- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing

How to Put a Quote in an Essay
Last Updated: November 28, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Danielle Blinka, MA, MPA . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 2,640,669 times.
Using a direct quote in your essay is a great way to support your ideas with concrete evidence, which you need to support your thesis. To select a good quote , look for a passage that supports your argument and is open to analysis. Then, incorporate that quote into your essay, and make sure you properly cite it based on the style guide you’re using.
Sample Quotes

Incorporating a Short Quote

- For instance, let's say this is the quote you want to use: "The brown leaves symbolize the death of their relationship, while the green buds suggest new opportunities will soon unfold."
- If you just type that sentence into your essay and put quotes around it, your reader will be disoriented. Instead, you could incorporate it into a sentence like this: "The imagery in the story mirrors what's happening in Lia's love life, as 'The brown leaves symbolize the death of their relationship, while the green buds suggest new opportunities will soon unfold.'"

- "Critic Alex Li says, 'The frequent references to the color blue are used to suggest that the family is struggling to cope with the loss of their matriarch.'"
- "According to McKinney’s research, 'Adults who do yoga at least three times a week have lower blood pressure, better sleeping patterns, and fewer everyday frustrations.'"
- "Based on several recent studies, people are more likely to sit on the park benches when they're shaded by trees."

- You still need to use quotation marks even if you're only quoting a few words.
- If you're in doubt, it's best to be cautious and use quotes.

- For example, let’s say you used the quote, “According to McKinney’s research, ‘Adults who do yoga at least three times a week have lower blood pressure, better sleeping patterns, and fewer everyday frustrations.’” Your commentary might read, “This shows that yoga can have a positive impact on people’s health, so incorporating it into the workplace can help improve employee health outcomes. Since yoga makes employees healthier, they’ll likely have reduced insurance costs.”

- When you use a paraphrase, you still need to provide commentary that links the paraphrased material back to your thesis and ideas.
Using a Long Quote

- The reader will recognize that the material is a direct quote because it's set off from the rest of the text. That's why you don't need to use quotation marks. However, you will include your citation at the bottom.

- "In The Things They Carried , the items carried by soldiers in the Vietnam war are used to both characterize them and burden the readers with the weight they are carrying: The things they carried were largely determined by necessity. Among the necessities or near-necessities were P-38 can openers, pocket knives, heat tabs, wristwatches, dog tags, mosquito repellent, chewing gum, candy cigarettes, salt tablets, packets of Kool-Aid, lighters, matches, sewing kits, Military Payment Certificates, C rations, and two or three canteens of water." (O'Brien 2)
Variation: When you're citing two or more paragraphs, you must use block quotes, even if the passage you want to quote is less than four lines long. You should indent the first line of each paragraph an extra quarter inch. Then, use ellipses (…) at the end of one paragraph to transition to the next.

- Your block quote will use the same spacing as the rest of your paper, which will likely be double-spacing.

- For example, “According to Li, “Rosa is the first sister to pick a rose because she’s the only one who’s begun to move on after their mother’s death” might become “According to Li, “Rosa is the first sister to pick a rose because she’s … begun to move on after their mother’s death.”
- Don’t eliminate words to change the meaning of the original text. For instance, it’s not appropriate to use an ellipsis to change “plants did not grow faster when exposed to poetry” to “plants did … grow faster when exposed to poetry.”

- For example, let’s say you want to use the quote, “All of them experienced a more relaxed, calmer disposition after doing yoga for 6 months.” This doesn’t tell the reader who you’re talking about. You could use brackets to say, “All of [the teachers in the study] experienced a more relaxed, calmer disposition after doing yoga for 6 months.”
- However, if you know the study is talking about teachers, you couldn’t use brackets to say, “All of [society experiences] a more relaxed, calmer disposition after doing yoga for 6 months.”

- If you don't explain your quote well, then it's not helping your ideas. You can't expect the reader to connect the quote back to your thesis for you.

- For instance, you may prefer to use a long block quote to present a passage from a literary work that demonstrates the author's style. However, let's say you were using a journal article to provide a critic's perspective on an author's work. You may not need to directly quote an entire paragraph word-for-word to get their point across. Instead, use a paraphrase.
Tip: If you’re unsure about a quote, ask yourself, “Can I paraphrase this in more concise language and not lose any support for my argument?” If the answer is yes, a quote is not necessary.
Citing Your Quote

- An MLA citation will look like this: (Lopez 24)
- For sources with multiple authors, separate their names with the word “and:” (Anderson and Smith 55-56) or (Taylor, Gomez, and Austin 89)
- If you use the author’s name in your lead-in to the quote, you just need to provide the year in parentheses: According to Luz Lopez, “the green grass symbolizes a fresh start for Lia (24).”

- An APA citation for a direct quote looks like this: (Ronan, 2019, p. 10)
- If you’re citing multiple authors, separate their names with the word “and:” (Cruz, Hanks, and Simmons, 2019, p. 85)
- If you incorporated the author’s name into your lead-in, you can just give the year and page number: Based on Ronan’s (2019, p. 10) analysis, “coffee breaks improve productivity.”

- For instance, a Chicago Style citation will look like this: (Alexander 2019, 125)
- If you’re quoting a source with multiple authors, separate them with the word “and:” (Pattinson, Stewart, and Green 2019, 175)
- If you already incorporated the author’s name into your quote, then you can just provide the year and page number: According to Alexander, “the smell of roses increases feelings of happiness” (2019, 125).

- For MLA, you'd cite an article like this: Lopez, Luz. "A Fresh Blossom: Imagery in 'Her Darkest Sunshine.'" Journal of Stories , vol. 2, no. 5, 2019, p. 15-22. [17] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- In APA, you'd cite an article like this: Lopez, Luz. (2019). A Fresh Blossom: Imagery in "Her Darkest Sunshine." Journal of Stories , 2(5), 15-22. [18] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- For Chicago Style, your article citation would look like this: Lopez, Luz. "A Fresh Blossom: Imagery in 'Her Darkest Sunshine.'" Journal of Stories 2 no. 4 (2019): 15-22. [19] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
Selecting a Quote

Tip: Quotes are most effective when the original language of the person or text you’re quoting is worth repeating word-for-word.

- If you’re struggling to explain the quote or link it back to your argument, then it’s likely not a good idea to include it in your essay.

- Paraphrases and summaries work just like a direct quote, except that you don’t need to put quotation marks around them because you’re using your own words to restate ideas. However, you still need to cite the sources you used.
Community Q&A

- Always cite your quotes properly. If you don't, it is considered plagiarism. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.ursinus.edu/live/files/1160-integrating-quotespdf
- ↑ https://lsa.umich.edu/sweetland/undergraduates/writing-guides/how-do-i-incorporate-quotes-.html
- ↑ https://helpfulprofessor.com/quotes/
- ↑ https://advice.writing.utoronto.ca/using-sources/quotations/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_formatting_quotations.html
- ↑ https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/apaquickguide/intext
- ↑ https://www.chicagomanualofstyle.org/tools_citationguide/citation-guide-2.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_formatting_and_style_guide.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/reference_list_articles_in_periodicals.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/chicago_manual_17th_edition/cmos_formatting_and_style_guide/periodicals.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/quotations/
About This Article

Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...
To put a quote in an essay, incorporate it directly into a sentence if it's shorter than 4 typed lines. For example, you could write "According to researchers," and then insert the quote. If a quote is longer than 4 typed lines, set it off from the rest of the paragraph, and don't put quotes around it. After the quote, include an in-text citation so readers know where it's from. The right way to cite the quote will depend on whether you're using MLA, APA, or Chicago Style formatting. For more tips from our English co-author, like how to omit words from a quote, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Did this article help you?
Bobby Hilltop
May 26, 2017
Sarah Okyere
Mar 29, 2019
May 19, 2019
Feb 6, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Offer of the decade FLAT 20% off + sign up bonus of $20 Order Now
- [email protected]
- +14159918581
Files Missing!
Please upload all relevant files for quick & complete assistance.
Put a Quote in an Essay
Home / Blog / How To Put A Quote In An Essay (with Examples)

Introduction
When writing an essay , it is essential to incorporate quotes from reputable sources to support your arguments and ideas. However, knowing how to use quotes effectively is crucial in maintaining the flow and clarity of your essay. This blog will discuss the proper ways to put a quote in an essay with examples.
Why Use Quotes in an Essay?
Quotes are used in an essay to support or reinforce the writer's arguments and ideas. They provide evidence for your claims and demonstrate that your argument is backed up by research and authority. Incorporating quotes also helps to provide context and depth to your writing and can add a unique perspective to your essay.
Types of Quotes
There are two types of quotes you can use in your essay: direct quotes and indirect quotes.
Direct Quotes: Direct quotes are the exact words used by the source that you are quoting. When using direct quotes, you need to use quotation marks and indicate the source.
Example: According to John Smith, "The Earth is round."
Indirect Quotes: Indirect quotes are a paraphrase of the original source. When using indirect quotes, you do not need to use quotation marks.
Example: John Smith claims that the Earth is round.
How to Put a Quote in an Essay
When using quotes in an essay, there are several rules that you need to follow to ensure that your writing is clear, accurate, and appropriate. Here are the steps to follow:
Step 1: Choose a Relevant Quote
Before you start writing your essay, identify the quotes that you want to use to support your arguments. Ensure that the quotes you select are relevant, reliable, and add value to your essay.
Step 2: Introduce the Quote
Introduce the quote by providing context and indicating who the source is. This will help the reader understand the significance of the quote and its relevance to your argument.
Example: According to Jane Doe, a renowned climate scientist, "Climate change is the biggest threat facing humanity."
Step 3: Use Quotation Marks
When using a direct quote, use quotation marks to indicate that you are using the exact words of the source.
Example: According to Jane Doe, "Climate change is the biggest threat facing humanity."
Step 4: Provide the Source
Provide the source of the quote, including the author's name, the title of the book or article, and the page number. This will help the reader find the source if they want to read it.
Example: According to Jane Doe, a renowned climate scientist, "Climate change is the biggest threat facing humanity." (Doe, The State of the Climate, p. 25)
Step 5: Punctuate Correctly
Punctuate the quote correctly by placing the comma or period inside the quotation marks, depending on whether it is a part of the quote or your sentence.
Step 6: Explain the Quote
Explain the significance of the quote in your own words. This will help the reader understand how the quote supports your argument.
Example: Jane Doe's quote highlights the urgency of addressing climate change as it poses a significant threat to human survival.
Step 7: Cite Your Sources
Ensure that you cite your sources correctly using the citation style specified by your instructor or the style guide for your discipline.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Quotes in an Essay
Using quotes in an essay can be tricky, and many students make mistakes that can impact the quality of their writing. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when using quotes in an essay:
Failing to provide context: It is essentialto provide context when using a quote in an essay. Failure to do so can confuse the reader and make the quote appear out of place. Always introduce the quote and provide some background information about the source and why you are using the quote.
Overusing quotes: While quotes can add value to your essay, it is essential not to overuse them. Use quotes sparingly and only when necessary. Overusing quotes can make your writing appear lazy, and it may give the impression that you are not confident in your own ideas.
Incorrectly citing sources: Always cite your sources correctly using the citation style specified by your instructor or the style guide for your discipline. Failure to do so can lead to accusations of plagiarism , which can have serious consequences.
Misquoting or altering a quote: When using a direct quote, it is essential to use the exact words of the source. Do not alter the quote or misquote the source as this can distort the meaning and accuracy of the quote.
Failing to explain the quote: When using a quote, it is important to explain its significance and how it supports your argument. Failure to do so can make the quote appear irrelevant and disconnected from your essay.
Examples of Quotes in an Essay
Here are some examples of how to use quotes in an essay:
Example 1: Argumentative Essay
Topic: Should students be required to wear school uniforms?
Quote: "School uniforms promote a sense of unity and equality among students, and they help to reduce instances of bullying based on clothing." (Johnson, School Uniforms, p. 10)
Explanation: The quote supports the argument that school uniforms can have a positive impact on student behavior and reduce instances of bullying. It is introduced with the source and provides context for the argument.
Example 2: Persuasive Essay
Topic: The importance of recycling
Quote: "Every ton of paper that is recycled saves 17 trees, 7,000 gallons of water, and 463 gallons of oil." (Environmental Protection Agency)
Explanation: The quote provides a powerful statistic that supports the importance of recycling. It is introduced with the source, and its significance is explained in the following sentences.
Example 3: Expository Essay
Topic: The history of the American Civil War
Quote: "Four score and seven years ago, our fathers brought forth on this continent, a new nation, conceived in Liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal." (Lincoln, Gettysburg Address)
Explanation: The quote is an iconic line from Abraham Lincoln's Gettysburg Address, which is a significant event in American history. It is introduced with the source, and its significance is explained in the following sentences.
Incorporating quotes in an essay can add depth, context, and authority to your writing. However, it is important to use quotes effectively and appropriately. Always choose relevant and reliable quotes, introduce them with context, use the correct punctuation, explain their significance, and cite your sources correctly. By following these guidelines, you can effectively use quotes in your essay and improve the quality of your writing.
Do you want to share?
You might also like.

Top 100 Persuasive Essay Topics/Ideas for Students

Discursive Essay Topics for Students

How to Write an Essay Introduction?

How to Write a Law Essay: Writing Guide with Examples

How to Choose Ideal Argumentative Essay Topics to Work On

PEEL Paragraph a Guide to Write a Perfect Essay

100 Effective Persuasive Essay Topics

How to Write a Descriptive Essay?- Guide with Examples

Who Am I Essay : How to Write it?
Leave a reply, place order.
Want Impressive Essay Help?
Submit your requirements here

-->Admin --> Published On Oct 3, 2023 | Updated on Oct 4, 2023

-->Admin --> Published On Sep 30, 2023 | Updated on Sep 30, 2023

-->Admin --> Published On Sep 26, 2023 | Updated on Sep 26, 2023

-->Admin --> Published On Sep 22, 2023 | Updated on Sep 26, 2023

-->Admin --> Published On Sep 5, 2023 | Updated on Sep 11, 2023
Assignment Help
Dissertation
Research Paper

-->Admin --> Published On Apr 18, 2019 | Updated on Aug 10, 2023

-->Admin --> Published On Sep 22, 2018 | Updated on Sep 12, 2023

-->Admin --> Published On Feb 13, 2019 | Updated on Aug 10, 2023

-->Admin --> Published On Apr 5, 2023 | Updated on Aug 10, 2023

-->Admin --> Published On Jun 22, 2020 | Updated on Aug 10, 2023
Subscribe Newsletter
You can place your order for free now. Simply submit your order and see what our writers can Subscribe to get regular update!
Thank you for commenting.
Thank you for subscribed newsletter.
Thank You For Commenting.
Get acquainted with the top essay helpers in the country and glide smoothly towards your academic goals with the necessary essay writing help online from US’s top professionals.
Want quick $20? Share your details with us.
Thank you for subscribing our newsletter
Have any Query? Contact with us
Have a thesis expert improve your writing
Check your thesis for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- How to Quote | Citing Quotes in Harvard & APA
How to Quote | Citing Quotes in Harvard & APA
Published on 15 April 2022 by Shona McCombes and Jack Caulfield. Revised on 3 September 2022.
Quoting means copying a passage of someone else’s words and crediting the source. To quote a source, you must ensure:
- The quoted text is enclosed in quotation marks (usually single quotation marks in UK English, though double is acceptable as long as you’re consistent) or formatted as a block quote
- The original author is correctly cited
- The text is identical to the original
The exact format of a quote depends on its length and on which citation style you are using. Quoting and citing correctly is essential to avoid plagiarism , which is easy to detect with a good plagiarism checker .

Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
How to cite a quote in harvard and apa style, introducing quotes, quotes within quotes, shortening or altering a quote, block quotes, when should i use quotes, frequently asked questions about quoting sources.
Every time you quote, you must cite the source correctly . This looks slightly different depending on the citation style you’re using.
Citing a quote in Harvard style
When you include a quote in Harvard style, you must add a Harvard in-text citation giving the author’s last name, the year of publication, and a page number if available. Any full stop or comma appears after the citation, not within the quotation marks.
Citations can be parenthetical or narrative. In a parenthetical citation , you place all the information in brackets after the quote. In a narrative citation , you name the author in your sentence (followed by the year), and place the page number after the quote.
- Evolution is a gradual process that ‘can act only by very short and slow steps’ (Darwin, 1859, p. 510) . Darwin (1859) explains that evolution ‘can act only by very short and slow steps’ (p. 510) .
Complete guide to Harvard style
Citing a quote in APA Style
To cite a direct quote in APA , you must include the author’s last name, the year, and a page number, all separated by commas. If the quote appears on a single page, use ‘p.’; if it spans a page range, use ‘pp.’
An APA in-text citation can be parenthetical or narrative. In a parenthetical citation , you place all the information in parentheses after the quote. In a narrative citation , you name the author in your sentence (followed by the year), and place the page number after the quote.
Punctuation marks such as full stops and commas are placed after the citation, not within the quotation marks.
- Evolution is a gradual process that ‘can act only by very short and slow steps’ (Darwin, 1859, p. 510) .
- Darwin (1859) explains that evolution ‘can act only by very short and slow steps’ (p. 510) .
Complete guide to APA
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing.
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Make sure you integrate quotes properly into your text by introducing them in your own words, showing the reader why you’re including the quote and providing any context necessary to understand it. Don’t present quotations as stand-alone sentences.
There are three main strategies you can use to introduce quotes in a grammatically correct way:
- Add an introductory sentence
- Use an introductory signal phrase
- Integrate the quote into your own sentence
The following examples use APA Style citations, but these strategies can be used in all styles.
Introductory sentence
Introduce the quote with a full sentence ending in a colon . Don’t use a colon if the text before the quote isn’t a full sentence.
If you name the author in your sentence, you may use present-tense verbs, such as “states’, ‘argues’, ‘explains’, ‘writes’, or ‘reports’, to describe the content of the quote.
- In Denmark, a recent poll shows that: ‘A membership referendum held today would be backed by 55 percent of Danish voters’ (Levring, 2018, p. 3).
- In Denmark, a recent poll shows that support for the EU has grown since the Brexit vote: ‘A membership referendum held today would be backed by 55 percent of Danish voters’ (Levring, 2018, p. 3).
- Levring (2018) reports that support for the EU has grown since the Brexit vote: ‘A membership referendum held today would be backed by 55 percent of Danish voters’ (p. 3).
Introductory signal phrase
You can also use a signal phrase that mentions the author or source but doesn’t form a full sentence. In this case, you follow the phrase with a comma instead of a colon.
- According to a recent poll, ‘A membership referendum held today would be backed by 55 percent of Danish voters’ (Levring, 2018, p. 3).
- As Levring (2018) explains, ‘A membership referendum held today would be backed by 55 percent of Danish voters’ (p. 3).
Integrated into your own sentence
To quote a phrase that doesn’t form a full sentence, you can also integrate it as part of your sentence, without any extra punctuation.
- A recent poll suggests that EU membership ‘would be backed by 55 percent of Danish voters’ in a referendum (Levring, 2018, p. 3).
- Levring (2018) reports that EU membership ‘would be backed by 55 percent of Danish voters’ in a referendum (p. 3).
When you quote text that itself contains another quote, this is called a nested quotation or a quote within a quote. It may occur, for example, when quoting dialogue from a novel.
To distinguish this quote from the surrounding quote, you enclose it in double (instead of single) quotation marks (even if this involves changing the punctuation from the original text). Make sure to close both sets of quotation marks at the appropriate moments.
Note that if you only quote the nested quotation itself, and not the surrounding text, you can just use single quotation marks.
- Carraway introduces his narrative by quoting his father: ‘ ‘ Whenever you feel like criticizing anyone, ‘ he told me, ‘ just remember that all the people in this world haven’t had the advantages that you’ve had ‘ ‘ (Fitzgerald 1).
- Carraway introduces his narrative by quoting his father: ‘”Whenever you feel like criticizing anyone,” he told me, “just remember that all the people in this world haven’t had the advantages that you’ve had “ (Fitzgerald 1).
- Carraway introduces his narrative by quoting his father: ‘“Whenever you feel like criticizing anyone,” he told me, “just remember that all the people in this world haven’t had the advantages that you’ve had”’ (Fitzgerald 1).
- Carraway begins by quoting his father’s invocation to ‘remember that all the people in this world haven’t had the advantages that you’ve had’ (Fitzgerald 1).
Note: When the quoted text in the source comes from another source, it’s best to just find that original source in order to quote it directly. If you can’t find the original source, you can instead cite it indirectly .
Often, incorporating a quote smoothly into your text requires you to make some changes to the original text. It’s fine to do this, as long as you clearly mark the changes you’ve made to the quote.
Shortening a quote
If some parts of a passage are redundant or irrelevant, you can shorten the quote by removing words, phrases, or sentences and replacing them with an ellipsis (…). Put a space before and after the ellipsis.
Be careful that removing the words doesn’t change the meaning. The ellipsis indicates that some text has been removed, but the shortened quote should still accurately represent the author’s point.
Altering a quote
You can add or replace words in a quote when necessary. This might be because the original text doesn’t fit grammatically with your sentence (e.g., it’s in a different tense), or because extra information is needed to clarify the quote’s meaning.
Use brackets to distinguish words that you have added from words that were present in the original text.
The Latin term ‘ sic ‘ is used to indicate a (factual or grammatical) mistake in a quotation. It shows the reader that the mistake is from the quoted material, not a typo of your own.
In some cases, it can be useful to italicise part of a quotation to add emphasis, showing the reader that this is the key part to pay attention to. Use the phrase ’emphasis added’ to show that the italics were not part of the original text.
You usually don’t need to use brackets to indicate minor changes to punctuation or capitalisation made to ensure the quote fits the style of your text.
If you quote more than a few lines from a source, you must format it as a block quote . Instead of using quotation marks, you set the quote on a new line and indent it so that it forms a separate block of text.
Block quotes are cited just like regular quotes, except that if the quote ends with a full stop, the citation appears after the full stop.
To the end of his days Bilbo could never remember how he found himself outside, without a hat, a walking-stick or any money, or anything that he usually took when he went out; leaving his second breakfast half-finished and quite unwashed-up, pushing his keys into Gandalf’s hands, and running as fast as his furry feet could carry him down the lane, past the great Mill, across The Water, and then on for a mile or more. (16)
Avoid relying too heavily on quotes in academic writing . To integrate a source , it’s often best to paraphrase , which means putting the passage into your own words. This helps you integrate information smoothly and keeps your own voice dominant.
However, there are some situations in which quotes are more appropriate.
When focusing on language
If you want to comment on how the author uses language (for example, in literary analysis ), it’s necessary to quote so that the reader can see the exact passage you are referring to.
When giving evidence
To convince the reader of your argument, interpretation or position on a topic, it’s often helpful to include quotes that support your point. Quotes from primary sources (for example, interview transcripts or historical documents) are especially credible as evidence.
When presenting an author’s position or definition
When you’re referring to secondary sources such as scholarly books and journal articles, try to put others’ ideas in your own words when possible.
But if a passage does a great job at expressing, explaining, or defining something, and it would be very difficult to paraphrase without changing the meaning or losing the weakening the idea’s impact, it’s worth quoting directly.
A quote is an exact copy of someone else’s words, usually enclosed in quotation marks and credited to the original author or speaker.
To present information from other sources in academic writing , it’s best to paraphrase in most cases. This shows that you’ve understood the ideas you’re discussing and incorporates them into your text smoothly.
It’s appropriate to quote when:
- Changing the phrasing would distort the meaning of the original text
- You want to discuss the author’s language choices (e.g., in literary analysis )
- You’re presenting a precise definition
- You’re looking in depth at a specific claim
Every time you quote a source , you must include a correctly formatted in-text citation . This looks slightly different depending on the citation style .
For example, a direct quote in APA is cited like this: ‘This is a quote’ (Streefkerk, 2020, p. 5).
Every in-text citation should also correspond to a full reference at the end of your paper.
In scientific subjects, the information itself is more important than how it was expressed, so quoting should generally be kept to a minimum. In the arts and humanities, however, well-chosen quotes are often essential to a good paper.
In social sciences, it varies. If your research is mainly quantitative , you won’t include many quotes, but if it’s more qualitative , you may need to quote from the data you collected .
As a general guideline, quotes should take up no more than 5–10% of your paper. If in doubt, check with your instructor or supervisor how much quoting is appropriate in your field.
If you’re quoting from a text that paraphrases or summarises other sources and cites them in parentheses , APA recommends retaining the citations as part of the quote:
- Smith states that ‘the literature on this topic (Jones, 2015; Sill, 2019; Paulson, 2020) shows no clear consensus’ (Smith, 2019, p. 4).
Footnote or endnote numbers that appear within quoted text should be omitted.
If you want to cite an indirect source (one you’ve only seen quoted in another source), either locate the original source or use the phrase ‘as cited in’ in your citation.
A block quote is a long quote formatted as a separate ‘block’ of text. Instead of using quotation marks , you place the quote on a new line, and indent the entire quote to mark it apart from your own words.
APA uses block quotes for quotes that are 40 words or longer.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & Caulfield, J. (2022, September 03). How to Quote | Citing Quotes in Harvard & APA. Scribbr. Retrieved 6 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/working-sources/quoting/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to paraphrase | step-by-step guide & examples, how to avoid plagiarism | tips on citing sources, the 5 types of plagiarism | explanations & examples.

What this handout is about
Used effectively, quotations can provide important pieces of evidence and lend fresh voices and perspectives to your narrative. Used ineffectively, however, quotations can clutter your text and interrupt the flow of your argument. This handout will help you decide when and how to quote like a pro.
When should I quote?
Use quotations at strategically selected moments. You have probably been told by teachers to provide as much evidence as possible in support of your thesis. But packing your paper with quotations will not necessarily strengthen your argument. The majority of your paper should still be your original ideas in your own words (after all, it’s your paper). And quotations are only one type of evidence: well-balanced papers may also make use of paraphrases, data, and statistics. The types of evidence you use will depend in part on the conventions of the discipline or audience for which you are writing. For example, papers analyzing literature may rely heavily on direct quotations of the text, while papers in the social sciences may have more paraphrasing, data, and statistics than quotations.
Discussing specific arguments or ideas
Sometimes, in order to have a clear, accurate discussion of the ideas of others, you need to quote those ideas word for word. Suppose you want to challenge the following statement made by John Doe, a well-known historian:
“At the beginning of World War Two, almost all Americans assumed the war would end quickly.”
If it is especially important that you formulate a counterargument to this claim, then you might wish to quote the part of the statement that you find questionable and establish a dialogue between yourself and John Doe:
Historian John Doe has argued that in 1941 “almost all Americans assumed the war would end quickly” (Doe 223). Yet during the first six months of U.S. involvement, the wives and mothers of soldiers often noted in their diaries their fear that the war would drag on for years.
Giving added emphasis to a particularly authoritative source on your topic.
There will be times when you want to highlight the words of a particularly important and authoritative source on your topic. For example, suppose you were writing an essay about the differences between the lives of male and female slaves in the U.S. South. One of your most provocative sources is a narrative written by a former slave, Harriet Jacobs. It would then be appropriate to quote some of Jacobs’s words:
Harriet Jacobs, a former slave from North Carolina, published an autobiographical slave narrative in 1861. She exposed the hardships of both male and female slaves but ultimately concluded that “slavery is terrible for men; but it is far more terrible for women.”
In this particular example, Jacobs is providing a crucial first-hand perspective on slavery. Thus, her words deserve more exposure than a paraphrase could provide.
Jacobs is quoted in Harriet A. Jacobs, Incidents in the Life of a Slave Girl, ed. Jean Fagan Yellin (Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 1987).
Analyzing how others use language.
This scenario is probably most common in literature and linguistics courses, but you might also find yourself writing about the use of language in history and social science classes. If the use of language is your primary topic, then you will obviously need to quote users of that language.
Examples of topics that might require the frequent use of quotations include:
Southern colloquial expressions in William Faulkner’s Light in August
Ms. and the creation of a language of female empowerment
A comparison of three British poets and their use of rhyme
Spicing up your prose.
In order to lend variety to your prose, you may wish to quote a source with particularly vivid language. All quotations, however, must closely relate to your topic and arguments. Do not insert a quotation solely for its literary merits.
One example of a quotation that adds flair:
President Calvin Coolidge’s tendency to fall asleep became legendary. As H. L. Mencken commented in the American Mercury in 1933, “Nero fiddled, but Coolidge only snored.”
How do I set up and follow up a quotation?
Once you’ve carefully selected the quotations that you want to use, your next job is to weave those quotations into your text. The words that precede and follow a quotation are just as important as the quotation itself. You can think of each quote as the filling in a sandwich: it may be tasty on its own, but it’s messy to eat without some bread on either side of it. Your words can serve as the “bread” that helps readers digest each quote easily. Below are four guidelines for setting up and following up quotations.
In illustrating these four steps, we’ll use as our example, Franklin Roosevelt’s famous quotation, “The only thing we have to fear is fear itself.”
1. Provide context for each quotation.
Do not rely on quotations to tell your story for you. It is your responsibility to provide your reader with context for the quotation. The context should set the basic scene for when, possibly where, and under what circumstances the quotation was spoken or written. So, in providing context for our above example, you might write:
When Franklin Roosevelt gave his inaugural speech on March 4, 1933, he addressed a nation weakened and demoralized by economic depression.
2. Attribute each quotation to its source.
Tell your reader who is speaking. Here is a good test: try reading your text aloud. Could your reader determine without looking at your paper where your quotations begin? If not, you need to attribute the quote more noticeably.
Avoid getting into the “they said” attribution rut! There are many other ways to attribute quotes besides this construction. Here are a few alternative verbs, usually followed by “that”:
Different reporting verbs are preferred by different disciplines, so pay special attention to these in your disciplinary reading. If you’re unfamiliar with the meanings of any of these words or others you find in your reading, consult a dictionary before using them.
3. Explain the significance of the quotation.
Once you’ve inserted your quotation, along with its context and attribution, don’t stop! Your reader still needs your assessment of why the quotation holds significance for your paper. Using our Roosevelt example, if you were writing a paper on the first one-hundred days of FDR’s administration, you might follow the quotation by linking it to that topic:
With that message of hope and confidence, the new president set the stage for his next one-hundred days in office and helped restore the faith of the American people in their government.
4. Provide a citation for the quotation.
All quotations, just like all paraphrases, require a formal citation. For more details about particular citation formats, see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . In general, you should remember one rule of thumb: Place the parenthetical reference or footnote/endnote number after—not within—the closed quotation mark.
Roosevelt declared, “The only thing we have to fear is fear itself” (Roosevelt, Public Papers, 11).
Roosevelt declared, “The only thing we have to fear is fear itself.”1
How do I embed a quotation into a sentence?
In general, avoid leaving quotes as sentences unto themselves. Even if you have provided some context for the quote, a quote standing alone can disrupt your flow. Take a look at this example:
Hamlet denies Rosencrantz’s claim that thwarted ambition caused his depression. “I could be bounded in a nutshell and count myself a king of infinite space” (Hamlet 2.2).
Standing by itself, the quote’s connection to the preceding sentence is unclear. There are several ways to incorporate a quote more smoothly:
Lead into the quote with a colon.
Hamlet denies Rosencrantz’s claim that thwarted ambition caused his depression: “I could be bounded in a nutshell and count myself a king of infinite space” (Hamlet 2.2).
The colon announces that a quote will follow to provide evidence for the sentence’s claim.
Introduce or conclude the quote by attributing it to the speaker. If your attribution precedes the quote, you will need to use a comma after the verb.
Hamlet denies Rosencrantz’s claim that thwarted ambition caused his depression. He states, “I could be bounded in a nutshell and count myself a king of infinite space” (Hamlet 2.2).
When faced with a twelve-foot mountain troll, Ron gathers his courage, shouting, “Wingardium Leviosa!” (Rowling, p. 176).
The Pirate King sees an element of regality in their impoverished and dishonest life. “It is, it is a glorious thing/To be a pirate king,” he declares (Pirates of Penzance, 1983).
Interrupt the quote with an attribution to the speaker. Again, you will need to use a comma after the verb, as well as a comma leading into the attribution.
“There is nothing either good or bad,” Hamlet argues, “but thinking makes it so” (Hamlet 2.2).
“And death shall be no more,” Donne writes, “Death thou shalt die” (“Death, Be Not Proud,” l. 14).
Dividing the quote may highlight a particular nuance of the quote’s meaning. In the first example, the division calls attention to the two parts of Hamlet’s claim. The first phrase states that nothing is inherently good or bad; the second phrase suggests that our perspective causes things to become good or bad. In the second example, the isolation of “Death thou shalt die” at the end of the sentence draws a reader’s attention to that phrase in particular. As you decide whether or not you want to break up a quote, you should consider the shift in emphasis that the division might create.
Use the words of the quote grammatically within your own sentence.
When Hamlet tells Rosencrantz that he “could be bounded in a nutshell and count [him]self a king of infinite space” (Hamlet 2.2), he implies that thwarted ambition did not cause his depression.
Ultimately, death holds no power over Donne since in the afterlife, “death shall be no more” (“Death, Be Not Proud,” l. 14).
Note that when you use “that” after the verb that introduces the quote, you no longer need a comma.
The Pirate King argues that “it is, it is a glorious thing/to be a pirate king” (Pirates of Penzance, 1983).
How much should I quote?
As few words as possible. Remember, your paper should primarily contain your own words, so quote only the most pithy and memorable parts of sources. Here are guidelines for selecting quoted material judiciously:
Excerpt fragments.
Sometimes, you should quote short fragments, rather than whole sentences. Suppose you interviewed Jane Doe about her reaction to John F. Kennedy’s assassination. She commented:
“I couldn’t believe it. It was just unreal and so sad. It was just unbelievable. I had never experienced such denial. I don’t know why I felt so strongly. Perhaps it was because JFK was more to me than a president. He represented the hopes of young people everywhere.”
You could quote all of Jane’s comments, but her first three sentences are fairly redundant. You might instead want to quote Jane when she arrives at the ultimate reason for her strong emotions:
Jane Doe grappled with grief and disbelief. She had viewed JFK, not just as a national figurehead, but as someone who “represented the hopes of young people everywhere.”
Excerpt those fragments carefully!
Quoting the words of others carries a big responsibility. Misquoting misrepresents the ideas of others. Here’s a classic example of a misquote:
John Adams has often been quoted as having said: “This would be the best of all possible worlds if there were no religion in it.”
John Adams did, in fact, write the above words. But if you see those words in context, the meaning changes entirely. Here’s the rest of the quotation:
Twenty times, in the course of my late reading, have I been on the point of breaking out, ‘this would be the best of all possible worlds, if there were no religion in it!!!!’ But in this exclamation, I should have been as fanatical as Bryant or Cleverly. Without religion, this world would be something not fit to be mentioned in public company—I mean hell.
As you can see from this example, context matters!
This example is from Paul F. Boller, Jr. and John George, They Never Said It: A Book of Fake Quotes, Misquotes, and Misleading Attributions (Oxford University Press, 1989).
Use block quotations sparingly.
There may be times when you need to quote long passages. However, you should use block quotations only when you fear that omitting any words will destroy the integrity of the passage. If that passage exceeds four lines (some sources say five), then set it off as a block quotation.
Be sure you are handling block quotes correctly in papers for different academic disciplines–check the index of the citation style guide you are using. Here are a few general tips for setting off your block quotations:
- Set up a block quotation with your own words followed by a colon.
- Indent. You normally indent 4-5 spaces for the start of a paragraph. When setting up a block quotation, indent the entire paragraph once from the left-hand margin.
- Single space or double space within the block quotation, depending on the style guidelines of your discipline (MLA, CSE, APA, Chicago, etc.).
- Do not use quotation marks at the beginning or end of the block quote—the indentation is what indicates that it’s a quote.
- Place parenthetical citation according to your style guide (usually after the period following the last sentence of the quote).
- Follow up a block quotation with your own words.
So, using the above example from John Adams, here’s how you might include a block quotation:
After reading several doctrinally rigid tracts, John Adams recalled the zealous ranting of his former teacher, Joseph Cleverly, and minister, Lemuel Bryant. He expressed his ambivalence toward religion in an 1817 letter to Thomas Jefferson:
Adams clearly appreciated religion, even if he often questioned its promotion.
How do I combine quotation marks with other punctuation marks?
It can be confusing when you start combining quotation marks with other punctuation marks. You should consult a style manual for complicated situations, but the following two rules apply to most cases:
Keep periods and commas within quotation marks.
So, for example:
According to Professor Poe, werewolves “represent anxiety about the separation between human and animal,” and werewolf movies often “interrogate those boundaries.”
In the above example, both the comma and period were enclosed in the quotation marks. The main exception to this rule involves the use of internal citations, which always precede the last period of the sentence. For example:
According to Professor Poe, werewolves “represent anxiety about the separation between human and animal,” and werewolf movies often “interrogate those boundaries” (Poe 167).
Note, however, that the period remains inside the quotation marks when your citation style involves superscript footnotes or endnotes. For example:
According to Professor Poe, werewolves “represent anxiety about the separation between human and animal,” and werewolf movies often “interrogate those boundaries.” 2
Place all other punctuation marks (colons, semicolons, exclamation marks, question marks) outside the quotation marks, except when they were part of the original quotation.
Take a look at the following examples:
I couldn’t believe it when my friend passed me a note in the cafe saying the management “started charging $15 per hour for parking”!
The coach yelled, “Run!”
In the first example, the author placed the exclamation point outside the quotation mark because she added it herself to emphasize the outrageous nature of the parking price change. The original note had not included an exclamation mark. In the second example, the exclamation mark remains within the quotation mark because it is indicating the excited tone in which the coach yelled the command. Thus, the exclamation mark is considered to be part of the original quotation.
How do I indicate quotations within quotations?
If you are quoting a passage that contains a quotation, then you use single quotation marks for the internal quotation. Quite rarely, you quote a passage that has a quotation within a quotation. In that rare instance, you would use double quotation marks for the second internal quotation.
Here’s an example of a quotation within a quotation:
In “The Emperor’s New Clothes,” Hans Christian Andersen wrote, “‘But the Emperor has nothing on at all!’ cried a little child.”
Remember to consult your style guide to determine how to properly cite a quote within a quote.
When do I use those three dots ( . . . )?
Whenever you want to leave out material from within a quotation, you need to use an ellipsis, which is a series of three periods, each of which should be preceded and followed by a space. So, an ellipsis in this sentence would look like . . . this. There are a few rules to follow when using ellipses:
Be sure that you don’t fundamentally change the meaning of the quotation by omitting material.
Take a look at the following example:
“The Writing Center is located on the UNC campus and serves the entire UNC community.”
“The Writing Center . . . serves the entire UNC community.”
The reader’s understanding of the Writing Center’s mission to serve the UNC community is not affected by omitting the information about its location.
Do not use ellipses at the beginning or ending of quotations, unless it’s important for the reader to know that the quotation was truncated.
For example, using the above example, you would NOT need an ellipsis in either of these situations:
“The Writing Center is located on the UNC campus . . .”
The Writing Center ” . . . serves the entire UNC community.”
Use punctuation marks in combination with ellipses when removing material from the end of sentences or clauses.
For example, if you take material from the end of a sentence, keep the period in as usual.
“The boys ran to school, forgetting their lunches and books. Even though they were out of breath, they made it on time.”
“The boys ran to school. . . . Even though they were out of breath, they made it on time.”
Likewise, if you excerpt material at the end of clause that ends in a comma, retain the comma.
“The red car came to a screeching halt that was heard by nearby pedestrians, but no one was hurt.”
“The red car came to a screeching halt . . . , but no one was hurt.”
Is it ever okay to insert my own words or change words in a quotation?
Sometimes it is necessary for clarity and flow to alter a word or words within a quotation. You should make such changes rarely. In order to alert your reader to the changes you’ve made, you should always bracket the altered words. Here are a few examples of situations when you might need brackets:
Changing verb tense or pronouns in order to be consistent with the rest of the sentence.
Suppose you were quoting a woman who, when asked about her experiences immigrating to the United States, commented “nobody understood me.” You might write:
Esther Hansen felt that when she came to the United States “nobody understood [her].”
In the above example, you’ve changed “me” to “her” in order to keep the entire passage in third person. However, you could avoid the need for this change by simply rephrasing:
“Nobody understood me,” recalled Danish immigrant Esther Hansen.
Including supplemental information that your reader needs in order to understand the quotation.
For example, if you were quoting someone’s nickname, you might want to let your reader know the full name of that person in brackets.
“The principal of the school told Billy [William Smith] that his contract would be terminated.”
Similarly, if a quotation referenced an event with which the reader might be unfamiliar, you could identify that event in brackets.
“We completely revised our political strategies after the strike [of 1934].”
Indicating the use of nonstandard grammar or spelling.
In rare situations, you may quote from a text that has nonstandard grammar, spelling, or word choice. In such cases, you may want to insert [sic], which means “thus” or “so” in Latin. Using [sic] alerts your reader to the fact that this nonstandard language is not the result of a typo on your part. Always italicize “sic” and enclose it in brackets. There is no need to put a period at the end. Here’s an example of when you might use [sic]:
Twelve-year-old Betsy Smith wrote in her diary, “Father is afraid that he will be guilty of beach [sic] of contract.”
Here [sic] indicates that the original author wrote “beach of contract,” not breach of contract, which is the accepted terminology.
Do not overuse brackets!
For example, it is not necessary to bracket capitalization changes that you make at the beginning of sentences. For example, suppose you were going to use part of this quotation:
“The colors scintillated curiously over a hard carapace, and the beetle’s tiny antennae made gentle waving motions as though saying hello.”
If you wanted to begin a sentence with an excerpt from the middle of this quotation, there would be no need to bracket your capitalization changes.
“The beetle’s tiny antennae made gentle waving motions as though saying hello,” said Dr. Grace Farley, remembering a defining moment on her journey to becoming an entomologist.
Not: “[T]he beetle’s tiny antennae made gentle waving motions as though saying hello,” said Dr. Grace Farley, remembering a defining moment on her journey to becoming an entomologist.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Barzun, Jacques, and Henry F. Graff. 2012. The Modern Researcher , 6th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage Learning.
Booth, Wayne C., Gregory G. Colomb, Joseph M. Williams, Joseph Bizup, and William T. FitzGerald. 2016. The Craft of Research , 4th ed. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Gibaldi, Joseph. 2009. MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers , 7th ed. New York: The Modern Language Association of America.
Turabian, Kate. 2018. A Manual for Writers of Term Papers, Theses, Dissertations , 9th ed. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
How to use Quotes in an Essay in 7 Simple Steps

A quote can be an effective and powerful literary tool in an essay, but it needs to be done well. To use quotes in an essay, you need to make sure your quotes are short, backed up with explanations, and used rarely. The best essays use a maximum of 2 quotes for every 1500 words.
Rules for using quotes in essays:
- Avoid Long Quotes.
- Quotes should be less than 1 sentence long.
- Match Quotes with Explanations and Examples.
- Use Max. 2 Quotes for 1500 words.
- Use page numbers when Citing Quotes.
- Don’t Italicize Quotes.
- Avoid quotes inside quotes.
Once you have mastered these quotation writing rules you’ll be on your way to growing your marks in your next paper.
How to use Quotes in an Essay
1. avoid long quotes.
There’s a simple rule to follow here: don’t use a quote that is longer than one line. In fact, four word quotes are usually best.
Long quotes in essays are red flags for teachers. It doesn’t matter if it is an amazing quote. Many, many teachers don’t like long quotes, so it’s best to avoid them.
Too many students provide quotes that take up half of a paragraph. This will lose you marks – big time.
If you follow my perfect paragraph formula , you know that most paragraphs should be about six sentences long, which comes out to about six or seven typed lines on paper. That means that your quote will be a maximum of one-sixth (1/6) of your paragraph. This leaves plenty of space for discussion in your own words.
One reason teachers don’t like long quotes is that they suck up your word count. It can start to look like you didn’t have enough to say, so you inserted quotes to pad out your essay. Even if this is only your teacher’s perception, it’s something that you need to be aware of.
Here’s an example of over-use of quotes in paragraphs:
Avoid Quotes that are Too Long
Children who grow up in poverty often end up being poor as adults. “Many adult Americans believe that hard work and drive are important factors on economic mobility. When statistics show that roughly 42% of children born into the bottom level of the income distribution will likely stay there (Isaacs, 2007), this Is a consequence of structural and social barriers.” (Mistry et al., 2016, p. 761). Therefore poverty in childhood needs to be addressed by the government.
This student made the fatal mistake of having the quote overtake the paragraph.
Simply put, don’t use a quote that is longer than one line long. Ever. It’s just too risky.
Personally, I like to use a 4-word quote in my essays. Four-word quotes are long enough to constitute an actual quote but short enough that I have to think about how I will fit that quote around my own writing. This forces me to write quotations that both show:
- I have read the original source, but also:
- I know how to paraphrase
2. Do not use a Quote to that takes up a full Sentence, Starts a Sentence, or Ends a Paragraph
These are three common but fatal mistakes.
Essay quotes that start sentences or end paragraphs make you appear passive.
If you use a quotation in an essay to start a sentence or end a paragraph, your teacher automatically thinks that your quote is replacing analysis, rather than supporting it.
You should instead start the sentence that contains the quote with your own writing. This makes it appear that you have an active voice .
Similarly, you should end a paragraph with your own analysis, not a quote.
Let’s look at some examples of quotes that start sentences and end paragraphs. These examples are poor examples of using quotes:
Avoid Quotes that Start Sentences The theorist Louis Malaguzzi was the founder of the Reggio Emilia Approach to Education. “Children have the ability to learn through play and exploration. Play helps children to learn about their surroundings” (Malaguzzi, 1949, p. 10). Play is better than learning through repetition of drills or reading. Play is good for all children.
Avoid Quotes that End Paragraphs Before Judith Butler gender was seen as being a binary linked to sex, men were masculine and women were feminine. Butler came up with this new idea that gender is just something society has made up over time. “Gender is a fluid concept” (Butler, 1990, p. 136).
Both these quotes are from essays that were shared with me by colleagues. My colleagues marked these students down for these quotes because of the quotes:
- took up full sentences;
- started sentences; and
- were used to end paragraphs.
It didn’t appear as if the students were analyzing the quotes. Instead, the quotes were doing the talking for the students.
There are some easy strategies to use in order to make it appear that you are actively discussing and analyzing quotes.
One is that you should make sure the essay sentences with quotes in them don’t start with the quote . Here are some examples of how we can change the quotes:
Example 1: Start Quote Sentences with an Active Voice The theorist Louis Malaguzzi was the founder of the Reggio Emilia Approach to Education. According to Malaguzzi (1949, p. 10), “children have the ability to learn through play and exploration.” Here, Malaguzzi is highlighting how to play is linked to finding things out about the world. Play is important for children to develop. Play is better than learning through repetition of drills or reading. Play is good for all children.
Here, the sentence with the quote was amended so that the student has an active voice. They start the sentence with According to Malaguzzi, ….
Similarly, in the second example, we can also insert an active voice by ensuring that our quote sentence does not start with a quote:
Example 2: Start Quote Sentences with an Active Voice In 1990, Judith Butler revolutionized Feminist understandings of gender by arguing that “gender is a fluid concept” (p. 136). Before Butler’s 1990 book Gender Trouble , gender was seen as being a binary linked to sex. Men were masculine and women were feminine. Butler came up with this new idea that gender is just something society has made up over time.
In this example, the quote is not at the start of a sentence or end of a paragraph – tick!
How to Start Sentences containing Quotes using an Active Voice
- According to Malaguzzi (1949, p. 10), “…”
- Malaguzzi (1949, p. 10) argues that “…”
- In 1949, Malaguzzi (p. 10) highlighted that “…”
- The argument of Malaguzzi (1949, p. 10) that “…” provides compelling insight into the issue.
3. Match Quotes with Explanations and Examples
Earlier on, I stated that one key reason to use quotes in essays is so that you can analyze them.
Quotes shouldn’t stand alone as explanations. Quotes should be there to be analyzed, not to do the analysis.
Let’s look again at the quote used in Point 1:
Example: A Quote that is Too Long Children who grow up in poverty often end up being poor as adults. “Many adult Americans believe that hard work and drive are important factors in economic mobility. When statistics show that roughly 42% of children born into the bottom level of the income distribution will likely stay there (Isaacs, 2007), this Is a consequence of structural and social barriers.” (Mistry et al., 2016, p. 761). Therefore poverty in childhood needs to be addressed by the government.
This student has included the facts, figures, citations and key details in the quote. Essentially, this student has been lazy. They failed to paraphrase.
Instead, this student could have selected the most striking phrase from the quote and kept it. Then, the rest should be paraphrased. The most striking phrase in this quote was “[poverty] is a consequence of structural and social barriers.” (Mistry et al., 2016, p. 761).
So, take that one key phrase, then paraphrase the rest:
Example: Paraphrasing Long Quotes Children who grow up in poverty often end up being poor as adults. In their analysis, Mistry et al. (2016) highlight that there is a misconception in American society that hard work is enough to escape poverty. Instead, they argue, there is evidence that over 40% of people born in poverty remain in poverty. For Mistry et al. (2016, p. 761), this data shows that poverty is not a matter of being lazy alone, but more importantly “a consequence of structural and social barriers.” This implies that poverty in childhood needs to be addressed by the government.
To recap, quotes shouldn’t do the talking for you . Provide a brief quote in your essay, and then show you understand it with surrounding explanation and analysis.
4. Know how many Quotes to use in an Essay
There’s a simple rule for how many quotes should be in an essay.
Here’s a good rule to follow: one quote for every five paragraphs. A paragraph is usually 150 words long, so you’re looking at one quote in every 750 words, maximum .
To extrapolate that out, you’ll want a maximum of about:
- 2 quotes for a 1500-word paper;
- 3 quotes for a 2000-word paper;
- 4 quotes for a 3000-word paper.
That’s the maximum , not a target. There’s no harm in writing a paper that has absolutely zero quotes in it, so long as it’s still clear that you’ve closely read and paraphrased your readings.
The reason you don’t want to use more quotes than this in your essay is that teachers want to see you saying things in your own words. When you over-use quotes, it is a sign to your teacher that you don’t know how to paraphrase well.
5. Always use page numbers when Citing Quotes in Essays
One biggest problem with quotes are that many students don’t know how to cite quotes in essays.
Nearly every referencing format requires you to include a page number in your citation. This includes the three most common referencing formats: Harvard, APA, and MLA. All of them require you to provide page numbers with quotes.
Citing a Quote in Chicago Style – Include Page Numbers
- Incorrect: “Gender is a fluid concept” (Butler 1990).
- Correct: “Gender is a fluid concept” (Butler 1990, 136).
Citing a Quote in APA and Harvard Styles – Include Page Numbers
- Incorrect: “Gender is a fluid concept” (Butler, 1990).
- Correct: “Gender is a fluid concept” (Butler, 1990, p. 136).
Citing a Quote in MLA Style – Include Page Numbers
- Incorrect: “Gender is a fluid concept” (Butler).
- Correct: “Gender is a fluid concept” (Butler 136).
Including a page number in your quotation makes a huge difference when a marker is trying to determine how high your grade should be.
This is especially true when you’re already up in the higher marks range. These little editing points can mean the difference between placing first in the class and third. Don’t underestimate the importance of attention to detail.
6. Don’t Italicize Quotes
For some reason, students love to use italics for quotes. This is wrong in absolutely every major referencing format, yet it happens all the time.
I don’t know where this started, but please don’t do it. It looks sloppy, and teachers notice. A nice, clean, well-formatted essay should not contain these minor but not insignificant errors. If you want to be a top student, you need to pay attention to minor details.
7. Avoid quotes inside quotes
Have you ever found a great quote and thought, “I want to quote that quote!” Quoting a quote is a tempting thing to do, but not worth your while.
I’ll often see students write something like this:
Poor Quotation Example: Quotes Inside Quotes Rousseau “favored a civil religion because it would be more tolerant of diversity than Christianity. Indeed ‘no state has ever been founded without religion as its base’ (Rousseau, 1913: 180).” (Durkheim, 1947, p. 19).
Here, there are quotes on top of quotes. The student has quoted Durkheim quoting Rousseau. This quote has become a complete mess and hard to read. The minute something’s hard to read, it loses marks.
Here are two solutions:
- Cite the original source. If you really want the Rousseau quote, just cite Rousseau. Stop messing around with quotes on top of quotes.
- Learn the ‘as cited in’ method. Frankly, that method’s too complicated to discuss here. But if you google it, you’ll be able to teach yourself.
When Should I use Quotes in Essays?
1. to highlight an important statement.
One main reason to use quotes in essays is to emphasize a famous statement by a top thinker in your field.
The statement must be important. It can’t be just any random comment.
Here are some examples of when to use quotes in essays to emphasize the words of top thinkers:
- The words of Stephen Hawking go a long way in Physics ;
- The words of JK Rowling go a long way in Creative Writing ;
- The words of Michel Foucault go a long way in Cultural Studies ;
- The words of Jean Piaget go a long way in Education Studies .
2. To analyze an Important Statement.
Another reason to use quotes in essays is when you want to analyze a statement by a specific author. This author might not be famous, but they might have said something that requires unpacking and analyzing. You can provide a quote, then unpack it by explaining your interpretation of it in the following sentences.
Quotes usually need an explanation and example. You can unpack the quote by asking:
- What did they mean,
- Why is it relevant, and
- Why did they say this?
You want to always follow up quotes by top thinkers or specific authors with discussion and analysis.
Quotes should be accompanied by:
- Explanations of the quote;
- Analysis of the ideas presented in the quote; or
- Real-world examples that show you understand what the quote means.
Remember: A quote should be a stimulus for a discussion, not a replacement for discussion.
What Bad Quotes Look Like
Many teachers I have worked with don’t like when students use quotes in essays. In fact, some teachers absolutely hate essay quotes. The teachers I have met tend to hate these sorts of quotes:
- When you use too many quotes.
- When you use the wrong citation format.
- When you don’t provide follow-up explanations of quotes.
- When you used quotes because you don’t know how to paraphrase .

Be a minimalist when it comes to using quotes. Here are the seven approaches I recommend for using quotes in essays:
- Avoid Long Quotes in Essays
- Do not use a Quote that takes up a full Sentence, Starts a Sentence, or Ends a Paragraph
- Match Quotes with Explanations and Examples
- Use a Maximum of 2 Quotes for every 1500 words
- Always use page numbers when Citing Quotes in Essays
- Don’t Italicize Quotes
- Avoid quotes inside quotes

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is IQ? (Intelligence Quotient)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
popular searches
- Request Info
Suggested Ways to Introduce Quotations
To introduce a quote in an essay, don't forget to include author's last name and page number (MLA) or author, date, and page number (APA) in your citation. Shown below are some possible ways to introduce quotations. The examples use MLA format.
Use A Full Sentence Followed by A Colon To Introduce A Quotation
- The setting emphasizes deception: "Nothing is as it appears" (Smith 1).
- Piercy ends the poem on an ironic note: "To every woman a happy ending" (25).
Begin A Sentence with Your Own Words, Then Complete It with Quoted Words
Note that in the second example below, a slash with a space on either side ( / ) marks a line break in the original poem.
- Hamlet's task is to avenge a "foul and most unnatural murder" (Shakespeare 925).
- The speaker is mystified by her sleeping baby, whose "moth-breath / flickers among the flat pink roses" (Plath 17).
Use An Introductory Phrase Naming The Source, Followed By A Comma to Quote A Critic or Researcher
Note that the first letter after the quotation marks should be upper case. According to MLA guidelines, if you change the case of a letter from the original, you must indicate this with brackets. APA format doesn't require brackets.
- According to Smith, "[W]riting is fun" (215).
- In Smith's words, " . . .
- In Smith's view, " . . .
Use A Descriptive Verb, Followed by A Comma To Introduce A Critic's Words
Avoid using says unless the words were originally spoken aloud, for instance, during an interview.
- Smith states, "This book is terrific" (102).
- Smith remarks, " . . .
- Smith writes, " . . .
- Smith notes, " . . .
- Smith comments, " . . .
- Smith observes, " . . .
- Smith concludes, " . . .
- Smith reports, " . . .
- Smith maintains, " . . .
- Smith adds, " . . .
Don't Follow It with A Comma If Your Lead into The Quotation Ends in That or As
The first letter of the quotation should be lower case.
- Smith points out that "millions of students would like to burn this book" (53).
- Smith emphasizes that " . . .
- Smith interprets the hand washing in MacBeth as "an attempt at absolution" (106).
- Smith describes the novel as "a celebration of human experience" (233).
Other Writing Resources
Enhance your academic writing skills by exploring our additional writing resources that will help you craft compelling essays, research papers, and more.

Your New Chapter Starts Wherever You Are
The support you need and education you deserve, no matter where life leads.
because a future built by you is a future built for you.
Too many people have been made to feel that higher education isn’t a place for them— that it is someone else’s dream. But we change all that. With individualized attention and ongoing support, we help you write a new story for the future where you play the starring role.
Quoting and integrating sources into your paper
In any study of a subject, people engage in a “conversation” of sorts, where they read or listen to others’ ideas, consider them with their own viewpoints, and then develop their own stance. It is important in this “conversation” to acknowledge when we use someone else’s words or ideas. If we didn’t come up with it ourselves, we need to tell our readers who did come up with it.
It is important to draw on the work of experts to formulate your own ideas. Quoting and paraphrasing the work of authors engaged in writing about your topic adds expert support to your argument and thesis statement. You are contributing to a scholarly conversation with scholars who are experts on your topic with your writing. This is the difference between a scholarly research paper and any other paper: you must include your own voice in your analysis and ideas alongside scholars or experts.
All your sources must relate to your thesis, or central argument, whether they are in agreement or not. It is a good idea to address all sides of the argument or thesis to make your stance stronger. There are two main ways to incorporate sources into your research paper.
Quoting is when you use the exact words from a source. You will need to put quotation marks around the words that are not your own and cite where they came from. For example:
“It wasn’t really a tune, but from the first note the beast’s eyes began to droop . . . Slowly the dog’s growls ceased – it tottered on its paws and fell to its knees, then it slumped to the ground, fast asleep” (Rowling 275).
Follow these guidelines when opting to cite a passage:
- Choose to quote passages that seem especially well phrased or are unique to the author or subject matter.
- Be selective in your quotations. Avoid over-quoting. You also don’t have to quote an entire passage. Use ellipses (. . .) to indicate omitted words. Check with your professor for their ideal length of quotations – some professors place word limits on how much of a sentence or paragraph you should quote.
- Before or after quoting a passage, include an explanation in which you interpret the significance of the quote for the reader. Avoid “hanging quotes” that have no context or introduction. It is better to err on the side of your reader not understanding your point until you spell it out for them, rather than assume readers will follow your thought process exactly.
- If you are having trouble paraphrasing (putting something into your own words), that may be a sign that you should quote it.
- Shorter quotes are generally incorporated into the flow of a sentence while longer quotes may be set off in “blocks.” Check your citation handbook for quoting guidelines.
Paraphrasing is when you state the ideas from another source in your own words . Even when you use your own words, if the ideas or facts came from another source, you need to cite where they came from. Quotation marks are not used. For example:
With the simple music of the flute, Harry lulled the dog to sleep (Rowling 275).
Follow these guidelines when opting to paraphrase a passage:
- Don’t take a passage and change a word here or there. You must write out the idea in your own words. Simply changing a few words from the original source or restating the information exactly using different words is considered plagiarism .
- Read the passage, reflect upon it, and restate it in a way that is meaningful to you within the context of your paper . You are using this to back up a point you are making, so your paraphrased content should be tailored to that point specifically.
- After reading the passage that you want to paraphrase, look away from it, and imagine explaining the main point to another person.
- After paraphrasing the passage, go back and compare it to the original. Are there any phrases that have come directly from the original source? If so, you should rephrase it or put the original in quotation marks. If you cannot state an idea in your own words, you should use the direct quotation.
A summary is similar to paraphrasing, but used in cases where you are trying to give an overview of many ideas. As in paraphrasing, quotation marks are not used, but a citation is still necessary. For example:
Through a combination of skill and their invisibility cloak, Harry, Ron, and Hermione slipped through Hogwarts to the dog’s room and down through the trapdoor within (Rowling 271-77).
Important guidelines
When integrating a source into your paper, remember to use these three important components:
- Introductory phrase to the source material : mention the author, date, or any other relevant information when introducing a quote or paraphrase.
- Source material : a direct quote, paraphrase, or summary with proper citation.
- Analysis of source material : your response, interpretations, or arguments regarding the source material should introduce or follow it. When incorporating source material into your paper, relate your source and analysis back to your original thesis.
Ideally, papers will contain a good balance of direct quotations, paraphrasing and your own thoughts. Too much reliance on quotations and paraphrasing can make it seem like you are only using the work of others and have no original thoughts on the topic.
Always properly cite an author’s original idea, whether you have directly quoted or paraphrased it. If you have questions about how to cite properly in your chosen citation style, browse these citation guides . You can also review our guide to understanding plagiarism .
University Writing Center
The University of Nevada, Reno Writing Center provides helpful guidance on quoting and paraphrasing and explains how to make sure your paraphrasing does not veer into plagiarism. If you have any questions about quoting or paraphrasing, or need help at any point in the writing process, schedule an appointment with the Writing Center.
Works Cited
Rowling, J.K. Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone. A.A. Levine Books, 1998.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Edit Quotes in an Essay
4-minute read
- 29th April 2019
Quoting sources is vital when writing an essay . But what if the quote doesn’t fit the surrounding text? Or what if it’s too long?
The good news is you can change a quote if you need to. But you also need to highlight your edits clearly in the text. Check out our guide below, then, to find out how to edit quotes in academic writing.
Omitting Text from Quotations with Ellipses
If a quote is too long, it may interrupt the flow of your writing. For instance:
Smith (2007, p. 24) describes blancmange as “a sweet dessert that is generally made with milk or cream and sugar, although I also once had one that contained none of these ingredients, that has been thickened with gelatin, corn starch or Irish moss.”
The middle part of this quote isn’t necessary for describing blancmange, so we might want to leave it out. To do this, we would use an ellipsis to show where we had cut something from the original source:
Smith (2007, p. 24) describes blancmange as “a sweet dessert that is generally made with milk or cream and sugar…that has been thickened with gelatin, corn starch or Irish moss.”
We now have the text we wanted to quote, but we haven’t had to include the middle bit. This makes it clearer and more succinct.
Keep in mind, too, that you can write an ellipsis in several ways, including:
- In square brackets […]
- Spaced (. . .) or unspaced (…)
- With a space before and after the ellipsis or without spaces
As such, always check your style guide for advice on how to write ellipses. If you do not have a style guide, simply apply one type of ellipsis consistently.
Changing or Adding Words in Quotations
You can edit quotes by changing or adding words in order to:
- Integrate quoted text into your own writing
- Clarify the meaning of something
- Correct an error in the original text
If you do any of these, use square brackets to show where you have changed the original text. For example, imagine we found the following in a book:
Blancmange is delicious. The first time I ate it, I was in love.

Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
We might then want to quote the second sentence. But without the first sentence, it wouldn’t be clear what the “it” refers to. As such, we could edit the second sentence so that it works by itself:
Smith (2007, p. 31) says, “The first time I ate [blancmange], I was in love.”
It is now clear what Smith is saying without having to include the first sentence, but the reader can also see where we have changed the quote.
Marking Errors in Quotations
Finally, what if you don’t want to change an error in a quote? Or what if it contains something that looks like an error, such as an old-fashioned spelling?
In cases like these, you can use the Latin term “sic” to show that you’ve kept something non-standard from the original text. This is short for sic erat scriptum , which translates to “thus was it written.”
Usually, to use “sic” like this, you would place it in square brackets:
His writings were riddled with errors due to his addiction, which he described as “a terrible but delishus [sic] shame” (Smith 2017, p. 2).
The reader will then know that the spelling “delishus” comes from the quoted text, so it is not a transcription error.
Unless you have a good reason for preserving an error, though, it is usually better to fix it and put the correction in square brackets instead.
Summary: How to Edit Quotes in an Essay
If you need to edit quotes in your writing, keep the following in mind:
- Use an ellipsis to indicate omissions in the text. Check your style guide for how to format ellipses (e.g., in brackets or not, spaced or unspaced).
- Mark additions or changes by placing the edited text in square brackets .
- Use the term “[Sic]” to show that you’ve duplicated an error from a source. This will ensure the reader doesn’t think you’ve made a mistake yourself.
Different style guides may vary on these rules, so make sure to check yours if you have one. And don’t forget to have your work proofread .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
How can I add to or edit a quotation in an essay?

This is the third and final chapter about Quoting . To complete this reader, read each chapter carefully and then unlock and complete our materials to check your understanding.
– Introduce five ways in which quotations can be altered
– Provide directions for adding to and editing quotations
– Use examples to contextualise quotation usage
Chapter 1: What are quotations and why are they useful?
Chapter 2: How should I use quotations in academic writing?
Chapter 3: How can I add to or edit a quotation in an essay?
Before you begin reading...
- video and audio texts
- knowledge checks and quizzes
- skills practices, tasks and assignments
Having discussed why quotations are used in academic writing and how to include them correctly, the final aspect of quotation usage is about adding, editing and deleting text as well as dealing with errors in the original source and adding writer emphasis. Each one of these is dealt with below using the following example:

Once you’ve read about the different ways of editing quotations, you may wish to download our beginner-, intermediate– and advanced-level worksheets on this topic to check your comprehension.
1. Adding Text
There may be occasions when you wish to add text to a quotation , perhaps to clarify that quotation or explain a pronoun that’s been taken out of context. It’s perfectly OK to add text to a quotation in this way provided you inform the reader that you’ve done so. The way to do this is to include the new text within square brackets ([ ]), as is shown in the example below:

2. Editing Text
There may also be instances when you’ll need to edit the original text used in the quotation , although this shouldn’t be done without good reason. Generally, acceptable reasons to edit a quotation are to change the grammar or tense of that quotation so that it better fits within the flow of your writing, or to replace an unclear pronoun with a more specific noun or noun phrase . Again, much like when adding text to a quotation, square brackets are used to envelop the word that’s being inserted into the text:

3. Removing Text
It’s also possible to remove a section of text to make that quotation shorter (perhaps to save on words ), to join two distant pieces of text, or to remove unnecessary language. Again, square brackets are used to also remove text, except this time an ellipsis (three dots in a row) is placed within those square brackets to indicate that text has been removed:

4. Fixing Errors
There may even be scenarios in which you find genuine errors within the original text. Rather than fix those errors yourself, it’s simple enough to use the Latin word ‘sic’, meaning ‘so’ or ‘thus’ (although some people simply think of it as meaning ‘spelling is correct’), directly after the mistake in italics and square brackets .

Of course, do be sure to check that this mistake is indeed an error and not simply a spelling variant between British- and American-English dialects , for example.
5. Adding Emphasis
The final way in which you may wish to alter a quotation is to add emphasis to that quotation in the form of italicising particular text. If such italicised emphasis is added however, you must remember to also mention that you’ve done this in the related citation by including the phrase ‘my emphasis’:

Knowing how to manipulate a quotation any more than 10% of cited material as quotations within an assessed academic submission. Following this guidance, all that’s left to do now is check your comprehension of this topic by downloading and completing some of our professionally-made worksheets.
Downloadables
Once you’ve completed all three chapters about quoting , you might also wish to download our beginner, intermediate and advanced worksheets to test your progress or print for your students. These professional PDF worksheets can be easily accessed for only a few Academic Marks .
Our quoting academic reader (including all three chapters about this topic) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
Gain unlimited access to our quoting beginner worksheet, with activities and answer keys designed to check a basic understanding of this reader’s chapters.
To check a confident understanding of this reader’s chapters, click on the button below to download our quoting intermediate worksheet with activities and answer keys.
Our quoting advanced worksheet with activities and answer keys has been created to check a sophisticated understanding of this reader’s chapters.
To save yourself 3 Marks , click on the button below to gain unlimited access to all of our subject-verb agreement chapters and worksheets. The All-in-1 Pack includes every chapters on this topic, as well as our beginner, intermediate and advanced worksheets in one handy PDF.
Click on the button below to gain unlimited access to our quoting teacher’s PowerPoint, which should include everything you’d need to successfully introduce this topic.
Collect Academic Marks
- 100 Marks for joining
- 25 Marks for daily e-learning
- 100-200 for feedback/testimonials
- 100-500 for referring your colleages/friends
Table of Contents
Ai, ethics & human agency, collaboration, information literacy, writing process, inserting or altering words in a direct quotation.
- CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 by Nancy Lewis
What punctuation should be used when words are inserted or altered in a direct quotation?
When writers insert or alter words in a direct quotation, square brackets—[ ]—are placed around the change. The brackets, always used in pairs, enclose words intended to clarify meaning, provide a brief explanation, or to help integrate the quote into the writer’s sentence. A common error writers make is to use parentheses in place of brackets.
How are square brackets used around clarifying or explanatory words?
Let’s look at an example:
Quotation with brackets used correctly around a clarifying word:
“It [driving] imposes a heavy procedural workload on cognition that . . . leaves little processing capacity available for other tasks” (Salvucci and Taatgen 107). [1]
Note : Brackets are placed around the inserted word in this example to let the reader know that ‘driving’ clarifies the meaning of the pronoun ‘it.’
Quotation with parentheses incorrectly used in place of brackets:
“It (driving) imposes a heavy procedural workload on cognition that . . . leaves little processing capacity available for other tasks” (Salvucci and Taatgen 107).
Note : Parentheses are used incorrectly in place of brackets in this example, making the inserted word look like it could be part of the original text.
Let’s look at another example:
Quotation with brackets used correctly around an explanatory insert:
“[D]riving is not as automatic as one might think; in fact, it imposes a heavy procedural workload [visual and motor demands] on cognition that . . . leaves little processing capacity available for other tasks” (Salvucci and Taatgen 107).
Note : Brackets are placed around the inserted words in this example to provide further explanation of the “procedural workload” discussed in the original text.
“[D]riving is not as automatic as one might think; in fact, it imposes a heavy procedural workload (visual and motor demands) on cognition that . . . leaves little processing capacity available for other tasks” (Salvucci and Taatgen 107).
Note : Parentheses are used incorrectly in place of brackets in this example, making the inserted words look like they are part of the original text.
How are square brackets used to help integrate a quote properly?
Original direct quotation beginning with an upper case letter:
“The heavy cognitive workload of driving suggests that any secondary task has the potential to affect driver behavior” (Salvucci and Taatgen 108).
Integrated quotation with brackets used correctly to indicate a change in letter case:
Salvucci and Taatgen propose that “[t]he heavy cognitive workload of driving suggests that any secondary task has the potential to affect driver behavior” (108).
Note : Brackets are placed around the lower-case letter ‘t’ to indicate that the letter case has been changed. The quotation is introduced by a signal phrase, which makes the quote an integral part of the writer’s sentence; as a result of this syntactical change, the upper case ‘T’ in the original is changed to a lower case letter.
Original direct quotation written in the past tense:
“Not coincidentally, drivers have been increasingly engaging in secondary tasks while driving” (Salvucci and Taatgen 68).
Note : The authors’ words appear in the past tense in the original text.
Quotation with brackets used correctly to indicate a change in verb tense:
“Not coincidentally, drivers [are] increasingly engaging in secondary tasks while driving” (Salvucci and Taatgen 68).
Note : Brackets are placed around the word ‘are’ to indicate that the verb has been changed to the present tense, which is the preferred tense for most writing in MLA style. The past tense is preferred for APA style writing.
A word of caution : Bracketed insertions may not be used to alter or add to the quotation in a way that inaccurately or unfairly represents the original text. Quite simply, do not use bracketed material in a way that twists the author’s meaning.
Bracket Use: Quick Summary
[1] Salvucci, Dario D., and Niels A. Taatgen. Multitasking Minds . Oxford: Oxford UP, 2011. eBook Collection (EBSCOhost) . Web. 20 Feb. 2012.

Brevity – Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence – How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow – How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity – Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style – The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Speech & Writing
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
In-Text Citations: The Basics

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here .
Reference citations in text are covered on pages 261-268 of the Publication Manual. What follows are some general guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay.
Note: On pages 117-118, the Publication Manual suggests that authors of research papers should use the past tense or present perfect tense for signal phrases that occur in the literature review and procedure descriptions (for example, Jones (1998) found or Jones (1998) has found ...). Contexts other than traditionally-structured research writing may permit the simple present tense (for example, Jones (1998) finds ).
APA Citation Basics
When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
If you are referring to an idea from another work but NOT directly quoting the material, or making reference to an entire book, article or other work, you only have to make reference to the author and year of publication and not the page number in your in-text reference.
On the other hand, if you are directly quoting or borrowing from another work, you should include the page number at the end of the parenthetical citation. Use the abbreviation “p.” (for one page) or “pp.” (for multiple pages) before listing the page number(s). Use an en dash for page ranges. For example, you might write (Jones, 1998, p. 199) or (Jones, 1998, pp. 199–201). This information is reiterated below.
Regardless of how they are referenced, all sources that are cited in the text must appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
In-text citation capitalization, quotes, and italics/underlining
- Always capitalize proper nouns, including author names and initials: D. Jones.
- If you refer to the title of a source within your paper, capitalize all words that are four letters long or greater within the title of a source: Permanence and Change . Exceptions apply to short words that are verbs, nouns, pronouns, adjectives, and adverbs: Writing New Media , There Is Nothing Left to Lose .
( Note: in your References list, only the first word of a title will be capitalized: Writing new media .)
- When capitalizing titles, capitalize both words in a hyphenated compound word: Natural-Born Cyborgs .
- Capitalize the first word after a dash or colon: "Defining Film Rhetoric: The Case of Hitchcock's Vertigo ."
- If the title of the work is italicized in your reference list, italicize it and use title case capitalization in the text: The Closing of the American Mind ; The Wizard of Oz ; Friends .
- If the title of the work is not italicized in your reference list, use double quotation marks and title case capitalization (even though the reference list uses sentence case): "Multimedia Narration: Constructing Possible Worlds;" "The One Where Chandler Can't Cry."
Short quotations
If you are directly quoting from a work, you will need to include the author, year of publication, and page number for the reference (preceded by "p." for a single page and “pp.” for a span of multiple pages, with the page numbers separated by an en dash).
You can introduce the quotation with a signal phrase that includes the author's last name followed by the date of publication in parentheses.
If you do not include the author’s name in the text of the sentence, place the author's last name, the year of publication, and the page number in parentheses after the quotation.
Long quotations
Place direct quotations that are 40 words or longer in a free-standing block of typewritten lines and omit quotation marks. Start the quotation on a new line, indented 1/2 inch from the left margin, i.e., in the same place you would begin a new paragraph. Type the entire quotation on the new margin, and indent the first line of any subsequent paragraph within the quotation 1/2 inch from the new margin. Maintain double-spacing throughout, but do not add an extra blank line before or after it. The parenthetical citation should come after the closing punctuation mark.
Because block quotation formatting is difficult for us to replicate in the OWL's content management system, we have simply provided a screenshot of a generic example below.

Formatting example for block quotations in APA 7 style.
Quotations from sources without pages
Direct quotations from sources that do not contain pages should not reference a page number. Instead, you may reference another logical identifying element: a paragraph, a chapter number, a section number, a table number, or something else. Older works (like religious texts) can also incorporate special location identifiers like verse numbers. In short: pick a substitute for page numbers that makes sense for your source.
Summary or paraphrase
If you are paraphrasing an idea from another work, you only have to make reference to the author and year of publication in your in-text reference and may omit the page numbers. APA guidelines, however, do encourage including a page range for a summary or paraphrase when it will help the reader find the information in a longer work.
VCE Study Tips
English Language

Private Tutoring

Only one more step to getting your FREE text response mini-guide!
Simply fill in the form below, and the download will start straight away
How To Embed Quotes in Your Essay Like a Boss
October 2, 2012

Want insider tips? Sign up here!
Go ahead and tilt your mobile the right way (portrait). the kool kids don't use landscape....
Updated 30/12/2020
- What Are Quotes?
- Why Use Quotes?
- What You Want To Quote
- How Much You Want To Quote
- How That Quote Will Fit into Your Essay
- There Are Also Other Ways of Using Quotation Marks
- Questions You Must Ask Yourself When Weaving Quotes into Sentences
- How To Find Good Quotes
1. What Are Quotes?
Quotations, better known by their abbreviation ‘quotes’, are a form of evidence used in VCE essays. Using quotations in essays helps to demonstrate your knowledge of the text, and provides solid evidence for your arguments. The discussion on quotations in this study guide can be applied to all three areas of study in the VCAA English course which have been explained in detail in our Ultimate Guide s to VCE Text Response , Comparative and Language Analysis .
A quotation is the repetition of a group of words taken from a text by someone other than the original author. The punctuation mark used to indicate a repetition of another author’s work is presented through quotation marks. These quotation marks are illustrated by inverted commas, either single inverted commas (‘ ’) or double inverted commas (“ ”). There is no general rule in Australia regarding which type of inverted comma you must use for quotations. Single inverted commas are preferred in Australia as they follow the British standard. The American standard involves styling quotations with the double inverted comma. You can choose either style, just be consistent in your essays.
2. Why Use Quotes?
The usage of quotations in essays demonstrates:
- Your knowledge of the text
- Credibility of your argument
- An interesting and thoughtful essay
- The strength of your writing skills.
However, quotations must be used correctly, otherwise you risk (and these frequent mistakes will be discussed in detail later):
- Irrelevant quotations
- Overcrowding or overloading of quotations
- Broken sentences
How You Integrate a Quote into an Essay Depends on Three Factors:
- What you want to quote
- How much you want to quote
- How that quote will fit into your essay.
3. What You Want To Quote
As you discuss ideas in a paragraph, quotes should be added to develop these ideas further. A quote should add insight into your argument; therefore, it is imperative that the quote you choose relates intrinsically to your discussion. This is dependent on which aspect of the text you are discussing, for example:
- Description of theme or character
- Description of event or setting
- Description of a symbol or other literary technique
Never quote just for the sake of quoting. Quotations can be irrelevant if a student merely adds in quotes as ‘sentence fillers’. Throwing in quotations just to make your essay appear more sophisticated will only be more damaging if the quotation does not adequately reinforce or expand on your contention. Conversely, an essay with no quotations will not achieve many marks either.
4. How Much You Want To Quote
A quotation should never tell the story for you. Quotations are a ‘support’ system, much like a back up for your ideas and arguments. Thus, you must be selective in how much you want to quote. Generally speaking, the absolute minimum is three quotes per paragraph but you should not overload your paragraphs either. Overcrowding your essay with too many quotations will lead to failure to develop your ideas, as well as your work appearing too convoluted for your assessor. Remember that the essay is your piece of work and should consist mainly of your own ideas and thoughts.
Single Word Quotations
The word ‘evaporates’, used to characterise money and happiness intends to instill the idea that happiness as a result of money is only temporary. (VCAA ‘Can Money Buy Happiness’ Language Analysis)
Single worded quotations can often leave the largest impression on the assessor. This is because you are able to demonstrate that you can focus on one word and develop an entire idea around it.
Phrase Quotations
Sunil Badami ‘still found it hard to tie my Indian appearance to my Australian feeling', showing that for Sunil, his culture was not Indian, but Australian due to his upbringing. ( Sticks and Stones and Such-like, Sunil Badami in Growing Up Asian in Australia )
A phrase quotation is the most common quotation length you will use in essays.
Long Quotations
The multitudes of deaths surrounding Anna began to take its toll on her, burdening her with guilt as ‘sometimes, if I walked the main street of the village in the evening, I felt the press of their ghosts. I realised then that I had begun to step small and carry myself all hunched, keeping my arms at my sides and my elbows tucked, as if to leave room for them.’ ( Year of Wonders, Geraldine Brooks )
Long quotations comprise of more than one sentence – avoid using them as evidence. Your assessor will not mark you highly if the bulk of your paragraphs consists of long quotations. You should aim to keep your quotations to less than 2 lines on an A4 writing page. If you have a long quotation you wish to use, be selective. Choose only the important phrases or key words, and remove the remaining sentence by replacing it with an ellipsis (…).
Here is the same example again, with the student using ellipsis:
The multitudes of deaths surrounding Anna began to take its toll on her, burdening her with guilt as she felt ‘the press of their ghosts…[and] begun to step small and carry myself all hunched…as if to leave room for them.’ ( Year of Wonders, Geraldine Brooks)
In this case, we have deleted: ‘sometimes, if I walked the main street of the village in the evening’ and ‘I realised then that I had’ by using an ellipsis – a part of the quotation that is not missed because it does not represent the essence of the student’s argument. You would have noticed that a square bracket ([ ]) was used. This will be discussed in detail under Blending Quotes.
5. How That Quote Will Fit into Your Essay
You must never take the original author’s words and use them in your essay without inserting them in quotation marks. Failure to do so leads to ‘plagiarism’ or cheating. Plagiarism occurs when you take someone else’s work and pass it off as your own. You must make sure that you use quotation marks whenever you use evidence from your text.
The following is plagiarism:
Even a single flicker of the eyes could be mistaken for the essential crime that contained all other crimes in itself – thought crime. (1984, George Orwell)
Using quotation marks however, avoids plagiarism:
Even ‘a single flicker of the eyes’ could be mistaken for ‘the essential crime that contained all other crimes in itself – thought crime.’ (1984, George Orwell)
There are serious consequences for plagiarism. VCAA will penalise students for plagiarism. VCAA uses statistical analysis to compare a student’s work with their General Achievement Test (GAT), and if the cross-referencing indicates that the student is achieving unexpectedly high results with their schoolwork, the student’s school will be notified and consequential actions will be taken.
Plagiarism should not be confused with:
- Paraphrasing : to reword or rephrase the author’s words
- Summarising: to give a brief statement about the author’s main points
- Quoting : to directly copy the author’s words with an indication (via quotation marks) that it is not your original work
Blending Quotations
You should always aim to interweave quotations into your sentences in order to achieve good flow and enhanced readability of your essay. Below is a good example of blending in quotations:
John Proctor deals with his own inner conflict as he is burdened with guilt and shame of his past adulterous actions. Yet during the climatic ending of the play, Proctor honours his principles as he rejects signing a false confession. This situation where Proctor is confronted to ‘sign [himself] to lies’ is a stark epiphany, for he finally acknowledges that he does have ‘some shred of goodness.’ ( The Crucible, Arthur Miller)
There are three main methods in how you can blend quotations into an essay:
1. Adding Words
Broken sentences are a common mistake made when students aim to integrate quotations into their sentences. Below are examples of broken sentences due to poor integration of a quotation:
‘Solitary as an oyster’. Scrooge is illustrated as a person who is isolated in his own sphere. ( A Christmas Carol, Charles Dickens)
Never write a sentence consisting of only a quotation. This does not add insight into your argument, nor does it achieve good flow or readability.
Scrooge, ‘solitary as an oyster’, is illustrated as a person who is isolated in his own sphere. (A Christmas Carol, Charles Dickens)
This example is better, however the sentence is still difficult to read. In order to blend quotations into your sentences, try adding in words that will help merge the quotation and your own words together:
Described as being as ‘solitary as an oyster’, Scrooge is illustrated as a person who is isolated in his own sphere. (A Christmas Carol, Charles Dickens)
Scrooge is depicted as a person who is ‘solitary as an oyster’, illustrating that he is isolated in his own sphere. (A Christmas Carol, Charles Dickens)
Tip: If you remove the quotation marks, the sentence should still make sense.
2. Square Brackets ([ ])
These are used when you need to modify the original writer’s words so that the quotation will blend into your essay. This is usually done to:
Change Tense
Authors sometimes write in past (looked) , present (look) or future tense (will look) . Depending on how you approach your essay, you may choose to write with one of the three tenses. Since your tense may not always match the author’s, you will need to alter particular words.
Original sentence: ‘…puts his arm around Lewis’ shoulder’ ( Cosi, Louis Nowra)
Upon seeing Lewis upset, Roy attempts to cheer him up by ‘put[ting] his arm around Lewis’ shoulder’. ( Cosi, Louis Nowra)
Change Narrative Perspective
The author may write in a first (I, we) , second (you) or third person (he, she, they) narrative. Since you will usually write from an outsider’s point of view, you will refer to characters in third person. Thus, it is necessary to replace first and second person pronouns with third person pronouns. Alternatively, you can replace first and second person pronouns with the character’s name.
The original sentence: ‘Only now can I recognise the scene for what it was: a confessional, a privilege that I, through selfishness and sensual addiction, failed to accept…’ (Maestro, Peter Goldsworthy)
When Keller was finally ready to share his brutal past with Paul, the latter disregarded the maestro, as he was too immersed in his own adolescent interests. However, upon reflection, Paul realises that ‘only now can [he] recognise the scene for what it was: a confessional, a privilege that [he], through selfishness and sensual addiction, failed to accept’. (Maestro, Peter Goldsworthy)
Insert Missing Words
Sometimes, it may be necessary to insert your own words in square brackets so that the quotation will be coherent when incorporated into your sentences.
The original sentence: ‘His heels glow.’ ( Ransom, David Malouf)
Achilles, like Priam, feels a sense of refreshment as highlighted by ‘his heels [which] glow.’ ( Ransom, David Malouf)
It is important to maintain proper grammar while weaving in quotations. The question is: does the punctuation go inside or outside the final quotation mark?
The rule is: If the quoted words end with a full stop (or comma), then the full stop goes inside the quotation marks. If the quoted words do not end with a full stop, then the full stop goes outside the quotation marks.
Original sentence: 'Sagitty’s old place plus another hundred acres that went from the head waters of Darkey Creek all the way down to the river.’ ( The Secret River, Kate Grenville)
Punctuation inside:
During the past decade, Thornhill became the wealthiest man in the area, owning ‘Sagitty’s old place plus another hundred acres that went from the head waters of Darkey Creek all the way down to the river.’ ( The Secret River, Kate Grenville)
Punctuation outside:
During the past decade, Thornhill became the wealthiest man in the area, owning ‘Sagitty’s old place plus another hundred acres’. ( The Secret River, Kate Grenville)
6. There Are Also Other Ways of Using Quotation Marks
Title of text.
When including the title of the text in an essay, use single quotation marks.
Directed by Elia Kazan, ‘On The Waterfront’ unveils the widespread corruption among longshoremen working at New Jersey docks. ( On The Waterfront, Elia Kazan)
Alternatively, you can underline the title of the text instead of using single quotation marks. Many teachers and examiners prefer this option.
Quotation Within a Quotation
When you quote the author who is quoting someone else, then you will need to switch between single and double quotation marks. You firstly need to enclose the author’s words in single quotation marks, and then enclose the words they quote in double quotation marks. If you're following the American standard, you'll need to do this the opposite way - that is, using double quotation marks for the author's words and and then single quotation marks for the quote. We recommend sticking to the preferred Australian style though, which is single and then double.
Original sentence: ‘…something bitter and stringy, too difficult to swallow. “It’s just that – I – um, I hate it…It’s too – it’s too Indian!”’ ( Sticks and Stones and Such-like, Sunil Badami in Growing Up Asian in Australia)
Sunil’s unusual name leads him to believe that it is ‘…something bitter and stringy, too difficult to swallow. “It’s just that – I – um, I hate it…It’s too – it’s too Indian!”’ ( Sticks and Stones and Such-like, Sunil Badami in Growing Up Asian in Australia)
As you can see, the student has quoted the author’s words in single quotation marks. The dialogue used by the author is surrounded by double quotation marks. This demonstrates that the dialogue used in the text still belongs to the author.
Using Quotations to Express Irony
When you wish to express irony, you use quotation marks to illustrate that the implied meaning of the actual word or phrase is different to the normal meaning.
As a young girl, Elaine is a victim of Mrs Smeath and her so called ‘friends’. Her father’s interest in insects and her mother’s lack of housework presents Elaine as an easy bullying target for other girls her age who are fit to fulfill Toronto’s social norms. ( Cat’s Eye, Margaret Atwood)
In this case, ‘friends’ is written in inverted commas to indicate that Elaine’s peers are not truly her friends but are in fact, bullies.
7. Questions You Must Ask Yourself When Weaving Quotes into Sentences
1. Does the quote blend into my sentence?
2. Does my sentence still make sense?
3. Is it too convoluted for my readers to understand?
4. Did I use the correct grammar?
8. How To Find Good Quotes
Tip One: Do not go onto Google and type in 'Good quotes for X text', because this is not going to work. These type of quotes are generally the most famous and the most popular quotes because, yes they are good quotes, but does that necessarily mean that it's going to be a good quote in your essay? Probably not. But why? Well, it's because these quotes are the most likely to be overused by students - absolutely every single person who has studied this text before you, and probably every single person who will study this text after you. You want to be unique and original. So, how are you going to find those 'good quotes'? Recognise which quotes are constantly being used and blacklist them. Quotes are constantly used in study guides are generally the ones that will be overused by students. Once you eliminate these quotes, you can then go on to find potentially more subtle quotes that are just as good as the more popular or famous ones. Tip Two: Re-read the book. There is nothing wrong with you going ahead and finding your own quotes. You don't need to find quotes that already exist online or in study guides. Go and find whatever gels with you and whatever you feel like has a lot of meaning to it. I had a friend back in high school who was studying a book by Charles Dickens. I haven't read the book myself, but there was a character who couldn't pronounce the letter S, or he had a lisp of some sort. What my friend did was he found this one word where, throughout the entire book, the guy with the lisp only ever said the S one time and that was a massive thing. So, he used that. This is something that is really unique and original. So, go ahead and try to find your own quotes. Tip Three: Realise that good quotes do not necessarily have to come from the main character. Yes, the main character does often have good quotes associated with whatever they're saying, but just know that you do have minor characters who can say something really relevant and have a really good point too. Their quote is going to be just as strong in your essay as a main character's quote, which will probably be overused and overdone by so many other students. Tip Four: Develop a new interpretation of a famous or popular quote. Most of the time, the really popular quotes are analysed in very much the same way. But if you can offer a new insight into why it's being said or offer a different interpretation, then this is automatically going to create a really good quote that's going to offer a refreshing point of view. For example, if we look at The Great Gatsby , one of the most famous quotes that is constantly being used is, 'He found what a grotesque thing a rose is and how raw the sunlight was upon the scarcely created grass.' What most people will do is they will analyse the part about the 'grotesque thing a rose', because that's the most significant part of the quote that stands out. But what you could do instead, is focus on a section of that quote, for example the 'raw'. Why is the word raw being used? How does the word raw contribute extra meaning to this particular quote? This way you're honing in on a particular section of the quote and really trying to offer something new. This automatically allows you to investigate the quote in a new light. Tip Five: Just remember that the best quotes do not have to be one sentence long. Some of the best quotes tend to be really short phrases or even just one particular word. Teachers actually love it when you can get rid of the excess words that are unnecessary in the sentence, and just hone in on a particular phrase or a particular word to offer an analysis. And also, that way, when you spend so much time analysing and offering insight into such a short phrase or one sentence, it shows how knowledgeable you are about the text and that you don't need to rely on lots and lots of evidence in order to prove your point. Those are my five quick tips on how to find good quotes from your texts!
Need more help with quotes? Learn about 5 Ways You're Using Quotes Wrong .
Resources for texts mentioned/referenced in this blog post:
Comparing: Stasiland and 1984 Study Guide
A Killer Text Guide: Cosi (ebook)
Cosi By Louis Nowra Study Guide
Cosi Study Guide
Growing Up Asian in Australia Study Guide
A Killer Text Guide: On the Waterfront (ebook)
A Killer Text Guide: Ransom (ebook)
Ransom Study Guide
The Crucible by Arthur Miller Study Guide
A Killer Text Guide: The Crucible (ebook)
The Crucible and Year of Wonders Prompts
Comparing: The Crucible and Year of Wonders Study Guide
The Great Gatsby Study Guide
A Killer Text Guide: The Secret River (ebook)
The Secret River by Kate Grenville Study Guide
Get our FREE VCE English Text Response mini-guide
Now quite sure how to nail your text response essays? Then download our free mini-guide, where we break down the art of writing the perfect text-response essay into three comprehensive steps. Click below to get your own copy today!

Struggling to answer the essay topic?
Has your teacher ever told you:
"You're not answering the prompt"
"You're going off topic"
Then you're not alone! If you struggle to understand and stay on topic, learn how to answer the prompt every time with our How To Write A Killer Text Response study guide.

Introduction
Not gonna lie, this novel is a bit of a tricky one to introduce. World War II, arguably one of the darkest events of human history, has been the basis of so much writing across so many genres; authors, academics, novelists have all devoted themselves to understanding the tragedies, and make sense of how we managed to do this to one another. Many reflect on the experiences of children and families whose lives were torn apart by the war.
In some ways, Doerr is another author who has attempted this. His novel alludes to the merciless anonymity of death in war, juxtaposes individualism with collective national mindlessness, and seeks out innocence amidst the brutality of war.
What makes this novel difficult to introduce is the way in which Doerr has done this; through the eyes of two children on opposite sides of the war, he explores how both of them struggle with identity, morality and hope, each in their own way. Their storylines converge in the bombing of Saint-Malo, demonstrating that war can be indiscriminate in its victims—that is, it does not care if its victims are children or adults, innocent or guilty, French or German. However, their interaction also speaks to the humanity that lies in all of us, no matter how deeply buried.
A very quick history lesson
Fast Five Facts about World War II:
- Lasting 1939-1945, the war was fought between the Axis powers (Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (basically everyone else, but mainly England, France, and later the US). Whilst it was Germany who started the war, the intervention of the US at the end of five long years of fighting ultimately helped the Allies win.
- Various forms of technology were first used, or found new uses, during the war. Aircraft carriers and various planes (fighters, bombers etc.) became more important than ever, while Hitler’s use of tanks allowed him to take over much of Europe very quickly.
- Other forms of new technology included one of the world’s first electronic computers that was used to codebreak (stop reading now and watch The Imitation Game if you haven’t already! Totally counts as studying, right?), as well as radio and radar, used to communicate and also to detect enemies in the field.
- World War II is also referred to as the Holocaust, the name given to Hitler’s attempted genocide of the Jewish people. 6 million Jews died in the war, and as many as 15 million others died in total.
- Germany’s initial conquest of Europe was swift and brutal. Within a month, Poland had already surrendered and within a year, so had France. However, there were also resistance groups all over these countries which sought to undermine the Nazi regime in a number of ways, both big and small.
My best attempt to give a general plot overview of this very long book
Disclaimer: this is a very, very broad overview of the novel and it is absolutely not a substitute for actually reading it (please actually read it).
Chronologically, we start in 1934, five years before the war. Marie-Laure is a French girl who lives with her father Daniel Leblanc, working at the Museum of Natural History in Paris. As she starts to go blind, Daniel teaches her Braille, and makes her wooden models of their neighbourhood to help her navigate. Six years later, the Nazis invade France, and they flee the capital to find Daniel’s uncle Etienne, who lives in the seaside town of Saint-Malo; Daniel was also tasked with safeguarding a precious gem, the Sea of Flames, from the Nazis.
In Saint-Malo, Daniel also builds Marie-Laure a model of the town, hiding the gem inside. Meanwhile, she befriends Etienne, who suffers from agoraphobia as a result of the trauma from the First World War. He is charming and very knowledgeable about science, having made a series of scientific radio broadcasts with his brother Henri (who died in WWI). She also befriends his cook, Madame Manec, who participates in the resistance movement right up until she falls ill and dies.
Her father is also arrested (and would ultimately die in prison), and the loss of their loved ones prompts both Etienne and Marie-Laure to begin fighting back. Marie-Laure is also given a key to a grotto by the seaside which is full of molluscs, her favourite kind of animal.
On the other side of the war, Werner is, in 1934, an 8 year-old German boy growing up in an orphanage with his sister Jutta in the small mining town of Zollverein. They discover a radio, which allows them to listen to a broadcast from miles away (it was Henri and Etienne’s), and Werner learns French to try and understand it. One day, he repairs the radio of a Nazi official, who recruits him to the Hitler Youth on account of his ingenuity (and his very blonde hair and very blue eyes, considered to be desirable traits by the regime). Jutta grows increasingly distant from Werner during this time, as she questions the morality of the Nazis.
Werner is trained to be a soldier along with a cohort of other boys, and additionally learns to use radio to locate enemy soldiers. He befriends Frederick, an innocent kid who was only there because his parents were rich—Frederick would eventually fall victim to the brutality of the instructors, and Werner tries to quit out of solidarity. Unfortunately, he is sent into the army to apply his training to actual warfare. He fights with Frank Volkheimer, a slightly ambiguous character who a tough and cruel soldier, but also displays a capacity to be kind and gentle (including a fondness for classical music). The war eventually takes them to Saint-Malo.
Also around 1943 or so, a Nazi sergeant, Reinhold von Rumpel, begins to track down the Sea of Flames. He would have been successful ultimately had it not been for Werner, who stops him in order to save Marie Laure.
As America begins to turn the war around, Werner is arrested and dies after stepping on a German landmine; Marie-Laure and Etienne move back to Paris. Marie-Laure eventually becomes a scientist specialising in the study of molluscs and has an extensive family of her own by 2014. Phew.
What kind of questions does Doerr raise through this plot? To some degree, the single central question of the novel is one of humanity, and this manifests in a few different ways.
Firstly, to what extent are we in control of our own choices? Do we truly have free will to behave morally ? The Nazi regime throws a spanner in the works here, as it makes incredibly inhumane demands on its people. Perhaps they fear punishment and have no choice—Werner, for instance, does go along with everything. At the same time, his own sister manages to demonstrate critical thinking and moral reasoning well beyond her years, and it makes you wonder if there was potential for Werner to be better in this regard. There’s also the question of whether or not he redeemed himself in the end.
That being said, Werner is far from the only character who struggles with this—consider the perfumer, Claude Levitte, who becomes a Nazi informer, or even ordinary French citizens who simply accept the German takeover. Do they actually have free will to resist, or is it even moral for them to do so?
Hannah Arendt famously coined the phrase “the banality of evil,” referring to how broader movements of inhumanity (such as the Holocaust) can be compartmentalised until individual actions feel perfectly banal, commonplace and ordinary. This is what allowed people to do evil things without actually feeling or even being inherently evil—they were just taking orders, after all. Consider the role of free will in this context.
This brings us to the broader ‘theme’ of war in general: in particular, what kinds of acts are suddenly justifiable in war? Etienne and Madame Manec, for instance, even disagree on the morality of resistance, which can frequently involve murder. Etienne’s pacifist stance is a result of the scale of deaths in the previous world war. At the same time, the climactic event of the novel is an allied bombing of Saint-Malo, a French town, just because it had become a German outpost. Risking lives both French and German, this also highlights the ‘necessity’ of some inhumane actions in times of war.
On a more optimistic note, a human quality that Doerr explores is our natural curiosity towards science . This is abundant in the childhoods of both protagonists, as Werner demonstrates dexterity with the radio at a very young age, and Marie-Laure a keen interest in marine biology. In particular, her blindness pushes her into avenues of science which she can experience without literal sight, such as the tactile sensations of mollusc shells. The title may hint at this—for all the light she cannot see, she seeks enlightenment through knowledge, which in turn gives her hope, optimism and purpose.
At the same time, the human desire to better understand the world can also be used inhumanely—Werner used radio to learn through Etienne and Henri’s broadcasts, but he would later in life also use it to help his compatriots murder enemy soldiers. This alludes to the banality of evil again; by focusing on his very technical role and his unique understanding of the science behind radios, he is able to blind himself to the bigger picture of the evils he is abetting. Science is something that is so innately human, yet can also be used inhumanely as well.
For these reasons, I’d suggest humanity is at the heart of the novel. There is a certain cruel randomness to death in war, but just because so many did perish doesn’t mean that there aren’t human stories worth searching for in the destruction. This is the lens that Doerr brings to the WWII narrative.
Some symbols
To some degree, a lot of these symbols relate to humanity, which I’ve argued is the crux of the novel. I’ll keep this brief so as to not be too repetitive.
One major symbol is the radio , with its potential for good as well as for evil. On one hand, it is undoubtedly used for evil purposes, but it also acts as a source of hope, purpose, conviction and connection in the worst of times. It is what ultimately drives Werner to save Marie-Laure.
Along the same vein, whelks are also a major symbol, particularly for Marie-Laure. While an object of her fascination, they also represent strength for her, as they remain fixed onto rocks and withstand the beaks of birds who try to attack them. In fact, she takes “the Whelk” as a code-name for herself while aiding the resistance movement. It’s also noteworthy that, given the atrocities of war, maybe animals are the only innocent beings left. As Saint-Malo is destroyed and the Sea of Flames discarded, it is the seaside ecosystem that manages to live on, undisturbed. In this sense, the diamond can be seen as a manifestation of human greed, harmless once removed from human society.
Finally, it’s also worth considering the wooden models that Daniel builds for Marie-Laure. They represent his immense love for her, and more broadly the importance of family, but the models also attempt to shrink entire cities into a predictable, easily navigable system. As we’ve seen, this is what causes people to lose sight of the forest for the trees—to hone in on details and lose track of the bigger picture around them. The models are an oversimplification of life, and an illusion of certainty, in a time when life was complicated and not at all certain for anyone.
Identity, morality and hope—these things pretty much shape what it means to be human. Throughout All the Light We Cannot See though, characters sometimes struggle with all three of them at the same time.
And yet they always manage to find something within themselves, some source of strength, some sense of right and wrong, some humanity in trying times. Doerr explores this capacity amply in this novel, and in this sense his novel is not just another story about WWII—it’s a story about the things that connect us, always.
Essay prompt breakdown
Transcription
Through the prompt that we’ll be looking at today, the main message I wanted to highlight was to always try and look for layers of meaning. This could mean really being across all of the symbols, motifs and poetic elements of a text, and it’s especially important for a novel as literary as this one.
You might not have been particularly happy to find out you’re going to have to study All The Light We Cannot See— it is probably the longest text on the entire text list—but it’s also a really beautiful, well-written book that deservedly took out the Pulitzer Prize for fiction in 2015.
In this novel, Anthony Doerr tells the World War 2 story through a unique lens, or rather a unique combination of lenses, as he sets a 16-year-old French girl and a 17-year-old German boy on an unlikely path of convergence. Through the dangers and difficulties that they face, Doerr’s novel is one of growth and self-assuredness in a time when this seemed virtually impossible.
The essay topic we’ll be looking at today is:
All The Light We Cannot See is a literal title for the novel, in that it exposes the darkness, evil and cruelty of which humans are demonstrably capable. Is this an accurate interpretation?
As usual, let’s define some keywords.
I want to leave ‘darkness’ for a little later, but let’s start with ‘evil and cruelty.’ By themselves, they generally just mean immorality or inhumanity, but also keep in mind how they come across in characters’ actions, since those will be the focus of our analysis. The word ‘demonstrably’ highlights this, since it means that any ‘evil’ you discuss needs to be demonstrated or proven.
With ‘darkness’, that’s a bit more of a tricky term because it can mean any number of things. Here, it might be taken to mean bad intentions, corruption or anything like that, because it fits with ‘evil and cruelty’. However, this is where the ‘interpretation’ aspect of the prompt comes in—an interpretation being a way of explaining meaning, how do you explain the meaning of ‘darkness’ in relation to the title? Darkness in this sense could be any number of things.
Now, how should we plan for this topic? Let’s first consider if there’s any room to challenge, since the prompt seems to only focus on the more negative, pessimistic side of the book. I’d argue that with darkness, there is also some light in the form of kindness, charity and hope.
This all sounds pretty profound, but I’m just trying to link it back to the book’s title! I mean, that’s what the topic is asking about, right?
Let’s break this down into paragraphs.
For our first paragraph, a good starting point might be analysing the literal forms of darkness in the novel, and seeing what other interpretations we can get from those. A character that comes to mind is Marie-Laure, the French girl who cannot see any ‘light’ due to her blindness. The title could be seen as an allusion to her character and by extension, the hopelessness that blindness might cause in the midst of a war. We could compare Marie-Laure’s situation with that of Werner, who faces the industrialization of his childhood town, watching it become more and more enveloped in ‘darkness’ and as such, hopelessness.
For our next paragraph, we might drill down to deeper levels of interpreting darkness, because it’s often used as a metaphor for inhumanity. It isn’t difficult to find inhumanity in the novel. There’s plenty of it peppered throughout Werner’s storyline, particularly at Schulpforta, where the Hitler Youth were ‘trained’, (to put it lightly). He and his peers are routinely drilled to “drive the weakness from the corps” in humiliating exercises led by cruel instructors. They are also sometimes driven to cruelty towards one another, and Frederick, Werner’s bunkmate, is relentlessly bullied for his perceived weakness.
So by now, it’s clear that the novel demonstrates the human capacity for experiencing ‘darkness’ as well as inflicting it upon others. But, across these two layers of meaning, could there perhaps be some room to challenge these interpretations? This is something we should look at for our final paragraph.
Here, I would probably argue that just as Doerr explores various forms of darkness, there is also enough ‘light’ which allows some characters to overcome or escape from the darkness. These manifestations of light also require you to think about the different symbolic layers of the novel. On one level for example, looking at light literally, there’s the message on Werner’s radio that teaches us that, even though the brain is sealed in darkness, “the world it constructs…is full of light.” A deeper level of meaning to this may refer to the sense of scientific wonder and discovery which sometimes brings light to Werner, and also Frederick, his bunkmate at Schulpforta, when their lives there are at their most dark.
Consider how, just as darkness has levels of interpretation and symbolism in this book, so does light and hope and joy, rather than just evil and cruelty.
And that’s it! Always delving deeper for meaning helps you to really make use of the symbols, imagery and motifs in a text, and I hope this novel in particular illustrates that idea.
From year 7-10 the traditional essays we have written have had an introduction, three body paragraphs and a conclusion. In these essays we write about characters, plot points and themes. Hence, it is understandable that upon entering English Language in year 11 or 12, it can be difficult to grasp a hold on how to write an essay without characters, plots or themes. To be precise, the requirement in an English Language essay is to ‘use key linguistic concepts and metalanguage appropriately to discuss/analyse/investigate…in an objective and systematic way” (English Language Study Design) .
What does this mean?
Essentially, in section C of the exam, you are required to present a discussion of a given idea. The word ‘discussion’ is defined as ‘a conversation or debate about a specific topic.’ In this sense, your essay is effectively a written conversation which needs to display an understanding of both sides of the topic.
In saying that, it is still important to form a contention, such as ‘indeed non-standard varieties are more acceptable in speaking than in writing in the Australian context’ however in arguing this contention, you must to explore both sides to show the examiner your understanding of language in Australian society.
The overarching idea of the essay is presented to you in the form of a prompt. For example, in the 2016 VCAA exam, a possible essay prompt given was: “In Australia today, variations from the standard tends to be more acceptable in speaking than in writing.”
In this prompt, the idea to be discussed is standard vs. non-standard Australian English. The main idea or topic forms an umbrella under which the essay is formed. This is the foundation of your essay. Each main argument will relate to this topic. In this example, standard vs non-standard Australian English is a topic from which an array of sub-topics can be extracted, the choice of which is to your discretion.
The sub-topics you choose to delve into will depend on your preferences and strengths. You may choose to discuss online-speak, ethnolects or Australian slang in relation to non-standard English, or legal and political jargon in relation to standard English.
Regardless of the choice of sub-topic, each body paragraph must explicitly link to three things; the prompt, the topic sentence and the contention. This is the criteria for your discussion. Ensuring clear links to these three will assure the examiner that you have confidence in the material you are discussing.
Your body paragraphs should be used to show the examiner how the ideas you have chosen to talk about relate to the prompt provided. Here it is necessary to use a combination of contemporary media examples, personal examples and linguist quotes as a means to prove the link between your chosen paragraph idea, your contention and the prompt. Try to find the most relevant examples which clearly demonstrate your line of thinking to the examiner. You don’t want to give them a reason to question the arguments you choose to present.
It is also important to be wary of this so that your essay flows in an orderly, sequential manner. Each idea presented within a paragraph and across the essay itself should follow a pathway, one leading into another. Use the ending of each body paragraph to come back to your essay prompt and reiterate your contention. This ensures you stay on topic and the examiner can clearly visualize your understanding of your topic.
In the end, your job in your essay is to present a discussion of a given prompt; an understanding of both sides. Use examples and explanations to show your examiner that you comprehend how the prompt can be debated.
Helpful Hints:
- Writing the very first sentence of your essay can be difficult. Sometimes, to get yourself into the flow of writing, it can be helpful to integrate a linguistic quote into your first sentence. This also helps solidify your contention. For example:
- “One’s idiolect, particularly lexical choices and accent can be strongly indicative of their unique identity and the social groups to which they belong; it is the most natural badge of symbol of public and private identity (David Crystal)”
- Your topic sentence for each paragraph should contain a link to the essay prompt, to the topic of your paragraph and to your contention. A link to all three elements should be identifiable. Below is an example of a topic sentence for the given essay prompt. “The language we use is the best indicator of who we are, individually, socially and culturally. Discuss.”
- Ethnolects are a quintessential indicator of cultural identity as they are strongly identifiable by their unique phonological characteristics.
- This topic sentence shows a clear identification of the topic of the paragraph (ethnolects), a connection with the prompt, (cultural belonging) and a contention, (ethnolects are indeed indicative of cultural identity)
- Rather than introducing linguist quotes with expressions such as “in the words of…” or “as said by…” using linguist quotes discretely where they are integrated as part of the sentence will improve the flow of your essay. Consider this example.
- “The use of the interjectory ‘reh’ expresses the cultural identity individuals associate themselves with and is part of the language they use as ‘a means to an end of understanding who [they] are and what society is like (David Crystal).”
- Not all your contemporary essay examples need to come from news articles or social media. Students can often get caught up doing aimless research trying to find examples through research which really isn’t all that necessary. You should try to find examples of language use in every-day life. Perhaps consider other school subjects you study and the jargon you used within these subjects. You can quite easily discuss this use of language in your essays. Here is an example of a student using the metalanguage from VCE Accounting as an example for their essay.
- Jargon and taboo language are often used to express social identity as they are demonstrative of social groups one wishes to belong to. Jargon terms such as, ‘equity,’ ‘profit margin’, ‘cash flow statement,’ ‘debt ratio’ and ‘accrued’ belong to the financial and accounting semantic field. Their use suggests the individual is knowledgeable in business and finance and further suggests they are likely to be working in the business sector. The use of jargon in one’s vernacular can therefore provide hints of the individual’s social identity and is significant to their individual identity.
Link to David Crystal interviews to pick out quotes and ideas for your essays:
Link to Kate Burridge on TED Talk talking about Euphemisms; a good source for examples of euphemisms and how they are used in society. This can be used as foundation for a paragraph in your essays:
We’ve explored historical context, themes, essay planning and essay topics over on our Like a House on Fire by Cate Kennedy blog post. If you need a quick refresher or you’re new to studying this text, I highly recommend checking it out!
[Video Transcript]
‘Liz sits there helpless’
• From the beginning of the short story we can see that Liz isn’t, or doesn’t feel in control of her situation. The step by step process where she needs to ‘put the key in the ignition and turn it. Fire up the car and drive away’ showcases how the smallest details of starting the car, something that should be so simple instead requires immense mental effort on her behalf.
‘And he’s in there, alone, where she’s left him’.
• Her guilt bubbles to the surface here because it’s as though she’s the villain here, and she’s to blame for leaving him alone.
‘Abandoned him to a roomful of rampaging strangers’
• What’s really interesting here is her description of the other children. Instead of seeing this as an opportunity for Daniel to befriend others and have a great time, she describes them as ‘rampaging strangers’, giving us a sense that Daniel is subject to an unfamiliar environment that is wild, frenzied, rioting.
“Guerilla warfare”, “Jungle gym”, "seasoned commanders”
• These "fighter” phrases reveal Liz’s anxious mindset, as she imagines a world where her son is almost in the wilderness, every man for himself, as though it’s the survival of the fittest - and which Liz so fearfully express, “not that there’s going to be anybody with enough time to notice that Daniel needs help”, is not an environment where Daniel belongs.
“She digs in her bag for her lipstick, her fingers searching for the small cylinder, and pulls out a crayon, then a battery, then a tampon, then a gluestick.”
• Her everyday objects are splashed with Daniel’s belongings - the crayon, the gluestick, and demonstrate how intertwined her life is now with her child. This foreshadows her return to her pre-baby life - that things will not be the same.
“The smell of the place, that’s what throws her, the scent of it all, adult perfumes, air breathed out by computers and printers and photocopiers.”
• Even her sense of smell betrays her being away from Daniel. There’s a sense of alienation, of nausea that shows readers like us that Liz doesn’t feel like she belongs. This is in contrast to later in the story when she is reunited with Daniel and is comforted by ‘inhaling[ing] the scent of him again’.
“Same computer, same shiny worn spot on the space bar…"
• The repetition of ’same’ actually heightens how much has actually changed for Liz. Her entire world is now Daniel, whereas everything in the office is as it used to be. Therefore, there’s this sense that the people’s lives in the office remain unchanged, highlighting again Liz’s alienation.
“Yeah, yeah, yeah, they’re right, of course they are.”
• This sarcastic internal monologue reflects Liz’s current state of mind, where she’s experiencing a disconnect from her coworkers, and ’the land of the living’.
"Delete, she presses. Punching the key like a bird pecking. Delete, delete, delete.”
• We can feel Liz’s exasperation at this stage. The simile ‘like a bird pecking’ automates Liz’s actions in the workplace, as though she is doing it by switching to a ‘mechanical form’ of herself. The repetition of ‘delete, delete, delete’ gives us the sense that she’s frustratingly attempting to ‘delete’ her self-acknowledged, perhaps over-the-top anxiety surrounding Daniel, or trying to delete herself out of her situation. Whichever is unclear and left up to interpretation. Perhaps both ring true.
‘Returning to work after maternity leave’
• Liz’s narrative interspersed with new mum’s pamphlet. The juxtaposition of the pamphlet’s words ‘being a stay-at-home mum can begin to seem mundane and repetitive’ is contrasted with Liz’s love of motherhood - she is at odds with what society tells her she should be feeling.
‘[Daniel]’d have his thumb in his mouth right now. Not smiling, that’s for sure.’
• There’s a self-projection of anxiety here with Liz assuming that the childcarers are unable to look after Daniel properly, and that he’s suffering.
‘God, these endless extended moments where you’re left in limbo, the time dangling like a suspended toy on a piece of elastic.’
• This simile highlights how her mindset is completely consumed with Daniel, as she likens her daily experiences with objects and things related to Daniel and childhood. She struggles to switch between her identity as a mother, and her previous identity as a colleague in the workplace.
‘Caroline, Julie and Stella had laughed dutifully enough, but their faces had shown a kind of pained disappointment, something faintly aggrieved.’
• Perhaps this is Cate Kennedy's commentary on society and motherhood. The expectations others have on you as a new mother, and how you should be feeling.
‘He doesn’t run over when he sees her’.
• The opening of this chapter is blunt and brutal. Liz has longed to see Daniel all day, her anxiety getting the best of her, and yet at the moment of their reunion, it’s not as she expects. In this sense, we can to feel that Liz is very much alone in her anxiety and despair and, not the other way around with Daniel.
’She’s fighting a terrible nausea, feeling the sweat in the small of her back.’
• Unlike other stories in this collection, her pain isn’t because the absence of love, but because of its strength. Her love for Daniel is so intense that it’s physiological, making her unwell to have been away from him.
• The symbol of cake represents her pre-baby life, a time when she was concerned with the ‘account of Henderson’s’ and ‘delete fourth Excel column’. Her priorities have now shifted, and the celebrated ‘cake’ tradition in the workplace, one that is at the centre of several conversations, is no longer to significance to Liz. Her husband, Andrew’s attempt to celebrate Liz’s first day back at work with cake is highly ironic. The societal expectation that Liz is happy to be back at work even extends to her husband, and heightens how Liz is very much alone in her experience.
If you found this close analysis helpful, then you might want to check out our Like a House on Fire Study Guide where we analyse EVERY story in the text and pinpoint key quotes and symbols!
Watch our YouTube Video on Like A House On Fire Essay Topic and Body Paragraphs Breakdown
Like a House on Fire by Cate Kennedy
Like a House on Fire Essay Topic Breakdown
How To Get An A+ On Your Like A House On Fire Essay
Close Analysis Of 'Cake' From Like A House On Fire
3. Sample Essay Topics
4. A+ Essay Topic Breakdown
Things Fall Apart is usually studied in the Australian curriculum under Area of Study 1 - Text Response. For a detailed guide on Text Response, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Text Response .
Things Fall Apart is set in a fictional group of Igbo villages called Umuofia, around the beginning of the twentieth century. The first half of the novel is dedicated to an almost anthropological depiction of Igbo village life and culture through following the life of the protagonist Okonkwo . Okonkwo is the greatest wrestler and warrior alive in the nine villages and beyond. He has dedicated his life to achieving status and proving his strength to avoid becoming like his father Unoka – a lazy, improvident, but gentle man. Weakness is Okonkwo’s greatest fear. After men in another village kill a woman from Umuofia, a boy named Ikemefuna is given to Umuofia as compensation and lives in Okonkwo’s compound until the Gods decide his fate. Ikemefuna quickly becomes part of Okonkwo’s family; he is like a brother to Okonkwo’s son Nwoye and is secretly loved by Okonkwo as well. Over the next three years, the novel follows Okonkwo’s family through harvest seasons, religious festivals, cultural rituals, and domestic disputes. Okonkwo is shown to be more aggressive than other Igbo men and is continually criticized and rebuked by the village for his violence and temper . When the Oracle of the Hills and Caves decides that Ikemefuna must be killed, Okonkwo is warned by a respected elder to have no hand in the boy’s death because Ikemefuna calls him ‘father’. However, afraid of being thought weak, when Ikemefuna runs to Okonkwo in hope of protection, Okonkwo delivers the fatal blow. Ikemefuna’s brutal death deeply distresses Nwoye who becomes afraid of his father.
At the end of Part One, Okonkwo accidentally kills a clansman at a funeral after his faulty gun explodes and is exiled to his motherland, Mbanta. During his exile, British missionaries arrive in Mbanta and establish a church. Nwoye, disillusioned with his own culture and Gods after Ikemefuna’s death, is attracted to Christianity and is an early convert . This is a heartbreaking disappointment to Okonkwo. When Okonkwo and his family return from exile after seven years they find that the missionaries and colonial governors have established Umuofia as the center of their new colonial government . Clashes of culture and morality occur, and as the British make the Igbo more dependent on them through introducing trade and formal education, the Igbo way of life is continually undermined . When a Christian convert unmasks an egwugwu during a tribal ritual, a sin amounting to the death of an ancestral spirit, the egwugwu burn down the village church. The men who destroyed the church are arrested and humiliated by the District Commissioner, and Okonkwo beheads a court messenger at a village council in rebellion. When none of his clansmen rise with him against the British, Okonkwo realizes his culture and way of life is lost and commits suicide in despair. Suicide is a crime against the Earth Goddess, Ani , so Okonkwo is left to rot above ground in the Evil Forest, like his father Unoka – a shameful fate he spent his life desperate to avoid. The final paragraph, written from the perspective of the District Commissioner, reduces Okonkwo’s life to a single sentence about his death in his planned book The Pacification of the Primitive Tribes of The Lower Niger . Achebe has filled an entire novel with evidence of the complexity and sophistication of Okonkwo’s individual and social life and the District Commissioner’s casual dismissal and belittling of him causes us to flinch with horror and dismay. This is a metaphor for the reduction of Igbo culture in the eyes of its colonizers.
The title gives away the plot of the novel and anticipates the collapse of Okonkwo and his society. Things Fall Apart is about the connection between the tragic downfall of Okonkwo , who fate and temperamental weakness combine to destroy, and the destruction of his culture and society as the Igbo way of life is assailed by forces they do not understand and are unprepared to face .
A Full and Fair Representation of Ibo Traditional Life
The first part of the novel presents the traditional world of the Ibo with specificity and vibrancy . The imbedded descriptions of the patterns of interaction, daily routines and seasonal rituals of Ibo life creates an overwhelming impression of community and shared culture. We see the established system of values which regulates collective life and how closely related this is to natural cycles and environments. The Ibo’s moral values are contained in sayings and stories, rituals and festivals. Achebe depicts a comprehensive and sustaining social, spiritual, economic, agricultural, and legal order. (Chapters to consider: 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 12, 19)
While Ibo society is marked by the internal coherence of its organization and the poetry of its rituals, this coherence is partially formed by the repression of the individual and the inflexibility of social norms. Achebe shows the violence, dehumanization, and discrimination vulnerable groups experience in Umuofia due to the rigid adherence to tradition and superstition. This includes the customary abandonment of newborn twins, the sacrificial murder of Ikemefuna in the name of justice, and the discriminatory caste structure that denies inclusion to the osu (Chapters 7, 18).
Obierika’s questioning of the stern logic of some customs suggests that many laws are enacted from a sense of duty and inevitability rather than from a firm conviction in their justice or efficacy (Chapter 13). The cultural demand for conformity places a huge moral and psychological burden on individuals who must reckon with the sometimes heartless will of the gods . This internal tension is epitomized in the character of Okonkwo, discussed below.
Clash of Cultures
When the Ibo are confronted with rival institutions a mirror is held up to their society. Fall Apart honestly considers and reflects on Ibo practices, customs, values, and beliefs. The novel is a frank articulation of the nature of the African past and its relevance to the present and future . Achebe wants to illuminate Ibo culture to dispense with lingering colonial prejudices, but he is not sentimental or nostalgic for the past. Instead he is shifting through it to identify the valuable aspects of Ibo culture to bring into the future and help define Nigeria’s post-independence identity .
Achebe recognises that the colonial encounter which led, swiftly and seemingly inevitably, to the disintegration of Ibo culture revealed its profound weaknesses. Achebe suggests that with the arrival and contrast against another culture, a cultural reckoning was inevitable for the Ibo. However, cultural reckoning and revaluation is not the same thing as destruction and erasure . The British colonialists were a hostile force seeking cultural domination. By pointing out some of the weaknesses of the Ibo tradition, Achebe in no way excuses or justifies colonial domination or diminishes the pain and tragedy of the cultural erasure that occurred.
Colonial Domination
The anti-colonial position and purpose of the novel is powerfully clear. Achebe depicts the process of colonial initial establishment and the resultant cultural suspension of Ibo society. The British colonizers believed in their inherent cultural superiority and arrived in Umuofia with the intention to “bring civilization” (p.151) to Africa. They wanted to achieve full control by supplanting Ibo religion and culture with their own.
The British arrived quietly and non-confrontationally with their religion and the clans allow them to stay, misinterpreting their silence as peaceability . An Ibo proverb warns that there is danger in silence and nothing to fear from someone who reveals their motivations (Chapter 15). Obierika recognizes how the white man’s strategy disguised their intentions and gave them the freedom to grow and fortify. He explains the political consequences for the clan, now divided by the new religion, they can no longer act as one (Chapter 20). Without strength in unity, the Ibo are vulnerable to further encroachment of British control in their other institutions .
As only a small number of Ibo initially converted to Christianity, the church was only able to establish itself firmly in the villages because of the Ibo’s religious tolerance (Chapter 2, 22). Mr Brown learns about Ibo religion and his willful blindness to its complexity shows how the colonizers justified their colonial rule and imposition through labelling their subjects ‘primitive’ . Mr Brown understands that Christianity held no appeal for people well integrated in Ibo society, concluding that “a frontal attack on it would not succeed” (p.132) and thus introduces education as a new method of cultural displacement and erasure . Additionally, trade also increased the Ibo’s dependence on the introduced economy (Chapter 21).
From the very first introduction of the colonizers we understand that violence and fear were tools of oppression and dominance , forcing the Ibo to submit and keeping them unresisting (Chapter 15, 20, 23). Not only do the British impose foreign rule on the Ibo and judge them by standards they do not recognize, the District Commissioner’s personal brand of ‘justice’ is corrupt and hypocritical. When the elders are arbitrarily and falsely imprisoned, he tells them that what they have done “must not happen in the dominion of our queen” (p.141), combining personal corruption with a state apparatus of paternalism, hegemony, and occupation (Chapter 20, 23).
Dogmatic zealot, Reverend Smith, encourages fanaticism in his converts, motivating them to insult and humiliate the clan (Chapter 22). Under Reverend Smith’s wrathful guidance, the colonial agenda becomes transparently aggressive . The grief and pathos of the Ibo’s situation and collective trauma is displayed evocatively in the final episodes as Achebe depicts this painful moment of acute crisis (Chapter 22, 23, 24, 25).
A recurring thematic question in Things Fall Apart is to what degree the collapse of the Ibo and the downfall of Okonkwo are due to their own internal weaknesses or the whims of a pernicious fate .
The Ibo understand fate to be in a dynamic and somewhat ambiguous relationship with personal agency . This is evident in their proverb “when a man says yes his chi says yes also” (p.20) which acknowledges and privileges the role of an individual’s choices in shaping their destiny (Chapter 4). The saying “as a man danced so the drums were beaten for him” (p.135) also relates this idea – fate is a response to one’s behaviour. Okonkwo is warned that killing Ikemefuna, his surrogate son, is the “kind of action for which the goddess wipes out whole families” (p.49).This demonstrates the clan’s belief that the goddess’s (or fate’s) punishments are not arbitrary but the result of individual action (Chapter 8).
Although there is an element of chance in Okonkwo’s gun accidentally exploding and killing someone, his exile carries the suggestion of just comeuppance in its echo of the guns failure to shoot when purposely aimed at Ekwefi (Chapter 5, 13). Likewise, although the arrival of the Christians was unexpected and chanced, Nwoye’s rejection of his father is traceable directly to Okonkwo’s choice to kill Ikemefuna (Chapter 7). The desertion of people injured by Ibo traditions is a blow to the clan that feels equally earned (Chapters 16, 17, 18).
After his exile, Okonkwo believes his chi has turned against him (Chapter 14). He renunciates the wisdom of his elders by denying the active role he had in directing the course of events. His refusal to reflect on the connection between his actions and punishment reflect his fatal flaws: hubris and willful lack of self-knowledge. By refusing to self-analyze and self-correct, Okonkwo loses the opportunity of redemption. Comparably, the Ibo, despite believing in a relationship between action and fate, do not reflect on the cause of their kinsmen’s desertion to Christianity. Achebe provides numerous examples of the clan’s dogma and brutal traditions denying people such as Ikemefuna or twins control over their lives (Chapter 2, 7). It was the shortcomings of the Ibo social and religious order that made members susceptible to the attraction of a competing value system with a more articulated concept of individuality. The Ibo’s cultural lack of self-apprehension meant they could not adjust their traditions to save themselves .
However, just as Achebe shows how individuals in the clan are at the mercy of rigid overarching authority, he shows how the fateful forces of history constrain human agency . The British’s hostile intention to erase and supplant the Ibo way of life is a punishment greater than the Ibo deserve and a force stronger than they can rise to. In his description of the grief and trauma of colonial imposition, Achebe demonstrates his compassion and sorrow for the Ibo as they faced the sweeping and unforgiving forces of change in their moment of historical crisis .
Sample Essay Topics
1. "Things Fall Apart demonstrates how the values and customs of a society help us to deal with the familiar but not with change." Discuss.
2. "Traditional ideas of honour dominate Okonkwo's life and finally they destroy him." Discuss.
3. "Nwoye knew that it was right to be masculine and to be violent, but somehow he still preferred the stories his mother used to tell." How does Achebe explore masculinity in Things Fall Apart ?
Now it's your turn! Give these essay topics a go. For more sample essay topics, head over to our Things Fall Apart Study Guide to practice writing essays using the analysis you've learnt in this blog!
A+ Essay Topic Breakdown
Whenever you get a new essay topic, you can use LSG’s THINK and EXECUTE strategy , a technique to help you write better VCE essays. This essay topic breakdown will focus on the THINK part of the strategy. If you’re unfamiliar with this strategy, then check it out in How To Write A Killer Text Response .
Within the THINK strategy, we have 3 steps, or ABC. These ABC components are:
Step 1: A nalyse
Step 2: B rainstorm
Step 3: C reate a Plan
Let's look at an essay prompt in this video below:
In Things Fall Apart , women suffer the most and are victimised by men. Discuss.
Whenever you are breaking a prompt down. Ask yourself...
- What are the key words/ ideas that you need to address?
- Which theme is the prompt referring to?
- Do you agree with prompt? Or do you disagree with it?
The keywords of this prompt would be women, suffer,, victimised and men. The prompt requires us to address the role of women in the text and the ways in which they suffer in a society that is pervaded by patriarchal values. It also asks us, ‘Who is to blame?’ Are men solely responsible for the maltreatment or are there other causes to their suffering? The word ‘most’ in this prompt is actually there to give us a bit of room for discussion. Yes, women do suffer, but do they suffer the most? Or do men suffer as well?
Now that we’ve thought about the prompt, we can move on to the second step of the THINK part of the THINK and EXECUTE technique. To find out more about this unique strategy, I’d recommend downloading a free sample of our How to Write a Killer Text Response eBook!
Now, before we write our ideas in beautiful topic sentences, it’s often easier to simplify everything first. One way to do this is to work out whether the paragraph agrees or disagrees with the prompt at hand. We could follow this structure…
Yes, the prompt is true because X Yes, another reason it is true is X While it is true, it is limited by X
By elucidating the ways in which women are seen as inferior to their male counterparts, the writer establishes his critique on a society that victimises and oppresses women. From the outset of the book, Okonkwo is characterised as a violent man who ‘rules his household with a heavy hand’, placing his wives in perpetual fear. The frequent beating and violence fortifies the portrayal of him as a man who is governed by his hatred of ‘gentility and idleness’, further showing the terror that his wives are forced to be living in.
"Do what you are told woman. When did you become one of the ndichie (meaning elders) of Umuofia?"
He also sees his wife’s mere act of questioning as disrespect, as evidenced through the ways in which he implies that she is overstepping her role.
“There were many women, but they looked on from the fringe like outsiders"
This simile also shows how women are often marginalised and treated as outcasts, underlining the overarching yearning for social justice throughout the text. This pitiful image of women looking ‘on from the fringe’ also helps Achebe relay his criticism of gender double standards and the unfairness that Igbo women are forced to live with. Achebe’s sympathy for women’s suffering and condemnation of men’s mistreatment towards are also evident through his depiction of a society that normalises misogyny.
‘His mother and sisters worked hard enough, but they grew women’s crops… Yam, the king of crops, was a man’s crops’
The personification of the crops, in particular, the men’s crops, the ‘yam’, being the ‘king of crops’ establishes this gender hierarchy in yet another way. More specifically, the position of men in the social hierarchy is highlighted and the negative connotation attached to the ‘women’s crops’ undermine their hard work, rendering it in significant. While women are the main victims of Igbo gendered prejudice, Achebe does not disregard the undue burden that societal expectations impose on men.
‘He was afraid of being thought weak.’
Achebe explores the burdens of unrealistic expectations that are placed on both men and women. This quote exemplifies societal expectations on men to be strong, powerful and fearless leaders who never show emotions. Achebe’s sympathies regarding these expectations show us that this is an important critique in Things Fall Apart that we can analyse.
If you find this helpful, then you might want to check out our Things Fall Apart: A Killer Text Guide where we cover 5 A+ sample essays (written by a 50 study scorer!) with EVERY essay annotated and broken down on HOW and WHY these essays achieved A+ so you reach your English goals! Let's get started.
The Ultimate Guide to VCE Text Response
How To Write A Killer Text Response Study Guide
How to embed quotes in your essay like a boss
How to turn your Text Response essays from average to A+
5 Tips for a mic drop worthy essay conclusion
With contributions from Lindsey Dang.
1. 'The fantasy never got beyond that—I didn't let it—and though the tears rolled down my face, I wasn't sobbing or out of control. I just waited a bit, then turned back to the car, to drive off to wherever it was I was supposed to be.'
Compare how a perceived sense of control shapes characters in both Never Let Me Go and Stasiland .
2. Compare how the texts explore the importance of memory in defining identity.
3. 'To conform is to be safe and to survive.'
Compare how this idea is examined in both texts.
4. 'I'll have Hailsham with me, safely in my head, and that'll be something no one can take away.' (Never Let Me Go)
Compare how these texts explore the consequences of denying history for affected individuals.
5. Compare how Never Let Me Go and Stasiland examine what it means to be human.
6. Compare how both texts explore the influence of being an outsider on one's understanding of society and their place in the world.
7. 'This society, it was built on lies – lie after lie after lie.' ( Stasiland )
Compare what the two texts say about wilful ignorance in society.
8. 'It is impossible to be free when you are unaware of your confines.'
Compare how the two texts explore freedom and confinement.
9 . 'When I got out of prison, I was basically no longer human.' ( Stasiland )
'Poor creatures. What did we do to you?' ( Never Let Me Go )
Compare how Never Let Me Go and Stasiland explore how humanity can be irreparably broken.
10. Compare how these texts examine the sacrifices required for societal progression and change.
11. Compare what the two texts say about the inevitability of change and being forgotten.
12. Compare the ways these texts explore the influence of different types of human relationships on the individual.
13. 'Things have been put behind glass, but they are not yet over.' ( Stasiland )
Compare how Never Let Me Go and Stasiland demonstrate differing attitudes towards reality and the past.
14. Compare what the two texts suggest about the factors which shape an individual's world view.
15. 'We took away your art because we thought it would reveal your souls. Or to put it more finely, we did it to prove you had souls at all.' ( Never Let Me Go )
'...a soul buckled out of shape, forever.' ( Stasiland )
Compare how Never Let Me Go and Stasiland explore the concept of souls in relation to one's identity.
We’ve all been doing Text Response essays from as young as Year 7. At this point in VCE, we should be feeling relatively comfortable with tackling themes and characters in our essays. However, the danger with just discussing themes and characters is that we often fall into the trap of simply paraphrasing the novel, or retelling the story. So how do we elevate our essays to become more sophisticated and complex analyses that offer insight?
Before reading on, make sure you've read our Ultimate Guide to VCE Text Response .
An important distinction to be aware of is that the expectation of Year 11 English was geared more toward themes and characters. However in Year 12, teachers and examiners expect students to focus on the author’s construction of the text . By keeping in mind that the text is a DELIBERATE CONSTRUCTION, this can help eliminate retelling. A good guideline to follow is to include the author’s name at least once every paragraph.
Some examples are:
- (author) elicits
- (author) endorses or condemns
- (author) conveys
Move beyond talking about character and relationships. How are those characters used to explore ideas? How are they used to show readers what the author values?
To explore the text BEYOND characters, themes and ideas, tackle the following criteria:
Social, cultural and historical values embodied in text
In other words, this means the context in which the text was written. Think about how that influenced the author, and how those views and values are reflected in the text. How does the author create social commentary on humanity?
For a more in-depth look into this issue and how to get it right in your essays, read Context and Authorial Intention in VCE English .
Linguistic structures and features
These involve the author’s use of symbols, metaphors, subtext, or genres. Consider why the author chose those particular words, images or symbols? What effect did it evoke within the reader? What themes or characters are embodied within these literary devices? Metalanguage is essential in VCE essays, so ensure you are confident in this field.
If the text is a film, it’s important to include why the director chose certain cinematography techniques . Comment on the mise-en-scene, camera angles, overview shots, close ups, flashbacks, soundtrack, to name a few. Or if it’s a play, examine the stage directions. These contain great detail of the author’s intentions.
How text is open to different interpretations
“While some may perceive… others may believe…” is a good guideline to follow in order to explore different angles and complexities of the text.
Skilful weaving in of appropriate quotes
This is how to create a well-substantiated essay. To weave in textual evidence, don’t simply ‘plonk’ in sentence long quotes. Instead, use worded quotes within your sentences so the transition is seamless.
Do you know how to embed quotes like a boss? Test yourself with our blog post here .
Strong turn of phrase
Ensure your essay is always linked to the prompt; don’t go off on an unrelated tangent. Linking words such as “conversely” or “furthermore” increase coherence within your essay. Begin each paragraph with a strong topic sentence, and finish each paragraph with a broader perception that links back to the topic and the next paragraph. To see what this looks like in practice, check out What Does Improving Your English Really Look Like? for multiple sample paragraphs.
This is also where having a wide range of vocabulary is crucial to presenting your ideas in a sophisticated manner. Create a word bank from assessor’s reports, sample essays, or teacher’s notes, and by the end of the year you’ll have an extensive list to choose from. Also, referring to literary devices contributes to a great vocabulary, exhibiting a strong turn of phrase!
Consider the topic

What does it imply? Find the underlying message and the implications behind the prompt. There is always tension within the topic that needs to be resolved by the conclusion of your essay. A must-know technique to ensure you actually answer the prompt is by knowing the 5 types of different essay topics, and how your essay structure changes as a result. The How To Write A Killer Text Response ebook is a great way to learn how to identify the type of essay topic you have in front of you immediately, and start writing an A+ essay.
Finally, simply enjoy writing about your text! It will help you write with a sense of personal voice and a personal engagement with the text, which the teachers and assessors will always enjoy.
The majority, yes the majority of your peers this year will hire tutors for extra assistance in their studies. It's perfectly understandable since VCE is only getting more and more competitive, and students are looking for that edge that will set them apart from others! If you are a student who is currently looking for that one ideal tutor in whatever subject it may be, then this guide is for you. You might be in the same situation as I was a few years ago, someone who has gone through so many tutors that you can't even keep count. And why is that? Probably because you simply weren't satisfied with them. And you know what?
If you're not 100% happy with your tutor, then don't settle!
Let me tell you now, there is definitely that perfect tutor who is: knowledgeable, passionate, highly regarded, and someone who strives to help you succeed in VCE! Let's have a look at a few factors that you should take into consideration when looking for the best tutor for you:
1. Just because a tutor didn't get a study score of 50, don't overlook them.
A study score of 50 means that this person has fantastic English skills - we can't deny that. However, teaching a subject is very different to learning it. To be able to communicate well with a student, recognise their strengths and weaknesses, and cater tutoring sessions to suit you so that you achieve the most benefit is more importan t than simply being top of the class.
2. Tuition class structure.
Next, you need to consider whether the tutor's teaching method matches well with your preferred way of learning. There are tuition schools which often follow a strict syllabus structure week by week. Other tutors are more flexible with a 'we-will-focus-on-what-you'd-like-to-focus-on' approach. Which one do you prefer?
3. Assistance inside and outside of classes.
To put it plainly, tutoring is a highly paid job, which means that some people are only in it for the money. You want to find a tutor who will be more than happy to go that extra mile to ensure that you can benefit as much as possible from their tutoring. Are they willing to help you outside of class sessions through email or text messages? Are they happy to organise extra tutoring sessions if you need? Will they do extra work on the side so they can be adequately prepared for your next session? This year I taught an EAL student who particularly struggled with certain grammar and sentence structures. Since I had less experience in teaching EAL, I spent my own private time deciphering out the best way to teach him, and how he could overcome these challenges. Try to find a tutor who isn't just in the business for the money, but puts you , the student as their first priority.
4. Cost $$$.
Let's be honest. How much you will pay a tutor is also a major consideration. Generally, the higher the price, the more credentials that tutor has. Many VCE teachers are going for $100+ an hour, and that value is increasing! Also find out, what else apart from tutoring will you get? Will you be offered extra resources (study guides, A+ essays and more), can you contact your tutor outside of tutoring hours, will you receive reports on your progress? It's not enough now to simply have one hour of tutoring each week, you should be looking for tutors who will go that extra mile for you.
5. 'Freshness'.
'Freshness' is basically my way of asking, how up-to-date is the tutor with the current syllabus? Some tutors only teach what they studied in school, continue to use the same resources and provide the same advice year after year. It's a good idea to seek a tutor who actively aims to upgrade their knowledge and resources each year. This shows how staying relevant is important to them, and demonstrates that their ability to cater to their students' needs is a priority. However, it is important to keep in mind that just because a tutor is 10 years out of school, doesn't mean that they're not up-to-date. This goes both ways - a tutor who is 2 years out of school may seem current because they've only just graduated, yet if they haven't spent the time to learn the new syllabus changes, then that speaks for itself!
6. Personality.
Tutors with personality are always a big bonus. Tutor personality plays a major role in how effectively they communicate with you, as the student. Have you noticed how some of your favourite teachers are probably your favourite because of their great personality and how they use that to teach? By making class fun, it helps to stimulate your interest and encourages your curiosity to learn. So you can see how a tutor who is enthusiastic and passionate in their teaching will make you want to be a better student too!
7. Plagiarism.
Under no circumstances should you hire a tutor to do your homework for you! Nor should that tutor offer to write you an essay in return for compensation. In Year 11 Literature, my tutor told me she would write an essay for me, which I understood as writing an essay then showing it to me the week after. What I didn't realise was that the next week, she presented me with the essay, and told me I had to pay for it. Because I was quite shy, I didn't say anything and took her essay. But I didn't feel right using her work and after that, I stopped attending her sessions because I felt too uncomfortable. A good tutor is well aware of their part in helping you with your studies. They know that the best way for you to improve is to support you, not encourage you to copy their work. Remember that in the end, when you're sitting in that SAC or exam hall, you only have yourself to rely on. In the end, I did show my Literature teacher both copies, my own and my tutor's (I did explain to her that the second essay was not my own), and asked her if she could grade both. How ironic, because my essay had actually scored a higher mark than my tutors!
8. Credentials.
The best form of credentials for any tutor is word-of-mouth. Hearing that a tutor is good at what they do from others is always a sure sign that you're choosing somebody right. If you are recommended somebody, then they're probably worth looking into. If you are feeling out of the loop, start asking family and friends if they know anybody they could recommend you. Another form of credentials is a tutor's success stories. As a tutor, I often boast my own teaching successes rather than my own study score. I achieved 45 in my English studies and while tutoring over the past 6 years, I've actually facilitated several students to gain higher marks than myself! Now that I'm proud of!
Most importantly, don't settle. If there's something you're unhappy about your tutor, firstly speak to your tutor about it. Your tutor is there to help you and if they're not interested in adapting to how you'd like to learn, then perhaps they're not the tutor for you. There are so many different tutors out there, with so many different approaches to tutoring that you're bound to find the right person!
At Lisa's Study Guides, we take pride in our specialised VCE English (EAL, Literature, and English Language) tutoring service. We have a small, select team of tutors who have achieved study scores of 45 and above (the top 2% of their year level). All tutors have been especially selected because of their fantastic personality and ability to hone in on students' strengths and weaknesses, and cater tutoring sessions to optimise student results. We also ensure that we are up-to-date with any study design changes, so that we can stay on top of the VCE game. If you're interested in finding out more, check out our private tutoring page here !
Easily the most common question I get asked post-VCE-results has been: “How did you do it?”
For a lot of people, they think getting a 50 in English is just a distant dream for them, that they don’t have the skills or drive to achieve that elusive number.
I didn’t believe I was one of these students last year, and I can’t tell you how I did it. There are a huge number of variables involved in obtaining a 50, and many of them you can’t control. But I do know now that the work I did during last year gave me every chance of being one of those select students, and that I should’ve believed my work habits gave me every chance to achieve that dream number.
Keep in mind that I wasn’t getting full marks on my English SAC’s at any point last year, so don’t think that to get a 50 you need perfect marks consistently through the year. Perfect marks help obviously, but don’t be disheartened if you’ve just missed out. Those close-to-perfect scores are actually quite valuable, because they should make you feel confident that you have all the capability of writing a perfect essay on the end of year exam, while giving you the tidbit of feedback you need to fine-tune your writing.
If you’re in that top rung of students consistently getting perfect or near perfect scores on SAC’s, the most important thing you can do to keep achieving such high scores is to take on every piece of advice your teacher gives you. Most often when you’re at such a high level of writing, it’s advanced skills like the clarity in the way you communicate the ideas within a text, or zooming in on specific points of discussion or symbolism to add some zing to your essay. These skills come with practice – I would know. So be patient with English; it takes time to build up the technique and expertise required to cook up a perfect essay.
So for all the people wondering what they can do to crack that 50 study score – there is no such thing as a guaranteed 50, and most certainly no one way to “think” like a 50 student, but there are many things you can do during 3/4 English to give yourself the best shot at one.
Here’s what I did, and how it might help set you on the path to a 50.
PREP: The early days
Take clear, organised, easy-to-navigate notes.
I cannot emphasise enough how much writing and keeping well set-out notes helped keep me sane through the insanity of Year 12.
Right from the get go, make sure you have a system of note-taking that works for you. Whether it be writing them out in a notebook or keeping them in a document on your laptop, ensure that you write down every little helpful tidbit of information you might be told during class by a teacher, or even read on a website. This will ensure you don’t have that horrible feeling of regret when it comes to later down the track closer to the SAC (*can rhyme*) and are kicking yourself for not writing down that sentence about a character, or idea about a theme.
AND when I say “writing them out in a notebook or keeping them in a document on your laptop”, I don’t mean throwing everything in random nonsensical order on your page – separate your notes into headings. Keep your “characters” separate from your “themes”, so your ideas don’t get muddled up and you don’t confuse yourself into a state of breakdown two nights before the SAC when attempting to decode your notes.
Trust me, keeping solid notes is perhaps the most important self-care tip of Year 12. It may take some more time and effort, but you will be thanking yourself over and over when it comes to SAC and exam time.
Start learning quotes
If you had a dollar for every time a teacher had told you this you’d be able to pay your way to Schoolies, but they say it for a reason. And having been there and done that, I can validate that their hassling is completely reasonable.
Learning quotes sooner rather than later not only means you won’t be rushing to memorise them in the days before the SAC/exam, but it’ll help you get a grip on themes within, and the chronological order, of the text.
The most effective way I found to learn quotes is to split your total lot of quotes up into even groups. List your quotes in order from hardest (the ones that might be longer or have more complex language involved) to easiest to learn, then split them into small groups depending on how many weeks out you are from your SAC/exam - say you have 35 total, split them into groups of 7 to learn over, for example, 5 weeks.
Start with the hardest ones and focus on learning them throughout that first week. Then the following week, once you’ve memorized that first lot, add in the second hardest group and learn them while still going over the first group. Then the third week, add in the third group to learn while still going over the last two, and so on.
Using this method ensures you have 1. An even workload leading up to the SAC/exam and 2. More time to nail the quotes that are more difficult and will take longer to memorise.
PREP: The week before
Plan essays on a range of topics.
Ask any student who slays at English and they’ll tell you that they have planned topics until they never want to see another essay plan again. Planning topics is the best way to work out your strengths and your weaknesses in regards to the themes involved in your text. You can nail a plan for a topic you know you can smash, and sit down and really think about solid paragraph ideas and examples for a topic that would normally make you want to run out of the room crying if you got it in the SAC/exam. This way you’re literally planning for the worst case scenario and making sure that if you do get a topic you don’t love, you’ve still got a solid plan you can use for it. If you plan for all the topics you don’t want to get in an essay, you won’t have to worry about that “OMG I don’t know how to write an essay on this” panic setting in – who cares if you can’t think of ideas on the spot, you already have a killer plan you prepared earlier, you clever cookie.
Let’s just clarify what planning means though. Simply writing down three or four 5-word ideas for paragraphs is not going to be much help to you during the actual assessment. Writing full, articulate topic sentences and putting down examples of quotes and/or events you’ll use to support your arguments, INCLUDING how they explain your point, is what you’ll find helpful when you’re looking over them in the days before/the day of.
Drill quotes every night
You might be thinking “I’ve been learning quotes for 5 weeks now, she’ll be right – I’ll take this week off just to focus on planning”.
No, my friend, that is not what you should be thinking. No matter how much you might hate learning quotes, you’ll never forgive yourself when you’re sitting in the assessment and have forgotten how the quotes you’re looking to use are worded, or when they’re said, or even who said them, because you haven’t been over them the last few days.
Don’t back off revising quotes in the last week. Quotes are what make your whole essay, and the more and better you can embed in your essay, the higher your mark is likely to be. You don’t want to do yourself dirty by switching your focus to planning and completely neglecting quotes – think about how easy it is to forget things once you’re sitting at a desk with nerves running through you on SAC/exam day. It ain’t going to end well if you ignore your quotes in that last week.
Make mind maps
Regardless if you’re a visual learner or not, I’ve found mind maps are a really smart, time savvy way to organise your notes and knowledge. You might think it’s a waste of time, but in the course of making them you’re forced to consolidate your notes into the smallest but most informative piece of information you can, you’re writing it down, and you’re literally connecting your ideas together. It’s a perfect recipe to help make sense of your text.
Mind maps also come in really handy for exam time, as you can stick them up on whatever surface of your choosing to have them to look at and help you revise. Not only that, but on SAC day when you don’t want to overwhelm yourself by rereading all your notes and bombarding your brain, mind maps are a great way to revise and remind yourself of the connecting ideas within your text.
Ignore the ‘stress merchants’
Don’t get caught up in all the “I don’t know any quotes” and “I don’t know how to write an essay” stress that other students pass around in those hours before the SAC and exam. These are the people you don’t want to touch with a 50-foot pole. It’s so easy for you to forget about all the hard work, planning, quote learning and essay writing you’ve done in the last few weeks when you’re surrounded by the stress from other people who are way underprepared.
Structure your thoughts
If you’re going to write a flowing, connected, non-clunky essay, you need to think in a flowing, connected, non-clunky way. Keep your thoughts clean – instead of looking at your topic and thinking something along the lines of “Oh ok this isn’t what I expected have I done a practice essay on this topic no ok omg so what paragraphs am I meant to write how am I meant to plan this” and on and on, take a breath and steady yourself. Take another look at the topic and break it down: pick out the focus words, being those that relate to the theme the topic focuses on or characters it concerns, and pull your paragraph ideas from those focus words. When you’re writing your paragraphs, you want to keep your thoughts structured. Focus on your wording, write each sentence at a time and try not to rush ahead, and make sure at the end of each sentence you think about what purpose you want the next one to serve. Is it a segway into your next example? Is it explaining your example and connecting it back to your overall theme? This thought pattern is really key to ensuring you write a coherent and eloquent essay.
Back yourself
This is really where that 50-student mindset comes in – remind yourself about how hard you’ve worked, and how ready you are for this assessment. Chances are you’re going in more prepared than about 90% of the other students in your cohort. Stay calm, because you don’t need to stress. Nerves are ok though – it means you care! Just make sure you take a minute to breathe before you start and clear your head so you can go straight into planning mode once that clock starts.
If there’s anything that’s a clear indication that you’re thinking like a 50 student, it’s working smarter, not harder – changing the way you approach writing and preparation to incorporate the most effective methods for you and make the most of the time you have is a surefire way to set yourself up for the best chance at a 50.
Best of luck.
VCE is a two-year journey which involves a high degree of academic and personal growth. Young adults experiencing these two years of life will encounter a number of challenges which, albeit rewarding, are nonetheless a cause of much anxiety and pressure. It is important to recognise that the process is, at the end of the day, a team effort – VCE students are as reliant on their teachers for learning material as they are upon their parents for support, just as they rely upon friends to offer an outlet of distraction and ease. As a parent, your fundamental role during your child’s years of VCE is to help him/her manage their time, stress and aspirations to ultimately reach their goals. The purpose of this article is to provide a tangible, how-to guide to fulfil a healthy parent-student relationship during VCE. The below strategies detail the importance of communication, teamwork and compromise as the three cornerstones necessary to achieve conjunctive family and academic success.
Communication
Communication is pivotal during Year 11 and 12. It is important to ensure that all members of your VCE team, whoever this may involve, remain on the same page. Miscommunication is a messy way to disrupt a streamlined VCE journey – continuous and multi-way communication allows you to take positive steps towards your child receiving the most stress-free experience. To adopt this approach within your own family:
Ensure that your child knows that their happiness and education is your first priority.
It is easy to forget the purpose of VCE given the mayhem of it all. It is crucial to reassure your child that you are present as a support network and that you hold a stake in their journey. Rather than present their results as a source of positivity or negativity, create the perception that a healthy and committed approach to VCE is of the highest importance. If your child knows that your role is centred around their happiness and success, they will be more relaxed and willing to share their journey with you.
Frequently reinforce your pride in their achievements.
VCE is a long, tough effort. It is two years of high expectations and insurmountable workload which culminates in the endgame of a four-digit number. For a student undergoing VCE, it is difficult to remove yourself from this mindset. As a parent, remember to appreciate the small successes and the baby steps towards a more recognisable achievement. Even a little acknowledgement, such as praising consistent grades or offering a “Good work!” can remind your child that they are on the right track and that you are aware – and proud – of this.
Take notice of, and respect, the cues that your child presents.
VCE is often described as a rollercoaster. This is a metaphor which accurately summarises the highs and lows that are bound to accompany such an important stage of a young person’s life. It may be tricky to understand why your child may come home one day in seemingly ‘meh’ spirits and so forth. Regardless, these actions (or lack thereof) are designed to subtly inform you of their headspace and mindset at a particular time. If you can form a limited understanding of these cues, they will enable you to provide relevant solutions and/or support. For example, if your child is repeatedly answering to you with curt or brief responses, this may indicate that their mind is elsewhere, and they would appreciate the opportunity to study in quiet for some time. On the other hand, if work progress seems to slow down, a distraction and time-out from study may be necessary. Sometimes, just a brief chat about their day will make a significant difference to motivation levels.
Maintain two-way communication with your child’s teachers.
Communication should flow freely between the classroom and your home. Remaining aware of how your child is progressing at school will give you the best ability to support them in a relevant and sustainable way, while also drawing attention to areas of improvement or growth and enabling you to respond to these developments appropriately. Parent-Teacher Interviews are a great way to keep in touch. Alternatively, a brief email every so often will inform your child’s teacher that you are committed to their progress and want consistent updates.
At the end of the day, VCE is a team effort! Without a doubt, your child’s work and dedication is the driving force, yet the role of parents, teachers, friends and others provides a crucial support network. It is important to maintain this vision and to acknowledge your place within this team. To implement this strategy yourself:
Be prepared to discuss your child’s studies with them.
Basic, genuine attempts to form some understanding of what your child is learning will assure them of your stake within their academic journey. This discussion does not have to be profound – if your child is studying Biology, do not think it is essential for you to gain a strong understanding of the metabolic processes performed by animals, for example. It will never be necessary for you to be an expert at any VCE subject. Rather, simply encouraging your child to share their knowledge with you will contribute to their learning. Carrying on with the example of Biology, you can ask your child to briefly explain the stages of photosynthesis. This technique will result in a number of benefits; your child will be challenged to demonstrate their knowledge and thereby increase their own understanding, and you will find a source of discussion which fosters growth (both academically and emotionally) between yourself and your child.
Express a genuine interest in their work.
It is easy for VCE students to attain a tunnel vision and lean towards route learning during the crunch point of their studies. Articulating your intrigue to learn about their studies will boost student engagement and remind your child that subjects can be extended beyond the classroom. Simply asking natural questions and/or clarifying content will demonstrate your stake in their progress and exemplify the team mindset which promotes cohesive growth. Just discussing your child’s English text with them will position him/her to articulate their ideas and, in turn, contribute to the level of analysis they are able to perform when writing an essay.
Consider investing in tutoring as a way to extend your child’s education beyond the classroom.
A tutor performs the unique role of a mentor, friend and teacher who has the exclusive ability to provide one-on-one support. A tutor can further your child’s skills in a focused and familiar environment, sustaining growth throughout the year and tackling gaps in understanding as soon as these concerns arise. Ultimately, a tutor is an invaluable addition to your child’s VCE team! Lisa's Study Guides provides a one-of-a-kind, specialised tutoring service which offers a wealth of curated resources, 24/7 support and lessons with the state’s most high-performing recent graduates. To find out more about what Lisa's Study Guides can do for you, click here .
VCE is a period of significant change and it is important to remain flexible. By acknowledging the importance of focused study time, you can adjust your family’s schedule to meet the requirements of each individual. Encouraging your child to demonstrate two-way communication and positive habits, such as informing you of upcoming commitments, will ensure that compromise can occur in a swift and agreeable fashion. The following advice will contribute to healthy negotiation within your home:
Understand that your child’s priorities have changed.
It is inevitable that Year 11 and 12 are going to require intense focus and a dedication, on your child’s part, to his/her studies. Designating specific study blocks is a good way to ensure that you highlight the importance of routine and consistent study. Despite this fact, it can be difficult to come to terms with the reality of such change. During VCE, it is unlikely that your child will have the ability to sustainably divide their time in a way which is familiar to you. This shift may be significant or subtle depending on the consistency of your child’s study habits, their non-scholarly commitments and a range of other factors. Regardless, it is important to remain adaptable and understand that your child’s response to VCE is a natural reaction to the major change involved.
Be flexible and offer alternatives where necessary.
VCE is often unpredictable and assignments can arise out of the blue. Workloads may be relatively easy-going one moment, before three new assessments come up the next school day and suddenly extra work is required. While it is helpful to theoretically organise family time or outings, it may eventuate that these plans are not always compatible with your child’s schedule. Try postponing events where necessary and approach the situation with a neutral attitude – reassuring your child that Thursday is as good as Tuesday to catch the latest Marvel flick will buoy their spirits and link these events to positive emotions.
Commit to reaching solutions which work for you, your VCE student and the rest of your family.
Settling for an option which disgruntles yourself, your Year 11/12 student or other members of your family is an unsustainable way to manage family expectations during VCE. While it may not be ideal to find a day of the week which is suitable for everyone, or if it looks like cancelling is the easier option, keep in mind the potential repercussions that these decisions may have. Due to its limited nature, time spent as a family is especially precious when a child is undergoing VCE. Reaching mutually agreeable solutions is the best way to meet both family and school needs and will have a significant impact on morale in the long term.
Consider introducing a family timetable developed around your VCE student’s study habits.
It may be useful to organise your family’s priorities and represent these ideals in an accessible timetable. Doing so will ensure that your needs as a family are met without the potential for certain elements to be overlooked and inform family members in advance of upcoming plans. Organise your standard week by priority and create a tangible, week-to-week routine like illustrated:

VCE is an undoubtedly testing stage for a student and their family – yet, it does not have to be overwhelming. Successful navigation through Year 11 and 12 will occur as the result of a cohesive relationship between a student and his/her support network. As a parent, your role is centred around support. Offering your child the confidence of your time, patience and effort will make a world of difference to their morale and, in turn, results. Simple family adjustments, as listed above, will contribute to the sustained growth between yourself and your child. Implementing these strategies and anchoring your focus on the themes of communication, teamwork and compromise will ensure that your family’s VCE experience occurs smoothly.
Can you believe that the eagerly awaited July holidays are finally here? It’s a bit scary to think that this marks the half-way point until end of year exams. We all know that the VCE year travels on too quickly, leaving us feeling that there is always too little time, and too much to do! As time ticks away and end-of-year exams draw closer, it is important to make efficient use out of your mid-year holidays. Listed below are 5 ideas that you might like to take onboard:
- Take a break! It’s pretty clear that during holidays you’re supposed to be on a holiday. However, with ongoing VCE stresses, you might feel inclined to continue studying throughout your 2 or 3 week mid-year break. It’s a great idea to keep up your studies, just make sure that you do give yourself a chance to rest and recover, or you may risk getting ‘burnt-out’. Try to catch up with friends, have a good night out or whatever activity that will give you a few good hours of relaxation and fun!
- Revise. While it’s important to have a break, these few weeks can be vital for your studies. Rather than putting everything aside until the end of the year, it is a good opportunity for you to revise your previous unit work. During this time, you should focus any weak areas and aim to strengthen them. By adopting this method, you have a greater chance of making major improvements compared to smaller improvements when revising the areas you are already skilled in.
- Study ahead. Familiarising yourself with the topics coming up can give you an advantage over other students who see topics for the first time in-semester. If the topics are based on work you’ve done previously in year 11 or even the first half of year 12, it may be useful for you to review that work so that you are prepared for the coming unit.
- Look into university preferences. The July / August period is a busy time to think about your future. University preferences are due, and many of you will be participating in the Undergraduate Medicine and Health Sciences Admission Test (UMAT). Since the next couple of months will be hectic, you don’t want to rush any decisions regarding career, course, and university. If you get serious these holidays and do some research into what path you’d like to take in the future, it will be less stressful for you when you start school again. If you're unsure about your university preferences, watch my tips in the video below!
- Prepare for English. If you haven’t read or watched your texts for the next unit, this is the time to do so. It’s always best to read just for reading sake the first time round, and at a pace that you’re happy with. This gives you the chance to soak up some knowledge on characters, plots and themes so that when your teacher begins discussions in class, you’ll already have a head start.
Depending on how you like to study, your approach to these holidays may be different to others. However, the take home message is to ensure you have a well-deserved break while still maintaining a healthy level of study. These few weeks can really make a difference in your VCE studies, so do what you think will help you improve the most. That’s all today, enjoy your holidays!
It’s around that time of the year when you start to contemplate which one of two texts you’ll most likely use in the Text Response component of the exam. And it’s not necessarily an easy choice to make! There are several factors worth considering, and you should definitely take your time deciding which text is best for you – after all, it can make a massive difference in your studying habits leading up to the exam and also how well you perform in the final exam. I’ll share with you a few of the common remarks made by students in regards to the exam and how things generally aren’t as straightforward as they seem!
1. ‘I’ll just spend all my time on one text because I’m not that great with the other one.’
Whoa! Stop right there! The first thing you should keep in mind is that you have 2 texts to choose from for a reason. The moment you decide to stick with one text, you have essentially put all your eggs into one basket. The negative side is exactly that – if you’ve placed all your chances of doing well into that one text, what if things don’t go as planned? Like two incredibly difficult exam prompts that you’ve never come across, a massive freak out I-just-realised-I-know-a-lot-less-than-I-thought leading up to the exam, or worse , that last-minute decision to switch texts for the exam. When eliminating the other option, you’ve basically got no backup. I’m sure you, like myself, have been told to back up your work on the computer and at some point, you didn’t and what happened? Of course, your computer crashed and you lost all your work. If you’re willing to take the risk, then of course go for it. Having a backup or at least having two text options ready provides you with a safety net. Even with two texts at hand, it’s completely natural for you to lean towards one text than the other. The best option, which I believe most of you would agree on, would be to focus more time on one text, but still have the other one at your disposal.
2. ‘I’ll select the text that scores the highest marks in past exams.’
Having a look at past exam marks can give you a good indication of the number of students that select a particular text and also the average mark scored by those students. The table below shows what VCAA used to produce in their Assessment Reports:

As you can see, the novel Year of Wonders has received the highest average mark. This by no means indicates that examiners are any more lenient on this text, nor do they favour it. What it really means is that it just so happened that the percentage of students who decided to write on this text were higher-than-average English students. Since 2013, VCAA has published a much more realistic table that gives us a better indication of what type of students were writing on these texts:

VCAA then stated:
From this table it can be seen that students achieved the highest scores on average for Henry IV, Part I. However, it can also be seen that on average this same set of students achieved well in the other sections of the English examination. Conversely, students who selected Così had the lowest average score in Section A, but also had low scores in Sections B and C.
UPDATE: It's 2017, so I thought I'd show you last year's examination report just below.
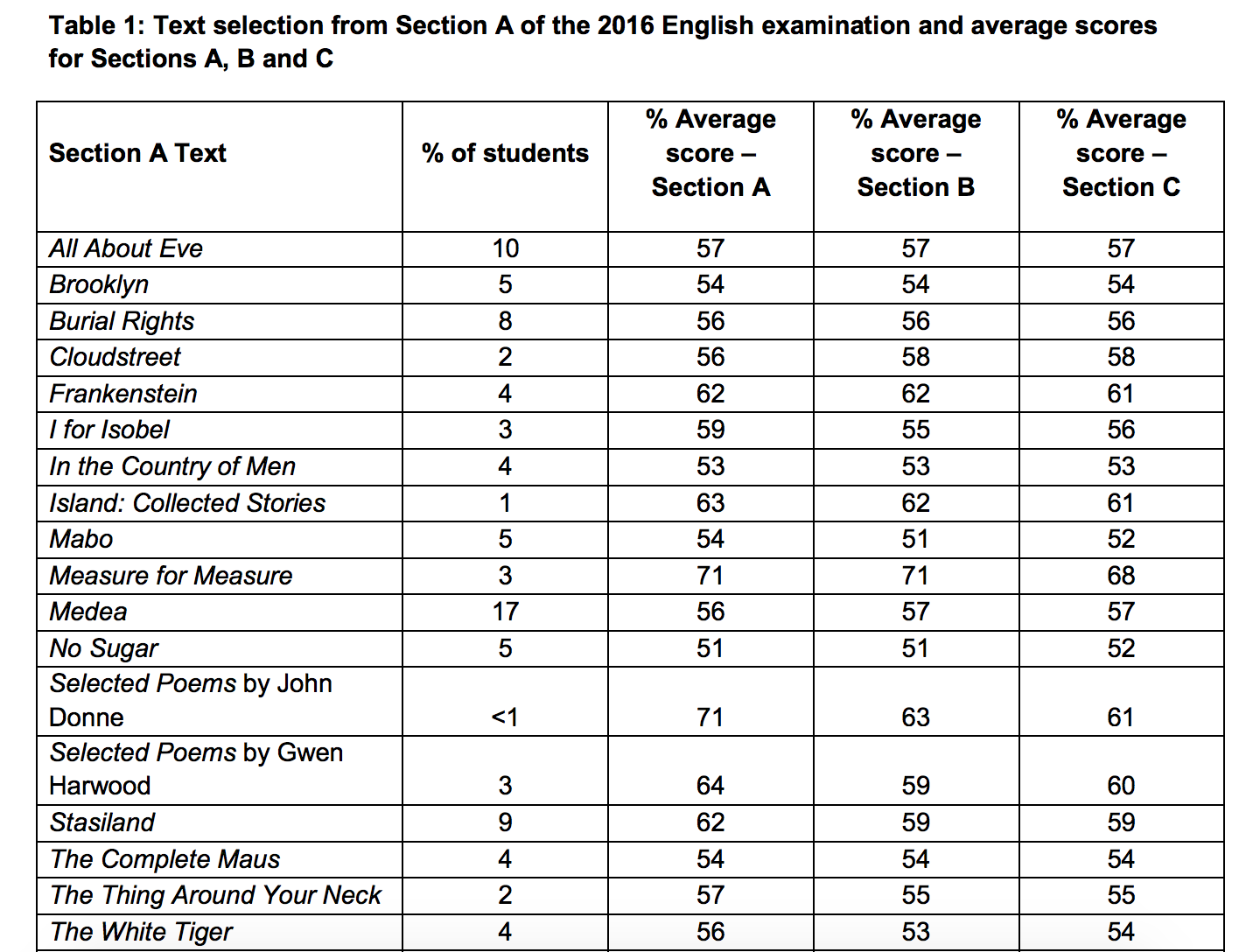
So what’s the take home message here? Don’t simply choose your text because it seemed to score well in recent years.
3. ‘I’ll do the film because it’s easier.’
Don’t be fooled! Films does not equal easy! Perhaps reviewing the film will be quicker than re-reading a text but films have so many layers of intricacy that you’d be silly to think that you’re automatically going to do better in the exam. It’s very hard to be successful just by writing about dialogue and plot. You have to analyse the film techniques , especially those that aren’t going to be mentioned by majority of students in the exam in order to stand out!
4. ‘I won’t do a text because it’s the first year it’s being assessed and I don’t know what to expect.’
Well hey, this is fair enough. But you can probably see it as an advantage. Although you don’t know what to expect, keep in mind that the examiners themselves probably won’t know what to expect from VCE students either. It goes both ways! If you don’t know what to expect, adequately prepare yourself. Collect and practice as many essay prompts as you can, read whatever notes or study guides you can get your hands on, and seek out your teacher and ask them if they have any thoughts on the exam!
5. “I’ll select the text that is newer to the syllabus as many students will not pick this and I will be able to get a better mark.”
The thing is, you really can’t tell how many students will choose a certain text. At the end of the day, examiners cross-mark several different texts which means that one text isn’t going to score better simply because less students choose it. A particular text may appear to receive higher scores because it’s less popular but really it means that the people who chose to write on it were higher-than-average English students (just refer to the tables shown above from VCAA Assessment Reports)!
With all these common remarks from students mentioned above, it comes down to one simple point, but often a point that needs to be reiterated – choose the text that you’re most familar and most comfortable with. Afterall, it’s going to be your writing that speaks out to the examiner. You can be strategic as you like, but choosing the text you’re best at is definitely the best strategy of all! Hope this helps any of you who have been contemplating some of these questions. Keep it up everyone!
So…you’ve just begun the school year and you’re feeling pretty excited about English. You’re determined to put aside all distractions this year and to only focus on studying, studying and studying. But…the minute you sit down at your desk, you find that your mind goes completely blank and that you are left only with one dreadful question: What now?
If this sounds all too familiar to you, you are definitely not alone. English can often make you feel like you don’t even know where to start. So, here is a quick guide that can help you to plan out your year, to break free from procrastination and to find some sparks of motivation when you feel like there is simply no road ahead.
Step 1: Read Your Text !
This may seem like the most obvious step, but it can make all the difference when done thoughtfully and thoroughly. One thing that VCAA English examiners always look for when reading text responses is in-depth knowledge and understanding of the text, and the best way to develop and gain this knowledge is to read, read, and read again! Try to treat your text like a blank map, full of unexplored territories and winding roads that are there for you to uncover each time you read the text.
When you read your text for the first time, look out for the major roads and landmarks; the setting and premise, the plot, the characters, the broad ideas, the authorial voice and style etc. Once you’ve gotten a good grasp of the major elements of your text, read it again, and focus on adding more detail to your map; fleshing out characters, understanding their motives, understanding the author’s purpose, and underlining key quotations and particular passages that encompass a broader idea. If you’re a forgetful person like me, you might find it helpful to note down some key observations as you go and to create a summary you can always refer back to throughout the year.
Step 2: Read Around Your Text
While reading and rereading your text will definitely help you to know your text in and out, in order to fully tick the box of knowledge and understanding, it is also important to read around the text; to understand the context of when and why the text was written, for whom it was written, and the impact the text has had on both its original audience and its audience today. Especially for texts that are rooted in history, like The Women of Troy or Rear Window , understanding context and background information is essential in understanding the text itself. After all, Rear Window just wouldn’t be Rear Window if it weren’t for the McCarthyistic attitudes that were so prevalent at the time, and The Women of Troy would have been a far more different play had it not been written during wartime. Each text is a product of both its creator and its time, so make the effort to research the writer, playwright or filmmaker , and the historical, cultural, social and political context of your text.
When doing your research, it can be helpful to use a set of questions like the one below as a guideline, to ensure that the information you’re finding is always relevant.
- Who is the writer/playwright/filmmaker?
- Who is the audience?
- When/where was your text written?
- When/where is your text set?
- Why was your text written?
- What is the style/genre of your text?
Step 3: Study Your Text
Here’s where it gets a bit more difficult. Now that you’ve drawn out your map, and dotted it with various landmarks, rivers and roads, it is time to actually use your map to go somewhere; to make use of all the knowledge and background information you have gathered so that you can begin to analyse and dissect your text in greater detail. Studying a subject with as large of a cohort as VCE English can oftentimes mean that ideas are recycled and exams are repetitive, so in order to distinguish yourself from the pack, try to look for ways to craft your own original path ; a view of the text that is distinctly your own, instead of following others. The best way to do this is to do a bit of thinking at home; to create your own original set of notes and observations and to spend time analysing each section of your text in greater detail than you may have done in class.
Constructing a notes table like the one below can help you greatly in sorting and fleshing out your ideas, and, when done consistently throughout the year, can save a lot of time and effort when it comes to studying for the exam!
The Women of Troy Notes Table:
%20(1).png)
Step 4: Target Your Study to Your SAC
So...you’ve made it all the way to your SAC. You may be feeling nervous at this point, even a little burnt out, but there is no need to worry. Studying for your SAC simply requires a bit of adjusting to your normal studying routine; changing it up so that instead of simply brainstorming ideas, you’re actually using these ideas in topic sentences, and instead of collating a list of quotes, you’re embedding these quotes into a practice paragraph. These are all examples of targeted study: taking all the information you’ve gathered on your text, all the notes you’ve made, and all the work you’ve done in class, and putting it into practice.
Targeted study could be done in the form of an essay plan, or unpacking an essay question
As an example, I've unpacked an essay prompt below using LSG’s THINK and EXECUTE strategy , a technique to help you write better VCE essays. If you’re unfamiliar with this strategy, then check it out in How To Write A Killer Text Response .
Step 1: A nalyse Step 2: B rainstorm Step 3: C reate a Plan
The Prompt:
‘I ask you not to hate me. With the greatest reluctance / I must tell you the news…’ Euripides softens the brutality of the Greeks’ behaviour through his characterisation of Talthybius.
Step 1: Analyse
- This is an example of a quote-based prompt ( learn about the 5 different prompt types here )
- Bold keywords from the prompt: ‘I ask you not to hate me . With the greatest reluctance / I must tell you the news…’ Euripides softens the brutality of the Greeks’ behaviour through his characterisation of Talthybius.
- To what extent do you agree? This part is asking me to adopt a specific viewpoint, whether you agree, disagree or are somewhere in between.
Step 2: Brainstorm
Unpack the keywords in the topic:
- 'not to hate me' , 'greatest reluctance' – Talthybius’ desire to be liked, his understanding of the actions of Greeks
- Softens the brutality – Talthybius serves as the opposing force to the Greeks’ brutal behaviour, makes the Greeks more sympathetic
- Characterisation – Talthybius’ personality, behaviour, actions, language
Step 3: Create a Plan
Contention: While Talthybius is used by Euripides to evoke some sympathy for the Greeks, ultimately, he serves to exacerbate the cruelty of the Greeks’ actions and the devastating consequences of their fall from a civilised, sacred people to a bestial, impulse-driven group of men.
Paragraph 1: Certainly, amongst his peers which are excoriated by Euripides for their cruel, unfeeling behaviour, Talthybius is depicted to be the most humane of the Greeks due to his conflicted nature, evoking sympathy amongst the audience, and reinstating some humanity to the Greeks’ otherwise sullied reputation.
Targeted study could also be done in the form of unpacking quotes, and analysing their significance
We can also use the ABC steps here. For example:
'Like the mother bird to her plundered nest, my song has become a scream'
Step 1: Analyse
Demonstrates the dehumanisation of the Trojan women, and the heinous, beastly actions of the Greek men, who, like their 'war machine' description, have subverted all that is natural to become violent, and all that is beautiful to become grotesque
Step 2: Brainstorm
- 'Mother bird' - animal imagery, maternalistic
- 'My song has become a scream' - demonstrates devastation, contrast between melody to dissonance
Embed the quote into a sentence, e.g.:
Euripides’ description of Hecuba as a 'mother bird' at her 'plundered nest' demonstrates the innately maternal nature of her character through animal imagery, while also emphasising the vulnerability of the Trojan women, who have been reduced to defenceless prey as a result of the Greeks’ predatory and beastly behaviour.
Planning essays and breaking down prompts/quotes are extremely time-efficient ways to approach your texts and SACs. Rather than slaving away for hours and hours writing full essays, these simpler forms of targeted study can and will save you the burnout and will get you feeling confident faster.
Only move on to writing a full practice essay or some practice paragraphs once you feel you have a good in-depth understanding of how to plan an essay and once you have already naturally memorised some important quotes that you can use in your essay ( learn how to embed your quotes like a boss here ). Remember, quality over quantity, so spend your time before your SAC revising thoughtfully and carefully, targeting your revision, and taking things slowly, rather than robotically churning out essay after essay.
Step 5: Embrace the Exam!
The end of every VCE English journey is the highly anticipated, dreaded and feared English exam. Now, while you may be reading those words with a horror movie soundtrack playing in your mind, the English exam, despite being a gruelling 3 hours of essay-writing, really isn’t as horrific as it sounds. Preparing for it is also much less intense than you might think it to be, because essentially, from the very first time you read your text, you will have already begun preparing for the exam. All that is left to do before the English exam is to polish up on some of your weaknesses identified in your SACs, to look over all the notes and information you have gathered throughout the year, to freshen up on essay writing and essay planning , and to do a couple of practices, so that you can feel as ready as you can for the real thing.
In particular, I found that in the leadup to my English exam, studying with my friends and peers was not only a welcome stress reliever, but a really good way to expand my own knowledge by helping others and being helped myself. Having your peers review your essays and helping to give feedback on theirs is always an excellent way to improve your own essay-writing skills, and, a great way to provide good constructive criticism is to follow the GIQ rule (I’m not sure if this is a real rule…but it works!)
- What was GOOD about the piece? e.g. Your sentences flow really well, and you embed quotes into sentences phenomenally!
- What could be IMPROVED? e.g. Perhaps adding a couple of sentences elaborating on this idea could make your essay even better!
- What QUESTIONS do you have about the piece? e.g. I don’t really understand this sentence, what were you trying to say here?
Hopefully, these tips will be able to help you out throughout the year in staying motivated and feeling okay about English! Remember, this is just here as a guide to help you, and not a strict regimen to follow, because everyone studies differently, and has different goals in English.
However, now that you have a clearer pathway and plan for learning your texts in-depth, what’s next? Well, it’s pretty important that you learn about the different areas of study so that you understand how you’ll actually apply all of your new-found text knowledge to each of your SACs and the exam. Our Ultimate Guide to Text Response and Ultimate Guide to Comparative give you a full rundown of what is required in these two areas of study (where you will have to learn specific texts) so I would highly recommend having a read!
Get exclusive weekly advice from Lisa, only available via email.
Power-up your learning with free essay topics, downloadable word banks, and updates on the latest VCE strategies.
latest articles
Check out our latest thought leadership on enterprise innovation., vce creative writing: how to structure your story.

VCE English Unit 3, Area of Study 2: Creating Texts - What Is It?

Breaking Down Themes & Key Quotes in The Erratics by Vicki Laveau-Harvie

Keep in touch
Have questions? Get in touch with us here - we usually reply in 24 business hours.
Unfortunately, we won't be able to answer any emails here requesting personal help with your study or homework here!

Copyright © Lisa's Study Guides. All Rights Reserved. The VCAA does not endorse and is not affiliated with Lisa's Study Guides or vcestudyguides.com. The VCAA provides the only official, up to date versions of VCAA publications and information about courses including the VCE. VCE® is a registered trademark of the VCAA.
03 9028 5603 Call us: Monday to Friday between 3pm - 6pm or leave us a message and we'll call you back! Address: Level 2 Little Collins St Melbourne 3000 VIC

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
If you use the author's name in your lead-in to the quote, you just need to provide the year in parentheses: According to Luz Lopez, "the green grass symbolizes a fresh start for Lia (24).". 2. Include the author's last name, the year, and the page number for APA format. Write the author's name, then put a comma.
Citing a quote in APA Style. To cite a direct quote in APA, you must include the author's last name, the year, and a page number, all separated by commas. If the quote appears on a single page, use "p."; if it spans a page range, use "pp.". An APA in-text citation can be parenthetical or narrative.
Step 6: Explain the Quote. Explain the significance of the quote in your own words. This will help the reader understand how the quote supports your argument. Example: Jane Doe's quote highlights the urgency of addressing climate change as it poses a significant threat to human survival.
Citing a quote in APA Style. To cite a direct quote in APA, you must include the author's last name, the year, and a page number, all separated by commas. If the quote appears on a single page, use 'p.'; if it spans a page range, use 'pp.'. An APA in-text citation can be parenthetical or narrative.
when an author has said something memorably or succinctly, or. when you want to respond to exact wording (e.g., something someone said). Instructors, programs, editors, and publishers may establish limits on the use of direct quotations. Consult your instructor or editor if you are concerned that you may have too much quoted material in your paper.
What this handout is about. Used effectively, quotations can provide important pieces of evidence and lend fresh voices and perspectives to your narrative. Used ineffectively, however, quotations can clutter your text and interrupt the flow of your argument. This handout will help you decide when and how to quote like a pro.
A quote can be an effective and powerful literary tool in an essay, but it needs to be done well. To use quotes in an essay, you need to make sure your quotes are short, backed up with explanations, and used rarely. The best essays use a maximum of 2 quotes for every 1500 words. Rules for using quotes in essays: Avoid Long Quotes.
Revised on June 16, 2022. A direct quote is a piece of text copied word-for-word from a source. You may quote a word, phrase, sentence, or entire passage. There are three main rules for quoting in APA Style: If the quote is under 40 words, place it in double quotation marks. If the quote is 40 words or more, format it as a block quote.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays, research papers, and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises). Add a citation whenever you quote, paraphrase, or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
For quotations that are more than four lines of prose or three lines of verse, place quotations in a free-standing block of text and omit quotation marks. Start the quotation on a new line, with the entire quote indented 1/2 inch from the left margin while maintaining double-spacing. Your parenthetical citation should come after the closing ...
To introduce a quote in an essay, don't forget to include author's last name and page number (MLA) or author, date, and page number (APA) in your citation. Shown below are some possible ways to introduce quotations. The examples use MLA format. Use A Full Sentence Followed by A Colon To Introduce A Quotation Examples:
Important guidelines. When integrating a source into your paper, remember to use these three important components: Introductory phrase to the source material: mention the author, date, or any other relevant information when introducing a quote or paraphrase. Source material: a direct quote, paraphrase, or summary with proper citation.
If you need to edit quotes in your writing, keep the following in mind: Use an ellipsis to indicate omissions in the text. Check your style guide for how to format ellipses (e.g., in brackets or not, spaced or unspaced). Mark additions or changes by placing the edited text in square brackets. Use the term " [Sic]" to show that you've ...
Tip #3: Seamlessly integrate quotes. Another strategy you might consider when adding quotes in your paper is to seamlessly integrate them in the middle of a sentence, much like you would a paraphrase. In this case, the quote isn't introduced by a signal phrase but is part of the sentence. Here's an example from a paper about mandatory ...
3. Interject the Author's Name into the Middle of the Quote. "In 2005, less than 10% of Johnson & Roe's employees reported their political affiliation," Yang (2007) reports, "but more than 50% reporteddiscussing politics with their colleagues.". Phrases & Words to Introduce Quotes. Phrases to Introduce the Quote.
The way to do this is to include the new text within square brackets ( [ ]), as is shown in the example below: 2. Editing Text. There may also be instances when you'll need to edit the original text used in the quotation, although this shouldn't be done without good reason. Generally, acceptable reasons to edit a quotation are to change the ...
The quotation is introduced by a signal phrase, which makes the quote an integral part of the writer's sentence; as a result of this syntactical change, the upper case 'T' in the original is changed to a lower case letter. ... Bracketed insertions may not be used to alter or add to the quotation in a way that inaccurately or unfairly ...
Integrating sources means incorporating another scholar's ideas or words into your work. It can be done by: Quoting. Paraphrasing. Summarizing. By integrating sources properly, you can ensure a consistent voice in your writing and ensure your text remains readable and coherent. You can use signal phrases to give credit to outside sources and ...
In-text citation capitalization, quotes, and italics/underlining. Always capitalize proper nouns, including author names and initials: D. Jones. If you refer to the title of a source within your paper, capitalize all words that are four letters long or greater within the title of a source: Permanence and Change.
There are three main methods in how you can blend quotations into an essay: 1. Adding Words. Broken sentences are a common mistake made when students aim to integrate quotations into their sentences. Below are examples of broken sentences due to poor integration of a quotation: 'Solitary as an oyster'.
Some other citation styles also require indentation on the right side, different spacing, or a smaller font. To format a block quote in Microsoft Word, follow these steps: Hit Enter at the beginning and end of the quote. Highlight the quote and select the Layout menu. On the Indent tab, change the left indent to 0.5″.