- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works

74 Best Social Media Research Paper Topics

Whether in college or high school, you will come across research writing as a student. In most cases, the topic of research is assigned by your teacher/professor. Other times, students have to come up with their topic. Research writing in school is inescapable. It’s a task you are bound to undertake to fulfill your academic requirements. If you are in college, there are several topics for research depending on your discipline. For high school students, the topic is usually given. In this article, we focus on social media and topics about social media.
A social media paper is a research paper about social media that studies social media generally or an aspect of it. To write research papers on social media, you’ll need to conduct thorough research for materials and scholarly materials that’ll assist you. For social media, most of the scholarly works will be media-focused.
Sometimes, Professors or teachers ask students to write an essay or research a topic without narrowing it down. In that case, students will have to develop specific research topics. If you’re writing a paper on social media, we’ve provided you with helpful topics to consider for research.
How to Start a Social Media Research Paper
Social media topics to write about, social media research topics for college students, interesting topics to research for fun, research questions about social media, social media essay topics for high school students, narrow research topic ideas students can consider, research paper on social media marketing, good social topics for research papers, easy social issues to write about, social science research topics for college students, interesting research topics for high school students, comprehensive social networking research papers, final words about social media topics.
Before giving a research writing, Professors and teachers believe students already know how to write one. Not every student knows how to write a research paper in most cases.
Research writing follows a systematic pattern, which applies to research on social media. Below is the pattern of a research paper to use;
- Paper title
- Introduction
- Statement of problem
- Research methodology
- Research objective
- Critical analysis
- Results and discussion
Every research follows this basic pattern, and it also applies to your research paper on social media.
Social media has become a powerful tool for engagement of various kinds. Before now, social media was merely apps used for interpersonal affairs. Today, with the modification of digital technology, social media encompasses a lot more. Below are some social media topics to write about.
- The impact of social media in promoting interpersonal relationships
- A study on how social media is a vital tool for social change
- Social media censorship: A new form of restriction on freedom of speech
- The constantly growing oversharing nature of social media
- Social media is a vital tool for political campaign
- The proliferation of social media platforms into a buying space
- The juxtaposition of personal engagement and business on social media platforms
There is a wide range of topics to coin from social media for college students because social media is a platform with diverse issues that can form into topics. Here are some research topics about social media to consider.
- Breach of Privacy: A study on the ability of the government to monitor personal affairs on social media
- A study of the toxicity brewing within social media
- The increased cyberbullying perpetrated on social media platforms
- The evolution of Twitter into a space for diverse conversations
- A study of the emergence and growth of social media over the years
- Effects of social media: How social media is breeding laziness amongst children
- Social media as a distraction tool for students
If you are searching for interesting topics, there are many interesting research topics on social media. Examples of research paper topics that sound fun to choose from include;
- A study on how the emergence of social media and social media advertising has infiltrated its primary purpose
- An evaluation of how social media has created employment opportunities for people
- Social media influence and its negative impact on society
- Advertising on social media: Will influencer businesses take over advertising agencies?
- A study on ways to improve advertisement for social media engagement
- A look into how social media creates a distorted view of real life
- Social media and real-life: Does social media obscure reality?
Research questions are helpful when carrying out research in a particular field. To know more about your thesis on social media, you will need to create research questions on social media to help inform your writing. Some social media research questions to ask are;
- Are social media platforms designed to be addictive?
- What is a social media Algorithm, and how to navigate it?
- To what extent are personal data stored on social app databases protected?
- Can social media owners avoid government monitoring?
- Should parents allow their children to navigate social media before they are 15?
- Have social media jobs come to stay, or are they temporary?
- Is social media influencer culture overtaking celebrity culture?
- To what extent can social media help to curb racism and homophobia?
- Does social media exacerbate or curb discriminatory practices?
- Is social media an effective tool for learning?
Everyone has access to social media apps until they’ve reached a certain age. There are several social media essay topics for high school students to write about. Some social media titles for essays include;
- How social media affects the academic performance of students
- Why the use of social media is prohibited during school hours
- Why students are obsessed with Tiktok
- Running a profitable social media business while in high school and the challenges
- The dangers of overusing editing apps
- A critical essay on how editing apps and filters promote an unrealistic idea of beauty
- The death of TV: how social media has stolen student’s interest
The challenge students have with their topic ideas for research papers is that they’re broad. A good social media thesis topic should be narrowed down. Narrowing a topic down helps you during research to focus on an issue.
Some narrow social media topics for the research paper include;
- A study of how social media is overtaking Television in entertainment
- A study of how social media has overtaken traditional journalism
- An evaluation of the rise of influencer culture on Instagram
- YouTube and how it has created sustainable income for black content creators
- A comparative study of social media managers and content creators
- A study of the decline of Instagram since the emergence of Tiktok
- How Twitter breeds transphobic conversations
There are several areas of social media to focus your research on. If you are looking for some social media marketing topics, below are some social media research paper topics to consider;
- Influencer culture and a modified model of mouth-to-mouth marketing
- The growth of video marketing on Instagram
- Social media managers as an essential part of online marketing
- A study on how social media stories are optimized for marketing
- An analysis of social media marketing and its impact on customer behavior
- An evaluation of target marketing on social media
There are so many topics to choose from in this aspect. Some social issues research paper topics to explore are;
- The growth of cyberattacks and cyberstalking in social media
- Social media and how it promotes an unrealistic idea of life
- Social media and the many impacts it has on users and businesses
- Social media detox: Importance of taking scheduled social media breaks
- How social media enable conversation on social challenges
Writing a research paper on social issues touches on various areas. Some are challenging, while others are easier to navigate.
Below are some of the easy social issues topics to choose from.
- The growing issue of women’s and trans people’s rights
- Religious bigotry and how it affects social progress
- Sustainable living and why it’s important to the society
- The social impact of climate change and global warming
Social science is a broad discipline. If you are looking for social science essay topics, below are some social science topics for research papers to look into;
- Consumerism and how it’s perpetrated on social media
- How religious beliefs impact social relationships
- Inflation and how it affects the economy of a nation
- A study of the limited availability of work opportunities for minority groups
- A look into the concept of “low wage” jobs
Research writing is not always technical or challenging. Sometimes, it can be fun to write. It all depends on your choice of topic. Below are some topics on social media that are fun to work on;
- The importance of social media branding for small businesses
- A look into the monetization of Instagram
- User engagement and how it can be converted into business leads
- The study of emojis and their role in social media engagement
- From Instagram to Tiktok: the poaching nature of social media apps
Research writing on social media networking studies social networking and its design and promotion on social media platforms. Some research papers on social media networking are;
- The impact of social media networking on business owners
- Social media networking and how it impacts influencer culture
- Social media and how it’s used to build and develop social relationships
- How social media made social networking services easier
Social media research writing is one of the most interesting research to conduct. It cuts across several interesting areas. The writer can handle almost every aspect of the dissertation or thesis statement about social media . But, students who find it challenging should seek professional help. You can reach out to our expert team of writers to help you handle every element of your writing. We have the best on our team who are always ready to give you their best.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
234 Social Media Research Topics & Ideas
18 January 2024
last updated
Social media research encompasses a broad range of different topics that delve into the ever-evolving digital landscape. People investigate the impact of social platforms on society, exploring subjects, such as online identity formation, self-presentation, the psychology of virtual interactions, and others. Additionally, studies examine the influence of social media on politics, activism, and public opinion, uncovering patterns of information dissemination and polarization. Privacy concerns, cyberbullying, and online safety are also explored in-depth, seeking strategies to mitigate the associated risks. In this article, people can find many social media research topics, ideas, and examples.
Hot Social Media Research Topics
- Impacts of Social Media and Internet Algorithms on User Experience
- The Rise of TikTok: A Socio-Cultural Analysis
- Dealing With Cyberbullying: Strategies and Solutions
- Understanding the Phenomenon of Social Media ‘Cancel Culture’
- NFTs and Social Media: The Future of Digital Art?
- Ethical Concerns in the Era of Influencer Marketing
- Social Media’s Role in Accelerating E-Commerce Growth
- Impacts of Internet and Social Media on Journalism and News Reporting
- Understanding the Psychology of Viral Challenges on Social Platforms
- Cryptocurrency and Social Media: The Intersection
- Mitigating Misinformation and ‘Fake News’ on Social Media
- Augmented Reality (AR) in Social Media: A Game Changer?
- Evaluating the Impact of Social Media on Political Campaigns
- Social Media’s Influence on Fashion and Beauty Trends
- Privacy, Safety, and Security Concerns in the Age of Social Networking
- Roles of Free Access and Social Media in Promoting Sustainable Practices
- Implications of Social Media Addiction on Mental Health
- Examining Social Media’s Role in Crisis Communication
- The Power of User-Generated Content in Branding
- Influence of Social Media on Food Culture and Dining Trends
Easy Social Media Research Topics
- Impacts of Online Videos and Social Media on Mental Health
- Influencer Marketing: Efficacy and Ethical Concerns
- Evolution of Privacy Policies Across Social Platforms
- Understanding Virality: What Makes Content Shareable?
- Cyberbullying: Prevalence and Prevention Strategies
- Social Media and Political Polarization: An In-Depth Study
- Role of Social Media in Modern Business Strategies
- Effect of Social Media on Interpersonal Relationships
- Social Platforms as Tools for Social Change
- Navigating Online Hate Speech: A Legal Perspective
- Emerging Trends in Social Media Advertising
- Online Identity Construction and Self-Presentation
- The Psychology of Social Media Addiction
- Social Media’s Role in Crisis Management and Communication
- Sentiment Analysis in Social Media and Its Implications
- Social Media Algorithms: Bias and Implications
- The Phenomenon of Cancel Culture on Social Platforms
- Cybersecurity Threats in the Era of Social Media
- Analyzing Adverse Impacts of Social Media on Consumer Behavior

Interesting Social Media Research Topics
- Evaluating the Effects of Social Media on Language and Communication
- Roles of Social Media in Fostering Political Engagement
- Misinformation and Propaganda Spread Through Social Platforms
- Analyzing the Shift From Traditional Media to Social Media
- Dark Patterns in Social Media: Hidden Manipulative Tactics
- Social Media and Digital Activism: Revolutionizing Advocacy
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Its Impact on Social Networking
- Exploring Cybersecurity Issues in Social Media Platforms
- Roles and Effects of Social Media and News in Mental Health Promotion
- Strategies for Effective Social Media Crisis Management
- The Power of Live Streaming for Brands and Influencers
- Using Social Media to Enhance Classroom Learning
- Analyzing the Influence of Memes on Internet Culture
- Impacts of Social Media Algorithms on User Behavior
- Assessing the Correlation Between Social Media and Loneliness
- Geotagging and Its Implications for Personal Privacy
- Social Media and E-commerce: A Cross-Industry Study
- The Ethics of Digital Advertising on Social Platforms
- Understanding the Psychology of Social Media Trolls
- The Cultural Shift Caused by Social Media Localization
Social Media Research Paper Topics for High School
- The Phenomenon of Cyberbullying: Prevention and Strategies
- How Does Social Media Influence Teen Body Image?
- Evaluating the Educational Potential of Social Media Platforms
- Impacts of Social Media on Adolescents’ Self-Esteem
- Roles of Free Connection and Social Media in Modern Political Activism
- Exploring the Concept of ‘Digital Citizenship’ Among Teenagers
- The Ethics of Social Media Privacy: User Rights and Responsibilities
- Social Media Addiction: Understanding Its Causes and Effects
- Influence of Social Media on Modern Communication Styles
- Analyzing Positive Roles of Social Media in Promoting Reading Culture
- Social Media and Mental Health: Correlation or Causation?
- The Role of Social Media in Global Environmental Awareness
- Examining Social Media’s Impact on Real-Life Social Skills
- Social Media Platforms: Tools for Personal Branding or Narcissism?
- Influence of Social Media Trends on Youth Fashion Choices
- Impacts of Social Media on Teenagers’ Sleep Patterns
- Online Safety: The Role of Parents and Schools in Social Media Usage
- How Does Social Media Influence Teenagers’ Views on Relationships?
- Social Media and Empathy: Does Online Interaction Decrease Compassion?
Social Media Research Paper Topics for College Students
- Evaluating the Impact of Social Media on Body Image and Self-Esteem
- The Influence of Social Media on Voting Patterns Among Young Adults
- Social Media as a Valid Tool for Social Change: A Case Study Approach
- Unveiling the Psychology of Social Media Addiction
- Social Media’s Role in Modern Journalism: Opportunities and Challenges
- Privacy Implications of Data Collection on Social Media Platforms
- Cyberbullying in the Age of Social Media: Scope and Solutions
- The Ethical Aspects of Social Media Influencer Marketing
- Roles and Effects of Social Media in Crisis Communication and Management
- Social Media and Its Effects on Interpersonal Communication Skills
- Analyzing Social Media Strategies of Successful Businesses
- Impacts of Internet Use and Social Media on Mental Health Among College Students
- The Roles That Social Media Has in Modern Political Campaigns
- Understanding the Social Media Algorithm: Bias and Implications
- Social Media and Consumer Behavior: The Power of Influencer Marketing
- Fake News, Authors, and Disinformation Spread Through Social Media Platforms
- Exploring Direct Links Between Social Media Use and Academic Performance
- Social Media’s Role in Promoting Sustainable Lifestyle Choices
- Regulation of Hate Speech and Offensive Content on Social Media
- The Power and Peril of Virality in the Age of Social Media
Social Media Research Paper Topics for University
- The Effect That Social Media Has on Global Politics
- The Ethics of Data Mining in Social Media
- Roles of Social Media in Business Marketing Strategies
- Social Media, Internet Use, and Their Impacts on Mental Health: A Systematic Review
- Algorithmic Bias in Social Media Platforms: Causes and Consequences
- The Influence of Colors and Social Media on Consumer Behavior
- Exploring Possible Relationships Between Social Media Use and Academic Performance
- Privacy, Morality, and Security Concerns in the Age of Social Media
- Social Media as a Platform for Digital Activism
- Impacts of Social Media on Interpersonal Communication and Relationships
- Cyberbullying on Social Media: Scope, Impact, and Preventive Measures
- The Role of Social Media in Spreading Health-Related Misinformation
- Analyzing the Effect of Social Media on Journalism Practices
- Understanding the Influence of Social Media on Body Image Perceptions
- Social Media’s Role in Crisis Management: Case Studies
- The Power and Effectiveness of Influencer Marketing on Social Media
- Fake News and Disinformation in the Social Media Age
- Regulatory Approaches to Hate Speech on Social Media Platforms
- The Economic Implications of Social Media: From Startups to Giants
Social Media Research Paper Topics for Masters
- Advanced Algorithms and Their Role in Shaping Social Media Interactions
- Evaluating the Impact of Social Media on Democratic Processes Globally
- The Intersection of Privacy, Data Mining, and Ethics in Social Media
- Quantitative Analysis of Social Media’s Impact on Consumer Buying Behavior
- Cybersecurity Threats in Social Media: Mitigation and Prevention Strategies
- Analyzing the Psychological Implications of Social Media Addiction
- Using Social Media Data to Predict Market Trends: An Econometric Approach
- Role of Social Media in Crisis Management: A Comparative Study
- The Sociolinguistic Impact of Social Media on Communication
- Machine Learning and AI in Social Media: An Examination of Emerging Trends
- Social Media as a Valid Tool for Public Health: Opportunities and Challenges
- Social Media’s Influence on Modern Journalism: A Critical Analysis
- Mapping Social Networks: A Graph Theory Approach
- Evaluating the Efficacy of Social Media Campaigns in Social Change Movements
- Analyzing the Role of Social Media in Corporate Reputation Management
- Data Privacy Laws and Social Media: A Comparative Study
- The Use of Small and Big Data Analytics in Social Media Marketing
- Social Media and Its Role in Strengthening Democracy: A Deep Dive
- The Impact of Social Media on Cultural Assimilation and Identity
- Ethics of Artificial Intelligence in Social Media Content Moderation
Social Media Research Paper Topics for Ph.D.
- Analyzing the Impact of Social Media Algorithms on User Behavior and Perceptions
- Deciphering the Influence of Social Media on Political Campaign Strategies
- Examining the Role of Social Media in Corporate Social Responsibility Initiatives
- Social Media and Mental Health: A Comprehensive Analysis of Recent Studies
- Effects of Social Media and Internet Use on Consumer Buying Behavior: An Econometric Approach
- Social Media and Digital Diplomacy: A Critical Analysis
- Ethical Implications of Data Mining Techniques in Social Media Platforms
- Unpacking the Psychological Mechanisms of Social Media Addiction
- Role of Social Media in Contemporary Journalism: Opportunities and Challenges
- Social Media and Privacy: A Comparative Study of Data Protection Laws
- Machine Learning and AI in Social Media: Identifying Future Trends
- Social Media’s Possible Influence on People, Body Image, and Self-Esteem: A Meta-Analysis
- Analyzing the Role of Social Media in Crisis Management and Communication
- Impacts of Social Media on Different Language and Communication Styles
- Cybersecurity in Social Media: An Analysis of Current Threats and Mitigation Strategies
- Social Media as a Good Tool for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention
- Effects of Social Media on Children and Their Parents: Social Skills and Interpersonal Relationships
- Roles of Social Media in Promoting Gender Equality and Women’s Rights
- Social Media and its Influence on Cultural Assimilation and Identity Formation
Social Media Research Topics for Argumentative Papers
- Impacts of Social Media on Social and Political Discourses: Enhancing or Hindering Democratic Engagement?
- Social Media and Mental Health: Exploring the Association Between Excessive Usage and Psychological Well-Being
- Fostering Online Activism and Social Movements: The Role of Social Media
- Balancing Personal Information Sharing and Data Protection: Social Media and Privacy
- Exploring the Effects of Social Media on Body Image and Self-Esteem
- Social Media and Political Polarization: Reinforcing Echo Chambers or Encouraging Diverse Perspectives?
- Youth Culture and Identity Formation: The Influence of Social Media
- Fake News and Misinformation: Combating Inaccurate Information in the Era of Social Media
- Social Media and Cyberbullying: Examining the Impact on Mental Health and Well-Being
- The Ethics of Social Media Research: Privacy, Informed Consent, and Ethical Considerations
- Relationships in the Digital Age: Exploring the Influence of Social Media Use
- The Influence of Internet, Technology, and Social Media on Consumer Behavior and Buying Decisions
- Analyzing the Role of Online Platforms in Elections: Social Media and Political Campaigns
- Social Media in Education: Exploring the Benefits and Challenges of Integration in the Classroom
- Impacts of Social Media and Interface on News Consumption and Journalism Practices
- Body Politics in the Digital Space: Examining Representations of Gender, Race, and Body Image on Social Media
- Addressing Ethical and Security Concerns in the Digital Age: Social Media and Cybersecurity
- Shaping Consumer Behavior and Brand Perception: The Role of Social Media Influencers
- Civic Engagement in the Digital Era: Assessing the Role of Social Media Platforms
- The Influence of Social Media Algorithms on Information Consumption and Personalization
Social Media Research Topics for Persuasive Papers
- The Power of Social Media in Driving Social and Political Change
- Promoting Digital Literacy: Empowering Users to Navigate the Complexities of Social Media
- Social Media as a Catalyst for Social Justice Movements: Amplifying Marginalized Voices
- Countering Fake News and Misinformation on Social Media: Strategies for Critical Thinking
- Harnessing the Influence of Social Media for Environmental Activism and Sustainability
- The Dark Side of Social Media: Addressing Online Harassment and Cyberbullying
- Influencer Marketing: Ethical Considerations and Consumer Protection in the Digital Age
- Leveraging Social Media for Public Health Campaigns: Increasing Awareness and Behavioral Change
- Social Media and Mental Health: Promoting Well-Being in a Hyperconnected World
- Navigating the Privacy Paradox: Balancing Convenience and Personal Data Protection on Social Media
- Roles of Social Media and Internet in Fostering Civic Engagement and Democratic Participation
- Promoting Positive Body Image on Social Media: Redefining Beauty Standards and Empowering Individuals
- Enhancing Online Safety: Developing Policies and Regulations for Social Media Platforms
- Social Media and the Spread of Disinformation: Combating the Infodemic
- Roles of Social Media and Technology in Building and Sustaining Relationships: Connecting in a Digital Era
- Influencer Culture and Materialism: Examining the Impact on Consumer Behavior
- Social Media and Education: Maximizing Learning Opportunities and Bridging the Digital Divide
- The Power of Viral Hashtags: Exploring Social Movements and Online Activism
- Social Media and Political Polarization: Bridging Divides and Encouraging Constructive Dialogue
Social Media Topics for Pros and Cons Research Papers
- Examining the Social Effects of Digital Connectivity: Pros and Cons of Using Social Media
- Balancing Privacy Concerns in the Digital Age: Evaluating the Cons and Risks of Social Media Use
- Information Sharing in the Digital Era: Uncovering the Advantages of Social Media Platforms
- Building Online Communities: Analyzing the Strengths and Weaknesses of Social Media Interaction
- Navigating Political Discourse in the Digital Age: The Disadvantages of Social Media Engagement
- Mental Health in the Digital Sphere: Understanding the Benefits and Drawbacks of Social Media
- Combating Cyberbullying: Addressing the Negative Side of Online Social Interactions
- Personal Branding in the Digital Landscape: Empowerment vs. Self-Objectification on Social Media
- Establishing Meaningful Connections: Exploring the Pros and Cons of Social Media Relationships
- Leveraging the Educational Potential of Digital Platforms: Examining the Benefits of Social Media in Learning
- Body Image and Self-Esteem in the Age of Social Media: Weighing the Positives and Negatives
- From Digital Activism to Political Change: Assessing the Opportunities and Limitations of Social Media
- Unraveling the Influence: Social Media and Consumer Behavior in the Digital Marketplace
- Misinformation in the Digital Landscape: The Pros and Cons of Social Media in the Spread of Disinformation
- Crisis Communication in the Digital Age: Navigating the Benefits and Challenges of Social Media
- Tackling Fake News: Navigating Misinformation in the Era of Social Media
- Maximizing Business Opportunities: Evaluating the Advantages and Disadvantages of Social Media Marketing
- The Psychology of Social Media: Analyzing the Upsides and Downsides of Digital Engagement
- Exploring the Impact of Social Media on Socialization: Benefits, Drawbacks, and Implications
- Online Activism: The Power and Limitations of Social Media Movements
Social Media Topics for Cause and Effect Research Papers
- Enhancing Political Activism: Exploring the Relationship Between Social Media and Civic Engagement
- The Psychological Effects of Digital Connectivity: Investigating the Relationship Between Mental Health of People and Social Media Use
- Political Polarization in the Online Sphere: Understanding the Impact of Digital Networks
- Disrupted Sleep Patterns in the Digital Era: Exploring the Role of Online Platforms
- Digital Distractions and Academic Performance: Analyzing the Effects of Online Engagement
- Navigating Online Relationships: Understanding the Impacts of Digital Interactions
- The Digital Marketplace: Exploring Consumer Behavior in the Age of Online Platforms
- The Loneliness Epidemic: Investigating the Relationship Between Social Media Use and Social Isolation
- Redefining Political Participation: The Influence of Digital Networks on Democracy
- Unmasking Digital Identities: The Psychological Effects of Social Media Use
- News Consumption in the Digital Era: Exploring the Impacts of Online Platforms
- Cyberbullying in the Virtual World: Analyzing the Effects of Online Interactions
- The Digital Campaign Trail: Investigating the Influence of Online Platforms on Voter Behavior
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) in the Digital Age: Exploring the Psychological Consequences
- Body Dissatisfaction in the Digital Sphere: Understanding the Impacts of Online Presence
- Information Overload: Coping With the Digital Deluge in the Information Age
- Privacy Concerns in the Online Landscape: Analyzing the Implications of Digital Footprints
- Unveiling the Dark Side: Exploring the Relationship Between Online Activities and Substance Abuse
- Bridging the Political Divide: The Impact of Digital Networks on Sociopolitical Polarization
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles
431 music essay topics & ideas, essay on my escape from north korea.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » 300+ Social Media Research Topics
300+ Social Media Research Topics

Social media has become an integral part of our lives, and it has transformed the way we communicate, share information, and interact with each other. As social media platforms continue to evolve and gain popularity, they have also become a rich source of data for researchers. Social media research is a rapidly growing field that encompasses a wide range of topics , from understanding the psychological and social effects of social media to analyzing patterns of user behavior and identifying trends in online conversations. In this era of data-driven decision-making, social media research is more important than ever, as it provides insights into how we use and are influenced by social media. In this post, we will explore some of the most fascinating and relevant social media research topics that are shaping our understanding of this powerful medium.
Social Media Research Topics
Social Media Research Topics are as follows:
- The effects of social media on mental health
- The role of social media in political polarization
- The impact of social media on relationships
- The use of social media by businesses for marketing
- The effects of social media on body image and self-esteem
- The influence of social media on consumer behavior
- The use of social media for education
- The effects of social media on language use and grammar
- The impact of social media on news consumption
- The role of social media in activism and social change
- The use of social media for job seeking and career development
- The effects of social media on sleep patterns
- The influence of social media on adolescent behavior
- The impact of social media on the spread of misinformation
- The use of social media for personal branding
- The effects of social media on political participation
- The influence of social media on fashion trends
- The impact of social media on sports fandom
- The use of social media for mental health support
- The effects of social media on creativity
- The role of social media in cultural exchange
- The impact of social media on language learning
- The use of social media for crisis communication
- The effects of social media on privacy and security
- The influence of social media on diet and exercise behavior
- The impact of social media on travel behavior
- The use of social media for citizen journalism
- The effects of social media on political accountability
- The role of social media in peer pressure
- The impact of social media on romantic relationships
- The use of social media for community building
- The effects of social media on gender identity
- The influence of social media on music consumption
- The impact of social media on academic performance
- The use of social media for social support
- The effects of social media on social skills
- The role of social media in disaster response
- The impact of social media on nostalgia and memory
- The use of social media for charity and philanthropy
- The effects of social media on political polarization in developing countries
- The influence of social media on literary consumption
- The impact of social media on family relationships
- The use of social media for citizen science
- The effects of social media on cultural identity
- The role of social media in promoting healthy behaviors
- The impact of social media on language diversity
- The use of social media for environmental activism
- The effects of social media on attention span
- The influence of social media on art consumption
- The impact of social media on cultural values and norms.
- The impact of social media on mental health
- The impact of social media on mental health.
- The impact of social media on body image and self-esteem.
- The use of social media for political activism and social justice movements.
- The role of social media in promoting cultural diversity and inclusivity.
- The impact of social media on romantic relationships and dating.
- The use of social media for customer service and support.
- The impact of social media on mental health and well-being among young adults.
- The impact of social media on political polarization and partisanship.
- The use of social media for health communication and behavior change.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards vaccination.
- The impact of social media on political participation and civic engagement.
- The impact of social media on political polarization and echo chambers.
- The use of social media for political campaigning and the manipulation of public opinion.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards vaccination and public health.
- The impact of social media on news consumption and trust in journalism.
- The use of social media for promoting sustainable fashion practices and ethical consumption.
- The role of social media in influencing beauty standards and body image.
- The impact of social media on the music industry and the role of social media influencers.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among healthcare professionals.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards gun violence and gun control policies.
- The impact of social media on social activism and advocacy.
- The use of social media for promoting cross-cultural communication and intercultural understanding.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards climate change and environmental policies.
- The impact of social media on public health during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The use of social media for promoting financial literacy and access to financial services for low-income individuals.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards immigration policies and refugee crises.
- The impact of social media on political activism and social movements.
- The use of social media for promoting digital literacy and technology education in developing countries.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards gender and sexual orientation.
- The impact of social media on consumer behavior in the food and beverage industry.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among first responders.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards racial justice and police brutality.
- The impact of social media on privacy concerns and data security.
- The use of social media for promoting interfaith dialogue and religious tolerance.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards income inequality and economic justice.
- The impact of social media on the film and television industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among military personnel.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards privacy and data security.
- The impact of social media on the hospitality industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting intergenerational communication and understanding.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards animal welfare and animal rights.
- The impact of social media on the gaming industry and gamer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting digital literacy and technology skills among seniors.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards renewable energy and sustainability.
- The impact of social media on the advertising industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among children and adolescents.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards online privacy and security.
- The impact of social media on the beauty industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting cultural preservation and heritage tourism.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards criminal justice reform.
- The impact of social media on the automotive industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among marginalized communities.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards sustainable development goals.
- The impact of social media on the fashion industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting intercultural communication in the workplace.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards mental health policies.
- The impact of social media on the travel industry and sustainable tourism practices.
- The use of social media for health information seeking and patient empowerment.
- The role of social media in promoting environmental activism and sustainable practices.
- The impact of social media on consumer behavior and brand loyalty.
- The use of social media for promoting education and lifelong learning.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards mental health issues.
- The impact of social media on the fashion industry and fast fashion practices.
- The use of social media for promoting social entrepreneurship and social innovation.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards gun control.
- The impact of social media on the mental health and well-being of adolescents.
- The use of social media for promoting intercultural exchange and understanding.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards climate change.
- The impact of social media on political advertising and campaign strategies.
- The use of social media for promoting healthy relationships and communication skills.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards police brutality and racial justice.
- The use of social media for promoting financial literacy and personal finance management.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards LGBTQ+ rights.
- The impact of social media on the music industry and fan engagement.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among marginalized populations.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards immigration and border policies.
- The impact of social media on the professional development and networking of journalists.
- The use of social media for promoting community building and social cohesion.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards healthcare policies.
- The impact of social media on the food industry and consumer behavior.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards gender equality.
- The impact of social media on the sports industry and athlete-fan interactions.
- The use of social media for promoting financial inclusion and access to banking services.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards animal welfare.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among college students.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards privacy and data security.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards income inequality and poverty.
- The use of social media for promoting digital literacy and technology skills.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards renewable energy.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among elderly populations.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards online privacy and security.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards criminal justice reform.
- The impact of social media on online activism and social movements.
- The use of social media for business-to-business communication and networking.
- The role of social media in promoting civic education and engagement.
- The impact of social media on the fashion industry and sustainable fashion practices.
- The use of social media for promoting cultural diversity and inclusion.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards police reform.
- The impact of social media on the mental health and well-being of frontline healthcare workers.
- The use of social media for promoting financial literacy and investment education.
- The role of social media in promoting environmental sustainability and conservation.
- The impact of social media on body image and self-esteem among adolescent girls.
- The use of social media for promoting intercultural dialogue and understanding.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards immigration policies and refugees.
- The impact of social media on the professional development and networking of healthcare professionals.
- The use of social media for promoting community resilience and disaster preparedness.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards the Black Lives Matter movement.
- The impact of social media on the music industry and artist-fan interactions.
- The use of social media for promoting healthy eating habits and nutrition education.
- The role of social media in promoting mental health and well-being among college students.
- The impact of social media on the entertainment industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting workplace diversity and inclusion.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards climate change policies.
- The impact of social media on the travel industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among military veterans.
- The role of social media in promoting intergenerational dialogue and understanding.
- The impact of social media on the professional development and networking of educators.
- The use of social media for promoting animal welfare and advocacy.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards reproductive rights.
- The impact of social media on the sports industry and fan behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting financial inclusion and literacy among underprivileged populations.
- The role of social media in promoting mental health and well-being among LGBTQ+ populations.
- The impact of social media on the food and beverage industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting interfaith dialogue and understanding.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards gun ownership.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among caregivers.
- The role of social media in promoting sustainable tourism practices.
- The impact of social media on the gaming industry and gamer culture.
- The use of social media for promoting cultural heritage tourism and preservation.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards public transportation policies.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among homeless populations.
- The role of social media in promoting mental health and well-being among immigrants and refugees.
- The use of social media for promoting financial literacy and entrepreneurship among youth.
- The use of social media for political mobilization and participation in authoritarian regimes.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards immigration policies.
- The impact of social media on the professional development of teachers and educators.
- The use of social media for emergency communication during public health crises.
- The role of social media in promoting LGBTQ+ rights and advocacy.
- The impact of social media on body positivity and self-acceptance among women.
- The use of social media for public diplomacy and international relations.
- The impact of social media on the mental health and well-being of marginalized communities.
- The use of social media for crisis management and disaster response in the corporate sector.
- The role of social media in promoting environmental activism and conservation.
- The impact of social media on the professional development and networking of entrepreneurs.
- The use of social media for medical education and healthcare communication.
- The role of social media in promoting cultural exchange and understanding.
- The impact of social media on social capital and civic engagement among young adults.
- The use of social media for disaster preparedness and community resilience.
- The role of social media in promoting religious pluralism and tolerance.
- The use of social media for promoting healthy lifestyles and wellness.
- The use of social media for fundraising and philanthropy in the non-profit sector.
- The role of social media in promoting interfaith dialogue and understanding.
- The impact of social media on the travel and tourism industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for customer engagement and brand loyalty in the retail sector.
- The impact of social media on the political attitudes and behaviors of young adults.
- The use of social media for promoting gender equality and women’s empowerment.
- The use of social media for promoting animal welfare and adoption.
- The role of social media in promoting mental health and well-being among the elderly.
- The impact of social media on the art industry and artist-fan interactions.
- The use of social media for promoting healthy food choices and nutrition.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards income inequality.
- The use of social media for promoting political satire and humor.
- The role of social media in promoting disability rights and advocacy.
- The use of social media for promoting voter registration and participation.
- The role of social media in promoting entrepreneurship and small business development.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among incarcerated populations.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards gun violence prevention.
- The use of social media for promoting cultural heritage and preservation.
- The impact of social media on mental health and well-being.
- The relationship between social media use and academic performance.
- The use of social media for emergency communication during natural disasters.
- The impact of social media on traditional news media and journalism.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and discourse.
- The use of social media for online learning and education.
- The impact of social media on the fashion and beauty industry.
- The use of social media for brand awareness and marketing.
- The impact of social media on privacy and security.
- The use of social media for job searching and recruitment.
- The impact of social media on political polarization and extremism.
- The use of social media for online harassment and cyberbullying.
- The role of social media in promoting environmental awareness and sustainability.
- The impact of social media on youth culture and identity formation.
- The use of social media for travel and tourism marketing.
- The impact of social media on consumer behavior and decision-making.
- The role of social media in shaping beauty standards and body positivity.
- The use of social media for crisis communication and disaster response.
- The impact of social media on the music industry.
- The use of social media for fundraising and philanthropy.
- The role of social media in promoting healthy lifestyles and wellness.
- The impact of social media on sports fandom and fan behavior.
- The use of social media for political lobbying and advocacy.
- The impact of social media on the entertainment industry.
- The use of social media for healthcare communication and patient engagement.
- The role of social media in promoting gender equality and feminism.
- The impact of social media on the restaurant and food industry.
- The use of social media for volunteerism and community service.
- The role of social media in promoting religious tolerance and interfaith dialogue.
- The impact of social media on the art industry.
- The use of social media for political satire and humor.
- The role of social media in promoting disability awareness and advocacy.
- The impact of social media on the real estate industry.
- The use of social media for legal advocacy and justice reform.
- The role of social media in promoting intercultural communication and understanding.
- The impact of social media on the automotive industry.
- The use of social media for pet adoption and animal welfare advocacy.
- The role of social media in promoting mental health and wellness for marginalized communities.
- The impact of social media on the retail industry.
- The use of social media for promoting civic engagement and voter participation.
- The impact of social media on the film and television industry.
- The use of social media for fashion and style inspiration.
- The role of social media in promoting activism for human rights and social issues.
- The effectiveness of social media for political campaigns.
- The role of social media in promoting fake news and misinformation.
- The impact of social media on self-esteem and body image.
- The impact of social media on romantic relationships.
- The use of social media for online activism and social justice movements.
- The impact of social media on traditional news media.
- The impact of social media on interpersonal communication skills.
- The impact of social media on the fashion industry.
- The use of social media for social support and mental health awareness.
- The use of social media for political lobbying and activism.
- The impact of social media on travel and tourism behavior.
- The use of social media for customer feedback and market research.
- The impact of social media on the restaurant industry.
- The role of social media in political activism
- The effect of social media on interpersonal communication
- The relationship between social media use and body image concerns
- The impact of social media on self-esteem
- The role of social media in shaping cultural norms and values
- The use of social media by celebrities and its impact on their image
- The role of social media in building and maintaining personal relationships
- The use of social media for job searching and recruitment
- The impact of social media on children and adolescents
- The use of social media by political candidates during election campaigns
- The role of social media in education
- The impact of social media on political polarization
- The use of social media for news consumption
- The effect of social media on sleep habits
- The use of social media by non-profit organizations for fundraising
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion
- The influence of social media on language and communication patterns
- The use of social media in crisis communication and emergency management
- The role of social media in promoting environmental awareness
- The influence of social media on music preferences
- The impact of social media on body positivity movements
- The role of social media in shaping beauty standards
- The influence of social media on sports fandom
- The use of social media for health promotion and education
- The impact of social media on political participation
- The role of social media in shaping parenting practices
- The influence of social media on food preferences and eating habits
- The use of social media for peer support and mental health advocacy
- The role of social media in shaping religious beliefs and practices
- The influence of social media on humor and comedy
- The use of social media for online activism and social justice advocacy
- The impact of social media on public health awareness campaigns
- The role of social media in promoting cultural diversity and inclusion
- The influence of social media on travel behavior and decision-making
- The use of social media for international diplomacy and relations
- The impact of social media on job satisfaction and employee engagement
- The role of social media in shaping romantic preferences and dating behavior
- The influence of social media on language learning and language use
- The use of social media for political satire and humor
- The impact of social media on social capital and community building
- The role of social media in shaping gender identity and expression
- The influence of social media on fashion and beauty advertising.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

200+ Funny Research Topics

500+ Sports Research Topics

300+ American History Research Paper Topics

500+ Cyber Security Research Topics

500+ Environmental Research Topics

500+ Economics Research Topics
Explore your training options in 10 minutes Get Started
- Graduate Stories
- Partner Spotlights
- Bootcamp Prep
- Bootcamp Admissions
- University Bootcamps
- Coding Tools
- Software Engineering
- Web Development
- Data Science
- Tech Guides
- Tech Resources
- Career Advice
- Online Learning
- Internships
- Apprenticeships
- Tech Salaries
- Associate Degree
- Bachelor's Degree
- Master's Degree
- University Admissions
- Best Schools
- Certifications
- Bootcamp Financing
- Higher Ed Financing
- Scholarships
- Financial Aid
- Best Coding Bootcamps
- Best Online Bootcamps
- Best Web Design Bootcamps
- Best Data Science Bootcamps
- Best Technology Sales Bootcamps
- Best Data Analytics Bootcamps
- Best Cybersecurity Bootcamps
- Best Digital Marketing Bootcamps
- Los Angeles
- San Francisco
- Browse All Locations
- Digital Marketing
- Machine Learning
- See All Subjects
- Bootcamps 101
- Full-Stack Development
- Career Changes
- View all Career Discussions
- Mobile App Development
- Cybersecurity
- Product Management
- UX/UI Design
- What is a Coding Bootcamp?
- Are Coding Bootcamps Worth It?
- How to Choose a Coding Bootcamp
- Best Online Coding Bootcamps and Courses
- Best Free Bootcamps and Coding Training
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Community College
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Self-Learning
- Bootcamps vs. Certifications: Compared
- What Is a Coding Bootcamp Job Guarantee?
- How to Pay for Coding Bootcamp
- Ultimate Guide to Coding Bootcamp Loans
- Best Coding Bootcamp Scholarships and Grants
- Education Stipends for Coding Bootcamps
- Get Your Coding Bootcamp Sponsored by Your Employer
- GI Bill and Coding Bootcamps
- Tech Intevriews
- Our Enterprise Solution
- Connect With Us
- Publication
- Reskill America
- Partner With Us
- Resource Center
- Bachelor’s Degree
- Master’s Degree
The Top 10 Most Interesting Social Media Research Topics
Finding social media research topics you’re interested in is tricky. Social media is a fairly new field, and the constant arrival of new technology means that it’s always evolving. So, students have a lot to think about in their search for topics.
In this article, we’re going to walk you through social media research paper topics that are timely and relevant. We’ll also show you examples of social media research topics you can get inspiration from. Lastly, we’re going to lay out some social media research questions you can ponder while formulating your topic.
Find your bootcamp match
What makes a strong social media research topic.
A strong social media research topic requires clarity of focus. This means that your topic must be timely, relevant, and coherent. This allows your research topic to be compelling and easily understandable to others.
Tips for Choosing a Social Media Research Topic
- Know the trends. Learning what social media topics are trending allows you to know the relevant issues and emergent themes in the field of social media. This also lets you know what topics are well-researched and which ones are still emerging.
- Explore knowledge gaps. Knowing what previous researchers have written prevents you from repeating knowledge that has already been explored and shared. Nobody wants to reinvent the wheel when doing research. Exploring knowledge gaps lets you increase the impact of your work and identify opportunities for further research.
- Choose something that you’re interested in. Diving deep into a topic that you’re interested in motivates you to learn more about it. The research process becomes more engaging when you know you care about your topic.
- Be specific. Knowing what you want to research and what you don’t want to research are keys to the research process. This entails narrowing down your topic to a specific area, subject, theme, or relationship. You want to know the scope and the limitations of your study.
- Check your timeframe. Limiting your topic to a specific timeframe helps in narrowing down what you need to study. For example, you can decide to study a phenomenon that has emerged in just the last three years. By doing this, you’re making sure that your research is both specific and relevant.
What’s the Difference Between a Research Topic and a Research Question?
The difference between a research topic and a research question is in the scope. Research topics tend to be broader than research questions. Research topics focus on a specific area of study within a larger field, while a research question further narrows down what you are researching. A good research question allows you to write on your topic with greater precision.
How to Create Strong Social Media Research Questions
The key to creating strong social media research questions is learning enough about your topic to know where the gaps are. This means that you have to conduct a thorough social media literature review, reading previous studies until you have a handle on what’s been said and what questions are still unanswered. Your question will emerge from this preliminary research.
Top 10 Social Media Research Paper Topics
1. a comparative review of facebook, instagram, and tiktok as primary marketing platforms for small businesses.
A lot of small businesses have flocked to various social media sites to market their products and services. Social networking sites like Facebook, Instagram, and Tiktok are platforms that deliver constant online content to their users. Comparing the marketing and advertising strategies of these online platforms will shed light on how social media helps businesses .
2. The Influence of Social Media on Mental Health
Mental health has been an important topic in social media research these past few years. Social media use and its connection to mental health has even been the subject of systematic reviews. This means that there’s a huge body of previous studies that you can look to when developing your research question.
Exploring both the positive effects and negative impacts of social media sites on mental health helps people and firms establish guidelines that help user communities. This research topic might also cover strategies for helping social media users improve their mental health.
3. The Role of Social Media in Political Campaigning
Social media is a new tool for political campaigning. Exploring what social media strategies have been conducted by politicians running for office helps in determining how social media aids in political campaigning. Studying new strategies like user-generated content for political campaigning allows you to know how voters interact with political candidates.
4. The Role of Social Media in Disinformation
The rise of fake news has coincided with the rise of social networking websites. This topic involves dissecting how social media technologies allow certain types of online content to thrive and make it easier for bad actors to spread disinformation.
5. How Social Media Can Benefit Communities
More and more social issues have been popularized through online content. Diving deep into how social media can facilitate organizational networking lets you compare the traditional and new organizing strategies being created in digital spaces. It also lets you understand how social media activity influences trends in virtual communities.
6. The Effects of Social Media Exposure on Child Development
Children also use social media sites. Some children use social networking sites under the supervision of their parents, and some do not. Social interaction, online or not, affects how children develop. Studying the psychological effects of social media exposure lets you know how social media may improve or derail the growth of children.
7. How Communication Has Evolved Through Social Media
Body language, tone of voice, and other non-verbal cues are absent in online forms of communication. In their place, emojis and other new ways to express thoughts and emotions have appeared. Learning how social media changes the way we talk to one another allows you to develop a theory of communication that takes into account the role of digital communities.
8. Social Media Platforms as Primary News Sources
A lot of people now are getting their daily dose of news and current events through social media. News networks have also established their social media presence on platforms that they can use to deliver news and current events to their audiences. Researching this topic lets you investigate the changes and innovations in information dissemination.
9. How Social Media Paves Way for Non-Traditional Advertising
Regular social media posts, advertisements, and other forms of online content aren’t the only ways businesses market to their audiences. Social media has paved the way for user-generated content and other non-traditional types of online marketing. With this topic, you can learn social media marketing strategies that have been capitalized on the social connection fostered by social networking websites.
10. Impacts of Social Media Presence on Corporate Image
More businesses increasingly build and curate their digital presence through various social networks. Knowing how a business can improve its corporate image through social media influence clarifies the role of technology in modern economics and online marketing.
Other Examples of Social Media Research Topics & Questions
Social media research topics.
- Social Media Addiction and Adolescent Mental Health
- The Rise of Social Media Influencers
- The Role of Social Media Sites as Political Organizing Tools Under Repressive Governments
- Social Media Influencers and Adolescent Mental Health
- How Social Media Is Used in Natural Disasters and Critical Events
Social Media Research Questions
- How was Facebook used as a political campaigning tool in the 2020 United States presidential election?
- What social platforms are the most effective in influencing consumer behavior?
- How does user-generated content boost the credibility of a business?
- How do different types of online content disseminated through popular networks affect the attention span of people?
- What are the most effective forms of online content and social media strategies for increasing sales conversions for small businesses?
Choosing the Right Social Media Research Topic
Choosing the right social media research topic helps you create meaningful contributions to the discipline of social media studies. Knowing the most popular topics in the field can make you an expert on social media. By reading up on previous studies, you will not only be more informed but you will also be in a position to make a positive impact on future studies.
Studying the relationship between social media and different fields produces valuable knowledge. Even if you’re only interested in exploring one social platform or a single social media event or phenomenon, your research can help people better understand how social media engagement changes the face of social relationships in the world at large.
Social Media Research Topics FAQ
Social media is a computer-based technology that allows digital communities to exchange information through user networks. Various social media networks specialize in text, photo, or video transfer. All of these are ways for people on the Internet to share information and ideas with each other.
Social media research is important because it helps you contribute to the growing body of knowledge about digital social settings. In 2021, according to DataReportal, at least 4.88 billion people around the world use the Internet . The more that people connect with each other through the social media domain, the more their quality of life changes, for better or worse.
According to Statista, the most popular social media platforms right now are Facebook, YouTube, and WhatsApp , each of which has at least two billion users. These social networks allow users to share text, picture, and video content with one another.
People use social media to connect with each other, share information, and entertain themselves. Social media sites can broadly serve all of these purposes or be focused on just one of these functions.
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication .
What's Next?
Get matched with top bootcamps
Ask a question to our community, take our careers quiz.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *


- Board Members
- Management Team
- Become a Contributor
- Volunteer Opportunities
- Code of Ethical Practices
KNOWLEDGE NETWORK
- Search Engines List
- Suggested Reading Library
- Web Directories
- Research Papers
- Industry News

- Become a Member
- Associate Membership
- Certified Membership
- Membership Application
- Corporate Application

- CIRS Certification Program
- CIRS Certification Objectives
- CIRS Certification Benefits
- CIRS Certification Exam
- Maintain Your Certification

- Upcoming Events
- Live Classes
- Classes Schedule
- Webinars Schedules

- Latest Articles
- Internet Research
- Search Techniques
- Research Methods
- Business Research
- Search Engines
- Research & Tools
- Investigative Research
- Internet Search
- Work from Home
- Internet Ethics
- Internet Privacy
MRA Guide to the Top 16 Social Media Research Questions

MRA and IMRO published this simple guide to Social Media Research (SMR) in 2010 in order to help researchers identify and find answers to the most important questions to SMR techniques.
Introduction Social networks engulf everyday life. They represent a place to share news, ideas, and information of all kinds. The connections made among people in these networks, and the resulting information shared, can have a profound effect on the thoughts, attitudes, and beliefs of individuals. Moreover, even the flow of information itself can be a powerful predictor of key business and program outcomes.
Recognizing the power of social networks, opinion researchers have increasingly begun to take advantage of social media to answer critical business questions. In doing so, the research profession has invented new tools and methods to supplement an already impressive array of techniques. The Marketing Research Association (MRA) has developed this guide in order to describe the current landscape of social media research as well as to facilitate and advance further development of the technique. Ultimately, it is the goal of the Association and its members to foster universally accepted and practiced standards and best practices for these and other research methods.
What is Social Media?
There are many definitions of social media but, at its core, social media uses Internet-based technologies that facilitate the creation and exchange of user-generated content. Social media refers to Web sites that permit people to interact with the site and with each other using simple interfaces. At the time of publication, Facebook, qq.com, Twitter and YouTube are among the most popular social media sites.
Social media refers to the information that people share on those sites, including status updates, image and video comments, responses to blogs and forums, and any other individual contributions to the online space. This information reflects naturally occurring conversations among people who may or may not personally know each other.
What is Social Media Research?
Though evolving rapidly, social media research (SMR) is the application of marketing and opinion research methods to social media data for the purposes of conducting research (e.g., usage and attitude studies, social media research tracking studies, custom research, etc.). Similar to other types of marketing research usage and attitude studies, tracking studies, research goals and objectives are developed, methodologies are prepared, and social media data are analyzed quantitatively and/or qualitatively depending on the goals of the project.
SMR is distinct from other forms of marketing research in that it uses social media as its data source as opposed to surveys, focus groups and other data collection modes and techniques. SMR can be a complementary or stand-alone analytical tool for researchers, providing them with a unique opportunity to listen and measure the opinions of potentionally vast numbers of people who communicate online, some of whom may not normally or easily be accessible through non-observational forms of research.
About the Authors MRA is grateful to the following for their contributions to this Guide to the Top 16 Social Media Research Questions: Jim Longo, PRC, Itracks, Committee Chair; Janet Savoie, PRC, Online Survey Solution; Annie Pettit, Conversition Strategies; Ray Poynter, The Future Place; Ellie Schwartz; Ed Sugar, PRC, OLC Global; Tamara Barber, Forrester Research; Tamara Kenworthy, PRC, On Point Strategies; Steven Runfeldt, Schwartz Consulting; Benjamin Smithee, Spych Market Analytics; Aaron Hill, PRC, Sawtooth Software; Susan Saurage-Altenloh, PRC; Steffen Hück, HVYE; and Patrick Glaser, MRA.
THE ROLE OF SOCIAL MEDIA RESEARCH
#1. what are the advantages and disadvantages of smr.
From a capacity standpoint, SMR provides the ability to collect and analyze information from the past as well as in real-time, as it is generated. Moreover, the richness of data available on social media networks is conducive to both qualitative designs (e.g., digital ethnographies) as well as quantitative designs, including numerical aggregation of large quantities of data.
In terms of methodological considerations, SMR utilizes an observational form of data collection. Information is collected from Web sites as posted by individuals who may not be specifically aware of the research role. As such, social media communications are thought to be free of, or less subject to, response biases that occurs in interviewer-administered, and even self-administered, forms of opinion surveys and focus groups. However, social media is inherently a public form of communication, with varying degrees of privacy which may affect some social media users’ willingness to reveal information, particularly sensitive or potentially embarrassing personal details.
From an ethical standpoint, SMR has the additional advantage of eliminating the burden that would otherwise be placed on a research participant. Social media users do not participate in “active” data collection (e.g., survey, focus group). They generate data simply by engaging in their natural online communications. However, SMR presents unique ethical considerations of which researchers must be aware (see “Ethical and Legal Issues”).
SMR offers researchers a host of benefits, a few of which include:
- Ease of adjusting research criteria throughout the study
- Potential cost savings and reduced logistical burden
- Ease of application across locations
- Access to hard-to-reach research participants
- Benchmarking (e.g., reported vs. observed opinions)
Likewise, researchers should be aware of various challenges associated with SMR. For example, researchers who are new to SMR methods will need to familiarize themselves with both the characteristics of social media users as well as specific SM sites in order to properly draw conclusions about research findings. Additional considerations include the need to learn and become proficient with:
- SM tools and techniques including sentiment and content analysis
- Indicators of SMR validity and reliability at each stage of the process
- Relevant types of biases, particularly those arising from unique SMR tools
- The types of brands and categories that are more likely to be successful carrying out SMR, e.g., due to volume of data or consumer importance
#2. What data sources are typically used in SMR?
Millions of Web sites (small and large) currently facilitate the practice of social media research. However, online sites, which currently facilitate social media communications come and go, and change very rapidly. Researchers involved in SMR need to stay abreast of changes in social media communication patterns and trends, including the rise of mobile access, and popular SM vehicles. Current examples of SM Web sites that generate data suitable for SMR include:
- Social Networking Sites:Social News: e.g., Digg, Reddit, Mashable, Technorati Facebook: Search, Community Pages, Fan Pages, Groups, Chat, Facebook-based Apps
Twitter: Location-based Application, Real-time Search, Advanced Search (search.twitter.com)
LinkedIn: Search, Groups, Q&A
- Photo/Video Sharing: e.g., YouTube, Flickr
- Online Communities: Industry, Topic-related, Branded or Unbranded
- Blogs: e.g., Blogger, Posterous, Wordpress
- Forums: Industry or Topic-related
- Questions and Answers: e.g., Yahoo Answers, Linkedin Answers, Yedda
- Commenting: e.g., Disqus, Backtype
- Traditional News: e.g., CNN, BusinessWeek
#3. How does SMR interact with other forms of traditional and non-traditional research, including online, offline, in-person, and qualitative and quantitative?
SMR can effectively stand on its own, but may also be integrated with traditional research methods to create a holistic research solution. In fact, SMR may sometimes springboard or support other forms of traditional research. Examples of SMR integration with other research methods include:
- Observing the flow of conversation in real time, thus prompting the most effective methodology for further research
- Accessing user supplied media such as photos and video
- Measuring trending topics for further “traditional” research
- Assisting in the preparation of discussion guides or surveys
- Identifying key influencers in an industry or on a topic
- Reaching a segment of the population that may not otherwise be reachable
- Comparing community-based insights to natural observational social media insights
- Establishing trust between researcher and participant, potentially for further recruitment into another form of research
- Exploring, and discovering “unknowns” via observations
#4. How reliable are SMR results?
Validity refers to the degree to which results reflect truth or reality while reliability reflects the degree to which results can be replicated if someone else were to conduct a similar study. Because research suppliers have different methods, standards of quality, and processing rules, research consumers must conduct their own validity and reliability analysis of any potential supplier to ensure the quality of work is sufficient. As with all types of marketing research, the validity and reliability of social media research varies greatly:
What is the validity and reliability of the sentiment and/or content analysis processes? If manual coders are used, reliability might be lower. If automated coders are used, validity might be lower.
- Given that sentiment differs by Web site (e.g., Twitter is more negative while blogs are more positive), what is the range of social media venues that are measured and what percentage of the Internet population do they represent? Do any of the sites overwhelm the data collection strategy in a proportion that does not reflect the Internet space? Does the vendor know how and why to sample and weight data?
- To what extent is the intended target group reflected by the social media venues being used?
- Is the intention to measure and generalize to the general Internet population or to a particular segment of the Internet?
- How is geographic and demographic information being measured in order to assess the validity of generalizing outside of the sample?
- What timeframe is appropriate for the research objectives? Though small samples may be acceptable for long-term research, shorter time frames must use larger sample sizes.
#5. Within businesses and organizations, how will SMR activities be tracked and aggregated, and whose responsibility is it to handle each of those functions?
Social media research may be executed in multiple ways. For example, numerous departments within a single company may be involved in SMR, including internal research departments, and cross-functional teams from marketing, customer relationship management, public relations, public affairs, and other departments. SMR may also be outsourced to vendors who may or may not specialize in research. Regardless, the skill set of the user must be appropriate for the function.
#6. What additional knowledge, skills, and abilities will a corporate researcher need to learn in order to improve their level of competency with SMR?
SMR may involve several different methods and analytical approaches. As such, corporate researchers may find it most advantageous to learn a wide breadth of relevant techniques while continually honing their skills and knowledge in the areas that are most relevant to their organization. Commonly used techniques include both sentiment analysis and content analysis. Additionally, researchers will need to learn about, and become comfortable with, important explanatory variables beyond traditional “respondent” demographics, such as how different types of Web sites (e.g., blogs, forums, media, etc.) generate and facilitate different types of data (e.g., whether data is more positive versus negative, descriptive versus condensed, etc.).
#7. Are the participants aware that their usergenerated content is under observation?
Research contributors have demonstrated the occasional tendency to provide sub-optimal information when they are aware that others are studying or observing them. Oftentimes, this is attributable to concerns over the privacy of sensitive information or feelings of being compelled to give a socially-desirable response to a question. In SMR, though it commonly is understood that conversations are generally public and open to viewing by almost anyone, the individual under observation may or may not be aware of the presence of a researcher.
At the same time, participation in the social media space offers varying degrees of privacy. Users may participate for personal and/or professional reasons and they may or not seek relationships with other users. Researchers should be aware of the potential and likelihood for “social observational bias” and the effect it will have on the type, candor and direction of the user’s comments.
Ethical and Legal Issues
#8. how are sources cited in research reports and on research web portals are the citations different based on the source, e.g., twitter, blogger, forums.
As in traditional forms of research, it is important to protect the privacy of contributors. As such, without prior express consent, data transmitted from vendor to client should not include direct references or citations to individuals that would reveal their identity.
However, sources may be recorded for validation purposes as well as for potential data quality checks. Any data or reporting intended for transfer to an outside entity should be purged of personally identifiable information (PII) prior to changing-hands. This includes IP addresses, usernames, user id numbers, user photos, e-mail addresses, and other types of commonly available online data.
Where detailed information must be shared for the purposes of data quality or validation, the data should include source citations using the current link of the information (e.g., http:// twitter.com/xxxx/xxxx/). Notably, links should be expected to expire or become “broken” overtime. Researchers should plan to record any pertinent administrative or relevant source data (e.g., date/time, source identifier, query details, etc.) to be used in validation at the time of data collection.
#9. What are the controversies and legal issues regarding the rights of the people whose data is being used?
Social media is a relatively new form of communication and individuals from every stakeholder group, including the public, researchers and governments, are participating in an on-going conversation about the nature of its privacy and ethics. For this reason, it’s critical for researchers to understand that they have a responsibility to respect social media user’s privacy and that the definition and expectations for social media user’s privacy can and will change over time. Some brief areas of consideration are described below.
Privacy: Individuals and their social media privacy expectations should be respected. If an individual has posted information on a public Web site under a public “privacy” setting, they may be considered to have a very low or no expectation of privacy for the information they reveal. Even so, researchers who collect and analyze this information should take care to protect it from becoming identifiable to an individual.
Conversations should not be copied verbatim into reports as those direct quotes can be searched and identities discovered. A small number of relevant conversations can be summarized, without losing their flavor, in reports. Moreover, full quotations can be used with permission.
Interacting with individuals: Clients must never use information collected during or for social media research for the purpose of direct marketing or otherwise influencing the opinions and behaviors of the data subject. Marketing may only occur in places like branded and client communities where contributors would naturally expect those types of conversations to take place.
Combining data from multiple sources where privacy policies differ: In general, the policy provisions that tend to favor the rights and needs of the contributors should be given weight. Best practices call for researchers to respect the coded crawling terms of every Web site they visit. Where Web sites are coded to indicate that crawling is not permitted, those Web sites should not be crawled even if it is technically possible. Researchers must not join Web sites under the pretense of being a member so that they then have access to crawl a Web site that prohibits such crawling otherwise – this condition holds for both automated and manual crawling. Where researchers do join groups, they must immediately make it explicit that they are there for the purposes of marketing research. Notably, issues concerning access to data sources are paramount to the conduct of social media research and can be expected to be a major focus of the opinion research industry moving forward, both in terms of how to ethically gain access to the widest net of sources as well as appropriate ways to handle and adjust for cases where this is not possible.
SM Research Processes & Providers
#10. what is the level of expertise and industry qualifications of social media researchers and/or smr companies.
Anyone selecting a social media research vendor must be aware that the technique is relatively new. They must be careful to select a research partner with the appropriate level of expertise and skill in the practice of SMR. Some relevant questions to ask include:
- Is the company primarily an IT or social media company that expanded into research, or a research company that expanded into social media? While IT and social media companies may have expertise in social media, crawling and data collection techniques, research companies have expertise in data analysis techniques.
- Does the company focus on research exclusively or do they maintain other functions as well? For example, companies that conduct SMR may specialize in buzz monitoring, customer relationship management, public relations, research, or some other social media function.
- Does the company specialize in qualitative methods, quantitative methods, or a combination of both?
- Is the provider aware of traditional research practices such as sampling and weighting and, if so, how and when do they apply those practices?
- For the practice of ethics and standards of quality, does the provider classify themselves as a researcher or as some other profession?
#11. What are the standard data and/or research outputs?
Since SMR is relatively new, industry standards for outputs have not yet been developed. It is important to understand the vendor’s policies and capacities for standard and custom reporting. Relevant questions include:
- Does the company offer a full-service model of data collection, analysis and presentation or do they offer a self-service tool such as a portal?
- In cases where the vendor offers full-service reporting and presentation, what substantive outputs may be expected? What technical explanation and reporting may be expected (e.g., a technical appendix)?
- Are the SMR analyses incorporated with traditional types of marketing research and does the company have expertise doing so?
- Does the provider offer standardized or customized tools?
- How often are outputs updated and/or delivered?
#12. What is the process for gathering data?
Like other forms of opinion research, a wide variety of approaches exist for the implementation of SMR. It is important to understand the company policies undertaken. Relevant questions include:
- Does the company gather its own data or is a data collection vendor used?
- How many Web sites are crawled and how are those Web sites selected?
- Does the company seek out permission-based relationships with the sites they crawl?
- Does the company honor the electronic privacy notifications of individual Web sites?
#13. What data quality processes are implemented in each stage of the SMR?
What quality and validation protocols have been adopted and implemented to safeguard the quality of the research at each stage of the process? Are there validation processes in place for initial data collection, scoring and coding, etc.? Does the organization collect and retain information at the initial stages for validation purposes while removing/anonymizing data for reporting purposes?
#14. Does the company provide sentiment scoring?
Sentiment scoring is a process of assigning a positive or negative emotion to a conversation. Some vendors may provide strictly positive or negative emotions, while others may assign a continuum ranging from positive to neutral, to negative. If the vendor provides sentiment scoring, is the process an internal proprietary method, a third party purchased product, or some combination of the two? How is the sentiment scored (e.g., dictionary, bayesian, manually)?
#15. If sentiment scoring is provided, what is the process for validating results?
Simple and commonly-used systems of sentiment validation may prove to be inadequate. More rigorous approaches should be used, specifically blinded methods. For example:
For automated systems, researchers should receive a list of uncoded conversations and then code them manually. The manual codes should then be matched back and compared to the automated codes to derive a percentage match (i.e., validation coefficient).
For manual systems, two unique raters should independently code conversations. A validation coefficient may be derived from a comparison of the two outputs.
The above processes are two relatively simple examples of validation systems. More complicated calculations are available, but their use should be weighed according to the capacity of stakeholders to understand the meaning and method of the technique.
Language constantly changes and evolves due to new and lapsed slang, terminology, and speech patterns. As such, simple systems of sentiment validation may prove to be inadequate. When conducting SMR, rigorous and constantly monitored approaches to sentiment analysis are most appropriate.
#16. What, if any, methods are used for determining the geography associated with the data?
Demographic and geographic information can often be an important and meaningful element for research and validation purposes. When considering SMR, what geographic information is available and how precise is the information (e.g., city or town, region, country, unknown)? What types of demographic data are available (e.g., age, gender, income, education)?
Researchers must take care to specify the methodology and sample size associated with the information. Inferred methods (based on Web site sources or language) may be associated with large sample sizes but have low validity. On the other hand, precise information is currently only available for an extremely tiny percentage of conversations and therefore often has insufficient generalizability.
The “Top 16 Questions” presented in this guide represent the core matters of importance to the research field with respect to social media research. They include issues of reliability, execution, interaction with other kinds of research, ethics and legal compliance, data quality, process, and outputs.
Importantly, the 16 questions in this document do not stand as the only ones the opinion research profession needs to address, nor do they take the place of standards of practice. Instead, they provide a starting point for experts and professionals to debate and discuss development toward this goal. As in any profession, a reasonable consensus should be reached in order to validly define and represent an industry standard of best practice. It is the goal of the Marketing Research Association that this document be widely distributed and contribute as such.
Latest from Anthony Frank
- The Deep Web: The forbidden fruit of the cyber world
- 90% of Gmail Users Not Properly Protecting Accounts
- Using the internet makes people more likely to vote Labour, research shows
Live Classes Schedule
World's leading professional association of Internet Research Specialists - We deliver Knowledge, Education, Training, and Certification in the field of Professional Online Research. The AOFIRS is considered a major contributor in improving Web Search Skills and recognizes Online Research work as a full-time occupation for those that use the Internet as their primary source of information.
Get Exclusive Research Tips in Your Inbox
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Advertising Opportunities
- Knowledge Network
Social media research: Step-by-step tutorial with examples
- Introduction: What is social media research?
- Step 1: Develop a research design
- Step 2: Collect & import your social media data
- Step 3: Data preparation
Step 4: Get an overview
- Step 5: Categorize your data
- Step 6: Aggregate & present your results
Further learning materials
Friday, January 5, 2024

How to conduct social media research with MAXQDA?
Social Media has drastically changed the way we communicate. Nowadays it’s a lot easier for an individual to communicate with a large audience or with strangers living on the other side of the planet, and to find and communicate with others researching similar topics. Companies, organizations, and political parties can target a specific group of people for their campaign and receive immediate feedback. So, it’s not a surprise that online communication has become more prevalent, which in turn has increased the significance of social media platforms.
Researchers and marketers alike benefit from the wealth of data available on social media platforms, gaining insights into the public’s opinions, communication patterns, and more. Social media research describes the process of collecting and analyzing social media data, such as posts, comments, and likes in order to understand communication patterns, public opinions, and trends.
Who conducts social media research?
Compared to other data collection instruments, such as focus group discussions, collecting social media data is less resource-intensive as the data is easily accessible. However, researchers are confronted with extensive data when performing social media research. Depending on the topic thousands and thousands of posts and comments exist. Consequently, social media researchers need QDA software that is well-equipped for challenges like these, such as MAXQDA. MAXQDA can facilitate your social media research with its numerous data organization and analysis tools. MAXQDA’s auto-coding and sentiment analysis are particularly useful tools, allowing you to explore many posts without reading each one individually. Furthermore, AI Assist, MAXQDA’s AI-based features, are well-suited to handle big data. In the present guide we aim to explain how you can perform social media research with MAXQDA.

Step 1: Develop a research design for social media research
As for any other research project, we advise you to develop a research design before starting your social media research. A research design serves as a structured plan outlining how a researcher intends to answer a specific research question. Determine the specific social media data you wish to analyze and define the precise methodology for your analysis. Among other considerations, ask yourself which social media platform(s) you want to consider, whether there is a time frame of interest; and if you plan to exclusively focus on social media posts containing particular hashtags or keywords. You must address these questions to develop a well-designed study that ensures reliable and valid results. We recommend reading our Research Design guide if you need clarification on what a research design entails.
Please note that the order of the steps presented here is flexible and depends on your research design and research question.
Step 2: Collect & import your social media data
With MAXQDA, you have several options for importing your social media data. On the one side, MAXQDA provides specialized import tools for YouTube comments and specialized analysis tools for YouTube data and X (formerly known as Twitter) data. Suppose you want to import and analyze data from a different social media platform. Then, you can either use MAXQDA’s WebCollector to collect and import entire webpages into MAXQDA or another social media data collection service, saving the data in a MAXQDA-compatible format, like an Excel file. There are several online tools for exporting social media data.
MAXQDA’s WebCollector
You can use MAXQDA’s WebCollector – a free Chrome Browser extension – to export entire websites in a format that can be imported into MAXQDA. The free MAXQDA WebCollector is availale on the Chrome WebStore.
Get the MAXQDA WebCollector
After installing the extension, export the webpage from your social media platform of interest. In the case of X (formerly known as Twitter) you have two options. You can either export only top-level posts or a specific top-level post, including all its replies. Search for a hashtag and export the search results, i.e., all posts containing this hashtag, by opening the WebCollector extension and clicking “Collect.” If you want, you can add notes in the Document Memo section, such as the time frame or other parameters of your search. Upon import into MAXQDA, these notes will be imported as a Document Memo.
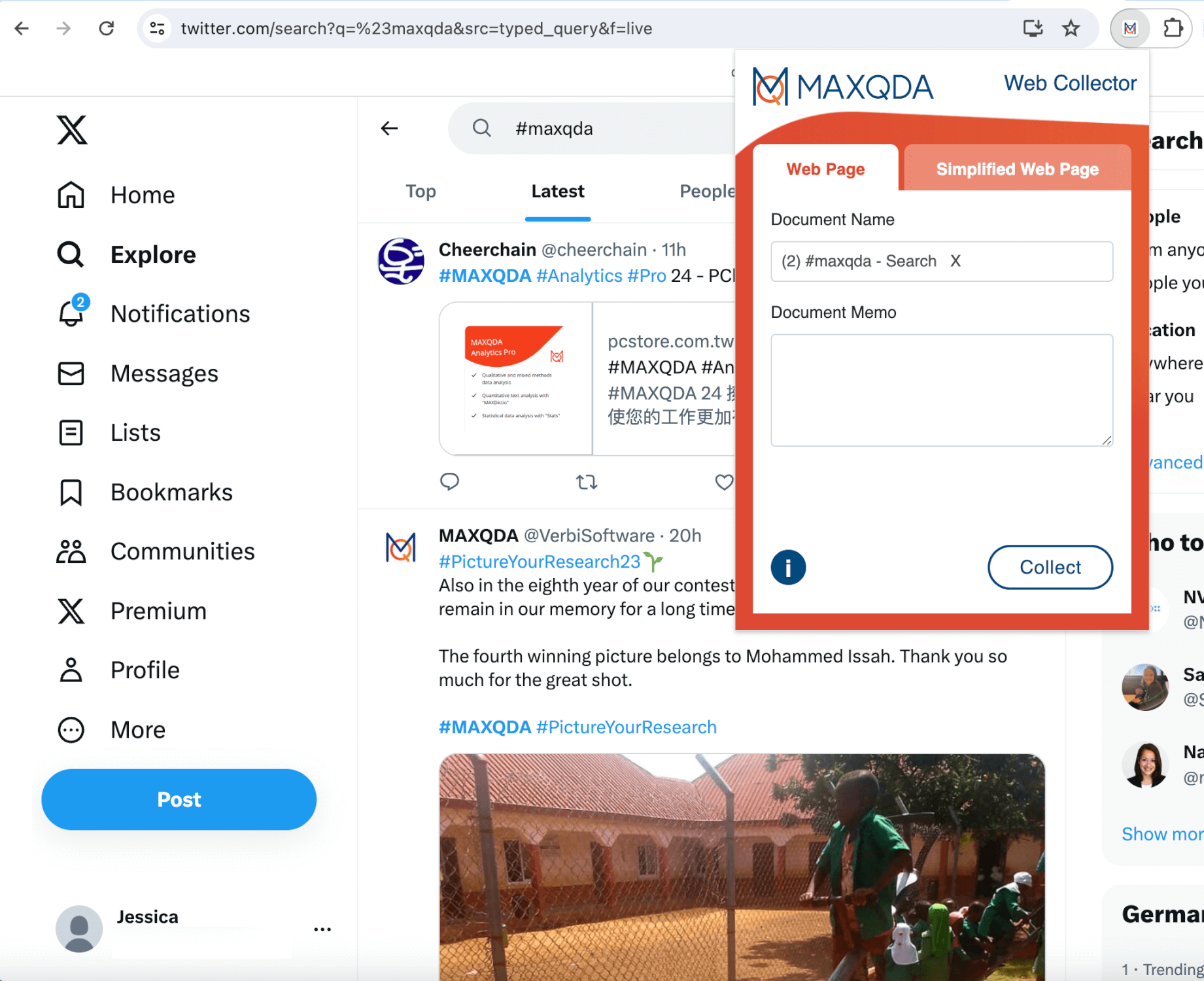
Use the MAXQDA WebCollector to export social media data
In the case you are specifically interested in specific posts, e.g., posts from a certain account or posts with a lot of replies, click on the post so that the original post and all comments are displayed. Now, export the website with MAXQDA’s WebCollector to compile the original posts, including all replies.
Step 3: Social media research data preparation
Before starting the actual analysis, you might want to clean and organize your data in a meaningful way. For example, you could remove irrelevant and duplicate posts. You could also organize your data in document groups, e.g., based on the social media platform, a time range, a hashtag, or whatever category is important to your social media research.
Organize your data in Document groups
You may add variables to the imported social media data depending on your research design. For example, when investigating social media trends over time, it can be handy for further analysis to add variables such as the date and timing of the post. To do so, simply go to the “Variables” tab and click “List of Document Variables.” By clicking “New variable,” you can add new variables, specify their type, and define missing values.
Add document variables to improve your social media research
Depending on your research approach, you might benefit from an overview of the data before creating and applying codes, e.g., when following an inductive approach. In other cases, you might already have codes in mind and use them prior to summarizing the data, e.g., in deductive approaches.
When following an inductive approach, you might want to get a basic understanding of the collected social media data and base your codes on the actual content. MAXQDA offers numerous tools, allowing you to get a quick overview. Especially useful when working with big data, such as in social media research, are MAXQDA’s auto-coding and AI-based tools.
Summarize social media data with AI Assist
We acknowledge that AI can assist researchers in qualitative data analysis as well as in other areas of life. Therefore, we developed the AI Assist add-on – your virtual research assistant. AI Assist features several tools that can facilitate your social media research. AI Assist’s Summarize Document function is handy for a quick content overview. This feature creates a summary of entire documents, e.g., of a post and its replies, which it stores in Document Memos. To let AI Assist summarize your document, right-click on it in the Documents window, and choose AI Assist > Summarize Document. You can edit and refine the summary within the Document Memo. These summaries might help you get an idea about the key points discussed and develop codes accordingly.
With AI-generated summaries you can speed up your social media research
Automatically analyze the public’s sentiment
Often, people performing social media research are not interested in every single opinion of every single individual but in the general sentiment towards a topic, politician, issue, or product. With MAXQDA, you can perform a sentiment analysis in no time. To perform a sentiment analysis, open the Smart Coding Tool in the Codes tab. Since the Smart Coding tool works on the level of coded segments, you need to dummy-code your data prior to the sentiment analysis. When importing YouTube comments, comments and replies are automatically coded. However, when importing data through other means, such as via the WebCollector, you may want to manually create the codes ‘post’ and ‘reply’ to quickly code your data. Subsequently, you can perform automatic sentiment analysis by clicking on the button “Analyze Sentiments.” To autocode your social media data with the respective sentiment, click “Autocode Segments with Sentiment.” Then, MAXQDA creates the code ‘Sentiment’ with the identified sentiments as subcodes. By looking at the code frequencies you get a first impression of the general public sentiment.
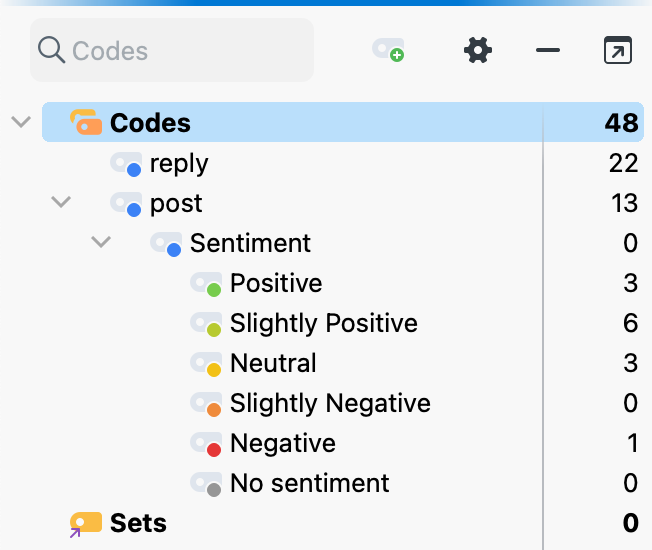
Autocode the sentiment of your social media data
Subsequently, you can use MAXQDA’s retrieval function to, e.g., focus your social media research on negative posts. To do so, simply activate the documents of interest and the code ‘Sentiment’ > ‘Negative’. All text segments coded with this code will be displayed in the Retrieved Segments window. If you plan to create subcodes, for example to divide the negative sentiment into reasons why people dislike your product, you can again use the Smart Coding tool. Select the code ‘Negative’ from the Code tree on the left site and MAXQDA will display only the segments with a negative sentiment to which you can apply additional codes.
Summarize coded segments with AI Assist
Rather than going through the ‘Negative’ posts individually, you can again use the power of artificial intelligence to create a summary of the coded segments. To do so, right-click the code ‘Negative’ in the Codes window and select AI Assist > Summarize coded segments. Similarly, to the Summarize Document feature, AI Assist will add the summary in a memo.
Step 5: Categorize your social media research data
In many qualitative research projects, including social media research, coding/categorizing your data is an important step. When working inductively, the AI-generated summaries might provide initial ideas for codes. When working deductively, you probably already have codes in mind. With MAXQDA you can easily create codes, assign code colors, and define rules for coding in the New Code window regardless of your approach. Furthermore, you can organize your codes hierarchically. But there is more – MAXQDA allows you to create emoticodes which might come handy when analyzing social media data. For more information on various coding methods, you can refer to:
Learn more about coding with MAXQDA
Autocode your social media data
Especially useful for big data is MAXQDA’s Text Search & Autocode feature, which is located in the Analysis tab. This feature allows you to search for keywords and automatically code them. You can also use logical operators, such as OR, to search for a list of keywords simultaneously e.g., to find all synonyms of a word with just one search. If you are interested in certain concepts, you can create dictionaries of keywords defining the concept and search for multiple concepts at once (search for the whole dictionary). To do so, you first need to create a dictionary. Therefore, go to the MAXDictio tab and select Dictionaries.
Search & autocode important keywords for your social media research
Generate subcode suggestions with AI Assist
In the coding of qualitative data, researchers often start with broad codes, intending to refine them in a later step of the social media research. Alongside the Smart Coding Tool, which is ideal for code refinement, as explained earlier, AI Assist’s “Suggest Subcodes” is another valuable tool. You can use this feature to to get subcode suggestions. Simply, right-click on a code and select AI Assist > Subcode Suggestions.
Step 6: Aggregate & present your results
A crucial step involves consolidating your social media research results into a format that is easily understandable for others. For example, charts and visualisations can aggregate huge amount of data in an easily comprehensible graph that answers your research question. Of course, MAXQDA has integrated visualisation and charting tools. Some tools that might be especially useful for presenting social media data are presented in the following sections.
Word Cloud for visualizing the most frequent words
MAXQDA’s World Cloud, which can also be used with data that hasn’t been coded, is one of the most appropriate visualization tools in social media research. Select the document(s) that serve as the basis for your word cloud and generate a visual representation of the most recurring words. To exclude frequent, yet non-informative words such as ‘the’ or ‘a,’ you can apply a stop word list to the data, effectively filtering out these ubiquitous terms. We offer several Stop Word Lists in several languages on our website, so you don’t have to create one yourself.
Get Stop Word Lists
Word Cloud displaying the most frequent words of YouTube comments
Visualize trends
If your social media research analyzes a topic over time, the Trends function might also interest you. Currently, MAXQDA offers Word Trends, Code Trends, and Dictionary Categories Trends. To explore how code or word frequencies change across time, you should store your social media data in distinct documents – one document per time range. While Word Trends can be used even when the data is not coded, Code Trends requires coded data. No matter whether you are using Code or Word trends, select Trends for multiple documents. Then, select the documents (and codes) of interest and MAXQDA will visualize them. For example, you can use the Code Trends tool on auto-generated sentiment codes to investigate how sentiments towards a topic change over time.
Aside from analyzing trends across time, you can also use MAXQDA’s Trends tool to compare reactions, e.g., between different social media plattforms. To do this, you need to organize your data as follows: create a separate document for each social media plattform containing all posts of interest. Next, choose your preferred Trends tool and again choose trends for multiple documents. In case you are interested in how a discussion evolves in a comment section, given that the data is stored in one document, you can opt for the single document trends feature. MAXQDA splits the document in 10 segments, allowing you to see how word/code frequencies look across them.
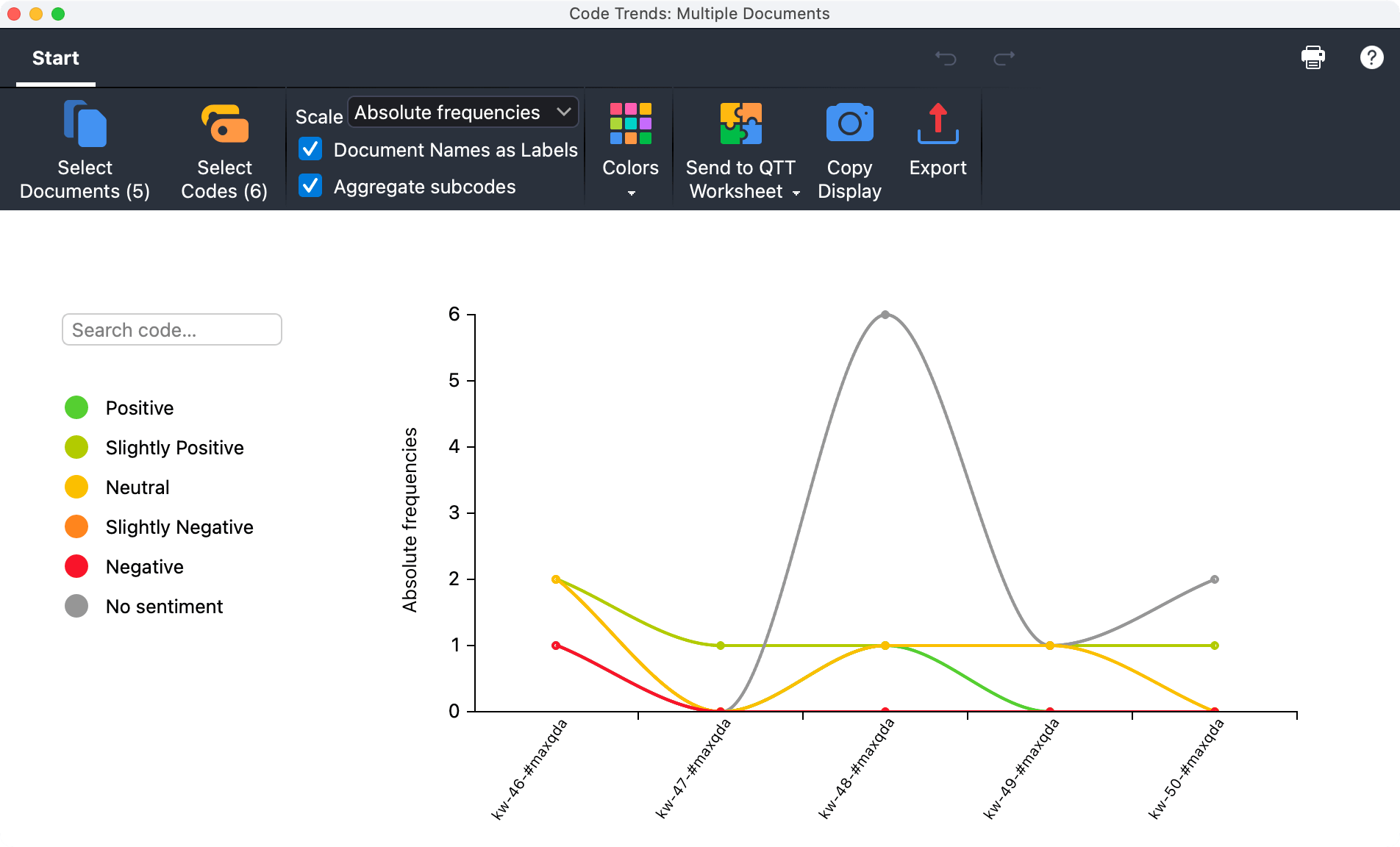
Visualizing sentiment trends for #maxqda across weeks
Write your report with QTT
Questions-Themes-Theories (QTT) provides an innovative workspace for gathering important visualizations, notes, segments, and other analytical results. It is an excellent tool for organizing your thoughts and crafting your social media research report. To get started, create a dedicated worksheet for your topics and research questions, and populate it with pertinent analysis elements extracted from other MAXQDA functions. For example, you can incorporate your Trends visualization to a QTT worksheet by clicking on the button, as shown in the screenshot below. Exploratory coded segments related to a set of social media posts can be added to the QTT worksheet via the context menu. For each imported element you can add insights. Furthermore, you have the option to add your conclusions and theories, as well as your research design. Subsequently, you can view all analysis elements and insights to write your final conclusion. The new Questions-Themes-Theories tool is designed to assist you finalize your social media research. With just one click, you can export your worksheet and use it as a starting point for your social media research report.
Add a visualization to a QTT worksheet
We offer a variety of complimentary learning materials to help you get started with your social media research. Check out the recording of a spotlight session on analyzing social media data with MAXQDA which was held at the MAXDAYS conference in 2023. In addition, the free book “The Practice of Qualitative Data Analysis,” provides ten case studies with brief real-world examples, demonstrating MAXQDA’s practical applications.
Spotlight Session: Analyzing Social Media Data with MAXQDA
The Practice of Qualitative Data Analysis

MAXQDA Newsletter
Our research and analysis tips, straight to your inbox.
- By submitting the form I accept the Privacy Policy.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Office of the Surgeon General (OSG). Social Media and Youth Mental Health: The U.S. Surgeon General’s Advisory [Internet]. Washington (DC): US Department of Health and Human Services; 2023.

Social Media and Youth Mental Health: The U.S. Surgeon General’s Advisory [Internet].
Critical questions remain unanswered.
Nearly every teenager in America uses social media, and yet we do not have enough evidence to conclude that it is sufficiently safe for them. Our children have become unknowing participants in a decades-long experiment. It is critical that independent researchers and technology companies work together to rapidly advance our understanding of the impact of social media on children and adolescents. This section describes the known gaps and proposes additional areas for research that warrant urgent consideration.
Known Evidence Gaps
- How do in-person vs. digital social interactions differ in terms of the impact on health, and what are the unique contributions of social media behavior to social connectedness, social isolation, and mental health symptoms?
How does social comparison affect one’s sense of life satisfaction and in-person relationships?
How does the use of social media, including specific designs and features, relate to dopamine pathways involved in motivation, reward, and addiction?
- What type of content, and at what frequency and intensity, generates the most harm? Through which modes of social media access (e.g., smartphone, computer) and design features? For which users and why?
- What are the beneficial effects of social media? For whom are the benefits greatest? In what ways, and under what circumstances?
- What individual-, community-, and societal-level factors may protect youth from the negative effects of social media?
- What types of strategies and approaches are effective in protecting the mental health and well-being of children and adolescents on social media (e.g., programs, policies, design features, interventions, norms)?
- How does social media use interact with a person’s developmental stage for measuring risk of mental health impact?
It is critical that independent researchers and technology companies work together to rapidly advance our understanding of the impact of social media on children and adolescents.
Unless otherwise noted in the text, all material appearing in this work is in the public domain and may be reproduced without permission. Citation of the source is appreciated.
- Cite this Page Office of the Surgeon General (OSG). Social Media and Youth Mental Health: The U.S. Surgeon General’s Advisory [Internet]. Washington (DC): US Department of Health and Human Services; 2023. Critical Questions Remain Unanswered.
- PDF version of this title (1005K)
Other titles in this collection
- Publications and Reports of the Surgeon General
Recent Activity
- Critical Questions Remain Unanswered - Social Media and Youth Mental Health Critical Questions Remain Unanswered - Social Media and Youth Mental Health
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
Media Studies
Developing a research question.
- Finding Sources
- Evaluating Sources
- Writing Tips
- Citing Sources
- News & Newspapers
- Television & Ratings Data
- Accessing Our Collections
- Foundational Texts
- Reference Sources
- Primary Sources & Archival Collections
- Journals and Newspapers
- Image, Stock Photo, and Audiovisual Resources
- Open Access & Additional Resources
- Resources & Services for Scholars
- Instructional Support
- MSCH F306 Writing Media Criticism
- MSCH J450 History of Journalism
- Campus & Community Resources
- Monthly Community Celebrations
- Collection & Subject Spotlights
- Representation in Media
- Other Features
- Indigenous Heritage & History Month
Ask a Librarian (Chat)
Selecting and narrowing a topic, choose an area of interest to explore. .
For you to successfully finish a research project, it is important to choose a research topic that is relevant to your field of study and piques your curiosity. The flip side is that curiosity can take you down long and winding paths, so you also need to consider scope in how to effectively cover the topic in the space that you have available. If there's an idea or concept you've recently learned that's stuck with you, that might be a good place to start !
Gather background information.
You may not know right away what your research question is - that's okay! Start out with a broad topic, and see what information is out there through cursory background research. This will help you explore possibilities and narrow your topic to something manageable. Do a few quick searches in OneSearch@IU or in other relevant sources. See what other researchers have already written to help narrow your focus.
Narrow your topic.
Once you have a sense of how other researchers are talking about the topics you’re interested, narrow down your topic by asking the 5 Ws
- Who – population or group (e.g., working class, college students, Native Americans)
- What – discipline or focus (e.g., anthropological or art history)
- Where – geographic location (e.g., United States; universities; small towns; Standing Rock)
- When – time period or era (17 th century; contemporary; 2017)
- Why – why is the topic important? (to the class, to the field, or to you)
Broad topic: Native American representations in museums
Narrowed topic: Museum efforts to adhere to NAGPRA
Adapted from: University of Michigan. (2023 Finding and Exploring your topic. Retrieved from https://guides.lib.umich.edu/c.php?g=283095&p=1886086
From Laurier Library.
From Topic to Research Question
So, you have done some background research and narrowed down your topic. Now what? Start to turn that topic into a series of questions that you will attempt to answer the course of your research. Keep in mind that you will probably end up changing and adjusting the question(s) you have as you gather more information and synthesize it in your writing. However, having a clear line of inquiry can help you maintain a sense of your direction, which will then in turn help you evaluate sources and identify relevant information throughout your research process.
Exploratory questions.
These are the questions that comes from a genuine curiosity about your topic. When narrowing down your topic, you got a good sense of the Who, What, When, and Where of things. Now it’s time to consider
- Asking open-ended “how” and “why” questions about your general topic, which can lead you to better explanations about a phenomenon or concept
- Consider the “so what?” of your topic. Why does this topic matter to you? Why should it matter to others? What are the implications of the information you’re discovering through the search process to the Who and the What of your topic?
Evaluate your research question.
Use the following to determine if any of the questions you generated would be appropriate and workable for your assignment.
- Is your question clear ? Do you have a specific aspect of your general topic that you are going to explore further? Will the reader of your research be able to keep it in mind?
- Is your question focused? Will you be able to cover the topic adequately in the space available? Are you able to concisely ask the question?
- Is your question and arguable ? If it can be answered with a simple Yes or No, then dig deeper. Once you get to “it depends on X, Y, and Z” then you might be getting on the right track.
Hypothesize.
Once you have developed your research question, consider how you will attempt to answer or address it.
- What connections can you make between the research you’ve read and your research question? Why do those connections matter?
- What other kinds of sources will you need in order to support your argument?
- If someone refutes the answer to your research question, what is your argument to back up your conclusion?
- How might others challenge your argument? Why do those challenges ultimately not hold water?
Adapted from: George Mason University Writing Center. (2018). How to write a research question. Retrieved from https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/writing-resources/research-based-writing/how-to-write-a-research-question
Sample research questions.
A good research question is clear, focused, and has an appropriate level of complexity. Developing a strong question is a process, so you will likely refine your question as you continue to research and to develop your ideas.
Unclear : Why are social networking sites harmful?
Clear: How are online users experiencing or addressing privacy issues on such social networking sites as Facebook and TikTok?
Unfocused: What is the effect on the environment from global warming?
Focused: How is glacial melting affecting penguins in Antarctica?
Simple vs Complex
Too simple: How are doctors addressing diabetes in the U.S.?
Appropriately Complex: What are common traits of those suffering from diabetes in America, and how can these commonalities be used to aid the medical community in prevention of the disease?
- Last Updated: Feb 19, 2024 9:49 AM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.indiana.edu/mediastudies
Social media
- Instagram for Herman B Wells Library
- Facebook for IU Libraries
Additional resources
Featured databases.
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) OneSearch@IU
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Academic Search (EBSCO)
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) ERIC (EBSCO)
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Nexis Uni
- Resource available without restriction HathiTrust Digital Library
- Databases A-Z
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Google Scholar
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) JSTOR
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Web of Science
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Scopus
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) WorldCat
IU Libraries
- Diversity Resources
- About IU Libraries
- Alumni & Friends
- Departments & Staff
- Jobs & Libraries HR
- Intranet (Staff)
- IUL site admin

- Services Paper editing services Paper proofreading Business papers Philosophy papers Write my paper Term papers for sale Term paper help Academic term papers Buy research papers College writing services Paper writing help Student papers Original term papers Research paper help Nursing papers for sale Psychology papers Economics papers Medical papers Blog

193 Great Social Media Research Topics For Successful Paper

Social media sites are those that facilitate the sharing of ideas, thoughts, and information through virtual networks or communities. Social media is internet-based and gives users effective electronic communication of content. On social media sites, you can send messages, images, documents, videos, or other forms of data. The various large social media networks include; Facebook, YouTube, TikTok, Instagram, Snapchat, and Twitter.
Characteristics of a Good Social Media Research Paper
To write a good social media research paper, follow this procedure:
- Check The Instructions: Check the instructions on what is required. You also need to consult the professor to know what is expected. This will help you to choose the right topic that will lead to a proper research paper. You can check whether the essay needs to be persuasive, engaging, or argumentative.
- Choose A Topic: Choose a topic that is not too complex. Additionally, it should be something that you are passionate about. Browse various sample papers online to know the best topic to use.
- Research Well: Once you choose a topic and seek approval from your professor, you now need to do proper research. You can use scholarly articles, documentaries, films, and other data to find the relevant needed information.
- Draft It Out: Write out the key points and know how the introduction body and conclusion will be. If doing a project, thesis, or dissertation, write a great abstract. The draft should contain all the relevant information. Remember to write titles that correspond to the main points.
- Write The Final Paper: Once you are done, write the final paper and proofread to ensure that everything you’ve written is as it should be.
Social Media Research Topics
Social media is a great place to interact with friends, colleagues, family, bloggers, and even celebrities. They make the world seem a bit smaller with the amount of information you can get from it.
- The factors that lead to the growth of social media sites.
- Evaluate how social media fuels rebellion among teenagers.
- How are social network websites used for political affairs?
- The best ways to deal with children’s addiction in social sites.
- How can social media sites be used during certain country disasters?
- Evaluate how data protection is done on social media sites.
- In your own opinion, do you think there should be an age restriction on the use of social networks?
- Evaluate the various reasons that companies are opting to advertise more on Facebook.
- The major factors that lead to the popularity of social media sites like Instagram.
- Evaluate the growth of social media in the past 10 years – what has changed?
- Is there a relationship between social media and mental problems?
- Discuss how the major changes that have occurred in communication are due to social media sites.
- Evaluate the evolution of Twitter from its inception to date.
- The best tactics to build a strong social media presence.
Social Media Research Questions
Did you know that social media sites can play with the psychology of a teen? They will see society differently than they were used to.
- Which are the best ways to monitor children’s access to social media platforms?
- Among all the social media platforms, which is the best to use when starting a business?
- Which are the positive and negative effects of using social media sites?
- How do social networks make people commit suicide?
- Which are the negative effects of children using social media sites?
- How can addiction to social media occur? The best methods to use to curb it.
- Which are the advantages and disadvantages of parents monitoring their children’s social media presence?
- How do social media networks help whenever there is a disaster?
- How effective is Twitter when providing some information globally?
- Do you think that social media connects and disconnects people equally?
- How do social media networks facilitate kidnapping and assaults?
- How effective is the social media network when providing good PR?
- How effective is data protection on the internet?
- Is it safe to do a job on any of the social media platforms?
Research Papers On Social Media
Have you ever come across a social media political campaign? Well, yes, there are social media politics. A couple of politicians have gained popularity through social media exposure.
- Evaluate the changes that have occurred in human values after social media prevalence.
- Should there be a restriction on social media activities for both adults and children?
- Does social media enhance or prevent stereotyping?
- The best way to recognize valid advertisements and spam.
- The best way social media can help to stop racism.
- The effects of online games.
- The negative effects of social media on crime cases.
- The best way to manage social media pressure among celebrities globally.
- How do social media sites boost personal branding?
- The positive effects of social media on improving the corporate image.
- How does influence marketing help in boosting businesses?
- The influence of chatbots in boosting communication in companies.
- The best strategies to use to create a strong online presence.
- Evaluate the evolution of social media.
Interesting Social Media Research Topic
There is a close relationship between social media and relationships. This is because it plays a major role in how people relate. This is in families, couples, friends, and colleagues.
- The power of online communities.
- The impact of business branding in increasing sales.
- The major roles of images in boosting online communication.
- The best methods to use to monitor kids’ activities on social media.
- Social empowerment on the use of social media sites.
- The impact of social media in boosting spirituality in individuals.
- The major impacts of social media on job creation.
- The effects of cybercrime on different individuals.
- How do social media relationships occur?
- The safety of social media relationships in the modern age.
- The importance of social media in new products marketing.
- How does social media help in marketing?
- The negative and positive impacts of social media in religious missions.
- The role of social media in breaking news to the public.
Social Media Research Papers
Of late many people have been indulging in the social media business. This is because of its diversity. There is a lot of areas that still require exploration in the digital world.
- Evaluate the impact of social media on modern times.
- The effectiveness of government communication through social media.
- How has social media influenced education?
- The impact of social media in journalism.
- The effectiveness of mobile technology in marketing.
- The various regulations put in place for online activities.
- The most effective email marketing strategies.
- How is social media being used to boost food security?
- How does social media affect the behaviors of children at school and home?
- The global regulations on online activities.
- The various online marketing modes used by various social media marketers.
- The best way to use social media networks to boost your content visibility.
- How can startups use social media to boost their customer service experience?
- Do you think information overload influences our health?
More Social Media Research Paper Topics
Narcissism behaviors can also be seen easily on social media sites. These are some of the best social media research papers that you can start with. Therefore, use our research paper writing services to get a professional help with your papers.
- How social media aids in fighting stereotypes?
- Do you think terrorists use social networks to recruit new members?
- Which kind of information should be restricted on social media sites?
- The best way social sites help to attract people’s attention to social problems.
- How do you think social media aids to make us educated?
- Why do you think people use more time using social media sites?
- The negative effects of information overload.
- Do you think social media is the best place to seek justice?
- How does social media stimulate mental issues?
- The effects of using women’s bodies for advertisements globally.
- Do you think social media sites are 100% effective for communication?
- The healthy ways of self-realization through social media.
- The best way to earn from social media sites.
- How can blogging help to boost the education system?
Research Topic On Social Media
These are some of the best media topics. You can also find some multimedia topics that you can use for your research paper. Digital media is interesting and you get a lot of information from it.
- Evaluate business growth in the past and present due to social media networks.
- How does social media help us to find inspiration?
- The amount of time to use when using social media sites.
- Why do you think people always crave likes on social media sites?
- Why do you think people are often aggressive when using social media sites?
- Why do you think cyberbullying is rampant on social media?
- What do you think makes marketing great on social media?
- Has social media influenced what is considered beautiful and what is not?
- The best way to depoliticize is through social media.
- The best ways to interact positively with people through social media.
- Do you think it is effective to find a relationship partner through social media?
- It is recommended for employers to always check the social media accounts of their employees?
- Do you think it is wise to check a candidate’s social media presence before hiring?
- The best way to boost your social media presence as a brand ambassador.
Informative Research Questions On Social Media
Are you looking for good and interesting research questions on social media? Look no further! You can start with these. Also, remember to do thorough research to meet the end goal.
- Which are the lessons gotten from social media network usage?
- The only time when children should be allowed to use social sites.
- The best way to raise funds for sick people using social media.
- The best ways social media can be used for acts of mercy.
- How social media is a new culture.
- Do you think social media makes us accept violence easily?
- How do you think social media sites are used to plan crimes?
- The relation between social media and violence.
- The relation between social media and culture.
- The most popular kinds of posts on social media sites.
- The influence of Instagram on women.
- The best way to find your perfect target audience.
- How are social media sites used to unite human beings?
Best Social Media Paper Ideas
It is important to submit high-quality work to your professor. Try our college paper writing service and discover the benefits of high-quality and cheap paper writing help. This will help you to gain top grades while in college.
- Why do some accounts gain more followers than others?
- How businesses can use social media in client service development?
- The best methods to stop cyberbullying on social media sites.
- Do you think it is recommended to trust bloggers’ views before making a purchase?
- How have social sites become a platform for new business destinies?
- The best methods to use to become a celebrity on media sites.
- Should teachers keep their accounts closed to prevent students from knowing them?
- The various professions emerged due to the developing of social media.
- How to find your perfect social media audience.
- Customer engagement on social media platforms.
- The best way social media can be used is to make students more aware of their surroundings.
- How can social media be used to track a lost person?
- The use of mass media on the development of the education system.
- Why do you think people love reading gossip on various social media sites?
Argumentative Research Topics About Social Media
These research topics about social media will make you think deeper and see the online world differently. Through research, you will also learn why the” future is digital.”
- How do social media sites help in enriching students with presentation skills?
- The best way social media can be used to educate students on real-life scenarios.
- The best way to reduce theft on social media sites.
- The best way to crowdsource different people to achieve something,
- How do social media sites invade people’s privacy?
- Which should be an age limit for using certain social media sites?
- The best way to learn through social media.
- The policies and regulations needed for social media usage.
- The effectiveness of social media sites during elections
- How has social media led to family breakups?
- How easy is it to get information online?
- Evaluate all the Twitter limitations.
- How do people fake it on social media?
- Evaluate how to make the online space safe.
Amazing Social Media Paper Topics
As a student, you need to strive to achieve diligently in your course units. Here are some amazing topics that you can use.
- The amount of bandwidth used when using social media.
- The negative effects of joining social media platforms when too young.
- The network connectivity issues that occur on social sites.
- The best legislations that can be put in place for social media
- The best way to earn through online games.
- The effectiveness of digital dating sites on boosting relationships.
- Data protection policies on social media sites.
- The best way start-ups can use to boost their companies online.
- Do you think social media networks are increasing suicide cases?
- The best way to gain followers on Twitter.
- The various causes of addiction on social media.
- The best way to reduce addiction to social media among the youth.
- The best way to improve social sites for all ages.
- The various ways Twitter has been used to save lives
Engaging Social Networks Topics
Social media emerged as a way to interact with family and friends. However, with time, businesses started to take advantage of the popular new communication method.
- The diverse relation between social sites and religion.
- Is it ethical to monitor your employee’s social networks?
- The various modes being used to improve interaction online.
- Is parent-child protection necessary while online to prevent bullying?
- The dangers of posting pictures online.
- Evaluate how social media is disconnecting people?
- The censorship policies that are being put in place for mass media.
- The mass media bias during elections.
- How does cyberbullying occur online?
- The business of mass media during elections in different regions of the world.
- The various important mass media ethics.
- Evaluate phone journalism
- How are images important when giving a story on social media sites?
- The interrelation between politics and media.
- The history of mass communication
Unique Social Networking Topics
Social media sites have made it easier to get real-time information fast. Additionally, you get to learn about the latest trends and technologies.
- The impact of fake news on modern society.
- How does accreditation of journalists occur online?
- Evaluate the currency of news.
- The advantages and disadvantages of mass communication.
- The relation between mental illnesses and social media
- The relation between media, ethics, and public relation.
- The relation between media, fashion, and aesthetics.
- The positive and negative effects of media cliché.
- How can media be used as an instrument of propaganda?
- The relation between terrorism and media.
- The common major media industries.
- The movement rules and politics about media.
- The relation between reality shows, privacy, and ethics
- How does media get information overloading?
- How are social media sites making us lonely?

Social Media Research Paper Thesis
Social media marketing has grown over time and is slowly gaining popularity. These are some of the best social media research papers that you can use for your thesis.
- The best way to protect children online.
- Evaluate the world-famous influencers on social media.
- The effect of social media on our relationships.
- Evaluate addiction in social media in different age groups.
- How does social media use lead to anxiety?
- The negative and positive effects of social media on the youth.
- The importance of social media presence on recruitment.
- The real value of social media
- The effects of social media on human beings.
Trying To Finish Your Social Media Paper?
Are you looking for someone who can do a research paper for you? Look no further! We will provide the best writing help. We have experts who specialize in different things, with the majority being writers. You can also get the required customer support when you need it. The writers are often available and reliable enough to provide the best work. Your professors will be happy. As students, it is important to give it your best while at school.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Terms & Conditions Loyalty Program Privacy Policy Money-Back Policy
Copyright © 2013-2024 MyPaperDone.com
The Library Is Open
The Wallace building is now open to the public. More information on services available.
- RIT Libraries
- Social/Behavioral Sciences Research Guide
Research Question
This InfoGuide assists students starting their research proposal and literature review.
- Introduction
- Research Process
- Types of Research Methodology
- Data Collection Methods
- Anatomy of a Scholarly Article
- Finding a topic
- Identifying a Research Problem
- Problem Statement
- Research Design
- Search Strategies
- Psychology Database Limiters
- Literature Review Search
- Annotated Bibliography
- Writing a Literature Review
- Writing a Research Proposal
A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to discover in your work. A good research question is essential to guide your research paper.
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
You will usually write a single research question to guide your progress in a research paper. Your answer then forms your thesis statement—the central assertion or position that your paper will argue for.
You can follow these steps to develop a strong research question:
- Choose your topic
- Do some preliminary reading about the current state of the field
- Narrow your focus to a specific niche
- Identify the research problem that you will address
Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to refine them. The criteria below can help you evaluate the strength of your research question.
Research Objectives & Question Formulations
- What are the characteristics of X?
- How has X changed over time?
- What are the causes of X?
- How has X dealt with Y?
- What is the relationship between X and Y?
- What is the role of X in Y?
- What is the impact of X on Y?
- How does X influence Y?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of X?
- How effective is X ?
- How can X be improved?
Criteria & Explanation 1
Criteria & explanation 3: your research question is complex and arguable, example research problem & question, criteria & explanation 2: your research question is feasible and specific, criteria & explanation 4: your research question should be relevant and original..
- << Previous: Problem Statement
- Next: Research Design >>
Edit this Guide
Log into Dashboard
Use of RIT resources is reserved for current RIT students, faculty and staff for academic and teaching purposes only. Please contact your librarian with any questions.
Help is Available
Email a Librarian
A librarian is available by e-mail at [email protected]
Meet with a Librarian
Call reference desk voicemail.
A librarian is available by phone at (585) 475-2563 or on Skype at llll
Or, call (585) 475-2563 to leave a voicemail with the reference desk during normal business hours .
Chat with a Librarian
Social/behavioral sciences research guide infoguide url.
https://infoguides.rit.edu/researchguide
Use the box below to email yourself a link to this guide
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
For more open and equitable public discussions on social media, try “meronymity”
Press contact :, media download.

*Terms of Use:
Images for download on the MIT News office website are made available to non-commercial entities, press and the general public under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license . You may not alter the images provided, other than to crop them to size. A credit line must be used when reproducing images; if one is not provided below, credit the images to "MIT."

Previous image Next image
Have you ever felt reluctant to share ideas during a meeting because you feared judgment from senior colleagues? You’re not alone. Research has shown this pervasive issue can lead to a lack of diversity in public discourse, especially when junior members of a community don’t speak up because they feel intimidated.
Anonymous communication can alleviate that fear and empower individuals to speak their minds, but anonymity also eliminates important social context and can quickly skew too far in the other direction, leading to toxic or hateful speech.
MIT researchers addressed these issues by designing a framework for identity disclosure in public conversations that falls somewhere in the middle, using a concept called “meronymity.”
Meronymity (from the Greek words for “partial” and “name”) allows people in a public discussion space to selectively reveal only relevant, verified aspects of their identity.
The researchers implemented meronymity in a communication system they built called LiTweeture, which is aimed at helping junior scholars use social media to ask research questions.
In LiTweeture, users can reveal a few professional facts, such as their academic affiliation or expertise in a certain field, which lends credibility to their questions or answers while shielding their exact identity.
Users have the flexibility to choose what they reveal about themselves each time they compose a social media post. They can also leverage existing relationships for endorsements that help queries reach experts they otherwise might be reluctant to contact.
During a monthlong study, junior academics who tested LiTweeture said meronymous communication made them feel more comfortable asking questions and encouraged them to engage with senior scholars on social media.
And while this study focused on academia, meronymous communication could be applied to any community or discussion space, says electrical engineering and computer science graduate student Nouran Soliman.
“With meronymity, we wanted to strike a balance between credibility and social inhibition. How can we make people feel more comfortable contributing and leveraging this rich community while still having some accountability?” says Soliman, lead author of a paper on meronymity .
Soliman wrote the paper with her advisor and senior author David Karger, professor in the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and a member of the Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL), as well as others at the Semantic Scholar Team at Allen Institute for AI, the University of Washington, and Carnegie Mellon University. The research will be presented at the ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems.
Breaking down social barriers
The researchers began by conducting an initial study with 20 scholars to better understand the motivations and social barriers they face when engaging online with other academics.
They found that, while academics find X (formerly called Twitter) and Mastodon to be key resources when seeking help with research, they were often reluctant to ask for, discuss, or share recommendations.
Many respondents worried asking for help would make them appear to be unknowledgeable about a certain subject or feared public embarrassment if their posts were ignored.
The researchers developed LiTweeture to enable scholars to selectively present relevant facets of their identity when using social media to ask for research help.
But such identity markers, or “meronyms,” only give someone credibility if they are verified. So the researchers connected LiTweeture to Semantic Scholar, a web service which creates verified academic profiles for scholars detailing their education, affiliations, and publication history.
LiTweeture uses someone’s Semantic Scholar profile to automatically generate a set of meronyms they can choose to include with each social media post they compose. A meronym might be something like, “third-year graduate student at a research institution who has five publications at computer science conferences.”
A user writes a query and chooses the meronyms to appear with this specific post. LiTweeture then posts the query and meryonyms to X and Mastodon.
The user can also identify desired responders — perhaps certain researchers with relevant expertise — who will receive the query through a direct social media message or email. Users can personalize their meronyms for these experts, perhaps mentioning common colleagues or similar research projects.
Sharing social capital
They can also leverage connections by sharing their full identity with individuals who serve as public endorsers, such as an academic advisor or lab mate. Endorsements can encourage experts to respond to the asker’s query.
“The endorsement lets a senior figure donate some of their social capital to people who don’t have as much of it,” Karger says.
In addition, users can recruit close colleagues and peers to be helpers who are willing to repost their query so it reaches a wider audience.
Responders can answer queries using meronyms, which encourages potentially shy academics to offer their expertise, Soliman says.
The researchers tested LiTweeture during a field study with 13 junior academics who were tasked with writing and responding to queries. Participants said meronymous interactions gave them confidence when asking for help and provided high-quality recommendations.
Participants also used meronyms to seek a certain kind of answer. For instance, a user might disclose their publication history to signal that they are not seeking the most basic recommendations. When responding, individuals used identity signals to reflect their level of confidence in a recommendation, for example by disclosing their expertise.
“That implicit signaling was really interesting to see. I was also very excited to see that people wanted to connect with others based on their identity signals. This sense of relation also motivated some responders to make more effort when answering questions,” Soliman says.
Now that they have built a framework around academia, the researchers want to apply meronymity to other online communities and general social media conversations, especially those around issues where there is a lot of conflict, like politics. But to do that, they will need to find an effective, scalable way for people to present verified aspects of their identities.
“I think this is a tool that could be very helpful in many communities. But we have to figure out how to thread the needle on social inhibition. How can we create an environment where everyone feels safe speaking up, but also preserve enough accountability to discourage bad behavior? says Karger.
“Meronymity is not just a concept; it's a novel technique that subtly blends aspects of identity and anonymity, creating a platform where credibility and privacy coexist. It changes digital communications by allowing safe engagement without full exposure, addressing the traditional anonymity-accountability trade-off. Its impact reaches beyond academia, fostering inclusivity and trust in digital interactions,” says Saiph Savage, assistant professor and director of the Civic A.I. Lab in the Khoury College of Computer Science at Northeastern University, and who was not involved with this work.
This research was funded, in part, by Semantic Scholar.
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- Nouran Soliman
- David Karger
- Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
- Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
Related Topics
- Computer science and technology
- Social media
- Social networks
- Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL)
- Electrical Engineering & Computer Science (eecs)
Related Articles
Empowering social media users to assess content helps fight misinformation

Q&A: Alexey Makarin on why social media harms youth mental health

On social media platforms, more sharing means less caring about accuracy
Previous item Next item
More MIT News

Featured video: Moooving the needle on methane
Read full story →
The many-body dynamics of cold atoms and cross-country running

Heather Paxson named associate dean for faculty of the School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences

Preparing MIT’s campus for cardiac emergencies

Researching extreme environments

To build a better AI helper, start by modeling the irrational behavior of humans
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
Send us an email
25 answers to the most common social media questions
Written by by Jacqueline Zote
Published on March 26, 2021
Reading time 7 minutes
With the social media landscape evolving constantly, there’s always something new to learn for both novice and experienced marketers alike. Naturally, you might have a lot of pressing social media marketing questions that you’re embarrassed to ask because they seem like common knowledge. But no question is too simple because it can be challenging to catch up.
In this post, we answer some of the most common and important questions about social media. Besides general social media FAQs, we’ll also tackle platform-specific questions with a focus on Instagram FAQs. Let’s get started.
Want to unlock social media success in 2022? Check out these five resources designed to inspire stronger content, campaigns and customer care.

General social media questions
1. how many people are on social media.
As of April 2020, a total of 3.81 billion people around the world use social media, putting the worldwide social media penetration rate at 49%.
2. What is the most popular social media platform?
Based on user count alone, Facebook continues to be the most popular social media platform. It had garnered 2.6 billion monthly active users by Q1 of 2020. The Sprout Social Index XV: Empower & Elevate also found that it’s the most popular platform for both marketers and consumers. Eighty-nine percent of marketers surveyed used the platform while 83% of consumers surveyed used it.
3. How long does the average person spend on social media per day?
In 2019, the average social media user spent around 1 hour and 15 minutes per day on social media. eMarketer predicts that this average will increase by 8.8% in 2020 due to social distancing and people spending more time indoors during the pandemic. So we can expect that social media users will spend around 1 hour and 22 minutes on average using social media every day.

4. What is the fastest growing social media platform?
While Instagram once held this coveted position, the platform’s growth has tapered off for a while. In fact, its US user growth rate dropped to 6.7% in 2019. Meanwhile, TikTok saw a 97.5% increase in its US user base. Granted, these numbers will decline as the hype dies down, projections still show that the platform will continue to see a double-digit growth rate in the coming years.

5. What’s the best time to post on social media?
The best time to post on social media depends on several factors. While your choice of platform and your industry both matter, your audience activity plays the biggest role. So ideally, you should look at your post performance to get valuable data about the perfect post timing for your business.
You can also use our guide on the best time to post as a starting point before you find what works best for your business and industry.
6. How often should I post on social media?
Again, this largely depends on your audience. While you definitely should publish at least one post every day, you should see if posting more often will make any difference in your performance. Once you find a posting frequency that works for you, create a publishing calendar , and follow it consistently.
7. Which social media platform should I use to promote my business?
While the natural assumption is that you should be on all the popular platforms, this can be counterproductive if not executed with a strategy. Instead, focus on a couple of platforms that are highly popular among your target audience. So the best platforms to use will vary for each business. Check out our guide on how to choose the best social media channels for your business.
8. How do I get started with social media marketing?
There are a few things you need to begin marketing on social media – a goal, a target audience and a strategy. Find out what you want to achieve through social media marketing and what types of people you want to attract. Then create a social media strategy to streamline and organize your approach.
9. What kind of content should I post?
This also depends on your industry and what appeals to your target audience, although visuals typically take the cake on social media. Try out some of our social media post ideas and see which ones perform the best to find out what type of content your audience likes.
10. How can I get more followers on social media?
Growing your social media following involves a lot of planning and strategizing as well as posting the right content and targeting the right audience. Use our comprehensive guide on how to grow your social media audience to get started.
Instagram FAQs
11. what is the average age of instagram users.
On average, most Instagram users are between the ages of 18 and 34. Learn more Instagram demographic stats .

12. How many followers does the average Instagram user have?
Since the purpose of personal Instagram accounts is to connect with family and friends, the average Instagram personal account has about 150 followers .
13. What percentage of Instagram followers sees your post?
While Instagram hasn’t made anything official, many users have noticed that their posts reach only about 7% of their followers. This is mainly because the platform prioritizes posts from accounts you regularly interact with.
14. How many Instagram posts are there?
Since its inception, Instagram has seen over 50 billion photos uploaded on the platform. And there is an average of 100 million photos and videos uploaded every day.
15. Does Instagram sell your information?
While Instagram doesn’t sell your information, it shares analytics data about users’ activity and preferences with third-party partners such as advertisers and analytics services. In Instagram’s data policy , Instagram promises to never sell your information.
16. What information does Instagram collect?
Besides your device information, Instagram collects the content, communication and information you provide. This can include metadata about your content such as the location, for instance. It also collects information about how you use the platform as well as the people, accounts and hashtags you interact with. Read the full Instagram data policy to learn more on what information is collected.
17. Can you export Instagram followers?
Yes. While not in the Instagram app itself, there are several tools out there such as IGExport and Phantombuster that will let you export your Instagram followers into a .csv file.
18. Is there a way to download Instagram posts?
Instagram gives you an option to download a copy of all the posts you’ve shared on the platform. Find out how to do this through the Instagram Help Center . As for posts shared by other people, Instagram won’t let you download them directly but you can use third-party apps like DownloadGram and Ingramer for this. Keep in mind that recent changes in Instagram’s terms of use affects any image downloading, reposting and embedding that you may want to do.
19. How do you save someone else’s picture on Instagram?
Instagram lets you save someone else’s post so you can easily find it again later. For this, just click on the “Save” button at the bottom of the post and Instagram will add it to your collection. Note that this isn’t the same as downloading the photo or video. As mentioned in the previous answer, you’ll need to use third-party apps to actually download the photo or video to your device.

20. How can I see who saved my pictures on Instagram?
While Instagram doesn’t give you the option to see who’s saved your posts, Instagram Business Profiles can find out how many times a post has been saved. You can find this information under the Post Insights, but this only shows you the number of saves and not the details of people who’ve saved it to their collection.
21. How do you get pictures off of Instagram?
To remove pictures or videos you’ve posted on Instagram, tap on the options button above your post and then choose “Delete.” You’ll need to tap “Delete” again to confirm that you want to remove the post from Instagram.
22. How do you get your “Top Live” on Instagram?
Just as Instagram recommends posts based on your activity and the accounts you interact with the most, it used to give suggestions for live videos you might want to watch. You could access this “Top Live” section at the top of your “Explore” page before, but Instagram has since removed it.
23. How can I share live video replays?
Instagram gives you the option to share a replay of your live video to IGTV once the broadcast ends. Just choose “Share to IGTV” when you see the option at the bottom of your screen. You’ll also get the option to “Download Video” in case you want to save it to your camera roll or “Delete Video” if you don’t want to keep it.
24. How can I see who is live on Instagram?
When someone you follow goes live on Instagram, you’ll see their profile picture at the top of your Feed and it will have a colorful ring around it along with the word “Live.” Just tap on the profile picture to start watching their live video.
25. How can I see active users on Instagram?
Instagram lets you see the active status of only people you follow or have exchanged direct messages with. If they’re currently active, you’ll see a green dot next to their profile picture and username. Note that you won’t be able to see if users have turned off their activity status..
Bonus Question
Did we answer most of your social media questions?
Let us know if you have any other pressing questions about social media or Instagram FAQs that you’d like us to answer. We understand that things change quickly and you need answers just as fast. Be sure to check out our social media stats to understand the landscape better across all social platforms.
- Social Media Strategy
11 YouTube analytics tools to improve your marketing in 2024
- Sprout in Action
14 Sprout Social features you might not know about
- Social Media Content
Post Performance Report: Brands creating AI-generated content with intention
400+ Instagram captions and ideas to get you through every season in 2024
- Now on slide
Build and grow stronger relationships on social
Sprout Social helps you understand and reach your audience, engage your community and measure performance with the only all-in-one social media management platform built for connection.
19 Frequently Asked Social Media Questions [ANSWERED]
What do social media managers do? How does social media work? How often should I post? Behold—answers to all the top social media questions.

What do a family BBQ and a professional networking event have in common? The fact that someone is going to ask you, “How do I go viral?” or other social media questions, like, “Do you just post on Instagram all day?” #no
Most people know social media is great for business, but sometimes those at the top don’t always understand specifically how it works. Whether it’s the C suite you need to bring up to speed, a hiring manager, or your nosy aunt Meg, be prepared with these answers to the most popular social media questions.
Table of Contents
Bonus: Get a free social media strategy template to quickly and easily plan your own strategy. Also use it to track results and present the plan to your boss, teammates, and clients.
19 frequently asked social media questions
1. what is a social media manager and what do they do.
A social media manager is someone who manages social media for a brand or multiple brands.
A social media manager’s responsibilities can span across social media marketing strategy, content creation, performance analysis, social listening, community management, and, sometimes, customer service.
Alongside their team, they social media managers also plan organic and paid campaigns , develop a content calendar, and network with other brands and influencer partners.
Sometimes social media managers are called digital marketing managers, community managers, or brand creators.
Large companies typically hire in-house social media staff, or rely on long-term agency contracts. Small businesses may only have the budget to hire one full-time person, resulting in them being a “jack-of-all-trades” social media manager. These versatile marketers often do everything from strategy to shooting videos and everything in between. Or, they may outsource to freelance experts in design, production, or writing to help out.
2. How much does social media marketing cost?
How much does a car cost? Depends if it’s a Kia or a Mercedes. The same goes for social media marketing: You can spend a lot or a little. But, the amount you spend isn’t a guarantee of how quickly you’ll reach your goals. After all, a Kia and a Mercedes can both get you to the same place at the time.
Running tons of ads or hiring an experienced agency to manage your accounts can result in faster growth. But, money can’t replace strategy. No matter how much you invest in social media marketing, you need to know your target audience, set measurable goals, create a content strategy , test different types of social media content, and more. You also need to understand social media ROI to know how much you can spend on promoting your products and services on social media and still make profit.
Even if you manage everything in-house, you still need to cover the expense of your time (or your team’s), plus:
- software/tools to produce and manage content,
- product or payment for influencer marketing campaigns,
Not sure what you should be spending? We have a guide on how to create a social media budget for businesses of all sizes.
3. Is being a social media manager a real job?
Hopefully by now, most people realize working in social media is a real job. As of 2021, 91% of companies with over 100 employees use social media marketing.
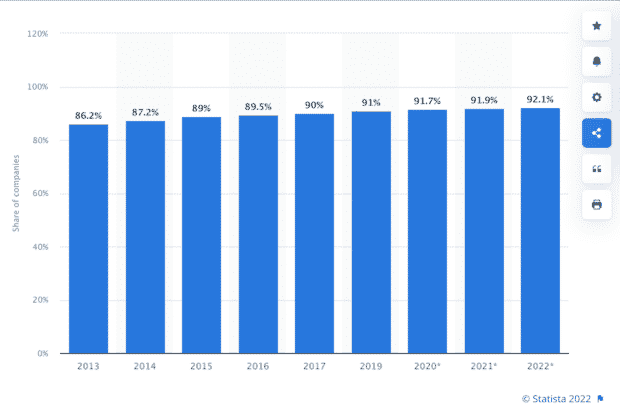
The public expects most companies to have a social media presence, so the full-time jobs to manage those accounts are very real. Besides working directly for a company, social media managers can also work for agencies representing multiple clients, or freelance.
Content creators —who used to be called influencers—are also a form of social media managers, but they’re focused on building their own brands instead of a company’s. This used to be seen as a one-in-a-million shot at success but is becoming increasingly more common and financially viable as the creator economy continues to take off.
4. How do I get more followers, especially on a brand new account?
Consistently post high-quality, relevant content your target audience wants to see. Experiment often to discover which types of content work best.
But how do you do that? Sticking to a focused editorial calendar and regularly repurposing content .
In the meantime, if you can’t stand staring at “0 followers” at the beginning of a new account, and you have the budget for it, consider running ads to bring in your first couple hundred followers.
In previous years, cost-per-like campaigns were cheap, but skyrocketed to an average of $0.52 per like in 2021. In 2022 and beyond, you can get a better bang for your buck while still building a following with retargeting campaigns.
5. Is buying followers really that bad?
Yes. Don’t do it.
Need proof? We’ve run multiple experiments and the results are clear: Buying followers damages your reputation and can potentially lead to your account getting blacklisted. Some services are outright scams, while others deliver what they promise—thousands of followers—but those followers aren’t real, don’t comment or like, and they don’t do anything to increase the metrics that matter, like your engagement rate.
Want to spend money to boost your followers in a legit way? Congrats, that’s called advertising. Here’s how to get the most out of your social ad campaigns as a newbie.
6. How do you go viral?
One does not simply “go viral.”
The black gates leading to the social media elites are guarded by more than just a few viral posts. There is content there that does not sleep. The analytics are ever watchful. It is a bustling wasteland, riddled with Instagram Reels , selfies, and sponsorships. The air there is an intoxicating fume. Not with a ten thousand person camera crew could you do this.
As Boromir famously says in The Lord of the Rings: “It is folly.”
Perhaps Boromir would have felt differently about walking into Mordor if he would’ve had a guide such as this one on the best social media trends to go viral.
7. Which social media platforms should I use?
The only correct answer is, “Not all of them.” You can be successful with one social media channel, though keep it to a max of three or four main ones to focus on. (Unless you’ve got a big team to handle more than that—then by all means, go for gold.)
When choosing which social platforms to use, look for matches that:
- are where your audience hangs out
- have advertising or other promotional options
- align with the types of content you want to create
Whether you’re setting up new business accounts or auditing your performance, knowing which platforms to use relies on having up-to-date statistics on each platform. Lucky for you, we have our free, in-depth Social Trends 2022 report with all the demographics you need to decide where to focus your time this year.
8. How many people use social media?
As of Q1 2022, 4.62 billion people use social media, which is 58.4% of the world’s population. That’s also an 8% jump from 2021, when just over 50% of the world was on social.
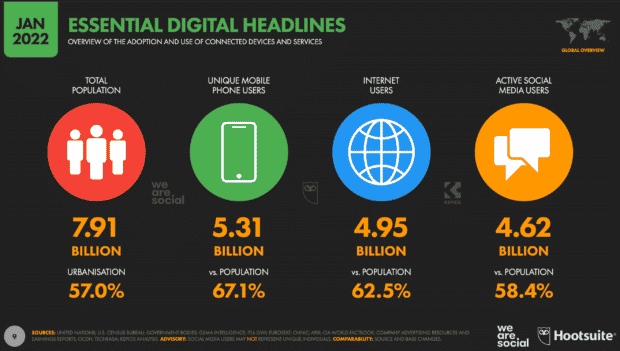
9. What is the most popular social network?
Facebook with 2.9 billion monthly active users . Next up is YouTube with 2.5 billion monthly active users, then WhatsApp (2 billion) and Instagram (1.47 billion).
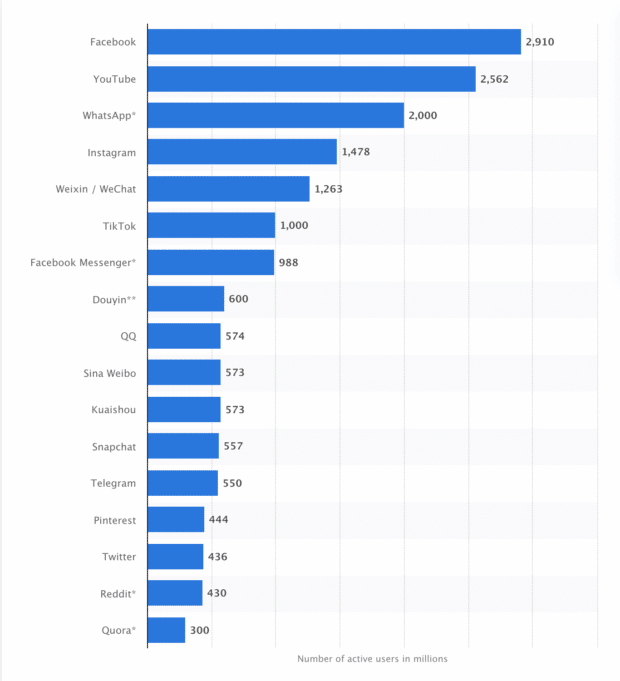
As the parent company of Facebook, Instagram, Facebook Messenger, and WhatsApp, Meta reaches 3.64 billion users per month. That’s 78% of the world’s 4.6 billion social media users.
Technical social media questions
10. how do you create a good social media strategy.
There isn’t a one-size-fits-all social media strategy. Your strategy is specific to your business. But one thing that is the same across every successful social media strategy? Making everything about serving your audience.
Brand new to developing a strategy, or looking to add something new to your toolbox? Check out the following resources:
- Free Social Media Strategy Template
- How to Set S.M.A.R.T. Social Media Goals
- Social Media Best Practices
Want full guidance on every aspect of creating and optimizing your social strategy? Try the Hootsuite Social Marketing course.
11. How do you calculate engagement rate?
Your engagement rate per post is the percentage of your followers who interacted with that post. Your overall engagement rate is the average engagement each post received during a specific time period.
To calculate it, take the total number of engagements on your post and divide it by your total follower count.
(Engagements / Total followers) x 100 = Engagement rate
Want a shortcut? Try our free engagement rate calculator , which includes benchmarks to measure your performance.
So what counts as an engagement?
- Save (on Instagram)
For formats like Instagram Stories , engagement could also be a DM reply, clicking a link sticker, answering a poll, or other Story actions. Engagement options vary by platform but those are the ones most have in common.
12. How many hashtags should I use?
Each platform has its own rules about this. For example, Instagram allows a maximum of 30 hashtags per post.
But should you use them all? Nope.
While algorithms change all the time, our experiments show that using fewer hashtags can actually boost your reach by as much as 15%. Instagram now recommends using only 3-5 hashtags, even though they still allow up to 30.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Instagram’s @Creators (@creators)
What about Facebook, Twitter, and every other network? We’ve got you with a complete hashtag guide , including how to find the right ones for you.
13. How often should I post?
The “perfect” posting schedule changes as often as the platforms change their algorithms (which is a lot). What works right now likely won’t in six months.
You don’t need to alter your schedule every week, but you should be switching things up at least once a quarter to see if posting more or less often boosts your engagement. Your audience’s behavior—how often they’re online—and preferences will determine how successful your posting schedule is. It’s different for everyone.
Remember : your schedule needs to be something you can keep up with. Want to post five Reels a week but only have time to make one? Be realistic when planning.
OK, but how often should you really post right now? Here’s the answer:
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Hootsuite 🦉 (@hootsuite)
14. What are the image sizes for each social platform?
Image specs have changed over the years as platforms redesign their apps and feeds. Check out our complete guide to all current social media image sizes for 2022.
Here’s a sneak peek of the most popular platforms and formats:
15. What social media tools do I need?
Technically, you don’t really need anything. You can manage your social media completely for free. But, having the following types of tools will dramatically improve your growth and save time and money.
Content scheduling
This is what most social media managers look to automate first, for obvious time-saving reasons. Beyond scheduling posts, your ride-or-die tool should also allow you to:
- Visually plan content and campaigns,
- Collaborate with your team,
- Optimize content for each platform (e.g. tagging the right @mentions, media size editing),
- Allow for bulk uploading and scheduling.
As you may have guessed, Hootsuite fills the bill on all those. Check out how Hootsuite brings planning and scheduling together to simplify your workflow:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c_xYkyfivDI
Start your free trial. (You can cancel anytime.)
Content creation
If you don’t have a team supporting you, you’ll likely need help. A few of our faves are Canva for graphics and ContentGems for content curation. Plus, you can connect both to your Hootsuite account for max efficiency.
Social media analytics
Once you create and publish your content, you’re going to want to track how it performs to get an understanding of what your audience likes and dislikes. A good social media analytics tool (like Hootsuite!) will help you track the data that matters across multiple social media accounts and networks, and generate comprehensive reports for your team and boss.
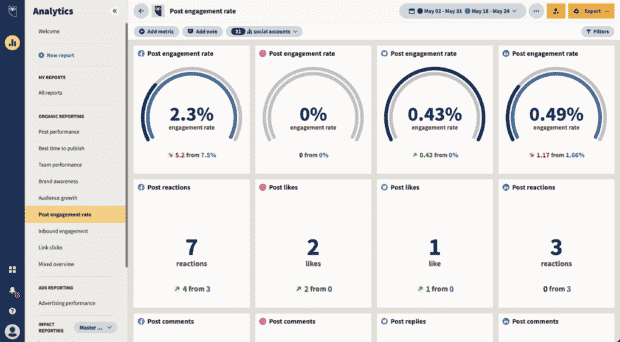
Learn more about the different types of social media management tools and how to pick the best one for your needs.
Social media manager interview questions
Applying for social media manager positions? Check how your skills measure up, and grab our free resume template .
Already landed an interview? Prep for these social media interview questions:
16. As a social media manager, how do you balance work and life?
Being a social media manager often feels like a 24/7 responsibility, but thanks to technology, you don’t have to be “on” 24/7. Schedule content in advance, set aside specific times to respond to DMs and comments, and most importantly, use automation to help you enjoy your downtime worry-free.
Launch a chatbot to answer customer questions during off hours, and use an app like Smart Moderation to scan for spam or inappropriate comments while you’re away.
17. How do you respond to trolls?
How a company handles negative comments depends a lot on their content strategy, but as a rule: Everyone knows you don’t feed the trolls.
It’s a fine line between ensuring you’re addressing all legitimate customer complaints and filtering out trolls who only want to waste your time. When in doubt? Respond politely and professionally. It may not matter to the troll, but it will protect your reputation with your real customers who are watching.
18. Which social platforms do you have the strongest presence on and how did you grow them (for your work or personal use)?
Well, I can’t answer that for ya. But here’s where you want to wow your interviewer with case studies, percentages, and facts. Sure, you grew Al’s Window Emporium’s Instagram followers, but by how much? What percent increase was that year-over-year?
Facts = results, and results are what companies are hiring you for. Take the time to collect notable statistics from your career to demonstrate your capabilities.
19. We are just starting out and want to grow our following quickly. What do you suggest we do first?
Answer: relationship building for cross-promotion and/or running an influencer campaign . Have a budget? Run ads.
Networking with other complementary businesses is the fastest way to grow a new, unknown account for free. How you do this will vary, but the essential steps are:
- Identify potential partners (e.g. businesses in your industry/a related industry who aren’t competitors).
- Start slow: Follow them, leave thoughtful and professional comments on their posts. Do this for several weeks (if not longer!) before ever approaching them or asking to partner up.
- After you’ve built positive rapport with your comments, it’s time to slide into the DMs… or emails. Try to find an email contact. Use LinkedIn to search for the company’s social media or PR team, or check their website.
- Send a personalized introduction—starting with what a cross-promotion would do for them. Why should they want to partner with you? What’s in it for them? Approach everything with this mindset and you’ll be ahead of most.
- So, what is in it for them? Probably money. If your company is more established, a trade or other promotional opportunity may work instead.
- If you don’t hear back, follow up.
Let Hootsuite help you manage it all effortlessly with content planning and scheduling right alongside powerful analytics reporting. Plus all the advanced tools like social listening and ads management to take your growth to the next level. Try it free today.
Get Started
Do it better with Hootsuite , the all-in-one social media tool. Stay on top of things, grow, and beat the competition.
Become a better social marketer.
Get expert social media advice delivered straight to your inbox.
As an ex-agency strategist turned freelance WFH fashion icon, Michelle is passionate about putting the sass in SaaS content. She's known for quickly understanding and distilling complicated technical topics into conversational copy that gets results. She has written for Fortune 500 companies and startups, and her clients have earned features in Forbes, Strategy Magazine and Entrepreneur.
Related Articles

How to Become a Social Media Manager in 2024 [Free Resume Template]
From content creation to customer service to PR to sales, businesses often rely on their social media manager to wear many hats.

The 11 Best Social Media Apps for Marketers
Which social media apps do you need to know about? Here’s a list of the top apps in terms of size and value.

109 Social Media Demographics Marketers Need to Know in 2024
Understanding social media demographics will help you fine-tune your marketing strategy and reach the right people with your message.

How to Create a Social Media Marketing Strategy in 9 Easy Steps [Free Template]
Creating your social media marketing strategy doesn’t need to be painful. Create an effective plan for your business in 9 simple steps.

Sprinklr Service
Sprinklr Social
Works Best With
Sprinklr Insights
Sprinklr Marketing
Marketing Teams
Customer Service Teams
- Unified-CXM
- Customers Customer Stories Sprinklr Champions
- Company Our Story Leadership Newsroom Partners Careers Culture & Talent Investor Relations Security & Data Privacy
- Resources Learn Services Support CX-WISE Podcast Analyst Reports Product Demo Days eBooks & Reports Events & Webinars Blog Unified-CXM Guide Our Services Training For Agencies Help Center Release Notes Contact Us
- Platform & Technology
- Customer Service
- Marketing & Advertising
- Research & Insights
- Social Media Management
- Customer Stories
- Announcements
- Culture & Talent
13 Most Common Social Media Questions (+ Answers)
September 22, 2023 • 7 min read

Share this Article
You’re absolutely right! You check your social media notifications!
Social media has become an integral part of our daily life, enabling us to connect with friends, family and even strangers worldwide. It’s also an ever-changing landscape with new concepts evolving every day. So, it’s natural for people to feel overwhelmed by all the information and developments that it brings. But just so you feel more comfortable navigating all the digital craziness, we’re here to lighten the load by answering some of the most commonly asked social media questions of all time.
So, with that, let‘s begin with the basics.
How do I leverage social media for professional networking?
Social media platforms are a great way to connect with peers and build valuable relationships. You can grow your professional network if you:
Create a professional profile , especially on platforms like LinkedIn, and accurately show your skills, experience and professional aspirations
Join industry-specific groups focused on specific industries or areas of interest
Share relevant content regularly , like articles, research papers or thought-provoking insights related to your field of expertise
Attend online networking events hosted on platforms like LinkedIn or professional forums
Technologies and trends come and go but where does the future lie in social media? Let's talk about it.
Survey Features
Social media research questions.
Get your current survey solution evaluated by our experts.
Social media surveys are a part of online surveys. You can use social media platforms to run surveys across a wider audience on a global scale. It helps you reach your current customers, prospects, target audience, and competitors’ customers.
What is social media research?
In market research, social media research is the method of collecting data directly from customers using various social media platforms. You can simply share/upload your survey on a social media platform and gather data from a vast audience.
It is important to remember that while conducting such research, you should deploy surveys on channels that are preferred by your target audience. When your target audience is 30-40, you can’t run a survey on TikTok and expect to gather data.
Social media research questions help you gather reliable and accurate opinions quickly and easily. Therefore, identifying the platform widely used by your target audience can increase the response rate and ensure statistical significance.
Gather customer feedback across multiple channels.
Get a complete view of customer data with the Voxco omnichannel platform.
Loved by 500+ global brands in 40+ countries.
What are the benefits of social media research questions?
Now more than ever, customers spend most of their time reviewing products on social media . Using social media platforms to ask research questions can help brands achieve higher engagement and gather real-time feedback.
1. Gather data at the right time:
Real-time is the right time. Social media research questions allow you to gather data at the right time from your target audience. When designed and executed correctly, it can reach the right audience at the right moment and help you gather rich data.
2. Wider reach:
58.&% of the world’s population is actively using social media. This means you can gather global views at any point in time.
Instead of sending surveys to a pre-selected list of contacts, you can reach your customers across geographical boundaries and ask for their feedback.
3. Higher volume of data:
Another benefit of social media research questions is that people are more likely to share their opinion. Your audience may not respond to an email or a phone survey, believing it to be spam. However, people are more likely to engage when you run a social media survey from your verified account.
What are the uses of social media research?
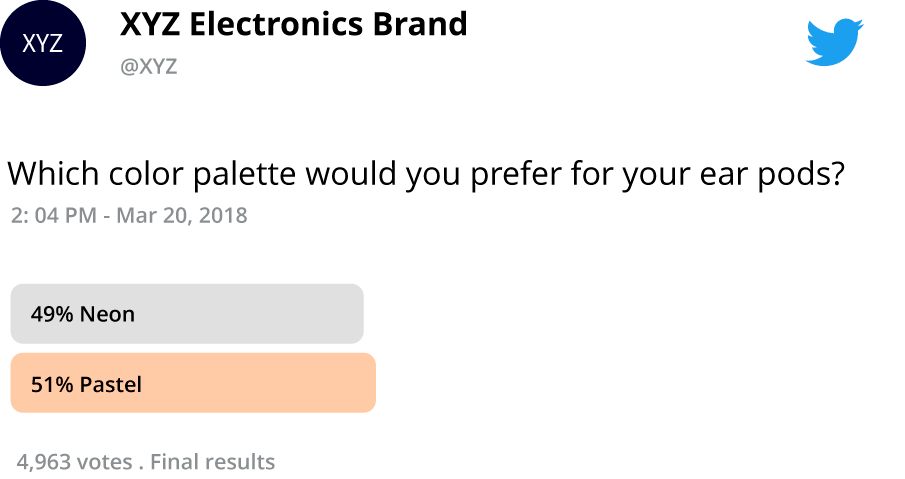
Social media research questions can be used to understand current trends, customer preferences, dislikes, and more.
1. To reach large demography:
Social media can give you access to audiences from different demographics. It can help you segment your customers and create buyer personas to help shape your marketing efforts.
2. To measure experience:
You can reach out to your entire target market to gather customer experience feedback. Instead of a point-of-sale survey, you can simply run an experience survey anytime to measure customer experience.
3. To test brand loyalty:
With social media, you can simply run a poll or a micro-survey to measure brand loyalty within your customer base. Social media research questions engage more people and make the audience feel included and valued by the brand.
4. To understand customer satisfaction:
Use social media to target customers who may not be in your current customer base. The platform can help you reach one-time buyers or past customers, enabling you to gauge their satisfaction level with your brand and product.
For example, you may also gather feedback from people who may have received your product as a gift.
Reach audience beyond geographical borders and uncover insightful data.
Browse through Online, Offline, and Phone channels and decide the best channel to engage your audience.
How to design social media research questions?
Social media platforms create the opportunity to engage in a straightforward and public conversation with your audience. It is the best research method to gather unbiased and honest opinions.
Here are 5 factors you should remember when designing social media surveys.
1. Identify the right platform.
Find the right demography of each platform to ensure that you run the right survey on the right platform. For example, LinkedIn is most popular within B2B communities. While Facebook is used by mixed demography of older and younger people.
2. Keep the research question simple.
Ask a single question and make it direct. Engage people in a conversation on a single and focused topic instead of asking too many questions.
3. Design a mobile-friendly survey.
Ensure your social media research question is responsive to mobile devices. Design it as per user experience and interface to ensure higher engagement.
4. Ask closed-ended questions.
Short and closed-ended questions can lead to a higher response rate. Find the most suitable closed-ended question type, which is also responsive to the mobile device and the social media platform.
5. Run surveys at the right time.
Find the right time to deploy your surveys. Choose the time when your target market is most active on a specific platform and deploy the survey.
Experience Innovative Survey Features and Drive Informed Decision-Making with Voxco Insights
✓ Drag-and-drop Interface
✓ 100+ Question Types
✓ Skip Logic and Branching
Related Features

Thurstone scale | Survey Features | Voxco

Concept Testing |Market Research | Voxco

Types of Survey with Examples
Voxco is trusted by top 50 market research firms, global brands & universities in 40 countries. voxco offers full omnichannel capability including cati, predictive dialler, online surveys, offline capi, and panel management..
Follow Voxco on
We use cookies in our website to give you the best browsing experience and to tailor advertising. By continuing to use our website, you give us consent to the use of cookies. Read More
Does drinking soy milk cause men’s breasts to grow bigger?
Experts offer their research-based takes on claims swirling all over social media.

Is it true that drinking soy milk can cause men’s breasts to enlarge?
The idea is all over social media, but the answer is almost certainly no. “It’s highly unlikely that drinking soy milk promotes breast growth in men,” says Donald Hensrud, associate professor of nutrition and preventive medicine at the Mayo Clinic College of Medicine. “I haven’t seen good evidence that soy milk has any feminizing effects on men.”
Concerns about soy’s effect on men probably arose because soybeans and other legumes contain isoflavones. These are phytoestrogens, or estrogen compounds structurally similar to human estrogen. However, “they have different biological properties than human estrogen and don’t promote harmful estrogen effects on the body,” Hensrud says. “In fact, they may be protective.”
Studies generally do not support the notion that drinking soy milk will cause men to grow breasts, or experience any other feminizing effects. Studies also refute the notion that soy increases the risk of breast cancer in women.
“I haven’t seen any data that leads me to believe that drinking soy milk or eating soy products promotes feminization in men, meaning breast growth, or any similar adverse health effects, such as breast cancer, in women,” says David Jenkins, university professor in the departments of nutritional sciences and medicine, Temerty Faculty of Medicine, at the University of Toronto. “I recommend soy intake to my patients — both sexes. I don’t think it has any ill effects.” He added that no major health organization has warned of any dangers associated with soy consumption.
At least two early studies each described a single case of soy consumption linked to feminizing effects in men, among them enlarged breasts, erectile dysfunction and decreased libido. But experts pointed out that the two subjects each consumed unusually high amounts of soy — in one instance, three quarts of soy milk a day — which is many times the intake in the average diet.
“That is a very large amount of soy milk on a consistent basis — most people don’t drink that much water daily,” Hensrud says. “These are two unusual cases, and they are not representative of the overall evidence on soy phytoestrogens.”
“Breast growth — gynecomastia — does occur occasionally in men and adolescent males,” he says, referring to other causes of gynecomastia in young men. “Most important, there is strong evidence that soy intake provides numerous health benefits with little risk.”
Many studies have also found that soy milk and other soy products may lower the risk of breast cancer, possibly accounting for the low incidence of breast cancer among Japanese women, whose traditional diets are heavy in soy. Soy intake also may lower the risk of breast cancer recurrence in women, according to studies.
Women who have estrogen-positive breast cancer may worry about soy, but Hensrud says data does not point to a greater risk. Other research indicates that breast cancer rates rise among Japanese women who reduce their soy consumption and adopt a Western diet.
Moreover, soy milk can have cardiovascular benefits by reducing blood pressure, inflammation and low-density lipoprotein (the bad) cholesterol, according to studies. Additional research shows soy appears to reduce the risk of prostate cancer and might prevent memory loss associated with aging and cognitive impairment.
What else you should know
Soy milk is a processed food that may contain added sugar, flavorings and other ingredients. Also, those who have a soy allergy should avoid it.
In addition to isoflavones, soy foods are rich in B vitamins, fiber, potassium and magnesium. Also, unlike some plant proteins, soy protein contains all nine essential amino acids, making it a complete protein. Soy foods can be unfermented or fermented, the latter meaning it has been cultured with beneficial bacteria, yeast or mold.
“Fermented soy milk may have even more health benefits, similar to other fermented foods,” Hensrud says.
Get Well+Being tips straight to your inbox

Read more from Well+Being
Well+Being shares news and advice for living well every day. Sign up for our newsletter to get tips directly in your inbox.
Are you taking your meds wrong ? Many patients make these common mistakes.
Centenarians give their advice about everything.
The wall sit is a simple exercise that can lower your blood pressure.
Tart cherries — more specifically, tart cherry juice — may help with inflammation and pain.
Do you self-sabotage ? Here’s how to stop.

Trump's defense used a jury consultant to research and help them select jurors

The New Yorkers who could decide Donald Trump’s fate were vetted in real time on Friday by the former president’s defense team.
As the potential alternate jurors were being questioned by prosecutors seeking to convict Trump of illegally paying hush money to a porn star , and by defense attorneys trying to keep him out of jail, a jury consultant hired by Trump's legal team was watching the candidates closely for telltale signs of possible bias while simultaneously feeding the defense attorneys her impressions.
Follow along for live updates
Meanwhile, other jury consultants say, it is likely that a team of researchers working with the jury consultant were doing social media and other online searches to fill out the picture of every potential juror and sending that information to Trump’s lawyers in the courtroom.
“All this has to happen relatively quickly,” said veteran jury consultant Jo-Ellan Dimitrius of Dimitrius & Associates, who has been following the case and identified the firm working for Trump as Magna Legal Services.
The Philadelphia-based firm did not respond to a call from NBC News but court records show that Magna served as Trump’s jury consultant when was ordered to pay $83.3 million in damages to writer E. Jean Carroll for defaming her in 2019.
It was not immediately clear if the Manhattan District Attorney’s office used its own jury consultant to vet jurors and a spokesperson for the agency did not return numerous phone calls from NBC News.
By midday, jury selection had been completed and Trump's first trial was heading for opening arguments.
Using jury consultants for vetting has become a fairly common practice.
“In my experience, there’s usually a consultant sitting behind the lawyers with a laptop who is feeding information to the lawyer doing the questioning of jurors,” Dimitrius said. “They usually have the home office doing the social media checks and other searches because the primary role of the consultant in the courtroom is to listen and watch the jurors and give feedback to the lawyers.”
Sometimes the background checks of potential jurors are being done even before the questioning begins, Dimitrius said.
“Generally on the morning of jury selection you get a list of potential jurors,” she said. “So we will take an iPhone photo of the list and send it back to the office where they’ll start their searches.”
Tampa-based jury consultant Michael Boucher of TCS, who has worked on a number of high-profile cases in New York City, like former Alaska Gov. Sarah Palin’s failed libel case versus the New York Times, echoed Dimitrius.
“In a case like this, we would set up a laptop on the podium and use a messaging app to stay in contact with the lawyers questioning the jurors,” Boucher said. “Not only are you feeding the lawyer information, you are finding on the jurors online, you’re trying to help guide the lawyer asking the questions. Lawyers, at times, sometimes get too far into the weeds and they need assistance so they can come up with follow-up questions.”
At the same time, Boucher said, “We’re watching the reactions of the other jurors waiting to be questioned and feeding that information to our legal team. That way, when the next potential juror steps up we already have a sense of where they stand.”
Boucher said in his experience Manhattan jury pools tend to be sophisticated, well-educated and thoughtful. But cases involving polarizing figures like Trump or Palin “sometime attract what we call 'motivated jurors,' with strong feelings either for or against" them.
“It’s very hard to find anybody who doesn’t have an opinion about Trump,” he said.
NBC News Legal Analyst Danny Cevallos, an attorney who practices in New York and elsewhere, agreed.
“In virtually every other case in the world, there’s not a strong chance that the jurors have tweeted about the defendant or posted on social media," Cevallos said. "This is the rare one-in-a-million case where there’s a good chance all of us have retweeted or tweeted something about Donald Trump."
Renato Stabile, managing director at Dubin Research & Consulting in New York City, said the ability to track social media has revolutionized the way juries get picked — and how jury consultants do their jobs.
“Before you just had to rely on what jurors said in court, and I think lawyers depended a lot more on their experience and gut, and maybe unfortunately, stereotypes that were either correct or incorrect and their past experience," Stabile said. "Now you just get such a better sense of what jurors are really all about based on the articles they’re liking, what they’re reposting."
Examining social media is "probably the most important part of jury selection,” said David Oscar Markus, a criminal defense attorney who, among others, successfully defended former Tallahassee mayor Andrew Gillum against charges of lying to the FBI .
“Lots of folks will come into court and say, ‘Yes, of course, I can be fair,’ or, ‘I have feelings about this one way or the other, but I can put all those aside and give the prosecution and defense a fair shake'," Markus said. "But then, once you see posts, even if they’re old posts, they reveal sort of the jurors’ true feelings.”
Lisa Rubin and Corky Siemaszko reported from New York City, Megan Lebowitz reported from Washington, D.C.
Lisa Rubin is an MSNBC legal correspondent and a former litigator.
Megan Lebowitz is a politics reporter for NBC News.
Corky Siemaszko is a senior reporter for NBC News Digital.

Adolescence
More research questions the “social media hypothesis” of mental health, a new study shows that social media does not lead to anxiety or depression..
Posted August 10, 2023 | Reviewed by Gary Drevitch
- What Changes During Adolescence?
- Find a therapist to support kids and teens
- Many believe that social media causes teens to experience depression and anxiety, despite lacking evidence.
- A new study found that when teenagers used social media more, their mental health did not change over time.
- Mainstream media should devote more coverage to studies like this one.

As I’ve discussed previously , conventional wisdom suggests that using social media promotes poor mental health, especially in teenagers . But there is good reason to question this idea. As more high-quality research becomes available, we can see room for nuance and see that social media is not consistently detrimental to everyone’s well-being.
A critical limitation in many existing studies on this topic is that they are cross-sectional. This means all variables are assessed only once, and at the same time. This isn’t necessarily a bad thing; it just means we don’t know how behavioral changes over time might be associated with changes in emotional variables. Longitudinal research helps us to better understand how change happens by measuring these variables repeatedly over a period of months or even years.
Longitudinal research is especially valuable in this case because some young people may use social media to alleviate distress , so we might observe that increases in depression or anxiety will predict increases in social media use , rather than the reverse. On the other hand, if the social media hypothesis is correct, then as teenagers spend more and more time online, this should be followed by decreased mental health (i.e., greater anxiety/depression). But that’s not what the data reveal.
What Researchers Found
A research team in Norway recently published a study in which they tracked young people aged 10-16, and assessed them every 2 years. Each time, the researchers interviewed participants about their behaviors online (e.g., posting photos, “liking,” or commenting on others' posts), and they conducted clinical assessments of depression and anxiety with standardized psychiatric measures. The researchers found no evidence that increased social media use was followed by elevated anxiety or depression. This means that as these teenagers used more social media, their mental health did not change. These findings directly contradict the idea that social media use leads to poor psychological well-being.
The authors are careful to note that even though social media did not make teenagers feel worse, on average, it also did not make them feel better. So, social media use may not have an overall negative or positive effect for the average teenager. This idea is consistent with what I have argued previously , which is that social media use may have differential effects depending on the user’s initial motivations. When people are motivated to use social media because they find it interesting or rewarding, then it’s likelier to make them happy, whereas when they feel compelled or obligated to use it, then it’s likelier to make them feel worse. Motivations matter more than the technology itself.
The researchers also suggest that perhaps subgroups of teenagers may experience different outcomes following social media use, such as those who are bullied or have low self-esteem . The specific content that people view on social media may also play a role. It is also true that digital technologies change rapidly and we cannot assume that all future forms of social media will operate the same way psychologically. New applications have the potential to be better or worse than what people currently use.
Time Trend Data Are Inconclusive
Those who hold with the “social media hypothesis” of mental health will often point to time trend data as evidence. They argue that because social media use has risen in teenagers over the past 15 years, and that teen depression and anxiety has also risen over the same period of time, then those two trends are likely connected.
But if that were true, we ought to be able to observe this trend happening during teenagers’ lives. The fact is, we do not observe this pattern, and these null findings should make us skeptical about such claims. When researchers track teenagers’ mental health over a span of years, there is no link between their social media use and their experiences of depression or anxiety. In the words of the authors , “ the frequency with which adolescents engage in behaviors like posting, liking, and commenting on others’ posts does not influence their risk for symptoms of depression and anxiety .”
It would be great to see more mainstream media coverage of studies like this, especially considering the widespread belief that if young people are permitted to use social media, their mental health will deteriorate. Perhaps parents of teenagers can take some comfort in the fact that for the average user, there is little risk of this.
Cauberghe, V., Van Wesenbeeck, I., De Jans, S., Hudders, L., & Ponnet, K. (2021). How Adolescents Use Social Media to Cope with Feelings of Loneliness and Anxiety During COVID-19 Lockdown. Cyberpsychology, behavior and social networking , 24 (4), 250–257. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2020.0478
Puukko, K., Hietajärvi, L., Maksniemi, E., Alho, K., & Salmela-Aro, K. (2020). Social Media Use and Depressive Symptoms—A Longitudinal Study from Early to Late Adolescence. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 17 (16), 5921. MDPI AG. Retrieved from http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165921
Steinsbekk, S., Nesi, J., & Wichstrøm, L. (2023). Social media behaviors and symptoms of anxiety and depression. A four-wave cohort study from age 10–16 years. Computers in Human Behavior , 147 , 107859.

Dylan Selterman, Ph.D., is an Associate Teaching Professor at Johns Hopkins University in the Department of Psychological and Brain Sciences. He teaches courses and conducts research on personality traits, happiness, relationships, morality/ethics, game theory, political psychology, and more.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Teletherapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
81% of U.S. adults – versus 46% of teens – favor parental consent for minors to use social media
More than 40 states and the District of Columbia are suing Meta , the parent company of Facebook and Instagram, alleging its platforms purposefully use addictive features that harm children’s mental health.
Amid this news, U.S. adults and teens are more likely to support than oppose requiring parental consent for minors to create a social media account and requiring people to verify their age before using these platforms, according to a pair of new Pew Research Center surveys. But adults are far more supportive than teens of these measures, as well as limiting how much time minors can spend on social media.
Pew Research Center conducted this study to understand American adults’ and teens’ views on ways social media companies could limit minors’ use of their platforms. This analysis uses data from two separate surveys, allowing us to compare the views of U.S. teens ages 13 to 17 with U.S. adults ages 18 and older.
For the analysis of teens, the Center conducted an online survey of 1,453 U.S. teens from Sept. 26 to Oct. 23, 2023, via Ipsos. Ipsos recruited the teens via their parents who were a part of its KnowledgePanel , a probability-based web panel recruited primarily through national, random sampling of residential addresses. The survey is weighted to be representative of U.S. teens ages 13 to 17 who live with parents by age, gender, race and ethnicity, household income and other categories. This research was reviewed and approved by an external institutional review board (IRB), Advarra, an independent committee of experts specializing in helping to protect the rights of research participants.
For the separate analysis of adults, the Center surveyed 8,842 U.S. adults from Sept. 25 to Oct. 1, 2023. Everyone who took part in the survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP). This online survey panel is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race and ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology .
Here’s a closer look at the findings from the two new surveys – one of adults and one of teens – which we conducted in late September through October, before the states’ lawsuit against Meta.
Adults’ views on social media policies aimed at minors
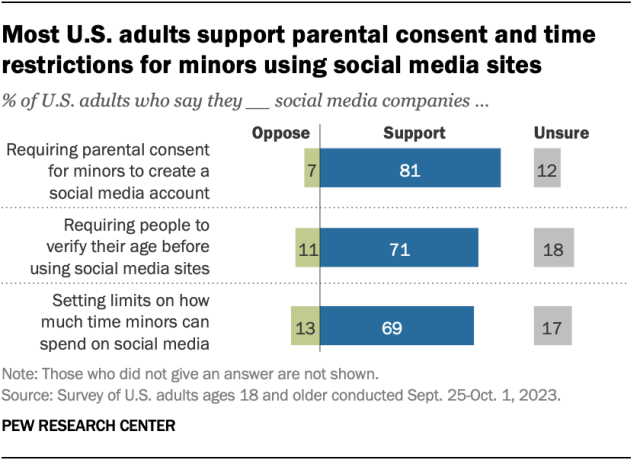
Most U.S. adults (81%) say they support social media companies requiring parental consent for minors to create a social media account. About seven-in-ten favor requiring people to verify their age before using social media sites (71%) and setting limits on how much time minors can spend on these platforms (69%). Only about one-in-ten adults oppose each of these three measures.
Still, some adults are uncertain. For example, roughly one-in-five adults are unsure if companies should require age verification (18%) or set time limits for minors (17%).
Views among adults by age, party and parental status
Many social media companies do not allow those under 13 to use their sites. Still, there’s a growing movement to develop stricter age verification measures , such as requiring users to provide government-issued identification. Legislators have pushed for mandatory parental consent and time restrictions for those under 18, arguing this will help parents better monitor what their children do on social media.
Our survey finds there is strong bipartisan support for these types of policies. Clear majorities of Republicans and Democrats – including independents who lean to either party – support parental consent, time limits for minors and age verification.
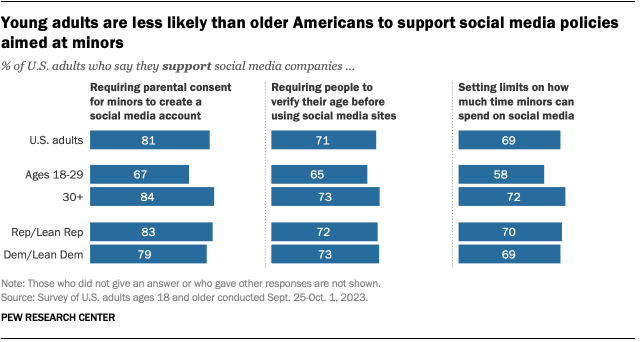
Majorities of adults across age groups support social media companies introducing these measures. But young adults are less supportive than their older counterparts. For example, 67% of those ages 18 to 29 say social media sites should require parental consent for minors to create an account, but this share rises to 84% among those ages 30 and older.
Additionally, majorities of parents and those without children back each of these measures, though support is somewhat higher among parents.
Teens’ views on social media policies for minors
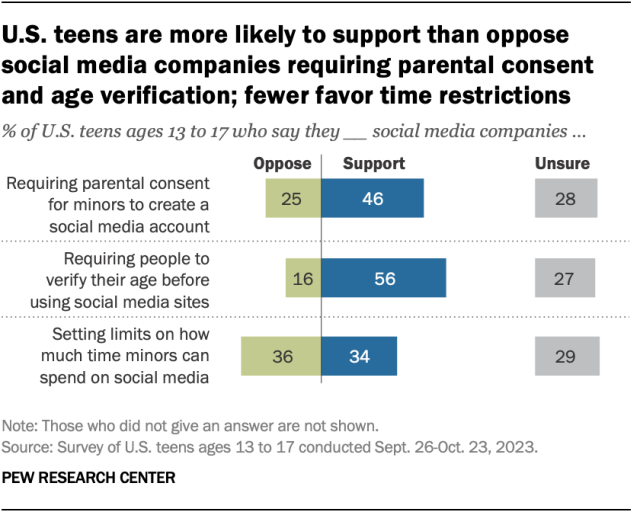
Building on the Center’s previous studies of youth and social media, we asked U.S. teens ages 13 to 17 about their views on these measures.
Teens are more likely to support than oppose social media companies requiring parental consent for minors to create an account (46% vs. 25%). There’s even more support for requiring people to verify their age before using these sites – 56% of teens favor this, while 16% oppose it.
But their views are more divided when it comes to setting limits on how long minors can use these sites. Similar shares of teens support and oppose this (34% vs. 36%).
For each of these policies, about three-in-ten teens report being unsure if this is something social media companies should do.
How adults’ and teens’ views on social media policies differ
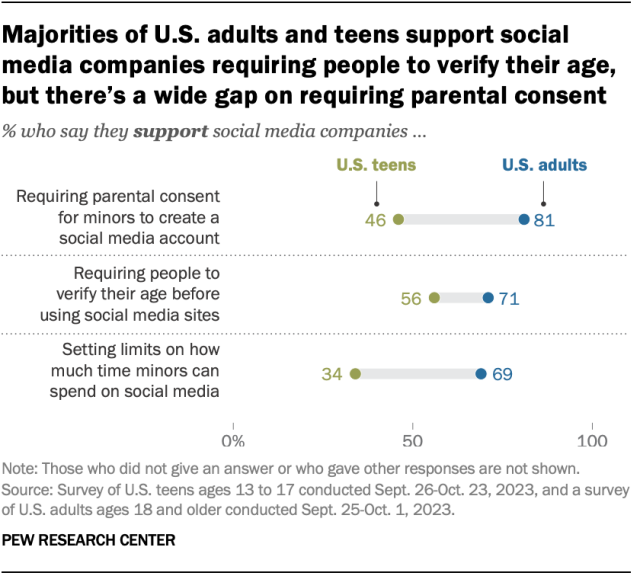
Adults are considerably more supportive of all three measures we asked about than are teens.
While 81% of U.S. adults support social media companies requiring parental consent for minors to create an account, that share drops to 46% among U.S. teens.
Adults are also about twice as likely as teens to support setting limits on how much time minors can spend on social media sites (69% vs. 34%).
But majorities of adults and teens alike support requiring people to verify their age before using social media sites. But on this, too, adults are more supportive than teens (71% vs. 56%).
Note: Here are the questions used for this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology .
- Social Media
- Technology Policy Issues
- Teens & Tech

6 facts about Americans and TikTok
Whatsapp and facebook dominate the social media landscape in middle-income nations, how teens and parents approach screen time, germans stand out for their comparatively light use of social media, majorities in most countries surveyed say social media is good for democracy, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Some social issues research paper topics to explore are; The growth of cyberattacks and cyberstalking in social media. Social media and how it promotes an unrealistic idea of life. Social media and the many impacts it has on users and businesses. Social media detox: Importance of taking scheduled social media breaks.
18 January 2024. last updated. Social media research encompasses a broad range of different topics that delve into the ever-evolving digital landscape. People investigate the impact of social platforms on society, exploring subjects, such as online identity formation, self-presentation, the psychology of virtual interactions, and others.
Social media research is a rapidly growing field that encompasses a wide range of topics, from understanding the psychological and social effects of social media to analyzing patterns of user behavior and identifying trends in online conversations. In this era of data-driven decision-making, social media research is more important than ever, as ...
Top 10 Social Media Research Paper Topics. 1. A Comparative Review of Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok as Primary Marketing Platforms for Small Businesses. A lot of small businesses have flocked to various social media sites to market their products and services.
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
The development of the current systematic review is based on the main research question: how does social media affect mental health? Review. Research strategy. The research was conducted to identify studies analyzing the role of social media on mental health. Google Scholar was used as our main database to find the relevant articles.
The "Top 16 Questions" presented in this guide represent the core matters of importance to the research field with respect to social media research. They include issues of reliability, execution, interaction with other kinds of research, ethics and legal compliance, data quality, process, and outputs. Importantly, the 16 questions in this ...
What is Social Media and What Questions Can Social Media Research Help Us Answer? In: The SAGE Handbook of Social Media Research Methods By: Lori McCay-Peet & Anabel Quan-Haase Pub. Date: 2018 Access Date: October 18, 2021 Publishing Company: SAGE Publications Ltd City: 55 City Road Print ISBN: 9781473916326 Online ISBN: 9781473983847
Step 6: Aggregate & present your results. A crucial step involves consolidating your social media research results into a format that is easily understandable for others. For example, charts and visualisations can aggregate huge amount of data in an easily comprehensible graph that answers your research question.
To examine Americans' trust in the information from national and local news organizations, as well as social media sites, Pew Research Center surveyed 12,147 U.S. adults from July 18 to Aug. 21, 2022. Everyone who completed the survey is a member of the Center's American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through ...
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
Critical Questions Remain Unanswered. Nearly every teenager in America uses social media, and yet we do not have enough evidence to conclude that it is sufficiently safe for them. Our children have become unknowing participants in a decades-long experiment. It is critical that independent researchers and technology companies work together to ...
Start to turn that topic into a series of questions that you will attempt to answer the course of your research. Keep in mind that you will probably end up changing and adjusting the question (s) you have as you gather more information and synthesize it in your writing. However, having a clear line of inquiry can help you maintain a sense of ...
The researchers found no evidence that increased social media use was followed by elevated anxiety or depression. This means that as these teenagers used more social media, their mental health did ...
These are some of the best social media research papers that you can use for your thesis. The best way to protect children online. Evaluate the world-famous influencers on social media. The effect of social media on our relationships. Evaluate addiction in social media in different age groups.
1 answer. Aug 20, 2019. Social media research is gaining ground , so is the search for theories other than spawned by old media research in terms of media control, technology, audiences and ...
Hypersensitivity to social feedback. Brain development starting at ages 10-13 (i.e., the outset of puberty) until approximately the mid-twenties is linked with hypersensitivity to social feedback/stimuli. iv In other words, youth become especially invested in behaviors that will help them get personalized feedback, praise, or attention from peers.. AI-recommended content has the potential to ...
Facebook - which recently celebrated its 15th anniversary - remains one of the most widely used social media sites among adults in the U.S. Roughly seven-in-ten adults (69%) say they ever use the platform. (A separate 2018 Center survey showed Facebook use among U.S. teens had dropped in recent years.) YouTube is the only other online ...
A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to discover in your work.A good research question is essential to guide your research paper. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue; Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources; Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints; Specific enough to answer thoroughly
Caption: The researchers implemented meronymity in a communication system they built called LiTweeture, which is aimed at helping junior scholars use social media to ask research questions. Here, an example tweet shows a Meronymous contribution posted through LiTweeture. The tweet incorporates the contribution message with a paper recommendation and the meronym composed by the contributor.
It had garnered 2.6 billion monthly active users by Q1 of 2020. The Sprout Social Index XV: Empower & Elevate also found that it's the most popular platform for both marketers and consumers. Eighty-nine percent of marketers surveyed used the platform while 83% of consumers surveyed used it. 3.
Girls are more likely than boys to say it would be difficult for them to give up social media (58% vs. 49%). Older teens are also more likely than younger teens to say this: 58% of those ages 15 to 17 say it would be very or somewhat hard to give up social media, compared with 48% of those ages 13 to 14. Teens are more likely to say social ...
We have a guide on how to create a social media budget for businesses of all sizes. 3. Is being a social media manager a real job? Hopefully by now, most people realize working in social media is a real job. As of 2021, 91% of companies with over 100 employees use social media marketing.
It has become a powerful tool for self-expression and communication. Thе realm of social mеdia includes wеll-known wеbsitеs, such as Facеbook, Instagram, Twittеr, LinkеdIn and several others. Each platform has distinct characteristics and sеrvеs specific dеmographics.
Social media research questions allow you to gather data at the right time from your target audience. When designed and executed correctly, it can reach the right audience at the right moment and help you gather rich data. 2. Wider reach: 58.&% of the world's population is actively using social media.
Wong has transformed his social media presence in recent years to appeal more to youth, as attested by his TikTok base of 120,000 followers; If he hopes to win over the Gen Z segment in the next ...
The idea is all over social media, but the answer is almost certainly no. "It's highly unlikely that drinking soy milk promotes breast growth in men," says Donald Hensrud, associate ...
A jury consultant hired by the former president's legal team watched potential jurors for signs of bias while researchers conducted social media searches to vet them. IE 11 is not supported.
Those who hold with the "social media hypothesis" of mental health will often point to time trend data as evidence. They argue that because social media use has risen in teenagers over the ...
81% of U.S. adults - versus 46% of teens - favor parental consent for minors to use social media. By. Monica Anderson and Michelle Faverio. More than 40 states and the District of Columbia are suing Meta, the parent company of Facebook and Instagram, alleging its platforms purposefully use addictive features that harm children's mental ...