
Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.

How to Give an Impromptu Speech, with Examples
March 2, 2021 - Dom Barnard
An impromptu speech is when you’re asked to speak in public without prior notice. It can be one of the most terrifying speeches you’ll ever do; standing up in front of a crowd and having to speak for a few minutes without preparation is daunting, even for the most seasoned speakers.
It’s not likely to happen often, however when it does, you don’t want to be caught completely off-guard. Here are a few things to bear in mind if you’re asked to speak at short notice.
Impromptu speech definition
An impromptu speech is given with little or no preparation, yet almost always with some advance knowledge on the topic. This is sometimes referred to as “off the cuff” or “spur of the moment”.
For example, in class, a teacher may ask a student to give a short impromptu speech about a topic that was in the assigned readings. Business meetings may also start with everyone talking briefly about what they have done recently on the project.
In small informal meetings, the audience will interrupt an impromptu speech and ask questions, which helps guide the speech and the information that is presented.
When campaigning, politicians sometimes respond to reporters or voters almost anywhere and at any time.
Comedians are well known for their impromptu replies to hecklers, which are sometimes planned, but usually made up on the spot.
Tips on giving an impromptu speech
If you are about to make an impromptu speech and have a few minutes to prepare, follow these two tips:
1. Make some quick notes
The first thing you should do when asked to speak is to grab a pen and a piece of paper (or napkin – whatever you can find to write on). Jot down a few initial ideas, or even just a few words that you can expand upon during your speech.
If you don’t write anything else, make sure you’ve written down your starting and ending sentences, as these are the most important.
2. Decide on the tone
Next, think about what tone to speak in. This will depend on the type of event you’re at. For example, at a wedding, you would speak informally, and you can have fun with the speech, whereas at a business conference you would speak more formally and stick to a professional tone.

Impromptu speech frameworks
This is when it gets easy. Pick one of these frameworks to use as a structure for your impromptu speech, and you’ll instantly feel more prepared. They’re easy to remember, so you won’t have to write them down – instead write down keywords for each point.
1. The 5 Ws
Useful for when you’re speaking about a person or specific event
Following the 5 Ws provides instant structure to your speech, and you’ll be able to organise your thoughts in an easy-to-follow way. You don’t even need to change the order – starting with ‘who’ gives context to the speech and ending with ‘why’ leaves the audience with the most important, relatable point.
- Who – who is involved in the event or who is attending
- What – what event are you at and what are the common goals?
- Where – where is the event, how did the initiative the event revolves around start?
- When – is the timing of the event important? What does the future hold?
- Why – why is everyone there? Why are you there?
For example, if you’re talking about a fundraising event, you could say who started the charity, what the goals are, where it is heading, when the event is happening, and why it’s important.
2. Diplomatic framework
Useful for formal occasions such as a business conference.
For this impromptu speech, start by talking about the advantages and disadvantages of the subject topic , then end with a conclusion.
This will make your speech informative and enable you to talk for a longer period of time than the 5 Ws. It’s important not to be afraid of silence when using this framework.
Given that there is less room for creativity, you may find you need to pause to think about what you’re going to say next. While you think, you could walk up and down the stage slightly as if you are letting your last point settle, ask if there are any questions, or ask for a glass of water.
These techniques all buy you more time if your mind goes blank and save you (and your audience) from feeling awkward about a prolonged silence.
3. Storytelling
Useful for informal events such as weddings and book launches.
Storytelling is a powerful method of speaking and is an easy way of connecting with the audience . When having to speak when you aren’t prepared, start off small, then medium, and end large. Basically, talk about the event from an individual perspective, then a group or national perspective, and end with the bigger picture.
For example, if you’re asked to give a speech at a wedding , you could talk about when you met the couple and your experiences with them (small), what their relationship and marriage means to the rest of the wedding guests (medium), and end with the future of their relationship and their family legacy.
Practice impromptu speeches
Impromptu speeches, by their nature, are hard to practice for. You don’t know what the topic will be or the type of audience you’ll be facing. However, the more you practice, the better you’ll be when the impromptu situation arises.
We’ve designed an impromptu speaking exercise with the following:
- Speak about what’s on a random slide for 30 seconds each slide
- Feedback on your performance so you can identify areas that need improving
- Audio of the practice session is recorded so that you can listen back and self-evaluate your performance
You’ll practice quick thinking by talking about a series of random slides for 30 seconds each. You’ll be able to give speeches at short notice and answer questions more easily with this brain training.
Examples of an impromptu speech
Here are two examples of impromptu speeches. The videos skip the short preparation time and start when the speaker starts speaking.
Being able to deliver an impromptu speech is an important skill to have and will save you a lot of anxiety when you’re asked to speak at the last minute.
To prepare yourself for the unknown, try an impromptu practice exercise so that your brain is trained to think on the spot. Not only is this an effective way to learn, but it’s also fun!
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact
- Impromptu speaking tips
- Impromptu speech outlines
Impromptu speech outline: 7 formats
How to prepare for an impromptu speech.
By: Susan Dugdale
Using a speech outline to prepare an impromptu speech seems counterintuitive, doesn't it? After all, impromptu means of the moment, spontaneous, without preparation. So, what is an impromptu speech outline?
Quite simply it’s the structure, or format of your speech. It’s how you order your material from the time you open your mouth at the beginning of your speech, until you close it at the end.
An outline doesn’t need to be a written document or put on note cards to be effective. An experienced impromptu speaker will have an assortment of structural patterns memorized. When they’re asked to speak, they’ll mentally flick through them and choose the most appropriate.
Following an outline lessens the possibility of rambling aimlessly off topic. And, given my flibberty gibbet tendencies it's vital! Maybe yours too?☺
What's on this page
Seven structural patterns , each with example impromptu speech outlines and a printable blank outline template to download.
How to use these structural patterns : guidelines for practice
About the printable impromptu speech outlines
How to reframe a topic : examples of openings showing how to adapt a topic.
The patterns are:
- Point, Reason, Example, Point (PREP)
Past, Present, Future
Problem, solution.
- Pros/Cons, Positives/Negatives, For/Against, Advantages/Disadvantages
Cause, Effect, Remedy
- Before/The Event/The Result
Local, National, International

How to use these structural patterns
To become a competent impromptu speaker you need to get familiar with them. So initially just play with them for practice either with a friend or by yourself.
- Get a subject to talk about. (Click for 150 impromptu speaking topics ).
- Choose yourself a pattern to form the body of speech.
- Now go. Open your mouth and speak.
You’ll need an introduction followed by your material organized according to whatever pattern you’ve selected, and then a conclusion.
Keep it simple. You don’t need to try hard to say devastatingly intelligent insightful things. The starting goal is to get used to thinking, then speaking, without a great deal of prior preparation.
This is impromptu speaking, ‘off the cuff’, largely spontaneous. Be honest and where you can, add personal stories. Your own experiences, plus your knowledge of the subject, will establish rapport and credibility. Don’t be afraid to experiment, or 'fail', as that's how you'll learn.
If your content at this stage is trite nonsense and you putter out of ideas too soon, so be it. At the beginning it’s more important to learn to let go of feeling anxious, inadequate and the need for perfection.
Once you’re used to a pattern, and can follow it easily without having to stop and think about which part comes next, you’ll naturally come up with better material.
Along with examples of each impromptu speech outline structure there's a link to a blank printable. There are seven of them: one for each pattern. They are there for you to use as a guide. You'll find the links for them below the example outlines.
Each outline has the same four step format.
The first step is mentally preparing yourself: sorting out your topic, considering your audience and working out what tone best fits with them, as well as your speech purpose.
The second step covers preparing the introduction, the third, the body, and the fourth and final step, the conclusion.
Your chosen structural pattern is the body
The third step, the body of your speech, holds the specific pattern you’re working with. It’s this step, the body, you’ll want to focus on first when you’re practicing. After you’ve set your topic allow yourself a few minutes to think it through (or make notes) using the pattern headings as a guide.
Once you feel comfortable with the body, you’ll find the openings and conclusions become much easier.
Getting the time and content balance right
The overall length of your speech or the time you take to deliver it is, to a large part, determined by how much information you put into the body. Obviously one or two main points and their supporting material will take less time than three or four.
( Practice will help you confidently and reliably get the balance of time to content right. Click the link for examples of one minute speeches prepared using the Point-Reason-Example-Point (PREP) pattern. They'll give you an idea of what's required.)
Practice, practice, and then do it some more
You don’t need to follow each of the four steps of the outline slavishly. However, to use that old cliché, before you can run, you need to know how to walk. So before giving yourself permission to try to improvise and dazzle publicly, ground yourself in structure. Give yourself a solid baseline to work from.
There’s no secret behind becoming more confident and competent reasonably quickly. It’s practice. Lots of it.
Time and record yourself. Play it back and listen carefully.
Is there a good opening? Have you followed the pattern you chose in the body of the speech? Is it clear? Have you got clean transitions between each part of your speech and the one following it? Is there a strong ending? And are the words you’ve chosen, as well as the way you use them, right for your subject, the purpose of the speech and your intended audience?
And lastly, learn one pattern well before you work with another.
Effective impromptu speech activities
If you teach a public speaking or communication class or lead a public speaking group, here's a comprehensive bundle of 17 proven fun and effective impromptu speech activities , complete with full guidelines and printables. They ease, rather than jettison, students into impromptu speaking one step at a time.

How to reframe a topic
Sometimes when you're asked to speak on a topic you'll find yourself needing to modify it before going ahead.
Or maybe you want confirmation that you've understood what you're being asked to speak about.
Here are examples of three ways to reframe the topic as part of your opening. They are particularly useful for Question and Answer sessions.
Add them to your practice too.
1. Give the topic a scope. This establishes what you're prepared to cover.
For example: Thanks. That’s a great question. I am happy to share what has happened since I joined the organization in 2020.
Or: Thanks, that’s a great, and very big question. I don’t have time right now to cover all aspects of it. So here’s the first part. If anybody would like me to follow up with the second and third, please see me later and we’ll make a time.
2. Summarize and ask for confirmation. Use this technique to make sure you’ve understood what’s being asked of you before you answer.
Example: Thank you for your question. It's an important one and I want to make sure I’ve understood it correctly before answering. You want to know why we’re not mobilizing the Defense Force to clear protesters from the streets, is that right?
3. Redirecting, reshaping the question or angle, before responding . This can be useful when you want to give a bigger picture, or establish context - something the original question didn't allow for.
Example: You’ve asked about using the Defense Force to clear the streets. Let’s consider the precedents for that: the 1951 Waterfront Dispute, Bastion Point, 1978, and the anti-Springbok rugby tour protest in 1981. What have they taught us?
7 impromptu speech outline patterns
Please note, these examples are not complete speech outlines. In most instances they don't include the opening or the conclusion. What they do is illustrate seven ways to organize material in the body of the speech. And some of the examples are more fleshed out than others.
PREP: Point, Reason, Example, Point
PREP is an acronym for: Point, Reason, Example, Point. The pattern adapts well to most situations.
Here are two PREP impromptu speech outline examples: one for a social setting and one for business or workplace audiences. You can also see it in action on this page of one minute speech topics where I've used it in three sample one minute speech outlines.
PREP impromptu speech outline: workplace
Topic: Cameras off during a virtual team meeting
Point: Human Resources are reporting numerous requests from employees to be allowed to leave their cameras off during routine virtual (zoom) meetings.
Reason: The reason most frequently given is fatigue due to strain
Examples: It is hard to:
- maintain focus while looking at a grid of faces for the length of an entire meeting,
- see yourself on camera and NOT respond to it,
- be physically constrained in a small space in order to remain on camera,
- arrange life so it doesn’t intrude in the form of kittens, babies or anything else while on camera,
- have your colleagues in your home without having issued the invitation yourself.
Point: And that’s why we’ve asked Human Resources to develop a set of guidelines to cover when cameras should be on, and when they can be turned off. If you have any suggestions or points you’d like them to consider, please get them by Friday.
For more:
- Bailenson, J. N. (2021). Nonverbal Overload: A Theoretical Argument for the Causes of Zoom Fatigue . Technology, Mind, and Behavior, 2(1).
- Should We Require Students to Turn Their Cameras On in the Zoom Classroom? Anna Lännström, Stonehill College. Published by Wabash Center, 2020
PREP impromptu speech outline example: social
A toast to acknowledge friend’s engagement
Point: It’s a joy to join you celebrating Ryan and Mary’s engagement.
Reason(s): There’s dozens of reasons for my being pleased to be here. We haven’t got time for them all. So here’s three. The first goes back a long way to when we were ten years old. I’m never going going to get married, he said. Thanks to Mary, look at you now! I am delighted you have to eat those words. The second reason is quite selfish. At least the field is cleared now because he’s well and truly spoken for. Hi ya singletons out there! And the third and most important is because I’ve never seen Ryan quite so deliriously crazy happy, ever, in all the years I’ve known him.
Example(s): This is the man who has spent all his weekends for last year renovating the house they share. You know it’s got to be the real thing when unclogging drains, getting rid of rat nests and replacing rotten window frames is better than time out with me and the boys. When you add making significant positive changes to his eating and drinking habits, throw in running a kilometer or two or three or more, several times a week, it’s proof. You’ve got be happy to do any of that!
Point: Which in turn, makes me happy too. Here's to Ryan and Mary!
Download PREP impromptu speech outline
Click the link to download a printable pdf file to use: PREP impromptu speech outline

Use this pattern if you want apply a time line treatment to a subject.
Topic: In your experience what's an effective way of getting children to eat vegetables?
In the past:
When I was a child not eating whatever was served was not an option. It didn’t matter if it was something dreaded like cauliflower, broccoli or spinach. It was on the plate. Therefore it needed to be chewed and swallowed. If it wasn’t you were in for a long sit at the table. Because both you and the plate of food remained in place until the plate was cleared. This as a technique was a failure. It built resentment rather than a love of vegetables.
That kind of stand off would not happen nowadays. I have more tolerance than my parents for children whose taste buds do not thrill to strong tasting vegetables. The only thing I ask of my kids, is that they try a little of each new one when it is served. If they don’t like it, they can put it to one side. Alongside that, we use vegetables as snacks, sneak them into purees and sauces, get the kids involved in choosing and cooking them, and set an example by eating copious quantities of them ourselves.
Our diets are changing. They are becoming increasingly plant based. Vegetables are no longer an accompaniment, an after-thought. Instead they’re center plate – up front and proud.
Perhaps the infamous battle over vegetables will disappear entirely. It’s my hope that through showing greater tolerance of our children’s preferences and by being more creative with how we introduce them into their diets, that the issue will simply cease to be one.
Vive la broccoli!
Topic: What are the most popular and enduring toys for children?
Past : Toys that sold well: Teddy bears, named after Theodore Roosevelt 1902, yo-yos – 1928, Silly Putty, 1955, GI Joe – dolls for boys, 1960s, including two that have kept right on selling;
Present: Lego from Denmark, 1932, and Barbie from USA, 1959
Future : More Lego, more Barbies who are more diverse, more skin types and shapes. Both seem set for along time yet.
Download Past, Present, Future outline
Click the link to download a printable pdf file to use: Past, Present, Future impromptu speech outline

This is a simple two part pattern: here’s the problem. Now here’s the solution.
Example: The problem is congestion on our main city roads during peak hours.
The solution is to:
- reroute heavy vehicles over those hours
- look carefully at the current design of the roundabouts, on and off ramps and laybys and update them if necessary
- adjust the speed limit
Example: The problem is maintaining a work routine while working from home
- make yourself a dedicated work space.
- set yourself regular hours for getting up, having breakfast, being at your desk, lunch etc.
- establish clear boundaries around your work time for family and friends. Being in the same room or the next one, doesn’t mean you’re available.
- prioritize your tasks for the day each morning.
Download Problem, Solution outline
Click the link to download a printable pdf file to use: Problem, Solution impromptu speech outline

Pros and Cons, Positives and Negatives
This is a useful beginning point toward answering the classic ‘what shall I do?’ dilemmas.
Setting out the pros and cons * of a situation gives us an overview, which we can then use to help make a rational, considered decision.
* 16th century: from Latin prō for + con, from contrā against
Dilemma: Whether or not to go to university
- New experiences, new people, broadens outlook
- Builds networking opportunities, long term friendships, & professional relationships
- After graduation enter workforce at different level – a leg up because core competencies already established
- Scholarships available
- Leadership and extension activities/clubs available
- High levels of personal debt
- Difficult to sustain oneself mentally, physically and financially without support
- Doesn’t guarantee a job on graduation
- Doesn’t train you for a specific vocation
- Doesn’t automatically mean entry into higher paying job
Dilemma: Whether or not to buy cheap or fast fashion
- Affordable – instantly gratifying
- Up to the minute clothing – democratization of fashion – not just for elite rich
- Can follow the trend – included rather than excluded on price
- Can change mind and buy more if don’t like what you have – not going to cause you hardship
- Profitable for retailers and manufacturers
- pollution: people throw out their clothes which then enter land fills
- waste: breeds throwaway mentality – chuck rather than mend
- loss of skills: how to mend clothing: sew on buttons, fix a fallen hem, patch a rip etc.
- exploitation of woman and children in 3rd world countries: low wages, and unsafe workplaces
For more: Fast Fashion by Adam Hayes, April 2021, investopedia.com
Download Pros and Cons outline
Click the link to download a printable pdf file to use: Pros and Cons impromptu speech outline

This is a three-part problem solving pattern.
- What is the cause of something?
- What is its effect?
- And what is the remedy?
Topic: Public speaking anxiety
Cause(s) of public speaking anxiety:
- feeling self conscious in front of others
- fearing repeat of past poor experiences
- fear of being judged
- fearing not being as good as you’d like to be, or as good as others
- breathing poorly which doesn’t support the voice
- becoming overwhelmed by symptoms of fear: shaking limbs, quivering voice, racing heart beat, forgetting what had been practiced
- gabbling through speech at break neck speed
- becomes a cycle which intensifies each time a person has to speak in public
- limits personal potential in many ways: at work and socially
- take a public speaking course, join a public speaking club
- practice a great deal, get good support and practical feedback you can use
- and take every opportunity to speak in front of others as it will lessen the fear.
Topic: Procrastination
Cause(s) of procrastination:
- boredom: not being interested in the task that needs completing
- fear of failure: thinking the task will prove too difficult - would rather not begin it, than risk failure, perfectionism
- unable to prioritize what needs to be done against what isn’t so urgent
- overwhelmed: too many things to do, and too little energy
Effect(s) of procrastination:
- pressure: rushing to catch up on what should have been done which leads to poor decision making
- failure: letting oneself, friends, family and workmates down, compromised work standards, reputation
- losing time, opportunities, limiting your career options
- escalating low self-esteem issues and health risks
- Create incremental to-do lists – a bit at a time rather than one huge overwhelming piece of work.
- Create a stimulating work-place for yourself – surround yourself with what you genuinely like to see.
- Time-line your work realistically - what needs to happen. today, tomorrow and the next day to arrive at the due date with the work completed to your satisfaction.
- Get rid of the temptations you know you are distracted by. Put your phone on mute. Remove bookmarked sites.
- Find a mentor, someone you admire and who will hold you to account.
Download Cause, Effect, Remedy outline
Click the link to download a printable pdf file to use: Cause, Effect, Remedy impromptu speech outline

Before, The Event, The Result
This three-part pattern is a time line centered around an event. The result of event (eg. a natural disaster or a personal or societal change, large or small) profoundly changes what came before it. Sometimes the end result is much better, and sometimes far worse.
It’s a pattern much loved by advertisers who imply that the event (the purchase and use of whatever product or service they are selling) will result in whatever is desired: health, wealth, beauty, popularity, longevity, peace, love, intelligence... It's the classic Before and After format.
Topic: Covid-19 - its impact on the tourism industry in NZ
Total annual tourism expenditure had increased by almost $15 billion, or 55%, in the seven years prior to 2020.
- Tourism was New Zealand’s biggest export industry, contributing 20.1% of total exports.
- Tourism generated a direct annual contribution to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of $16.4 billion, or 5.5%, and a further indirect contribution of $11.3 billion, another 3.8% of New Zealand’s total GDP.
Then along came Covid–19. The borders were closed in an effort to keep it out for as long as possible. Good for the population: fewer deaths and hospitalizations compared to other first world countries: USA, UK, Australia but not so good for tourism.
The result:
- total tourism expenditure was $26.1 billion, a decrease of 37.3 percent ($15.6 billion) from the previous year.
- international tourism’s overall contribution to New Zealand’s total exports of goods and services fell to 2.1 percent from 20.0 percent
- tourism generated a direct contribution to GDP of $8.5 billion, or 2.9 percent, a decrease of 47.5 percent ($7.7 billion), or 2.6 percentage points
Reference: https://www.tia.org.nz/about-the-industry/quick-facts-and-figures/
Here’s a feel-good-hard-work-pays-off story using the format, the sort you might hear on your local TV or radio station.
Topic: the house makeover
Before the makeover:
- dark and dingy – very few windows, dated décor
- very poor heat retention – no insulation
- no outdoor – indoor flow
- small poky kitchen with limited storage
- one bathroom – not adjacent to either living areas or bedrooms
The Event: the makeover of the worst house in the best street, a perfect project for husband (builder) and wife (interior decorator), 12 month time line, carefully planned
The Result:
- jump in value of property
- a house which is a pleasure to live in, fabulous garden, everybody is happy, reporters come calling for house and garden magazine before and after spreads☺
- an inspirational example of talent plus effort
Download Before, The Event, The Result outline
Click the link to download a printable pdf file to use: Before, The Event, The Result impromptu speech outline

This structure is excellent for comparisons and overviews spanning spatial areas.
Topic: Deaths from Covid-19 in New Zealand as at 22nd February 2022
Local: none
National: 56
International: 5,905,942
Reference: Google News - Covid 19 map - New Zealand
Topic: Who follows the news? A survey of 38 countries, 2018
Local news : Global median = 78%. 78% of respondents are more likely to follow the news if in own area and own country.
National news : Global median = 86%. 86% of respondents are more likely to follow if the news is about own country.
International news : Global median = 57%. Comparatively significantly less of the respondents are likely to follow the news. That changes with the amount of education a person has. If they have more education, they are more likely to follow the news.
Reference: Publics around the world follow national and local news more closely than international : Pew Research Center report, 2018
Download Local, National, International outline
Click the link to download a printable pdf file to use: Local, National, International impromptu speech outline

speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Communication Skills
- Public Speaking
How to Give a Great Impromptu Speech
Last Updated: March 19, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Lynn Kirkham . Lynn Kirkham is a Professional Public Speaker and Founder of Yes You Can Speak, a San Francisco Bay Area-based public speaking educational business empowering thousands of professionals to take command of whatever stage they've been given - from job interviews, boardroom talks to TEDx and large conference platforms. Lynn was chosen as the official TEDx Berkeley speaker coach for the last four years and has worked with executives at Google, Facebook, Intuit, Genentech, Intel, VMware, and others. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 407,181 times.
Most speeches are the result of careful planning, revision and practice. There may be times, however, when a situation demands that you give an impromptu speech with little or no time to prepare. When you find yourself in an unexpected public speaking scenario, you’ll be improvising what you say, which means you’ll have to be able to think on your feet. Following a basic structure, pacing yourself and staying composed will help you deliver an oration you can be proud of, or at least survive with minimal embarrassment.
Setting Up an Unexpected Speech

- Most of the time when you’re giving an impromptu speech, you’ll be singled out to say a few words on the spot. Since you’ll only have a few moments, preparing yourself is more about getting yourself in the right state of mind than it is knowing exactly what you’re going to say.
- If you really need to milk it, you can buy yourself some extra time by shaking hands, exchanging pleasantries or adjusting the microphone stand before speaking.

- Assume that everyone around you wants to see you succeed. This will help put you at ease. Expecting yourself to fail will only destroy your composure and make you more fearful of your audience.
- Confront the reality of your situation to avoid being blindsided by panic. Accept that you have to give a speech and then focus all your resources on giving a good one.

- Oftentimes, the more confident you make yourself appear, the more confident you’ll feel.
- Relax! Speaking in front of a crowd is not that big a deal. Even if you make a mistake, it’s not the end of the world.

- Don’t just jump right into the main idea of your speech. Test the waters by getting used to speaking and sharing a little about yourself first.
Delivering an Effective Speech

- Use simple sentences that follow a logical progression and enunciate your words carefully to keep yourself from getting tongue-tied.
- Slowing yourself down a little will give your mind time to catch up and formulate new ideas.

- Two minutes will fly by once you start speaking. Despite your reservations about being put on the spot, you may actually find it harder to give a short speech than a long one.

- A good way to give your speech a solid beginning, middle and end is to present details chronologically. For example start with “when I first became friends with John, he…”, follow that up with “now that we’re coworkers, we have more fun than ever…” and conclude with “I have no doubt that the future of our friendship will be just as entertaining.”
- When describing personal experiences, avoid sharing opinions on irrelevant controversial subjects.

- Humor is a great icebreaker and also makes it easier to hold your audience’s attention.
- Be sure any jokes you make are suitable for the age and demographic of your audience, as well as the occasion itself.
Ending on a High Note

- As with the rest of your speech, keep your conclusion brief. It’s alright to sign off with a simple “thank you for your time” or “let’s hear it for the newlyweds.”

- If you’re planning on making a specific request or appeal, as for a business conference, the end of your speech is the proper time to do it.
- The conclusion is the perfect occasion to come out with something especially heartfelt. Emotions will run high and the crowd will be moved by your sentiments.

- You don’t have to thank every important figure at the event individually. A general expression of gratitude is all that’s needed.
- Be clear who you’re supposed to hand the microphone or floor off to so that you don’t end your speech by looking around in confusion. [11] X Research source

- Impromptu speeches are mostly appraised by the willingness of the speaker to rise to the occasion. There’s no sense in being too critical of your performance since you’ll have had no time to work on it beforehand.
Expert Q&A

- Practice for unexpected speaking scenarios by volunteering to give impromptu speeches at casual events. Thanks Helpful 16 Not Helpful 2
- If you're using a microphone, stay within optimal range for your voice to be amplified. Don't move the microphone too close or too far away from your mouth. Thanks Helpful 14 Not Helpful 2
- While brainstorming, quickly come up with three or four main points to cover. Thanks Helpful 18 Not Helpful 4

- Steer clear of subjects you don't know much about. Thanks Helpful 13 Not Helpful 2
- Be careful not to offend your audience. Not only is it bad form and will make your speech be perceived as a failure, it could actually harm your standing among your acquaintances. Thanks Helpful 12 Not Helpful 3
- Take a moment to get your appearance in order before presenting yourself. Steal a quick glance in the mirror or have a trusted friend tell you if your hair is a mess, your shirt is untucked, you have food stuck in your teeth, etc. Thanks Helpful 10 Not Helpful 3
- Don't use generic, pre-written speeches pulled from the internet or oration guidebooks. These can easily come off as stilted and inorganic. Your audience will be able to tell if you're simply going through the motions. Thanks Helpful 9 Not Helpful 4
You Might Also Like

- ↑ Lynn Kirkham. Public Speaking Coach. Expert Interview. 20 November 2019.
- ↑ http://wittcom.com/how-to-develop-confidence-speaking/
- ↑ http://sixminutes.dlugan.com/how-to-impromptu-speech/
- ↑ http://www.askmen.com/money/body_and_mind_150/192b_better_living.html
- ↑ http://www.write-out-loud.com/how-to-use-humor-effectively.html
- ↑ https://speakingwithoutnet.wordpress.com/2012/02/08/ending-on-a-high-note-the-last-sentence/
- ↑ https://www.workingvoices.com/insights/presenting-how-to-react-when-you-make-a-mistake/
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Bridget Harris
Mar 1, 2023
Did this article help you?
Veeraraghavan. Santhanam
Jul 21, 2017
Dharyl Bizu
Mar 27, 2017
Apr 30, 2017
Sameed Ahsan
Jan 28, 2019

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
- Internet , Productivity
15 Best Impromptu Speech Tips (With Examples)
An impromptu speech is often the scariest type of speech you can make because you don’t get to prepare or predetermine what you’re going to say.
The speaker only gets a topic given in the form of a quotation, object, or proverb, and they have to do their best to deliver long-awaited answers.
Impromptu speech doesn’t have to be a full speech on its own. It can be a combination of answers to short quotations or terms provided during interviews or live discussions broadcast on the television.
While you can’t prepare yourself for the impromptu speech since you might not have any idea what you’ll be asked, you can still work on improving your speech and dialog with the help of the tips below!
I have also listed some great examples of impromptu speeches to give you an idea of what I am talking about.
Also Read : Common Weaknesses List & Examples
15 Best Impromptu Speech Tips
These 15 tips will let you know exactly how to behave during an impromptu speech, how to know what and when to say, and how to guide your speech without having too many pauses or breaks in between.
1. Hold it Together (Be Confident)

Impromptu speeches might happen suddenly for many reasons, and often, you might find yourself in front of the audience without even agreeing to it.
No matter what happens during the speech, you have to assure yourself that you’ll be alright. This means you should look up, never avoid eye contact, and breathe deeply. Thinking about something positive is a confidence boost you might need to get through the speech.
2. Focus on Your Audience
When you’re starting your impromptu speech, keep in mind that you’re not going against the audience, yet the audience will be on your side.
Therefore, you should work with the audience and focus your speech around something positive and helpful to the audience.
The goal is to have the audience listen and understand what you’re saying in your impromptu speech but also respond to the things you’re saying. Being confident in front of the audience is one thing you should do, while the other is to focus on the audience and plan a structure you’ll learn in the next tip.
3. Plan a Structure
Even though you might not be prepared for a speech, you will still be able to quickly develop a speech structure in your head as soon as you hear the topic, question, or object you’re given to talk about.
Every speech structure should include three steps and the speech can be structured around almost anything. The most popular structures are:
- Past/present/future
- Cause/effect/remedy
- Before/the event/the result
Think of the structure as a guideline of your speech that will help you get from start to finish as smoothly as possible. Another thing to keep in mind is that you can tell your structure/plan to your audience so they can easily keep up with your speech and know what to expect from it.
Check Out : Professional Development Goal Examples
4. Don’t Ramble
When you come up with a quick structure for your impromptu speech, you’re left to deliver the speech, but one thing you should keep in mind is not to ramble.
Rambling won’t get you anywhere; you’ll feel unease, and your audience won’t follow your speech easily.
Instead, it would help if you stuck to the “less is more” saying, stick to the target, and keep things short and to the point.
With a proper structure plan, you’ll have three key points (no matter what they are), so by splitting your speech into three sections, you’ll be able to judge how much time you should spend talking about each section.
5. Stand Out

Many try to stand out by actions, gestures, and confidence during their impromptu speech. While this is also important, there’s something even more important.
The first and the last sentence are the most memorable. It’s all about the primacy and recency, and most of the audience will most likely remember the first and the last thing you say.
Therefore, starting and finishing with powerful sentences that go well with your given topic and are linked to the message you deliver in the speech is super important as it will have the biggest impact if properly executed.
6. Talk as if You Were Talking to a Friend
Talking in front of the audience can be scary, but without preparation, talking in front of the audience can be even scarier.
Instead of feeling the pressure, feeling uncomfortable, or sweating buckets, you should go on with your impromptu speech as if you were talking to a group of friends.
You don’t have to fake anything, as the audience will see right through it. Instead, be yourself and try to do your best as this will always provide a better result.
Also Read : Best Executive Summary Examples
7. Tell a Relevant Story to Personalize Your Speech
The great thing about impromptu speeches is that they can go in your favor. If you don’t know what to talk about or what to include in your speech, here’s one tip that can help change the way you do your speech.
Try to think of a personal story that will be relevant to the subject of your impromptu speech. This will give you a topic to talk about, you won’t have to do any research or try to come up with facts that you will have to somehow back up, and your audience will love a personal story.
Personal stories are always easier to follow, and they’ll always go down well with any audience. Another piece of advice is to include a personal story in the middle section of your speech, but you can place it somewhere near the beginning of the speech.
8. Pay Attention to Your Voice Tone
When you take care of everything else before the speech and during the speech itself, many speakers forget to think of the voice tone.
There’s not much to overthink and you should speak slowly. Rushing might get you near the end sooner, but your speech won’t be a smooth ride.
Instead, take your time, focus on your breathing, rely on pauses, and have an impact while you deliver the key parts of the speech.
9. Make Sure to Follow Your Speech with Confident Actions

Confident actions are the most powerful body language actions that are not hard to get right, yet you might have to remind yourself to be “presentable”.
Standing tall on both your feet, not slouching over, keeping eye contact, using hand gestures, and avoiding fiddling are some of the things that will make you look confident.
Such confident actions will go well with your speech structure, confident voice tone, and relaxed, personalized speech.
Learning a couple of hand gestures will also put you at ease as you won’t have to wonder what to do with your hands during the speech.
10. Don’t Aim for Perfection
Every speaker wishes for their speech to be perfect, but an impromptu speech is the worst time to expect a perfect speech from yourself.
Therefore, it’s okay to lower the bar and focus on the execution and let the main goal be the smooth flow.
Setting the bar too high will only put you under pressure. In reality, most impromptu speeches happen due to unpredicted reasons, so if you’re put under the spotlight unwillingly and unprepared, the audience will notice, and they’ll understand, so there’s nothing to be afraid of.
Explore : Goal vs Objective – Difference & Examples
11. Practice Beforehand
You might not ever be prepared for a specific impromptu speech, but if you’ve been put into the spotlight once, you can be put under the spotlight again.
What you can do is practice quickly coming up with a speech structure on any given topic. Even if you have only a couple of minutes, you can develop a quick and concise structure and rehearse it in your head or in front of a mirror before you go in front of the audience.
And if you have a couple of hours, you can do a lot of practicing and even go through all these tips and be fully ready, no matter what the audience throws at you.
12. Use Humor to Break the Ice

No matter what the speech is about, you can always add a bit of humor to it. Don’t overdo it, but even a tiny bit of humor can help you make a better connection with your audience, ensure they pay attention to what you’re saying, and that they’re intrigued to hear what’s next.
Followed with a personalized story, you’ll have the audience hooked up until the end of the speech.
Of course, humor should come naturally, and you shouldn’t do it if you feel like you have to force it. But keep in mind that humor can be a great ice breaker, so it’s never a bad idea to keep it as a “secret weapon”.
13. The Meaningful Pause
Unfortunately, you’ll likely feel stuck or not know what to say next during your impromptu speech.
Just the thought of this can paralyze many speakers who are put under the spotlight. However, there’s a quick tip you can use to turn the block in your head into an advantage.
Instead of worrying if your audience noticed, try to “fake” a meaningful pause whenever you’re feeling stuck. During this pause, you can relax, and sooner than you know it, you will think of something.
The best thing is, your audience will never notice that “something’s wrong”, and yet this will also give them a breather and help them continue following your speech.
14. Keep Things Short
Less is more, and during impromptu speeches that can go extremely wrong, it’s better to cut your speech short and yet deliver everything you believe is valuable to the audience.
In other words, it’s better to regret not saying something than to say too much and then be on the spot from where you can’t turn back.
Also, keeping things short will help you stay in control of your impromptu speech and even look a lot more confident during your performance!
15. Try Turning the Impromptu Speech into Q&A Session

Since most impromptu speeches happen unexpectedly, not only will you have to come up with something from nothing, but you’ll also have to give the audience something you’re looking for.
Therefore, depending on the setting of your speech, you might try and turn your impromptu speech into a Q&A session, just like the journalistic interview type.
This will help you think less about what your whole speech will look like and focus on things the audience asks you in pieces.
You’ll still have full control over the answer, so turning a speech into a Q&A session is never a bad idea.
Check Out : Motivational, Funny, & Uplifting Sales Quotes
Best Impromptu Speech Examples
We’ll now take a look at some of the best examples of impromptu speeches to draw inspiration from.
University of Kentucky – Speech and Debate Team
In this impromptu speech example, the speaker only took two minutes for a quick structure plan from where she was put under the spotlight straight away.
A great start with a personalized story that leads straight into the argument. During the argument, clear signs of uncertainty are visible, but the speaker did well by slowing the speech down and taking a couple of very short meaningful pauses.
Prepared with examples which is a bonus, the speaker went through her speech structure with ease. There were moments where the speaker was nervous, but she kept it well together and even seemed confident in her speech at times.
Use gestures, confident actions, eye contact with the audience, and all other positive things you can learn from the tips above.
Closing the speech without any rumbling and getting the point straight across to the audience is a memorable way to end the speech, which is why this is one of many perfect examples of an impromptu speech.
Interesting Post : Popular Digital Marketing Quotes
Chris Gurrie Impromptu Speech Example
This is a short yet educative impromptu speech example where the speaker, Chris Gurrie, gets assigned a random topic by the audience and then guides the viewers of this video on how to plan a perfect impromptu speech structure.
While you would usually have around two minutes for the planning and practice process, Chris does it in about 30 seconds.
Chris starts his impromptu speech with many questions that come from a personalized story that then leads into the main topic of the speech.
What Chris also does is focuses on his audience and he shares his planned structure.
Chris’s impromptu speech is full of valuable information the audience might not have been aware of, which then ties to things on a larger scale. Even though Chris only took 30 seconds to work on the speech plan, he looks very relaxed, confident, with a strong game right until the end of the speech.
What’s interesting enough is that if you didn’t know this was an impromptu speech, you might not even know. Therefore, this is a perfect example of how good you can get at impromptu speeches without knowing the subject beforehand.
Toastmaster International – Impromptu Speaking
If you prefer learning from a video example, this four-minute video is everything you’ll need to gain the confidence to do an impromptu speech.
In this example, you’ll learn opportunities where impromptu speaking might be required. Of course, all of the opportunities are the ones where you don’t have much time to prepare.
However, with the techniques covered in this example video, you’ll learn how to manage last-minute speeches.
Lastly, the video will teach you all the benefits of holding impromptu speeches.
Even though this is an educational-type video, if you have a better look, you would notice that this whole video is less than five minutes long, and it’s scripted in a way to serve as yet another impromptu speech example.
Therefore, as you learn how to perform an impromptu speech, you’re watching an impromptu speech which is a brilliant idea.
Preparing yourself for an impromptu speech is only half the job, so in this video, you also learn how to deliver your impromptu speech with more useful tips.
Impromptu Speech Example: Thesis-Point-Story Format
Planning a structure for your impromptu speech is super important. The thing about the structure is that you can develop any three- or four-step process that will get you through the speech.
This video is a perfect example of a thesis-point-story format where Chris, the speaker, gets assigned a random topic from where he creates the thesis-point structure, shares it with the students, and gets down to the speech itself.
With word play, Chris slowly introduces the topic to the audience, and while he speaks to his students as his friends, he is getting down to the story’s main point.
As Chris goes through his impromptu speech, you can also notice that he asks the audience plenty of questions, and by answering his questions, he is slowly revealing the whole story behind the point of his impromptu speech.
Even though this example might be a bit complicated to understand, you can also learn from Chris’s body language, how he speaks, and how he controls his speech as he’s a highly skilled impromptu speaker.
Angel Anderson – Impromptu Speech Example
In this four-minute impromptu speech example video, Angel Anderson teaches you exactly what impromptu speaking is, how to practice it, and even shows an example full of important tips that can help you develop the same skills.
Angel uses a question-style topic, after which he sets the timer for two minutes for his impromptu speech.
With this type of question, Angel starts his impromptu speech with a personal story that gets interesting, which ensures that the audience follows him.
Not only did Angel answer a question, but he also shared an anecdotal story, and even then, he shared some more information connected to this story.
By far, Angel’s video is not the perfect impromptu speech, but it’s a real example of how easily you can work on your impromptu speech, practice, and learn as you progress.
Of course, this example is ideal for all interview-type impromptu speeches, which can be as hard as the topic-type speeches.
Impromptu speech can seem scary at first, but with plenty of preparation and practice, you will be able to speak on any topic without much preparation.
These 15 tips are everything you’ll need to start, develop, and finish your impromptu speech while being confident both verbally and nonverbally.
On top of that, these five examples show you how impromptu speech is done first-hand. Remember that you shouldn’t aim for perfection, but even tiny improvements are a good step forward to achieving a decent impromptu speech.
Tom loves to write on technology, e-commerce & internet marketing. I started my first e-commerce company in college, designing and selling t-shirts for my campus bar crawl using print-on-demand. Having successfully established multiple 6 & 7-figure e-commerce businesses (in women’s fashion and hiking gear), I think I can share a tip or 2 to help you succeed.
How to Give an Impromptu Speech
No Time to Prepare? Don't Despair
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
An impromptu speech is a speech that you have to make without much or any time to prepare. In life, this can happen when you attend special events, like weddings or celebrations. In school, teachers use impromptu speeches as homework assignments to help you develop communication skills and to help you prepare for those future life surprises.
While this may seem like a cruel trick from a student's point of view, it actually builds confidence and is great preparation for life.
Rarely will you be asked to stand and deliver a speech with no warning and no time to organize your thoughts. This would be unusual in the classroom unless the teacher is attempting to make a point about the importance of preparedness.
At some point in your life, however, you may be asked to speak without notice. There are a few things you can do to avoid panic and embarrassment.
- Grab a pen and a piece of paper. If you have a few moments before your speech is expected to begin, grab a writing utensil and something to write on, whether it's a napkin, envelope, or the back of a receipt you have on hand, and jot down a few thoughts .
- Highlight a few interesting or significant points. Keep in mind, your impromptu speech doesn't have to be long. A little-known fact about effective speeches is that if you start with a good line and then end with a really great punch, the speech will be perceived as a total success. So the beginning and ending markers are critical. The middle portion of your speech should relate to the event you're attending or the class assignment, but if you have to choose one great moment, your ending line is particularly important. If you can walk away gracefully, your speech will be a hit, so keep your big zinger for last.
- Try to memorize key points. If you have time before your speech, create an outline of the major themes or points and commit it to memory with a memorization trick, like an acronym. Don't try to remember the entire speech in detail like this; just remember important points.
- Hijack the topic. There is an old trick that politicians use when they're being interviewed on TV, and once you realize this, you can use it yourself. They think of questions ahead of time (or topics to discuss), prepare some talking points, and talk about those, despite the topic or question they're given. This is a handy trick when you're facing a hard question or asked to discuss a topic with which you're unfamiliar.
- Remember you're in charge of this time. Your goal is to deliver a one-sided conversation, off the cuff, so you are in complete control. Relax and make it your own. If you want to make this a funny story about your pesky little brother who always bothers you during homework time, then do it. Everyone will applaud your effort.
- Feel free to acknowledge that you have not prepared for a speech. If you are speaking in front of friends or family, it may ease your nervousness to express your lack of preparation. This should not be an attempt to garner pity, but rather a way to put yourself and your audience at ease. Then, take a deep breath before you begin speaking. Zone out the audience or choose someone specific to focus on, whichever makes you more comfortable.
- Begin with your introductory sentence, elaborate, then start working your way to your ending sentence. Fill in the middle space with as many points as you can, elaborating on each one as you go. Just concentrate on the zinger you've reserved for the end.
- As you deliver your speech, concentrate on diction and tone. If you are thinking about this, you won't be thinking about the eyes watching you. Your mind can't think about too many things at once, so think about breathing, enunciating your words, and controlling your tone, and you'll maintain more control.
What to Do If You Draw a Blank
If you suddenly lose your train of thought or draw a complete blank, there are a few you can do to keep from panicking.
- Pretend you're pausing on purpose. Walk back and forth slowly, as if you're letting your last point sink in.
- There is always a jokester or friendly person who will stand out in the crowd. Make eye contact and try to draw a response from him or her while you think.
- If you need more time to think, you may want to ask the audience a question. Have a few prepared ahead, like "Do you have any questions," or "Can everyone hear me okay?"
- If you still can't remember what you were going to say, make up a reason to pause the speech. You can say, "I'm sorry, but my throat is very dry. Can I please get a glass of water?" Someone will go to get you a drink, and you will have time to think of two or three points to talk about.
If these tricks don't appeal to you, think of your own. The goal is to have something ready for every possible scenario ahead of time. If you know you may be asked to give an impromptu speech soon, try going through the entire preparation process with a few common speech topics .
When caught off guard, many people can suffer extreme anxiety about speaking off the cuff. That's why the best speakers are always prepared.
- 50 Topics for Impromptu Student Speeches
- Impromptu Speech Activities
- Practice Speaking Skills With Impromptu Speeches
- Memorable Graduation Speech Themes
- Effective Speech Writing
- How to Write a Graduation Speech as Valedictorian
- 5 Tips on How to Write a Speech Essay
- Give a Speech People Remember
- Speech Topics to Meet Oral Communication Standards
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- What Is a Compelling Introduction?
- How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- How to Write a Research Paper That Earns an A
- How to Prepare for an Oral Report
- How to Lead a Book Club Discussion
- Audience Analysis in Speech and Composition

12 effective impromptu speech tips you should use
- Filed under: Featured articles , Public speaking articles , Public speaking tips and tricks , Speaking tips , Speech delivery , Speech preparation
An impromptu speech is something most people are afraid of even more than public speaking . There’s hardly any time to prepare, and, sometimes, this speech must be longer than just a few minutes.
So, what is an impromptu speech? An impromptu speech is a speech which is given without any thorough preparation. It is five- to eight-minute speech with a characteristically short preparation time of a couple of minutes.
This can be frightening, but it’s not the hardest of things. Today, I’ll give you 12 good tips you can use in the future. That said if you want even more information about impromptu speech and public speaking then definitely check out this list of the best public speaking books I have compiled for you.
Table of Contents
12 impromptu speech tips (short version)
Video: 12 effective impromptu speech tips you should use.
Why give an impromptu speech? Here are the reasons:
- The actual speaker is running late or you have to give a speech totally last moment instead of the actual speaker.
- At a meeting , you are unexpectedly asked to give a longer overview of what’s happening.
- You are forced (or decide for yourself) to take part in a discussion (e.g., parents’ meeting).
- A cheering speech at a birthday party or other similar event (e.g., colleague’s birthday).
- An unexpected (or even agreed beforehand) interview .
- You must unexpectedly introduce yourself at an event or talk about your area of activity .
- Unexpected questions during a Q&A session following your presentation.
Remember that the better public speaker you are, the more people will be pointing in your direction, because no-one wants to go out there. So, get ready to be teased, „James, we all know you can do it so well…“
12 impromptu speech tips that will make you shine
1. a good speech has a structure.
There are several speech structures, but I use the one called the FAT system.
- F = Feeling . Express how you feel about the subject of your speech
- A = Anecdote . Tell a story related to it. If it’s funny, even better.
- T = Tie back . Link the story to the subject.
F = Feeling
Share your feelings about the subject. If it makes you sad, show it. If it makes you happy, express it with all your nature.
A = Anecdote
The anecdote doesn’t necessarily mean making a joke. Indeed, if your story is funny and related to the subject, that’s just great. Keep in mind that the make-a-point-tell-a-story approach usually works well.
T = Tieback
When you’re done with your story, keep in mind that now is the time to link it to the subject. For example: if your topic is „Your Favourite Car Brand“ and you told a good story about which bad (or good) cars you’ve come across, now is the time, to sum up, the topic pointing out why you chose a particular car brand.
2. Practice giving a speech
Mark Twain once said, „It usually takes more than three weeks to prepare a good impromptu speech“. In other words, it can be practiced. The more you practice and the more topics you go through, the easier it will be .
You can practice alone or with your friends. One of the ways to do it with your friends is to play a game. Scroll down for instructions!
As a side note, I wrote an article (with 10 effective tips) about how to practice a speech. You can read it here.
3. Go on stage and give speeches whenever you get an opportunity
The more experience you gain, the better you will be able to handle unexpected situations. You’ll also learn how to deal with tricky questions and smarty pants.
Recommended books
How to Deliver a TED Talk: Secrets of the World's Most Inspiring Presentations
Jeremy Donovan
Resonate: Present Visual Stories that Transform Audiences
Nancy Duarte
Confessions of a Public Speaker
Scott Berkun
Talk Like TED: The 9 Public-Speaking Secrets of the World's Top Minds
Carmine Gallo
The Checklist Manifesto: How to Get Things Right
Atul Gawande
The First 20 Hours: How to Learn Anything... Fast!
Josh Kaufman
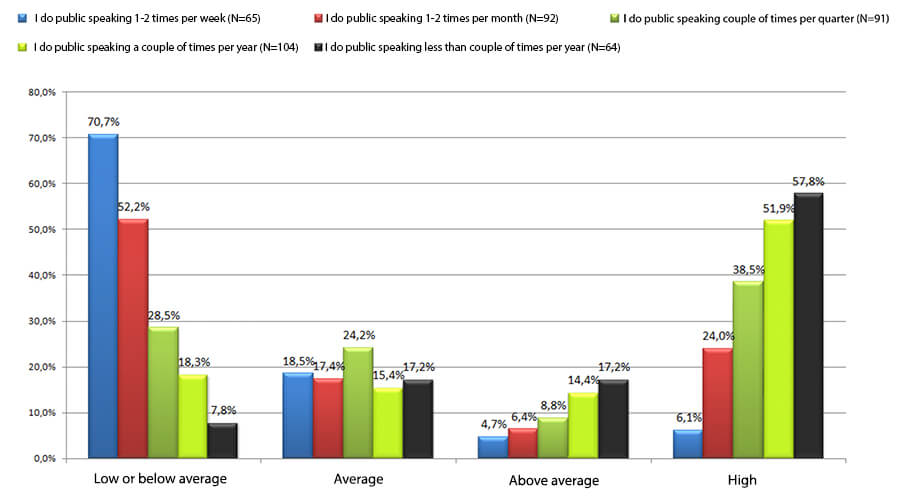
By the way, I did my MA thesis on the fear of public speaking, in which I also studied the way in which the level of the fear of public speaking and the frequency of its occurrence is related. It revealed that the people who do public speaking more often suffer from the fear of public speaking significantly less than those who do it rarely.
Have a look at the figure below:
4. Believe you can do it
If you only focus on the idea of potentially failing, you focus on the wrong thing . You’re not the most important person at the moment of giving a presentation. Your listeners are. Anyway, if you don’t believe in yourself, why should I as a listener? Oftentimes, the audience is your allie , and you should keep that in mind at all times.
Why is the audience your Allie ? Because the better you do, the more they will benefit from your presentation.
5. You could mention it’s an impromptu speech
An impromptu speech is just like any other speech, that is, it’s not a good idea to start your speech with an excuse. If the listeners are aware of the situation anyway, it might be worth mentioning. Do it in a brief and professional manner and avoid futile apologies.
Briefly explain why the speech is improvisation and get to the subject. If you use the above-mentioned FAT structure, it’ll be much easier for you to give a good speech.
6. Don’t forget about humor
For example: if you mention that it’s an impromptu speech, make a joke about the situation . Already today, it would be a good idea to think of a funny story or two about yourself for such occasions.
At the same time, keep in mind that if you’re not particularly good at making jokes , don’t try to overdo it . Equally important, never say „I’m going to tell you a funny story“ because you set the expectations high. Just say that you’re going to tell a story, and if the audience finds it funny, great success!
7. Think of universal introductions or stories to use in the future
Getting started with a story is always a good idea, especially, if it’s a personal one. For example, you can start with a story of how you had to give a speech once and what went wrong.
Sometimes, it may happen that you have to give a speech so unexpectedly that there’s no time whatsoever to think of a story introducing the subject. In this case, after making an introduction, you can make a transition in the form of a joke about yourself.
For example, you could say, „Some of you will wonder how this story is related to my presentation. It’s not, really… I just had to give a speech so unexpectedly that this story was the first thing that sprang to mind. Speaking of the subject… (and you go on with the actual subject)“.
But there’s a lot more to it so I wrote a complete guide on how to make a speech introduction that grabs the attention which you can read here.
8. If you get stuck, pretend it’s a meaningful pause
Remember that one speaker from Ancient Greece once summed up the fundamental truths about public speaking tips:
- Speak clearly to be heard.
- Stand straight to be seen.
- Be quiet to be enjoyable.
Take your time and try to avoid unnecessary voiced sounds during the pause – most people won’t even realize there’s something going on.
9. Customize the topic and make it your statement
Sometimes, it’s the only solution. For example: if I’m unexpectedly asked to talk about maths for 15 minutes, I have to admit this is a subject I don’t know anything about.
So I have a couple of stories about how I wasn’t very good at maths at school and that there’s one thing I’m very good at when it comes to maths. Calculating percentages by cross-multiplying. Then, I’ll be talking about how it really helped me in practice and how the audience could use it.
To sum it up, if the subject is something you don’t know much about, you will adjust it a little and change the focus , talking about it from a perspective you feel more confident about.
10. In relation to your speech, find answers to the following five questions:
- What (or about what)?
For example: if you have to talk about the fact that you’re afraid to speak publicly, your speech could answer the following questions:
- Who are you?
- What have you done to cope with it and what could others learn from it?
- When did you succeed (or fail) in relation to the subject (add a short story here)?
- Where could your tips be used?
- Why is it important at all?
It’s essentially the same as the FAT structure but explained from another angle.
11. Turn your presentation into a Q&A session
If you have no idea what to say in the beginning, go for a Q&A session. For example, your topic is „How to Give a Speech“, but you don’t have any good idea. So you start with something like „Dear all, today, we’ll be talking about how to give a speech. How many of you have given an impromptu speech or done public performances unexpectedly? Yes, Paul, what were the circumstances?“
This way, you’ll get hints from the listeners about what you could talk about, and you can smoothly go over to your speech.
But if you say „Today, we’ll be talking about how to give a speech. First of all, you’ll be able to ask a few questions about what you find most important when it comes to our topic“, the questions asked by the listeners will give you an idea of what you should talk about.
Keep in mind that you have to encourage your listeners as they may be too shy to ask questions. If no-one asks a question, go back to one of the tips above.
12. Don’t blab all the time
To be brief is always a good thing . The longer you talk, the greater the likelihood that your speech becomes somewhat boring , and, as a result, the listeners lose interest.
An impromptu speech developing game you can play with your friends
It’s quite common to play different games in larger or smaller groups. The game I recommend is suitable for groups of all shapes and sizes.
- Beginner : On a piece of paper, each participant puts down a topic they are able to talk about for a minute or two, without preparation.
- Advanced : On a piece of paper, each participant puts down a completely random topic.
- Put all the topics together. Now, in turns, you pick one topic and start talking about it for about a minute or two, without preparation. If you pick the topic written by you, you put it back and pick a new one.
When one participant is finished, the next participant picks a new topic and starts with their speech.
- Other listeners shouldn’t interrupt the speaker during their speech.
- It is advisable to give feedback, especially by the person who has come up with the topic.
How does this game improve giving an impromptu speech?
First, you get used to talking about topics you don’t know anything about at a first glance.
Second, you get a wealth of experience in terms of how to customize a topic. For example: if you pick a topic entitled „My Trip to Spain“, but you’ve never been to Spain, you’ll be talking about „What I Could Do on my Next Trip to Spain“.
Third, you get feedback from other people about how you did. Pretty soon, you’ll discover that you’re actually much better than you think.
Finally, the more you play this game, the more comfortable you will feel in different situations . You will learn from experience, right?
An impromptu speech can be frightening, but it’s not the hardest of things. It’s all in your head, and you can start fixing it now.
Have a look at my 12 impromptu speech tips and think of the situations where you can use one or the other. And then… go on stage. First thing. The more you practice public speaking , the better you get.
Related questions
What is a persuasive speech? The main objective of a persuasive speech is to make your listeners do what you want them to do. For example, „buy my product“, „vote for me“, „believe what I’m talking about“, and so on. ( full article here)
What is the elevator pitch? An elevator pitch is a well-thought, meaningful, and repeatedly practiced brief (about 30-60 seconds long) overview of who you are, what you offer, and how your partner can benefit from it ( full article here ).
What is audience analysis? Audience analysis gives you the opportunity to get as much information about the background of your listeners as possible. Using this information, you can prepare your message so that it builds on the interests, needs, and expectations of your listeners. ( full article here )
Posts about public speaking you may also like

16 secret ways how to speak to a bored audience
One of the many nightmares of public speaking is having a bored audience. It happens to everyone, but it doesn’t make it any less worrisome.

Social anxiety disorder (social phobia) and the stage fear
I’m sometimes asked about what social anxiety disorder (SAD) is and whether it’s the same as social phobia. Since SAD is one of the subtypes

How to Give an Award Acceptance Speech?
You’ve been nominated for an award and now you have to give an acceptance speech. It might be an Academy Award where the whole world
- Tags: Art of public speaking , Effective speaking , Good speech , Impromptu presentation , Impromptu speaking , Impromptu talk , Making a speech , Prepare a speech , Presentation skills tips , Presentation techniques , Speech skills , Speech tips , Writing a speech
Recommended gear

Best Portable Speakers For The Presentations

Best Video Cameras for Public Speakers

Best rresenter remotes for public speakers

Best Portable Thumb Drives And Hard Drives for the Presentations
Who is janek tuttar.
My name is Janek Tuttar , and I am the founder and author of Speak and Conquer website.
I have been teaching public speaking at Estonian Entrepreneurship University of Applied Sciences
Here, I am sharing the wisdom of how to cope in different public speaking situations.
More information about Janek »

Share this post

Hi! My name is Janek Tuttar, and I am the founder and author of SpeakAndConquer.com.
I have been teaching and blogging about public speaking since spring 2007. Here, I am sharing the wisdom of how to cope in different public speaking situations.
Send me an e-mail: [email protected]
LEGAL INFORMATION
This site is owned and operated by Janek Tuttar. SpeakAndConquer.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com.
This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.

Best teleprompters

Best Computer Mice for the Presentations

Best Laptop Backpacks for Public Speakers
- Speech Writing
- Delivery Techniques
- PowerPoint & Visuals
- Speaker Habits
- Speaker Resources
Speech Critiques
- Book Reviews
- Browse Articles
- ALL Articles
- Learn About Us
- About Six Minutes
- Meet Our Authors
- Write for Us
- Advertise With Us
How to Ace the Impromptu Speech
Several readers sent in questions related to impromptu speeches, including Matthias K.:
I’m pretty comfortable when I have days or even weeks to prepare a speech, but I REALLY struggle when I’m asked to speak at a moment’s notice. Do you have any tips for impromptu speaking?
In this article, you’ll find a set of tips that will make you shine the next time you are asked to speak on the spur of the moment.
Impromptu Speech Scenarios
Impromptu speaking may not be as glamorous as prepared speaking, but it is an equally vital skill simply because there are so many scenarios where you find yourself speaking without more than a few moments of preparation. It’s no surprise that “impromptu speaking sessions” are found within Toastmasters meetings , college communications courses, and public speaking seminars.
Consider just a few situations where you find yourself speaking off the cuff:
- The scheduled speaker is unavailable (or late), and you’ve been asked to fill in.
- You are sitting on a panel answering questions from the audience.
- You are fielding questions after your own talk (yes, your Q&A session is impromptu speaking)
- You are being interviewed on television, radio, webinar, or telephone.
- You are invited (at the last moment) to say a few words at a company gathering.
- You are asked to provide a brief status report for your project at a department meeting.
- You are motivated to join the debate at the parent association meeting for your child’s school.
- You decide to give an unplanned toast at an event with family or friends.
It’s also worth noting the irony that the better you are at giving prepared speeches, the more often you will be invited to speak with no time for preparation at all. Your friends and colleagues will recognize your speaking skill, and when they need “someone” to say a few words… you’ll be that someone!
Winning Strategies for Impromptu Speeches
Although you may only have a few seconds to prepare for any particular impromptu situation, you certainly can prepare yourself to be ready when called upon.
Here are a few strategies you can use:
Anticipate situations where you may be called upon to speak. For example, if you are attending an engagement party for a close friend or family member, there’s a reasonable chance that you might be asked to speak. Similarly, if one of your close colleagues is scheduled to speak (e.g. your boss, your peer, or your report), it’s also reasonable to assume that you will find yourself speaking. As you head to the event, do a few mental exercises, trying to guess what you might be asked to speak about, and how you would respond. Even if your guess isn’t accurate, it’s amazing how those prior thoughts will help you think on your feet when you are asked to speak.
Wrap your response around a simple template, or framework. If you practice this a few times, you will find that your mini-speeches are much more polished and coherent. A few easy frameworks include:
- P.R.E.P. (Point. Reason. Example. Point) – Start off by clearly stating your point. Share the primary reason (or reasons, if you have more time). Then, share an example (preferably in story form) where your main point or reason is supported. Finally, conclude by summarizing your central point again. The template works well in many situations, and is easily adapted.
- Issue, Pros vs. Cons, Conclusions – Start off by framing the issue. Talk about the benefits, and then talk about the drawbacks. Conclude with your recommendation.
- 5W – In this pattern, you cover your topic by addressing the Who, What, When, Where, and Why elements. For example, if you’ve been asked to speak briefly about a fundraising initiative, you could talk about [1] who started it, and who is involved now; [2] what the goals are; [3] when it started, and the schedule for the future; [4] where does it take place; and [5] why are you involved. This template works nicely, largely because the “why?” comes last, because this is often the most critical information.
Turn your impromptu session into a Q&A session. In situations where you are asked to fill in when the schedule speaker is absent, it may not be wise to launch into a 45 minute impromptu speech. Even the most accomplished speakers are prone to meander in that situation. Instead, reframe the session as a Q&A session, which breaks it up into a series of very small impromptu speeches that are probably easier for you to answer individually. Plus, the content comes directly from the audience, so you are guaranteed to deliver what they are seeking.
Use personal stories. Storytelling is an essential skill for prepared speaking, but it is equally useful for impromptu speaking as well. Stories are emotional, real, and interesting. If you stick to personal stories, you’ll find that it is much easier to speak (even without preparation) because the events happened to you.
Avoid the tendency to go on, and on, and on. Craft a coherent message, and then be quiet. Rambling on will only weaken your overall speech. If you must fill more time, shift into a Q&A.
Go easy on yourself. We all want to speak perfectly every time, but demanding perfection from yourself in an impromptu speech is setting the bar too high. The audience (probably) recognizes that you’ve been thrown in at the last minute, and they will understand.
Your Turn: What’s Your Opinion?
Do you have any proven strategies for mastering the impromptu speech?
Please share in the comments .
Please share this...
This is one of many public speaking articles featured on Six Minutes . Subscribe to Six Minutes for free to receive future articles.
Image credit: Four Aces by FreeImages.com/B S K ( license )
Add a Comment Cancel reply
E-Mail (hidden)
Subscribe - It's Free!
Similar articles you may like....
- How to Deliver Group Presentations: The Unified Team Approach
- Leading the Perfect Q&A
- How to Prepare for Presenting to Senior Executives
- 10 Phrases Savvy Speakers Never Say
- How to Manage 8 Tough Personas in a Group Discussion
- How to Lead a Discussion Group
Find More Articles Tagged:
21 comments.
Great ideas – and I like the simple structures PREP, I-P&C-C, 5W – quick tools to put structure into your talk 2 minutes before standing up.
The real challenge is closing an impromptu speech – so often the lack of preparation of a good opening leaves it difficult to do a great closing – and you end up with a tepid “well… that’s it… thanks”
Always try to be prepared for the “Impromptu Speech.”
A Police Chief once told me he takes it as a given that when attending Chamber and other events, the emcee will usually say, “And let’s hear a few words from our city’s Top Cop. Come on up here, Chief!”
I like your idea, Andrew, of the Q&A Session. If you don’t know the answer, or just want to involve more people, the answer to the question can be thrown back to the audience.
Thanks for the Post!
I have always been an impromptu speaker. I loose my confidence when I prepare my speech. Which I do well, but at times, I miss out on important issues and also I can’t time my speech
At one point in my career, I was constantly confronted with impromptu speaking situations–the speech literally being planned between chair and podium.
The challenge was how to make the speech coherent and focused with no time to labor over an outline.
One speaker suggested simply picking an object on the way…and using the elements of that object as points for the speech. We might use an object that has an obvious connection with the topic, say a “ball point pen” used for points on communication, but that is not necessary, a shoe or a flower arrangement could be used as well.
So, it begins, “this common shoe tells us everything we need to know about time management…..” –first, like a good shoe, it has to fit you and your distinctive personality… –second, like the sole, it must both protect you from the dynamics of the outside world, and give you traction… –Finally, like the shoe in its totality, you must use it or it cannot fulfill its function no matter how well designed…
This actually works so well, I have used it to create outlines for writing and prepared speeches…a structured brain storming.
God bless and Merry Christmas
hi thanks so much for addressing an issue I had requested for too, only not so articulately.
If it is impromptu it is a not really a speech. It is more you giving your off the cuff thoughts about something. By the very nature of being unprepared you can be prepared for them. But you can learn to be good communicator and share your well organized thoughts about something *whenever* you are asked.
An “impromptu speech” is no different than a coworker or a spouse asking you your opinion about something.
The ‘template’ advice is spot on Andrew. A well structured speech will always sound professional. To what you’ve said here I’d add that when time to prepare is short, make best use of it by working out the opening (an arresting attention getter) and the close (something they’ll always remember). Somehow you’ll be able to speak your way from one to the other!
excellent suggestion! Will give it a go 🙂
I always enjoy your write ups. Impromptu speaking is the monster in many people’s nightmares. . . Your suggestions are very valid.
Nice! I remember my speech teacher getting me to use the 5W’s when doing impromptu speeches years ago. I’ve never been as strong with impromptu side of things in comparison to prepared speeches, so thanks for sharing your excellent strategies! Will use.
I really have a hard time getting my confidence. I thank you for sharing this knowledge and may help any body who wants to be a good public speaker. May God Bless You!
hi your articles are really great.they will be helpful during the public speaking competitions
I have an impromptu speaking competition coming up. I get any topic in the world from the adjudicator and have 5 minutes of preparation. I must speak for at least 2 minutes. I had a practice round yesterday, but it went really badly. My topic was ‘Know Your Limits’ and it came out a bit disastrous. Do you have a fully formed plan or something I could follow in regards to any topic that could come up? Thank you.
Hey Ashley, I realize you posted your comment months ago, but I also have an impromptu speaking competition coming up in days, just like yours. You must have finished your competition by now, and I was wondering whether you have any tips you could give me? I have the same problem you do. Thanks.
If you start with an intro Attention Getter – grab your audience Thesis – what is my topic Preview of Points – then talk about each point specifically then conclude with Review – what did i just talk about Thesis – what was the topic and a Tieback to the attention getter
This helps my students succeed. At least a minute of talking with an introduction and conclusion and a minute on each point, you have a minimum of a 4 minute speech! Just think, process and come up with points about your topic and you will do great!
I find the articles very interesting and informative.
I SOMETIMES EXPERIENCE SOME CHALLENGES WHEN REQUESTED TO GIVE AN IMPROMPTU SPEECH. I WOULD BE GLAD TO SUBSCRIBE SO THAT I CAN EQUIP MYSELF WITH SKILLS OF PUBLIC SPEAKING.
IMPROMPTU 1 Pick topic from here and now–I usually talk about talking impromptu 2 Quickly pick ending to guide your talk–I usually invite them to give an impromptu talk soon.
Love these tips. Spot on!
I have developed this website for practicing impromptu speech with an active time. Please feel free to use it impromptuspeech.net
This was helpful for a project in working on for the next few days
Recent Tweets
How to Ace the Impromptu Speech – https://t.co/lDPj5JHbRB — Rainmakers (@RainmakersIndy) Oct 28th, 2015
#CentralDelhiTM #TableTopicsContest TIPS to Ace the Impromptu Speech https://t.co/b6mgrbfoP3 by @6minutes — @CentralDelhiTM Mar 8th, 2016
Leaders: You are always on stage. Be ready! https://t.co/mFOuZ4n1Nw — @KurtGreene Jun 13th, 2016
#WednesdayWisdom Good article by @6minutes about impromptu speeches. Be confident off the cuff! https://t.co/zeLiJ8jY07 — PitchVantage (@pitchvantage) Jun 15th, 2016
How to Ace the Impromptu Speech https://t.co/vEKxFQcUED by @6minutes — @MarysReflection Oct 20th, 2016
https://t.co/pE1a9QxnEL この記事のP.R.E.P. (Point. Reason. Example. Point)の部分をPPAP的なノリで参考にしようと思った(意味不) — @mikueigo Nov 2nd, 2016
very helpful https://t.co/aPNHorseHb — @jonmarc_gordon Feb 21st, 2017
How to Ace the Impromptu Speech https://t.co/6yAangvFFJ by @6minutes #publicspeaking #coaching — @Seb_n_CHS Oct 17th, 2017
https://t.co/f9ZHdZCGH6 — @SpeakClearComm Jul 27th, 2018
Love the idea of using an (ironically-named) acronym – PREP – to give structure to impromptu speeches. @6minutes, d… https://t.co/EDuBwglGL9 — @speakupcamb Jul 31st, 2018
4 Blog Links
How to Ace the Short, Impromptu Speech | EFL Tips - Resources for EFL Students — Jan 19th, 2012
Impromptu speaking – strategies for winging it « Speak well, do well! — May 10th, 2012
Useful resources to help you get ready for the contests « Toast of CIBC Toastmasters Blog — Sep 12th, 2012
Donn King's Corner » Blog Archive » Prepare to speak without preparation — Nov 12th, 2012
Featured Articles
- Majora Carter (TED, 2006) Energy, Passion, Speaking Rate
- Hans Rosling (TED, 2006) 6 Techniques to Present Data
- J.A. Gamache (Toastmasters, 2007) Gestures, Prop, Writing
- Steve Jobs (Stanford, 2005) Figures of speech, rule of three
- Al Gore (TED, 2006) Humor, audience interaction
- Dick Hardt (OSCON, 2005) Lessig Method of Presentation
Books We Recommend
Six Minutes Copyright © 2007-2022 All Rights Reserved.
Read our permissions policy , privacy policy , or disclosure policy .
Comments? Questions? Contact us .
- Delivery Techniques →
Speaking Off-the-Cuff: How to Tackle an Impromptu Speech

Imagine you are at your best friend’s wedding and you are sitting at the table just enjoying the food and company.
You’re relaxed, and perhaps a little buzzed.
Then the emcee of the event (being weak at impromptu speaking) calls you.
“Why don’t you share a few words about your best friend, John?”
You look around. There are 30 tables and each table has 10 guests. 300 people. Oh oh.
Your heart starts pounding fast, you begin sweating and you start thinking of an excuse. But everyone starts clapping and cheering you on.
The emcee walks to you and passes you the microphone. The spotlight is on you.
What would you do?
Do you run away? Or do you take the mic and possibly embarrass yourself?
Wouldn’t you wish you had learnt to do impromptu speaking ?

Why Impromptu Speaking?
Impromptu speaking is an essential skill because there are so many situations where you may be called up to speak without preparation.
Here are some examples. Try to see if any of these sounds familiar:
- You get asked to give a brief status report for your project during a department meeting.
- Your colleague refers to you for input in the middle of a presentation, or worse, asks you to join him to present.
- The interviewer asks you a question that catches you off guard during a job interview.
- You get interviewed by a reporter on TV, radio, podcast or telephone.
- You are sitting on a panel answering questions you did not prepare.
- You are fielding questions during the Q&A session after your own presentation. (Yes, this is impromptu speaking)
- You get asked to fill in for a late or unavailable scheduled speaker.
- You join a debate at your child’s schools’ parents association meeting.
- You are invited to “say a few words” at a company’s event.
- Introducing yourself at a networking event.
- You decided to give a toast at a friend or family member’s wedding.
- You have to inspire your team when morale is low.
- You want to acknowledge a departing employee with a goodbye speech.
- You get chosen to share what you have learnt in class or at a workshop.
These situations happen more often than you think.
Everyone can give a prepared speech well, but it is how you handle yourself when you are the least prepared, that demonstrates your confidence and leadership ability.
So what do you do when you find yourself in any of these situations?

Last Minute Tips for Speaking Off-the-Cuff
Anticipate such situations.
Before you land yourself in the spotlight , try to anticipate situations where you may be called up to speak.
For example, when you attend a training workshop, the trainer very likely will ask participants to share what they have learnt.
Similarly, when you attend a close friend’s wedding , you may be tempted to give a toast to your buddy.
Or when your team member is presenting a project, and even though you may not be scheduled to speak, there is a reasonable chance you will end up on stage as well.

Before the event starts, take out your phone and make a note of the possible questions you may be asked. Then answer these questions.
It is like preparing a Q&A session after your presentation; you predict the questions that may be asked. Even if the questions are not the same, being mentally prepared to get called up will help calm your nerves and think on your feet.
When you get called up to speak, don’t panic. Rushing up will make you feel more anxious.
Instead, slow down your movements . Take your time. Breathe deep. Get up from your seat slowly.
As you walk to the stage (slowly), use that time to think about what to say. The longer you take to walk up, the more time you have to organize your thoughts.
Slow, controlled movements also signals your confidence . Nervous people fidget, confident people move calmly.
Once you’re on stage, or after you receive your question, pause.
Don’t underestimate the power of the pause .
Pausing not only allows you to organize your thoughts, it lets the audience contemplate the question and form their own thoughts on the subject matter.

Pausing signifies confidence, because only confident speakers do not fear silence. Unconfident speakers think it will be awkward, and it shows through their sub-communications.
Pausing boosts your credibility because it shows you have thought your answer through.
Pausing also ensures that the first few words you utter are not filler words like “umm, well, err…”
Remember, time always seems to appear slower for you - the speaker. What might feel like an eternity for you seldom feel the same to the audience.
Have a Clear Structure
Like any speech, prepared or otherwise, an impromptu speech should have a clear structure . This ensures that your audience can follow along easily.
I often see new speakers answer a question directly, somehow forgetting everything they have learnt about crafting a speech.
At the very least, there should be an introduction , a body and a conclusion.
The introduction serves to capture the audiences’ attention. It also sets the context of the speech. It could also be as simple as repeating/rephrasing the question asked.
The body is for your main points. Ideally, 1-3 points depending on the time allowed. To beef up the main body of your speech, back up the points with some anecdotes, examples or statistics.
Anything more than 3 points and you might lose your audiences’ attention. Keep your speech concise, clear, relevant and try not to be too long-winded.
The conclusion is a recapping of your points, answering of the question, sharing of your main message or a Call-to-Action.
Often, speakers miss the conclusion and end their speech with a very weak “yeah, that is all.”
As Dale Carnegie said:
Tell the audience what you're going to say, say it; then tell them what you've said."

Dale Carnegie
There are many other structures you can use; like the PREP (Point, reason, example, point), the Pendulum Method and the Timeline Method.
To read more about these different impromptu speaking structures (8 to be exact), and see some examples, read our post here: Terrific Tips to Tackle Table Topics .
Tell Personal Stories
When you speak from personal experience, you are sharing something you intimately know.
There’s no need to research or memorize anything . You’ll find that it is easier to tell because the event happened to you. Stories are emotional, real and (usually) interesting.
So when you’re unsure what to say, tell a story that is related to the situation. It makes your input unique and valuable.

Stick to the Truth
This goes hand-in-hand with telling personal stories . There’s no need to exaggerate or stretch the truth. This is not a Tall Tales contest .
Share how you really feel. Are you nervous? Are you excited? Are you afraid?
If you don’t know about something, then say you don’t know.
Telling the truth makes you seem more authentic.
Now, telling the truth doesn’t mean divulging your buddy’s embarrassing secrets during his wedding or telling your boss you hate him.
It just means that you stick to the truth in the moment and not embellish anything.
Humour is a good way to break the ice and to connect with your audience .
Joke about the elephant in the room - that you are totally unprepared to get called on, but be warned, do it weakly and it shows a lack of confidence.
If you can make them laugh, they’ll ignore the fact that you may be unprepared or can’t answer the topic.
In Toastmasters table topics, the speaker who draws the biggest laughters often wins the ‘Best Table Topic Speaker’ ribbon.
As Maya Angelou said:
“At the end of the day people won't remember what you said or did, they will remember how you made them feel.”

Maya Angelo
Civil Rights Activist
Make them laugh.
Never Apologise
How would you feel if you travelled all the way to an event only to hear the speaker say “Sorry, I didn’t prepare for this talk.”
When you say that, you’re disrespecting the audience members’ time.
Often when a speaker apologises, it is to ‘set the standard low’ in case he screws up. But what it does instead is showing a serious lack of confidence.
In most impromptu situations, you are not wrong (to not be prepared), so why apologise?
Sure, you can mention that this is an impromptu speech, but keep it brief, professional and avoid futile apologies.
Turn it Into a Q&A Session
In cases where you have nothing to say, a smart way of still controlling the stage is to turn the talk into a Questions & Answers session.
This is especially useful for a long (~45min) impromptu talk where you have nothing prepared in advance.
Ask the audience what they think of the topic. Ask them what they want to know. Heck, ask them the question you were asked!
The audience’s input forms the content of your speech. It gives you ideas and threads to work on.
Don’t Drag On
Most people freeze when they get asked a question they know nothing about. But when they receive a question they are passionate about, they go on and on and on and on and on and on…
Once, a speaker spoke for a good 5 min during a 1 to 2 min table topic session . He was losing the audience’s attention but he was so oblivious that he kept going. We had to cut him off politely.
As you don’t rehearse for an impromptu speech, it is easy to go overtime without proper crafting. Hence, aim to keep your speech concise and to the point. Focus on just one message if you are too excited for the topic.
Respect the program agenda.

Start Talking
The mind works in a funny way.
When you stand in front of an audience, thinking of what to say, often times your mind remains blank.
But the moment you start talking, ideas flow automatically into your mind and out of your mouth. You’ve entered flow state, and you’re spewing gold left and right.
It happened to me multiple times and it happened to many speakers I saw.
So if nothing comes into your mind after pausing and thinking for a few seconds, then start talking.
Just say anything. Repeat the topic if you have to.
As cliche as it sounds, practice does make progress.
But the question is: how do you practice for an impromptu speech?
The best way I found is to join Toastmasters . Every Toastmasters meeting has a session called the table topics, which is a whole session dedicated to impromptu speaking.
You go on stage and the host gives you a topic and you talk about it for 1-2 min. That’s literally it.
As simple as it sounds, actually standing in front of an audience and speaking without preparation under pressure is tremendous practice.

If formal practice is not possible, then do it yourself. Search for a list of impromptu speech topics on Google, and answer them one by one.
I have a gratitude journal and on top of each page is a quote. Everyday after practicing gratitude, I practice impromptu speaking by saying something about the quote. Just 1-2 min a day works wonders.
Another ‘game’ I have is called verbal association . I think of an object, and without filter, I just talk about it and the next thing that pops into my mind, I talk about that thing, and the next association, and the next.
You must do this with NO filter, NO judgement and NO pondering. Just free flow. Whatever you say won’t be logical. It simply trains you to associate one object with another.
For instance: book.
The book on my table is very thick and it makes me wonder how many trees were cut just for this book? Trees are really amazing things as they take in carbon dioxide and give out oxygen. Oxygen is essential for life. You know what else is essential for life? Water. Be like water my friend. Water adapts and fills up the shape of the container it enters. A container reminds me of tupperware. Tupperware parties are so interesting. A whole bunch of housewives coming together selling tupperware. I read somewhere that this is a multi-level marketing scheme. MLM reminds me of the pyramids and oh, I am heading to Egypt next week. Can’t wait!
Crazy how I start with a book on my table and ended up with Egypt.
This trains your association muscle and helps with thinking on your feet. Don’t just do this silently. Say it out loud!
As Mark Twain said:
It usually takes me more than three weeks to prepare a good impromptu speech.

Practice , my friend!
Conclusion: On Impromptu Speaking Off-the-Cuff
The next time you get called up to give a talk last minute , remember these tips.
Move slowly, pause, crack a joke, tell the truth, share a story, stick to the point and if nothing else works, turn it into a Q&A session.
I hope this post helps you ease your fear of impromptu speaking. Let me know in the comments what questions you have.
For more impromptu speech structures, read our post: Terrific Tips to Tackle Table Topics .
Oratory Club
Public Speaking Helpline

How to Deliver an Impromptu Speech
To give an impromptu speech, gather your thoughts quickly and structure your speech with a strong opening, clear points, and a memorable conclusion. Being prepared with confidence and engaging body language will help deliver a successful impromptu speech.
Impromptu speaking, the art of delivering a speech without any prior planning or preparation, can be a daunting task for many. Whether in a professional setting or a social gathering, the ability to think on your feet and express your ideas effectively is a valuable skill to have.
We will discuss some practical tips and techniques to help you give an impromptu speech with confidence and ease. From organizing your thoughts to engaging your audience, we will explore the essential elements of a successful impromptu speech. So, if you find yourself unexpectedly called upon to speak, don’t panic! With the right approach and a few simple strategies, you can give an impressive impromptu speech that will leave a lasting impact.

Credit: virtualspeech.com
Table of Contents
Preparing Mentally And Emotionally
Discover the key to delivering a successful impromptu speech by focusing on mental and emotional preparation. Boost your confidence, gather your thoughts, and engage your audience effectively with these essential tips.
Overcoming The Fear Of Public Speaking:
- Visualize success: Close your eyes, take deep breaths, and imagine yourself delivering a confident and impactful speech. Visualizing success can help calm your nerves and boost your confidence.
- Practice, practice, practice: The more prepared you are, the less anxious you’ll be. Practice your impromptu speaking skills regularly to become more comfortable with thinking on your feet.
- Embrace the nerves: Instead of fighting your nervousness, reframe it as excitement. Channel the adrenaline rush into enthusiasm and energy, using it to fuel your impromptu speech.
- Start small: Begin by speaking in front of small groups or in low-pressure situations. Gradually work your way up to larger audiences, building your confidence along the way.
- Focus on the message, not yourself: Shift your attention away from your own insecurities and focus on delivering a meaningful message to your audience. Remember, they are there to hear what you have to say, not to judge you.
Developing Quick Thinking Skills:
- Enhance your general knowledge: Read widely on different topics to broaden your knowledge base. This will provide you with a good foundation to draw upon when speaking impromptu on various subjects.
- Engage in brainstorming exercises: Train your brain to think quickly by practicing brainstorming sessions either alone or with others. Challenge yourself to come up with as many ideas or solutions as possible within a specific timeframe.
- Play improv games: Improvisational games and exercises can sharpen your ability to think on your feet. These activities require quick thinking and adaptability, boosting your overall impromptu speaking skills.
- Stay up-to-date with current events: Follow the news and stay informed about current events. This will help you stay relevant and provide you with relevant talking points in impromptu speaking situations.
Building Confidence And Self-Assurance:
- Acknowledge your strengths: Identify your unique strengths as a speaker and draw confidence from them. Recognize the aspects of your speaking style that are effective and use them to your advantage.
- Seek constructive feedback: Ask trusted friends, colleagues, or mentors to provide feedback on your impromptu speaking skills. Their insights can help you improve and build confidence in areas that may need attention.
- Practice positive self-talk: Challenge negative thoughts and replace them with positive affirmations. Remind yourself of past successes and praise yourself for your efforts in becoming a better impromptu speaker.
- Embrace mistakes as learning opportunities: Understand that mistakes are a natural part of the learning process. Instead of dwelling on them, use them as opportunities to grow and refine your impromptu speaking skills.
- Maintain good body language: Stand tall, make eye contact, and use open gestures. Strong and confident body language can enhance your self-assurance and leave a lasting impact on your audience.
Remember, impromptu speaking may feel challenging in the beginning, but with practice and the right mindset, you can become more comfortable and effective at delivering speeches on the spot.
Organizing Your Thoughts On The Spot
Learn how to give an impromptu speech with ease by organizing your thoughts on the spot. Discover effective strategies to deliver a confident and coherent presentation without any prior preparation.
Analyzing The Topic Or Prompt:
- Take a moment to analyze the topic or prompt before you begin speaking. This will help you gather your thoughts and form a coherent response.
- Consider the key points or main ideas that you want to address in your impromptu speech.
- Identify any supporting evidence or examples that you can use to strengthen your points.
- Think about the overall message or takeaway you want to convey to your audience.
Creating A Structured Outline In Your Mind:
- Once you have analyzed the topic or prompt, create a mental outline to organize your thoughts.
- Begin by determining the main points or sections of your speech.
- Prioritize these main points in a logical order that flows well and makes sense to your audience.
- Think about how you can transition smoothly from one point to another.
- Consider using keywords or phrases to help you remember the main ideas of each section.
Utilizing The Rule Of Three For Content Organization:
- The rule of three is a powerful technique for organizing your content and making it more memorable for your audience.
- Divide your speech into three main sections or points.
- Ensure that each of the three sections is distinct and focused on a specific aspect of the topic.
- Use bullet points or subheadings within each section to further organize and clarify your ideas.
- Remember to provide supporting evidence or examples for each of the main points.
By following these strategies for organizing your thoughts on the spot, you can deliver a well-structured and coherent impromptu speech. Taking the time to analyze the topic, create a mental outline, and utilize the rule of three will help you deliver a confident and impactful speech that engages your audience.
Delivering An Effective Impromptu Speech
Learn how to give an impromptu speech effectively with these expert tips. Discover how to start strong, maintain clarity and confidence, and engage your audience with concise and impactful sentences. Master the art of thinking on your feet and delivering a compelling impromptu speech that captivates your listeners.
Opening With A Strong And Attention-Grabbing Introduction
- Begin your impromptu speech with a powerful statement or a thought-provoking question to capture your audience’s attention right from the start.
- Share a fascinating statistic or a surprising fact that relates to your speech topic.
- Start with a relevant quote from a notable figure or a famous saying that resonates with the theme of your speech.

Using Persuasive Techniques To Engage The Audience
- Utilize rhetorical devices, such as repetition, alliteration, or rhetorical questions, to make your speech more engaging and memorable.
- Appeal to the emotions of your audience by using storytelling or personal anecdotes that tug at their heartstrings.
- Use vivid language and descriptive metaphors to paint a picture in the minds of your listeners and make your speech more persuasive.
Incorporating Personal Anecdotes Or Storytelling To Connect With Listeners
- Begin by sharing a personal experience or an anecdote that relates to your speech topic and offers a unique perspective.
- Use storytelling techniques to weave a narrative that captures the attention and imagination of your audience.
- Ensure that your personal anecdotes are relatable and relevant to the main points of your impromptu speech.
Navigating Through The Main Points Smoothly And Coherently
- Clearly outline the main points you wish to discuss in your impromptu speech and provide a brief introduction for each point.
- Use transition words, such as “firstly,” “secondly,” and “finally,” to guide your audience through the different sections of your speech.
- Maintain a logical flow throughout your speech by connecting each point to the next and reinforcing their relevance to the overall topic.
Concluding With A Memorable Ending
- Summarize the key points you have covered in your impromptu speech and restate them in a concise and memorable manner.
- End with a call to action or a thought-provoking question that encourages your audience to reflect or take action based on your speech.
- Finish with an impactful quote or a powerful statement that leaves a lasting impression on your listeners.
Remember, in an impromptu speech, it’s essential to think on your feet, engage your audience, and deliver your message effectively. By opening with a captivating introduction, using persuasive techniques, incorporating personal anecdotes, navigating smoothly through the main points, and concluding memorably, you’ll be well on your way to delivering an exceptional impromptu speech.
Practicing And Improving Impromptu Speaking Skills
Learn effective strategies to practice and improve impromptu speaking skills with these invaluable tips for delivering a successful impromptu speech. Discover techniques to think on your feet, engage your audience, and deliver a compelling message without any prior preparation.
Impromptu speaking can be a nerve-wracking experience for many individuals. However, with practice and dedication, anyone can improve their impromptu speaking skills. Here are some effective strategies to help you become a confident impromptu speaker:
Participating In Improvisation Exercises Or Classes:
- Join improv classes or workshops to enhance your ability to think on your feet.
- Engage in improvisation exercises that require you to respond spontaneously to given prompts.
- Practice improvisation techniques such as word association and role-playing to sharpen your impromptu speaking skills.
Frequenting Public Speaking Clubs And Events:
- Attend public speaking clubs like toastmasters to gain exposure and practice impromptu speaking.
- Take advantage of opportunities to deliver impromptu speeches at networking events, conferences, or other public speaking engagements.
- Observe and learn from experienced impromptu speakers, paying attention to their delivery techniques and strategies.
Utilizing Technology For Self-Recording And Evaluation:
- Use your smartphone or a recording device to capture your impromptu speeches for self-evaluation.
- Watch recordings of your impromptu speaking sessions and identify areas for improvement, such as clarity, body language, and vocal projection.
- Analyze your strengths and weaknesses and set specific goals for improvement based on your self-assessment.
Seeking Feedback And Incorporating Constructive Criticism:
- Share your impromptu speaking sessions with trusted friends, colleagues, or mentors to receive honest feedback.
- Embrace constructive criticism and use it to refine your impromptu speaking skills.
- Practice incorporating feedback by delivering impromptu speeches on a regular basis and implementing suggested improvements.
Remember, becoming a skilled impromptu speaker takes time and dedication. By participating in improvisation exercises, joining public speaking clubs, utilizing technology for self-recording and evaluation, and seeking constructive feedback, you can continuously improve your impromptu speaking skills and become a confident and persuasive speaker.
Handling Unexpected Challenges During An Impromptu Speech
Handling unexpected challenges during an impromptu speech requires quick thinking and adaptability. Speakers must maintain composure, focus on the main points, and engage the audience through concise and confident delivery. Success lies in preparation, being aware of potential obstacles, and having a flexible mindset to tackle any unforeseen situations that may arise.
**dealing with time constraints:**
- Prioritize your key points: Determine the most important points you want to convey and ensure they are delivered within the given time frame.
- Be concise: Avoid unnecessary details and focus on delivering your message in a clear and succinct manner.
- Time management techniques: Practice timed impromptu speeches to build awareness of how long different sections take. Use tactics like using an internal timer or dividing your speech into equal time segments to ensure you stay on track.
- Adjust your pace: If you find yourself running short on time, speak slightly faster to cover all the essential points. Conversely, if you have extra time, pause momentarily and emphasize key ideas.
**adapting to unfamiliar topics:**
- Seek common ground: Look for connections between the unfamiliar topic and your existing knowledge or experiences. Find related concepts that you can use to build your speech.
- Analyze the prompt: Break down the topic into different components and explore each one individually. This will help you understand the topic better and provide a structured approach for your speech.
- Use personal anecdotes: Relate the unfamiliar topic to real-life experiences or personal stories to help make it relatable and engaging for both you and the audience.
- Draw from general knowledge: Utilize general knowledge or popular culture references to add depth and context to your speech. This can also help in creating a connection with the audience.
**handling technical difficulties and distractions:**
- Be prepared: Familiarize yourself with the technical equipment and rehearse with it beforehand. This will enable you to troubleshoot any technical difficulties quickly.
- Stay focused: Concentrate on your speech and maintain eye contact with your audience. This will help minimize distractions and keep you engaged with the listeners.
- Pause and adapt: If a technical issue arises during your speech, remain calm and composed. Take a short pause to address the problem, and if needed, continue without the aid of the technology or transition to another part of your speech.
- Use humor: Incorporate humor to help diffuse the situation and maintain a positive atmosphere. Engaging the audience with a light-hearted comment can help overcome technical difficulties.
**recovering from mistakes or forgotten points:**
- Stay composed: If you make a mistake or forget a point, take a deep breath and maintain your composure. Remember that the audience is supportive and wants you to succeed.
- Reiterate main ideas: Summarize the main ideas you have already presented to reinforce your message and provide a smooth transition back into your speech.
- Improvise: Think on your feet and adapt your speech if necessary. Use your existing knowledge on the topic to fill any gaps and continue your delivery seamlessly.
- Pause strategically: If you forget a point, take a momentary pause, gather your thoughts, and continue with the next point. Avoid drawing attention to the mistake or getting flustered.
Navigating unexpected challenges during an impromptu speech can be intimidating, but with adequate preparation and a positive mindset, you can overcome them effectively. By managing time constraints, adapting to unfamiliar topics, handling technical difficulties and distractions, and recovering from mistakes, you can deliver an engaging and impactful impromptu speech.
Overcoming Common Impromptu Speaking Errors
Discover effective strategies for delivering impromptu speeches flawlessly with “overcoming common impromptu speaking errors. ” Learn practical techniques to confidently speak on the spot and captivate your audience without stumbling over commonly overused phrases. Be prepared to effortlessly handle impromptu speaking situations with ease and poise.
Overcoming Common Impromptu Speaking Errors:
Impromptu speeches can be nerve-wracking, causing many people to make common errors. To deliver a successful impromptu speech, it’s essential to avoid these mistakes:
- Avoiding rambling or going off-topic: Stay focused and concise by following these tips:
- Prepare a mental outline: Organize key points in your mind to avoid rambling.
- Stick to the topic: Keep your speech on track by constantly reminding yourself of the main subject.
- Use transitions: Smoothly transition between ideas to maintain coherence and avoid going off-topic.
- Refraining from fillers or verbal crutches: Minimize the use of fillers or verbal crutches to enhance your speech’s clarity and professionalism. Consider the following strategies:
- Practice pausing: Instead of using filler words, pause briefly to gather your thoughts or emphasize a point.
- Be aware of fillers: Recognize your habitual fillers (such as “um,” “like,” or “you know”) and consciously eliminate them.
- Speak slowly: Speaking at a slower pace allows you to think more clearly, reducing the need for fillers.
- Maintaining appropriate body language and eye contact: Non-verbal cues play a crucial role in effective impromptu speaking. Remember the following techniques:
- Stand tall and relaxed: Project confidence and professionalism by maintaining good posture.
- Establish eye contact: Engage your audience by making eye contact with individuals throughout your speech.
- Use open gestures: Utilize appropriate hand movements to emphasize key points and maintain a connection with your listeners.
- Modulating voice and using effective gestures: To further enhance your impromptu speech, focus on voice modulation and gestures:
- Vary your pitch, tone, and volume: Use these vocal elements to convey emotion, emphasize important ideas, and keep your audience engaged.
- Incorporate purposeful gestures: When appropriate, use hand gestures or body movements to enhance your speech’s impact and expressiveness.
Impromptu speaking can be daunting, but by avoiding rambling, eliminating fillers, maintaining appropriate body language and eye contact, and utilizing effective voice modulation and gestures, you can overcome common errors and deliver an engaging impromptu speech. Practice these techniques to improve your impromptu speaking skills and build confidence in your ability to speak off-the-cuff.
Building A Repertoire Of Impromptu Speech Topics
Discover the secrets to giving an impromptu speech with our guide on building a repertoire of topics. Learn how to captivate your audience with confidence and deliver an engaging speech on the spot. Master the art of impromptu speaking with our expert tips and techniques.
Impromptu speeches can be daunting, but with the right skills and preparation, you can tackle them with confidence. Building a repertoire of impromptu speech topics is an essential step in becoming an effective and engaging speaker. In this section, we’ll explore two strategies to help you expand your general knowledge and stay informed, as well as practice brainstorming techniques for quick topic generation.
Additionally, we’ll discuss the importance of creating a list of go-to topics for practice purposes.
Expanding General Knowledge And Staying Informed:
- Read widely: Explore a variety of topics by reading books, articles, and online content from reputable sources. This will broaden your knowledge base and expose you to different viewpoints and ideas.
- Follow news outlets: Stay updated on current events by following trustworthy news outlets. This will not only keep you informed but also provide you with potential impromptu speech topics.
- Engage in discussions: Participating in conversations with others who have diverse perspectives can enhance your understanding of various subjects. This can be done through joining clubs, attending workshops, or even online forums.
Practicing Brainstorming Techniques For Quick Topic Generation:
- Mind mapping: Start with a central topic and brainstorm related subtopics or ideas around it. This visual representation can help you quickly generate impromptu speech topics.
- Word association: Connect different words or concepts that are related or evoke similar thoughts. By linking these associations, you can uncover potential impromptu speech topics.
- Random prompts: Utilize random word generators or ask someone to give you a random word. Challenge yourself to quickly come up with impromptu speech topics related to that word.
Creating A List Of Go-To Topics For Practice Purposes:
- Personal experiences: Reflect on your own life and identify significant moments, challenges, or achievements that can serve as impromptu speech topics.
- Educational or professional expertise: Consider topics related to your field of study or work that you can confidently discuss and share insights on.
- Popular subjects: Compile a list of frequently discussed topics such as technology, environment, health, or social issues. This will provide you with a range of topics to practice impromptu speeches on.
By expanding your general knowledge, practicing brainstorming techniques, and creating a list of go-to topics, you’ll be well-equipped to deliver impromptu speeches confidently and captivatingly. Remember, the key is to embrace the challenge and embrace the opportunity to share your thoughts and ideas spontaneously.
So, let’s get started and enhance your impromptu speaking skills!
Leveraging Opportunities To Give Impromptu Speeches
Discover how to deliver compelling impromptu speeches by seizing opportunities to speak off-the-cuff. Gain confidence, clarity, and the ability to engage any audience with these essential tips and techniques. Experience the power of spontaneous speaking and unlock your true potential as a communicator.
Impromptu speeches can be nerve-wracking, but they also present great opportunities to showcase your communication skills. By volunteering for impromptu speaking moments, seizing spontaneous opportunities, and utilizing these speeches as chances to demonstrate your abilities, you can become a confident and skilled impromptu speaker.
Volunteering For Impromptu Speaking Opportunities:
- Actively participate in group discussions or meetings that provide impromptu speaking chances.
- Offer to lead a team discussion or present a topic at a meeting when the opportunity arises.
- Volunteer to give impromptu speeches at toastmasters or similar speaking clubs.
- Join panel discussions or roundtable events where spontaneous speaking opportunities may arise.
- Seek out events or conferences where impromptu speaking is encouraged, such as tedx open-mic nights.
Seizing Spontaneous Public Speaking Moments:
- Be attentive and aware of situations that may require impromptu speaking, such as someone unexpectedly asking for your opinion.
- Take the initiative to share your thoughts in casual conversations or social gatherings.
- Embrace unexpected opportunities to speak publicly, even if it is outside your comfort zone.
- Respond to impromptu speaking prompts during training sessions or workshops.
- Emulate impromptu speaking scenarios by practicing speaking extemporaneously with friends or colleagues.
Using Impromptu Speeches As A Chance To Showcase Skills:
- Focus on a concise and clear message that relays your expertise on the topic.
- Highlight your ability to think on your feet and provide thoughtful responses.
- Utilize storytelling techniques to engage and captivate the audience.
- Incorporate humor or personal anecdotes to make your impromptu speech memorable.
- Maintain confident body language and eye contact to enhance your overall delivery.
Remember, giving impromptu speeches may be daunting at first, but with practice and a positive mindset, you can turn these unexpected moments into opportunities for personal and professional growth. Embrace the chance to speak spontaneously, showcase your skills, and watch your confidence soar as an impromptu speaker.
Keep in mind: successful impromptu speaking is not about perfection; it’s about effectively delivering your message and engaging your audience. So, embrace the challenge, prepare by practicing impromptu speeches, and grow into a confident and skilled impromptu speaker.
Frequently Asked Questions On How To Give An Impromptu Speech
How do you prepare for an impromptu speech.
To prepare for an impromptu speech, focus on organizing your thoughts, practicing concise delivery, and familiarizing yourself with the topic beforehand. By developing good communication skills and staying current on various subjects, you can feel more confident and ready to deliver a impromptu speech effectively.
What Are Some Tips For Speaking Confidently During An Impromptu Speech?
To speak confidently during an impromptu speech, maintain good posture, make eye contact with the audience, and use gestures to emphasize key points. Take a deep breath before speaking and speak slowly and clearly. Remember that confidence comes with practice, so don’t be afraid to take on opportunities to speak spontaneously.
How Can I Structure An Impromptu Speech?
Structure an impromptu speech by starting with a strong introduction that grabs the audience’s attention, followed by a brief outline of your main points. Develop these points with clear examples or evidence, and conclude with a concise summary or call to action.
Practice this structure in various impromptu scenarios to become more proficient.
Mastering the art of giving an impromptu speech is a valuable skill that can greatly benefit anyone, whether in personal or professional settings. By following these simple guidelines, such as organizing your thoughts, maintaining eye contact, and speaking with confidence, you can deliver a successful impromptu speech that leaves a lasting impact on your audience.
Remember to embrace the opportunity for growth and improvement, as practice makes perfect. Keep in mind that it is normal to feel nervous, but with preparation and a positive mindset, you can overcome any challenges that come your way. So, next time you are faced with the daunting task of giving an impromptu speech, approach it with enthusiasm and trust in your abilities.
With these techniques in your arsenal, you will be well-equipped to rise to the occasion and deliver an impressive impromptu speech every time.
Similar Posts
How to show confidence: mastering body language and communication.
Confidence is a quality that many of us admire and aspire to possess. It’s that magnetic aura that instantly captivates a room and commands respect. But have you ever wondered how some people effortlessly exude confidence while others struggle to project even a hint of it? Former FBI agent and body language expert Joe Navarro…

How to Give An Extemporaneous Speech?
To give an extemporaneous speech, prepare key points beforehand and practice speaking in a clear and confident manner. Having a solid foundation of knowledge on the topic will also aid in delivering a well-structured and engaging speech. Additionally, maintain eye contact, use gestures to emphasize important points, and manage time effectively to ensure an impactful…

Breathing Exercises for Presentations
Breathing exercises can enhance presentation skills by reducing anxiety and improving focus. In today’s fast-paced and competitive world, effective communication is crucial. Whether you are giving a speech, presenting a proposal, or leading a meeting, mastering breathing techniques can help you calm your nerves, increase your confidence, and deliver a more compelling presentation. By incorporating…
Public Speaking Events to Sharpen Your Skills
Public speaking events are dynamic gatherings where individuals communicate ideas and information to a live audience. These events provide opportunities for speakers to share knowledge, inspire others, and build connections. Public speaking events foster personal development, enhance communication skills, and boost confidence. They can be found in various settings, such as conferences, seminars, workshops, and…
What Are The Types Of Public Speaking?
Public speaking is an art form that has been practiced for centuries, captivating audiences and inspiring change. From delivering persuasive speeches to informative presentations, there are various types of public speaking that cater to different purposes and styles. Whether it’s the power of storytelling or the ability to influence, understanding these types can help individuals…
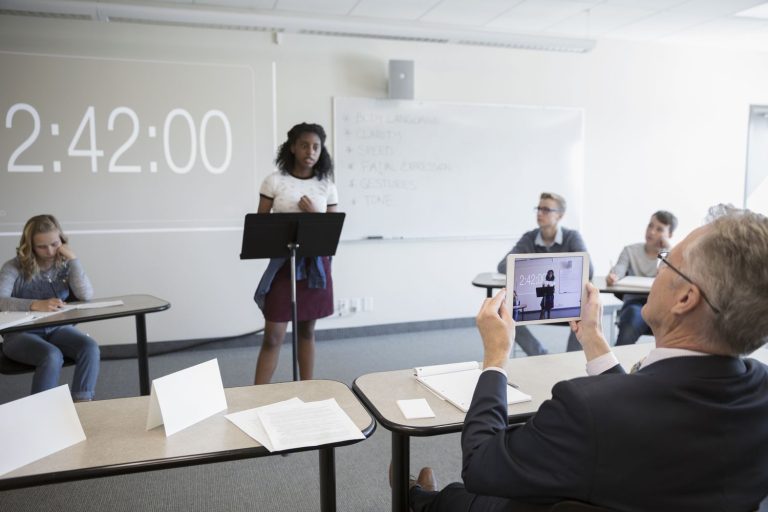

Is Public Speaking Class Hard?
Public Speaking Class can be challenging for some individuals due to the requirement of speaking in front of a crowd, but with practice and guidance, it can become easier. The skill of public speaking is one that can be developed and honed over time. Confidence, preparation, and effective communication techniques are key factors in succeeding…

Impromptu Speech

If delivering a speech can get nerve-racking for some people, just imagine if they are to deliver an impromptu speech. When we know we are to deliver a speech, we would often go out of our ways just to plan, rehearse, and practice for days, even weeks for some, just to make sure we could ace it. However, when we are asked to deliver a speech on the spot, that’s when things would get challenging for us.
- Church Welcome Speech Examples – PDF
- Salutatorian Speech Examples – PDF
Even though the moments when you would be asked to deliver an impromptu speech could be unexpected, there are some moments when you are most likely to deliver one and such moments are weddings, award presentations or recognition, and even project updates in your workplace. Whatever it is, people would expect that you would be able to deliver an impromptu speech that is smart, witty, insightful, and informative, especially if it’s a formal setting.
If you are not really good at making an impromptu speech but you would always find yourself to be asked to deliver one, then you have to ace your game and surprise everyone who has already witnessed your countless nail-biting situations with the help of the impromptu speech examples that we have compiled here in this article. We have also included some tips on how to deliver an impromptu speech that will surely be of help when you are asked to deliver another impromptu speech.
What is Impromptu Speech? – Definition An impromptu speech is a type of speech that is given without prior preparation or notice . It requires the speaker to quickly organize their thoughts and ideas on a given topic and deliver a coherent and persuasive presentation on the spot. Unlike prepared speeches, where the speaker has time to research, plan, and rehearse, impromptu speeches are spontaneous and demand a high level of quick thinking, adaptability, and the ability to articulate thoughts clearly and effectively under pressure. Impromptu speaking is a valuable skill in various contexts, including everyday conversations, business meetings, interviews, social gatherings, and competitive speaking events. It tests a speaker’s ability to think on their feet, use language creatively, and engage with an audience without the safety net of prepared materials. Mastering impromptu speaking can enhance one’s communication skills, confidence, and ability to handle unexpected situations gracefully.
Tips on giving an impromptu speech

- Stay Calm and Composed : The key to successful impromptu speaking starts with your mindset. Take a deep breath, stay calm, and approach the task with confidence. Remember, your audience is more forgiving than you think.
- Listen Carefully : If you’re given a topic or question, listen carefully to understand it fully. Clarify if necessary before you start speaking to ensure your response is relevant.
- Structure Your Thoughts Quickly : Organize your speech with a clear beginning, middle, and end. You might use the simple structure of stating your main point, supporting it with a few details or examples, and then concluding by summarizing your point.
- Use the PREP Method : Point, Reason, Example, Point (PREP) is a straightforward formula for organizing your thoughts. State your main point, give a reason why it’s important, provide an example or evidence, and restate your point.
- Draw on Personal Experience : Personal stories or examples can make your speech more engaging and relatable. Don’t hesitate to draw on your own experiences when relevant.
- Keep It Simple and Clear : Avoid trying to cover too much in a short speech. Focus on one or two key points that you can discuss clearly and succinctly.
- Engage Your Audience : Make eye contact, use gestures for emphasis, and modulate your voice to keep the audience engaged. Showing enthusiasm for your topic can also help captivate your listeners.
- Practice Active Listening : Improve your impromptu speaking skills by practicing active listening in daily conversations. This helps you become better at formulating quick and coherent responses.
- Embrace Silence : It’s okay to take a moment to collect your thoughts before responding or to pause briefly during your speech. These pauses can actually improve your speech’s clarity and pacing.
- Learn from Every Experience : After each impromptu speech, reflect on what went well and what could be improved. Continuous self-reflection and practice are key to becoming a more effective speaker.
- Stay Informed : Being well-read and informed about a variety of topics can provide you with a wealth of material to draw from when asked to speak spontaneously.
- Practice Under Pressure : Challenge yourself by practicing impromptu speeches in different settings or under time constraints. This can help build your confidence and improve your quick-thinking skills
Impromptu speech frameworks
Impromptu speech frameworks are structured approaches that help speakers organize their thoughts quickly and deliver a coherent speech on the spot. These frameworks provide a guideline for arranging your points, making it easier to speak confidently and clearly under pressure. Here are several effective frameworks for impromptu speaking:
PREP (Point, Reason, Example, Point)
Point : Start by stating your main point or argument. Reason : Explain why this point is important or relevant. Example : Provide an example or evidence to support your reason. Point : Conclude by restating your main point, reinforcing your argument.
PEEL (Point, Explain, Evidence, Link)
- Point : Begin with the main point you intend to make.
- Explain : Elaborate on your point, providing more detail.
- Evidence : Offer evidence, examples, or anecdotes to support your explanation.
- Link : Conclude by linking back to your main point, showing how the evidence supports it.
What? So What? Now What?
What? : Describe the situation or topic you’re addressing. So What? : Discuss the importance or impact of the situation/topic. Now What? : Suggest a course of action or a conclusion based on the discussion.
5 Ws (Who, What, When, Where, Why) and How
This framework is especially useful for informative or explanatory speeches. Address each of the “5 Ws” to cover the topic comprehensively, followed by “How” to explain processes or solutions.
Problem-Solution-Benefit
Problem : Start by describing a problem. Solution : Propose a solution to the problem. Benefit : Highlight the benefits or positive outcomes of implementing the solution.
Cause-Effect-Solution
Cause : Explain the cause of a particular issue or situation. Effect : Describe the effects or consequences of this cause. Solution : Offer solutions to mitigate the cause or address its effects.
Compare and Contrast
This framework involves comparing two or more ideas, situations, or objects, highlighting similarities and differences. It’s effective for persuasive speeches or when making a choice between options.
Past-Present-Future
Past : Start by discussing the history or background of your topic. Present : Describe the current state or relevance of the topic. Future : Predict future trends or implications related to the topic.
Three-Point Structure
Choose three main points you want to make about your topic. This straightforward structure is flexible and can be adapted to most topics, providing clarity and depth without overwhelming the audience.
Impromptu Speech Samples
- Impromptu Speech for Students
- Impromptu Speech for Kids
- Impromptu Speech for Beginners
- Impromptu Speech for Grade 10
- Impromptu Speech for Love
- Impromptu Speech for Family
- Impromptu Speech for Bullying
- Impromptu Speech for Public Speaking
- Impromptu Speech for Education
- Impromptu Speech for Events
- Impromptu Speech for Political Rallies
- Impromptu Speech for Social Media Influencers
- Impromptu Speech for Educational Leaders
- Impromptu Speech for Health And Wellness Coaches
- Impromptu Speech for Technological Innovations
- Impromptu Speech for Corporate Success
- Impromptu Speech for Graduates
Assignment Impromptu Speech Example

Evaluation Impromptu Speech Example

One-Minute Elevator Impromptu Speech Example

Preparing an Impromptu Speech

Presentation Program Impromptu Speech Example

Strategies Impromptu Speech

Topics Impromptu Speech Example

Situations You’d Likely Deliver an Impromptu Speech
As mentioned above, the moments you’d be asked to deliver an impromptu speech is unexpected but there are certain moments and events wherein you would most likely be asked to deliver one. With that, we have listed down some of the situations that you would most likely get asked an impromptu speech:
- The scheduled speaker had informed that he or she would not be able to make it at the last minute and you have been asked to fill in for him or her.
- When you are one of the panelists in a contest, a report or status update, or a project presentation and when you are the one doing the project presentation or a status update and that one of the panelists would ask you questions.
- When you would initiate a question-and-answer session after your prepared speech (the answers you reply to the questions thrown at you by the audience is considered as an impromptu speaking).
- When you would be asked to be interviewed, be it on television, radio, seminars or webinars, or even phone interviews.
- When you would be asked to say a few words or a toast at any kind of gathering, be it among your friends, family members, colleagues, or company.
- When you would join a debate in school or even in your workplace or even when your teacher in class would decide that he or she is going to hold a debate on the spot.
Winning Tips and Strategies for Creating and Delivering Impromptu Speeches
If there is one thing you cannot do with impromptu speeches, it’s the fact that you can never prepare them. However, you can always prepare yourself for when you would be encountering such moments. With that, we have listed down some tips and strategies you can use when you would be asked to deliver a speech right on the spot:
Anticipate the possible situations where you might be called upon to deliver an impromptu speech. We have already listed down the possible and common situations and events above and you could also add on some more situations especially if you have already countless experiences when you would just be caught off guard because you are, again, asked to deliver an impromptu speech. Even though you can never prepare an impromptu speech because you can never know what would happen in a situation, having the knowledge of these situations will enable you to at least prepare and compose yourself.
If you are a prominent person or an individual people have high regard for, just expect that you will always be asked to speak even if you know it yourself that you are not good at public speaking, especially if it is an impromptu one. This is why you should make it a point to have a personal impromptu speech structure that can serve as your default template, framework, or guide when you are asked to deliver an impromptu speech. Having such structure decreases the chances of you rambling in front of your audience since you would already have something to follow in your head.
If you could not think of any personal impromptu speech structure, you could make use or get inspired with some of this easy impromptu speech structure or framework:
- P.R.E.P. which stands for Point, Reason, Example, Point. This structure is easy to follow: you can start off by clearly stating your points, followed by sharing the reasons or your defense as to why you have these points, followed by examples that would illustrate and explain to the audience why you made those points and the reasons for those points, and lastly, end your impromptu speech with the summary of your central point again.
- Issue, Pros vs. Cons, Conclusions. Here is another easy structure that you can follow. You start off by talking about the issue. Then, you follow it by talking about the benefits people can get from it, followed by talking about its drawbacks, and finally end it with your recommendations.
- Answering the 5Ws and 1H. This structure is centralized in addressing and answering the 5Ws and 1H questions or the Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How elements or questions.
Turn your impromptu session into a question-and-answer session. Having a Q and A session always works wonders especially when you are only tasked to fill in for the absence of a scheduled speaker. Most of the time, a scheduled speaker would be given at least 30- to 45-minute speech but in your case where you are only given the task to fill in his or her time without preparation, it would not be wise to dive into having a 30- to 45-minute impromptu speech. Even if you are fully aware and knowledgeable about the topic that you will be making an impromptu speech out of, it is still not easy to prepare a speech about it right on this spot. If you would re-frame the time with a Q and A session, you would be able to easily break up the given time into a series of very small but extremely manageable impromptu speeches which makes it easier for you to answer and generate an impromptu speech out of. The best part of it is that the questions would come directly from the audience, which means that the answers you give to them is something they wanted to hear.
Using your personal stories also works wonders as well because even if you are not really a good speaker to begin with, you would suddenly be an expert at it especially if you would be creating an impromptu speech using your emotional, real, and interesting personal stories. This is because it is much easier for you to speak about the things that happened based on personal experiences.
Most of all, just go easy on yourself. You may be a good speaker but if you are too tensed and you put so much pressure on yourself, you can still go downhill. Don’t aim too much for perfection and just strive to deliver a message that your audience will get insights from. Your audience could probably recognize that you are only asked to give a speech right on the spot and they will surely understand.
Do you feel like you could take on every moment that you’d be asked to deliver an impromptu speech after reading this article? You may also be interested in Commercial Speech Examples in PDF.
Benefits and Opportunities of Impromptu Speech
- Enhanced Communication Skills : Regular practice of impromptu speaking sharpens your ability to express thoughts clearly and concisely, improving overall communication skills.
- Quick Thinking : Impromptu speaking fosters quick thinking and mental agility, enabling you to formulate and articulate ideas on the spot.
- Confidence Building : Facing the challenge of speaking without preparation builds self-confidence, not just in public speaking situations but in everyday interactions as well.
- Adaptability : It teaches adaptability, allowing you to adjust your message based on the audience, setting, or feedback you receive in real-time.
- Listening Skills : Effective impromptu speaking often requires active listening, especially when responding to questions or comments, thus enhancing your listening abilities.
- Persuasion Skills : As you learn to construct arguments and convey messages spontaneously, your ability to persuade and influence others improves.
- Stress Management : Over time, engaging in impromptu speaking can help you manage stress and anxiety associated with public speaking and other high-pressure situations.
- Creativity and Innovation : The need to think on your feet can boost creativity, encouraging innovative thinking and problem-solving skills.
Opportunities
- Leadership : Strong impromptu speaking skills are invaluable in leadership roles, where the ability to communicate effectively and make decisive comments is crucial.
- Career Advancement : Effective communication is a key competency in the workplace. Proficiency in impromptu speaking can open doors to promotions and other career opportunities.
- Networking : Impromptu speaking skills can enhance your networking abilities, making it easier to engage in conversations, make connections, and leave a positive impression.
- Public Speaking : For those interested in public speaking, debate, or politics, impromptu speaking serves as a foundational skill that can lead to more formal speaking engagements and opportunities.
- Educational Benefits : Students can benefit significantly from impromptu speaking, improving their academic presentations, classroom participation, and overall learning experience.
- Social Interactions : On a personal level, the confidence and skills gained from impromptu speaking can enrich social interactions, making you a more engaging and persuasive communicator in social settings.
- Crisis Management : In professional settings, the ability to speak eloquently and calmly during unexpected situations is invaluable, especially in crisis management roles.
- Personal Satisfaction : Mastering impromptu speaking can bring a deep sense of personal achievement and satisfaction, knowing you can handle spontaneous speaking challenges with poise.
How to Build Impromptu Speaking Skills
Building impromptu speaking skills is a valuable endeavor that can enhance your communication abilities across many areas of life. Here are steps and strategies to improve your impromptu speaking skills:
1. Understand the Basics
- Familiarize yourself with the structure of impromptu speeches and common frameworks, such as PREP (Point, Reason, Example, Point) or the 5 Ws (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How).
2. Practice Regularly
- Engage in daily practice by giving short, impromptu speeches on random topics. Use a list of prompts or have someone suggest topics.
- Join clubs or groups that practice public speaking, such as Toastmasters International, where you can practice impromptu speaking in a supportive environment.
3. Embrace Opportunities to Speak
- Seize every opportunity to speak in public, whether it’s answering questions in a meeting, giving a toast, or participating in discussions. The more you practice in real situations, the more comfortable you’ll become.
4. Read Widely and Stay Informed
- A broad knowledge base will give you more material to draw from during impromptu speeches. Stay informed about current events, and read widely across different subjects.
5. Listen and Observe
- Pay attention to effective speakers and analyze what makes their impromptu speeches work. Notice their structure, how they engage their audience, and how they handle unexpected questions.
6. Think on Your Feet
- Practice thinking on your feet by putting yourself in situations that require quick thinking. Activities like debating or even improvisational comedy can improve your ability to come up with ideas quickly.
7. Focus on Clear Structure
- Even in impromptu situations, strive to have a clear beginning, middle, and end to your speeches. A clear structure helps keep your thoughts organized and makes your speech more coherent to your audience.
8. Develop Your Listening Skills
- Good impromptu speaking often involves responding to others. By developing your listening skills, you can more effectively tailor your responses to what has been said.
9. Work on Delivery
- Practice using effective body language, making eye contact, and modulating your voice to add interest and emphasis to your speeches.
10. Record and Review
- Record your practice speeches and review them to identify areas for improvement. Pay attention to your ums and ahs, pacing, clarity, and how well you stick to your structure.
11. Seek Feedback
- Get feedback from peers, mentors, or through public speaking groups. Constructive criticism can help you identify strengths and areas for improvement.
12. Embrace Mistakes
- Understand that making mistakes is part of the learning process. Each mistake is an opportunity to improve. Reflect on what went wrong and how you can do better next time.
13. Challenge Yourself
- Gradually increase the complexity of your speech topics or the pressure of your speaking situations to continue pushing your boundaries.
14. Stay Positive
- Maintain a positive attitude toward impromptu speaking. View it as an opportunity to improve and showcase your skills rather than something to fear.
15. Reflect and Adjust
- After each impromptu speech, take a moment to reflect on what went well and what didn’t. Use these insights to adjust and improve for next time.
How to Give a Great Impromptu Speech
- Listen and Understand the Topic
- Structure Your Speech
- Use a Familiar Framework
- Open Strong
- Focus on Key Points
- Use Personal Experiences
- Engage Your Audience
- Conclude with Impact
- Practice Active Listening
- Embrace Pauses
- Learn from Every Experience
- Stay Informed
- Practice Regularly
How Do You Prepare for Impromptu Speaking?
To prepare for impromptu speaking, regularly practice speaking on random topics, stay informed about various subjects, and improve your quick thinking and listening skills. Familiarizing yourself with speech structures like PREP can also help.
What Are the Three Parts of an Impromptu Speech?
The three parts of an impromptu speech include the introduction, where you present your main idea, the body, where you expand on your idea with details or examples, and the conclusion, where you summarize and reinforce your main points.
Are Impromptu Speeches Short?
Yes, impromptu speeches are typically short, often ranging from two to five minutes. Their brevity requires the speaker to convey their message concisely and effectively within a limited timeframe.
Why Is Impromptu Speech Difficult?
Impromptu speech is difficult because it requires quick thinking, the ability to organize thoughts rapidly, and confidence in speaking without preparation. The challenge lies in delivering a coherent and engaging speech on the spot.
Is Impromptu Speech a Talent?
While some individuals may naturally excel at impromptu speaking, it is more accurately described as a skill that can be developed and refined with practice, rather than a talent. Continuous practice and learning can significantly improve impromptu speaking abilities.
Speech Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a speech on the importance of teamwork in school projects
Generate a speech encouraging students to participate in school sports.
Deliver an Impromptu Speech on the Benefits of Reading Books over Watching TV.
Create an Impromptu Speech discussing the Pros and Cons of Remote Work.
Generate an Impromptu Speech on Ways to Reduce Environmental Pollution.
Deliver an Impromptu Speech on the Role of Technology in Education.
Create an Impromptu Speech about the Value of Traveling and Experiencing Different Cultures.
Generate an Impromptu Speech on How Volunteering Benefits Both the Volunteer and the Community
Deliver an Impromptu Speech on the Importance of Mental Health Awareness
Create an Impromptu Speech discussing the Future of Renewable Energy Sources.
- All Insights
- Top-Rated Articles
- How-to Guides
- For Parents
How to Organize Your Five-Minute Impromptu Speech: Building Your Introduction (Part 1)
What do five minutes feel like to you? You could tell us that it’s made of up 300 seconds, in which time corn on the cob could be microwaved, a round of commercials could be played, and one kilometer be could run – at least for some of us. But the experience of five minutes is relative. It feels a lot longer if you’re waiting in traffic, than if you’re running late for class. So in this article, you’ll learn what five minutes should feel like when making an impromptu speech, by breaking down the different parts of your speech in order to create a structure that’s both organized and timely. All organized speeches have a beginning, middle, and end, also known as the introduction, body, and conclusion. Knowing how to plan the content of these parts is key to reaching a five-minute impromptu speech, especially because of the limitations you’re under with only two minutes of prep time. Why is this important? Two reasons. One: without keeping track of your time, you may end up finishing early and leaving out essential analysis. Two: many of us have a tendency to ramble and go off-topic, confusing both you and your audience in the process. So, as you map out the structure of your speech, you’ll learn how much time to allow for each part, and what content should be included to reach that timing. Let’s start with impromptu introductions, which require five key ingredients. First, the hook. All good speeches should create a strong first impression. For impromptu, hooks generally come in the form of a personal or well-known anecdote that’s related to the meaning of your prompt and thesis. If you choose a famous story, consider picking something simple that you know well, like the plot of a fable you’ve been taught or a movie you’ve watched. These anecdotes are the quickest to think of and can often be told smoothly without much preparation. For instance, if we suddenly asked you to retell the tale of Snow White, or your vacation last summer, you probably remember quite well what happened. In total, you should spend approximately 40 seconds on your hook, which is about six sentences. Second, the transition sentence or sentences. It’s important to link your hook to the prompt so the audience can see how they relate together. This link should be approximately one to two sentences, no more than ten seconds. For instance, let’s say the last sentence of your hook is, “The story of Snow White ends as a happy one, as the princess wakes up after true love’s kiss from her Prince Charming.” You wouldn’t want to immediately follow it with, “This quote by Stephen King says, “The trust of the innocent is the liar's most useful tool.” Why? Because the audience wouldn’t understand how Snow White is related to “innocence” or “liars.” So, ask yourself, what do the story and the quote have in common? Well, if you recall, Snow White was too innocent, trusting the old lying granny who sold her the apple. Let’s try to use this information to link the hook and the quote together. Your transition might be: “Fairytales such as these don’t exist, with innocent people often getting hurt rather than living out their ‘happily ever after.’” Notice how this sentence makes the connection between the hook and prompt by comparing how fairytales are different from real life. Third, the prompt and your interpretation. Even with a transition sentence, it’s helpful to add a dependent clause before you present your prompt. A dependent clause is a group of words that cannot be used alone; they instead provide additional information for the independent clause, which in this case, is your prompt. Avoid directly saying things like, “the prompt I got today is…” Be a little bit more subtle in your language. You could do this one in of two ways. One: link specific parts of the hook directly to the prompt. You could say something like this: “Snow White’s trusting actions are exactly what Stephen King described in his quote…” Two: If your transition sentence is already clear, use a conventional phrase like: “This brings me to today’s quote…”, or “Which is why we see in today’s quote…”, or “This story is fitting with today’s quote…” You can of course replace the word “quote” with proverb, word, or picture, depending on what type of prompt you’re given. Now for your interpretation. If your prompt is a quote or proverb, spending a sentence to explain its meaning is enough. Elaborate on who or what the prompt refers to and what kind of tone it sets. If there are any hidden meanings, then you might add an extra sentence or two. For word prompts, take more time to describe or define it, giving an example of how this word is commonly used. For picture prompts, read off any text, and describe the picture and its purpose. In total, introducing the prompt and your interpretation of it should take about 20 seconds. Fourth: the thesis statement, which its main objective is summed up in one clear, concise, and debatable sentence. This should take no more than five seconds. Finally, your roadmap (also called the preview), which outlines your speech’s three main points. Usually, in other speeches, your roadmap would include your three claims. However, because most impromptu speakers don’t have time to fully brainstorm these claims during prep, it’s common practice to simply introduce the three stories you plan to talk about in two or three sentences, which is your final 15 seconds. The best way to make this short and simple is to create story titles for each example or to refer to the names of the people or groups you plan to talk about. And there you have, five key parts and their timeline for building a one-minute and 30-second introduction. In the second part of this article, you’ll see an example of a good introduction, and then we’ll break down body paragraphs and conclusions.

Related Insights
How to incorporate humor in your speech: use appropriate tones (part 2), 3 ways to include humour in your speech (part 1), using stage movements and gestures as foundations of persuasion: learn these 3 ways (part 2).

- 5 Prep Tips for BP
- Top Speech Introductions
- Public Speaking and Debate Competitions
- Incorporating Humor
- Logical Fallacies
- How-To: Prepare for Debate Tournaments
- How-To: Judge a Debate
- How-To: Win a BP Debate
- How-To: Win An Argument
- How-To: Improve at Home
- Team China Wins World Championship
- Ariel Wins Tournament
- Jaxon Speaks Up
- Tina Improves

Personal Development
How to give an impromptu speech, with examples.
Communication
Productivity
Work Skills
What is an Impromptu Speech?
An impromptu speech is a type of address given with little or no prior preparation and can also be referred to as "off the cuff" or "spur of the moment" speaking. Examples of an impromptu speech involve a teacher asking a student to present a quick address on a topic from their lesson or a business meeting opening with all participants discussing recent progress on project. Politicians might have to unexpectedly respond to reporters or voters during the course of their campaign or comedians might have to perform a complete or partial improv to an audience or heckler.
Tips for Giving an Impromptu Speech
Though it might be daunting to give an impromptu speech, there are a few techniques to help you feel more prepared and organized when the time comes. Here are two key tips for preparing an impromptu speech:
- Take notes - Get a piece of paper or something to write on and create a few ideas, or even just a few words, to use in your speech. Be sure to include the introduction and ending of your speech for a more structured presentation.
- Pick the right tone - The tone of your speech will be determined by the type of event. For instance, a wedding would usually involve a more informal, lighthearted speech, while a business conference should be more professional and formal in nature.
Frameworks for an Impromptu Speech
Using frameworks is an effective way to give structure to an impromptu speech. Here are a couple essential frameworks to remember:
- The 5 Ws - This framework can be useful when speaking about a specific person or event. The 5 Ws provide a reliable structure, beginning with "who" for context and concluding with "why" for the most important and relevant point.
- Diplomatic framework - This framework is ideal for more formal events, such as business conferences. Begin by talking about the pros and cons of the topic then move on to a conclusion. Take a moment to think of what to say next.
Having the capability to give an impromptu speech is an essential skill and can help alleviate any stress associated with speaking on the spot. You can practice delivering impromptu speeches for an enjoyable and unforgettable way to learn.
To ensure your speech flows well structure wise, begin smaller and move on to bigger points. For instance, when giving a wedding speech, start with your personal experiences with the couple, discuss how their relationship and marriage will affect the wedding guests, and lastly talk about their future and legacy as a couple.
Buying More Time When You Go Blank
If you ever find yourself with a mental block, there are methods you can use to give yourself more time and prevent yourself and the audience from feeling uncomfortable. Techniques such as rephrasing the previous point or asking a question related to the topic can help stall for time while you come up with more content.
Achieve Your Goals
Join shiken for free.

AI-powered learning tools. Create, relax, learn.
Try Shiken Premium for Free
How to Make an Impromptu Speech: 5 Strategies for Success
December 13, 2022

“So, Justine. What’s the status of your project?” If your name is Justine, you might have just panicked a little bit. Certainly, you can identify. We’ve all been in situations — at a meeting or a social gathering — when all eyes turn to us. They expect us to say something.
Worry not! Public speaking coach Lisa Kleiman, the founder of Speaktopia, has five strategies you can use on Yoodli to improve your public speaking, especially impromptu speaking. Impromptu speaking is all about confidence, and you can build that confidence by practicing in Yoodli’s pressure-free environment.
You can’t possibly have a ready response in every situation, but you can have a ready structure to use in any scenario. Continue reading to learn how to make an impromptu speech with Kleiman’s winning strategies.
Strategy #1: The 5 Ws
Speaking with or to people is easier when you have some sort of connection — some knowledge about what you’re like, what you know, or what you care about. They’re more likely to listen to you if they feel a bond with you.
If you’re called on to speak with or to people you’ve just met, that connection isn’t there — yet. But, you can make that connection by using the 5 Ws strategy . It involves asking questions:
- Who … ?
- What … ?
- Why … ?
- Where … ?
- When … ?
Here’s an example of how to make an impromptu speech using the 5 Ws strategy. Let’s say that you’re asked to lead a team discussion about the work-from-home policy — right now. You could try to articulate the policy and share how you think it’s working. You might assume that everyone already knows what it is and not state it. If you’re wrong in your assumption, some people will be confused. Is anyone still listening to you at this point?
Now let’s say that you know how to make an impromptu speech with the 5 Ws strategy. You start off by asking, “Who has clarity about what our current policy is?” The question engages your audience, getting them to think and respond. It also helps you know whether you need to review the policy. Then you ask, “What kind of feedback have you received about the policy?” Again, they’re thinking and responding. You’re getting information that helps you know which direction to take the discussion.
This strategy helps you establish a bond with your audience at the beginning because it instantly engages you in a conversation. This works even when you’re speaking in front of a large audience. Although it’s less of a dialogue, you can ask for a show of hands or use rhetorical questions to get them to listen and engage.
You can practice this impromptu speaking strategy with the “Record Speech” feature on the free Yoodli app. Click on “Not sure what to say? Try with a fun prompt.” See what W questions you can come up with!
Strategy #2: P.R.E.P.
Sometimes you’re prepared to speak, but you’re not ready for the curve balls that get thrown at you in the form of questions or remarks. Suddenly, your prepared speech turns into an impromptu speech. The P.R.E.P. strategy works for any kind of speech. Here’s how it works:
- Point — Make a singular point.
- Reasoning — Share the reasoning behind your point. This is the why to your what .
- Evidence — Share a concrete example or two that supports your point and your reasoning.
- Point — Circle back to your point and summarize it.
Here’s an example of how to make an impromptu speech using the P.R.E.P. strategy. You’re asked what you think should be added to the budget next quarter.
- Point — “I think we should hire a part-time assistant for Charles.”
- Reasoning — “I see Charles doing a lot of tasks that anyone can do, and he should be freed up to do what only he can do as the Development Director.”
- Evidence — “I saw this dynamic at the last organization I worked for. When the director was released of administrative tasks, she was able to spend a lot more time meeting with potential donors, and contributions went up and eventually covered the cost of the assistant and more.”
- Point — “A part-time assistant for Charles should be a budget priority for us if we want to see long-term growth in contributions.”
Strategy #3: S.E.E.
If you can appeal to someone’s logic or their emotions, you’re doing well. What if you could appeal to both? You’re likely to win them over to your idea. It’s great when you have a chance to prepare for a specific scenario, but sometimes you won’t get that chance. Still, you can be prepared with a strategy. The S.E.E. strategy is easy to remember and will help you appeal to your audience’s logic and emotions in impromptu situations.
Here’s what it stands for:
- Statement — Make a simple statement.
- Evidence — Provide evidence (facts) to support your statement and appeal to your audience’s reasoning.
- Emotion — Provide something (perhaps a story about a person) to support your statement and appeal to your audience’s emotions.
Here’s an example of how to make an impromptu speech using the S.E.E. strategy. You’re asked whether you think the company should have a holiday party this year.
- Statement — “We definitely should have a company holiday party.”
- Evidence — “Our team surveys indicate that it’s a significant morale boost and a major team bonding experience, and research shows that morale and bonding directly impact productivity.”
- Emotion — “You know Derrick? He used to show up at 9:00 every day, leave at 5:00, and barely talk to anyone in between. At last year’s party, he really came out of his shell when we brought out the karaoke machine. Now he’s taking on leadership roles with a confidence he (and we) never knew he had!”
You can practice this strategy with Yoodli’s free Interview Practice tool . Pick a question such as “Describe your leadership style” or any others that catch your eye.
Strategy #4: The 3 Ts
You’re probably familiar with the Introduction/Body/Conclusion communication structure. That’s essentially what the 3 Ts strategy is.
Here’s how it works:
- Tell them what you’re going to tell them. This buys you time and allows you to clarify what question your answering.
- Tell them. This is the meat of your response. After your introduction, you can go into detail.
- Tell them what you told them. This is a summary and a chance to give them a takeaway or a call to action.
Here’s an example of how to make an impromptu speech using the 3 Ts strategy. Let’s say that you’re asked to give a brief update on your project.
- Tell them what you’re going to tell them. “Sure, I’d be happy to give a quick progress report on my video project.”
- Tell them. “I’ve captured the raw footage, and I’m now in the editing process. I expect that to take a couple more days, and then I’ll get some feedback on it before finalizing it.”
- Tell them what you told them. “I’m on track with the video project, and your feedback will be helpful in a couple of days, so I’ll reach out then.”
Strategy #5: C.A.R.
Sometimes you’re asked on the spur of the moment to address a problem. The C.A.R. strategy for impromptu speaking is a great way to handle this. It lets you demonstrate that you have a good grasp of the problem and that your solution is worth exploring. Here’s how it works:
- Challenge — State the problem.
- Action — Offer a solution.
- Result — Cast a vision for the post-problem future.
Here’s an example of how to make an impromptu speech using the C.A.R. strategy. Your teammate comes to you, clearly anxious, and says that your team project is due tomorrow and it’s not on track to be completed.
- Challenge — “So, the project is due at tomorrow’s 3:00 meeting, and we still need to gather the sales data and get it into the presentation.”
- Action — “I can put my current task on hold and get the first quarter data, and I’ll ask Cate to get second quarter. If you’re comfortable prepping the template from the last presentation and plugging in the data we give you, that should be all we need.”
- Result — “The boss is going to love the presentation, and we’ll breathe easy when it’s done!”
Practice These Strategies
Now that you know how to make an impromptu speech with Kleiman’s five strategies,
it’s time to practice each one with your own AI speech coach at Yoodli. It will help you improve your speaking skills and overcome anxiety about being called on to speak.
If you’re feeling a little competitive, you can try one of the Yoodli impromptu speaking warmup exercises to beat your own high score. Get a daily streak of five, and you’ll see noticeable improvement.
If you haven’t done so already, sign up for free and take advantage of the practical tools and fun games. Yoodli’s AI analytics can train you to take whatever comes at you and respond with confidence and clarity.
Start practicing with Yoodli.
Getting better at speaking is getting easier. Record or upload a speech and let our AI Speech Coach analyze your speaking and give you feedback.
How to Present an Impromptu Speech: A Complete Guide to Ace Your Next Speech
I like building and growing simple yet powerful products for the world and the worldwide web.
Published Date : February 15, 2024
Reading Time :
If you have ever participated in a debate, you will admit to having to stay on your toes for the whole presentation. You are meant to come up with new counter-arguments quickly without much time to prepare. Coming up with impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics or presenting them can make people without glossophobia suffer from the fear of public speaking .
We all know that you can’t read the mind of the impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics generator, so you must understand the concept of impromptu speaking to ace your next speaking opportunity . I am here with a detailed guide to help you understand impromptu speaking and coming up with examples of impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics examples.
I am going to:
- Help you understand the concept of impromptu speaking.
- The structure and characteristics of impromptu speeches
- Share funny impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics and give examples of impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics.
- Talk about the disadvantages of impromptu speaking and more.
I can’t advise skipping any of these segments, as each will help you better understand impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics. However, if you are already a pro at impromptu speaking, you can skip to the end, where I summarize all I have said and conclude.
What is the Definition?
The word impromptu means something done in the spur of the moment. As the word impromptu implies, an impromptu or extemporaneous Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech is a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech a speaker delivers with little to no prior preparation.
Here, someone assigns random Impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics to speakers to think over for a few seconds and come up with relevant content.
Impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics are common during declamation contests, debates, Public Speaking <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking refers to any live presentation or speech. It can cover a variety of topics on various fields and careers (you can find out more about public speaking careers here: https://orai.com/blog/public-speaking-careers/. Public speaking can inform, entertain, or educate an audience and sometimes has visual aids.</p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking is done live, so the speakers need to consider certain factors to deliver a successful speech. No matter how good the speech is, if the audience doesn't connect with the speaker, then it may fall flat. Therefore, speakers have to use a lot more nonverbal communication techniques to deliver their message. </p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:heading --> <h2>Tips for public speaking</h2> <!-- /wp:heading --><br /><!-- wp:list --> <ul> <li>Have a sense of humor.</li> <li>Tell personal stories that relate to the speech you're giving.</li> <li>Dress appropriately for the event. Formal and business casual outfits work best.</li> <li>Project a confident and expressive voice.</li> <li>Always try to use simple language that everyone can understand.</li> <li>Stick to the time given to you.</li> <li>Maintain eye contact with members of your audience and try to connect with them.</li> </ul> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/public-speaking/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">public speaking courses, panel discussions, school, group discussions, and more. In debates, the Impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics generator is usually the argument the opponent raises.
Impromptu speaking is a huge part of communication since we don’t have a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech structure when talking to colleagues and friends. Extemporaneous Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech delivery is becoming more popular, so understanding and getting better will help you in different aspects of life.
See this video:
How to Deliver a Good Impromptu Speech?
We have already established that impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topic presentations do not give you ample time to prepare (that is if they provide you with any preparation time at all). Sometimes, the need to present such extemporaneous speeches happens at defining moments in your career , like:
- When you have to fill in for a late or absent speaker at an event
- Being on a discussion panel and being hit with a question you did not anticipate or prepare for
- Self-introduction at networking events
- Interview by a reporter
- An unexpected question at a job interview
- When you give an idea in a meeting and face an unanticipated rebuff and suddenly need to defend your point further
- When someone refers to you mid-presentation for an input
- Having to give an unplanned toast at a company party
- Being pulled to provide an update in a meeting you were not originally part of
- When your boss suddenly asks you to give a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech at your goodbye party.
However, we all know that an excellent Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech presentation requires presentation and ample practice. So, how do you deliver your impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics presentation and excel at it without enough preparation time?
Sometimes, like debates or extemporaneous Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech competitions, you may get time to brainstorm ideas and develop a structure. The judges will typically grade the result of the Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech based on the balance between time spent talking and relevance.
So, how do you make your impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech balance between time and relevance? How do you even create a worthy structure in little to no time? I will be answering these questions in the following subheading.
What Are Great Ways To Structure this Speech?
First, an impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech requires an introduction, body, and conclusion, which I will discuss soon. How do you create a structure that includes these and still has an excellent delivery?
I have four tips to help you create a great impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech structure.
Telling the Truth is Perfect
When mentally planning your impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , it’s best to choose impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics that center around the truth.
There is no need to exaggerate or develop a new scenario. Your brain already has difficulty figuring out perfect impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics, so you do not need to add to the burden.
With impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics, it is best to:
- Stick to facts
- Say what is valid at the moment.
- Summarize and try to be better next time― if you feel you are at your wit’s end.
Choose Speech Topics You Know Very Well
Like every Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics are better focused on an area where you have a proper education. With other public speaking categories , it is easy for the presenter to run in-depth studies on topics they aren’t familiar with and prepare properly to give a spectacular Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech .
The case is different for extemporaneous speaking since you do not have enough time to properly research your impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topic examples. Therefore, it’s best to stick with a topic in a field you have prior knowledge of.
Sharing Personal Experience is Helpful
When you think of impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics, it is best to center it around your personal experience, except you have a separate impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics generator. Talking from experience doesn’t need special memory aids or research.
Understandably, we have limited experience as humans, so you may not have any experience with the assigned impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topic. The best thing to do here is to search your memory for any time someone has told you a story about it or when you read it in a book.
For example, if you were to talk about the meaning of life, you could share a near-death experience, a quote on it, a friend’s experience, or something you read in a book that made you question the meaning of life.
The best part of sharing from personal experiences is that you could try your luck with funny, impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics.
When You Have Time to Practice, Do It Out Loud.
If you have enough time to practice, it’s best to practice aloud to make sense of what you are saying. One way to practice easily is by using the Orai app since it can give you feedback.
However, you can start practicing today to build confidence by
Check these videos out for help with Public Speaking <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking refers to any live presentation or speech. It can cover a variety of topics on various fields and careers (you can find out more about public speaking careers here: https://orai.com/blog/public-speaking-careers/. Public speaking can inform, entertain, or educate an audience and sometimes has visual aids.</p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking is done live, so the speakers need to consider certain factors to deliver a successful speech. No matter how good the speech is, if the audience doesn't connect with the speaker, then it may fall flat. Therefore, speakers have to use a lot more nonverbal communication techniques to deliver their message. </p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:heading --> <h2>Tips for public speaking</h2> <!-- /wp:heading --><br /><!-- wp:list --> <ul> <li>Have a sense of humor.</li> <li>Tell personal stories that relate to the speech you're giving.</li> <li>Dress appropriately for the event. Formal and business casual outfits work best.</li> <li>Project a confident and expressive voice.</li> <li>Always try to use simple language that everyone can understand.</li> <li>Stick to the time given to you.</li> <li>Maintain eye contact with members of your audience and try to connect with them.</li> </ul> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/public-speaking/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">public speaking :
Now that we have seen tips on creating an impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech let us discuss proper structure. As I said earlier, the design of an impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech includes:
Introduction
Creating a structure is essential because it helps organize your thoughts to avoid meaningless rambling and gives you a sense of direction.
Start by addressing whoever called you up like a chairperson. Afterward, you could go for a one-line about your impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topic.
Next, share your honest feelings or opinions on your impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topic. It gives a form of background and serves as a great introductory point.
Shed more light on the topic. You can share an anecdote or tell a story related to the topic. Remember the four tips we spoke of earlier and keep them in mind. Here, you should:
- Use two or three main points to discuss a central theme.
- Use relevant supporting details like the stories we talked about earlier.
If you have no relevant story related to your impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topic, it is best to conduct a direct old-fashioned discussion or a question-and-answer section.
The best way to end is to relate your story or discussion to your main point for relevance. You can also share final pointers as you round up. Remember to keep things simple and acknowledge the chairperson.
What are the Characteristics?
Most of the characteristics of impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics center around its nature of spontaneity. Impromptu speeches are characterized by:
- Little to no preparation time
- Spontaneously organized points
- Short presentation time
How To Give A One-Minute Speech?
Giving one-minute speeches can be a scary ordeal. Combined with the sudden nature of an impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , it could be a nightmare.
The easiest way to give an impromptu one-minute Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech is to:
- State your point
- Share your reason for choosing your point.
- Give an example of your point.
- Bring it back and relate what you said to your main point.
Before you realize it, your one minute is up, and you can move on.
How do you give an imp impromptu speech within a minute?
When you have your impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topic and want to present a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech within a minute, focusing on a single message is the best direction to follow. As stated in the previous section, keeping things around a point makes your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech more meaningful and impactful.
No matter how long your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech is, if you have a single message, it helps your audience remember what you said.
Even if you want to present funny, impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics, focusing on a central comedy theme is best. Too many aspects make it difficult to keep your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech within a minute.
It is also essential to remember that all the rules of impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech presentation still apply here. One of the best ways to start a one-minute funny, impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topic presentation is by letting your audience know you plan to keep things short.
Remember to keep it simple and end with your core point (nothing too dramatic is necessary).
How Can One Improve Impromptu Speech?
How do you improve your impromptu speaking skills so they stop being the bane of your existence? I will share seven strategies you can apply to win in impromptu speaking.
- Anticipate possible scenarios where you must give an impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech and prepare for it.
- Keep it simple by organizing your thoughts around a simple template. You can use the one-minute Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech guide.
- Frame your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech as a Q&A section to help you direct your address.
- Storytelling is a speaker’s best friend.
- Try not to ramble and overstress a single point.
- Don’t set the bar too high. Try to improve within realistic standards.
- Practice for impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech moments in your comfort zone. You can always consult orai to be your Speech Coach <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:411">A <strong>speech coach</strong> is a trained professional who provides personalized guidance and support to individuals seeking to improve their <strong>public speaking</strong> skills. Whether you aim to <strong>master public speaking</strong> for professional presentations, overcome stage fright, or simply hone your everyday communication, a <strong>speech coach</strong> can tailor their expertise to meet your needs and goals.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:32"><strong>What Does a Speech Coach Do?</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-13:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:124"><strong>Conduct assessments:</strong> Analyze your strengths, weaknesses, and communication style through evaluations and observations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:149"><strong>Develop personalized plans:</strong> Create a customized roadmap with exercises, techniques, and feedback to address your specific areas of improvement.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:167"><strong>Offer expert instruction:</strong> We will guide you through various aspects of public speaking, including vocal control, body language, content delivery, and overcoming anxiety.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:168"><strong>Provide practice opportunities:</strong> Facilitate mock presentations, simulations, and role-playing scenarios to refine your skills in a safe and supportive environment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-11:114"><strong>Offer constructive feedback:</strong> Identify areas for improvement and suggest strategies for achieving your goals.</li> <li data-sourcepos="12:1-13:0"><strong>Boost confidence and motivation:</strong> Encourage and support you throughout your journey, empowering you to become a confident and impactful communicator.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="14:1-14:40"><strong>Who Can Benefit from a Speech Coach?</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="16:1-20:0"> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:174"><strong>Professionals:</strong> Refining public speaking skills can benefit executives, entrepreneurs, salespeople, leaders, and anyone who presents in professional settings.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:160"><strong>Students:</strong> Teachers, public speakers, debaters, and students wanting to excel in presentations or classroom settings can gain valuable skills with a coach.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-18:176"><strong>Individuals who fear public speaking:</strong> Coaching can help those who experience anxiety or nervousness when speaking in public develop strategies and gain confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="19:1-20:0"><strong>Anyone seeking to improve communication:</strong> A coach can provide guidance to individuals seeking to enhance their communication skills for personal or professional development.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="21:1-21:28"><strong>Types of Speech Coaches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="23:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:110"><strong>Private coaches:</strong> Work one-on-one with individuals to provide highly personalized attention and feedback.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:130"><strong>Group coaches:</strong> Offer workshops or classes in group settings, often at a lower cost but with less individualized attention.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Specialization coaches:</strong> Some coaches specialize in executive communication, storytelling, or presentation design.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:35"><strong>Finding the Right Speech Coach:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-33:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:91"><strong>Identify your goals:</strong> What areas do you want to improve? What are your specific needs?</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:109"><strong>Research credentials and experience:</strong> Look for qualified coaches with relevant experience and expertise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:122"><strong>Consider availability and budget:</strong> Set a budget and explore options that fit your schedule and financial constraints.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-33:0"><strong>Schedule consultations:</strong> Talk to potential coaches to assess their personality, approach, and compatibility with your needs.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="34:1-34:418"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="34:1-34:418">Investing in a <strong>speech coach</strong> can be a transformative experience, enhancing your communication skills, boosting your confidence, and empowering you to achieve your communication goals. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting your journey, consider exploring the potential of working with a <strong>speech coach</strong> to unlock your full potential as a communicator and <strong>master public speaking</strong>.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech-coach/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech coach .
What Are Some Great Examples?
Although it seems like I have only been referring to funny impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics, there are numerous examples of impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics.
So, funny impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics aside, what examples of extemporaneous Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech exist?
Persuasive Impromptu Speech Topics
- The government should stop receiving foreign aid.
- Painkillers should become prescription drugs.
- Social media is creating sociopaths.
- We learn the most outside the school environment.
- Try making immigration laws more flexible.
- Do churches need to pay taxes?
Debate Impromptu Speech Topics
- Is being an adult as hard as young adults make it seem?
- Does the end always justify the means?
- Are government officials receiving more than their world?
- Should plastic production completely stop?
- Is democracy essential when everyone is apathetic?
- Should schools stop having orthodox class sessions?
Personal Impromptu Speech Topics
- Overcoming my worst fear
- Things I cannot live without
- The most important person in the world to me
- My favorite season
- Why I will never go swimming again
- What I fear the most about the future
Abstract Impromptu Speech Topics
- Patience is a fool’s virtue.
- Everything is beautiful to its soulmate.
- The unity in factions
- I got flowers today
- The bane of my existence
- Something worth more than gold
Humorous Or Funny Impromptu Speech Topics
- Most awkward nickname
- Making reality disappear
- What is worse than always being broke?
- Does normal exist?
- Is laughter a better medicine than water?
- Should you marry for love or money?
Here is an example of a funny impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topic presentation:
Business Impromptu Speech Topics
- How to improve return on investment
- Can you decrease the cost of production for a higher profit margin?
- Preventing financial fraud
- Navigating unfavorable government policies
- Getting the best internal auditor
- Strategic solutions to e-marketing
Demonstrative Impromptu Speech Topics
- Starting a blog and excelling at it
- Applying for your dream job/ to your dream college
- Improving your etiquette
- Giving an impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech in one minute
- How to sell anything
Student’s Impromptu Speech Topics
- What does Christmas mean to you?
- Why do schools have dress policies?
- My dream job opportunity
- What I would do if I were invisible for a day
- Why do earthquakes occur?
An example of an impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech presentation is https://youtu.be/XS8IIjngJ8M.
What are some good mindsets to have?
Honestly, I believe the best mindset to face funny impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics opportunities is with a positive attitude. It is best to anticipate all the possibilities of facing an extemporaneous speaking moment and prepare accordingly.
What are the Disadvantages of an Impromptu Speech?
What are the disadvantages of impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ? Its nature alone is a disadvantage since it does not give you enough time to prepare.
Other disadvantages of impromptu speeches are:
- There is no room to verify facts.
- You cannot take back the words you say
- It is a high-stress situation.
- It is possible to make numerous grammatical errors, but you can reduce the chance with enough practice.
Why is delivering an impromptu speech an important skill to have?
Delivering impromptu speeches, a critical skill for personal and professional settings, alleviates anxiety, fosters quick thinking, and enhances communication. Honing this skill through practice trains your brain to respond eloquently, equipping you to confidently navigate unforeseen speaking situations and making it an essential tool for life’s unpredictable moments.
How can impromptu speeches be practiced?
Impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech practice involves various techniques: speaking on random slides for 30 seconds to improve quick thinking, receiving feedback to identify areas for improvement, self-evaluating through audio recordings to gain insights, and finally, enhancing spontaneous speaking abilities. These exercises simulate real-life scenarios, training your brain to think quickly and adapt, ultimately making you more confident and impactful in unexpected speaking situations.
What are some tips for giving an impromptu speech?
Master the art of impromptu speeches with this comprehensive guide! Start by clearly stating your main point, explaining your focus, and using a relatable example. Keep it concise and tie it all back for maximum impact. Anticipate scenarios, use simple templates, consider Q&A formats, weave in stories, avoid rambling, set realistic goals, and practice with tools like Orai. Be confident, impactful, and ready to speak on the spot!
As promised, I will give a summary of my main points. An impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech is already high-stress without the additional tension you place on yourself. In these situations, a bit of knowledge proves truly helpful.
Some points to remember are:
- Practice as much impromptu speaking as possible with random impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics in your free time. It helps.
- Stick to what is factual and correct to avoid unnecessary stress
- Know the kinds of situations that may call for an impromptu Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech and educate yourself on topics in that niche
- Keep it simple and around a central idea.
I hope these tips help you, and good luck on your next impromptu speaking opportunity! Orai is an AI-powered Speech Coach <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:411">A <strong>speech coach</strong> is a trained professional who provides personalized guidance and support to individuals seeking to improve their <strong>public speaking</strong> skills. Whether you aim to <strong>master public speaking</strong> for professional presentations, overcome stage fright, or simply hone your everyday communication, a <strong>speech coach</strong> can tailor their expertise to meet your needs and goals.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:32"><strong>What Does a Speech Coach Do?</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-13:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:124"><strong>Conduct assessments:</strong> Analyze your strengths, weaknesses, and communication style through evaluations and observations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:149"><strong>Develop personalized plans:</strong> Create a customized roadmap with exercises, techniques, and feedback to address your specific areas of improvement.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:167"><strong>Offer expert instruction:</strong> We will guide you through various aspects of public speaking, including vocal control, body language, content delivery, and overcoming anxiety.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:168"><strong>Provide practice opportunities:</strong> Facilitate mock presentations, simulations, and role-playing scenarios to refine your skills in a safe and supportive environment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-11:114"><strong>Offer constructive feedback:</strong> Identify areas for improvement and suggest strategies for achieving your goals.</li> <li data-sourcepos="12:1-13:0"><strong>Boost confidence and motivation:</strong> Encourage and support you throughout your journey, empowering you to become a confident and impactful communicator.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="14:1-14:40"><strong>Who Can Benefit from a Speech Coach?</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="16:1-20:0"> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:174"><strong>Professionals:</strong> Refining public speaking skills can benefit executives, entrepreneurs, salespeople, leaders, and anyone who presents in professional settings.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:160"><strong>Students:</strong> Teachers, public speakers, debaters, and students wanting to excel in presentations or classroom settings can gain valuable skills with a coach.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-18:176"><strong>Individuals who fear public speaking:</strong> Coaching can help those who experience anxiety or nervousness when speaking in public develop strategies and gain confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="19:1-20:0"><strong>Anyone seeking to improve communication:</strong> A coach can provide guidance to individuals seeking to enhance their communication skills for personal or professional development.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="21:1-21:28"><strong>Types of Speech Coaches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="23:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:110"><strong>Private coaches:</strong> Work one-on-one with individuals to provide highly personalized attention and feedback.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:130"><strong>Group coaches:</strong> Offer workshops or classes in group settings, often at a lower cost but with less individualized attention.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Specialization coaches:</strong> Some coaches specialize in executive communication, storytelling, or presentation design.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:35"><strong>Finding the Right Speech Coach:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-33:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:91"><strong>Identify your goals:</strong> What areas do you want to improve? What are your specific needs?</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:109"><strong>Research credentials and experience:</strong> Look for qualified coaches with relevant experience and expertise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:122"><strong>Consider availability and budget:</strong> Set a budget and explore options that fit your schedule and financial constraints.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-33:0"><strong>Schedule consultations:</strong> Talk to potential coaches to assess their personality, approach, and compatibility with your needs.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="34:1-34:418"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="34:1-34:418">Investing in a <strong>speech coach</strong> can be a transformative experience, enhancing your communication skills, boosting your confidence, and empowering you to achieve your communication goals. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting your journey, consider exploring the potential of working with a <strong>speech coach</strong> to unlock your full potential as a communicator and <strong>master public speaking</strong>.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech-coach/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech coach that fits in your pocket and can help you with your needs for public speaking ! Orai offers a customized learning experience based on your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech recordings and helps you learn new Public Speaking <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking refers to any live presentation or speech. It can cover a variety of topics on various fields and careers (you can find out more about public speaking careers here: https://orai.com/blog/public-speaking-careers/. Public speaking can inform, entertain, or educate an audience and sometimes has visual aids.</p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking is done live, so the speakers need to consider certain factors to deliver a successful speech. No matter how good the speech is, if the audience doesn't connect with the speaker, then it may fall flat. Therefore, speakers have to use a lot more nonverbal communication techniques to deliver their message. </p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:heading --> <h2>Tips for public speaking</h2> <!-- /wp:heading --><br /><!-- wp:list --> <ul> <li>Have a sense of humor.</li> <li>Tell personal stories that relate to the speech you're giving.</li> <li>Dress appropriately for the event. Formal and business casual outfits work best.</li> <li>Project a confident and expressive voice.</li> <li>Always try to use simple language that everyone can understand.</li> <li>Stick to the time given to you.</li> <li>Maintain eye contact with members of your audience and try to connect with them.</li> </ul> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/public-speaking/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">public speaking techniques. They provide instant feedback on your pronunciation, Conciseness <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:326">In the realm of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>conciseness</strong> refers to the ability to express your message clearly and effectively using the fewest possible words. It's about conveying your ideas precisely, avoiding unnecessary details and rambling while maintaining your message's essence and impact.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:33"><strong>Benefits for Public Speakers:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:137"><strong>Engaged audience:</strong> A concise speech keeps your audience focused and prevents them from losing interest due to excessive information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:117"><strong>Increased clarity:</strong> By removing unnecessary clutter, your core message becomes clearer and easier to understand.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:137"><strong>Enhanced credibility:</strong> Concise communication projects professionalism and efficiency, making you appear more confident and prepared.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Knowing you have a clear and concise message can help manage <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong> by minimizing the pressure to fill time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:35"><strong>Challenges for Public Speakers:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:126"><strong>Striking a balance:</strong> Knowing where to draw the line between conciseness and omitting important information can be tricky.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:115"><strong>Avoiding oversimplification:</strong> Complex topics may require elaboration to ensure clarity and understanding.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Overcoming natural tendencies:</strong> Some speakers naturally use more words than others, requiring a conscious effort to be concise.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:41"><strong>Strategies for Achieving Conciseness:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="20:1-25:0"> <li data-sourcepos="20:1-20:92"><strong>Identify your core message:</strong> What is your audience's main point to remember?</li> <li data-sourcepos="21:1-21:128"><strong>Prioritize and eliminate:</strong> Analyze your content and remove any information not directly supporting your core message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:133"><strong>Use strong verbs and active voice:</strong> This makes your sentences more impactful and avoids passive constructions that can be wordy.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:109"><strong>Simplify your language:</strong> Avoid jargon and technical terms unless they are essential and clearly defined.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-25:0"><strong>Practice and refine:</strong> Rehearse your speech aloud and identify areas where you can tighten your wording or eliminate redundancies.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="26:1-26:20"><strong>Additional Tips:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="28:1-31:0"> <li data-sourcepos="28:1-28:93"><strong>Use storytelling:</strong> Engaging narratives can convey complex ideas concisely and memorably.</li> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:110"><strong>Focus on the visuals:</strong> Powerful visuals can support your message without extensive explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-31:0"><strong>Embrace silence:</strong> Pausing deliberately can emphasize key points and give your audience time to absorb your message.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="32:1-32:404"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="32:1-32:404"><strong>Conciseness</strong> is a powerful tool for <strong>public speakers</strong>. By eliminating unnecessary words and focusing on your core message, you can create a more engaging, impactful, and memorable presentation for your audience. This can also help manage <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong> by reducing the pressure to fill time and enabling you to focus on delivering your message with clarity and confidence.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/conciseness/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">conciseness , and more! Start your free trial today!
You might also like
How many words is a 5-minute speech, good attention getters for speeches with 10+ examples, quick links.
- Presentation Topics
Useful Links
- Start free trial
- The art of public speaking
- improve public speaking
- mastering public speaking
- public speaking coach
- professional speaking
- public speaking classes - Courses
- public speaking anxiety
- © Orai 2023
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance

How To Judge Impromptu
Basic understanding.
Impromptu is a public speaking event where students have seven minutes to select a topic, brainstorm their ideas, outline the speech, and finally, deliver the speech. The speech is given without notes and uses an introduction, body, and conclusion. The speech can be light-hearted or serious. The speech can be based upon prompts that range from nursery rhymes, current events, celebrities, organizations, and more.
In an Impromptu round the speaker draws three prompts from an envelope. After drawing the three prompts, the student must select one and begin brainstorming their ideas for the speech. In total, a student has seven minutes. This seven minutes may be divided up by the student however they see fit. For instance, they could brainstorm and outline their ideas for three minutes and then deliver a four-minute speech; or they could brainstorm and outline for one minute and speak for six minutes. There is no minimum amount of time required for brainstorming and no minimum amount of time for speaking. Therefore, the student should work to develop the best possible structure and reasoning in as short amount of time as possible. Sometimes students think it’s more impressive to speak longer, but if the ideas aren’t clear or well developed, it can detract from the overall performance.
Conversely, a well-thought out but short speech restricts a student’s ability to spend adequate time analyzing the prompt. Therefore, examine which students struck the best balance between preparation and speaking. An Impromptu speech follows a basic structure in which a student presents an introduction, body, and conclusion. Similar to other public speaking events, the introduction should provide adequate context for the trajectory of the speech. If a student has illustrated an example, conveyed their chosen prompt, and provided a thesis statement for the speech, they have created a structurally sound introduction! The most common formulation for the body of the speech is to explore two or three topic areas in greater depth. For example, if a student’s thesis focuses on cultivating innovation, they would likely introduce two effective ways to do so and use examples to prove their point. Following this, the student will conclude the speech by reiterating the prompt, thesis, and main arguments.
As a judge, ask yourself if the speaker has created sound arguments, used a structure that was easy to follow, and held your attention for the duration of their speaking time. Students who do well in those three categories have demonstrated effective Impromptu speaking skills.
Evaluating the Round
When evaluating an Impromptu round, consider three main criteria.
First, organization . Does the student have a clear structure to their speech? Are transitions used to move effectively between each part of the speech? Does the development of the speech make sense?
Second, analysis . Does the student directly address the prompt? Does the student develop justifications for their ideas and establish significance to the points?
Third, delivery . Does the student use voice, movement, and expression effectively? Is the speaker confident? Is there consistent eye contact? Is the volume appropriate?
Filling Out the Ballot
Performers are ranked compared to the other students in their room with the best performance receiving the one ranking. The judge may also assign speaker points, typically in a range from 90 and 100, with 100 being outstanding.
The judge writes on the ballot how the speaker can improve (e.g., eye contact, clarity, emotion, etc.) and what the student did well. This is an educational activity and all feedback is welcome. Please make sure the feedback is constructive and not merely critical.
404 Not found
15 Powerful Speech Opening Lines (And How to Create Your Own)
Hrideep barot.
- Public Speaking , Speech Writing

Powerful speech opening lines set the tone and mood of your speech. It’s what grips the audience to want to know more about the rest of your talk.
The first few seconds are critical. It’s when you have maximum attention of the audience. And you must capitalize on that!
Instead of starting off with something plain and obvious such as a ‘Thank you’ or ‘Good Morning’, there’s so much more you can do for a powerful speech opening (here’s a great article we wrote a while ago on how you should NOT start your speech ).
To help you with this, I’ve compiled some of my favourite openings from various speakers. These speakers have gone on to deliver TED talks , win international Toastmaster competitions or are just noteworthy people who have mastered the art of communication.
After each speaker’s opening line, I have added how you can include their style of opening into your own speech. Understanding how these great speakers do it will certainly give you an idea to create your own speech opening line which will grip the audience from the outset!
Alright! Let’s dive into the 15 powerful speech openings…
Note: Want to take your communications skills to the next level? Book a complimentary consultation with one of our expert communication coaches. We’ll look under the hood of your hurdles and pick two to three growth opportunities so you can speak with impact!
1. Ric Elias
Opening: “Imagine a big explosion as you climb through 3,000 ft. Imagine a plane full of smoke. Imagine an engine going clack, clack, clack. It sounds scary. Well I had a unique seat that day. I was sitting in 1D.”
How to use the power of imagination to open your speech?
Putting your audience in a state of imagination can work extremely well to captivate them for the remainder of your talk.
It really helps to bring your audience in a certain mood that preps them for what’s about to come next. Speakers have used this with high effectiveness by transporting their audience into an imaginary land to help prove their point.
When Ric Elias opened his speech, the detail he used (3000 ft, sound of the engine going clack-clack-clack) made me feel that I too was in the plane. He was trying to make the audience experience what he was feeling – and, at least in my opinion, he did.
When using the imagination opening for speeches, the key is – detail. While we want the audience to wander into imagination, we want them to wander off to the image that we want to create for them. So, detail out your scenario if you’re going to use this technique.
Make your audience feel like they too are in the same circumstance as you were when you were in that particular situation.
2. Barack Obama
Opening: “You can’t say it, but you know it’s true.”
3. Seth MacFarlane
Opening: “There’s nowhere I would rather be on a day like this than around all this electoral equipment.” (It was raining)
How to use humour to open your speech?
When you use humour in a manner that suits your personality, it can set you up for a great speech. Why? Because getting a laugh in the first 30 seconds or so is a great way to quickly get the audience to like you.
And when they like you, they are much more likely to listen to and believe in your ideas.
Obama effortlessly uses his opening line to entice laughter among the audience. He brilliantly used the setting (the context of Trump becoming President) and said a line that completely matched his style of speaking.
Saying a joke without really saying a joke and getting people to laugh requires you to be completely comfortable in your own skin. And that’s not easy for many people (me being one of them).
If the joke doesn’t land as expected, it could lead to a rocky start.
Keep in mind the following when attempting to deliver a funny introduction:
- Know your audience: Make sure your audience gets the context of the joke (if it’s an inside joke among the members you’re speaking to, that’s even better!). You can read this article we wrote where we give you tips on how you can actually get to know your audience better to ensure maximum impact with your speech openings
- The joke should suit your natural personality. Don’t make it look forced or it won’t elicit the desired response
- Test the opening out on a few people who match your real audience. Analyze their response and tweak the joke accordingly if necessary
- Starting your speech with humour means your setting the tone of your speech. It would make sense to have a few more jokes sprinkled around the rest of the speech as well as the audience might be expecting the same from you
4. Mohammed Qahtani
Opening: Puts a cigarette on his lips, lights a lighter, stops just before lighting the cigarette. Looks at audience, “What?”
5. Darren Tay
Opening: Puts a white pair of briefs over his pants.
How to use props to begin your speech?
The reason props work so well in a talk is because in most cases the audience is not expecting anything more than just talking. So when a speaker pulls out an object that is unusual, everyone’s attention goes right to it.
It makes you wonder why that prop is being used in this particular speech.
The key word here is unusual . To grip the audience’s attention at the beginning of the speech, the prop being used should be something that the audience would never expect. Otherwise, it just becomes something that is common. And common = boring!
What Mohammed Qahtani and Darren Tay did superbly well in their talks was that they used props that nobody expected them to.
By pulling out a cigarette and lighter or a white pair of underwear, the audience can’t help but be gripped by what the speaker is about to do next. And that makes for a powerful speech opening.
6. Simon Sinek
Opening: “How do you explain when things don’t go as we assume? Or better, how do you explain when others are able to achieve things that seem to defy all of the assumptions?”
7. Julian Treasure
Opening: “The human voice. It’s the instrument we all play. It’s the most powerful sound in the world. Probably the only one that can start a war or say “I love you.” And yet many people have the experience that when they speak people don’t listen to them. Why is that? How can we speak powerfully to make change in the world?”
How to use questions to open a speech?
I use this method often. Starting off with a question is the simplest way to start your speech in a manner that immediately engages the audience.
But we should keep our questions compelling as opposed to something that is fairly obvious.
I’ve heard many speakers start their speeches with questions like “How many of us want to be successful?”
No one is going to say ‘no’ to that and frankly, I just feel silly raising my hand at such questions.
Simon Sinek and Jullian Treasure used questions in a manner that really made the audience think and make them curious to find out what the answer to that question is.
What Jullian Treasure did even better was the use of a few statements which built up to his question. This made the question even more compelling and set the theme for what the rest of his talk would be about.
So think of what question you can ask in your speech that will:
- Set the theme for the remainder of your speech
- Not be something that is fairly obvious
- Be compelling enough so that the audience will actually want to know what the answer to that question will be
8. Aaron Beverley
Opening: Long pause (after an absurdly long introduction of a 57-word speech title). “Be honest. You enjoyed that, didn’t you?”
How to use silence for speech openings?
The reason this speech opening stands out is because of the fact that the title itself is 57 words long. The audience was already hilariously intrigued by what was going to come next.
But what’s so gripping here is the way Aaron holds the crowd’s suspense by…doing nothing. For about 10 to 12 seconds he did nothing but stand and look at the audience. Everyone quietened down. He then broke this silence by a humorous remark that brought the audience laughing down again.
When going on to open your speech, besides focusing on building a killer opening sentence, how about just being silent?
It’s important to keep in mind that the point of having a strong opening is so that the audience’s attention is all on you and are intrigued enough to want to listen to the rest of your speech.
Silence is a great way to do that. When you get on the stage, just pause for a few seconds (about 3 to 5 seconds) and just look at the crowd. Let the audience and yourself settle in to the fact that the spotlight is now on you.
I can’t put my finger on it, but there is something about starting the speech off with a pure pause that just makes the beginning so much more powerful. It adds credibility to you as a speaker as well, making you look more comfortable and confident on stage.
If you want to know more about the power of pausing in public speaking , check out this post we wrote. It will give you a deeper insight into the importance of pausing and how you can harness it for your own speeches. You can also check out this video to know more about Pausing for Public Speaking:
9. Dan Pink
Opening: “I need to make a confession at the outset here. Little over 20 years ago, I did something that I regret. Something that I’m not particularly proud of. Something that in many ways I wish no one would ever know but that here I feel kind of obliged to reveal.”
10. Kelly McGonigal
Opening: “I have a confession to make. But first I want you to make a little confession to me.”
How to use a build-up to open your speech?
When there are so many amazing ways to start a speech and grip an audience from the outset, why would you ever choose to begin your speech with a ‘Good morning?’.
That’s what I love about build-ups. They set the mood for something awesome that’s about to come in that the audience will feel like they just have to know about.
Instead of starting a speech as it is, see if you can add some build-up to your beginning itself. For instance, in Kelly McGonigal’s speech, she could have started off with the question of stress itself (which she eventually moves on to in her speech). It’s not a bad way to start the speech.
But by adding the statement of “I have a confession to make” and then not revealing the confession for a little bit, the audience is gripped to know what she’s about to do next and find out what indeed is her confession.
11. Tim Urban
Opening: “So in college, I was a government major. Which means that I had to write a lot of papers. Now when a normal student writes a paper, they might spread the work out a little like this.”
12. Scott Dinsmore
Opening: “8 years ago, I got the worst career advice of my life.”
How to use storytelling as a speech opening?
“The most powerful person in the world is the storyteller.” Steve Jobs
Storytelling is the foundation of good speeches. Starting your speech with a story is a great way to grip the audience’s attention. It makes them yearn to want to know how the rest of the story is going to pan out.
Tim Urban starts off his speech with a story dating back to his college days. His use of slides is masterful and something we all can learn from. But while his story sounds simple, it does the job of intriguing the audience to want to know more.
As soon as I heard the opening lines, I thought to myself “If normal students write their paper in a certain manner, how does Tim write his papers?”
Combine such a simple yet intriguing opening with comedic slides, and you’ve got yourself a pretty gripping speech.
Scott Dismore’s statement has a similar impact. However, just a side note, Scott Dismore actually started his speech with “Wow, what an honour.”
I would advise to not start your talk with something such as that. It’s way too common and does not do the job an opening must, which is to grip your audience and set the tone for what’s coming.
13. Larry Smith
Opening: “I want to discuss with you this afternoon why you’re going to fail to have a great career.”
14. Jane McGonigal
Opening: “You will live 7.5 minutes longer than you would have otherwise, just because you watched this talk.”
How to use provocative statements to start your speech?
Making a provocative statement creates a keen desire among the audience to want to know more about what you have to say. It immediately brings everyone into attention.
Larry Smith did just that by making his opening statement surprising, lightly humorous, and above all – fearful. These elements lead to an opening statement which creates so much curiosity among the audience that they need to know how your speech pans out.
This one time, I remember seeing a speaker start a speech with, “Last week, my best friend committed suicide.” The entire crowd was gripped. Everyone could feel the tension in the room.
They were just waiting for the speaker to continue to know where this speech will go.
That’s what a hard-hitting statement does, it intrigues your audience so much that they can’t wait to hear more! Just a tip, if you do start off with a provocative, hard-hitting statement, make sure you pause for a moment after saying it.
Silence after an impactful statement will allow your message to really sink in with the audience.
Related article: 5 Ways to Grab Your Audience’s Attention When You’re Losing it!
15. Ramona J Smith
Opening: In a boxing stance, “Life would sometimes feel like a fight. The punches, jabs and hooks will come in the form of challenges, obstacles and failures. Yet if you stay in the ring and learn from those past fights, at the end of each round, you’ll be still standing.”
How to use your full body to grip the audience at the beginning of your speech?
In a talk, the audience is expecting you to do just that – talk. But when you enter the stage and start putting your full body into use in a way that the audience does not expect, it grabs their attention.
Body language is critical when it comes to public speaking. Hand gestures, stage movement, facial expressions are all things that need to be paid attention to while you’re speaking on stage. But that’s not I’m talking about here.
Here, I’m referring to a unique use of the body that grips the audience, like how Ramona did. By using her body to get into a boxing stance, imitating punches, jabs and hooks with her arms while talking – that’s what got the audience’s attention.
The reason I say this is so powerful is because if you take Ramona’s speech and remove the body usage from her opening, the entire magic of the opening falls flat.
While the content is definitely strong, without those movements, she would not have captured the audience’s attention as beautifully as she did with the use of her body.
So if you have a speech opening that seems slightly dull, see if you can add some body movement to it.
If your speech starts with a story of someone running, actually act out the running. If your speech starts with a story of someone reading, actually act out the reading.
It will make your speech opening that much more impactful.
Related article: 5 Body Language Tips to Command the Stage
Level up your public speaking in 15 minutes!
Get the exclusive Masterclass video delivered to your inbox to see immediate speaking results.
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Final Words
So there it is! 15 speech openings from some of my favourite speeches. Hopefully, these will act as a guide for you to create your own opening which is super impactful and sets you off on the path to becoming a powerful public speaker!
But remember, while a speech opening is super important, it’s just part of an overall structure.
If you’re serious about not just creating a great speech opening but to improve your public speaking at an overall level, I would highly recommend you to check out this course: Acumen Presents: Chris Anderson on Public Speaking on Udemy. Not only does it have specific lectures on starting and ending a speech, but it also offers an in-depth guide into all the nuances of public speaking.
Being the founder of TED Talks, Chris Anderson provides numerous examples of the best TED speakers to give us a very practical way of overcoming stage fear and delivering a speech that people will remember. His course has helped me personally and I would definitely recommend it to anyone looking to learn public speaking.
No one is ever “done” learning public speaking. It’s a continuous process and you can always get better. Keep learning, keep conquering and keep being awesome!
Lastly, if you want to know how you should NOT open your speech, we’ve got a video for you:
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

7 Keys to Emcee Like a Pro: Unlock Your Hosting Potential

8 Ways to Rise Above the Noise to Communicate Better

How to Negotiate: The Art of Getting What You Want

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Kindly drop your contact details so that we can arrange call back
Select Country Afghanistan Albania Algeria AmericanSamoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Colombia Comoros Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Rwanda Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe land Islands Antarctica Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brunei Darussalam Cocos (Keeling) Islands Congo, The Democratic Republic of the Cote d'Ivoire Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Guernsey Holy See (Vatican City State) Hong Kong Iran, Islamic Republic of Isle of Man Jersey Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Lao People's Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Macao Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Mozambique Palestinian Territory, Occupied Pitcairn Réunion Russia Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sao Tome and Principe Somalia Svalbard and Jan Mayen Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tanzania, United Republic of Timor-Leste Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S.


COMMENTS
Tips on giving an impromptu speech. If you are about to make an impromptu speech and have a few minutes to prepare, follow these two tips: 1. Make some quick notes. The first thing you should do when asked to speak is to grab a pen and a piece of paper (or napkin - whatever you can find to write on). Jot down a few initial ideas, or even just ...
Talk about experiences from your life. Keep the speech short and don't take up too much time. Start with a story. Make eye contact with portions of the audience, not individual people. Do this by dividing the audience into halves or quarters. Don't tell the audience you were asked to give an impromptu speech.
7 impromptu speech outline patterns. Please note, these examples are not complete speech outlines. In most instances they don't include the opening or the conclusion. What they do is illustrate seven ways to organize material in the body of the speech. And some of the examples are more fleshed out than others. PREP: Point, Reason, Example, Point
Take a few slow, deep breaths to collect yourself. [1] Let your mind settle so you can concentrate on the task at hand. Shut out all unnecessary distractions that might steal your attention and stifle anxious thoughts that might cause you to doubt yourself. Assume that everyone around you wants to see you succeed.
Impromptu is like all other speeches. The ending is the part that sticks with the judge and can often make or break a performance. In an Impromptu speech, the conclusion is often the shortest part of the speech. At this point, you have already given the prompt and the meaning. You've provided evidence and how it is related.
Thinking about something positive is a confidence boost you might need to get through the speech. 2. Focus on Your Audience. When you're starting your impromptu speech, keep in mind that you're not going against the audience, yet the audience will be on your side. Therefore, you should work with the audience and focus your speech around ...
1. Practice at Home With Your Family. The best way to deliver an impromptu speech is to practice more. Ask your family members to give you a topic on-spot every day. It can be a short 5 min session where you practice one topic or one-hour session where each family member takes turns and speaks on any given topic.
RESOURCES & LINKS: _____Impromptu Speech Article: https://www.orai.com/blog/impromptu-speech-topics/Download App:Andro...
Grab a pen and a piece of paper. If you have a few moments before your speech is expected to begin, grab a writing utensil and something to write on, whether it's a napkin, envelope, or the back of a receipt you have on hand, and jot down a few thoughts. Highlight a few interesting or significant points. Keep in mind, your impromptu speech ...
Here are the reasons: 12 impromptu speech tips that will make you shine. 1. A good speech has a structure. 2. Practice giving a speech. 3. Go on stage and give speeches whenever you get an opportunity. 4.
Craft a coherent message, and then be quiet. Rambling on will only weaken your overall speech. If you must fill more time, shift into a Q&A. Go easy on yourself. We all want to speak perfectly every time, but demanding perfection from yourself in an impromptu speech is setting the bar too high.
Turn it Into a Q&A Session. In cases where you have nothing to say, a smart way of still controlling the stage is to turn the talk into a Questions & Answers session. This is especially useful for a long (~45min) impromptu talk where you have nothing prepared in advance. Ask the audience what they think of the topic.
By OratoryCDC August 22, 2023. To give an impromptu speech, gather your thoughts quickly and structure your speech with a strong opening, clear points, and a memorable conclusion. Being prepared with confidence and engaging body language will help deliver a successful impromptu speech. Impromptu speaking, the art of delivering a speech without ...
Don't overdo it. Just once a day is enough. 2. Speak in a group. Practicing in front of a group and getting professional feedback is the best way to learn impromptu speaking. I know that this option is harder than practicing on your own for many reasons. Not finding the right group, not finding the time are just a few.
Here are steps and strategies to improve your impromptu speaking skills: 1. Understand the Basics. Familiarize yourself with the structure of impromptu speeches and common frameworks, such as PREP (Point, Reason, Example, Point) or the 5 Ws (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How). 2.
In total, introducing the prompt and your interpretation of it should take about 20 seconds. Fourth: the thesis statement, which its main objective is summed up in one clear, concise, and debatable sentence. This should take no more than five seconds. Finally, your roadmap (also called the preview), which outlines your speech's three main points.
An impromptu speech is a type of address given with little or no prior preparation and can also be referred to as "off the cuff" or "spur of the moment" speaking. Examples of an impromptu speech involve a teacher asking a student to present a quick address on a topic from their lesson or a business meeting opening with all participants ...
Reasoning — Share the reasoning behind your point. This is the why to your what. Evidence — Share a concrete example or two that supports your point and your reasoning. Point — Circle back to your point and summarize it. Here's an example of how to make an impromptu speech using the P.R.E.P. strategy.
Here, you should: Use two or three main points to discuss a central theme. Use relevant supporting details like the stories we talked about earlier. If you have no relevant story related to your impromptu speechtopic, it is best to conduct a direct old-fashioned discussion or a question-and-answer section. Conclusion.
In an Impromptu round the speaker draws three prompts from an envelope. After drawing the three prompts, the student must select one and begin brainstorming their ideas for the speech. In total, a student has seven minutes. This seven minutes may be divided up by the student however they see fit. For instance, they could brainstorm and outline ...
Impromptu speaking is a speech that a person delivers without predetermination or preparation. The speaker is most commonly provided with their topic in the form of a quotation, but the topic may also be presented as an object, proverb, one-word abstract, or one of the many alternative possibilities. While specific rules and norms vary with the organization and level of competition, the ...
Tips on giving an impromptus speech. Wenn you are about go make an impromptu speech and have a few minutes to prepare, follow these two tips: 1. Make some quick notes. The first thing you should do when question to speaker is to grab a pen furthermore a piece of papers (or napkin - whatever i can detect to write on).
Analyze their response and tweak the joke accordingly if necessary. Starting your speech with humour means your setting the tone of your speech. It would make sense to have a few more jokes sprinkled around the rest of the speech as well as the audience might be expecting the same from you. 4. Mohammed Qahtani.