241 Abortion Essay Topics & Research Questions + Examples
Abortion is a highly controversial issue because it involves a conflict between a woman’s bodily autonomy and a fetus’s right to life. Due to the complicated nature of this problem, one can come up with many research questions on abortion. On this page, you’ll find plenty of interesting and thought-provoking abortion title ideas and essay examples. Read on to get inspired!

📚 Subtopics for Abortion Essays
🏆 best essay topics on abortion, 👍 good abortion research topics & essay examples, ✍️ abortion essay topics for college, 🎓 most interesting abortion research titles, 💡 simple abortion paper topics, 🌶️ hot abortion ideas to write about, 🤔 abortion research questions, 📝 abortion argumentative essay topics, ✏️ abortion questions for essay, 🔎 questions about abortion for research paper.
Do you need to write a paper on pregnancy termination but don’t know where to begin? Here are some general abortion topics to write about. You can use them as a starting point for developing more nuanced research questions about abortion for your assignment.
- Analysis of Advantages and Disadvantages of Abortion
- Ethical Egoist and Social Contract Ethicist: On Abortion
- Why Abortions Should Be Legal?
- Should Abortion Be Banned?
- Should Abortions be Legal?
- The Controversy Around Morality of Abortion
- Abortion in Hanafi and Maliki Schools of Islamic Thought
- The Dilemma of Abortions: Consequentialist and Deontological Points of View
- Deductive and Inductive Arguments: Granting Abortion Rights
- Abortion: An Ethical Dilemma
- Reproductive Health and Abortion Practices in Fiji The legalization of abortion has always been a difficult and contentious topic of discussion, both in the academic field and in politics.
- Utilitarianism and Abortion: Mill’s Principle of Utility and Bentham’s Felicific Calculus The issue of abortion is often approached from spiritual or religious standpoints, and utilitarianism arguably has the potential to provide a refreshing perspective.
- “Why Abortion Is Immoral” the Article by Don Marquis The selected text for analysis relates to the ethical issue of abortion since its title is “Why Abortion is Immoral” by Don Marquis.
- The Moral and Legal Status of Abortion This paper discusses Warren’s work “On the Moral and Legal Status of Abortion,” which raises a question about the status of any given fetus and whether it made the latter a person.
- Ethics and the Right to Abortion The paper discusses a case in which a gynecologist must decide to perform an abortion for a woman who is a survivor of abuse in a state that prohibits the practice.
- Discussion of Legalization of Abortion The paper presents annotated bibliography of sources aims at providing a clear view of various policies and laws around the globe on abortion.
- Social Exchange Theory and Abortion Legalization While the risk of having financial issues influences individuals, they will be more likely to refuse to give birth to a child because of the possible losses in the future.
- Legal and Ethical Issues Concerning Abortion in the United Kingdom Samantha can legally have an abortion if she meets the legal requirements stipulated in the United Kingdom abortion Act of 1967.
- Abortion in Marquis’, Bentham’s, Biblical Theories Some people believe that abortion is impermissible under any circumstances, even if the child is ill or if it was conceived as a result of rape.
- Is Abortion Beneficial or Harmful To a Teenager? Abortion is the removal of a pregnancy before it is due. It is the elimination of a fetus or embryo from the mother’s uterus before it is due for birth.
- Abortion: Comparing Advantages and Disadvantages Pro-life and pro-choice have their respective stands regarding the issue of abortion. The question is whether to terminate or keep the pregnancy.
- Thompson’s ‘A Defense of Abortion’ and Hursthouse’s ‘Virtue Theory and Abortion’ This paper is a reading summary of two articles on the ethics of abortion, such as ‘A defense of abortion’ and ‘Virtue theory and abortion’.
- Debate of the Dangerous Consequences of Abortion In order to cope with the various problems resulting from abortion, it is mandatory to create an awareness campaign that informs people of the dangerous consequences of abortion.
- Abortion Nursing Care and Patient’s Rights The U.S. has many abortion laws and limitations; furthermore, the procedure is widely frowned-upon in the American society.
- Abortion and Its Moral Status Sometimes, our decisions inevitably affect other people’s lives and therefore involve a wide range of moral issues. This is the case with abortion.
- The Judith Thomson vs. Don Marquis Abortion Debate Thompson agrees that murder is immoral, as the Marquis believes, but a woman has every right to get rid of the fetus, and outsiders have the right to help her.
- The Advantages and the Dangers of Abortion The paper states that the right to abortion allows a woman the freedom to control their body. It also empowers pregnant people to manage their health.
- Reflection on “A Defense of Abortion” by Judith Jarvis Thomson In her moral philosophy essay, “A Defense of Abortion,” Judith Jarvis Thomson implements thought experiments to argue in support of abortion based on two core premises
- Abortions: Pro-Choice vs. Pro-Life The issue of abortions has always been a controversial one leading to multiple clashes between irreconcilable ideologies.
- Abortion: Analysis of the Main Causes The causes of abortion are not universal around the world; they vary depending on the country and region of residence.
- Violinist Analogy in Thomson’s “A Defense of Abortion” This example of Thompson’s article demonstrates what kind of a burden women are obliged to deal with in case they live in a society that prohibits abortions.
- Ethics in Society. Abortion Debates: Different Sides The history of abortion witnessed that “millions of women suffered injury or death at the hands of abortionists operating illegally”.
- The Issue of Abortion: Ethics Challenges The debate about abortion in terms of ethics has been in place for decades ever since this medical procedure was first legalized by the government.
- The Need for Abortion and the Moral Status of the Fetus The people who rely on religious postulates are likely to see a fetus as a creature that is supposed to have the same rights as the child that is already born.
- A Defense on Abortion: Ethical Issues Abortion is considered the intended action to expel a fetus from the womb of a woman. The expulsion of a fetus leads to death, the intentional expulsion of a fetus is murder.
- Abortion: Women’s Health as Their Integral Right This paper will elaborate on the thesis that a woman should have the right to abortion as the best ethical decision to ensure her physical and psychological health.
- Abortion Policies: History, Current Issues, and Social Workers’ Roles This discussion is aimed at discussing abortion policies with regard to the Constitution, their history, current issues on abortion, and social workers’ roles.
- Abortion Dilemma in Pragmatic Ethics The moral acceptability of abortions has always been a disputable issue. From the perspective of pragmatic ethics, the decision to make an abortion can be acceptable and moral.
- Pros and Cons of Abortion Undergoing abortion is a very difficult step to take for any woman and it takes a lot of guts to take the decision. This paper will throw light upon the pros and cons of abortion.
- Abnormal Fetus, Its Moral Status and Abortion Ethics Abortion is a medical procedure that involves the surgical elimination of the fetus from a female’s womb with the purpose of ending a pregnancy.
- Abortion: Pros and Cons Abortion should be illegal because unborn babies are considered human beings by the US Government, making abortion murder.
- Fetal Abnormality and Ethical Dilemms of Abortion In the case study “Fetal Abnormality,” four characters face the same problem: an abnormal condition of a fetus and the necessity to decide if to save a child or consider abortion.
- Should Abortions Be Legal? The paper states that doing an abortion before 20 weeks is permissible and has to be an option for women willing to stop their pregnancy.
- Abortion: Arguments for Defense Abortion should be accepted as a way of curbing unnecessary maternal death and showing compassion to rape victims.
- Abortion: Arguments in Support This essay will explore the medical reason for an abortion to be performed. It will ask the pertinent question of why abortion should remain legal with limitations.
- Abortion: The Ethically Appropriate Procedure Based on the available evidence and the considerations of women’s rights, treating abortions as an ethically appropriate procedure seems to be a more reasonable position.
- Social Justice Protests Regarding Abortions This study aims to understand abortion rights and how they were significant in women’s equality. Roe v. Rode was a case that challenged the rule about abortion.
- Abortion in Christian and Non-Christian Ethics The Christian ethical system approaches the issue of abortion through God’s image and character while utilitarianism is concerned with maximizing happiness.
- Abortion Is a Woman’s Right and Should Be Legal Abortion is one of the most controversial topics in our society. Some believe that a woman has the right to choose what happens to her body and believe that abortion is murder.
- The Controversy Around Abortion in the US In the US, the issue of abortion has been facing controversy. The disagreement from society is making it difficult to address the problem.
- Abortion With Limitations: Analysis Since abortion remains a divisive issue due to the presence of divergent opinions, permitting it with specific limitations is a good decision.
- The Abortion Prohibition Issue Analysis The paper analyzes the issue of the irrationality of abortion prohibition due to the ideological, sociological, medical, and legal perspectives.
- Abortion Should Be Available in Modern Society Abortions should be allowed for every woman within the framework of respect for human rights and eliminating undesirable consequences for a woman’s health.
- Ethical Aspects of Abortion: A Moral Dilemma This paper discusses the ethical aspects of abortion, a controversial and highly debated topic that raises religious, moral, and other fundamental issues.
- Justifying Abortion From Utilitarian Position This paper argues that abortion should be justified since a woman’s body, health and future should depend on her own consensual and conscious decisions.
- Abortion Ban and Its Negative Consequences The choice to ban abortion will have a severe impact on women; doctors must engage judges in case a clinical feticide are necessary, causing a delay that might result in death.
- Abortion Abolitionists and Pro-Life Activists While both abortion abolitionists and pro-life activists share a variety of fundamental beliefs, they also vary in their approach and interpretation of women’s rights to abortion.
- American Democrats’ Pro-Abortion Beliefs The US political system consists of liberal Democrats and conservative Republicans. The chosen news article elaborates more on the Federal Abortion ban from these two perspectives.
- Sex-Selective Abortions Around the World Sex-selective abortion is a problem that must be addressed if we take into account the place of women in society and the effects of sex choice on interpersonal relationships.
- Decriminalizing Abortion for Women’s Health’s Sake The debate for and against abortion has caused controversies worldwide, with some groups ruling out the act as heinous.
- Ban on Abortions as Current Civil Rights Issue Even if a woman leaves a child for upbringing due to an unplanned pregnancy, it will be difficult to talk about a good emotional climate in a family.
- The Morality of Selective Abortion and Genetic Screening The paper states that the morality of selective abortion and genetic screening is relative. This technology should be made available and legal.
- Right to Abortion and Related Ethical Issues This paper applies the utilitarianism approach to ethics in showing that women that have been raped or have some health complications should be free to terminate their pregnancy.
- “Why Abortion is Immoral” by Don Marquis Don Marquis is an author of an essay that argues that abortions are immoral from a non-religious standpoint. He begins with a general discussion on why killing is wrong.
- Abortion: A Pro-Choice Rally in Charlotte The article discusses the author’s experience at a pro-choice rally in Charlotte, NC, where a Christian preacher attempted to reason with the protestors and spread God’s message.
- Women’s Reasons for Seeking Abortions The cause-effect essay aims to contribute to the ongoing discussion by exploring the reasons why women seek abortions.
- Supreme Court’s Abortion Ruling Sets Off New Court Fights The article discusses the Supreme Court’s decision to ban abortions and give states the right to decide on their local level whether they want to prohibit it or not.
- Abortion in Public Opinion and Legislation Supporters of abortion believe that embryos and fetuses cannot have full human rights since the fetus is not yet a human being.
- Right to Abortion: Ethical Issues On the one hand, abortion is the woman’s right to protect her life; on the other hand, abortion touches upon two lives minimum.
- Women’s Right to Abortion: Religious Perspective Some religious people are right to accept the US court decision on limiting women’s right to abortion. They believe that the act is murder because life starts at conception.
- Ethical Issue: Abortion Should Be Legal Abortions should be lawful because morally justifiable activities should be legal: it is an injustice to punish behaviors that are not bad.
- Roe v. Wade: Abortion Rights in the United States Since the beginning of May, the United States has been discussing the possible cancellation of the decision in the Roe v. Wade case.
- “A Defense of Abortion” by Judith Thomson and Abortion Discussion “A Defense of Abortion” by Judith Thomson tries to bridge the gap between supporters of abortion, and opponents, who believe that a fetus is a person.
- Ethics: Women’s Right to Abortion In the current paradigm of medicine and healthcare, abortion has become a relatively safe operation due to the increased quality of competencies and equipment.
- “Abortion Law and Policy Around the World”: Source Evaluation The paper analyzes article “Abortion law and policy around the world” which was written by Marge Berer and published in June, 2017.
- Abortion: The Lifesaving Procedure Even though abortion is a form of right to life deprivation, the act is not a crime, as some believe hence should be legalized. It can potentially be a lifesaving procedure.
- Abortion: Effects and Legalization The social stigma surrounding abortion has a negative impact on people’s mental health and their willingness to seek safe abortion services despite the legal laws.
- The Right to Abortion Must Be Protected Legal abortion means respecting women’s reproductive freedom, ensuring that all children grow up wanted in safe environments, and improving the general conditions of society.
- Abortion Legalization and List of Circumstances In some cases where the expectant mother cannot handle a child, abortion in such a scenario needs legalization.
- Discussion: Legalization of Abortion Aspects The paper argues abortion needs legalization under exceptional grounds, such as when a mother’s life is at risk.
- Abortion Issues and Safe Practices Fathalla’s Safe abortion discusses solutions to preventing unsafe abortions, including sexual education, increased access to contraceptives, provision of safe abortions, etc.
- The Abortion Issue Regarding Human Rights This article raises the question of how people should determine what rights should be guaranteed by the constitution and what rights are core rights from birth.
- The Controversy Over Abortion Rights The paper states that the confrontation between the two movements over the years has led to the fact that abortion has become a controversial topic.
- The Future of Abortions in the United States This paper examines the different ways United States legislators have used their power to politicize abortion and argues about the future of abortion rights.
- The Morality of the Abortion Case Abortion is perceived as a morally incorrect action. This paper investigates the morality of the case and which action is supposed to be right or wrong.
- The Issues Surrounding Abortion This paper aims to find solutions to the issues surrounding abortion and to justify why the proposals need to be considered when implementing abortion laws.
- Abortion: Comparison and Contrast of Arguments Abortion has been a controversial issue for many decades, with both sides of the argument often feeling very strongly about it.
- Disagreeing With Abortion Encouragement This essay argues that abortions should not be publicly encouraged as it represents a serious decision for women that should be undertaken without pressure.
- Abortion: The Indispensable Woman’s Right A woman’s freedom to safe, legal abortion is an integral part of her right to privacy and physical and psychological health.
- Women’s Mental Health after Receiving or Being Denied an Abortion: Summary The results infer women who were refused abortion experienced higher levels of anxiety, lower levels of contentment, and a similar level of depression as those who had an abortion.
- President’s Power to Affect National Policy: The Case of Abortion Probably, none of the important and controversial policies can be implemented without the participation of the country’s chief executive.
- Affordable Abortions as a Reproductive Right of Women This paper examines the issue of abortion affordability as a public health and human right concern from legal and judicial perspectives.
- Women’s Bodies, Women’s Rights: A Case for Abortion If one holds that a woman has the moral right to make decisions about her health and existence, the only reasonable conclusion is to acknowledge the right to abortion.
- Abortion Safety as Topic of Sociological Studies Sociological studies show that about half of all abortions are unsafe, while every third abortion is performed in dangerous circumstances.
- Abortion and Its Permissibility Issue Abortion during pregnancy is one of the discussed topics in the modern world, which sometimes becomes more acute in connection with certain incidents.
- Christianity Views on Abortion Concepts, the Big Bang, and the Evolution Theory The Bible and other Christian articles provide information related to contemporary society, views on abortion concepts, the big bang, and the evolution theory.
- Debates: Abortions Must Be Legal Access to safe and effective abortions is not only a universal human right but also an indicator of social development concerning women.
- A Controversial Topic of Abortion Abortion has been a controversial topic globally for many decades. The side of the argument an individual chooses to support depends on many factors.
- Ethical Issues and Concerns Regarding Abortion The paper is addressing contemporary ethical issues and concerns regarding abortion. The debate over this subject involves ethical arguments.
- Way Forward for Improving Abortion Healthcare The healthcare field should ensure the safety of those who want to terminate the pregnancy, the first step towards changing the situation is training enough personnel.
- Moral Arguments Regarding Abortion The paper describes that abortion laws within the US vary dramatically between states, and to understand the reason for this disparity, it is critical to list the moral arguments.
- “No Taxpayer Funding for Abortion” Act and the Judeo-Christian Worldview The purpose of this paper is to analyze the H.R. 7 “No Taxpayer Funding for Abortion” act within the framework of the Judeo-Christian worldview and ethics.
- Ethical, Medical, and Legal Aspects of Abortion Abortion is a medical procedure aimed at termination of pregnancy “before the fetus is able to live independently in the extrauterine environment”.
- Abortions’ Negative Impacts on Modern Society Abortion is an immoral act or rather a crime that has diverse negative implications for individuals and the entire society.
- The Moral Status of a Fetus and the Acceptability of Abortion The case study involves four individuals presenting their views on the moral status of a fetus and the acceptability of abortion.
- Decriminalizing Abortion in Victoria, Australia The issue of abortion had been rampant in Australia, particularly in Victoria, to the point that it was considered a crime until 2007 when the government decriminalized it.
- Abortions. Perspectives, Federalism, Court Cases Abortion has been one of the most provocative topics across the globe. People have different views on whether a woman should be permitted to abort her child or not.
- The Problem of Alabama’s Latest Abortion Bill The problem revolves around Alabama’s latest abortion bill, which punishes abortion, providing doctors with lifetime sentencing.
- The Controversial Issue of Abortion Legal and ethical issues associated with abortion are becoming controversial every day in modern society; some people support the idea of abortion, while others disagree.
- Policy Debate: Argument in Support of Abortion Abortion is a critical issue in the support of women’s rights because usually women are more affected by the debate than men (both as a gender and individuals).
- The Effects of Abortions on the Black Community The paper states that it cannot be confidently stated that the ‘trend’ on abortion among the black community is the result of political conspiracy.
- Why Abortion Should Be Included in the National Healthcare Plan The abortion debate is one of the most controversial and irrational issues that have lacked a concrete solution for a very long time in America.
- Abortions: Is It a Legalized Murder? The views about abortion are often based on the cultural and ethical values of people and on how an individual perceives the status of the fetus.
- Ethics of Smoke-Free Legislation and Abortion Laws There are laws that are clear for the population and their importance is undeniable. A bright example is smoke-free legislation, which is crucial for the health of non-smokers.
- Providing the Argument Against Abortion The paper questions the argument against abortion that is associated with the fact that every aborted child may become a great composer, an artist, or some other prominent person.
- Fetus Abnormality and Morality of Abortion
- An Exploration of the Abortion Debate
- Mandating Ultrasound Prior to Having an Abortion
- “Reasons U.S. Women Have Abortions” by Finer
- Abortion Should Be Encouraged in the United States
- Should Abortions Be Legal? Arguments For and Against
- The Abortion Debate: The Conservative and Liberal Arguments Against
- Abortion and Catholic Church’s Attitude
- Abortion Topic in “A Defense of Abortion” by Thomson
- The Abortion Dilemma: Islam vs. Christianity
- Judith Jarvis Thomson’s Views on Abortion
- Abortion: The Issue of Legalization and Ethical Considerations
- ‘A Defense of Abortion’ by Judith Jarvis Thomson: Major Arguments for Abortion
- Abortion Issues: Credible and Non-Credible Sources of Information
- The Legalized of Abortion in the United States
- Summary of the Research Article About Abortion
- The Decision to Seek Abortions
- Pro-choice vs. Pro-life: The Question of Abortion
- Abortion as the Fundamental Right of Women
- Women Have the Right to Decide the Abortion
- The Issue of Abortion Eligibility
- Overview of the Abortion as a Legal Issue
- The Ethics of Abortion and Reproductive Rights
- The Controversy About Abortion Prohibition and Women’s Rights
- Abortions Through the Prism of Christianity
- Women Have the Right to Decide Whether to Have an Abortion
- Legality of Abortion in the USA: Discussion
- Abortion: Negative Impacts on Women
- Pro-Abortion Ethics Case and Argument
- The Abortion Law in Ireland and Canada
- The Issue Of Abortion in the United States: Arguments For and Against
- Abortion: Arguments for and Against
- Abortion as a Legal Women’s Right
- The Problem of Abortion
- Abortion: G. Marino’s Controversial Points of View
- Abortion and Moral Status of Fetus with Abnormality
- Abortion and Moral Theory
- Debate on Abortion Insurance in South Dakota
- Health Insurance Abortion Ban in South Dakota
- Abortion Policy in the United States
- Abortion in the US: Human Behavior and Social Environment
- Abortions in Australia Discussed in Media
- Abortion as a Woman’s Choice and Right
- Abortion: Legal, Medical, Moral, Religious Issues
- Abortion from Legal and Public Health Perspectives
- Abortion in Feminist and Care Ethics
- Abortion and Maternal Health: the Global Health Crisis
- Ethics in Practice: Abortion Choice
- President Obama’s Fallacy in Abortion Arguments
- Abortion in Texas as a Political Issue
- Ethics of Abortion and Over-the-Counter Drugs
- Abortion Clinic Access Policy and Women’s Health
- Abortion in Case of Down Disease in Fetus
- Abortion as a Moral Controversy in the US
- Abortions and Rights of a Fetus in the US
- Florida Abortion Policies and Health Insurance
- Policy Analysis: Abortion Clinic Access
- “A Defense of Abortion” by Judith Jarvis Thomson
- Abortion: Reasons and Issues
- Abortion as a Public Issue: The New York Times Views
- Anti-Abortion Advocacy of Pro-Life Movement
- Canadian Abortion Laws and Women’s Rights
- Abortion: Judith Thomson’s Ethical Perspective
- Fetal Abnormality and Abortion: Ideal and Discretionary Theories
- The Ethics of Abortion: Women’s Rights
- Abortion: Legal, Ethical and Professional Evidence
- Moral Argument in Support of Abortion
- Should Abortion be Legal or Illegal?
- Abortion as a Controversy
- Possible Effects After Abortion
- Abortion’s Physical and Psychological Effects
- What Does the Bible Say About Abortion?
- What Kind of Connection Exist Between Abortion and Mental Health?
- Does Abortion Relieve Overpopulation?
- Why Many Christians Oppose Abortion
- What Similar Features Are Seen Between Abortion and Slavery?
- Does Male Age Have an Influence on the Risk of Spontaneous Abortion?
- What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Abortion?
- Why Abortion Should Remain Legal?
- What Are the Reasons for the Choice of Abortion in American Women?
- What Are the Pros and Cons of Abortion, Prostitution and Gun Control?
- What Are Opposition and Conflicting Feelings on Abortion?
- Does Rape Justify Abortion?
- What Are the Ethical Issues Raised With Abortion?
- Who Should Decide the Legality of Abortion?
- Does Abortion Have Severe Psychological Effects?
- Why Abortion Attitudes Will Always Be Controversial?
- Does Abortion Affect Subsequent Pregnancy?
- Why the Abortion Controversy Is Often So Bitter Essay
- Why the Government Should Ban Abortion Essay
- Why Has Abortion Become Such a Political Issue? Who Should Have the Final Say?
- Why Doctors Should Not Perform Induced Abortion?
- What Are the Religious Arguments Concerning Contraception and Abortion?
- What Social, Moral and Ethical Dilemma Causes Abortion?
- Why Abortion Laws Should Be Changed for Teens?
- Does abortion promote gender equality?
- Should parental consent be required for minors seeking an abortion?
- Is a fetus’s right to life more important than a woman’s right to choose?
- Is abortion acceptable in case of rape or incest?
- Should waiting periods and pre-abortion counseling be mandatory?
- Abortion: a relief or a toll on a woman’s physical and mental health?
- Is abortion justified in case of failed contraception?
- Should medical professionals be allowed to refuse to perform abortions?
- Should medically unnecessary abortions be criminalized?
- Abortion: a personal choice or a social matter?
- How do religious beliefs affect opinions about the legality of abortions?
- How do restrictive abortion laws influence women’s access to safe healthcare?
- What is the role of informed consent in abortion?
- How do socioeconomic disparities affect women’s decisions regarding abortion?
- What is the impact of sex education programs on the demand for abortions?
- What do women experience before, during, and after abortion?
- How does the media shape public attitudes toward abortion?
- How do societal attitudes toward abortion differ across the world?
- How did abortion laws evolve over time?
- Do the psychological effects of abortion differ from one woman to another?
- How do cultural perceptions of motherhood affect women’s abortion decisions?
- How does abortion accessibility influence the rates of self-induced and unsafe abortions?
- What is the role of grassroots movements in shaping abortion policies?
- What are the long-term health consequences of multiple abortions?
- How do technological advancements shape how the public perceives the fetus?
- How do mandatory waiting periods affect women’s mental well-being?
- Does telemedicine improve rural women’s access to safe abortion?
- What is the emotional impact of mandatory pre-abortion ultrasounds on women?
- How does the availability of abortion affect women’s economic stability?
- How do personal narratives help reduce the stigma surrounding abortion?
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, September 9). 241 Abortion Essay Topics & Research Questions + Examples. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/abortion-essay-topics/
"241 Abortion Essay Topics & Research Questions + Examples." StudyCorgi , 9 Sept. 2021, studycorgi.com/ideas/abortion-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) '241 Abortion Essay Topics & Research Questions + Examples'. 9 September.
1. StudyCorgi . "241 Abortion Essay Topics & Research Questions + Examples." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/abortion-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "241 Abortion Essay Topics & Research Questions + Examples." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/abortion-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "241 Abortion Essay Topics & Research Questions + Examples." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/abortion-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Abortion were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 5, 2024 .

- Services Paper editing services Paper proofreading Business papers Philosophy papers Write my paper Term papers for sale Term paper help Academic term papers Buy research papers College writing services Paper writing help Student papers Original term papers Research paper help Nursing papers for sale Psychology papers Economics papers Medical papers Blog

159 Abortion Research Paper Topics: Creative Ideas List

Abortion is a very controversial issue discussed in different panels all over the world. Because of how vast the topic of abortion is, many interesting research papers can be written about it. For many students, picking the right topic to build their abortion thesis on can seem complicated, and finding the right topic is the bedrock to writing an excellent essay. This article aims at exposing all students to interesting abortion research topics that will help them write high-quality and in-depth research papers on abortion for their university programs. Abortion is simply a medical procedure that intentionally ends a pregnancy before a fetus is born. There are a lot of opinions about abortion, with some opposing it, stating various religious or ethical reasons why it is wrong. Those who support it do that with human rights and medical backing.
What Makes a Good Abortion Thesis Paper?
The first step to writing your essay is picking the right topic, but after you do that, there is a structure to put your thoughts into writing to deliver the best quality thesis paper. This section highlights how to outline and arrange your ideas to produce a good paper at the end. Follow the below outline when writing your abortion essay.
Before Beginning the Paper
Don’t just start writing immediately, do the below pre-writing activities first
Select a Topic : As mentioned above, an essential part of writing an essay is picking the right topic. The right topic should be interesting to you and appeal to your readers. State your Argument : Now that you know the abortion topic you want to write on, what is your argument? Are you going to oppose or support the issue? Your answer will help build a research paper on the topic. Conduct a Research : without proper research, you might end up misinforming your audience. Take time out to dig deep and find evidence that backs up your research. Organize your References : Your references need to be credible. The evidence shows you have done research to back your thesis.
Writing the Paper
After completing your pre-writing exercises, it is time to write your essay properly. Use this as a guideline.
- The Introduction : your Introduction should aim at grabbing the reader’s interest and ensuring that they are interested enough to read the rest of your paper. The opening is what starts the report. It also lets the reader know that your paper is worth reading.
- The Body : The body is the main section of the paper. This is where you present your actual writing. Here you state each idea and back it up with evidence. Your tone, style, and grammar must be concise, making your paper interesting enough for your professor to read. Do not miss out on any detail here. You are allowed to be as descriptive as you want.
- Conclusion : Here, you summarize the main points of your paper and highlight what you would like the reader to remember from reading your work.
Many students find writing a research paper challenging. Following the above structure will help you write a proper essay that will guarantee the best scores. Now that you know how to write a great paper, here are some good topics to help you begin. Before you get acquainted with our perfect list, remember you always have an opportunity to buy a custom research paper from our team of professional helpers. Just c ontact us with a “ do my research paper ” request and get a top grade.
Abortion Topics for Research Paper
Abortion is a topic that has different opinions and conversations. These are some topics you can explore when writing about abortion.
- Explore the possible side effects of abortion.
- Medical reasons for abortions.
- Different religions and their stands on abortion.
- Why the government should ban abortion
- History of abortion.
- The abortion procedure explained.
- General misinformation about abortion.
- What other gender-borne concerns can be connected to abortion?
- Considering that the legislators who pass pro-life regulations are male, can abortion be considered reproductive control?
- The Problems of Abortion in Modern Society.
- Pro-life and Pro-choice Sides of Abortion. Who is right?
- Is Africa ready to embrace abortion?
- Abortion and virtue ethics.
- Legalizing Abortion: Advantages and Justification.
- Legalization of Abortion for Underage Girls.
- Abortion as a Crime and the Fight Against It
- Teenage Pregnancy, Abortion and Sex Education.
- Abortion in Ireland: Law and Public Opinion.
- The Safety and Quality of Abortion Care in Canada.
- Abortion: An Unsolvable Dilemma?
- Abortion: Premeditated Murder or a Reasonable Way Out?
- Abortion: Strengths and Limitations
- Is the abortion rate declining? What are the factors contributing to it?
- Abortion is legal but is it ethical?
- The upward trend and demand for abortion in the United States.
- What is abortion counseling, and who should provide it?
Essay Topics on Abortions
To write a proper essay on abortion, you need to look at different perspectives before deciding on your topic. Here are some essay topics that explore different perspectives of the abortion discussion.
- Has the legalization of abortion played any part in reducing crime rates in the United States?
- How Have Abortion Laws Changed Around the World?
- How Has Abortion and Birth Control Affected the 20th and 21st Century?
- Who Should Decide the Legality of Abortion?
- Why Has Abortion Created Serious Debates and Controversies Among the Mainline?
- Should the Right to Have an abortion lay on the woman alone?
- Why Should Abortion Remain Legal and With Limitations?
- Historically, what were the main reasons women of various titles abort children?
- What were the methods used for abortion before the development of modern medicine?
- Is the history of abortion relevant to the contemporary debate? Why or why not?
- Understanding the risks of teenage abortion.
- Is Self-Defense Abortion Permissible?
- Should women have the right to abortion if serious handicaps are detected in their children?
- Third-trimester abortions: Are they ever morally permissible?
- Is it immoral to force a woman to carry a pregnancy to term against her will?
- Who can teenagers talk to if they want to get an abortion?
- Some medical effects of abortion on the woman’s body.
- How lack of resources affects the occurrences of unsafe abortions in developing countries.
- Is a woman who has had an abortion considered a mother?
- Republican and Democratic views on abortion.
- The roles religion plays in the social discussion and perception of abortion.
- Is abortion about women’s health, or is it a choice of convenience?
- What does early and late abortion mean?
- Who has more rights when it concerns abortion, and why?
- Should health insurance cover abortions?
- Abortion and how it affects adoptions.
- Why do teenagers need consent from a parent before having an abortion?
- In cases of incest, is abortion morally right?
- Abortion is always wrong. Explain
- How do we reduce the rate of abortion in the United States while keeping abortion safe and accessible to all women?
- What are the rights of a fetus?
- The effects of repeated abortions on future pregnancies.
- Abortion rights and patriarchy.
- The perception of abortion in different cultures.
- Why do the abortion policies differ per state in the United States?
Abortion Argumentative Topics
Everyone has a different view about abortion, which sometimes leads to intelligent arguments. Some topics that can present your points argumentatively include:
- Moral and ethical arguments concerning abortion.
- Abortion laws and how it contradicts women’s fundamental human rights.
- What are the pros and cons of having an abortion?
- Under what circumstances should abortion be considered?
- The abortion and mental health controversy.
- Abortion in older women. Is it safe?
- The rights of a father in the abortion decision.
- Christianity and abortion.
- Who should have the final say on abortion? The woman, the hospital, or the government?
- Cultural arguments surrounding abortion.
- Examine the generation gap in abortion support.
- How accessible is abortion in Africa?
- Mental health consequences of refused abortions.
- Is abortion a mortal sin?
- Why is there a stigma surrounding abortion?
- Abortions due to medical mistakes, should there be legal actions?
- Do mothers regret their actions after abortion?
- A cross-study of abortion laws in Malawi.
- Side effects of illegal abortions.
- The role of parents in the minor’s decision to abort.
- When is the best time to have an abortion?
- Psychiatric aspects of abortion.
Abortion Research Questions
There are many complex ethical, moral, legal, and religious perspectives concerning abortion. Some interesting questions you can research include:
- Should Abortions be legal?
- In what countries are abortions legal?
- How does abortion relate to mental health?
- What issues are agreeable reasons for abortions?
- Does rape justify abortion?
- Will abortion affect subsequent pregnancies?
- What are the abortion laws surrounding teenagers?
- Why is abortion such a controversial issue?
- What are the current laws regarding abortion?
- What do women want from abortion services?
- Has abortion been politicized?
- Why is abortion still illegal in some countries?
- Why is abortion such a controversial issue worldwide?
College Research Topics about Abortion
College students are responsible for writing clear and concise research papers built on good topics. The following are some interesting topics college students can write on.
- The Physiological effects of having an abortion
- Controversies surrounding abortion.
- A critical look at the United States laws concerning abortion?
- Common misconceptions about abortion.
- What is incomplete abortion, and how does it affects the woman’s health?
- Abortion amongst teenagers and adolescents.
- Understanding induced abortion.
- The process of legalization of abortion in Japan.
- When is abortion denied?
- The adverse effects of self-induced abortions.
- Post-abortion complications as a result of visiting illegal abortion centers.
- Childhood trauma and its connection to women seeking an abortion.
- What is a post-abortion syndrome?
- Understanding why some women opt for abortion.
- Barriers to access to abortion
- Different abortion methods, pros, and cons.
- Do the fathers have their say in abortion?
- Abortion laws and restrictions. A cross-examination of The United States and India.
- Clandestine abortion and all it entails.
- Abortion laws around the world: progress and pushbacks.
- Abortion and how it is linked to population growth and reduction.
- Looking at the punishment for abortion in countries where they ate illegal.
- Is abortion immoral?
- Should the rights of the unborn be more important than the mothers?
- What are the medical arguments for and against abortion?
- The evolution of abortion laws.
- What are the changes people opposing abortion are trying to effect?
- What changes are those supporting abortion trying to effect?
- What are the cultural arguments for and against abortion?
- History of the anti-abortion movement.
- Why do various religions have different views on abortion?
- Would a complete abortion ban be a correct solution from a religious viewpoint? Why or why not?
- When applied to abortion, what are the different ethical notions?
- What would be some negative consequences of an abortion ban?
- Why is abortion considered to be a feminist issue?
- Illegal abortions in India, and how it affects the girl child.
- Post-abortion discussion: How to avoid a repeat case of unwanted pregnancy.
Controversial Abortion Research Paper Topics
Abortion is one of the most controversial subjects in modern society, and there are many strong feelings for or against this topic. Some controversial abortion topics you can build on include:
- How has the rise of women’s rights affected abortion rates in The United States?
- What is late-term abortion?
- What is the difference between the morality and legality of abortion?
- When is abortion the right option?
- Why women should be able to have an abortion whenever they please.
- Canada and China have no legal restrictions on abortion. Any woman in these countries can get an abortion whenever she pleases. Should there be any restrictions on abortion? If not, why not? If so, what should those restrictions be and why?
- Does life begin at conception?
- Should we consider the fetus a separate being, or is it a part of its mother?
- What is a better option: abort an unplanned pregnancy or have the child neglected after birth?
- Adoption as an alternative to Abortion: Discuss
- How has legalizing abortion impacted the birth rate?
- Discuss the abortion debate and human rights.
- Why does the public support for legal termination of pregnancy remain high?
- Should men be allowed to discuss the termination of pregnancy?
- How race, poverty, and choice affect the abortion rate.
- Abortion vs. using embryos for research and IVF: Evaluate
- Should an aborting woman go through forced sterilization?
- Should birth control be considered as wrong as abortions?
- Why is it hard for some women to have an abortion even if something is wrong with a fetus?
- Why do many married couples have abortions?
- Is it better to have an abortion or give birth and place a baby in the orphanage?
- Is abortion a simple operation, or is it a severe psychological trauma for women?
- A woman’s life before and after abortion: what changes exactly?
- Canadian Abortion Laws and Women’s Rights.
- Debate on Abortion: Ethics and Principles.
Writing Help For Your Saviour
The success of an essay is first determined by the topic you write on. But picking the topic is not the only important factor. You are also required to write a detailed and concise essay. With all the workload of a college student, it might be tough to deliver your best when you write an essay. Sometimes, you should allow experts and professionals from different disciplines to provide thesis help and write the perfect essay. We provide custom research papers that can be delivered to you fast. Our team of writers consists of University graduates, professors, and teachers who can write essays suitable for undergraduate and Ph.D. students alike. Our research paper services are affordable, secure, and easily accessed by everyone online.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Terms & Conditions Loyalty Program Privacy Policy Money-Back Policy
Copyright © 2013-2024 MyPaperDone.com
245 Abortion Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
📑 aspects to cover in an abortion essay, 🏆 best abortion topic ideas & essay examples, 🥇 most interesting abortion topics to write about, 💡 good essay topics on abortion, 📌 simple & easy abortion essay titles, 📑 good research topics about abortion, 🎓 abortion argumentative essay topics, ❓ questions about abortion for research paper.
If you need to write an abortion essay, you might be worried about the content, arguments, and other components of the paper. Don’t panic – this guide contains the key aspects that will make your essay on abortion outstanding.
Historical Perspectives
First of all, you should think about the historical perspectives on abortion. It is true that unwanted pregnancies were a thing long before any legislation in this area has been enacted. If you want to write on this topic, consider the following:
- Historically, what were the main reasons for women of various titles to abort children?
- What were the methods used for abortion before the development of modern medicine?
- Were there any famous historical examples of women who aborted?
- Is the history of abortion relevant to the contemporary debate? Why or why not?
Religious Arguments
In an abortion essay, pro-life arguments usually stem from religious beliefs. Hence, there are plenty of possibilities for you to explore religious arguments related to the debate on abortion. Here are some things to think about:
- What are the ideas about abortion in different religions?
- Why do various religions have different views on abortion?
- Were there any other factors that affected how different religions saw abortion (e.g., political or social)?
- Would an complete abortion ban be a correct solution from a religious viewpoint? Why or why not?
Moral Arguments
Abortion is probably one of the most popular topics in the study of ethics. Moral arguments exist for both pro-choice and pro-life views on abortion, and you can thus explore both sides of the debate in your paper. These questions will help you to get started:
- Why is abortion considered an ethical dilemma?
- What do different ethical theories show when applied to abortion?
- From a moral viewpoint, should the life of an unborn child be more important than the physical, psychological, and socioeconomic well being of the mother? Why or why not?
- What would be some negative consequences of an abortion ban?
Women’s Rights
Abortion essay topics are often linked to the issue of women’s rights. According to most feminists, abortion is related to women’s bodily autonomy, and thus, legislators should not try to limit access to safe abortions. If you wish to explore the relationship between women’s rights and abortion, focus on the following:
- Why is abortion considered to be a feminist issue?
- Who should be involved in decisions about abortion?
- Considering that most legislators who pass pro-life laws are male, is it correct to understand abortion legislation as reproductive control?
- What are other gender issues associated with abortion?
- From the feminist viewpoint, what would be the best way to approach the problem of high abortion rates?
Essay Structure
The structure of your essay is just as important as its content, so don’t forget about it. Here is what you could do to make your paper stand out:
- Read sample papers on abortion to see how other people structure their work.
- Write a detailed abortion essay outline before you start working.
- Make sure that your points follow in a logical sequence – this will make your paper more compelling!
- For a good abortion essay conclusion, do not introduce any new sources or points in the final paragraph.
By covering the aspects above, you will be able to write an influential paper that will earn you an excellent mark. Before you begin researching, check our website for free abortion essay examples and other useful content to help you get an A*!
- Pros and Cons of Abortion to the Society Argumentative Essay In the case of rape or incest, keeping a pregnancy is very traumatizing to the person raped as no one would wish to keep a child that is a result of this, and the best […]
- Abortions: Causes, Effects, and Solutions The principal causes for the abortion problem are the social cause, which mandates ethical attitudes; the political cause, which affects legislation; and the environmental cause, which illuminates the initial stages of human development.
- Abortion: To Legalize or Not If a mother is denied an abortion due to its illegality, that mother then will be forced to go through the pregnancy, the labor, the birth, and the raising of an unwanted child. Another concern […]
- Should Abortion Be Legal In addition to the burden of carrying the unborn baby, in most cases research findings have indicated that, majority of individuals who father some babies are unwilling to take the responsibility of contributing to the […]
- Abortion and Virtue Ethics Those who support the right of a woman to an abortion even after the final trimester makes the assertion that the Constitution does not provide any legal rights for a child that is still within […]
- Ethics and Abortion In weighing the options concerning whether to perform an abortion and how to care for the patient, a healthcare entity must consider the legal implications, the patient’s and provider’s beliefs as well as the health […]
- Social Problem: Abortion The willingness of the students to partake in the procurement of abortion was significantly correlated with the views that they held regarding the issue of abortion, the extent to which they would be required to […]
- Christian Ethics Issues and Abortion As for the rights and interests of the mother, when comparing them with the rights and interests of the child, there is a possibility of an axiological preference for the goods of the latter.
- The Mother and the Challenges of Abortion In conclusion, it is clear that despite having procured abortions in the past, she wanted to be a mother to her children.
- An Abortion Versus Fetus’s Right Dilemma On the other hand, she is afraid that the child will serve as a reminder of the rapist and she has set a lot of plans for her studies and career path.
- Conservative and Liberal Arguments on Abortion Governments and health organizations’ move to control access to abortion led to the emergence of groups and movements supporting and opposing abortion.
- Abortion From the Utilitarian Perspective First and foremost, the majority of people will not abide by her since abortion is considered to be an immoral act of human murder.
- Abortion in Marquis’s vs. Thompson’s Arguments Overall, the argument against the morality of abortion using the premise that the fetus has a right to live just like the mother is self-defeating in nature. It would be beneficial for the opponents of […]
- Abortion: An Unsolvable Dilemma? We know that Christians are composed of three congregations: the Protestants, Roman Catholics, and Those who believe in the Bible, it is clear that the Bible is straightforward on life, that is that God is […]
- Abortion in Thomas Aquinas’ Religious View Abortion is aimed at the destruction of blastocyst, foetus, embryo or zygote and in the process kills the innocence any life that would be there.
- Abortion’s Pros and Cons Abortion, if legalized would curb unnecessary maternal deaths, in that, it would be done in the open and mothers would not be afraid of consulting qualified personnel for the same.
- Arguments Against the Abortion The other danger associated with abortion is that it poses a danger to the reproductive system of women in the future.
- Elizabeth Leiter’s The Abortion Divide Review Undeniably, The Abortion Divide film adequately shows the gradual growth in differences between the pro-choice and pro-life supporters but fails to bring a solution to the moral problem of abortion.
- Abortion in Teenagers: Proposal Argument In the overwhelming majority of cases, the teenager who has encountered such problems is inclined to violate the law, which often leads her to illegal and sometimes unsafe abortion. According to WHO, it is the […]
- Abortion: Why It Should Be Banned Most people are suffering from various pregnancy-related traumas as more and more couples are experiencing conceiving difficulties due to the current unhealthy food intake and environmental conditions; thus, having a baby could change a lot […]
- Discussion of Abortions: Advantages and Disadvantages The topic of abortions is, arguably, one of the most controversial and emotionally charged in the medical history, and it continues to cause a divide in healthcare even today.
- Abortion: An Ethical Dilemma and Legal Position The core concerns in the controversy are whether women should have the right to decide to terminate a pregnancy or whether the unborn child has the right to life.
- Abortion: Ethical Dilemma in Pope John Paul II’s View This paper tries to examine the abortion ethical dilemma from the lens of the Pope’s thoughts and proposals. Towards the end of the 20th century, new ideas and thoughts began to emerge in different parts […]
- Abortion Law in Canada For instance, in the report released by the Canada government in 2005, the overall rate of abortion in the country was approximately 14%, which was less than the 20% incidents reported in the United States, […]
- Abortion and the Aspects of Pro-Abortion There are occasions where somebody can have an untimely pregnancy that might end up enslaving her to the man and this can be sorted out through abortion A foetus is not a baby and there […]
- Moral Issues in the Abortion The moral authority termination of life lies in the hands of the mother despite the influence of the society about the issue.
- Debating the Issue of Abortion The psychological price to pay for abortion is irredeemable and not unless anyone wants to live a downtrodden life, she should refrain from abortion.
- Abortion-Related Ethical Considerations As a health practitioner, following the required professional standards and regulations on abortion will enable me to avoid the wrath of the law.
- Texas Abortion Ban as Current Political Topic Furthermore, denying women the right to make decisions regarding their bodies leads to the denial of bodily autonomy, which, in turn, must be regarded as a severe infringement on basic human rights.
- Abortion in Australia: Legal and Ethical Issues A woman’s sexual companion is not needed to be informed of an abortion, and the judicial system does not give orders to stop the termination even when the complainant is the biological father of the […]
- Abortion Law Reform and Maternal Mortality: Global Study Some of the criteria for selecting a credible source include the authors’ reputation, the time elapsed since published, and the legality of the publishing company or database.”Abortion Laws Reform May Reduce Maternal Mortality: An Ecological […]
- The Ethics of Abortion in Nursing The sanctity of human life, non-maleficence, and the right to autonomy and self-determination are some of the fundamental ethical ideas frequently addressed regarding abortion.
- Utilitarian Permissive Concept for Women’s Right to Choose Abortion Utilitarians believe that the right to choose abortion should be protected under the law as a matter of justice since a woman should have the right to make decisions concerning her own body and health.
- Abortion: Positive and Negative Sides To sum up, despite abortion being presented as an illegal intervention against human life, proponents believe that as a safe medical procedure, it protects the lives of mothers.
- Abortion vs. Right to Life Among Evangelical Protestants The issue of abortion is critical to many citizens, especially women. In addition to restricting women’s rights, the issue of abortion affects well-being.
- Abortion and Significant Health Complications Considering the effects of abortion, such as excessive bleeding, infection, and perforation of the uterus, surgical abortion procedures due to incomplete abortion or even death abortion can be fatal to life and one’s health.
- Abortion as an Ethical Issue in Medicine In resolving the conflict between the decision to obtain an abortion from a minor adolescent and the nurse, there may be the following solution.
- Teen Abortion: Legal and Ethical Implications The second legal implication is that the patient has the right to medical privacy and confidentiality, and the doctor may not be able to legally tell the patient’s mother about the pregnancy or abortion without […]
- Abortion as a Medical Necessity Moreover, in case of fetal death, abnormalities, ectopic pregnancy, or harm to the woman’s health, it is obligatory to follow the recommendations of doctors who objectively assess the situation. Hence, individual factors influence the development […]
- Abortion Ban: Ethical Controversies and History of Laws Abortion bans are the attempt to restrict the rights of women to procure an abortion when needed. On the other hand, arguments against the abortion ban focus on the bodily autonomy of women and the […]
- Impact of Abortion Bans on Black Women Black women and other females of color will be disproportionately affected by the United States Supreme Court’s ruling to invalidate the right to an abortion as guaranteed by the Constitution.
- The Problem of Late-Term Abortion Late-term abortion is associated with high-risk complications for the mother and inhumane treatment of the unborn child. There is an immense violation of the child’s rights if abortion is to be done after 20 weeks […]
- Abortion With Limitations: Discussion Such insights support the notion that such a medical practice could be pursued in a professional manner when the life of the mother appears to be at risk.
- Abortion and Mental Health as Controversial Issues There have been issues related to the use of face masks and the number of cases of infected people. The topic of autism is a huge controversy due to denial or a lack of awareness.
- Philosophical Reasoning About Deliberately Induced Abortion The philosophical discussion about the relationship between the right to life and bodily autonomy has become especially aggravated in the modern world.
- The Abortion Theme in Society and Literature The author does not directly mention whether the couple or the parent had opted for abortion but relating to how society handles unwanted pregnancy, the thought must have crossed people’s minds, and that is how […]
- Abortion: Pro-Life and Pro-Choice Positions Traditionally, those concerned with the abortion dilemma take one of two positions – pro-life, in which it is required to keep the fetus alive, and pro-choice, following which a woman has the right to end […]
- Nursing Ethics Regarding Abortion Currently, several articles exist that highlight different facets of this issue in nursing, including the ability of nurses to object to abortion, their confrontation with the law, and their perception of specific types of abortion.
- The Government Stance on Abortion as an Ethical Issue Throughout the years, the practice has been both legalized and prohibited in the US, with the government’s shift in attitudes being central to the ambiguity of the issue.
- Is Abortion Moral From Kantian Standpoint? The difficulties in using Kantian deontology to discuss the morality of abortion are defining whether the fetus is a human, and the role ethics play in actual decision-making.
- Abortion of a Fetus With Disability It is worth paying attention to the fact that it is precise because of such things that terminations of pregnancy occur so that a person does not come into contact with obvious prejudices still actively […]
- Pro-Abortion Arguments and Justification In general, terminating a pregnancy is the key to a woman’s prosperity, social and moral well-being, and ability to control the future.
- Law of Interest: Abortion Restrictions In the current paper, I will discuss the Texas Senate Bill 8, which is the legislation related to abortion restrictions. Therefore, the bill is interesting from the standpoint of ethical considerations, which are double-natured.
- Researching of Abortion Rights The authors of the three articles support my viewpoint by depicting the health-related and ethical risks that may take place if abortion laws continue to be restrictive.
- Aspects Against Abortion Rights Having reviewed both the supporters and opponents of abortion in the legal and ethical contexts, the writers express their pro-life views, saying that life should be respected while offering their ideas on the aforementioned contexts.
- Religious Beliefs and Medical Ethics: The Dilemma of Abortion in Cuban Society The process of giving birth to a child is considered a holiday for Cubans, and the family supports the woman after giving birth in every possible way.
- Legislative Powers in Texas: Case of Abortions In this particular situation, the Speaker of the House supports my position in the role of trustee, but here the position of the lieutenant governor is much more critical since the bill is heard in […]
- Abortion Backlash and Leadership Issues Although the issue of abortion in the United States remains one of the weightiest issues, with a high possibility of affecting the well-being of the people, it has been entirely politicized.
- Anti-Abortion Laws: The Roe v. Wade Case Therefore, the Roe case is similar to the Griswold case, making the use of the latter as a precedent justifiable. The precedent case in Roe v.
- Majority Opinion on Abortion Legalization vs. Prohibition Abortion is not the result of a nation’s historical or even cultural experience but merely the result of the adoption of restrictions.
- The “Why Abortion Is Immoral” Article by Don Marquis Don Marquis gives a different argument regarding the immorality of abortion from the standard anti-abortion argument in his “Why Abortion Is Immoral” article.
- Judith Jarvis Thomson on Women’s Right to Abortion The most serious objection to Thompson’s argument might be the one addressing abortion as a killing of a child, given that the fetus is considered a human being from the moment of conception.
- The Right to Abortion: Childless Women The issue of inferential statistics in this example is motivated by considering the possibility of extrapolating results from the sample to the general population in the context of the population mean, i.e, no children for […]
- Abortion and Women’s Right to Control Their Bodies However, the decision to ban abortions can be viewed as illegal, unethical, and contradicting the values of the 21st century. In such a way, the prohibition of abortion is a serious health concern leading to […]
- Role of Abortion Policies Discussion The introduction of regulation and informed consent measures in the case of abortion policies is feasible from the perspective of eliminating health risks for the population.
- Abortion-Related Racial Discrimination in the US In spite of being a numerical minority, Black women in the U.S.resort to abortion services rather often compared to the White population.
- Should Abortions Be Illegal as Form of Homicide? When it comes to the difference between my opinion and the status quo, I believe that abortions cannot be considered a form of homicide and cannot be persecuted.
- Abortions: Abortions Stigmatization Another issue regards the unavailability of abortions and the consequences of women being denied in abortions, and the necessity of choice for women to terminate or not terminate a pregnancy.
- Socio-Psychological Factors of Abortion in Women of Different Age Groups It is necessary to conduct a theoretical analysis of the pregnancy termination problem, reflected in psychological research. In addition, it is essential to improve the state of social stability.
- Women in Marriage & Sex, Abortion, and Birth Control The historical period chosen is from the eighteenth to the twentieth century to demonstrate the advancement of social structures for women.
- Constitutional Issues of Abortion Rights Constitution, regulating the fundamental rights and freedoms of citizens, laid the legal basis for the practical implementation of the American concept of civil rights. The amendments that were passed later on the base of the […]
- Abortion Trends in the United States The history of the legalization of abortion in the United States has a history of several decades and is still the problem of reproductive rights today is quite acute.
- Texas Abortion Laws for Victims of Sexual Assault A female will have approximately two weeks in the law to evaluate her situation, verify the conception with a test, determine how to handle the pregnancy, and undergo an abortion.
- Discussion of Abortion Accesion for Women Other individuals perceive abortion as a rather reasonable and necessary procedure that should exist as a part of healthcare and be accessible to the women who refuse to give birth to a child due to […]
- A Controversial Process of Abortion Abortion is morally wrong and should not occur at any stage of human life because it only deprives the fetus of a right to life.
- Abortion Politics and Moral Concerns Supporters of the third position think that abortion is a form of killing a person since the embryo is a person with the right to life from the moment of conception.
- “On the Moral and Legal Status of Abortion” Article by Warren In the first section of the paper, Mary Ann Warren suggests that it is impossible to establish whether abortion is morally permissible, provided one accepts that the fetus is a being with a full right […]
- Abortion on the Grounds of Disability Removing a fetus from the woman’s womb results in death which is contrary to the morals of the community that is against killing.
- Abortion: The Role of Nursing Staff In addition, the task of the nurse may be to inform the patient about the abortion process and its possible consequences. Medical personnel must respect the decision and rights of a woman who decides to […]
- Abortion and Its Physical and Psychological Effects Physiological and physical disorders that may develop in the long run due to abortion have a wide range of unfavorable consequences.
- Discussion of Abortion Rights Aspects 1, 2017, pp. It would be best used to illustrate the argument in favor of abortion rights based on the [regnant women’s right to health, which is its major strength.
- Do We Need to Legalize Abortions? Therefore, every person should take a moment to research this uncomfortable subject and think about the consequences of unsafe and illegal abortion for women, children, and society.
- Ethical Dilemma of Abortion Triumphalism In this issue and other matters, the affected person’s experience may not be a determining factor for the expression of opinion but is unique.
- The Texas Abortion Law: A Signal of War on Women’s Rights and Bodies The purpose of this paper is to examine the structure and implications of the Texas Abortion Law in order to demonstrate its flaws.
- Abortion and Menstrual Health and Society’s Views Limited resources, menstrual materials, and access to facilities are often a result of the lack of policy dedicated to the sexual health of individuals.
- The Problem of Abortion in Today’s World Therefore, the choice of the topic of late abortion is justified because of the importance and need to cover this issue.
- Abortion in the Context of Ethics and Laws The aim of this paper is to analyze abortion in the context of the law, ethics, and human rights and to identify the solution to the issue.
- Societal Approach to Abortion at Various Levels Due to its relevance in society, the issue of abortion has those affirmative, the proposers, and those who think that abortion is a vice against humanity and unethical, the opposers.
- The Problem of Abortion: Key Aspects Abortion should not be permitted because any procedure that results in the termination of pregnancy before viability is contrary to the religious idea.
- The Issue of Prohibitions on Abortions in Texas I want to talk about the indifference to women’s problems on the part of those who have vowed to be the guardians of justice in our country.
- Abortion as a Modern-Day Dilemma for the US Community For this reason, the right for abortion must be seen as the integral part of a system of human rights, specifically, those that must be given solely to women based on the reality of their […]
- Abortion: Ethical and Religious Aspects From the Christian perspective, the miracle of human life is the most valuable gift, as the creation of human beings in imago Dei allows them to experience the blessings of life and exercising the service […]
- The Ethical Dilemma on Abortion From the perspective of the Christian philosophy, a person is a product and manifestation of the love of God, hence the sanctity of any human life.
- “What I Saw at the Abortion” by Richard Selzer This sight made Selzer imagine that the fetus was struggling with the needle in this way, that he was scared and hurt, that he was trying to save itself.
- Abortion: Pro-Life and Pro-Choice Argumentation To convince the States to provide access to abortion services for women legally, the article’s author refers to standards of human rights to health and other fundamental human rights. The article’s author refers to international […]
- The Effects of Age and Other Personal Characteristics on Abortion Attitudes This is tantamount to seeking a face-saving compromise where the core issues are in black and white and is similar to the uncompromising stands of those for and against homosexual marriage; of pederasts, pedophiles and […]
- Supporting the Women Undergoing Abortion One in every five pregnancies in the world results in abortions. The main aim of the paper is to study the perceptions of nurses attending to abortion patients.
- The Politics of Abortion in Modern Day Jamaica In the first part of the dissertation, the influence of the Offences Against the Person Act of 1861 was discussed on abortion practices and laws around the world, including Jamaica.
- Abortion as Moral and Ethical Dilemma Despite the conflicting approaches to solving the moral and ethical dilemma of abortion, experts agree that it is possible to reduce the severity of the problem with the help of more excellent sexual education of […]
- Regarding Abortion vs. Adoption In such cases, the couple, or more specifically, the woman is forced to face the reality of her situation and make a decision that will definitely affect the rest of her life.
- Class Action Against the Enforcement of Texas Abortion The specific grounds of inconsistency are that the laws seek to prohibit an attempt to obtain or the actual procurement of an abortion regardless of the circumstances with the exception of the special circumstance of […]
- Ethics in Health Care-Pro-Abortion There has been myriad of reported cases of failure to uphold the integrity of the unborn and the possible health related problems that would affect a mother’s health especially in the event of unsuccessful abortion.
- The Benefits of Declining an Abortion Procedure The women may feel that they do not deserve the love of their children, and a sincere act such s a child refusing to suckle is perceived as the child directing hatred to the mother […]
- Hills Like White Elephants. Abortion or Breakup It is used to demonstrate the stalemate in the couples’ relationships the necessity to choose between an abortion and a breakup.
- Parental Consent in Minors’ Abortions Thus, the parents or guardians of the teenage girl ought to be aware of the planned abortion and explain the possible consequences of abortion to the girl.
- Ethics and Reproduction Health: Surrogacy, Multiple Pregnancies, Abortion When the child is born, the contracting woman becomes the mother of the child, but she is not a biological mother because the child has the genes of the husband and the surrogate mother.
- Applying the Moral Model to Evaluate Abortion Issue The MORAL model could be used to evaluate the issue by following the five components of the model. Upon reviewing the aspects, a nurse may want to know the current health status of the patient.
- Induced and Spontaneous Abortion and Breast Cancer Incidence Among Young Women There is also no question as to whether those who had breast cancer was only as a result of abortion the cohort study does not define the total number of women in population.
- Abortion-Related-Maternal Death in Dominican Republic There is need to focus the effort in pressuring the lawmakers to respect the rights of women. The Dominican law prohibits women from abortion even the life of woman and the child is in danger.
- How Do Abortion Laws and Regulations Affect Anti-Abortion Violence? Moreover, support for anti-abortion violence can also be considered as a political weapon against women’s rights that is linked to the tolerance of violence against women.
- Benefits of Abortion Overview Therefore, although some believe that abortion is equal to murder, many are still for abortion because it allows women to have control over their bodies, achieve full potential, and avoid engaging in hazardous abortion methods.
- Abortion Techniques and Ban in Nicaragua The case of Nicaragua has shown to be particularly challenging as the country’s leaders are adhering to the patriarchal worldview that does not consider the rights and the health of women, and the importance of […]
- How Christians View Abortion There are people who claim that the act of abortion is okay since it does not amount to the death of a live being.
- Abortion and the Theory of Act Utilitarianism One possible philosophical approach to the problem of choice in such sensitive issues as abortion is the theory of Utilitarianism measuring the moral value of the action.
- Teen Pregnancy: Abortion Rates Rise In the spotlight was the matter of teen pregnancy since teen births and abortion are both consequences of the former. That teen pregnancy rates fell in the 1990s and rose in the middle of this […]
- Abortion and Its Side Effects in the United States One of the most dominant restrictions in the 1992 ruling is that parents are supposed to be involved in the decision making platform before an abortion can be carried out.
- Cider House Rules Movie and Abortion However, upon raping her own daughter and making her pregnant, a reason was introduced for Homer to follow the path of his mentor as he becomes an abortionist for the first time.
- Maryland State Bill on Abortion According to the bill, women are supposed to see the ultrasound image in the uterus before an abortion is performed on them.
- Legalizing Abortion in the USA: Pros and Cons Since abortion was legalized in the US in the year 1973, the rates of abortion have gone up to approximately 1.
- Pro-Choice: The Issue of Abortion Abortion has become a highly debatable issue in the United States because of the ethics and morality involved in the act and the possibility of resorting to it in an elective manner.
- The Ethics of Abortion: Discussion The essay first examines the philosophical and religious concept of life and how the decision to abort affects the right to life of the fetus as also the existential dilemma that may arise when a […]
- Is Abortion Right or Wrong: A Dilemma The supporters of abortion feel that a woman should be given the chance to decide on abortion as being pregnant and having a baby involves dealing with many consequences.
- Medical Ethics. Should Abortion Be Banned? However, in the present situation of the world in general and the United States in particular, there is no doubt that abortion is a bad practice that deserves to be banned in all cases except […]
- Legalities of Carrying Out Abortion Discussion This led to the emergence of such groupings as pro-life, who advocate for the consideration of abortion as murder, and pro-choice who are of the view that women should have the right of choice of […]
- Issue of Abortion Abortion in Islam and Christianity This law justifies the humanity of the unborn baby and places the child in the same level of an adult being who has caused the miscarriage.
- Abortion Is Legal but Is It Ethical? It is not difficult to understand how God’s words can be considered open to analysis but the difficulty of the abortion issue is that the breadth of the interpretation is very wide.
- Ethical Problem of Abortion However, the major point of contention has not been whether the mother is the victim or not; but more on where does the fetus really attain the status of a person with rights and the […]
- Abortions and Birth Control As a result the overall mortality of women increases in the countries where legal abortions take place. The general point of view in decreasing the number of abortions is the use of contraceptives as a […]
- Abortion as an Unmerciful and Irresponsible Act Abortion is a very big risk to the health of the woman who opts to undergo an abortion. The biggest risk is to the life of the woman who opts for an abortion.
- Abortion in Islamic View If a woman finds that she is pregnant, and does not want to be, what is the best way out for her, the potential baby that she is carrying, and all the other people concerned […]
- Noonan and Thomson’s View on Abortion A more disarming approach is that of Thomson who maintains that the mother’s right to control her own body overrides the right to life of the fetus unless the mother has a special responsibility to […]
- Factors Contributing to the Decline in Abortion A considerable decline in abortion has been witnessed and I propose to assess the factors that have contributed to the decline in abortion. The next is the reason for the decline in the number of […]
- Bioethics. When Abortion Is Morally Permissible Abortion as we all know is the deliberate removal of a foetus from the womb of a female resulting in the death of the foetus.
- Abortion Debate: Overview of Both Positions Daniel Oliver appears to be the supporter of the pro-life side of the debate, even though he does not impose his opinion on the reader and does not write that abortion is wrong.
- Abortion: Strengths and Limitations They believe that it is the right of a woman to have an abortion when they want to, and they should also not be forced to have an abortion if they want to give birth.
- Importance of Legalizing of Abortions Three of the most common reasons why women choose abortion is that they do not have the financial resources to raise a child, the others feel that they are not ready to have a child, […]
- Ethical Issues of Counseling: Abortion and Divorce Personal values and beliefs, world views, and attitudes of both a counselor and a client have a great impact on the therapeutic relationship and effective treatment.
- Contemporary Argument on Abortion Review Abortion is treated differently as some find it a moral crime, others think that it is a reasonable way out from the unwanted pregnancy situation, and there is also a viewpoint that abortion is the […]
- Abortion: Premeditated Murder or a Reasonable Way Out? Speaking of the second point the supporters of abortion have, we should say that they find abortion as the mother’s attempt to protect the unborn child from the various hardship she will fail to fight.
- Women’s Health Issues: Abortion Reasons and Laws As one can see, the physical, psychological, and social risks of limiting access to abortion or proposing hostile policies are apparent.
- View of Abortion: The Question of Human Life and Death In order to describe the question of abortion it is important to define and explain it.”Abortion’ as a ‘spontaneous or induced termination of pregnancy”, and “miscarriage’ as the ‘the spontaneous loss of an early pregnancy […]
- Unsafe Abortions Concepts Analysis The overall attitudes to abortion were negative, and women who succeeded in aborting pregnancy faced opposition from their partners, social ostracism, and quasi-legal sanctions.
- New Jersey Bill A495 on Abortion This paper aims to review the New Jersey Bill A495, the differences in the legislation process between New Jersey and other states, provide a personal position on the issue of abortion, and discuss the impact […]
- Social Work Framework for the Abortion Seeking Experience In countries that do allow abortion, the law has to be adhered to and I would have to do the abortion or give the needed advice despite my ethical or religious beliefs.
- The Safety and Quality of Abortion Care in the United States What is the association between the appropriateness of specific abortion services and various clinical circumstances? What are the physical and mental health effects of abortion?
- The Abortion Debate: The Moral Status of the Fetus All arguments about abortion do not come down to the question of what is the moral status of the fetus since there are other aspects involved, including the health conditions of the mother, the fetus’s […]
- Abortion in Ireland: Law and Public Opinion Abortion in Ireland is a highly controversial issue despite the May 26, 2018 landslide victory, which saw the repealing of the Eighth Amendment of the constitution to allow women to abort albeit under certain circumstances.
- Anti-Abortion Social Movements and Legislators’ Role In the described cases, the main task for the representatives is to make law as flexible as possible, and this is one of the most complicated things to do.
- The Politics of Abortion
- Abortion Is Too Complex to Feel All One Way About
- The Last Abortion Clinic
- Why Abortion Is Immoral?
- Abortion, Its Causes and Psychological Problems
- Abortion Debates of Pro-Life and Pro-Choice Parties
- Abortion as a Constitutional Right of US Women
- Is Abortion Morally Justified?
- Abortion Debate: Immoral Aspect of Pregnancy Termination
- Abortion Counseling and Psychological Support
- Teenage Pregnancy, Abortion, and Sex Education
- Barriers to Access to Abortion Services
- Anti-Abortion Legislation and Services in Texas
- Elective Abortion For and Against
- Should Abortions Be Legal?
- Abortion Rights: Roe vs. Wade Case
- Abortion as a Crime and the Fight Against It
- Canadian vs. American Post-Abortion Care
- Abortion: Quality of Life and Genetic Abnormalities
- Teenage Pregnancy and Abortion: Articles Evaluation
- Abortion in the Middle East
- Abortion Practice in the Middle East
- The Minimum Hourly Wages and the Abortions
- Conflicting Viewpoints: Should Abortion Be Legal?
- “The Last Abortion Clinic”: Documentary Analysis
- Ethical Dilemma: Political Involvement in Abortion
- Legalization of Abortion for Underage Girls
- Legalizing Abortion: Advantages and Justification
- Abortion Incidence in the United State
- Ethics of Abortion: Controversial Issues
- “A Defence of Abortion” by Thomson
- Social Issues: Abortions Prohibition
- Abortion Law Importance in Canada
- Abortion: Theories and Moral Issues
- Anti- and Pro-Abortion Arguments
- A Woman Has A Natural Right To Get An Abortion
- Controversial Question About Abortion
- Abortion: Pro-Choice and Pro-Life Movement
- The Issue of Abortion in the African Continent
- State of Abortion Laws
- Moral Problems of Abortion
- President Reagan’s Thoughts on Abortion
- Abortion and Parental Consent
- Analysis of Abortion as an Ethical Issue
- Ethics in Professional Psychology: Abortion Issue
- Abortion as a Health Ethics Issue
- Abortion as a Current Public Policy Issue
- A Call to Legalize Abortion
- Should Canada Have An Abortion Law?
- Abortion’s Merits and Demerits of in the Global Perspectives
- Freedom of Women to Choose Abortion
- Compare and Contrast Analysis Socio-Political and Moral Agenda of Abortion
- Abortions Legal in the U.S.A.
- Abortion: Analysis of Pro-Abortion Arguments
- The Role of US Government on Abortions
- Exploiting Nazism in Abortion Debate
- Abortion Principles – Case of George and Linda
- Is Self-Defense Abortion Permissible?
- Africa Is Not Ready to Embrace Abortion
- The Ethics of Abortion
- The Debate About Abortion
- Moral Controversies of Abortion
- The Issue of Abortion
- The Case Against Legalization of Abortion
- The Burning Debate on Abortion
- Teen Abortion: Understanding the Risks
- Conflicting Views on Abortion
- Pro-Life and Pro-Choice Sides of Abortion
- No More Abortion: Anti-Abortion Debate
- The Right to Abortion
- The Problem of Legality or Illegality of Terminating Pregnancy (Abortion)
- Abortion and Its Effects
- The True Extremist on Abortion: The Analysis of Tom Trinkon’s Essay
- The Problems of Abortion in Modern Society
- Social Problem of Abortion: Dealing With Media
- Abortion as a Controversial Issue
- How Christians Respond to the Issue of Abortion?
- Did Legalizing Abortion Reduce Crime Rate in the US?
- Does Abortion Have Severe Psychological Effects?
- Does Increased Abortion Lead To Lower Crime?
- Does Natural Law Allow Abortion?
- What Are Economic Incentives for Sex-Selective Abortion in India?
- How Christians Might Put Their Beliefs About Abortion Into Action?
- How Christian Teachings May Be Used in a Discussion About Abortion?
- How Abortion Laws Have Changed Around the World?
- How Are Religious and Ethical Principles Used in the Abortion?
- How Has Abortion and Birth Control Affected the 20th and 21st Century?
- How Roman Catholics Might Put Their Beliefs About Abortion Into Practice?
- How Useful Are Kantian Ethics for Drawing Conclusions About Abortion?
- How Women Are Psychologically Impacted by Abortion?
- What Are the Ethical Issues Raised With Abortion?
- Who Should Decide the Legality of Abortion?
- Why Abortion Should Remain Legal and With Limitations?
- Why Has Abortion Created Serious Debates and Controversies Among the Mainline?
- Why the Government Should Ban Abortion?
- Women Should Have the Right to Have Abortion?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 2). 245 Abortion Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/abortion-essay-examples/
"245 Abortion Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 2 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/abortion-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '245 Abortion Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 2 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "245 Abortion Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/abortion-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "245 Abortion Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/abortion-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "245 Abortion Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/abortion-essay-examples/.
- Human Development Research Ideas
- Parenting Research Topics
- Parent Essay Ideas
- Family Titles
- Affordable Care Act Essay Titles
- Women’s Rights Titles
- Reproductive Health Essay Titles
- Health Promotion Research Topics
Home — Blog — Topic Ideas — 50 Abortion Essay Topics: Researching Abortion-Related Subjects
50 Abortion Essay Topics: Researching Abortion-Related Subjects
Abortion remains a contentious social and political issue, with deeply held beliefs and strong emotions shaping the debate. It is a topic that has been at the forefront of public discourse for decades, sparking heated arguments and evoking a range of perspectives from individuals, organizations, and governments worldwide.
The complexity of abortion stems from its intersection with fundamental human rights, ethical principles, and societal norms. It raises questions about the sanctity of life, individual autonomy, gender equality, and public health, making it a challenging yet critically important subject to explore and analyze.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the significance of choosing the right abortion essay topics and abortion title ideas , offering valuable insights and practical advice for students navigating this challenging yet rewarding endeavor. By understanding the multifaceted nature of abortion and its far-reaching implications, students can make informed decisions about their topic selection, setting themselves up for success in producing well-researched, insightful, and impactful essays.
Choosing the Right Abortion Essay Topic
For students who are tasked with writing an essay on abortion, choosing the right topic is essential. A well-chosen topic can be the difference between a well-researched, insightful, and impactful piece of writing and a superficial, uninspired, and forgettable one.
This guide delves into the significance of selecting the right abortion essay topic, providing valuable insights for students embarking on this challenging yet rewarding endeavor. By understanding the multifaceted nature of abortion and its far-reaching implications, students can identify topics that align with their interests, research capabilities, and the overall objectives of their essays.
Abortion remains a contentious social and political issue, with deeply held beliefs and strong emotions shaping the debate on abortion topics . It is a topic that has been at the forefront of public discourse for decades, sparking heated arguments and evoking a range of perspectives from individuals, organizations, and governments worldwide.
List of Abortion Argumentative Essay Topics
Abortion argumentative essay topics typically revolve around the ethical, legal, and societal aspects of this controversial issue. These topics often involve debates and discussions, requiring students to present well-reasoned arguments supported by evidence and persuasive language.
- The Bodily Autonomy vs. Fetal Rights Debate: A Balancing Act
- Exploring Abortion Rights: An Argumentative Analysis
- Gender Equality and Reproductive Freedom in the Abortion Debate
- Considering Abortion as a Human Right
- The Impact of Abortion Stigma on Women's Mental Health
- Abortion: A Controversial Issue
- Persuasive Speech Outline on Abortion
- Laughing Matters: Satire and the Abortion Debate
- Abortion Is Bad
- Discussion on Whether Abortion is a Crime
- Abortion Restrictions and Women's Economic Opportunity
- Government Intervention in Abortion Regulation
- Religion, Morality, and Abortion Attitudes
- Parental Notification and Consent Laws
- A Persuasive Paper on the Issue of Abortion
Ethical Considerations: Abortion raises profound ethical questions about the sanctity of life, personhood, and individual choice. Students can explore these ethical dilemmas by examining the moral implications of abortion, the rights of the unborn, and the role of personal conscience in decision-making.
Legal Aspects: The legal landscape surrounding abortion is constantly evolving, with varying regulations and restrictions across different jurisdictions. Students can delve into the legal aspects of abortion by analyzing the impact of laws and policies on access, safety, and the well-being of women.
Societal Impact: Abortion has a significant impact on society, influencing public health, gender equality, and social justice. Students can explore the societal implications of abortion by examining its impact on maternal health, reproductive rights, and the lives of marginalized communities.
Effective Abortion Topics for Research Paper
Research papers on abortion demand a more in-depth and comprehensive approach, requiring students to delve into historical, medical, and international perspectives on this multifaceted issue.
Medical Perspectives: The medical aspects of abortion encompass a wide range of topics, from advancements in abortion procedures to the health and safety of women undergoing the procedure. Students can explore medical perspectives by examining the evolution of abortion techniques, the impact of medical interventions on maternal health, and the role of healthcare providers in the abortion debate.
Historical Analysis: Abortion has a long and complex history, with changing attitudes, practices, and laws across different eras. Students can engage in historical analysis by examining the evolution of abortion practices in ancient civilizations, tracing the legal developments surrounding abortion, and exploring the shifting social attitudes towards abortion throughout history.
International Comparisons: Abortion laws and regulations vary widely across different countries, leading to diverse experiences and outcomes. Students can make international comparisons by examining abortion access and restrictions in different regions, analyzing the impact of varying legal frameworks on women's health and rights, and identifying best practices in abortion policies.
List of Abortion Research Paper Topics
- The Socioeconomic Factors and Racial Disparities Shaping Abortion Access
- Ethical and Social Implications of Emerging Abortion Technologies
- Abortion Stigma and Women's Mental Health
- Telemedicine and Abortion Access in Rural Areas
- International Human Rights and Abortion Access
- Reproductive Justice and Other Social Justice Issues
- Men's Role in Abortion Decision-Making
- Abortion Restrictions and Social Disparities
- Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Abortion Access
- Alternative Approaches to Abortion Regulation
- Political Ideology and Abortion Policy Debates
- Public Health Campaigns for Informed Abortion Decisions
- Abortion Services in Conflict-Affected Areas
- Healthcare Providers and Medical Ethics of Abortion
- International Cooperation on Abortion Policies
By exploring these topics and subtopics for abortion essays , students can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the multifaceted nature of the abortion debate and choose a specific focus that aligns with their interests and research objectives.
Choosing Abortion Research Paper Topics
When selecting research paper topics on abortion, it is essential to consider factors such as research feasibility, availability of credible sources, and the potential for original contributions.
Abortion is a complex and multifaceted issue that intersects with various aspects of society and individual lives. By broadening the scope of abortion-related topics, students can explore a wider range of perspectives and insights.
- Abortion Social Issue
- Exploring the Complexity of Abortion: Historical, Medical and Personal Perspectives
- Abortion: A Comprehensive Research
- An Examination of Abortion and its Health Implications on Women
- Abortion Introduction
- Comparative Analysis of Abortion Laws Worldwide
- Historical Evolution of Abortion Rights and Practices
- Impact of Abortion on Public Health and Maternal Mortality
- Abortion Funding and Access to Reproductive Healthcare
- Role of Misinformation and Myths in Abortion Debates
- International Perspectives on Abortion and Reproductive Freedom
- Abortion and the UN Sustainable Development Goals
- Abortion and Gender Equality in the Global Context
- Abortion and Human Rights: A Legal and Ethical Analysis
- Religious and Cultural Influences on Abortion Perceptions
- Abortion and Social Justice: Addressing Disparities and Marginalization
- Anti-abortion and Pro-choice Movements: Comparative Analysis and Impact
- Impact of Technological Advancements on Abortion Procedures and Access
- Ethical Considerations of New Abortion Technologies and Surrogacy
- Role of Advocacy and Activism in Shaping Abortion Policy and Practice
- Measuring the Effectiveness of Abortion Policy Interventions
Navigating the complex landscape of abortion-related topics can be a daunting task, but it also offers an opportunity for students to delve into a range of compelling issues and perspectives. By choosing the right topic, students can produce well-researched, insightful, and impactful essays that contribute to the ongoing dialogue on this important subject.
The 50 abortion essay ideas presented in this guide provide a starting point for exploring the intricacies of abortion and its far-reaching implications. Whether students are interested in argumentative essays that engage in ethical, legal, or societal debates or research papers that delve into medical, historical, or international perspectives, this collection offers a wealth of potential topics to ignite their curiosity and challenge their thinking.

We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Open access
- Published: 28 June 2021
Impact of abortion law reforms on women’s health services and outcomes: a systematic review protocol
- Foluso Ishola ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8644-0570 1 ,
- U. Vivian Ukah 1 &
- Arijit Nandi 1
Systematic Reviews volume 10 , Article number: 192 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
21k Accesses
2 Citations
3 Altmetric
Metrics details
A country’s abortion law is a key component in determining the enabling environment for safe abortion. While restrictive abortion laws still prevail in most low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), many countries have reformed their abortion laws, with the majority of them moving away from an absolute ban. However, the implications of these reforms on women’s access to and use of health services, as well as their health outcomes, is uncertain. First, there are methodological challenges to the evaluation of abortion laws, since these changes are not exogenous. Second, extant evaluations may be limited in terms of their generalizability, given variation in reforms across the abortion legality spectrum and differences in levels of implementation and enforcement cross-nationally. This systematic review aims to address this gap. Our aim is to systematically collect, evaluate, and synthesize empirical research evidence concerning the impact of abortion law reforms on women’s health services and outcomes in LMICs.
We will conduct a systematic review of the peer-reviewed literature on changes in abortion laws and women’s health services and outcomes in LMICs. We will search Medline, Embase, CINAHL, and Web of Science databases, as well as grey literature and reference lists of included studies for further relevant literature. As our goal is to draw inference on the impact of abortion law reforms, we will include quasi-experimental studies examining the impact of change in abortion laws on at least one of our outcomes of interest. We will assess the methodological quality of studies using the quasi-experimental study designs series checklist. Due to anticipated heterogeneity in policy changes, outcomes, and study designs, we will synthesize results through a narrative description.
This review will systematically appraise and synthesize the research evidence on the impact of abortion law reforms on women’s health services and outcomes in LMICs. We will examine the effect of legislative reforms and investigate the conditions that might contribute to heterogeneous effects, including whether specific groups of women are differentially affected by abortion law reforms. We will discuss gaps and future directions for research. Findings from this review could provide evidence on emerging strategies to influence policy reforms, implement abortion services and scale up accessibility.
Systematic review registration
PROSPERO CRD42019126927
Peer Review reports
An estimated 25·1 million unsafe abortions occur each year, with 97% of these in developing countries [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. Despite its frequency, unsafe abortion remains a major global public health challenge [ 4 , 5 ]. According to the World health Organization (WHO), nearly 8% of maternal deaths were attributed to unsafe abortion, with the majority of these occurring in developing countries [ 5 , 6 ]. Approximately 7 million women are admitted to hospitals every year due to complications from unsafe abortion such as hemorrhage, infections, septic shock, uterine and intestinal perforation, and peritonitis [ 7 , 8 , 9 ]. These often result in long-term effects such as infertility and chronic reproductive tract infections. The annual cost of treating major complications from unsafe abortion is estimated at US$ 232 million each year in developing countries [ 10 , 11 ]. The negative consequences on children’s health, well-being, and development have also been documented. Unsafe abortion increases risk of poor birth outcomes, neonatal and infant mortality [ 12 , 13 ]. Additionally, women who lack access to safe and legal abortion are often forced to continue with unwanted pregnancies, and may not seek prenatal care [ 14 ], which might increase risks of child morbidity and mortality.
Access to safe abortion services is often limited due to a wide range of barriers. Collectively, these barriers contribute to the staggering number of deaths and disabilities seen annually as a result of unsafe abortion, which are disproportionately felt in developing countries [ 15 , 16 , 17 ]. A recent systematic review on the barriers to abortion access in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) implicated the following factors: restrictive abortion laws, lack of knowledge about abortion law or locations that provide abortion, high cost of services, judgmental provider attitudes, scarcity of facilities and medical equipment, poor training and shortage of staff, stigma on social and religious grounds, and lack of decision making power [ 17 ].
An important factor regulating access to abortion is abortion law [ 17 , 18 , 19 ]. Although abortion is a medical procedure, its legal status in many countries has been incorporated in penal codes which specify grounds in which abortion is permitted. These include prohibition in all circumstances, to save the woman’s life, to preserve the woman’s health, in cases of rape, incest, fetal impairment, for economic or social reasons, and on request with no requirement for justification [ 18 , 19 , 20 ].
Although abortion laws in different countries are usually compared based on the grounds under which legal abortions are allowed, these comparisons rarely take into account components of the legal framework that may have strongly restrictive implications, such as regulation of facilities that are authorized to provide abortions, mandatory waiting periods, reporting requirements in cases of rape, limited choice in terms of the method of abortion, and requirements for third-party authorizations [ 19 , 21 , 22 ]. For example, the Zambian Termination of Pregnancy Act permits abortion on socio-economic grounds. It is considered liberal, as it permits legal abortions for more indications than most countries in Sub-Saharan Africa; however, abortions must only be provided in registered hospitals, and three medical doctors—one of whom must be a specialist—must provide signatures to allow the procedure to take place [ 22 ]. Given the critical shortage of doctors in Zambia [ 23 ], this is in fact a major restriction that is only captured by a thorough analysis of the conditions under which abortion services are provided.
Additionally, abortion laws may exist outside the penal codes in some countries, where they are supplemented by health legislation and regulations such as public health statutes, reproductive health acts, court decisions, medical ethic codes, practice guidelines, and general health acts [ 18 , 19 , 24 ]. The diversity of regulatory documents may lead to conflicting directives about the grounds under which abortion is lawful [ 19 ]. For example, in Kenya and Uganda, standards and guidelines on the reduction of morbidity and mortality due to unsafe abortion supported by the constitution was contradictory to the penal code, leaving room for an ambiguous interpretation of the legal environment [ 25 ].
Regulations restricting the range of abortion methods from which women can choose, including medication abortion in particular, may also affect abortion access [ 26 , 27 ]. A literature review contextualizing medication abortion in seven African countries reported that incidence of medication abortion is low despite being a safe, effective, and low-cost abortion method, likely due to legal restrictions on access to the medications [ 27 ].
Over the past two decades, many LMICs have reformed their abortion laws [ 3 , 28 ]. Most have expanded the grounds on which abortion may be performed legally, while very few have restricted access. Countries like Uruguay, South Africa, and Portugal have amended their laws to allow abortion on request in the first trimester of pregnancy [ 29 , 30 ]. Conversely, in Nicaragua, a law to ban all abortion without any exception was introduced in 2006 [ 31 ].
Progressive reforms are expected to lead to improvements in women’s access to safe abortion and health outcomes, including reductions in the death and disabilities that accompany unsafe abortion, and reductions in stigma over the longer term [ 17 , 29 , 32 ]. However, abortion law reforms may yield different outcomes even in countries that experience similar reforms, as the legislative processes that are associated with changing abortion laws take place in highly distinct political, economic, religious, and social contexts [ 28 , 33 ]. This variation may contribute to abortion law reforms having different effects with respect to the health services and outcomes that they are hypothesized to influence [ 17 , 29 ].
Extant empirical literature has examined changes in abortion-related morbidity and mortality, contraceptive usage, fertility, and other health-related outcomes following reforms to abortion laws [ 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 ]. For example, a study in Mexico reported that a policy that decriminalized and subsidized early-term elective abortion led to substantial reductions in maternal morbidity and that this was particularly strong among vulnerable populations such as young and socioeconomically disadvantaged women [ 38 ].
To the best of our knowledge, however, the growing literature on the impact of abortion law reforms on women’s health services and outcomes has not been systematically reviewed. A study by Benson et al. evaluated evidence on the impact of abortion policy reforms on maternal death in three countries, Romania, South Africa, and Bangladesh, where reforms were immediately followed by strategies to implement abortion services, scale up accessibility, and establish complementary reproductive and maternal health services [ 39 ]. The three countries highlighted in this paper provided unique insights into implementation and practical application following law reforms, in spite of limited resources. However, the review focused only on a selection of countries that have enacted similar reforms and it is unclear if its conclusions are more widely generalizable.
Accordingly, the primary objective of this review is to summarize studies that have estimated the causal effect of a change in abortion law on women’s health services and outcomes. Additionally, we aim to examine heterogeneity in the impacts of abortion reforms, including variation across specific population sub-groups and contexts (e.g., due to variations in the intensity of enforcement and service delivery). Through this review, we aim to offer a higher-level view of the impact of abortion law reforms in LMICs, beyond what can be gained from any individual study, and to thereby highlight patterns in the evidence across studies, gaps in current research, and to identify promising programs and strategies that could be adapted and applied more broadly to increase access to safe abortion services.
The review protocol has been reported using Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) guidelines [ 40 ] (Additional file 1 ). It was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) database CRD42019126927.
Eligibility criteria
Types of studies.
This review will consider quasi-experimental studies which aim to estimate the causal effect of a change in a specific law or reform and an outcome, but in which participants (in this case jurisdictions, whether countries, states/provinces, or smaller units) are not randomly assigned to treatment conditions [ 41 ]. Eligible designs include the following:
Pretest-posttest designs where the outcome is compared before and after the reform, as well as nonequivalent groups designs, such as pretest-posttest design that includes a comparison group, also known as a controlled before and after (CBA) designs.
Interrupted time series (ITS) designs where the trend of an outcome after an abortion law reform is compared to a counterfactual (i.e., trends in the outcome in the post-intervention period had the jurisdiction not enacted the reform) based on the pre-intervention trends and/or a control group [ 42 , 43 ].
Differences-in-differences (DD) designs, which compare the before vs. after change in an outcome in jurisdictions that experienced an abortion law reform to the corresponding change in the places that did not experience such a change, under the assumption of parallel trends [ 44 , 45 ].
Synthetic controls (SC) approaches, which use a weighted combination of control units that did not experience the intervention, selected to match the treated unit in its pre-intervention outcome trend, to proxy the counterfactual scenario [ 46 , 47 ].
Regression discontinuity (RD) designs, which in the case of eligibility for abortion services being determined by the value of a continuous random variable, such as age or income, would compare the distributions of post-intervention outcomes for those just above and below the threshold [ 48 ].
There is heterogeneity in the terminology and definitions used to describe quasi-experimental designs, but we will do our best to categorize studies into the above groups based on their designs, identification strategies, and assumptions.
Our focus is on quasi-experimental research because we are interested in studies evaluating the effect of population-level interventions (i.e., abortion law reform) with a design that permits inference regarding the causal effect of abortion legislation, which is not possible from other types of observational designs such as cross-sectional studies, cohort studies or case-control studies that lack an identification strategy for addressing sources of unmeasured confounding (e.g., secular trends in outcomes). We are not excluding randomized studies such as randomized controlled trials, cluster randomized trials, or stepped-wedge cluster-randomized trials; however, we do not expect to identify any relevant randomized studies given that abortion policy is unlikely to be randomly assigned. Since our objective is to provide a summary of empirical studies reporting primary research, reviews/meta-analyses, qualitative studies, editorials, letters, book reviews, correspondence, and case reports/studies will also be excluded.
Our population of interest includes women of reproductive age (15–49 years) residing in LMICs, as the policy exposure of interest applies primarily to women who have a demand for sexual and reproductive health services including abortion.
Intervention
The intervention in this study refers to a change in abortion law or policy, either from a restrictive policy to a non-restrictive or less restrictive one, or vice versa. This can, for example, include a change from abortion prohibition in all circumstances to abortion permissible in other circumstances, such as to save the woman’s life, to preserve the woman’s health, in cases of rape, incest, fetal impairment, for economic or social reasons, or on request with no requirement for justification. It can also include the abolition of existing abortion policies or the introduction of new policies including those occurring outside the penal code, which also have legal standing, such as:
National constitutions;
Supreme court decisions, as well as higher court decisions;
Customary or religious law, such as interpretations of Muslim law;
Medical ethical codes; and
Regulatory standards and guidelines governing the provision of abortion.
We will also consider national and sub-national reforms, although we anticipate that most reforms will operate at the national level.
The comparison group represents the counterfactual scenario, specifically the level and/or trend of a particular post-intervention outcome in the treated jurisdiction that experienced an abortion law reform had it, counter to the fact, not experienced this specific intervention. Comparison groups will vary depending on the type of quasi-experimental design. These may include outcome trends after abortion reform in the same country, as in the case of an interrupted time series design without a control group, or corresponding trends in countries that did not experience a change in abortion law, as in the case of the difference-in-differences design.
Outcome measures
Primary outcomes.
Access to abortion services: There is no consensus on how to measure access but we will use the following indicators, based on the relevant literature [ 49 ]: [ 1 ] the availability of trained staff to provide care, [ 2 ] facilities are geographically accessible such as distance to providers, [ 3 ] essential equipment, supplies and medications, [ 4 ] services provided regardless of woman’s ability to pay, [ 5 ] all aspects of abortion care are explained to women, [ 6 ] whether staff offer respectful care, [ 7 ] if staff work to ensure privacy, [ 8 ] if high-quality, supportive counseling is provided, [ 9 ] if services are offered in a timely manner, and [ 10 ] if women have the opportunity to express concerns, ask questions, and receive answers.
Use of abortion services refers to induced pregnancy termination, including medication abortion and number of women treated for abortion-related complications.
Secondary outcomes
Current use of any method of contraception refers to women of reproductive age currently using any method contraceptive method.
Future use of contraception refers to women of reproductive age who are not currently using contraception but intend to do so in the future.
Demand for family planning refers to women of reproductive age who are currently using, or whose sexual partner is currently using, at least one contraceptive method.
Unmet need for family planning refers to women of reproductive age who want to stop or delay childbearing but are not using any method of contraception.
Fertility rate refers to the average number of children born to women of childbearing age.
Neonatal morbidity and mortality refer to disability or death of newborn babies within the first 28 days of life.
Maternal morbidity and mortality refer to disability or death due to complications from pregnancy or childbirth.
There will be no language, date, or year restrictions on studies included in this systematic review.
Studies have to be conducted in a low- and middle-income country. We will use the country classification specified in the World Bank Data Catalogue to identify LMICs (Additional file 2 ).
Search methods
We will perform searches for eligible peer-reviewed studies in the following electronic databases.
Ovid MEDLINE(R) (from 1946 to present)
Embase Classic+Embase on OvidSP (from 1947 to present)
CINAHL (1973 to present); and
Web of Science (1900 to present)
The reference list of included studies will be hand searched for additional potentially relevant citations. Additionally, a grey literature search for reports or working papers will be done with the help of Google and Social Science Research Network (SSRN).
Search strategy
A search strategy, based on the eligibility criteria and combining subject indexing terms (i.e., MeSH) and free-text search terms in the title and abstract fields, will be developed for each electronic database. The search strategy will combine terms related to the interventions of interest (i.e., abortion law/policy), etiology (i.e., impact/effect), and context (i.e., LMICs) and will be developed with the help of a subject matter librarian. We opted not to specify outcomes in the search strategy in order to maximize the sensitivity of our search. See Additional file 3 for a draft of our search strategy.
Data collection and analysis
Data management.
Search results from all databases will be imported into Endnote reference manager software (Version X9, Clarivate Analytics) where duplicate records will be identified and excluded using a systematic, rigorous, and reproducible method that utilizes a sequential combination of fields including author, year, title, journal, and pages. Rayyan systematic review software will be used to manage records throughout the review [ 50 ].
Selection process
Two review authors will screen titles and abstracts and apply the eligibility criteria to select studies for full-text review. Reference lists of any relevant articles identified will be screened to ensure no primary research studies are missed. Studies in a language different from English will be translated by collaborators who are fluent in the particular language. If no such expertise is identified, we will use Google Translate [ 51 ]. Full text versions of potentially relevant articles will be retrieved and assessed for inclusion based on study eligibility criteria. Discrepancies will be resolved by consensus or will involve a third reviewer as an arbitrator. The selection of studies, as well as reasons for exclusions of potentially eligible studies, will be described using a PRISMA flow chart.
Data extraction
Data extraction will be independently undertaken by two authors. At the conclusion of data extraction, these two authors will meet with the third author to resolve any discrepancies. A piloted standardized extraction form will be used to extract the following information: authors, date of publication, country of study, aim of study, policy reform year, type of policy reform, data source (surveys, medical records), years compared (before and after the reform), comparators (over time or between groups), participant characteristics (age, socioeconomic status), primary and secondary outcomes, evaluation design, methods used for statistical analysis (regression), estimates reported (means, rates, proportion), information to assess risk of bias (sensitivity analyses), sources of funding, and any potential conflicts of interest.
Risk of bias and quality assessment
Two independent reviewers with content and methodological expertise in methods for policy evaluation will assess the methodological quality of included studies using the quasi-experimental study designs series risk of bias checklist [ 52 ]. This checklist provides a list of criteria for grading the quality of quasi-experimental studies that relate directly to the intrinsic strength of the studies in inferring causality. These include [ 1 ] relevant comparison, [ 2 ] number of times outcome assessments were available, [ 3 ] intervention effect estimated by changes over time for the same or different groups, [ 4 ] control of confounding, [ 5 ] how groups of individuals or clusters were formed (time or location differences), and [ 6 ] assessment of outcome variables. Each of the following domains will be assigned a “yes,” “no,” or “possibly” bias classification. Any discrepancies will be resolved by consensus or a third reviewer with expertise in review methodology if required.
Confidence in cumulative evidence
The strength of the body of evidence will be assessed using the Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) system [ 53 ].
Data synthesis
We anticipate that risk of bias and heterogeneity in the studies included may preclude the use of meta-analyses to describe pooled effects. This may necessitate the presentation of our main findings through a narrative description. We will synthesize the findings from the included articles according to the following key headings:
Information on the differential aspects of the abortion policy reforms.
Information on the types of study design used to assess the impact of policy reforms.
Information on main effects of abortion law reforms on primary and secondary outcomes of interest.
Information on heterogeneity in the results that might be due to differences in study designs, individual-level characteristics, and contextual factors.
Potential meta-analysis
If outcomes are reported consistently across studies, we will construct forest plots and synthesize effect estimates using meta-analysis. Statistical heterogeneity will be assessed using the I 2 test where I 2 values over 50% indicate moderate to high heterogeneity [ 54 ]. If studies are sufficiently homogenous, we will use fixed effects. However, if there is evidence of heterogeneity, a random effects model will be adopted. Summary measures, including risk ratios or differences or prevalence ratios or differences will be calculated, along with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Analysis of subgroups
If there are sufficient numbers of included studies, we will perform sub-group analyses according to type of policy reform, geographical location and type of participant characteristics such as age groups, socioeconomic status, urban/rural status, education, or marital status to examine the evidence for heterogeneous effects of abortion laws.
Sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analyses will be conducted if there are major differences in quality of the included articles to explore the influence of risk of bias on effect estimates.
Meta-biases
If available, studies will be compared to protocols and registers to identify potential reporting bias within studies. If appropriate and there are a sufficient number of studies included, funnel plots will be generated to determine potential publication bias.
This systematic review will synthesize current evidence on the impact of abortion law reforms on women’s health. It aims to identify which legislative reforms are effective, for which population sub-groups, and under which conditions.
Potential limitations may include the low quality of included studies as a result of suboptimal study design, invalid assumptions, lack of sensitivity analysis, imprecision of estimates, variability in results, missing data, and poor outcome measurements. Our review may also include a limited number of articles because we opted to focus on evidence from quasi-experimental study design due to the causal nature of the research question under review. Nonetheless, we will synthesize the literature, provide a critical evaluation of the quality of the evidence and discuss the potential effects of any limitations to our overall conclusions. Protocol amendments will be recorded and dated using the registration for this review on PROSPERO. We will also describe any amendments in our final manuscript.
Synthesizing available evidence on the impact of abortion law reforms represents an important step towards building our knowledge base regarding how abortion law reforms affect women’s health services and health outcomes; we will provide evidence on emerging strategies to influence policy reforms, implement abortion services, and scale up accessibility. This review will be of interest to service providers, policy makers and researchers seeking to improve women’s access to safe abortion around the world.
Abbreviations
Cumulative index to nursing and allied health literature
Excerpta medica database
Low- and middle-income countries
Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols
International prospective register of systematic reviews
Ganatra B, Gerdts C, Rossier C, Johnson BR, Tuncalp O, Assifi A, et al. Global, regional, and subregional classification of abortions by safety, 2010-14: estimates from a Bayesian hierarchical model. Lancet. 2017;390(10110):2372–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31794-4 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Guttmacher Institute. Induced Abortion Worldwide; Global Incidence and Trends 2018. https://www.guttmacher.org/fact-sheet/induced-abortion-worldwide . Accessed 15 Dec 2019.
Singh S, Remez L, Sedgh G, Kwok L, Onda T. Abortion worldwide 2017: uneven progress and unequal access. NewYork: Guttmacher Institute; 2018.
Book Google Scholar
Fusco CLB. Unsafe abortion: a serious public health issue in a poverty stricken population. Reprod Clim. 2013;2(8):2–9.
Google Scholar
Rehnstrom Loi U, Gemzell-Danielsson K, Faxelid E, Klingberg-Allvin M. Health care providers’ perceptions of and attitudes towards induced abortions in sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia: a systematic literature review of qualitative and quantitative data. BMC Public Health. 2015;15(1):139. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-015-1502-2 .
Say L, Chou D, Gemmill A, Tuncalp O, Moller AB, Daniels J, et al. Global causes of maternal death: a WHO systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2(6):E323–E33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(14)70227-X .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Benson J, Nicholson LA, Gaffikin L, Kinoti SN. Complications of unsafe abortion in sub-Saharan Africa: a review. Health Policy Plan. 1996;11(2):117–31. https://doi.org/10.1093/heapol/11.2.117 .
Abiodun OM, Balogun OR, Adeleke NA, Farinloye EO. Complications of unsafe abortion in South West Nigeria: a review of 96 cases. Afr J Med Med Sci. 2013;42(1):111–5.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Singh S, Maddow-Zimet I. Facility-based treatment for medical complications resulting from unsafe pregnancy termination in the developing world, 2012: a review of evidence from 26 countries. BJOG. 2016;123(9):1489–98. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.13552 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Vlassoff M, Walker D, Shearer J, Newlands D, Singh S. Estimates of health care system costs of unsafe abortion in Africa and Latin America. Int Perspect Sex Reprod Health. 2009;35(3):114–21. https://doi.org/10.1363/3511409 .
Singh S, Darroch JE. Adding it up: costs and benefits of contraceptive services. Estimates for 2012. New York: Guttmacher Institute and United Nations Population Fund; 2012.
Auger N, Bilodeau-Bertrand M, Sauve R. Abortion and infant mortality on the first day of life. Neonatology. 2016;109(2):147–53. https://doi.org/10.1159/000442279 .
Krieger N, Gruskin S, Singh N, Kiang MV, Chen JT, Waterman PD, et al. Reproductive justice & preventable deaths: state funding, family planning, abortion, and infant mortality, US 1980-2010. SSM Popul Health. 2016;2:277–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssmph.2016.03.007 .
Banaem LM, Majlessi F. A comparative study of low 5-minute Apgar scores (< 8) in newborns of wanted versus unwanted pregnancies in southern Tehran, Iran (2006-2007). J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2008;21(12):898–901. https://doi.org/10.1080/14767050802372390 .
Bhandari A. Barriers in access to safe abortion services: perspectives of potential clients from a hilly district of Nepal. Trop Med Int Health. 2007;12:87.
Seid A, Yeneneh H, Sende B, Belete S, Eshete H, Fantahun M, et al. Barriers to access safe abortion services in East Shoa and Arsi Zones of Oromia Regional State, Ethiopia. J Health Dev. 2015;29(1):13–21.
Arroyave FAB, Moreno PA. A systematic bibliographical review: barriers and facilitators for access to legal abortion in low and middle income countries. Open J Prev Med. 2018;8(5):147–68. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojpm.2018.85015 .
Article Google Scholar
Boland R, Katzive L. Developments in laws on induced abortion: 1998-2007. Int Fam Plan Perspect. 2008;34(3):110–20. https://doi.org/10.1363/3411008 .
Lavelanet AF, Schlitt S, Johnson BR Jr, Ganatra B. Global Abortion Policies Database: a descriptive analysis of the legal categories of lawful abortion. BMC Int Health Hum Rights. 2018;18(1):44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12914-018-0183-1 .
United Nations Population Division. Abortion policies: A global review. Major dimensions of abortion policies. 2002 [Available from: https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/publications/abortion/abortion-policies-2002.asp .
Johnson BR, Lavelanet AF, Schlitt S. Global abortion policies database: a new approach to strengthening knowledge on laws, policies, and human rights standards. Bmc Int Health Hum Rights. 2018;18(1):35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12914-018-0174-2 .
Haaland MES, Haukanes H, Zulu JM, Moland KM, Michelo C, Munakampe MN, et al. Shaping the abortion policy - competing discourses on the Zambian termination of pregnancy act. Int J Equity Health. 2019;18(1):20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12939-018-0908-8 .
Schatz JJ. Zambia’s health-worker crisis. Lancet. 2008;371(9613):638–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60287-1 .
Erdman JN, Johnson BR. Access to knowledge and the Global Abortion Policies Database. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2018;142(1):120–4. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijgo.12509 .
Cleeve A, Oguttu M, Ganatra B, Atuhairwe S, Larsson EC, Makenzius M, et al. Time to act-comprehensive abortion care in east Africa. Lancet Glob Health. 2016;4(9):E601–E2. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(16)30136-X .
Berer M, Hoggart L. Medical abortion pills have the potential to change everything about abortion. Contraception. 2018;97(2):79–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2017.12.006 .
Moseson H, Shaw J, Chandrasekaran S, Kimani E, Maina J, Malisau P, et al. Contextualizing medication abortion in seven African nations: A literature review. Health Care Women Int. 2019;40(7-9):950–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/07399332.2019.1608207 .
Blystad A, Moland KM. Comparative cases of abortion laws and access to safe abortion services in sub-Saharan Africa. Trop Med Int Health. 2017;22:351.
Berer M. Abortion law and policy around the world: in search of decriminalization. Health Hum Rights. 2017;19(1):13–27.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Johnson BR, Mishra V, Lavelanet AF, Khosla R, Ganatra B. A global database of abortion laws, policies, health standards and guidelines. B World Health Organ. 2017;95(7):542–4. https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.17.197442 .
Replogle J. Nicaragua tightens up abortion laws. Lancet. 2007;369(9555):15–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60011-7 .
Keogh LA, Newton D, Bayly C, McNamee K, Hardiman A, Webster A, et al. Intended and unintended consequences of abortion law reform: perspectives of abortion experts in Victoria, Australia. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2017;43(1):18–24. https://doi.org/10.1136/jfprhc-2016-101541 .
Levels M, Sluiter R, Need A. A review of abortion laws in Western-European countries. A cross-national comparison of legal developments between 1960 and 2010. Health Policy. 2014;118(1):95–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthpol.2014.06.008 .
Serbanescu F, Morris L, Stupp P, Stanescu A. The impact of recent policy changes on fertility, abortion, and contraceptive use in Romania. Stud Fam Plann. 1995;26(2):76–87. https://doi.org/10.2307/2137933 .
Henderson JT, Puri M, Blum M, Harper CC, Rana A, Gurung G, et al. Effects of Abortion Legalization in Nepal, 2001-2010. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(5):e64775. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0064775 .
Goncalves-Pinho M, Santos JV, Costa A, Costa-Pereira A, Freitas A. The impact of a liberalisation law on legally induced abortion hospitalisations. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2016;203:142–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2016.05.037 .
Latt SM, Milner A, Kavanagh A. Abortion laws reform may reduce maternal mortality: an ecological study in 162 countries. BMC Women’s Health. 2019;19(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-018-0705-y .
Clarke D, Muhlrad H. Abortion laws and women’s health. IZA discussion papers 11890. Bonn: IZA Institute of Labor Economics; 2018.
Benson J, Andersen K, Samandari G. Reductions in abortion-related mortality following policy reform: evidence from Romania, South Africa and Bangladesh. Reprod Health. 2011;8(39). https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4755-8-39 .
Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. Bmj-Brit Med J. 2015;349.
William R. Shadish, Thomas D. Cook, Donald T. Campbell. Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for generalized causal inference. Boston, New York; 2002.
Bernal JL, Cummins S, Gasparrini A. Interrupted time series regression for the evaluation of public health interventions: a tutorial. Int J Epidemiol. 2017;46(1):348–55. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyw098 .
Bernal JL, Cummins S, Gasparrini A. The use of controls in interrupted time series studies of public health interventions. Int J Epidemiol. 2018;47(6):2082–93. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyy135 .
Meyer BD. Natural and quasi-experiments in economics. J Bus Econ Stat. 1995;13(2):151–61.
Strumpf EC, Harper S, Kaufman JS. Fixed effects and difference in differences. In: Methods in Social Epidemiology ed. San Francisco CA: Jossey-Bass; 2017.
Abadie A, Diamond A, Hainmueller J. Synthetic control methods for comparative case studies: estimating the effect of California’s Tobacco Control Program. J Am Stat Assoc. 2010;105(490):493–505. https://doi.org/10.1198/jasa.2009.ap08746 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Abadie A, Diamond A, Hainmueller J. Comparative politics and the synthetic control method. Am J Polit Sci. 2015;59(2):495–510. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajps.12116 .
Moscoe E, Bor J, Barnighausen T. Regression discontinuity designs are underutilized in medicine, epidemiology, and public health: a review of current and best practice. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2015;68(2):132–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2014.06.021 .
Dennis A, Blanchard K, Bessenaar T. Identifying indicators for quality abortion care: a systematic literature review. J Fam Plan Reprod H. 2017;43(1):7–15. https://doi.org/10.1136/jfprhc-2015-101427 .
Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, Elmagarmid A. Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016;5(1):210. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0384-4 .
Jackson JL, Kuriyama A, Anton A, Choi A, Fournier JP, Geier AK, et al. The accuracy of Google Translate for abstracting data from non-English-language trials for systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med. 2019.
Reeves BC, Wells GA, Waddington H. Quasi-experimental study designs series-paper 5: a checklist for classifying studies evaluating the effects on health interventions-a taxonomy without labels. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017;89:30–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.02.016 .
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, et al. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ. 2008;336(7650):924–6. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD .
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539–58. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.1186 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank Genevieve Gore, Liaison Librarian at McGill University, for her assistance with refining the research question, keywords, and Mesh terms for the preliminary search strategy.
The authors acknowledge funding from the Fonds de recherche du Quebec – Santé (FRQS) PhD doctoral awards and Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) Operating Grant, “Examining the impact of social policies on health equity” (ROH-115209).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Epidemiology, Biostatistics and Occupational Health, Faculty of Medicine, McGill University, Purvis Hall 1020 Pine Avenue West, Montreal, Quebec, H3A 1A2, Canada
Foluso Ishola, U. Vivian Ukah & Arijit Nandi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
FI and AN conceived and designed the protocol. FI drafted the manuscript. FI, UVU, and AN revised the manuscript and approved its final version.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Foluso Ishola .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1:.
PRISMA-P 2015 Checklist. This checklist has been adapted for use with systematic review protocol submissions to BioMed Central journals from Table 3 in Moher D et al: Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Systematic Reviews 2015 4:1
Additional File 2:.
LMICs according to World Bank Data Catalogue. Country classification specified in the World Bank Data Catalogue to identify low- and middle-income countries
Additional File 3: Table 1
. Search strategy in Embase. Detailed search terms and filters applied to generate our search in Embase
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Ishola, F., Ukah, U.V. & Nandi, A. Impact of abortion law reforms on women’s health services and outcomes: a systematic review protocol. Syst Rev 10 , 192 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-021-01739-w
Download citation
Received : 02 January 2020
Accepted : 08 June 2021
Published : 28 June 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-021-01739-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Abortion law/policies; Impact
- Unsafe abortion
- Contraception
Systematic Reviews
ISSN: 2046-4053
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]

The Safety and Quality of Abortion Care in the United States (2018)
Chapter: 1 introduction, 1 introduction.
When the Institute of Medicine (IOM) 1 issued its 1975 report on the public health impact of legalized abortion, the scientific evidence on the safety and health effects of legal abortion services was limited ( IOM, 1975 ). It had been only 2 years since the landmark Roe v. Wade decision had legalized abortion throughout the United States and nationwide data collection was just under way ( Cates et al., 2000 ; Kahn et al., 1971 ). Today, the available scientific evidence on abortion’s health effects is quite robust.
In 2016, six private foundations came together to ask the Health and Medicine Division of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to conduct a comprehensive review of the state of the science on the safety and quality of legal abortion services in the United States. The sponsors—The David and Lucile Packard Foundation, The Grove Foundation, The JPB Foundation, The Susan Thompson Buffett Foundation, Tara Health Foundation, and William and Flora Hewlett Foundation—asked that the review focus on the eight research questions listed in Box 1-1 .
The Committee on Reproductive Health Services: Assessing the Safety and Quality of Abortion Care in the U.S. was appointed in December 2016 to conduct the study and prepare this report. The committee included 13 individuals 2 with research or clinical experience in anesthesiology,
___________________
1 In March 2016, the IOM, the division of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine focused on health and medicine, was renamed the Health and Medicine Division.
2 A 14th committee member participated for just the first 4 months of the study.
obstetrics and gynecology, nursing and midwifery, primary care, epidemiology of reproductive health, mental health, health care disparities, health care delivery and management, health law, health professional education and training, public health, quality assurance and assessment,
statistics and research methods, and women’s health policy. Brief biographies of committee members are provided in Appendix A .
This chapter describes the context for the study and the scope of the inquiry. It also presents the committee’s conceptual framework for conducting its review.
ABORTION CARE TODAY
Since the IOM first reviewed the health implications of national legalized abortion in 1975, there has been a plethora of related scientific research, including well-designed randomized controlled trials (RCTs), systematic reviews, and epidemiological studies examining abortion care. This research has focused on examining the relative safety of abortion methods and the appropriateness of methods for different clinical circumstances ( Ashok et al., 2004 ; Autry et al., 2002 ; Bartlett et al., 2004 ; Borgatta, 2011 ; Borkowski et al., 2015 ; Bryant et al., 2011 ; Cates et al., 1982 ; Chen and Creinin, 2015 ; Cleland et al., 2013 ; Frick et al., 2010 ; Gary and Harrison, 2006 ; Grimes et al., 2004 ; Grossman et al., 2008 , 2011 ; Ireland et al., 2015 ; Kelly et al., 2010 ; Kulier et al., 2011 ; Lohr et al., 2008 ; Low et al., 2012 ; Mauelshagen et al., 2009 ; Ngoc et al., 2011 ; Ohannessian et al., 2016 ; Peterson et al., 1983 ; Raymond et al., 2013 ; Roblin, 2014 ; Sonalkar et al., 2017 ; Upadhyay et al., 2015 ; White et al., 2015 ; Wildschut et al., 2011 ; Woodcock, 2016 ; Zane et al., 2015 ). With this growing body of research, earlier abortion methods have been refined, discontinued, and new approaches have been developed ( Chen and Creinin, 2015 ; Jatlaoui et al., 2016 ; Lichtenberg and Paul, 2013 ). For example, the use of dilation and sharp curettage is now considered obsolete in most cases because safer alternatives, such as aspiration methods, have been developed ( Edelman et al, 1974 ; Lean et al, 1976 ; RCOG, 2015 ). The use of abortion medications in the United States began in 2000 with the approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of the drug mifepristone. In 2016, the FDA, citing extensive clinical research, updated the indications for mifepristone for medication abortion 3 up to 10 weeks’ (70 days’) gestation ( FDA, 2016 ; Woodcock, 2016 ).
Box 1-2 describes the abortion methods currently recommended by U.S. and international medical, nursing, and other health organizations that set professional standards for reproductive health care, including the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), the Society of Family Planning, the American College of Nurse-Midwifes, the National Abortion Federation (NAF), the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) (in the United Kingdom), and the World
3 The terms “medication abortion” and “medical abortion” are used interchangeably in the literature.
Health Organization ( ACNM, 2011 , 2016 ; ACOG, 2013 , 2014 ; Costescu et al., 2016 ; Lichtenberg and Paul, 2013 ; NAF, 2017 ; RCOG, 2011 ; WHO, 2014 ).
A Continuum of Care
The committee views abortion care as a continuum of services, as illustrated in Figure 1-1 . For purposes of this study, it begins when a woman, who has decided to terminate a pregnancy, contacts or visits a provider seeking an abortion. The first, preabortion phase of care includes an initial clinical assessment of the woman’s overall health (e.g., physical examination, pregnancy determination, weeks of gestation, and laboratory and other testing as needed); communication of information on the risks and benefits of alternative abortion procedures and pain management options; discussion of the patient’s preferences based on desired anesthesia and weeks of gestation; discussion of postabortion contraceptive options if desired; counseling

and referral to services (if needed); and final decision making and informed consent. The next phases in the continuum are the abortion procedure itself and postabortion care, including appropriate follow-up care and provision of contraceptives (for women who opt for them).
A Note on Terminology
Important clinical terms that describe pregnancy and abortion lack consistent definition. The committee tried to be as precise as possible to avoid misinterpreting or miscommunicating the research evidence, clinical practice guidelines, and other relevant sources of information with potentially significant clinical implications. Note that this report follows Grimes and Stuart’s (2010) recommendation that weeks’ gestation be quantified using cardinal numbers (1, 2, 3...) rather than ordinal numbers (1st, 2nd, 3rd...). It is important to note, however, that these two numbering conventions are sometimes used interchangeably in the research literature despite having different meanings. For example, a woman who is 6 weeks pregnant has completed 6 weeks of pregnancy: she is in her 7th (not 6th) week of pregnancy.
This report also avoids using the term “trimester” where possible because completed weeks’ or days’ gestation is a more precise designation, and the clinical appropriateness of abortion methods does not align with specific trimesters.
Although the literature typically classifies the method of abortion as either “medical” or “surgical” abortion, the committee decided to specify methods more precisely by using the terminology defined in Box 1-2 . The term “surgical abortion” is often used by others as a catchall category that includes a variety of procedures, ranging from an aspiration to a dilation and evacuation (D&E) procedure involving sharp surgical and other instrumentation as well as deeper levels of sedation. This report avoids describing abortion procedures as “surgical” so as to characterize a method more accurately as either an aspiration or D&E. As noted in Box 1-2 , the term “induction abortion” is used to distinguish later abortions that use a
medication regimen from medication abortions performed before 10 weeks’ gestation.
See Appendix B for a glossary of the technical terms used in this report.
Regulation of Abortion Services
Abortion is among the most regulated medical procedures in the nation ( Jones et al., 2010 ; Nash et al., 2017 ). While a comprehensive legal analysis of abortion regulation is beyond the scope of this report, the committee agreed that it should consider how abortion’s unique regulatory environment relates to the safety and quality of abortion care.
In addition to the federal, state, and local rules and policies governing all medical services, numerous abortion-specific federal 4 and state laws and regulations affect the delivery of abortion services. Table 1-1 lists the abortion-specific regulations by state. The regulations range from prescribing information to be provided to women when they are counseled and setting mandatory waiting periods between counseling and the abortion procedure to those that define the clinical qualifications of abortion providers, the types of procedures they are permitted to perform, and detailed facility standards for abortion services. In addition, many states place limitations on the circumstances under which private health insurance and Medicaid can be used to pay for abortions, limiting coverage to pregnancies resulting from rape or incest or posing a medical threat to the pregnant woman’s life. Other policies prevent facilities that receive state funds from providing abortion services 5 or place restrictions on the availability of services based on the gestation of the fetus that are narrower than those established under federal law ( Guttmacher Institute, 2017h ).
Trends and Demographics
National- and state-level abortion statistics come from two primary sources: the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC’s) Abortion
4 Hyde Amendment (P.L. 94-439, 1976); Department of Defense Appropriations Act (P.L. 95-457, 1978); Peace Corps Provision and Foreign Assistance and Related Programs Appropriations Act (P.L. 95-481, 1978); Pregnancy Discrimination Act (P.L. 95-555, 1977); Department of the Treasury and Postal Service Appropriations Act (P.L. 98-151, 1983); FY1987 Continuing Resolution (P.L. 99-591, 1986); Dornan Amendment (P.L. 100-462, 1988); Partial-Birth Abortion Ban (P.L. 108-105, 2003); Weldon Amendment (P.L. 108-199, 2004); Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (P.L. 111-148 as amended by P.L. 111-152, 2010).
5 Personal communication, O. Cappello, Guttmacher Institute, August 4, 2017: AZ § 15-1630, GA § 20-2-773; KS § 65-6733 and § 76-3308; KY § 311.800; LA RS § 40:1299 and RS § 4 0.1061; MO § 188.210 and § 188.215; MS § 41-41-91; ND § 14-02.3-04; OH § 5101.57; OK 63 § 1-741.1; PA 18 § 3215; TX § 285.202.
TABLE 1-1 Overview of State Abortion-Specific Regulations That May Impact Safety and Quality, as of September 1, 2017
a Excludes laws or regulations permanently or temporarily enjoined pending a court decision.
b States have abortion-specific requirements generally following the established principles of informed consent.
c The content of informed consent materials is specified in state law or developed by the state department of health.
d In-person counseling is not required for women who live more than 100 miles from an abortion provider.
e Counseling requirement is waived if the pregnancy is the result of rape or incest or the patient is younger than 15.
f Maximum distance requirement does not apply to medication abortions.
g Some states also exempt women whose physical health is at severe risk and/or in cases of fetal impairment.
h Some states have exceptions for pregnancies resulting from rape or incest, pregnancies that severely threaten women’s physical health or endanger their life, and/or in cases of fetal impairment.
SOURCES: Guttmacher Institute, 2017b , c , d , e , f , g , h , i , 2018b .
Surveillance System and the Guttmacher Institute’s Abortion Provider Census ( Jatlaoui et al., 2016 ; Jerman et al., 2016 ; Jones and Kavanaugh, 2011 ; Pazol et al., 2015 ). Both of these sources provide estimates of the number and rate of abortions, the use of different abortion methods, the characteristics of women who have abortions, and other related statistics. However, both sources have limitations.
The CDC system is a voluntary, state-reported system; 6 , 7 three states (California, Maryland, and New Hampshire) do not provide information ( CDC, 2017 ). The Guttmacher census, also voluntary, solicits information from all known abortion providers throughout the United States, including in the states that do not submit information to the CDC surveillance system. For 2014, the latest year reported by Guttmacher, 8 information was obtained directly from 58 percent of abortion providers, and data for nonrespondents were imputed ( Jones and Jerman, 2017a ). The CDC’s latest report, for abortions in 2013, includes approximately 70 percent of the abortions reported by the Guttmacher Institute for that year ( Jatlaoui et al., 2016 ).
Both data collection systems report descriptive statistics on women who have abortions and the types of abortion provided, although they define demographic variables and procedure types differently. Nevertheless, in the aggregate, the trends in abortion utilization reported by the CDC and Guttmacher closely mirror each other—indicating decreasing rates of abortion, an increasing proportion of medication abortions, and the vast majority of abortions (90 percent) occurring by 13 weeks’ gestation (see Figures 1-2 and 1-3 ) ( Jatlaoui et al., 2016 ; Jones and Jerman, 2017a ). 9 Both data sources are used in this chapter’s brief review of trends in abortions and throughout the report.
Trends in the Number and Rate of Abortions
The number and rate of abortions have changed considerably during the decades following national legalization in 1973. In the immediate years after
6 In most states, hospitals, facilities, and physicians are required by law to report abortion data to a central health agency. These agencies submit the aggregate utilization data to the CDC ( Guttmacher Institute, 2018a ).
7 New York City and the District of Columbia also report data to the CDC.
8 Guttmacher researchers estimate that the census undercounts the number of abortions performed in the United States by about 5 percent (i.e., 51,725 abortions provided by 2,069 obstetrician/gynecologist [OB/GYN] physicians). The estimate is based on a survey of a random sample of OB/GYN physicians. The survey did not include other physician specialties and other types of clinicians.
9 A full-term pregnancy is 40 weeks.

national legalization, both the number and rate 10 of legal abortions steadily increased ( Bracken et al., 1982 ; Guttmacher Institute, 2017a ; Pazol et al., 2015 ; Strauss et al., 2007 ) (see Figure 1-2 ). The abortion rate peaked in the
10 Reported abortion rates are for females aged 15 to 44.
1980s, and the trend then reversed, a decline that has continued for more than three decades ( Guttmacher Institute, 2017a ; Jones and Kavanaugh, 2011 ; Pazol et al., 2015 ; Strauss et al., 2007 ). Between 1980 and 2014, the abortion rate among U.S. women fell by more than half, from 29.3 to 14.6 per 1,000 women ( Finer and Henshaw, 2003 ; Guttmacher Institute, 2017a ; Jones and Jerman, 2017a ) (see Figure 1-2 ). In 2014, the most recent year for which data are available, the aggregate number of abortions reached a low of 926,190 after peaking at nearly 1.6 million in 1990 ( Finer and Henshaw, 2003 ; Jones and Jerman, 2017a ). The reason for the decline is not fully understood but has been attributed to several factors, including the increasing use of contraceptives, especially long-acting methods (e.g., intrauterine devices and implants); historic declines in the rate of unintended pregnancy; and increasing numbers of state regulations resulting in limited access to abortion services ( Finer and Zolna, 2016 ; Jerman et al., 2017 ; Jones and Jerman, 2017a ; Kost, 2015 ; Strauss et al., 2007 ).
Weeks’ Gestation
Length of gestation—measured as the amount of time since the first day of the last menstrual period—is the primary factor in deciding what abortion procedure is most appropriate ( ACOG, 2014 ). Since national legalization, most abortions in the United States have been performed in early pregnancy (≤13 weeks) ( Cates et al., 2000 ; CDC, 1983 ; Elam-Evans et al., 2003 ; Jatlaoui et al., 2016 ; Jones and Jerman, 2017a ; Koonin and Smith, 1993 ; Lawson et al., 1989 ; Pazol et al., 2015 ; Strauss et al., 2007 ). CDC surveillance reports indicate that since at least 1992 (when detailed data on early abortions were first collected), the vast majority of abortions in the United States were early-gestation procedures ( Jatlaoui et al., 2016 ; Strauss et al., 2007 ); this was the case for approximately 92 percent of all abortions in 2013 ( Jatlaoui et al., 2016 ). With such technological advances as highly sensitive pregnancy tests and medication abortion, procedures are being performed at increasingly earlier gestational stages. According to the CDC, the percentage of early abortions performed ≤6 weeks’ gestation increased by 16 percent from 2004 to 2013 ( Jatlaoui et al., 2016 ); in 2013, 38 percent of early abortions occurred ≤6 weeks ( Jatlaoui et al., 2016 ). The proportion of early-gestation abortions occurring ≤6 weeks is expected to increase even further as the use of medication abortions becomes more widespread ( Jones and Boonstra, 2016 ; Pazol et al., 2012 ).
Figure 1-3 shows the proportion of abortions in nonhospital settings by weeks’ gestation in 2014 ( Jones and Jerman, 2017a ).
Abortion Methods
Aspiration is the abortion method most commonly used in the United States, accounting for almost 68 percent of all abortions performed in 2013 ( Jatlaoui et al., 2016 ). 11 Its use, however, is likely to decline as the use of medication abortion increases. The percentage of abortions performed by the medication method rose an estimated 110 percent between 2004 and 2013, from 10.6 to 22.3 percent ( Jatlaoui et al., 2016 ). In 2014, approximately 45 percent of abortions performed up to 9 weeks’ gestation were medication abortions, up from 36 percent in 2011 ( Jones and Jerman, 2017a ).
Fewer than 9 percent of abortions are performed after 13 weeks’ gestation; most of these are D&E procedures ( Jatlaoui et al., 2016 ). Induction abortion is the most infrequently used of all abortion methods, accounting for approximately 2 percent of all abortions at 14 weeks’ gestation or later in 2013 ( Jatlaoui et al., 2016 ).
Characteristics of Women Who Have Abortions
The most detailed sociodemographic statistics on women who have had an abortion in the United States are provided by the Guttmacher Institute’s Abortion Patient Survey. Respondents to the 2014/2015 survey included more than 8,000 women who had had an abortion in 1 of 87 outpatient (nonhospital) facilities across the United States in 2014 ( Jerman et al., 2016 ; Jones and Jerman, 2017b ). 12 Table 1-2 provides selected findings from this survey. Although women who had an abortion in a hospital setting are excluded from these statistics, the data represent an estimated 95 percent of all abortions provided (see Figure 1-3 ).
The Guttmacher survey found that most women who had had an abortion were under age 30 (72 percent) and were unmarried (86 percent) ( Jones and Jerman, 2017b ). Women seeking an abortion were far more likely to be poor or low-income: the household income of 49 percent was below the federal poverty level (FPL), and that of 26 percent was 100 to 199 percent of the FPL ( Jerman et al., 2016 ). In comparison, the
11 CDC surveillance reports use the catchall category of “curettage” to refer to nonmedical abortion methods. The committee assumed that the CDC’s curettage estimates before 13 weeks’ gestation refer to aspiration procedures and that its curettage estimates after 13 weeks’ gestation referred to D&E procedures.
12 Participating facilities were randomly selected and excluded hospitals. All other types of facilities were included if they had provided at least 30 abortions in 2011 ( Jerman et al., 2016 ). Jerman and colleagues report that logistical challenges precluded including hospital patients in the survey. The researchers believe that the exclusion of hospitals did not bias the survey sample, noting that hospitals accounted for only 4 percent of all abortions in 2011.
TABLE 1-2 Characteristics of Women Who Had an Abortion in an Outpatient Setting in 2014, by Percent
NOTE: Percentages may not sum to 100 because of rounding.
SOURCES: (a) Jones and Jerman, 2017b (n = 8,098); (b) Jerman et al., 2016 (n = 8,380).
corresponding percentages among all women aged 15 to 49 are 16 and 18 percent. 13 Women who had had an abortion were also more likely to be women of color 14 (61.0 percent); overall, half of women who had had an abortion were either black (24.8 percent) or Hispanic (24.5 percent) ( Jones and Jerman, 2017b ). This distribution is similar to the racial and ethnic distribution of women with household income below 200 percent of the FPL, 49 percent of whom are either black (20 percent) or Hispanic (29 percent). 15 Poor women and women of color are also more likely than others to experience an unintended pregnancy ( Finer and Henshaw, 2006 ; Finer et al., 2006 ; Jones and Kavanaugh, 2011 ).
Many women who have an abortion have previously experienced pregnancy or childbirth. Among respondents to the Guttmacher survey, 59.3 percent had given birth at least once, and 44.8 percent had had a prior abortion ( Jerman et al., 2016 ; Jones and Jerman, 2017b ).
While precise estimates of health insurance coverage of abortion are not available, numerous regulations limit coverage. As noted in Table 1-1 , 33 states prohibit public payers from paying for abortions and other states have laws that either prohibit health insurance exchange plans (25 states) or private insurance plans (11 states) sold in the state from covering or paying for abortions, with few exceptions. 16 In the Guttmacher survey, only 14 percent of respondents had paid for the procedure using private insurance coverage, and despite the disproportionately high rate of poverty and low income among those who had had an abortion, only 22 percent reported that Medicaid was the method of payment for their abortion. In 2015, 39 percent of the 25 million women lived in households that earned less than 200 percent of the FPL in the United States were enrolled in Medicaid, and 36 percent had private insurance ( Ranji et al., 2017 ).
Number of Clinics Providing Abortion Care
As noted earlier, the vast majority of abortions are performed in nonhospital settings—either an abortion clinic (59 percent) or a clinic offering a variety of medical services (36 percent) ( Jones and Jerman, 2017a ) (see Figure 1-4 ). Although hospitals account for almost 40 percent of facilities offering abortion care, they provide less than 5 percent of abortions overall.
13 Calculation by the committee based on estimates from Annual Social and Economic Supplement (ASEC) to the Current Population Survey (CPS) .
14 Includes all nonwhite race and ethnicity categories in Table 1-2 . Data were collected via self-administered questionnaire ( Jones and Jerman, 2017b ).
15 Calculation by the committee based on estimates from Annual Social and Economic Supplement (ASEC) to the Current Population Survey (CPS) .
16 Some states have exceptions for pregnancies resulting from rape or incest, pregnancies that endanger the woman’s life or severely threaten her health, and in cases of fetal impairment.

The overall number of nonhospital facilities providing abortions—especially specialty abortion clinics—is declining. The greatest proportional decline is in states that have enacted abortion-specific regulations ( Jones and Jerman, 2017a ). In 2014, there were 272 abortion clinics in the United States, 17 percent fewer than in 2011. The greatest decline (26 percent) was among large clinics with annual caseloads of 1,000–4,999 patients and clinics in the Midwest (22 percent) and the South (13 percent). In 2014, approximately 39 percent of U.S. women aged 15 to 44 resided in a U.S. county without an abortion provider (90 percent of counties overall) ( Jones and Jerman, 2017a ). Twenty-five states have five or fewer abortion clinics; five states have one abortion clinic ( Jones and Jerman, 2017a ). A recent analysis 17 by Guttmacher evaluated geographic disparities in access to abortion by calculating the distance between women of reproductive age (15 to 44) and the nearest abortion-providing facility in 2014 ( Bearak et al., 2017 ). Figure 1-5 highlights the median distance to the nearest facility by county.
17 The analysis was limited to facilities that provided at least 400 abortions per year and those affiliated with Planned Parenthood that performed at least 1 abortion during the period of analysis.

The majority of facilities offer early medication and aspiration abortions. In 2014, 87 percent of nonhospital facilities provided early medication abortions; 23 percent of all nonhospital facilities offered this type of abortion ( Jones and Jerman, 2017a ). Fewer facilities offer later-gestation procedures, and availability decreases as gestation increases. In 2012, 95 percent of all abortion facilities offered abortions at 8 weeks’ gestation, 72 percent at 12 weeks’ gestation, 34 percent at 20 weeks’ gestation, and 16 percent at 24 weeks’ gestation ( Jerman and Jones, 2014 ).
STUDY APPROACH
Conceptual framework.
The committee’s approach to this study built on two foundational developments in the understanding and evaluation of the quality of health

care services: Donabedian’s (1980) structure-process-outcome framework and the IOM’s (2001) six dimensions of quality health care. Figure 1-6 illustrates the committee’s adaptation of these concepts for this study’s assessment of abortion care in the United States.
Structure-Process-Outcome Framework
In seminal work published almost 40 years ago, Donabedian (1980) proposed that the quality of health care be assessed by examining its structure, process, and outcomes ( Donabedian, 1980 ):
- Structure refers to organizational factors that may create the potential for good quality. In abortion care, such structural factors as the availability of trained staff and the characteristics of the clinical setting may ensure—or inhibit—the capacity for quality.
- Process refers to what is done to and for the patient. Its assessment assumes that the services patients receive should be evidence based and correlated with patients’ desired outcomes—for example, an early and complete abortion for women who wish to terminate an unintended pregnancy.
- Outcomes are the end results of care—the effects of the intervention on the health and well-being of the patient. Does the procedure achieve its objective? Does it lead to serious health risks in the short or long term?
Six Dimensions of Health Care Quality
The landmark IOM report Crossing the Quality Chasm: A New Health System for the 21st Century ( IOM, 2001 ) identifies six dimensions of health care quality—safety, effectiveness, patient-centeredness, timeliness, efficiency, and equity. The articulation of these six dimensions has guided public and private efforts to improve U.S. health care delivery at the local, state, and national levels since that report was published ( AHRQ, 2016 ).
In addition, as with other health care services, women should expect that the abortion care they receive meets well-established standards for objectivity, transparency, and scientific rigor ( IOM, 2011a , b ).
Two of the IOM’s six dimensions—safety and effectiveness—are particularly salient to the present study. Assessing both involves making relative judgments. There are no universally agreed-upon thresholds for defining care as “safe” versus “unsafe” or “effective” versus “not effective,” and decisions about safety and effectiveness have a great deal to do with the context of the clinical scenario. Thus, the committee’s frame of reference for evaluating safety, effectiveness, and other quality domains is of necessity a
relative one—one that entails not only comparing the alternative abortion methods but also comparing these methods with other health care services and with risks associated with not achieving the desired outcome.
Safety—avoiding injury to patients—is often assessed by measuring the incidence and severity of complications and other adverse events associated with receiving a specific procedure. If infrequent, a complication may be characterized as “rare”—a term that lacks consistent definition. In this report, “rare” is used to describe outcomes that affect fewer than 1 percent of patients. Complications are considered “serious” if they result in a blood transfusion, surgery, or hospitalization.
Note also that the term “effectiveness” is used differently in this report depending on the context. As noted in Box 1-3 , effectiveness as an attribute of quality refers to providing services based on scientific knowledge to all who could benefit and refraining from providing services to those not likely to benefit (avoiding underuse and overuse, respectively). Elsewhere in this report, effectiveness denotes the clinical effectiveness of a procedure, that
is, the successful completion of an abortion without the need for a follow-up aspiration.
Finding and Assessing the Evidence
The committee deliberated during four in-person meetings and numerous teleconferences between January 2017 and December 2017. On March 24, 2017, the committee hosted a public workshop at the Keck Center of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine in Washington, DC. The workshop included presentations from three speakers on topics related to facility standards and the safety of outpatient procedures. Appendix C contains the workshop agenda.
Several committee workgroups were formed to find and assess the quality of the available evidence and to draft summary materials for the full committee’s review. The workgroups conducted in-depth reviews of the epidemiology of abortions, including rates of complications and mortality, the safety and effectiveness of alternative abortion methods, professional standards and methods for performing all aspects of abortion care (as described in Figure 1-1 ), the short- and long-term physical and mental health effects of having an abortion; and the safety and quality implications of abortion-specific regulations on abortion.
The committee focused on finding reliable, scientific information reflecting contemporary U.S. abortion practices. An extensive body of research on abortion has been conducted outside the United States. A substantial proportion of this literature concerns the delivery of abortion care in countries where socioeconomic conditions, culture, population health, health care resources, and/or the health care system are markedly different from their U.S. counterparts. Studies from other countries were excluded from this review if the committee judged those factors to be relevant to the health outcomes being assessed.
The committee considered evidence from randomized controlled trials comparing two or more approaches to abortion care; systematic reviews; meta-analyses; retrospective cohort studies, case control studies, and other types of observational studies; and patient and provider surveys (see Box 1-4 ).
An extensive literature documents the biases common in published research on the effectiveness of health care services ( Altman et al., 2001 ; Glasziou et al., 2008 ; Hopewell et al., 2008 ; Ioannidis et al., 2004 ; IOM, 2011a , b ; Plint et al., 2006 ; Sackett, 1979 ; von Elm et al., 2007 ). Thus, the committee prioritized the available research according to conventional principles of evidence-based medicine intended to reduce the risk of bias in a study’s conclusions, such as how subjects were allocated to different types of abortion care, the comparability of study populations, controls
for confounding factors, how outcome assessments were conducted, the completeness of outcome reporting, the representativeness of the study population compared with the general U.S. population, and the degree to which statistical analyses helped reduce bias ( IOM, 2011b ). Applying these principles is particularly important with respect to understanding abortion’s
long-term health effects, an area in which the relevant literature is vulnerable to bias (as discussed in Chapter 4 ).
The committee’s literature search strategy is described in Appendix D .

ORGANIZATION OF THE REPORT
Chapter 2 of this report describes the continuum of abortion care including current abortion methods (question 1 in the committee’s statement of task [ Box 1-1 ]); reviews the evidence on factors affecting their safety and quality, including expected side effects and possible complications (questions 2 and 3), necessary safeguards to manage medical emergencies (question 6), and provision of pain management (question 7); and presents the evidence on the types of facilities or facility factors necessary to provide safe and effective abortion care (question 4).
Chapter 3 summarizes the clinical skills that are integral to safe and high-quality abortion care according to the recommendations of leading national professional organizations and abortion training curricula (question 5).
Chapter 4 reviews research examining the long-term health effects of undergoing an abortion (question 2).
Finally, Chapter 5 presents the committee’s conclusions regarding the findings presented in the previous chapters, responding to each of the questions posed in the statement of task. Findings are statements of scientific evidence. The report’s conclusions are the committee’s inferences, interpretations, or generalizations drawn from the evidence.
ACNM (American College of Nurse-Midwives). 2011. Position statement: Reproductive health choices . http://www.midwife.org/ACNM/files/ACNMLibraryData/UPLOADFILENAME/000000000087/Reproductive_Choices.pdf (accessed August 1, 2017).
ACNM. 2016. Position statement: Access to comprehensive sexual and reproductive health care services . http://www.midwife.org/ACNM/files/ACNMLibraryData/UPLOADFILENAME/000000000087/Access-to-Comprehensive-Sexual-and-Reproductive-Health-Care-Services-FINAL-04-12-17.pdf (accessed August 1, 2017).
ACOG (American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists). 2013. Practice Bulletin No. 135: Second-trimester abortion. Obstetrics & Gynecology 121(6):1394–1406.
ACOG. 2014. Practice Bulletin No. 143: Medical management of first-trimester abortion (reaffirmed). Obstetrics & Gynecology 123(3):676–692.
AHRQ (Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality). 2016. The six domains of health care quality. https://www.ahrq.gov/professionals/quality-patient-safety/talkingquality/create/sixdomains.html (accessed May 3, 2017).
Altman, D. G., K. F. Schulz, D. Moher, M. Egger, F. Davidoff, D. Elbourne, P. C. Gøtzsche, and T. Lang. 2001. The revised CONSORT statement for reporting randomized trials: Explanation and elaboration. Annals of Internal Medicine 134(8):663–694.
Ashok, P. W., A. Templeton, P. T. Wagaarachchi, and G. M. Flett. 2004. Midtrimester medical termination of pregnancy: A review of 1002 consecutive cases. Contraception 69(1):51–58.
Autry, A. M., E. C. Hayes, G. F. Jacobson, and R. S. Kirby. 2002. A comparison of medical induction and dilation and evacuation for second-trimester abortion. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 187(2):393–397.
Bartlett, L. A., C. J. Berg, H. B. Shulman, S. B. Zane, C. A. Green, S. Whitehead, and H. K. Atrash. 2004. Risk factors for legal induced abortion-related mortality in the United States. Obstetrics & Gynecology 103(4):729–737.
Bearak, J. M., K. L. Burke, and R. K. Jones. 2017. Disparities and change over time in distance women would need to travel to have an abortion in the USA: A spatial analysis. The Lancet Public Health 2(11):e493–e500.
Borgatta, L. 2011. Labor induction termination of pregnancy. Global library for women’s medicine . https://www.glowm.com/section_view/heading/Labor%20Induction%20Termination%20of%20Pregnancy/item/443 (accessed September 13, 2017).
Borkowski, L., J. Strasser, A. Allina, and S. Wood. 2015. Medication abortion. Overview of research & policy in the United States . http://publichealth.gwu.edu/sites/default/files/Medication_Abortion_white_paper.pdf (accessed January 25, 2017).
Bracken, M. B., D. H. Freeman, Jr., and K. Hellenbrand. 1982. Hospitalization for medical-legal and other abortions in the United States 1970–1977. American Journal of Public Health 72(1):30–37.
Bryant, A. G., D. A. Grimes, J. M. Garrett, and G. S. Stuart. 2011. Second-trimester abortion for fetal anomalies or fetal death: Labor induction compared with dilation and evacuation. Obstetrics & Gynecology 117(4):788–792.
Cates, Jr., W., K. F. Schulz, D. A. Grimes, A. J. Horowitz, F. A. Lyon, F. H. Kravitz, and M. J. Frisch. 1982. Dilatation and evacuation procedures and second-trimester abortions. The role of physician skill and hospital setting. Journal of the American medical Association 248(5):559–563.
Cates, Jr., W., D. A. Grimes, and K. F. Schulz. 2000. Abortion surveillance at CDC: Creating public health light out of political heat. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 19(1, Suppl. 1):12–17.
CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention). 1983. Surveillance summary abortion surveillance: Preliminary analysis, 1979–1980—United States. MMWR Weekly 32(5): 62–64. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/00001243.htm (accessed September 18, 2017).
CDC. 2017. CDC’s abortion surveillance system FAQs . https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/data_stats/abortion.htm (accessed June 22, 2017).
Chen, M. J., and M. D. Creinin. 2015. Mifepristone with buccal misoprostol for medical abortion: A systematic review. Obstetrics & Gynecology 126(1):12–21.
Cleland, K., M. D. Creinin, D. Nucatola, M. Nshom, and J. Trussell. 2013. Significant adverse events and outcomes after medical abortion. Obstetrics & Gynecology 121(1):166–171.
Costescu, D., E. Guilbert, J. Bernardin, A. Black, S. Dunn, B. Fitzsimmons, W. V. Norman, H. Pymar, J. Soon, K. Trouton, M. S. Wagner, and E. Wiebe. 2016. Medical abortion. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada 38(4):366–389.
Donabedian, A. 1980. The definition of quality and approaches to its assessment. In Explorations in quality assessment and monitoring. Vol. 1. Ann Arbor, MI: Health Administration Press.
Edelman, D. A., W. E. Brenner, and G. S. Berger. 1974. The effectiveness and complications of abortion by dilatation and vacuum aspiration versus dilatation and rigid metal curettage. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 119(4):473–480.
Elam-Evans, L. D., L. T. Strauss, J. Herndon, W. Y. Parker, S. V. Bowens, S. Zane, and C. J. Berg. 2003. Abortion surveillance—United States, 2000. MMWR Surveillance Summaries 52(SS-12):1–32. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/ss5212a1.htm (accessed September 18, 2017).
FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration). 2016. MIFEPREX ® : Highligh ts of prescribing information. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/020687s020lbl.pdf (accessed September 11, 2017).
Finer, L. B., and S. K. Henshaw. 2003. Abortion incidence and services in the United States in 2000. Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health 35(1):6–15.
Finer, L. B., and S. K. Henshaw. 2006. Disparities in rates of unintended pregnancy in the United States, 1994 and 2001. Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health 38(2):90–96.
Finer, L. B., and M. R. Zolna. 2016. Declines in unintended pregnancy in the United States, 2008–2011. New England Journal of Medicine 374(9):843–852.
Finer, L. B., L. F. Frohwirth, L. A. Dauphinee, S. Singh, and A. M. Moore. 2006. Timing of steps and reasons for delays in obtaining abortions in the United States. Contraception 74(4):334–344.
Frick, A. C., E. A. Drey, J. T. Diedrich, and J. E. Steinauer. 2010. Effect of prior cesarean delivery on risk of second-trimester surgical abortion complications. Obstetrics & Gynecology 115(4):760–764.
Gary, M. M., and D. J. Harrison. 2006. Analysis of severe adverse events related to the use of mifepristone as an abortifacient. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 40(2):191–197.
Glasziou, P., E. Meats, C. Heneghan, and S. Shepperd. 2008. What is missing from descriptions of treatment in trials and reviews? British Medical Journal 336(7659):1472–1474.
Grimes, D. A., and G. Stuart. 2010. Abortion jabberwocky: The need for better terminology. Contraception 81(2):93–96.
Grimes, D. A., S. M. Smith, and A. D. Witham. 2004. Mifepristone and misoprostol versus dilation and evacuation for midtrimester abortion: A pilot randomised controlled trial. British Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology 111(2):148–153.
Grossman, D., K. Blanchard, and P. Blumenthal. 2008. Complications after second trimester surgical and medical abortion. Reproductive Health Matters 16(31 Suppl.):173–182.
Grossman, D., K. Grindlay, T. Buchacker, K. Lane, and K. Blanchard. 2011. Effectiveness and acceptability of medical abortion provided through telemedicine. Obstetrics & Gynecology 118(2 Pt. 1):296–303.
Guttmacher Institute. 2017a. Fact sheet: Induced abortion in the United States. https://www.guttmacher.org/fact-sheet/induced-abortion-united-states (accessed November 10, 2017).
Guttmacher Institute. 2017b. Bans on specific abortion methods used after the first trimester. https://www.guttmacher.org/state-policy/explore/bans-specific-abortion-methods-used-after-first-trimester (accessed September 12, 2017).
Guttmacher Institute. 2017c. Counseling and waiting periods for abortion. https://www.guttmacher.org/state-policy/explore/counseling-and-waiting-periods-abortion (accessed September 12, 2017).
Guttmacher Institute. 2017d. Medication abortion. https://www.guttmacher.org/state-policy/explore/medication-abortion (accessed September 12, 2017).
Guttmacher Institute. 2017e. An overview of abortion laws. https://www.guttmacher.org/state-policy/explore/overview-abortion-laws (accessed September 12, 2017).
Guttmacher Institute. 2017f. Requirements for ultrasound. https://www.guttmacher.org/state-policy/explore/requirements-ultrasound (accessed September 12, 2017).
Guttmacher Institute. 2017g. State funding of abortion under Medicaid. https://www.guttmacher.org/state-policy/explore/state-funding-abortion-under-medicaid (accessed September 12, 2017).
Guttmacher Institute. 2017h. State policies on later abortions. https://www.guttmacher.org/state-policy/explore/state-policies-later-abortions (accessed September 12, 2017).
Guttmacher Institute. 2017i. Targeted regulation of abortion providers. https://www.guttmacher.org/state-policy/explore/targeted-regulation-abortion-providers (accessed September 12, 2017).
Guttmacher Institute. 2018a. Abortion reporting requirements. https://www.guttmacher.org/state-policy/explore/abortion-reporting-requirements (accessed January 22, 2018).
Guttmacher Institute. 2018b. Restricting insurance coverage of abortion. https://www.guttmacher.org/state-policy/explore/restricting-insurance-coverage-abortion (accessed January 24, 2018).
Hopewell, S., M. Clarke, D. Moher, E. Wager, P. Middleton, D. G. Altman, K. F. Schulz, and the CONSORT Group. 2008. CONSORT for reporting randomized controlled trials in journal and conference abstracts: Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Medicine 5(1):e20.
Ioannidis, J. P., S. J. Evans, P. C. Gøtzsche, R. T. O’Neill, D. G. Altman, K. Schulz, D. Moher, and the CONSORT Group. 2004. Better reporting of harms in randomized trials: An extension of the CONSORT statement. Annals of Internal Medicine 141(10):781–788.
IOM (Institute of Medicine). 1975. Legalized abortion and the public health . Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
IOM. 2001. Crossing the quality chasm: A new health system for the 21st century. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
IOM. 2011a. Clinical practice guidelines we can trust. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
IOM. 2011b. Finding what works in health care: Standards for systematic reviews. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
Ireland, L. D., M. Gatter, and A. Y. Chen. 2015. Medical compared with surgical abortion for effective pregnancy termination in the first trimester. Obstetrics & Gynecology 126(1):22–28.
Jatlaoui, T. C., A. Ewing, M. G. Mandel, K. B. Simmons, D. B. Suchdev, D. J. Jamieson, and K. Pazol. 2016. Abortion surveillance—United States, 2013. MMWR Surveillance Summaries 65(No. SS-12):1–44.
Jerman, J., and R. K. Jones. 2014. Secondary measures of access to abortion services in the United States, 2011 and 2012: Gestational age limits, cost, and harassment. Women’s Health Issues 24(4): e419–e424.
Jerman J., R. K. Jones, and T. Onda. 2016. Characteristics of U.S. abortion patients in 2014 and changes since 2008 . https://www.guttmacher.org/sites/default/files/report_pdf/characteristics-us-abortion-patients-2014.pdf (accessed October 17, 2016).
Jerman, J., L. Frohwirth, M. L. Kavanaugh, and N. Blades. 2017. Barriers to abortion care and their consequences for patients traveling for services: Qualitative findings from two states. Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health 49(2):95–102.
Jones, R. K., and H. D. Boonstra. 2016. The public health implications of the FDA update to the medication abortion label. New York: Guttmacher Institute. https://www.guttmacher.org/article/2016/06/public-health-implications-fda-update-medication-abortion-label (accessed October 27, 2017).
Jones, R. K., and J. Jerman. 2017a. Abortion incidence and service availability in the United States, 2014. Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health 49(1):1–11.
Jones, R. K., and J. Jerman. 2017b. Characteristics and circumstances of U.S. women who obtain very early and second trimester abortions. PLoS One 12(1):e0169969.
Jones, R. K., and M. L. Kavanaugh. 2011. Changes in abortion rates between 2000 and 2008 and lifetime incidence of abortion. Obstetrics & Gynecology 117(6):1358–1366.
Jones, R. K., L. B. Finer, and S. Singh. 2010. Characteristics of U.S. abortion patients, 2008. New York: Guttmacher Institute.
Kahn, J. B., J. P. Bourne, J. D. Asher, and C. W. Tyler. 1971. Technical reports: Surveillance of abortions in hospitals in the United States, 1970. HSMHA Health Reports 86(5):423–430.
Kelly, T., J. Suddes, D. Howel, J. Hewison, and S. Robson. 2010. Comparing medical versus surgical termination of pregnancy at 13–20 weeks of gestation: A randomised controlled trial. British Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology 117(12): 1512–1520.
Koonin, L. M., and J. C. Smith. 1993. Abortion surveillance—United States, 1990. MMWR Surveillance Summaries 42(SS-6):29–57. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/00031585.htm (accessed September 18, 2017).
Kost, K. 2015. Unintended pregnancy rates at the state level: Estimates for 2010 and trends since 2002. New York: Guttmacher Institute.
Kulier, R., N. Kapp, A. M. Gulmezoglu, G. J. Hofmeyr, L. Cheng, and A. Campana. 2011. Medical methods for first trimester abortion. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (11):CD002855.
Lawson, H. W., H. K. Atrash, A. F. Saftlas, L. M. Koonin, M. Ramick, and J. C. Smith. 1989. Abortion surveillance, United States, 1984–1985. MMWR Surveillance Summaries 38(SS-2):11–15. https://www.cdc.gov/Mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/00001467.htm (accessed September 18, 2017).
Lean, T. H., D. Vengadasalam, S. Pachauri, and E. R. Miller. 1976. A comparison of D & C and vacuum aspiration for performing first trimester abortion. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 14(6):481–486.
Lichtenberg, E. S., and M. Paul. 2013. Surgical abortion prior to 7 weeks of gestation. Contraception 88(1):7–17.
Lohr, A. P., J. L. Hayes, and K. Gemzell Danielsson. 2008. Surgical versus medical methods for second trimester induced abortion. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1):CD006714.
Low, N., M. Mueller, H. A. Van Vliet, and N. Kapp. 2012. Perioperative antibiotics to prevent infection after first-trimester abortion. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (3):CD005217.
Mauelshagen, A., L. C. Sadler, H. Roberts, M. Harilall, and C. M. Farquhar. 2009. Audit of short term outcomes of surgical and medical second trimester termination of pregnancy. Reproductive Health 6(1):16.
NAF (National Abortion Federation). 2017. 2017 Clinical policy guidelines for abortion care . Washington, DC: NAF.
Nash, E., R. B. Gold, L. Mohammed, O. Cappello, and Z. Ansari-Thomas. 2017. Laws affecting reproductive health and rights: State policy trends at midyear, 2017 . Washington, DC: Guttmacher Institute. https://www.guttmacher.org/article/2017/07/laws-affecting-reproductive-health-and-rights-state-policy-trends-midyear-2017 (accessed September 21, 2017).
Ngoc, N. T., T. Shochet, S. Raghavan, J. Blum, N. T. Nga, N. T. Minh, V. Q. Phan, B. Winikoff. 2011. Mifepristone and misoprostol compared with misoprostol alone for second-trimester abortion: A randomized controlled trial. Obstetrics & Gynecology 118(3):601–608.
Ohannessian, A., K. Baumstarck, J. Maruani, E. Cohen-Solal, P. Auquier, and A. Agostini. 2016. Mifepristone and misoprostol for cervical ripening in surgical abortion between 12 and 14 weeks of gestation: A randomized controlled trial. European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology 201:151–155.
Pazol, K., A. A. Creanga, and S. B. Zane. 2012. Trends in use of medical abortion in the United States: Reanalysis of surveillance data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2001–2008. Contraception 86(6):746–751.
Pazol, K., A. A. Creanga, and D. J. Jamieson. 2015. Abortion surveillance—United States, 2012. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 64(SS-10):1–40.
Peterson, W. F., F. N. Berry, M. R. Grace, and C. L. Gulbranson. 1983. Second-trimester abortion by dilatation and evacuation: An analysis of 11,747 cases. Obstetrics & Gynecology 62(2):185–190.
Plint, A. C., D. Moher, A. Morrison, K. Schulz, D. G. Altman, C. Hill, and I. Gaboury. 2006. Does the CONSORT checklist improve the quality of reports of randomised controlled trials? A systematic review. Medical Journal of Australia 185(5):263–267.
Ranji, U., A. Salganicoff, L. Sobel, C. Rosenzweig, and I. Gomez. 2017. Financing family planning services for low-income women: The role of public programs. https://www.kff.org/womens-health-policy/issue-brief/financing-family-planning-services-for-low-income-women-the-role-of-public-programs (accessed September 9, 2017).
Raymond, E. G., C. Shannon, M. A. Weaver, and B. Winikoff. 2013. First-trimester medical abortion with mifepristone 200 mg and misoprostol: A systematic review. Contraception 87(1):26–37.
RCOG (Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists). 2011. The care of women requesting induced abortion (Evidence-based clinical guideline number 7). London, UK: RCOG Press. https://www.rcog.org.uk/globalassets/documents/guidelines/abortion-guideline_web_1.pdf (accessed July 27, 2017).
RCOG. 2015. Best practice in comprehensive abortion care (Best practice paper no. 2). London, UK: RCOG Press. https://www.rcog.org.uk/globalassets/documents/guidelines/best-practice-papers/best-practice-paper-2.pdf (accessed September 11, 2017).
Roblin, P. 2014. Vacuum aspiration. In Abortion care, edited by S. Rowlands. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Sackett, D. L. 1979. Bias in analytic research. Journal of Chronic Diseases 32(1–2):51–63.
Sonalkar, S., S. N. Ogden, L. K. Tran, and A. Y. Chen. 2017. Comparison of complications associated with induction by misoprostol versus dilation and evacuation for second-trimester abortion. International Journal of Gynaecology & Obstetrics 138(3):272–275.
Strauss, L. T., S. B. Gamble, W. Y. Parker, D. A. Cook, S. B. Zane, and S. Hamdan. 2007. Abortion surveillance—United States, 2004. MMWR Surveillance Summaries 56 (SS-12):1–33.
Upadhyay, U. D., S. Desai, V. Zlidar, T. A. Weitz, D. Grossman, P. Anderson, and D. Taylor. 2015. Incidence of emergency department visits and complications after abortion. Obstetrics & Gynecology 125(1):175–183.
von Elm, E., D. G. Altman, M. Egger, S. J. Pocock, P. C. Gøtzsche, and J. P. Vandenbrouke. 2007. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. PLoS Medicine 4(10):e296.
White, K., E. Carroll, and D. Grossman. 2015. Complications from first-trimester aspiration abortion: A systematic review of the literature. Contraception 92(5):422–438.
WHO (World Health Organization). 2012. Safe abortion: Technical and policy guidance for health systems (Second edition). http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/70914/1/9789241548434_eng.pdf (accessed September 12, 2017).
WHO. 2014. Clinical practice handbook for safe abortion. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Press. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/97415/1/9789241548717_eng.pdf?ua=1&ua=1 (accessed November 15, 2016).
Wildschut, H., M. I. Both, S. Medema, E. Thomee, M. F. Wildhagen, and N. Kapp. 2011. Medical methods for mid-trimester termination of pregnancy. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1):Cd005216.
Woodcock, J. 2016. Letter from the director of the FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research to Donna Harrison, Gene Rudd, and Penny Young Nance. Re: Docket No. FDA-2002-P-0364. Silver Spring, MD: FDA.
Zane, S., A. A. Creanga, C. J. Berg, K. Pazol, D. B. Suchdev, D. J. Jamieson, and W. M. Callaghan. 2015. Abortion-related mortality in the United States: 1998–2010. Obstetrics & Gynecology 126(2):258–265.
Abortion is a legal medical procedure that has been provided to millions of American women. Since the Institute of Medicine first reviewed the health implications of national legalized abortion in 1975, there has been a plethora of related scientific research, including well-designed randomized clinical trials, systematic reviews, and epidemiological studies examining abortion care. This research has focused on examining the relative safety of abortion methods and the appropriateness of methods for different clinical circumstances. With this growing body of research, earlier abortion methods have been refined, discontinued, and new approaches have been developed.
The Safety and Quality of Abortion Care in the United States offers a comprehensive review of the current state of the science related to the provision of safe, high-quality abortion services in the United States. This report considers 8 research questions and presents conclusions, including gaps in research.
READ FREE ONLINE
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
Switch between the Original Pages , where you can read the report as it appeared in print, and Text Pages for the web version, where you can highlight and search the text.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.
Abortion Research Paper: Example, Outline, & Topics
The long-standing debate surrounding abortion has many opponents and advocates. Groups known as Pro-Choice and Pro-Life argue which approach is better, with no easy solution in sight. This ethical complexity is what makes abortion a popular topic for argumentative writing. As a student, you need to tackle it appropriately.
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!

If this task sounds daunting, read this guide by our custom-writing experts to get excellent writing tips on handling this assignment. You will also find here:
- abortion topics and prompts,
- a research paper outline,
- a free essay sample.
- 🤔 Why Is Abortion a Good Topic?
- ☑️ Research Paper Prompts
- 👨⚕️ Abortion Research Questions
- 📚 Research Topics
- 🔬 Before You Start
- ✍️ Step-by-Step Writing Guide
📋 Abortion Research Paper Example
🔍 references, 🤔 why is abortion a good research topic.
Abortion studies are a vast area of research and analysis. It touches upon numerous domains of life, such as politics, medicine, religion, ethics, and human rights perspectives.
Like gun control or euthanasia, the abortion debate offers no evident answers to what kind of regulation is preferable. According to a recent survey, 61% of US adults are in favor of abortion , while 37% think it should be illegal. The arguments from both sides make sense, and there is no “yes-no” solution.
All this makes investigating the abortion debate a valuable exercise to hone your critical analysis skills. It will teach you to back up your claims with sound evidence while giving credit to counterarguments. Besides, expanding the body of abortion research is beneficial for the American community and women’s rights.
☑️ Abortion Research Paper Prompts
The first step to writing a successful paper is choosing an appropriate topic. Abortion is surrounded by numerous legal, medical, ethical, and social debates. That’s why the choice of ideas is virtually endless.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
Don’t know where to start? Check out the prompts and creative titles below.
Should Abortion Be Legal: Research Paper Prompt
You can approach this question from several perspectives. For example, propose a new legal framework for regulating eligibility for abortion. Some states allow the procedure under certain circumstances, such as a threat to a woman’s health. Should it be made legal in less extreme situations, too?
Anti-Abortion Research Paper Prompt
The legal status of abortions is still disputed in many countries. The procedure’s most ardent opponents are Catholic religious groups. In an anti-abortion paper, you may list ethical or faith-based claims. Focus on the right-to-life arguments and give scientific evidence regarding embryo’s rights.
Abortion and Embryonic Stem Cell Research Prompt
Stem cell research is a dubious issue that faces strong opposition from ethical and religious activists. Here are some great ideas for an essay on this topic:
- Start by explaining what stem cells are.
- Outline the arguments for and against their use in research.
- Link this discussion to the status of abortion.
Abortion Law Research Paper Prompt
If you get an abortion-related assignment in your Legal Studies class, it’s better to take a legislative approach to this issue. Here’s what you can do:
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 15% off your first order!
- Study the evolution of abortion laws in the US or other countries.
- Pinpoint legal gaps.
- Focus on the laws’ strengths and weaknesses.
Abortion Breast Cancer Research Prompt
Increasing research evidence shows the link between abortion and breast cancer development . Find scholarly articles proving or refuting this idea and formulate a strong argument on this subject. Argue it with credible external evidence.
Abortion Ethics Research Paper Prompt
Here, you can focus on the significance of the discussion’s ethical dimension. People who are against abortion often cite the ethics of killing an embryo. You can discuss this issue by quoting famous thinkers and the latest medical research. Be sure to support your argument with sound evidence.
👨⚕️ Questions about Abortion for Research Paper
- How does technology reframe the abortion debate?
- Is there new ethics of abortion in the 21 st century?
- How did the abortion debate progress before the Roe v. Wade decision?
- How is the abortion debate currently being shaped on social media?
- How do abortion rights advocates conceptualize the meaning of life ?
- Can the abortion debate be called a culture war?
- What are women’s constitutional abortion rights?
- How does abortion reshape the concept of a person?
- How does the abortion debate fit in the post-Socialist transition framework of the European community?
- Where does the abortion debate stand in the politics of sexuality?
📚 Abortion Topics for Research Paper
- The changing legal rhetoric of abortion in the US.
- Constructing abortion as a legal problem.
- Regendering of the US’ abortion problem.
- Evolution of public attitudes to abortion in the US.
- Choice vs. coercion in the abortion debate.
- Abortion and sin in Catholicism.
- Artificial wombs as an innovative solution to the abortion debate.
- Religious belief vs. reason in the abortion debate.
- Introduction of pregnant women’s perspectives into the abortion debate: dealing with fetal abnormalities.
- The role of ultrasound images in the evolution of women’s abortion intentions.
🔬 Research Papers on Abortions: Before You Start
Before discussing how to write an abortion paper, let’s focus on the pre-writing steps necessary for a stellar work. Here are the main points to consider.
Abortion Research Design
Before you start exploring your topic, you need to choose between a qualitative and quantitative research design:
💬 Qualitative studies focus on words and present the attitudes and subjective meanings assigned to the concept of abortion by respondents.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
🧪 Quantitative studies , in turn, focus on numbers and statistics. They analyze objective evidence and avoid subjective interpretations.
Pick a research design based on your research skills and the data you’re planning to analyze:
- If you plan to gain insight into people’s opinions, attitudes, and life experiences related to abortion, it’s better to go for an interview and qualitative analysis.
- If you have a survey and want to focus on descriptive statistics, it’s better to stick to quantitative methods .
Abortion Research Paper Outline Format
Next, it’s time to choose the format of your paper’s outline. As a rule, students use one of the 3 approaches:
You can learn more about these formats from our article on how to write an outline .
Choosing Headings & Subheadings
A strong title can save your paper, while a poor one can immediately kill the readers’ interest. That’s why we recommend you not to underestimate the importance of formulating an attention-grabbing, exciting heading for your text.
Here are our best tips to make your title and subheadings effective:
- A good title needs to be brief. It’s up to 5 words, as a rule. Subheadings can be longer, as they give a more extended explanation of the content.
- Don’t be redundant. Make sure the subheadings are not duplicating each other.
- Mind the format. For instance, if your paper is in the APA format, you need to use proper font size and indentation. No numbering of headings and subheadings is necessary as in the outline. Ensure the reader understands the hierarchy with the help of heading level distinctions.
Components of an Effective Outline
According to academic writing conventions, a good outline should follow 4 essential principles:
- Parallelism . All components of your outline need to have a similar grammatical structure. For example, if you choose infinitives to denote actions, stick to them and don’t mix them with nouns and gerunds.
- Coordination . Divide your work into chunks with equal importance. This way, you will allocate as much weight to one point as to all the others. Your outline’s sections of similar hierarchy should have equal significance.
- Subordination . The subheadings contained within one heading of a higher order should all be connected to the paper’s title.
- Division . The minimum number of subheadings in each outline heading should be 2. If you have only one point under a heading, it’s worth adding another one.
Use this list of principles as a cheat sheet while creating your outline, and you’re sure to end up with well-organized and structured research!
Abortion Research Paper Outline Example
To recap and illustrate everything we’ve just discussed, let’s have a look at this sample abortion outline. We’ve made it in the decimal format following all effective outlining principles—check it out!
- History of abortion laws in the USA.
- Problem: recent legal changes challenge Roe vs. Wade .
- Thesis statement: the right to abortion should be preserved as a constitutional right
- The fundamental human right to decide what to do with their body.
- Legal abortions are safer.
- Fetuses don’t feel pain at the early stages of development.
- Abortion is murder.
- Fetuses are unborn people who feel pain at later stages.
- Abortion causes lifelong psychological trauma for the woman.
- Roe vs. Wade is a pro-choice case.
- The constitutional right to privacy and bodily integrity.
- Conclusion.
✍️ Abortion Research Paper: How to Write
Now, let’s proceed to write the paper itself. We will cover all the steps, starting with introduction writing rules and ending with the body and conclusion essentials.
Abortion Introduction: Research Paper Tips
When you begin writing an abortion paper, it’s vital to introduce the reader to the debate and key terminology. Start by describing a broader issue and steadily narrow the argument to the scope of your paper. The intro typically contains the key figures or facts that would show your topic’s significance.
For example, suppose you plan to discuss the ethical side of abortion. In this case, it’s better to structure the paper like this:
- Start by outlining the issue of abortion as a whole.
- Introduce the arguments of pro-choice advocates, saying that this side of the debate focuses on the woman’s right to remove the fetus from her body or leave it.
- Cite the latest research evidence about fetuses as living organisms, proceeding to debate abortion ethics.
- End your introduction with a concise thesis statement .
Thesis on Abortion for a Research Paper
The final part of your introduction is a thesis—a single claim that formulates your paper’s main idea. Experienced readers and college professors often focus on the thesis statement’s quality to decide whether the text is worth reading further. So, make sure you dedicate enough effort to formulate the abortion research paper thesis well!
Don’t know how to do it? These pro tips will surely help you write a great thesis:
Abortion Research Paper Body
Now, it’s time to proceed to the main body of your paper. It should expand on the main idea in more detail, explaining the details and weighing the evidence for and against your argument.
The secret of effective writing is to go paragraph by paragraph . Your essay’s body will have around 2-5 of them, and the quality of each one determines the value of the whole text.
Here are the 4 easy steps that can help you excel in writing the main part of your essay:
- Start each paragraph with a topic sentence. It functions as a mini-thesis statement and communicates the paragraph’s main idea.
- Then, expand it with additional facts and evidence. It’s better to back that information with external sources, showing that it’s not your guesswork. Make sure you properly analyze the citations and show how they fit into your broader research.
- A paragraph should end with a concise wrap-up. Write a concluding sentence restating the topic sentence or a transition linking to the next section.
Research Papers on Abortions: Conclusion
The conclusion of an abortion paper also plays a major role in the overall impression that your paper will produce. So, how do you make it interesting?
Instead of simply restating the thesis and enumerating your points, it’s better to do the following:
- Focus on the broader implications of the issue you’ve just discussed.
- Mention your study’s limitations and point out some directions for further research.
- It’s also a good idea to include a call to action , which can help create a sense of urgency in the readers.
Abortion Articles for Research Paper & Other Sources
Every research paper ends with “works cited” or a reference page enumerating the sources used for the assignment. A rule of thumb is to cite credible, authoritative publications from governmental organizations and NGOs and academic articles from peer-reviewed journals. These sources will make your research more competent and professional, supporting your viewpoint with objective scientific information.
Here are some databases that can supply top-quality data to back the abortion-related claims in a research paper:
Feel free to check these databases for studies related to your subject. It’s best to conduct preliminary research to see whether your topic has enough supporting evidence. Also, make sure there are plenty of new studies to back your arguments! Abortion is a fast-changing field of research, so it’s best only to use publications no more than 5 years old.
To learn more about credible research sources, check out our guide on choosing reliable websites .
We’ve taught you all you need to write a well-researched and thoughtful abortion paper. Finally, we want to give you an example of an essay on the topic “ Should Abortion Rights Be Preserved? ” Check it out to gain inspiration.
Now you know all the details of abortion paper writing. Use our tips to choose a topic, develop sound arguments, and impress your professor with a stellar piece on this debatable subject!
❓ Abortion Research Paper FAQs
- First, you need to pick a debatable topic about abortion and develop a thesis statement on that subject.
- Next, choose the arguments to support your claim and use external evidence to back them up.
- End the paper with a concise wrap-up.
- Begin your introduction with a catchy fact or shocking statistics on the issue of abortion.
- Ask a rhetorical question to boost your readers’ interest.
- Cite a famous person’s words about the pros and cons of legal abortion.
To compose a strong opening for your abortion essay, make sure to provide some background and context for further discussion. Explain why the debate about abortions is so acute and what the roots of the problem are.
There are many interesting topics related to abortion, spanning the areas of sociology, ethics, and medicine. You can focus on the progression of the abortion debate along with civil rights or discuss abortion from a feminist perspective.
You can choose between qualitative and quantitative approaches for your abortion research. Hold a survey among women and report the findings of your qualitative study in a short report. Or, you can measure factual information in numbers and conduct quantitative research.
- The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Research Paper: Grammarly
- Scholarly Articles on Abortion: Gale
- Unintended Pregnancy and Abortion Worldwide: Guttmacher Institute
- Why Abortion Should Be Legal: News 24
- Pro and Con: Abortion: Britannica
- Organizing Academic Research Papers: The Introduction: Sacred Heart University
- How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Research Paper: Steps and Examples: Research.com
- Abortion: American Psychological Association
- Writing a Research Paper: University of Wisconsin-Madison
- Writing a Research Paper: Purdue University
- A Process Approach to Writing Research Papers: University of California, Berkeley
- What Is Qualitative vs. Quantitative Study?: Grand Canyon University
- Decimal Outlines: Texas A&M University
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

What is the most important part of any essay or research paper? Of course, it’s the thesis statement—a sentence that expresses the paper’s main idea and guides the readers through your arguments. But where do you place the thesis? You’ve probably answered, “in the introduction.” However, that’s not all of...

If you’re a student, you’ve heard about a formal essay: a factual, research-based paper written in 3rd person. Most students have to produce dozens of them during their educational career. Writing a formal essay may not be the easiest task. But fear not: our custom-writing team is here to guide...

Rhetorical analysis is never a simple task. This essay type requires you to analyze rhetorical devices in a text and review them from different perspectives. Such an assignment can be a part of an AP Lang exam or a college home task. Either way, you will need a solid outline...

Narrative essays are unlike anything you wrote throughout your academic career. Instead of writing a formal paper, you need to tell a story. Familiar elements such as evidence and arguments are replaced with exposition and character development. The importance of writing an outline for an essay like this is hard...

Discourse is the way people talk about any specific topic. It’s also the way in which language is used to convey social and historical meanings. Discourse analysis is the process that helps to understand the underlying message of what is being said. Sounds interesting? Keep reading to learn more. This in...

A précis is a brief synopsis of a written piece. It is used to summarize and analyze a text’s main points. If you need to write a précis for a research paper or the AP Lang exam, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide by Custom-Writing.org, you’ll...

A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place! In this guide by our custom writing team,...

Do you know how to make your essay stand out? One of the easiest ways is to start your introduction with a catchy hook. A hook is a phrase or a sentence that helps to grab the reader’s attention. After reading this article by Custom-Writing.org, you will be able to...

A critical analysis essay is an academic paper that requires a thorough examination of theoretical concepts and ideas. It includes a comparison of facts, differentiation between evidence and argument, and identification of biases. Crafting a good paper can be a daunting experience, but it will be much easier if you...

Critical thinking is the process of evaluating and analyzing information. People who use it in everyday life are open to different opinions. They rely on reason and logic when making conclusions about certain issues. A critical thinking essay shows how your thoughts change as you research your topic. This type...

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: process analysis and its typesa process analysis outline tipsfree examples and other tips that might be helpful for your college assignment So,...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 02 January 2024
Psychological traits and public attitudes towards abortion: the role of empathy, locus of control, and need for cognition
- Jiuqing Cheng 1 ,
- Ping Xu 2 &
- Chloe Thostenson 1
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 11 , Article number: 23 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
2239 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Social policy
In the summer of 2022, the U.S. Supreme Court overturned the historic Roe v. Wade ruling, prompting various states to put forth ballot measures regarding state-level abortion rights. While earlier studies have established associations between demographics, such as religious beliefs and political ideologies, and attitudes toward abortion, the current research delves into the role of psychological traits such as empathy, locus of control, and need for cognition. A sample of 294 U.S. adults was obtained via Amazon Mechanical Turk, and participants were asked to provide their attitudes on seven abortion scenarios. They also responded to scales measuring empathy toward the pregnant woman and the unborn, locus of control, and need for cognition. Principal Component Analysis divided abortion attitudes into two categories: traumatic abortions (e.g., pregnancies due to rape) and elective abortions (e.g., the woman does not want the child anymore). After controlling for religious belief and political ideology, the study found psychological factors accounted for substantial variation in abortion attitudes. Notably, empathy toward the pregnant woman correlated positively with abortion support across both categories, while empathy toward the unborn revealed an inverse relationship. An internal locus of control was positively linked to support for both types of abortions. Conversely, external locus of control and need for cognition only positively correlated with attitudes toward elective abortion, showing no association with traumatic abortion attitudes. Collectively, these findings underscore the significant and unique role psychological factors play in shaping public attitudes toward abortion. Implications for research and practice were discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Death anxiety as mediator of relationship between renunciation of desire and mental health as predicted by Nonself Theory
The Psychological Science Accelerator’s COVID-19 rapid-response dataset
Conservatives and liberals have similar physiological responses to threats
The U.S. Supreme Court overturned the long-time landmark ruling of Roe v. Wade in 2022 summer. Debates and legal challenges regarding legal abortion in the U.S. have been heated (Felix et al., 2023 ). Furthermore, residents in several states have or will cast their vote on a ballot measure to determine abortion rights at the state level. A Gallup poll released in 2023 summer found that about one third of voters indicated that they would only vote for a candidate who shared their views on abortion (Saad, 2023 ). Therefore, it is imperative to understand people’s attitudes toward abortion. Past research on such attitudes have mainly focused on the role of political ideology and religious belief (e.g., Hess and Rueb, 2005 ); however, to our knowledge, relatively few studies have been done to examine the psychological underpinnings. Here we propose that examining the correlations between psychological factors and attitudes toward abortion has the potential to make contributions from the perspectives of both research and practice.
First, compared to attitudes in everyday life such as attitudes toward a product or brand, attitudes toward abortion are unique because it often elicits strong emotional response and conflict experience (Foster et al., 2012 ; Scott, 1989 ). Moreover, such an attitude goes beyond individual preference as it is deeply intertwined with one’s moral and religious beliefs, cultural background, and societal norms. Debate on abortion is not merely about a personal choice; it is about the definitions of life, rights, and autonomy (Osborne et al., 2022 ; Scott, 1989 ). For abortion, the contrasting views may lead to polarized opinions. In contrast, disagreements about a product or brand preference are typically less emotionally charged and do not carry the same societal weight. Therefore, given the unique nature of attitudes toward abortion as described above, it remains unclear whether psychological factors that correlate with attitudes in other areas still apply and, if so, in what capacity they do so. Additionally, as introduced below, several studies in this area employed a qualitative approach (interview). While the qualitative approach offered valuable insights into individuals’ perspectives on abortion, we aim to expand upon these findings by employing a quantitative approach. Especially, the quantitative approach allows us to explore the unique relationship between psychology and abortion attitudes after statistically controlling for other powerful factors like religious belief and political ideology. Together, a major goal of the present study is to provide initial empirical evidence for the correlations between attitudes toward abortion and certain psychological factors. We will further detail how our study might fill research gaps when introducing specific psychological factors as described below.
Second, examining the correlations between psychological factors and attitudes toward abortion may also offer practical insights. Consider the role of thinking style, for instance. The decision to pursue an abortion is imperative and often a prominently salient one, impacting not just the pregnant woman but also her family and extensive social network. Such a decision is complex and challenging due to intense feelings (e.g., conflict) and the balance between a woman’s bodily autonomy and fetal rights. From this viewpoint, there might be a correlation between attitudes toward abortion and one’s thinking style, especially their willingness to address complex and difficult issues. Past research has highlighted the connection between rational decision-making and the availability of relevant information (Shafir and LeBoeuf, 2002 ). Hence, to facilitate informed decisions, comprehensive knowledge about abortion is both essential and beneficial. The present study will examine the relationship between thinking style and abortion attitudes. Should a correlation be identified, our study would suggest individuals engage more deeply in critical thinking about the issues of abortion to enhance abortion-related education and informed decision-making.
Together, the present study aims to shed more light on the unique role of psychology in abortion attitudes, particularly in the presence of political ideology and religious belief. Specifically, we choose to examine the factors of empathy, locus of control, and thinking style (need for cognition) based on three considerations. Firstly, from a face validity perspective, the psychological constructs are predicted to exhibit a relationship with abortion attitudes. For example, the internal locus of control aligns well with the pro-choice mantra, ‘my body, my choice. Secondly, as detailed below, although these constructs have been explored in previous studies, they have only received limited attention and their relations with abortion attitudes remain inconclusive. Hence, our study aims to fill the gaps from past research by further clarifying their roles in attitudes toward abortion. Thirdly, research has indicated significant intersections between elements like cognitive style, empathy, and locus of control with various decisions, especially in health contexts (Marton et al., 2021 ; Pfattheicher et al., 2020 ; Xu and Cheng, 2021 ). These elements are tied to motivation, information analysis, and make trade-offs (Fischhoff and Broomell, 2020 ). Building on this, our study seeks to explore the applicability of these factors to the deeply sensitive and polarizing decision of abortion. On the other hand, it is worth noting that the psychological factors examined in our study are not exhaustive or driven by theoretical considerations. However, as mentioned in recent publications (Osborne et al., 2022 ; Valdez et al., 2022 ), past research on abortion attitudes with a psychological perspective is still limited. Therefore, our hope is that the present study could provide initial yet meaningful empirical evidence to exhibit the sophisticated role of psychology in attitudes toward abortion. We detail our rationales for each factor below.
Empathy refers to a variety of cognitive and affective responses, including sharing and understanding, toward others’ experiences (Pfattheicher et al., 2020 ). Previous studies have demonstrated a positive association between empathy and prosocial behaviors, such as caring for others (Moudatsou et al., 2020 ; Klimecki et al., 2016 ), as well as a reduction in conflict and stigma (Batson et al., 1997 ; Klimecki, 2019 ). Recently, Pfattheicher et al. ( 2020 ) also demonstrated that inducing empathy for the vulnerable people could promote taking preventative measures during the Covid-19 pandemic. While researchers advocated for incorporating empathy into abortion-related mental health intervention (Brown et al., 2022 ), the role of empathy in attitudes toward abortion remains understudied. Hunt ( 2019 ) investigated the impact of empathy toward pregnant women by presenting testimonial videos in which a pregnant woman described the challenges she faced due to legal abortion restrictions in Arkansas. However, this manipulation did not significantly reduce participants’ support for the abortion restrictions. Research has found that people’s views on abortion tends to be stable over time (Jelen and Wilcox, 2003 ; Pew Research Center, 2022 ). Hence, a short video used in Hunt ( 2019 ) might not be able to change people’s long-held views on abortion. Instead, we here hypothesize that the pre-existing but not temporality induced empathy play a role in abortion attitudes.
Furthermore, in addition to the empathy toward pregnant woman, it is also reasonable to assume that (some) people may feel empathy toward the unborn. For instance, interviews with Protestant religious leaders exhibited empathy toward both pregnant women and unborn (Dozier et al., 2020 ). Embree ( 1998 ) asked participants to indicate their opinions when responding to different scenarios of abortion. As a result, the study found that 64% and 17% of participants showed a moderate and strong level of empathy for the unborn, respectively. Despite the informative findings, the relationship between attitudes toward abortion and empathy toward the unborn remains unclear, particularly when taking empathy toward pregnant woman and other factors (e.g., political ideology) into account.
Together, we raise three hypotheses regarding the role of empathy as shown below.
H1a: Empathy toward pregnant woman and unborn can coexist.
H1b: People’s empathy toward pregnant woman are positively related to the support toward abortion.
H1c: People’s empathy toward unborn are negatively related to the support toward abortion.
As empathy has been highlighted in the intervention process when dealing with abortion-related mental health issues (Brown et al., 2022 ; Whitaker et al., 2015 ), we hope our findings could generate implications for future research and practice.
Locus of control
Locus of control (LOC) refers to people’s beliefs regarding whether their life outcomes are controlled and determined by their own (internal LOC) or external resources (fate, chance and/or powerful people, external LOC) (Levenson, 1981 ). Before delving into details, it is important to note that the internal and external LOC refer to different dimensions and are not mutually exclusive (Levenson, 1981 ; Reknes et al., 2019 ). For example, a person’s success may be determined by both hardworking and support from others. Regarding abortion attitudes, Sundstrom et al. ( 2018 ) analyzed interview contents and found that some women’s thoughts on pregnancy and abortion aligned with an internal locus of control (e.g., “As women, we need to take control as much as possible of our reproductive health”), while others aligned with an external locus of control (e.g., “leave it in God’s hands…we’ll just play it by ear and if I get pregnant, I get pregnant”).
The findings from Sundstrom et al. ( 2018 ) were informative and consistent with common sense. For example, at face value level, the slogan of “my body my choice” well aligns with the concept of internal LOC. However, the role of internal LOC in abortion attitudes may be more complicated. That is, religious belief may complicate the association between internal LOC and abortion attitudes. Past studies, including a meta-analysis and a study with over 20,000 participants, found a positive relationship between internal LOC and religious belief (Coursey et al., 2013 ; Falkowski, 2000 ; Iles-Caven et al., 2020 ). As noted in these articles, there are similarities between internal LOC and religious belief. For instance, religious beliefs often provide individuals with a sense of meaning, purpose, and guidance in life. Meanwhile, people higher in internal LOC are more likely to report higher levels of existential well-being and purpose in life, which can be associated with religious belief and engagement (Kim-Prieto et al., 2005 ; Krause and Hayward, 2013 ). Thus, the relationship between internal LOC and religious belief may complicate how internal LOC is involved in the abortion attitudes. Sundstrom et al. ( 2018 ) used interviews to explore the role of LOC in thoughts about abortion. However, this method might not sufficiently differentiate the influence of religious beliefs. In this study, we adopt a quantitative approach, using a classical scale to measure LOC. We aim to empirically assess the relationship between internal LOC and attitudes toward abortion, especially when accounting for religious belief. Furthermore, considering that the relationship between internal LOC and abortion attitudes might be intertwined with religious beliefs, we refrain from positing a specific hypothesis at this point.
External LOC, on the other hand, does not appear to have a significant relationship with religious belief. Additionally, a few studies found that people higher in external LOC tended to attribute outcomes to external reasons (Falkowski, 2000 ; Reknes et al., 2019 ). Building on this concept, individuals with a higher external locus of control (LOC) may be more inclined to attribute pregnancy to external factors and place less emphasis on personal responsibility. Accordingly, we predict the hypothesis below.
H2: External LOC will be positively related to the support toward abortion.
Need for cognition
Based on face validity, thinking style might pertain to one’s perception of abortion. For instance, individuals who prioritize comprehensive and empirical data might arrive at a different conclusion than those who lean on personal stories and emotional narratives. A few studies have tapped into the relationship between thinking style and attitudes toward abortion. Valdez et al. ( 2022 ) conducted qualitative interviews on abortion and employed natural language processing techniques to analyze the interviews. The study identified analytical thinking, which involved considering abortion from multiple perspectives, had a negative relationship with the number of cognitive distortions (such as polarized and rigid thinking about abortion). However, such a finding conflicted with another study by Hill ( 2004 ) where the concept of cognitive complexity (thinking beyond surface-level observations) did not correlate with attitudes toward abortion. The inconsistency might be due to methodological issues. For example, the correlations described above in Valdez et al. ( 2022 ) were derived from a small sample consisting of 16 participants. A low reliability of the cognitive complexity scale used in Hill ( 2004 ) might (partly) address the non-significant relationship. Thus, the present study will utilize the Need for Cognition scale, a widely recognized and validated instrument that measures thinking style, to examine its correlation with attitudes toward abortion in a larger sample.
Need for cognition (NFC) pertains to the inclination to derive satisfaction from and actively participate in effortful thinking (Cacioppo et al., 1984 ). Consistent with its concept, past research demonstrated that NFC was positively correlated with information seeking (Verplanken et al., 1992 ), academic achievement (Richardson et al., 2012 ), and logical reasoning performance (Ding et al., 2020 ). As for attitudes toward abortion, we hypothesize the following.
H3: There will be a positive correlation between NFC and attitudes toward abortion.
Our prediction is based on two reasons. First, NFC drives individuals to actively seek and update information and knowledge. It was discovered that acquiring a deeper understanding of abortion correlated with increased support for it (Hunt, 2019 ; Mollen et al., 2018 ). Second and relatedly, NFC was found to be negatively associated with various stereotype memories and positively related to non-prejudicial social judgments (Crawford and Skowronski, 1998 ; Curşeu and de Jong, 2017 ).
In sum, the present study aims to provide empirical evidence for the association between attitudes toward abortion and psychology by examining and clarifying the role of empathy, locus of control, and need for cognition. Past research has repeatedly found the involvement of political ideology and religious belief in abortion attitudes (e.g., Hess and Rueb, 2005 ; Holman et al., 2020 ; Jelen, 2017 ; Osborne et al., 2022 ; Prusaczyk and Hodson, 2018 ). Given their powerful and robust effect, it is crucial to gather additional empirical evidence to elucidate the distinct contribution of psychology to attitudes toward abortion, while considering the influence of political ideology and religious beliefs. Additionally, when describing attitudes toward abortion, the dichotomization of “pro-choice” and “pro-life” have been widely used for decades. However, some studies have criticized that the dichotomization oversimplified attitudes toward abortion (Hunt, 2019 ; Osborne et al., 2022 ; Rye and Underhill, 2020 ). That is, people’s views on abortion vary across different scenarios and reasons. For instance, people showed less support toward abortion with elective reasons than with traumatic reasons (Hoffmann and Johnson, 2005 ). With confirmatory analysis, Osborne et al. ( 2022 ) derived two types of abortion: traumatic (e.g., pregnancy due to rape) vs. elective (e.g., the woman does not want the child anymore). Building on prior research, the current study aims exploring potential variations in attitudes across different abortion reasons. Furthermore, we also intend to examine whether the psychological factors described above have varying associations with different types of abortion.
Participants
The study was approved by IRB before data collection. Participants were recruited from Amazon Mechanical Turk (mTurk) on October 20th, 2022. To be eligible for the study, participants must be an adult, a U.S. citizen, and have an approval rating greater than 98% in mTurk. A total of 300 participants were enrolled into the study. Each participant received $3 for compensation. Six participants did not complete at least 80% of the items and were removed from the study. Thus, the effective sample size was 294. Demographics are presented in the Results section.
Materials and procedures
Participants took an online survey developed by Qualtrics. Our study did not set a specific time restriction. Across 294 participants, the average survey completion time was 682.8 s (SD = 286.6 s). The median completion time was 595.0 s (IQR = 344.8 s). The following questionnaires were completed.
Attitudes toward abortion
Hoffmann and Johnson ( 2005 ) and Osborne et al. ( 2022 ) analyzed attitudes toward abortion with six different scenarios (scenarios a-f below) that were measured by the U.S. General Social Survey. We further added an additional item regarding underage pregnancy for two reasons. First, compared to other Western industrialized nations, the U.S. has historically had a higher rate of underage pregnancies. Additionally, underage pregnant individuals tended to have a higher likelihood of seeking abortions compared to their older counterparts (Lantos et al., 2022 ; Kearney and Levine, 2012 ; Sedgh et al., 2015 ). Second, underage pregnancy is linked to various adverse outcomes, such as increased risk during childbirth, heightened stress and depression, disruptions in education, and financial challenges (Eliner et al., 2022 ; Hodgkinson et al., 2014 ; Kearney and Levine, 2012 ). Given the significance and prevalence of underage pregnancy, we chose to include it as a scenario to understand the public’s perception. Additionally, we understood that people might feel conflict or uncertain toward one or more scenarios. Hence, instead of using binary response (yes/no format) adopted in the U.S. General Social Survey, we employed a 1 to 7 Likert scale for each scenario, with a higher score indicating stronger support for a pregnant woman to obtain legal abortion.
The seven scenarios in the present study included: (a) there is a strong chance of serious defect in the baby; (b) the woman’s own health is seriously endangered by the pregnancy; (c) the woman became pregnant as a result of rape; (d) the woman is married and does not want any more children; (e) the family has a very low income and cannot afford any more children; (f) the woman is not married and does not want to marry the man; and (g) the woman is underage.
Following the wording used to measure empathy in Pfattheicher et al. ( 2020 ), we developed six items to measure the empathy toward the pregnant woman and unborn or fetus, respectively. The scale of empathy toward pregnant woman included: (a) I am very concerned about the pregnant woman who may lose access to legal abortion; (b) I feel compassion for the pregnant women who may lose access to legal abortion; and (c) I am quite moved by the pregnant women who may lose access to legal abortion. The scale of empathy toward unborn included: (a) I am very concerned about the fetus or unborn child; (b) I feel compassion for the fetus or unborn child; and (c) I am quite moved by the fetus or unborn child. Participants rated each item on a five-point Likert scale, with 1 being strongly disagree and 5 being strongly agree. Thus, a higher score demonstrated stronger empathy toward the target. The Cronbach’s α for the scale of toward pregnant woman was 0.90 in the present study. The Cronbach’s α for the scale of toward unborn was 0.92.
The need for cognition scale (NFC, Cacioppo et al., 1984 ) intends to measure the tendency to engage into deep thinking. It has 18 items, such as “I only think as hard as I have to” and “I find satisfaction in deliberating hard and for long hours”. Participants rated each item on a five-point Likert scale, with a higher score indicating a greater tendency to enjoy deep thinking. In the present study, the reliability of this scale was 0.93.
The present study adopted Levenson multidimensional locus of control scale (Levenson, 1981 ). Across 24 items, this scale measures three dimensions of locus of control: internality (sample item: Whether or not I get to be a leader depends mostly on my ability); powerful others (sample item: I feel like what happens in my life is mostly determined by powerful people); and chance (sample item: To a great extent my life is controlled by accidental happenings). In the present study, participants rated each item on a 1 to 6 Likert scale, with a higher score indicating a stronger belief that fate was controlled by self, powerful others, or chance. The Cronbach’s α for the subscales of internality, powerful others, and chance was 0.84, 0.91, and 0.93, respectively. As shown below, there was a high agreement between powerful others and chance subscales ( r = 0.87, p < 0.001). Hence, we combined these two subscales to form an external locus of control composite.
Demographics
After completing the scales described above, participants were asked to report their demographic information including race, age, gender, education, annual household income, current relationship status, abortion experience, religious belief, and political ideology. Gender was coded with 1 = male, 2 = female, and 3 = other. Race was coded with 1 = White or Caucasian, 2 = Hispanic or Latinx, 3 = Black or African American, 4 = Asian or Asian American, and 5 = Other. Education was coded with six levels: 1 = Less than high school graduate, 2 = High school graduate or equivalent, 3 = Some college or associate degree, 4 = Bachelor’s degree, 5 = Master’s degree, 6 = Doctoral degree. Annual household income was categorized into 13 levels and ranged between under $9,999 and above $120,000 with increments of $9,999. Current relationship status was coded into six levels: 1 = single and not dating, 2 = single but in a relationship, 3 = married, 4 = divorced, 5 = widowed, 6 = other. For abortion experience participants were asked “For any reason, have you had an abortion?”. For this question, the answer was coded with 1 = yes and 2 = no.
Religious belief was measured with three items. The first item asked “How often do you attend religious services?” Participants selected one option out of the following: 1 = never, 2 = a few times per year, 3 = once a month, 4 = 2–3 times a month, 5 = once a week or more. The second item asked “How important is religion to you personally?” Participants rated this question on a five-point Likert point, with 5 being most important. The third question asked “How would you describe your religious denomination”. The options included 1 = Christian, 2 = Islam, 3 = Judaism, 4 = Buddhism, 5 = Hinduism, 6 = other or atheism. In the present study, the first two items were highly correlated ( r = 0.77, p < 0.001). Following Hunt ( 2019 ), we combined the two items to form a general religiosity composite, with a higher score indicating a stronger religious belief.
Political ideology was measured with two items: (a) Generally, how would you describe your views on most social political issues (e.g., education, religious freedom, death penalty, gender issues, etc.)? and (b) Generally, how would you describe your views on most economic political issues (e.g., minimum wage, taxes, welfare programs, etc.)? Participants rated each item with a five-point Likert scale, with 1 = strongly conservative 2 = conservative 3 = moderate 4 = liberal 5 = strongly liberal. We found a strong correlation between the two political ideology items, r = 0.76, p < 0.001. Hence, we combined the two items to form a general political ideology composite.
SPSS 24.0 was employed to perform all the analyses. Across 294 participants, age ranged from 21 to 79, with a mean of 40.4 and a standard deviation of 12.4. Table 1 displays the descriptive statistics for the variables of gender, race, education, annual household income, current relationship status, religious denomination, and abortion experience.
Table 2 presents the descriptive statistics of attitudes toward abortion in different scenarios, religious belief, political ideology, and the scores of the psychological scales. Similar to the results obtained from the large-scale surveys in the U.S. and New Zealand (Osborne et al., 2022 ), the support toward abortion was strong (neutral = 4) across all scenarios.
To examine the structure of attitudes toward abortion in different scenarios, a Principal Component Analysis (PCA) with a Varimax orthogonal rotation was performed on all seven scenarios. With eigenvalue ≥ 1 as the threshold, two components were generated, accounting for 81.34% of the variability. Table 3 presents the PCA results. As shown, we obtained two distinct components. The first one included the scenarios of baby defection, pregnant woman’s health being endangered, pregnancy caused by rape, and underage pregnancy. The second component included the scenarios of not wanting the child, low income, and not wanting to marry. Such a differentiation between the two components was consistent with the notion in Osborne et al. ( 2022 ). Following this paper and the face validity of the scenarios, we labeled the two components traumatic abortion and elective abortion, respectively. Accordingly, we also computed a composite score for each component by averaging the corresponding items. In line with previous research (Hoffmann and Johnson, 2005 ), the support was significantly stronger toward the traumatic abortion (mean = 5.84, SD = 1.24) than the elective abortion (mean = 4.94, SD = 1.74), t (293) = 11.51, p < 0.001, Cohen’s d = 0.67.
Table 4 presents the zero-order correlations between attitudes toward traumatic and elective abortions, demographics, and scores of the psychological factors. Consistent with the findings from past research (e.g., Hess and Rueb, 2005 ; Holman et al., 2020 ), a stronger religious belief was negatively related to the support toward both types of abortions. A stronger liberal ideology was positively related to the support toward both types of abortions. Additionally, empathy toward the pregnant woman was positively associated with the support toward both types of abortions whereas empathy toward unborn or fetus had an opposite effect. Based on the zero-order correlation, we did not find a significant relationship between internal locus of control and attitudes toward either type of abortion. The external locus of control (either powerful others or chance), on the other hand, was positively related to the support toward elective but not traumatic abortion. As there was a high agreement between the two external locus of control subscales ( r = 0.87, p < 0.001), we formed a general external locus of control composite by averaging the two items in the following regressions. Finally, need for cognition was positively related to attitudes toward elective abortion but not traumatic abortion.
While the zero-order correlations were informative, we were mindful that the Type I error might be greatly inflated due to a vast amount of repeated testing. Moreover, one goal of the study was to examine the role of psychological factors in the presence of religious belief and political ideology. Thus, we performed a hierarchical linear regression on each type of abortion, with age, gender, income, and education in the first block, religious belief and political ideology in the second block, and psychological factors in the third block. We separated the regression between the two types of abortion because the role of predictors might vary. This approach was also employed in Osborne et al. ( 2022 ). Table 5 exhibits the regression results.
As shown in Table 5 , the demographic variables of age, gender, education, and income did not account for a significant portion of the variability in attitudes toward either type of abortion. The present study added to the literature that there might not necessarily be a difference in attitudes toward abortion between males and females (Bilewicz et al., 2017 ; Jelen and Wilcox, 1997 ). By contrast, in the second block, religious belief and political ideology collectively explained a sizable portion of the variability in attitudes toward both types of abortion. In block 3, in the presence of demographic variables including religious belief and political ideology, psychological factors could still account for a significant portion of the variability.
Looking at the individual psychological predictors (for more detailed interpretations please refer to the discussion part), consistent with our hypothesis, empathy toward the pregnant woman was positively associated with the support toward both types of abortion. By contrast, empathy toward the unborn or fetus was negatively associated the support toward abortion. For the factor of locus of control, the internal locus of control was not related to any type of abortion attitudes when zero-order correlation was used (Table 4 ); yet it was positively related to abortion attitudes after all other predictors were taken into account, indicating a suppressing effect. Upon further examination, we identified two suppressors: religious belief and empathy toward the unborn. After removing these two variables, internal locus of control was no longer significant. The observed pattern reflected our previous prediction, indicating that the role of internal locus of control could be complicated by religious beliefs. External locus of control, on the other hand, was positively correlated with the support toward elective abortion. Similarly, need for cognition (NFC) also had a positive relationship with the support toward elective abortion. Neither external locus of control nor NFC had a significant correlation with attituded toward traumatic abortion. Hence, our hypotheses regarding external locus of control and NFC were partially supported. We detailed out interpretation and discussion of the results below.
The present study aimed to provide empirical evidence for the correlations between psychological factors and attitudes toward abortion. As introduced earlier, while it is common to find the involvement of psychology in everyday life attitudes and preferences, attitudes toward abortion are unique and drastically different. Given its unique nature, it lacks empirical evidence regarding whether psychological factors that interplay with attitudes in other areas still apply and, if so, in what capacity they do so. Past research has primarily focused on the role of religious belief and political ideology. Our study demonstrated a substantial involvement ( R 2 change = 0.27 and 0.24 for traumatic and elective abortion, respectively) of the psychological factors, after controlling for religious belief and political ideology. More importantly, these effects were comparable to the variability accounted for by religious belief and political ideology combined, particularly in the elective abortion category. The results highlighted the influential role of psychological factors in shaping attitudes toward abortion.
Additionally, past research has shown the interconnection between psychology and the public’s attitudes toward major societal events. For example, during the Covid-19 pandemic, while the perception of mask-wearing and/or social distancing was highly politicized, studies found that attitudes toward these preventative measures to be related to thinking style, self-control, numeracy, and working memory capacity (Steffen and Cheng, 2023 ; Xie et al., 2020 ; Xu and Cheng, 2021 ). In line with this, our study further underscored the significant influence of psychology on another pressing societal topic: abortion. In the sections below, we detail our findings and relevant implications. We are fully aware that our study was preliminary and hope it could serve as a starting point for future research and practice. We also acknowledge the limitations of our study and address them at the end.
Some past studies on empathy and abortion only considered the empathy toward the pregnant woman (e.g., Brown et al., 2022 ; Homaifar et al., 2017 ; Hunt, 2019 ; Whitaker et al., 2015 ). The present study identified two types of empathy when dealing abortion: empathy toward the pregnant woman and empathy toward the unborn. In the presence of each other, we found that greater empathy toward the pregnant woman was associated with more support toward abortion, whereas greater empathy toward the unborn or fetus was associated with less support toward abortion. Such a pattern suggested that empathy might be a source of conflict feeling. That is, when considering abortion, concerns and care toward pregnant woman and unborn could coexist, potentially leading to conflict and dilemma when people thought about abortion. While the present study examined the public’s attitudes toward abortion with a diverse sample, pregnant women might have a similar pattern of empathy and hence feel conflict and dilemma when thinking about abortion. To cope with such a conflict, it might be beneficial for a counselor to acknowledge conflicting emotions that arise from empathizing with both the unborn and the pregnant individual. Moreover, the counselor could guide the client through the process of reconciling these emotions to alleviate feelings of isolation or confusion the client may experience. Future research in the realms of mental health and counseling should consider integrating these dual empathy perspectives and empirically assess the efficacy of such therapeutic interventions.
Additionally, Hunt ( 2019 ) did not find a significant influence of empathy on abortion attitudes change when participants were exposed to testimonial videos featuring pregnant women discussing the legal obstacles they faced. The disparity between Hunt’s ( 2019 ) findings and our own could potentially be attributed to the inherent stability and longstanding nature of abortion attitudes. Research has found that people’s views on abortion tends to be stable over time (Jelen and Wilcox, 2003 ; Pew Research Center, 2022 ). As a result, it is possible that pre-existing empathy, rather than empathy induced temporarily, was the factor correlated with individuals’ perception and consideration of abortion. Our findings were consistent with this possibility. Together, our findings supported H1a to H1c. Moreover, our study shed more light on empathy by showing its association with distinct views on abortion. The results suggest that future research could investigate how different types of empathy are formed and how they influence the shaping and persuasion of abortion attitudes.
Through qualitative interviews, Sundstrom et al. ( 2018 ) unveiled individual differences in the locus of control when discussing opinions on abortion. However, these interviews might not have fully captured the interplay between internal and external locus of control and other factors involved attitudes toward abortion. To fill the gap, our study employed a quantitative approach to delve deeper into how locus of control correlated with abortion attitudes. Consistent with Levenson ( 1981 ) and Reknes et al. ( 2019 ), we found that the constructs internal locus of control and external locus of control were differentiated but not unidimensional. For internal locus of control, interestingly, we found a suppressing effect. As discussed earlier, the role of internal locus of control in abortion attitudes might be complicated. That is, on the one hand, by face validity, the internal locus of control well aligned with the concept of “my body, my choice” (Sundstrom et al., 2018 ). On the other hand, in line with past research (Coursey et al., 2013 ; Falkowski, 2000 ; Iles-Caven et al., 2020 ), our study found that internal locus of control was positively related to religious belief. Furthermore, as shown in Table 4 , internal locus of control was also positively related to the empathy toward the unborn, and such a relationship was significantly mediated by religious belief (mediation effect = 0.21, SE = 0.5, 95% CI = [0.13, 0.31]). Therefore, when using zero-order correlation, the effect of internal locus of control might be neutralized by the two opposite parts (“my body, my choice” vs. religious belief) discussed above. By contrast, in regression, the “my body, my choice” part stood out because the religiosity part was partialled out by the variables of religious belief and empathy toward the unborn.
In addition to internal locus of control, we also discovered that external locus of control was involved in abortion attitudes. Specifically, we found a positive relationship between external locus of control and support toward elective abortion (H2 was partially supported). Past research has found that locus of control is related to attribution (Falkowski, 2000 ; Reknes et al., 2019 ). Thus, our finding was in line with the notion that those with a greater level of external locus of control might be more likely to attribute unwanted pregnancy to external reasons (not personal responsibility), and hence showed more support toward abortion.
Our findings regarding locus of control suggest that individuals might simultaneously believe in personal autonomy (“my body, my choice”) while also feeling that certain life events, like unwanted pregnancies, are influenced by external factors beyond their control. This is particularly true when thinking about elective abortion. Education and counseling practices might be designed to reflect this duality. For example, materials and discussions could simultaneously emphasize the importance of personal choices and responsibilities, while also exploring societal, cultural, or circumstantial factors that might influence abortion decision. Incorporating both perspectives would allow to create a supportive environment where individuals feel seen and acknowledged in their complexities.
As introduced earlier, past research on the relationship between thinking style and abortion attitudes was inconclusive. To clarify the relationship, the present study adopted the validated need for cognition scale. Need for cognition has demonstrated its involvement in consequential events, such as political elections and the adoption of preventive measures during the Covid-19 pandemic (Sohlberg, 2019 ; Xu and Cheng, 2021 ). In the present study, we discovered that need for cognition was positively related to the support toward elective abortion. Such a finding was consistent with the notion that need for cognition was negatively related to stereotypes (Crawford and Skowronski, 1998 ; Curşeu and de Jong, 2017 ). Additionally, as need for cognition drives individuals to seek and update knowledge, our result was also in line with the finding that gaining knowledge about abortion led to more positive view on abortion (Hunt, 2019 ; Mollen et al., 2018 ). Our study implied that future research could empirically evaluate if indeed abortion knowledge mediates the relationship between need for cognition and abortion attitudes.
It is worth noting that the present study also clarified the role of need for cognition in attitudes toward abortion by examining a potential artifact. Specifically, the observed positive relationship between need for cognition and support for abortion might be an artifact, given that liberal ideology is positively correlated with both abortion attitudes and need for cognition (Young et al., 2019 ). However, as shown in our regression, the relationship between need for cognition and elective abortion remained significant in the presence of other variables, including political ideology. Thus, the finding suggested that at least part of the relationship between need for cognition and attitude toward abortion was unique and not driven by political ideology.
Our findings related to need for cognition had an implication on abortion-related education. As discussed earlier, having adequate knowledge about abortion could facilitate the support for making informed decisions. As need for cognition was found to be related to openness and motivation to seek and update information (Russo et al., 2022 ), our finding suggested that cultivating willingness to engage into critical thinking might be beneficial for education on abortion and reproductive rights. While we are fully aware that correlation does not equate to causation, our study still offers a starting point for future research and practice on abortion-related education.
Traumatic abortion vs. elective abortion
While some researchers argued that the dichotomization of “pro-choice” and “pro-life” was oversimplified, to date, only two studies have empirically examined attitude variation between different abortion scenarios (Hoffmann and Johnson, 2005 ; Osborne et al., 2022 ). Both studies demonstrated that public views on abortion can be grouped into two categories: traumatic and elective. Our research not only replicated these findings but also introduced two significant advancements. First, we incorporated a scenario addressing underage pregnancy, given its high prevalence and significance. Secondly, instead of a binary response, we employed a 7-point Likert scale, allowing us to more accurately capture potential conflicting attitudes among participants.
Furthermore, our findings revealed that the roles of external locus of control and need for cognition varied in relation to attitudes toward the two types of abortion. Interestingly, we observed that neither of these variables significantly related to attitudes toward traumatic abortion, as indicated by both zero-order correlation and regression analyses. Conceptually, the scenarios of traumatic abortion (e.g., pregnancy caused by rape; mother life endangered) tend to be more extreme and emergent than the scenarios of elective abortion. Hence, there might be less room for psychological factors, such as thinking or attribution, to function in traumatic abortion than in elective abortion. Our interpretation was also consistent with the statistical pattern between the two abortions. That is, compared to elective abortion, the standard deviation of traumatic abortion was smaller. Additionally, there were more participants rated seven on the Likert scale in the scenarios of traumatic abortion (29.6%) than in the scenarios of elective abortion (18%). Despite the difference between the two types of abortion, it is essential to acknowledge that elective abortion does not imply a stress-free experience. Both traumatic and elective abortions involve significant levels of stress and emotional challenges. While traumatic abortion scenarios can be considered more extreme, it is crucial to recognize that individuals undergoing elective abortion may also experience considerable emotional distress.
Taken together, with concrete evidence, our study demonstrated that the public’s attitude toward abortion depended on abortion reasons. Our study also implied that future research should focus on attitudes toward specific abortion scenarios rather than a holistic concept of abortion. Furthermore, the differentiation between the traumatic and elective abortions suggested the limitation and potential ineffectiveness of one-size-fits-all legislative solutions. Given the varying and often conflicting attitudes that people harbor, it would be reasonable for legislative frameworks to be flexible, adaptive, and cognizant of the different circumstances surrounding abortion. This will not only be more reflective of public opinions but also more supportive of individuals who undergo different types of abortion experiences, each of which carries its own set of emotional and psychological challenges.
Expanding findings with a quantitative approach
Some past studies employed a qualitive approach when dealing with attitudes toward abortion (e.g., Dozier et al., 2020 ; Sundstrom et al., 2018 ; Valdez et al., 2022 ; Woodruff et al., 2018 ). These investigations have provided insights and served as inspirations for our own research. However, the relationship between abortion attitudes and pertinent factors may remain somewhat opaque. This is particularly true when considering the intricate interconnectedness among these factors. The present study demonstrated that findings from qualitative studies could be extended and enriched with a quantitative approach. For instance, we utilized quantitative scales to measure empathy toward the unborn —a variable that was previously identified through interviews in the study by Dozier et al. ( 2020 ). Moreover, we further exhibited the role of empathy toward the unborn when statistically controlled other variables, including empathy toward the pregnant. Similarly, the role of internal locus of control was revealed in interviews in Sundstrom et al. ( 2018 ). With validated scales, we exhibited the correlation with internal locus of control in both types of abortion. Furthermore, by detecting and interpreting a suppressing effect, we showed the interplay between internal locus of control, religious belief, and attitude toward abortion. Thus, our study implied that using quantitative scales and analyses was a viable approach to examine attitude toward abortion and could deepen the understanding of relevant factors.
Limitations and future directions
Despite the contributions, limitations should be acknowledged as well. First and foremost, we believe our study was still in the explorative stage. The specific psychological factors tested in the present study were not exhaustive and not theoretically driven. We hope the present study could provide initial empirical evidence to show the sophisticated role of psychology in attitudes toward abortion. Future studies could use a more theoretical driven approach to examine the specific psychological involvement in abortion attitudes. For example, given the correlation between need for cognition and attitudes toward abortion, future research could further elucidate the role of thinking style in attitudes toward abortion by incorporating the Dual-Process Theory (Evans, 2008 ). The Dual-Process Theory posits that humans have two distinct systems of information processing: System 1, which is intuitive, automatic, and fast; and System 2, which is deliberate, analytical, and slower. By examining the interplay between these two systems, researchers might gain insights into how intuitive emotional responses versus more deliberate cognitive analyses influence individuals’ attitudes toward abortion. For instance, are individuals who predominantly rely on System 1 more swayed by emotive narratives or imagery related to abortion?
Second, when analyzing and discussing the results, we proposed several possible underlying mechanisms that might elucidate the relationships observed. To illustrate, we employed the concept of attribution to shed light on the role of an external locus of control, positing that individuals with a strong external locus might attribute abortion decisions to external factors or circumstances rather than personal choices. Furthermore, we suggested that the observed positive relationship between the need for cognition and abortion attitudes might be mediated through abortion knowledge. This implies that individuals with a higher need for cognition could potentially seek out more information on abortion, leading to more informed attitudes. However, while these interpretations offer potential insights, we recognize their speculative nature. It’s crucial to emphasize that our proposed mechanisms require rigorous empirical testing for validation. For example, it would be of interest to test whether indeed, gaining various types of abortion knowledge improves views of abortion.
Third, as described above, we strived to show how our findings could be potentially used in abortion-related counseling. However, we acknowledge that our study is explorative but not counseling focused. Therefore, while we believe our findings offer meaningful implications, we caution against over-extrapolating their direct applicability to counseling contexts. Future research could delve into empirically investigating how psychological factors, such as varying empathy types and loci of control, could be utilized to alleviate negative feelings associated with abortion decisions. Additionally, understanding how various psychological factors interact with cultural and social norms could further help tailor counseling approaches.
Fourth, the present study did not include an attention check item. We believe the quality of our survey could have been improved had we included one or more attention check items. However, the reliabilities of our scales were relatively high (ranged from 0.84 to 0.93). Additionally, we also replicated some major findings from previous research (e.g., the associations between attitudes toward abortion and religious belief and political ideology). Thus, we believe that overall, inattention did not affect the quality of our data. Future online surveys could consider using attention check items for quality control.
In conclusion, the present study demonstrates the unique contribution of empathy, locus of control, and need for cognition to how people perceived abortion in different scenarios. The findings suggests that attitudes toward complex moral issues like abortion are shaped by individual psychological traits and cognitive needs, in addition to societal, religious, and cultural norms. Future research could use our study as a starting point to expand on these findings, exploring other psychological traits and cognitive processes that may similarly affect perceptions of abortion and other controversial subjects.
Data availability
Data included in this project may be found in the online repository, https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/E5AB5R .
Batson CD, Polycarpou MP, Harmon-Jones E, Imhoff HI, Mitchener EC, Highberger L et al. (1997) Empathy and attitudes: can feeling for a member of a stigmatized group improve feelings toward the group? J Person Soc Psychol 72(1):105–118
Article CAS Google Scholar
Bilewicz M, Mikołajczak G, Babińska M (2017) Speaking about the preborn. How specific terms used in the abortion debate reflect attitudes and (de)mentalization. Person Individ Differ 111:256–262
Article Google Scholar
Brown L, Swiezy S, McKinzie A, Komanapalli S, Bernard C (2022) Evaluation of family planning and abortion education in preclinical curriculum at a large midwestern medical school. Heliyon 8(7):e09894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09894
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cacioppo JT, Petty RE, Kao CF (1984) The efficient assessment of need for cognition. J Person Assess 48(3):306–307. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327752jpa4803_13
Comrey AL, Lee HB (1992) A first course in factor analysis (2nd ed.). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc
Coursey LE, Kenworthy JB, Jones JR (2013) A meta-analysis of the relationship between intrinsic religiosity and locus of control. Arch Psychol Relig 35:347–368. https://doi.org/10.1163/15736121-12341268
Crawford MT, Skowronski JJ (1998) When motivated thought leads to heightened bias: high need for cognition can enhance the impact of stereotypes on memory. Person Soc Psycholo Bull 24(10):1075–1088. https://doi.org/10.1177/01461672982410005
Curşeu PL, de Jong JP (2017) Bridging social circles: need for cognition, prejudicial judgments, and personal social network characteristics. Front Psychol 8:1251. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01251
Ding D, Chen Y, Lai J, Chen X, Han M, Zhang X (2020) Belief bias effect in older adults: roles of working memory and need for cognition. Front Psychol 10:2940. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02940
Dozier JL, Hennink M, Mosley E, Narasimhan S, Pringle J, Clarke L, Blevins J, James-Portis L, Keithan R, Hall KS, Rice WS (2020) Abortion attitudes, religious and moral beliefs, and pastoral care among Protestant religious leaders in Georgia. PloS one 15(7):e0235971. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0235971
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Eliner Y, Gulersen M, Kasar A, Lenchner E, Grünebaum A, Chervenak FA, Bornstein E (2022) Maternal and neonatal complications in teen pregnancies: a comprehensive study of 661,062 patients. J Adolesc Health 70(6):922–927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2021.12.014
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Embree RA (1998) Attitudes toward elective abortion: preliminary evidence of validity for the personal beliefs scale. Psychol Rep 82(3 Pt 2):1267–1281. https://doi.org/10.2466/pr0.1998.82.3c.1267
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Evans JSTBT (2008) Dual-processing accounts of reasoning, judgment and social cognition. Ann Rev Psychol 59:255–278. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.59.103006.093629
Falkowski CK (2000) Locus of control, religious values, work values and social policy choices. Diss Abstracts Int. Sec B: Sci Eng 61:1694
Google Scholar
Felix., M., Sobel, L., & Salganicoff, A. (2023). Legal challenges to state abortion bans since the dobbs decision. Kaiser Family Foundation . Retrieved from https://www.kff.org/womens-health-policy/issue-brief/legal-challenges-to-state-abortion-bans-since-the-dobbs-decision/
Fischhoff B, Broomell SB (2020) Judgment and decision making. Ann Rev Psychol 71:331–355
Foster DG, Gould H, Taylor J, Weitz TA (2012) Attitudes and decision making among women seeking abortions at one U.S. clinic. Perspect Sexual Reprod Health 44(2):117–124. https://doi.org/10.1363/4411712
Hess JA, Rueb JD (2005) Attitudes toward abortion, religion, and party affiliation among college students. Curr Psychol 24(1):24–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-005-1002-0
Hill A (2004) The relationship between attitudes about abortion and cognitive complexity. UW-J Undergrad Res VII:1–6
ADS Google Scholar
Hodgkinson S, Beers L, Southammakosane C, Lewin A (2014) Addressing the mental health needs of pregnant and parenting adolescents. Pediatrics 133(1):114–122. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2013-0927
Hoffmann JP, Johnson SM (2005) Attitudes toward abortion among religious traditions in the United States: change or continuity. Soc Relig 66(2):161–182. https://doi.org/10.2307/4153084
Holman M, Podrazik E, Silber Mohamed H (2020) Choosing choice: how gender and religiosity shape abortion attitudes among Latinos. J Race Ethnicity Politics 5(2):384–411. https://doi.org/10.1017/%20rep.2019.51
Homaifar N, Freedman L, French V (2017) “She’s on her own”: a thematic analysis of clinicians’ comments on abortion referral. Contraception 95(5):470–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2017.01.007
Hunt ME (2019) Shifting Abortion Attitudes using an Empathy-based Media Intervention: a randomized controlled study. graduate theses and dissertations Retrieved from https://scholarworks.uark.edu/etd/3256
Jelen TG (2017) Public attitudes toward abortion and LGBTQ issues: a dynamic analysis of region and partisanship. SAGE Open 7(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244017697362
Jelen TG, Wilcox C (1997) Attitudes toward abortion in Poland and the United States. Soc Sci Q 78(4):907–921
Jelen TG, Wilcox C (2003) Causes and consequences of public attitudes toward abortion: a review and research agenda. Political Res Q 56(4):489–500. https://doi.org/10.2307/3219809
Kearney MS, Levine PB (2012) Why is the teen birth rate in the United States so high and why does it matter. J Econ Perspect 26(2):141–166. https://doi.org/10.1257/jep.26.2.141
Kim-Prieto C, Diener E, Tamir M, Scollon C, Diener M (2005) Integrating the diverse definitions of happiness: a time-sequential framework of subjective well-being. J Happiness Studies 6(3):261–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-005-7226-8
Klimecki O, Mayer S, Jusyte A et al. (2016) Empathy promotes altruistic behavior in economic interactions. Sci Rep 6:31961. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31961
Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Klimecki OM (2019) The role of empathy and compassion in conflict resolution. Emotion Rev 11(4):310–325
Krause N, Hayward RD (2013) Prayer beliefs and change in life satisfaction over time. J Relig Health 52:674–694
Lantos, H., Pliskin, E., Wildsmith, E., & Manlove, J. (2022). State-level abortion restrictions will negatively impact teens and children. Child Trend s. Retrieved from https://www.childtrends.org/blog/state-level-abortion-restrictions-will-negatively-impact-teens-and-children
Levenson H (1981) Differentiating among internality, powerful others, and chance. In: Lefcourt HM (Ed.) Research with the Locus of Control Construct. Academic Press, New York, NY, p 15–63. 10.1016/b978-0-12-443201-7.50006-3
Iles-Caven Y, Gregory S, Ellis G, Golding J, Nowicki S (2020) The relationship between locus of control and religious behavior and beliefs in a large population of parents: an observational study. Front Psychol 11:1462. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01462
Marton G, Pizzoli SFM, Vergani L, Mazzocco K, Monzani D, Bailo L, Pancani L, Pravettoni G (2021) Patients’ health locus of control and preferences about the role that they want to play in the medical decision-making process. Psychol Health Med 26(2):260–266. https://doi.org/10.1080/13548506.2020.1748211
Mollen D, Hargons C, Klann EM, Mosley DV (2018) Abortion knowledge and attitudes among psychologists and graduate students. Counseling Psychol 46(6):738–760. https://doi.org/10.1177/0011000018795296
Moudatsou M, Stavropoulou A, Philalithis A, Koukouli S (2020) The role of empathy in health and social care professionals. Healthcare 8(1):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8010026
Osborne D, Huang Y, Overall NC, Sutton RM, Petterson A, Douglas KM, Davies PG, Sibley CG (2022) Abortion attitudes: an overview of demographic and ideological differences. Political Psychol 43:29–76. https://doi.org/10.1111/pops.12803
Pew Research Center. (2022, May 17). Public Opinion on Abortion. Retrieved from https://www.pewresearch.org/religion/fact-sheet/public-opinion-on-abortion/
Pfattheicher S, Nockur L, Böhm R, Sassenrath C, Petersen MB (2020) The emotional path to action: empathy promotes physical distancing and wearing of face masks during the COVID-19 pandemic. Psychol Sci 31(11):1363–1373. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797620964422
Prusaczyk E, Hodson G (2018) Left-right differences in abortion policy support in America: clarifying the role of sex and sexism in a nationally representative 2016 sample. Person Individual Differ 127:22–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2018.01.030
Reknes I, Visockaite G, Liefooghe A, Lovakov A, Einarsen SV (2019) Locus of control moderates the relationship between exposure to bullying behaviors and psychological strain. Front Psychol 10:446169. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01323
Richardson M, Abraham C, Bond R (2012) Psychological correlates of university students’ academic performance: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol Bull 138(2):353–387. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0026838
Russo D, Masegosa AR, Stol KJ (2022) From anecdote to evidence: the relationship between personality and need for cognition of developers. Empir Software Eng 27:71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10664-021-10106-1
Rye BJ, Underhill A (2020) Pro-choice and pro-life are not enough: an investigation of abortion attitudes as a function of abortion prototypes. Sexuality Culture 24:1829–1851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12119-020-09723-7
Saad, L. (2023, June 21). Abortion remains a potent issue for pro-choice voters. Gallup . Retrieved from https://news.gallup.com/poll/507527/abortion-remains-potent-issue-pro-choice-voters.aspx
Sedgh G, Finer LB, Bankole A, Eilers MA, Singh S (2015) Adolescent pregnancy, birth, and abortion rates across countries: levels and recent trends. J Adolesc Health 56(2):223–30
Scott J (1989) Conflicting beliefs about abortion: legal approval and moral doubts. Soc Psychol Q 52(4):319–326. https://doi.org/10.2307/2786995
Shafir E, LeBoeuf RA (2002) Rationality. Ann Rev Psychol 53(1):491–517. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.53.100901.135213
Sohlberg J (2019) Elections are (not) exciting: need for cognition and electoral behaviour. Scand Political Stud 42(2):138–150. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9477.12138
Steffen J, Cheng J (2023) The influence of gain-loss framing and its interaction with political ideology on social distancing and mask wearing compliance during the COVID-19 pandemic. Curr Psychol 42(10):8028–8038. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-02148-x
Sundstrom B, Szabo C, Dempsey A (2018) “My Body. My Choice”: a qualitative study of the influence of trust and locus of control on postpartum contraceptive choice. J Health Commun 23(2):162–169. https://doi.org/10.1080/10810730.2017.1421728
Valdez D, Jozkowski KN, Haus K et al. (2022) Assessing rigid modes of thinking in self-declared abortion ideology: natural language processing insights from an online pilot qualitative study on abortion attitudes. Pilot Feasib Stud 8:127. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40814-022-01078-0
Verplanken B, Hazenberg PT, Palenéwen GR (1992) Need for cognition and external information search effort. J Res Person 26(2):128–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-6566(92)90049-A
Whitaker AK, Quinn MT, Martins SL, Tomlinson AN, Woodhams EJ, Gilliam M (2015) Motivational interviewing to improve postabortion contraceptive uptake by young women: development and feasibility of a counseling intervention. Contraception 92(4):323–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2015.06.015
Woodruff K, Biggs MA, Gould H, Foster DG (2018) Attitudes toward abortion after receiving vs. being denied an abortion in the USA. Sexuality Res Soc Policy 15(4):452–463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13178-018-0325-1
Xie W, Campbell S, Zhang W (2020) Working memory capacity predicts individual differences in social distancing compliance during the COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S. PNAS 117(30):17667–17674
Article ADS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Xu P, Cheng J (2021) Individual differences in social distancing and mask-wearing in the pandemic of COVID-19: the role of need for cognition, self-control and risk attitude. Person Individual Differ 175:110706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2021.110706
Young DG, Bagozzi BE, Goldring A, Poulsen S, Drouin E (2019) Psychology, political ideology, and humor appreciation: why is satire so liberal. Psychol Popular Media Culture 8(2):134–147. https://doi.org/10.1037/ppm0000157
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Northern Iowa, Cedar Falls, IA, 50614, USA
Jiuqing Cheng & Chloe Thostenson
Wenzhou University, Wenzhou, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JC: conceptualization, data curation and analysis, writing, review& editing; PX: conceptualization, writing, review; CT: conceptualization, data curation and analysis, review.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jiuqing Cheng .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional review board (IRB 23-0018) at the University of Northern Iowa with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Cheng, J., Xu, P. & Thostenson, C. Psychological traits and public attitudes towards abortion: the role of empathy, locus of control, and need for cognition. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11 , 23 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-02487-z
Download citation
Received : 18 July 2023
Accepted : 30 November 2023
Published : 02 January 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-02487-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

- MJC Library & Learning Center
- Research Guides
- Abortion Research
Start Learning About Your Topic
Create research questions to focus your topic, featured current news, find articles in library databases, find web resources, find books in the library catalog, cite your sources, key search words.
Use the words below to search for useful information in books and articles .
- birth control
- pro-choice movement
- pro-life movement
- reproductive rights
- Roe v. Wade
- Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization (Dobbs v. Jackson)
Background Reading:
It's important to begin your research learning something about your subject; in fact, you won't be able to create a focused, manageable thesis unless you already know something about your topic.
This step is important so that you will:
- Begin building your core knowledge about your topic
- Be able to put your topic in context
- Create research questions that drive your search for information
- Create a list of search terms that will help you find relevant information
- Know if the information you’re finding is relevant and useful
If you're working from off campus , you'll be prompted to sign in if you aren't already logged in to your MJC email or Canvas. If you are prompted to sign in, use the same credentials you use for email and Canvas.
Most current background reading
- Issues and Controversies: Should Women in the United States Have Access to Abortion? June 2022 article (written after the Supreme Court overturned Roe v Wade) that explores both sides of the abortion debate.
- Access World News: Abortion The most recent news and opinion on abortion from US newspapers.
More sources for background information
- CQ Researcher Online This link opens in a new window Original, comprehensive reporting and analysis on issues in the news. Check the dates of results to be sure they are sufficiently current.
- Gale eBooks This link opens in a new window Authoritative background reading from specialized encyclopedias (a year or more old, so not good for the latest developments).
- Gale In Context: Global Issues This link opens in a new window Best database for exploring the topic from a global point of view.
Choose the questions below that you find most interesting or appropriate for your assignment.
- Why is abortion such a controversial issue?
- What are the medical arguments for and against abortion?
- What are the religious arguments for and against abortion?
- What are the political arguments for and against abortion?
- What are the cultural arguments for and against abortion?
- What is the history of laws concerning abortion?
- What are the current laws about abortion?
- How are those who oppose access to abortion trying to affect change?
- How are those who support access to abortion trying to affect change?
- Based on what I have learned from my research, what do I think about the issue of abortion?
- State-by-State Abortion Laws Updated regularly by the Guttmacher Institute
- What the Data Says About Abortion in the U.S. From the Pew Research Center in June 2022, a look at the most recent available data about abortion from sources other than public opinion surveys.
Latest News on Abortion from Google News
All of these resources are free for MJC students, faculty, & staff.
- Gale Databases This link opens in a new window Search over 35 databases simultaneously that cover almost any topic you need to research at MJC. Gale databases include articles previously published in journals, magazines, newspapers, books, and other media outlets.
- EBSCOhost Databases This link opens in a new window Search 22 databases simultaneously that cover almost any topic you need to research at MJC. EBSCO databases include articles previously published in journals, magazines, newspapers, books, and other media outlets.
- Facts on File Databases This link opens in a new window Facts on File databases include: Issues & Controversies , Issues & Controversies in History , Today's Science , and World News Digest .
- MEDLINE Complete This link opens in a new window This database provides access to top-tier biomedical and health journals, making it an essential resource for doctors, nurses, health professionals and researchers engaged in clinical care, public health, and health policy development.
- Access World News This link opens in a new window Search the full-text of editions of record for local, regional, and national U.S. newspapers as well as full-text content of key international sources. This is your source for The Modesto Bee from January 1989 to the present. Also includes in-depth special reports and hot topics from around the country. To access The Modesto Bee , limit your search to that publication. more... less... Watch this short video to learn how to find The Modesto Bee .
Browse Featured Web Sites:
- American Association of Pro-Life Obstetricians and Gynecologists Medical information and anti-abortion rights advocacy.
- American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Use the key term "abortion" in the search box on this site for links to reports and statistics.
- Guttmacher Institute Statistics and policy papers with a world-wide focus from a "research and policy organization committed to advancing sexual and reproductive health and rights worldwide."
- NARAL Pro-Choice America This group advocates for pro-abortion rights legislation. Current information abortion laws in the U.S.
- National Right to Life Committee This group advocates for anti-abortion rights legislation in the U.S.
Why Use Books:
Use books to read broad overviews and detailed discussions of your topic. You can also use books to find primary sources , which are often published together in collections.
Where Do I Find Books?
You'll use the library catalog to search for books, ebooks, articles, and more.
What if MJC Doesn't Have What I Need?
If you need materials (books, articles, recordings, videos, etc.) that you cannot find in the library catalog , use our interlibrary loan service .
Your instructor should tell you which citation style they want you to use. Click on the appropriate link below to learn how to format your paper and cite your sources according to a particular style.
- Chicago Style
- ASA & Other Citation Styles
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 1:28 PM
- URL: https://libguides.mjc.edu/abortion
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0 and CC BY-NC 4.0 Licenses .
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- America’s Abortion Quandary
1. Americans’ views on whether, and in what circumstances, abortion should be legal
Table of contents.
- Abortion at various stages of pregnancy
- Abortion and circumstances of pregnancy
- Parental notification for minors seeking abortion
- Penalties for abortions performed illegally
- Public views of what would change the number of abortions in the U.S.
- A majority of Americans say women should have more say in setting abortion policy in the U.S.
- How do certain arguments about abortion resonate with Americans?
- In their own words: How Americans feel about abortion
- Personal connections to abortion
- Religion’s impact on views about abortion
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology
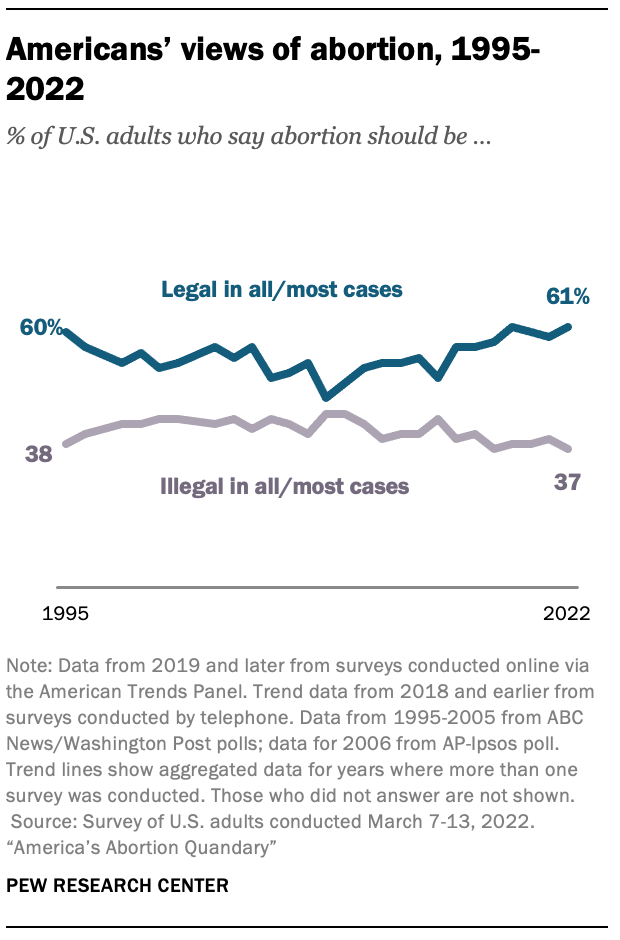
As the long-running debate over abortion reaches another key moment at the Supreme Court and in state legislatures across the country , a majority of U.S. adults continue to say that abortion should be legal in all or most cases. About six-in-ten Americans (61%) say abortion should be legal in “all” or “most” cases, while 37% think abortion should be illegal in all or most cases. These views have changed little over the past several years: In 2019, for example, 61% of adults said abortion should be legal in all or most cases, while 38% said it should be illegal in all or most cases. Most respondents in the new survey took one of the middle options when first asked about their views on abortion, saying either that abortion should be legal in most cases (36%) or illegal in most cases (27%).
Respondents who said abortion should either be legal in all cases or illegal in all cases received a follow-up question asking whether there should be any exceptions to such laws. Overall, 25% of adults initially said abortion should be legal in all cases, but about a quarter of this group (6% of all U.S. adults) went on to say that there should be some exceptions when abortion should be against the law.
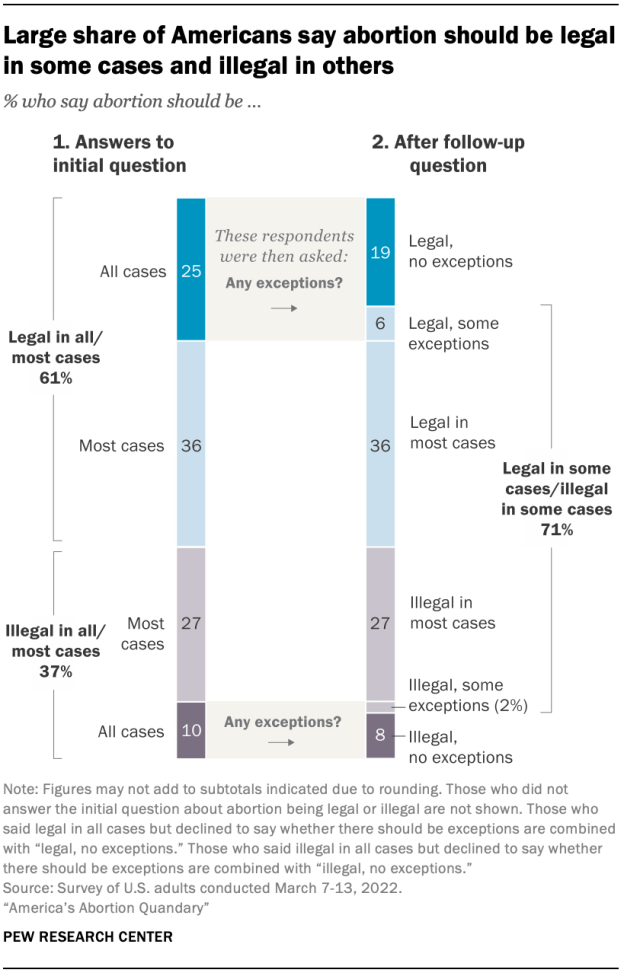
One-in-ten adults initially answered that abortion should be illegal in all cases, but about one-in-five of these respondents (2% of all U.S. adults) followed up by saying that there are some exceptions when abortion should be permitted.
Altogether, seven-in-ten Americans say abortion should be legal in some cases and illegal in others, including 42% who say abortion should be generally legal, but with some exceptions, and 29% who say it should be generally illegal, except in certain cases. Much smaller shares take absolutist views when it comes to the legality of abortion in the U.S., maintaining that abortion should be legal in all cases with no exceptions (19%) or illegal in all circumstances (8%).
There is a modest gender gap in views of whether abortion should be legal, with women slightly more likely than men to say abortion should be legal in all cases or in all cases but with some exceptions (63% vs. 58%).
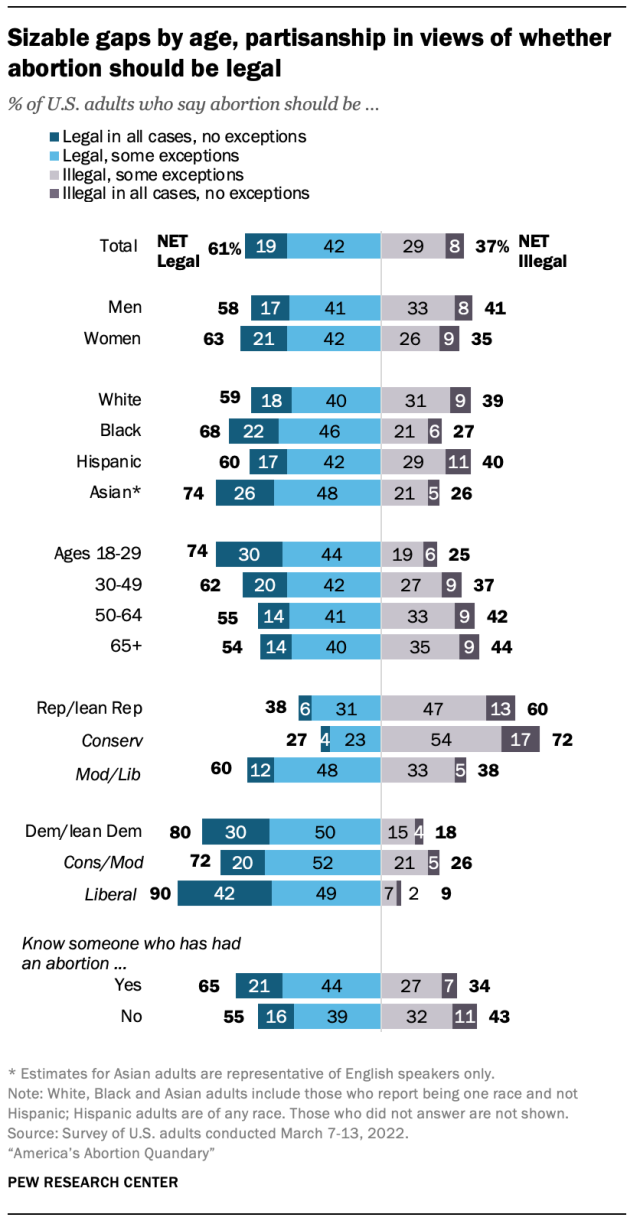
Younger adults are considerably more likely than older adults to say abortion should be legal: Three-quarters of adults under 30 (74%) say abortion should be generally legal, including 30% who say it should be legal in all cases without exception.
But there is an even larger gap in views toward abortion by partisanship: 80% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, compared with 38% of Republicans and GOP leaners. Previous Center research has shown this gap widening over the past 15 years.
Still, while partisans diverge in views of whether abortion should mostly be legal or illegal, most Democrats and Republicans do not view abortion in absolutist terms. Just 13% of Republicans say abortion should be against the law in all cases without exception; 47% say it should be illegal with some exceptions. And while three-in-ten Democrats say abortion should be permitted in all circumstances, half say it should mostly be legal – but with some exceptions.
There also are sizable divisions within both partisan coalitions by ideology. For instance, while a majority of moderate and liberal Republicans say abortion should mostly be legal (60%), just 27% of conservative Republicans say the same. Among Democrats, self-described liberals are twice as apt as moderates and conservatives to say abortion should be legal in all cases without exception (42% vs. 20%).
Regardless of partisan affiliation, adults who say they personally know someone who has had an abortion – such as a friend, relative or themselves – are more likely to say abortion should be legal than those who say they do not know anyone who had an abortion.
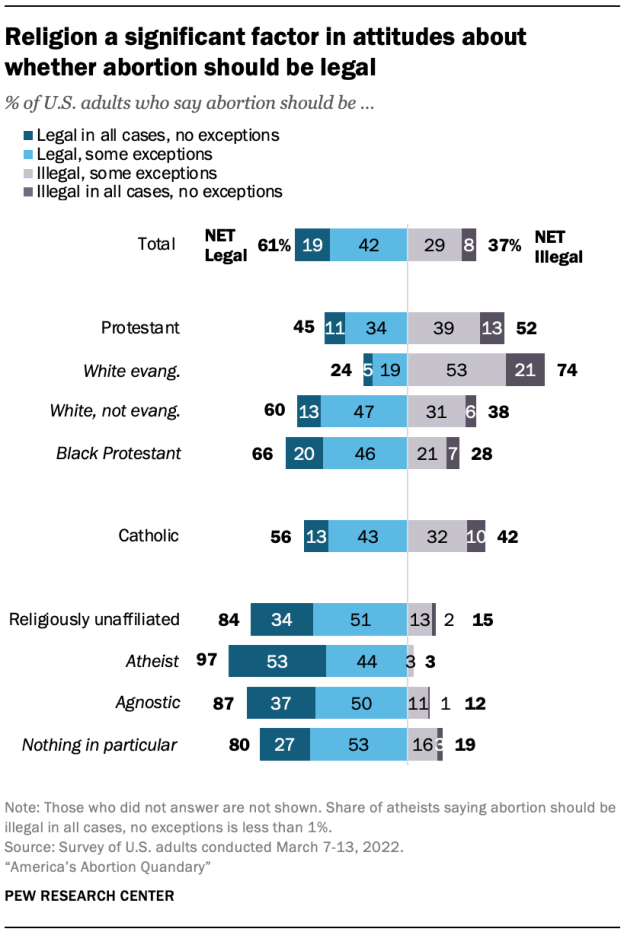
Views toward abortion also vary considerably by religious affiliation – specifically among large Christian subgroups and religiously unaffiliated Americans.
For example, roughly three-quarters of White evangelical Protestants say abortion should be illegal in all or most cases. This is far higher than the share of White non-evangelical Protestants (38%) or Black Protestants (28%) who say the same.
Despite Catholic teaching on abortion , a slim majority of U.S. Catholics (56%) say abortion should be legal. This includes 13% who say it should be legal in all cases without exception, and 43% who say it should be legal, but with some exceptions.
Compared with Christians, religiously unaffiliated adults are far more likely to say abortion should be legal overall – and significantly more inclined to say it should be legal in all cases without exception. Within this group, atheists stand out: 97% say abortion should be legal, including 53% who say it should be legal in all cases without exception. Agnostics and those who describe their religion as “nothing in particular” also overwhelmingly say that abortion should be legal, but they are more likely than atheists to say there are some circumstances when abortion should be against the law.
Although the survey was conducted among Americans of many religious backgrounds, including Jews, Muslims, Buddhists and Hindus, it did not obtain enough respondents from non-Christian groups to report separately on their responses.
As a growing number of states debate legislation to restrict abortion – often after a certain stage of pregnancy – Americans express complex views about when abortion should generally be legal and when it should be against the law. Overall, a majority of adults (56%) say that how long a woman has been pregnant should matter in determining when abortion should be legal, while far fewer (14%) say that this should not be a factor. An additional one-quarter of the public says that abortion should either be legal (19%) or illegal (8%) in all circumstances without exception; these respondents did not receive this question.
Among men and women, Republicans and Democrats, and Christians and religious “nones” who do not take absolutist positions about abortion on either side of the debate, the prevailing view is that the stage of the pregnancy should be a factor in determining whether abortion should be legal.
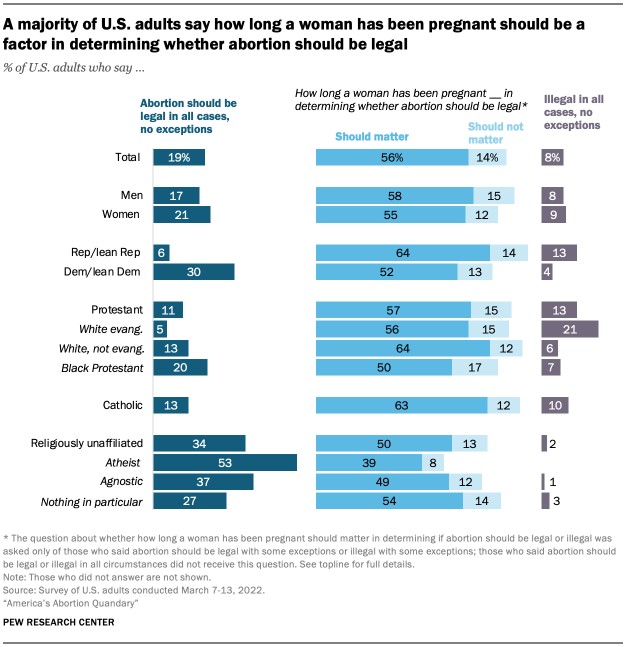
Americans broadly are more likely to favor restrictions on abortion later in pregnancy than earlier in pregnancy. Many adults also say the legality of abortion depends on other factors at every stage of pregnancy.
Overall, a plurality of adults (44%) say that abortion should be legal six weeks into a pregnancy, which is about when cardiac activity (sometimes called a fetal heartbeat) may be detected and before many women know they are pregnant; this includes 19% of adults who say abortion should be legal in all cases without exception, as well as 25% of adults who say it should be legal at that point in a pregnancy. An additional 7% say abortion generally should be legal in most cases, but that the stage of the pregnancy should not matter in determining legality. 1
One-in-five Americans (21%) say abortion should be illegal at six weeks. This includes 8% of adults who say abortion should be illegal in all cases without exception as well as 12% of adults who say that abortion should be illegal at this point. Additionally, 6% say abortion should be illegal in most cases and how long a woman has been pregnant should not matter in determining abortion’s legality. Nearly one-in-five respondents, when asked whether abortion should be legal six weeks into a pregnancy, say “it depends.”
Americans are more divided about what should be permitted 14 weeks into a pregnancy – roughly at the end of the first trimester – although still, more people say abortion should be legal at this stage (34%) than illegal (27%), and about one-in-five say “it depends.”
Fewer adults say abortion should be legal 24 weeks into a pregnancy – about when a healthy fetus could survive outside the womb with medical care. At this stage, 22% of adults say abortion should be legal, while nearly twice as many (43%) say it should be illegal . Again, about one-in-five adults (18%) say whether abortion should be legal at 24 weeks depends on other factors.
Respondents who said that abortion should be illegal 24 weeks into a pregnancy or that “it depends” were asked a follow-up question about whether abortion at that point should be legal if the pregnant woman’s life is in danger or the baby would be born with severe disabilities. Most who received this question say abortion in these circumstances should be legal (54%) or that it depends on other factors (40%). Just 4% of this group maintained that abortion should be illegal in this case.
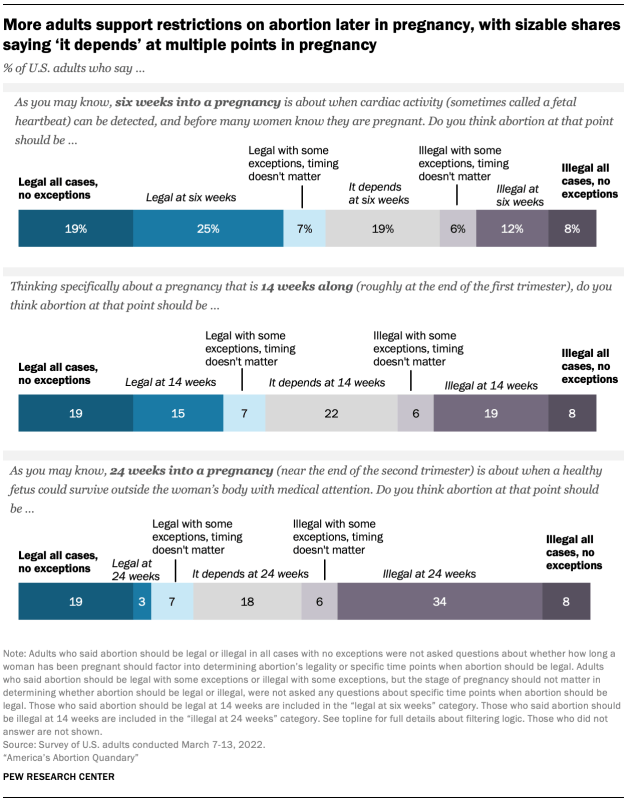
This pattern in views of abortion – whereby more favor greater restrictions on abortion as a pregnancy progresses – is evident across a variety of demographic and political groups.
Democrats are far more likely than Republicans to say that abortion should be legal at each of the three stages of pregnancy asked about on the survey. For example, while 26% of Republicans say abortion should be legal at six weeks of pregnancy, more than twice as many Democrats say the same (61%). Similarly, while about a third of Democrats say abortion should be legal at 24 weeks of pregnancy, just 8% of Republicans say the same.
However, neither Republicans nor Democrats uniformly express absolutist views about abortion throughout a pregnancy. Republicans are divided on abortion at six weeks: Roughly a quarter say it should be legal (26%), while a similar share say it depends (24%). A third say it should be illegal.
Democrats are divided about whether abortion should be legal or illegal at 24 weeks, with 34% saying it should be legal, 29% saying it should be illegal, and 21% saying it depends.
There also is considerable division among each partisan group by ideology. At six weeks of pregnancy, just one-in-five conservative Republicans (19%) say that abortion should be legal; moderate and liberal Republicans are twice as likely as their conservative counterparts to say this (39%).
At the same time, about half of liberal Democrats (48%) say abortion at 24 weeks should be legal, while 17% say it should be illegal. Among conservative and moderate Democrats, the pattern is reversed: A plurality (39%) say abortion at this stage should be illegal, while 24% say it should be legal.
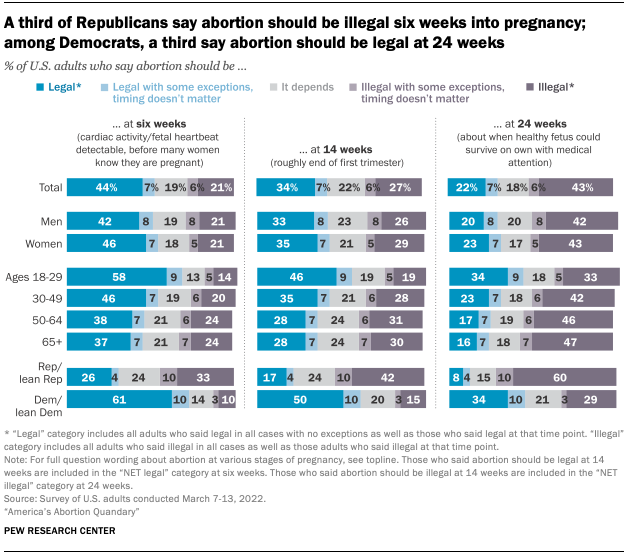
Christian adults are far less likely than religiously unaffiliated Americans to say abortion should be legal at each stage of pregnancy.
Among Protestants, White evangelicals stand out for their opposition to abortion. At six weeks of pregnancy, for example, 44% say abortion should be illegal, compared with 17% of White non-evangelical Protestants and 15% of Black Protestants. This pattern also is evident at 14 and 24 weeks of pregnancy, when half or more of White evangelicals say abortion should be illegal.
At six weeks, a plurality of Catholics (41%) say abortion should be legal, while smaller shares say it depends or it should be illegal. But by 24 weeks, about half of Catholics (49%) say abortion should be illegal.
Among adults who are religiously unaffiliated, atheists stand out for their views. They are the only group in which a sizable majority says abortion should be legal at each point in a pregnancy. Even at 24 weeks, 62% of self-described atheists say abortion should be legal, compared with smaller shares of agnostics (43%) and those who say their religion is “nothing in particular” (31%).
As is the case with adults overall, most religiously affiliated and religiously unaffiliated adults who originally say that abortion should be illegal or “it depends” at 24 weeks go on to say either it should be legal or it depends if the pregnant woman’s life is in danger or the baby would be born with severe disabilities. Few (4% and 5%, respectively) say abortion should be illegal at 24 weeks in these situations.
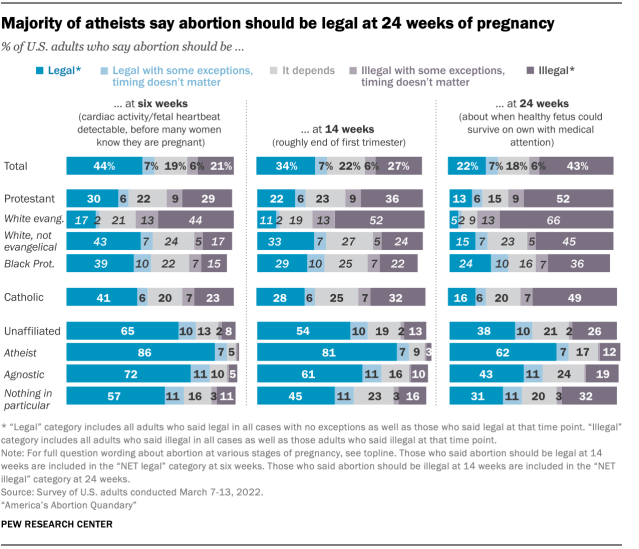
The stage of the pregnancy is not the only factor that shapes people’s views of when abortion should be legal. Sizable majorities of U.S. adults say that abortion should be legal if the pregnancy threatens the life or health of the pregnant woman (73%) or if pregnancy is the result of rape (69%).
There is less consensus when it comes to circumstances in which a baby may be born with severe disabilities or health problems: 53% of Americans overall say abortion should be legal in such circumstances, including 19% who say abortion should be legal in all cases and 35% who say there are some situations where abortions should be illegal, but that it should be legal in this specific type of case. A quarter of adults say “it depends” in this situation, and about one-in-five say it should be illegal (10% who say illegal in this specific circumstance and 8% who say illegal in all circumstances).
There are sizable divides between and among partisans when it comes to views of abortion in these situations. Overall, Republicans are less likely than Democrats to say abortion should be legal in each of the three circumstances outlined in the survey. However, both partisan groups are less likely to say abortion should be legal when the baby may be born with severe disabilities or health problems than when the woman’s life is in danger or the pregnancy is the result of rape.
Just as there are wide gaps among Republicans by ideology on whether how long a woman has been pregnant should be a factor in determining abortion’s legality, there are large gaps when it comes to circumstances in which abortions should be legal. For example, while a clear majority of moderate and liberal Republicans (71%) say abortion should be permitted when the pregnancy is the result of rape, conservative Republicans are more divided. About half (48%) say it should be legal in this situation, while 29% say it should be illegal and 21% say it depends.
The ideological gaps among Democrats are slightly less pronounced. Most Democrats say abortion should be legal in each of the three circumstances – just to varying degrees. While 77% of liberal Democrats say abortion should be legal if a baby will be born with severe disabilities or health problems, for example, a smaller majority of conservative and moderate Democrats (60%) say the same.
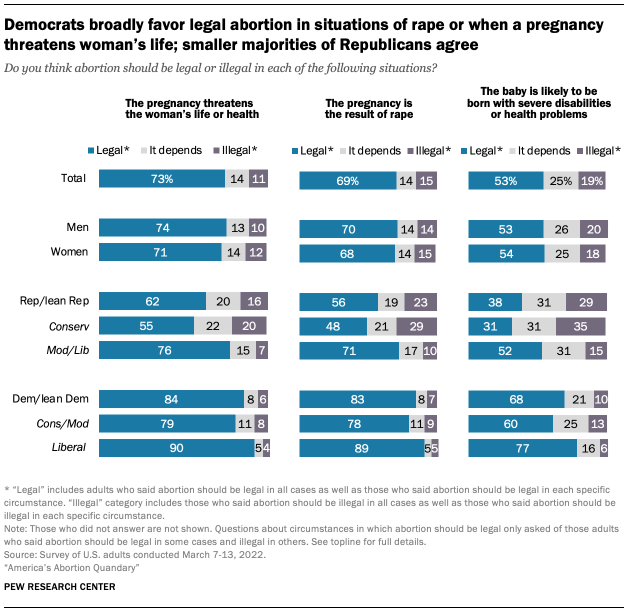
White evangelical Protestants again stand out for their views on abortion in various circumstances; they are far less likely than White non-evangelical or Black Protestants to say abortion should be legal across each of the three circumstances described in the survey.
While about half of White evangelical Protestants (51%) say abortion should be legal if a pregnancy threatens the woman’s life or health, clear majorities of other Protestant groups and Catholics say this should be the case. The same pattern holds in views of whether abortion should be legal if the pregnancy is the result of rape. Most White non-evangelical Protestants (75%), Black Protestants (71%) and Catholics (66%) say abortion should be permitted in this instance, while White evangelicals are more divided: 40% say it should be legal, while 34% say it should be illegal and about a quarter say it depends.
Mirroring the pattern seen among adults overall, opinions are more varied about a situation where a baby might be born with severe disabilities or health issues. For instance, half of Catholics say abortion should be legal in such cases, while 21% say it should be illegal and 27% say it depends on the situation.
Most religiously unaffiliated adults – including overwhelming majorities of self-described atheists – say abortion should be legal in each of the three circumstances.
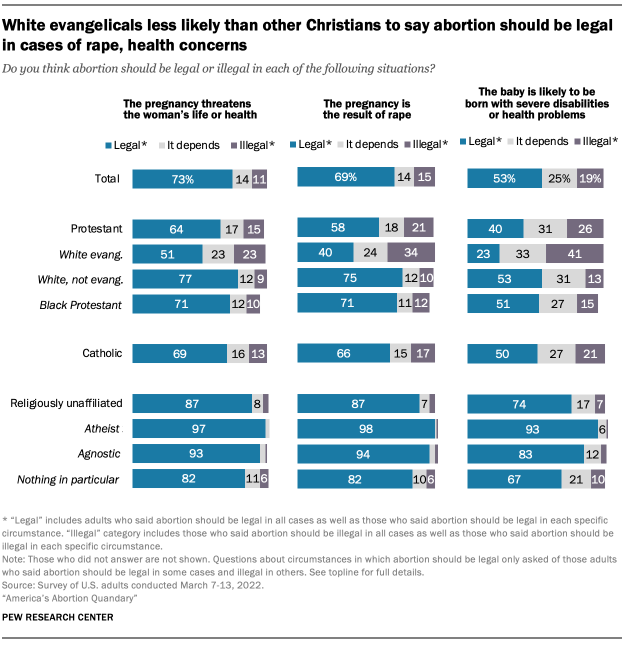
Seven-in-ten U.S. adults say that doctors or other health care providers should be required to notify a parent or legal guardian if the pregnant woman seeking an abortion is under 18, while 28% say they should not be required to do so.
Women are slightly less likely than men to say this should be a requirement (67% vs. 74%). And younger adults are far less likely than those who are older to say a parent or guardian should be notified before a doctor performs an abortion on a pregnant woman who is under 18. In fact, about half of adults ages 18 to 24 (53%) say a doctor should not be required to notify a parent. By contrast, 64% of adults ages 25 to 29 say doctors should be required to notify parents of minors seeking an abortion, as do 68% of adults ages 30 to 49 and 78% of those 50 and older.
A large majority of Republicans (85%) say that a doctor should be required to notify the parents of a minor before an abortion, though conservative Republicans are somewhat more likely than moderate and liberal Republicans to take this position (90% vs. 77%).
The ideological divide is even more pronounced among Democrats. Overall, a slim majority of Democrats (57%) say a parent should be notified in this circumstance, but while 72% of conservative and moderate Democrats hold this view, just 39% of liberal Democrats agree.
By and large, most Protestant (81%) and Catholic (78%) adults say doctors should be required to notify parents of minors before an abortion. But religiously unaffiliated Americans are more divided. Majorities of both atheists (71%) and agnostics (58%) say doctors should not be required to notify parents of minors seeking an abortion, while six-in-ten of those who describe their religion as “nothing in particular” say such notification should be required.
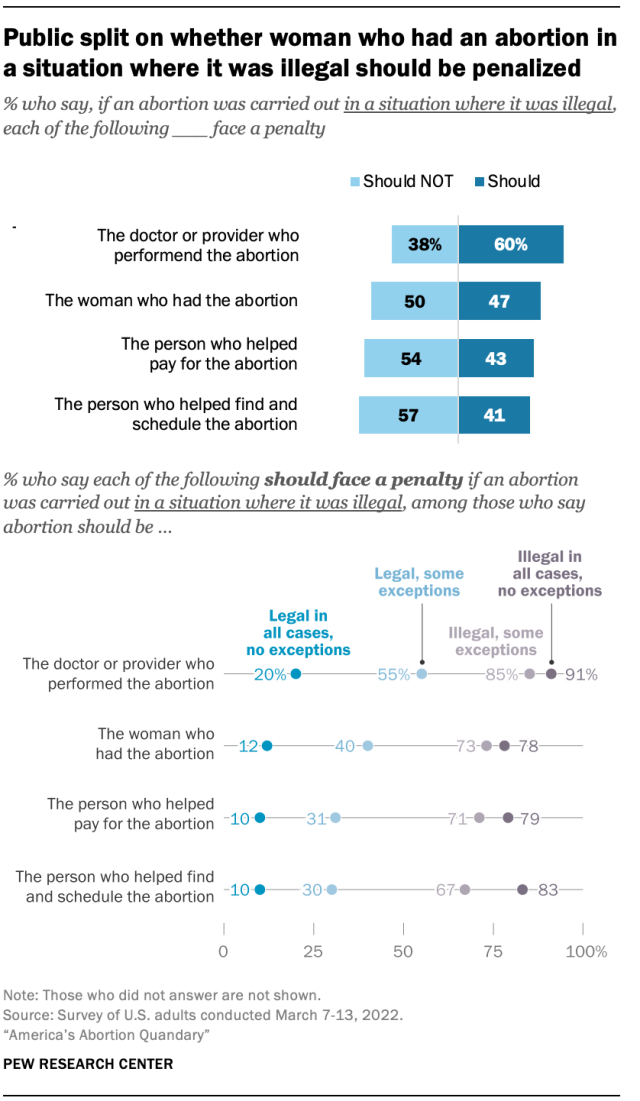
Americans are divided over who should be penalized – and what that penalty should be – in a situation where an abortion occurs illegally.
Overall, a 60% majority of adults say that if a doctor or provider performs an abortion in a situation where it is illegal, they should face a penalty. But there is less agreement when it comes to others who may have been involved in the procedure.
While about half of the public (47%) says a woman who has an illegal abortion should face a penalty, a nearly identical share (50%) says she should not. And adults are more likely to say people who help find and schedule or pay for an abortion in a situation where it is illegal should not face a penalty than they are to say they should.
Views about penalties are closely correlated with overall attitudes about whether abortion should be legal or illegal. For example, just 20% of adults who say abortion should be legal in all cases without exception think doctors or providers should face a penalty if an abortion were carried out in a situation where it was illegal. This compares with 91% of those who think abortion should be illegal in all cases without exceptions. Still, regardless of how they feel about whether abortion should be legal or not, Americans are more likely to say a doctor or provider should face a penalty compared with others involved in the procedure.
Among those who say medical providers and/or women should face penalties for illegal abortions, there is no consensus about whether they should get jail time or a less severe punishment. Among U.S. adults overall, 14% say women should serve jail time if they have an abortion in a situation where it is illegal, while 16% say they should receive a fine or community service and 17% say they are not sure what the penalty should be.
A somewhat larger share of Americans (25%) say doctors or other medical providers should face jail time for providing illegal abortion services, while 18% say they should face fines or community service and 17% are not sure. About three-in-ten U.S. adults (31%) say doctors should lose their medical license if they perform an abortion in a situation where it is illegal.
Men are more likely than women to favor penalties for the woman or doctor in situations where abortion is illegal. About half of men (52%) say women should face a penalty, while just 43% of women say the same. Similarly, about two-thirds of men (64%) say a doctor should face a penalty, while 56% of women agree.
Republicans are considerably more likely than Democrats to say both women and doctors should face penalties – including jail time. For example, 21% of Republicans say the woman who had the abortion should face jail time, and 40% say this about the doctor who performed the abortion. Among Democrats, far smaller shares say the woman (8%) or doctor (13%) should serve jail time.
White evangelical Protestants are more likely than other Protestant groups to favor penalties for abortions in situations where they are illegal. Fully 24% say the woman who had the abortion should serve time in jail, compared with just 12% of White non-evangelical Protestants or Black Protestants. And while about half of White evangelicals (48%) say doctors who perform illegal abortions should serve jail time, just 26% of White non-evangelical Protestants and 18% of Black Protestants share this view.
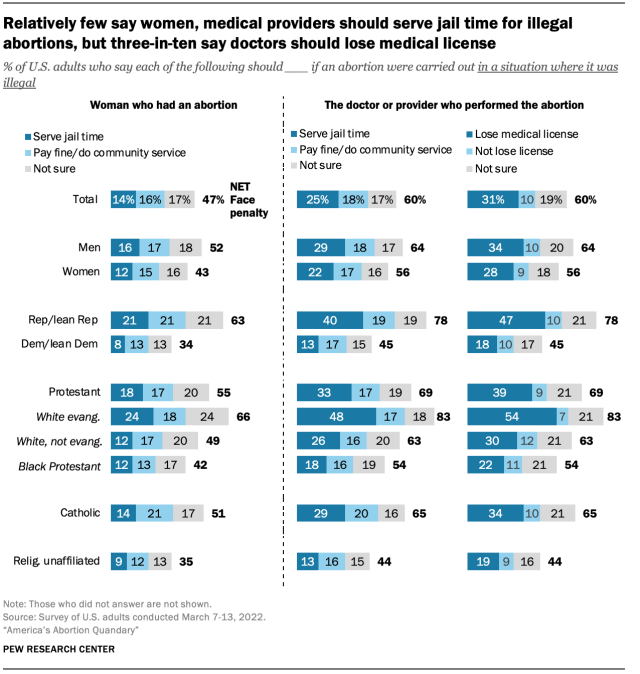
- Only respondents who said that abortion should be legal in some cases but not others and that how long a woman has been pregnant should matter in determining whether abortion should be legal received questions about abortion’s legality at specific points in the pregnancy. ↩
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Christianity
- Evangelicalism
- Political Issues
- Politics & Policy
- Protestantism
- Religion & Abortion
- Religion & Politics
- Religion & Social Values
Americans are less likely than others around the world to feel close to people in their country or community
Growing partisan divisions over nato and ukraine, as biden and trump seek reelection, who are the oldest – and youngest – current world leaders, more than 80% of americans believe elected officials don’t care what people like them think, voters’ views of trump and biden differ sharply by religion, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.

- May 10, 2024 • 27:42 Stormy Daniels Takes the Stand
- May 9, 2024 • 34:42 One Strongman, One Billion Voters, and the Future of India
- May 8, 2024 • 28:28 A Plan to Remake the Middle East
- May 7, 2024 • 27:43 How Changing Ocean Temperatures Could Upend Life on Earth
- May 6, 2024 • 29:23 R.F.K. Jr.’s Battle to Get on the Ballot
- May 3, 2024 • 25:33 The Protesters and the President
- May 2, 2024 • 29:13 Biden Loosens Up on Weed
- May 1, 2024 • 35:16 The New Abortion Fight Before the Supreme Court
- April 30, 2024 • 27:40 The Secret Push That Could Ban TikTok
- April 29, 2024 • 47:53 Trump 2.0: What a Second Trump Presidency Would Bring
- April 26, 2024 • 21:50 Harvey Weinstein Conviction Thrown Out
- April 25, 2024 • 40:33 The Crackdown on Student Protesters
Stormy Daniels Takes the Stand
The porn star testified for eight hours at donald trump’s hush-money trial. this is how it went..
Hosted by Michael Barbaro
Featuring Jonah E. Bromwich
Produced by Olivia Natt and Michael Simon Johnson
Edited by Lexie Diao
With Paige Cowett
Original music by Will Reid and Marion Lozano
Engineered by Alyssa Moxley
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music | YouTube
This episode contains descriptions of an alleged sexual liaison.
What happened when Stormy Daniels took the stand for eight hours in the first criminal trial of former President Donald J. Trump?
Jonah Bromwich, one of the lead reporters covering the trial for The Times, was in the room.
On today’s episode

Jonah E. Bromwich , who covers criminal justice in New York for The New York Times.

Background reading
In a second day of cross-examination, Stormy Daniels resisted the implication she had tried to shake down Donald J. Trump by selling her story of a sexual liaison.
Here are six takeaways from Ms. Daniels’s earlier testimony.
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Dan Farrell, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Renan Borelli, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson and Nina Lassam.
Jonah E. Bromwich covers criminal justice in New York, with a focus on the Manhattan district attorney’s office and state criminal courts in Manhattan. More about Jonah E. Bromwich
Advertisement
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Machine Learning
Title: kan: kolmogorov-arnold networks.
Abstract: Inspired by the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem, we propose Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) as promising alternatives to Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs). While MLPs have fixed activation functions on nodes ("neurons"), KANs have learnable activation functions on edges ("weights"). KANs have no linear weights at all -- every weight parameter is replaced by a univariate function parametrized as a spline. We show that this seemingly simple change makes KANs outperform MLPs in terms of accuracy and interpretability. For accuracy, much smaller KANs can achieve comparable or better accuracy than much larger MLPs in data fitting and PDE solving. Theoretically and empirically, KANs possess faster neural scaling laws than MLPs. For interpretability, KANs can be intuitively visualized and can easily interact with human users. Through two examples in mathematics and physics, KANs are shown to be useful collaborators helping scientists (re)discover mathematical and physical laws. In summary, KANs are promising alternatives for MLPs, opening opportunities for further improving today's deep learning models which rely heavily on MLPs.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Abortion research paper topics can study the health effects of different pregnancy termination methods, like medications and surgeries. You can write an abortion essay in psychology. For example, research strategies to cope with grief after pregnancy termination and the role of pre and post-abortion counseling.
Abortion Topics for Research Paper. Abortion is a topic that has different opinions and conversations. These are some topics you can explore when writing about abortion. Explore the possible side effects of abortion. Medical reasons for abortions. Different religions and their stands on abortion. History of abortion.
Looking for a good essay, research or speech topic on Abortion? Check our list of 245 interesting Abortion title ideas to write about! Clear. Writing Help Login Writing Tools. ... Abortion essay topics are often linked to the issue of women's rights. According to most feminists, abortion is related to women's bodily autonomy, and thus ...
Abortion argumentative essay topics typically revolve around the ethical, legal, and societal aspects of this controversial issue. These topics often involve debates and discussions, requiring students to present well-reasoned arguments supported by evidence and persuasive language. The Bodily Autonomy vs. Fetal Rights Debate: A Balancing Act.
The analysis of abortion by means of medical and social documents. Abortion means a pregnancy interruption "before the fetus is viable" [] or "before the fetus is able to live independently in the extrauterine environment, usually before the 20 th week of pregnancy" [].]. "Clinical miscarriage is both a common and distressing complication of early pregnancy with many etiological ...
Abortion services are a vital component of reproductive health care. Since the Supreme Court's 2022 ruling in Dobbs v.Jackson Women's Health Organization, access to abortion services has been increasingly restricted in the United States. Jung and colleagues review current practice and evidence on medication abortion, procedural abortion, and associated reproductive health care, as well as ...
Research on abortion decision-making and preferences has repeatedly demonstrated that aspects of the abortion process like accessibility, cost, privacy, confidentiality and security, legal risk, and being treated with dignity and respect are paramount in peoples' abortion decision-making and assessment of the quality of their abortion care. 15.
Abortion is a common medical or surgical intervention used to terminate pregnancy. Although a controversial and widely debated topic, approximately 73 million induced abortions occur worldwide each year, with 29% of all pregnancies and over 60% of unintended pregnancies ending in abortion. Abortions are considered safe if they are carried out using a method recommended by WHO, appropriate to ...
Introduction. Globally, access to safe abortion is limited. As a result, an estimated 25 million unsafe abortion occur each year, and at least 22 800 women die from resulting complications, almost all in low- and middle-income countries. 1 This is often due to restrictive laws which prohibit abortion; but even in contexts where abortion is legal, other barriers, such as cost, distance and ...
A country's abortion law is a key component in determining the enabling environment for safe abortion. While restrictive abortion laws still prevail in most low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), many countries have reformed their abortion laws, with the majority of them moving away from an absolute ban. However, the implications of these reforms on women's access to and use of health ...
Legal abortion is a safe clinical procedure, with extremely low rates of complications and death. 1 Conversely, the risk of death associated with childbirth is 14 times that associated with legal ...
Existing scholarship on abortion attitudes spans the "worldviews" and mobilizing tactics of activists [e.g., (3, 8, 9)]; dominant political and cultural messaging [e.g., (10-13)]; and how everyday Americans' views on legality correlate with personal demographic characteristics [e.g., (14, 15), see also ()].We add to this important work the concept of an abortion imaginary: a set of ...
1 Introduction. When the Institute of Medicine (IOM) 1 issued its 1975 report on the public health impact of legalized abortion, the scientific evidence on the safety and health effects of legal abortion services was limited ().It had been only 2 years since the landmark Roe v.Wade decision had legalized abortion throughout the United States and nationwide data collection was just under way ...
The Standardizing Abortion Research (STAR) outcomes project aims to define a core outcome set for abortion-related research. Abortion is a common experience worldwide, with an estimated 73 million abortions annually . Robust, well-developed clinical trials and guidelines on abortion provide information that can enhance safety, effectiveness ...
Abortion Articles for Research Paper & Other Sources Every research paper ends with "works cited" or a reference page enumerating the sources used for the assignment. A rule of thumb is to cite credible, authoritative publications from governmental organizations and NGOs and academic articles from peer-reviewed journals.
Abortion access is a component of economic justice because parenthood is expensive. In the USA, 49% of abortion patients have incomes below the poverty line and an additional 26% have low incomes; 73% of abortion patients list "can't afford a baby now" as one of their reasons, and 23% list it as "the most important reason".
Research has found that people's views on abortion tends to be stable over time (Jelen and Wilcox, 2003; Pew Research Center, 2022). As a result, it is possible that pre-existing empathy, rather ...
On May 15, 2019, the Alabama State Senate passed a bill that restricts the right to abortion by criminalising doctors who do the procedure. This was followed the next day by the Missouri State Senate passing a law forbidding abortions after 8 weeks of pregnancy. These two bills are the latest in a rapidly escalating attack on a woman's constitutionally protected right to an abortion. Alabama ...
Here are some examples to help you get started. Abortion Essay Titles. 1. The Abortion Dilemma: How Duty to Protect Life Gave Way to a Focus on Political Rights in the 1960s. 2. Pro-Choice Does Not Mean Pro-Murder: Why Women Who Would Never Personally Have an Abortion Still Support Others' Right to Have Them. 3.
From the Pew Research Center in June 2022, a look at the most recent available data about abortion from sources other than public opinion surveys. Two Republican state senators are expected to join Democrats in Arizona on Wednesday to pass a bill to repeal the 1864 abortion ban.
In "Association of Texas' 2021 Ban on Abortion in Early Pregnancy with the Number of Facility-Based Abortion in Texas and Surrounding States," White et al. used a large dataset containing information before and after the passage of SB8 in September 2021. 1 This bill banned most abortions after 6 weeks in the state of Texas.
Fewer adults say abortion should be legal 24 weeks into a pregnancy - about when a healthy fetus could survive outside the womb with medical care. At this stage, 22% of adults say abortion should be legal, while nearly twice as many (43%) say it should be illegal. Again, about one-in-five adults (18%) say whether abortion should be legal at ...
This episode contains descriptions of an alleged sexual liaison. What happened when Stormy Daniels took the stand for eight hours in the first criminal trial of former President Donald J. Trump?
Our focus is on quasi-experimental research because we are interested in studies evaluating the effect of population-level interventions (i.e., abortion law reform) with a design that permits inference regarding the causal effect of abortion legislation, which is not possible from other types of observational designs such as cross-sectional ...
Inspired by the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem, we propose Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) as promising alternatives to Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs). While MLPs have fixed activation functions on nodes ("neurons"), KANs have learnable activation functions on edges ("weights"). KANs have no linear weights at all -- every weight parameter is replaced by a univariate function ...