Transitional Words and Phrases
One of your primary goals as a writer is to present ideas in a clear and understandable way. To help readers move through your complex ideas, you want to be intentional about how you structure your paper as a whole as well as how you form the individual paragraphs that comprise it. In order to think through the challenges of presenting your ideas articulately, logically, and in ways that seem natural to your readers, check out some of these resources: Developing a Thesis Statement , Paragraphing , and Developing Strategic Transitions: Writing that Establishes Relationships and Connections Between Ideas.
While clear writing is mostly achieved through the deliberate sequencing of your ideas across your entire paper, you can guide readers through the connections you’re making by using transitional words in individual sentences. Transitional words and phrases can create powerful links between your ideas and can help your reader understand your paper’s logic.
In what follows, we’ve included a list of frequently used transitional words and phrases that can help you establish how your various ideas relate to each other. We’ve divided these words and phrases into categories based on the common kinds of relationships writers establish between ideas.
Two recommendations: Use these transitions strategically by making sure that the word or phrase you’re choosing matches the logic of the relationship you’re emphasizing or the connection you’re making. All of these words and phrases have different meanings, nuances, and connotations, so before using a particular transitional word in your paper, be sure you understand its meaning and usage completely, and be sure that it’s the right match for your paper’s logic. Use these transitional words and phrases sparingly because if you use too many of them, your readers might feel like you are overexplaining connections that are already clear.
Categories of Transition Words and Phrases
Causation Chronology Combinations Contrast Example
Importance Location Similarity Clarification Concession
Conclusion Intensification Purpose Summary
Transitions to help establish some of the most common kinds of relationships
Causation– Connecting instigator(s) to consequence(s).
accordingly as a result and so because
consequently for that reason hence on account of
since therefore thus
Chronology– Connecting what issues in regard to when they occur.
after afterwards always at length during earlier following immediately in the meantime
later never next now once simultaneously so far sometimes
soon subsequently then this time until now when whenever while
Combinations Lists– Connecting numerous events. Part/Whole– Connecting numerous elements that make up something bigger.
additionally again also and, or, not as a result besides even more
finally first, firstly further furthermore in addition in the first place in the second place
last, lastly moreover next second, secondly, etc. too
Contrast– Connecting two things by focusing on their differences.
after all although and yet at the same time but
despite however in contrast nevertheless nonetheless notwithstanding
on the contrary on the other hand otherwise though yet
Example– Connecting a general idea to a particular instance of this idea.
as an illustration e.g., (from a Latin abbreviation for “for example”)
for example for instance specifically that is
to demonstrate to illustrate
Importance– Connecting what is critical to what is more inconsequential.
chiefly critically
foundationally most importantly
of less importance primarily
Location– Connecting elements according to where they are placed in relationship to each other.
above adjacent to below beyond
centrally here nearby neighboring on
opposite to peripherally there wherever
Similarity– Connecting to things by suggesting that they are in some way alike.
by the same token in like manner
in similar fashion here in the same way
likewise wherever
Other kinds of transitional words and phrases Clarification
i.e., (from a Latin abbreviation for “that is”) in other words
that is that is to say to clarify to explain
to put it another way to rephrase it
granted it is true
naturally of course
finally lastly
in conclusion in the end
to conclude
Intensification
in fact indeed no
of course surely to repeat
undoubtedly without doubt yes
for this purpose in order that
so that to that end
to this end
in brief in sum
in summary in short
to sum up to summarize


Improving Your Writing Style
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Clear, Concise Sentences
Use the active voice
Put the action in the verb
Tidy up wordy phrases
Reduce wordy verbs
Reduce prepositional phrases
Reduce expletive constructions
Avoid using vague nouns
Avoid unneccessarily inflated words
Avoid noun strings
Connecting Ideas Through Transitions
Using Transitional Words and Phrases
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
The Ultimate List of Linking Words for Your Essay

Let’s face it: You can’t write an essay (or any other writing piece) without linking words.
Also known as connecting words or transition words, they serve to make your writing flow and help those reading your work follow the flow of your thoughts, ideas , and arguments .
This post is your guide to linking words and their role in writing. Not only will you learn the types of these words, examples, and reasons to use them, but you’ll also get a massive list of transition words and phrases as well as linking words PDF to download and use whenever necessary.
Table of Contents:
What are Linking Words?
Why use transition words in essays, linking words examples, addition/agreement/similarity, contrast/contradiction/limitation/opposition, comparison/concession/condition, clarification, cause/effect/result, emphasis/example, generalization, illustration, location/place/space, reason/reference, time/sequence, summary/conclusion/restatement.
- The Ultimate List of Linking Words: Download
Linking words are lexical items (words and phrases) we use to connect ideas in writing and get a reader to the next sentence or paragraph.
They aren’t about essay writing only:
Whether you write a fiction book, marketing content , academic works, autobiography , or poems, you’ll need to connect ideas. That’s what transition words do:
They link your thoughts and arguments into a chain to show how they relate to each other. Also known as transition words, these phrases often start a sentence or a paragraph. However, you’ll also use them in the middle of sentences to bring ideas together.
The most common places for linking words in essays are:
- the start of a paragraph
- the start of a sentence introducing a new idea or extending an argument
- the beginning of a concluding statement
Essay linking words is an integral part of academic writing. Put it simply, you can’t write a paper without using them; otherwise, your writing won’t make any sense for readers.
Transition words for essay serve to:
- connect ideas in writing
- create a flow of thoughts and arguments for readers to understand what you want to say
- guide readers from one idea to another, demonstrating how they relate to each other
- hook readers and encourage them to read the next sentence or paragraph
- add more information
- support or contrast a point
- show the result, conclude, demonstrate an effect of this or that point
Using essay maker and connecting words, each sentence and paragraph must pass readers on to the next one. These connecting words serve as an instrument to guide readers from one thought or point to the next.
Linking words examples are many, and it’s clear why: every piece of writing contains tons of connecting and transition words. Let’s take an essay sample from Bid4Papers writers to see the example of linking words in academic writing:

This one was an essay introduction .
Now, why not take a step further and look for essay linking words in essay conclusions ?

Types and List of Linking Words to Use in Essays
Below you’ll find the ultimate list of transition words for essays by categories. Choose the role you need a word to play (reason, contrast, emphasis, restatement, etc.) and consider the corresponding table of transitions.
If you need the whole transition words list in one place, jump to the next category of this post to find the downloadable linking words pdf.
And now, for connecting words categories:
These words serve to add info to what you’ve previously stated, demonstrate the commonality between arguments, and support your thoughts.
Linking words for contrast is your instrument to show how things are different and provide counterarguments. They work best in persuasive and critical essays.
These lexical items will help you if you need to provide conditions to your statements, show how things are different/similar, or accept a point with reservation.
These words will help you with personal or narrative essays: They are linking words in opinion writing that indicates you’re going to explore ideas in more detail.
Expository essays will win with these words too.
Cause and effect connecting words do what their name says exactly: demonstrating a cause of some point and providing the result of what has been done or started.
These words are for putting forward your point more forcefully, providing examples.
Perfect transition words for hypothesis essays , generalization lexical items serve to make a general statement you’ll then specify and prove in detail.
These words and phrases are for you to provide examples in essays.
Use these words to provide order and reference or clarify spatial relationships between your points or ideas.
These transitional words will help you demonstrate relationships between ideas and provide reasons for what and why has started or occurred.
Use these words in your essay when you need to indicate the time and order of what you say.
Restatement words will help you express an alternative to what you previously stated. They work for all essay types, including rhetorical precis and dialectic essays .
Use summary and conclusion transitional phrases to sum up your points and come up with the final paragraph of your writing.
The Ultimate List of Connecting Words: Download
And now, for the most interesting and practical part:
Below you can find the linking words worksheet that gathers all the most commonly used transitional words in essays. Feel free to download this linking words PDF and refer to it every time you write an essay and experience writer’s block:
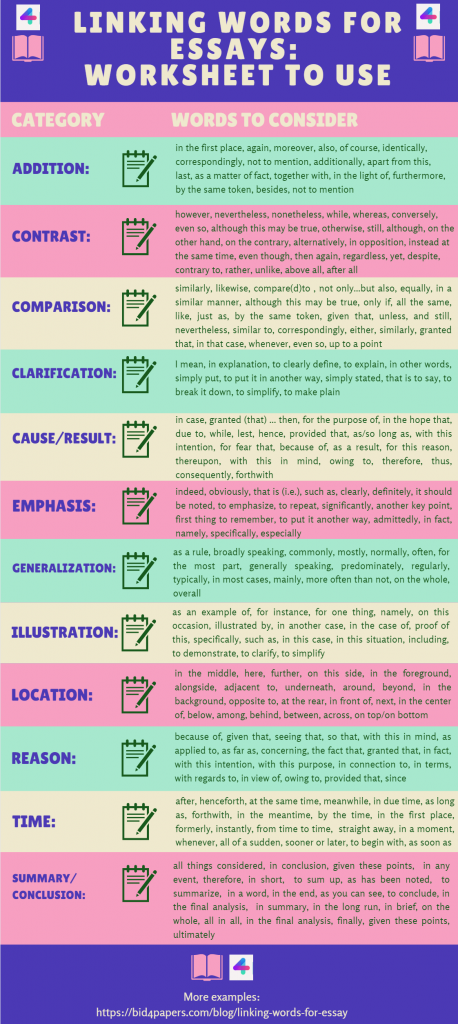
Do you need more guides and worksheets like this to assist you with academic writing? Please share your ideas in the comments, and our writers will be happy to help!
Related posts
- What Is the Difference between Primary and Secondary Sources
- Common Types of Plagiarism with Examples
- Exemplification Essay – Ideas and Tips
Our Writing Guides
We’re reviewing our resources this spring (May-August 2024). We will do our best to minimize disruption, but you might notice changes over the next few months as we correct errors & delete redundant resources.
Transition Words and Phrases
Transitions are connecting words or phrases that strengthen the internal cohesion of your writing. Transition words tell the reader how one idea relates to another. Using them appropriately makes your argument more convincing because the reader is able to understand the flow between and within paragraphs, including the relationship between different ideas, evidence, and analysis.
Types of Transition Words and Phrases
- additionally
- coupled with
- furthermore
- equally important
- in addition
Cause and Effect
- accordingly
- as consequence
- as a result
- at that time
- concurrently
- consequently
- followed by
- for this purpose
- for this reason
- subsequently
- comparatively
- correspondingly
- in the same way
- on the one han
- together with
Contrast/Exception/Concession
- a different view is
- alternatively
- despite/in spite of (+ noun)
- differing from
- even though
- in contrast
- it could also be said that
- nevertheless
- notwithstanding (+ noun)
- nonetheless
- on the contrary
- on (the) one hand
- on the other hand
- regardless of (+ noun)
- in particular
- particularly
Example/Illustration
- as an example
- as an illustration
- for example
- for instance
- illustrated by
- in the/this case
- on this occasion
- specifically
- to demonstrate
- to illustrate
- all things considered
- at the same time
- in other words
- on the whole
- that is to say
- to put it differently
- first, second, third, etc.
Summary/Conclusion
- by and large
- in any case
- in any event
- in conclusion
- to conclude
- to summarize
- at that/this point
- at that/this time
- immediately
- in the future
- in the meantime
- in the past
- simultaneously
Sample Transition Words
While (1) qualitative data is helpful in gauging graduate student responses to Boot Camp, it is also crucial that we undertake data-driven analysis to support the value of the four-day writing event. Currently (2), quantitative measures of satisfaction of Dissertation Boot Camp participants are tracked in two ways: through a formal survey posted through SurveyMonkey and an informal survey that is handwritten at the end of the Camp. In fact (3), to ensure reliable data for analysis, the SurveyMonkey questionnaire is filled out by students at three different times: before Camp, on the first day of Camp, and 30 days after Camp. The decision to send the survey at three different times was made in order to ensure that attitudes prior to Camp matched attitudes on the first day, and to then compare that to results after Camp. However (4) the current survey questions are somewhat informal, and none have been psychometrically tested. In order to improve the reliability and usefulness of the collected data, we will need to revise some of our Likert-scale based questions using currently-available test questions from other indices. Ultimately (5) , this combination of quantitative and qualitative data will help us to make decisions about the program as it is offered in subsequent semesters.
(1) Comparison
(3) Emphasis
(4) Contrast/Exception/Concession
(5) Summary/Conclusion
- Academic Skills
- Reading, writing and referencing
- Writing effectively
Connecting ideas
How to connect ideas at the sentence and paragraph level in academic writing.
What is cohesion?
Cohesion refers to the way we use vocabulary and grammatical structures to make connections between the ideas within a text. It provides flow and sequence to your work and helps make your paragraphs clear for the reader.
Cohesive devices are words and expressions that show relationships between parts of text and ideas, such as cause and effect, time, addition, or comparison and contrast.
Watch the video to learn how to make your ideas link together and your narrative flow.
How can I create cohesion?
Let’s look at types of cohesive devices.
Linking words
Academic writing usually deals with complex ideas. To enable the reader to follow your thoughts, they need to be clearly and smoothly linked. To join ideas and sentences, we use a number of connecting words and phrases. For example:
Additionally, and, also, apart from this, as well (as), in addition, moreover, further, furthermore.
If, in that case, provided that, unless.
Correspondingly, equally, for the same reason, in a similar manner, in comparison, in the same way, on the one hand, similarly.
Alternatively, although, but, conversely, despite, even so, even though, however, in contrast, in spite of, instead, on the contrary, contrary to, nevertheless, nonetheless, notwithstanding, on the other hand, rather, still, though, yet, whereas, while.
Again, in fact, interestingly, indeed, it should be noted (that), more important(ly), most importantly, to repeat, (un)fortunately, unquestionably.
A further instance of this is..., an example of this is…, for example, for instance, such as, thus, as follows.
In other words, more simply, namely, simply put, to put it differently / another way, such as, that is.
A / the consequence of, because, due to, for, the effect of …, since, the result of …
Accordingly, as a result/consequence, consequently, for this reason, hence, so, therefore, thus.
Admittedly, although, clearly though, even though, however, indeed, obviously.
As a rule, for the most part, generally, in general, in most cases, normally, on the whole, usually.
First, second, third (etc), next, before, earlier, finally, following, given the above, later, meanwhile, subsequently, then, to conclude, while.
A note about presentation and style
Check a usage guide for exact rules for punctuation. Many introductory phrases have a comma after them. For example, 'therefore,' and 'in addition,'.
Referring backwards
To avoid repeating words and phrases many times, we use cohesive devices to make references to other parts of a text, such as:
- Pronouns: it, he, she, his, her, they, their
- Demonstratives: this, that, these, those
- Articles: a, the
- Adverbs: previously, subsequently
The Australian prime minister has called an early election. The date was selected to coincide with the start of the Olympic Games. This decision was based on the views of his ministerial advisors, who predicted that voter confidence in the government’s policies would be strong at this time . As previously mentioned , decisions on the timing of elections are based on predictions of voter confidence in the existing government.
In the example above:
- The date - refers back to the election date
- This decision - refers to the prime minister calling an early election
- His - refers to the Australian prime minister
- this time - refers to the start of the Olympic Games
- As previously mentioned - refers to all of the earlier information about the selection of election dates
Looking forward
We often use words and phrases to highlight new information for the reader. This helps make a smooth transition from one point to another. Such phrases include: the following, as follows, below, next, subsequently .
The following dates have been proposed for the forthcoming election: September 8, September 15 and 3 October.
The next issue to be discussed is the influence of the media on voter confidence in the government.
Connecting paragraphs
Apart from using the linking words / phrases above, showing the link between paragraphs could involve writing ‘hand-holding’ sentences. These are sentences that link back to the ideas of the previous paragraph. For instance, when outlining the positive and negative issues about a topic you could use the following:
Example (from beginning of previous paragraph):
- One of the main advantages of X is…
When you are ready to move your discussion to the negative issues, you could write one of the following as a paragraph opener:
- Having considered the positive effects of X, negative issues may now need to be taken into account…
- Despite the positive effects outlined above, negative issues also need to be considered...
It is always important to make paragraphs part of a coherent whole text; they must not remain isolated units.
Checking for paragraph links in your own work
When you are editing your next written assignment, ask yourself the following questions as you read through your work (Gillett, Hammond, & Martala, 2009):
- Does the start of my paragraph give my reader enough information about what the paragraph will be about?
- Does my paragraph add to or elaborate on a point made previously and, if so, have I made this explicit with an appropriate linking word / phrase?
- Does my paragraph introduce a completely new point or a different viewpoint to before and, if so, have I explicitly shown this with a suitable connective?
- Have I used similar connectives repeatedly? If yes, try to vary them using the above list.
Strategies to improve cohesion
- Select a piece of writing, preferably from a textbook or journal article, from your area of study.
- Choose a paragraph and underline or highlight all the different forms of cohesion used, such as using linking words, referring backwards, looking forwards or adding synonyms.
- Which forms are the most common?
- Choose a couple that you think are effective and practice using them in your own writing.
- Try to use a variety of ways to show the relationship between your ideas.

Looking for one-on-one advice?
Get tailored advice from an Academic Skills Adviser by booking an Individual appointment, or get quick feedback from one of our Academic Writing Mentors via email through our Writing advice service.
Go to Student appointments
- Academic writing
- Commonly confused words
- Critical thinking
- PEEL Paragraphs
- Linking/transition words
- Paraphrasing
- Proofreading
- Terms and definitions
- Action Words: What is description, application, analysis and evaluation
Linking/transition words: Things you need to know...
All assignments are written in formal language. You need to ensure that you demonstrate your knowledge and understanding alongside your ability to answer the question/solve the problem.
Below are some ideas to help you to develop your structure and flow.
- Linking / transition words and phrases join ideas, sentences and paragraphs together. They should be used within sentences and to move from one idea to another (between sentences).
These words and phrases indicate the direction, order and flow of ideas. Significantly, they strengthen the quality and structure of your work.
- Redundant Words - less is more. P articularly when trying to reduce the word count, it is important to look for phrases which can be replaced with a single word.
Linking/Transition Words
Transitions link one main idea to another separated by a semi-colon or full-stop. When the transition word is at the beginning of the sentence, it should be followed by a comma:
Among other functions, they can signal cause and effect or sequencing (see examples in the table below).
Linking words: conjunctions
Linking words within a sentence are referred to as coordinating conjunctions. Do not worry about the term: think about the function.
Conciseness / redundant words
Microsoft Word now has an additional feature within the Edito r - it is called conciseness or wordiness.
- If you cannot see the Editor menu a quick tip is to hold down the function (fn key at the bottom left of the keyboard) + F7 (top line of keys).
- From the Refinements section - select Conciseness - if there are any suggestions a number will appear in the box alongside this option
- A dotted line will appear under any groups of groups
- Either select the identified text by clicking with your right mouse button OR click on the down down next to the Conciseness menu.
- MS Word will display any alternative words which you can either select and they will be replaced in your text or reject if you want to keep the original phrases.
Examples: try to replace phrases with a single words which mean the same.
Need to know more...
- Related pages
- External links
- Academic writing Illustrates the main features of academic writing so that you are aware of what it is and what it involves
- Critical Thinking Academic work involves thinking, not just accepting what you read or are told.
- Terms and Definitions Important words appear in your assignments and examinations. The aim of this factsheet is to help you to fully understand what they mean.
Additional resources to help you to improve your confidence and grades:-
- Writing Effectively demonstrates the importance of: clarity, structure, relevance, argument and precision.
- Writing Mechanics gives further examples and resources on areas including: sentence structure, vocabulary, spelling, punctuation and grammar.
Linking/Transition words - Scribbr https://www.scribbr.co.uk/syntax/transition-words-examples/ [Accessed 10 February 2023]
There are many books concerning academic writing, look around Dewey number 808
- << Previous: PEEL Paragraphs
- Next: Paraphrasing >>
- Last Updated: Mar 13, 2024 6:24 PM
- URL: https://libguides.staffs.ac.uk/academic_writing
- Library and Learning Services, Staffordshire University, College Road, Stoke-on-Trent, ST4 2DE
- Accessibility
- Library Regulations
- Appointments
- Library Search

33 Transition Words and Phrases
Transitional terms give writers the opportunity to prepare readers for a new idea, connecting the previous sentence to the next one.
Many transitional words are nearly synonymous: words that broadly indicate that “this follows logically from the preceding” include accordingly, therefore, and consequently . Words that mean “in addition to” include moreover, besides, and further . Words that mean “contrary to what was just stated” include however, nevertheless , and nonetheless .
as a result : THEREFORE : CONSEQUENTLY
The executive’s flight was delayed and they accordingly arrived late.
in or by way of addition : FURTHERMORE
The mountain has many marked hiking trails; additionally, there are several unmarked trails that lead to the summit.
at a later or succeeding time : SUBSEQUENTLY, THEREAFTER
Afterward, she got a promotion.
even though : ALTHOUGH
She appeared as a guest star on the show, albeit briefly.
in spite of the fact that : even though —used when making a statement that differs from or contrasts with a statement you have just made
They are good friends, although they don't see each other very often.
in addition to what has been said : MOREOVER, FURTHERMORE
I can't go, and besides, I wouldn't go if I could.
as a result : in view of the foregoing : ACCORDINGLY
The words are often confused and are consequently misused.
in a contrasting or opposite way —used to introduce a statement that contrasts with a previous statement or presents a differing interpretation or possibility
Large objects appear to be closer. Conversely, small objects seem farther away.
used to introduce a statement that is somehow different from what has just been said
These problems are not as bad as they were. Even so, there is much more work to be done.
used as a stronger way to say "though" or "although"
I'm planning to go even though it may rain.
in addition : MOREOVER
I had some money to invest, and, further, I realized that the risk was small.
in addition to what precedes : BESIDES —used to introduce a statement that supports or adds to a previous statement
These findings seem plausible. Furthermore, several studies have confirmed them.
because of a preceding fact or premise : for this reason : THEREFORE
He was a newcomer and hence had no close friends here.
from this point on : starting now
She announced that henceforth she would be running the company.
in spite of that : on the other hand —used when you are saying something that is different from or contrasts with a previous statement
I'd like to go; however, I'd better not.
as something more : BESIDES —used for adding information to a statement
The city has the largest population in the country and in addition is a major shipping port.
all things considered : as a matter of fact —used when making a statement that adds to or strengthens a previous statement
He likes to have things his own way; indeed, he can be very stubborn.
for fear that —often used after an expression denoting fear or apprehension
He was concerned lest anyone think that he was guilty.
in addition : ALSO —often used to introduce a statement that adds to and is related to a previous statement
She is an acclaimed painter who is likewise a sculptor.
at or during the same time : in the meantime
You can set the table. Meanwhile, I'll start making dinner.
BESIDES, FURTHER : in addition to what has been said —used to introduce a statement that supports or adds to a previous statement
It probably wouldn't work. Moreover, it would be very expensive to try it.
in spite of that : HOWEVER
It was a predictable, but nevertheless funny, story.
in spite of what has just been said : NEVERTHELESS
The hike was difficult, but fun nonetheless.
without being prevented by (something) : despite—used to say that something happens or is true even though there is something that might prevent it from happening or being true
Notwithstanding their youth and inexperience, the team won the championship.
if not : or else
Finish your dinner. Otherwise, you won't get any dessert.
more correctly speaking —used to introduce a statement that corrects what you have just said
We can take the car, or rather, the van.
in spite of that —used to say that something happens or is true even though there is something that might prevent it from happening or being true
I tried again and still I failed.
by that : by that means
He signed the contract, thereby forfeiting his right to the property.
for that reason : because of that
This tablet is thin and light and therefore very convenient to carry around.
immediately after that
The committee reviewed the documents and thereupon decided to accept the proposal.
because of this or that : HENCE, CONSEQUENTLY
This detergent is highly concentrated and thus you will need to dilute it.
while on the contrary —used to make a statement that describes how two people, groups, etc., are different
Some of these species have flourished, whereas others have struggled.
NEVERTHELESS, HOWEVER —used to introduce a statement that adds something to a previous statement and usually contrasts with it in some way
It was pouring rain out, yet his clothes didn’t seem very wet.
Word of the Day
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Games & Quizzes

Usage Notes
Prepositions, ending a sentence with, is 'irregardless' a real word, 8 more grammar terms you used to know: special verb edition, point of view: it's personal, 31 useful rhetorical devices, grammar & usage, primary and caucus: what is the difference, words commonly mispronounced, merriam-webster’s great big list of words you love to hate, more commonly misspelled words, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, 12 words for signs of spring, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), 13 unusually long english words, the words of the week - may 10, a great big list of bread words.

Down and Dirty Tips: Narrative and Descriptive Essays: Narrative Transitions
- Narrative Start
- Descriptive Start
- Narrative Organization
- Descriptive Organization
- Narrative Transitions
- Descriptive Transitions
Adding Transitions: Narrative Essay
Narrative Essay
Narrative (Timeline) Transitions
- << Previous: Adding Transitions
- Next: Descriptive Transitions >>
- Last Updated: Oct 23, 2023 11:02 AM
- URL: https://spcollege.libguides.com/narrative_descriptive

Useful Linking Words and Phrases to Use in Your Essays
By: Author Sophia
Posted on Last updated: October 26, 2023
Sharing is caring!
Linking words and phrases are used to show relationships between ideas. They can be used to join two or more sentences or clauses.
We can use linking words to give a result , add information , summarize , give illustrations , emphasize a point , sequence information , compare or to contrast idea .
Useful Linking Words and Phrases
In this article, you will learn about the most common linking words and phrases:

Giving a Result
Usage : To provide the result of what has been stated or has occurred
Linking W ords :
- As a result
- As a consequence
- Consequently
- For this reason
- His wife left him. As a result , he became very depressed.
- She has lived in France, and as a consequence she speaks French fluently.
- We do not have enough money. T herefore we cannot afford to buy the new car.
- We do not own the building. Thus , it would be impossible for us to make any major changes to it.
- There has been a great deal of rain and consequently the reservoirs are full.
- The customer was displeased with her meal, hence the chef prepared a replacement.
- For this reason , they are not a good choice for exterior use.
- Due to a broken wing, this bird can’t fly.

Adding Information
Usage : To add to what has been previously stated
Linking Words:
- Additionally / an additional
- Furthermore
- As well as that
- In addition
- In addition to this
- Apart from this
- Additionally , the bus service will run on Sundays, every two hours.
- He said he had not discussed the matter with her. Furthermore , he had not even contacted her.
- We are unable to repair this watch. Also , this is the fourth time this has happened.
- I love wearing earrings. I design and make them too .
- We went to the park today. As well as that , we did some shopping.
- Along with parties and parliaments, elections have lost their charm.
- I can’t afford to go to the concert. Besides , I don’t really like classical music.
- You haven’t paid the rent yet. In addition , you owe me money.
- The report is badly presented. Moreover , it contains inaccuracies.
- John’s grades are terrible because he has been so lazy these days. In addition to this , his relationship to his parents got worse.
- Apart from this paragraph, the report contains a number of sensible initiatives.
Summarizing
Usage : To sump up what has been previously stated
Linking words :
- In conclusion
- To summarize
- To conclude
- In conclusion , walking is a cheap, safe, enjoyable and readily available form of exercise.
- To summarize , this is a clever approach to a common problem.
- The food was good and we loved the music. Altogether it was a great evening.
- His novels belong to a great but vanished age. They are, in short , old-fashioned.
- To sum up , there are three main ways of tackling the problem…
- In summary , this was a disappointing performance.
- Briefly , our team is now one of the best in the world.
- To conclude , I want to wish you all a very happy holiday season.
Giving Examples
Usage : To provide examples
Linking words:
- For example/ For instance
- In this case
- Proof of this
- There are many interesting places to visit in the city, for example / for instance , the botanical garden or the art museum.
- I prefer to wear casual clothes, such as jeans and a sweatshirt.
- Including Christmas Day and Boxing Day, I’ve got a week off work.
- We need to concentrate on our target audience, namely women aged between 20 and 30.
- I think I would have made a difference in this case .
- This building are a living proof of this existence, so we must preserve it.
- I also make other jewellery like rings and bracelets.
Emphasizing a Point
Usage : To put forward a point or idea more forcefully
- Undoubtedly
- Particularly / in particular
- Importantly
- Without a doubt
- It should be noted
- Unquestionably
- Undoubtedly , the story itself is one of the main attractions.
- I don’t mind at all. Indeed , I would be delighted to help.
- Obviously , we don’t want to spend too much money.
- I love silver earrings, in particular ones from Mexico
- The car is quite small, especially if you have children.
- Clearly , this will cost a lot more than we realized.
- More importantly , can he be trusted?
- He’s an absolutely brilliant cook.
- I definitely remember sending the letter.
- We still believe we can win this series without a doubt .
- I’m neve r surprised at what I do.
- It should be noted that if you have something to note, then note it
- Unquestionably , teaching has been a paramount part of his career.
- Above all , this forest is designed for wear and tear.
- This is positively the worst thing that I can even imagine.

Sequencing Ideas
Usage : To indicate the order of what is being said
- First/ firstly (Second/ secondly, Third/ thirdly, Finally)
- At this time
- Subsequently
- Lastly and most importantly
- Last but not least
- First and foremost
- Firstly , I prefer the train because I can see the landscape.
- At this time , the young man leapt into the air and flew off towards sunset.
- They arrived on Monday evening and we got there the following day.
- I had visited them three days previously .
- Your name is before mine on the list.
- Subsequently , new guidelines were issued to all employees.
- Above all , keep in touch.
- Lastly, and most importantly , you should be optimistic.
- Last but not least , I find I seriously cannot relate to women.
- We will continue to focus on our players first and foremost .

Comparing Ideas
Usage: To show how things are similar
- Compare / compare(d) to(with)
- By the same token
- In the same way
- Correspondingly
- Similarly , the basketball and hockey games draw nearly full attendance.
- Equally , not all customers are honest.
- Her second marriage was likewise unhappy.
- She’s just as smart as her sister.
- Working with housecats is just like working with lions or tigers.
- Some people say I have a running style similar to him.
- Having a power is not the same as using the power.
- He gets the ball off quickly compared to two years ago.
- Teenagers should be more respectful; by the same token , parents should be more understanding.
- Alex enjoys telling jokes; in the same way/similarly/likewise ,his son adores funny stories.
- Correspondingly , the roles each of them played were soon different.
Contrasting Ideas
Usage : To show how things are different
- Nevertheless
- On the other hand
- Nonetheless
- Despite / in spite of
- In contrast (to)
- Alternatively
- Differing from
- Contrary to
- Unlike most systems, this one is very easy to install.
- There is little chance that we will succeed in changing the law. Nevertheless , it is important that we try.
- Laptops are convenient; O n the other hand , they can be expensive.
- The problems are not serious. Nonetheless , we shall need to tackle them soon.
- Despite/ In spite of the rain, I went for a walk.
- In contrast to the diligent bee, the butterfly flies hither and yon with no apparent purpose.
- The agency will make travel arrangements for you. Alternatively , you can organize your own transport.
- Northern European countries had a great summer. On the contrary/conversely , Southern Europe had poor weather.
- Even so , many old friends were shocked at the announcement.
- Differing from his white colleagues, he preferred instructing his scholars to the ambition of acquiring personal renown.
- The situation in Ireland is quite contrary to this principle.

Linking Words for Essays | Images
Below is a handy list of words that are both useful and appropriate to academic language:

Other linking words to give an example or an illustration:
- In this case,
- In another case
- Take the case of
- To illustrate
- As an
- Illustration
- To take another example
- That is
- As shown by
- As illustrated by
- As expressed by

- Recent Posts
- Plural of Process in the English Grammar - October 3, 2023
- Best Kahoot Names: Get Creative with These Fun Ideas! - October 2, 2023
- List of Homophones for English Learners - September 30, 2023
Related posts:
- Linking Words and Phrases: Reasons and Results
- Useful Words and Phrases to Use as Sentence Starters to Write Better Essays
- Popular Linking Words and Transitional Phrases in English
- Transition Words You Need to Know to Master English Writing
Sunday 26th of November 2023
Must say extremely helpful . Stranded as I was nd I found this .theeeee best 10 /10
Momovi Burain
Thursday 10th of November 2022
Very very educational
Sunday 16th of October 2022
what the dog doing
Tuesday 23rd of August 2022
good website with good information
Friday 21st of January 2022
dijah said it is goooooooooooooooooood
Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- 40 Useful Words and Phrases for Top-Notch Essays

To be truly brilliant, an essay needs to utilise the right language. You could make a great point, but if it’s not intelligently articulated, you almost needn’t have bothered.
Developing the language skills to build an argument and to write persuasively is crucial if you’re to write outstanding essays every time. In this article, we’re going to equip you with the words and phrases you need to write a top-notch essay, along with examples of how to utilise them.
It’s by no means an exhaustive list, and there will often be other ways of using the words and phrases we describe that we won’t have room to include, but there should be more than enough below to help you make an instant improvement to your essay-writing skills.
If you’re interested in developing your language and persuasive skills, Oxford Royale offers summer courses at its Oxford Summer School , Cambridge Summer School , London Summer School , San Francisco Summer School and Yale Summer School . You can study courses to learn english , prepare for careers in law , medicine , business , engineering and leadership.
General explaining
Let’s start by looking at language for general explanations of complex points.
1. In order to
Usage: “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument. Example: “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.”
2. In other words
Usage: Use “in other words” when you want to express something in a different way (more simply), to make it easier to understand, or to emphasise or expand on a point. Example: “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.”
3. To put it another way
Usage: This phrase is another way of saying “in other words”, and can be used in particularly complex points, when you feel that an alternative way of wording a problem may help the reader achieve a better understanding of its significance. Example: “Plants rely on photosynthesis. To put it another way, they will die without the sun.”
4. That is to say
Usage: “That is” and “that is to say” can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: “Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.”
5. To that end
Usage: Use “to that end” or “to this end” in a similar way to “in order to” or “so”. Example: “Zoologists have long sought to understand how animals communicate with each other. To that end, a new study has been launched that looks at elephant sounds and their possible meanings.”
Adding additional information to support a point
Students often make the mistake of using synonyms of “and” each time they want to add further information in support of a point they’re making, or to build an argument . Here are some cleverer ways of doing this.
6. Moreover
Usage: Employ “moreover” at the start of a sentence to add extra information in support of a point you’re making. Example: “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…”
7. Furthermore
Usage:This is also generally used at the start of a sentence, to add extra information. Example: “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…”
8. What’s more
Usage: This is used in the same way as “moreover” and “furthermore”. Example: “What’s more, this isn’t the only evidence that supports this hypothesis.”
9. Likewise
Usage: Use “likewise” when you want to talk about something that agrees with what you’ve just mentioned. Example: “Scholar A believes X. Likewise, Scholar B argues compellingly in favour of this point of view.”

10. Similarly
Usage: Use “similarly” in the same way as “likewise”. Example: “Audiences at the time reacted with shock to Beethoven’s new work, because it was very different to what they were used to. Similarly, we have a tendency to react with surprise to the unfamiliar.”
11. Another key thing to remember
Usage: Use the phrase “another key point to remember” or “another key fact to remember” to introduce additional facts without using the word “also”. Example: “As a Romantic, Blake was a proponent of a closer relationship between humans and nature. Another key point to remember is that Blake was writing during the Industrial Revolution, which had a major impact on the world around him.”
12. As well as
Usage: Use “as well as” instead of “also” or “and”. Example: “Scholar A argued that this was due to X, as well as Y.”
13. Not only… but also
Usage: This wording is used to add an extra piece of information, often something that’s in some way more surprising or unexpected than the first piece of information. Example: “Not only did Edmund Hillary have the honour of being the first to reach the summit of Everest, but he was also appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire.”
14. Coupled with
Usage: Used when considering two or more arguments at a time. Example: “Coupled with the literary evidence, the statistics paint a compelling view of…”
15. Firstly, secondly, thirdly…
Usage: This can be used to structure an argument, presenting facts clearly one after the other. Example: “There are many points in support of this view. Firstly, X. Secondly, Y. And thirdly, Z.
16. Not to mention/to say nothing of
Usage: “Not to mention” and “to say nothing of” can be used to add extra information with a bit of emphasis. Example: “The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.”
Words and phrases for demonstrating contrast
When you’re developing an argument, you will often need to present contrasting or opposing opinions or evidence – “it could show this, but it could also show this”, or “X says this, but Y disagrees”. This section covers words you can use instead of the “but” in these examples, to make your writing sound more intelligent and interesting.
17. However
Usage: Use “however” to introduce a point that disagrees with what you’ve just said. Example: “Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion.”
18. On the other hand
Usage: Usage of this phrase includes introducing a contrasting interpretation of the same piece of evidence, a different piece of evidence that suggests something else, or an opposing opinion. Example: “The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.”
19. Having said that
Usage: Used in a similar manner to “on the other hand” or “but”. Example: “The historians are unanimous in telling us X, an agreement that suggests that this version of events must be an accurate account. Having said that, the archaeology tells a different story.”
20. By contrast/in comparison
Usage: Use “by contrast” or “in comparison” when you’re comparing and contrasting pieces of evidence. Example: “Scholar A’s opinion, then, is based on insufficient evidence. By contrast, Scholar B’s opinion seems more plausible.”
21. Then again
Usage: Use this to cast doubt on an assertion. Example: “Writer A asserts that this was the reason for what happened. Then again, it’s possible that he was being paid to say this.”
22. That said
Usage: This is used in the same way as “then again”. Example: “The evidence ostensibly appears to point to this conclusion. That said, much of the evidence is unreliable at best.”
Usage: Use this when you want to introduce a contrasting idea. Example: “Much of scholarship has focused on this evidence. Yet not everyone agrees that this is the most important aspect of the situation.”
Adding a proviso or acknowledging reservations
Sometimes, you may need to acknowledge a shortfalling in a piece of evidence, or add a proviso. Here are some ways of doing so.
24. Despite this
Usage: Use “despite this” or “in spite of this” when you want to outline a point that stands regardless of a shortfalling in the evidence. Example: “The sample size was small, but the results were important despite this.”
25. With this in mind
Usage: Use this when you want your reader to consider a point in the knowledge of something else. Example: “We’ve seen that the methods used in the 19th century study did not always live up to the rigorous standards expected in scientific research today, which makes it difficult to draw definite conclusions. With this in mind, let’s look at a more recent study to see how the results compare.”
26. Provided that
Usage: This means “on condition that”. You can also say “providing that” or just “providing” to mean the same thing. Example: “We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.”
27. In view of/in light of
Usage: These phrases are used when something has shed light on something else. Example: “In light of the evidence from the 2013 study, we have a better understanding of…”
28. Nonetheless
Usage: This is similar to “despite this”. Example: “The study had its limitations, but it was nonetheless groundbreaking for its day.”
29. Nevertheless
Usage: This is the same as “nonetheless”. Example: “The study was flawed, but it was important nevertheless.”
30. Notwithstanding
Usage: This is another way of saying “nonetheless”. Example: “Notwithstanding the limitations of the methodology used, it was an important study in the development of how we view the workings of the human mind.”
Giving examples
Good essays always back up points with examples, but it’s going to get boring if you use the expression “for example” every time. Here are a couple of other ways of saying the same thing.
31. For instance
Example: “Some birds migrate to avoid harsher winter climates. Swallows, for instance, leave the UK in early winter and fly south…”
32. To give an illustration
Example: “To give an illustration of what I mean, let’s look at the case of…”
Signifying importance
When you want to demonstrate that a point is particularly important, there are several ways of highlighting it as such.
33. Significantly
Usage: Used to introduce a point that is loaded with meaning that might not be immediately apparent. Example: “Significantly, Tacitus omits to tell us the kind of gossip prevalent in Suetonius’ accounts of the same period.”
34. Notably
Usage: This can be used to mean “significantly” (as above), and it can also be used interchangeably with “in particular” (the example below demonstrates the first of these ways of using it). Example: “Actual figures are notably absent from Scholar A’s analysis.”
35. Importantly
Usage: Use “importantly” interchangeably with “significantly”. Example: “Importantly, Scholar A was being employed by X when he wrote this work, and was presumably therefore under pressure to portray the situation more favourably than he perhaps might otherwise have done.”
Summarising
You’ve almost made it to the end of the essay, but your work isn’t over yet. You need to end by wrapping up everything you’ve talked about, showing that you’ve considered the arguments on both sides and reached the most likely conclusion. Here are some words and phrases to help you.
36. In conclusion
Usage: Typically used to introduce the concluding paragraph or sentence of an essay, summarising what you’ve discussed in a broad overview. Example: “In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.”
37. Above all
Usage: Used to signify what you believe to be the most significant point, and the main takeaway from the essay. Example: “Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that…”
38. Persuasive
Usage: This is a useful word to use when summarising which argument you find most convincing. Example: “Scholar A’s point – that Constanze Mozart was motivated by financial gain – seems to me to be the most persuasive argument for her actions following Mozart’s death.”
39. Compelling
Usage: Use in the same way as “persuasive” above. Example: “The most compelling argument is presented by Scholar A.”
40. All things considered
Usage: This means “taking everything into account”. Example: “All things considered, it seems reasonable to assume that…”
How many of these words and phrases will you get into your next essay? And are any of your favourite essay terms missing from our list? Let us know in the comments below, or get in touch here to find out more about courses that can help you with your essays.
At Oxford Royale Academy, we offer a number of summer school courses for young people who are keen to improve their essay writing skills. Click here to apply for one of our courses today, including law , business , medicine and engineering .
Comments are closed.
IELTS Preparation with Liz: Free IELTS Tips and Lessons, 2024
- Test Information FAQ
- Band Scores
- IELTS Candidate Success Tips
- Computer IELTS: Pros & Cons
- How to Prepare
- Useful Links & Resources
- Recommended Books
- Writing Task 1
- Writing Task 2
- Speaking Part 1 Topics
- Speaking Part 2 Topics
- Speaking Part 3 Topics
- 100 Essay Questions
- On The Day Tips
- Top Results
- Advanced IELTS
Linking Words for IELTS Writing Task 2
The linking words list below is essential for IELTS writing task 2 for high score. The examiner needs to see a range of linking words in your essay to award you a high score for the criterion of Coherence and Cohesion which is 25% of your marks. You will be checked on your range, accuracy and your flexibility of linking words in IELTS writing task 2. These connecting words are suitable for all types of essay writing as well as GT IELTS writing task 2

Download PDF: Linking Words for IELTS Writing Task 2
This is often used to either put your paragraphs in order or used inside the paragraph to list your supporting points.
- lastly /last but not least / finally
Adding Information
You will need to support your main points in your IELTS essay. These linkers inform the reader that extra information is about to be presented.
- in addition
- additionally
- furthermore
- not only … but also
Giving Examples
It is often useful to give examples to support your ideas in IELTS writing task 2. Make sure you use this range of linking words to do so.
- for example
- one clear example is
- for instance
- to illustrate
- in other words
To learn how to put examples in sentences for essay writing, please follow this link: How to Add Examples to Essays .
Results and Consequences
These linking devices can be used for solution essays or any essay when you need to explain the consequences of something.
- as a result
- consequently
- for this reason
Highlighting and Stressing
It is important to be clear about what you mean in your essay. These linking words help you stress particular points.
- particularly
- in particular
- specifically
Concessions and Contrasts
You often need to give opposite ideas, particularly for discussion essays so the linking words below will help you show the reader when you want to introduce an opposite point. Also you might want to give exceptions to a rule for a concession.
- nevertheless
- even though
- in spite of
- on the other hand
- by contrast
- in comparison
- alternatively
- another option could be
Reasons and Causes
These connecting words will help you explain reasons and causes for something which is very common in IELTS writing task 2, especially for cause / solution essays.
Giving your Opinion
- in my opinion
- I concur / agree
- I disagree / I cannot accept
Don’t make a mistake with the way you express your opinion. Watch this video for useful tips on giving your opinion and how to avoid mistakes: IELTS: Presenting your Opinion
Concluding Linkers
- in conclusion
- to conclude
To get more tips and advice on linking words to start your IELTS conclusion, please watch this video lesson: IELTS Conclusion Linkers
Practice with Linking Words
Improve your use of linking words by fill in the gaps below with linking words from the above list.
- There are a number of drawbacks to people using Facebook as a way of communicating (1)………………… it is (2)…………….. one of the most common social networking platforms for both individuals and businesses.
- (3)……………………….. the lack of exercise taken by average people, obesity and other weight related problems are on the rise.
- Unemployment and poverty, (4) ………….. in urban areas, is often deemed to be the cause of rising crime rate.
- (5) ……….. the rise in urban crime, more and more people continue to move to cities looking for a better life.
- More children are becoming obese and (6)…………….. schools should be encouraged to provide more sports lessons and outdoor activities.
Click below to reveal the answers:
- Due to / Owing to ( you can’t have “because of” because it is at the beginning of a sentence)
- particularly / especially / specifically
- therefore / so / for this reason
IELTS Speaking Linking Words
Linking words for IELTS speaking . Both word list and tips.
Recommended
- All Linking Word Practice Exercises
- All Writing task 2 Model Answers, Tips and Videos
Main IELTS Pages Develop your IELTS skills with tips, model answers, lessons, free videos and more. IELTS Listening IELTS Reading IELTS Writing Task 1 IELTS Writing Task 2 IELTS Speaking Vocabulary for IELTS IELTS Test Information (FAQ) Home Page: IELTS Liz
Get my free lessons by email
Subscribe for free to get my new IELTS lessons sent to your email inbox.
Email Address
Hi liz, Could you please provide the marking scheme writing and reading module of IELTS or in other words I am asking for the factors on which student’s band score is decided.
You can find those linked in the main sections for Writing Task 1, Writing Task 2 and Reading, which are all linked by the RED Menu Bar at the top of the website. Marking for reading is based on correct or incorrect answers, but for the writing and speaking test, it’s based on marking criteria. You can also find a link by clicking on the TEST INFO option on the RED Menu Bar which shows band score information.
I just saw on the IDP IELTS website it says, “Don’t overuse basic linking words like firstly (instead, try using ‘The first reason for/ The primary reason for this”). Is that really better? Can I continue using ‘firstly’ like you do?
Sincerely, Draven
It is fine to use it. But don’t then use Secondly, Thirdly. When you write like a machine, you get a lower score in Coherence and Cohesion, which counts for 25% of your marks. You could try: Firstly / Another point to consider The first point to consider is / A further consideration it You shouldn’t just learn one option. The linking words you use will depend on the points you want to present. You must learn how to use them flexibily.
liz thank you lot for making all videos. take care of you
You’re welcome 🙂
Hello Liz, Thank you for this very educative blog. when giving examples in task 2 writing for the academic test, are correct statistics important or can one just use made-up stats?
Your are marked on ideas, supporting ideas, developing ideas, but not numbers. The examiner is not going to check statistical data in task 2. The examiner is marked Task Response, Coherence & Cohesion, Vocabulary and Grammar. This means writing numbers does even help your score that much. Which is better: 1) 75% of people in urban areas feel public transport could be improved. 2) The majority of people living in urban areas feel the public transport could be improved. The second option boosts your vocab score. It is a simple essay based on relevance, not stats and research.
Hi Ms. Liz. Thank you for your lessons 🙂
Thank you very much for your lessons..you deserve to ” The most effective IELTS teacher award ” Thanks once again
It is a misfortune that IELTS mandates the use of linking words for high scores. Especially at the beginning of sentences, linking words quickly tire the reader being pushed around.
If linking words tire the reader, they are not being used properly. You are being tested on using them flexibly in a way that supports the reader.
mam I would like to share a small problem which I facing almost last 10 days in IELTS classes. I’m not good in writing even I don’t know what to write or what to add .and what to think . could you tell me how can I improve .I will looking for your generous response
You can find model essays and tips on the main writing task 2 page of this website for free: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-writing-task-2/ . But for some people, they need more training. My advanced lessons take you step by step through each paragraph and explain the content of each type of essay. You can find these lessons in my online store: https://elizabethferguson.podia.com/ . You can also find an Ideas for Essay Topics E-book, which contains ideas and vocabulary for topics. You memorise the ideas and adapt them to your essay topic. There’s also a Grammar E-book with many examples of sentence structures to help you. Hopefully all these will help you be clearer about how to tackle an IELTS essay and what to write.
Hi Liz, Can you allocate me some of the pre-ready templates which can be used as a topic statement in starting of the paragraph.
I do not provide them because they are the worst thing to do for your IELTS essay. IELTS does not accept memorised language and the higher band scores are all about flexibility, not templates. Writing task 1 is more formulaic than task 2 because task 1 is a report and most reports are pretty standard. But writing task 2 is all about creating unique sentences connected directly to the topic. This website is about learning and preparing for IELTS the right way.
very clear explanation Liz, Thanks !
Could i use the word “To recapitulate” in position of “To Conclude”? However l really impressed a lot to see your tremendous efforts for students. THANK YOU SOO MUCH MAM. may God bless you. Love from india 🇮🇳
Yes, you can use it but it won’t increase your score.
Teacher Liz, this is just a general question. Will points be deducted if literary words/phrases are used in IELTS Writing (or Speaking). Is literary factor considered informal? Thank you very much! Looking forward to hearing from your
I’m not exactly sure what you mean as you’ve provided no examples. However, to help understand: The writing test is formal. So, this means all informal language will cause you to lose marks. The only exception is the informal letter in GT writing task 1. The speaking test is informal and you can use all types of language and be as casual as you want in chatting to the examiner. But language should be used naturally, not poetically or in an overemphasized manner. You should talk as though you were talking to a friend.
I love you mam your are such a great teacher i appreciate your work 👍
Hey liz, I wanted to ask that for conclusion using “all in all” and “to wrap it up” are correct to use or not ?
They are informal and Writing Task 2 is formal.
Hi, Liz! You said in one of your videos that “to sum up” is rather informal for IELTS writing task 2. Why is it in the concluding linkers list then? Can I use it or not?
It is an option but some examiners think it is too informal. There are no rules in IELTS which have word lists that lower your score. It is examiner interpretation. I do not teach this linking word for a conclusion, but other teachers do. This is why it is in the list. My recommendations are recommendations, not rules.
Hi Liz, all your videos are very helpful to have a quick look on the respective modules. Thank you so much for sharing them.
You’re welcome.
Thanks for response
Hello Liz 👋, is it true that reading books or newspapers will improve our writing skills. If yes, what books or newspapers can you suggest to read.
They will certainly help you develop your writing, but they won’t help you develop your writing for IELTS.
I wonder if I am allowed to use specialized words in writing task 2 (as long as they are related to the task rubrics and the usage and the collocation is contextually appropriate). For instance, if the topic of the essay is “imprisonment”, am I allowed to use words like “criminals set free might resort to recidivism”? what happens if the examiner doesn’t know that term? I already know that IELTS guidelines demand that the underlying assumption in the writing exam be the candidate is writing for an academic “non-specialist” reader. Is this fact in contradiction with using technical terms?
With regards, Reza
It is not a case of being allowed or not allowed. It is about how you use language. If you are pushing high level words into your essay for effect, the language in the essay will become unnatural and will be marked down. So, never aim to impress. However, your example is completely fine. The word “recidivism” is an appropriate word to use for that sentence. Certainly not many candidates will know this word, but it is 100% accurate and appropriate. So, my advice is to use language naturally with the right intent and appropriacy based on your level of English. The examiner will not be specialised in law or other fields – bear that in mind. Your aim here is to hit band score 8 or 9, not to showcase specialised vocabulary. This is a basic English language test, not a test of legal language for example. Pay attention to the context of the essay – it isn’t an essay for a university degree in law. You don’t need to use specialised language to achieve your aim in IELTS. I would not recommend using such specialised language that a layperson would not understand. That isn’t an IELTS rule, it is just logical – use such language as is appropriate for the audience and the context.
Many thanks for the exhaustive response. You’re simply the best in the field, bar none!
I wonder if it is appropriate to use some linking words like ‘Moreover, Furthermore, Further’ to start a new paragraph? or they should be used to link ideas in between the sentence?
Thank you, Micaela
There are no rules about this. Linking is about being logical. I personally use these linking words for within the paragraph to add more information. When starting a new body paragraph I tend to use something more flexible, such as “Another point to consider is ..” – basically indicating the start of a brand new point rather than additional information to an existing point.
Can we use listing linkers (firstly, secondly etc) for inside the paragraphs? Or is it better to use linkers for organising paragraphs?
I believe we should use the additonal information linkers to support our main idea or present extended ideas.
Any thoughts?
Best using them within paragraphs. To each paragraph, try: Firstly, Another point, Finally. But to be honest, you can’t learn formulas like this for task 2. It all depends what your ideas are as to what linking words to use. You need to learn flexibility if you want a high score. Yes, you should use a good range of linking words in your essay.
Hlo madam , tomorrow will be my ILETS exam
Hi Liz, Do we need to use comm a after these linking word . If yes then in what circumstances. For instance if we use these linking words at the start of sentence what will the case. Also what will be case if we use these linking words in middle of sentence ?
This is an aspect of grammar that you need to study in depth. In a few weeks, I’ll be releasing a Grammar E-book. It will explain all of that and much much more.
Can I use ‘For one’ instead of ‘Firstly’? Can I continue using ‘Secondly’ and ‘Finally’ with ‘For one’ or it’s not correct usage?
“For one”, is informal and not suitable for IELTS essays. Be flexible with your use of linking devices but stick with formal ones.
Hi Liz, Thanks for the article. Is it safe to use comma (,) after every linking word?
Thanks Sirdhar
It depends which linking word and how the sentence is constructed.
”Poor sanitary conditions lead to wide range of bacterial and viral diseases as well as become a dangerous spot for the growth of dengue leading to dengue fever which is fatal.In order to avoid such consequences, my endeavour would be to construct underground pipes which prove to be effective giving a sensation of cleanliness.” Ma’am this is my answer to a direct question,” If you could change your hometown to make it a better place what changes would you make? ” Plz tell me the mistakes in structure or anything.
That question usually comes from speaking part 1. In part 1, they are relatively short answers – not deep discussions. The examiner would interrupt this answer. Just be direct and then add a bit more for part 1: “I’d change the sanitary conditions because … ” – then add one of two more sentences. Be chatty, not formal. You really need to start paying attention to what each part of the speaking test is like. There’s no point developing answers that aren’t appropriate to the section of the test. Your answer would be possible in part 3.
being a teacher, I feel that you the best.
Hello Liz. I just wanted to confirm that can I start the arguments in general by saying, “On the other hand, it is argued by some that …”. Can I use this to introduce people’s opinion? Please reply ASAP, I have my IELTS test in 2 days.
“On the other hand” is used to introduce an opposing view. “it is argued by some that” is used to express other people’s views.
Hi, Liz! I love your website! I have a question, though. Would it be helpful if I used paragraph links instead of standard transitional devices? Say, instead of starting a paragraph with a word such as “Secondly” or “On the other hand”, I could use either a word-link or idea-link. I don’t want my writing to look so mechanical. Will it affect my score if I try making my transitions “smoother”?
It is not necessary to start a paragraph with a linking word. You are right. It needs to be less mechanical. You can actually start your body paragraph with any word you want. Just make sure it is coherent and cohesive.
Hello Liz, are the following phrases ok? 1- tethered to this idea is its conjugate (in discussion essays where i am mentioning opposing views) ex: on the other hand, tethered to the previous idea is its conjugate. where some people believe that …… 2- a few bad apples spoil the batch (is it informal?) 3- X issue is not black and white.
Do not use descriptive language in a formal IELTS essay.
Hey! Lizz what about your ebook is it going to be published soon or not?
I just want to say how much I appreciate your hard work and love for putting these lessons together!
I am also so happy that you have offered us 50 discount! I am so happy! <3 Thank you very much!
Hello liz…. I have a confusion some of the Ielts trainers say that ‘Firstly’ isn’t exist in English language means it’s not a word…. We can’t use it…. I want to ask to you is this true???
I need to get a good dictionary (English – English). You shouldn’t be preparing for an English language test without one: https://dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/firstly
Hi.. I just want to ask that is it necessary to use linkers in writing as firsty, secondly, etc. while writing reasons or advantages. And on the other hand etc for starting new paragraph in opinion essay
The choice of linking words is not fixed. You use them flexibly, not in an automated way. There are many linking words you can use and also different methods of linking.
Hye Liz…your way of teaching is so clear..When I attend your lessons through videos, I feel your devotion to your work and really seems that you want to do your best for our best…may Allah bless you more and more.
I’m really pleased that my lessons are useful 🙂
Hello Liz pls can you discover an e book for the students which contains ideas, linking words and ….
I will be releasing an Ideas for IELTS Essay Topics E-book this month or early next month. I am also writing a Grammar for IELTS Writing Task 2 E-book which will be ready at the end of the year.
Your lessons are wonderful. Thanks.
Hello Liz, Have you released ideas book for IELTS writing Task-2 or not yet? Regards
Yes, you can find it here: https://elizabethferguson.podia.com/
I am really worried for Reading section it’s too much difficult to handle within short time. kindly let me know appropriate techniques as I have very short time, please.
Regards Khan
Click on “Reading” on the RED BAR at the top of the website – you will find the main page with tips, lessons etc to help you.
I need to say Liz, I have so much fun reading your answers, you are the best sincere person I have ever known. Continue like this please! Pietra
Thanks 🙂 Funny 🙂
Thank Liz for your help my question is that I want to know if I there is any number of times for the linking words to appear in my easy Wishing you successfull ending love your lecture
Linking words should not be repeated. You are being marked on your ability to use a range. However, words such as “and” or “but” are naturally going to be used a few times. Words such as “for example” can be paraphrased as “such as” or “namely” or “for instance”.
What it is meant by ‘the linking words shouldn’t be mechanical’?
This means to use them like a machine. For example, always putting them at the start of a sentence or starting every sentence with a linking word. Be flexible.
To use some less common linking words, Could you advise whether its appropriate to write ‘on the whole’ rather than ‘in conclusion’?
Also, in some model answers written by examiners in official ielts books, they start their last paragraph with “in my opinion”, and they dont say anything like “to conclude”. Is this risky to do?
Linking words are linking words – they do not need to be less common. Do not confuse vocabulary with linking words – they are part of different marking criterion.
Hello Liz. I am learning a lot from your tips. Thank you! Can you please elaborate more the linking phrases ‘moreover’ and ‘furthermore’. Thank you!
I’m not sure what else I can say. They are used when you want to add information to an existing point.
In one of articles relating to capital letters (link below) you mentioned that you should never start with – “But/ Because/ And”. In essays which require us to share multiple contrasting views, sometimes we may start a sentence with “But”. What are your views on that ?
No writing task 2 essay should have a sentence that starts with “But/And/Because”. You can use “However” instead of But.
Hi Liz. Which is the best book to practice for IELTS. Please suggest. I have been struggling to find a suitable book.
The reason I wrote over 300 pages of free lessons and tips is because didn’t like the IELTS books on offer. Have you completed the 300 pages of free lessons?
I didn’t find 300 pages of free lessons.
Because you didn’t read the HOME PAGE properly. The HOME page explains that you access the main pages through the RED BAR at the top of the site. The main pages contain over 300 pages of tips, lessons etc. Did you use the RED BAR?
I am convinced that you are best tutor ,I have best wishes for you ,thank you so much from your excellent site
Thank you so much for the useful information!
I have a question about the linking phrase “on the other hand”. Is it possible to use it independently, without mentioning ”on the one hand’? Or would it be a mistake?
Thank you in advance!
Yes. You can use “On the other hand” without “on the one hand”.
Hi Liz In one comment you’ve mentioned that you’ll publish a book discussing required grammars for writing task-2. Has it been published? Thanks. Mostafa
No, it is being written at this moment. I don’t know how long it will take to finish, but it will be this year.
Thank You for the reply. Mostafa
Why is apparently not there in the above list? Is it frequently used word, hence ommited deliberately Liz?
It’s fine to use that word.
This lecture is helpful.your god gifted voice is sweat ,crystal and clear. I respect it.may your voice always reply to untold question of liseners who are similar to me.
HI LIZ, thank you for your helpful information i need to ask whether words like ( IT , AS , IF, SO , THE )are counted as words to reach 150 words in letter writing ?
All words are counted – small, big – all words.
Thanks a lot Kiz for doing this great job
btw, does linking-word need to be followed by a comma? (,)
Depends on the linking words and how it’s used.
You are really doing a wonderful job, what baffles me your ability to reply these long comments , you are really awesome. However, I want to ask you about linking words such as , firstly, secondly, thirdly. I read it somewhere that they are old fashioned, is that true???
It isn’t about being old fashioned at all. It’s about flexibility which is what the examiner is looking for. It’s fine to use them inside one paragraph to show support points. It isn’t flexible to use them at the start of each body paragraph – that is called being “mechanical”, which means using them like a machine – that is a characteristic of band 6 in Coherence and Cohesion.
Hi Liz , Somewhere in your topics you have mentioned that one should not use ” last but not the least” as a linking word
But here it is written under heading of linking words.. Kindly guide on this
The linking word is : last but not least – no “the”. Also it depends HOW it is used. It’s about using them effectively. It shouldn’t be used a conclusion linking words. See this page for all tips: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-writing-task-2/
hi liz HOW TO ADD EXAMPLE IN AN ESSAYon this page is not opening. can you please share the link?
The link opened for me – it might be a problem with your internet Try it again: https://ieltsliz.com/how-to-put-examples-in-your-essay/
Honestly, you are the best tutor ever in this IELTS course, how I wish I knew you before, I could use only materials to help me pass well. My Test is after tomorrow and I have just landed your very impressing training work. Thanks a lot for sharing this wonderful knowledge with us. Am sure I will pass with a band 9.0 God bless you Liz
You can learn a lot in one day – focus on the areas you most wish to understand and improve. Good luck tomorrow! Keep your eye on the clock for reading and writing!
dear Liz I have met your page by yesterday,many thanks for such a great page,
Hi Liz, I hope, you are doing good. Actually, I appeared for ielts exam today but due to poor time management, I was not able to complete task 2 of writing. I wasted a lot of time on Task 1. I know, because of this, I would not be able to score 6 or more than that, as the task 2 holds more weightage. So, I have applied for the exam again. I have some concerns regarding writing section, I don’t know about the proper use of punctuation, especially commas. Also, sometime I write out of the context in essay writing. Please could you provide me some help with this. I would be really thankful.
The use of commas is simple. Just them to divide appropriate clauses. Punctuation is marked, but not at a high level. The main point is that commas are used in clauses, correctly and that full stops are used at the end of a sentence. Also that sentences are not too long. A very long sentence shows lack of punctuation because the person isn’t controlling the length of sentences. For ideas, it’s all about planning properly. See my advanced lessons: https://elizabethferguson.podia.com/ . You also need to prepare ideas for topics – you do this by googling ideas on line.
Thank you so much for the response 🙂 So, is it okay, if we use short sentences instead of long? Using them won’t be a reason to deduct marks? And, what about the complex sentences? Would it be advisable to attempt task 2 first and then task 1, as it carries more weightage, because I always face the issue of time management but I am working on it.
A complex sentence does not need to be very long. It just needs to be a sentence which is not simple – this is a way the sentences are categorised for IELTS examiners, not for grammar books. Having short, simple sentences is not a good idea if you are aiming for a higher band score. You need to show control and a good range of sentence structures. I am currently writing an e-book which is a Grammar List for IELTS Writing Task 2 – I’ll post a notice when it’s finished and ready to buy.
I’ll keep these points in my mind. Yes, please let me know, whenever you have completed E-book. Thankyou Liz 🙂
Hello teacher! I have a query about other words that can be used, besides the word “overall”, for the overview part. Can I use ” as a whole” or “in general” instead of that? Are those words considered as formal writing in IELTS?
Please enlighten me! Also, thank you so much for giving out this linking words. 🙂
It is possible to use those words, but the word “Overall”is the most logical to use and the most appropriate.
Thank you so much for the reply! 🙂
Under the Adding Information section, I have a doubt on below sentence
These linkers inform the reader or read?
Thanks, Kishore
Thanks – a typo 🙂
You are the best teacher ever and I hope you are doing fine.
I wanted to ask you whether it is okay use “i.e.” in my IELTS writing exam ?
You are being assessed on your use of linking words, “ie” is not a word. Don’t use it. Use “for instance” or “for example” – the list is given on the page above.
I like your teaching.and I appreciate it.
Thank you soo much mam..That was really really helpful..
to conclude to sum up these are very short pharse i want write a long pharse for example Before putting my pen down i would like to deduce tha ….
This page is about linking words and signposting. It is fine to learn linking words which are part of coherence and cohesion. It is NOT good to memorise phrases for IELTS. See all tips on this page: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-writing-task-2/
Hello Liz, How to use the linking phrase ” last but not least” ? Should it comes at the last body paragraph or the conclusion paragraph?
It indicates the final main point – it does not indicate a conclusion.
hello liz , I am not form any English specking country, i’m thinking that i’m good at specking.But my main problem is at spellings, how can i decline my spelling mistakes
See this page: https://ieltsliz.com/useful-websites-and-resources-for-ielts/
Hi,Liz How are you? Thank you for your suggestion,it’s so useful
Hi Liz, love your blog, would like to know if there is a direct link to all your pdf’s. It would be very helpful.
I don’t have my pdf files ready yet.
Hi Liz, Can we use “Because of that” in blank 6???
The word “because” can’t be put at the beginning of a sentence in formal essay writing for IELTS.
Thank you liz i wasn’t aware
Thank you, again and again…
Hi Liz, Can I conclude the essay by writing, ‘Hammering the last nail, I reckon that..’ or ‘I pen down by saying that..’?
No, you can’t. I am very confused. This whole page offers all the best linking words for a high score – even up to band 9. Use them, learn them. Stop trying to improve them. Do you want band 10? Just relax and start using appropriate language and linking words.
Thanks a lot mam!
Thanks a lot mam for your guidance. I have scored overall score of 8.50 with L-9.0, R-8.5, W-7.5 and S-8.5 as individual scores. I followed you religiously and I just can’t thank you enough! 🙂
Brilliant !! Very well done 🙂 Thanks for letting me know 🙂
I really appreciate the way you have described the small errors we all students keep on doing in daily essay writing. I have few questions in my mind, but without wasting your time I will put only one basic question that I am facing daily with the essay writing. If the topic of the essay mention ” to what extend do you agree”. So, in such essay do we have to write only paragraph in the notion of the topic. As my aim is to score band 7.5 and this confusion. IELTS have a feeling of schadenfreude when they see my low score in writing only.
I don’t understand your question. When you give your opinion, the whole essay will explain it. You will give an opinion based on the issue or issues given to you in the question.
hi mam I’m very bad in speaking part I have no Idea how to improve and how imagine more idea
See this page: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-speaking-free-lessons-essential-tips/
Hello Liz, My handwriting is poor and somewhat clumsy …. To improve legibility may I write in alternate lines on ielts answer sheet… Do you recommend it?… In case, if i need extra sheet, do they provide?…
I don’t recommend doing as you are planning. It makes it difficult to identify paragraphs and can be confusing for the reader. Just try to keep your handwriting as clear as possible so that the examiner can read it. Practice, practice and do more practice. Yes, you can ask for extra paper. Usually you just put your hand up and then explain you need more paper. But I have heard from one student that they wasted precious minutes waiting for the extra paper.
Hi Liz, thank you for precious advices, in your opinion is the use of Latin expression, such as “e.g.” or “i.e” useful in writing tasks for the academic module?
Avoiding using them. Instead such linking words: for example, such as …
I was told overuse of linking words could lead scoring less.is that true?
Yes. There is a criterion for marking which states that if you overuse linking words or if you use them mechanically (this means without flexibility), your score will not go higher in that marking criterion. This related to Coherence and Cohesion which is 25% of your marks for writing task 2. See my advanced lessons if you need training: https://elizabethferguson.podia.com/
What about an expression “all in all”?Can it be used in a conclusion paragraph?
I have known students use this. But I would stay with linking words most suitable for a conclusion = In conclusion
Thank you Liz for this useful lesson The answer is for instance , still , because , especially , consequently , therefore
Check the answers on the page above.
Thank you for your great lessons. It really helps a lot. I have a question about a linking word ‘and’. Would it be okay to start a sentence with ‘and’?
For example, this is mainly because of lack of physical activity and the poor quality of food. People are too busy. And in spite of economic growth, the quality of food has diminished.
Not in IELTS writing task 2. Never use “and, but, because” at the start of a sentence in writing task 2.
Thank you for your answer. I highly appreciate your great lessons and help.!
I am not clear why a sentence can not be started using “because”. Since we have mentioned both: subordinating clause and main clause, there should not be any issue to the examiner.
The words “because, and, but” should not be placed at the start of a sentence in formal writing. They come between clauses in formal writing.
Please guide me, how i can get good score in writing, Is it good to use idioms, Phrasal verbs in writing task 2
On this page: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-writing-task-2/ you will find advice about idioms
Hi Liz Can I expree my opinion by using this sentence (in my own point of view) or it’s informal Thanks
No, it’s not right to use that. See this page: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-writing-task-2-expressing-your-opinion/
Hello Liz I have question . If I use idioms or slangs to essay , could they help me to get higher score
They might help you get a lower score. See this page: https://ieltsliz.com/using-quotes-or-idioms-in-your-ielts-essay/
Hi Liz I have a problem with writing task, I can’t have enough time for task 2, I’m constantly thinking about what to write next. can you give me some suggestion? Thanks Abdullah
See this page: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-writing-task-2-essay-planning-tips/
hi madam if we are confused or not sure about answer can we can we write both the answer by using // in the middle
Hi Liz Can we use the phrase “my personal sentiments” to give opinion in task 2 instead of I believe or I think
thanks alot
No. It is informal and not suitable for writing task 2. See this page: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-writing-task-2-expressing-your-opinion/ and then check all writing task 2 tips: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-writing-task-2/
Hi mam, Thanks for your kind initiatives for the IELTS students like us. It is really fortune for me to have an online teacher like you. Please keep continuing.
Hi mam.. What is the procedure? to send u ielts writing for checking …..
Plz plz tell me…
There is a teacher who can help you on this page: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-essay-correction/
HI! I’m one of your avid fan. I just want to say thank you. I recently got the score I needed for Writing after 2 takes. I used all your guidelines in making it coherent and scoring higher using your tips on having a balance essay for every kind of questions. I also did task2 first to make me more calm and relax in writing the ardous part. THANKS FOR EVERYTHING!
That’s really great news!! Well done!! Thanks for letting me know 🙂
thanks Liz ,was very efficiently significant
I had written my IELTS test twice before coming across your website. Both the times I scored 6.5 in Writing which scoring above 7 in all the other 3 sections. I needed 7 in writing and hence I enrolled for the third time. I came across your website 3 weeks before my test and went through all the study material in your web pages. I got my scores last week and was ecstatic to see that I managed 7 in my writing section.
I am thankful to you and your website for helping me achieve my goal. You are doing such a commendable work. Keep it up.
That’s really good news! I’m so pleased for you. It can be hard to hit that elusive band 7 in writing. Well done 🙂
Hi Liz, are you available to correct my essay? If not, could you suggest another teacher? Thanks.
You can find a teacher called Tony to help you on this page: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-essay-correction/
My God! You are doing a beautiful job. More I’m studying from your website more I’m impressed! I can’t explain how much I feel grateful. Thanks a lot.
Hi liz, Is the writing matters for writing task 1 and 2? If so then whether we need to write in cursive or just clear.. I mean is any writing method acceptable?
You just need clear writing. As long as the examiner can read it, you are fine. It doesn’t matter what style of handwriting you choose.
hi mam, Task 2 which you provided is for BC or IDP.Because i am taking idp exam,pls give me reply
The tests are the same in IDP and BC – they are both owners of IELTS.
Hi Liz thank you a lot for giving us all this informative lectures and publishes. But why different teachers give different IELTS writing rules. Example you teach us hooking in your introduction is not important, but other teachers demonstrate that it is very important. And if we add hook to our writing could it reduce our marks?
Some teachers have completed the IELTS examiner training and others have not.
Hi Liz, beautifully you have explained variety of expression, i am preparing for ielts and having many issues while putting pencil on paper to write answer for Writing task 2, would you please suggest how to get it done within stipulated time frame such as in month so that i can fulfill my dream to study abroad…..
Firstly try to develop as many ideas for writing task 2 topics as you can. You can do this by taking ideas from model essays and other sites online. See this page for common topics: https://ieltsliz.com/100-ielts-essay-questions/ . For techniques, see my advanced lessons: http://subscriptions.viddler.com/IELTSLizStore
First, I would like to say to you thank you for very nice lessons. I was wondering to ask if you correct essay task 2 ?
https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-essay-correction/
thank you very much.
hlo mam, i just wanted to say that you are the best teacher.
Hi mam i need your help how to write task 2 to get 8 band can you give 9band samples writing answer pls
You can find model answers on the main writing task 2 page of this blog.
hi liz, i will give my ielts test after three month please help me in all. modules plss
There are 300 free pages of help on this blog. If you need more help with writing task 2, see my advanced lessons: http://subscriptions.viddler.com/IELTSLizStore
Hope you are fine.
My name is Gagandeep. I have IELTS test on 16th July and I feel I am not able to structure my ideas in writing task 1 and task 2 both. Please let me know how can I bulid my ideas perfectly to get band 8.
Regards Gagandeep
At present, I can only suggest you get my advanced writing task 2 lessons: http://subscriptions.viddler.com/IELTSLizStore
Thank you so much for being replying to people i have recently got the IELTS date which is on 16th of jun its my second time i am giving ielts the first time i got 5 bands and i need at lest 6.5 so how can i improve my grammar and vocabulary i have just 20 days remaining..
please do reply me soon.
It is normally best to take the test when you repeatedly get the score you want in practice tests. To improve English in just 20 days is a challenge. I can only suggest you decide what your main grammar problems are and deal with them one at a time. For vocabulary, review common topics for speaking ad writing – you can find word lists on google.
this is my first query from you. please clarify.
how to use furthermore,morever,in addition in an essay please clarify.
Excessive use of computers has many detrimental effects on childrens health.Firstly, frequent joint pain and fatigue are most likely to be experienced by young individuals and these issue seems to be prevaile till the death.Morever(do we use morever here to introduce new idea such effect of exceissive computer usage and academic grades or do we have to discuss another health related issue)(moreover will be used to introduce new idea such as school performance or anyother health related issue?
thank you very much
Sorry I don’t comment on writing.
thanksssssssssssss
Thank you for all the tips on how to write a meaningful essay. However could you please help out on how to paraphrase the question as that part is posing a lot more difficulty for me at the moment.
https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-liz-news/
Thank you so much for the tips on how to write a meaningful essay. However could you please help out with how to paraphrase the question, which is posing as the most difficult part for me right now.
Hi liz i am going to take my test in 3days , i am not perfect at task2 i can”t able to know how many word are of mandetatory can i write more than 250 words , can you please give me any suggestion how to get good score in task2 any key words etc
You can find information and tips for writing task 2 on this page: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-writing-task-2/ and you can find advanced training on this page: http://subscriptions.viddler.com/IELTSLizStore
thank you very much. I’m going to take IELTS on 16th April)
hey liz i am learn many things related to ielts but my writing skill is not development and is it important strength of the sentence suggest me about this
https://ieltsliz.com/liz-notice-2015-2016/
A.A mam my problem is vocabulary. Plz help me by giving tips and vocab words. I need 7 in ielts.
Hi Liz. My general english is good. I can cope up with more complex sentence structures too. But when it comes to writing task 2 , my brain just stops working. My main problem is I cant brainstorm on the topic. How can I improve my brainstorming for different topics. Thanks.
Hello Mam,can you assess my writing task if i mail it to you please? Further I do not have good command on spelling. how can i improve it within one month effectivly.
I can found some problems in writing task2 and i can not used rich vocabulary and some time i can’t get good points.so how can i improve???
Hi Liz, I know that native english speakers rarely use ” moreover”. Is it safe to use it in IELTS Essay?
Thank you for your useful lessons. I have a question that worries me lately. Would the assessor count repetitive words? For example if I used the word “students” 9 times in the whole essay? Or another example, if in writing task 1, I used countries’ names all the time (besides making it nationality: Britain = British).
Each word is counted. It is the same as using word count on a word document. Liz
Hi Liz Are the following answers appropriate for the respective questions? 1. because 2. obviously Thank you for the help Lahari
No, both answers can’t be used. Liz
Hi Liz, I appreciate your help on this question: can we use FIRST AND FOREMOST and LAST BUT NOT LEAST in Academic Writing? Thank you. Trang
Yes, but they are over used. Liz
Dear Liz, This question is not about the linking words, its about grammar. In the 2nd question, why you have not use ” ……. problems ARE on the rise.” instead of ” …… problems IS on the rise”?
Well spotted!
Hello liz thanks for your good websites. how can i submit my writing for checking? thanks in advance baazoft
Unfortunately, I don’t offer essay marking and I don’t have any teachers to recommend. All the best Liz
i wanna ask that sometimes like ….to…. like question are there in listening task what is the right way to answer this. it is 4to5 or it is4,5
Just “4 5”. You don’t need punctuation. Just make sure the numbers are easily read and separate. If you write “4 to 5” is would be marked wrong. Liz
Mam I weak in writing I Write only simple sentence then I lose band score…… What I use to get high score
You need to improve your English. This is a language test – make sure your English is good. Get a teacher and start learning from English language websites. Do this before you do IELTS.
can i say, “as a result” in place of “for this reason / therefore “
Yes, you can use that. Liz
We shouldn’t use these terms in the speaking part, should we? – The first thing i should mention is… – And i shouldn’t forget to mention – There’s a mixed variety of things but i guess the most popular one is… I think that i had better answer directly and spend time on expressing my ideas rather than using these phrases, but my teacher told me that i should use these to help organize my answer
You can use those phrases if they help you explain your ideas but they won’t necessarily give you a higher score. In part 1, you must answer quickly and directly so don’t use them. In part 3, you might use them to explain your ideas. The most important thing is to speak naturally. All the best Liz
Thank you for your help. 🙂
I just want to ask about the appropriate answers for a listening practice test 🙂 The questions are about ticket prices: $30 (1)…, or (2)… return According to what i heard, (1) is “one(-)way”. So is this written with or without a hyphen? For the second blank i heard “$45 in return” . so should i write down “$45 in” into the blank or just “$45” ? Thank you for your help.
One-way has a hyphen. For your second question, always look at the example they gave you. If the first one is “$30 one-way” then the second one must be “$45 return”. Always check the grammar. For note, form or table completion, grammar is rarely involved. All the best Liz
Thanks a lot. May all the best things come to you, teacher.
Can I answer questions 1 and 2 in a different way ? 1- .However, 2- still
It can’t be “However” because there is no full stop. Always check grammar. For the second question, “still” is possible. All the best Liz
Thank you so much.I really appreciate your reply.
Would my answer be correct if I used a full stop (.However, ) ?
I am asking because I could not see any grammatical difference in this sentence between using (even though ) or ( . However, ) .
That’s right. You need the full stop. Liz
Is not it possible to write the word this way: “…a way of communicating; however, it is…”?
You would need to write the full sentence for me to check. Liz
I meant the first sentence you gave to practice. You answered Ahmad that is not right to use “However” there, and decided to ask if it can be “1st sentence ;however, 2nd sentence”. Julia
Avoid using “;” in IELTS writing. Just use full stops or commas. Liz
You are great …God bless you.
Hi mam.i want to study with you online, if you have time please teach me.
At present the only lessons I offer are on my video course which I have only just started making. At present there is one lesson available for writing task 2 and tomorrow I hope to put my second lesson up: http://subscriptions.viddler.com/IELTSLizStore All the best Liz
Hello mam, Today while searching some helpful tips for ielts exam i went through your videos and i found it vry easy and helpful ways to improve our writing skills. Hope it will work during my exam too. Thank you mam for such a wonderful tips and guidance.
How i can improve my vocabulary please give me suggestion.my vocabulary is so poor.
Start reading. That is the surest way to develop vocabulary and understanding. Liz
Thank you so much
Thank you so much for your wonderful tips
Hello mam. I am Sandeep. Please help me. How i will get 6.5 band in writing task.
Take a look at the band scores to learn: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-writing-task-2-band-scores-5-to-8/ Liz
Dear Ms.Liz,
I have just received my Ielts result. Thanks to your help, I have got an overall band score of 7.5, 8.0 for the listening and reading test, 6.5 for the writing section and 7.0 for the speaking part. I am really delighted with this result because this is my first time ever studying on my own by using the materials on the Internet. Thank you so much for all of your lessons, I really appreciate what you have been doing and your dedication to teaching. May all the best thing come to you and your family.
Your Vietnamese student, Hanh Tran 😀
Hi Hanh Tran,
I’m really pleased to hear your result. 7.5 is a really good score, particular for your first try. In Vietnam the average is around band 6. So, band 7.5 puts you much higher than most students in your country. I hope you celebrated your result !
Good luck with your future plans 🙂 Liz
Thank you, teacher 😀
Hi liz I have my ielts exam on Thursday. I just wanna ask you that in writing task 2 general ielts training test ” in my opinion….” Should write in introduction or conclusion? I am little confused with that. And suggestions like “they should do that ……” That will come in conclusion or in body paragraphs? Where are they appropriate ? Looking forward for your reply thanks
You put your opinion in the introduction, if the instructions ask for your opinion or for you to answer a direct question. If the instructions don’t ask for your opinion, don’t give it. Please see my model essays to see how and where I put my opinion. There is also a separate lesson about giving your opinion on the writing task 2 page. Liz
Hi Liz, Is it advisable to use the listing words such as firstly, secondly, thirdly and finally at the last paragraph before the conclusion or I could use it also at my initial paragraph after the introduction? Thank you!
You use them as you want. They can order your paragraphs (although that is slightly mechanical) or you can use them to order supporting points in any paragraph you wish. Liz
Thank you for your response liz 🙂
Hello mam, i need your help how to complete reading task in one hour. There is some technic to do task as soon as possible because read full paragarh then find out ans. Is take so much time. Also how i improve my listening skills mam please help me.
Please read my tips about comprehension and strategy on the reading page. Thanks Liz
Hi Liz; I want to ask you about linking that are related to giving opinion. May I use them “I take the view that…” and “I subscribe to the theory that…” in writing Task 2 or just in Speaking.
Regards, Sherzod
Just be direct and don’t try to learn phrases – the examiner isn’t impressed by students who purposely learn phrases to boost their score and will not award points for it. You can use “In my opinion” or “I think” or “I agree” for task 2. You can also find a lesson on my task 2 page about how to give your opinion. For speaking, it is informal so you can use a range “I suppose”, ” I guess” or “I reckon” or “I think” etc. All the best Liz
Hi Liz, My ILETS exam was on the 4th of July and today I got my results’ message (listening 6, reading 6, writing 5.5, speaking 6.5). I am really shocked by my speaking and listening results. Do you you think I will get any new result if I reject and apply for remarking?
Listening rarely changes with a remark because it is marked by right or wrong answers and mistakes almost never happen. For speaking, band score 6.5 means you make more than a few mistakes in your grammar and vocabulary or possibly that your fluency is strong enough to be able to talk at length without effort. It is possible to get a remark for speaking but looking at your writing, it is even lower. So, it doesn’t give confidence that your score will go up with a remark. However, you must judge for yourself. All the best Liz
Dear Liz I have recently found out about your videos and website and I deeply appreciate your effort. I am preparing for an Academic module in a limited time so I found your lessons and instructions very useful to manage my studies. Although I am still struggling with Reading skill.
The key to reading is to spend time understanding the language in the questions and thinking about paraphrasing before you try and find the answers. The more time you spend with the questions, the quicker it is to find answers. You should also be writing down a list of paraphrases from all reading exercises you do. Lastly, spend time planning a strategy for each question type and learning which questions have answers that come in order. You can find a page about question types in the reading section of this blog. All the best Liz
Really this is a stategy
Dear Liz, Thank you for such a useful note, but it seems you missed contrast/opposite connection words.
Regards, Amir
You will find contrasting linking words in the concessions and contrast section. All the best Liz
Hello teacher,
I’m confused using between these two words. Is the same ” as a result ” and ” therefore”.?
Could you explain it to me, please? Thank you very much
They have the same meaning and you can alternate using them. All the best Liz
This is such a big help Ms. Liz. Thank you for always updating your site! Love you! 🙂
Please give me a common sentences of task 2 i can write in all type of essay
Sorry but that is not the right way to approach IELTS. The examiner is trained to spot learned sentences and you will lose marks. The sentences you should aim for are based on grammar structures or tenses: clauses, conditionals, prefect tenses, gerunds etc. Just review your grammar structures. All the best Liz
Hi Liz; Thanks to publish this useful words for writing task. I need 7 in that task while I was got 5.5 in my first attempt after that I had knew about your site and I register myself in it and from that day onwards I regularly follow your tips hope i will improve in my writing. Thanks again
Make sure you check your level of English to get band 7. In the message above, your first 9 words contain 2 mistakes and the second sentence contains 5 mistakes. You will need to reduce your errors to get band 7. Good luck Liz
Speak Your Mind Cancel reply
Notify me of new posts by email.
Advanced IELTS Lessons & E-books

Click Below to Learn:
- IELTS Test Information
Copyright Notice
Copyright © Elizabeth Ferguson, 2014 – 2024
All rights reserved.
Privacy Policy & Disclaimer
- Click here: Privacy Policy
- Click here: Disclaimer
Return to top of page
Copyright © 2024 · Prose on Genesis Framework · WordPress · Log in
Narrative Essays
Narrative: The spoken or written account of connected events; a story
Narrative Introductions
The introduction of a narrative essay sets the scene for the story that follows. Interesting introductions—for any kind of writing—engage and draw readers in because they want to know more.
Since narratives tell a story and involve events, the introduction of a narrative quite often starts in the middle of the action in order to bring the reader into the story immediately, as shown in examples 1, 3, and 5 below. Other effective introductions briefly provide background for the point of the story—often the lesson learned—as in 4 below and the first example on the reverse side.
Below are some strategies for writing effective openings. Remember your introduction should be interesting and draw your reader in. It should make your audience want to read more. If it's a person , begin with a description of the person and then say why that person mattered. If it's an event , begin with the action or begin by reflecting back on why the event mattered, then go into the narrative.
- "Potter...take off!" my coach yelled as I was cracking yet another joke during practice.
- Why do such a small percentage of high school athletes play Division One sports?
- It was a cold, rainy night, under the lights on the field. I lined up the ball on the penalty line under the wet grass. After glancing up at the tied score, I stared into the goalkeeper's eyes.
- My heart pounds in my chest. My stomach full of nervous butterflies. I hear the crowd talking and names being cheered.
- Slipping the red and white uniform over my head for the first time is a feeling I will never forget.
- "No football." Those words rang in my head for hours as I thought about what a stupid decision I had made three nights before.
- "SNAP!" I heard the startling sound of my left knee before I ever felt the pain.
- According to the NCAA, there are over 400,000 student-athletes in the United States.
Narrative Story
- Unified: Ensure all actions in your story develop a central idea or argument.
- Interesting: Draw your readers into your scene(s), making them feel as if they're experiencing them first-hand.
- Coherent: Indicate changes in time, location, and characters clearly (even if your story is not chronological).
- Climactic: Include a moment (the climax) when your ending is revealed or the importance of events is made clear.
- Remember the 5 W's : Who? What? When? Where? Why?
- Write vividly : Include significant sensory information in the scene (sight, sound, touch, smell, taste) to make readers feel they are there
- Develop " Thick Descriptions "
Clifford Geertz describes thick descriptions as accounts that include not only facts but also commentary and interpretation . The goal is to vividly describe an action or scene, often through the use of metaphors, analogies, and other forms of interpretation that can emote strong feelings and images in your readers' minds.
"The flatness of the Delta made the shack, the quarters, and the railroad tracks nearby seem like some tabletop model train set. Like many Mississippi shacks, this one looked as if no one had lived there since the birth of the blues. Four sunflowers leaned alongside a sagging porch. When the front door creaked open, cockroaches bigger than pecans scurried for cover [...] walls wept with mildew."
—from Bruce Watson's Freedom Summer
Narrative Checklist
- Does the story have a clear and unifying idea? If not, what could that idea be?
- If the story doesn't include a thesis sentence, is the unifying idea of the story clear without it?
- Is the story unified, with all the details contributing to the central idea?
- Is the story arranged chronologically? If not, is the organization of ideas and events still effective and clear?
- Do the transitions show the movement from idea to idea and scene to scene?
- Are there enough details?
- Is there dialogue at important moments?
- Is there a climax to the story—moment at which the action is resolved or a key idea is revealed?
501 E. High Street Oxford, OH 45056
- Online: Miami Online
- Main Operator 513-529-1809
- Office of Admission 513-529-2531
- Vine Hotline 513-529-6400
- Emergency Info https://miamioh.edu/emergency
1601 University Blvd. Hamilton, OH 45011
- Online: E-Campus
- Main Operator 513-785-3000
- Office of Admission 513-785-3111
- Campus Status Line 513-785-3077
- Emergency Info https://miamioh.edu/regionals/emergency
4200 N. University Blvd. Middletown, OH 45042
- Main Operator 513-727-3200
- Office of Admission 513-727-3216
- Campus Status 513-727-3477
7847 VOA Park Dr. (Corner of VOA Park Dr. and Cox Rd.) West Chester, OH 45069
- Main Operator 513-895-8862
- From Middletown 513-217-8862
Chateau de Differdange 1, Impasse du Chateau, L-4524 Differdange Grand Duchy of Luxembourg
- Main Operator 011-352-582222-1
- Email [email protected]
- Website https://miamioh.edu/luxembourg
217-222 MacMillan Hall 501 E. Spring St. Oxford, OH 45056, USA
- Main Operator 513-529-8600
Initiatives
- Miami THRIVE Strategic Plan
- Miami Rise Strategic Plan
- Boldly Creative
- Annual Report
- Moon Shot for Equity
- Miami and Ohio
- Majors, Minors, and Programs
- Inclusive Excellence
- Employment Opportunities
- University Safety and Security
- Parking, Directions, and Maps
- Equal Opportunity
- Consumer Information
- Land Acknowledgement
- Privacy Statement
- Title IX Statement
- Report an Accessibility Issue
- Annual Security and Fire Safety Report
- Report a Problem with this Website
- Policy Library
The Female-Midlife-Crisis Novel
Miranda July’s new book is full of estrangement, eroticism, and whimsy.

B ack when the word weird (or, in the spelling of the day, wyrd ) was first commonly used in English, it was not an adjective but a noun, and it functioned as a synonym for fate . A person wasn’t weird; instead a person had a weird, which was theirs alone, determined by forces beyond control and understanding. Shakespeare’s “Weird Sisters” in Macbeth helped transform the word, linking its supernatural connotations with an aesthetic quality. Those three crones know the future—they seem to know everything, standing astride the temporal and the miraculous as they do. In them, the old and the new weird s meet: They are creatures in touch with the workings of fate, but they are also inexplicable, creepy, queer, spooky, deviant from the norm.
Explore the June 2024 Issue
Check out more from this issue and find your next story to read.
I have been thinking about this word and its overtones since reading All Fours , the second novel by the idiosyncratic interdisciplinary artist Miranda July, probably best known for her work as a filmmaker . As I made my way through the book, I kept remarking to myself, and writing in the margins, “This is so weird.” That’s not a bad thing, in my personal lexicon, though in this instance I was registering a persistent feeling of bafflement. July’s middle-aged protagonist—a “semi-famous” artist known for her early multi-genre success (who, like July, has worked across film, writing, and performance)—consistently acted on instincts I didn’t understand and made choices I couldn’t imagine anyone making. As a narrator, she was not just unreliable but unpredictable, unsettling, shimmeringly strange.
Read: Miranda July on ‘Kajillionaire’ and nice people in Hollywood
This unnamed narrator—who, being a wry Los Angeles creative type, enjoys half-mockingly noting that she is a minor celebrity—is perplexing even to herself. Stalled out in her art practice and dissatisfied in her marriage (stable, loving, stale) to a music producer, she decides to drive to New York, leaving him and their young child behind for three weeks. She conceives the trip ostensibly to prove a point. At a party, her husband offhandedly suggests that people fall into two personality types: Drivers and Parkers. Drivers can immerse themselves in the ongoingness of life; they enjoy time with their children and pets; they’re good on road trips because they’re present and steady. Parkers “need a discrete task that seems impossible, something that takes every bit of focus and for which they might receive applause,” or they lapse into boredom and disappointment. The artist feels that she is being pegged as a Parker, and undertakes this road trip, she tells herself, to “finally become the sort of chill, grounded woman I’d always wanted to be.” That this is overly literal and somewhat illogical—leaving your family for three weeks doesn’t suggest a willingness to be present in daily ongoingness and child-rearing—doesn’t occur to her.
But even the artist is aware that this classic plot—a combination of the American road trip and the midlife crisis , both clichéd subgenres of the quest narrative—is the kind of trope that she typically wouldn’t bother with. Naturally, the road trip, and by extension the novel, goes sideways immediately. July herself has never been given to making chill, grounded art.
The narrator hasn’t gotten an hour away from her house before she makes eye contact with a young man at a gas station in Monrovia. A few minutes later, they run into each other at a nearby restaurant, and as they talk, he mentions that he works at Hertz and that he and his interior-decorator wife are trying to save $20,000 as a “nest egg.” For no discernible reason, the narrator proceeds to drive first to one of his Hertz locations and then to a dingy motel, where she rents a room. Soon after, she commissions the wife (without mentioning her encounter with the husband) to redecorate the motel room to look like a room at Le Bristol hotel, in Paris, for a fee of $20,000.

Is she stalking the Hertz guy, nearly 15 years her junior? Is this an art project? Whether July is presenting this as an earnest hero’s journey or as a self-skewering satire of the free spirit who does erratic things upon hitting her mid-40s and calls it art isn’t clear. That may sound like a huge flaw in the novel, and it does sometimes feel like a glitch, yet the ambiguity about what July and her narrator are up to makes the novel as intriguing as it is frustrating. July thwarts the reader’s instinct to decipher whether this is a narrative about miraculous fate or one about an odd character’s mundane sexual and hormonal odyssey. Instead, she writes as though there’s no difference.
I ’m not the first to be cheerfully confounded by July’s oeuvre, which amounts to a multipronged investigation of alienation from what the world sees as “normal.” Critics have often dismissively described her enterprise as “twee,” likely because she is fashionable and somewhat affectless, and her work features West Coast oddballs who blend quirkiness and borderline erotic perversity. Stylistically, she rides the line between deadpan humor and earnest absurdity. To take a representative example, in the first of her three feature-length films, Me and You and Everyone We Know (2005), a young video artist (played by July) fixates on a man whose wife has left him, and who recently set one of his hands on fire in an ill-conceived stunt to impress their children; secondary plotlines involve a middle-aged man leaving sexually explicit messages for two teen girls, and a woman planning to meet an internet stranger in the park after being titillated by his suggestion that they “poop back and forth” forever.
All of her projects, which revolve around a sort of randomness and mystery, probe shame and estrangement, but with a tonal lightness. “Who really knows why anyone does anything?” the narrator of All Fours remarks before she embarks on her zany motel-redecoration project. “Nobody knows what’s going on. We are thrown across our lives by winds that started blowing millions of years ago.” This aimlessness, her attunement to randomness, is entwined with her creativity. Yet as she keeps riffing, the narrator drifts toward a formulation of her experiment that’s more specific and ennobled, borrowing from feminist politics.
What kind of monster makes a big show of going away and then hides out right nearby? But this was no good, this line of thought. This was the thinking that had kept every woman from her greatness. There did not have to be an answer to the question why; everything important started out mysterious and this mystery was like a great sea you had to be brave enough to cross. How many times had I turned back at the first ripple of self-doubt? You had to withstand a profound sense of wrongness if you ever wanted to get somewhere new. So far each thing I had done in Monrovia was guided by a version of me that had never been in charge before. A nitwit? A madwoman? Probably. But my more seasoned parts just had to be patient, hold their tongues—their many and sharp tongues—and give this new girl a chance.
The appearance of the word monster comes as no surprise here. The female artist who does battle with what Virginia Woolf called “the Angel in the House” and leaves home to accomplish something inscrutable to her family and society at large still seems obligated to reckon with whether this act is horrific. As the critic Lauren Elkin observes in her recent book, Art Monsters , the impulse to demonize women who refuse domesticity in favor of creative exploration goes back hundreds of years (at least). So does the female artist’s own willingness to wonder whether her impulses are reprehensible .
July’s artist is consciously pushing back against this legacy here—she will not be kept from her greatness!—while July herself seems also to be lightly ridiculing the way her character’s politically enlightened logic is leading her into a foolish, perhaps unjustifiable set of actions. Her ghost self travels onward—she keeps track of where she should be, dutifully reporting home about the sights she isn’t seeing—while she remains installed in a Louis XIV–style motel room, where she is not busy making great art. Instead, she is masturbating furiously, overwhelmed with desire for a married stranger. This behavior is not monstrous, but it is wayward— weyward being an early spelling of weird .
Except that in a sense, it isn’t weyward at all: The narrator’s behavior (her erraticism, even her eroticism) is right on schedule. She has entered perimenopause , when estrogen levels begin to zigzag. This Rumspringa of hers is less about artistic evolution than the bewilderments of hormonal flux and (in her case) the problem of fitting wild, outsize desire into a life of monogamy, heterosexuality, and parenthood. Her yearnings converge: She wants to become more embodied, more honest and self-accepting, and creatively free—a state that she doesn’t entirely believe is possible. Her sexual awakening, experienced just as she’s learning that she’s likely nearing the end of her high-libido years, is baffling, transcendent, and abject. “This kind of desire made a wound you just had to carry with you for the rest of your life. But this was still better than never knowing.”
From the December 2014 issue: The real roots of midlife crisis
Continuing her old life now seems unbearable; leaving it behind is unthinkable. Whether as a woman, a wife, or an artist, July’s narrator has never, as yet, been an integrated person, believing instead in selectively presenting others with different selves, “each real, each with different needs.” For her, “the only dangerous lie was one that asked me to compress myself down into a single convenient entity that one person could understand.” And yet she still dreams of intimacy, of having a self that can be wholly expressed and held by another. “One fine day I would tell him all about me,” she fantasizes, thinking of her husband, “and this trip would be one of my stories. We would be holding each other in bed, saying everything, laughing and crying and being amazed at all the things we didn’t know about each other, the Great Reveal.”
The perimenopausal plotline—easily dismissed as niche and sentimental, unlike its cousin, the plotline of male midlife crisis—may in fact be the perfect form for July, who turns it into something appropriately whimsical and stark. She writes this hormonal crucible so well in part because she seems already positioned to capture precisely how heightened, bizarre, off-putting, confusing, absurd it is; these elements are the hallmarks of her style. In this context, the tone that might have been dismissed as irony or caprice in earlier work takes on a kind of embodied, material plausibility: “I was a throbbing, amorphous ball of light trying to get my head around a motherly, wifely human form,” the narrator reports with true desperation after returning home. What she has found in Monrovia may be weird, but it is also her weird—transgressiveness in search of honest intimacy, performative selfhood in search of authentic freedom. If this truest, weirdest self cannot be contained in the family structure or the social world that she occupies, perhaps breaking that structure counts as creative liberation.
Perimenopause, as the narrator experiences it, is a profound betrayal in that it begins transporting her into crone-hood without her consent, before she is ready. At the same time, the crone, the weird sister, is afforded proximity to the transporting, the repugnant, the queer, the prophetic. This is good for art, or it can be. In one climactic scene of the book—a sort of symbolic consummation with her future self—the artist has sex with an older woman with a connection to the Hertz attendant. “Her skin was beginning to thin with age, like a banana’s, but instead of being gross it felt incredible, velvety warm water. Well, knock me over with a feather , I thought.” After the encounter, in an epiphanic haze, she feels certain that promiscuity is the secret to life. This mania, as July renders it, is both completely earnest and totally laughable—a trademark tension in July’s work since her 20s.
Later, her narrator mulls:
I felt untethered from my age and femininity and thus swimming in great new swaths of freedom and time. One might shift again and again like this, through intimacies, and not outpace oldness exactly, but match its weirdness, its flagrant specificity, with one’s own.
Here, finally, she arrives at something that looks like a viable future, though after her return home from Monrovia, the book loses the fevered outlandishness that July achieves at its apex. The back half of the novel depends largely on an experiment with polyamory, presented as edgy, but an angsty middle-aged artist curing her ennui with an escapist lesbian affair is hardly radical. This delivers its share of tragicomic setbacks—and a banal, if true, realization that “the point was to keep going without a comprehensible end in sight.”
In Art Monsters , Elkin quotes an essay in which Woolf characterizes the two primary obstacles in her writing life: “The first—killing the Angel in the House—I think I solved. She died. But the second, telling the truth about my own experiences as a body, I do not think I solved. I doubt that any woman has solved it yet.” July frantically disassembles Woolf’s Angel in All Fours , without quite solving Woolf’s second challenge. (Has anyone?) Yet her entry into the canon of attempts to capture that truth, in all its flagrant specificity, is one only she could have produced: fascinating, jarringly funny, sometimes repellent, and strangely powerful.
This article appears in the June 2024 print edition with the headline “Miranda July’s Weird Road Trip.”
When you buy a book using a link on this page, we receive a commission. Thank you for supporting The Atlantic.
When did the U.S. Enter WWII? Examining the Factors Leading to America’s Involvement in the Global Conflict
This essay about the United States’ entry into World War II explores the significant factors that prompted its shift from isolationism to active involvement. It traces the historical context from post-World War I through the economic, political, and social conditions leading up to the Pearl Harbor attack, which catalyzed the U.S. declaration of war. The discussion highlights the multifaceted reasons behind this pivotal decision, including economic revival, the rise of totalitarian threats, and the broader implications for American security and democratic values.
How it works
In the broad narrative of history, the momentous decision for the United States to enter World War II stands as a deeply significant event. It represents a critical turning point where a nation previously on the margins of a global conflict stepped into a central role, influenced by a complex interplay of domestic and international factors.
The roots of American participation in World War II trace back to the aftermath of World War I. The Treaty of Versailles in 1919 had profound impacts on Europe, levying harsh penalties on Germany and planting the seeds for future unrest.
Meanwhile, the United States enjoyed an economic boom in the Roaring Twenties, but moved towards isolationism, disillusioned by the devastation of the earlier war and hesitant to engage in overseas disputes.
However, the rise of authoritarian regimes in Europe and Asia gradually cast a larger shadow worldwide. Adolf Hitler’s aggressive expansionism, along with Japan’s imperialist aims, signaled the brewing of a significant ideological and territorial conflict. Hitler’s bold takeover of Austria in 1938 and his moves into Czechoslovakia were clear signs of looming danger. In Asia, Japan’s advances into Manchuria and China indicated rising tensions that threatened to draw in more nations.
The conflict escalated with Germany’s invasion of Poland in September 1939, forcing the U.S. to confront a moral dilemma. While President Franklin D. Roosevelt initially supported the Allies through the Lend-Lease Act, providing crucial military aid, the prospect of entering another foreign conflict weighed heavily on the American public.
The decisive moment came with Japan’s unexpected attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941. This attack devastated the U.S. Pacific Fleet and abruptly ended any remaining sentiment for isolationism, compelling the U.S. into the war. President Roosevelt’s forceful address to Congress immediately after the attack unified the nation in a resolute declaration of war against Japan.
Entering the war was not merely a response to Pearl Harbor; it was the culmination of various factors that had gradually eroded isolationist tendencies, pushing the U.S. towards involvement. Economically, the war represented both a challenge and an opportunity. The ongoing impact of the Great Depression had deeply affected the nation, but the war effort kickstarted massive industrial mobilization, revitalizing the economy and ushering in a period of significant growth and prosperity.
Politically, the threat posed by totalitarian regimes was a direct challenge to democratic values. The horrific acts committed by Nazi Germany, especially the Holocaust, highlighted the urgent need to confront such tyranny.
On an international scale, the U.S. realized its security and future were closely linked to the outcome of the war. Supporting the Allies was not just a matter of ideology but a strategic imperative to maintain global stability and protect national interests.
Socially, the war effort became a unifying force, breaking down longstanding barriers among different races, genders, and social classes. The diverse contributions to the war effort helped to foster a new spirit of inclusivity and equality.
In conclusion, the U.S. entry into World War II is more than just a date; it is a story of transformation and determination. Emerging from the tragedy of Pearl Harbor, the U.S. became a nation fundamentally altered, united by the shared experience of war and committed to defending freedom against the darkness of tyranny and oppression.
Cite this page
When Did the U.S. Enter WWII? Examining the Factors Leading to America's Involvement in the Global Conflict. (2024, May 12). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/when-did-the-u-s-enter-wwii-examining-the-factors-leading-to-americas-involvement-in-the-global-conflict/
"When Did the U.S. Enter WWII? Examining the Factors Leading to America's Involvement in the Global Conflict." PapersOwl.com , 12 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/when-did-the-u-s-enter-wwii-examining-the-factors-leading-to-americas-involvement-in-the-global-conflict/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). When Did the U.S. Enter WWII? Examining the Factors Leading to America's Involvement in the Global Conflict . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/when-did-the-u-s-enter-wwii-examining-the-factors-leading-to-americas-involvement-in-the-global-conflict/ [Accessed: 12 May. 2024]
"When Did the U.S. Enter WWII? Examining the Factors Leading to America's Involvement in the Global Conflict." PapersOwl.com, May 12, 2024. Accessed May 12, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/when-did-the-u-s-enter-wwii-examining-the-factors-leading-to-americas-involvement-in-the-global-conflict/
"When Did the U.S. Enter WWII? Examining the Factors Leading to America's Involvement in the Global Conflict," PapersOwl.com , 12-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/when-did-the-u-s-enter-wwii-examining-the-factors-leading-to-americas-involvement-in-the-global-conflict/. [Accessed: 12-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). When Did the U.S. Enter WWII? Examining the Factors Leading to America's Involvement in the Global Conflict . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/when-did-the-u-s-enter-wwii-examining-the-factors-leading-to-americas-involvement-in-the-global-conflict/ [Accessed: 12-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
While transition words are essential to clear writing, it's possible to use too many of them. Consider the following example, in which the overuse of linking words slows down the text and makes it feel repetitive. The first experiment yielded a positive result. However, the second experiment yielded a negative result.
50 linking words to use in academic writing. academic writing. linkers. essay writing. thesis. ESL. English. It's very common for students to use long words they don't understand very well in their essays and theses because they have a certain idea of what academic writing should be.
Transitional words and phrases can create powerful links between ideas in your paper and can help your reader understand the logic of your paper. However, these words all have different meanings, nuances, and connotations. Before using a particular transitional word in your paper, be sure you understand its meaning and usage completely and be sure…
Level Up Your Team. See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. Transition words are useful for all types of writers. Whether you're attempting academic writing, blogging, speech writing, or writing fiction, transition words can help refine your text and create a narrative flow.
Linking words may help the reader understand additional comments or ideas in a statement. They may also express agreement or similarities. These words are also called additive transition words, commonly found in expository essays and narrative essays.
These transitional words (like finally) have the function of limiting, restricting, and defining time. They can be used either alone or as part of adverbial expressions. at the present time. from time to time. sooner or later. at the same time. up to the present time. to begin with.
Clear transitions are crucial to clear writing: They show the reader how different parts of your essay, paper, or thesis are connected. Transition sentences can be used to structure your text and link together paragraphs or sections. Example of a transition sentence for a new paragraph. In this case, the researchers concluded that the method ...
These words will help you with personal or narrative essays: They are linking words in opinion writing that indicates you're going to explore ideas in more detail. Expository essays will win with these words too. I mean. in explanation. in lay terms. to clearly define. to explain: in other words.
Transition Words and Phrases. Transitions are connecting words or phrases that strengthen the internal cohesion of your writing. Transition words tell the reader how one idea relates to another. Using them appropriately makes your argument more convincing because the reader is able to understand the flow between and within paragraphs, including ...
To join ideas and sentences, we use a number of connecting words and phrases. For example: Addition To add an idea. Additionally, and, also, apart from this, as well (as), in addition, moreover, further, furthermore. Condition to provide a condition. If, in that case, provided that, unless. For comparison To show how things are similar.
Transition Words/Phrases in Narrative Writing Transitional expressions can help tie ideas together. They also help your narrative flow from one paragraph or idea to the other. Try out a few in your paper. Be sure that any transition you use makes sense. The goal is to make your writing flow smoothly from sentence to sentence. After subsequently ...
Linking/Transition Words. Transitions link one main idea to another separated by a semi-colon or full-stop. When the transition word is at the beginning of the sentence, it should be followed by a comma: Among other functions, they can signal cause and effect or sequencing (see examples in the table below). Additional comments or ideas.
An extensive list of Transition Words and Phrases in English. They can be used at the start of new paragraphs in your essays. ... They can be used at the start of new paragraphs in your essays.
33 Transition Words and Phrases. 'Besides,' 'furthermore,' 'although,' and other words to help you jump from one idea to the next. Transitional terms give writers the opportunity to prepare readers for a new idea, connecting the previous sentence to the next one. Many transitional words are nearly synonymous: words that broadly indicate that ...
Linking words and phrases act as bridges between your ideas, helping to connect sentences and paragraphs in a way that makes your argument or narrative clear and easy to follow.
Down and Dirty Tips: Narrative and Descriptive Essays: Narrative Transitions. Tips for students on writing a Narrative / Descriptive essay. While this guide is not comprehensive, it does provide enough information for to students to follow and pass the assignment. This guide is especially helpful for those who don't have much time.
Sharing is caring! Linking words and phrases are used to show relationships between ideas. They can be used to join two or more sentences or clauses. We can use linking words to give a result, add information, summarize, give illustrations, emphasize a point, sequence information, compare or to contrast idea.
Use these worksheets to show how linking devices, such as phrases, clauses and time connectives, can help to link ideas in a narrative paragraph. This teaching resource include activities, such as: locating and underlining the linking devices within a narrative paragraph. building onto a sentence by adding a connecting phrase or clause.
4. That is to say. Usage: "That is" and "that is to say" can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: "Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.". 5. To that end. Usage: Use "to that end" or "to this end" in a similar way to "in order to" or "so".
The linking words list below is essential for IELTS writing task 2 for high score. The examiner needs to see a range of linking words in your essay to award you a high score for the criterion of Coherence and Cohesion which is 25% of your marks. You will be checked on your range, accuracy and your flexibility of linking words in IELTS writing ...
A narrative, at its essence, is a coherent sequence of events populated. Essay Example: Storytelling, an intrinsic human practice, transcends mere entertainment, embodying a profound method of communication that connects individuals, delineates cultures, and shapes our understanding of the world. A narrative, at its essence, is a coherent ...
Essay Example: Myths are the cultural bedrock of societies, pervasive narratives that give insight into the values, fears, and aspirations of the communities that cherish them. Far from being mere stories, myths serve as the complex connective tissue linking individuals with their cultural history
Narrative Introductions. The introduction of a narrative essay sets the scene for the story that follows. Interesting introductions—for any kind of writing—engage and draw readers in because they want to know more. Since narratives tell a story and involve events, the introduction of a narrative quite often starts in the middle of the ...
This essay about the fate of United Airlines Flight 93 contests the conspiracy theory that it was shot down by the U.S. military on September 11, 2001. It examines key points such as the widespread debris from the crash, the military's orders on that day, and eyewitness accounts, concluding that the evidence supports the official narrative.
It discusses the structure and purpose of Matthew, emphasizing its role in linking the Old and New Testaments and presenting Jesus as the fulfillment of Jewish prophecies. Highlighting key content such as the Sermon on the Mount, various parables, and miracles, the essay illustrates how these elements underscore Jesus' teachings and divine ...
The narrative outlines the Aztecs' transition from wanderers to empire builders, detailing their military prowess, strategic alliances, and innovative agricultural practices, like the chinampa system. It also explores the significant role of religion in Aztec society, which shaped their governance and cultural practices.
B ack when the word weird (or, in the spelling of the day, wyrd ) was first commonly used in English, it was not an adjective but a noun, and it functioned as a synonym for fate.A person wasn't ...
Essay Example: In the ongoing narrative of human existence, music remains an eternal guide, illuminating our complex emotional landscape. Among the myriad of tunes that accompany us on life's voyage, a song known as "Echoes of Resilience" uniquely touches the depths of our spirit, providing. Writing Service;
Essay Example: In the broad narrative of history, the momentous decision for the United States to enter World War II stands as a deeply significant event. It represents a critical turning point where a nation previously on the margins of a global conflict stepped into a central role, influenced. Writing Service;