Classroom Q&A
With larry ferlazzo.
In this EdWeek blog, an experiment in knowledge-gathering, Ferlazzo will address readers’ questions on classroom management, ELL instruction, lesson planning, and other issues facing teachers. Send your questions to [email protected]. Read more from this blog.

Eight Instructional Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking

- Share article
(This is the first post in a three-part series.)
The new question-of-the-week is:
What is critical thinking and how can we integrate it into the classroom?
This three-part series will explore what critical thinking is, if it can be specifically taught and, if so, how can teachers do so in their classrooms.
Today’s guests are Dara Laws Savage, Patrick Brown, Meg Riordan, Ph.D., and Dr. PJ Caposey. Dara, Patrick, and Meg were also guests on my 10-minute BAM! Radio Show . You can also find a list of, and links to, previous shows here.
You might also be interested in The Best Resources On Teaching & Learning Critical Thinking In The Classroom .
Current Events
Dara Laws Savage is an English teacher at the Early College High School at Delaware State University, where she serves as a teacher and instructional coach and lead mentor. Dara has been teaching for 25 years (career preparation, English, photography, yearbook, newspaper, and graphic design) and has presented nationally on project-based learning and technology integration:
There is so much going on right now and there is an overload of information for us to process. Did you ever stop to think how our students are processing current events? They see news feeds, hear news reports, and scan photos and posts, but are they truly thinking about what they are hearing and seeing?
I tell my students that my job is not to give them answers but to teach them how to think about what they read and hear. So what is critical thinking and how can we integrate it into the classroom? There are just as many definitions of critical thinking as there are people trying to define it. However, the Critical Think Consortium focuses on the tools to create a thinking-based classroom rather than a definition: “Shape the climate to support thinking, create opportunities for thinking, build capacity to think, provide guidance to inform thinking.” Using these four criteria and pairing them with current events, teachers easily create learning spaces that thrive on thinking and keep students engaged.
One successful technique I use is the FIRE Write. Students are given a quote, a paragraph, an excerpt, or a photo from the headlines. Students are asked to F ocus and respond to the selection for three minutes. Next, students are asked to I dentify a phrase or section of the photo and write for two minutes. Third, students are asked to R eframe their response around a specific word, phrase, or section within their previous selection. Finally, students E xchange their thoughts with a classmate. Within the exchange, students also talk about how the selection connects to what we are covering in class.
There was a controversial Pepsi ad in 2017 involving Kylie Jenner and a protest with a police presence. The imagery in the photo was strikingly similar to a photo that went viral with a young lady standing opposite a police line. Using that image from a current event engaged my students and gave them the opportunity to critically think about events of the time.
Here are the two photos and a student response:
F - Focus on both photos and respond for three minutes
In the first picture, you see a strong and courageous black female, bravely standing in front of two officers in protest. She is risking her life to do so. Iesha Evans is simply proving to the world she does NOT mean less because she is black … and yet officers are there to stop her. She did not step down. In the picture below, you see Kendall Jenner handing a police officer a Pepsi. Maybe this wouldn’t be a big deal, except this was Pepsi’s weak, pathetic, and outrageous excuse of a commercial that belittles the whole movement of people fighting for their lives.
I - Identify a word or phrase, underline it, then write about it for two minutes
A white, privileged female in place of a fighting black woman was asking for trouble. A struggle we are continuously fighting every day, and they make a mockery of it. “I know what will work! Here Mr. Police Officer! Drink some Pepsi!” As if. Pepsi made a fool of themselves, and now their already dwindling fan base continues to ever shrink smaller.
R - Reframe your thoughts by choosing a different word, then write about that for one minute
You don’t know privilege until it’s gone. You don’t know privilege while it’s there—but you can and will be made accountable and aware. Don’t use it for evil. You are not stupid. Use it to do something. Kendall could’ve NOT done the commercial. Kendall could’ve released another commercial standing behind a black woman. Anything!
Exchange - Remember to discuss how this connects to our school song project and our previous discussions?
This connects two ways - 1) We want to convey a strong message. Be powerful. Show who we are. And Pepsi definitely tried. … Which leads to the second connection. 2) Not mess up and offend anyone, as had the one alma mater had been linked to black minstrels. We want to be amazing, but we have to be smart and careful and make sure we include everyone who goes to our school and everyone who may go to our school.
As a final step, students read and annotate the full article and compare it to their initial response.
Using current events and critical-thinking strategies like FIRE writing helps create a learning space where thinking is the goal rather than a score on a multiple-choice assessment. Critical-thinking skills can cross over to any of students’ other courses and into life outside the classroom. After all, we as teachers want to help the whole student be successful, and critical thinking is an important part of navigating life after they leave our classrooms.

‘Before-Explore-Explain’
Patrick Brown is the executive director of STEM and CTE for the Fort Zumwalt school district in Missouri and an experienced educator and author :
Planning for critical thinking focuses on teaching the most crucial science concepts, practices, and logical-thinking skills as well as the best use of instructional time. One way to ensure that lessons maintain a focus on critical thinking is to focus on the instructional sequence used to teach.
Explore-before-explain teaching is all about promoting critical thinking for learners to better prepare students for the reality of their world. What having an explore-before-explain mindset means is that in our planning, we prioritize giving students firsthand experiences with data, allow students to construct evidence-based claims that focus on conceptual understanding, and challenge students to discuss and think about the why behind phenomena.
Just think of the critical thinking that has to occur for students to construct a scientific claim. 1) They need the opportunity to collect data, analyze it, and determine how to make sense of what the data may mean. 2) With data in hand, students can begin thinking about the validity and reliability of their experience and information collected. 3) They can consider what differences, if any, they might have if they completed the investigation again. 4) They can scrutinize outlying data points for they may be an artifact of a true difference that merits further exploration of a misstep in the procedure, measuring device, or measurement. All of these intellectual activities help them form more robust understanding and are evidence of their critical thinking.
In explore-before-explain teaching, all of these hard critical-thinking tasks come before teacher explanations of content. Whether we use discovery experiences, problem-based learning, and or inquiry-based activities, strategies that are geared toward helping students construct understanding promote critical thinking because students learn content by doing the practices valued in the field to generate knowledge.

An Issue of Equity
Meg Riordan, Ph.D., is the chief learning officer at The Possible Project, an out-of-school program that collaborates with youth to build entrepreneurial skills and mindsets and provides pathways to careers and long-term economic prosperity. She has been in the field of education for over 25 years as a middle and high school teacher, school coach, college professor, regional director of N.Y.C. Outward Bound Schools, and director of external research with EL Education:
Although critical thinking often defies straightforward definition, most in the education field agree it consists of several components: reasoning, problem-solving, and decisionmaking, plus analysis and evaluation of information, such that multiple sides of an issue can be explored. It also includes dispositions and “the willingness to apply critical-thinking principles, rather than fall back on existing unexamined beliefs, or simply believe what you’re told by authority figures.”
Despite variation in definitions, critical thinking is nonetheless promoted as an essential outcome of students’ learning—we want to see students and adults demonstrate it across all fields, professions, and in their personal lives. Yet there is simultaneously a rationing of opportunities in schools for students of color, students from under-resourced communities, and other historically marginalized groups to deeply learn and practice critical thinking.
For example, many of our most underserved students often spend class time filling out worksheets, promoting high compliance but low engagement, inquiry, critical thinking, or creation of new ideas. At a time in our world when college and careers are critical for participation in society and the global, knowledge-based economy, far too many students struggle within classrooms and schools that reinforce low-expectations and inequity.
If educators aim to prepare all students for an ever-evolving marketplace and develop skills that will be valued no matter what tomorrow’s jobs are, then we must move critical thinking to the forefront of classroom experiences. And educators must design learning to cultivate it.
So, what does that really look like?
Unpack and define critical thinking
To understand critical thinking, educators need to first unpack and define its components. What exactly are we looking for when we speak about reasoning or exploring multiple perspectives on an issue? How does problem-solving show up in English, math, science, art, or other disciplines—and how is it assessed? At Two Rivers, an EL Education school, the faculty identified five constructs of critical thinking, defined each, and created rubrics to generate a shared picture of quality for teachers and students. The rubrics were then adapted across grade levels to indicate students’ learning progressions.
At Avenues World School, critical thinking is one of the Avenues World Elements and is an enduring outcome embedded in students’ early experiences through 12th grade. For instance, a kindergarten student may be expected to “identify cause and effect in familiar contexts,” while an 8th grader should demonstrate the ability to “seek out sufficient evidence before accepting a claim as true,” “identify bias in claims and evidence,” and “reconsider strongly held points of view in light of new evidence.”
When faculty and students embrace a common vision of what critical thinking looks and sounds like and how it is assessed, educators can then explicitly design learning experiences that call for students to employ critical-thinking skills. This kind of work must occur across all schools and programs, especially those serving large numbers of students of color. As Linda Darling-Hammond asserts , “Schools that serve large numbers of students of color are least likely to offer the kind of curriculum needed to ... help students attain the [critical-thinking] skills needed in a knowledge work economy. ”
So, what can it look like to create those kinds of learning experiences?
Designing experiences for critical thinking
After defining a shared understanding of “what” critical thinking is and “how” it shows up across multiple disciplines and grade levels, it is essential to create learning experiences that impel students to cultivate, practice, and apply these skills. There are several levers that offer pathways for teachers to promote critical thinking in lessons:
1.Choose Compelling Topics: Keep it relevant
A key Common Core State Standard asks for students to “write arguments to support claims in an analysis of substantive topics or texts using valid reasoning and relevant and sufficient evidence.” That might not sound exciting or culturally relevant. But a learning experience designed for a 12th grade humanities class engaged learners in a compelling topic— policing in America —to analyze and evaluate multiple texts (including primary sources) and share the reasoning for their perspectives through discussion and writing. Students grappled with ideas and their beliefs and employed deep critical-thinking skills to develop arguments for their claims. Embedding critical-thinking skills in curriculum that students care about and connect with can ignite powerful learning experiences.
2. Make Local Connections: Keep it real
At The Possible Project , an out-of-school-time program designed to promote entrepreneurial skills and mindsets, students in a recent summer online program (modified from in-person due to COVID-19) explored the impact of COVID-19 on their communities and local BIPOC-owned businesses. They learned interviewing skills through a partnership with Everyday Boston , conducted virtual interviews with entrepreneurs, evaluated information from their interviews and local data, and examined their previously held beliefs. They created blog posts and videos to reflect on their learning and consider how their mindsets had changed as a result of the experience. In this way, we can design powerful community-based learning and invite students into productive struggle with multiple perspectives.
3. Create Authentic Projects: Keep it rigorous
At Big Picture Learning schools, students engage in internship-based learning experiences as a central part of their schooling. Their school-based adviser and internship-based mentor support them in developing real-world projects that promote deeper learning and critical-thinking skills. Such authentic experiences teach “young people to be thinkers, to be curious, to get from curiosity to creation … and it helps students design a learning experience that answers their questions, [providing an] opportunity to communicate it to a larger audience—a major indicator of postsecondary success.” Even in a remote environment, we can design projects that ask more of students than rote memorization and that spark critical thinking.
Our call to action is this: As educators, we need to make opportunities for critical thinking available not only to the affluent or those fortunate enough to be placed in advanced courses. The tools are available, let’s use them. Let’s interrogate our current curriculum and design learning experiences that engage all students in real, relevant, and rigorous experiences that require critical thinking and prepare them for promising postsecondary pathways.

Critical Thinking & Student Engagement
Dr. PJ Caposey is an award-winning educator, keynote speaker, consultant, and author of seven books who currently serves as the superintendent of schools for the award-winning Meridian CUSD 223 in northwest Illinois. You can find PJ on most social-media platforms as MCUSDSupe:
When I start my keynote on student engagement, I invite two people up on stage and give them each five paper balls to shoot at a garbage can also conveniently placed on stage. Contestant One shoots their shot, and the audience gives approval. Four out of 5 is a heckuva score. Then just before Contestant Two shoots, I blindfold them and start moving the garbage can back and forth. I usually try to ensure that they can at least make one of their shots. Nobody is successful in this unfair environment.
I thank them and send them back to their seats and then explain that this little activity was akin to student engagement. While we all know we want student engagement, we are shooting at different targets. More importantly, for teachers, it is near impossible for them to hit a target that is moving and that they cannot see.
Within the world of education and particularly as educational leaders, we have failed to simplify what student engagement looks like, and it is impossible to define or articulate what student engagement looks like if we cannot clearly articulate what critical thinking is and looks like in a classroom. Because, simply, without critical thought, there is no engagement.
The good news here is that critical thought has been defined and placed into taxonomies for decades already. This is not something new and not something that needs to be redefined. I am a Bloom’s person, but there is nothing wrong with DOK or some of the other taxonomies, either. To be precise, I am a huge fan of Daggett’s Rigor and Relevance Framework. I have used that as a core element of my practice for years, and it has shaped who I am as an instructional leader.
So, in order to explain critical thought, a teacher or a leader must familiarize themselves with these tried and true taxonomies. Easy, right? Yes, sort of. The issue is not understanding what critical thought is; it is the ability to integrate it into the classrooms. In order to do so, there are a four key steps every educator must take.
- Integrating critical thought/rigor into a lesson does not happen by chance, it happens by design. Planning for critical thought and engagement is much different from planning for a traditional lesson. In order to plan for kids to think critically, you have to provide a base of knowledge and excellent prompts to allow them to explore their own thinking in order to analyze, evaluate, or synthesize information.
- SIDE NOTE – Bloom’s verbs are a great way to start when writing objectives, but true planning will take you deeper than this.
QUESTIONING
- If the questions and prompts given in a classroom have correct answers or if the teacher ends up answering their own questions, the lesson will lack critical thought and rigor.
- Script five questions forcing higher-order thought prior to every lesson. Experienced teachers may not feel they need this, but it helps to create an effective habit.
- If lessons are rigorous and assessments are not, students will do well on their assessments, and that may not be an accurate representation of the knowledge and skills they have mastered. If lessons are easy and assessments are rigorous, the exact opposite will happen. When deciding to increase critical thought, it must happen in all three phases of the game: planning, instruction, and assessment.
TALK TIME / CONTROL
- To increase rigor, the teacher must DO LESS. This feels counterintuitive but is accurate. Rigorous lessons involving tons of critical thought must allow for students to work on their own, collaborate with peers, and connect their ideas. This cannot happen in a silent room except for the teacher talking. In order to increase rigor, decrease talk time and become comfortable with less control. Asking questions and giving prompts that lead to no true correct answer also means less control. This is a tough ask for some teachers. Explained differently, if you assign one assignment and get 30 very similar products, you have most likely assigned a low-rigor recipe. If you assign one assignment and get multiple varied products, then the students have had a chance to think deeply, and you have successfully integrated critical thought into your classroom.

Thanks to Dara, Patrick, Meg, and PJ for their contributions!
Please feel free to leave a comment with your reactions to the topic or directly to anything that has been said in this post.
Consider contributing a question to be answered in a future post. You can send one to me at [email protected] . When you send it in, let me know if I can use your real name if it’s selected or if you’d prefer remaining anonymous and have a pseudonym in mind.
You can also contact me on Twitter at @Larryferlazzo .
Education Week has published a collection of posts from this blog, along with new material, in an e-book form. It’s titled Classroom Management Q&As: Expert Strategies for Teaching .
Just a reminder; you can subscribe and receive updates from this blog via email (The RSS feed for this blog, and for all Ed Week articles, has been changed by the new redesign—new ones won’t be available until February). And if you missed any of the highlights from the first nine years of this blog, you can see a categorized list below.
- This Year’s Most Popular Q&A Posts
- Race & Racism in Schools
- School Closures & the Coronavirus Crisis
- Classroom-Management Advice
- Best Ways to Begin the School Year
- Best Ways to End the School Year
- Student Motivation & Social-Emotional Learning
- Implementing the Common Core
- Facing Gender Challenges in Education
- Teaching Social Studies
- Cooperative & Collaborative Learning
- Using Tech in the Classroom
- Student Voices
- Parent Engagement in Schools
- Teaching English-Language Learners
- Reading Instruction
- Writing Instruction
- Education Policy Issues
- Differentiating Instruction
- Math Instruction
- Science Instruction
- Advice for New Teachers
- Author Interviews
- Entering the Teaching Profession
- The Inclusive Classroom
- Learning & the Brain
- Administrator Leadership
- Teacher Leadership
- Relationships in Schools
- Professional Development
- Instructional Strategies
- Best of Classroom Q&A
- Professional Collaboration
- Classroom Organization
- Mistakes in Education
- Project-Based Learning
I am also creating a Twitter list including all contributors to this column .
The opinions expressed in Classroom Q&A With Larry Ferlazzo are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

BLOG | PODCAST NETWORK | ADMIN. MASTERMIND | SWAG & MERCH | ONLINE TRAINING

- Meet the Team
- Join the Team
- Our Philosophy
- Teach Better Mindset
- Custom Professional Development
- Livestream Shows & Videos
- Administrator Mastermind
- Academy Online Courses
- EDUcreator Club+
- Podcast Network
- Speakers Network
- EDUpreneur Mastermind
- Free Downloads
- Ambassador Program
- Free Facebook Group
- Professional Development
- Request Training
- Speakers Network Home
- Keynote Speakers
Strategies to Increase Critical Thinking Skills in students
Matthew Joseph October 2, 2019 Blog , Engage Better , Lesson Plan Better , Personalize Student Learning Better

In This Post:
- The importance of helping students increase critical thinking skills.
- Ways to promote the essential skills needed to analyze and evaluate.
- Strategies to incorporate critical thinking into your instruction.
We ask our teachers to be “future-ready” or say that we are teaching “for jobs that don’t exist yet.” These are powerful statements. At the same time, they give teachers the impression that we have to drastically change what we are doing .
So how do we plan education for an unknown job market or unknown needs?
My answer: We can’t predict the jobs, but whatever they are, students will need to think critically to do them. So, our job is to teach our students HOW to think, not WHAT to think.
Helping Students Become Critical Thinkers
My answer is rooted in the call to empower our students to be critical thinkers. I believe that to be critical thinkers, educators need to provide students with the strategies they need. And we need to ask more than just surface-level questions.
Questions to students must motivate them to dig up background knowledge. They should inspire them to make connections to real-world scenarios. These make the learning more memorable and meaningful.
Critical thinking is a general term. I believe this term means that students effectively identify, analyze, and evaluate content or skills. In this process, they (the students) will discover and present convincing reasons in support of their answers or thinking.
You can look up critical thinking and get many definitions like this one from Wikipedia: “ Critical thinking consists of a mental process of analyzing or evaluating information, particularly statements or propositions that people have offered as true. ”
Essential Skills for Critical Thinking
In my current role as director of curriculum and instruction, I work to promote the use of 21st-century tools and, more importantly, thinking skills. Some essential skills that are the basis for critical thinking are:
- Communication and Information skills
- Thinking and Problem-Solving skills
- Interpersonal and Self- Directional skills
- Collaboration skills
These four bullets are skills students are going to need in any field and in all levels of education. Hence my answer to the question. We need to teach our students to think critically and for themselves.
One of the goals of education is to prepare students to learn through discovery . Providing opportunities to practice being critical thinkers will assist students in analyzing others’ thinking and examining the logic of others.
Understanding others is an essential skill in collaboration and in everyday life. Critical thinking will allow students to do more than just memorize knowledge.
Ask Questions
So how do we do this? One recommendation is for educators to work in-depth questioning strategies into a lesson launch.
Ask thoughtful questions to allow for answers with sound reasoning. Then, word conversations and communication to shape students’ thinking. Quick answers often result in very few words and no eye contact, which are skills we don’t want to promote.
When you are asking students questions and they provide a solution, try some of these to promote further thinking:
- Could you elaborate further on that point?
- Will you express that point in another way?
- Can you give me an illustration?
- Would you give me an example?
- Will you you provide more details?
- Could you be more specific?
- Do we need to consider another point of view?
- Is there another way to look at this question?
Utilizing critical thinking skills could be seen as a change in the paradigm of teaching and learning. Engagement in education will enhance the collaboration among teachers and students. It will also provide a way for students to succeed even if the school system had to start over.
[scroll down to keep reading]
Promoting critical thinking into all aspects of instruction.
Engagement, application, and collaboration are skills that withstand the test of time. I also promote the integration of critical thinking into every aspect of instruction.
In my experience, I’ve found a few ways to make this happen.
Begin lessons/units with a probing question: It shouldn’t be a question you can answer with a ‘yes’ or a ‘no.’ These questions should inspire discovery learning and problem-solving.
Encourage Creativity: I have seen teachers prepare projects before they give it to their students many times. For example, designing snowmen or other “creative” projects. By doing the design work or by cutting all the circles out beforehand, it removes creativity options.
It may help the classroom run more smoothly if every child’s material is already cut out, but then every student’s project looks the same. Students don’t have to think on their own or problem solve.
Not having everything “glue ready” in advance is a good thing. Instead, give students all the supplies needed to create a snowman, and let them do it on their own.
Giving independence will allow students to become critical thinkers because they will have to create their own product with the supplies you give them. This might be an elementary example, but it’s one we can relate to any grade level or project.
Try not to jump to help too fast – let the students work through a productive struggle .
Build in opportunities for students to find connections in learning. Encouraging students to make connections to a real-life situation and identify patterns is a great way to practice their critical thinking skills. The use of real-world scenarios will increase rigor, relevance, and critical thinking.
A few other techniques to encourage critical thinking are:
- Use analogies
- Promote interaction among students
- Ask open-ended questions
- Allow reflection time
- Use real-life problems
- Allow for thinking practice
Critical thinking prepares students to think for themselves for the rest of their lives. I also believe critical thinkers are less likely to go along with the crowd because they think for themselves.
About Matthew X. Joseph, Ed.D.
Dr. Matthew X. Joseph has been a school and district leader in many capacities in public education over his 25 years in the field. Experiences such as the Director of Digital Learning and Innovation in Milford Public Schools (MA), elementary school principal in Natick, MA and Attleboro, MA, classroom teacher, and district professional development specialist have provided Matt incredible insights on how to best support teaching and learning. This experience has led to nationally publishing articles and opportunities to speak at multiple state and national events. He is the author of Power of Us: Creating Collaborative Schools and co-author of Modern Mentoring , Reimagining Teacher Mentorship (Due out, fall 2019). His master’s degree is in special education and his Ed.D. in Educational Leadership from Boston College.
Visit Matthew’s Blog

How to teach critical thinking, a vital 21st-century skill
A well-rounded education doesn’t just impart academic knowledge to students — it gives them transferable skills they can apply throughout their lives. Critical thinking is widely hailed as one such essential “ 21st-century skill ,” helping people critically assess information, make informed decisions, and come up with creative approaches to solving problems.
This means that individuals with developed critical thinking skills benefit both themselves and the wider society. Despite the widespread recognition of critical thinking’s importance for future success, there can be some ambiguity about both what it is and how to teach it . 1 Let’s take a look at each of those questions in turn.
What is critical thinking?
Throughout history, humanity has attempted to use reason to understand and interpret the world. From the philosophers of Ancient Greece to the key thinkers of the Enlightenment, people have sought to challenge their preconceived notions and draw logical conclusions from the available evidence — key elements that gave rise to today’s definition of “critical thinking.”
At its core, critical thinking is the use of reason to analyze the available evidence and reach logical conclusions. Educational scholars have defined critical thinking as “reasonable reflective thinking focused on deciding what to believe or do,” 2 and “interpretation or analysis, followed by evaluation or judgment.” 3 Some have pared their definition down to simply “good” or “skillful thinking.”
At the same time, being a good critical thinker relies on certain values like open-mindedness, persistence, and intellectual humility. 4 The ideal critical thinker isn’t just skilled in analysis — they are also curious, open to other points of view, and creative in the path they take towards tackling a given problem.
Alongside teaching students how to analyze information, build arguments, and draw conclusions, educators play a key role in fostering the values conducive to critical thinking and intellectual inquiry. Students who develop both skills and values are well-placed to handle challenges both academically and in their personal lives.
Let’s examine some strategies to develop critical thinking skills and values in the classroom.
How to teach students to think critically — strategies
1. build a classroom climate that encourages open-mindedness.

Fostering a classroom culture that allows students the time and space to think independently, experiment with new ideas, and have their views challenged lays a strong foundation for developing skills and values central to critical thinking.
Whatever your subject area, encourage students to contribute their own ideas and theories when addressing common curricular questions. Promote open-mindedness by underscoring the importance of the initial “brainstorming” phase in problem-solving — this is the necessary first step towards understanding! Strive to create a classroom climate where students are comfortable thinking out loud.
Emphasize to students the importance of understanding different perspectives on issues, and that it’s okay for people to disagree. Establish guidelines for class discussions — especially when covering controversial issues — and stress that changing your mind on an issue is a sign of intellectual strength, not weakness. Model positive behaviors by being flexible in your own opinions when engaging with ideas from students.
2. Teach students to make clear and effective arguments
Training students’ argumentation skills is central to turning them into adept critical thinkers. Expose students to a wide range of arguments, guiding them to distinguish between examples of good and bad reasoning.
When guiding students to form their own arguments, emphasize the value of clarity and precision in language. In oral discussions, encourage students to order their thoughts on paper before contributing.

In the case of argumentative essays , give students plenty of opportunities to revise their work, implementing feedback from you or peers. Assist students in refining their arguments by encouraging them to challenge their own positions.
They can do so by creating robust “steel man” counterarguments to identify potential flaws in their own reasoning. For example, if a student is passionate about animal rights and wants to argue for a ban on animal testing , encourage them to also come up with points in favor of animal testing. If they can rebut those counterarguments, their own position will be much stronger!
Additionally, knowing how to evaluate and provide evidence is essential for developing argumentation skills. Teach students how to properly cite sources , and encourage them to investigate the veracity of claims made by others — particularly when dealing with online media .
3. Encourage metacognition — guide students to think about their own and others’ thinking
Critical thinkers are self-reflective. Guide students time to think about their own learning process by utilizing metacognitive strategies, like learning journals or having reflective periods at the end of activities. Reflecting on how they came to understand a topic can help students cultivate a growth mindset and an openness to explore alternative problem-solving approaches during challenging moments.
You can also create an awareness of common errors in human thinking by teaching about them explicitly. Identify arguments based on logical fallacies and have students come up with examples from their own experience. Help students recognize the role of cognitive bias in our thinking, and design activities to help counter it.
Students who develop self-awareness regarding their own thinking are not just better at problem-solving, but also managing their emotions .
4. Assign open-ended and varied activities to practice different kinds of thinking
Critical thinkers are capable of approaching problems from a variety of angles. Train this vital habit by switching up the kinds of activities you assign to students, and try prioritizing open-ended assignments that allow for varied approaches.
A project-based learning approach can reap huge rewards. Have students identify real-world problems, conduct research, and investigate potential solutions. Following that process will give them varied intellectual challenges, while the real-world applicability of their work can motivate students to consider the potential impact their thinking can have on the world around them.

Classroom discussions and debates are fantastic activities for building critical thinking skills. As open-ended activities, they encourage student autonomy by requiring them to think for themselves.
They also expose students to a diversity of perspectives , inviting them to critically appraise these different positions in a respectful context. Class discussions are applicable across disciplines and come in many flavors — experiment with different forms like fishbowl discussions or online, asynchronous discussions to keep students engaged.
5. Use argument-mapping tools such as Kialo Edu to train students in the use of reasoning
One of the most effective methods of improving students’ critical thinking skills is to train them in argument mapping .
Argument mapping involves breaking an argument down into its constituent parts, and displaying them visually so that students can see how different points are connected. Research has shown that university students who were trained in argument mapping significantly out-performed their peers on critical thinking assessments. 5
While it’s possible — and useful — to map out arguments by hand, there are clear benefits to using digital argument maps like Kialo Edu. Students can contribute simultaneously to a Kialo discussion to collaboratively build out complex discussions as an argument map.
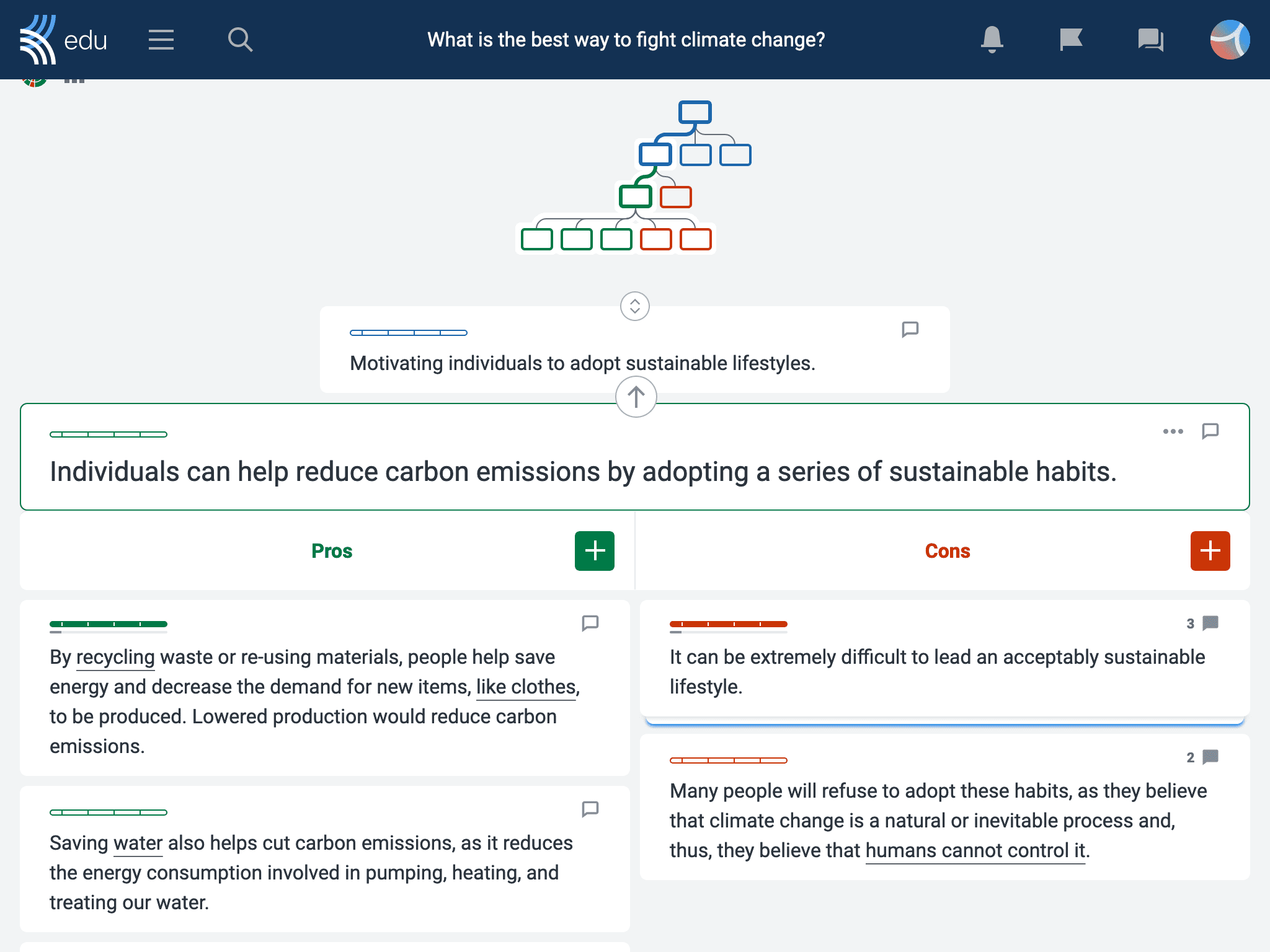
Individual students can plan essays as argument maps before writing. This helps them to stay focused on the line of argument and encourages them to preempt counterarguments. Kialo discussions can even be assigned as an essay alternative when teachers want to focus on argumentation as the key learning goal. Unlike traditional essays, they defy the use of AI chatbots like ChatGPT!
Kialo discussions prompt students to use their reasoning skills to create clear, structured arguments. Moreover, students have a visual, engaging way to respond to the content of the arguments being made, promoting interpretive charity towards differing opinions.
Best of all, Kialo Edu offers a way to track and assess your students’ progress on their critical thinking journey. Educators can assign specific tasks — like citing sources or responding to others’ claims — to evaluate specific skills. Students can also receive grades and feedback on their contributions without leaving the platform, making it easy to deliver constructive, ongoing guidance to help students develop their reasoning skills.
Improving students’ critical thinking abilities is something that motivates our work here at Kialo Edu. If you’ve used our platform and have feedback, thoughts, or suggestions, we’d love to hear from you. Reach out to us on social media or contact us directly at [email protected] .
- Lloyd, M., & Bahr, N. (2010). Thinking Critically about Critical Thinking in Higher Education. International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 4 (2), Article 9. https://doi.org/10.20429/ijsotl.2010.040209
- Ennis, R. H. (2015). Critical Thinking: A Streamlined Conception. In: Davies, M., Barnett, R. (eds) The Palgrave Handbook of Critical Thinking in Higher Education. Palgrave Macmillan, New York.
- Lang-Raad, N. D. (2023). Never Stop Asking: Teaching Students to be Better Critical Thinkers . Jossey-Bass.
- Ellerton, Peter (2019). Teaching for thinking: Explaining pedagogical expertise in the development of the skills, values and virtues of inquiry . Dissertation, The University of Queensland. Available here .
- van Gelder, T. (2015). Using argument mapping to improve critical thinking skills. In The Palgrave Handbook of Critical Thinking in Higher Education (pp. 183–192). doi:10.1057/9781137378057_12.
Want to try Kialo Edu with your class?
Sign up for free and use Kialo Edu to have thoughtful classroom discussions and train students’ argumentation and critical thinking skills.
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Win a $200 Amazon Gift Card in Today's Teacher Appreciation Giveaway 🎁!
10 Tips for Teaching Kids To Be Awesome Critical Thinkers
Help students dig deeper!

For more tips, check out Mentoring Minds’ Critical Thinking Strategies Guide —a flip chart packed with question stems and lesson ideas to help teach kids to become better critical and creative thinkers.
Getting students to dig deeper and answer questions using higher-level thinking can be a challenge. Here are our favorite tips for teaching critical thinking skills, adapted from Mentoring Minds’ Critical Thinking Strategies Guide, that help kids solve problems by going beyond the obvious response.
1. Slow down the pace.
It’s easy to fall into a routine of calling on one of the first kids who raises a hand. But if you wait even just 3 to 5 seconds after asking a question, you’ll probably find the pool of students willing to give an answer grows significantly. Plus, it helps the speedy kids learn that the first answer that pops into their head isn’t always the best. There are times you may even want to wait up to a minute or longer if the question is particularly complex or time-consuming. To avoid an awkward pause, you can let kids know that they have 10 seconds to think before answering the question or that you need to see 10 hands raised from volunteers before you hear a response.
2. Pose a Question of the Day.
Put a new spin on bell ringers by asking a Question of the Day. Use a questioning stem (e.g., create a riddle that uses the mathematics term “multiply” in one of the clues or write a letter to a classmate recommending this book) and put it on the board. Students can write answers in their critical-thinking journals. Then have a class discussion at the end of the day.
3. Make a response box.
Write a random critical-thinking question on the board, (e.g., Is there a better way to work out this problem? Explain your thinking.). Give students a specified amount of time to provide a written response and put it in the response box. Pull out entries one by one and read them aloud to the class. Alternatively, you can give a prize—like a homework pass or free time—to the student with the first appropriate response whose name is drawn from the box or to everyone who submitted appropriate answers.
4. Take a side.
First, read a statement that has two opposing views (e.g., Do you agree or disagree with the author? Why?). Ask kids who agree to stand on one side of the room and those who disagree to stand on the other side. Then have kids talk about why they chose each side. They can switch sides if they change their minds during the discussion.

5. Ask “why?” five times.
When you encounter a problem in class, you can help the class come up with a solution by using the Why? Five Times strategy. Ask the first why question (e.g., Why didn’t the class do well on the spelling test?), and after a response is given, ask why four more times (e.g., Why didn’t students study for the test?, Why didn’t students have time to study for the test?, etc.). The idea is that after the fifth question is asked, the problem will be solved.
6. Role-play.
Come up with an imaginary scenario and have kids work through the steps to solve a problem as a class. First, identify the problem and write it as a question (e.g., Why didn’t the science experiment work as planned?). Then brainstorm ideas to solve it and choose the best one to write as a solution statement. Finally, create an action plan to carry out the solution.
7. Go “hitchhiking.”
Practice creative thinking by collaborating on a storyboard. Write a problem on an index card and pin it on the top of a bulletin board. Then put different headings on index cards and pin them below the main card. Have kids brainstorm ideas that develop each of the heading cards and let kids pin them on the board. Encourage kids to “go hitchhiking” by building onto their classmates’ ideas.

8. Turn around.
A great way to focus on the positive in not-so-positive situations is the Turn Around thinking strategy. If a student forgets to bring his homework to school, you can ask, “What good can come of this?” The student can answer with ideas like, “I will change my routine before I go to bed.”
9. Put your pocket chart to good use.
Choose six completed questioning stems from different levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy and put them in a pocket chart. Choose some strips as mandatory and let kids pick two from the higher levels to answer aloud or in a journal.
10. Hold a Q&A session.
One way you can figure out how well kids are grasping critical-thinking skills is by holding question-and-answer sessions. Ask a variety of questions one-on-one or in small groups and take note of the levels of thought individual students use regularly and avoid over time. You can review your notes to help build more higher-order-thinking questions into your lessons.
FREE E-BOOK! How to Build a 36-Week Character Education Program . S upport social-emotional learning through a critical thinking lens with 36 projects and activities plus tips, research, and more!

You Might Also Like

5 Critical Thinking Skills Every Kid Needs To Learn (And How To Teach Them)
Teach them to thoughtfully question the world around them. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

- Instructors
- Institutions
- Teaching Strategies
- Higher Ed Trends
- Academic Leadership
- Affordability
- Product Updates
Try These Strategies for Building Critical-Thinking Skills

We hear all too often that critical-thinking skills are essential for students. But what, specifically, are critical-thinking skills, and how can instructors better help students build them? We’re breaking down what exactly critical-thinking skills are, and offering a few critical-thinking activities to add to your course.
What is critical thinking?
According to the Paul-Elder Framework , critical thinking is “that mode of thinking—about any subject, content, or problem—in which the thinker improves the quality of [their] thinking by skillfully taking charge of the structures inherent in thinking and imposing intellectual standards upon them.” Translation: It’s about analyzing the facts from as objective as a viewpoint as possible, while minimizing personal biases.
With 69.6% of employers claiming these skills are indicative of employee success, educators need to make sure their lessons help students build critical-thinking skills.
Assessing your students’ critical-thinking skills
Assessing your students’ critical-thinking skills is just as important as fostering them. According to the Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Framework , a “well-cultivated critical thinker” can:
- Raise vital questions and problems, formulating them clearly and precisely
- Gather and assess relevant information, using abstract ideas to interpret it effectively
- Come to well-reasoned conclusions and solutions, testing them against relevant criteria and standards
- Think open-mindedly within alternative systems of thought, recognizing and assessing, as need be, their assumptions, implications, and practical consequences
- Communicate effectively with others in figuring out solutions to complex problems
Think about if your syllabus checks these boxes. If not, try incorporating some of these strategies in your course.
Strategy 1: Use reflective thinking questions
Reflective thinking involves “consideration of the larger context, the meaning, and the implications of an experience or action.” In other words, reflection doesn’t just mean jotting down what you did or plan to do. It means considering why what you did or plan to do matters. It means writing to help you better understand something. It means exploring emotions, feelings, reactions and knowledges. And, it can even mean catharsis. Think of reflection as exploring the “so what” instead of just the “what.”
Check out this resource from the Colorado Department of Education for reflective thinking questions you can include in your course.
Strategy 2: Structure class discussions thoughtfully
Building critical-thinking skills is less about finding the right answer and more about the quest to get there. That quest is the thoughtful consideration and discussion that occurs amongst the students in your course. Try not to start with just one right answer in your head when you pose a question to your class, and instead think about the questions, comments and lines of thinking that your question — and potential answers for it — will spur.
For questions you can use to get your students thinking critically, check out these Universal Intellectual Standards .
Strategy 3: Use exercises to demonstrate biases
Here’s a $5 word to pull out at pub trivia night: Pareidolia . It’s the tendency to “perceive a specific, often meaningful image in a random or ambiguous visual pattern.” In practice, it could mean something as innocuous as seeing a human face in the whorls of a tree trunk or in a grilled cheese. Or, it might mean seeing a pattern that fits within your own biases without consideration for alternative meanings.
This exercise has your students analyze videos of animals communicating to analyze how their existing biases affect their views on a topic. Or, websites like School of Thought , a nonprofit organization dedicated to “promoting critical thinking, reason and understanding,” offer recourses surrounding logical fallacies and cognitive biases. Using hands-on activities helps students bridge the gap between learning about critical thinking in the abstract and applying it through tactile experiences.
More on critical-thinking skills
To learn more about strategies for engaging your students in critical thinking exercises and beyond, check out our guide on “Getting Started with Active Learning.”
Related articles

Why Schools Need to Change Yes, We Can Define, Teach, and Assess Critical Thinking Skills

Jeff Heyck-Williams (He, His, Him) Director of the Two Rivers Learning Institute in Washington, DC
Today’s learners face an uncertain present and a rapidly changing future that demand far different skills and knowledge than were needed in the 20th century. We also know so much more about enabling deep, powerful learning than we ever did before. Our collective future depends on how well young people prepare for the challenges and opportunities of 21st-century life.
Critical thinking is a thing. We can define it; we can teach it; and we can assess it.
While the idea of teaching critical thinking has been bandied around in education circles since at least the time of John Dewey, it has taken greater prominence in the education debates with the advent of the term “21st century skills” and discussions of deeper learning. There is increasing agreement among education reformers that critical thinking is an essential ingredient for long-term success for all of our students.
However, there are still those in the education establishment and in the media who argue that critical thinking isn’t really a thing, or that these skills aren’t well defined and, even if they could be defined, they can’t be taught or assessed.
To those naysayers, I have to disagree. Critical thinking is a thing. We can define it; we can teach it; and we can assess it. In fact, as part of a multi-year Assessment for Learning Project , Two Rivers Public Charter School in Washington, D.C., has done just that.
Before I dive into what we have done, I want to acknowledge that some of the criticism has merit.
First, there are those that argue that critical thinking can only exist when students have a vast fund of knowledge. Meaning that a student cannot think critically if they don’t have something substantive about which to think. I agree. Students do need a robust foundation of core content knowledge to effectively think critically. Schools still have a responsibility for building students’ content knowledge.
However, I would argue that students don’t need to wait to think critically until after they have mastered some arbitrary amount of knowledge. They can start building critical thinking skills when they walk in the door. All students come to school with experience and knowledge which they can immediately think critically about. In fact, some of the thinking that they learn to do helps augment and solidify the discipline-specific academic knowledge that they are learning.
The second criticism is that critical thinking skills are always highly contextual. In this argument, the critics make the point that the types of thinking that students do in history is categorically different from the types of thinking students do in science or math. Thus, the idea of teaching broadly defined, content-neutral critical thinking skills is impossible. I agree that there are domain-specific thinking skills that students should learn in each discipline. However, I also believe that there are several generalizable skills that elementary school students can learn that have broad applicability to their academic and social lives. That is what we have done at Two Rivers.
Defining Critical Thinking Skills
We began this work by first defining what we mean by critical thinking. After a review of the literature and looking at the practice at other schools, we identified five constructs that encompass a set of broadly applicable skills: schema development and activation; effective reasoning; creativity and innovation; problem solving; and decision making.
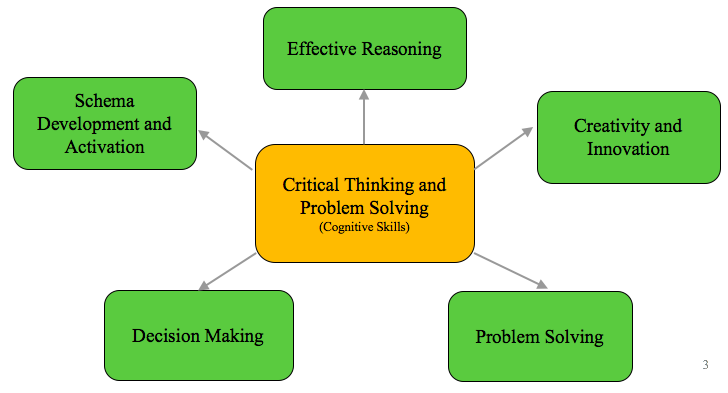
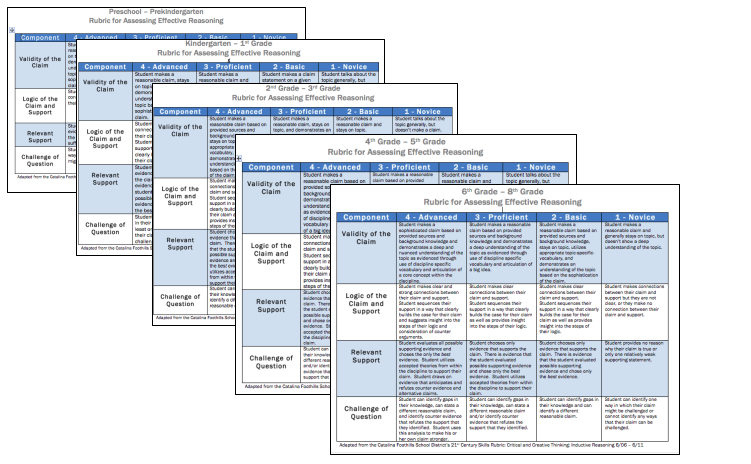
We then created rubrics to provide a concrete vision of what each of these constructs look like in practice. Working with the Stanford Center for Assessment, Learning and Equity (SCALE) , we refined these rubrics to capture clear and discrete skills.
For example, we defined effective reasoning as the skill of creating an evidence-based claim: students need to construct a claim, identify relevant support, link their support to their claim, and identify possible questions or counter claims. Rubrics provide an explicit vision of the skill of effective reasoning for students and teachers. By breaking the rubrics down for different grade bands, we have been able not only to describe what reasoning is but also to delineate how the skills develop in students from preschool through 8th grade.
Before moving on, I want to freely acknowledge that in narrowly defining reasoning as the construction of evidence-based claims we have disregarded some elements of reasoning that students can and should learn. For example, the difference between constructing claims through deductive versus inductive means is not highlighted in our definition. However, by privileging a definition that has broad applicability across disciplines, we are able to gain traction in developing the roots of critical thinking. In this case, to formulate well-supported claims or arguments.
Teaching Critical Thinking Skills
The definitions of critical thinking constructs were only useful to us in as much as they translated into practical skills that teachers could teach and students could learn and use. Consequently, we have found that to teach a set of cognitive skills, we needed thinking routines that defined the regular application of these critical thinking and problem-solving skills across domains. Building on Harvard’s Project Zero Visible Thinking work, we have named routines aligned with each of our constructs.
For example, with the construct of effective reasoning, we aligned the Claim-Support-Question thinking routine to our rubric. Teachers then were able to teach students that whenever they were making an argument, the norm in the class was to use the routine in constructing their claim and support. The flexibility of the routine has allowed us to apply it from preschool through 8th grade and across disciplines from science to economics and from math to literacy.

Kathryn Mancino, a 5th grade teacher at Two Rivers, has deliberately taught three of our thinking routines to students using the anchor charts above. Her charts name the components of each routine and has a place for students to record when they’ve used it and what they have figured out about the routine. By using this structure with a chart that can be added to throughout the year, students see the routines as broadly applicable across disciplines and are able to refine their application over time.
Assessing Critical Thinking Skills
By defining specific constructs of critical thinking and building thinking routines that support their implementation in classrooms, we have operated under the assumption that students are developing skills that they will be able to transfer to other settings. However, we recognized both the importance and the challenge of gathering reliable data to confirm this.
With this in mind, we have developed a series of short performance tasks around novel discipline-neutral contexts in which students can apply the constructs of thinking. Through these tasks, we have been able to provide an opportunity for students to demonstrate their ability to transfer the types of thinking beyond the original classroom setting. Once again, we have worked with SCALE to define tasks where students easily access the content but where the cognitive lift requires them to demonstrate their thinking abilities.
These assessments demonstrate that it is possible to capture meaningful data on students’ critical thinking abilities. They are not intended to be high stakes accountability measures. Instead, they are designed to give students, teachers, and school leaders discrete formative data on hard to measure skills.
While it is clearly difficult, and we have not solved all of the challenges to scaling assessments of critical thinking, we can define, teach, and assess these skills . In fact, knowing how important they are for the economy of the future and our democracy, it is essential that we do.
Jeff Heyck-Williams (He, His, Him)
Director of the two rivers learning institute.
Jeff Heyck-Williams is the director of the Two Rivers Learning Institute and a founder of Two Rivers Public Charter School. He has led work around creating school-wide cultures of mathematics, developing assessments of critical thinking and problem-solving, and supporting project-based learning.
Read More About Why Schools Need to Change

Bring Your Vision for Student Success to Life with NGLC and Bravely
March 13, 2024

For Ethical AI, Listen to Teachers
Jason Wilmot
October 23, 2023


Turning School Libraries into Discipline Centers Is Not the Answer to Disruptive Classroom Behavior
Stephanie McGary
October 4, 2023
K-12 Resources By Teachers, For Teachers Provided by the K-12 Teachers Alliance
- Teaching Strategies
- Classroom Activities
- Classroom Management
- Technology in the Classroom
- Professional Development
- Lesson Plans
- Writing Prompts
- Graduate Programs
Teaching Strategies to Promote Critical Thinking
Janelle cox.
- September 9, 2014

Critical thinking is an essential skill that all students will use in almost every aspect of their lives. From solving problems to making informed decisions, thinking critically is a valuable skill that will help students navigate the world’s complexities. In a post-COVID teaching environment , incorporating teaching strategies that help students think rationally and independently is an excellent way to strengthen students’ abilities and prepare them for any new challenges in the future.
There are several techniques to engage students and help strengthen these skills. Here are some teaching strategies that prove to be effective.
Encourage Students to Question Everything
We are now living in a world where AI ( artificial intelligence ) is slowly making its way into the classrooms. With these innovations, it’s imperative today, more than ever, for students to question everything and understand how to verify information when making an informed decision. AI has the potential to spread misinformation or be biased. Teach students to be careful of what is and is not a reliable source . Discuss credibility and bias and have students look for examples of both trusted content and misinformation. By using different forms of media for this exercise, students will need to use their critical thinking skills to determine the validity of the information.
Activate Student Curiosity
You can activate a student’s curiosity by using the inquiry-based learning model. This approach involves posing questions or problems for students to discover the answers on their own. In this method, students develop questions they want to know the answers to, and their teacher serves as their guide providing support as needed along the way. This approach nurtures curiosity and self-directed learning by encouraging students to think critically and independently. Recent research from 2019 supports the assertion that the use of this model significantly enhances students’ critical thinking abilities.
Incorporate Project-Based Learning
Immerse students in real-world problem scenarios by having them partake in project-based learning. Engaging in hands-on projects where students need to collaborate, communicate, analyze information, and find solutions to their challenges is a great way to develop their critical thinking skills. Throughout the project, students must engage in higher-order thinking while gathering their information and making decisions throughout various stages.
This approach pushes students to think critically while they connect to a real-world issue, and it helps them understand the relevance this issue has in their lives. Throughout the project, students will hone their critical thinking skills because PBL is a process that requires reflection and continuous improvement.
Offer Diverse Perspectives
Consider offering students a variety of viewpoints. Sometimes classrooms are filled with students who share similar perspectives on their beliefs and cultural norms. When this happens, it hinders learners from alternative viewpoints or experiences. Exposing students to diverse perspectives will help to broaden their horizons and challenge them to think beyond their perspectives. In addition, being exposed to different viewpoints encourages students to be more open-minded so they are more equipped to develop problem-solving strategies and analytical skills. It also helps them to cultivate empathy which is critical for critical thinking because it helps them appreciate others more and be concerned for them.
To support diverse viewpoints in the classroom, use various primary sources such as documentaries and articles from people who have experienced current events firsthand. Or invite in a few guest speakers who can offer varying perspectives on the same topic. Bring diverse perspectives into the classroom through guest speakers or by watching documentaries from varying experts.
Assign Tasks on Critical Writing
Assign writing tasks that encourage students to organize and articulate their thoughts and defend their position. By doing so, you are offering students the opportunity to demonstrate their critical thinking skills as well as effectively communicate their thoughts and ideas. Whether it’s through a research paper or an essay, students will need to support their claims and show evidence to prove their point of view. Critical writing also requires students to analyze information, scrutinize different perspectives, and question the reliability of sources, all of which contribute to the development of their critical thinking skills.
Promote Collaboration
Collaborative learning is a powerful tool that promotes critical thinking among students. Whether it’s through group discussions, classroom debates , or group projects, peer interaction will help students develop the ability to think critically. For example, a classroom debate will challenge students to articulate their thoughts, defend their viewpoints, and consider opposing viewpoints.
It will also challenge students to have a deep understanding of the subject matter as well as sharpen their communication skills. Any group setting where students can work together and be exposed to the thought processes of their classmates will help them understand that their way of thinking is not the only way. Through peer interaction, students will develop the ability to think critically.
Critical thinking requires consistency and commitment. This means that to make the above teaching strategies effective, they must be used consistently throughout the year. Encourage students to question everything and verify all information and resources. Activate student curiosity by using the inquiry-based learning model. Incorporate a real-world project that students can work on throughout the entire semester or school year. Assign critical writing tasks that require students to analyze information and prove their point of view. Finally, foster peer interaction where students work with their classmates to sharpen their communication skills and gain a deeper understanding of other perspectives.
The ultimate goal is for students to become independent thinkers who are capable of analyzing and solving their own problems. By modeling and developing student’s critical thinking skills in the classroom we are setting the stage for our student’s growth and success in the future.
- #CriticalThinking , #TeachingStrategies
More in Teaching Strategies

Learning Where You Live: The Power of Place-Based Education
Place-based learning is an innovative approach that engages students in their community. By…

Write On! Fun Ways to Help Kids Master Pencil Grip
Teaching children proper pencil grip will lay the foundation for successful writing. Holding…

Practical Strategies for Supporting Executive Function in the Classroom
Executive functions are self-regulating skills that we use every single day. Imagine a…

Helping Students Improve Their Handwriting
Despite the widespread use of technology in the classroom, handwriting remains an essential…
Complementary strategies for teaching collaboration and critical thinking skills
Subscribe to the center for universal education bulletin, tara barnett , tb tara barnett 4th grade teacher - knollwood school, fair haven, new jersey ben lawless , bl ben lawless history teacher - aiken college, melbourne, australia helyn kim , and helyn kim former brookings expert @helyn_kim alvin vista alvin vista former brookings expert @alvin_vista.
December 12, 2017
This is the fifth piece in a six-part blog series on teaching 21st century skills , including problem solving , metacognition , critical thinking , and collaboration, in classrooms.
In today’s changing world, students need a broader range of skills beyond traditional academic subject areas that they can apply to a wide range of real-life situations. Students will encounter many future situations where they have to bring together multiple complex skills to complete tasks. Using examples from the U.S. and Australia, we will outline two complementary methods that teach these complex skillsets. In the U.S., a 4th grade reading class uses a method to develop collaboration skills, while simultaneously developing critical thinking skills. Similarly, an example from Australia will show how a secondary level history class also teaches these two skills simultaneously, but with a different method.
An American classroom
Being able to discuss our ideas and opinions thoughtfully with others is a crucial life skill. Collaborative discussion relies on peer interaction, communication, sharing, and at times expert guidance to extend student thinking. Students—not teachers—should drive conversations as they present, defend, elaborate upon, and respond to each other. As they make connections, they will clarify their understanding, refine their thinking, and synthesize information. To help illustrate this important skill, Tara Barnett, a 4th grade teacher in Fair Haven, New Jersey, supports and enhances collaborative talk through a number of strategies.
When Tara thinks back to her own schooling, she remembers the many times she was asked questions designed to check her knowledge; rarely was she asked to engage in discussion around a text or issue. Now, it is common practice to ask students to turn and talk to each other. However, it is not enough just to provide opportunities; teachers need to teach collaborative discussion skills explicitly and systematically. Tara uses accountable talk stems as a strategy to structure meaningful conversation. This gives students the language they need to engage in discussion with each other. All too often, however, students go through the motions of talking without full engagement. Kids will say, “I agree” or “I disagree” and even give reasons, but conversations often stay at a surface level. They seem to think that using these phrases are the end rather than a means to an end.
To address this issue in classrooms, use the following strategies—they are related to literacy lessons but can, of course, be applied more widely.
1) Launch entire-class conversations before moving students to less-supported conversations with partners. Beginning with the entire class helps to establish norms for conversation in the classroom and gives a model for what a conversation can and should look like.
2) Give students a question in which they have to take a stance . In order to have good discussions, ideas need to be worth discussing. If the idea is simply stating the obvious or agreeing with a previously mentioned idea, the conversation will stall.
3) If you use accountable talk stems, preface them as a “way to enter the conversation” and list 1-2 stems for each path. The stems support students in thinking about what they are trying to accomplish by making their talk more purposeful and thoughtful. It might look something like what is described in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Entering a conversation
4) Explicitly teach vocabulary that will support students to enter a discussion. For example, when we want to discuss the characters in Fox by Margaret Wild and Ron Brooks , we introduce words like cunning , optimistic, and pessimistic . After introducing students to these words, they begin to see the connections between the words and the characters, which prompts students to use them in a discussion. Vocabulary support is a game changer for students.
5) Once students are having discussions more independently, have them record their discussions for the purpose of self-assessment. After the discussion, they can watch their discussion and ask themselves questions such as:
- Is there one person who is overpowering the discussion or one person who isn’t getting a chance to say much?
- Are we sticking with a topic for at least one round, maybe more? (Teach the students that they should be “catching” ideas and not just bouncing from one idea to the next like popcorn.)
Students can use their self-assessment to set goals. Reflection and goal setting really helps focus and elevate conversations and makes students accountable to themselves—an essential learning to learn characteristic.
An Australian classroom
On the other side of the world, Ben teaches secondary students at Aitken College, a co-educational independent school in Melbourne, Australia. Although Ben’s class subject is History, when people ask him what he teaches, Ben points out that he teaches “conceptual analysis.” This is his approach to developing critical thinking skills in a collaborative setting as the students learn history. Irrespective of the content or skills learned the ability to analyze material and concepts is crucial.
Conceptual analysis can be applied to building structures based on hierarchies or progressions, such as when students are tasked to create their own developmental or progression-based rubrics . It is important to demonstrate to students how rubrics are created and why they are useful because understanding rubrics also helps them structure their task output to match the task requirements. To help them with this skill, have the students to generate a rubric together. Pick a common school assignment, such as a history essay. Ask students to list some of the skills they use when producing a history essay; support the students in doing this by querying statements of what they produce to help them distinguish the actual processes they use. Choose three or four of these processes. Now ask students to describe what different levels of quality of these processes would look like, i.e., a description of an advanced example, and a middle-level example, and a basic level example.
Figure 2. Analyzing the skills used in a history essay

Figure 2 shows how this class activity would look like when completed as a grid, where for each step in “researching,” the students provided what they think are different levels of quality. Students are demonstrating sub-skills that are important components of conceptual analysis: differentiating, organizing, and attributing. They are differentiating by recognizing that the words generated in a brainstorm can be classified. They are organizing by placing them in different categories. We could extend the task by asking students to come up with sub-categories and sub-sub-categories. This helps students deconstruct a concept. Students who can understand how to break a task down like this are much more likely to develop and demonstrate the skills and sub-skills involved. With this task, we could also show students a few examples of other student work and ask them to grade them according to the rubric they created.
Critical thinking is a systematic way of looking at the world for the purposes of reasoning and making decisions effectively. Although we may define critical thinking in a more complex manner, it is essentially a practical or applied activity because reasoning and decisionmaking are applied activities. Conceptual analysis is a useful tool to help students do critical thinking activities collaboratively, and it can be taught in a team-based or collaborative setting.
Both conceptual analysis and collaborative discussion strategies show that they can be applied practically in diverse classroom tasks for teaching multiple complex skills such as working collaboratively and thinking critically—two of the 21st century skills that will become increasingly important as the new generation of students move into the workforce of the future.
Related Content
Loren Clarke, Esther Care
December 5, 2017
Kate Mills, Helyn Kim
October 31, 2017
Esther Care, Helyn Kim, Alvin Vista
October 17, 2017
Global Education K-12 Education
Global Economy and Development
Center for Universal Education
Jing Liu, Cameron Conrad, David Blazar
May 1, 2024
Vanessa Williamson
April 29, 2024
Sopiko Beriashvili, Michael Trucano
April 26, 2024
Our websites may use cookies to personalize and enhance your experience. By continuing without changing your cookie settings, you agree to this collection. For more information, please see our University Websites Privacy Notice .
Center for Excellence in Teaching and Learning
- Critical Thinking and other Higher-Order Thinking Skills
Critical thinking is a higher-order thinking skill. Higher-order thinking skills go beyond basic observation of facts and memorization. They are what we are talking about when we want our students to be evaluative, creative and innovative.
When most people think of critical thinking, they think that their words (or the words of others) are supposed to get “criticized” and torn apart in argument, when in fact all it means is that they are criteria-based. These criteria require that we distinguish fact from fiction; synthesize and evaluate information; and clearly communicate, solve problems and discover truths.
Why is Critical Thinking important in teaching?
According to Paul and Elder (2007), “Much of our thinking, left to itself, is biased, distorted, partial, uninformed or down-right prejudiced. Yet the quality of our life and that of which we produce, make, or build depends precisely on the quality of our thought.” Critical thinking is therefore the foundation of a strong education.
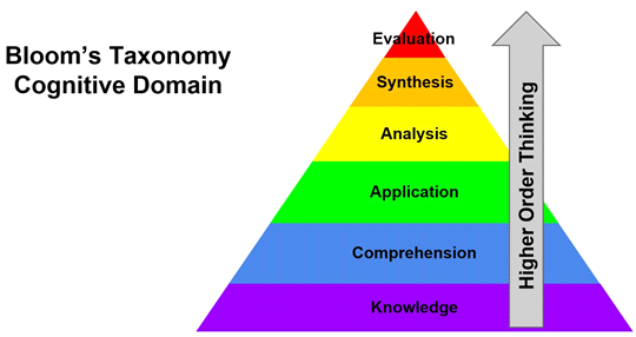
Using Bloom’s Taxonomy of thinking skills, the goal is to move students from lower- to higher-order thinking:
- from knowledge (information gathering) to comprehension (confirming)
- from application (making use of knowledge) to analysis (taking information apart)
- from evaluation (judging the outcome) to synthesis (putting information together) and creative generation
This provides students with the skills and motivation to become innovative producers of goods, services, and ideas. This does not have to be a linear process but can move back and forth, and skip steps.
How do I incorporate critical thinking into my course?
The place to begin, and most obvious space to embed critical thinking in a syllabus, is with student-learning objectives/outcomes. A well-designed course aligns everything else—all the activities, assignments, and assessments—with those core learning outcomes.
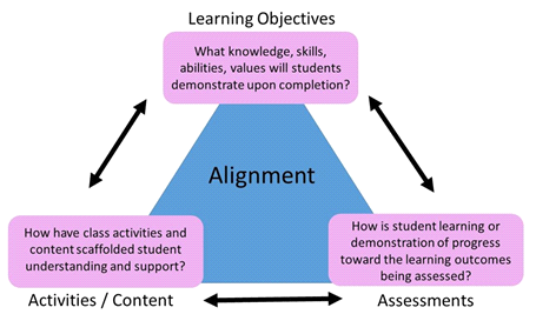
Learning outcomes contain an action (verb) and an object (noun), and often start with, “Student’s will....” Bloom’s taxonomy can help you to choose appropriate verbs to clearly state what you want students to exit the course doing, and at what level.
- Students will define the principle components of the water cycle. (This is an example of a lower-order thinking skill.)
- Students will evaluate how increased/decreased global temperatures will affect the components of the water cycle. (This is an example of a higher-order thinking skill.)
Both of the above examples are about the water cycle and both require the foundational knowledge that form the “facts” of what makes up the water cycle, but the second objective goes beyond facts to an actual understanding, application and evaluation of the water cycle.
Using a tool such as Bloom’s Taxonomy to set learning outcomes helps to prevent vague, non-evaluative expectations. It forces us to think about what we mean when we say, “Students will learn…” What is learning; how do we know they are learning?
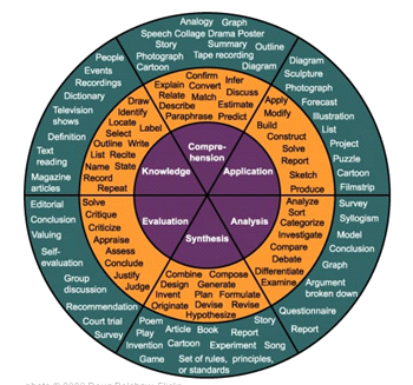
The Best Resources For Helping Teachers Use Bloom’s Taxonomy In The Classroom by Larry Ferlazzo
Consider designing class activities, assignments, and assessments—as well as student-learning outcomes—using Bloom’s Taxonomy as a guide.
The Socratic style of questioning encourages critical thinking. Socratic questioning “is systematic method of disciplined questioning that can be used to explore complex ideas, to get to the truth of things, to open up issues and problems, to uncover assumptions, to analyze concepts, to distinguish what we know from what we don’t know, and to follow out logical implications of thought” (Paul and Elder 2007).
Socratic questioning is most frequently employed in the form of scheduled discussions about assigned material, but it can be used on a daily basis by incorporating the questioning process into your daily interactions with students.
In teaching, Paul and Elder (2007) give at least two fundamental purposes to Socratic questioning:
- To deeply explore student thinking, helping students begin to distinguish what they do and do not know or understand, and to develop intellectual humility in the process
- To foster students’ abilities to ask probing questions, helping students acquire the powerful tools of dialog, so that they can use these tools in everyday life (in questioning themselves and others)
How do I assess the development of critical thinking in my students?
If the course is carefully designed around student-learning outcomes, and some of those outcomes have a strong critical-thinking component, then final assessment of your students’ success at achieving the outcomes will be evidence of their ability to think critically. Thus, a multiple-choice exam might suffice to assess lower-order levels of “knowing,” while a project or demonstration might be required to evaluate synthesis of knowledge or creation of new understanding.
Critical thinking is not an “add on,” but an integral part of a course.
- Make critical thinking deliberate and intentional in your courses—have it in mind as you design or redesign all facets of the course
- Many students are unfamiliar with this approach and are more comfortable with a simple quest for correct answers, so take some class time to talk with students about the need to think critically and creatively in your course; identify what critical thinking entail, what it looks like, and how it will be assessed.
Additional Resources
- Barell, John. Teaching for Thoughtfulness: Classroom Strategies to Enhance Intellectual Development . Longman, 1991.
- Brookfield, Stephen D. Teaching for Critical Thinking: Tools and Techniques to Help Students Question Their Assumptions . Jossey-Bass, 2012.
- Elder, Linda and Richard Paul. 30 Days to Better Thinking and Better Living through Critical Thinking . FT Press, 2012.
- Fasko, Jr., Daniel, ed. Critical Thinking and Reasoning: Current Research, Theory, and Practice . Hampton Press, 2003.
- Fisher, Alec. Critical Thinking: An Introduction . Cambridge University Press, 2011.
- Paul, Richard and Linda Elder. Critical Thinking: Learn the Tools the Best Thinkers Use . Pearson Prentice Hall, 2006.
- Faculty Focus article, A Syllabus Tip: Embed Big Questions
- The Critical Thinking Community
- The Critical Thinking Community’s The Thinker’s Guides Series and The Art of Socratic Questioning
Quick Links
- Developing Learning Objectives
- Creating Your Syllabus
- Active Learning
- Service Learning
- Case Based Learning
- Group and Team Based Learning
- Integrating Technology in the Classroom
- Effective PowerPoint Design
- Hybrid and Hybrid Limited Course Design
- Online Course Design
Consult with our CETL Professionals
Consultation services are available to all UConn faculty at all campuses at no charge.
Critical Thinking for Teachers
- First Online: 02 January 2023
Cite this chapter

- Diler Oner 3 &
- Yeliz Gunal Aggul 3
Part of the book series: Integrated Science ((IS,volume 13))
813 Accesses
2 Citations
Developing critical thinking is an important educational goal for all grade levels today. To foster their students’ critical thinking, future teachers themselves must become critical thinkers first. Thus, critical thinking should be an essential aspect of teacher training. However, despite its importance, critical thinking is not systematically incorporated into teacher education programs. There exist several conceptualizations of critical thinking in the literature, and these have different entailments regarding the guidelines and instructional strategies to teach critical thinking. In this paper, after examining the critical thinking literature, we suggested that critical thinking could be conceptualized in two distinct but complementary ways—as the acquisition of cognitive skills (instrumental perspective) and as identity development (situated perspective). We discussed the implications of these perspectives in teacher education. While the instrumental perspective allowed us to consider what to teach regarding critical thinking, the situated perspective enabled us to emphasize the broader social context where critical thinking skills and dispositions could be means of active participation in the culture of teaching.
Graphical Abstract/Art Performance

Critical thinking.
Everything we teach should be different from machines. If we do not change the way we teach, 30 years from now, we will be in trouble . Jack Ma
Jack Ma Co-founder of the Alibaba Group.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Burbules N-C, Berk R (1999) Critical thinking and critical pedagogy: relations, differences, and limits. In: Popkewitz T-S, Fendler L (eds) Critical theories in education. Routledge, New York, pp 45–65
Google Scholar
Hitchcock D (2018) Critical thinking. In: Zalta E-N (ed) The Stanford Encyclopedia of philosophy. https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/fall2018/entries/critical-thinking . Accessed 8 Aug 2020
Costa A-L (1985) Developing minds: preface to the revised edition. In: Costa A-L (ed) Developing minds: a resource book for teaching thinking. Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development, Virginia, pp ix–x
National Education Association (2012) Preparing 21st-century students for a global society: an educator’s guide to “the four Cs.” http://www.nea.org/assets/docs/A-Guide-to-Four-Cs.pdf . Accessed 08 Aug 2020
Oner D (2019) Education 4.0: the skills needed for the future. In: Paper presented at the 5th Turkish-German frontiers of social science symposium (TUGFOSS) by Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, Stiftung Mercator, and Koç University, Leipzig, Germany, 24–27 Oct 2019
Elder L, Paul R (1994) Critical thinking: why we must transform our teaching. J Dev Educ 18(1):34–35
Williams R-L (2005) Targeting critical thinking within teacher education: the potential impact on society. Teach Educ Q 40(3):163–187
Holder J-J (1994) An epistemological foundation for thinking: a Deweyan approach. Stud Philos Educ 13:175–192
Article Google Scholar
Dewey J (1910) How we think. D.C. Heath and Company, Lexington
Bruner J (1966) Toward a theory of instruction. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Laanemets U, Kalamees-Ruubel K (2013) The Taba-Tyler rationales. J Am Assoc Advance Curriculum Stud 9:1–12
McTighe J, Schollenberger J (1985) Why teach thinking? A statement of rationale. In: Costa A-L (ed) Developing minds: a resource book for teaching thinking. Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development, Alexandria, pp 2–5
Taba H (1962) The teaching of thinking. Element English 42(5):534–542
Pressesien B-Z (1985) Thinking skills: meanings and models revisited. In: Costa A-L (ed) Developing minds: a resource book for teaching thinking Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development, Alexandria, pp 56–62
Cohen J (1971) Thinking. Rand McNally, Chicago
Iowa Department of Education (1989) A guide to developing higher-order thinking across the curriculum. Department of Education, Des Moines (ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED-306-550)
Jonassen D (1996) Computers as mindtools for schools: engaging critical thinking. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Ennis R-H (1996) Critical thinking dispositions: their nature and accessibility. Informal Logic 18:165–182
Facione P (1990) Critical thinking: a statement of expert consensus for purposes of educational assessment and instruction. California Academic Press, Millbrae
Paul R-W (1985) Goals for a critical thinking curriculum. In: Costa A-L (ed) Developing minds: a resource book for teaching thinking. Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development, Alexandria, pp 77–84
Ennis R-H (1964) A definition of critical thinking. Read Teach 17(8):599–612
Ennis R-H (1985) Goals for a critical thinking curriculum. In: Costa A-L (ed) Developing minds: a resource book for teaching thinking. Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development, Alexandria, pp 68–71
Ennis R-H (2015) Critical thinking: a streamlined conception. In: Davies M, Barnett R (eds) The Palgrave handbook of critical thinking in higher education. Palgrave Macmillan, New York, pp 31–47
Chapter Google Scholar
Davies M (2015) A model of critical thinking in higher education. In: Paulsen M (ed) Higher education: handbook of theory and research, vol 30. Springer, Cham, pp 41–92
Walters K-S (1994) Introduction: beyond logicism in critical thinking. In: Walters K-S (ed) Re-thinking reason: new perspectives in critical thinking. SUNY Press, Albany, pp 1–22
Barnett R (1997) Higher education: a critical business. Open University Press, Buckingham
Phelan A-M, Garrison J-W (1994) Toward a gender-sensitive ideal of critical thinking: a feminist poetic. Curric Inq 24(3):255–268
Kaplan L-D (1991) Teaching intellectual autonomy: the failure of the critical thinking movement. Educ Theory 41(4):361–370
McLaren P (1994) Critical pedagogy and predatory culture. Routledge, London
Giroux H-A (2010) Lessons from Paulo Freire. https://www.chronicle.com/article/lessons-from-paulo-freire/ . Accessed 8 Aug 2020
Freire P (2000) Pedagogy of the oppressed. Continuum, New York
Giroux H-A (2011) On critical pedagogy. The Continuum International Publishing Group, Auckland
Volman M, ten Dam G (2015) Critical thinking for educated citizenship. In: Davies M, Barnett R (eds) The Palgrave handbook of critical thinking in higher education. Palgrave Macmillan, New York, pp 593–603
Belenky M-F, Clinchy B-M, Goldberger N-R, Tarule J-M (1997) Women’s ways of knowing: the development of self, voice, and mind. Basic Books, New York
Warren K-J (1994) Critical thinking and feminism. In: Walters K-S (ed) Re-thinking reason: new perspectives in critical thinking. SUNY Press, Albany, pp 199–204
Thayer-Bacon B (2000) Transforming critical thinking. Teachers College Press, New York
Atkinson D (1997) A critical approach to critical thinking in TESOL. TESOL Q 31(1):71–94
ten Dam G, Volman M (2004) Critical thinking as a citizenship competence: teaching strategies. Learn Instr 14:359–379
Sfard A (1998) On two metaphors for learning and the dangers of choosing just one. Educ Res 27:4–13
Tsui L (1999) Courses and instruction affecting critical thinking. Res High Educ 40(2):185–200
Abrami P-C, Bernard R-M, Borokhovski E, Waddington D-I, Anne Wade C, Persson T (2015) Strategies for teaching students to think critically: a meta-analysis. Rev Educ Res 85(2):275–314
Mpofu N, Maphalala M-C (2017) Fostering critical thinking in initial teacher education curriculums: a comprehensive literature review. Gender Behav 15(2):9226–9236
Ennis R-H (1989) Critical thinking and subject specificity: clarification and needed research. Educ Res 18(3):4–10
Norris S-P (1985) The choice of standard conditions in defining critical thinking competence. Educ Theory 35(1):97–107
Paul R-W (1985) McPeck’s mistakes. Informal Logic 7(1):35–43
Siegel H (1991) The generalizability of critical thinking. Educ Philos Theory 23(1):18–30
McPeck J-E (1981) Critical thinking and education. St Martin’s Press, New York
McPeck J-E (1984) Stalking beasts, but swatting flies: the teaching of critical thinking. Can J Educ 9(1):28–44
McPeck J-E (1990) Critical thinking and subject-specificity: a reply to Ennis. Educ Res 19(4):10–12
Adler M (1986) Why critical thinking programs won’t work. Educ Week 6(2):28
Brown A (1997) Transforming schools into communities of thinking and learning about serious matters. Am Psychol 52(4):399–413
Article CAS Google Scholar
Oner D (2010) Öğretmenin bilgisi özel bir bilgi midir? Öğretmek için gereken bilgiye kuramsal bir bakış. Boğaziçi Üniversitesi Eğitim Dergisi 27(2):23–32
Shulman L-S (1987) Knowledge and teaching: foundations of the new reform. Harvard Educ Rev 57(1):61–77. https://doi.org/10.17763/haer.57.1.j463w79r56455411
Oner D, Adadan E (2011) Use of web-based portfolios as tools for reflection in preservice teacher education. J Teach Educ 62(5):477–492
Oner D, Adadan E (2016) Are integrated portfolio systems the answer? An evaluation of a web-based portfolio system to improve preservice teachers’ reflective thinking skills. J Comput High Educ 28(2):236–260
Lave J, Wenger E (1991) Situated learning: legitimate peripheral participation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Book Google Scholar
Brookfield S (2012) Teaching for critical thinking: tools and techniques to help students question their assumptions. Jossey-Bass, San Francisco
Korthagen F-A-J (2010) Situated learning theory and the pedagogy of teacher education: towards an integrative view of teacher behavior and teacher learning. Teach Teach Educ 26(1):98–106
Putnam R-T, Borko H (2000) What do new views of knowledge and thinking have to say about research on teacher learning? Educ Res 29(1):4–15
Brown J-S, Collins A, Duguid P (1989) Situated cognition and the culture of learning. Educ Res 18(1):32–42
Scardamalia M, Bereiter C (1991) Higher levels of agency for children in knowledge building: a challenge for the design of new knowledge media. J Learn Sci 1(1):37–68
Shaffer D-W (2005) Epistemic games. Innovate J Online Educ 1(6):Article 2
Oner D (2020) A virtual internship for developing technological pedagogical content knowledge. Australas J Educ Technol 36(2):27–42
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Bogazici University, Istanbul, Turkey
Diler Oner & Yeliz Gunal Aggul
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Diler Oner .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Universal Scientific Education and Research Network (USERN), Stockholm, Sweden
Nima Rezaei
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Oner, D., Aggul, Y.G. (2022). Critical Thinking for Teachers. In: Rezaei, N. (eds) Integrated Education and Learning. Integrated Science, vol 13. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15963-3_18
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15963-3_18
Published : 02 January 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-15962-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-15963-3
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Our Mission

4 Strategies for Sparking Critical Thinking in Young Students
Fostering investigative conversation in grades K–2 isn’t easy, but it can be a great vehicle to promote critical thinking.
In the middle of class, a kindergartner spotted an ant and asked the teacher, “Why do ants come into the classroom?” Fairly quickly, educational consultant Cecilia Cabrera Martirena writes , students started sharing their theories: Maybe the ants were cold, or looking for food, or lonely.
Their teacher started a KWL chart to organize what students already knew, what they wanted to know, and, later, what they had learned. “As many of the learners didn’t read or write yet, the KWL was created with drawings and one or two words,” Cabrera Martirena writes. “Then, as a group, they decided how they could gather information to answer that first question, and some possible research routes were designed.”
As early elementary teachers know, young learners are able to engage in critical thinking and participate in nuanced conversations, with appropriate supports. What can teachers do to foster these discussions? Elementary teacher Jennifer Orr considered a few ideas in an article for ASCD .
“An interesting question and the discussion that follows can open up paths of critical thinking for students at any age,” Orr says. “With a few thoughtful prompts and a lot of noticing and modeling, we as educators can help young students engage in these types of academic conversations in ways that deepen their learning and develop their critical thinking skills.”
While this may not be an “easy process,” Orr writes—for the kids or the teacher—the payoff is students who from a young age are able to communicate new ideas and questions; listen and truly hear the thoughts of others; respectfully agree, disagree, or build off of their peers’ opinions; and revise their thinking.
4 Strategies for Kick-Starting Powerful Conversations
1. Encourage Friendly Debate: For many elementary-aged children, it doesn’t take much provoking for them to share their opinions, especially if they disagree with each other. Working with open-ended prompts that “engage their interest and pique their curiosity” is one key to sparking organic engagement, Orr writes. Look for prompts that allow them to take a stance, arguing for or against something they feel strongly about.
For example, Orr says, you could try telling first graders that a square is a rectangle to start a debate. Early childhood educator Sarah Griffin proposes some great math talk questions that can yield similar results:
- How many crayons can fit in a box?
- Which takes more snow to build: one igloo or 20 snowballs?
- Estimate how many tissues are in a box.
- How many books can you fit in your backpack?
- Which would take less time: cleaning your room or reading a book?
- Which would you rather use to measure a Christmas tree: a roll of ribbon or a candy cane? Why?
Using pictures can inspire interesting math discussions as well, writes K–6 math coach Kristen Acosta . Explore counting, addition, and subtraction by introducing kids to pictures “that have missing pieces or spaces” or “pictures where the objects are scattered.” For example, try showing students a photo of a carton of eggs with a few eggs missing. Ask questions like, “what do you notice?” and “what do you wonder?” and see how opinions differ.
2. Put Your Students in the Question: Centering students’ viewpoints in a question or discussion prompt can foster deeper thinking, Orr writes. During a unit in which kids learned about ladybugs, she asked her third graders, “What are four living and four nonliving things you would need and want if you were designing your own ecosystem?” This not only required students to analyze the components of an ecosystem but also made the lesson personal by inviting them to dream one up from scratch.
Educator Todd Finley has a list of interesting writing prompts for different grades that can instead be used to kick off classroom discussions. Examples for early elementary students include:
- Which is better, giant muscles or incredible speed? Why?
- What’s the most beautiful person, place, or thing you’ve ever seen? Share what makes that person, place, or thing so special.
- What TV or movie characters do you wish were real? Why?
- Describe a routine that you often or always do (in the morning, when you get home, Friday nights, before a game, etc.).
- What are examples of things you want versus things you need?
3. Open Several Doors: While some students take to classroom discussions like a duck to water, others may prefer to stay on dry land. Offering low-stakes opportunities for students to dip a toe into the conversation can be a great way to ensure that everyone in the room can be heard. Try introducing hand signals that indicate agreement, disagreement, and more. Since everyone can indicate their opinion silently, this supports students who are reluctant to speak, and can help get the conversation started.
Similarly, elementary school teacher Raquel Linares uses participation cards —a set of different colored index cards, each labeled with a phrase like “I agree,” “I disagree,” or “I don’t know how to respond.” “We use them to assess students’ understanding, but we also use them to give students a voice,” Linares says. “We obviously cannot have 24 scholars speaking at the same time, but we want everyone to feel their ideas matter. Even if I am very shy and I don’t feel comfortable, my voice is still heard.” Once the students have held up the appropriate card, the discussion gets going.
4. Provide Discussion Sentence Starters: Young students often want to add their contribution without connecting it to what their peers have said, writes district-level literacy leader Gwen Blumberg . Keeping an ear out for what students are saying to each other is an important starting point when trying to “lift the level of talk” in your classroom. Are kids “putting thoughts into words and able to keep a conversation going?” she asks.
Introducing sentence starters like “I agree…” or “I feel differently…” can help demonstrate for students how they can connect what their classmate is saying to what they would like to say, which grows the conversation, Blumberg says. Phrases like “I’d like to add…” help students “build a bridge from someone else’s idea to their own.”
Additionally, “noticing and naming the positive things students are doing, both in their conversation skills and in the thinking they are demonstrating,” Orr writes, can shine a light for the class on what success looks like. Celebrating when students use these sentence stems correctly, for example, helps reinforce these behaviors.
“Students’ ability to clearly communicate with others in conversation is a critical literacy skill,” Blumberg writes, and teachers in grades K–2 can get students started on the path to developing this skill by harnessing their natural curiosity and modeling conversation moves.
- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free
What Are Critical Thinking Skills and Why Are They Important?
Learn what critical thinking skills are, why they’re important, and how to develop and apply them in your workplace and everyday life.
![3 strategies for teaching critical thinking skills [Featured Image]: Project Manager, approaching and analyzing the latest project with a team member,](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/1SOj8kON2XLXVb6u3bmDwN/62a5b68b69ec07b192de34b7ce8fa28a/GettyImages-598260236.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
We often use critical thinking skills without even realizing it. When you make a decision, such as which cereal to eat for breakfast, you're using critical thinking to determine the best option for you that day.
Critical thinking is like a muscle that can be exercised and built over time. It is a skill that can help propel your career to new heights. You'll be able to solve workplace issues, use trial and error to troubleshoot ideas, and more.
We'll take you through what it is and some examples so you can begin your journey in mastering this skill.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to interpret, evaluate, and analyze facts and information that are available, to form a judgment or decide if something is right or wrong.
More than just being curious about the world around you, critical thinkers make connections between logical ideas to see the bigger picture. Building your critical thinking skills means being able to advocate your ideas and opinions, present them in a logical fashion, and make decisions for improvement.
Build job-ready skills with a Coursera Plus subscription
- Get access to 7,000+ learning programs from world-class universities and companies, including Google, Yale, Salesforce, and more
- Try different courses and find your best fit at no additional cost
- Earn certificates for learning programs you complete
- A subscription price of $59/month, cancel anytime
Why is critical thinking important?
Critical thinking is useful in many areas of your life, including your career. It makes you a well-rounded individual, one who has looked at all of their options and possible solutions before making a choice.
According to the University of the People in California, having critical thinking skills is important because they are [ 1 ]:
Crucial for the economy
Essential for improving language and presentation skills
Very helpful in promoting creativity
Important for self-reflection
The basis of science and democracy
Critical thinking skills are used every day in a myriad of ways and can be applied to situations such as a CEO approaching a group project or a nurse deciding in which order to treat their patients.
Examples of common critical thinking skills
Critical thinking skills differ from individual to individual and are utilized in various ways. Examples of common critical thinking skills include:
Identification of biases: Identifying biases means knowing there are certain people or things that may have an unfair prejudice or influence on the situation at hand. Pointing out these biases helps to remove them from contention when it comes to solving the problem and allows you to see things from a different perspective.
Research: Researching details and facts allows you to be prepared when presenting your information to people. You’ll know exactly what you’re talking about due to the time you’ve spent with the subject material, and you’ll be well-spoken and know what questions to ask to gain more knowledge. When researching, always use credible sources and factual information.
Open-mindedness: Being open-minded when having a conversation or participating in a group activity is crucial to success. Dismissing someone else’s ideas before you’ve heard them will inhibit you from progressing to a solution, and will often create animosity. If you truly want to solve a problem, you need to be willing to hear everyone’s opinions and ideas if you want them to hear yours.
Analysis: Analyzing your research will lead to you having a better understanding of the things you’ve heard and read. As a true critical thinker, you’ll want to seek out the truth and get to the source of issues. It’s important to avoid taking things at face value and always dig deeper.
Problem-solving: Problem-solving is perhaps the most important skill that critical thinkers can possess. The ability to solve issues and bounce back from conflict is what helps you succeed, be a leader, and effect change. One way to properly solve problems is to first recognize there’s a problem that needs solving. By determining the issue at hand, you can then analyze it and come up with several potential solutions.
How to develop critical thinking skills
You can develop critical thinking skills every day if you approach problems in a logical manner. Here are a few ways you can start your path to improvement:
1. Ask questions.
Be inquisitive about everything. Maintain a neutral perspective and develop a natural curiosity, so you can ask questions that develop your understanding of the situation or task at hand. The more details, facts, and information you have, the better informed you are to make decisions.
2. Practice active listening.
Utilize active listening techniques, which are founded in empathy, to really listen to what the other person is saying. Critical thinking, in part, is the cognitive process of reading the situation: the words coming out of their mouth, their body language, their reactions to your own words. Then, you might paraphrase to clarify what they're saying, so both of you agree you're on the same page.
3. Develop your logic and reasoning.
This is perhaps a more abstract task that requires practice and long-term development. However, think of a schoolteacher assessing the classroom to determine how to energize the lesson. There's options such as playing a game, watching a video, or challenging the students with a reward system. Using logic, you might decide that the reward system will take up too much time and is not an immediate fix. A video is not exactly relevant at this time. So, the teacher decides to play a simple word association game.
Scenarios like this happen every day, so next time, you can be more aware of what will work and what won't. Over time, developing your logic and reasoning will strengthen your critical thinking skills.
Learn tips and tricks on how to become a better critical thinker and problem solver through online courses from notable educational institutions on Coursera. Start with Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking from Duke University or Mindware: Critical Thinking for the Information Age from the University of Michigan.
Article sources
University of the People, “ Why is Critical Thinking Important?: A Survival Guide , https://www.uopeople.edu/blog/why-is-critical-thinking-important/.” Accessed May 18, 2023.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.
- WordPress.org
- Documentation
- Learn WordPress
- Members Newsfeed
14 Strategies to Help Students Improve Their Critical Thinking Skills
- Uncategorized
Are you looking for strategies to help students improve their critical thinking skills? If so, keep reading.
1. Provide the learner duties that require logical thinking (e.g., designate the learner to water plants and give a watering can and a glass, telling the learner to use the most appropriate container, etc.).
2. Every day, give the learner problem-solving situations that require logical thinking (e.g., “A stranger takes you by the arm in a department store. What do you do?” “You see smoke coming out of a neighbor’s house and no one is home. What do you do?” etc.).
3. Make sure the learner experiences the consequences of their behavior (e.g., appropriate behavior results in positive consequences while unacceptable behavior results in negative consequences).
4. Give the learner a list of questions involving logic to answer orally (e.g., “Why do we post ‘wet’ paint signs?” “Why do we have stop signs at intersections?” “Why do we wear seat belts?” etc.).
5. On occasions where something is broken, lost, etc., have the learner find what could have been done to prevent the situation. Talk with the learner about the value of properly keeping and organizing learning materials.
6. Get the learner to read stories involving a moral (e.g., The Tortoise and the Hare, The Boy Who Cried Wolf, etc.) and explain the reason for the outcome of the story.
7. Get the learner to read short stories without endings and require the learner to create logical endings for the stories.
8. Provide the learner situations/images and have them explain what variables are related (e.g., “Snow is falling, and the wind is blowing: Is the temperature hot or cold? What should you wear outdoors?”).
9. Get the learner to sequence rearranged cartoon strips and explain the logic of the sequence they created.
10. Provide the learner fill-in-the-blank statements requiring an appropriate response from multiple-choice possibilities (e.g., “The boy’s dog was dirty, so the boy decided to give his dog a _ [ dog biscuit, bath, toy].”).
11. Present the learner with images of dangerous situations and have them explain why they are dangerous (e.g., a child running into the street from between parked cars, a child riding a bicycle without using their hands, etc.).
12. Utilize cause-and-effect relationships as they relate to nature and people. Talk about what led up to a specific situation in a story or an image and what could happen next, etc.
13. Consider using an education app designed to help students improve their critical thinking skills. Click here to view our list of recommended apps.
14. Consider using edtech to encourage students to work on their critical thinking skills. Here is an article that we wrote on the subject .
Your email address will not be published.
Related Articles

Agriculture is a diverse industry with a vast array of job opportunities.…

Public health is a field that sees a high demand for professionals,…
Have you ever dreamed of becoming a millionaire? While the path to…

Pedagogue is a social media network where educators can learn and grow. It's a safe space where they can share advice, strategies, tools, hacks, resources, etc., and work together to improve their teaching skills and the academic performance of the students in their charge.
If you want to collaborate with educators from around the globe, facilitate remote learning, etc., sign up for a free account today and start making connections.
Pedagogue is Free Now, and Free Forever!
- New? Start Here
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Registration
Don't you have an account? Register Now! it's really simple and you can start enjoying all the benefits!
We just sent you an Email. Please Open it up to activate your account.
I allow this website to collect and store submitted data.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Students grappled with ideas and their beliefs and employed deep critical-thinking skills to develop arguments for their claims. Embedding critical-thinking skills in curriculum that students care ...
Students must learn to amass the proper expertise to inform their thinking. Teaching critical thinking skills can be supported by an understanding of how to analyze, organize, and clarify information. 6. Utilize Peer Groups. There is comfort in numbers, as the saying goes.
Critical thinking helps students make informed decisions, develop analytical skills, and promotes independence. 3. What are some strategies to cultivate critical thinking in students? Strategies can include Socratic questioning, debates and discussions, teaching metacognition, and problem-solving activities. 4. How can I assess my students ...
Teach Reasoning Skills. Reasoning skills are another key component of critical thinking, involving the abilities to think logically, evaluate evidence, identify assumptions, and analyze arguments. Students who learn how to use reasoning skills will be better equipped to make informed decisions, form and defend opinions, and solve problems.
Some essential skills that are the basis for critical thinking are: Communication and Information skills. Thinking and Problem-Solving skills. Interpersonal and Self- Directional skills. Collaboration skills. These four bullets are skills students are going to need in any field and in all levels of education.
How to teach students to think critically — strategies. 1. Build a classroom climate that encourages open-mindedness. 2. Teach students to make clear and effective arguments. 3. Encourage metacognition — guide students to think about their own and others' thinking. 4. Assign open-ended and varied activities to practice different kinds of ...
10. Hold a Q&A session. One way you can figure out how well kids are grasping critical-thinking skills is by holding question-and-answer sessions. Ask a variety of questions one-on-one or in small groups and take note of the levels of thought individual students use regularly and avoid over time.
6 Hats Thinking is a model for divergent thinking. 6. 6 Strategies for Teac h ing With Bloom's Taxonomy 7. An Intro To Critical Thinking, a 10-minute video from wireless philosophy that takes given premises, and walks the viewer through valid and erroneous conclusions. 8. Why Questions Are More Important Than Answers by Terry Heick. 9. 20 ...
Inspire creativity. Imagination is key to teaching critical thinking in elementary school. Teachers should seek out new ways for students to use information to create something new. Art projects are an excellent way to do this. Students can also construct inventions, write a story or poem, create a game, sing a song—the sky's the limit.
Strategy 2: Structure class discussions thoughtfully. Building critical-thinking skills is less about finding the right answer and more about the quest to get there. That quest is the thoughtful consideration and discussion that occurs amongst the students in your course. Try not to start with just one right answer in your head when you pose a ...
Yes, We Can Define, Teach, and Assess Critical Thinking Skills. Critical thinking is a thing. We can define it; we can teach it; and we can assess it. While the idea of teaching critical thinking has been bandied around in education circles since at least the time of John Dewey, it has taken greater prominence in the education debates with the ...
This article summarizes the available empirical evidence on the impact of instruction on the development and enhancement of critical thinking skills and dispositions and student achievement. The review includes 341 effects sizes drawn from quasi- or true-experimental studies that used standardized measures of CT as outcome variables.
These seven strategies can help students cultivate their critical thinking skills. (These strategies can be modified for all students with the aid of a qualified educator.) 1. Encourage Questioning. One of the fundamental pillars of critical thinking is curiosity. Encourage students to ask questions about the subject matter and challenge ...
Although there are some quite diverse definitions of critical thinking, nearly all emphasize the ability and tendency to gather, evaluate, and use information effectively (Beyer, 1985). In this article, we discuss skills related to critical thinking and three specific strategies for teaching these skills: 1) Building Categories, 2) Finding ...
Critical thinking requires consistency and commitment. This means that to make the above teaching strategies effective, they must be used consistently throughout the year. Encourage students to question everything and verify all information and resources. Activate student curiosity by using the inquiry-based learning model.
Complementary strategies for teaching collaboration and critical thinking skills. This is the fifth piece in a six-part blog series on teaching 21st century skills, including problem solving ...
Teaching for Thoughtfulness: Classroom Strategies to Enhance Intellectual Development. Longman, 1991. Brookfield, Stephen D. Teaching for Critical Thinking: Tools and Techniques to Help Students Question Their Assumptions. Jossey-Bass, 2012. Elder, Linda and Richard Paul. 30 Days to Better Thinking and Better Living through Critical Thinking ...
Our critical thinking skills framework. The focus on critical thinking skills has its roots in two approaches: the cognitive psychological approach and the educational approach (see for reviews, e.g. Sternberg Citation 1986; Ten Dam and Volman Citation 2004).From a cognitive psychological approach, critical thinking is defined by the types of behaviours and skills that a critical thinker can show.
3.1 Critical Thinking as Cognitive Processes and Skills. The emphasis on teaching thinking led to an initial conceptualization of critical thinking as cognitive processes and skills. In the book Developing Minds, by the Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development in the US, which is an early effort to provide a resource guide for educators to teach "thinking," Pressesien ...
4 Strategies for Kick-Starting Powerful Conversations. 1. Encourage Friendly Debate: For many elementary-aged children, it doesn't take much provoking for them to share their opinions, especially if they disagree with each other.
for teaching CT skills. KEYWORDS: Critical thinking skills, teaching critical thinking, assisting critical thinking, technology to promote critical thinking. INTRODUCTION Although the importance of Critical Thinking (CT) skills in the learning process is agreed upon, there is less agreement about how CT is defined (Alfadhli 2008).
According to the University of the People in California, having critical thinking skills is important because they are [ 1 ]: Universal. Crucial for the economy. Essential for improving language and presentation skills. Very helpful in promoting creativity. Important for self-reflection.
CT skills, assessing CT skills, strategies to teac h CT skills, CT skills taxonomy, and using technology to teach CT skills). Later, these five topics were used to for m the base of the conceptual ...
6. Get the learner to read stories involving a moral (e.g., The Tortoise and the Hare, The Boy Who Cried Wolf, etc.) and explain the reason for the outcome of the story. 7. Get the learner to read short stories without endings and require the learner to create logical endings for the stories. 8.
1 The Basics. To understand the role of questioning in teaching critical thinking, it's essential to grasp what constitutes a good question. A good question is open-ended, meaning it doesn't have ...
Journal of Research in Education and Science (IJRES), 2 (1), 190-200. This article may be used for research, teaching, and private study purposes. Any substantial or systematic reproduction, redistribution, reselling, loan, sub-licensing, systematic supply, or distribution in any form to anyone is expressly forbidden.
Discover how teachers can inspire students to become self-motivated learners with strategies that foster curiosity, critical thinking, and resilience.
1 Encourage Questions. Encouraging your clients to ask questions is a powerful way to develop their critical thinking skills. Questions drive deeper understanding and stimulate intellectual ...