British Council Malaysia
- English schools
- myClass Login
- Show search Search Search Close search

How to write a cohesive essay

When it comes to writing, people usually emphasise the importance of good grammar and proper spelling. However, there is a third element that actually helps authors get their thoughts across to readers, that is cohesiveness in writing.
In writing, cohesiveness is the quality that makes it easier for people to read and understand an essay’s content. A cohesive essay has all its parts (beginning, middle, and end) united, supporting each other to inform or convince the reader.
Unfortunately, this is an element that even intermediate or advanced writers stumble on. While the writer’s thoughts are in their compositions, all too often readers find it difficult to understand what is being said because of the poor organisation of ideas. This article provides tips on how you can make your essay cohesive.
1. Identify the thesis statement of your essay
A thesis statement states what your position is regarding the topic you are discussing. To make an essay worth reading, you will need to make sure that you have a compelling stance.
However, identifying the thesis statement is only the first step. Each element that you put in your essay should be included in a way that supports your argument, which should be the focus of your writing. If you feel that some of the thoughts you initially included do not contribute to strengthening your position, it might be better to take them out when you revise your essay to have a more powerful piece.
2. Create an outline
One of the common mistakes made by writers is that they tend to add a lot of details to their essay which, while interesting, may not really be relevant to the topic at hand. Another problem is jumping from one thought to another, which can confuse a reader if they are not familiar with the subject.
Preparing an outline can help you avoid these difficulties. List the ideas you have in mind for your essay, and then see if you can arrange these thoughts in a way that would make it easy for your readers to understand what you are saying.
While discursive essays do not usually contain stories, the same principle still applies. Your writing should have an introduction, a discussion portion and a conclusion. Again, make sure that each segment supports and strengthens your thesis statement.
As a side note, a good way to write the conclusion of your essay is to mention the points that you raised in your introduction. At the same time, you should use this section to summarise main ideas and restate your position to drive the message home to your readers.
3. Make sure everything is connected
In connection to the previous point, make sure that each section of your essay is linked to the one after it. Think of your essay as a story: it should have a beginning, middle, and end, and the way that you write your piece should logically tie these elements together in a linear manner.
4. Proofread before submitting your essay
Make sure to review your composition prior to submission. In most cases, the first draft may be a bit disorganised because this is the first time that your thoughts have been laid out on paper. By reviewing what you have written, you will be able to see which parts need editing, and which ones can be rearranged to make your essay more easily understood by your readers. Try to look at what you wrote from the point of view of your audience. Will they be able to understand your train of thought, or do you need to reorganise some parts to make it easier for them to appreciate what you are saying? Taking another look at your essay and editing it can do wonders for how your composition flows.
Writing a cohesive essay could be a lot easier than you think – especially when you follow these steps. Don’t forget that reading complements writing: try reading essays on various topics and see if each of their parts supports their identified goal or argument.

Cohesion And Coherence In Essay Writing
Table of contents, introduction.
Coherent essays are identified by relevance to the central topic. They communicate a meaningful message to a specific audience and maintain pertinence to the main focus. In a coherent essay, the sentences and ideas flow smoothly and, as a result, the reader can follow the ideas developed without any issues.
To achieve coherence in an essay, writers use lexical and grammatical cohesive devices. Examples of these cohesive devices are repetition, synonymy, antonymy, meronymy, substitutions , and anaphoric or cataphoric relations between sentences. We will discuss these devices in more detail below.
This article will discuss how to write a coherent essay. We will be focusing on the five major points.
- We will start with definitions of coherence and cohesion.
- Then, we will give examples of how a text can achieve cohesion.
- We will see how a text can be cohesive but not coherent.
- The structure of a coherent essay will also be discussed.
- Finally, we will look in detail at ways to improve cohesion and write a coherent essay.

Before illustrating how to write coherent essays, let us start with the definitions of coherence and cohesion and list the ways we can achieve cohesion in a coherent text.
Definitions Cohesion and Coherence
In general, coherence and cohesion refer to how a text is structured so that the elements it is constituted of can stick together and contribute to a meaningful whole. In coherent essays, writers use grammatical and lexical cohesive techniques so that ideas can flow meaningfully and logically.
What is coherence?
Coherence refers to the quality of forming a unified consistent whole. We can describe a text as being coherent if it is semantically meaningful, that is if the ideas flow logically to produce an understandable entity.
If a text is coherent it is logically ordered and connected. It is clear, consistent, and understandable.
Coherence is related to the macro-level features of a text which enable it to have a sense as a whole.
What is cohesion?
Cohesion is commonly defined as the grammatical and lexical connections that tie a text together, contributing to its meaning (i.e. coherence.)
While coherence is related to the macro-level features of a text, cohesion is concerned with its micro-level – the words, the phrases, and the sentences and how they are connected to form a whole.
If the elements of a text are cohesive, they are united and work together or fit well together.
To summarize, coherence refers to how the ideas of the text flow logically and make a text semantically meaningful as a whole. Cohesion is what makes the elements (e.g. the words, phrases, clauses, and sentences) of a text stick together to form a whole.
How to Achieve Cohesion And Coherence In Essay Writing
There are two types of cohesion: lexical and grammatical. Writers connect sentences and ideas in their essays using both lexical and grammatical cohesive devices.
Lexical cohesion
We can achieve cohesion through lexical cohesion by using these techniques:
- Repetition.
Now let’s look at these in more detail.
Repeating words may contribute to cohesion. Repetition creates cohesive ties within the text.
- Birds are beautiful. I like birds.
You can use a word or phrase that means exactly or nearly the same as another word to achieve cohesion.
- Paul saw a snake under the mattress. The serpent was probably hiding there for a long time.
Antonymy refers to the use of a word of opposite meaning. This is often used to create links between the elements of a text.
- Old movies are boring, the new ones are much better.
This refers to the use of a word that denotes a subcategory of a more general class.
- I saw a cat . The animal was very hungry and looked ill.
Relating a superordinate term (i.e. animal) to a corresponding subordinate term (i.e. cat) may create more cohesiveness between sentences and clauses.
Meronymy is another way to achieve cohesion. It refers to the use of a word that denotes part of something but which is used to refer to the whole of it for instance faces can be used to refer to people as in “I see many faces here”. In the following example, hands refer to workers.
- More workers are needed. We need more hands to finish the work.
Grammatical cohesion
Grammatical cohesion refers to the grammatical relations between text elements. This includes the use of:
- Cataphora .
- Substitutions.
- Conjunctions and transition words.
Let us illustrate the above devices with some examples.
Anaphora is when you use a word referring back to another word used earlier in a text or conversation.
- Jane was brilliant. She got the best score.
The pronoun “she” refers back to the proper noun “Jane”.
Cataphora is the opposite of anaphora. Cataphora refers to the use of a word or phrase that refers to or stands for a following word or phrase.
- Here he comes our hero. Please, welcome John .
The pronoun “he” refers back to the proper noun “John”.
Ellipsis refers to the omission from speech or writing of a word or words that are superfluous or able to be understood from contextual clues.
- Liz had some chocolate bars, and Nancy an ice cream.
In the above example, “had” in “Nancy an ice cream” is left because it can be understood (or presupposed) as it was already mentioned previously in the sentence.
Elliptic elements can be also understood from the context as in:
- A: Where are you going?
Substitutions
Substitutions refer to the use of a word to replace another word.
- A: Which T-shirt would you like?
- B: I would like the pink one .
Conjunctions transition words
Conjunctions and transition words are parts of speech that connect words, phrases, clauses, or sentences.
- Examples of conjunctions: but, or, and, although, in spite of, because,
- Examples of transition words: however, similarly, likewise, specifically, consequently, for this reason, in contrast to, accordingly, in essence, chiefly, finally.
Here are some examples:
- I called Tracy and John.
- He was tired but happy.
- She likes neither chocolates nor cookies.
- You can either finish the work or ask someone to do it for you.
- He went to bed after he had done his homework.
- Although she is very rich, she isn’t happy.
- I was brought up to be responsible. Similarly , I will try to teach my kids how to take responsibility for their actions.
Cohesive but not coherent texts
Sometimes, a text may be cohesively connected, yet may still be incoherent.
Learners may wrongly think that simply linking sentences together will lead to a coherent text.
Here is an example of a text in which sentences are cohesively connected, yet the overall coherence is lacking:
The player threw the ball toward the goalkeeper. Balls are used in many sports. Most balls are spheres, but American football is an ellipsoid. Fortunately, the goalkeeper jumped to catch the ball. The crossbar in the soccer game is made of iron. The goalkeeper was standing there.
The sentences and phrases in the above text are decidedly cohesive but not coherent.
There is a use of:
- Repetition of: the ball, goalkeeper, the crossbar.
- Conjunctions and transition words: but, fortunately.
The use of the above cohesive devices does not result in a meaningful and unified whole. This is because the writer presents material that is unrelated to the topic. Why should a writer talk about what the crossbar is made of? And is talking about the form balls in sports relevant in this context? What is the central focus of the text?
A coherent essay has to be cohesively connected and logically expressive of the central topic.
How to write a coherent essay?
1. start with an outline.
An outline is the general plan of your essays. It contains the ideas you will include in each paragraph and the sequence in which these ideas will be mentioned.
It is important to have an outline before starting to write. Spending a few minutes on the outline can be rewarding. An outline will organize your ideas and the end product can be much more coherent.
Here is how you can outline your writing so that you can produce a coherent essay:
- Start with the thesis statement – the sentence that summarizes the topic of your writing.
- Brainstorm the topic for a few minutes. Write down all the ideas related to the topic.
- Sift the ideas brainstormed in the previous step to identify only the ideas worth including in your essay.
- Organize ideas in a logical order so that your essay reflects the unified content that you want to communicate.
- Each idea has to be treated in a separate paragraph.
- Think of appropriate transitions between the different ideas.
- Under each idea/paragraph, write down enough details to support your idea.
After identifying and organizing your ideas into different paragraphs, they have to fit within the conventional structure of essays.

2. Structure your essay
It is also important to structure your essay so that you the reader can identify the organization of the different parts of your essay and how each paragraph leads to the next one.
Here is a structure of an essay
3. Structure your paragraphs
Paragraphs have to be well-organized. The structure of each paragraph should have:
- A topic sentence that is usually placed at the beginning,
- Supporting details that give further explanation of the topic sentence,
- And a concluding sentence that wraps up the content of the paragraph.
The supporting sentences in each paragraph must flow smoothly and logically to support the purpose of the topic sentence. Similarly, each paragraph has to serve the thesis statement, the main topic of the essay.
4. Relevance to the main topic
No matter how long the essay is, we should make sure that we stick to the topic we want to talk about. Coherence is about making everything flow smoothly to create unity. So, sentences and ideas must be relevant to the central thesis statement.
The writer has to maintain the flow of ideas to serve the main focus of the essay.
5. Stick to the purpose of the type of essay you’re-writing
Essays must be clear and serve a purpose and direction. This means that the writer’s thoughts must not go astray in developing the purpose of the essay.
Essays are of different types and have different purposes. Accordingly, students have to stick to the main purpose of each genre of writing.
- An expository essay aims to inform, describe, or explain a topic, using essential facts to teach the reader about a topic.
- A descriptive essay intends to transmit a detailed description of a person, event, experience, or object. The aim is to make the reader perceive what is being described.
- A narrative essay attempts to tell a story that has a purpose. Writers use storytelling techniques to communicate an experience or an event.
- In argumentative essays, writers present an objective analysis of the different arguments about a topic and provide an opinion or a conclusion of positive or negative implications. The aim is to persuade the reader of your point.
6. Use cohesive devices and signposting phrases
Sentences should be connected using appropriate cohesive devices as discussed above:
Cohesive devices such as conjunctions and transition words are essential in providing clarity to your essay. But we can add another layer of clarity to guide the reader throughout the essay by using signpost signals.
What is signposting in writing?
Signposting refers to the use of phrases or words that guide readers to understand the direction of your essay. An essay should take the reader on a journey throughout the argumentation or discussion. In that journey, the paragraphs are milestones. Using signpost signals assists the reader in identifying where you want to guide them. Signposts serve to predict what will happen, remind readers of where they are at important stages along the process, and show the direction of your essay.
Essay signposting phrases
The following are some phrases you can use to signpost your writing:
It should be noted though that using cohesive devices or signposting language may not automatically lead to a coherent text. Some texts can be highly cohesive but remain incoherent. Appropriate cohesion and signposting are essential to coherence but they are not enough. To be coherent, an essay has to follow, in addition to using appropriate cohesive devices, all the tips presented in this article.
7. Draft, revise, and edit
After preparing the ground for the essay, students produce their first draft. This is the first version of the essay. Other subsequent steps are required.
The next step is to revise the first draft to rearrange, add, or remove paragraphs, ideas, sentences, or words.
The questions that must be addressed are the following:
- Is the essay clear? Is it meaningful? Does it serve the thesis statement (the main topic)?
- Are there sufficient details to convey ideas?
- Are there any off-topic ideas that you have to do without?
- Have you included too much information? Does your writing stray off-topic?
- Do the ideas flow in a logical order?
- Have you used appropriate cohesive devices and transition words when needed?
Once the revision is done, it is high time for the editing stage. Editing involves proofreading and correcting mistakes in grammar and mechanics. Pay attention to:
- Verb tense.
- Subject-verb agreement.
- Sentence structure. Have you included a subject a verb and an object (if the verb is transitive.)
- Punctuation.
- Capitalization.
Coherent essays are identified by relevance to the thesis statement. The ideas and sentences of coherent essays flow smoothly. One can follow the ideas discussed without any problems. Lexical and grammatical cohesive devices are used to achieve coherence. However, these devices are not sufficient. To maintain relevance to the main focus of the text, there is a need for a whole process of collecting ideas, outlining, reviewing, and editing to create a coherent whole.
More writing lessons are here .
Related Pages:
- Figures of speech
- Articles about writing

- I nfographics
- Show AWL words
- Subscribe to newsletter
- What is academic writing?
- Academic Style
- What is the writing process?
- Understanding the title
- Brainstorming
- Researching
- First draft
- Proofreading
- Report writing
- Compare & contrast
- Cause & effect
- Problem-solution
- Classification
- Essay structure
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Book review
- Research proposal
- Thesis/dissertation
What is cohesion?
- Cohesion vs coherence
Transition signals
- What are references?
- In-text citations
- Reference sections
- Reporting verbs
- Band descriptors
Show AWL words on this page.
Levels 1-5: grey Levels 6-10: orange
Show sorted lists of these words.
Any words you don't know? Look them up in the website's built-in dictionary .
Choose a dictionary . Wordnet OPTED both
Cohesion How to make texts stick together
Cohesion and coherence are important features of academic writing. They are one of the features tested in exams of academic English, including the IELTS test and the TOEFL test . This page gives information on what cohesion is and how to achieve good cohesion. It also explains the difference between cohesion and coherence , and how to achieve good coherence. There is also an example essay to highlight the main features of cohesion mentioned in this section, as well as some exercises to help you practise.
For another look at the same content, check out YouTube or Youku , or the infographic .
It is important for the parts of a written text to be connected together. Another word for this is cohesion . This word comes from the verb cohere , which means 'to stick together'. Cohesion is therefore related to ensuring that the words and sentences you use stick together.
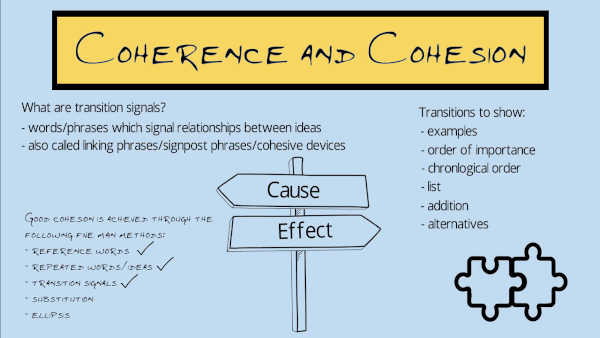
Good cohesion is achieved through the following five main methods, each of which is described in more detail below:
- repeated words/ideas
- reference words
- transition signals
- substitution
Two other ways in which cohesion is achieved in a text, which are covered less frequently in academic English courses, are shell nouns and thematic development . These are also considered below.
Repeated words/ideas

Check out the cohesion infographic »
One way to achieve cohesion is to repeat words, or to repeat ideas using different words (synonyms). Study the following example. Repeated words (or synonyms) are shown in bold.
Cohesion is an important feature of academic writing . It can help ensure that your writing coheres or 'sticks together', which will make it easier for the reader to follow the main ideas in your essay or report . You can achieve good cohesion by paying attention to five important features . The first of these is repeated words. The second key feature is reference words. The third one is transition signals. The fourth is substitution. The final important aspect is ellipsis.
In this example, the word cohesion is used several times, including as a verb ( coheres ). It is important, in academic writing, to avoid too much repetition, so using different word forms or synonyms is common. The word writing is also used several times, including the phrase essay or report , which is a synonym for writing . The words important features are also repeated, again using synonyms: key feature , important aspect .
Reference words
Reference words are words which are used to refer to something which is mentioned elsewhere in the text, usually in a preceding sentence. The most common type is pronouns, such as 'it' or 'this' or 'these'. Study the previous example again. This time, the reference words are shown in bold.
Cohesion is an important feature of academic writing. It can help ensure that your writing coheres or 'sticks together', which will make it easier for the reader to follow the main ideas in your essay or report. You can achieve good cohesion by paying attention to five important features. The first of these is repeated words. The second key feature is reference words. The third one is transition signals. The fourth is substitution. The final important aspect is ellipsis.
The words it , which and these are reference words. The first two of these, it and which , both refer to 'cohesion' used in the preceding sentence. The final example, these , refers to 'important features', again used in the sentence that precedes it.
Transition signals, also called cohesive devices or linking words, are words or phrases which show the relationship between ideas. There are many different types, the most common of which are explained in the next section on transition signals . Some examples of transition signals are:
- for example - used to give examples
- in contrast - used to show a contrasting or opposite idea
- first - used to show the first item in a list
- as a result - used to show a result or effect
Study the previous example again. This time, the transition signals are shown in bold. Here the transition signals simply give a list, relating to the five important features: first , second , third , fourth , and final .
Substitution
Substitution means using one or more words to replace (substitute) for one or more words used earlier in the text. Grammatically, it is similar to reference words, the main difference being that substitution is usually limited to the clause which follows the word(s) being substituted, whereas reference words can refer to something far back in the text. The most common words used for substitution are one , so , and auxiliary verbs such as do, have and be . The following is an example.
- Drinking alcohol before driving is illegal in many countries, since doing so can seriously impair one's ability to drive safely.
In this sentence, the phrase 'doing so' substitutes for the phrase 'drinking alcohol before driving' which appears at the beginning of the sentence.
Below is the example used throughout this section. There is just one example of substitution: the word one , which substitutes for the phrase 'important features'.
Ellipsis means leaving out one or more words, because the meaning is clear from the context. Ellipsis is sometimes called substitution by zero , since essentially one or more words are substituted with no word taking their place.
Below is the example passage again. There is one example of ellipsis: the phrase 'The fourth is', which means 'The fourth [important feature] is', so the words 'important feature' have been omitted.
Shell nouns
Shell nouns are abstract nouns which summarise the meaning of preceding or succeeding information. This summarising helps to generate cohesion. Shell nouns may also be called carrier nouns , signalling nouns , or anaphoric nouns . Examples are: approach, aspect, category, challenge, change, characteristics, class, difficulty, effect, event, fact, factor, feature, form, issue, manner, method, problem, process, purpose, reason, result, stage, subject, system, task, tendency, trend, and type . They are often used with pronouns 'this', 'these', 'that' or 'those', or with the definite article 'the'. For example:
- Virus transmission can be reduced via frequent washing of hands, use of face masks, and isolation of infected individuals. These methods , however, are not completely effective and transmission may still occur, especially among health workers who have close contact with infected individuals.
- An increasing number of overseas students are attending university in the UK. This trend has led to increased support networks for overseas students.
In the example passage used throughout this section, the word features serves as a shell noun, summarising the information later in the passage.
Cohesion is an important feature of academic writing. It can help ensure that your writing coheres or 'sticks together', which will make it easier for the reader to follow the main ideas in your essay or report. You can achieve good cohesion by paying attention to five important features . The first of these is repeated words. The second key feature is reference words. The third one is transition signals. The fourth is substitution. The final important aspect is ellipsis.
Thematic development
Cohesion can also be achieved by thematic development. The term theme refers to the first element of a sentence or clause. The development of the theme in the rest of the sentence is called the rheme . It is common for the rheme of one sentence to form the theme of the next sentence; this type of organisation is often referred to as given-to-new structure, and helps to make writing cohere.
Consider the following short passage, which is an extension of the first example above.
- Virus transmission can be reduced via frequent washing of hands, use of face masks, and isolation of infected individuals. These methods, however, are not completely effective and transmission may still occur, especially among health workers who have close contact with infected individuals. It is important for such health workers to pay particular attention to transmission methods and undergo regular screening.
Here we have the following pattern:
- Virus transmission [ theme ]
- can be reduced via frequent washing of hands, use of face masks, and isolation of infected individuals [ rheme ]
- These methods [ theme = rheme of preceding sentence ]
- are not completely effective and transmission may still occur, especially among health workers who have close contact with infected individuals [ rheme ]
- health workers [ theme, contained in rheme of preceding sentence ]
- [need to] to pay particular attention to transmission methods and undergo regular screening [ rheme ]
Cohesion vs. coherence
The words 'cohesion' and 'coherence' are often used together with a similar meaning, which relates to how a text joins together to make a unified whole. Although they are similar, they are not the same. Cohesion relates to the micro level of the text, i.e. the words and sentences and how they join together. Coherence , in contrast, relates to the organisation and connection of ideas and whether they can be understood by the reader, and as such is concerned with the macro level features of a text, such as topic sentences , thesis statement , the summary in the concluding paragraph (dealt with in the essay structure section), and other 'bigger' features including headings such as those used in reports .
Coherence can be improved by using an outline before writing (or a reverse outline , which is an outline written after the writing is finished), to check that the ideas are logical and well organised. Asking a peer to check the writing to see if it makes sense, i.e. peer feedback , is another way to help improve coherence in your writing.
Example essay
Below is an example essay. It is the one used in the persuasion essay section. Click on the different areas (in the shaded boxes to the right) to highlight the different cohesive aspects in this essay, i.e. repeated words/ideas, reference words, transition signals, substitution and ellipsis.
Title: Consider whether human activity has made the world a better place.
History shows that human beings have come a long way from where they started. They have developed new technologies which means that everybody can enjoy luxuries they never previously imagined. However , the technologies that are temporarily making this world a better place to live could well prove to be an ultimate disaster due to , among other things, the creation of nuclear weapons , increasing pollution , and loss of animal species . The biggest threat to the earth caused by modern human activity comes from the creation of nuclear weapons . Although it cannot be denied that countries have to defend themselves, the kind of weapons that some of them currently possess are far in excess of what is needed for defence . If these [nuclear] weapons were used, they could lead to the destruction of the entire planet . Another harm caused by human activity to this earth is pollution . People have become reliant on modern technology, which can have adverse effects on the environment . For example , reliance on cars causes air and noise pollution . Even seemingly innocent devices, such as computers and mobile phones, use electricity, most of which is produced from coal-burning power stations, which further adds to environmental pollution . If we do not curb our direct and indirect use of fossil fuels, the harm to the environment may be catastrophic. Animals are an important feature of this earth and the past decades have witnessed the extinction of a considerable number of animal species . This is the consequence of human encroachment on wildlife habitats, for example deforestation to expand cities. Some may argue that such loss of [animal] species is natural and has occurred throughout earth's history. However , the current rate of [animal] species loss far exceeds normal levels [of animal species loss] , and is threatening to become a mass extinction event. In summary , there is no doubt that current human activities such as the creation of nuclear weapons , pollution , and destruction of wildlife , are harmful to the earth . It is important for us to see not only the short-term effects of our actions, but their long-term ones as well. Otherwise , human activities will be just another step towards destruction .
Aktas, R.N. and Cortes, V. (2008), 'Shell nouns as cohesive devices in published and ESL student writing', Journal of English for Academic Purposes , 7 (2008) 3-14.
Alexander, O., Argent, S. and Spencer, J. (2008) EAP Essentials: A teacher's guide to principles and practice . Reading: Garnet Publishing Ltd.
Gray, B. (2010) 'On the use of demonstrative pronouns and determiners as cohesive devices: A focus on sentence-initial this/these in academic prose', Journal of English for Academic Purposes , 9 (2010) 167-183.
Halliday, M. A. K., and Hasan, R. (1976). Cohesion in English . London: Longman.
Hinkel, E. (2004). Teaching Academic ESL Writing: Practical Techniques in Vocabulary and Grammar . Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc Publishers.
Hyland, K. (2006) English for Academic Purposes: An advanced resource book . Abingdon: Routledge.
Thornbury, S. (2005) Beyond the Sentence: Introducing discourse analysis . Oxford: Macmillan Education.

GET FREE EBOOK
Like the website? Try the books. Enter your email to receive a free sample from Academic Writing Genres .
Below is a checklist for essay cohesion and coherence. Use it to check your own writing, or get a peer (another student) to help you.
Next section
Find out more about transition signals in the next section.
- Transitions
Previous section
Go back to the previous section about paraphrasing .
- Paraphrasing
Exercises & Activities Some ways to practise this area of EAP
You need to login to view the exercises. If you do not already have an account, you can register for free.
- Register
- Forgot password
- Resend activiation email

Author: Sheldon Smith ‖ Last modified: 03 February 2022.
Sheldon Smith is the founder and editor of EAPFoundation.com. He has been teaching English for Academic Purposes since 2004. Find out more about him in the about section and connect with him on Twitter , Facebook and LinkedIn .
Compare & contrast essays examine the similarities of two or more objects, and the differences.
Cause & effect essays consider the reasons (or causes) for something, then discuss the results (or effects).
Discussion essays require you to examine both sides of a situation and to conclude by saying which side you favour.
Problem-solution essays are a sub-type of SPSE essays (Situation, Problem, Solution, Evaluation).
Transition signals are useful in achieving good cohesion and coherence in your writing.
Reporting verbs are used to link your in-text citations to the information cited.

Writing Resources: Developing Cohesion
Cohesion is a characteristic of a successful essay when it flows as a united whole ; meaning, there is unity and connectedness between all of the parts. Cohesion is a writing issue at a macro and micro level. At a macro-level, cohesion is the way a paper uses a thesis sentence, topic sentences, and transitions across paragraphs to help unify and focus a paper. On a micro-level, cohesion happens within the paragraph unit between sentences; when each sentence links back to the previous sentence and looks ahead to the next, there is cohesion across sentences. Cohesion is an important aspect of writing because it helps readers to follow the writer’s thinking.
Misconceptions & Stumbling Blocks
Many writers believe that you should avoid repetition at all costs. It’s true that strong writing tends to not feel repetitive in terms of style and word choice; however, some repetition is necessary in order to build an essay and even paragraphs that build on each other and develop logically. A pro tip when you’re drafting an essay would be to build in a lot of repetition and then as you revise, go through your essay and look for ways you can better develop your ideas by paraphrasing your argument and using appropriate synonyms.
Building Cohesion
Essay focus: macro cohesion.
Locate & read your thesis sentence and the first and last sentence of each paragraph. You might even highlight them and/or use a separate piece of paper to make note of the key ideas and subjects in each (that is, making a reverse outline while you’re reading).
- How do these sentences relate?
- How can you use the language of the thesis statement again in topic sentences to reconnect to the main argument?
- Does each paragraph clearly link back to the thesis? Is it clear how each paragraph adds to, extends, or complicates the thesis?
- Repetition of key terms and ideas (especially those that are key to the argument)
- Repetition of central arguments; ideally, more than repeating your argument, it evolves and develops as it encounters new supporting or conflicting evidence.
- Appropriate synonyms. Synonyms as well as restating (paraphrasing) main ideas and arguments both helps you to explain and develop the argument and to build cohesion in your essay.
Paragraph Focus: Micro Cohesion
For one paragraph, underline the subject and verb of each sentence.
- Does the paragraph have a consistent & narrow focus?
- Will readers see the connection between the sentences?
- Imagine that the there is a title for this paragraph: what would it be and how would it relate to the underlined words?
- Repetition of the central topic and a clear understanding of how the evidence in this paragraph pushes forward or complicates that idea.
- Variations on the topic
- Avoid unclear pronouns (e.g., it, this, these, etc.). Rather than using pronouns, try to state a clear and specific subject for each sentence. This is an opportunity to develop your meaning through naming your topic in different ways.
- Synonyms for key terms and ideas that help you to say your point in slightly new ways that also push forward your ideas.
Sentence to Sentence: Micro Cohesion
Looking at one paragraph, try to name what each sentence is doing to the previous: is it adding further explanation? Is it complicating the topic? Is it providing an example? Is it offering a counter-perspective? Sentences that build off of each other have movement that is intentional and purposeful; that is, the writer knows the purpose of each sentence and the work that each sentence accomplishes for the paragraph.
- Transition words (look up a chart) to link sentence and to more clearly name what you’re doing in each sentence (e.g., again, likewise, indeed, therefore, however, additionally, etc.)
- Precise verbs to help emphasize what the writer is doing and saying (if you’re working with a source/text) or what you’re doing and saying.
- Again, clear and precise subjects that continue to name your focus in each sentence.
A Link to a PDF Handout of this Writing Guide
Achieving coherence
“A piece of writing is coherent when it elicits the response: ‘I follow you. I see what you mean.’ It is incoherent when it elicits the response: ‘I see what you're saying here, but what has it got to do with the topic at hand or with what you just told me above?’ ” - Johns, A.M
Transitions
Parallelism, challenge task, what is coherence.
Coherence in a piece of writing means that the reader can easily understand it. Coherence is about making everything flow smoothly. The reader can see that everything is logically arranged and connected, and relevance to the central focus of the essay is maintained throughout.

Repetition in a piece of writing does not always demonstrate cohesion. Study these sentences:
So, how does repetition as a cohesive device work?
When a pronoun is used, sometimes what the pronoun refers to (ie, the referent) is not always clear. Clarity is achieved by repeating a key noun or synonym . Repetition is a cohesive device used deliberately to improve coherence in a text.
In the following text, decide ifthe referent for the pronoun it is clear. Otherwise, replace it with the key noun English where clarity is needed.
Click here to view the revised text.
Suggested improvement
English has almost become an international language. Except for Chinese, more people speak it (clear reference; retain) than any other language. Spanish is the official language of more countries in the world, but more countries have English ( it is replaced with a key noun) as their official or unofficial second language. More than 70% of the world's mail is written in English ( it is replaced with a key noun). It (clear reference; retain) is the primary language on the Internet.
Sometimes, repetition of a key noun is preferred even when the reference is clear. In the following text, it is clear that it refers to the key noun gold , but when used throughout the text, the style becomes monotonous.
Improved text: Note where the key noun gold is repeated. The deliberate repetition creates interest and adds maturity to the writing style.
Gold , a precious metal, is prized for two important characteristics. First of all, gold has a lustrous beauty that is resistant to corrosion. Therefore, it is suitable for jewellery, coins and ornamental purposes. Gold never needs to be polished and will remain beautiful forever. For example, a Macedonian coin remains as untarnished today as the day it was made 23 centuries ago. Another important characteristic of gold is its usefulness to industry and science. For many years, it has been used in hundreds of industrial applications. The most recent use of gold is in astronauts’ suits. Astronauts wear gold -plated shields when they go outside spaceships in space. In conclusion, gold is treasured not only for its beauty but also its utility.
Pronoun + Repetition of key noun
Sometimes, greater cohesion can be achieved by using a pronoun followed by an appropriate key noun or synonym (a word with a similar meaning).
Transitions are like traffic signals. They guide the reader from one idea to the next. They signal a range of relationships between sentences, such as comparison, contrast, example and result. Click here for a more comprehensive list of Transitions (Logical Organisers) .
Test yourself: How well do you understand transitions?
Which of the three alternatives should follow the transition or logical organiser in capital letters to complete the second sentence?
Using transitions/logical organisers
Improve the coherence of the following paragraph by adding transitions in the blank spaces. Use the italicised hint in brackets to help you choose an apporpriate transition for each blank. If you need to, review the list of Transitions (Logical Organisers) before you start.
Using transitions
Choose the most appropriate transition from the options given to complete the article:
Overusing transitions
While the use of appropriate transitions can improve coherence (as the previous practice activity shows), it can also be counterproductive if transitions are overused. Use transitions carefully to enhance and clarify the logical connection between ideas in extended texts. Write a range of sentences and vary sentence openings.
Study the following examples:
Identifying cohesive devices

- Subject Guides
Academic writing: a practical guide
- Structure & cohesion
- Academic writing
- The writing process
- Academic writing style
- Criticality in academic writing
- Working with evidence
- Referencing
- Assessment & feedback
- Dissertations
- Reflective writing
- Examination writing
- Academic posters
- Feedback on Structure and Organisation
- Feedback on Argument, Analysis, and Critical Thinking
- Feedback on Writing Style and Clarity
- Feedback on Referencing and Research
- Feedback on Presentation and Proofreading
Structure & cohesion
General advice for structuring all types of academic writing.
For advice on structuring specific types of writing, visit the relevant page under 'Types of academic writing'.
Structure in academic writing
Academic writing has a clear, logical structure to communicate your points and show the connections between them; a well-structured assignment is easy for the reader to follow and understand.
These general principles apply to structuring most types of academic writing:
- Use a linear structure where points build on each other - don't jump backward and forwards.
- Start with more general and then move to the more specific ideas and points.
- Put more relevant/important information first.
- Everything is relevant to the main argument or point of the paragraph.
- Use cohesion to join ideas and points clearly - don't make the reader do the work.
- Follow any structural requirements for your assignment or type of writing.
It has a beginning, a middle and an end: a guide to structuring academic writing [Google Slides]

Planning structure
The best way to write a well-structured assignment is to have a good plan before you start writing. What's your argument? What are the main points you want to include? What's a logical way to order these points? Don't just launch into writing with no idea of where you're going!
To make a general plan:
- Make a list of the information and points to include.
- Organise similar points into groups.
- Put the groups in a logical order.
- Within each group, organise the points logically.
- Check the plan to make sure it meets task requirements.
Here's a step-by-step demonstration of planning assignment structure:
Planning: general structure [YouTube] | Planning: general structure [Google Doc]
Paragraph structure
A well-structured paragraph contains one main point or idea - all the information included is relevant to this point. If it's not related to the main point, it probably shouldn't be there!
There are many ways to structure a paragraph, but they generally all include:
- a topic sentence showing the main point
- development of the point: more detail, examples etc.
- evidence to support the point
- critical analysis showing how evidence relates to the main point
- a final wrap-up linking to the overall argument or next paragraph
However, this is only a guide - there are many ways to structure a paragraph. Reading sources from your field will help you to get a feel of ways to organise paragraphs.
Paragraph structure [Google Slides]
If the structure is the order of your points, cohesion is what ties them together and guides the reader through your argument.
Create cohesion using words and phrases that show the relationships between points. For example:
- basic connectives: and, or, but, so
- giving more detail: for example, to illustrate, an example of this is
- showing contrast: however, although, while, conversely, alternatively
- showing similarity: another, also, similarly, collectively, taken together
- cause/effect: leading to, the effect of this is, therefore, this may stem from
- referencing words: this/that, who, which/that, the groups, these findings
- showing implications: this suggests that, these findings may mean that, based on this
Cohesive words and phrases are shown in bold in this example paragraph about how language background affects maths skills development :
The time taken to pronounce number words is another linguistic factor that could affect children’s arithmetical development. If number words take longer to pronounce, fewer items can be held in working memory, which could affect the strategies used to solve arithmetic problems (Geary et al., 1993; Geary et al., 1996). In East Asian languages, number words are generally short, one-syllable words, while in English and other languages they can be much longer. The effect of this on working memory is seen in Chinese children’s longer digit span memory compared to their American peers (Geary et al., 1993). It also seems to influence the choice of strategies used by the two groups to solve arithmetic problems, with Chinese children using faster processes than American children (Geary et al., 1996). This limitation of working memory may mean speakers of less transparent languages rely more on slow procedural strategies than speakers of a transparent language, extending even to adulthood (Campbell & Xue, 2001).
More detailed advice and examples:
- << Previous: Academic writing style
- Next: Criticality in academic writing >>
- Last Updated: Apr 3, 2024 4:02 PM
- URL: https://subjectguides.york.ac.uk/academic-writing
It appears you have javascript disabled. Please enable javascript to get the full experience of gustavus.edu
Cohesion concerns the flow of sentences and paragraphs from one to another. It involves the tying together of old information and new. When we write academic essays, particularly in the humanities, we work hard to foster cohesion structurally, which enhances a reader's understanding of our ideas.
Essay organization
The first paragraph should include a thesis statement, which announces the main idea or argument of the paper.The rest of the sentences should lead up to or anticipate the thesis, either directly or indirectly.
The body paragraphs should support the thesis statement and should be arranged in a clear hierarchy.
Readers should be able to understand how each paragraph relates to what has come before it. This can be accomplished by the use of transition sentences.
Repetition helps to enhance a reader's understanding of what the author has written. Pointers are used as a tool in sentences to use repetition for better understanding.
Pointers are words, phrases, or ideas that appear in a sentence, and are repeated in the next.
Example : Epilepsy is a brain or neurological disorder where excess electrical energy causes seizures. Seizures result when the brain's nerve cells, or neurons, produce an excessive or abnormal amount of electrical activity. Depending on this activity …
Example : Depending on this activity, three results may occur. First, the seizure may start and stop in one location. Next, it may spread a bit and stop. Finally, it may go through the body's nervous system before stopping.
To prevent repetitions from becoming dull, an author may use:
- Variations of the word (golf, golfer, golfing)
- Pronouns (doctors…they)
- Synonyms (jump, hop, bounce)
Transitions
Transitional words and phrases, also known as tags, are used to hold a paper together.They can be simple conjunctions, like and and but, or they can be more complex. Here is a chart of transitional devices accompanied by a simplified definition of their function:
Table of Contents
Ai, ethics & human agency, collaboration, information literacy, writing process, coherence – how to achieve coherence in writing.
- © 2023 by Joseph M. Moxley - University of South Florida
Coherence refers to a style of writing where ideas, themes, and language connect logically, consistently, and clearly to guide the reader's understanding. By mastering coherence , alongside flow , inclusiveness , simplicity, and unity , you'll be well-equipped to craft professional or academic pieces that engage and inform effectively. Acquire the skills to instill coherence in your work and discern it in the writings of others.

What is Coherence?
Coherence in writing refers to the logical connections and consistency that hold a text together, making it understandable and meaningful to the reader. Writers create coherence in three ways:
- logical consistency
- conceptual consistency
- linguistic consistency.
What is Logical Consistency?
- For instance, if they argue, “If it rains, the ground gets wet,” and later state, “It’s raining but the ground isn’t wet,” without additional explanation, this represents a logical inconsistency.
What is Conceptual Consistency?
- For example, if you are writing an essay arguing that regular exercise has multiple benefits for mental health, each paragraph should introduce and discuss a different benefit of exercise, all contributing to your main argument. Including a paragraph discussing the nutritional value of various foods, while interesting, would break the conceptual consistency, as it doesn’t directly relate to the benefits of exercise for mental health.
What is Linguistic Consistency?
- For example, if a writer jumps erratically between different tenses or switches point of view without clear demarcation, the reader might find it hard to follow the narrative, leading to a lack of linguistic coherence.
Related Concepts: Flow ; Given to New Contract ; Grammar ; Organization ; Organizational Structures ; Organizational Patterns ; Sentence Errors
Why Does Coherence Matter?
Coherence is crucial in writing as it ensures that the text is understandable and that the ideas flow logically from one to the next. When writing is coherent, readers can easily follow the progression of ideas, making the content more engaging and easier to comprehend. Coherence connects the dots for the reader, linking concepts, arguments, and details in a clear, logical manner.
Without coherence, even the most interesting or groundbreaking ideas can become muddled and lose their impact. A coherent piece of writing keeps the reader’s attention, demonstrates the writer’s control over their subject matter, and can effectively persuade, inform, or entertain. Thus, coherence contributes significantly to the effectiveness of writing in achieving its intended purpose.
How Do Writers Create Coherence in Writing?
- Your thesis statement serves as the guiding star of your paper. It sets the direction and focus, ensuring all subsequent points relate back to this central idea.
- Acknowledge and address potential counterarguments to strengthen your position and add depth to your writing.
- Use the genres and organizational patterns appropriate for your rhetorical situation . A deductive structure (general to specific) is often effective, guiding the reader logically through your argument. Yet different disciplines may privilege more inductive approaches , such as law and philosophy.
- When following a given-to-new order, writers move from what the reader already knows to new information. In formal or persuasive contexts, writers are careful to vet new information for the reader following information literacy laws and conventions .
- Strategic repetition of crucial terms and your thesis helps your readers follow your main ideas and evidence for claims
- While repetition is useful, varying language with synonyms can prevent redundancy and keep the reader engaged.
- Parallelism in sentences can provide rhythm and clarity, making complex ideas easier to follow.
- Consistent use of pronouns avoids confusion and helps in maintaining a clear line of thought.
- Arrange your ideas in a sequence that naturally builds from one point to the next, ensuring each paragraph flows smoothly into the next .
- Signposting , or using phrases that indicate what’s coming next or what just happened, can help orient the reader within your argument.
- Don’t bother repeating your argument in your conclusion. Prioritize conciseness. Yet end with a call to action or appeal to kairos and ethos .
Recommended Resources
- Organization
- Organizational Patterns

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.

Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Speech & Writing
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Revising for Cohesion

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Writing a cohesive paper takes time and revision. This resource will focus primarily on topic sentences that begin each paragraph and on topics, or main points, within a paragraph. This resource will also enable students to look closely at their sentences and see how each sentence relates to another within a paragraph. This material is adapted from Style: Ten Lessons in Clarity and Grace , by Joseph Williams.
For a video guide to cutting unnecessary essay content, visit the Purdue OWL's vidcast on cutting.
- Begin sentences with short, simple words and phrases.
- These phrases should communicate information that appeared in previous sentences, or build on knowledge that you share with your reader.
- Within a paragraph, keep your topics, or main points, direct and reasonably consistent.
Tip: Create a list of words to draw from that intuitively tells the reader what to focus on. If your words progress from “investigate, remedy, resolve” or “negate, discover, re-invent” the reader should be able to follow the line of action and they will feel like your ideas cohere.
Exercise: Diagnosis, Analysis, Revision
- Underline the first few words of every sentence in a paragraph, ignoring short introductory phrases such as "In the beginning," or "For the most part."
- If you can, underline the first few words of every clause. (Remember that a clause has a subject and verb)
- Read your underlined words. Is there a consistent set of related topics?
- Will your reader see these connections among the topics?
- Imagine that the passage has a title. The words in the title should identify what should be the topics of most of the sentences.
- Decide what you will focus on in each paragraph.
- In most sentences, make your topics subjects that do the action in the sentences.
- Move your topics to the beginning of your sentences. Avoid hiding your topic behind long introductory phrases or clauses.
Sample Passage
Topics are crucial for readers because readers depend on topics to focus their attention on particular ideas toward the beginning of sentences . Topics tell readers what a whole passage is "about." If readers feel that a sequence of topics is coherent, then they will feel they are moving through a paragraph from a cumulatively coherent point of view. But if throughout the paragraph readers feel that its topics shift randomly, then they have to begin each sentence out of context, from no coherent point of view. When that happens, readers feel dislocated , disoriented, and out of focus.
Analysis of the Sample Passage:
1. Read your underlined words. Is there a consistent set of related topics?
Here are some significant words from the clauses that are underlined in the above example: topics , readers, topics, readers, they, readers, they, readers. Do these words help guide your reader along?
2. Will your reader see these connections among the topics?
Utilize repetition and patterns of progression. What this sample passage does really well is that it works with repetition. It also has a pattern of progression: in the first sentence, the phrase, “topics are crucial” is used and then the writer explains how topics are crucial in the rest of this sentence and the next. In terms of repetition, the phrase “readers feel that” is used twice. The third time it is used, there’s a variation to the pattern. This variation is direct, concise, and surprising: “Readers feel dislocated,” begins this clause.
3. Imagine that the passage has a title. The words in the title should identify what should be the topics of most of the sentences.
Sample Title: “How Topics Coherently Guide the Reader” Do the themes in the above passage match with this title?
4. Decide what you will focus on in each paragraph.
Think about the importance of your topics and what happens to the paragraph if these topics are not utilized. In the sample passage, the highlighted phrase seems out of place. Consider this revision:
Topics are crucial for readers. Topics tell readers what a whole passage is "about." Readers depend on topics to focus their attention on particular ideas toward the beginning of sentences . If readers feel that a sequence of topics is coherent, then they will feel they are moving through a paragraph from a cumulatively coherent point of view.
In this revision, the phrase “what a passage is ‘about,’” comes before “Readers depend…” This coheres better than the initial draft because the writer sets the reader up for a definition, or in-depth explanation of what the word “about”’ means.
Questions to ask yourself as you revise
On a sentence level:
1. Do your sentences "hang together"? Readers must feel that sentences in a paragraph are not just individually clear, but are unified with each other. Readers should be able to move easily from one sentence to the next, feeling that each sentence "coheres" with the one before and after it.
One way of thinking about this is as if you are giving your readers sign posts or clues they can follow throughout your passage. These will act as signals that guide the reader into your argument.
2. Does the sentence begin with information that’s familiar to the reader? Readers will be familiar with your information if it has already been touched upon in the previous sentence.
It’s important to address how readers feel about unfamiliar information. As a writer, we sometimes forget that readers have different assumptions, values and beliefs than we do. Their bodies of knowledge are not the same as ours. Thus, it’s important to clearly build your progression of thought or argument in a cohesive paper. In the sample passage, the writer clearly defines why readers depend on topics: “Topics tell the reader what a passage is ‘about.’”
3. Does the sentence end with interesting information the reader would not anticipate?
In the case of the sample passage, the last sentence has a sharp and unexpected ending. The last few words, “out of focus” are an unexpected way to end the paragraph because the entire paragraph has been about how topics are cohesive tools. Ending on this note leaves the reader feeling uneasy about leaving topics out of context, which is the aim of the sample passage.
On a paragraph level:
Will your reader be able to identify quickly the "topic" of each paragraph?
Note: it is easier to see coherence and clarity in other people's writing because by the time we reach a final draft, everything we write seems old or familiar to us. Improving on this takes practice. Try giving yourself a few days between writing and revising to get a fresh look.
- Departments
- For Students
- For Faculty
- Book Appointment
Flow and Cohesion
- Reverse Outline
- Paper Skeleton
- Creating a Research Space
- Personal Statements
- Literature Reviews
Our Writing Center gets a lot of students who are concerned about the flow of their writing, but this can mean a lot of different things. When we talk about "flow" we mean cohesion or how ideas and relationships are communicated to readers. Flow can involve the big-picture (how parts of the essay fit together and the way the sequence of these parts affect how readers understand it) and the sentence-level (how the structure of a sentence affects the ways meanings and relationships come across to readers). This page has an overview of ways to think about revising the flow of an essay on both of these levels.
Big-Picture Revision Strategies
Reading out-loud.
Oftentimes, you can identify places that need some extra attention sharing your writing with a friend, or reading it out loud to yourself. For example, if it's hard to actually say a sentence at a normal conversational pace, this might indicate that there's something you can change about the structure that will make it easier to say (and probably, easier to understand). A few more tips:
- When you read out-loud, make sure to slow down . If you are talking too fast, you might fill-in gaps or otherwise not notice things you want to change. You also want to give yourself time to process what you're saying as you say it.
- If there's nobody around, there are also many computer programs that can convert text to speech and read to you, including Microsoft Word .
- Take notes while you read. While you might want to fix things as you read, if you're worried about flow, it's also good to read your essay all the way through so that you can hear how parts fit together. If you don't want to interrupt your reading, you can take notes by doing things like putting a checkmark in the margins, using a highlighter, or making a list on a separate sheet of paper.
Structure and Sequence
Sometimes issues of flow and cohesion might actually be structural. It's good to reflect on the structure of an essay, the order of the different parts, and how they all fit together. If you want to revise the structure of your essay, consider trying one of the following activities.
Sign-Posting and Transitions
A great way to help readers comprehend the flow of ideas is include things like sign-posts and transitions. A sign-post is basically just language to point out different parts of the essay for readers in order to help them navigate your ideas. For example, strong topic sentences are a good as sign-posts because they tell readers what upcoming paragraphs are going to be about. Transition sentences can help readers understand how the ideas you were just discussing in a previous paragraph relate to what's coming up with the next paragraph. Here are a couple questions that can help you brainstorm sign-posting statements. After you brainstorm, you can then revise these sign-posting sentences so they fit better with your writing.
- Try starting a sentence by writing "In this paragraph, I will discuss..." After you complete this sentence, you can then revise it to make it fit better with your writing.
- "In the previous paragraph I discuss [purpose of paragraph 1] and this helps better understand [purpose of paragraph 2] because..."
- This paragraph supports my argument because..."
- While I discuss [previous idea or concept] above, I will now talk about [new idea or concept] because..."
Revision on the Sentence-Level
Verbs, or stuff we do.
A sentence seems clear when its important actions are in verbs. Compare these sentences where the actions are in bold and the verbs are UPPERCASE:
Because we LACKED data, we could not EVALUATE whether the UN HAD TARGETED funds to areas that most needed assistance. Our lack of data PREVENTED evaluation of UN actions in targeting funds to areas most in need of assistance .
Nominalization
Turning a verb or adjective into a noun is called a “nominalization.” No element of style more characterizes turgid writing, writing that feels abstract, indirect, and difficult, than lots of nominalizations, especially as the subjects of verbs.
Our request IS that you DO a review of the data. vs. We REQUEST that you REVIEW the data.
Try this: when editing, underline the actions in your sentences. Are those actions in the form of verbs? If not, you might try rewriting your sentences to turn those actions into the main verbs in the sentence.
Active and Passive Verbs
Some critics of style tell us to avoid the passive everywhere because it adds a couple of words and often deletes the agent, the “doer” of the action. But in fact, the passive is sometimes the better choice. To choose between the active and passive, you have to answer two questions:
- The president was rumored to have considered resigning.
- Those who are found guilty can be fined .
- Valuable records should always be kept in a safe.
- Because the test was not done , the flaw was not corrected .
- The weight given to industrial competitiveness as opposed to the value we attach to liberal arts will determine our decision.
- Our decision will be determined by the weight we give to industrial competitiveness as opposed to the value we attach to the liberal arts .
Try this: We need to find our passive verbs before we can evaluate whether or not to change them. While you’re editing, try underlining all the “to be” verbs, since these are often paired with other verbs to make passive constructions. The verbs you’re looking for are: am, are, is, was, were, be, become, became. Once you’ve identified these verbs, check to see if they are necessary, or if the sentence would be clearer or stronger without them. Example: “There is one explanation in the story…” vs “The story explains…”
Writing is more coherent when readers are able to make connections across sentences and paragraphs. On the sentence level, this can include when the last few words of one set up information that appears in the first few words of the next. That’s what gives us our experience of flow.
- Begin sentences with information familiar to your readers. Readers get that information from two sources: first, they remember words from the sentence they just read. Second, readers bring to a sentence a general knowledge of its subject. In a paper on black holes, for example, readers would find references to “astronomers” familiar, even without prior mention.
- End sentences with information that readers cannot anticipate. Readers prefer to read what’s easy before what’s hard, and what’s familiar and simple is easier to understand that what’ new and complex.
Compare these two passages:
Try this: While editing, check for these words: this, these, that, those, another, such, second, or more. Writers often refer to something in a previous sentence with these kinds of words. When you use any of those signals, try to put them at or close to the beginning of the sentence that you use them in.
Here are some tips to help your writing become more precise and cut out extra words.
- Delete what readers can infer. This can include redundant categories like “period of time,” “pink in color,” or “shiny in appearance.
- Can you make sense of the negatives in this sentence?
Except when you have failed to submit applications without documentation, benefits will not be denied.
This handout contains excerpts from Joseph M. Williams' Style: Ten Lessons in Clarity and Grace ( New York: Longman, 2000).
Pasco-Hernando State College
- Unity and Coherence in Essays
- The Writing Process
- Paragraphs and Essays
- Proving the Thesis/Critical Thinking
- Appropriate Language
Test Yourself
- Essay Organization Quiz
- Sample Essay - Fairies
- Sample Essay - Modern Technology
Related Pages
- Proving the Thesis
Unity is the idea that all parts of the writing work to achieve the same goal: proving the thesis. Just as the content of a paragraph should focus on a topic sentence, the content of an essay must focus on the thesis. The introduction paragraph introduces the thesis, the body paragraphs each have a proof point (topic sentence) with content that proves the thesis, and the concluding paragraph sums up the proof and restates the thesis. Extraneous information in any part of the essay which is not related to the thesis is distracting and takes away from the strength of proving the thesis.
An essay must have coherence. The sentences must flow smoothly and logically from one to the next as they support the purpose of each paragraph in proving the thesis. .
Just as the last sentence in a paragraph must connect back to the topic sentence of the paragraph, the last paragraph of the essay should connect back to the thesis by reviewing the proof and restating the thesis.
Example of Essay with Problems of Unity and Coherence
Here is an example of a brief essay that includes a paragraph that does not support the thesis “Many people are changing their diets to be healthier.”
People are concerned about pesticides, steroids, and antibiotics in the food they eat. Many now shop for organic foods since they don’t have the pesticides used in conventionally grown food. Meat from chicken and cows that are not given steroids or antibiotics are gaining in popularity even though they are much more expensive. More and more, people are eliminating pesticides, steroids, and antibiotics from their diets.
Eating healthier also is beneficial to the environment since there are less pesticides poisoning the earth. Pesticides getting into the waterways is creating a problem with drinking water. Historically, safe drinking water has been a problem. It is believed the Ancient Egyptians drank beer since the water was not safe to drink. Brewing beer killed the harmful organisms and bacteria in the water from the Nile.
There is a growing concern about eating genetically modified foods, and people are opting for non-GMO diets. Some people say there are more allergic reactions and other health problems resulting from these foods. Others are concerned because there are no long-term studies which clearly show no adverse health effects such as cancers or other illnesses. Avoiding GMO food is another way people are eating healthier food.
See how just one paragraph can take away from the effectiveness of the essay in showing how people are changing to healthier food since the unity and coherence are affected. There is no longer unity among all the paragraphs. The thought pattern is disjointed and the essay loses its coherence.
Transitions and Logical Flow of Ideas
Transitions are words, groups of words, or sentences that connect one sentence to another or one paragraph to another.
They promote a logical flow from one idea to the next and overall unity and coherence.
While transitions are not needed in every sentence or at the end of every paragraph, they are missed when they are omitted since the flow of thoughts becomes disjointed or even confusing.
There are different types of transitions:
Time – before, after, during, in the meantime, nowadays
Space – over, around, under
Examples – for instance, one example is
Comparison – on the other hand, the opposing view
Consequence – as a result, subsequently
These are just a few examples. The idea is to paint a clear, logical connection between sentences and between paragraphs.
- Printer-friendly version

Understanding the Fundamentals of A Perfect Cohesive Essay
Cohesiveness in writing is one of the most important traits of good writing pieces because it helps convey a writer’s thoughts to the readers. Check out this blog to learn more about how to write a cohesive essay. We, as a top custom essay writing service, are dedicated to assisting students in achieving the best grades.
Table of Contents
What is a Cohesive Essay?
Cohesion is a quality of a piece of writing that keeps the reader hooked till the end. This essay focuses on a particular subject and then moves on to support the main argument with evidence and relevant statistics to maintain cohesiveness in writing. Cohesive academic essays follow a fluent and fluid approach of content to convey the thoughts of writers directly to the readers. All the paragraphs in such essays are interlinked and connected.
Struggling to write a cohesive essay? Feel free to reach out to our professional essay writers to complete your assignments and essays.
How To Write A Cohesive Essay?
A cohesive essay can be challenging because it’s not always easy to bring cohesion in an essay and hook the reader till the end. Many students make mistakes in writing cohesively because they are not well aware of the structure and outline of such essays. The poor organization of ideas and irrelevance of the paragraphs with each other will destroy the primary task of making the essay more cohesive and structured. Following are some expert tips on how to write perfectly by keeping the cohesion in an essay.
The very first thing you need to do is to brainstorm ideas to write an essay about. It would be best if you pick some satire essay topics to write this essay.
If your instructor has already assigned you a topic, you need to sit in silence and let your brain think about ideas that you can incorporate into that topic.
If your instructor has given you the freedom to choose a topic, then select something you are passionate about.
Selecting a topic you can relate to is always a good idea because that will help you write more cohesively and aid in persuading the audience with your ideas.
Brainstorm for the new and unique ideas you can write about. You can also look into the previous research on that topic in order to get a clearer idea of what you are dealing with and what more you can add to the already existing research.
Brainstorming will also help you gather the potential points and essay questions you will unfold in your essay body. It will help in outlining your essay in a more comprehensive and cohesive way.

Secure Your Custom Essay Writing Solution
Identify the Thesis Statement
Thesis statements are very important to identify because they describe what you are trying to defend and support through your essay.
A clear thesis statement is the foundation of a perfect essay.
The thesis statement should be made clear in the very first paragraph of the introduction to make it easy for the reader to detect what the essay is about and what they can expect from it.
Identifying a thesis statement is the first step of writing a cohesive essay, and it should include the main argument and point of discussion.
The thesis statement mirrors your thoughts and ideas and helps proceed with a powerful approach to convey the message perfectly without leaving any confusion and ambiguity on the writer’s end.
If you feel like your thesis statement is not strong enough, you can always change it or modify it in this initial step.
Outline The Cohesive Essay
Outlining your essay helps in gathering and positioning all the potential points of discussion and structuring them in a way that ensures fluency of essay content.
Outlining your essay will help you not miss any important discussion points and cover every logical evidence that will help you explain your topic better.
A clear outline will make the essay more accurate, comprehensive, and concise.
Essays that follow an outline will have a natural flow of events in the context and will have more chance to be cohesive.
Outlining your essay will help you arrange your thoughts in a way that makes it easy for readers to understand your point of view and perspective.
Ensure Connectivity Between Paragraphs
The primary aim of a cohesive essay is to write in a way that everything is connected to each other in the context.
It would help if you made sure that the last line of every paragraph is linked with the first line of the next paragraph.
Your essay shouldn’t have irrelevant information or evidence that doesn’t link with each other and to the main thesis statement of the essay.
Everything that you will add to your essay body should be interlinked with each other and arranged properly, like the scene sequence in a novel.
You can’t add something that doesn’t reflect your initial thesis statement and the main argument of your essay. Because doing this will only make your reader confused and your essay ambiguous.
Make sure that every paragraph and every point of discussion is tied together and focused on the longevity of the thesis statement for your essay.
You can make your essay more connected by answering the main question of the essay after every paragraph and how every piece of evidence you mentioned contributes to your essay.
Proofread Your Cohesive Essay
After you are done writing with cohesion in an essay, make sure you proofread your piece of writing to ensure that there are no errors.
Proofreading also helps eliminate unnecessary points and irrelevant information from your essay and makes it more concise.
Your first draft might not be as well arranged as you want it to be; that’s why proofread thoroughly to arrange your content to convey your thoughts even better.
You can also simplify some difficult sentences that you first thought could reflect your thoughts perfectly. Make sure to make the content as simple and easy to understand as possible.
Thoroughly read your essay or use free tool options online that will check your content for spelling and other potential errors that you might have missed.

Structure of Cohesion Essay
The cohesive essay follows a comprehensive structure to ensure coherence in the contents of the essay. Let’s take a look at the checklist of sections in your research paper:
The abstract is a summary of your essay that summarizes everything you have discussed further in your essay. It includes hypotheses, research methods, and key findings of your research. It contains a single paragraph that precisely provides an overview of the entire essay to inform readers what they can expect from the essay.
Introduction
The introduction is the very first section of an essay that plays an important part in hooking the readers to keep on reading the essay. It provides an overview of the subject which the writer is going to discuss further in the paper. It gives a clear idea of what the essay is about and what the main point of discussion would be.
Research Hypothesis
The research hypothesis is going to discuss what your research is about and what the main research question you will be proving with the help of supporting evidence. It introduces the audience to the thesis statement and research question and clarifies what this particular essay is aiming to discuss.
Methodology
This section details what would be the research methodology the writers are going to use in proving their research question and thesis statement. It will describe the techniques and procedures used to identify and analyze the available literature and evaluate it to find the answers to research questions.
Literature Review
This section overviews all the available information regarding the subject briefly and helps the readers to get to know more about the background of the subject. It also covers the history and the results of the previous research done on the topic. By discussing the previous research, the writer will be able to introduce their research question and explain how it is going to be different from the previous research.
Data Analysis
This section discusses the supporting evidence, research, articles, and statistics regarding the subject. The writer aims to analyze and explain how the result of the data information contributes to the main thesis question of the essay.
This section of the essay will summarize all the important points discussed in the essay and what are the key findings and results of the essay. It also lists the key suggestions that writers wanted to give regarding future research opportunities on the topic. The writer will make sure that the main research question is answered and that the results of the research align with the main thesis statement.
This section cites all the sources of information used as supporting documents in the essay. References help in giving credit to the original researchers of those articles and research papers. References are formatted according to the recommended style by the instructor. Popular referencing styles are MLA, APA, and Chicago, which are used in worldwide academic institutions.
Cohesion Words To Use In An Essay

Get Your Custom Essay Written with 50% Discount Act Now!
Still Confused?
A cohesive essay can be quite challenging due to its requirement to write every point of discussion cohesively. If you are struggling with your essay, you can always contact our assignment writing service to get professional assistance.
Ending How to Write a Cohesive Essay
The primary aim of a cohesive essay is to convert the thoughts and ideas of the writer in such a close-knit way that it reaches the audience accordingly. In this blog, we have discussed how you can effectively write a cohesive academic essay by following some expert tips.
What is coherence in an essay?
Coherence refers to the quality of an essay that ensures that the reader has understood all the points of discussion and thoughts related to the subject. The writer needs to make sure that all the evidence and logical explanations are interconnected to each other and arranged properly to ensure that the reader can easily understand the focus point of the essay.
What are cohesion words in an essay?
Cohesion words are different based on the purpose they serve. Some of the most popular cohesion words are for example, for instance, in other words, moreover, furthermore, in addition to, in conclusion, and in the end.
What is cohesive and coherent?
Cohesion refers to the process that precedes coherence. Cohesion is a process that connects the sentences and coherence is the achieved results of connected ideas that a reader can understand.
What is a cohesive sentence?
A cohesive sentence aims to connect all the sentences around it. These sentences are added at the start, end, or in the middle of a paragraph in order to interlink the points with each other. It helps fit all other sentences around it and make sense of the whole argument.
Why is cohesion important?
Just like how all the ingredients in a dish are mixed together to create a delicious taste that achieves the ideal goal of perfection for that dish. In essays, cohesion helps in mixing all the potential points and logical explanations to achieve the goal of a perfect, interconnected, concise, and comprehensive essay.
First Time Order? Get Custom FREE ESSAY
No Plagiarism & No AI Content
Timely Deliveries
Premium Quality
Unlimited Revisions

We are a team of professional writers providing quality-assured essays, research papers, and assignments. We bring the most affordable services for you with multiple revisions. Get plagiarism-free content with Turnitin pass and on-time delivery. We Create Great Content, Value, & Reliability!
- Biography Writing Services
- Opinion Essay Writing Service
- Personal Statement Writing Service
- Cover Letter Writing Services
- College Essay Writing Service
- Our Writers

28 Cohesion Examples

Cohesion refers to the unity of multiple things. If those things are cohesive, they fit and work well together, making sense as a unified whole.
We can use this term to refer to the unity of people within a group, the unity of ideas in a text, or even the unity of elements in chemistry:
- Linguistic Cohesion: If we look at it through the lens of linguistics, a cohesive text is one that makes sense as a whole. This occurs through the artful organization of ideas so they’re all relevant and interconnected.
- Group Cohesion: On the other hand, in the context of group work , cohesion relates to the integration, unity, and the strong bond among members that helps in achieving a common objective. To put it succinctly, irrespective of the context, cohesion is about connecting elements together to form a cooperative, rational, and harmonious unit.
- Cohesion in Chemistry: In chemistry, cohesion refers to the intermolecular forces that hold particles of the same substance together.
Below, we’ll explore examples from multiple categories. Use the table of contents to scan for examples relevant to you!
Cohesion Examples
1. linguistic cohesion.
Linguistic cohesion refers to the process whereby words, ideas, and concepts are woven together to generate a cohesive idea through words and text. For example, transition words help to cohere paragraphs together, showing how they relate and interact.
- Conjunctions Conjunctions connect clauses or sentences, introducing a relationship between them. Essential conjunctions like ‘and’, ‘or’, ‘but’ and ‘so’ weave together distinct ideas, crafting articulate and cohesive narratives. Conjunctions help use to understand how the first and second half of the sentence go together, demonstrating whether they agree with each other, disagree, and so on.
- Transitional phrases Terms like ‘however’, ‘therefore’, and ‘on the other hand’ also add cohesion to a text. These phrases assist in navigating from one idea to another, signaling changes or connections. They guide the reader through the logical structure of the text, ensuring cohesive movement. They act as conduits, connecting disparate sections of text into a single unified whole.
- Pronouns Pronouns act as handy replacements for specific nouns or noun phrases, playing a vital role in achieving linguistic cohesion. They maintain the coherence in discourse by ensuring that we don’t need to repeat nouns unnecessarily. For instance, instead of repeating ‘John’ in a sentence, we can replace ‘John’ with ‘he’ in the succeeding sections of the text. This not only prevents repetition but is pivotal in creating a smooth flow of information.
- Demonstratives Demonstratives, such as ‘this’ and ‘that’, bring people or objects already mentioned back into focus. They spotlight previously mentioned entities for the listener or reader, making the discourse cohesive. For example, instead of repeating a person’s name or a thing, ‘this’ or ‘that’ can effectively substitute. Such a strategy creates a logical continuity within the text, making it well-connected.
- Synonyms Synonyms are different words with identical or similar meanings. They ensure diversity in expression while maintaining the thematic unity of the text. Functioning as alternatives for repeated words or phrases, they foster linguistic cohesion. For instance, using ‘joyful’ instead of repeatedly using ‘happy’ in a text helps maintain coherence .
- Repetition of a word Word repetition in a text is an important cohesive device. It reinforces the key concepts or ideas being communicated. Repetition bolsters cohesion by creating a consistent thread connecting various parts of a discourse. However, the balance is key as excessive repetition can undermine clarity and interest.
- Ellipsis Employing ellipsis refers to the omission of certain words, relying on the context for completion of meaning. This technique contributes to linguistic cohesion by allowing a smoother, more concise exchange. It reduces redundancy while maintaining a logical and consistent narrative. This works because the reader fills in the missing information from the previous text, linking the parts together.
- Substitution Substitution is a linguistic device where one word or phrase is replaced by another to avoid repetition. This method aids in maintaining relevancy and continuity in a text. The substituted word leads reader’s comprehension, relying on previously provided context. For instance, using ‘one’ instead of repeating a noun fosters linguistic cohesion.
The Cohesive Essay
One key example of linguistic cohesion is in essay writing. A cohesive essay will contain a set of concepts that make sense to one another, are all relevant to the essay question, and build a story that successfully prosecutes your argument. An incohesive essay jumps from idea to idea without a clear connection between them, making it difficult for readers to follow what you’re saying.
2. Social Cohesion
Social cohesion is a sociological concept explaining how societies and groups come together and stay together peacefully. In the most simple term, it demonstrates how societies continue to function, rather than breaking down.
- Shared cultural practices Cultural practices unite individuals belonging to the same society, binding them in a web of shared symbols, rituals, and norms. They create a sense of community, promoting mutual understanding and empathy among its members. A commonly shared custom or ritual, for example, Halloween or Thanksgiving, contributes to social harmony. These shared practices create an environment conducive for cohesion, enhancing societal integration.
- Common language Language is a fundamental tool for communication within a society, playing an essential role in social cohesion. It offers a medium through which thoughts and feelings can be shared, fostering social bonds . Furthermore, a common language can reinforce societal identity, further solidifying cohesion. Societies with a common language tend to be more cohesive than linguistically diverse societies, as the language barrier can often hamper mutual understanding.
- Shared religious beliefs Religion can act as a strong unifying force in a society, often promoting cohesion through shared values and belief systems . These shared beliefs offer common ground upon which connections can be formed, fostering a shared sense of identity among believers. Additionally, religious practices often encourage certain behaviors and moral systems shared by its practitioners, enhancing societal cohesion. The predictable and familiar routines of religious practices can provide stability and structure, reinforcing social cohesion.
- National holidays National holidays serve to commemorate historical events or cultural traditions significant to a society. These shared celebrations engage all members of the society, fostering unity and appreciation for shared history. For instance, Independence Day in the United States or Bastille Day in France encourages national solidarity and societal cohesion. They serve as societal rituals that strengthen the collective identity of a nation, thereby promoting cohesion.
- Common educational systems Tightly woven into the fabric of a society are its educational systems. Uniform educational experiences can share societal values, histories, and systems of thought, therefore promoting social unity. By fostering similar skills and attitudes, education helps equip individuals to participate effectively and harmoniously in society. In this way, the education system provides foundational knowledge and shared experiences, promoting societal cohesion.
- Shared historical experiences The collective memory of historical events and experiences can serve as a strong binding force for any society. Whether these shared experiences are of triumph or tragedy, they shape a society’s collective consciousness and identity. These historical narratives can stimulate feelings of shared heritage and destiny, strengthening societal bonds. Shared history not only forms part of a society’s collective identity but also fosters cohesion by uniting individuals through their shared past.
- Legal systems and laws The rule of law is a cornerstone of social cohesion. It ensures a harmonious coexistence by regulating social behavior and enforcing societal norms. Fair laws, applied universally, promote mutual respect and cooperation. In essence, a fair and efficient legal system safeguards societal interests, depicting the interdependence inherent in a cohesive society.
- National symbols National symbols, such as flags and anthems, play a pivotal role in reinforcing cohesion through shared identity. They serve as a joint representation of a nation’s history, values, and dreams. Logan (1986) posits these symbols often provoke emotional responses that transcend individual differences, fostering a sense of commonality. Thus, national symbols contribute massively to societal cohesion by instilling a shared sense of national identity and pride.
Durkheim and the Cohesive Society
Sociologist Emile Durkheim came up with two ways to describe how societies stick together. These are mechanical and organic solidarity.
- Organic solidarity refers to the process by which small societies cohere by being homogenous (sharing norms and belief systems).
- Mechanical solidarity refers to the process by which large societies cohere not by cultural homogeneity , but common self-interest: we rely on each other for goods and services, so we tolerate one another and respect shared rules.
3. Group Cohesion Examples
When talking about group cohesion, we are referring to the multitudes of ways we ensure the personalities in a group work together. By bringing out the best in all team members, giving them clear roles, and having them all work toward the same goal, we can achieve more than the sum of our parts.
- Clear group goals Clearly defined objectives are the mainstay of any successful collaborative endeavor. They provide a shared understanding of what the collective is aiming to achieve. Thus, team goals play a critical role in fostering cohesion, serving as a guiding light that aligns the efforts of all members. This unified focus on a common objective promotes cooperation and collaborative effort among group members.
- Effective communication Communication is an essential ingredient for cohesion in group work. Open, honest, and effective communication fosters understanding and mitigates misunderstandings. It creates a conducive environment where members can express their ideas freely, ensuring effective collaboration. With all members clearly understanding their tasks and the overall objectives, effective communication leads to harmonious group dynamics .
- Defined roles and responsibilities Clear delineation of roles and responsibilities is pivotal for successful group work. It ensures that every member knows what is expected of them, reducing chances of confusion or conflict. Furthermore, it fosters accountability and facilitates efficient completion of tasks. This clear hierarchy and distribution of work among members lead to a cohesive, functional, and efficient group.
- Trust among members Trust is the bedrock of a cohesive group, facilitating open communication, mutual respect, and interdependence among members. Here, each person trusts others to fulfill their responsibilities and believes in the group’s collective competence. This trust creates a sense of security and promotes the sharing of ideas, thereby strengthening cohesion. Essentially, trust catalyzes connections and cooperation within the group, thereby fostering group cohesion.
- Collaborative problem-solving In cohesive groups, problems are viewed as challenges to be overcome collectively. Solutions are conjured as a joint effort, relying on the group’s diverse skills and perspectives. When members work together to solve problems, they unify their efforts towards a common goal. This not only enhances the group’s problem-solving capacity but also fosters cohesion by promoting shared victories and learnings.
- Regular feedback sessions Constructive feedback , when delivered and received correctly, aids in maintaining group cohesion. These sessions allow members to express their views and offer improvements, ensuring each member feels heard and valued. Equally, it provides a platform for performance enhancement and course correction. Regular feedback thus strengthens group cohesion by promoting transparency, mutual respect, and open dialogue.
- Team-building activities Activities specifically designed to strengthen relationships among group members naturally cultivate group cohesion. Such activities enhance members’ understanding of each other’s strengths and weaknesses, fostering tolerance and empathy. They also create opportunities for collaboration outside the task-oriented dynamics, infusing elements of fun and relaxation. Consequently, team-building activities can greatly enhance group cohesion by fostering camaraderie and mutual appreciation.
- Shared rewards and recognitions Celebrating achievements together and acknowledging individual contributions to shared success preserve group cohesion. This practice validates members’ efforts, promoting a sense of shared satisfaction and belonging. It also motivates continued cooperative engagement and investment in group success. Hence, shared rewards and recognitions underline the idea of ‘all for one and one for all’, strengthening the cohesiveness of the group.
4. Cohesion in Science
In science, cohesion refers to the attraction between particles of the same substance, causing them to stick together. This phenomenon is often observed in liquids, such as the tendency of water molecules to cling to one another due to hydrogen bonding.
- Water molecules sticking together This phenomenon, known as cohesion, is attributed to hydrogen bonding among neighboring water molecules. When water molecules bond, they create a network of strong, cohesive forces. It’s this bonding and consequent cohesion that cause phenomena like water’s surface tension and capillary action. These connected water molecules illustrate scientific cohesion, with components working closely for collective behavior .
- Gravitational pull between celestial bodies In a cosmic context, gravity is the cohesive force that holds celestial bodies together. The gravitational attraction ensures that planets, stars, and satellites maintain their orbits and do not drift aimlessly in space. Therefore, gravity embodies cohesion at a cosmic scale, driven by the mutual attraction of celestial bodies, thus exemplifying cohesion in the realm of astrophysics.
- Surface tension on liquids Surface tension is a direct result of cohesive forces in liquids. Surface molecules experience an inward pull from neighboring molecules, minimizing surface area and creating a “film-like” surface. This phenomenon, attributable to cohesive forces, enables certain lightweight objects to float on a liquid surface without sinking. Hence, surface tension on liquids highlights the role of cohesion in everyday science.
- Intermolecular forces in solids In a solid substance, intermolecular forces bind the particles together, constraining their movement and keeping them tightly packed. It’s these forces that give a solid its definite shape and volume. The continuous interaction of these forces ensures the solidity of an object. Thus, intermolecular forces in solids also demonstrate scientific cohesion.
Cohesion fosters interconnectedness, harmony, and mutual cooperation within a system, be it cells in a body, members of a team, or words in a sentence. Grasping the idea of cohesion enables us to understand the complex interplay of elements in these systems, reflecting the essence of unity in diversity.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is IQ? (Intelligence Quotient)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- A Beginner’s Guide to IELTS
- Common Grammar Mistakes [for IELTS Writing Candidates]
Writing Correction Service
- Free IELTS Resources
- Practice Speaking Test
Select Page
How to Use Cohesive Devices Correctly [for IELTS Writing]
Posted by David S. Wills | Dec 7, 2020 | IELTS Tips , Writing | 0
If you look at IELTS websites and YouTube videos, you might learn that cohesive devices are very important and that you should use as many of them as possible. However, this is incorrect. You should use them when necessary, but you should not overuse them.
Cohesive devices certainly are important for IELTS writing but you should aim to use them sparingly and accurately. This article will tell you everything you need to know about them.
What are Cohesive Devices?
A cohesive device is a word that helps join parts of your essay together. They are also known as linkers, linking devices, transitions, transitional phrases, or signposting language. However, as the IELTS marking rubric refers to them as “cohesive devices,” then I shall also use that term today.
There are different types of cohesive devices because technically any word that joins ideas or clauses is cohesive by nature. However, in most cases we mean conjunctive adverbs. These are words that link two independent clauses in a compound sentence or else introduce an independent clause at the start of a new sentence.
Conjunctive adverbs include:
- Consequently
- For example
- As a result
- In conclusion
- On the one hand
How to Use Cohesive Devices
As I mentioned above, there are different types of cohesive devices. For this reason, you should use them according to the grammatical rules required. For example, a conjunctive adverb would be used differently from a subordinating conjunction, and these would each be different from a coordinating conjunction.
You can see the difference between those three types of cohesive device here:
Today, we will mostly focus on conjunctive adverbs. These begin an independent clause and that will come after a full stop or a semi-colon. For example:
- She’d had a bad morning; however, she stayed positive and hoped the afternoon would be better.
- She’d had a bad morning. However, she stayed positive and hoped the afternoon would be better.
The meaning is basically the same. We use a semi-colon when the connection between the two clauses is close and obvious. Sometimes they are interchangeable.
For IELTS essays, conjunctive adverbs most commonly are used as signposting language to guide the reader logically from one point to the next. It is very common to see these cohesive devices in task 2 essays:
- To begin with
- On the other hand
- In other words
You always need to keep in mind that these must be both logical and grammatical . That is really important if you want a good score for Coherence and Cohesion.
Problems with Cohesive Devices in IELTS Essays
Let’s now look at some problems people face with cohesive devices in IELTS essays.
Overusing Cohesive Devices
There are various problems that IELTS candidates face when using cohesive devices. The most common problem is overusing them. This is due to a misunderstanding of how English works and the fact that most IELTS tutors say, “Use as many cohesive devices as possible!”
In fact, you should use device devices sometimes in order to logically link parts of your writing, but you should definitely avoid using them too much or your work will sound mechanical and dull. Look at an essay by a native speaker of English. How many cohesive devices do they use? Not many.
The IELTS marking rubric specifically states that you will not score more than band 7 for Coherence and Cohesion if you overuse cohesive devices:
uses a range of cohesive devices appropriately although there may be some under-/over-use British Council
You can see how strange it sounds to overuse them in this example:
I have a full lesson on the overuse of cohesive devices here .
Picking the Wrong Cohesive Device
Another problem is that people often pick the wrong cohesive device. This is a bit less common than overusing them, but I still see it pretty frequently when marking essays for my IELTS writing correction service .
Here is an example:
Many people believe that governments should increase taxes on electrical devices in order to fund disposal programmes to ensure that they are recycled. For example, many devices are just thrown away with other trash, contributing to the destruction of the environment.
The problem here is that the cohesive device “for example” is not really appropriate. The second sentence is not actually an example of the first. It is related to the first but it further explains the ideas of the first sentence rather than providing any sort of example. To fix this, we might say:
Many people believe that governments should increase taxes on electrical devices in order to fund disposal programmes to ensure that they are recycled. For example, a small tax levied on all electrical goods could be used to establish drop-off points in easily accessible locations, where electrical goods are collected and sent to specialist sites to be re-used or broken into component parts that can be safely disposed.
Now, the second sentence gives a full example of the idea expressed in the first sentence.
Another commonly misused cohesive device is “meanwhile.” People seem to confuse this with “however” or “therefore.” It really means “at the same time as.” You can see that here:
To solve the trash crisis, we need to take various approaches. Perhaps the most important one is educating people of the damage that they are doing to our planet. Meanwhile, we also need to punish people who drop litter or dump chemicals because we cannot just wait for education to have an impact. That could take years.
In this case, “meanwhile” shows that punishment needs to happen at the same time as education .
Altering the Form of Cohesive Devices
One really common problem is people changing cohesive devices. Perhaps they just misremember them, but sometimes people try to be creative. Unfortunately, these parts of speech should be changed or else they become incorrect.
As you can see from the above picture, it is quite common for people to make an error with “On the one hand… On the other hand…” When you change either of these, the result is an incorrect phrase. There is no way to change them correctly, so don’t bother.
I also see people trying to be creative with other cohesive devices, like “in conclusion” or “for example.” They say things like “to be conclusion” or “for examples.” However, both of these are totally incorrect. Another strange one that I have seen is “first and most of all.”
Informal or Outdated Devices
It is also common to see people misusing cohesive devices by picking really informal ones or really old and unusual ones.
One of the most common mistakes is saying “to recapitulate.” This is a term that almost no native speaker would use nowadays. You can see here on Google that it is no longer a commonly used term:
Unfortunately, many IELTS candidates use this because lots of uninformed teachers tell them that it is a special word to dazzle the examiner.
Similarly, people use phrases like “last but not least.” This is a way of introducing people in spoken English. We might use it to introduce a speaker who has come last in a list of people. It is a comical and friendly way of saying “He’s last but that is just a random order.” It is totally inappropriate for an IELTS essay because it is so informal .
Confusing Types of Cohesive Devices
Another quite common problem is mixing up the different types of cohesive device. I stated earlier that we would focus on conjunctive adverbs in this lesson, but cohesive devices can technically include subordinative conjunctions or coordinating conjunctions. These are different parts of speech with different grammatical rules to govern them.
We use conjunctive adverbs after a period or semi-colon and follow them with a comma, but subordinating conjunctions do not have a comma after them. Conjunctive adverbs link two independent clauses but subordinating ones begin a dependent clause:
- INCORRECT: Although, the Earth is warming at an alarming temperature, some people refuse to admit that climate change is real.
- CORRECT: Although the Earth is warming at an alarming temperature, some people refuse to admit that climate change is real.
- CORRECT: Some people refuse to admit that climate change is real although the Earth is warming at an alarming temperature.
- ALSO CORRECT: Some people refuse to admit that climate change is real; however, the Earth is warming at an alarming temperature.
I have a full lesson on the difference between conjunctive adverbs and subordinating conjunctions here .
Most Common Cohesive Devices
It is honestly better to stick with standard language. The people who regularly are disappointed by their IELTS results are the ones who try to use fancy language as a means of taking a shortcut. Instead, stick with the most frequently used cohesive devices and make sure that you use them correctly:
- Additionally
These words and phrases are really useful and can help you to link your ideas logically. Don’t worry about them being “basic” or “boring.” They are important words and as long as you don’t overuse them in your essay then there is no problem.
Cohesive Device Examples
Finally, let’s look at a list of cohesive devices, divided by type. This is not an exhaustive list, of course. It is just a small sample of the vast array of cohesive devices that exist. However, maybe you will find it useful.
About The Author
David S. Wills
David S. Wills is the author of Scientologist! William S. Burroughs and the 'Weird Cult' and the founder/editor of Beatdom literary journal. He lives and works in rural Cambodia and loves to travel. He has worked as an IELTS tutor since 2010, has completed both TEFL and CELTA courses, and has a certificate from Cambridge for Teaching Writing. David has worked in many different countries, and for several years designed a writing course for the University of Worcester. In 2018, he wrote the popular IELTS handbook, Grammar for IELTS Writing and he has since written two other books about IELTS. His other IELTS website is called IELTS Teaching.
Related Posts
Describe a Polite Person
September 20, 2021
IELTS Speaking Topic: Cooking
May 6, 2018
Books and Reading [IELTS Speaking Topic]
July 17, 2023
10 IELTS Listening Tips
April 7, 2016
Leave a reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Download my IELTS Books
Recent Posts
- How to Improve your IELTS Writing Score
- Past Simple vs Past Perfect
- Complex Sentences
- How to Score Band 9 [Video Lesson]
- Taxing Fast Food: Model IELTS Essay
Recent Comments
- Francisca on Adverb Clauses: A Comprehensive Guide
- Mariam on IELTS Writing Task 2: Two-Part Questions
- abdelhadi skini on Subordinating Conjunction vs Conjunctive Adverb
- David S. Wills on How to Describe Tables for IELTS Writing Task 1
- anonymous on How to Describe Tables for IELTS Writing Task 1
- Lesson Plans
- Model Essays
- TED Video Lessons
- Weekly Roundup
- Research Paper
- College Paper
- Dissertation Service
- Research Proposal Writing Service
- Writing Help Online
- Write My Term Paper
- Legitimate Essay Writing Service
What Is a Cohesive Essay and Its Feature
- May 21, 2020
- Posted by: admin
- Category: Blog ,
If you have an immense wish and ambition to know what is a cohesive essay, you should invest quite a lot of effort into finding information, because this category of an essay is not at all so simple. However, you must complete this task at the end of your first year of study, so it makes no sense to avoid it. Although, you could easily ask our legit essay service to help you with this task!
Predominantly, it is important to figure out the cohesive essay meaning correctly. It is a non-scientific work of philosophical, literary, historical, journalistic or other subjects, of a small volume with a structured composition on a private subject, which is interpreted subjectively and usually incomplete.
In other words, the cohesive article is a consistently revealed issue with the help of interrelated thoughts and common arguments. But, how to organize your endeavor in a way to get an outstanding cohesive essay? Here are the most valuable aspects that will push you to write it like a pro.
Cohesive Essay Definition for a Better Understanding
A cohesive essay is an academic type of writing that must have a hierarchy of interrelated beliefs as well as attitudes, any element of which is called a cohesive paragraph. The primary purpose of any cohesive essay is to convince the reader that you are well aware of the topic and the clarification of your thoughts has a logical relation that leads to a definite conclusion.
The key concept is coherence, which means the desire to hold all things together, to make logical sense. What does it mean? Each cohesive paragraph should stick along with the other. Your thoughts should be opened up like a flower blossom, petal by petal one after another. Only after that, the final picture becomes visible. This best describes the correct mechanism for expressing thoughts in a cohesive essay. Remember this metaphor, and you will never make a mistake.
Cohesive Essay Format Which Should Be Followed
The cohesive essay format, as well as the format of any other essay, is not a set of complicated rules, as it seems at first glance. It is worth to clear this up once and for all simply by following marks:
- The specific issue and personal explanation. An essay cannot keep a lid on many themes or ideas at the same time. It expresses only one particular opinion and cultivates it purely. That is, an essay answers only one question.
- Free composition — an essential component of any essay. This assignment by its nature does not accept any formal scheme in the expression of your ideas. However, this rule does not apply to stylistics, which will be highlighted later.
- Ease stories. It is highly substantial to arrange a trusting style of sharing information with the reader; in order to be clear, you must avoid intentionally complex, obscure, unnecessarily rigorous constructions.
- The propensity for contradictions. An essay destined to dazzle the reader. The starting point is typically an aphoristic, vivid assertion or antagonistic interpretation that makes the reader be involved in the theme.
- Internal semantic harmony. That means the flexibility of the central theses and judgments, the internal wholeness of arguments and reflections.
- Focus on the simplicity of speech. At the same time, slang, verbal clichés, word abbreviations should be avoided.
Therefore, when writing an essay, it is imperative to comprehend the subject matter, to create the required volume and identify the intention of each component.
Cohesive Essay Outline Step-by-Step
A cohesive essay outline should definitely be followed for the successful implementation of the assignment. With the intention to be assured that everything flows smoothly in your essay, check the following points:
- Thesis statement. It should be clear, strong and debatable.
- Evidence. It is necessary to use evidence, which means using quotes, charts, statistics, etc. The evidence is your foundation on which the whole essay is kept, and if it is unstable, then your work will not receive anything but a crash.
- Analysis. No less important aspect is the analysis of evidence; it should be explanatory as well as your personal attitude towards it.
- Reflection. Your personal opinion, which confirms the analysis.
- Structure and style. Follow the standard essay structure, and do not be afraid to use your own narrative style. Use your imagination.
To write a cohesive essay is a somewhat tricky task that requires a lot of work. However, if you learn how to do it — you will not only become a professional in writing but also learn to justify your own opinion in a variety of life circumstances. Do not be reluctant to spend time learning the principles of writing a cohesive essay — this is the most complex and easiest way at the same time. But it is totally worth it. However, our college essay service is always ready to help you with any writing assignment!
Essay Custom Writing
Order Your Best Graduated Paper
While our prices is the lowest.
PLACE AN ORDER
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
The Happiness Gap Between Left and Right Isn’t Closing

By Thomas B. Edsall
Mr. Edsall contributes a weekly column from Washington, D.C., on politics, demographics and inequality.
Why is it that a substantial body of social science research finds that conservatives are happier than liberals?
A partial answer: Those on the right are less likely to be angered or upset by social and economic inequities, believing that the system rewards those who work hard, that hierarchies are part of the natural order of things and that market outcomes are fundamentally fair.
Those on the left stand in opposition to each of these assessments of the social order, prompting frustration and discontent with the world around them.
The happiness gap has been with us for at least 50 years, and most research seeking to explain it has focused on conservatives. More recently, however, psychologists and other social scientists have begun to dig deeper into the underpinnings of liberal discontent — not only unhappiness but also depression and other measures of dissatisfaction.
One of the findings emerging from this research is that the decline in happiness and in a sense of agency is concentrated among those on the left who stress matters of identity, social justice and the oppression of marginalized groups.
There is, in addition, a parallel phenomenon taking place on the right as Donald Trump and his MAGA loyalists angrily complain of oppression by liberals who engage in a relentless vendetta to keep Trump out of the White House.
There is a difference in the way the left and right react to frustration and grievance. Instead of despair, the contemporary right has responded with mounting anger, rejecting democratic institutions and norms.
In a 2021 Vox article, “ Trump and the Republican Revolt Against Democracy ,” Zack Beauchamp described in detail the emergence of destructive and aggressive discontent among conservatives.
Citing a wide range of polling data and academic studies, Beauchamp found:
More than twice as many Republicans (39 percent) as Democrats (17 percent) believed that “if elected leaders won’t protect America, the people must act — even if that means violence.”
Fifty-seven percent of Republicans considered Democrats to be “enemies,” compared with 41 percent of Democrats who viewed Republicans as “enemies.”
Among Republicans, support for “the use of force to defend our way of life,” as well as for the belief that “strong leaders bend rules” and that “sometimes you have to take the law in your own hands,” grows stronger in direct correlation with racial and ethnic hostility.
Trump has repeatedly warned of the potential for political violence. In January he predicted bedlam if the criminal charges filed in federal and state courts against him damaged his presidential campaign:
I think they feel this is the way they’re going to try and win, and that’s not the way it goes. It’ll be bedlam in the country. It’s a very bad thing. It’s a very bad precedent. As we said, it’s the opening of a Pandora’s box.
Before he was indicted in New York, Trump claimed there would be “potential death and destruction” if he was charged.
At an Ohio campaign rally in March, Trump declared, “If I don’t get elected, it’s going to be a blood bath for the whole country.”
In other words, Trump and his allies respond to adversity and what they see as attacks from the left with threats and anger, while a segment of the left often but not always responds to adversity and social inequity with dejection and sorrow.
There are significant consequences for this internalization.
Jamin Halberstadt , a professor of psychology at the University of Otago in New Zealand and a co-author of “ Outgroup Threat and the Emergence of Cohesive Groups : A Cross-Cultural Examination,” argued in his emailed reply to my inquiry that because “a focus on injustice and victimhood is, by definition, disempowering (isn’t that why we talk of ‘survivors’ rather than ‘victims’?), loss of control is not good for self-esteem or happiness.”
But, he pointed out:
this focus, while no doubt a part of the most visible and influential side of progressive ideology, is still just a part. Liberalism is a big construct, and I’m reluctant to reduce it to a focus on social justice issues. Some liberals have this view, but I suspect their influence is outsized because (a) they have the social media megaphone and (b) we are in a climate in which freedom of expression and, in particular, challenges to the worldview you characterize have been curtailed.
Expanding on this line of argument, Halberstadt wrote:
I’m sure some self-described liberals have views that are counterproductive to their own happiness. One sub-ideology associated with liberalism is, as you describe, a sense of victimhood and grievance. But there is more than one way to respond to structural barriers. Within that group of the aggrieved, some probably see systemic problems that cannot be overcome, and that’s naturally demoralizing and depressing. But others see systemic problems as a challenge to overcome.
Taking Halberstadt’s assessment of the effects of grievance and victimhood a step farther, Timothy A. Judge , the chairman of the department of management and human resources at Notre Dame, wrote in a 2009 paper, “ Core Self-Evaluations and Work Success ”:
Core self-evaluations (C.S.E.) is a broad, integrative trait indicated by self-esteem, locus of control, generalized self-efficacy and (low) neuroticism (high emotional stability). Individuals with high levels of C.S.E. perform better on their jobs, are more successful in their careers, are more satisfied with their jobs and lives, report lower levels of stress and conflict, cope more effectively with setbacks and better capitalize on advantages and opportunities.
I asked Judge and other scholars a question: Have liberal pessimists fostered an outlook that spawns unhappiness as its adherents believe they face seemingly insurmountable structural barriers?
Judge replied by email:
I do share the perspective that a focus on status, hierarchies and institutions that reinforce privilege contributes to an external locus of control. And the reason is fairly straightforward. We can only change these things through collective and, often, policy initiatives — which tend to be complex, slow, often conflictual and outside our individual control. On the other hand, if I view “life’s chances” (Virginia Woolf’s term) to be mostly dependent on my own agency, this reflects an internal focus, which will often depend on enacting initiatives largely within my control.
Judge elaborated on his argument:
If our predominant focus in how we view the world is social inequities, status hierarchies, societal unfairness conferred by privilege, then everyone would agree that these things are not easy to fix, which means, in a sense, we must accept some unhappy premises: Life isn’t fair; outcomes are outside my control, often at the hands of bad, powerful actors; social change depends on collective action that may be conflictual; an individual may have limited power to control their own destiny, etc. These are not happy thoughts because they cause me to view the world as inherently unfair, oppressive, conflictual, etc. It may or may not be right, but I would argue that these are in fact viewpoints of how we view the world, and our place in it, that would undermine our happiness.
Last year, George Yancey , a professor of sociology at Baylor University, published “ Identity Politics, Political Ideology, and Well-Being : Is Identity Politics Good for Our Well-Being?”
Yancey argued that recent events “suggest that identity politics may correlate to a decrease in well-being, particularly among young progressives, and offer an explanation tied to internal elements within political progressiveness.”
By focusing on “political progressives, rather than political conservatives,” Yancey wrote, “a nuanced approach to understanding the relationship between political ideology and well-being begins to emerge.”
Identity politics, he continued, focuses “on external institutional forces that one cannot immediately alleviate.” It results in what scholars call the externalization of one’s locus of control, or viewing the inequities of society as a result of powerful if not insurmountable outside forces, including structural racism, patriarchy and capitalism, as opposed to believing that individuals can overcome such obstacles through hard work and collective effort.
As a result, Yancey wrote, “identity politics may be an important mechanism by which progressive political ideology can lead to lower levels of well-being.”
Conversely, Yancey pointed out, “a class-based progressive cognitive emphasis may focus less on the group identity, generating less of a need to rely on emotional narratives and dichotomous thinking and may be less likely to be detrimental to the well-being of a political progressive.”
Yancey tested this theory using data collected in the 2021 Baylor Religion Survey of 1,232 respondents.
“Certain types of political progressive ideology can have contrasting effects on well-being,” Yancey wrote. “It is plausible that identity politics may explain the recent increase well-being gap between conservatives and progressives.”
Oskari Lahtinen , a senior researcher in psychology at the University of Turku in Finland, published a study in March, “ Construction and Validation of a Scale for Assessing Critical Social Justice Attitudes ,” that reinforces Yancey’s argument.
Lahtinen conducted two surveys of a total of 5,878 men and women to determine the share of Finnish citizens who held “critical social justice attitudes” and how those who held such views differed from those who did not.
Critical social justice proponents, on Lahtinen’s scale,
point out varieties of oppression that cause privileged people (e.g., male, white, heterosexual, cisgender) to benefit over marginalized people (e.g., woman, Black, gay, transgender). In critical race theory, some of the core tenets include that (1) white supremacy and racism are omnipresent and colorblind policies are not enough to tackle them, (2) people of color have their own unique standpoint and (3) races are social constructs.
What did Lahtinen find?
The critical social justice propositions encountered
strong rejection from men. Women expressed more than twice as much support for the propositions. In both studies, critical social justice was correlated modestly with depression, anxiety, and (lack of) happiness, but not more so than being on the political left was.
In an email responding to my inquiries about his paper, Lahtinen wrote that one of the key findings in his research was that “there were large differences between genders in critical social justice advocacy: Three out of five women but only one out of seven men expressed support for the critical social justice claims.”
In addition, he pointed out, “there was one variable in the study that closely corresponded to external locus of control: ‘Other people or structures are more responsible for my well-being than I myself am.’”
The correlation between agreement with this statement and unhappiness was among the strongest in the survey:
People on the left endorsed this item (around 2 on a scale of 0 to 4) far more than people on the right (around 0.5). Endorsing the belief was determined by political party preference much more than by gender, for instance.
Such measures as locus of control, self-esteem, a belief in personal agency and optimism all play major roles in daily life.
In a December 2022 paper, “ The Politics of Depression : Diverging Trends in Internalizing Symptoms Among U.S. Adolescents by Political Beliefs,” Catherine Gimbrone , Lisa M. Bates , Seth Prins and Katherine M. Keyes , all at Columbia’s Mailman School of Public Health, noted that “trends in adolescent internalizing symptoms diverged by political beliefs, sex and parental education over time, with female liberal adolescents experiencing the largest increases in depressive symptoms, especially in the context of demographic risk factors, including parental education.”
“These findings,” they added, “indicate a growing mental health disparity between adolescents who identify with certain political beliefs. It is therefore possible that the ideological lenses through which adolescents view the political climate differentially affect their mental well-being.”
Gimbrone and her co-authors based their work on studies of 85,000 teenagers from 2005 to 2018. They found that
while internalizing symptom scores worsened over time for all adolescents, they deteriorated most quickly for female liberal adolescents. Beginning in approximately 2010 and continuing through 2018, female liberal adolescents reported the largest changes in depressive affect, self-esteem, self-derogation and loneliness.
In conclusion, the authors wrote, “socially underprivileged liberals reported the worst internalizing symptom scores over time, likely indicating that the experiences and beliefs that inform a liberal political identity are ultimately less protective against poor mental health than those that inform a conservative political identity.”
From another vantage point, Nick Haslam , a professor of psychology at the University of Melbourne, argued in his 2020 paper “ Harm Inflation: Making Sense of Concept Creep ” that recent years have seen “a rising sensitivity to harm within at least some Western cultures, such that previously innocuous or unremarked phenomena were increasingly identified as harmful and that this rising sensitivity reflected a politically liberal moral agenda.”
As examples, Haslam wrote that the definition of “trauma” has been
progressively broadened to include adverse life events of decreasing severity and those experienced vicariously rather than directly. “Mental disorder” came to include a wider range of conditions, so that new forms of psychopathology were added in each revision of diagnostic manuals and the threshold for diagnosing some existing forms was lowered. “Abuse” extended from physical acts to verbal and emotional slights and incorporated forms of passive neglect in addition to active aggression.
Haslam described this process as concept creep and argued that “some examples of concept creep are surely the work of deliberate actors who might be called expansion entrepreneurs.”
Concept expansion, Haslam wrote, “can be used as a tactic to amplify the perceived seriousness of a movement’s chosen social problem.” In addition, “such expansion can be effective means of enhancing the perceived seriousness of a social problem or threat by increasing the perceived prevalence of both ‘victims’ and ‘perpetrators.’”
Haslam cited studies showing that strong “correlates of holding expansive concepts of harm were compassion-related trait values, left-liberal political attitudes and forms of morality associated with both.” Holding expansive concepts of harm was also “associated with affective and cognitive empathy orientation and most strongly of all with endorsement of harm- and fairness-based morality.” Many of these characteristics are associated with the political left.
“The expansion of harm-related concepts has implications for acceptable self-expression and free speech,” Haslam wrote. “Creeping concepts enlarge the range of expressions judged to be unacceptably harmful, thereby increasing calls for speech restrictions. Expansion of the harm-related concepts of hate and hate speech exemplifies this possibility.”
While much of the commentary on the progressive left has been critical, Haslam takes a more ambivalent position: “Sometimes concept creep is presented in an exclusively negative frame,” he wrote, but that fails to address the “positive implications. To that end, we offer three positive consequences of the phenomenon.”
The first is that expansionary definitions of harm “can be useful in drawing attention to harms previously overlooked. Consider the vertical expansion of abuse to include emotional abuse.”
Second, “concept creep can prevent harmful practices by modifying social norms.” For example, “changing definitions of bullying that include social exclusion and antagonistic acts expressed horizontally rather than only downward in organizational hierarchies may also entrench norms against the commission of destructive behavior.”
And finally:
The expansion of psychology’s negative concepts can motivate interventions aimed at preventing or reducing the harms associated with the newly categorized behaviors. For instance, the conceptual expansion of addiction to include behavioral addictions (e.g., gambling and internet addictions) has prompted a flurry of research into treatment options, which has found that a range of psychosocial treatments can be successfully used to treat gambling, internet and sexual addictions.
Judge suggested an approach to this line of inquiry that he believed might offer a way for liberalism to regain its footing:
I would like to think that there is a version of modern progressivism that accepts many of the premises of the problem and causes of inequality but does so in a way that also celebrates the power of individualism, of consensus and of common cause. I know this is perhaps naïve. But if we give in to cynicism (that consensus can’t be found), that’s self-reinforcing, isn’t it? I think about the progress on how society now views sexual orientation and the success stories. The change was too slow, painful for many, but was there any other way?
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here's our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Thomas B. Edsall has been a contributor to the Times Opinion section since 2011. His column on strategic and demographic trends in American politics appears every Wednesday. He previously covered politics for The Washington Post. @ edsall

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
3. Make sure everything is connected. In connection to the previous point, make sure that each section of your essay is linked to the one after it. Think of your essay as a story: it should have a beginning, middle, and end, and the way that you write your piece should logically tie these elements together in a linear manner. 4.
Coherence is about making everything flow smoothly to create unity. So, sentences and ideas must be relevant to the central thesis statement. The writer has to maintain the flow of ideas to serve the main focus of the essay. 5. Stick to the purpose of the type of essay you're-writing.
A cohesive essay focuses on one subject and uses supporting evidence and analysis to defend the topic. Cohesive essay writing relies on order and structure for the fluency of the message. Planning ...
Cohesion is an important feature of academic writing. It can help ensure that your writing coheres or 'sticks together', which will make it easier for the reader to follow the main ideas in your essay or report. You can achieve good cohesion by paying attention to five important features. The first of these is repeated words.
Cohesion is a characteristic of a successful essay when it flows as a united whole; meaning, there is unity and connectedness between all of the parts. Cohesion is a writing issue at a macro and micro level. At a macro-level, cohesion is the way a paper uses a thesis sentence, topic sentences, and transitions across paragraphs to help unify and focus a paper.
Cohesion and Coherence. A well-organized paper uses techniques to build cohesion and coherence between and within paragraphs to guide the reader through the paper by connecting ideas, building details, and strengthening the argument. Although transitions are the most obvious way to display the relationship between ideas, consider some of the ...
Coherence in a piece of writing means that the reader can easily understand it. Coherence is about making everything flow smoothly. The reader can see that everything is logically arranged and connected, and relevance to the central focus of the essay is maintained throughout. Two key aspects of coherence. Cohesion: This relates to the linking ...
The purpose of these aspects of writing is to think about, understand, and write for your readers. You can improve the clarity and organization of your writing by knowing the differences between concrete versus abstract language and making your paragraphs cohesive and coherent. Source: Williams, J.M., & Bizup, J. (2017).
Cohesive writing helps to avoid reader confusion and instead leaves a memorable impression. Cohesion also affects the flow of the essay, meaning that readers can move from one item to the next ...
Cohesion. If the structure is the order of your points, cohesion is what ties them together and guides the reader through your argument. Create cohesion using words and phrases that show the relationships between points. For example: basic connectives: and, or, but, so. giving more detail: for example, to illustrate, an example of this is.
Cohesion concerns the flow of sentences and paragraphs from one to another. It involves the tying together of old information and new. When we write academic essays, particularly in the humanities, we work hard to foster cohesion structurally, which enhances a reader's understanding of our ideas.. Essay organization
Coherence is crucial in writing as it ensures that the text is understandable and that the ideas flow logically from one to the next. When writing is coherent, readers can easily follow the progression of ideas, making the content more engaging and easier to comprehend. Coherence connects the dots for the reader, linking concepts, arguments ...
Revising for Cohesion. Writing a cohesive paper takes time and revision. This resource will focus primarily on topic sentences that begin each paragraph and on topics, or main points, within a paragraph. This resource will also enable students to look closely at their sentences and see how each sentence relates to another within a paragraph.
Harvard College Writing Center 2 Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt When you receive a paper assignment, your first step should be to read the assignment
Flow and Cohesion. Our Writing Center gets a lot of students who are concerned about the flow of their writing, but this can mean a lot of different things. When we talk about "flow" we mean cohesion or how ideas and relationships are communicated to readers. Flow can involve the big-picture (how parts of the essay fit together and the way the ...
Cohesive Writing Connects Topic and Stress: Sentences are cohesive when the stress of one sentence is used as the topic of the next. Below, the first example reads like a list of facts. The ideas are related but the sentences don't connect. The second example connects the topics and stress which creates a sense of flow.
Unity. Unity is the idea that all parts of the writing work to achieve the same goal: proving the thesis. Just as the content of a paragraph should focus on a topic sentence, the content of an essay must focus on the thesis. The introduction paragraph introduces the thesis, the body paragraphs each have a proof point (topic sentence) with ...
A cohesive essay can be challenging because it's not always easy to bring cohesion in an essay and hook the reader till the end. Many students make mistakes in writing cohesively because they are not well aware of the structure and outline of such essays. The poor organization of ideas and irrelevance of the paragraphs with each other will ...
Cohesive writing helps readers understand how the details relate to the overall argument of a text and to follow it easily. The quality of cohesion in a written text is achieved by various means, which make different elements of the text hold together well: logical conjunction, grammatical referencing, lexical choice and paragraphing.
The Cohesive Essay. One key example of linguistic cohesion is in essay writing. A cohesive essay will contain a set of concepts that make sense to one another, are all relevant to the essay question, and build a story that successfully prosecutes your argument. An incohesive essay jumps from idea to idea without a clear connection between them ...
A cohesive device is a word that helps join parts of your essay together. They are also known as linkers, linking devices, transitions, transitional phrases, or signposting language. However, as the IELTS marking rubric refers to them as "cohesive devices," then I shall also use that term today.
In a cohesive essay, all the parts stick together. Readers clearly understand what you are writing about and how you get from point to point. You probably know that a good essay should include an introduction, a body and a conclusion, but once you've made sure those main elements are there, try revising your essay to check for cohesive markers - the glue that binds them into a unified whole.
Cohesive Essay Definition for a Better Understanding. A cohesive essay is an academic type of writing that must have a hierarchy of interrelated beliefs as well as attitudes, any element of which is called a cohesive paragraph. The primary purpose of any cohesive essay is to convince the reader that you are well aware of the topic and the ...
The battle for 2024 is turning out to be the most audacious election in India's electoral history, even more daring than the 1977 elections, when opposition forces in India were up against Prime ...
Here is a selection of views from around the world. France: Warnings of 'Wokisme' Many in France, including Prime Minister Gabriel Attal, see the pro-Palestinian protests as another example of ...
Xi's selected destinations in Europe - France, Serbia, and Hungary - carry a strong narrative significance.
Mr. Edsall contributes a weekly column from Washington, D.C., on politics, demographics and inequality. Why is it that a substantial body of social science research finds that conservatives are ...