

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to ace the ap world history dbq: rubric, examples, and tips.
Advanced Placement (AP)
AP World History is a challenging class, and in order to get credit for it you’ll have to take an equally challenging exam. And one of the toughest parts of the test is the AP World History document-based question, or AP World DBQ. This question asks you to read and analyze documents on the fly, then write an argumentative essay…all in one hour.
It can be hard to know what–and how–to study for the AP World History DBQ, especially when you don’t know which documents you’ll receive on test day. But don’t worry: we’ll break down everything you need to know about the AP World History DBQ so you can ace it on test day. (We’ll even give you AP World History DBQ example questions and an AP World History DBQ rubric example!)
Here’s what we’ll cover:
- An explanation of what the AP World History DBQ is
- A look at how the DBQ works on the AP World History exam
- A step-by-step process for tackling the AP World History DBQ
- A guide to studying for and answering the AP World History DBQ
Let’s get going!

What Is an AP World History DBQ?
The document-based question (DBQ) is a question on the AP World History exam in which you are given a selection of seven documents and are asked to write an essay that incorporates information from at least six of them in a coherent argument based on a given prompt.
In other words: you’ll be writing an essay on a topic and incorporating resources that you’re given on the day of the exam!
The DBQ tests over a wide range of skills , like writing, organizing thoughts, making arguments, making connections between different perspectives, and having a knowledge of world history. Yeah, the DBQs are definitely tough! That’s why it’s important to understand what the DBQ APWH is and how to best tackle it.
How DBQs Work on the AP World History Exam
The DBQ format AP World History uses consists of a single open-ended prompt , and will focus on the time period of 1450-2001 .
Of the two free response questions, one is a long essay (worth 15%) and one is a DBQ. This means that the sole DBQ is, by itself, worth 25% of your total grade, making it the single most heavily-weighted question on the AP World History exam.
Here are some actual AP World History DBQ examples from previous years’ AP World History exams:
- “Evaluate the extent to which economic factors led to the outbreak of the Mexican Revolution (1910–1920).” ( 2021 )
- “Evaluate the extent to which the Portuguese transformed maritime trade in the Indian Ocean in the sixteenth century.” ( 2019 )
- “Evaluate the extent to which railroads affected the process of empire-building in Afro-Eurasia between 1860 and 1918.” ( 2018 )
Of course, one of the things that makes AP DBQ questions unique is that you’ll be given seven documents to analyze as part of your essay response. Not only will you have to read and analyze these documents on exam day, you’ll have to include them as evidence in your essay to prove your argument!
The seven documents you’ll receive will be a mixture of:
- Primary texts : texts that were actually written in the time period you’re being asked about
- Secondary texts : texts written by later historians that explain or interpret the time period
- Images: usually either political cartoons or artwork from the time period
How many of each type of document you get varies by year, so you’ll need to be comfortable using all three types to support an essay-based argument.
To answer the AP World History DBQ, you’ll have to read through all seven documents and write an argumentative essay that answers the prompt. So not only will you have to come up with an arguable point, you’ll have to prove that thesis using evidence contained in at least three of the seven documents. If you want to earn full credit for your DBQ, you’ll actually have to use six of the seven documents to support your position!

Just like in a sport, understanding how to score points on your DBQ is key to doing well on your exam.
Understand the AP World DBQ Rubric
First, y ou need to understand what the expectations are and how your answer will be graded. Doing this will help you figure out what you need to study and which skills you need to brush up on. It’ll also ensure that you know exactly what a great DBQ response requires so that you earn as many points as possible!
The good news is that the College Board has provided the AP World History DBQ rubric 2021 as part of their 2021 AP World History: Modern Sample Student Responses and Scoring Commentary document. The AP World History DBQ rubric contains all the information you need to know about how your response will be scored.
Here’s how the rubric breaks down:
Thesis (1 Point)
First you’ll need to create a thesis that “responds to the prompt with a historically defensible thesis/claim that establishes a line of reasoning.” In order to get this point you’ll need to make an arguable claim based on the documents that answers the question of the prompt.
Contextualization (1 Point)
In order to get a point for contextualization you’ll need to “accurately describe a context relevant” to the time period covered by the prompt. What this means is that you’ll have to describe the political, social, or economic events and trends that contributed to the topic you’re writing about.
Some of this you’ll know from the provided documents, but some of it you will also be expected to know based on what you’ve studied in AP World History class. You’ll also need to relate your knowledge to “broader historical events, developments, or processes that occur before, during, or continue after the time frame of the question.” In other words, you’ll have to show how the events of this time period are relevant now or how they are similar to some other historical situation.
Evidence (3 Points)
This category assigns points based on how well you use the documents provided to you on the test.
For this category, you get one of the potential three points solely for if you incorporate specific evidence that does not come from the provided documents in a way that is relevant to your thesis.
However, in order to earn the other two points, you must support your argument by using even more evidence from the documents provided . If you use three to five documents, you’ll earn an additional point. If you integrate six or more documents in your response, you can earn up to two points…and full credit for this category!
Just remember: You can’t just randomly throw information from the documents into your essay, though, you have to use it in a way that supports your argument and accurately represents what the documents are saying .
Analysis and Reasoning (2 Points)
For the analysis and reasoning section, you get one point for explaining “how or why the document’s point of view, purpose, historical situation, and/or audience is relevant to an argument,” and you get one point for “complexity,” showing that you understand the time period that the prompt covers and use evidence to prove your understanding and back up your argument .
Here’s what that means: you’ll have to prove how the documents are relevant to your argument, and your argument has to show that you understand the period you’re writing about. Additionally, you’ll need to write an essay that proves your argument in a way that shows you understand that there are a variety of possible perspectives about that time period or issue, and that not everyone in that period had the same experiences.

If all that sounds like a lot...that's because it is! But don't worry. We'll walk you through the steps you can take to get prepared for your DBQ.
5 Steps for Tackling an AP World History DBQ
The AP World History DBQ is a complicated question that tests you over several different skills, so there isn’t a simple technique to ace it. However, if you master each of the individual skills it takes to do well on the DBQ examples, you’ll set yourself up to write a successful DBQ! response!
Here are five steps you can follow to prepare for–and tackle!--the AP World History DBQ.
Step 1: Use Past AP World DBQ Prompts to Practice
Taking practice exams is a great way to prepare for any standardized test–including the AP World exam. Not only do you get a chance to test your knowledge, practice tests also give you the opportunity to familiarize yourself with the test format…which is really important when it comes to AP World DBQs.
There’s good news when it comes to AP World DBQ prompts, though. College Board’s website has the actual AP World DBQ prompts from 2002-2020 available to download. This means you can take almost 20 practice AP World History exams, as well as access AP World History DBQ example responses and AP World History DBQ rubrics, for free!
It’s good to take one practice test before you start studying intensely for it because that will let you know where your skills are now (and it’ll let you track your progress). However, the nature of a free response means that it won’t be easy for you to grade by yourself. When it comes to assessing your response, use the AP World History DBQ rubric and honestly assess whether or not you incorporated the information thoroughly and accurately. If that doesn’t work for you, you can always ask a family member, tutor, or teacher to give you feedback on your response as well!
Don’t be afraid to use multiple AP World DBQ prompts as part of your test prep strategy. The more DBQs you do, the better prepared you’ll be on test day!
Step 2: Practice Creating a Thesis
A thesis statement is a sentence or two, located in your essay’s introduction, that explains what your essay will be about. In this case, your thesis will outline the argument you make in your AP World DBQ.
The most important aspect of your thesis is that it has to make a claim that is both arguable and relevant to the prompt you’re given. However, you don’t want to just restate the prompt in your thesis!
Here’s what we mean. Say you’re given the following prompt:
“Evaluate the extent to which economic factors led to the outbreak of the Mexican Revolution (1910–1920).”
You don’t want your thesis to be “Economic factors led to the outbreak of the Mexican Revolution,” since that just restates the prompt without adding in your own argument. To write a great DBQ, you want to make a specific claim about how and why economic factors led to the Mexican Revolution, and you want to be able to use the AP World History DBQ documents provided to prove it!
Here are two AP World History DBQ examples that College Board considers acceptable theses for this prompt:
- “Mexico’s inability to resist the political dominance of the United States and European powers was the most significant factor in leading to the revolution because foreign dominance prevented the Mexican government from enacting economic reforms.”
- “Ethnic tensions were just as important in leading to the Mexican Revolution as economic factors because much of the economic exploitation that was occurring in Mexico affected poor indigenous communities.”
See how these two examples both make specific claims? The first argues that foreign influences prevented the Mexican government from enacting economic reforms. This is a claim that the author can prove by showing how foreign governments interfered with the Mexican government, and how that action led to reforms being stalled.
The second AP World History DBQ example thesis addresses something more complex: how ethnic tensions led to economic exploitation. The author can then use the provided documents as evidence that poor indigenous communities were exploited, and can argue that those actions led to the Mexican Revolution.

Outlines take a little time, but they'll keep your DBQ from derailing. (Staying on topic is key!)
Step 3: Practice Creating an Outline
Remember the AP World History DBQ is timed, and you’ll only have one hour to complete it! To keep your writing organized and on track, it’s a good idea for you to create a quick outline before you jump into writing your essay.
Having said that, you’ll need to be careful not to spend too much time on your outline so you have enough time to write your DBQ. That’s why we recommend spending 15 minutes reading documents, 5 minutes outlining your essay, and 40 minutes writing your response.
The most important things that your outline will need are an introduction and conclusion ! Your introduction sets up your thesis while your conclusion restates your thesis and explains how it’s relevant to the reader in some way–perhaps by showing that a similar claim could be made about another time period, or that the effects of the thesis are still being felt today.
Apart from your intro and conclusion, you’ll need body paragraphs. Since you only have about 45 minutes to write this essay, you don’t want too many of them. Three or four body paragraphs will be enough to make your argument. The most important thing about your body paragraphs is that each of them supports your argument and incorporates information from the documents!
To help you out, here is an example of a usable outline for the AP World History DBQ:
- Set up your argument and include your thesis.
- You can break down your thesis into several steps, which will then become the topics of each body paragraph
- Tell the reader what they need to know about the historical situation.
- Include any information you might already know from outside the provided documents.
- Make the first point you mentioned in your introduction.
- Use information from the documents to illustrate and prove your point.
- Include two or three documents that support your point
- Just like the previous paragraph, use two or three different documents to prove the second point of your thesis
- If you make a third point in your thesis, explain it here using one or two different documents as evidence
- Restate your thesis and summarize the main points you’ve made.
- Show how it’s relevant to the reader.
Your outline doesn’t need to be anything fancy–it just needs to give you an idea of how to structure your DBQ. Trust us: outlining might seem like a waste of time, but having a guide will make writing go much faster.
Step 4: Practice Incorporating Quotes and References
As you write your essay, you’ll need to use examples from the documents provided–and each time you do, you’ll need to indicate which documents you pulled the information from . You’ll do this whether you are quoting your source or just paraphrasing it.
Here are two attribution examples that College Board considers acceptable for the AP World History DBQ:
- (Document 1): “The finance minister tells strikers that unemployment is the result of supply and demand and is out of the government’s hands, a position which probably increased people’s discontent with the government because they were unwilling to help.”
- (Document 2): “The newspaper cartoon shows that the government was willing to use violence to put down popular protests against a rigged election system. Such oppressive government policies may have contributed to increased support for the eventual revolution.”
Note that both of these connect the contents of the document to the argument the author is trying to make. They don’t just paraphrase or quote the contents of the document for the sake of using them– you should use documents to support your argument!
Keep in mind that the College Board is pretty specific about how they want you to use AP World history DBQ documents. In the 2021 AP World History Scoring Guidelines rubric, College Board makes the point that you should “ describe and explain ” the contents of the document: By “describe'' they mean you should point out to your reader what about the document is relevant and illustrate it as if the reader did not have the document in front of them.
From there, you’ll need to explain the document. That means you should use the document to show the reader why changes or situations in history have happened or why there is a relationship between two factors you’re writing about.
Step 5: Understand Time Management
One of the most important skills you can acquire by taking multiple attempts at the AP World DBQ practice test will be time management.
When you’re in the actual test environment, you won’t be able to use your phone to set a timer or alarm, so it’ll be difficult to keep track of how much time you’re spending on reading and re-reading the documents, brainstorming, and outlining. You want to leave yourself the majority of the time allowed (which will be one hour) for writing.
College Board’s AP World History DBQ rubric recommends that you spend 15 minutes reading the documents and 45 minutes writing the essay . When you write your practice DBQs, be sure to use this format so you can get a feel for how much time you do (or don’t!) have for the question. Practicing with a timer is a great way to make sure you’re using your time wisely on test day!

4 Tips for Studying for and Answering the AP World History DBQs
Now that you’ve read our step-by-step process for tackling the AP World History DBQ and have seen several AP World History DBQ examples, here are some expert tips on doing well on the AP World History DBQ . We’ve developed these tips based on the AP World History rubric to make sure you earn as many points as possible!
Tip 1: Know Your Rubric
Go through the AP World History DBQ rubric 2021 and notice that it tells you exactly how to earn points in each category . Most categories are worth multiple points, so you need to know how to earn all the points possible.
For example, the rubric is clear about how to earn points for your thesis statement. You’ll have to make sure that you have a thesis that states outright what argument you are trying to make if you want to earn credit for that category of the rubric!
The scoring for the DBQ is pretty objective, and knowing exactly what the scorers are looking for will help you earn the most points possible.
Tip 2: Your Essay Can Contain Errors
In an AP World History DBQ, you’ll be able to make tiny errors and still be able to earn full credit for your response.
Before you get too excited, there are big (and we mean big!) limits to this rule. For instance, you can’t misrepresent a document by saying an author makes one claim when they clearly aren’t. You also can’t write something that is obviously wrong, like that America continues under British rule because the revolution was unsuccessful!
But you can make minor errors that don’t detract from your argument as long as you are demonstrating a knowledge of the time period and the ability to incorporate evidence to make an argument. So for example, you can make the mistake of saying that President Nixon’s impeachment hearings began in July 1974 (instead of May, when they actually began), and still earn full credit as long as you aren’t making an argument that depends on the accuracy of those dates.
Tip 3: Write for Clarity
One thing to keep in mind is that you’re graded on the quality of your argument and how well you prove it– you don’t get graded on how beautifully or fluently you write !
So, while you’ll want to use correct grammar and write as clearly as you can, don’t spend too much time making your writing beautiful. Instead, focus on clearly explaining your ideas!
To this end, you won’t have points taken away for grammatical errors unless they make it difficult for the graders to see how you’ve used the evidence to make an argument. So while you want your writing to be as error-free as possible, it’s more important that you’re making your argument as clearly–and as persuasively–as possible.
Tip 4: Write for Relevance
As you’re outlining and writing your AP World DBQ, ask yourself, why is this relevant to today’s readers? To earn a perfect score, you’ll have to tie your argument to another time period or historical situation.
This is your chance to show that while the period you’re writing about may have been long in the past, the events are still relevant to us today ! This is why we read, write, and study history in the first place. So as you outline and write your DBQ, make sure you’re doing your best to show your reader why this historical moment or event is still important.

What’s Next?
No matter what AP course you’re taking, you’ll want to have a study plan in place when it comes to exam time. This blog article can help you put together a prep strategy that works.
Not sure what a “good” AP test score is for AP World History? This list of the average AP test scores for every exam will help you understand how your scores stack up.
Perfect test scores are great, but do you really need a perfect AP World History score? Our experts will explain the pros and cons of getting perfect 5s on your AP exams .

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
4 Steps to Writing a Good APUSH Long Essay

- Patterns of connectivity (argue whether history changed or remained the same)
- Compare and contrast
- Periodization
No matter which type of essay you face, here are 4 steps to help you write a good APUSH long essay.
Focus on Writing a Solid Thesis
Your thesis is the most important part. It’s going to set up the entire essay. It’s also the first thing that the grader is going to see, so start with a strong thesis!
Your introductory paragraph should be about 2-5 sentences in length. Start with a hook before including your thesis . Your thesis should be original. Don’t just copy the question prompt!
Make sure that your thesis contains the following three things:
- Your stance (or answer) to the prompt
- A counterargument to address
- The 3 strongest supporting points for your thesis
Describe and Explain Your Supporting Points
To support your thesis, you need three specific examples. If you’re having a hard time coming up with examples, think about PERSIA : political, economic, religious, social, intellectual, and artistic.
Describe each example as much as possible. Then, don’t forget to reflect back to the thesis. This is the most important part, so spend plenty of time circling back to the thesis for each point.

Make Connections
When writing the body paragraphs, try to connect to events from different time periods, geographical areas, and themes whenever possible. Making connections is especially important when it comes to the rebuttal for your argument.
Synthesis across history is important to show that you have a deep understanding of U.S. history and that you’ve developed the historical thinking skills you need.
Don’t Forget the Conclusion
Some people skip over the conclusion . With only 35 minutes to write a polished essay, they would rather spend time developing the introductory and body paragraphs.
However, if you’ve practiced your timing for the APUSH long essay, you should have a few extra minutes for a conclusion. The conclusion should restate your thesis and strongest points in different words.
You’ve spent the entire school year preparing for your APUSH long essay. You’ve studied the concepts and themes. You have the information that you need to write a 6-worthy essay. Follow these tips as you practice writing APUSH long essays, so you can practice crafting these essays within the 35-minute time period. The more you practice, the better prepared you’ll be to write your essay on exam day.

Jamie graduated from Brigham Young University- Idaho with a degree in English Education. She spent several years teaching and tutoring students at the elementary, high school, and college level. She currently works as a contract writer and curriculum developer for online education courses. In her free time, she enjoys running and spending time with her boys!
View all posts
More from Magoosh

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

AP® US History
Ensuring your students earn the contextualization point on the dbq.
- The Albert Team
- Last Updated On: March 1, 2022

The redesign has brought a great deal of uncertainty and confusion amongst APUSH teachers. In many ways, we are all “rookie” teachers, as all of us have the challenge of implementing fundamental curricular and skills-based changes into our classrooms.
One of the more significant changes is to the structure of one essay on the AP® exam, the Document Based question (DBQ). The rubric for the DBQ was previously a more holistic essay that combined a strong thesis, and use of documents and outside information to support the argument. This has been transformed into a much more structured and formulaic skills-based rubric. The change has led to a healthy debate about the pros and cons of both types of essays, but in general the core of the essay has remained the same: write a thesis and support it with evidence in the form of documents and outside information. If students continue to apply these basic writing skills, they are likely to earn 3 or 4 out of the seven total points for the Document Based Question .
In this post, we will explore one of these points students will be looking to earn to help their chances at passing the APUSH exam this May: the Contextualization point.
What is Contextualization?
According to the College Board, contextualization refers to a:
Historical thinking skill that involves the ability to connect historical events and processes to specific circumstances of time and place as well as broader regional, national, or global processes. ( College Board AP® Course and Exam Description, AP® US History, Fall 2015 )
Contextualization is a critical historical thinking skill that is featured in the newly redesigned course. In my opinion, this is a skill of fundamental importance for students to utilize in the classroom. Often times, students find history difficult or boring because they don’t see connections between different historical time periods and the world they live in today. They assume that events occur in a vacuum, and don’t realize that the historical context is critical in helping explain people’s beliefs and points of view in that period of time. Putting events into context is something I always thought was important, but now that the College Board explicitly has established the skill, it has forced me to be more proactive in creating lessons and assignments that allow students to utilize this way of thinking.
The place that contextualization is most directly relevant on the actual AP® exam itself is the Document Based Question. In order to earn the point for contextualization, students must:
Situate historical events, developments, or processes within the broader regional, national, or global context in which they occurred in order to draw conclusions about their relative significance. (College Board AP® Course and Exam Description, AP® US History, Fall 2015)
In other words, students are asked to provide background before jumping right into their thesis and essay and paint a picture of what is going on at the time of the prompt. Although there is no specific requirement as to where contextualization should occur, it makes natural sense to place it in the introduction right before a thesis point. Placing this historical background right at the beginning sets the stage for the argument that will occur in the body of the essay, and is consistent with expectations many English teachers have in how to write an introduction paragraph.
I explain contextualization to students by using the example of Star Wars. Before the movie starts, the film begins with “A long time ago in a galaxy far, far away…” and continues with background information on the characters, events, and other information that is crucial to understanding the film. Without this context, the viewer would not know what is going on, and might miss key events or be lost throughout the film. This is what contextualization aims to do in student essays. It sets the stage for their thesis, evidence, and argument that is to follow.
Contextualization vs. Historical Context
One aspect of the DBQ rubric that can be a bit confusing initially is that students are asked to do this contextualization, but there is also another area which gives them the option to use historical context. So what is the difference?
Contextualization refers to putting the entire essay into a broader context (preferably in the introduction). However, when writing their essays, students are also required to analyze four of the documents that they utilize by either examining the author’s point of view, describing the intended audience of the source, identifying the author’s purpose or putting the source into historical context. The latter sounds similar to contextualization (and it is essentially the same skill), but historical context is only focused on the specific document being analyzed, not the entire essay, like the contextualization point. For example, if a document is a map that shows slavery growing dramatically from 1820 to 1860, a student might point out that this growth can be explained in the context of the development of the cotton gin, which made the production of cotton much more profitable and let to the spread of slavery in the Deep South. While essentially the same skill, historical context focuses on one specific document’s background.
Examples of Successful Student Contextualization Points
One of the biggest pitfalls that prevent students from earning the contextualization point is that they are too brief or vague. In general, it would be difficult for students to earn the point if they are writing only a sentence or two. Early in the year, I assigned students a DBQ based on the following prompt:
Evaluate the extent in which the Civil War was a turning point in the lives of African Americans in the United States. Use the documents and your knowledge of the years 1860-1877 to construct your response.

This was the third DBQ we had written, and students were now getting brave enough to move beyond a thesis and document analysis and started attempting to tackle the contextualization point. However, the attempts were all over the map. One student wrote:
The Civil War was a bloody event that led to the death of thousands of Americans.
Of course this is a true statement, but is extremely vague. What led to the Civil War? Why was it so deadly? Without any specific detail, this student could not earn the contextualization point.
Another student wrote:
Slavery had existed for hundreds of years in the United States. It was a terrible thing that had to be abolished.
Again, this is a drive-by attempt at earning contextualization. It mentions things that are true, but lacks any meaningful details or explanation that would demonstrate understanding of the time period in discussion. What led to the beginning of slavery in the colonies? How did it develop? What made it so horrible? How did individuals resist and protest slavery? These are the types of details that would add meaning to contextualization.
One student nailed it. She wrote:
The peculiar institution of slavery had been a part of America’s identity since the founding of the original English colony at Jamestown. In the early years, compromise was key to avoiding the moral question, but as America entered the mid 19th century sectional tensions and crises with popular sovereignty, Kansas, and fugitive slaves made the issue increasingly unavoidable. When the Civil War began, the war was transformed from one to simply save the Union to a battle for the future of slavery and freedom in the United States.
Now THAT is contextualization! It gives specific details about the beginning of slavery and its development. It discusses attempts at compromise, but increasing sectional tensions that led to the Civil War. The writer paints a vivid and clear picture of the situation, events, and people that set the stage for the Civil War. Students don’t want to write a 6-8 sentence paragraph (they will want to save time for their argument in the body), but they need to do more than write a vague sentence that superficially addresses the era.
Strategies for Teaching Contextualization to Students
Analyze Lots of Primary Sources One of the best ways to prepare for the DBQ is for students to practice reading and comprehending primary source texts, particularly texts that are written by people who use very different language and sentence structure from today. This helps them understand and analyze documents, but it also can be helpful in practicing contextualization. Looking at different perspectives and points of view in the actual historical time periods they are learning is key in allowing students to understand how the era can impact beliefs, values and events that occur.
Assign Many DBQ Assessments and Share Specific Examples The more often students write DBQs, the more comfortable students will get with the entire process and skill set involved, including contextualization. One thing that has been especially successful in my classroom is to collect a handful of student attempts at the contextualization point and share them with students. Students then get to examine them and look at effective and less effective attempts at earning contextualization. Often the best way for students to learn what to do or how to improve is to see what their classmates have done.
Incorporating In-Class Activities The course is broken into nine distinct time periods from 1491 to present. In each period or unit students are assigned activities that force them to put a specific policy, event, or movement into context. For example, we did lecture notes on the presidency of JFK, learning about the Man on the Moon Speech, Cuban Missile Crisis, and creation of the Peace Corps. Students had to write 3-4 sentences that asked them to put these events in historical context using the Cold War. This allowed students to understand that each of these seemingly unrelated historical events were shaped by the tension between the United States and Soviet Union: winning the space race, stopping a communist nuclear threat less than 100 miles from Florida, and spreading goodwill into nations that might otherwise turn to communism all are strategies the United States used to thwart the Soviet threat. By doing this activity, students gain an appreciation for how historical context shapes events and decisions of the day.

Teach Cause and Effect in United States History It is very easy to get caught up as a teacher in how to best get lots of minutia and factoids into students heads quickly and efficiently. However, if we can teach history not as a series of independent and unrelated events, but as a series of events that have a causal relationship that impact what happens next, this helps students grasp and understand contextualization. For example, in the lead-up to World War I, students create a timeline of events that led to America entering the conflict. As students examine the torpedoing of the Lusitania, unrestricted submarine warfare, the Zimmermann telegram, etc., they gain an understanding that it was not a random decision by President Wilson, but rather a series of events that precipitated the declaration of war. This is what contextualization is: the background that sets the stage for a particular moment in American history.
Examine Contextualization with Current Events I know what you are thinking, I have one school year (less if your school year starts in September) to get through 1491 to Present and now I am supposed to make this a current events class as well? The answer is yes and no. Will stuff from the news pages be content the students need to know for the exam: absolutely not. However, it is a great opportunity for students to understand that our past explains why our country is what it is today.
For example, President Obama’s decision to work towards normalizing relations with Cuba makes more sense if students think about it through the lens of contextualization. The United States invaded Cuba in 1898 in the Spanish-American War and set up a protectorate. Cubans, upset with what they perceived as U.S. meddling and intervention led a communist revolution in 1959, ousting the American-backed government and setting the stage for one of the scariest moments in the Cold War : the Cuban Missile Crisis. Looking at how the past shapes current events today helps students understand this skill, and it also helps them gain a deeper appreciation of how important history is in shaping the world around them.

Any time changes happen, there is a temptation to be reactionary and reject them. I have found that by being more deliberate about helping students understand historical context, their engagement and understanding have improved significantly. Teachers always are fighting that battle between covering the content (which is daunting in an AP® course) and helping students understand the “so what?” question. Why does this matter to me? By making connections, students can see that history does not every happen in a vacuum. Our shared narrative is a series of events and ideas that continuously evolve and build off of each other. When students gain a firm understanding of how the past impacts their lives today, it makes learning way more meaningful and fun.
Contextualization is tough for students at first, but it is a skill application that can be perfected and improved to maximize your students’ chances of earning that point and rocking the AP® exam.
Looking for AP® US History practice?
Kickstart your AP® US History prep with Albert. Start your AP® exam prep today .
We also go over five-steps to writing effective FRQs for AP® US History in this video:

Ben Hubing is an educator at Greendale High School in Greendale, Wisconsin. Ben has taught AP® U.S. History and AP® U.S. Government and Politics for the last eight years and was a reader last year for the AP® U.S. History Short Answer. Ben earned his Bachelors degree at The University of Wisconsin-Madison and Masters degree at Cardinal Stritch University in Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
Interested in a school license?
4 thoughts on “ensuring your students earn the contextualization point on the dbq”.
great very helpful!
Glad it helped!
Very useful, thank you.
Glad it was helpful!
Comments are closed.
Popular Posts

AP® Score Calculators
Simulate how different MCQ and FRQ scores translate into AP® scores

AP® Review Guides
The ultimate review guides for AP® subjects to help you plan and structure your prep.

Core Subject Review Guides
Review the most important topics in Physics and Algebra 1 .

SAT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall SAT® score

ACT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall ACT® score

Grammar Review Hub
Comprehensive review of grammar skills

AP® Posters
Download updated posters summarizing the main topics and structure for each AP® exam.
Calculate for all schools
Your chance of acceptance, your chancing factors, extracurriculars, creating a thesis for ap lit.
This year, I'm taking AP Lit and I'm struggling with writing thesis statements for my essays. Does anyone have any tips or insight on how to write a solid thesis statement for AP Lit essays?
I can definitely give you some advice on how to create a solid thesis statement for your AP Lit essays. In AP Lit, your thesis statement should provide a clear, original, and specific claim about your chosen literary work, which your essay will then analyze and support with textual evidence.
Here are a few steps you can follow to create a strong thesis statement:
1. Read the prompt carefully: Make sure you understand what the prompt is asking you to do, whether it's analyzing a specific aspect of the text, exploring a theme, or discussing a particular character.
2. Choose a clear and specific focus: Decide what aspect of the work you want to explore, such as characterization, theme, symbolism, or structure. Your thesis statement should be specific enough that your analysis doesn't become too broad or unfocused.
3. Make an original claim: Your thesis statement should present an original argument or interpretation, rather than merely stating an obvious fact or restating the prompt. Make sure your claim is one that can be both supported by evidence from the text and challenged by other interpretations.
4. Include some direction for your essay: A strong thesis statement not only makes a claim but also gives some indication of how your essay will support that claim. This helps guide your reader and sets up the organization of your essay.
For example: In The Great Gatsby , F. Scott Fitzgerald uses the contrasting settings of East Egg, West Egg, and the Valley of Ashes to illustrate the corrupting influence of wealth and social class on the characters and their ultimate disillusionment with the American Dream.
In this thesis statement, the focus is on the contrasting settings and their impact on the characters, making a specific claim about the author's intent. It provides direction for the essay, indicating that the writer will explore how Fitzgerald uses these settings to convey his message.
Remember, writing a strong thesis statement takes practice, so keep working at it and tweaking it until you feel confident in your ability to craft a well-argued and coherent claim about the text. Good luck in your AP Lit class!
About CollegeVine’s Expert FAQ
CollegeVine’s Q&A seeks to offer informed perspectives on commonly asked admissions questions. Every answer is refined and validated by our team of admissions experts to ensure it resonates with trusted knowledge in the field.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

Why universities turn to the police to end student protests − and why that can spiral out of control
Professor Emeritus of Criminal Justice, University of Alabama at Birmingham
Disclosure statement
John J Sloan, III has received funding from the National Science Foundation, Bureau of Justice Assistance, Office of Community Oriented Policing, and the National Institute of Justice.
View all partners
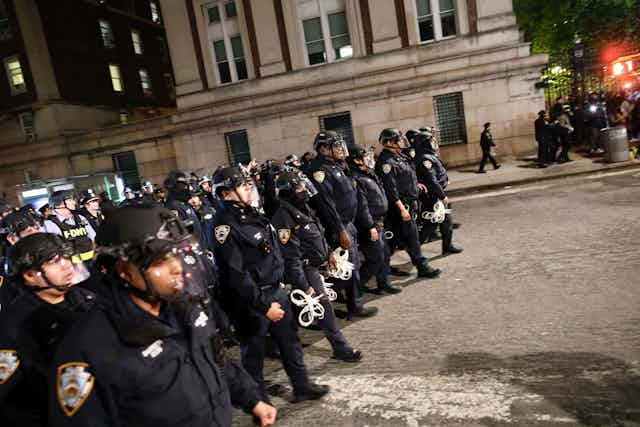
A two-week standoff between Columbia University administration and student protesters who advocated for the school to divest from companies that work in or support Israel culminated on April 30, 2024, one day after a group of students occupied a campus building, Hamilton Hall.
New York police arrested 109 demonstrators at Columbia and 173 other demonstrators at City College, in uptown Manhattan, on April 30.
The Conversation U.S. politics and society editor Amy Lieberman spoke with John J. Sloan III , a scholar of crime and police on college campuses at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, to better understand the different roles that police play on university and college campuses.

How do universities differ in working with police?
The first documented appearance of a sworn police officer patrolling a college campus was in 1894 at Yale University.
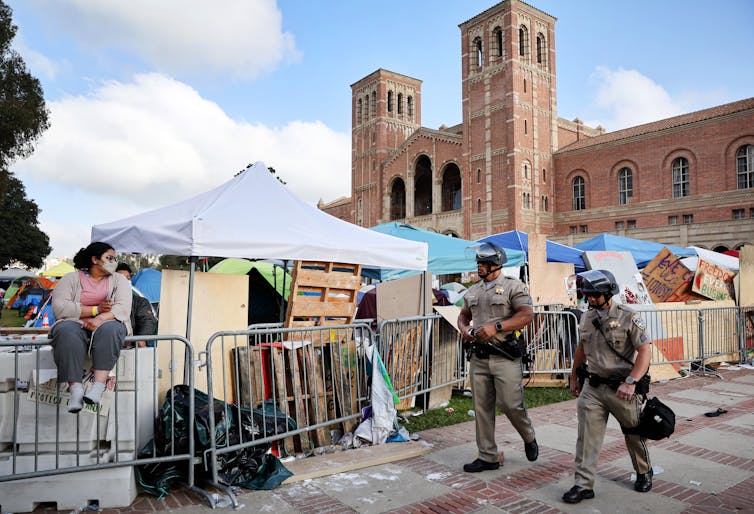
Generally, there have been two approaches to police on university or college campuses. Initially, university administrators asked local police to respond to issues with antiwar demonstrators during the Vietnam War and with women’s rights protests in the 1960s. When many of those encounters did not go very well for anyone , campus police departments were created. Today, about two-thirds of universities and colleges – mainly public ones, like University of California, Los Angeles – have their own campus police departments . There is no difference between these campus police officers and their municipal counterparts, in terms of training or legal authority.
Another one-third of colleges and universities ultimately chose to instead hire their own private security guards – not police officers. Columbia and other Ivy League schools, as well as other private institutions like Johns Hopkins University, are in this group. Increasingly, many of these guards are armed .
One reason different options were taken was because the legalities of creating a police department at a private school are more complex than are those for creating police departments at public universities. Aside from these logistics, there have also been image concerns about whether schools really wanted to have armed, uniformed police on their campuses.
Does this difference in police or private security matter, practically?
Colleges and universities that have their own police departments frequently have a memorandum of understanding or mutual aid agreement that formalizes the relationship between campus and municipal police. Often, both groups will train together to better coordinate their response to, say, a mass shooting on campus. It’s likely that in the post-George Floyd era, mutual training included responding to campus protests.
For schools without campus police, security personnel may lack extensive training in how to deal with demonstrations. As a result, things can spiral very quickly. I would imagine that Columbia’s president made the most recent call to bring in the NYPD because of a combination of factors – including that private security personnel may not have been fully trained and equipped to address the situation, plus the perceived urgency of the situation of students taking over a university building.
What else is notable about how different schools have responded to these protests?
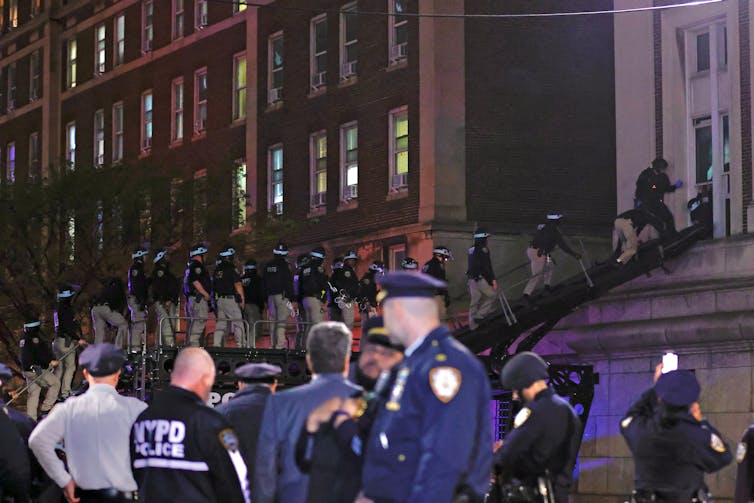
There appears to be a wide range in both university and police responses to the protests. On the one end is the Columbia situation, where you literally had NYPD officers using drones and other types of military tactics to take the building back that the students first occupied on April 29.
At the University of Wisconsin, Madison – which has its own campus police department – the university president also made the decision to call in the Madison police , perhaps for different reasons. This gets to the question of how university administrators want to deal with these protests. Do they want to wait out the protesters? And if they don’t want to wait them out, then how quickly do they want the campus cleared?
I certainly understand there is a need to ensure that the campus is secure. But when you invite local or state police to campus to address protests, you are turning over control of the situation to them and you are relying on them having the necessary training and preparation to come in and not create more problems. What I have seen so far, at least, is those who have called in outside law enforcement are going to have to answer questions about the use of force that was used against protesters.

What is important to know about the police’s tactical response to the protests?
New York Mayor Eric Adams spoke at a press conference and explained the NYPD’s approach to entering and clearing the Columbia campus and it reminded me of military tactics. He talked about how the NYPD had drones flying around to pinpoint better access points into the building and where the students were. He discussed encrypting the police’s radio frequency, so no one could listen to them. The garb that the police were wearing and the visuals of so many officers marching down the street reminded me of an army.
Adams said that no one was hurt at Columbia, but there are reports that show three students were hurt , as well as potentially some police officers. There have also been reports of police officers being injured at University of Wisconsin, Madison.
In other places, like UCLA, there has been a heavy outside police presence on campus, as well as reports of police officers using pepper spray and tear gas on protesters there and in other places like Florida . And at the University of Texas, Austin, officials called in state troopers to arrest protesters this week. Police using pepper spray and other aggressive tactics were reported there as well.
Part of this phenomenon involves the extent the police, nationwide, are becoming more and more militarized as a standard operating procedure. The Ohio State University purchased a surplus military armored personnel carrier for its police team in 2013, for example.
In the post-9/11 era, initial law enforcement concerns were with terrorism; now, the concern is mass shooters. In response, many police departments, including those at colleges and universities, are now routinely using military-grade surveillance, communications, equipment and training as part of their operations, such that it can look like you have the military on your campus .
- Anti-Semitism
- US campus protests
- Demonstrations
- 2024 campus protests
- Columbia University

Scheduling Analyst

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship

Executive Dean, Faculty of Health

Lecturer/Senior Lecturer, Earth System Science (School of Science)

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
By practicing thesis writing, you'll be able to create a detailed-and defensible!--statement that will help you create a convincing DBQ argument. An outline will serve as a roadmap that'll help you write a great essay—and it'll help you manage your time, too. Step 3: Practice Creating an Outline
If you're taking AP World History or AP United States History and feel unsure about how to approach the DBQ thesis, you've come to the right place! In this post, you'll learn about a DBQ thesis formula that you can use to: A) consistently earn the thesis point and
Types of Thesis Statements: 1. Direct: This a straightforward statement that clearly and directly answers the question. To a remarkable degree Jacksonian democrats succeeded in implementing their vision of American society. 2. Compound: Use this approach when trying to prove two main points. Use the word "and.".
A good idea is to write a concluding paragraph that might extend your original thesis. Think of a way to restate your thesis, adding information from your analysis of the documents. The thesis is that part of your essay that 1) specifically addresses the terms of the question and 2) sets up the structure for the rest of your essay.
Step 1: Analyze the Prompt. Each long essay question will ask you to "evaluate the extent" of some factor in American history. Since you are evaluating, you will need to develop an argument that addresses the prompt. Make sure to read all three prompts carefully. Think of the evidence you could use and the argument you could develop in ...
During Step 1: Analyze the Prompt. Use the 15-minute reading period to read the documents and organize them into groups for analysis. Feel free to write notes in the test booklet and underline important words in both the source line and the document itself. Nothing in the booklet is read as part of the essay scoring.
The thesis statement of an AP History essay is the most critical element of the essay. It will be establishing the basis of the entire paper, and if done properly will outline a comprehensive well-thought out essay. For this reason, a lot of planning needs to be done for the thesis statement as your examples and phrasing could be the key to a ...
Start with a Clearly Stated Thesis. Some good essay writers begin with a thesis statement, back it up with supporting evidence from documents and outside knowledge, and, if time permits, restate the thesis at the end. Other writers analyze the material and build up logically to their thesis statement. On an AP Exam, you should use whichever ...
AP US History DBQ example 1. Google Classroom. About. Transcript. The document-based question (DBQ) is one of two main essays on the AP US History exam and usually requires analyzing changes or continuities over time in US history. In this video, learn about the structure of DBQs and tips and tricks to help you succeed on this challenging part ...
Don't be afraid to use multiple AP World DBQ prompts as part of your test prep strategy. The more DBQs you do, the better prepared you'll be on test day! Step 2: Practice Creating a Thesis. A thesis statement is a sentence or two, located in your essay's introduction, that explains what your essay will be about.
And while obviously I can't sit here and write a whole essay on the screen, I do wanna outline things for you, and give you a general sense of what you could talk about where. For the DBQ we're gonna do a standard five-paragraph essay, which means introduction. . . with a thesis statement, paragraph 1, paragraph 2, paragraph 3.
Resources from Heimler's History: To master all the WRITING SKILLS you need, get my ESSAY CRAM COURSE: +AP Essay CRAM Course (DBQ, LEQ, SAQ Help): https://bi...
All documents are used as evidence to support a claim. The essay makes a complex and nuanced argument supported by strong evidence and analysis that goes beneath the surface. This sample essay was written in order to provide teachers and students with possible approaches to completing the AP US History DBQ.
Thesis Statement Dos and Don'ts. DO: Directly answer the question being asked. Be specific. Write a thesis statement like the first example. Don't: Answer the question in a confusing way or answer some other question you think the test SHOULD be asking. Be general. Synthesis in Document Based Questions. This is a newer component of the DBQ.
1. Respond to the prompt. Your thesis must be a specific answer to the actual prompt, not a variation of the prompt or something more generally on the topic of the prompt. This means that you have to read the question multiple times and identify everything you must do to address it. It's a good idea to mark up the prompt and underline key words.
In this video, I review how to write an introduction and thesis statement for AP free-response questions, and document-based questions. If you would like to ...
The prompts fall into 4 categories: Patterns of connectivity (argue whether history changed or remained the same) Compare and contrast. Causation. Periodization. No matter which type of essay you face, here are 4 steps to help you write a good APUSH long essay.
The intent of this question was to assess students' ability to articulate and defend an argument based on evidence provided by a select set of historical documents. The Document-Based Question (DBQ) asked students to evaluate the extent to which European imperialism had an impact on the economies of Africa and/or Asia.
Use the documents and your knowledge of the years 1860-1877 to construct your response. This was the third DBQ we had written, and students were now getting brave enough to move beyond a thesis and document analysis and started attempting to tackle the contextualization point. However, the attempts were all over the map.
AP United States History. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday ...
Use the word "and.". Jacksonian democrats successfully portrayed themselves as guardians of American ideals and did indeed achieve a remarkable degree of success in protecting those ideals. 3. Split:This approach splits the thesis into several categories. In essence it combines the thesis statement with the plan of attack/themes of the essay.
Step 1: Start with a question. You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis, early in the writing process. As soon as you've decided on your essay topic, you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
4. Develop your thesis statement: Practice creating clear and concise thesis statements that directly address the prompt. A strong thesis will help guide the rest of your essay. 5. Practice outlining: Time management is crucial during the DBQ. Before diving into writing the essay, quickly outline your main points, document connections, and ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Here are a few steps you can follow to create a strong thesis statement: 1. Read the prompt carefully: Make sure you understand what the prompt is asking you to do, whether it's analyzing a specific aspect of the text, exploring a theme, or discussing a particular character. 2. Choose a clear and specific focus: Decide what aspect of the work ...
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
One of the most unsettling statistics from the recent survey is that 32% of Americans think that "rule by a strong leader or the military would be a good way of governing their country."
Disclosure statement. John J Sloan, III has received funding from the National Science Foundation, Bureau of Justice Assistance, Office of Community Oriented Policing, and the National Institute ...