

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to write a perfect synthesis essay for the ap language exam.
Advanced Placement (AP)

If you're planning to take the AP Language (or AP Lang) exam , you might already know that 55% of your overall exam score will be based on three essays. The first of the three essays you'll have to write on the AP Language exam is called the "synthesis essay." If you want to earn full points on this portion of the AP Lang Exam, you need to know what a synthesis essay is and what skills are assessed by the AP Lang synthesis essay.
In this article, we'll explain the different aspects of the AP Lang synthesis essay, including what skills you need to demonstrate in your synthesis essay response in order to achieve a good score. We'll also give you a full breakdown of a real AP Lang Synthesis Essay prompt, provide an analysis of an AP Lang synthesis essay example, and give you four tips for how to write a synthesis essay.
Let's get started by taking a closer look at how the AP Lang synthesis essay works!
Synthesis Essay AP Lang: What It Is and How It Works
The AP Lang synthesis essay is the first of three essays included in the Free Response section of the AP Lang exam.
The AP Lang synthesis essay portion of the Free Response section lasts for one hour total . This hour consists of a recommended 15 minute reading period and a 40 minute writing period. Keep in mind that these time allotments are merely recommendations, and that exam takers can parse out the allotted 60 minutes to complete the synthesis essay however they choose.
Now, here's what the structure of the AP Lang synthesis essay looks like. The exam presents six to seven sources that are organized around a specific topic (like alternative energy or eminent domain, which are both past synthesis exam topics).
Of these six to seven sources, at least two are visual , including at least one quantitative source (like a graph or pie chart, for example). The remaining four to five sources are print text-based, and each one contains approximately 500 words.
In addition to six to seven sources, the AP Lang exam provides a written prompt that consists of three paragraphs. The prompt will briefly explain the essay topic, then present a claim that students will respond to in an essay that synthesizes material from at least three of the sources provided.
Here's an example prompt provided by the College Board:
Directions : The following prompt is based on the accompanying six sources.
This question requires you to integrate a variety of sources into a coherent, well-written essay. Refer to the sources to support your position; avoid mere paraphrase or summary. Your argument should be central; the sources should support this argument .
Remember to attribute both direct and indirect citations.
Introduction
Television has been influential in United States presidential elections since the 1960's. But just what is this influence, and how has it affected who is elected? Has it made elections fairer and more accessible, or has it moved candidates from pursuing issues to pursuing image?
Read the following sources (including any introductory information) carefully. Then, in an essay that synthesizes at least three of the sources for support, take a position that defends, challenges, or qualifies the claim that television has had a positive impact on presidential elections.
Refer to the sources as Source A, Source B, etc.; titles are included for your convenience.
Source A (Campbell) Source B (Hart and Triece) Source C (Menand) Source D (Chart) Source E (Ranney) Source F (Koppel)
Like we mentioned earlier, this prompt gives you a topic — which it briefly explains — then asks you to take a position. In this case, you'll have to choose a stance on whether television has positively or negatively affected U.S. elections. You're also given six sources to evaluate and use in your response. Now that you have everything you need, now your job is to write an amazing synthesis essay.
But what does "synthesize" mean, exactly? According to the CollegeBoard, when an essay prompt asks you to synthesize, it means that you should "combine different perspectives from sources to form a support of a coherent position" in writing. In other words, a synthesis essay asks you to state your claim on a topic, then highlight the relationships between several sources that support your claim on that topic. Additionally, you'll need to cite specific evidence from your sources to prove your point.
The synthesis essay counts for six of the total points on the AP Lang exam . Students can receive 0-1 points for writing a thesis statement in the essay, 0-4 based on incorporation of evidence and commentary, and 0-1 points based on sophistication of thought and demonstrated complex understanding of the topic.
You'll be evaluated based on how effectively you do the following in your AP Lang synthesis essay:
Write a thesis that responds to the exam prompt with a defensible position
Provide specific evidence that to support all claims in your line of reasoning from at least three of the sources provided, and clearly and consistently explain how the evidence you include supports your line of reasoning
Demonstrate sophistication of thought by either crafting a thoughtful argument, situating the argument in a broader context, explaining the limitations of an argument
Make rhetorical choices that strengthen your argument and/or employ a vivid and persuasive style throughout your essay.
If your synthesis essay meets the criteria above, then there's a good chance you'll score well on this portion of the AP Lang exam!
If you're looking for even more information on scoring, the College Board has posted the AP Lang Free Response grading rubric on its website. ( You can find it here. ) We recommend taking a close look at it since it includes additional details about the synthesis essay scoring.

Don't be intimidated...we're going to teach you how to break down even the hardest AP synthesis essay prompt.
Full Breakdown of a Real AP Lang Synthesis Essay Prompt
In this section, we'll teach you how to analyze and respond to a synthesis essay prompt in five easy steps, including suggested time frames for each step of the process.
Step 1: Analyze the Prompt
The very first thing to do when the clock starts running is read and analyze the prompt. To demonstrate how to do this, we'll look at the sample AP Lang synthesis essay prompt below. This prompt comes straight from the 2018 AP Lang exam:
Eminent domain is the power governments have to acquire property from private owners for public use. The rationale behind eminent domain is that governments have greater legal authority over lands within their dominion than do private owners. Eminent domain has been instituted in one way or another throughout the world for hundreds of years.
Carefully read the following six sources, including the introductory information for each source. Then synthesize material from at least three of the sources and incorporate it into a coherent, well-developed essay that defends, challenges, or qualifies the notion that eminent domain is productive and beneficial.
Your argument should be the focus of your essay. Use the sources to develop your argument and explain the reasoning for it. Avoid merely summarizing the sources. Indicate clearly which sources you are drawing from, whether through direct quotation, paraphrase, or summary. You may cite the sources as Source A, Source B, etc., or by using the descriptions in parentheses.
On first read, you might be nervous about how to answer this prompt...especially if you don't know what eminent domain is! But if you break the prompt down into chunks, you'll be able to figure out what the prompt is asking you to do in no time flat.
To get a full understanding of what this prompt wants you to do, you need to identify the most important details in this prompt, paragraph by paragraph. Here's what each paragraph is asking you to do:
- Paragraph 1: The prompt presents and briefly explains the topic that you'll be writing your synthesis essay about. That topic is the concept of eminent domain.
- Paragraph 2: The prompt presents a specific claim about the concept of eminent domain in this paragraph: Eminent domain is productive and beneficial. This paragraph instructs you to decide whether you want to defend, challenge, or qualify that claim in your synthesis essay , and use material from at least three of the sources provided in order to do so.
- Paragraph 3: In the last paragraph of the prompt, the exam gives you clear instructions about how to approach writing your synthesis essay . First, make your argument the focus of the essay. Second, use material from at least three of the sources to develop and explain your argument. Third, provide commentary on the material you include, and provide proper citations when you incorporate quotations, paraphrases, or summaries from the sources provided.
So basically, you'll have to agree with, disagree with, or qualify the claim stated in the prompt, then use at least three sources substantiate your answer. Since you probably don't know much about eminent domain, you'll probably decide on your position after you read the provided sources.
To make good use of your time on the exam, you should spend around 2 minutes reading the prompt and making note of what it's asking you to do. That will leave you plenty of time to read the sources provided, which is the next step to writing a synthesis essay.
Step 2: Read the Sources Carefully
After you closely read the prompt and make note of the most important details, you need to read all of the sources provided. It's tempting to skip one or two sources to save time--but we recommend you don't do this. That's because you'll need a thorough understanding of the topic before you can accurately address the prompt!
For the sample exam prompt included above, there are six sources provided. We're not going to include all of the sources in this article, but you can view the six sources from this question on the 2018 AP Lang exam here . The sources include five print-text sources and one visual source, which is a cartoon.
As you read the sources, it's important to read quickly and carefully. Don't rush! Keep your pencil in hand to quickly mark important passages that you might want to use as evidence in your synthesis. While you're reading the sources and marking passages, you want to think about how the information you're reading influences your stance on the issue (in this case, eminent domain).
When you finish reading, take a few seconds to summarize, in a phrase or sentence, whether the source defends, challenges, or qualifies whether eminent domain is beneficial (which is the claim in the prompt) . Though it might not feel like you have time for this, it's important to give yourself these notes about each source so you know how you can use each one as evidence in your essay.
Here's what we mean: say you want to challenge the idea that eminent domain is useful. If you've jotted down notes about each source and what it's saying, it will be easier for you to pull the relevant information into your outline and your essay.
So how much time should you spend reading the provided sources? The AP Lang exam recommends taking 15 minutes to read the sources . If you spend around two of those minutes reading and breaking down the essay prompt, it makes sense to spend the remaining 13 minutes reading and annotating the sources.
If you finish reading and annotating early, you can always move on to drafting your synthesis essay. But make sure you're taking your time and reading carefully! It's better to use a little extra time reading and understanding the sources now so that you don't have to go back and re-read the sources later.
A strong thesis will do a lot of heavy lifting in your essay. (See what we did there?)
Step 3: Write a Strong Thesis Statement
After you've analyzed the prompt and thoroughly read the sources, the next thing you need to do in order to write a good synthesis essay is write a strong thesis statement .
The great news about writing a thesis statement for this synthesis essay is that you have all the tools you need to do it at your fingertips. All you have to do in order to write your thesis statement is decide what your stance is in relationship to the topic provided.
In the example prompt provided earlier, you're essentially given three choices for how to frame your thesis statement: you can either defend, challenge, or qualify a claim that's been provided by the prompt, that eminent domain is productive and beneficial . Here's what that means for each option:
If you choose to defend the claim, your job will be to prove that the claim is correct . In this case, you'll have to show that eminent domain is a good thing.
If you choose to challenge the claim, you'll argue that the claim is incorrect. In other words, you'll argue that eminent domain isn't productive or beneficial.
If you choose to qualify, that means you'll agree with part of the claim, but disagree with another part of the claim. For instance, you may argue that eminent domain can be a productive tool for governments, but it's not beneficial for property owners. Or maybe you argue that eminent domain is useful in certain circumstances, but not in others.
When you decide whether you want your synthesis essay to defend, challenge, or qualify that claim, you need to convey that stance clearly in your thesis statement. You want to avoid simply restating the claim provided in the prompt, summarizing the issue without making a coherent claim, or writing a thesis that doesn't respond to the prompt.
Here's an example of a thesis statement that received full points on the eminent domain synthesis essay:
Although eminent domain can be misused to benefit private interests at the expense of citizens, it is a vital tool of any government that intends to have any influence on the land it governs beyond that of written law.
This thesis statement received full points because it states a defensible position and establishes a line of reasoning on the issue of eminent domain. It states the author's position (that some parts of eminent domain are good, but others are bad), then goes on to explain why the author thinks that (it's good because it allows the government to do its job, but it's bad because the government can misuse its power.)
Because this example thesis statement states a defensible position and establishes a line of reasoning, it can be elaborated upon in the body of the essay through sub-claims, supporting evidence, and commentary. And a solid argument is key to getting a six on your synthesis essay for AP Lang!

Step 4: Create a Bare-Bones Essay Outline
Once you've got your thesis statement drafted, you have the foundation you need to develop a bare bones outline for your synthesis essay. Developing an outline might seem like it's a waste of your precious time, but if you develop your outline well, it will actually save you time when you start writing your essay.
With that in mind, we recommend spending 5 to 10 minutes outlining your synthesis essay . If you use a bare-bones outline like the one below, labeling each piece of content that you need to include in your essay draft, you should be able to develop out the most important pieces of the synthesis before you even draft the actual essay.
To help you see how this can work on test day, we've created a sample outline for you. You can even memorize this outline to help you out on test day! In the outline below, you'll find places to fill in a thesis statement, body paragraph topic sentences, evidence from the sources provided, and commentary :
- Present the context surrounding the essay topic in a couple of sentences (this is a good place to use what you learned about the major opinions or controversies about the topic from reading your sources).
- Write a straightforward, clear, and concise thesis statement that presents your stance on the topic
- Topic sentence presenting first supporting point or claim
- Evidence #1
- Commentary on Evidence #1
- Evidence #2 (if needed)
- Commentary on Evidence #2 (if needed)
- Topic sentence presenting second supporting point or claim
- Topic sentence presenting three supporting point or claim
- Sums up the main line of reasoning that you developed and defended throughout the essay
- Reiterates the thesis statement
Taking the time to develop these crucial pieces of the synthesis in a bare-bones outline will give you a map for your final essay. Once you have a map, writing the essay will be much easier.
Step 5: Draft Your Essay Response
The great thing about taking a few minutes to develop an outline is that you can develop it out into your essay draft. After you take about 5 to 10 minutes to outline your synthesis essay, you can use the remaining 30 to 35 minutes to draft your essay and review it.
Since you'll outline your essay before you start drafting, writing the essay should be pretty straightforward. You'll already know how many paragraphs you're going to write, what the topic of each paragraph will be, and what quotations, paraphrases, or summaries you're going to include in each paragraph from the sources provided. You'll just have to fill in one of the most important parts of your synthesis—your commentary.
Commentaries are your explanation of why your evidence supports the argument you've outlined in your thesis. Your commentary is where you actually make your argument, which is why it's such a critical part of your synthesis essay.
When thinking about what to say in your commentary, remember one thing the AP Lang synthesis essay prompt specifies: don't just summarize the sources. Instead, as you provide commentary on the evidence you incorporate, you need to explain how that evidence supports or undermines your thesis statement . You should include commentary that offers a thoughtful or novel perspective on the evidence from your sources to develop your argument.
One very important thing to remember as you draft out your essay is to cite your sources. The AP Lang exam synthesis essay prompt indicates that you can use generic labels for the sources provided (e.g. "Source 1," "Source 2," "Source 3," etc.). The exam prompt will indicate which label corresponds with which source, so you'll need to make sure you pay attention and cite sources accurately. You can cite your sources in the sentence where you introduce a quote, summary, or paraphrase, or you can use a parenthetical citation. Citing your sources affects your score on the synthesis essay, so remembering to do this is important.

Keep reading for a real-life example of a great AP synthesis essay response!
Real-Life AP Synthesis Essay Example and Analysis
If you're still wondering how to write a synthesis essay, examples of real essays from past AP Lang exams can make things clearer. These real-life student AP synthesis essay responses can be great for helping you understand how to write a synthesis essay that will knock the graders' socks off .
While there are multiple essay examples online, we've chosen one to take a closer look at. We're going to give you a brief analysis of one of these example student synthesis essays from the 2019 AP Lang Exam below!
Example Synthesis Essay AP Lang Response
To get started, let's look at the official prompt for the 2019 synthesis essay:
In response to our society's increasing demand for energy, large-scale wind power has drawn attention from governments and consumers as a potential alternative to traditional materials that fuel our power grids, such as coal, oil, natural gas, water, or even newer sources such as nuclear or solar power. Yet the establishment of large-scale, commercial-grade wind farms is often the subject of controversy for a variety of reasons.
Carefully read the six sources, found on the AP English Language and Composition 2019 Exam (Question 1), including the introductory information for each source. Write an essay that synthesizes material from at least three of the sources and develops your position on the most important factors that an individual or agency should consider when deciding whether to establish a wind farm.
Source A (photo) Source B (Layton) Source C (Seltenrich) Source D (Brown) Source E (Rule) Source F (Molla)
In your response you should do the following:
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis presents a defensible position.
- Select and use evidence from at least 3 of the provided sources to support your line of reasoning. Indicate clearly the sources used through direct quotation, paraphrase, or summary. Sources may be cited as Source A, Source B, etc., or by using the description in parentheses.
- Explain how the evidence supports your line of reasoning.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating your argument.
Now that you know exactly what the prompt asked students to do on the 2019 AP Lang synthesis essay, here's an AP Lang synthesis essay example, written by a real student on the AP Lang exam in 2019:
[1] The situation has been known for years, and still very little is being done: alternative power is the only way to reliably power the changing world. The draw of power coming from industry and private life is overwhelming current sources of non-renewable power, and with dwindling supplies of fossil fuels, it is merely a matter of time before coal and gas fuel plants are no longer in operation. So one viable alternative is wind power. But as with all things, there are pros and cons. The main factors for power companies to consider when building wind farms are environmental boon, aesthetic, and economic factors.
[2] The environmental benefits of using wind power are well-known and proven. Wind power is, as qualified by Source B, undeniably clean and renewable. From their production requiring very little in the way of dangerous materials to their lack of fuel, besides that which occurs naturally, wind power is by far one of the least environmentally impactful sources of power available. In addition, wind power by way of gearbox and advanced blade materials, has the highest percentage of energy retention. According to Source F, wind power retains 1,164% of the energy put into the system – meaning that it increases the energy converted from fuel (wind) to electricity 10 times! No other method of electricity production is even half that efficient. The efficiency and clean nature of wind power are important to consider, especially because they contribute back to power companies economically.
[3] Economically, wind power is both a boon and a bone to electric companies and other users. For consumers, wind power is very cheap, leading to lower bills than from any other source. Consumers also get an indirect reimbursement by way of taxes (Source D). In one Texan town, McCamey, tax revenue increased 30% from a wind farm being erected in the town. This helps to finance improvements to the town. But, there is no doubt that wind power is also hurting the power companies. Although, as renewable power goes, wind is incredibly cheap, it is still significantly more expensive than fossil fuels. So, while it is helping to cut down on emissions, it costs electric companies more than traditional fossil fuel plants. While the general economic trend is positive, there are some setbacks which must be overcome before wind power can take over as truly more effective than fossil fuels.
[4] Aesthetics may be the greatest setback for power companies. Although there may be significant economic and environmental benefit to wind power, people will always fight to preserve pure, unspoiled land. Unfortunately, not much can be done to improve the visual aesthetics of the turbines. White paint is the most common choice because it "[is] associated with cleanliness." (Source E). But, this can make it stand out like a sore thumb, and make the gargantuan machines seem more out of place. The site can also not be altered because it affects generating capacity. Sound is almost worse of a concern because it interrupts personal productivity by interrupting people's sleep patterns. One thing for power companies to consider is working with turbine manufacturing to make the machines less aesthetically impactful, so as to garner greater public support.
[5] As with most things, wind power has no easy answer. It is the responsibility of the companies building them to weigh the benefits and the consequences. But, by balancing economics, efficiency, and aesthetics, power companies can create a solution which balances human impact with environmental preservation.
And that's an entire AP Lang synthesis essay example, written in response to a real AP Lang exam prompt! It's important to remember AP Lang exam synthesis essay prompts are always similarly structured and worded, and students often respond in around the same number of paragraphs as what you see in the example essay response above.
Next, let's analyze this example essay and talk about what it does effectively, where it could be improved upon, and what score past exam scorers awarded it.
To get started on an analysis of the sample synthesis essay, let's look at the scoring commentary provided by the College Board:
- For development of thesis, the essay received 1 out of 1 possible points
- For evidence and commentary, the essay received 4 out of 4 possible points
- For sophistication of thought, the essay received 0 out of 1 possible points.
This means that the final score for this example essay was a 5 out of 6 possible points . Let's look more closely at the content of the example essay to figure out why it received this score breakdown.
Thesis Development
The thesis statement is one of the three main categories that is taken into consideration when you're awarded points on this portion of the exam. This sample essay received 1 out of 1 total points.
Now, here's why: the thesis statement clearly and concisely conveys a position on the topic presented in the prompt--alternative energy and wind power--and defines the most important factors that power companies should consider when deciding whether to establish a wind farm.
Evidence and Commentary
The second key category taken into consideration when synthesis exams are evaluated is incorporation of evidence and commentary. This sample received 4 out of 4 possible points for this portion of the synthesis essay. At bare minimum, this sample essay meets the requirement mentioned in the prompt that the writer incorporate evidence from at least three of the sources provided.
On top of that, the writer does a good job of connecting the incorporated evidence back to the claim made in the thesis statement through effective commentary. The commentary in this sample essay is effective because it goes beyond just summarizing what the provided sources say. Instead, it explains and analyzes the evidence presented in the selected sources and connects them back to supporting points the writer makes in each body paragraph.
Finally, the writer of the essay also received points for evidence and commentary because the writer developed and supported a consistent line of reasoning throughout the essay . This line of reasoning is summed up in the fourth paragraph in the following sentence: "One thing for power companies to consider is working with turbine manufacturing to make the machines less aesthetically impactful, so as to garner greater public support."
Because the writer did a good job consistently developing their argument and incorporating evidence, they received full marks in this category. So far, so good!
Sophistication of Thought
Now, we know that this essay received a score of 5 out of 6 total points, and the place where the writer lost a point was on the basis of sophistication of thought, for which the writer received 0 out of 1 points. That's because this sample essay makes several generalizations and vague claims where it could have instead made specific claims that support a more balanced argument.
For example, in the following sentence from the 5th paragraph of the sample essay, the writer misses the opportunity to state specific possibilities that power companies should consider for wind energy . Instead, the writer is ambiguous and non-committal, saying, "As with most things, wind power has no easy answer. It is the responsibility of the companies building them to weigh the benefits and consequences."
If the writer of this essay was interested in trying to get that 6th point on the synthesis essay response, they could consider making more specific claims. For instance, they could state the specific benefits and consequences power companies should consider when deciding whether to establish a wind farm. These could include things like environmental impacts, economic impacts, or even population density!
Despite losing one point in the last category, this example synthesis essay is a strong one. It's well-developed, thoughtfully written, and advances an argument on the exam topic using evidence and support throughout.

4 Tips for How to Write a Synthesis Essay
AP Lang is a timed exam, so you have to pick and choose what you want to focus on in the limited time you're given to write the synthesis essay. Keep reading to get our expert advice on what you should focus on during your exam.
Tip 1: Read the Prompt First
It may sound obvious, but when you're pressed for time, it's easy to get flustered. Just remember: when it comes time to write the synthesis essay, read the prompt first !
Why is it so important to read the prompt before you read the sources? Because when you're aware of what kind of question you're trying to answer, you'll be able to read the sources more strategically. The prompt will help give you a sense of what claims, points, facts, or opinions to be looking for as you read the sources.
Reading the sources without having read the prompt first is kind of like trying to drive while wearing a blindfold: you can probably do it, but it's likely not going to end well!
Tip 2: Make Notes While You Read
During the 15-minute reading period at the beginning of the synthesis essay, you'll be reading through the sources as quickly as you can. After all, you're probably anxious to start writing!
While it's definitely important to make good use of your time, it's also important to read closely enough that you understand your sources. Careful reading will allow you to identify parts of the sources that will help you support your thesis statement in your essay, too.
As you read the sources, consider marking helpful passages with a star or check mark in the margins of the exam so you know which parts of the text to quickly re-read as you form your synthesis essay. You might also consider summing up the key points or position of each source in a sentence or a few words when you finish reading each source during the reading period. Doing so will help you know where each source stands on the topic given and help you pick the three (or more!) that will bolster your synthesis argument.
Tip 3: Start With the Thesis Statement
If you don't start your synthesis essay with a strong thesis statement, it's going to be tough to write an effective synthesis essay. As soon as you finish reading and annotating the provided sources, the thing you want to do next is write a strong thesis statement.
According to the CollegeBoard grading guidelines for the AP Lang synthesis essay, a strong thesis statement will respond to the prompt— not restate or rephrase the prompt. A good thesis will take a clear, defensible position on the topic presented in the prompt and the sources.
In other words, to write a solid thesis statement to guide the rest of your synthesis essay, you need to think about your position on the topic at hand and then make a claim about the topic based on your position. This position will either be defending, challenging, or qualifying the claim made in the essay's prompt.
The defensible position that you establish in your thesis statement will guide your argument in the rest of the essay, so it's important to do this first. Once you have a strong thesis statement, you can begin outlining your essay.
Tip 4: Focus on Your Commentary
Writing thoughtful, original commentary that explains your argument and your sources is important. In fact, doing this well will earn you four points (out of a total of six)!
AP Lang provides six to seven sources for you on the exam, and you'll be expected to incorporate quotations, paraphrases, or summaries from at least three of those sources into your synthesis essay and interpret that evidence for the reader.
While incorporating evidence is very important, in order to get the extra point for "sophistication of thought" on the synthesis essay, it's important to spend more time thinking about your commentary on the evidence you choose to incorporate. The commentary is your chance to show original thinking, strong rhetorical skills, and clearly explain how the evidence you've included supports the stance you laid out in your thesis statement.
To earn the 6th possible point on the synthesis essay, make sure your commentary demonstrates a nuanced understanding of the source material, explains this nuanced understanding, and places the evidence incorporated from the sources in conversation with each other. To do this, make sure you're avoiding vague language. Be specific when you can, and always tie your commentary back to your thesis!

What's Next?
There's a lot more to the AP Language exam than just the synthesis essay. Be sure to check out our expert guide to the entire exam , then learn more about the tricky multiple choice section .
Is the AP Lang exam hard...or is it easy? See how it stacks up to other AP tests on our list of the hardest AP exams .
Did you know there are technically two English AP exams? You can learn more about the second English AP test, the AP Literature exam, in this article . And if you're confused about whether you should take the AP Lang or AP Lit test , we can help you make that decision, too.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis Essay + Example
Do you know how to improve your profile for college applications.
See how your profile ranks among thousands of other students using CollegeVine. Calculate your chances at your dream schools and learn what areas you need to improve right now — it only takes 3 minutes and it's 100% free.
Show me what areas I need to improve
What’s Covered:
What is the ap lang synthesis essay, how will ap scores affect my college chances.
AP English Language and Composition, commonly known as AP Lang, is one of the most engaging and popular AP classes offered at most high schools, with over 535,000 students taking the class . AP Lang tests your ability to analyze written pieces, synthesize information, write rhetorical essays, and create cohesive and concrete arguments. However, the class is rather challenging as only 62% of students were able to score a three or higher on the exam.
The AP Lang exam has two sections. The first consists of 45 multiple choice questions which need to be completed in an hour. This portion counts for around 45% of your total score. These questions ask students to analyze written pieces and answer questions related to each respective passage. All possible answer choices can be found within the text, and no prior knowledge of literature is needed to understand the passages.
The second section contains three free-response questions to be finished in under two hours and 15 minutes. This section counts for 55% of your score and includes the synthesis essay, the rhetorical essay, and the argumentative essay.
- The synthesis essay requires you to read 6-7 sources and create an argument using at least three sources.
- The rhetorical analysis essay requires you to describe how a piece of writing evokes specific meanings and symbolism.
- The argumentative essay requires you to pick a perspective of a debate and create an argument based on the evidence provided.
In this post, we will take a look at the AP Lang synthesis essay and discuss tips and tricks to master this part of the exam. We will also provide an example of a well-written essay for review.
The AP Lang synthesis essay is the first of three essays included in the Free Response section of the AP Lang exam. The exam presents 6-7 sources that are organized around a specific topic, with two of those sources purely visual, including a single quantitative source (like a graph or pie chart). The remaining 4-5 sources are text-based, containing around 500 words each. It’s recommended that students spend an hour on this essay—15 minute reading period, 40 minutes writing, and 5 minutes of spare time to check over work.
Each synthesis essay has a topic that all the sources will relate to. A prompt will explaining the topic and provide some background, although the topics are usually broad so you will probably know something related to the issue. It will also present a claim that students will respond to in an essay format using information from at least three of the provided sources. You will need to take a stance, either agreeing or disagreeing with the position provided in the claim.
According to the CollegeBoard, they are looking for essays that “combine different perspectives from sources to form a support of a coherent position.” This means that you must state your claim on the topic and highlight relationships between several sources that support your specific position on the topic. Additionally, you’ll need to cite clear evidence from your sources to prove your point.
The synthesis essay counts for six points on the AP Lang exam. Students can receive 0-1 points for writing a thesis statement, 0-4 based on the incorporation of evidence and commentary, and 0-1 points based on the sophistication of thought and demonstration of complex understanding.
While this essay seems extremely overwhelming, considering there are a total of three free-response essays to complete, with proper time management and practiced skills, this essay is manageable and straightforward. In order to enhance the time management aspect of the test to the best of your ability, it is essential to divide the essay up into five key steps.
Step 1: Analyze the Prompt
As soon as the clock starts, carefully read and analyze what the prompt asks from you. It might be helpful to markup the text to identify the most critical details. You should only spend around 2 minutes reading the prompt so you have enough time to read all the sources and figure out your argument. Don’t feel like you need to immediately pick your stance on the claim right after reading the prompt. You should read the sources before you commit to your argument.
Step 2: Read the Sources Carefully
Although you are only required to use 3 of the 6-7 sources provides, make sure you read ALL of the sources. This will allow you to better understand the topic and make the most educated decision of which sources to use in your essay. Since there are a lot of sources to get through, you will need to read quickly and carefully.
Annotating will be your best friend during the reading period. Highlight and mark important concepts or lines from each passage that would be helpful in your essay. Your argument will probably begin forming in your head as you go through the passages, so you will save yourself a lot of time later on if you take a few seconds to write down notes in the margins. After you’ve finished reading a source, reflect on whether the source defends, challenges, or qualifies your argument.
You will have around 13 minutes to read through all the sources, but it’s very possible you will finish earlier if you are a fast reader. Take the leftover time to start developing your thesis and organizing your thoughts into an outline so you have more time to write.
Step 3: Write a Strong Thesis Statement
In order to write a good thesis statement, all you have to do is decide your stance on the claim provided in the prompt and give an overview of your evidence. You essentially have three choices on how to frame your thesis statement: You can defend, challenge or qualify a claim that’s been provided by the prompt.
- If you are defending the claim, your job will be to prove that the claim is correct .
- If you are challenging the claim, your job will be to prove that the claim is incorrect .
- If you choose to qualify the claim, your job will be to agree to a part of the claim and disagree with another part of the claim.
A strong thesis statement will clearly state your stance without summarizing the issue or regurgitating the claim. The CollegeBoard is looking for a thesis statement that “states a defensible position and establishes a line of reasoning on the issue provided in the prompt.”
Step 4: Create a Minimal Essay Outline
Developing an outline might seem like a waste of time when you are up against the clock, but believe us, taking 5-10 minutes to outline your essay will be much more useful in the long run than jumping right into the essay.
Your outline should include your thesis statement and three main pieces of evidence that will constitute each body paragraph. Under each piece of evidence should be 2-3 details from the sources that you will use to back up your claim and some commentary on how that evidence proves your thesis.
Step 5: Write your Essay
Use the remaining 30-35 minutes to write your essay. This should be relatively easy if you took the time to mark up the sources and have a detailed outline. Remember to add special consideration and emphasis to the commentary sections of the supporting arguments outlined in your thesis. These sentences are critical to the overall flow of the essay and where you will be explaining how the evidence supports or undermines the claim in the prompt.
Also, when referencing your sources, write the in-text citations as follows: “Source 1,” “Source 2,” “Source 3,” etc. Make sure to pay attention to which source is which in order to not incorrectly cite your sources. In-text citations will impact your score on the essay and are an integral part of the process.
After you finish writing, read through your essay for any grammatical errors or mistakes before you move onto the next essay.
Here are six must-have tips and tricks to get a good score on the synthesis essay:
- Cite at least four sources , even though the minimum requirement is three. Remember not to plagiarize and cite everything you use in your arguments.
- Make sure to develop a solid and clear thesis . Develop a stable stance for the claim and stick with it throughout the entire paper.
- Don’t summarize the sources. The summary of the sources does not count as an argument.
- You don’t necessarily have to agree with the sources in order to cite them. Using a source to support a counterargument is still a good use of a source.
- Cite the sources that you understand entirely . If you don’t, it could come back to bite you in the end.
- Use small quotes , do not quote entire paragraphs. Make sure the quote does not disrupt the flow or grammar of the sentence you write.

Discover your chances at hundreds of schools
Our free chancing engine takes into account your history, background, test scores, and extracurricular activities to show you your real chances of admission—and how to improve them.
Here is an example prompt and essay from 2019 that received 5 of the 6 total points available:
In response to our society’s increasing demand for energy, large-scale wind power has drawn attention from governments and consumers as a potential alternative to traditional materials that fuel our power grids, such as coal, oil, natural gas, water, or even newer sources such as nuclear or solar power. Yet the establishment of large-scale, commercial-grade wind farms is often the subject of controversy for a variety of reasons.
Carefully read the six sources, found on the AP English Language and Composition 2019 Exam (Question 1), including the introductory information for each source. Write an essay that synthesizes material from at least three of the sources and develops your position on the most important factors that an individual or agency should consider when deciding whether to establish a wind farm.
Source A (photo)
Source B (Layton)
Source C (Seltenrich)
Source D (Brown)
Source E (Rule)
Source F (Molla)
In your response you should do the following:
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis presents a defensible position.
- Select and use evidence from at least 3 of the provided sources to support your line of reasoning. Indicate clearly the sources used through direct quotation, paraphrase, or summary. Sources may be cited as Source A, Source B, etc., or by using the description in parentheses.
- Explain how the evidence supports your line of reasoning.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating your argument.
[1] The situation has been known for years, and still very little is being done: alternative power is the only way to reliably power the changing world. The draw of power coming from industry and private life is overwhelming current sources of non-renewable power, and with dwindling supplies of fossil fuels, it is merely a matter of time before coal and gas fuel plants are no longer in operation. So one viable alternative is wind power. But as with all things, there are pros and cons. The main factors for power companies to consider when building wind farms are environmental boon, aesthetic, and economic factors.
[2] The environmental benefits of using wind power are well-known and proven. Wind power is, as qualified by Source B, undeniably clean and renewable. From their production requiring very little in the way of dangerous materials to their lack of fuel, besides that which occurs naturally, wind power is by far one of the least environmentally impactful sources of power available. In addition, wind power by way of gearbox and advanced blade materials, has the highest percentage of energy retention. According to Source F, wind power retains 1,164% of the energy put into the system – meaning that it increases the energy converted from fuel (wind) to electricity 10 times! No other method of electricity production is even half that efficient. The efficiency and clean nature of wind power are important to consider, especially because they contribute back to power companies economically.
[3] Economically, wind power is both a boon and a bone to electric companies and other users. For consumers, wind power is very cheap, leading to lower bills than from any other source. Consumers also get an indirect reimbursement by way of taxes (Source D). In one Texan town, McCamey, tax revenue increased 30% from a wind farm being erected in the town. This helps to finance improvements to the town. But, there is no doubt that wind power is also hurting the power companies. Although, as renewable power goes, wind is incredibly cheap, it is still significantly more expensive than fossil fuels. So, while it is helping to cut down on emissions, it costs electric companies more than traditional fossil fuel plants. While the general economic trend is positive, there are some setbacks which must be overcome before wind power can take over as truly more effective than fossil fuels.
[4] Aesthetics may be the greatest setback for power companies. Although there may be significant economic and environmental benefit to wind power, people will always fight to preserve pure, unspoiled land. Unfortunately, not much can be done to improve the visual aesthetics of the turbines. White paint is the most common choice because it “[is] associated with cleanliness.” (Source E). But, this can make it stand out like a sore thumb, and make the gargantuan machines seem more out of place. The site can also not be altered because it affects generating capacity. Sound is almost worse of a concern because it interrupts personal productivity by interrupting people’s sleep patterns. One thing for power companies to consider is working with turbine manufacturing to make the machines less aesthetically impactful, so as to garner greater public support.
[5] As with most things, wind power has no easy answer. It is the responsibility of the companies building them to weigh the benefits and the consequences. But, by balancing economics, efficiency, and aesthetics, power companies can create a solution which balances human impact with environmental preservation.
More examples can be found here at College Board.
While AP Scores help to boost your weighted GPA, or give you the option to get college credit, AP Scores don’t have a strong effect on your admissions chances . However, colleges can still see your self-reported scores, so you might not want to automatically send scores to colleges if they are lower than a 3. That being said, admissions officers care far more about your grade in an AP class than your score on the exam.
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

Calculate for all schools
Your chance of acceptance, your chancing factors, extracurriculars, writing a synthesis essay for ap lang.
I have to write a synthesis essay this week for my AP Lang class, but I'm not 100% sure what exactly that entails. Can someone explain what the process is like and maybe share some tips on how to write a strong synthesis essay?
Sure, a synthesis essay is a type of essay that requires you to use multiple sources to create an argument. In an AP Lang synthesis essay, you'll typically be provided with the sources and will need to analyze them, identify the main ideas, and then connect those ideas to your central argument or thesis.
Here's a step-by-step breakdown of how to write a strong synthesis essay for AP Lang:
1. Understand the prompt : Carefully read the prompt and make sure you understand what's being asked. Identify the main issue or topic you'll be addressing.
2. Develop a thesis statement : Your thesis statement should make a clear and specific claim about the topic. It should be an arguable point that you'll support using evidence from the sources provided.
3. Read and analyze the sources : Read through each source, taking notes on key ideas, evidence, and arguments related to your thesis. Think about how each source contributes to your argument and look for connections between sources.
4. Outline your essay : Create an outline that organizes your ideas and evidence into a logical sequence. Typically, a synthesis essay will have an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Each body paragraph should focus on a specific point related to your thesis and include evidence from multiple sources to support the point.
5. Write the introduction : Begin with a hook to engage the reader and introduce the topic. Then, give some brief background information about the issue before presenting your thesis statement.
6. Write the body paragraphs : In each body paragraph, start with a topic sentence that introduces the main point of the paragraph. Then, provide evidence and analysis from the sources to support the point, making sure to cite your sources according to the citation style required by your instructor. Try to incorporate evidence from multiple sources and emphasize the connections between them.
7. Address counterarguments : It's important to address any opposing views or counterarguments to show that you've considered different perspectives. You can either refute counterarguments or concede some validity while still maintaining your overall argument.
8. Write the conclusion : Summarize your main points and restate your thesis statement in a new way. You can also suggest further implications of your argument or propose a call to action. Avoid introducing new information in the conclusion.
Some additional tips for writing a strong synthesis essay:
- Make sure your analysis connects effectively to your thesis statement.
- Clearly explain how the evidence from the sources supports your argument.
- Use appropriate transitions to guide your reader through the essay and help them understand the connections between ideas.
- Edit and revise your essay for clarity, grammar, and punctuation.
Good luck with your AP Lang synthesis essay!
About CollegeVine’s Expert FAQ
CollegeVine’s Q&A seeks to offer informed perspectives on commonly asked admissions questions. Every answer is refined and validated by our team of admissions experts to ensure it resonates with trusted knowledge in the field.
Essay Papers Writing Online
Mastering the art of crafting a stellar synthesis essay – top tips, techniques, and examples to boost your writing skills and academic success.

Are you ready to embark on a journey of discovery, where you meld ideas, thoughts, and arguments into a seamless tapestry? The synthesis essay offers you a unique opportunity to showcase your ability to synthesize various sources and present your ideas in a coherent and convincing manner. In this article, we will explore some tried-and-true strategies to help you master the art of crafting a compelling synthesis essay that will leave a lasting impression on your readers.
First and foremost, it is essential to develop a strong grasp of the central theme or topic of your essay. This theme serves as the thread that will tie all the different sources and ideas together. By understanding the underlying essence of your essay, you can better navigate through the vast sea of information and select the most relevant and persuasive sources to support your arguments.
Once you have identified the central theme, it is crucial to critically analyze the various sources at your disposal. Remember, the key is not just to summarize these sources but to analyze them in relation to your thesis statement. Look for patterns, contradictions, and connections between the different sources. Highlight the key arguments and evidence that are relevant to your essay’s central theme, and be prepared to present counterarguments that address opposing viewpoints.
Understand the Prompt
In order to write an effective synthesis essay, it is crucial to fully understand the prompt provided. The prompt serves as a guide, outlining the specific topic or issue that needs to be addressed in the essay.
When analyzing the prompt, it is important to carefully examine the keywords and phrases used. These words may provide valuable insight into the expectations of the essay and the specific elements that should be included. It is also crucial to identify any limitations or guidelines outlined in the prompt.
Understanding the prompt also involves determining the purpose of the essay. Is it meant to inform, persuade, or argue a specific point? By grasping the purpose, you can tailor your writing style and arguments to best meet the objectives of the prompt.
Additionally, it is essential to consider the context and audience of the essay. Who will be reading your essay? What are their expectations and knowledge on the topic? By considering these factors, you can better adjust your writing style and tone to effectively communicate your ideas.
Overall, understanding the prompt is the first step towards writing an effective synthesis essay. By carefully analyzing the prompt, identifying key elements, and considering the purpose and audience, you can ensure that your essay is well-focused, coherent, and meets the requirements of the assignment.
Conduct Thorough Research
When it comes to crafting a compelling and well-supported synthesis essay, conducting thorough research is crucial. A successful essay requires a deep understanding of the topic at hand, as well as a comprehensive exploration of different perspectives and sources. Simply put, conducting thorough research means digging deep and gathering a wide range of relevant and reliable information that will enrich your synthesis essay and make it more convincing.
Research is the foundation on which your essay will be built. It allows you to gather facts, statistics, and expert opinions that support your thesis and strengthen your arguments. By conducting thorough research, you can demonstrate your knowledge and expertise on the topic, as well as present a well-rounded perspective that takes into account different viewpoints and evidence.
It is essential to use a variety of sources during your research process. This includes academic journals, books, reputable websites, and studies conducted by experts in the field. By consulting a diverse range of sources, you can ensure that your synthesis essay is well-informed and comprehensive.
When conducting research, it is important to critically evaluate the sources you come across. Not all sources are created equal, and it is your responsibility as an essay writer to determine their credibility and reliability. Look for sources that are peer-reviewed, published by reputable scholars or organizations, and have a track record of accuracy and reliability.
In addition to gathering information from various sources, you should also take notes and organize your research in a systematic and structured manner. This will make it easier to refer back to specific information when writing your essay and ensure that you include all relevant facts and data in your synthesis.
In conclusion, conducting thorough research is a critical step in writing an effective synthesis essay. It enables you to gather a wealth of relevant information, evaluate its credibility, and present a well-informed and comprehensive perspective on the topic. By investing time and effort into research, you can ensure that your essay is well-supported, convincing, and showcases your knowledge and understanding of the subject matter.
Create a Strong Thesis Statement
One of the most essential elements for writing a successful synthesis essay is the creation of a strong thesis statement. A thesis statement serves as the guiding principle and main argument of your essay, offering a clear and focused direction for your synthesis. This statement should be concise and powerful, encapsulating the main idea or theme that you will explore throughout your essay.
To create a strong thesis statement, it is important to consider the main points or ideas that you want to convey in your essay. Think about the connections and relationships between these points, and how they contribute to the overall theme or argument of your synthesis. Your thesis statement should reflect these connections and provide a clear stance or perspective on the topic.
Additionally, your thesis statement should be specific and avoid vague or general language. It should clearly state your main argument or position, and highlight the unique perspective or insights that you will bring to the topic. Avoid using clichés or common phrases, as they can weaken the impact of your thesis statement.
Lastly, make sure that your thesis statement is arguable. A strong thesis statement should invite discussion and debate, rather than stating an obvious or universally agreed-upon fact. It should be a statement that can be supported or refuted through evidence and logical reasoning.
By creating a strong thesis statement, you lay the foundation for a compelling and cohesive synthesis essay. It will guide your writing process and help you maintain a clear focus throughout your essay. Take the time to craft a thesis statement that is powerful, specific, and arguable, and you will set yourself up for success in writing an effective synthesis essay.
Organize Your Ideas

When it comes to crafting a compelling synthesis essay, one of the most important steps is organizing your ideas. Effective organization ensures that your thoughts flow smoothly and cohesively, allowing your readers to easily follow your argument. By structuring your essay in a logical and coherent manner, you can effectively convey your message and make a strong impact.
A key aspect of organizing your ideas involves creating an outline. This serves as a roadmap for your essay, helping you to visualize the overall structure and flow of your argument. Start by brainstorming your main ideas and supporting evidence, then arrange them in a logical order. This can be done using a variety of methods, such as creating a mind map or a hierarchical list.
Once you have established your outline, it’s important to consider the most effective way to present your ideas. One option is to use a chronological or sequential order, where you present your arguments in a logical progression. Another option is to use a thematic approach, grouping related ideas together to create a cohesive narrative. Whichever approach you choose, make sure to clearly introduce each main point and provide sufficient evidence to support your claims.
In addition to organizing your ideas structurally, it’s also important to consider the cohesiveness of your writing. Use transitional words and phrases to guide your readers through your argument, signaling shifts in ideas or providing connections between different points. This will help your essay to flow smoothly and prevent any misunderstandings.
Lastly, don’t forget to revise and refine your organization as you go. After completing a first draft, take the time to review your essay and make any necessary adjustments. This may involve reordering paragraphs, adding or deleting sections, or rephrasing sentences for clarity. By continuously revising and refining your organization, you can ensure that your essay is well-structured and easy to follow.
By organizing your ideas effectively, you can elevate your synthesis essay and make a strong impression on your readers. Take the time to carefully plan and structure your argument, and you’ll be well on your way to writing an impactful and persuasive essay.
Use Evidence and Examples from Various Sources
One crucial aspect of writing a synthesis essay is the use of evidence and examples from different sources to support your claims and arguments. By drawing from a variety of sources, such as scholarly articles, books, interviews, and research studies, you can strengthen the validity and credibility of your essay.
When selecting evidence and examples, it’s important to consider the diversity of viewpoints and perspectives. Including evidence from multiple sources allows you to present a well-rounded argument and demonstrate that you have considered various opinions on the topic.
Moreover, using evidence and examples from different sources helps to avoid biases and ensure that your essay is objective and comprehensive. By incorporating a variety of sources, you can present a more balanced and informed analysis.
Additionally, when using evidence and examples, be sure to provide proper citations and references. This not only gives credit to the original authors but also strengthens the credibility of your essay. Make sure to follow the appropriate citation style, such as APA or MLA, and include in-text citations and a reference list or bibliography.
In conclusion, by utilizing evidence and examples from various sources, you can enhance the effectiveness of your synthesis essay. By incorporating different viewpoints and perspectives, avoiding biases, and providing proper citations, you can create a well-supported and persuasive argument.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, tips and techniques for crafting compelling narrative essays.
Synthesis Essay

Writing a Perfect Synthesis Essay: Definition & Examples
16 min read
Published on: Mar 1, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

People also read
Interesting Synthesis Essay Topics You Must Consider
Synthesis Essay Examples: Learn From Powerful Example
Share this article
Do you have a ton of research to synthesize but don't know how? Or maybe you're not sure what a synthesis essay is and how to write a good synthesis essay.
We know writing a synthesis essay is not an easy task to do; it’s challenging for most of us. But it can be perfectly done with the right guidance and preparation.
In this blog, we'll walk you through all the necessary information to craft a perfect synthesis essay. So you can get done with your assignments confidently!
Let’s get started.
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Synthesis Essay?
Synthesis essay definition states:
It is a piece of writing that takes a unique perspective on a central idea, topic, or theme. Then backs it up with evidence from multiple sources.
A synthesis essay is an important part of academic writing. The main purpose of this essay is to show your ability to prove an argument.
To make sense of these arguments, you need to use different credible sources. It demonstrates your basic understanding of the main subject. This type of essay help to enhance your critical, analytical, and research skills.
A synthesis essay is made up of ideas and conclusions based on the information reviewed. Also, this essay asks you to summarize the topic and add your own thoughts about it in relation to what you have read.
Furthermore, the synthesis essays can be similar to analytical essays , argumentative essays , or compare and contrast essays .
Synthesis Essay Types
There are three types of a synthesis essay:
1. Argument Synthesis Essay
This essay's purpose is to debate or argue on a certain topic or issue. It justifies its claims by providing evidence in the body of the essay.
In contrast to the explanatory essay, you will perform the same thing as if you were writing a typical argumentative paper. First, state your argument, make supporting statements, and back up each claim with reliable facts.
2. Review Essay
A review essay is frequently written as a preparatory essay to an argument synthesis. Review essays are commonly used in social science and medicine classes.
It is a discussion of what has already been published on a topic, with a critical examination of the sources mentioned.
An unwritten thesis statement is added to it, which is not final and indicates that further study is needed in that area.
3. Explanatory Synthesis Essay
In this essay, the writer helps the reader to grasp deeper knowledge about the topic. Rather than arguing or debating on some points, the goal of this essay is to explain a certain topic.
Like any other essay, it needs backing up with supporting claims and credible sources.
How to Start a Synthesis Essay?
The following are some helpful techniques for writing an essay. These will help you start the process and avoid common errors that plague many writers.
1. Choosing a Synthesis Essay Topic
A prompt for a synthesis paper must be arguable. Based on your project, you may be required to select primary content. Select a book that may include contrasting perspectives. Here are some important tips for choosing a topic for a synthesis essay.
- Look through the themes and ideas. Read from sources and investigate specific topics thoroughly to see if any of them catch your interest.
- Select a topic and collect relevant and valuable references for your synthesis paper.
- Outline your synthesis essay using concepts or ideas from the sources. This should make writing a lot simpler and save you a lot of time.
It is necessary to find an arguable topic to make your synthesis essay effective. Another reason is that these topics have been discussed in public for decades.
Examples of good synthesis essay topics are;
- The process of hiring in the age of social media
- Social networks promote suicide
- Should higher education be free?
- Is it necessary to remove marks in education
- The importance of getting a good education
- 3D printers are not used efficiently nowadays.
- Is technology really helping people?
- Why has technology made surgery safe and effective?
- What is the cause of widespread obesity in teens?
- What is the role of gender today?
2. Analyze Your Topic
Here's how you can fully understand your synthesis essay topic.
- Grasp the Idea of a Synthesis Essay
A synthesis essay's purpose is to establish meaningful connections between sections of a work. When conducting research on a topic, you have to look for connections to build a strong viewpoint on the subject. The ultimate goal of the essay is to present and prove a claim about a topic .
- Select a Topic Appropriate for a Synthesis Essay
The subject and topic must be extensive enough to include multiple relevant sources. If you have a free hand in deciding what to write about, some preparatory research may assist you in researching and choosing the right topic.
- Select and Study Your Sources Carefully
Research and find relevant information and sources. Generally, choose at least three references for your essay. It's a good idea to learn one or two additional sources for better understanding but no matter what it is, make sure that you study it properly.
Remember that it is better to read three sources properly than five sources poorly.
Compile each source by writing notes in the margins. This allows you to keep track of your thoughts, fresh ideas, and so on.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
- Reread the Source Material
Reread your source material for elements that will help to support your argument.
Examine your sources for important statements, figures, thoughts, and facts that support your thesis. Make a note of them when you come across them. This will be very useful throughout your writing process.
3. Develop a Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement will be the central idea of your essay. It should cover the topic and express your viewpoint on it. After reading the sources and conducting your research, form an opinion on your topic.
It should be stated as a complete sentence. Based on the essay, your thesis statement could be the first sentence of the essay or the last sentence of the first paragraph.
- Structure Your Thesis Statement Creatively
To present your thesis, use a more creative structure. You can use a more elaborate structure than the one outlined above. You can develop your essay using the following approaches:
Straw man: In this approach, you will present the counter-arguments first. Then demonstrate their weaknesses and flaws.
Such an approach demonstrates your awareness of the opposition as well as your readiness to respond to it. You present the counter-argument immediately following your thesis statement, followed by evidence to refute it. And conclude with a positive argument that supports your thesis.
Concession: In structure, concessions in essays are similar to the straw man. But this approach acknowledges the validity of the counter-argument while demonstrating that your argument is stronger. This structure is suitable for presenting papers to readers who hold opposing views.
Illustration/ Example: It could be a thorough narrative, synopsis, or quotation from your source material that provides support for your position. However, you should not make your paper a collection of examples at the expense of supporting your thesis statement.
Comparison and Contrast: In this approach, similarities and differences between two subjects or sources demonstrate both aspects. It requires a thorough reading of your source material to identify both subtle and major points of comparison.
This type of essay can present its arguments source by source or by points of similarity or difference.
4. Create an Outline for Your Essay
An essay outline is a method for outlining the framework of your essay. Hereâs what you have to do. Outlining can help you structure and plan your synthesis paper.
The standard outline of a synthesis essay is divided into three sections:
Need detailed guidance on how to write a synthesis essay? Check out this video?
How to Write a Synthesis Essay?
For writing a great essay, you have to do extensive research on your subject. This essay connects sections of multiple works and develops a strong viewpoint on a subject.
There are some major steps of the process:
1. Start Writing Your Essay
After getting done with the preparation part, start to write your synthesis essay.
2. Write Your First Draft Using Your Outline as a Guide
But be prepared to change your strategy if you discover fresh ideas and information. And make sure it supports your thesis and the source material.
Your essay should have an introduction paragraph with your thesis statement at the end of it. A body with evidence that supports your main topic and thesis statement. Lastly, a conclusion that summarizes your point of view.
3. Use Transitions
To make the content flow logically, use transitions between paragraphs. Transition words are an excellent method to highlight areas where your sources complement one another.
Longer quotes of three lines or more should be presented as block quotes to draw emphasis to them.
4. Wrap Up Your Essay
Here you have completed the writing process, but still, you need to make sure that your essay is flawless.
5. Revise Your Essay
This is the time to enhance transitions between points and paragraphs and to reinforce arguments. You should strive to make your argument as concise and clear to understand as possible. It is beneficial to read your essay aloud so you can spot problematic phrases or unclear ideas.
Request someone else to proofread your paper. Have you heard the cliché "two heads are better than one"? Is it still valid?
Ask a friend or coworker what they would add or eliminate from the paper. Most importantly, does your thesis statement make sense, and are your references clearly supporting it?
Answer these questions in your essay.
6. Proofread Your Content
Examine your document for any grammatical, punctuation, or spelling mistakes.
Are all the terms, names, and words accurately spelled? Are there any extraneous English language or sentence fragments? As you go, correct them.
Read the essay loudly to ensure that you don't accidentally add or remove words when reading in your mind. If possible, ask a friend or classmate to edit your writing.
7. Must Cite Sources
Use footnotes to mention information in the body paragraph and bibliography of cited books at the conclusion. Footnotes and in-text citations should be used for any information that is quoted, paraphrased, or cited.
8. Title Your Essay
The point of view expressed in your thesis statement and supporting arguments should be reflected in your title. Therefore, choose a title that suits your essay rather than constructing your essay to fit the title.
Synthesis Essay Format
The format of your synthesis paper is chosen by your high school, college, or university professor. MLA, APA, and Chicago styles are the most often used styles.
The APA format is followed in the disciplines of science, education, and psychology. Chicago is commonly followed in the field of history, fine arts, and business. And MLA is the style of citation used in the humanities.
APA Style Format
The following are some APA style important details:
- Add a page header to the top of each page.
- Times New Roman, 1â margins, 12 pt. Font, double-spaced.
- The format of a synthesis essay should be separated into four sections: title page, abstract, main body, and references.
- Insert a page number in the upper right corner.
Chicago Style Format
The following are some Chicago style key points:
- Use double-spacing between the paper's lines.
- Make margins of one inch.
- Font size: 12 pt. Times New Roman font style.
- Create text that is left-justified with a rugged edge.
- Mention the full name of a person, place, or organization.
- At the start of the paragraph, use half-inch indents.
- The bibliography should be on its own page.
MLA Style Format
The following are some MLA style significant points:
- The title must be centered.
- Font: Times New Roman, 1â margins, 12 pt font size, double-spaced
- Mention your name, professor's name, the course number, and the date (dd/mm/yy).
- On each page, the top right corner displays the last name and page number.
- The final page provides a âWorks Citedâ list.
Synthesis Essay Rubric
A rubric is essentially a list of criteria that your professor will use to grade your paper.
Knowing how each criterion is weighted can help make sure you get the best grade possible on your synthesis essay.
The Basics of the Synthesis Essay Rubric
The basic elements of any synthesis essay rubric include organization, focus/development, and language use/style.
- Organization refers to how well you structure your paper. It should flow logically and have clear transitions between sections.
- Focus/development looks at how well you develop your argument throughout the paper. Are you able to clearly explain why each point supports your thesis?
- Language use/style focuses on grammar, punctuation, and spelling. Was the paper proofread thoroughly or did careless errors slip in?
For example , your synthesis essay thesis statement is
âCapital punishment should be abolished in all states."
Do you provide evidence from different angles, such as legal history, religious beliefs, or moral arguments to back up this claim?
Does this evidence prove why capital punishment should be abolished?
How to Write a Synthesis Essay - Ap Lang
Are you an AP Lang student whoâs been assigned the dreaded synthesis essay? Hereâs how to write a successful synthesis essay for AP Lang.
- Understand the Prompt
The first step in writing any synthesis essay is to read and understand the prompt. Itâs also important to note any specific requirements such as word count, formatting style, or sources that must be used in your essay.
- Organize Your Argument
Once you have all the information necessary, itâs time to start organizing your argument.
Start by identifying any common themes or ideas between the various sources of evidence and create an outline with these points at its core.
- Write Your Essay
Now comes the fun partâwriting!
You should now have a comprehensive outline of all the points and evidence you want to include in your essay. So use this as a guide when crafting your argument.
Make sure that each point has supporting evidence from credible sources and that everything flows logically from one point to another.
Finally, donât forget to proofread and edit before submitting so that there are no errors in grammar or spelling. These small details can make all the difference!
Synthesis Essay Tips
Working on a synthesis paper requires a thorough study of a particular given prompt. To evaluate it properly, you must first understand the promptâs goal, argument, authorâs claim, and rhetoric.
To compose a successful synthesis essay, here are some helpful tips to keep in mind.
- Use Multiple Reasons
It is well recognized that the use of various reasons (generally two) is a very successful approach.
Present one argument against your strong thesis statement. This type of evidence presents an introduction and description. The advantage of this method is to teach awareness of the other side of the argument. It is followed by the opposing view and a decisive factor.
This is one of the most basic ways of organizing. It enables you to summarise the sources that are most relevant to you. The problem is that this technique excludes any of your individual thinking.
- Compare and Contrast
Comparing reveals similarities, while contrasting reveals distinctions. It is feasible to show an in-depth analysis of your chosen topic. It allows writers to compare and contrast two sources at the same time.
Write quotations from sources in your own words. This approach also allows the usage of quotable sources. Ensure to cite the reference when you use the reference.
This method depicts the opposing point of view. It demonstrates that the positives outweigh the negatives.
Writing a synthesis essay is not as difficult as it may seem. You can also try our AI essay writer to generate plagiarism-free content and make the process easier.
However, if you are having trouble understanding the concepts or writing a synthesis essay, it is best to hire professionals.
Our synthesis essay writing service is the perfect solution to your problems. We have a team of skilled writers who will help you through each step of the essay-writing process.
You contact our professionals at CollegeEssay.org to get essay writing help online . Our essay writer service is always ready to ace your assignments.
So don't hesitate and order your essay now!
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you end a synthesis essay.
A strong ending fulfills these 3 things:
- Restate your thesis.
- Summarize or synthesize key points.
- Make your argument's context explicit.
What is a synthesis paragraph?
A synthesis is a textual debate that includes support from multiple sources with opposing viewpoints. This type of work requires analysis by using different sources and determining their relevance to your thesis.
Why is synthesis important?
It is important because it allows us to:
- Test and validate hypotheses.
- Comprehend key processes.
- Plan future research efforts.
How to conclude a synthesis essay?
Synthesize rather than summarize your argument. No need to go over your entire paper again. Instead, include a brief summary of the main points of the paper and explain to your reader how you've made points.
What is an example of a synthesis?
Making connections or putting things together is all that is required. We naturally synthesize information to assist others in seeing connections between things. For example, synthesis occurs when you report to a friend what other friends have said about a film or book.
How many paragraphs is a synthesis essay?
According to the standard outline provided, you should stick to the basic five-to-six paragraph structure. In rare cases, there may be more paragraphs in the main body.
Caleb S. (Literature, Marketing)
Caleb S. has extensive experience in writing and holds a Masters from Oxford University. He takes great satisfaction in helping students exceed their academic goals. Caleb always puts the needs of his clients first and is dedicated to providing quality service.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Find what you need to study
2024 AP English Language and Composition Exam Guide
12 min read • august 18, 2023
Your guide to the 2024 AP English Language and Composition exam
We know that studying for your AP exams can be stressful, but Fiveable has your back! We created a study plan to help you crush your AP English Language and Composition exam. This guide will continue to update with information about the 2024 exams, as well as helpful resources to help you do your best on test day. Unlock Cram Mode for access to our cram events—students who have successfully passed their AP exams will answer your questions and guide your last-minute studying LIVE! And don't miss out on unlimited access to our database of thousands of practice questions.
Format of the 2024 AP English Language and Composition exam
This year, all AP exams will cover all units and essay types. The 2024 AP English Language and Composition exam format will be:
Section I: Multiple Choice - 45% of your score
45 questions in 1 hour
Section II: Free Response Section - 55% of your score
2 hours and 15 minutes for:
1 synthesis essay
1 rhetorical analysis essay
1 argument essay
Scoring Rubric for the 2024 AP Lang Essays
Synthesis Essay
1 point for a defensible thesis that responds to the prompt
Evidence and Commentary
Max of 4 points for providing evidence from at least 3 sources that support the line of reasoning AND commentary that explains and analyzes the evidence
Sophistication
1 point any of the following:
Creating a nuanced argument
Showing the limitations of the argument
Making effective rhetorical choices
Employing a style that is vivid and persuasive
Rhetorical Analysis Essay
1 point for a defensible thesis that analyzes rhetorical choices
Max of 4 points for providing specific evidence AND consistently explaining how the evidence relates to the line of reasoning AND showing how the rhetorical choices contribute to the author's message .
1 point for any of the following:
Explaining the significance of the rhetorical choices ( rhetorical situation )
Explaining the complexities of the passage and their purpose
Argument Essay
1 point for a defensible thesis
Max of 4 points for providing specific evidence AND consistently explaining the relevance of that evidence .
Crafting a nuanced argument by identifying complexities
Explaining the limitations of the argument by placing it in a broader context
Making rhetorical choices to improve the argument
Check out our study plan below to find resources and tools to prepare for your AP English Language and Composition exam.
When is the 2024 AP English Language and Composition Exam and How Do I Take It?
How should i prepare for the ap lang exam.
First, take stock of your progress in the course so far. What areas have you excelled and which sections need more focus? Download the AP English Language Cheatsheet PDF - a single sheet that covers everything you need to know at a high level. Take note of your strengths and weaknesses!
Build your study plan to review every unit and question type, but focus most on the areas that need the most improvement and practice. We’ve put together this plan to help you study between now and May. This will cover all of the units and essay types to prepare you for your exam
Practice essays are your best friends! The more essays you write, the more automatic the process will come, and the easier the AP exam will be!
Try some of the past exam questions here
We've put together the study plan found below to help you study between now and May. This will cover all of the units and essay types to prepare you for your exam. Pay special attention to the units that you need the most improvement in.
Study, practice, and review for test day with other students during our live cram sessions via Cram Mode . Cram live streams will teach, review, and practice important topics from AP courses, college admission tests, and college admission topics. These streams are hosted by experienced students who know what you need to succeed.
Pre-Work: Set Up Your Study Environment
Before you begin studying, take some time to get organized.
🖥 Create a study space.
Make sure you have a designated place at home to study. Somewhere you can keep all of your materials, where you can focus on learning, and where you are comfortable. Spend some time prepping the space with everything you need and you can even let others in the family know that this is your study space.
📚 Organize your study materials.
Get your notebook, textbook, prep books, or whatever other physical materials you have. Also, create a space for you to keep track of review. Start a new section in your notebook to take notes or start a Google Doc to keep track of your notes. Get yourself set up!
📅 Plan designated times for studying.
The hardest part about studying from home is sticking to a routine. Decide on one hour every day that you can dedicate to studying. This can be any time of the day, whatever works best for you. Set a timer on your phone for that time and really try to stick to it. The routine will help you stay on track.
🏆 Decide on an accountability plan.
How will you hold yourself accountable to this study plan? You may or may not have a teacher or rules set up to help you stay on track, so you need to set some for yourself. First, set your goal. This could be studying for x number of hours or getting through a unit. Then, create a reward for yourself. If you reach your goal, then x. This will help stay focused!
2024 AP Lang Study Guide
🚧 unit 1 foundations of rhetoric: analysis of the rhetorical situation and claims ., big takeaways:.
Unit 1 is an introductory unit that lays the foundations for the reading skills associated with how to understand and analyze complex texts. Skills here include identifying the ASPECTS of a text, analyzing the claim given and the evidence used to support that claim, and determining the function of the “chunks” in the argument. Because the content in this unit is very foundational, it is looped throughout the rest of the course instruction.
Definitely do this:
📚 Read these study guides:
Unit 1 Overview: Claims , Reasoning , and Evidence
1.1 Identifying the purpose and intended audience of a text
1.2 Examining how evidence supports a claim
1.3 Developing paragraphs as part of an effective argument
🎥 Watch these videos:
College Board’s Instructional Video: Overview of The Rhetorical Situation .
Fiveable’s How to Read Like an AP Student .
Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statements
Rhetorical Analysis Body Paragraphs
✍️ Practice:
Use the Fiveable ASPECTS Guidesheet to help you break down a complex text.
🗺 Can you identify these rhetorical devices?
You won’t be asked to name drop on the exam, but it can be helpful to use devices when discussing strategies. Try this Quizlet to help prepare.
Unit 2 Foundations of Argument: Analysis of an author’s choices in appeals and evidence
Unit 2 is an introductory unit that builds onto the foundations of rhetorical ASPECTS and moves toward planning and writing your own arguments. This unit focuses on the relationships between subject, speaker, and message, including examination of the structure and purpose of the given argument. The unit then moves into the developing thesis statements and building your own arguments with a clear line of reasoning .
Unit 2 Overview: Organizing Information for a Specific Audience
2.1 Analyzing audience and its relationship to the purpose of an argument
2.2 Building an argument with relevant and strategic evidence
2.3 Developing thesis statements
2.4 Developing structure and integrating evidence to reflect a line of reasoning
College Board’s Instructional Video: Identify Rhetorical Situation in a Pre 20th Century Text .
Fiveable’s video on How to Find Rhetorical Devices
📰 Check out these articles:
Here’s a list of recommended rhetorical devices with definitions and examples!
Use the Fiveable Rhetorical Precis Guidesheet to help you break down a complex text.
🗺 Can you identify these elements of practical argument?
You won’t be asked to name drop of the exam, but it can be helpful to use devices when discussing strategies. Try this Quizlet to help prepare.
👥 Unit 3 Confluence: Synthesis of multiple sources in argumentation
Unit 3 approaches multiple perspectives in argument through the lens of synthesis (that’s FRQ 1). In this study, you learn to identify effective and faulty reasoning while integrating a variety of evidence from credible resources that is properly cited in an original text.
Unit 3 Overview: Perspectives and How Arguments Relate
3.1 Interpreting character description and perspective
3.2 Identifying and avoiding flawed lines of reasoning
3.3 Introducing and integrating sources and evidence
3.4 Using sufficient evidence for an argument
3.5 Attributing and citing references
3.6 Developing parts of a text with cause-effect and narrative methods
Fiveable’s Introduction into Synthesis Essays and How to Begin Your Argument
College Board’s Instructional Video: Complexity in Argument .
🗺 Can you identify these elements of synthesis?
👀 Unit 4 Reasoning : Analysis of argument from introduction to conclusion
Unit 4 includes a greater depth of focus on the writing of effective arguments -- the line of reasoning created in the introduction, built with modes of discourse, and strengthened in the conclusion. An important note about these skills of argumentation is that they build toward all parts of every FRQ.
Unit 4 Overview: How writers develop arguments, intros, and conclusion
4.1 Developing and connecting thesis statements and lines of reasoning
4.2 Developing introductions and conclusions
4.3 Adjusting an argument to address new evidence
College Board’s Instructional Video: Understanding a Line of Reasoning .
Fiveable’s Effective Annotations .
Try Fiveable’s Guide to LOR Body Paragraphs .
🗺 Can you identify the rhetorical modes?
You won’t be asked to name drop them on the exam, but it can be helpful to use devices when discussing strategies. Try this Quizlet to help prepare.
🧐 Unit 5 Commentary and Analysis: Analysis of complex argument and intentional rhetoric
In Unit 5, the skills look at the minutiae involved in argumentation: development of the line of reasoning that produces strong commentary and maintains the primary claim through all parts of the writing. To achieve these goals, this unit includes a focus on transitions , modifiers , and qualifications for argumentative perspective .
Unit 5 Overview
5.1 Maintaining ideas throughout an argument
5.2 Developing commentary throughout paragraphs
5.3 Using modifiers to qualify an argument and convey perspective
5.4 Using transitions
Fiveable’s video on How to Improve Analysis Part 1 and Part 2
As well as how to Embed Quotes into Body Paragraphs
Rhetorical Analysis Body Paragraphs
Synthesis Essay Body Paragraphs
Argument Essay Body Paragraphs
Tara Seale’s adaptation for Creating a Line of Reasoning .
🏃♂️ Unit 6 Rhetorical Risks: Analysis of multiple perspectives , bias , and shifts with new evidence
In Unit 6, you will notice a direct link building on the ideas of Unit 3 as this instruction looks at position and perspectives while synthesizing information strategically to support a claim. For greater depth, this unit moves to modify a current argument to include new evidence .
Unit 6 Overview: Position, Perspective , and Bias
6.1 Incorporating multiple perspectives strategically into an argument
6.2 Recognizing and accounting for bias
6.3 Adjusting an argument to new evidence
6.4 Analyzing tone and shifts in tone
College Board’s Instructional Video: Creating a Nuanced Argument .
Fiveable’s video on Tracking an Author’s Argument
🚀 Unit 7 Complex Argumentation: Analysis of effective arguments, including concession and refutation
The skills of Unit 7 are about putting all units of study together to look at the complexity of a given argument and the effectiveness of the pieces built into that argument. Though many teachers will have addressed counterarguments, concessions, and refutations before reaching this unit, those skills are highly scrutinized in this segment of learning.
Unit 7 Overview: Successful and Unsuccessful Arguments
7.1 Examining complexities in issues
7.2 Considering how words, phrases, and clauses can modify and limit an argument
7.3 Examining how counterargument or alternative perspectives affect an argument
7.4 Exploring how sentence development affects an argument
Fiveable’s video on Arguments and Counterarguments
College Board’s Instructional Video: How Argument Demonstrates Understanding .
Check your progress with Fiveable’s AP Language Skills Matrix .
📝 Unit 8 Style: Analysis of how style influences the audience movement
Unit 8 covers how to understand the influence style has on the audience , and the purpose behind each decision. By analyzing these various tactics, students are able to understand the author’s audience , and how to effectively persuade them. Style is an important part in connecting the rest of the course and understanding how the rhetorical choices and devices are used to accomplish a purpose .
Unit 8 Overview: Stylistic Choices
8.1 Choosing comparisons based on an audience
8.2 Considering how sentence development and word choice affect how the writer is perceived by an audience
8.3 Considering how all choices made in an argument affect the audience
8.4 Considering how style affects an argument
Fiveable’s Analysis of the Mindset of the Audience
College Board’s Instructional video: Analyzing and Understanding the Audience
College Board’s explanation of Elements and Context for Style
Review this quizlet on Elements of Style for more practice.
✏️ Unit 9 Craft: Creation of your own complex argument with synthesis and rhetoric
The final unit of AP Language and Composition covers how to effectively form your own arguments by acknowledging and understanding complexities to create a nuanced and sophisticated argument. It focuses on your ability to comprehend and connect multiple sources to create a well reasoned, and detailed argument as well as how to add in your own rhetorical devices and choices to make your writing more persuasive and effective.
Unit 9 Overview: Developing a Complex Argument
9.1 Strategically conceding, rebutting, or refuting information
9.2 Crafting an argument through stylistic choices like word choice and description
Fiveable’s video on Creating your own Synthesis Arguments
College Board’s video on Complexities within Arguments and How to Create a Nuanced Argument
Key Terms to Review ( 38 )
Argument Structure
Author's Message
Cause-Effect Method
Comparisons
Conclusions
Counterargument
Introductions
Line of Reasoning
Multiple Perspectives
Narrative Method
Objective Reasoning
Perspective
Qualifications
Rhetorical Choices
Rhetorical Situation
Sentence Development
Stylistic Choices
Subjective Reasoning
Textual Evidence
Thesis Development
Thesis Statement
Tone Shifts
Transitions
Word Choice

Stay Connected
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website.
How to Write a Synthesis Essay in 7 Steps

Samuel Gorbold
Starting to write synthesis essays can feel exciting but also overwhelming. Synthesis essays are all about blending different sources to build a strong argument. Whether you're new to this or looking to improve your skills, this article is here to help. We'll break down the process, from understanding what synthesis is to gathering sources, structuring your essay, and making your points effectively. Think of it as your guide to crafting synthesis essays that are clear, persuasive, and engaging. For starters, let's dive into what a synthesis essay is! If you’re in a hurry, you can use our essay writing service online to expedite the process.
What Is a Synthesis Essay?
A synthesis essay is an academic paper that combines ideas from multiple sources to create a coherent argument or thesis statement. Unlike other types of essays that primarily rely on the writer's opinions or analysis, synthesis essays require you to gather information from various sources, such as articles, books, or research studies, and synthesize them into a unified whole. The goal is to present a nuanced understanding of a topic by drawing connections, identifying patterns, and evaluating different perspectives. There are two main types of synthesis essays:
- Explanatory Synthesis
In an explanatory synthesis essay, your primary objective is to explain a topic by synthesizing information from multiple sources. You provide an overview of the subject matter, analyze different viewpoints, and present a comprehensive understanding of the topic to your audience. This type of synthesis essay is common in academic settings and often requires thorough research and critical thinking skills.
- Argumentative Synthesis
Argumentative synthesis essays go beyond merely explaining a topic; they also require you to take a stance or make a claim about the subject matter. You integrate information from various sources to support your argument or thesis statement. Additionally, you must anticipate counterarguments and address them effectively to strengthen your position. Argumentative synthesis essays aim to persuade the reader of the validity of your viewpoint by presenting well-supported evidence and logical reasoning.
Both types of synthesis essays require careful analysis, synthesis of information, and effective communication of ideas. If that sounds like a challenge, simply order essay writing from competent academic authors and relieve yourself from this chore.
Synthesis Essay Structure
The structure and format of a synthesis essay typically follow a standardized approach to effectively convey your argument and synthesize information from various sources. Here's a breakdown of the typical structure and format:
Introduction
- Start with a hook to grab the reader's attention and introduce the topic.
- Provide some background information on the subject matter to contextualize the discussion.
- Present your thesis statement, which clearly states your main argument or position on the topic.
Body Paragraphs
- Each body paragraph should focus on a specific aspect or subtopic related to your thesis.
- Begin each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main point or argument.
- Provide evidence from your sources to support your claims. This may include paraphrases, summaries, or direct quotations.
- Analyze and evaluate the information presented in the sources to demonstrate your understanding of the topic.
- Use transitions to smoothly connect ideas between paragraphs and ensure coherence.
Counterargument and Rebuttal
- Acknowledge potential counterarguments or alternative perspectives on the topic.
- Present evidence or reasoning to refute opposing viewpoints.
- This section strengthens your argument by demonstrating that you have considered different perspectives and can effectively defend your position.
- Summarize the main points of your essay and restate your thesis statement.
- Reflect on the significance of your argument and its implications for the broader topic.
- Offer insights or suggestions for further research or discussion.
- End with a compelling closing statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
- If required, include a list of references or a bibliography at the end of your essay.
- Follow the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA) for citing sources used in your essay.
When formatting your synthesis essay, ensure consistency in font size, spacing, margins, and citation style according to the guidelines provided by your instructor or the academic institution. Additionally, proofread your essay carefully to eliminate any grammatical or typographical errors and ensure clarity and coherence in your writing. If you say, ‘ help me write my essay ,’ our experts will respond within minutes with a tangible solution.
How to Write a Synthesis Essay?
Writing a synthesis essay involves several steps to effectively synthesize information from multiple sources and construct a coherent argument. Here's a guide to writing a synthesis essay in seven steps:

Understand the Prompt
Take the time to thoroughly comprehend the synthesis essay prompt. Identify the central topic or issue you're expected to explore. Pay attention to any specific instructions or guidelines provided by your instructor, such as the number of sources required or the formatting style to be used. If there are terms or concepts in the prompt that are unclear, clarify them before proceeding.
Conduct comprehensive research on the topic by gathering information from a variety of sources. These may include academic journals, books, reputable websites, and other scholarly materials. Be sure to critically evaluate the credibility and reliability of each source. Take detailed notes as you read, highlighting key ideas, arguments, and evidence that you can use to support your synthesis essay thesis.
Formulate Your Thesis
Based on your research and analysis, develop a strong thesis statement that clearly states your main argument or position on argumentative synthesis essays topics. Your thesis should be specific, debatable, and concise, providing a roadmap for the rest of your essay. Consider the main points or arguments you plan to make in your essay and how they contribute to your overall thesis.
Outline Your Essay
Organize your thoughts and ideas by creating an outline for your essay. Start with a brief introduction that introduces the topic and provides context for your argument. Then, outline the main points or arguments you'll address in each body paragraph, along with supporting evidence from your sources. Finally, plan your conclusion to summarize your main points and restate your thesis. For more outlining tips, please consult our guide on how to format an essay .
Write Your Introduction
Begin your essay with an attention-grabbing hook that draws the reader in and sets the tone for your essay. Provide some background information on the topic to give context to your argument. Finally, end your introduction with a clear thesis statement that previews the main points you'll be discussing in the body of your essay.
Compose Your Body Paragraphs
In the body of your essay, develop each main point or argument in separate paragraphs. Start each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph. Then, provide evidence from your sources to support your argument, using quotes, paraphrases, or summaries as needed. Analyze the significance of the evidence and explain how it relates to your overall thesis.
Craft Your Conclusion
Summarize the main points of your essay in the conclusion, emphasizing how they support your thesis. Avoid introducing new information or arguments in the conclusion; instead, focus on reinforcing the key ideas you've already presented. End to write synthesis essays with a thought-provoking statement or a call to action that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.

Useful Tips for Writing a Synthesis Essay
Here are some useful tips you can use to write a better synthesis essay:
- Choose Strong Sources
Select credible and relevant sources to support your argument before writing a synthesis essay. Look for sources that provide diverse perspectives on the topic and include a mix of primary and secondary sources.
- Analyze Your Sources
Don't just summarize the sources; critically analyze them. Consider the author's credibility, biases, and the evidence presented. Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each source and how they contribute to your argument.
- Develop a Strong Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement should clearly articulate the main argument or position of your essay. It should be specific, debatable, and supported by evidence from your sources.
- Organize Your Essay
Create a clear and logical structure for your essay. Start with an introduction that provides context for your argument and ends with a strong thesis statement. Then, organize your body paragraphs around key themes or arguments, with each paragraph focusing on a single idea supported by evidence.
- Use Transitions
Use transitional words and phrases to guide the reader through your essay. Transitions help to create coherence and flow between paragraphs and ideas, making your argument easier to follow.
- Blend Sources Seamlessly
Integrate information from your sources smoothly into your own writing. Avoid simply listing sources or relying too heavily on quotations. Instead, paraphrase or summarize the information in your own words and cite your sources appropriately.
- Provide Analysis and Interpretation
Don't just present evidence; analyze and interpret each essential component of a synthesis essay. Explain how each piece of evidence supports your argument and what it reveals about the topic. Use critical thinking to evaluate the significance of the evidence in relation to your thesis.
- Address Counterarguments
Anticipate and address potential counterarguments to your thesis. Acknowledge opposing viewpoints and provide evidence or reasoning to refute them. This demonstrates that you have considered multiple perspectives and strengthens your argument.
- Revise and Edit
Take the time to revise and edit your essay carefully. Check for clarity, coherence, and consistency in your argument and writing style. Proofread for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors, and ensure that your citations are accurate and properly formatted. For more tips, please consult our guide on how to write an academic essay .

Samuel Gorbold , a seasoned professor with over 30 years of experience, guides students across disciplines such as English, psychology, political science, and many more. Together with EssayHub, he is dedicated to enhancing student understanding and success through comprehensive academic support.
- updated the text structure;
- the how-to section was made more specific.
- https://www.bgsu.edu/content/dam/BGSU/learning-commons/documents/writing/synthesis/planning-synthesis-essay.pdf
- https://www.bellevuecollege.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/161/2014/09/synthesis.pdf
- Osborn, S. Synthesis Essays: A Step-by-Step How-To Guide. https://writingcenterofprinceton.com/synthesis-essays-a-step-by-step-how-to-guide/

- Plagiarism Report
- Unlimited Revisions
- 24/7 Support

AP® English Language
Five strategies that will score you a 9 on the ap® english language synthesis frq.
- The Albert Team
- Last Updated On: March 1, 2022

The Advanced Placement (AP) English Language course aligns to an introductory college level rhetoric and writing curriculum. The AP® English Free Response Questions (FRQ’s) are aimed to evaluate students’ ability to develop evidence-based analytic and argumentative essays that go through several stages, which is especially true of the synthesis FRQ.
The synthesis FRQ gives students six sources with which to form and argue for a position on a topic the test provides. In order to score an 8 on the synthesis FRQ question, students need to write an essay that effectively argues a position, synthesizes at least 3 of the sources, uses appropriate and convincing evidence, and showcases a wide range of the elements of writing. Essays that score a 9 do all of that and demonstrate sophistication in their argument.
So how do you write an essay that does all of that in just 40 minutes? First, take a deep breath. And remember, you don’t have to do it on the fly. Prepare yourself. You are given a 15-minute planning period, so make sure that you use it to read the documents, label them, and ask yourself questions about them. Then, while writing the essay, interact with the sources. Don’t just regurgitate them. Use them to support your arguments and question them.
Use these strategies to calm down, be prepared, and write an essay that will earn you a 9 on the AP® English synthesis FRQ.
Read, Carefully, then Label Your Documents.
The AP® English test gives you fifteen minutes to read over the documents. Make sure that you use them! Read over the documents carefully, don’t skim them. Fully comprehend them, and try to understand their meaning. A deeper understanding of the documents will help you much more than a few extra minutes of writing time.
It can seem overwhelming to try and carefully read six sources in fifteen minutes. But the creators of the AP® English Language test don’t want to overwhelm you. Each source is roughly one page and one of the sources is visual–a graph, chart, or photograph. You have time to carefully read all of the documents that the AP® Language synthesis FRQ provides.
After you read each document, it’s a good idea to take a moment to label the documents. Think of the annotations as notes to a friend.
If you had to text your friend right before a test and tell them what this document was about, what would you say? Just write down one sentence or less that explains what the author said. It will help cement your understanding of the source and will help you keep track of all of them.
Here’s an example of a source from the 2014 AP® English synthesis FRQ.

As you are reading, circle and underline things that could be helpful to your later, like the words of the honor code in the first paragraph or the 157 students involved in the cheating scandal in the fourth. But after you have finished reading, write a one-sentence summary near the top of the source. Think of this as your quick-label. For this source, a good example would be a sentence like: “Despite emphasis on not cheating, elite private school caught up in cheating scandal.” The label at the top will help you keep track of the documents. The labels within the documents will help you pull the best evidence to support your arguments. Reading the documents carefully helps you pull out the most important information.
Talk to Yourself. No, Really, it’s a Good Idea.
Before you start writing, craft a thesis. The thesis should be thoughtful and present an argument. One of the best ways to come up with a thesis for the synthesis FRQ, which asks students to formulate an argument, is to come up with several possible positions that you could take.
Then pick one. It can feel a little quick to be asked to form an opinion like that, and some students worry that the argument they come up with from this process won’t be good enough.
Don’t waffle on your opinion. The AP® FRQ is designed to evaluate how well students can synthesize documents and use them to support an argument. In other words, there is no right or wrong answer. As long as you can support your opinion with a well-crafted argument, it’s a good opinion. If you find yourself questioning it in the middle of your essay, just remind yourself to not worry about it.
Your thesis needs to be direct and specific. It shouldn’t give the reader any question as to what opinion you have decided to argue for. It should encompass your entire essay in just one sentence.
The 2014 AP® English synthesis FRQ asked students to synthesize information from six sources and “incorporate it into a coherent, well-developed argument for your own position on whether your school should establish, maintain, revise, or eliminate an honor code or honor system.” For this question:
Good thesis: My school should eliminate our current honor code because honor codes do not adequately prevent cheating and are often used in place of teaching students the ethical reasons for not cheating, as shown by recent scandals both in and out of school.
This thesis breaks down a chronological argument whose evidence can be drawn from the documents. Just reading the thesis tells you that this student’s essay will a) prove that honor codes do not prevent cheating, b) discuss the idea that honor codes promote repeat-after-me ethics over actual understanding and c) draw on examples of cheating in school and out of school (which will be drawn from the documents).
Bad thesis: My school should maintain their current honor code because I don’t cheat, but it should revise it for all the other students who do.
This is not a good thesis because it is not at all clear whether the student is going to argue that their school should maintain their honor code or revise their honor code. The student is waffling on their opinion and the reader will definitely have some questions. The thesis is not specific or direct.
Take your well-crafted thesis and try pretending, briefly, that you sent your thesis to the author of the sources. What would they say? Would they agree or disagree? What parts of their own sources would they bring up? Use that imaginary conversation to help write your outline.
Talking to yourself like this may feel odd, but in the context of writing an essay, it is the best way to organize your thoughts. It will help you to come up with several ideas, pick an opinion, craft a good thesis, and sketch out a good outline.
Resist the Urge to Summarize the Sources.
It is so tempting to summarize the sources, especially when you are in the middle of your synthesis essay and worried you are running out of time. Resist that temptation.
It is important to use the sources in front of your to inform your FRQ response. But the graders of the AP® English test do not want you to simply summarize the sources. They’ve read them.
Try to take a deep breath and instead go for short quotations and paraphrasing. Go back to your notes and read what you underlined to see if it is helpful for quick quotations.
Look at another source from the 2014 AP® English synthesis FRQ:
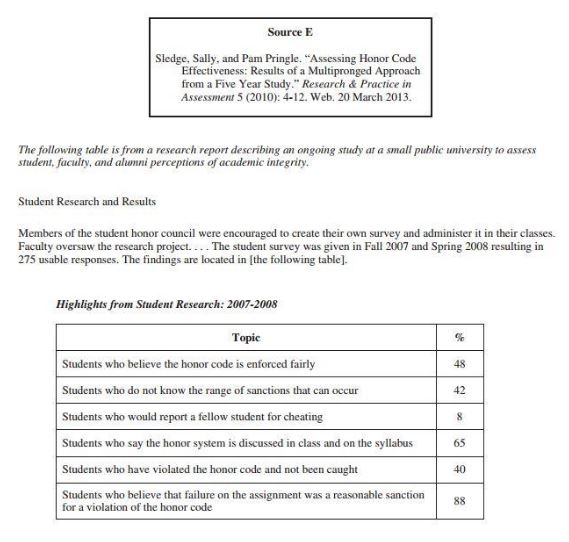
If a student wanted to use this source as support for eliminating honor codes on the basis that they do not work, here is an example of summarizing the source and analyzing the analysis for support.
Summary : Honor codes do not work because only 48% of survey respondents at a small public university believed the honor code was enforced fairly. Only 42% knew the range of sanctions that can occur and just 8% would report a fellow student for cheating. 65% of students say the honor system is discussed in class and on the syllabus and 40% of students have violated the honor code and not been caught. Clearly, honor codes do not work.
Instead of adding to the information from the source, the student just rewrote the information from the source. The student does not include information that the reader cannot get from reading the document.
Analysis: Honor codes are ineffective at preventing cheating. Often, the perception of the honor code varies from the intention of the honor code. It is written to sound as if it will be strictly enforced, but students do not perceive it to be. For example, when students from a small, public university were surveyed, 40% of them admitted to having violated the honor code and gotten away with it, and only 8% of them would report another student for having violated it. While the wording of the honor code was not provided, and so it is unclear how harsh the punishments it promises are, clearly students do not take it seriously. There’s a disconnect between intent and execution, where the school says the honor code is important, but student think it is enforced unfairly, often because they have violated it themselves or they know someone who has.
This paragraph uses the source to support a point. The student is trying to convey that the school appears to take honor codes seriously, but students do not perceive that they do so. The student does not summarize the entire source, but instead pulls two statistics from it and use them to support their argument.
Remember, even if you are running out of time, that quality is always better than quantity on the AP® Language FRQ responses. Take the time to really support your arguments with good quotations instead of stuffing up the rest of your space with summary.
Question the Sources.
Don’t just accept the sources at face value. Pretend that, instead of encountering the sources on the AP® English exam you found them on the Internet. Would you buy them? Why or why not?
The AP® synthesis FRQ graders will appreciate that same type of thinking. Each source comes with a description, at the top, with the name, origin, and author of the source. Use that information to question the sources. Be cynical about the sources and be critical of the information they provide you, if it is appropriate.
Take this excerpt from Source B of the 2016 AP® English synthesis FRQ.

The 2016 question had to do with the educational benefits of learning a foreign language. This David Thomas piece is one of the sources. Here’s a good way to question that source:
Look at the top–the little box at the top of the source contains a treasure trove of information. It says who wrote the article, when they wrote it, and who published the article.
In the case of this source, it was published by Mail Online , an online magazine. As students know, online magazines compete for page views and are interested in selling ads. Rehashing the same ideas does not attract viewers in the same way that being a little controversial does. So, in the case of David Thomas, this piece was written partially to say something different than the rest of the UK and to attract attention to an online magazine.
Questioning the sources does not mean dismissing them. The above analysis isn’t to suggest that David Thomas does not believe what he has written, or that he was simply trying to be contrarian; only that the purpose of an article written for an online opinion column is fundamentally different than an article written in an academic journal, for example. That purpose is reflected in the language and subject matter of the piece.
Treat the sources on the AP® English test the way you would treat sources in the real world. If you wouldn’t believe it if someone shared it as a Facebook status, bringing that disbelief into your essay demonstrates your critical thinking abilities. Just make sure you can back it up and give good reasons for questioning your sources.
Plan to Address the Opposition.
Remember when you came up with several possible responses you could have made to the prompt? Addressing some of them increases the sophistication of your argument astronomically.
The AP® English synthesis FRQ is largely about how well you can handle making an argument. A huge part of good argument involves thinking about the opposition. Take time to engage with the opposite opinion to the one you put forward.
Following these five strategies will ensure a 9 on the AP® English synthesis FRQ and, hopefully, a 5 on the AP® English test. Prepare yourself by reading carefully and labeling the documents. Interact with the documents by explaining them to yourself, using them for support, and questioning them when necessary.
Featured Image Source

Let’s put everything into practice. Try this AP® English Language practice question:
Looking for more AP® English Language practice?
Check out our other articles on AP® English Language .
You can also find thousands of practice questions on Albert.io. Albert.io lets you customize your learning experience to target practice where you need the most help. We’ll give you challenging practice questions to help you achieve mastery of AP® English Language.
Start practicing here .
Are you a teacher or administrator interested in boosting AP® English Language student outcomes?
Learn more about our school licenses here .
Interested in a school license?
Popular posts.

AP® Score Calculators
Simulate how different MCQ and FRQ scores translate into AP® scores

AP® Review Guides
The ultimate review guides for AP® subjects to help you plan and structure your prep.

Core Subject Review Guides
Review the most important topics in Physics and Algebra 1 .

SAT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall SAT® score

ACT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall ACT® score

Grammar Review Hub
Comprehensive review of grammar skills

AP® Posters
Download updated posters summarizing the main topics and structure for each AP® exam.
Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.
How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay (With Example)
November 27, 2023
Feeling intimidated by the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? We’re here to help demystify. Whether you’re cramming for the AP Lang exam right now or planning to take the test down the road, we’ve got crucial rubric information, helpful tips, and an essay example to prepare you for the big day. This post will cover 1) What is the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? 2) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Rubric 3) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis: Sample Prompt 4) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example 5)AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Why It Works
What is the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is one of three essays included in the written portion of the AP English Exam. The full AP English Exam is 3 hours and 15 minutes long, with the first 60 minutes dedicated to multiple-choice questions. Once you complete the multiple-choice section, you move on to three equally weighted essays that ask you to synthesize, analyze, and interpret texts and develop well-reasoned arguments. The three essays include:
Synthesis essay: You’ll review various pieces of evidence and then write an essay that synthesizes (aka combines and interprets) the evidence and presents a clear argument. Read our write up on How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis Essay here.
Argumentative essay: You’ll take a stance on a specific topic and argue your case.
Rhetorical essay: You’ll read a provided passage, then analyze the author’s rhetorical choices and develop an argument that explains why the author made those rhetorical choices.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Rubric
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is graded on just 3 rubric categories: Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication . At a glance, the rubric categories may seem vague, but AP exam graders are actually looking for very particular things in each category. We’ll break it down with dos and don’ts for each rubric category:
Thesis (0-1 point)
There’s nothing nebulous when it comes to grading AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay thesis. You either have one or you don’t. Including a thesis gets you one point closer to a high score and leaving it out means you miss out on one crucial point. So, what makes a thesis that counts?
- Make sure your thesis argues something about the author’s rhetorical choices. Making an argument means taking a risk and offering your own interpretation of the provided text. This is an argument that someone else might disagree with.
- A good test to see if you have a thesis that makes an argument. In your head, add the phrase “I think that…” to the beginning of your thesis. If what follows doesn’t logically flow after that phrase (aka if what follows isn’t something you and only you think), it’s likely you’re not making an argument.
- Avoid a thesis that merely restates the prompt.
- Avoid a thesis that summarizes the text but does not make an argument.
Evidence and Commentary (0-4 points)
This rubric category is graded on a scale of 0-4 where 4 is the highest grade. Per the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis rubric, to get a 4, you’ll want to:
- Include lots of specific evidence from the text. There is no set golden number of quotes to include, but you’ll want to make sure you’re incorporating more than a couple pieces of evidence that support your argument about the author’s rhetorical choices.
- Make sure you include more than one type of evidence, too. Let’s say you’re working on your essay and have gathered examples of alliteration to include as supporting evidence. That’s just one type of rhetorical choice, and it’s hard to make a credible argument if you’re only looking at one type of evidence. To fix that issue, reread the text again looking for patterns in word choice and syntax, meaningful figurative language and imagery, literary devices, and other rhetorical choices, looking for additional types of evidence to support your argument.
- After you include evidence, offer your own interpretation and explain how this evidence proves the point you make in your thesis.
- Don’t summarize or speak generally about the author and the text. Everything you write must be backed up with evidence.
- Don’t let quotes speak for themselves. After every piece of evidence you include, make sure to explain your interpretation. Also, connect the evidence to your overarching argument.
Sophistication (0-1 point)
In this case, sophistication isn’t about how many fancy vocabulary words or how many semicolons you use. According to College Board , one point can be awarded to AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essays that “demonstrate sophistication of thought and/or a complex understanding of the rhetorical situation” in any of these three ways:
- Explaining the significance or relevance of the writer’s rhetorical choices.
- Explaining the purpose or function of the passage’s complexities or tensions.
- Employing a style that is consistently vivid and persuasive.
Note that you don’t have to achieve all three to earn your sophistication point. A good way to think of this rubric category is to consider it a bonus point that you can earn for going above and beyond in depth of analysis or by writing an especially persuasive, clear, and well-structured essay. In order to earn this point, you’ll need to first do a good job with your thesis, evidence, and commentary.
- Focus on nailing an argumentative thesis and multiple types of evidence. Getting these fundamentals of your essay right will set you up for achieving depth of analysis.
- Explain how each piece of evidence connects to your thesis.
- Spend a minute outlining your essay before you begin to ensure your essay flows in a clear and cohesive way.
- Steer clear of generalizations about the author or text.
- Don’t include arguments you can’t prove with evidence from the text.
- Avoid complex sentences and fancy vocabulary words unless you use them often. Long, clunky sentences with imprecisely used words are hard to follow.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis: Sample Prompt
The sample prompt below is published online by College Board and is a real example from the 2021 AP Exam. The prompt provides background context, essay instructions, and the text you need to analyze. For sake of space, we’ve included the text as an image you can click to read. After the prompt, we provide a sample high scoring essay and then explain why this AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay example works.
Suggested time—40 minutes.
(This question counts as one-third of the total essay section score.)
On February 27, 2013, while in office, former president Barack Obama delivered the following address dedicating the Rosa Parks statue in the National Statuary Hall of the United States Capitol building. Rosa Parks was an African American civil rights activist who was arrested in 1955 for refusing to give up her seat on a segregated bus in Montgomery, Alabama. Read the passage carefully. Write an essay that analyzes the rhetorical choices Obama makes to convey his message.
In your response you should do the following:
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis that analyzes the writer’s rhetorical choices.
- Select and use evidence to support your line of reasoning.
- Explain how the evidence supports your line of reasoning.
- Demonstrate an understanding of the rhetorical situation.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating your argument.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
In his speech delivered in 2013 at the dedication of Rosa Park’s statue, President Barack Obama acknowledges everything that Parks’ activism made possible in the United States. Telling the story of Parks’ life and achievements, Obama highlights the fact that Parks was a regular person whose actions accomplished enormous change during the civil rights era. Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did.
Although it might be a surprising way to start to his dedication, Obama begins his speech by telling us who Parks was not: “Rosa Parks held no elected office. She possessed no fortune” he explains in lines 1-2. Later, when he tells the story of the bus driver who threatened to have Parks arrested when she refused to get off the bus, he explains that Parks “simply replied, ‘You may do that’” (lines 22-23). Right away, he establishes that Parks was a regular person who did not hold a seat of power. Her protest on the bus was not part of a larger plan, it was a simple response. By emphasizing that Parks was not powerful, wealthy, or loud spoken, he implies that Parks’ style of activism is an everyday practice that all of us can aspire to.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example (Continued)
Even though Obama portrays Parks as a demure person whose protest came “simply” and naturally, he shows the importance of her activism through long lists of ripple effects. When Parks challenged her arrest, Obama explains, Martin Luther King, Jr. stood with her and “so did thousands of Montgomery, Alabama commuters” (lines 27-28). They began a boycott that included “teachers and laborers, clergy and domestics, through rain and cold and sweltering heat, day after day, week after week, month after month, walking miles if they had to…” (lines 28-31). In this section of the speech, Obama’s sentences grow longer and he uses lists to show that Parks’ small action impacted and inspired many others to fight for change. Further, listing out how many days, weeks, and months the boycott lasted shows how Parks’ single act of protest sparked a much longer push for change.
To further illustrate Parks’ impact, Obama incorporates Biblical references that emphasize the importance of “that single moment on the bus” (lines 57-58). In lines 33-35, Obama explains that Parks and the other protestors are “driven by a solemn determination to affirm their God-given dignity” and he also compares their victory to the fall the “ancient walls of Jericho” (line 43). By of including these Biblical references, Obama suggests that Parks’ action on the bus did more than correct personal or political wrongs; it also corrected moral and spiritual wrongs. Although Parks had no political power or fortune, she was able to restore a moral balance in our world.
Toward the end of the speech, Obama states that change happens “not mainly through the exploits of the famous and the powerful, but through the countless acts of often anonymous courage and kindness” (lines 78-81). Through carefully chosen diction that portrays her as a quiet, regular person and through lists and Biblical references that highlight the huge impacts of her action, Obama illustrates exactly this point. He wants us to see that, just like Parks, the small and meek can change the world for the better.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Why It Works
We would give the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay above a score of 6 out of 6 because it fully satisfies the essay’s 3 rubric categories: Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication . Let’s break down what this student did:
The thesis of this essay appears in the last line of the first paragraph:
“ Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did .”
This student’s thesis works because they make a clear argument about Obama’s rhetorical choices. They 1) list the rhetorical choices that will be analyzed in the rest of the essay (the italicized text above) and 2) include an argument someone else might disagree with (the bolded text above).
Evidence and Commentary:
This student includes substantial evidence and commentary. Things they do right, per the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis rubric:
- They include lots of specific evidence from the text in the form of quotes.
- They incorporate 3 different types of evidence (diction, long lists, Biblical references).
- After including evidence, they offer an interpretation of what the evidence means and explain how the evidence contributes to their overarching argument (aka their thesis).
Sophistication
This essay achieves sophistication according to the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay rubric in a few key ways:
- This student provides an introduction that flows naturally into the topic their essay will discuss. Before they get to their thesis, they tell us that Obama portrays Parks as a “regular person” setting up their main argument: Obama wants all regular people to aspire to do good in the world just as Rosa Parks did.
- They organize evidence and commentary in a clear and cohesive way. Each body paragraph focuses on just one type of evidence.
- They explain how their evidence is significant. In the final sentence of each body paragraph, they draw a connection back to the overarching argument presented in the thesis.
- All their evidence supports the argument presented in their thesis. There is no extraneous evidence or misleading detail.
- They consider nuances in the text. Rather than taking the text at face value, they consider what Obama’s rhetorical choices imply and offer their own unique interpretation of those implications.
- In their final paragraph, they come full circle, reiterate their thesis, and explain what Obama’s rhetorical choices communicate to readers.
- Their sentences are clear and easy to read. There are no grammar errors or misused words.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay—More Resources
Looking for more tips to help your master your AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? Brush up on 20 Rhetorical Devices High School Students Should Know and read our Tips for Improving Reading Comprehension . If you’re ready to start studying for another part of the AP English Exam, find more expert tips in our How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis blog post.
Considering what other AP classes to take? Read up on the Hardest AP Classes .
- High School Success
Christina Wood
Christina Wood holds a BA in Literature & Writing from UC San Diego, an MFA in Creative Writing from Washington University in St. Louis, and is currently a Doctoral Candidate in English at the University of Georgia, where she teaches creative writing and first-year composition courses. Christina has published fiction and nonfiction in numerous publications, including The Paris Review , McSweeney’s , Granta , Virginia Quarterly Review , The Sewanee Review , Mississippi Review , and Puerto del Sol , among others. Her story “The Astronaut” won the 2018 Shirley Jackson Award for short fiction and received a “Distinguished Stories” mention in the 2019 Best American Short Stories anthology.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight
“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
Writing a Multiple-Source (Synthesis) Essay
DEVELOPING YOUR PARAGRAPHS:
To develop a body paragraph, follow a basic " three-step " approach:
1.) Decide on a main point and then state that main point in a sentence (the topic sentence for the paragraph). For example :
- � One common theme that emerges from these essays is that watching movies and reading books are social acts .�
- "One noticeable similarity in the Dillard and Hughes essays is that children are causing trouble for adults."
- "A main element in the process of death is the stage of grief."
2.) Next, reread the essays looking for �evidence� to use to support your main idea. For example :
- I might look for examples or quotes in the Ebert, Welty, Toth, and King essays about the "social" act of watching movies and reading books.
- I would summarize the parts of the Dillard and Hughes essays where the children are causing trouble for the adults.
- I would summarize or quote from the Woolf and Momaday essays when the writers talk about grieving the loss of the animal or family member.
3.) Finally, you don�t want to abruptly end your paragraph and just leave the examples , summaries, or quotes just hanging there. You want to �drive home� your point, emphasize what is important about it, add your own commentary (thoughts, feelings, opinions) or your own experiences about the main idea and/or the examples.
- In essence, you want to ask and answer the question, �So What?�
For more information and examples (from a different essay) about developing paragraphs, click here .
DOCUMENTING YOUR SOURCES:
Whenever you use someone else's words or ideas in your writing, you must let the reader know the source of those words or ideas. It really doesn't matter whether you have paraphrased , summarized , or quoted -- in each case, you must let the reader know whose material you are using.
Up to this point, your writing assignments have focused on one reading selection at a time. In them you have used simple transitions to tell the reader when you were using material from the reading selection. There are, however, more formal methods of documentation that you will need to learn to use as you write in college classes.
The MLA (Modern Language Association) is one method of documentation, used primarily in the humanities. It uses parentheses within the paper to identify the author and page number of a particular passage that is paraphrased, summarized, or quoted. It also uses a separate page at the end of the paper to give more detailed and complete identification of the sources used. Because we are using "common texts" in this class -- texts that everyone has, either from our book or on handouts I have provided -- you do not need to write a separate "Works Cited" page for this paper.
Use these guidelines to help you:
- Each paraphrase, summary, and quotation should be identified by author and page number in parentheses. Do not use the author's first name within the parentheses.
- If the author's name is already included in the "signal phrase" in the sentence, it does not need to be repeated in the parentheses.
- No punctuation is placed between the author's last name and the page number.
- The parenthetical citation is placed at the end of the borrowed material but before the period at the end of the sentence.
MORE INFORMATION ABOUT USING SOURCES :
You have three choices when you take someone else�s words / ideas from their writing to put into your own writing:
1.) QUOTATION: copy the words and punctuation exactly like it is in the other writer�s essay; be extremely accurate; use quotation marks.
2.) SUMMARY: you use your own words to �shrink� down another writer�s ideas to the main things you want to highlight or emphasize; even though you use your own words, you must still give credit to the writer.
3.) PARAPHRASE: you use your own words to �translate� or �restate� more clearly another writer�s ideas; your paraphrase should be roughly the same length as the passage you are paraphrasing; you will need to change both many of the words and the sentence structure(s) of the passage you are paraphrasing; even though you use your own words, you must still give credit to the writer.
Finally, there are three steps to take to put a summary, a paraphrase, or a quotation into your paper :
1.) First, use a �signal phrase.� Here, you are giving credit to the person who the words/ideas belong to and you are �signaling� to your reader that you are putting something in your paper that doesn�t belong to you. Examples of signal phrases include �According to Annie Dillard, ... � or �As George Orwell says , ... � or � Susan Allen Toth states that ... �
2.) Second, put in the summary, paraphrase, or quotation. (You can also use a combination of summary, paraphrase, and quotation.)
3.) Third, use a �parenthetical citation.� If you have put the author�s name in your sentence, all you need in the citation is the page number, for example (16). If you did not put the author�s name in your sentence, then include the name with the page number, for example ( Dillard 16).
How to Write a Synthesis Essay: Your Guide From Start to Finish

Today, we're swamped with information, like reading 174 newspapers every day. It comes from all over—news, social media, science, and more. This flood might make you feel overwhelmed and lost in a sea of facts and opinions. But being able to make sense of it all is crucial.
This guide isn't just about handling all that info; it's about using it to write awesome essays. We'll show you step by step how to pick a topic and organize your essay. Let's dive in and learn how to turn scattered facts into powerful essays that really stand out.
What Is a Synthesis Essay
The synthesis essay is a powerful tool in writing. It's not just about gathering facts but about connecting them to make a clear and strong argument.
Writing a synthesis essay allows you to dive deep into ideas. You have to find similarities between different sources—like articles, studies, or arguments—and use them to tell a convincing story.
In today's world, where we're bombarded with information, synthesis essays are more important than ever. They let us explore how different ideas fit together and help us express our thoughts on complex topics. Whether you're writing about literature, science, history, or current events, a synthesis essay shows off your ability to analyze and understand a topic from all angles. And if you're struggling with this task, just ask us to ' write paper for me ,' and we'll handle your assignment for you.
Explanatory vs. Argumentative Synthesis Essays
In synthesis writing, there are two main types: explanatory and argumentative. Understanding these categories is key because they shape how you approach your essay.
Explanatory:
An explanatory synthesis essay does just what it says—it explains. These essays aim to give a balanced view of a topic by gathering information from different sources and presenting it clearly. They don't try to persuade; instead, they focus on providing information and making things easier to understand. They're like comprehensive summaries, breaking down complex ideas for a broader audience. These essays rely heavily on facts and expert opinions, avoiding personal bias.
Argumentative:
On the flip side, argumentative synthesis essays are all about persuasion. Their main goal is to take a stance on an issue and convince the reader. They gather information from various sources not only to present different views but also to build a strong argument. Argumentative essays aim to sway the reader's opinion by using gathered information as evidence. These essays express opinions and use rhetorical strategies to persuade.
And if you're keen on knowing how to write an informative essay , we've got you covered on that, too!
Synthesis Essay Structure
To craft a strong synthesis essay, you need a solid foundation. Here's a structured approach to help you nail it:
Introductory Paragraph:
- To kick things off, grab your reader's attention with a catchy hook or interesting fact. Give a bit of background info about your topic and the sources you'll be using, as it can help readers understand your topic better! Then, lay out your main argument in a clear thesis statement.
Body Paragraphs:
- Each paragraph should focus on a different aspect of your topic or source. Start with a topic sentence that links back to your thesis. Introduce the source you're discussing and highlight its main points. Also, using quotes, paraphrases, or summaries from your sources can make your arguments stronger.
Synthesis :
- This part is where your essay comes together. Look for common themes or differences among your sources. Use your analysis to build a strong argument. Don't forget to address any opposing viewpoints if they're relevant!
Conclusion :
- Wrap things up by restating your thesis and summarizing your main points. Explain why your argument is important and what it means in the bigger picture. End with a thought-provoking statement to leave a lasting impression.
References :
- Finally, don't forget to list all your sources properly using the right citation style, like MLA or APA. Do you know that different citation styles have different rules? So, make sure you follow the right one!
Choosing a Synthesis Essay Topic
Picking essay topics is just the beginning. To write a great synthesis essay, you need to carefully evaluate and connect different sources to build a strong argument or viewpoint. Here's a step-by-step infographic guide to help you choose the right synthesis essay topics wisely.

How to Write a Synthesis Essay with Easy Steps
Writing a synthesis essay is similar to a compare and contrast essay . It requires a methodical approach to blend information from different sources into a strong and persuasive argument. Here are some crucial steps and tips to help you along the way.
- Clarify Your Purpose: First, decide if you're writing an explanatory or argumentative synthesis essay. This choice will set the tone and direction for your essay.
- Source Selection and Analysis: Choose credible and relevant sources for your topic, balancing different types like articles, books, and websites. Analyze each source carefully, noting the main ideas and evidence presented.
- Formulate a Strong Thesis Statement: Create a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your essay. It should express your main argument or perspective.
- Structure Your Essay: Organize your essay with a clear synthesis essay outline, including an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each body paragraph should focus on a specific aspect of your topic.
- Employ Effective Transition Sentences: Use transition sentences to connect your ideas and paragraphs smoothly, ensuring a cohesive flow in your essay.
- Synthesize Information: Blend information from your sources within your paragraphs. Discuss how each source contributes to your thesis and highlight common themes or differences.
- Avoid Simple Summarization: Don't just summarize your sources—analyze them critically and use them to build your argument.
- Address Counterarguments (if applicable): Acknowledge opposing viewpoints and counter them with well-supported arguments, showing a deep understanding of the topic.
- Craft a Resolute Conclusion: Summarize your main points and restate your thesis in the conclusion. Emphasize the importance of your argument or insights, and end with a thought-provoking statement or call to action.
- Revise and Proofread: Check your essay for clarity, coherence, and grammar mistakes. Ensure your citations are correct and follow the chosen citation style, like MLA or APA.
Ready to Transform Your Synthesis Essay from Bland to Grand?
Let's tap into the magic of our expert wordsmiths, who will create an essay that dances with ideas and dazzles with creativity!
Synthesis Essay Format
Choosing the right citation style can enhance the credibility and professionalism of your paper. The format of your synthesis paper depends on the specific guidelines given by your instructor. They usually fall into one of the popular styles: MLA, APA, or Chicago, each used in different academic fields.

1. MLA (Modern Language Association):
- Uses in-text citations with the author's last name and page number.
- Includes a 'Works Cited' page at the end listing all sources.
- Focuses on the author and publication date.
- Often used in humanities essays, research papers, and literary analyses.
2. APA (American Psychological Association):
- Uses in-text citations with the author's last name and publication date in parentheses.
- Includes a 'References' page listing all sources alphabetically.
- Emphasizes the publication date and scientific precision.
- Commonly used in research papers, scholarly articles, and scientific studies.
3. Chicago Style:
- Offers two documentation styles: Notes-Bibliography and Author-Date.
- Notes-Bibliography uses footnotes or endnotes for citations, while Author-Date uses in-text citations with a reference list.
- Suitable for various academic writing, including research papers and historical studies.
- Provides flexibility in formatting and citation methods, making it adaptable to different disciplines.
Synthesis Essay Example
Here are two examples of synthesis essays that demonstrate how to apply the synthesis process in real life. They explore interesting topics and offer practical guidance for mastering the art of writing this type of paper.
Synthesis Essay Tips
Crafting a strong synthesis essay requires careful planning and effective techniques. Here are five essential tips to help you write your best paper:
- Diverse Source Selection : Choose a range of reliable sources that offer different viewpoints on your topic. Make sure they're recent and relevant to your subject.
- Seamless Source Integration : Avoid just summarizing your sources. Instead, blend them into your essay by analyzing and comparing their ideas. Show how they connect to build your argument.
- Balanced Tone : Maintain an impartial tone in your writing, even if you have personal opinions. Synthesis essays require objectivity, so they present different viewpoints without bias.
- Focus on Synthesis : Remember, synthesis essays are about linking ideas, not just summarizing sources. Explore how your sources relate to each other to create a cohesive argument.
- Address Counterarguments : Like in persuasive essays topics , acknowledge opposing viewpoints and explain why your perspective is stronger. This demonstrates your understanding of the topic and adds depth to your argument.
Concluding Thoughts
When writing a synthesis essay, it's essential to pick trustworthy sources, blend them effectively to build your argument and stay objective. Use smooth transitions, address counterarguments thoughtfully, and focus on analyzing rather than just summarizing. By following these steps, you'll create essays that inform, persuade, and engage your readers!
Want an Essay that Sings, Sparkles, and Stuns?
Fear not! Our expert wordsmiths are here to turn your thoughts into a symphony of ideas!
How Should You Conclude a Synthesis Essay?

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Related Articles
%20(3).webp)
How to Write a Synthesis Essay: Examples, Topics, & Outline
A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place!
In this guide by our custom writing team, you will find:
- a step-by-step writing guide;
- a list of 34 synthesis essay topics;
- a full essay sample in MLA format.
- 📚 Synthesis Essay Definition
- 📝 Essay Types
- ✅ Step-by-Step Guide
- ✍️ Topics & Prompts
- 📑 Example & Formatting Tips
📚 What Is a Synthesis Essay?
A synthesis essay is an assignment that requires a unique interpretation of a particular topic using several reliable sources. To write it, you need to understand, analyze, and synthesize information. That is why this type of essay is used in the AP Lang exam to assess students’ reasoning skills.
The key features of the synthesis essay are:
- Debatable topic . If your goal is to write a good synthesis essay, it’s necessary to choose an arguable topic. It’s best to choose something that people have different opinions about. This will allow you to use many sources with various viewpoints for your synthesis.
- Clear thesis statement. It’s a sentence that briefly describes the main idea of your essay.
- Reliable sources to prove your thesis . For a synthesis essay, your opinion is not enough. You also need to find the evidence. Keep in mind that simply reading an online encyclopedia won’t do; make sure to choose only reliable sources.
What Does It Mean to Synthesize Information?
Synthesis is a process that has huge importance in nature, science, and our everyday life. The word stems from Ancient Greek “synthesis,” which means “putting together.” In general, synthesis is the combination of components to form a connected whole.
In everyday life, we usually resort to it to synthesize information . This means taking the data from different sources and bringing it together. This process is the opposite of analyzing:
- For an analysis , you break problems into pieces,
- For a synthesis , you combine separate elements into a whole.
We use synthesis for analysis papers, research papers, argument papers, and business reports.
What Does Synthesis Mean in Writing?
Synthesis in writing means summarizing and connecting different sources considering a particular topic. Although synthesis and analysis are two opposite things, they usually go together in synthesis essays. The process consists of 2 stages:
- Conduct the analysis. For that, you break down a problem into parts and analyze the sources. It’s helpful to highlight everything regarding your topic while reading.
- Carry out the synthesis. The next step is to formulate an opinion and combine the highlighted information from the sources.
Synthesis is not only used in writing but also in reading comprehension . It’s useful to do this kind of reading while studying your sources. There are three reading comprehension stages:
- Your previous knowledge about the topic.
- Expansion of your knowledge while you are reading.
- Understanding of the problem when you have finished reading.
So, synthesized reading comprehension means combining three stages in one and formulating one statement.
Synthesis vs Summary: What Is the Difference?
A summary is a paraphrasing of the written source in your own words. For a good summary, it’s necessary to include all of the text’s key elements. Meanwhile, synthesis means combining different ideas from different sources. You don’t have to include all the key points; just choose everything related to your topic.
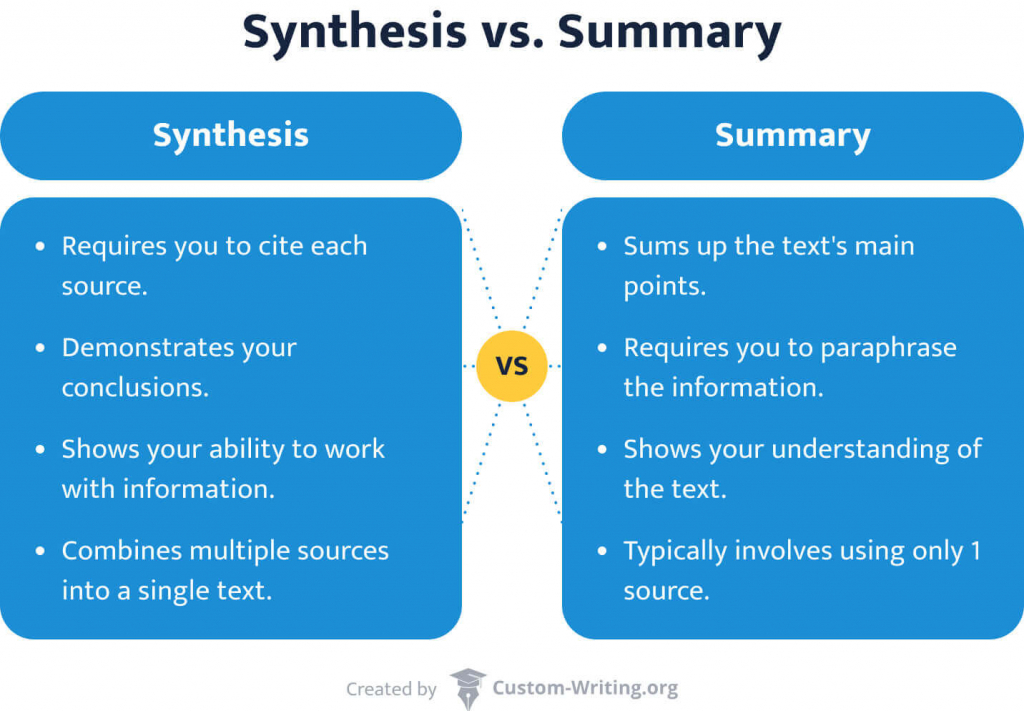
Both of these techniques are used for the synthesis essay:
- The summary goes in the conclusion. You briefly sum up your paper’s main ideas.
- Synthesis goes in the body paragraphs. Here, you combine multiple sources to prove a point.
📝 Synthesis Essay Types
There are two main types of a synthesis essay: argument and explanatory synthesis.
Both of them require working with multiple reliable sources and analyzing information. The only difference is that an argument synthesis essay requires your own opinion, while an explanatory synthesis essay does not.
Argument Synthesis Essay: Outline and Definition
As you already know, an argument synthesis essay requires you to state your own opinion about the given topic and back it up with several reliable sources. The purpose of such an essay is to persuade the reader that your point is correct.
Here’s what an argument synthesis essay consists of:
Explanatory Synthesis Essay: Definition and How to Write
An explanatory informative synthesis essay requires you to stay neutral towards the problem you are discussing. This means you cannot express your own opinion considering the given question or a problem. Your task is just to inform the reader. That’s why this essay type is also called informative synthesis.
Check out this explanatory essay outline:
✅ How to Write a Synthesis Essay Step by Step
When it comes to the synthesis essay outline, it’s not too different from other assignments. Have a look at this template:
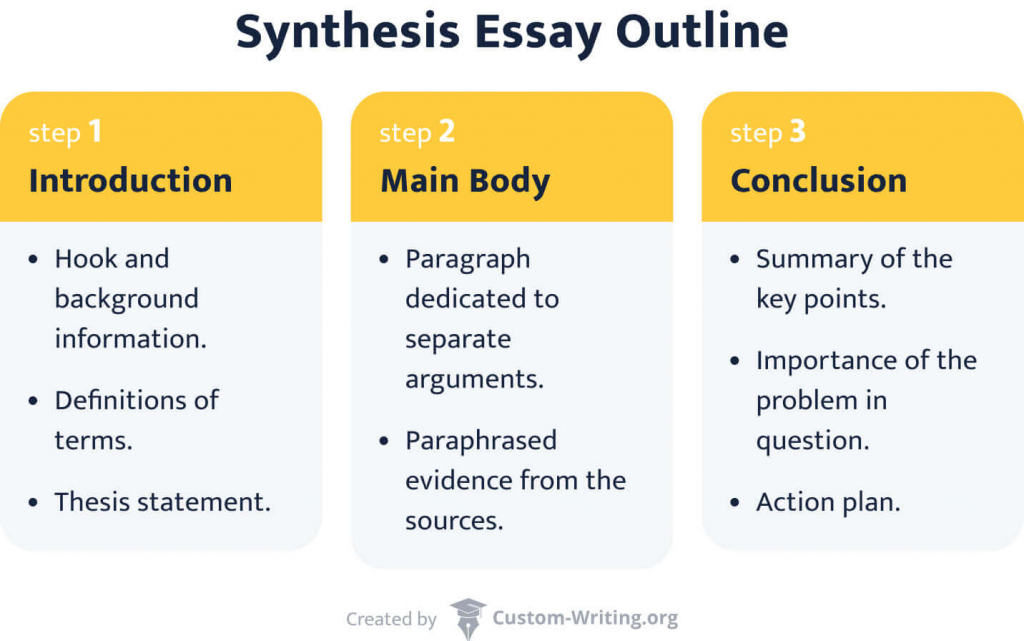
How to Synthesize: Working with Sources
After you’ve decided on your topic, it’s time to figure out how to synthesize articles into one text. This is how you do it:
- Choose reliable sources: the ones printed in journals or published on academic websites.
- Become familiar with them and see if they fit into your essay.
- Try to find a few sources for each point. It will increase your essay’s reliability.
- Relate each source to your arguments and see similarities between them.
- Don’t forget to list every source in the references.
When you are done with a comprehensive analysis of related literature, try to step back and imagine a person who has a different opinion on this topic. Think of some arguments that they can provide to prove their opinion. After you have the list of arguments, find the written evidence of why they are wrong and put them in your essay.
Analyzing and organizing sources is the first and very important step for the synthesis essay. So make sure you do understand what the text means before using it as a reference.
Synthesis Essay Outline: How to Write
For structuring your essay, it’s useful to try mapping . This technique means combining the information from different sources and rearranging it to create a new direction. To do it, you need to analyze the authors’ ideas and come up with your own conclusions.
The best way to do that is called synthesis matrix or graphic organizer. It’s a chart that you can make when you start working on your essay. Here you have a horizontal column that states the main ideas and a few vertical columns that present sources. Your task is to take sources you have chosen and write down the main ideas from them.
Here’s an example of a matrix chart:
While doing that, you will see how many sources contain the same ideas. When you analyze them, you will be able to formulate your thesis backed up with evidence. The synthesis matrix also helps to see new arguments you can cover in your synthesis paper.
How to Write an Introduction for a Synthesis Essay
Now it’s time to start writing the paper. In the introductory part of the essay, you can include:
- A short yet catchy sentence or a quotation that would present the topic. The start of your essay should make people interested. It’s best to make the first sentence not only informative but also easy to understand.
- The texts that are used for the essay. Provide the titles and the authors’ names (use the appropriate guidelines depending on the writing style.)
- The background information which is needed to understand your essay. Definitions of terms or unknown words considering the topic can be included in this part. Otherwise, people may find it hard to understand what they are reading about.
How to Write a Thesis for a Synthesis Essay
A thesis statement is a point of view on a certain problem that you will defend in your essay. It should contain the key points that you want to include in your paper. Here’s how to create a perfect thesis statement:
- Find several central ideas in the chart.
- Choose the ones that are repeated the most often and the ones that you feel need to be in your essay.
- Combine them, and you have a thesis statement with all the key points.
- Make a draft of the thesis statement. Try to formulate the main idea you want to present in your essay.
- Elaborate on this idea. Add some details and expand it a bit further.
If the whole picture is coherent, and it conveys exactly what you wanted, then this is your perfect thesis statement. See the example below:
Gender inequality still exists at the workplace: women are less likely to get the most responsible positions, easily lose careers due to maternity leave, and often receive less pay for the same amount of work.
How to Write Synthesis Paragraphs for the Main Body
Your essay’s main body consists of a few paragraphs. Each of them presents a different argument considering the topic. When you start a paragraph, make sure to begin with a topic sentence, which informs the reader about the paragraph’s main idea. Then, include the synthesized sources and elaborate on them.
Here’s what you should and shouldn’t do when writing the main body:
You can use the following words to present the ideas from your sources. They will help you reflect the authors’ tone:
How to Conclude a Synthesis Essay
There are quite a few ways to conclude the synthesis paper. Have a look at some of the options:
- Paraphrase the thesis. As you remember, the thesis is the main idea of your essay. The conclusion is a good place to remind your readers about it. When they are done with the reading, they remember the most important thing from your essay.
- Synthesize the arguments. There is no need to repeat everything you wrote in your essay. Just briefly summarize the most crucial points.
- Answer the “So what” question. Tell the readers why this topic matters, why you’ve chosen it, and why it’s valuable for the reader.
- Provide a closure. It’s an effective strategy when you want to make the reader think. Leave them with a strong statement at the end of your essay.
Synthesis Paper Proofreading Tips
When you have finally written your paper, there is still one important thing left to do. You need to check your paper for any grammatical and contextual mistakes. You certainly can do it yourself, but it would be perfect if you could ask somebody else to read it.
The first thing you need to check grammar-wise is the tense you are using. There is no single tense you need to use for the synthesis essay. It depends on the format:
- If you’re writing in MLA format, use the present tense;
- For APA essays, you use the past tense.
The next step is to check whether your synthesis essay has everything that’s required. For that, we have prepared the checklist of questions you can ask yourself to proofread your essays.
- Is there a clear thesis statement?
- Did you include all of the key points from the synthesis?
- Are there clear transitions between paragraphs?
- Did you organize a paragraph around a single idea?
- Did you use reliable and up-to-date sources?
- Did you analyze sources rather than just summarize them?
- Did you mention every source you’ve used?
If you’ve answered “yes” to all the questions—congratulations, you are done with the essay! Otherwise, you need to come back and fix everything that you’ve answered “no” to.
✍️ Synthesis Essay Topics and Prompts
Sometimes, when you don’t have a topic , it is tough to come up with a suitable idea. That is why we have prepared two lists of topics that you can use for any synthesis essay type.
Explanatory Synthesis Essay Topics
The topics below are suitable for an explanatory synthesis essay:
- The beginning of Hollywood cinema . Cinema is a huge industry in the USA. Tell the readers about its history. Describe what it was like in the beginning, which movie was the first one, and who started this industry.
- Tactics on dealing with noisy children. Sometimes kids can be very loud, especially in public places. Write about different tactics that can help with this issue.
- The effects of climate change on the water cycle. Climate change has affected the water cycle significantly. Your task is to explain how.
- The best American cities to live in. Provide the list of the best cities and explain why you’ve included them.
- The importance of a healthy diet . Keeping a healthy diet is beneficial in many ways. Write about all the advantages it brings.
- Who can become an entrepreneur? Entrepreneurship is not for everybody. In this essay, you can describe the qualities needed for having your own business.
- The correlation between overpopulation and poverty . Describe how overpopulation leads to poverty and vice versa.
- The advantages of taking an active vacation.
- Cultural shock as a part of moving to a different country.
- The consequences of the first wave of feminism.
- Synthesis of Tan and Rodriguez’ essays ideas.
- Difficulties you may encounter during the job interview.
- How does reading prevent Alzheimer’s disease?
- The effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on businesses.
- The connection between religion and politics in ruling the country.
- What can non-verbal signals tell you about a person ?
- The psychology of leadership .
- The origins of the most common stereotypes about Americans.
- Role of social media in business communication .
- The synthesis of personal nursing philosophy concept.
- Behavioral components of schizophrenia and psychosis.
- Main components of successful entrepreneurship.
- Critical components of scientific research.
- Change in religion and human beliefs throughout history.
- The effect of global warming on modern life.
Argument Synthesis Paper Topics
The list of topics for the Argument Synthesis Essay:
- Vaping is better than smoking. People are starting to exchange cigarettes for vapes and e-cigarettes. In what ways are they less harmful?
- Rich people should pay higher taxes. The same percentage of money doesn’t equal for rich and poor people. Explain why the ones who can afford more should share with others.
- Depression is a disease. Prove that psychological problems must be recognized as real health issues that should be cured and not ignored.
- Social media affects young people’s lives. Social media has a massive influence on people. In this essay, you can discuss which life spheres are the most affected.
- Beauty pageants should be banned. Provide the reasons why they should be banned and tell the reader about psychological problems they can cause.
- People should cut meat from their diet to stop global warming. Describe how the meat industry influences climate change.
- The voting age should be 25+. Your task is to show the reasons why the votes of people under 25 should not be taken into account during elections.
- A healthy lifestyle requires a lot of money.
- Each healthy man should serve in the military.
- School bullying should be punished by immediate exclusion.
- Does friendship exist between men and women?
- Drinking coffee is a bad habit.
- Working hard is more important than being talented.
- Everybody should visit a therapist at least once.
- Should universities be free?
- Artificial intelligence will cause huge unemployment rates.
- Gaming should not be allowed to children under 18.
- Components and strategies of social responsibility
- Integration of relevant ethical theory and conceptual principles in health care
- Children under 10 should be banned from gadgets .
- Social media platforms facilitate cyberbullying.
- Issues of distance education .
- Social media addiction is a serious disease.
- Deforestation critically contributes to global warming.
- Healthcare should be free for everyone.
📑 Synthesis Essay Example & Synthesis Essay Format Tips
Now let’s talk about formatting. There are two writing styles you can use for a synthesis essay: APA or MLA. You need to choose the one that is required for your assignment.
We will start with the paper in APA format. It is usually used in science and education.
And these are MLA formatting rules:
Finally, we’ve prepared a synthesis essay sample for you to check out. Feel free to download the PDF file below:
First introduced in the Civil Rights Act of 1964, affirmative action policies aim to mitigate the discrepancy in opportunities available for underrepresented social groups by taking into account one’s minority background. The policies have become a pressing public issue that obstructs previously marginalized individuals, particularly in the educational environment.
Thank you for reading the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing. We hope you found it helpful. Don’t forget to share it with your friends. Good luck with your assignments!
🔍 References
- Writing a Synthesis Essay: Bowling Green State University
- What Is Synthesis: University of Manitoba
- Synthesis: Biology Online
- Reading Strategies: Difference Summarizing and Synthesizing: WordPress
- Summary, Analysis, Synthesis Definitions: University of Utah
- Argumentative Synthesis: University of Arkansas
- How to Synthesize Written Information: Simply Psychology
- Mapping of Synthesis Essay: University of Nevada, Reno
- Writing a Literature Review and Using a Synthesis Matrix: Florida International University
- Synthesis Essay: Cleveland State University
- Literature Review: Synthesizing Multiple Sources: Louisiana State University
- Writing a Conclusion: Texas Women’s University
- General APA Guidelines: Purdue University
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Do you know how to make your essay stand out? One of the easiest ways is to start your introduction with a catchy hook. A hook is a phrase or a sentence that helps to grab the reader’s attention. After reading this article by Custom-Writing.org, you will be able to...

A critical analysis essay is an academic paper that requires a thorough examination of theoretical concepts and ideas. It includes a comparison of facts, differentiation between evidence and argument, and identification of biases. Crafting a good paper can be a daunting experience, but it will be much easier if you...

Critical thinking is the process of evaluating and analyzing information. People who use it in everyday life are open to different opinions. They rely on reason and logic when making conclusions about certain issues. A critical thinking essay shows how your thoughts change as you research your topic. This type...

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: process analysis and its typesa process analysis outline tipsfree examples and other tips that might be helpful for your college assignment So,...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...
![how to write synthesis essay aplac Critical Writing: Examples & Brilliant Tips [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/fingers-note-report-journalist-filling-284x153.jpg)
Any critique is nothing more than critical analysis, and the word “analysis” does not have a negative meaning. Critical writing relies on objective evaluations of or a response to an author’s creation. As such, they can be either positive or negative, as the work deserves. To write a critique, you...

If you are assigned to write a rhetorical analysis essay, you have one significant advantage. You can choose a text from an almost infinite number of resources. The most important thing is that you analyze the statement addressed to an audience. The task of a rhetorical analysis essay is to...

Any literary analysis is a challenging task since literature includes many elements that can be interpreted differently. However, a stylistic analysis of all the figurative language the poets use may seem even harder. You may never realize what the author actually meant and how to comment on it! While analyzing...

As a student, you may be asked to write a book review. Unlike an argumentative essay, a book review is an opportunity to convey the central theme of a story while offering a new perspective on the author’s ideas. Knowing how to create a well-organized and coherent review, however, is...

The difference between an argumentative and persuasive essay isn’t always clear. If you’re struggling with either style for your next assignment, don’t worry. The following will clarify everything you need to know so you can write with confidence. First, we define the primary objectives of argumentative vs. persuasive writing. We...
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Synthesis Essay
Last Updated: April 7, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,123,116 times.
Writing a synthesis essay requires the ability to digest information and present it in an organized fashion. While this skill is developed in high school and college classes, it translates to the business and advertising world as well. Scroll down to Step 1 to begin learning how to write a synthesis essay.
Examining Your Topic

- Argument synthesis: This type of essay has a strong thesis statement that presents the writer's point of view. It organizes relevant information gathered from research in a logical manner to support the thesis' point of view. Business white papers known as position papers often take this form. This is the type of synthesis essay that students will write during the AP test.
- Review: Often written as a preliminary essay to an argument synthesis, a review essay is a discussion of what has been written previously on a topic, with a critical analysis of the sources covered. Its unstated thesis is usually that more research needs to be done in that area or that the topic problem has not been adequately addressed. This type of paper is common in social science classes and in medicine.
- Explanatory/background synthesis: This type of essay helps readers understand a topic by categorizing facts and presenting them to further the reader's understanding. It does not advocate a particular point of view, and if it has a thesis statement, the thesis is a weak one. Some business white papers take this form, although they are more likely to have a point of view, if understated.

- Example of a broad topic narrowed down into a reasonable synthesis essay topic: Instead of the broad topic of Social Media, you could discuss your view on the effects texting has had on the English language.
- If you've been assigned a topic as part of a class, make sure you read the prompt carefully and fully understand it.

- Keep in mind that it's better to do three sources well than to do five sources incompletely.
- Annotate each source by writing notes in the margins. This allows you to keep track of your train of thought, developing ideas, etc.

- Example: Texting has had a positive impact on the English language as it has helped the millennial generation create their own form of the language.

- If you wish to take on a claim by an opponent of your idea, and to poke holes in it, you should also find some ideas or quotes that go against your thesis statement, and plan ways to disprove them. This is called a concession, refutation, or rebuttal, which can strengthen your argument if you do it well.
- Example : For the thesis statement listed above, excellent sources would include quotes from linguists discussing the new words that have developed through 'text-speak', statistics that show the English language has evolved with almost every generation, and facts that show students still have the ability to write with the use of grammar and spelling (which your opponents would bring up as the main reason texting has had a negative effect on the English language).
Outlining Your Essay

- The introductory paragraph: 1. An introductory sentence that acts as a hook, capturing the reader's interest. 2. Identification of the issue you will be discussing. 3. Your thesis statement.
- The body paragraphs: 1. Topic sentence that gives one reason to support your thesis. 2. Your explanation and opinion of the topic sentence. 3. Support from your sources that backs up the claim you just made. 4. Explanation of the significance of the source(s).
- The conclusion paragraph: 1. State further significance of your topic from the evidence and reasons you discussed in the essay. 2. A profound thought or thoughtful ending for your paper.

- Example/illustration. This may be a detailed recount, summary, or direct quote from your source material that provides major support for your point of view. You may use more than one example or illustration, if your paper calls for it. You should not, however, make your paper a series of examples at the expense of supporting your thesis.
- Straw man. With this technique, you present an argument opposed to the argument stated in your thesis, then show the weaknesses and flaws of the counter-argument. This format shows your awareness of the opposition and your readiness to answer it. You present the counter-argument right after your thesis, followed by the evidence to refute it, and end with a positive argument that supports your thesis. [5] X Research source
- Concession. Essays with concessions are structured similar to those using the straw man technique, but they acknowledge the validity of the counter-argument while showing that the original argument is stronger. This structure is good for presenting papers to readers who hold the opposing viewpoint.
- Comparison and contrast. This structure compares similarities and contrasts differences between two subjects or sources to show the facets of both. Writing an essay with this structure requires a careful reading of your source material to find both subtle and major points of similarity and difference. This kind of essay can present its arguments source-by-source or by points of similarity or difference.

- Summary. This structure presents summaries of each of your relevant sources, making a progressively stronger argument for your thesis. It provides specific evidence to support your point of view, but usually omits presenting your own opinions. It's most commonly used for background and review essays.
- List of reasons. This is a series of sub-points that flow from the main point of your paper as stated in its thesis. Each reason is supported with evidence. As with the summary method, reasons should become progressively more important, with the most important reason last.
Writing Your Essay

- Your essay should have an introductory paragraph that includes your thesis , a body to present evidence that supports your thesis, and a conclusion that summarizes your point of view.

- Lengthy quotes of three lines or more should generally be set off as block quotes to better call attention to them. [7] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
Finalizing Your Essay

- Ask someone else to proofread your paper. The saying “two heads are better than one” still holds true. Ask a friend or colleague what would they add or remove from the paper. Most importantly, does your argument make sense, and is it clearly supported by your sources?

- Read the paper aloud to guarantee that you don't accidentally add in or take out words when reading in your head.
- If you can, get a friend or classmate to proofread your essay as well.

- Example of citing in an AP synthesis essay: McPherson claims “texting has changed the English language in a positive way--it has given a new generation their own unique way to communicate” (Source E).
- For college essays, you'll most likely use MLA format. Whichever format you use, be consistent in its use. You may also be asked to use APA or Chicago style.

- Example title: : English and the iPhone: Exploring the Benefits of 'Text-Speak'
Outline Template

Community Q&A
- Just as your title should fit your essay instead of writing your essay to fit the title, your thesis, once chosen, should direct your subsequent research instead of subsequent research altering your thesis � unless you find you've adopted an unsupportable thesis. Thanks Helpful 21 Not Helpful 8

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://success.uark.edu/get-help/student-resources/synthesis-paper.php
- ↑ https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/student-resources/writing-speaking-resources/mapping-a-synthesis-essay
- ↑ https://www.bgsu.edu/content/dam/BGSU/learning-commons/documents/writing/synthesis/planning-synthesis-essay.pdf
- ↑ https://writingcenterofprinceton.com/synthesis-essays-a-step-by-step-how-to-guide/
- ↑ https://owl.excelsior.edu/argument-and-critical-thinking/logical-fallacies/logical-fallacies-straw-man/
- ↑ https://writingcommons.org/section/rhetoric/rhetorical-stance/point-of-view/third-person-point-of-view/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_formatting_quotations.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/steps_for_revising.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/proofreading_suggestions.html
- ↑ https://www.edhs.org/ourpages/auto/2010/5/17/41759867/Synthesis%20Essay%20Introduction.pdf
- ↑ https://writing.umn.edu/sws/assets/pdf/quicktips/titles.pdf
About This Article

To write a synthesis essay, start by coming up with a thesis statement that you can support using all of the sources you've read for your essay. For example, your thesis statement could be "Texting has had a positive impact on the English language." Once you've got your thesis, go through your sources to find specific quotes, facts, and statistics that back up your claim. Structure your essay so it has an introduction that includes your thesis statement, a body that includes your arguments and evidence, and a conclusion that wraps everything up. For more tips on structuring your synthesis essay, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Aug 8, 2016
Did this article help you?
Adrian Mastrocola
Sep 29, 2016
Emmanuel Amoatey Djaba
Nov 26, 2016
Anna VonLeader
Jun 6, 2016
May 7, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter

Synthesis Essay
Synthesis essay generator.

A Synthesis Essay is a sophisticated form of writing that requires the integration of various sources and perspectives. Our resource provides a comprehensive look into this writing style, complete with insightful essay examples . These examples demonstrate how to effectively combine information from different texts, crafting a cohesive and well-argued narrative. Ideal for students and professionals alike, this guide will help you master the art of synthesizing diverse viewpoints into a single, compelling argument in your essays.
What is a Synthesis Essay?
A synthesis essay is a written discussion that draws on one or more sources. It involves combining information from various sources to make a cohesive argument or presentation on a specific topic. This type of essay requires the writer to analyze information, derive insights, and present them in a structured and coherent manner. The key to a successful synthesis essay is not just summarizing the sources but integrating them to create a new perspective or argument. Writers must cite their sources accurately, showing how each piece of information contributes to and supports their thesis or main argument. Synthesis essays are common assignments in academic settings, especially in higher education, testing students’ abilities to research, evaluate, synthesize complex information, and articulate their findings effectively.

Download Synthesis Essay Bundle
Essays depict the standpoints of a writer on a certain topic or issue. An essay often presents a point and either convinces a reader to agree or disagree to a certain subject matter. An effective essay does what it is intended to do when a reader is convinced of the writer’s stand point. Common college essays include writing a synthesis essay. Examples of synthesis essay can be found in the page and made available for your reference. The examples can also be downloaded via the download link button below the sample in order to get a closer look.
Synthesis involves combining different pieces of information to form a cohesive understanding. For instance, if you gather insights from various experts about the impact of climate change and weave them into a comprehensive article or report, you are performing synthesis. This process is distinct from merely summarizing since it requires critical thinking to integrate ideas and form new connections, rather than just listing details or differences like in comparison and contrast.
Synthesis Essay Structure
It helps in presenting your argument clearly and persuasively. Here’s a typical structure for a synthesis essay:
Introduction
Hook: Start with an engaging sentence to grab the reader’s attention. Background Information: Provide some context or background for the topic you will be discussing. Thesis Statement: Present your main argument or position on the topic, clearly stating how the different sources will support your thesis.
Body Paragraphs
Each body paragraph should focus on a specific point or aspect of your thesis, integrating multiple sources to support each point.
Topic Sentence: Introduce the main idea of the paragraph that supports your thesis. Evidence and Analysis: Include information from your sources as evidence to back up your point. This could be quotations, summaries, or paraphrased material. Analyze the evidence, showing how it supports your argument. Synthesis: Discuss how the evidence from different sources relates to each other and to your thesis. This is where you combine (synthesize) the information to build your argument. Concluding Sentence: Summarize the main point of the paragraph and how it supports your overall thesis.
Counterarguments (Optional)
Consider including a paragraph that addresses potential counterarguments or opposing views. Refute these arguments and show how your thesis still stands.
Summary: Briefly summarize the key points you made in your body paragraphs. Thesis Restatement: Restate your thesis in a new way, reflecting the insights and arguments developed in your essay. Final Thoughts: Offer some final thoughts on the topic, possibly suggesting areas for further research or implications of your argument.
Include a list of all sources cited in your essay, formatted according to the required academic style guide (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
How to Write a Synthesis Essay
Writing a synthesis essay involves gathering information from various sources and merging these insights to support a central thesis or argument. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Understand the Prompt
- Clarify the Task: Ensure you fully understand the essay prompt or assignment requirements. Know what type of synthesis essay you are writing (explanatory or argumentative).
- Identify the Main Ideas: Determine what themes or ideas you need to explore based on the prompt.
Conduct Research
- Gather Sources: Collect relevant sources that provide information on your topic. These can include academic papers, books, articles, and credible online resources.
- Evaluate Sources: Assess the credibility and relevance of each source to your topic.
Develop a Thesis Statement
- Formulate a Clear Argument: Based on your research, craft a thesis statement that encapsulates the main argument or perspective your essay will support.
Create an Outline
- Organize Your Points: Plan the structure of your essay, deciding how you will integrate information from your sources to support your thesis.
- Outline Body Paragraphs: Each paragraph should focus on a specific point or piece of evidence related to your thesis. Determine how you will synthesize information from different sources for each point.
Revise and Proofread
- Review Your Work: Check for clarity, coherence, and logical flow. Ensure each part of your essay effectively contributes to supporting your thesis.
- Proofread: Correct any grammatical, spelling, or punctuation errors. Make sure your citations and references are formatted correctly.
Cite Your Sources
- Follow Formatting Guidelines: Use the appropriate academic style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) to cite your sources within the text and in a bibliography or works cited page.
10+ Synthesis Essay Samples
- Synthesis Essay on Climate Change
- Synthesis Essay on Death
- Synthesis Essay on Education
- Synthesis Essay on Environment
- Synthesis Essay on Food
- Synthesis Essay on Gender Inequality
- Synthesis Essay on Internet
- Synthesis Essay on Social Media
- Synthesis Essay on Technology
- Synthesis Essay on Unemployment
10+ Synthesis Essay Examples

Free Download
College Synthesis Essay

High School Synthesis Essay

Student Synthesis Essay

Practice Synthesis Example

Synthesis Essay Outline

Poetry Synthesis Essay Sample

Argumentative Synthesis

Explanatory Essay Sample

Technology Synthesis

What is the Purpose of a Synthesis Essay?
Synthesis essays are used in different papers. Point is, a synthesis essay is used in creating a relationship between different sources and getting supplemental information from them to support the writer’s view point or make a coherent plan or proposal templates .
Essay examples in doc seen on the page offer more information regarding an essay. They are made available for your review by clicking on the individual link buttons under each sample.
Tips for Writing the Synthesis Essay
Writing a synthesis essay is a pivotal skill for students, particularly in high school and college. This type of essay goes beyond simple summarization and requires critical thinking, a skill essential in essay writing. Here are some key tips to help students craft an effective synthesis essay:
- Understand Your Sources : It’s crucial to thoroughly read and understand your sources. As a student essay , your synthesis essay should reflect a deep engagement with the materials, providing a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
- Develop a Strong Thesis Statement : The foundation of your essay is the thesis statement. It should clearly convey your central argument or perspective, integrating the various themes and ideas from your sources. In high school essay writing, a well-defined thesis is particularly important as it guides the structure and flow of your argument.
- Organize Your Essay Effectively : Structure your essay in a clear, logical manner. Start with an introduction that includes your thesis statement , followed by body paragraphs that explore your main points, and conclude with a summary that reinforces your thesis.
- Balance Your Sources : Synthesize the information from your sources in a way that provides a balanced perspective. Your synthesis essay should not just list points from each source but rather integrate them into a coherent argument.
- Use Evidence to Support Your Argument : Back up your claims with evidence from your sources. This will strengthen your argument and demonstrate your understanding of the material.
- Maintain a Formal and Objective Tone : A synthesis essay, particularly in an academic setting, should be written in a formal and objective tone. Avoid using first-person pronouns and keep your language professional.
- Cite Your Sources Appropriately : Proper citation is crucial in academic essay writing to avoid plagiarism. Make sure to follow the appropriate format for citations, whether it’s APA, MLA, or another style.
- Revise and Edit : After completing your essay, take the time to revise and edit. This includes checking for grammatical errors, ensuring your argument flows logically, and verifying that your thesis statement is clearly supported throughout the essay.
How Long Should a Synthesis Essay Take?
The time to write a synthesis essay varies, typically ranging from several hours to a few days. This includes time for research, planning, writing, and revising. Effective time management and early start can help streamline the process.
Should You Use “I” in a Synthesis Essay?
Generally, avoid using “I” in a synthesis essay, especially in academic settings. Aim for an objective tone by presenting evidence and analysis without personal bias. Exceptions may apply if personal reflection or perspective is explicitly requested.
How Do I Write a Good Synthesis Essay?
Writing a good synthesis essay involves thorough research, understanding your sources, creating a strong thesis, organizing your points logically, and synthesizing evidence from various sources to support your argument. Clear writing and proper citation are also crucial.
How Do You Start a Synthesis Essay?
Start a synthesis essay with an engaging hook, followed by brief background information on your topic. Clearly state your thesis, outlining the main argument or perspective your essay will support, setting the stage for your synthesis.
Is It Okay to Use First-Person in a Synthesis Essay?
Using first-person in a synthesis essay is generally discouraged in formal academic writing. It’s better to maintain an objective tone. However, if the assignment guidelines allow or if reflecting on personal experience, it may be acceptable.
Do You Directly Quote in a Synthesis Essay?
Yes, you can directly quote in a synthesis essay to support your points, but do so sparingly. Focus on synthesizing information by paraphrasing and analyzing evidence from your sources. Ensure all quotes are properly cited according to the required citation style.
In conclusion, synthesis essays are key in developing critical thinking and analytical skills. For further guidance on writing synthesis essays, Colorado State University provides an in-depth guide , which can be accessed here. This resource offers valuable insights into the process of synthesizing information from diverse sources.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write a Synthesis Essay on the integration of technology in education.
Create a Synthesis Essay comparing different leadership styles.
Analyze the impact of technology on education through synthesis.
Synthesize views on climate change from multiple sources.
Compare traditional vs. online learning in a synthesis essay.
Discuss the role of social media in politics synthesis.
Explore mental health effects of social isolation via synthesis.
Evaluate renewable energy sources' viability in a synthesis essay.
Synthesize historical perspectives on women's rights movement.
Examine the effects of globalization on culture through synthesis.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Paragraph 1: The prompt presents and briefly explains the topic that you'll be writing your synthesis essay about. That topic is the concept of eminent domain. Paragraph 2: The prompt presents a specific claim about the concept of eminent domain in this paragraph: Eminent domain is productive and beneficial.This paragraph instructs you to decide whether you want to defend, challenge, or ...
Step 5: Write your Essay. Use the remaining 30-35 minutes to write your essay. This should be relatively easy if you took the time to mark up the sources and have a detailed outline. Remember to add special consideration and emphasis to the commentary sections of the supporting arguments outlined in your thesis.
Students write essays that respond to 3 free-response prompts from the following categories: Synthesis Question: After reading 6-7 texts about a topic (including visual and quantitative sources), students will compose an argument that combines and cites at least 3 of the sources to support their thesis.
Synthesis Essay 6 points . Since the early 2000s, the United States government and a number of corporations have sponsored initiatives to improve education in the STEM ... Write an essay that synthesizes material from at least three of the sources and develops your position on the value, if any, of initiatives to improve STEM education and ...
The two synthesis essay questions below are examples of the question type that has been one of the three free-response questions on the AP English Language and Composition Exam as of the May 2007 exam. The synthesis question asks students to synthesize information from a variety of sources to inform their own discussion of a topic. Students are given a 15-minute reading period to accommodate ...
Sure, a synthesis essay is a type of essay that requires you to use multiple sources to create an argument. In an AP Lang synthesis essay, you'll typically be provided with the sources and will need to analyze them, identify the main ideas, and then connect those ideas to your central argument or thesis. Here's a step-by-step breakdown of how to write a strong synthesis essay for AP Lang: 1.
For everything you need to know about the AP English Language Exam, check out our ultimate guide: https://marcolearning.com/guide-to-the-ap-english-language-...
The writing process for composing a good synthesis essay requires curiosity, research, and original thought to argue a certain point or explore an idea. Synthesis essay writing involves a great deal of intellectual work, but knowing how to compose a compelling written discussion of a topic can give you an edge in many fields, from the social sciences to engineering.
If you use information from the sources, you have to cite it. If you take text out of a source, you have to put it in quotation marks. #2: Don't plagiarize. After you quote or paraphrase a source, cite it as you would in a paper: (Source F) or (Gilman). Be consistent. #3: Your essay needs a thesis. You need a strong, clear thesis.
Understand the Prompt. In order to write an effective synthesis essay, it is crucial to fully understand the prompt provided. The prompt serves as a guide, outlining the specific topic or issue that needs to be addressed in the essay. When analyzing the prompt, it is important to carefully examine the keywords and phrases used.
First, state your argument, make supporting statements, and back up each claim with reliable facts. 2. Review Essay. A review essay is frequently written as a preparatory essay to an argument synthesis. Review essays are commonly used in social science and medicine classes.
In this video, I'll show you how to write the AP English Language synthesis essay (Q1) step by step using the actual 2017 prompt. This tutorial also includes...
The 2024 AP English Language and Composition exam format will be: Section I: Multiple Choice - 45% of your score. 45 questions in 1 hour. Section II: Free Response Section - 55% of your score. 2 hours and 15 minutes for: 1 synthesis essay. 1 rhetorical analysis essay. 1 argument essay.
Summarize the main points of your essay and restate your thesis statement. Reflect on the significance of your argument and its implications for the broader topic. Offer insights or suggestions for further research or discussion. End with a compelling closing statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
In order to score an 8 on the synthesis FRQ question, students need to write an essay that effectively argues a position, synthesizes at least 3 of the sources, uses appropriate and convincing evidence, and showcases a wide range of the elements of writing. Essays that score a 9 do all of that and demonstrate sophistication in their argument.
The three essays include: Synthesis essay: You'll review various pieces of evidence and then write an essay that synthesizes (aka combines and interprets) the evidence and presents a clear argument. Read our write up on How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis Essay here. Argumentative essay: You'll take a stance on a specific topic and argue ...
You have three choices when you take someone else's words / ideas from their writing to put into your own writing: 1.) QUOTATION: copy the words and punctuation exactly like it is in the other writer's essay; be extremely accurate; use quotation marks. 2.) SUMMARY: you use your own words to "shrink" down another writer's ideas to the ...
Clarify Your Purpose: First, decide if you're writing an explanatory or argumentative synthesis essay. This choice will set the tone and direction for your essay. Source Selection and Analysis: Choose credible and relevant sources for your topic, balancing different types like articles, books, and websites.
For everything you need to know about the AP English Language Exam, check out our ultimate guide: https://marcolearning.com/guide-to-the-ap-english-language-...
Find several central ideas in the chart. Choose the ones that are repeated the most often and the ones that you feel need to be in your essay. Combine them, and you have a thesis statement with all the key points. Make a draft of the thesis statement. Try to formulate the main idea you want to present in your essay.
Annotate each source by writing notes in the margins. This allows you to keep track of your train of thought, developing ideas, etc. 4. Develop a thesis statement. Once you have read the sources you are provided with, or have done your own outside research, you will have to come up with an opinion on your topic.
A synthesis essay is a written discussion that draws on one or more sources. It involves combining information from various sources to make a cohesive argument or presentation on a specific topic. This type of essay requires the writer to analyze information, derive insights, and present them in a structured and coherent manner.