, 2006 ; Russell et al., 2008 ). In addition, many methodological approaches could effectively encapsulate the impact described above, as seen in entrepreneurship research. For instance, future studies could employ a longitudinal case study approach (Overall et al., 2018 ) to follow nascent entrepreneurs in their journey and determine the impact of BPC participation. Longitudinal studies have proven effective in capturing the factors and variables influencing entrepreneurial life over the years (Petty & Gruber, 2011 ).
Conclusions
The purpose of this SLR was to critically analyze the literature related to BPCs and set the future research agenda for the area of entrepreneurship. To the best of our knowledge, ours is the first SLR to review research focused on recent BPC literature (Tipu, 2018 ), thus making our contribution original in its approach. The originality of the study lies in it being the first attempt at conducting an SLR on the topic of BPCs and contributing to science in several ways, as depicted below. Our study on BPC research has several implications for both academics and practitioners. From a theoretical perspective, our study makes several contributions to BPC and entrepreneurship literature. It does so by not only synthesizing extant research, but also by providing a structured research agenda built upon the several gaps found amid BPC literature. A further contribution to science is the development of a theoretical framework that will enable future researchers to have a bird’s-eye view of the domain and structure their future contributions accordingly. From a practical perspective, the study is of interest to practitioners and nascent entrepreneurs, as it provides policymakers and practitioners with a BPC blueprint featuring state-of-the-art characteristics and several key implications on how and why participating in BPCs is beneficial to nascent entrepreneurs. We propose a more detailed look at both theoretical and practical implications below.
Implications for research
Our main research contribution is a detailed review of the recent literature on BPCs, which can be deemed original, as no authors have attempted to systematically synthesize the existing BPC research. Our approach to the design of the SLR was twofold. We first provided a descriptive overview of the sample in terms of annual scientific production and geographical relevance. We then applied qualitative content analysis to highlight key emerging themes that were used to identify foci for future research directions. Based on our classification, we contend that the theoretical advancement of this research area requires greater attention to both antecedents and consequences of BPC attendance.
Our second contribution was the development of a research framework to synthesize existing knowledge on BPCs and to provide new and original insights into the BPC literature stream. Our framework explicates the role played by BPCs in the professional lives of nascent entrepreneurs (McKenzie, 2018 ; Overall et al., 2018 ) in terms of how it affects their entrepreneurial behavior (Burton, 2020 ; Passaro et al., 2017 ) and identifies the specific characteristics BPCs should feature to be as effective as possible. The same framework also helps define the scope for future research, as it identifies several avenues that future entrepreneurship scholars should explore (Fichter & Tiemann, 2020 ; Li et al., 2019 ). The framework provides future researchers a bird’s-eye view of the existing knowledge base in the area, indicating, at the same time, what remains underexplored or ignored. Additionally, by profiling extant research on BPCs, we offer scholars a comprehensive overview of potentially appropriate outlets for their studies, along with the most widely used methods and theories that could help them design their future research.
Finally, we contribute by systematically uncovering crucial research gaps in the reviewed literature on BPCs from both a methodological and a content perspective. From a methodological perspective, our analysis has revealed the need for future research to broaden the methodological scope of BPC research (Efobi & Orkoh, 2018 ). Thus far, the BPC literature stream has been dominated by empirical research featuring case studies and experimental designs (Cervilla, 2008 ; Li et al., 2019 ; Mancuso et al., 2010 ). Quantitative and mixed-method research is needed to further expand upon the findings of exploratory BPC research and to test their validity on a larger scale. From a content perspective, our study has defined a structured research agenda synthesized from extant gaps. We have identified and listed several research questions that could drive future work on the topic. Additionally, our study has highlighted the uneven distribution of BPC research from a geographical standpoint. While their significance is equally pertinent for developed and emerging economies (Tipu, 2018 ) and BPC programs are becoming increasingly popular in developing countries (House-Soremenkun & Falola, 2011 ; Wong, 2011 ), our findings suggest that country-specific production is still lagging behind pioneering nations, namely the USA and the UK. Hence, there is a need for additional evidence from developing countries, along with cross-cultural analyses to highlight the cultural differences in BPC and entrepreneurial education.
Practical implications
Our study has multiple implications for BPC practices. First, it provides policymakers and practitioners with a BPC blueprint featuring state-of-the-art characteristics. Drawing on Cant’s ( 2018 ) BPC blueprint, which was an attempt to identify an ideal set of characteristics for BPCs, we reviewed and expanded upon their findings by adding new points of view taken from empirical studies found in our sample to add new insights and incorporate more contributions from the literature. Overall, the ideal BPC should feature active participation from industry professionals, as they can provide participants with valuable insights into the professional world (Botha & Robertson, 2014 ), which BPC research has shown to be important (Moultry, 2011 ). Furthermore, a serious effort should be made to guarantee BPC participants funds and financial resources for the early stages of their entrepreneurial lives, as material support and knowledge sharing are both crucial to increasing their chances of survival (Burton, 2020 ; Passaro et al., 2017 ).
Second, our study informs practitioners of the importance of longitudinally monitoring BPC participants throughout their entrepreneurial lives (Watson et al., 2018 ). Longitudinal data allow a better understanding of the factors and variables influencing entrepreneurial life (Petty & Gruber, 2011 ). This could help BPC organizers better weigh the design choices in their educational courses by monitoring the returns they get from the seeds planted during the developmental phase of nascent business ideas (Jiang et al., 2018 ). Longitudinal monitoring of BPC participants is valuable in several ways. As suggested by McKenzie ( 2017 ), BPC winners tend to possess a greater survival rate in entrepreneurial life, which contributes to the debate on whether the quality of business plans affects the future survival rate (Simón-Moya & Revuelto-Taboada, 2016 ). Practitioners and policymakers should be asked to monitor and support BPC participants after the competition. As noted by Cant ( 2018 ), building a long-lasting collaboration with BPC participants increases their chances of survival, regardless of whether they have won the actual competition. The role played by BPC organizers in building a post-competition collaborative network is vital and has a significant impact on the survival rate, employment, profits, and sales of ventures participating in BPCs (McKenzie, 2017 ).
Our study could also be beneficial to managers, entrepreneurs, and professionals alike, as it can provide them with several key implications on how and why participating in BPCs is beneficial to nascent entrepreneurs, in terms of visibility, knowledge development, and networking opportunities (Thomas et al., 2014 ; Passaro et al., 2020 ). This is true both for novel entrepreneurs who have yet to emerge and for industry professionals who are willing to get in touch with future generations of entrepreneurs and stimulate the discussion around the topic of BPCs (Barbini et al., 2021 ). While participants generally obtain more tangible benefits from winning BPCs, their very participation in the competition can provide several intangible benefits as well, primarily in terms of networking opportunities and skill development. In this regard, our study is of practical significance for nascent entrepreneurs willing to partake in BPCs, as it features a clear depiction of what to expect to gain from the competition.
Limitations and future research
We adopted an SLR methodology to analyze the available research on BPCs. Our systematic review of the BPC literature provided descriptive and original contributions to the field. Four research questions were addressed in this article. RQ1 was addressed by providing an overview of the current state of the art of BPC research in what we refer to as research profiling. Fifty-eight unique records were extracted from the Scopus and WoS databases and analyzed in terms of annual scientific production, publication sources, geographical contexts, and influence in terms of citations. We addressed RQ2 by adopting qualitative content analysis and identifying several emerging themes across the sample, which led to a structured overview of the existing knowledge on BPCs. In regards to RQ3, we were able to identify several research gaps in the empirical literature and suggest avenues for further research. Finally, we addressed RQ4 by developing a theoretical framework that uses the above sample as its foundation. The framework aims to investigate the multidimensional nature of BPCs and provide future researchers with a theoretical underpinning for their studies.
In regards to future research directions, our systematic review has highlighted several thematic areas of prior research and investigated extant gaps both in terms of topics and in terms of methodological choices. We have, thus, identified various possible avenues for future research and presented them in a theoretical framework, that acs as a synthesized view of the existing research, serves as the basis for identifying visible gaps in prior research and suggesting various theme-based research questions and avenues of future research. In other words, the framework aims to investigate the multidimensional nature of BPCs and provide future researchers with a theoretical underpinning for their studies.
There are a few caveats worth mentioning regarding this study, some of which are intrinsic to the SLR methodology. First, the sample may not have included a few records that did not appear in the online repository due to missing or different keywords. Although chain referencing reduces the chances of this happening, the risk is still there and needs to be addressed. Second, our research protocol included only peer-reviewed journal articles written in English, as conference proceedings, book chapters, and review articles were excluded from the sample. Future research could include gray literature and other sources to compare their results with those published in peer-reviewed journals. Third, the scope of the SLR was limited to BPCs. Therefore, it did not explore nascent entrepreneurs or the role of entrepreneurial education in universities in general, despite both topics being strongly related to BPCs. Future SLRs could take a broader approach and discuss the topic of entrepreneurial education, to which the BPC stream contributes.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
* Articles included in the sample of the Systematic Literature Review
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50 (2), 179–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-t
Article Google Scholar
* Arranz, N., Ubierbna, F., Arroyabe, M. F., Perez, C., & De Arroyabe, J. C. (2017). The Effect of Curricular and Extracurricular Activities on University Students’ Entrepreneurial Intention and Competences. Studies in Higher Education, 42 (11), 1979–2008.
Audretsch, D. B., Belitski, M., Caiazza, R., & Desai, S. (2022). The role of institutions in latent and emergent entrepreneurship. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 174 , 121263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121263
* Barbini, F. M., Corsino, M., & Giuri, P. (2021). How do universities shape founding teams? Social proximity and informal mechanisms of knowledge transfer in student entrepreneurship. The Journal of Technology Transfer, 46 (4), 1046–1082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10961-020-09799-1
Baregheh, A., Rowley, J., & Sambrook, S. (2009). Towards a multidisciplinary definition of innovation. Management Decision, 47 (8), 1323–1339. https://doi.org/10.1108/00251740910984578
* Bell, J. (2010). Student business plan competitions: Who really does have access? Moyak.com. Retrieved October 19, 2022, from http://www.moyak.com/papers/student-business-plan.pdf
* Botha, M., & Robertson, C. L. (2014). Potential entrepreneurs’ assessment of opportunities through the rendering of a business plan. South African Journal of Economic and Management Sciences, 17 (3), 249–265. https://doi.org/10.4102/sajems.v17i3.524
* Brentnall, C., Rodríguez, I. D., & Culkin, N. (2018). Enterprise Education Competitions: A Theoretically Flawed Intervention. In D. Higgins, P. Jones, & P. Mcgowan (Eds.), Contemporary Issues in Entrepreneurship Research (pp. 25–48). Emerald Publishing Limited.
Google Scholar
Buono, A. F. (2000). A review of Stuart crainer and Des dearlove’s gravy training: Inside the business of business schools. Business and Society Review, 105 (2), 299–304. https://doi.org/10.1111/0045-3609.00083
* Burton, J. (2020). Supporting entrepreneurs when it matters: Optimising capital allocation for impact. Journal of Entrepreneurship and Public Policy, 9 (3), 277–302. https://doi.org/10.1108/jepp-06-2019-0054
* Cant, M. C. (2016a). Entrants and winners of a business plan competition: Does marketing media play a role in success? Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 19 (2), 98–119.
* Cant, M. C. (2016b). Using social media to market a promotional event to SMEs: Opportunity or wasted effort? Problems and Perspectives in Management, 14 , 76–82. https://doi.org/10.21511/ppm.14(4).2016.09
* Cant, M. C. (2018). Blueprint for a business plan competition: Can it work? Management Journal of Contemporary Management Issues, 23 (2), 141–154. https://doi.org/10.30924/mjcmi/2018.23.2.141
* Cervilla, M. A. (2008). Celulab case: A “spin-off” de technoclinical solutions .
* Clingingsmith, D., Drover, W., & Shane, S. (2022). Examining the outcomes of entrepreneur pitch training: An exploratory field study. Small Business Economics . https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-022-00619-4
Coduras, A., Saiz-Alvarez, J. M., & Ruiz, J. (2016). Measuring readiness for entrepreneurship: Aninformation tool proposal. Journal of Innovation and Knowledge, 1 (2), 99–109.
Connell, R. (2013). The Neoliberal Cascade and Education: An Essay on the Market Agenda and its Consequences. Critical Studies in Education, 54 , 99–112.
Cornelissen, J. P., & Werner, M. D. (2014). Putting framing in perspective: A review of framing and frame analysis across the management and organizational literature. Academy of Management Annals, 8 (1), 181–235. https://doi.org/10.1080/19416520.2014.875669
Dana, L. P. (1992). Entrepreneurial Education in Europe. Journal of Education for Business, 68 (2), 74–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/08832323.1992.10117590
* Daub, C. -H., Hasler, M., Verkuil, A. H., & Milow, U. (2020). Universities talk, students walk: Promoting innovative sustainability projects. International Journal of Sustainability in Higher Education, 21 (1), 97–111. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijshe-04-2019-0149
Dee, N., Gill, D., Weinberg, C., & Mctavish, S. (2015). Start-up Support Programmes: What’s the Difference? NESTA.
Dhir, A., Talwar, S., Kaur, P., & Malibari, A. (2020). Food waste in hospitality and food services: A systematic literature review and framework development approach. Journal of Cleaner Production, 270 , 122861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122861
* Efobi, U., & Orkoh, E. (2018). Analysis of the impacts of entrepreneurship training on growth performance of firms: Quasi-experimental evidence from Nigeria. Journal of Entrepreneurship in Emerging Economies, 10 (3), 524–542. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEEE-02-2018-0024
Fafchamps, M., McKenzie, D., Quinn, S., & Woodruff, C. (2014). Microenterprise growth and the flypaper effect: Evidence from a randomized experiment in Ghana. Journal of Development Economics, 106 , 211–226. Elsevier BV. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdeveco.2013.09.010
* Fafchamps, M., & Quinn, S. (2017). Aspire. The Journal of Development Studies, 53 (10), 1615–1633. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220388.2016.1251584
* Fafchamps, M., & Woodruff, C. (2017). Identifying gazelles: Expert panels vs. Surveys as a means to identify firms with rapid growth potential. The World Bank Economic Review, 31 (3), 670–686. https://doi.org/10.1093/wber/lhw026
Farashahi, M., & Hafsi, T. (2009). Strategy of firms in unstable institutional environments. Asia Pacific Journal of Management, 26 (4), 643–666. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10490-008-9129-9
Fayolle, A. (2013). Personal Views on the Future of Entrepreneurship Education. Entrepreneurship & Regional Development, 25 (7), 692–701.
Fayolle, A., & Klandt, H. (2006). International Entrepreneurship Education . Edward Elgar Publishing.
Book Google Scholar
* Feldman, J., & Oden, L. D. (2007). Apples and oranges mean a new fruit crop: New business plan competition model integrates economic and community development. Community College Journal of Research and Practice, 31 (6), 505–506. https://doi.org/10.1080/10668920701359656
* Fichter, K., & Tiemann, I. (2020). Impacts of promoting sustainable entrepreneurship in generic business plan competitions. Journal of Cleaner Production, 267 , 122076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122076
Fishbein, M., & Ajzen, I. (1975). Belief, attitude, intention and behaviour: An introduction to theory and research . Addison-Wesley.
* Florin, J., Karri, R., & Rossiter, N. (2007). Fostering Entrepreneurial Drive in Business Education: An Attitudinal Approach. Journal of Management Education, 31 (1), 17–42.
Grichnik, D., Brinckmann, J., Singh, L., & Manigart, S. (2014). Beyond environmental scarcity: Human and social capital as driving forces of bootstrapping activities. Journal of Business Venturing, 29 (2), 310–326. Elsevier BV. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2013.02.006
Gumpert, D. E. (2003). Burn your business plan!: what investors really want from entrepreneur . Lauson Publishing.
* He, W., Hao, P., Huang, X., Long, L. -R., Hiller, N. J., & Li, S. -L. (2020). Different roles of shared and vertical leadership in promoting team creativity: Cultivating and synthesizing team members’ individual creativity. Personnel Psychology, 73 (1), 199–225. https://doi.org/10.1111/peps.12321
Hiebl, M. R. W. (2021). Sample selection in systematic literature reviews of management research. Organizational Research Methods, 109442812098685. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428120986851
House-Soremenkun, B., & Falola, T. (2011). Globalization and Sustainable Development in Africa . University Rochester Press.
Hu, Q., & Hughes, M. (2020). Radical innovation in family firms: A systematic analysis and research agenda. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behaviour & Research, 26 (6), 1199–1234. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijebr-11-2019-0658
Hyder, S., & Lussier, R. N. (2016). Why businesses succeed or fail: A study on small businesses in Pakistan. Journal of Entrepreneurship in Emerging Economies, 8 (1), 82–100. https://doi.org/10.1108/jeee-03-2015-0020
* Jiang, H., Zhang, Q. -P., & Zhou, Y. (2018). Dynamic creative interaction networks and team creativity evolution: A longitudinal study. The Journal of Creative Behavior, 52 (2), 168–196. https://doi.org/10.1002/jocb.141
* Jones, A., & Jones, P. (2011). “Making an impact”: A Profile of a Business Planning Competition in a University. Education + Training, 53 (8), 704–721.
* Kolb, C. (2006). Runway ruhr: Business plan competition medical economics. Medizintechnik, 126 (6), 228–229.
Kraus, S., Breier, M., & Dasí-Rodríguez, S. (2020). The art of crafting a systematic literature review in entrepreneurship research. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 16 (3), 1023–1042. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-020-00635-4
Kraus, S., & Schwarz, E. (2007). The role of pre-start planning in new small business. International Journal of Management and Enterprise Development, 4 (1), 1–17.
* Kwong, C. C. Y., Thompson, P., & Cheung, C. W. M. (2012). The effectiveness of social business plan competitions in developing social and civic awareness and participation. Academy of Management Learning and Education, 11 (3), 324–348. https://doi.org/10.5465/amle.2011.0007a
* Lange, J. E., Mollov, A., Pearlmutter, M., Singh, S., & Bygrave, W. D. (2007). Pre-start-up formal business plans and post-start-up performance: A study of 116 new ventures. Venture Capital, 9 (4), 237–256. https://doi.org/10.1080/13691060701414840
* Laud, R., Betts, S., & Basu, S. (2015). The ‘business concept’ competition as a ‘business plan’ alternative for new and growing entrepreneurship programs: What’s the big idea? Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 18 (2), 53–58.
Leadbeater, C., & Oakley, K. (2001). Surfing the Long Wave: Knowledge. Entrepreneurship in Britain. Demos.
* Lewellyn, K. B., & Muller-Kahle, M. I. (2016). A configurational approach to understanding gender differences in entrepreneurial activity: A fuzzy set analysis of 40 countries. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 12 (3), 765–790. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-015-0366-3
* Li, R., Qian, Z. C., Chen, Y. V., & Zhang, L. (2019). Design thinking driven interdisciplinary entrepreneurship. A case study of college students business plan competition. The Design Journal, 22 (sup1), 99–110. https://doi.org/10.1080/14606925.2019.1602993
* Licha, J., & Brem, A. (2018). Entrepreneurship education in Europe - insights from Germany and Denmark. International Journal of Entrepreneurship & Small Business, 33 (1), 1. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijesb.2018.088641
* Liñán, F., Rodríguez-Cohard, J. C., & Rueda-Cantuche, J. M. (2011). Factors affecting entrepreneurial intention levels: A role for education. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 7 (2), 195–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-010-0154-z
* Lu, V. N., Scholz, B., & Nguyen, L. T. V. (2018). Work integrated learning in International Marketing: Student insights. Australasian Marketing Journal (AMJ), 26 (2), 132–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ausmj.2018.05.002
* Lv, Y., Chen, Y., Sha, Y., Wang, J., An, L., Chen, T., Huang, X., Huang, Y., & Huang, L. (2021). How entrepreneurship education at universities influences entrepreneurial intention: Mediating effect based on entrepreneurial competence. Frontiers in Psychology, 12 , 655868. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.655868
* Mancuso, L. C., Alijani, G. S., Kwun, O., & Smith, L. D. (2010). Successful outcomes of teaching minority undergraduate students entrepreneurial business planning concepts using andragogy and service learning. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 13 , 37–44.
Mariani, M., Baggio, R., Fuchs, M., & Höepken, W. (2018). Business intelligence and big data in hospitality and tourism: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 30 (12), 3514–3554. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijchm-07-2017-0461
Mary George, N., Parida, V., Lahti, T., & Wincent, J. (2016). A systematic literature review of entrepreneurial opportunity recognition: Insights on influencing factors. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 12 (2), 309–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-014-0347-y
* Mboha, S. (2018). An assessment of the impact of business plan competitions on enterprise development in Kenya: A case study of Chora bizna enablish LaunchPad. European Scientific Journal, 14 (10), 390. https://doi.org/10.19044/esj.2018.v14n10p390
* McGowan, P., & Cooper, S. (2008). Promoting technology-based enterprise in higher education: The role of business plan competitions. Industry and Higher Education, 22 , 29–36. https://doi.org/10.5367/000000008783876968
* McKenzie, D. (2017). Identifying and spurring high-growth entrepreneurship: Experimental evidence from a business plan competition. American Economic Review, 107 (8), 2278–2307. https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.20151404
* McKenzie, D. (2018). Can business owners form accurate counterfactuals? Eliciting treatment and control beliefs about their outcomes in the alternative treatment status. Journal of Business & Economic Statistics: A Publication of the American Statistical Association, 36 (4), 714–722. https://doi.org/10.1080/07350015.2017.1305276
* McKenzie, D., & Sansone, D. (2019). Predicting entrepreneurial success is hard: Evidence from a business plan competition in Nigeria. Journal of Development Economics, 141 , 102369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdeveco.2019.07.002
* Mosey, S., Noke, H., & Binks, M. (2012). The influence of human and social capital upon the entrepreneurial intentions and destinations of academics. Technology Analysis and Strategic Management, 24 (9), 893–910. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537325.2012.718664
* Moultry, A. M. (2011). A mass merchandiser’s role in enhancing pharmacy students’ business plan development skills for medication therapy management services. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 75 (7), 133. https://doi.org/10.5688/ajpe757133
Olafsen, E., & Cook, P. A. (2016). Growth entrepreneurship in developing countries: a preliminary literature review.
* Olokundun, M. A., Ibidunni, A. S., Peter, F., Amaihian, A. B., & Ogbari, M. (2017). Entrepreneurship educator’s competence on university students’ commitment to learning and business plan writing. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 16 (2)
Olssen, M., & Peters, M. A. (2005). Neoliberalism, Higher Education and the Knowledge Economy: From the Free Market to Knowledge Capitalism. Journal of Education Policy, 20 (3), 313–345.
* Overall, J., Gedeon, S. A., & Valliere, D. (2018). What can universities do to promote entrepreneurial intent? An empirical investigation. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Venturing, 10 (3), 312. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijev.2018.093227
Paek, B., & Lee, H. (2018). Strategic entrepreneurship and competitive advantage of established firms: Evidence from the digital TV industry. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 14 (4), 883–925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-017-0476-1
Palacios-Marqués, D., Soto-Acosta, P., & Merigó, J. M. (2015). Analyzing the effects of technological, organizational and competition factors on Web knowledge exchange in SMEs. Telematics and Informatics, 32 (1), 23–32. Elsevier BV. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2014.08.003
* Parente, R., Feola, R., Cucino, V., & Catolino, G. (2015). Visibility and reputation of new entrepreneurial projects from academia: The role of start-up competitions. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 6 (3), 551–567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-015-0255-6
* Passaro, R., Quinto, I., & Thomas, A. (2017). Start-up competitions as learning environment to foster the entrepreneurial process. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behaviour & Research, 23 (3), 426–445. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijebr-01-2016-0007
* Passaro, R., Quinto, I., & Thomas, A. (2020). Supporting entrepreneurship policy: An overview of Italian start-up competitions. International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Innovation Management, 24 (1), 1. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijeim.2020.105274
Petty, J. S., & Gruber, M. (2011). In pursuit of the real deal. Journal of Business Venturing, 26 (2), 172–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2009.07.002
Poggesi, S., Mari, M., De Vita, L., & Foss, L. (2020). Women entrepreneurship in STEM fields: Literature review and future research avenues. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 16 (1), 17–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-019-00599-0
* Raveendra, P. V., Rizwana, M., Singh, P., Satish, Y. M., & Kumar, S. S. (2018). Entrepreneurship development through industry institute collaboration: An observation. International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology, 9 (6), 980–984.
Riviezzo, A., De, A., & Rosaria, M. (2012). Attractiveness of European higher education in entrepreneurship: A strategic marketing framework. Entrepreneurship - Creativity and Innovative Business Models. InTech.
Ross, L. W., & Byrd, K. A. (2011). Business plan competitions: Start-up ‘idols’ and their twenty-first century launch pads. Journal of Higher Education Theory and Practice, 11 (4), 53–64.
* Russell, R., Atchison, M., & Brooks, R. (2008). Business plan competitions in tertiary institutions: Encouraging entrepreneurship education. Journal of Higher Education Policy and Management, 30 (2), 123–138. https://doi.org/10.1080/13600800801938739
Saeed, S., Muffatto, M., & Yousafzai, S. (2014). A multi-level study of entrepreneurship education among Pakistani university students. Entrepreneurship Research Journal, 4 (3).Walter de Gruyter GmbH. https://doi.org/10.1515/erj-2013-0041
Salmony, F. U., & Kanbach, D. K. (2022). Personality trait differences across types of entrepreneurs: A systematic literature review. Review of Managerial Science, 16 (3), 713–749. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-021-00466-9
Schlaegel, C., & Koenig, M. (2014). Determinants of entrepreneurial intent: A meta–analytic test and integration of competing models. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 38 (2), 291–332. https://doi.org/10.1111/etap.1208
* Schwartz, M., Goethner, M., Michelsen, C., & Waldmann, N. (2013). Start-up competitions as an instrument of entrepreneurship policy: The German experience. European Planning Studies, 21 (10), 1578–1597. https://doi.org/10.1080/09654313.2012.722960
Shahid, M. S., Shehryar, H., & Inram, Y. (2017). Journal of Small Business & Entrepreneurship, 30 (2), 139–156.
Simón-Moya, V., & Revuelto-Taboada, L. (2016). Revising the predictive capability of business plan quality for new firm survival using qualitative comparative analysis. Journal of Business Research, 69 (4), 1351–1356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2015.10.106
Škare, M., Blanco-Gonzalez-Tejero, C., Crecente, F., & del Val, M. T. (2022). Scientometric analysis on entrepreneurial skills - creativity, communication, leadership: How strong is the association? Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 182 , 121851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121851
Tabares, A., Chandra, Y., Alvarez, C., & Escobar-Sierra, M. (2021). Opportunity-related behaviors in international entrepreneurship research: A multilevel analysis of antecedents, processes, and outcomes. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 17 (1), 321–368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-020-00636-3
* Tata, A., & Niedworok, A. (2018). Is beauty in the eye of the beholder? An empirical study of how entrepreneurs, managers, and investors evaluate business opportunities at the earliest stages. Venture Capital, 22 (1), 71–104. https://doi.org/10.1080/13691066.2018.1526449
Terán-Yépez, E., Jiménez-Castillo, D., & Sánchez-Pérez, M. (2022). The role of affect in international opportunity recognition and the formation of international opportunity beliefs. Review of Managerial Science, 1–43.
Thomas, D. F., Gudmundson, D., Turner, K., & Suhr, D. (2014). Business plan competitions and their impact on new ventures' business models. Journal of Strategic Innovation & Sustainability, 10(1).
Tipu, S. A. A. (2018). Business plan competitions in developed and emerging economies: What do we still need to know? Journal of Entrepreneurship in Emerging Economies, 11 (1), 81–97. https://doi.org/10.1108/jeee-12-2017-0102
* Tornikoski, E. T., & Puhakka, V. (2009). Exploring firm emergence: Initially conditioned or actively created? International Journal of Entrepreneurship & Small Business, 7 (1), 123. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijesb.2009.021613
* Waldmann, N., Schwartz, M., & Michelsen, C. (2010). From the intention to the foundation - start-up competitions in germany. List Forum Fur Wirtschafts- Und Finanzpolitik, 36 (4), 301–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03373978
* Wales, W., Cox, K. C., Lortie, J., & Sproul, C. R. (2019). Blowing smoke? How early-stage investors interpret hopeful discourse within entrepreneurially oriented business plans. Entrepreneurship Research Journal, 9 (3), 20180114. https://doi.org/10.1515/erj-2018-0114
* Watson, K., & McGowan, P. (2019). Emergent perspectives toward the business plan among nascent entrepreneur start-up competition participants. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 26 (3), 421–440. https://doi.org/10.1108/jsbed-02-2018-0038
* Watson, K., McGowan, P., & Cunningham, J. A. (2018). An exploration of the Business Plan Competition as a methodology for effective nascent entrepreneurial learning. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behaviour & Research, 24 (1), 121–146. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijebr-05-2017-0158
* Watson, K., McGowan, P., & Smith, P. (2015). Leveraging effectual means through business plan competition participation. Industry and Higher Education, 29 (6), 481–492. https://doi.org/10.5367/ihe.2015.0285
* Wegner, D., Thomas, E., Teixeira, E. K., & Maehler, A. E. (2019). University entrepreneurial push strategy and students’ entrepreneurial intention. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behaviour & Research, 26 (2), 307–325. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijebr-10-2018-0648
* Weisz, N., Vassolo, R. S., Mesquita, L., & Cooper, A. C. (2010). Diversity and social capital of nascent entrepreneurial teams in business plan competitions. Management Research the Journal of the Iberoamerican Academy of Management, 8 (1), 39–63. https://doi.org/10.1108/1536-541011047903
* Wen, C. T., & Chen, Y. W. (2007). The innovation process of entrepreneurial teams in dynamic business plan competition: From sense-making perspective. Journal International De La Gestion Technologique [international Journal of Technology Management], 39 (3/4), 346. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijtm.2007.013505
Wong, P. K. (2011). Academic Entrepreneurship in Asia: The Role and Impact of Universities in National Innovation Systems . Edward Elgar Publishing.
Zhou, W., Vredenburgh, D., & Rogoff, E. G. (2015). Informational diversity and entrepreneurial team performance: Moderating effect of shared leadership. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 11 (1), 39–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-013-0274-3
* Zhu, X., Yang, S., & Kromidha, E. (2022). The emergence of team entrepreneurial passion from team helping: An affective events theory perspective. International Small Business Journal, 026624262210894. https://doi.org/10.1177/02662426221089499
Download references
Open access funding provided by Università degli Studi di Torino within the CRUI-CARE Agreement.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Ecole de commerce Paris - ICD Business School, 12 Rue Alexandre Parodi, France, Paris, 75010, France
Léo-Paul Dana
Lappeenranta-Lahti University of Technology LUT, Yliopistonkatu 34, Lappeenranta, 53850, Finland
Department of Management, University of Turin, Corso Unione Sovietica, 218 bis, Turin, TO, 10134, Italy
Edoardo Crocco, Francesca Culasso & Elisa Giacosa
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Edoardo Crocco .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Dana, LP., Crocco, E., Culasso, F. et al. Business plan competitions and nascent entrepreneurs: a systematic literature review and research agenda. Int Entrep Manag J 19 , 863–895 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-023-00838-5
Download citation
Accepted : 19 January 2023
Published : 28 February 2023
Issue Date : June 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-023-00838-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Business plan competition
- Systematic literature review
- Higher education
- Small businesses
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Eugene McDermott Library
- University of Texas at Dallas
- Business Plans and Proposals
- Electronic Resources
Finding Journal Articles
Scholarly vs popular journals.
- Inside America's Economic Machine
- Useful Websites
- Getting Help
To find articles on topics in Business Plans, use a resource from the Business Management page. It is possible to begin with a database such as Business Source Complete. In the first search box type "business plan" and in the second search box type sample. Notice that there are quotes around business plan. Some of the search results will show examples of business plans.
To broaden your search, select a resource from the complete list .
How do I find peer-reviewed articles and journals?
- Ulrichsweb.com Ulrichsweb.com is an online directory of journals, magazines, and other periodicals. Ulrichsweb.com also indicates if a journal or magazine is refereed or peer reviewed.
- << Previous: Electronic Resources
- Next: Multimedia >>
- Last Updated: Nov 30, 2023 11:23 AM
- URL: https://libguides.utdallas.edu/business-plans-and-proposals
Librarians/Admins
- EBSCOhost Collection Manager
- EBSCO Experience Manager
- EBSCO Connect
- Start your research
- EBSCO Mobile App
Clinical Decisions Users
- DynaMed Decisions
- Dynamic Health
- Waiting Rooms
- NoveList Blog
Business Source Ultimate
Business Source Ultimate works for your students like a solid business plan – it offers an unprecedented wealth of peer-reviewed, full-text journals and other resources that provide historical information and current trends in business that spark discussion on future developments and changes in the business world.
Business Source Ultimate offers access to 3,512 active full-text journals, including many peer-reviewed publications. It spans various business topics, from current trends to historical information and global perspectives. It provides researchers with essential business journals such as Harvard Business Review, Forbes, and MIS Quarterly, plus business videos from top providers. With a total journal retail value of $1,176,557.27, it is the largest database within the Business Source family.
Active Full Text for FT50 Journals
The Financial Times publishes a yearly ranking of business schools that offer MBA, EMBA, and online MBA programs. These rankings include a research score, which is based on the number of faculty publications published in 50 academic and practitioner journals, known as the FT50 journal list . Here is how Business Source Ultimate compares to ABI/INFORM Collection across the FT50 journal list:
Strengthen Exposure to Open Access Journals
Business Source Ultimate includes rigorous curation and indexing of open access (OA) journals, which has resulted in a growing collection of 1,789 active global OA journals. Once validated and certified for inclusion, these OA journals are treated with high-quality subject indexing and sophisticated, precise/accurate full-text linking.
NOTE: EBSCOhost databases and EBSCO Discovery Service generate a lot more referrals for DOAJ than any other online platform .
The World's Highest-Quality Business Research Database — Includes Expanding International Content
The most comprehensive non-journal content of any business research database, business video collections.
With three important video collections, Business Source Ultimate offers researchers a variety of ways to gather unique content to supplement information found in journal articles. Students can access the new collection of 111 videos from Academy of Management plus thousands of Business & Economics videos as well as relevant videos from the Associated Press.
Business Source Ultimate helps students find academic business journal articles more quickly than other products and provides our best access to Harvard Business Review .
— Business Librarian, University in California
See what other librarians are saying about Business Source Ultimate .
Ahead of Print
Business Source Ultimate includes Ahead of Print content for relevant titles from key publishers.
Searchable Cited References
Business Source Ultimate includes 1,310 journals with searchable cited references.
The Highest Quality Subject Indexing
EBSCO has the premier and most highly regarded scholarly vocabularies curated by subject matter experts, covering all disciplines and major publishers.
EBSCO believes in breaking down barriers to information through Enhanced Subject Precision (ESP) mapping, bridging the gap between content and end users through inclusion of natural languages.
EBSCO databases support all learning types through textual and visual subject browse and information literacy training through subject access points in more than 30 languages. Watch video to learn more .
Business Source Ultimate includes 4,373 active indexed and abstracted journals. 3,175 of them are peer-reviewed.
Customers also bought

- Library databases
- Library website
Business Plans: Find Business Planning Articles
Find business planning articles.
Business plans are found in trade/professional journals (as opposed to scholarly/peer-reviewed journals, which are more likely to present research studies). You can search the ABI/INFORM Collection or Business Source Complete databases and limit your results to articles from Trade Publications.
Database links:
Search for business plans:
Enter the phrase "business plans" in the search box. You may wish to add other keywords describing a specific industry or type of company to narrow your search. For example:
First Search Box:
"business plans"
Second Search Box:
coffee shop
After entering your keywords, you will need to limit your search to Trade Publications to see articles from trade journals only.
Locate the Source Type limiter in ABI/Inform Complete . Click on the box next to Trade Journals.

Locate the Publication Type limiter in Business Source Complete. Under Publication Type , click on Trade Publication.

- Previous Page: Find Business Planning Books
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- Share full article

A Failed Crop Rattled the Chocolate Industry. Then Speculators Came.
After a production shortfall in West Africa, cocoa prices rose to $4,000 a metric ton from $2,500. Then they went nuts.
Credit... Carl Godfrey
Supported by

By J. Edward Moreno
- May 10, 2024
A failed crop, followed by a wave of financial speculation, put cocoa prices on a roller coaster this year, rattling an industry reliant on inexpensive crops and labor.
This is not how things normally go in the cocoa market. For much of the past decade, the price of cocoa in one key global benchmark hovered around $2,500 per metric ton. Last year, after poor harvests in West Africa, the price began to creep up — rising to $4,200 a ton by December, a threshold that hadn’t been crossed since the 1970s.
Then the financial speculators began to pile in — betting prices would rise further. They pushed the price above $6,000 a ton in February, $9,000 a ton in March and $11,000 a ton in mid-April. Since then, the price has swung wildly, falling nearly 30 percent in just two weeks before bouncing up again. By Thursday, the price was $8,699 a ton.
Large food companies have been raising prices and warning that they’ll have to continue to do so if cocoa doesn’t stabilize. Companies that use more pure cocoa — rather than the palm oil and other fillers that go into many candy bars — will be hit hardest, though some premium chocolate makers note that they’ve always paid much higher prices in order to compensate farmers fairly.
The situation doesn’t look as if it’s going to settle down soon. Here’s what you need to know.
What happened to the cocoa crop?
A combination of low rainfall, plant disease and aging trees led to a disappointing crop in Ivory Coast and Ghana in 2023. The two countries produce about two-thirds of the world’s cocoa, so the shortage hit the global market hard. It continues: The International Cocoa Organization recently forecast that global production will trail demand by 374,000 tons this season, which ends in September, after a 74,000-ton shortfall last year.
There’s no quick fix for this. The trees take years to produce fruit, giving farmers little incentive to plant more since they don’t know what the price of the crop will be when they bear fruit. Some may prefer to use more of their land for growing rubber or mining gold.

But while the production shortfall underpinned the initial price gains, speculation from investors like hedge funds took things to another level.
“Yes, there’s fundamentals that trigger the move, but then these financial considerations add to it and compound to the situation.” said Judy Ganes, a commodities consultant. “It’s money driven.”
How is the global price of cocoa set?
Like any commodity, cocoa has many different prices.
In Ghana and Ivory Coast , the government sets a seasonal rate that cocoa farmers are paid, in an effort to protect them from volatility in global prices. After market prices spiked in April, the Ivory Coast’s agriculture ministry agreed to raise that rate for the rest of the season — but it is still far less than the increase in global commodity markets.
In other countries, farmers are paid market rates.
But big buyers, like Hershey and Mondelez, and commodity traders buy and sell cocoa on global exchanges, where they trade physical beans as well as futures contracts that can require them to take a delivery of beans at a future date.
It’s in the global exchanges that prices have become disconnected from the reality on the farms.
The global benchmark for cocoa is a futures contract traded on the Intercontinental Exchange — and a buyer of that contract is agreeing to a price for a metric ton of cocoa beans to be delivered to one of several ports in the Eastern United States.
One big factor behind the price spike this year is that those futures contracts are settled with physical delivery of the cocoa — which means traders who are selling the contracts need to keep large reserves of cocoa beans on hand. That can result in an upward spiral, as traders are forced to buy more cocoa in order to replenish their inventories.
The volume of trading can also affect how the price changes.
In January, the number of active cocoa contracts jumped 30 percent from the year before, data from the Commodities Futures Trading Commission show. But that trading volume fell sharply starting in April — as prices peaked — and the smaller number of trades resulted in big price swings in the past two weeks.
Though prices have come down from their highest point, they’re likely to stay elevated for some time, said Paul Joules, an analyst at Rabobank, “because of the systemic issues that are going to take a while to resolve.”
Carla Martin, a Harvard professor who studies the cocoa industry, said the broader market might look more efficient if farmers had more price-setting power based on their supply.
“There’s actually a ton of money in cocoa, it’s just getting captured in very specific nodes of the supply chain,” Ms. Martin said. “The market itself does not actually solve these kinds of problems, the problems get solved by people.”
What does this mean for chocolate bars?
Chocolate prices are mostly rising. When Hershey and Mondelez, which owns brands like Cadbury and Toblerone, reported earnings recently, the price swings were a big topic of conversation.
Mondelez said it raised its prices about 6 percent in the first three months of the year, and Hershey about 5 percent, and both said they would be willing to push prices up more if the cost of cocoa stayed high. Both companies said their profits had increased by double-digit percentages over the previous year as consumers continued buying their products despite rising prices.
Luca Zaramella, the chief financial officer of Mondelez, told analysts on April 30 that the market was “overreacting” and that it would very likely correct itself in the latter half of the year.
Still, he said, “it’s absolutely critical for us to get ready for potentially cocoa staying at these levels.” Mondelez could protect its profits, Mr. Zaramella said, by trying to secure large orders of cocoa during market downswings or reducing costs for other inputs, like ingredients.
Some “bean to bar” chocolate makers, which have always paid a premium for the cocoa they get from smaller farmers, say they’re having a different experience.
“The premium cocoa price never changed,” said Dan Maloney, who runs Sol Cacao, a chocolate business in the Bronx, with his two brothers. “It’s almost like the bulk price caught up with the premium price, but we were always paying premium.”
Mr. Maloney said he was already paying $9,000 to $12,000 for a ton of premium cocoa, which he obtains from farmers around the world, particularly in Latin America and Africa. Sol Cacao charges $8 for a 1.86-ounce bar, while a four-ounce Hershey bar is about $2.
Mr. Maloney said he charged those prices to ensure the quality of the product and ethical treatment of farmers in the industry, which has a history of exploiting children and enslaved people for labor .
“They market chocolate as candy,” Mr. Maloney said of large manufacturers. “We market it more as a luxury, something to savor, like a bottle of wine.”
Some cocoa farmers see buyers like Mr. Maloney as allies who protect them from the whims of the financial markets.
Gustavo Mindineros, a cocoa farmer who leads a co-op of producers in Tumaco, Colombia, said farmers tended to favor smaller buyers when production was low because they bought fewer beans at a higher price.
“The large company guarantees volume, but they don’t recognize quality,” Mr. Mindineros said. “Smaller buyers do recognize quality, and they pay a premium for it.”
J. Edward Moreno is a business reporter at The Times. More about J. Edward Moreno
Explore Our Business Coverage
Dive deeper into the people, issues and trends shaping the world of business..
Elon Musk’s Diplomacy: The billionaire is wooing right-wing world leaders to push his own politics and expand his business empire.
Staying Connected: Some couples are using professional project-management software like Slack and Trello to maintain their relationships. Why does it bother other people ?
A Final Curtain Call: The animatronic band at Chuck E. Cheese, by turns endearing and creepy, will be phased out by year’s end at all but two locations. We visited one of them .
The ‘Betches’ Got Rich: Betches Media, the women’s media company that started as a raunchy college blog, is a rare financial success story. So what’s next ?
Retraining German Workers: As Germany’s industrial landscape shifts, companies have formed an alliance aimed at offering the skills and certification that employees need to find new jobs .
Advertisement
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
FACT SHEET: President Biden Takes Action to Protect American Workers and Businesses from China’s Unfair Trade Practices
President Biden’s economic plan is supporting investments and creating good jobs in key sectors that are vital for America’s economic future and national security. China’s unfair trade practices concerning technology transfer, intellectual property, and innovation are threatening American businesses and workers. China is also flooding global markets with artificially low-priced exports. In response to China’s unfair trade practices and to counteract the resulting harms, today, President Biden is directing his Trade Representative to increase tariffs under Section 301 of the Trade Act of 1974 on $18 billion of imports from China to protect American workers and businesses. The Biden-Harris Administration’s Investing in America agenda has already catalyzed more than $860 billion in business investments through smart, public incentives in industries of the future like electric vehicles (EVs), clean energy, and semiconductors. With support from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, CHIPS and Science Act, and Inflation Reduction Act, these investments are creating new American jobs in manufacturing and clean energy and helping communities that have been left behind make a comeback. As President Biden says, American workers and businesses can outcompete anyone—as long as they have fair competition. But for too long, China’s government has used unfair, non-market practices. China’s forced technology transfers and intellectual property theft have contributed to its control of 70, 80, and even 90 percent of global production for the critical inputs necessary for our technologies, infrastructure, energy, and health care—creating unacceptable risks to America’s supply chains and economic security. Furthermore, these same non-market policies and practices contribute to China’s growing overcapacity and export surges that threaten to significantly harm American workers, businesses, and communities. Today’s actions to counter China’s unfair trade practices are carefully targeted at strategic sectors—the same sectors where the United States is making historic investments under President Biden to create and sustain good-paying jobs—unlike recent proposals by Congressional Republicans that would threaten jobs and raise costs across the board. The previous administration’s trade deal with China failed to increase American exports or boost American manufacturing as it had promised. Under President Biden’s Investing in America agenda, nearly 800,000 manufacturing jobs have been created and new factory construction has doubled after both fell under the previous administration, and the trade deficit with China is the lowest in a decade—lower than any year under the last administration. We will continue to work with our partners around the world to strengthen cooperation to address shared concerns about China’s unfair practices—rather than undermining our alliances or applying indiscriminate 10 percent tariffs that raise prices on all imports from all countries, regardless whether they are engaged in unfair trade. The Biden-Harris Administration recognizes the benefits for our workers and businesses from strong alliances and a rules-based international trade system based on fair competition. Following an in-depth review by the United States Trade Representative, President Biden is taking action to protect American workers and American companies from China’s unfair trade practices. To encourage China to eliminate its unfair trade practices regarding technology transfer, intellectual property, and innovation, the President is directing increases in tariffs across strategic sectors such as steel and aluminum, semiconductors, electric vehicles, batteries, critical minerals, solar cells, ship-to-shore cranes, and medical products. Steel and Aluminum The tariff rate on certain steel and aluminum products under Section 301 will increase from 0–7.5% to 25% in 2024. Steel is a vital sector for the American economy, and American companies are leading the future of clean steel. Recently, the Biden-Harris Administration announced $6 billion for 33 clean manufacturing projects including for steel and aluminum, including the first new primary aluminum smelter in four decades, made possible by the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and the Inflation Reduction Act. These investments will make the United States one of the first nations in the world to convert clean hydrogen into clean steel, bolstering the U.S. steel industry’s competitiveness as the world’s cleanest major steel producer. American workers continue to face unfair competition from China’s non-market overcapacity in steel and aluminum, which are among the world’s most carbon intensive. China’s policies and subsidies for their domestic steel and aluminum industries mean high-quality, low-emissions U.S. products are undercut by artificially low-priced Chinese alternatives produced with higher emissions. Today’s actions will shield the U.S. steel and aluminum industries from China’s unfair trade practices. Semiconductors The tariff rate on semiconductors will increase from 25% to 50% by 2025. China’s policies in the legacy semiconductor sector have led to growing market share and rapid capacity expansion that risks driving out investment by market-driven firms. Over the next three to five years, China is expected to account for almost half of all new capacity coming online to manufacture certain legacy semiconductor wafers. During the pandemic, disruptions to the supply chain, including legacy chips, led to price spikes in a wide variety of products, including automobiles, consumer appliances, and medical devices, underscoring the risks of overreliance on a few markets. Through the CHIPS and Science Act, President Biden is making a nearly $53 billion investment in American semiconductor manufacturing capacity, research, innovation, and workforce. This will help counteract decades of disinvestment and offshoring that has reduced the United States’ capacity to manufacture semiconductors domestically. The CHIPS and Science Act includes $39 billion in direct incentives to build, modernize, and expand semiconductor manufacturing fabrication facilities as well as a 25% investment tax credit for semiconductor companies. Raising the tariff rate on semiconductors is an important initial step to promote the sustainability of these investments. Electric Vehicles (EVs) The tariff rate on electric vehicles under Section 301 will increase from 25% to 100% in 2024. With extensive subsidies and non-market practices leading to substantial risks of overcapacity, China’s exports of EVs grew by 70% from 2022 to 2023—jeopardizing productive investments elsewhere. A 100% tariff rate on EVs will protect American manufacturers from China’s unfair trade practices. This action advances President Biden’s vision of ensuring the future of the auto industry will be made in America by American workers. As part of the President’s Investing in America agenda, the Administration is incentivizing the development of a robust EV market through business tax credits for manufacturing of batteries and production of critical minerals, consumer tax credits for EV adoption, smart standards, federal investments in EV charging infrastructure, and grants to supply EV and battery manufacturing. The increase in the tariff rate on electric vehicles will protect these investments and jobs from unfairly priced Chinese imports. Batteries, Battery Components and Parts, and Critical Minerals The tariff rate on lithium-ion EV batteries will increase from 7.5%% to 25% in 2024, while the tariff rate on lithium-ion non-EV batteries will increase from 7.5% to 25% in 2026. The tariff rate on battery parts will increase from 7.5% to 25% in 2024. The tariff rate on natural graphite and permanent magnets will increase from zero to 25% in 2026. The tariff rate for certain other critical minerals will increase from zero to 25% in 2024. Despite rapid and recent progress in U.S. onshoring, China currently controls over 80 percent of certain segments of the EV battery supply chain, particularly upstream nodes such as critical minerals mining, processing, and refining. Concentration of critical minerals mining and refining capacity in China leaves our supply chains vulnerable and our national security and clean energy goals at risk. In order to improve U.S. and global resiliency in these supply chains, President Biden has invested across the U.S. battery supply chain to build a sufficient domestic industrial base. Through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, the Defense Production Act, and the Inflation Reduction Act, the Biden-Harris Administration has invested nearly $20 billion in grants and loans to expand domestic production capacity of advanced batteries and battery materials. The Inflation Reduction Act also contains manufacturing tax credits to incentivize investment in battery and battery material production in the United States. The President has also established the American Battery Materials Initiative, which will mobilize an all-of-government approach to secure a dependable, robust supply chain for batteries and their inputs. Solar Cells The tariff rate on solar cells (whether or not assembled into modules) will increase from 25% to 50% in 2024. The tariff increase will protect against China’s policy-driven overcapacity that depresses prices and inhibits the development of solar capacity outside of China. China has used unfair practices to dominate upwards of 80 to 90% of certain parts of the global solar supply chain, and is trying to maintain that status quo. Chinese policies and nonmarket practices are flooding global markets with artificially cheap solar modules and panels, undermining investment in solar manufacturing outside of China. The Biden-Harris Administration has made historic investments in the U.S. solar supply chain, building on early U.S. government-enabled research and development that helped create solar cell technologies. The Inflation Reduction Act provides supply-side tax incentives for solar components, including polysilicon, wafers, cells, modules, and backsheet material, as well as tax credits and grant and loan programs supporting deployment of utility-scale and residential solar energy projects. As a result of President Biden’s Investing in America agenda, solar manufacturers have already announced nearly $17 billion in planned investment under his Administration—an 8-fold increase in U.S. manufacturing capacity, enough to supply panels for millions of homes each year by 2030. Ship-to-Shore Cranes The tariff rate on ship-to-shore cranes will increase from 0% to 25% in 2024. The Administration continues to deliver for the American people by rebuilding the United States’ industrial capacity to produce port cranes with trusted partners. A 25% tariff rate on ship-to-shore cranes will help protect U.S. manufacturers from China’s unfair trade practices that have led to excessive concentration in the market. Port cranes are essential pieces of infrastructure that enable the continuous movement and flow of critical goods to, from, and within the United States, and the Administration is taking action to mitigate risks that could disrupt American supply chains. This action also builds off of ongoing work to invest in U.S. port infrastructure through the President’s Investing in America Agenda. This port security initiative includes bringing port crane manufacturing capabilities back to the United States to support U.S. supply chain security and encourages ports across the country and around the world to use trusted vendors when sourcing cranes or other heavy equipment. Medical Products The tariff rates on syringes and needles will increase from 0% to 50% in 2024. For certain personal protective equipment (PPE), including certain respirators and face masks, the tariff rates will increase from 0–7.5% to 25% in 2024. Tariffs on rubber medical and surgical gloves will increase from 7.5% to 25% in 2026. These tariff rate increases will help support and sustain a strong domestic industrial base for medical supplies that were essential to the COVID-19 pandemic response, and continue to be used daily in every hospital across the country to deliver essential care. The federal government and the private sector have made substantial investments to build domestic manufacturing for these and other medical products to ensure American health care workers and patients have access to critical medical products when they need them. American businesses are now struggling to compete with underpriced Chinese-made supplies dumped on the market, sometimes of such poor quality that they may raise safety concerns for health care workers and patients. Today’s announcement reflects President Biden’s commitment to always have the back of American workers. When faced with anticompetitive, unfair practices from abroad, the President will deploy any and all tools necessary to protect American workers and industry.
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
Exclusive: Corporate climate watchdog document deems carbon offsets largely ineffective
- Medium Text

- Company Amazon.com Inc Follow
- Company Microsoft Corp Follow
- Company Salesforce Inc Follow
POLICING THE QUALITY
Sign up here.
Reporting by Virginia Furness in London; Editing by Greg Roumeliotis and David Gregorio
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Sustainability Chevron

UAW trails in early unionization vote counting at Alabama Mercedes factory
The outcome of a vote on Friday by workers at a Mercedes-Benz factory in Alabama will be a key referendum on whether the United Auto Workers can maintain momentum in the historically anti-union South, but the union trails in early voting.

- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
United Airlines says it has regained some privileges that were suspended after problem flights
- Copy Link copied
CHICAGO (AP) — United Airlines said Thursday that federal regulators are letting it resume planning for growth after they imposed restrictions on the airline following a series of flight mishaps earlier this year, including an engine fire and a tire falling off a plane.
United said the Federal Aviation Administration “has allowed us to begin the process of restarting our certification activities, including new aircraft and routes.”
The FAA indicated, however, that it has not made any final decisions from its review of the airline, which began in March.
“The FAA has not approved any expansion of United Airlines’ routes or fleets,” an agency spokesperson said in a statement. The FAA said its review of the airline “is ongoing, and safety will determine the timeline for completing it.”
The FAA is insisting on being present when United personnel make final inspections of new planes that replace older ones.
In a memo to employees, United said the ability to resume planning for growth was “good news,” but it noted that FAA inspectors were still reviewing the airline’s work processes, manuals and facilities.
The FAA increased its oversight of Chicago-based United after a series of flight problems.
In one, a piece of aluminum skin fell off a plane flying from San Francisco to Oregon. Another plane lost a tire after takeoff from San Francisco, and another suffered an engine fire in Houston.
Pilots reported that rudder pedals used to steer on the runway failed after landing in Newark, New Jersey, and another plane rolled off a taxiway in Houston.
The incidents led United CEO Scott Kirby to assure customers the airline was safe.
Kirby said the events were unrelated but they “have our attention and have sharpened our focus.” He said United would review each incident to see if changes were needed in safety training and procedures.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Research: Negotiating Is Unlikely to Jeopardize Your Job Offer
- Einav Hart,
- Julia Bear,
- Zhiying (Bella) Ren

A series of seven studies found that candidates have more power than they assume.
Job seekers worry about negotiating an offer for many reasons, including the worst-case scenario that the offer will be rescinded. Across a series of seven studies, researchers found that these fears are consistently exaggerated: Candidates think they are much more likely to jeopardize a deal than managers report they are. This fear can lead candidates to avoid negotiating altogether. The authors explore two reasons driving this fear and offer research-backed advice on how anxious candidates can approach job negotiations.
Imagine that you just received a job offer for a position you are excited about. Now what? You might consider negotiating for a higher salary, job flexibility, or other benefits , but you’re apprehensive. You can’t help thinking: What if I don’t get what I ask for? Or, in the worst-case scenario, what if the hiring manager decides to withdraw the offer?
- Einav Hart is an assistant professor of management at George Mason University’s Costello College of Business, and a visiting scholar at the Wharton School. Her research interests include conflict management, negotiations, and organizational behavior.
- Julia Bear is a professor of organizational behavior at the College of Business at Stony Brook University (SUNY). Her research interests include the influence of gender on negotiation, as well as understanding gender gaps in organizations more broadly.
- Zhiying (Bella) Ren is a doctoral student at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania. Her research focuses on conversational dynamics in organizations and negotiations.
Partner Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The business plan should clearly and concisely define the mission, val-ues, strategy, measurable objectives, and key results the owner expects. It is important to set aside enough time to formulate the plan. Experts recommend starting the planning pro-cess at least 6 months before initiating a new business.
Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed. Summary. When asked about an opponent's plan for their impending fight, former world heavyweight champion Mike Tyson ...
Amy Gallo. People make business plans for all sorts of reasons — to attract funding, evaluate future growth, build partnerships, or guide development. Unfortunately, the vast majority of these ...
Typically, business planning has been analyzed as the single act of writing a business plan (e.g. Honig and Karlsson, 2004).However, business planning is made up of a variety of activities (Gruber, 2007), which entrepreneurs may utilize as a whole, or simply choose parts of the business planning process.It is worth noting that these specific activities are not mutually exclusive with lean ...
A Way Forward for Small Businesses. Summary. Small businesses with fewer than 500 employees account for 48% of American jobs and 43.5% of GDP, and they are facing an existential threat in the wake ...
Writing business plans is often the first step for entrepreneurs in developing new venture ideas. Trade press publications support their value and include templates or even software for crafting the business plan. ... (1997) "How to Write a Great Business Plan." Harvard Business Review 75(4), 99-110. Shane, S. and Delmar, F. (2004) "Planning ...
Cohn and Schwartz 7 outline typical components of a business plan in their review on the subject for a physician leadership audience. The table compares the components of a learning plan to a business plan and provides an example of how the process might play out. Although the components are presented in a numerical order, many of these may be ...
The Journal of Business Research aims to publish research that is rigorous, relevant, and potentially impactful. Recognizing the intricate relationships between the many areas of business activity, JBR examines a wide variety of business decision contexts, processes and activities, developing …. View full aims & scope.
Overview For the purposes of this special issue, we define strategic planning as a 'deliberative, disciplined effort to produce fundamental decisions and actions that shape and guide what an organization (or other entity) is, what it does, and why' (Bryson Citation 2011, 7-9).Strategic planning that fits this definition is an increasingly common practice in governments around the world ...
We focused on articles published in journals classified by the Social Sciences Citation Index because these journals are international in nature and use strict peer-review processes to enhance the quality of their articles (Walker and Andrews 2015). We included articles that mentioned "strategic planning" in the title or abstract.
Here are the key elements of a good business plan: Executive Summary: An executive summary gives a clear picture of the strategies and goals of your business right at the outset. Though its value is often understated, it can be extremely helpful in creating the readers' first impression of your business.
Strategic planning provides the structure to make day-to-day decisions that follow a larger vision, creates a direction for your practice, and maximizes your options for influencing your environment. In oncology practice, where dramatic changes in reimbursement, technology, and the marketplace are just a few of the driving forces, "the future ...
This article presents an approach to conceptualizing, planning, and monitoring project value and the risks to it. The approach does not solve all of the problems in the preceding paragraph, but it does address several—specifically, improving project definition and planning, clarifying the implications of project goals, including appropriate activities at appropriate times in the project ...
Informed by past JAMS editorials, four authors debated and selected keywords relevant to the three principles. 1 We used this curated set of keywords to identify and select articles published in the six leading marketing journals listed in the FT 50 journal ranking. 2 An initial search and article extraction performed on Scopus (www.scopus.com ...
Business plan competitions (BPCs) give nascent entrepreneurs the chance to present their business ideas to an industry and investment peer group tasked with judging each project and picking the most viable one (Overall et al., 2018).Winners are awarded various prizes (McGowan & Cooper, 2008).The purpose of BPCs is to stimulate new entrepreneurial activity and support novel entrepreneurial ...
To find articles on topics in Business Plans, use a resource from the Business Management page. It is possible to begin with a database such as Business Source Complete. In the first search box type "business plan" and in the second search box type sample. ... Scholarly/Peer Reviewed Journals (JAMA, Science, etc.) Intended for a general audience.
Business Source Ultimate works for your students like a solid business plan - it offers an unprecedented wealth of peer-reviewed, full-text journals and other resources that provide historical information and current trends in business that spark discussion on future developments and changes in the business world.
Coupling Strategy to Operating Plans. Operations strategy Magazine Article. John M. Hobbs. Donald F. Heany. In recent years a growing number of companies have expended considerable amounts of time ...
Business plans are found in trade/professional journals (as opposed to scholarly/peer-reviewed journals, which are more likely to present research studies). You can search the ABI/INFORM Collection or Business Source Complete databases and limit your results to articles from Trade Publications.
J. Edward Moreno is a business reporter at The Times. More about J. Edward Moreno A version of this article appears in print on , Section B , Page 1 of the New York edition with the headline: Why ...
Following an in-depth review by the United States Trade Representative, President Biden is taking action to protect American workers and American companies from China's unfair trade practices.
Velan Studios has secured new contracts that will keep the video game company from laying off as many workers as it had anticipated. In March, the company filed plans to layoff 46 employees — a ...
Umicore SA, a major supplier to Volkswagen AG, replaced its chief executive and will reassess spending plans for its battery materials business due to the industrywide slowdown in electric vehicle ...
Staff at an influential corporate climate action group whose board announced a plan to allow companies to offset greenhouse gas emissions from their supply chain with carbon credits has now found ...
United Airlines says it can plan for growth again as federal regulators continue their review of the airline's operations. ... unbiased news in all formats and the essential provider of the technology and services vital to the news business. More than half the world's population sees AP journalism every day. The Associated Press.
This article, as an opinion piece, considers the importance of developing a succession plan that can be implemented when a vacancy occurs in school leadership. While succession planning is a common practice within corporations, businesses and governments, schools also have to be thoughtful and prepared for change. ... Harvard Business Review 85 ...
Plan for public authority to gain control of Saint Rose campus gets key backing ... By Luke Nathan - Reporter, Albany Business Review. May 16, 2024. ... except with the prior written permission ...
Job seekers worry about negotiating an offer for many reasons, including the worst-case scenario that the offer will be rescinded. Across a series of seven studies, researchers found that these ...