
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications. If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Search Menu
- Advance articles
- Editor's Choice
- Supplements
- French Abstracts
- Portuguese Abstracts
- Spanish Abstracts
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- About International Journal for Quality in Health Care
- About the International Society for Quality in Health Care
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Contact ISQua
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
Primacy of the research question, structure of the paper, writing a research article: advice to beginners.
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Thomas V. Perneger, Patricia M. Hudelson, Writing a research article: advice to beginners, International Journal for Quality in Health Care , Volume 16, Issue 3, June 2004, Pages 191–192, https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzh053
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Writing research papers does not come naturally to most of us. The typical research paper is a highly codified rhetorical form [ 1 , 2 ]. Knowledge of the rules—some explicit, others implied—goes a long way toward writing a paper that will get accepted in a peer-reviewed journal.
A good research paper addresses a specific research question. The research question—or study objective or main research hypothesis—is the central organizing principle of the paper. Whatever relates to the research question belongs in the paper; the rest doesn’t. This is perhaps obvious when the paper reports on a well planned research project. However, in applied domains such as quality improvement, some papers are written based on projects that were undertaken for operational reasons, and not with the primary aim of producing new knowledge. In such cases, authors should define the main research question a posteriori and design the paper around it.
Generally, only one main research question should be addressed in a paper (secondary but related questions are allowed). If a project allows you to explore several distinct research questions, write several papers. For instance, if you measured the impact of obtaining written consent on patient satisfaction at a specialized clinic using a newly developed questionnaire, you may want to write one paper on the questionnaire development and validation, and another on the impact of the intervention. The idea is not to split results into ‘least publishable units’, a practice that is rightly decried, but rather into ‘optimally publishable units’.
What is a good research question? The key attributes are: (i) specificity; (ii) originality or novelty; and (iii) general relevance to a broad scientific community. The research question should be precise and not merely identify a general area of inquiry. It can often (but not always) be expressed in terms of a possible association between X and Y in a population Z, for example ‘we examined whether providing patients about to be discharged from the hospital with written information about their medications would improve their compliance with the treatment 1 month later’. A study does not necessarily have to break completely new ground, but it should extend previous knowledge in a useful way, or alternatively refute existing knowledge. Finally, the question should be of interest to others who work in the same scientific area. The latter requirement is more challenging for those who work in applied science than for basic scientists. While it may safely be assumed that the human genome is the same worldwide, whether the results of a local quality improvement project have wider relevance requires careful consideration and argument.
Once the research question is clearly defined, writing the paper becomes considerably easier. The paper will ask the question, then answer it. The key to successful scientific writing is getting the structure of the paper right. The basic structure of a typical research paper is the sequence of Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion (sometimes abbreviated as IMRAD). Each section addresses a different objective. The authors state: (i) the problem they intend to address—in other terms, the research question—in the Introduction; (ii) what they did to answer the question in the Methods section; (iii) what they observed in the Results section; and (iv) what they think the results mean in the Discussion.
In turn, each basic section addresses several topics, and may be divided into subsections (Table 1 ). In the Introduction, the authors should explain the rationale and background to the study. What is the research question, and why is it important to ask it? While it is neither necessary nor desirable to provide a full-blown review of the literature as a prelude to the study, it is helpful to situate the study within some larger field of enquiry. The research question should always be spelled out, and not merely left for the reader to guess.
Typical structure of a research paper
The Methods section should provide the readers with sufficient detail about the study methods to be able to reproduce the study if so desired. Thus, this section should be specific, concrete, technical, and fairly detailed. The study setting, the sampling strategy used, instruments, data collection methods, and analysis strategies should be described. In the case of qualitative research studies, it is also useful to tell the reader which research tradition the study utilizes and to link the choice of methodological strategies with the research goals [ 3 ].
The Results section is typically fairly straightforward and factual. All results that relate to the research question should be given in detail, including simple counts and percentages. Resist the temptation to demonstrate analytic ability and the richness of the dataset by providing numerous tables of non-essential results.
The Discussion section allows the most freedom. This is why the Discussion is the most difficult to write, and is often the weakest part of a paper. Structured Discussion sections have been proposed by some journal editors [ 4 ]. While strict adherence to such rules may not be necessary, following a plan such as that proposed in Table 1 may help the novice writer stay on track.
References should be used wisely. Key assertions should be referenced, as well as the methods and instruments used. However, unless the paper is a comprehensive review of a topic, there is no need to be exhaustive. Also, references to unpublished work, to documents in the grey literature (technical reports), or to any source that the reader will have difficulty finding or understanding should be avoided.
Having the structure of the paper in place is a good start. However, there are many details that have to be attended to while writing. An obvious recommendation is to read, and follow, the instructions to authors published by the journal (typically found on the journal’s website). Another concerns non-native writers of English: do have a native speaker edit the manuscript. A paper usually goes through several drafts before it is submitted. When revising a paper, it is useful to keep an eye out for the most common mistakes (Table 2 ). If you avoid all those, your paper should be in good shape.
Common mistakes seen in manuscripts submitted to this journal
Huth EJ . How to Write and Publish Papers in the Medical Sciences , 2nd edition. Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins, 1990 .
Browner WS . Publishing and Presenting Clinical Research . Baltimore, MD: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, 1999 .
Devers KJ , Frankel RM. Getting qualitative research published. Educ Health 2001 ; 14 : 109 –117.
Docherty M , Smith R. The case for structuring the discussion of scientific papers. Br Med J 1999 ; 318 : 1224 –1225.
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1464-3677
- Print ISSN 1353-4505
- Copyright © 2024 International Society for Quality in Health Care and Oxford University Press
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Summer 2024 Admissions Open Now. Sign up for upcoming live information sessions here (featuring former and current Admission Officers at Havard and UPenn).
How to Write a Research Paper

Undergrads often write research papers each semester, causing stress. Yet, it’s simpler than believing if you know how to write a research paper . Divide the task, get tips, a plan, and tools for an outstanding paper. Simplify research, writing, topic choice, and illustration use!
A research paper is an academic document that involves deep, independent research to offer analysis, interpretation, and argument. Unlike academic essays, research papers are lengthier and more detailed, aiming to evaluate your writing and scholarly research abilities. To write one, you must showcase expertise in your subject, interact with diverse sources, and provide a unique perspective to the discussion.
Research papers are a foundational element of contemporary science and the most efficient means of disseminating knowledge throughout a broad network. Nonetheless, individuals usually encounter research papers during their education; they are frequently employed in college courses to assess a student’s grasp of a specific field or their aptitude for research.
Given their significance, research papers adopt a research paper format – a formal, unadorned style that eliminates any subjective influence from the writing. Scientists present their discoveries straightforwardly, accompanied by relevant supporting proof, enabling other researchers to integrate the paper into their investigations.
This guide leads you through every steps to write a research paper , from grasping your task to refining your ultimate draft and will teach you how to write a research paper.
Understanding The Research Paper
A research paper is a meticulously structured document that showcases the outcomes of an inquiry, exploration, or scrutiny undertaken on a specific subject. It embodies a formal piece of academic prose that adds novel information, perspectives, or interpretations to a particular domain of study. Typically authored by scholars, researchers, scientists, or students as part of their academic or professional pursuits, these papers adhere to a well-defined format. This research paper format encompasses an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
The introduction provides context and outlines the study’s significance, while the literature review encapsulates existing research and situates the study within the broader academic discourse. The methodology section elucidates the research process, encompassing data collection and analysis techniques. Findings are presented in the results section, often complemented by graphical and statistical representations. Interpretation of findings, implications, and connection to existing knowledge transpire in the discussion section.
Ultimately, the conclusion encapsulates pivotal discoveries and their wider import.
Research papers wield immense significance in advancing knowledge across diverse disciplines, enabling researchers to disseminate findings, theories, and revelations to a broader audience. Before publication in academic journals or presentations at conferences, these papers undergo a stringent peer review process conducted by domain experts, ensuring their integrity, precision, and worth.
Academic and non-academic research papers diverge across several dimensions. Academic papers are crafted for scholarly circles to expand domain knowledge and theories. They maintain a formal, objective tone and heavily rely on peer-reviewed sources for credibility. In contrast, non-academic papers, employing a more flexible writing style, target a broader audience or specific practical goals. These papers might incorporate persuasive language, anecdotes, and various sources beyond academia. While academic papers rigorously adhere to structured formats and established citation styles, non-academic papers prioritize practicality, adapting their structure and citation methods to suit the intended readership.
The purpose of a research paper revolves around offering fresh insights, knowledge, or interpretations within a specific field. This formal document serves as a conduit for scholars, researchers, scientists, and students to communicate their investigative findings and actively contribute to the ongoing academic discourse.

Research Paper Writing Process – How To Write a Good Research Paper
Selecting a suitable research topic .
Your initial task is to thoroughly review the assignment and carefully absorb the writing prompt’s details. Pay particular attention to technical specifications like length, formatting prerequisites (such as single- vs. double-spacing, indentation, etc.), and the required citation style. Also, pay attention to specifics, including an abstract or a cover page.
Once you’ve a clear understanding of the assignment, the subsequent steps to write a research paper are aligned with the conventional writing process. However, remember that research papers have rules, adding some extra considerations to the process.
When given some assignment freedom, the crucial task of choosing a topic rests on you. Despite its apparent simplicity, this choice sets the foundation for your entire research paper, shaping its direction. The primary factor in picking a research paper topic is ensuring it has enough material to support it. Your chosen topic should provide ample data and complexity for a thorough discussion. However, it’s important to avoid overly broad subjects and focus on specific ones that cover all relevant information without gaps. Yet, approach topic selection more slowly; choosing something that genuinely interests you is still valuable. Aim for a topic that meets both criteria—delivering substantial content while maintaining engagement.
Conducting Thorough Research
Commence by delving into your research early to refine your topic and shape your thesis statement. Swift engagement with available research aids in dispelling misconceptions and unveils optimal paths and strategies to gather more material. Typically, research sources can be located either online or within libraries. When navigating online sources, exercise caution and opt for reputable outlets such as scientific journals or academic papers. Specific search engines, outlined below in the Tools and Resources section, exclusively enable exploring accredited sources and academic databases.
While pursuing information, it’s essential to differentiate between primary and secondary sources. Primary sources entail firsthand accounts, encompassing published articles or autobiographies, while secondary sources, such as critical reviews or secondary biographies, are more distanced. Skimming sources instead of reading each part proves more efficient during the research phase. If a source shows promise, set it aside for more in-depth reading later. Doing so prevents you from investing excessive time in sources that won’t contribute substantively to your work. You should present a literature review detailing your references and submit them for validation in certain instances.
Organizing And Structuring The Research Paper
According to the research paper format , an outline for a research paper is a catalogue of essential topics, arguments, and evidence you intend to incorporate. These elements are divided into sections with headings, offering a preliminary overview of the paper’s structure before commencing the writing process. Formulating a structural outline can significantly enhance writing efficiency, warranting an investment of time to establish one.
Start by generating a list encompassing crucial categories and subtopics—a preliminary outline. Reflect on the amassed information while gathering supporting evidence, pondering the most effective means of segregation and categorization.
Once a discussion list is compiled, deliberate on the optimal information presentation sequence and identify related subtopics that should be placed adjacent. Consider if any subtopic loses coherence when presented out of order. Adopting a chronological arrangement can be suitable if the information follows a straightforward trajectory.
Given the potential complexity of research papers, consider breaking down the outline into paragraphs. This aids in maintaining organization when dealing with copious information and provides better control over the paper’s progression. Rectifying structural issues during the outline phase is preferable to addressing them after writing.
Remember to incorporate supporting evidence within the outline. Since there’s likely a substantial amount to include, outlining helps prevent overlooking crucial elements.
Writing The Introduction
According to the research paper format , the introduction of a research paper must address three fundamental inquiries: What, why, and how? Upon completing the introduction, the reader should clearly understand the paper’s subject matter, its relevance, and the approach you’ll use to construct your arguments.
What? Offer precise details regarding the paper’s topic, provide context, and elucidate essential terminology or concepts.
Why? This constitutes the most crucial yet challenging aspect of the introduction. Endeavour to furnish concise responses to the subsequent queries: What novel information or insights do you present? Which significant matters does your essay assist in defining or resolving?
How? To provide the reader with a preview of the paper’s forthcoming content, the introduction should incorporate a “guide” outlining the upcoming discussions. This entails briefly outlining the paper’s principal components in chronological sequence.

Developing The Main Body
One of the primary challenges that many writers grapple with is effectively organizing the wealth of information they wish to present in their papers. This is precisely why an outline can be an invaluable tool. However, it’s essential to recognize that while an outline provides a roadmap, the writing process allows flexibility in determining the order in which information and arguments are introduced.
Maintaining cohesiveness throughout the paper involves anchoring your writing to the thesis statement and topic sentences. Here’s how to ensure a well-structured paper:
- Alignment with Thesis Statement: Regularly assess whether your topic sentences correspond with the central thesis statement. This ensures that your arguments remain on track and directly contribute to the overarching message you intend to convey.
- Consistency and Logical Flow: Review your topic sentences concerning one another. Do they follow a logical order that guides the reader through a coherent narrative? Ensuring a seamless flow from one topic to another helps maintain engagement and comprehension.
- Supporting Sentence Alignment: Each sentence within a paragraph should align with the topic sentence of that paragraph. This alignment reinforces the central idea, preventing tangential or disjointed discussions.
Additionally, identify paragraphs that cover similar content. While some overlap might be inevitable, it’s essential to approach shared topics from different angles, offering fresh insights and perspectives. Creating these nuanced differences helps present a well-rounded exploration of the subject matter.
An often-overlooked aspect of effective organization is the art of crafting smooth transitions. Transitions between sentences, paragraphs, and larger sections are the glue that holds your paper together. They guide the reader through the progression of ideas, enhancing clarity and creating a seamless reading experience.
Ultimately, while the struggle to organize information is accurate, employing these strategies not only aids in addressing the challenge but also contributes to the overall quality and impact of your writing.
Crafting A Strong Conclusion
The purpose of the research paper’s conclusion is to guide your reader out of the realm of the paper’s argument, leaving them with a sense of closure.
Trace the paper’s trajectory, underscoring how all the elements converge to validate your thesis statement. Impart a sense of completion by ensuring the reader comprehends the resolution of the issues introduced in the paper’s introduction.
In addition, you can explore the broader implications of your argument, outline your paper’s contributions to future students studying the subject, and propose questions that your argument raises—ones that might not be addressed in the paper itself. However, it’s important to avoid:
- Introducing new arguments or crucial information that wasn’t covered earlier.
- Extending the conclusion unnecessarily.
- Employing common phrases that signal the decision (e.g., “In conclusion”).
By adhering to these guidelines, your conclusion can serve as a fitting and impactful conclusion to your research paper, leaving a lasting impression on your readers.
Refining The Research Paper
- Editing And Proofreading
Eliminate unnecessary verbiage and extraneous content. In tandem with the comprehensive structure of your paper, focus on individual words, ensuring your language is robust. Verify the utilization of active voice rather than passive voice, and confirm that your word selection is precise and tangible.
The passive voice, exemplified by phrases like “I opened the door,” tends to convey hesitation and verbosity. In contrast, the active voice, as in “I opened the door,” imparts strength and brevity.
Each word employed in your paper should serve a distinct purpose. Strive to eschew the inclusion of surplus words solely to occupy space or exhibit sophistication.
For instance, the statement “The author uses pathos to appeal to readers’ emotions” is superior to the alternative “The author utilizes pathos to appeal to the emotional core of those who read the passage.”
Engage in thorough proofreading to rectify spelling, grammatical, and formatting inconsistencies. Once you’ve refined the structure and content of your paper, address any typographical and grammatical inaccuracies. Taking a break from your paper before proofreading can offer a new perspective.
Enhance error detection by reading your essay aloud. This not only aids in identifying mistakes but also assists in evaluating the flow. If you encounter sections that seem awkward during this reading, consider making necessary adjustments to enhance the overall coherence.
- Formatting And Referencing
Citations are pivotal in distinguishing research papers from informal nonfiction pieces like personal essays. They serve the dual purpose of substantiating your data and establishing a connection between your research paper and the broader scientific community. Given their significance, citations are subject to precise formatting regulations; however, the challenge lies in the existence of multiple sets of rules.
It’s crucial to consult the assignment’s instructions to determine the required formatting style. Generally, academic research papers adhere to either of two formatting styles for source citations:
- MLA (Modern Language Association)
- APA (American Psychological Association)
Moreover, aside from MLA and APA styles, occasional demands might call for adherence to CMOS (The Chicago Manual of Style), AMA (American Medical Association), and IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) formats.
Initially, citations might appear intricate due to their numerous regulations and specific details. However, once you become adept at them, citing sources accurately becomes almost second nature. It’s important to note that each formatting style provides detailed guidelines for citing various sources, including photographs, websites, speeches, and YouTube videos.

Tips For Writing An Effective Research Paper
By following these research paper writing tips , you’ll be well-equipped to create a well-structured, well-researched, and impactful research paper:
- Select a Clear and Manageable Topic: Choose a topic that is specific and focused enough to be thoroughly explored within the scope of your paper.
- Conduct In-Depth Research: Gather information from reputable sources such as academic journals, books, and credible websites. Take thorough notes to keep track of your sources.
- Create a Strong Thesis Statement: Craft a clear and concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or purpose of your paper.
- Develop a Well-Structured Outline: Organize your ideas into a logical order by creating an outline that outlines the main sections and their supporting points.
- Compose a Captivating Introduction: Hook the reader with an engaging introduction that provides background information and introduces the thesis statement.
- Provide Clear and Relevant Evidence: Support your arguments with reliable and relevant evidence, such as statistics, examples, and expert opinions.
- Maintain Consistent Tone and Style: Keep a consistent tone and writing style throughout the paper, adhering to the formatting guidelines of your chosen citation style.
- Craft Coherent Paragraphs: Each paragraph should focus on a single idea or point, and transitions should smoothly guide the reader from one idea to the next.
- Use Active Voice: Write in the active voice to make your writing more direct and engaging.
- Revise and Edit Thoroughly: Proofread your paper for grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and sentence structure. Revise for clarity and coherence.
- Seek Peer Feedback: Have a peer or instructor review your paper for feedback and suggestions.
- Cite Sources Properly: Accurately cite all sources using the required citation style (e.g., MLA, APA) to avoid plagiarism and give credit to original authors.
- Be Concise and Avoid Redundancy: Strive for clarity by eliminating unnecessary words and redundancies.
- Conclude Effectively: Summarize your main points and restate your thesis in the conclusion. Provide a sense of closure without introducing new ideas.
- Stay Organized: Keep track of your sources, notes, and drafts to ensure a structured and organized approach to the writing process.
- Proofread with Fresh Eyes: Take a break before final proofreading to review your paper with a fresh perspective, helping you catch any overlooked errors.
- Edit for Clarity: Ensure that your ideas are conveyed clearly and that your arguments are easy to follow.
- Ask for Feedback: Don’t hesitate to ask for feedback from peers, instructors, or writing centers to improve your paper further.
In conclusion, we’ve explored the essential steps to write a research paper . From selecting a focused topic to mastering the intricacies of citations, we’ve navigated through the key elements of this process.
It’s vital to recognize that adhering to the research paper writing tips is not merely a suggestion, but a roadmap to success. Each stage contributes to the overall quality and impact of your paper. By meticulously following these steps, you ensure a robust foundation for your research, bolster your arguments, and present your findings with clarity and conviction.
As you embark on your own research paper journey, I urge you to put into practice the techniques and insights shared in this guide. Don’t shy away from investing time in organization, thorough research, and precise writing. Embrace the challenge, for it’s through this process that your ideas take shape and your voice is heard within the academic discourse.
Remember, every exceptional research paper begins with a single step. And with each step you take, your ability to articulate complex ideas and contribute to your field of study grows. So, go ahead – apply these tips, refine your skills, and witness your research papers evolve into compelling narratives that inspire, inform, and captivate.
In the grand tapestry of academia, your research paper becomes a thread of insight, woven into the larger narrative of human knowledge. By embracing the writing process and nurturing your unique perspective, you become an integral part of this ever-expanding tapestry.
Happy writing, and may your research papers shine brightly, leaving a lasting mark on both your readers and the world of scholarship.
Related Posts

Steps To Write A Great Research Paper

CCIR Academy Featured by Nature, The World’s Most Prestigious Academic Publication
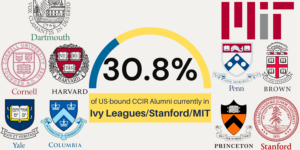
Our Exceptional Alumni: College Admission Results 2020-2023

High School Student Researcher Sailahari’s Paper on Machine Learning Approach in Predicting Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) in E. coli Accepted at the MIT URTC 2023

High School Student Researcher Hyojin on Understanding Psychopathy through Structural and Functional MRI

High School Student Researcher Abigail’s Paper on Quantifying Exam Stress Progressions Presented at the IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE) and Published in the IEEE Xplore Journal
Download Programme Prospectus
- Programme structure
- Research course catalogue
- Professor biographies
- Tuition and Scholarship
Start Your Application
Cambridge Future Scholar (Summer 24)
Admission is OPEN
Early Admissions Deadline: May 1
Regular Admissions Deadline: May 15
Rolling Admissions.
1-on-1 Research Mentorship Admission is open all year.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER BRIEF
- 08 May 2019
Toolkit: How to write a great paper
A clear format will ensure that your research paper is understood by your readers. Follow:
1. Context — your introduction
2. Content — your results
3. Conclusion — your discussion
Plan your paper carefully and decide where each point will sit within the framework before you begin writing.

Collection: Careers toolkit
Straightforward writing
Scientific writing should always aim to be A, B and C: Accurate, Brief, and Clear. Never choose a long word when a short one will do. Use simple language to communicate your results. Always aim to distill your message down into the simplest sentence possible.
Choose a title
A carefully conceived title will communicate the single core message of your research paper. It should be D, E, F: Declarative, Engaging and Focused.
Conclusions
Add a sentence or two at the end of your concluding statement that sets out your plans for further research. What is next for you or others working in your field?
Find out more
See additional information .
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-019-01362-9
Related Articles
How to get published in high impact journals

So you’re writing a paper
Writing for a Nature journal

‘Shrugging off failure is hard’: the $400-million grant setback that shaped the Smithsonian lead scientist’s career
Career Column 15 APR 24

Citizenship privilege harms science
Comment 15 APR 24

How I harnessed media engagement to supercharge my research career
Career Column 09 APR 24
Brazil’s postgraduate funding model is about rectifying past inequalities
Correspondence 09 APR 24
Declining postdoc numbers threaten the future of US life science
Assistant Professor - Cell Physiology & Molecular Biophysics
Opportunity in the Department of Cell Physiology and Molecular Biophysics (CPMB) at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC)
Lubbock, Texas
Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, School of Medicine
Postdoctoral Associate- Curing Brain Tumors
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Energy AI / Grid Modernization / Hydrogen Energy / Power Semiconductor Concentration / KENTECH College
21, Kentech-gil, Naju-si, Jeollanam-do, Republic of Korea(KR)
Korea Institute of Energy Technology
Professor in Macromolecular Chemistry
The Department of Chemistry - Ångström conducts research and education in Chemistry. The department has 260 employees and has a turnover of 290 mil...
Uppsala (Stad) (SE)
Uppsala University
Postdoctoral research fellow focused on generative modelling of synthetic cohorts in brain research
Lunds universitet, Institutionen för kliniska vetenskaper Malmö Lund University was founded in 1666 and is repeatedly ranked among the world’s top ...
Lund (Stad), Skåne (SE)
Lund University
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- How to write a research paper
Last updated
11 January 2024
Reviewed by
With proper planning, knowledge, and framework, completing a research paper can be a fulfilling and exciting experience.
Though it might initially sound slightly intimidating, this guide will help you embrace the challenge.
By documenting your findings, you can inspire others and make a difference in your field. Here's how you can make your research paper unique and comprehensive.
- What is a research paper?
Research papers allow you to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of a particular topic. These papers are usually lengthier and more detailed than typical essays, requiring deeper insight into the chosen topic.
To write a research paper, you must first choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to the field of study. Once you’ve selected your topic, gathering as many relevant resources as possible, including books, scholarly articles, credible websites, and other academic materials, is essential. You must then read and analyze these sources, summarizing their key points and identifying gaps in the current research.
You can formulate your ideas and opinions once you thoroughly understand the existing research. To get there might involve conducting original research, gathering data, or analyzing existing data sets. It could also involve presenting an original argument or interpretation of the existing research.
Writing a successful research paper involves presenting your findings clearly and engagingly, which might involve using charts, graphs, or other visual aids to present your data and using concise language to explain your findings. You must also ensure your paper adheres to relevant academic formatting guidelines, including proper citations and references.
Overall, writing a research paper requires a significant amount of time, effort, and attention to detail. However, it is also an enriching experience that allows you to delve deeply into a subject that interests you and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your chosen field.
- How long should a research paper be?
Research papers are deep dives into a topic. Therefore, they tend to be longer pieces of work than essays or opinion pieces.
However, a suitable length depends on the complexity of the topic and your level of expertise. For instance, are you a first-year college student or an experienced professional?
Also, remember that the best research papers provide valuable information for the benefit of others. Therefore, the quality of information matters most, not necessarily the length. Being concise is valuable.
Following these best practice steps will help keep your process simple and productive:
1. Gaining a deep understanding of any expectations
Before diving into your intended topic or beginning the research phase, take some time to orient yourself. Suppose there’s a specific topic assigned to you. In that case, it’s essential to deeply understand the question and organize your planning and approach in response. Pay attention to the key requirements and ensure you align your writing accordingly.
This preparation step entails
Deeply understanding the task or assignment
Being clear about the expected format and length
Familiarizing yourself with the citation and referencing requirements
Understanding any defined limits for your research contribution
Where applicable, speaking to your professor or research supervisor for further clarification
2. Choose your research topic
Select a research topic that aligns with both your interests and available resources. Ideally, focus on a field where you possess significant experience and analytical skills. In crafting your research paper, it's crucial to go beyond summarizing existing data and contribute fresh insights to the chosen area.
Consider narrowing your focus to a specific aspect of the topic. For example, if exploring the link between technology and mental health, delve into how social media use during the pandemic impacts the well-being of college students. Conducting interviews and surveys with students could provide firsthand data and unique perspectives, adding substantial value to the existing knowledge.
When finalizing your topic, adhere to legal and ethical norms in the relevant area (this ensures the integrity of your research, protects participants' rights, upholds intellectual property standards, and ensures transparency and accountability). Following these principles not only maintains the credibility of your work but also builds trust within your academic or professional community.
For instance, in writing about medical research, consider legal and ethical norms, including patient confidentiality laws and informed consent requirements. Similarly, if analyzing user data on social media platforms, be mindful of data privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with laws governing personal information collection and use. Aligning with legal and ethical standards not only avoids potential issues but also underscores the responsible conduct of your research.
3. Gather preliminary research
Once you’ve landed on your topic, it’s time to explore it further. You’ll want to discover more about available resources and existing research relevant to your assignment at this stage.
This exploratory phase is vital as you may discover issues with your original idea or realize you have insufficient resources to explore the topic effectively. This key bit of groundwork allows you to redirect your research topic in a different, more feasible, or more relevant direction if necessary.
Spending ample time at this stage ensures you gather everything you need, learn as much as you can about the topic, and discover gaps where the topic has yet to be sufficiently covered, offering an opportunity to research it further.
4. Define your research question
To produce a well-structured and focused paper, it is imperative to formulate a clear and precise research question that will guide your work. Your research question must be informed by the existing literature and tailored to the scope and objectives of your project. By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers.
5. Write a thesis statement
A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction. It serves as an overall guide to summarize the overall intent of the research paper for you and anyone wanting to know more about the research.
A strong thesis statement is:
Concise and clear: Explain your case in simple sentences (avoid covering multiple ideas). It might help to think of this section as an elevator pitch.
Specific: Ensure that there is no ambiguity in your statement and that your summary covers the points argued in the paper.
Debatable: A thesis statement puts forward a specific argument––it is not merely a statement but a debatable point that can be analyzed and discussed.
Here are three thesis statement examples from different disciplines:
Psychology thesis example: "We're studying adults aged 25-40 to see if taking short breaks for mindfulness can help with stress. Our goal is to find practical ways to manage anxiety better."
Environmental science thesis example: "This research paper looks into how having more city parks might make the air cleaner and keep people healthier. I want to find out if more green spaces means breathing fewer carcinogens in big cities."
UX research thesis example: "This study focuses on improving mobile banking for older adults using ethnographic research, eye-tracking analysis, and interactive prototyping. We investigate the usefulness of eye-tracking analysis with older individuals, aiming to spark debate and offer fresh perspectives on UX design and digital inclusivity for the aging population."
6. Conduct in-depth research
A research paper doesn’t just include research that you’ve uncovered from other papers and studies but your fresh insights, too. You will seek to become an expert on your topic––understanding the nuances in the current leading theories. You will analyze existing research and add your thinking and discoveries. It's crucial to conduct well-designed research that is rigorous, robust, and based on reliable sources. Suppose a research paper lacks evidence or is biased. In that case, it won't benefit the academic community or the general public. Therefore, examining the topic thoroughly and furthering its understanding through high-quality research is essential. That usually means conducting new research. Depending on the area under investigation, you may conduct surveys, interviews, diary studies, or observational research to uncover new insights or bolster current claims.
7. Determine supporting evidence
Not every piece of research you’ve discovered will be relevant to your research paper. It’s important to categorize the most meaningful evidence to include alongside your discoveries. It's important to include evidence that doesn't support your claims to avoid exclusion bias and ensure a fair research paper.
8. Write a research paper outline
Before diving in and writing the whole paper, start with an outline. It will help you to see if more research is needed, and it will provide a framework by which to write a more compelling paper. Your supervisor may even request an outline to approve before beginning to write the first draft of the full paper. An outline will include your topic, thesis statement, key headings, short summaries of the research, and your arguments.
9. Write your first draft
Once you feel confident about your outline and sources, it’s time to write your first draft. While penning a long piece of content can be intimidating, if you’ve laid the groundwork, you will have a structure to help you move steadily through each section. To keep up motivation and inspiration, it’s often best to keep the pace quick. Stopping for long periods can interrupt your flow and make jumping back in harder than writing when things are fresh in your mind.
10. Cite your sources correctly
It's always a good practice to give credit where it's due, and the same goes for citing any works that have influenced your paper. Building your arguments on credible references adds value and authenticity to your research. In the formatting guidelines section, you’ll find an overview of different citation styles (MLA, CMOS, or APA), which will help you meet any publishing or academic requirements and strengthen your paper's credibility. It is essential to follow the guidelines provided by your school or the publication you are submitting to ensure the accuracy and relevance of your citations.
11. Ensure your work is original
It is crucial to ensure the originality of your paper, as plagiarism can lead to serious consequences. To avoid plagiarism, you should use proper paraphrasing and quoting techniques. Paraphrasing is rewriting a text in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. Quoting involves directly citing the source. Giving credit to the original author or source is essential whenever you borrow their ideas or words. You can also use plagiarism detection tools such as Scribbr or Grammarly to check the originality of your paper. These tools compare your draft writing to a vast database of online sources. If you find any accidental plagiarism, you should correct it immediately by rephrasing or citing the source.
12. Revise, edit, and proofread
One of the essential qualities of excellent writers is their ability to understand the importance of editing and proofreading. Even though it's tempting to call it a day once you've finished your writing, editing your work can significantly improve its quality. It's natural to overlook the weaker areas when you've just finished writing a paper. Therefore, it's best to take a break of a day or two, or even up to a week, to refresh your mind. This way, you can return to your work with a new perspective. After some breathing room, you can spot any inconsistencies, spelling and grammar errors, typos, or missing citations and correct them.
- The best research paper format
The format of your research paper should align with the requirements set forth by your college, school, or target publication.
There is no one “best” format, per se. Depending on the stated requirements, you may need to include the following elements:
Title page: The title page of a research paper typically includes the title, author's name, and institutional affiliation and may include additional information such as a course name or instructor's name.
Table of contents: Include a table of contents to make it easy for readers to find specific sections of your paper.
Abstract: The abstract is a summary of the purpose of the paper.
Methods : In this section, describe the research methods used. This may include collecting data, conducting interviews, or doing field research.
Results: Summarize the conclusions you drew from your research in this section.
Discussion: In this section, discuss the implications of your research. Be sure to mention any significant limitations to your approach and suggest areas for further research.
Tables, charts, and illustrations: Use tables, charts, and illustrations to help convey your research findings and make them easier to understand.
Works cited or reference page: Include a works cited or reference page to give credit to the sources that you used to conduct your research.
Bibliography: Provide a list of all the sources you consulted while conducting your research.
Dedication and acknowledgments : Optionally, you may include a dedication and acknowledgments section to thank individuals who helped you with your research.
- General style and formatting guidelines
Formatting your research paper means you can submit it to your college, journal, or other publications in compliance with their criteria.
Research papers tend to follow the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), or Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) guidelines.
Here’s how each style guide is typically used:
Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS):
CMOS is a versatile style guide used for various types of writing. It's known for its flexibility and use in the humanities. CMOS provides guidelines for citations, formatting, and overall writing style. It allows for both footnotes and in-text citations, giving writers options based on their preferences or publication requirements.
American Psychological Association (APA):
APA is common in the social sciences. It’s hailed for its clarity and emphasis on precision. It has specific rules for citing sources, creating references, and formatting papers. APA style uses in-text citations with an accompanying reference list. It's designed to convey information efficiently and is widely used in academic and scientific writing.
Modern Language Association (MLA):
MLA is widely used in the humanities, especially literature and language studies. It emphasizes the author-page format for in-text citations and provides guidelines for creating a "Works Cited" page. MLA is known for its focus on the author's name and the literary works cited. It’s frequently used in disciplines that prioritize literary analysis and critical thinking.
To confirm you're using the latest style guide, check the official website or publisher's site for updates, consult academic resources, and verify the guide's publication date. Online platforms and educational resources may also provide summaries and alerts about any revisions or additions to the style guide.
Citing sources
When working on your research paper, it's important to cite the sources you used properly. Your citation style will guide you through this process. Generally, there are three parts to citing sources in your research paper:
First, provide a brief citation in the body of your essay. This is also known as a parenthetical or in-text citation.
Second, include a full citation in the Reference list at the end of your paper. Different types of citations include in-text citations, footnotes, and reference lists.
In-text citations include the author's surname and the date of the citation.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of each page of your research paper. They may also be summarized within a reference list at the end of the paper.
A reference list includes all of the research used within the paper at the end of the document. It should include the author, date, paper title, and publisher listed in the order that aligns with your citation style.
10 research paper writing tips:
Following some best practices is essential to writing a research paper that contributes to your field of study and creates a positive impact.
These tactics will help you structure your argument effectively and ensure your work benefits others:
Clear and precise language: Ensure your language is unambiguous. Use academic language appropriately, but keep it simple. Also, provide clear takeaways for your audience.
Effective idea separation: Organize the vast amount of information and sources in your paper with paragraphs and titles. Create easily digestible sections for your readers to navigate through.
Compelling intro: Craft an engaging introduction that captures your reader's interest. Hook your audience and motivate them to continue reading.
Thorough revision and editing: Take the time to review and edit your paper comprehensively. Use tools like Grammarly to detect and correct small, overlooked errors.
Thesis precision: Develop a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your paper. Ensure that your thesis aligns with your research's overall purpose and contribution.
Logical flow of ideas: Maintain a logical progression throughout the paper. Use transitions effectively to connect different sections and maintain coherence.
Critical evaluation of sources: Evaluate and critically assess the relevance and reliability of your sources. Ensure that your research is based on credible and up-to-date information.
Thematic consistency: Maintain a consistent theme throughout the paper. Ensure that all sections contribute cohesively to the overall argument.
Relevant supporting evidence: Provide concise and relevant evidence to support your arguments. Avoid unnecessary details that may distract from the main points.
Embrace counterarguments: Acknowledge and address opposing views to strengthen your position. Show that you have considered alternative arguments in your field.
7 research tips
If you want your paper to not only be well-written but also contribute to the progress of human knowledge, consider these tips to take your paper to the next level:
Selecting the appropriate topic: The topic you select should align with your area of expertise, comply with the requirements of your project, and have sufficient resources for a comprehensive investigation.
Use academic databases: Academic databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and JSTOR offer a wealth of research papers that can help you discover everything you need to know about your chosen topic.
Critically evaluate sources: It is important not to accept research findings at face value. Instead, it is crucial to critically analyze the information to avoid jumping to conclusions or overlooking important details. A well-written research paper requires a critical analysis with thorough reasoning to support claims.
Diversify your sources: Expand your research horizons by exploring a variety of sources beyond the standard databases. Utilize books, conference proceedings, and interviews to gather diverse perspectives and enrich your understanding of the topic.
Take detailed notes: Detailed note-taking is crucial during research and can help you form the outline and body of your paper.
Stay up on trends: Keep abreast of the latest developments in your field by regularly checking for recent publications. Subscribe to newsletters, follow relevant journals, and attend conferences to stay informed about emerging trends and advancements.
Engage in peer review: Seek feedback from peers or mentors to ensure the rigor and validity of your research. Peer review helps identify potential weaknesses in your methodology and strengthens the overall credibility of your findings.
- The real-world impact of research papers
Writing a research paper is more than an academic or business exercise. The experience provides an opportunity to explore a subject in-depth, broaden one's understanding, and arrive at meaningful conclusions. With careful planning, dedication, and hard work, writing a research paper can be a fulfilling and enriching experience contributing to advancing knowledge.
How do I publish my research paper?
Many academics wish to publish their research papers. While challenging, your paper might get traction if it covers new and well-written information. To publish your research paper, find a target publication, thoroughly read their guidelines, format your paper accordingly, and send it to them per their instructions. You may need to include a cover letter, too. After submission, your paper may be peer-reviewed by experts to assess its legitimacy, quality, originality, and methodology. Following review, you will be informed by the publication whether they have accepted or rejected your paper.
What is a good opening sentence for a research paper?
Beginning your research paper with a compelling introduction can ensure readers are interested in going further. A relevant quote, a compelling statistic, or a bold argument can start the paper and hook your reader. Remember, though, that the most important aspect of a research paper is the quality of the information––not necessarily your ability to storytell, so ensure anything you write aligns with your goals.
Research paper vs. a research proposal—what’s the difference?
While some may confuse research papers and proposals, they are different documents.
A research proposal comes before a research paper. It is a detailed document that outlines an intended area of exploration. It includes the research topic, methodology, timeline, sources, and potential conclusions. Research proposals are often required when seeking approval to conduct research.
A research paper is a summary of research findings. A research paper follows a structured format to present those findings and construct an argument or conclusion.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics.
- 10 research paper
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Research Paper

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The pages in this section provide detailed information about how to write research papers including discussing research papers as a genre, choosing topics, and finding sources.
The Research Paper
There will come a time in most students' careers when they are assigned a research paper. Such an assignment often creates a great deal of unneeded anxiety in the student, which may result in procrastination and a feeling of confusion and inadequacy. This anxiety frequently stems from the fact that many students are unfamiliar and inexperienced with this genre of writing. Never fear—inexperience and unfamiliarity are situations you can change through practice! Writing a research paper is an essential aspect of academics and should not be avoided on account of one's anxiety. In fact, the process of writing a research paper can be one of the more rewarding experiences one may encounter in academics. What is more, many students will continue to do research throughout their careers, which is one of the reasons this topic is so important.
Becoming an experienced researcher and writer in any field or discipline takes a great deal of practice. There are few individuals for whom this process comes naturally. Remember, even the most seasoned academic veterans have had to learn how to write a research paper at some point in their career. Therefore, with diligence, organization, practice, a willingness to learn (and to make mistakes!), and, perhaps most important of all, patience, students will find that they can achieve great things through their research and writing.
The pages in this section cover the following topic areas related to the process of writing a research paper:
- Genre - This section will provide an overview for understanding the difference between an analytical and argumentative research paper.
- Choosing a Topic - This section will guide the student through the process of choosing topics, whether the topic be one that is assigned or one that the student chooses themselves.
- Identifying an Audience - This section will help the student understand the often times confusing topic of audience by offering some basic guidelines for the process.
- Where Do I Begin - This section concludes the handout by offering several links to resources at Purdue, and also provides an overview of the final stages of writing a research paper.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.

CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
Loading metrics
Open Access
Ten simple rules for leading a successful undergraduate-intensive research lab
Roles Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation MIT-WHOI Joint Program in Oceanography/Applied Ocean Science & Engineering, Cambridge and Woods Hole, Massachusetts, United States of America
Roles Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliation Biology Department, Utah Valley University, Orem, Utah, United States of America
- KJE Hickman,
- Geoffrey Zahn

Published: April 11, 2024
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011994
- Reader Comments
Participating in mentored research is an enormous benefit to undergraduate students. These immersive experiences can dramatically improve retention and completion rates, especially for students from traditionally underserved populations in STEM disciplines. Scientists typically do not receive any formal training in management or group dynamics before taking on the role of a lab head. Thus, peer forums and shared wisdom are crucial for developing the vision and skills involved with mentorship and leading a successful research lab. Faculty at any institution can help improve student outcomes and the success of their labs by thoughtfully including undergraduates in their research programs. Moreover, faculty at primarily undergraduate institutions have special challenges that are not often acknowledged or addressed in public discussions about best practices for running a lab. Here, we present 10 simple rules for fostering a successful undergraduate research lab. While much of the advice herein is applicable to mentoring undergraduates in any setting, it is especially tailored to the special circumstances found at primarily undergraduate institutions.
Citation: Hickman K, Zahn G (2024) Ten simple rules for leading a successful undergraduate-intensive research lab. PLoS Comput Biol 20(4): e1011994. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011994
Editor: Russell Schwartz, Carnegie Mellon University, UNITED STATES
Copyright: © 2024 Hickman, Zahn. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
This is a PLOS Computational Biology Benchmarking paper.
Introduction
Undergraduate research (UR) is a high-impact practice that has been demonstrated to benefit student learning, persistence, and career preparation [ 1 , 2 ]. Undergraduate research serves as a robust intervention for students from underrepresented groups who are at risk of dropping out of college [ 3 , 4 ]. By engaging students during their early years of study, they develop a sense of community and gain access to faculty mentors. A preliminary introduction to the research environment gives students time to develop their science identity and makes them more resilient to difficulties encountered during their educational careers [ 5 ]. The literature on positive outcomes associated with participation in UR is broad [ 6 ], encompassing large public research institutions, private institutions, and liberal arts colleges.
Faculty at Primarily Undergraduate Institutions (PUIs) face a unique set of challenges to maintain scholarly productivity and “successful” research programs. They often have fewer external funding opportunities [ 7 ] and far higher teaching loads than faculty at research-intensive (R1) universities. Many R1 institutions provide research opportunities for undergraduates by incorporating them into ongoing projects led by graduate students and/or postdocs, via short-term programs or with course-based undergraduate research experiences (CUREs, see Rule 10), which can be successful at any type of institution. However, the luxury of graduate student and postdoc labor is not available to most faculty at a PUI—instead, they must rely on the involvement of undergraduate researchers.
Working with undergraduate students themselves presents some unique challenges. Typically, graduate students have a more refined set of skills and direction when they begin mentored research. They also have more financial support and time dedicated to research. Conversely, undergraduate students generally require a high investment toward training before they can be independent researchers. This is because undergraduates are enrolled in full-time coursework and are only with the lab for a short time before they graduate and move on to careers or graduate programs.
While there is considerable overlap in practices that lead to successful labs in both R1 and PUI settings, the unique challenges of running a lab at a PUI require specialized approaches for recruiting lab members and fostering lab success. There has been rich discourse on methods to increase the health and productivity of research labs [ 8 – 11 ]. However, we note that much of the advice (even when about undergraduate students) has been geared toward R1 labs with postdocs, graduate students, and reduced teaching expectations for faculty. Here, we discuss some “rules” tailored to the specific challenges facing the principal investigators of research labs at PUIs, particularly at public universities that serve a diverse student body.
Rule 1: Determine what “success” means in your lab
The crucial first step is to decide what “success” means for your PUI research lab. Setting this down in writing and communicating it to lab members will help to set the tone and focus of the lab. While external funding and publication quantity/quality are important metrics for lab “success” in some settings, we would argue that lab success at a PUI is most usefully defined as student success ( Fig 1 ).
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
Defining lab success as student success is foundational to the 9 other rules for running a successful undergraduate-intensive research lab. This definition is informed by lab standards, training methodologies, and recruitment strategies. Cultivating the principles endemic to each rule promotes student success which, in turn, provides further opportunities to strengthen the lab’s success. These mutually reinforcing processes build lab community and facilitate successful undergraduate research labs.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011994.g001
Student success can be measured in many ways, from retention and graduation in STEM, to increased science identity and critical thinking skills, to poster presentations, internal grant awards, and placement in graduate/professional programs. Selecting and tracking these metrics of importance will help you define your lab’s role in student success and prioritize your lab’s activities and engagement. Students who join your lab will have diverse educational and career goals, so it is imperative to have a plan in place for incorporating them into your lab’s pursuits. For example, a student planning on medical school might want to attend a different conference than one planning on graduate school, or a student considering other callings (communication, law, science policy, etc.) might benefit from altogether different career-development experiences. At all points, maintain an open dialogue with lab members about how their activities will lead to their own success in the context of the lab, and solicit feedback from each of them (individually) about what they view as “success” on short-term (approximately 3 to 6 months), medium-term (approximately 1 to 2 years), and long-term (>3 to 5 years) timescales.
The diversity of skill levels and interests you encounter with undergraduate lab members may shape your lab’s research goals in ways you did not anticipate. Some students may want to simply assist on someone else’s project, while others will be eager to start their own line of original research. Keeping a flexible research agenda to accommodate student interests and skills is fine, but undergraduates may want to push the boundaries of your lab’s unique focus beyond what you are capable of effectively supporting. Having a clear statement of “lab success” and putting lab goals in writing in a formal document will help you to guide students toward activities that support both them and your lab. An example undergraduate lab handbook has been archived online via Zenodo [ 12 ].
Rule 2: Approach students early
Science is a multifaceted and often slow process. With the high training investment and heavy course loads characteristic of undergraduate students, the research process is slowed even further. Be prepared for things to take much longer than you expect. Actively recruiting early-stage students, even local high-school students, is a winning strategy to overcome this challenge. This will provide you with ample time to test mentoring strategies, train the students in relevant methodologies, and benefit from their application of this training. Moreover, allotting sufficient time for the students’ training will facilitate their development into independent scientists with the ability to generate and investigate their own questions and ideas.
Freshmen and sophomores in your courses may not be aware that undergraduate research is even an option. PIs at teaching-focused institutions usually have consistent access to early students through the courses they teach. Spend a bit of time in class discussing research opportunities and benefits at your institution, and use examples of student research to highlight course content. Invite your current research students to present their projects in class to help you recruit, and invite interested students to shadow in the lab for a day. Highlighting the availability and inclusivity of undergraduate research and its importance to student success can help raise awareness in student populations who otherwise may have never been told that they could be a scientist.
Rule 3: Structure projects for peer collaboration
As a faculty member at a PUI, teaching is typically your first priority. With such restrictions on research time, a peer-mentor model can be a useful asset in your lab. This is analogous to the peer-mentor models employed by PIs at R1 institutions, with postdocs helping mentor PhD students [ 13 ]. In an undergraduate-only setting, the time and effort spent training students to serve as peer-mentors is significantly greater. After they are trained, peer-mentoring roles can be negotiated that lead to beneficial experiences for both mentor and mentee students [ 14 ]. This model can be an especially empowering role for the student mentor, developing their self-perception as a scientist. Moreover, this model develops teamwork skills and adds an element of peer-accountability which has been shown to improve retention and enjoyment of the scientific process [ 15 ].
In a PUI research setting, most students generally benefit from rotating through projects and/or duties. This variety exposes them to ideas and processes that may eventually shape their career path. Incorporating new students into senior students’ preexisting projects facilitates a flexible lab environment, which cultivates skill exploration, preparing them for independent research [ 16 , 17 ]. Good communication between the PI and the student research teams is also important for clearly defining roles, authorship credit, and project development. A collaborative lab environment will always be more successful than a competitive one, and you should take care to model and reinforce good collaborative practices.
Rule 4: Get students’ hands dirty
Undergraduate students typically seek out research labs because they have a vision of what research looks like and a perception of themselves as part of this process. For example, students may visualize researchers in a white coat at the lab bench, knee-deep in a bog, or logging onto a supercomputer. There are many ways to conduct research and these variations may not be equally recognized among undergraduates. Consequently, students should be engaged throughout various steps in the research process in order to enrich their contextual understanding and experience. There is no substitute for hands-on experience. Engaging students in active research protocols early on increases retention and improves chances of attaining high-skill positions in STEM [ 18 ].
A few roles on research projects in which new students can easily participate range, for example, from data collection and entry, to student–student peer review, to computational analyses, depending on student background. As students progress, this list can expand to include more intensive responsibilities. Allowing students to participate in a broad range of scientific tasks will equip them with an applied understanding of the hidden processes in science and build early intuition for this work [ 19 ].
Rule 5: Encourage a well-rounded education
Science is a highly creative pursuit and meaningful STEM careers can follow myriad paths. For example, a student may take interest in science communication, policy, or advocacy. Encourage your students’ diverse interests and allow them to follow their passion. This applies to the lab, their research questions, and their academic and personal life. They may want to take a ceramics class, learn to scuba dive, or spend time volunteering with campus organizations. Extracurricular activities and experiences build well-rounded individuals and more creative scientists, as well as making them more competitive applicants for jobs and postsecondary educational programs [ 20 ].
Talking to your students about their non-research passions may inspire new research paradigms or even inform how you communicate science from your lab. Promoting a healthy work/life balance and embracing the diversity of personal interests in your lab will make you more approachable and help foster an environment where lab members feel respected and fulfilled. Happy students do better science and have a positive effect on lab success.
Rule 6: Tailor your lab to your mentorship style
Different personalities and skill sets lead to different mentorship styles. When organizing your lab, it is helpful to do some self-reflection about what sort of mentor you want to be. Developing a formal mentoring philosophy can be facilitated through mentorship training from your institution, professional societies, and government agencies. These are excellent methods to spark introspection and define your strengths, weaknesses, and goals as a mentor.
How many students can you effectively supervise? How many different ongoing projects are feasible? The right answers to these and other questions will vary for every PI. Some may be comfortable establishing a large research group with formalized peer-mentoring and defined projects. Others may do better with a small group and closer interactions with each student. It takes time to develop trust and rapport with students, and without it, they may not feel comfortable failing or asking for help. It is important to be intentional and aware of your limitations. It is also important that each student in your lab gets the individual attention that they need.
Rule 7: Collaborate early and often
Science is inherently collaborative, and collaboration is a skill [ 21 ]. This is particularly important when running an undergraduate research lab where student training and graduation timelines do not leave much room for extensive data collection. Multiyear projects that students contribute to during their short tenure can leave most participants without tangible products to show as they apply for the next steps in their career pathway. To get things done on an undergraduate timeline, collaborations with external partners can be key.
Your lab will likely have some methodological focus that could be invaluable to other research teams. For example, if your undergraduate lab focuses on computational training, you will probably have external research labs eager for you to analyze data. Colleagues at R1 institutions often see PUI partners as a benefit for funding opportunities as well (e.g., NSF Broader Impacts). Use your professional network to advertise what your students can do and actively seek out collaborative opportunities with your academic, industry, and governmental contacts. This creates opportunities for your students to participate in projects they could not do alone, builds their professional networks, and teaches them how to be good collaborators.
Rule 8: Practice radical inclusivity
Building an inclusive lab takes effort and commitment. Most of the excellent advice for establishing an inclusive and antiracist lab [ 8 , 11 , 22 ] is directly applicable to undergraduate research settings as well, so we will not repeat it here. However, special considerations should be noted for PUIs. For example, you will likely encounter a greater proportion of first-generation/low-income and underrepresented students at a public PUI, as each stage of the educational pipeline successively excludes more students from those populations.
Students who are the first generation in their family to attend college, who come from low-income backgrounds, and/or who identify with underrepresented groups in STEM are far less likely to approach and interact with faculty either formally or informally [ 23 ]. This makes it crucial for faculty to proactively initiate discussions and actively recruit undergraduate lab members rather than wait for students to approach them. Underrepresented students benefit more from faculty-mentored research than any other group [ 24 ] and inclusion in undergraduate research has been shown to improve these students’ persistence in STEM [ 25 ]. Find the time to meet with students from these groups, whether in your classroom or by attending extracurricular events geared toward these student groups. Invest in creating a lab environment that will support a diverse group of students and then actively recruit them early in their educational journey.
Rule 9: Compensate students for their contributions
One of the most impactful differences between graduate and undergraduate researchers is that the latter are primarily full-time students, typically with no expectations or compensation for research activities. Finding ways to compensate undergraduates for research equalizes who can afford to participate. Your university may have internal grant mechanisms that pay or subsidize wages for undergraduate student research labor. Be proactive in finding these and other funding sources and, if paying your students is not an option, you may be able to compensate with course credit. Aside from equalizing access, compensating your students fosters mutual respect for their work/life balance which sets a precedent for students to respect their own time, manage expectations, and not overcommit.
Rule 10: Incorporate research into your teaching
While one-on-one mentoring has the highest impact on students [ 19 ], the time investment required for this practice is not always scalable. Course-based undergraduate research experiences (CUREs) offer a way to reach more students [ 6 ]. CUREs can make research participation more inclusive and available to students who may not be aware that mentored research is an option, and they reach a “captive audience” of students who may never have considered engaging in research. It also allows a wide range of students to add meaningful research experience to their professional portfolio while earning credits toward their degree. Teaching a CURE is separate from running a research lab, but it invariably extends and informs your mentoring. The pedagogical literature has many good examples of how to design and effectively manage a CURE in your classroom [ 26 – 30 ].
Conclusions
While the habits and attitudes that lead to successful research labs overlap considerably between an R1 and a PUI, there are unique features and special challenges in an undergraduate-only lab group that deserve special consideration. Here, we have tried to highlight some of the important practices that can transform those challenges into opportunities. Faculty at public PUIs play a critical role in preparing underserved students for careers in science, and often influence the types of scientists that these students will become. By teaching them how to be good scientists and collaborative community members, and how to cultivate a deep well of patience and compassion, you’re enabling their success. Framing “lab success” in terms of “student success” as a guiding principle will lead to positive outcomes for students and your lab.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Michael Rotter for constructive feedback on the original manuscript. Thanks to the bouncer at The Muddy Charles for providing invaluable feedback on the layout of Fig 1 . Finally, thanks to undergraduate researchers everywhere. This manuscript is the result of a collaboration between a PUI faculty member and a former undergraduate student.
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- PubMed/NCBI
How to write a research article to submit for publication
Pharmacists and healthcare professionals who are undertaking research should have an understanding of how to produce a research article for publication, and be aware of the important considerations relating to submission to a peer-reviewed journal.

Viennaslide / Alamy Stock Photo
Undertaking and performing scientific, clinical and practice-based research is only the beginning of the scholarship of discovery [1] . For the full impact of any research to be achieved and to have an effect on the wider research and scientific community, it must be published in an outlet accessible to relevant professionals [2] .
Scientific research is often published in peer-reviewed journals. Peer review is defined as the unbiased, independent, critical assessment of scholarly or research manuscripts submitted to journals by experts or opinion leaders [3] . The process and requirements of reviewers has been covered recently [4] . On account of this rigorous process, peer-reviewed scientific journals are considered the primary source of new information that impacts and advances clinical decision-making and practice [5] , [6] .
The development of a research article can be helpful for the promotion of scientific thinking [7] , [8] and the advancement of effective writing skills, allowing the authors to participate in broader scientific discussions that lie beyond their scope of practice or discipline [2] .
This article aims to provide pharmacists and healthcare professionals who are undertaking research with an understanding of how to produce a research article for publication, as well as points to consider before submission to a peer-reviewed journal.
Importance of the research question
This article will not go into detail about forming suitable research questions, however, in principle, a good research question will be specific, novel and of relevance to the scientific community (e.g. pharmacy – pharmacists, pharmaceutical scientists, pharmacy technicians and related healthcare professionals). Hulley et al . suggest using the FINER criteria (see ‘Figure 1: FINER criteria for a good research question’) to aid the development of a good research question [9] .
Figure 1: FINER criteria for a good research question
Source: Hulley S, Cummings S, Browner W et al . [9]
The FINER criteria highlight useful points that may generally increase the chances of developing a successful research project. A good research question should specify the population of interest, be of interest to the scientific community and potentially to the public, have clinical relevance and further current knowledge in the field.
Having a clear research question that is of interest to those working in the same field will help in the preparation of an article because it can be used as the central organising principle – all of the content included and discussed should focus on answering this question.
Preparing a first draft
Before writing the article, it is useful to highlight several journals that you could submit the final article to. It also helps to familiarise yourself with these journals’ styles, article structures and formatting instructions before starting to write. Many journals also have criteria that research articles should be able to satisfy. For example, all research article submissions to Clinical Pharmacist must demonstrate innovative or novel results that are sustainable, reproducible and transferable [10] .
Having researched potential target journals, you should have a clear idea about your target audience, enabling you to pitch the level of the article appropriately [11] (see ‘Box 1: Top tips to prepare for writing’).
Box 1: Top tips to prepare for writing
- Know the focus of the paper – identify two or three important findings and make these the central theme of the article;
- Gather important data, perform any analyses and make rough data plots and tables beforehand. These can then be refined for inclusion or submitted as supplementary information if needed;
- Organise your results to flow in a logical sequence;
- Know the structure and requirements of your target journals (check websites and author guidelines, as well as published articles);
- Think about the style of the piece and look to pitch the article at the level of the intended audience;
- Clarity should be your guiding principle.
Structuring a research article
Most research articles follow a similar structure and format that includes an abstract, introduction, methods, results and discussion, as well as a summary of the key points discussed in the article.
One approach is to start with the methods section, which can be derived from the protocol and any pilot phase. Many of the figures and tables can be constructed in advance, which will help with writing the results section. The questions addressed by the study can be used alongside the results to formulate the introduction, which can guide how the discussion is written [11] .
Clinical Pharmacist , like other peer-reviewed journals, has specific author guidelines and formatting instructions to help authors prepare their articles [10] , [12] , [13] . The following sections will discuss the required sections and important considerations for authors when writing.
Title, abstract and keywords
The title, abstract and keywords are essential to the successful communication of research. Most electronic search engines, databases (e.g. PubMed/MEDLINE) and journal websites extract words from them to determine whether your article will be displayed to interested readers [14] , [15] , [16] , [17] , enabling accurate dissemination and leading to future citations.
In addition, the title and abstract are usually freely available online. If an article is not published in an ‘open access’ format, (i.e. it is free and immediately available online and access is combined with the rights to use these articles fully in the digital environment) [18] , or if the reader does not have a subscription to the journal, they will have to decide on whether to pay to access the full article to continue reading. Therefore, it is imperative that they are informative and accurate.
The title should accurately reflect the research, identify the main issue and begin with the subject matter, while being both simple and enticing enough to attract the audience [19] . Authors should avoid using ‘a study of’, ‘investigations into’ and ‘observations on’ in titles. It is also worth remembering that abstracting and indexing services, such as MEDLINE, require accurate titles, because they extract keywords from them for cross-referencing [19] .
Many journals require the abstract to be structured in the same way as the main headings of the paper (e.g. introduction, methods, results, discussion and conclusion) and to be around 150–300 words in length [10] . In general, references should not be cited in the abstract.
Introduction
The introduction should provide the background and context to the study. Two or three paragraphs can be dedicated to the discussion of any previous work and identification of gaps in current knowledge. The rest of the introduction should then outline what this piece of work aims to address and why this is important, before stating the objectives of the study and the research question [20] .
The methods section should provide the reader with enough detail for them to be able to reproduce the study if desired [3] . The context and setting of the study should be described and the study design specified. The section should further describe the population (including the inclusion and exclusion criteria), sampling strategy and the interventions performed. The main study variables should be identified and the data collection procedures described [3] .
Authors should provide specific, technical and detailed information in this section. Several checklists and guidelines are available for the reporting of specific types of studies:
- CONSORT is used for developing and reporting a randomised controlled trial [21] ;
- The STARD checklist can help with designing a diagnostic accuracy study [22] ;
- The PRISMA checklist can be used when performing a metaâ€analyses or systematic review, but can also help with compiling an introduction [23] .
For the reporting of qualitative research studies, authors should explain which research tradition the study utilises and link the choice of methodological strategies with the research goals [24] .
For studies describing the development of new initiatives or clinical services, authors should describe the situation before the initiative began, the establishment of priorities, formulation of objectives and strategies, mobilisation of resources, and processes used in the methods section [10] .
The final portion of the methods section will include the statistical methods used to analyse the data [25] . The statistical methods employed should be described with enough detail to enable a knowledgeable reader with access to the original data to be able to judge its appropriateness for the study and verify the results [3] . For survey-based studies and information on sampling frame, size and statistical powers, see ‘When to use a survey in pharmacy practice research’ [26] .
Findings should be quantified and presented with appropriate indicators of measurement error or uncertainty (e.g. confidence intervals). Authors should avoid relying solely on statistical hypothesis testing, such as P values, because these fail to convey important information about effect size and precision of estimates [3] . Statistical terms, abbreviations and most symbols should be defined, and the statistical software package and versions used should be specified. Authors should also take care to distinguish prespecified from exploratory analyses, including subgroup analyses [3] .
The results section should be straightforward and factual and all of the results that relate to the research question should be provided, with detail including simple counts and percentages [27] . Data collection and recruitment should be commented on and the participants described. Secondary findings and the results of subgroup analyses can also be presented [27] .
Figures, schemes and tables
To present data and results of the research study, figures, schemes and tables can be used. They should include significant digits, error bars and levels of statistical significance.
Tables should be presented with a summary title, followed by caption, a sentence or two that describes the content and impact of the data included in the table. All captions should provide enough detail so that the table or figure can be interpreted and understood as stand-alone material, separate from the article.
Figures should also be presented with a summary title, a caption that describes the significant result or interpretation that can be made from the figure, the number of repetitions within the experiment, as well as what the data point actually represents. All figures and tables should be cited in the manuscript text [11] .
When compiling tables and figures, important statistics, such as the number of samples (n), the index of dispersion (standard deviation [SD], standard error of the mean [SEM]), and the index of central tendency (mean, median or mode), must be stated. The statistical analysis performed should also be included and specific statistical data should be indicated (e.g. P values) [11] .
Discussion and conclusions
The discussion section should state the main findings of the study. The main results should be compared with reference to previous research and current knowledge, and where this has been extended it should be fully described [2] , [11] , [25] . For clinical studies, relevant discussion of the implications the results may have on policy should be included [10] . It is important to include an analysis of the strengths and limitations of the study and offer perspectives for future work [2] . Excessive presentation of data and results without any discussion should be avoided and it is not necessary to cite a published work for each argument presented. Any conclusions should include the major findings, followed by a brief discussion of future perspectives and the application of this work to other disciplines [10] .
The list of references should be appropriate; important statements presented as facts should be referenced, as well as the methods and instruments used. Reference lists for research articles, however, unlike comprehensive reviews of a topic, do not necessarily have to be exhaustive. References to unpublished work, to documents in the grey literature (technical reports), or to any source that the reader will have difficulty finding or understanding should be avoided [27] . Most journals have reference limits and specific formatting requirements, so it is important to check the journal’s author guidelines [10] , [11] , [12] , [13] , [19] .
Authorship and acknowledgements
Determining contributors who qualify as authors and those who should be acknowledged can be difficult. Clinical Pharmacist follows guidance from the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors, which recommends that authorship be based on the following four criteria:
- Substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; AND
- Drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content; AND
- Final approval of the version to be published; AND
- Agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved [3] .
Therefore, only individuals who meet all four criteria should be identified as authors [3] . The contribution of individuals who do not meet all four criteria should instead be included in the acknowledgements.
In addition, a statement that recognises any funding sources for the work should be added to the acknowledgements. This statement should adhere to the guidelines provided by the funding institution [11] .
Supplementary and supporting information
A key principle of research publication is that others should be able to replicate and build upon an author’s published claims. Therefore, submitted manuscripts should contain the necessary detail about the study and analytical design, and the data must be available for editors and peer-reviewers to allow full evaluation to take place. This is now commonplace and is seen as best practice. Author guidelines now include sections related to misconduct and falsification of data [28] . By participating in self-archiving practices and providing full data sets, authors can play their part in transparency.
The Royal Pharmaceutical Society website hosts a database to help share data from research studies. The map of evidence collates existing evidence and ongoing initiatives that can ultimately inform policy and practice relating to pharmacy; enables the sharing and showcasing of good pharmacy practice and innovation; and aims to increase the knowledge exchange and learning in pharmacy and pharmaceutical sciences [29] .
Revising your article prior to submission
Once a draft research article has been prepared, it should be shared among all of the co-authors for review and comments. A full revision of the draft should then take place to correct grammar and check flow and logic before journal submission. All authors will have to agree on the authenticity of the data and presentation before formal submission can take place [3] (see ‘Box 2: Common mistakes and reasons why research articles are rejected for publication’).
Box 2: Common mistakes and reasons why research articles are rejected for publication
- Lack of novelty and importance of the research question;
- Poor study design;
- Methods not accurately and adequately described;
- Results poorly reported, along with little analysis of data;
- Lack of statistical analysis;
- Not acknowledging the study’s limitations;
- Providing unsupported conclusions or overstating the results of the study;
- Poor writing;
- Not following the journal’s style and formatting guidance;
- Submitting a manuscript that is incomplete or outside of the aims and scope.
Selecting a journal and submitting your manuscript
It is important to select a journal for submission wisely because this choice can determine the impact and dissemination of your work [13] . Impact factor (a measure of the frequency with which the average article in a journal has been cited in a particular year), the scope and readership of a title may also influence your choice.
Furthermore, approval and adequate disclosures must be obtained from all co-authors. A conflict of interests form is also completed as part of the submissions process (normally completed by the lead author on behalf of all authors).
Many journals now request that a cover letter is also submitted to the editor, putting the study in context and explaining why the research is of importance to their audience and why it should be considered for publication in their journal.
Once this is all completed, the article can be formally submitted (usually via email or an online submission system). Figure 2 provides a sample process for a manuscript once submitted to a journal for consideration for publication.
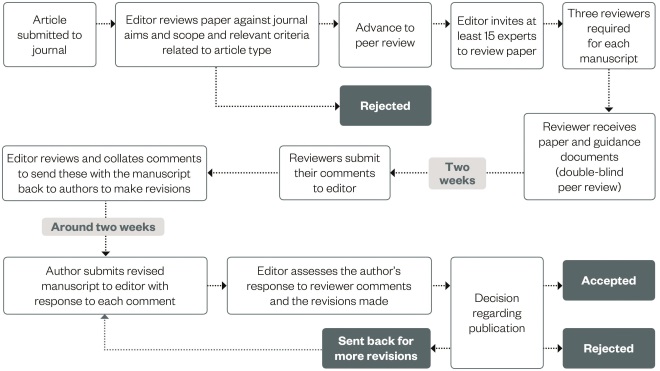
Figure 2: Sample process for a submitted manuscript
Source: The Pharmaceutical Journal
All journals follow a similar process for article submissions, whether they use a formal online submissions system or simply email. Clinical Pharmacist uses a process similar to this and it is useful for authors to be aware of how their submission may progress once submitted to a journal for publication.
Useful Links
- The EQUATOR Network
- Research4Life – Authorship skills modules
- Pharmacy Research UK
Reading this article counts towards your CPD
You can use the following forms to record your learning and action points from this article from Pharmaceutical Journal Publications.
Your CPD module results are stored against your account here at The Pharmaceutical Journal . You must be registered and logged into the site to do this. To review your module results, go to the ‘My Account’ tab and then ‘My CPD’.
Any training, learning or development activities that you undertake for CPD can also be recorded as evidence as part of your RPS Faculty practice-based portfolio when preparing for Faculty membership. To start your RPS Faculty journey today, access the portfolio and tools at www.rpharms.com/Faculty
If your learning was planned in advance, please click:
If your learning was spontaneous, please click:
[1] Boyer E. Scholarship reconsidered: Priorities for the professoriate . 1990. Princeton, NJ: The Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching.
[2] Hoogenboom BJ & Manske RC. How to write a scientific article. Int J Sports Phys Ther . 2012;7(5):512–517. PMCID: PMC3474301
[3] International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Recommendations for the conduct, reporting, editing, and publication of scholarly work in medical journals. 2014. Available at: http://www.icmje.org/icmje-recommendations.pdf (accessed November 2016).
[4] Dowdall M. How to be an effective peer reviewer. Clinical Pharmacist 2015;7(10). doi: 10.1211/CP.2015.20200006
[5] Nahata MC. Tips for writing and publishing an article. Ann Pharmaco . 2008;42:273–277. doi: 10.1345/aph.1K616
[6] Dixon N. Writing for publication: A guide for new authors. Int J Qual Health Care . 2001;13:417–421. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/13.5.417
[7] Keys CW. Revitalizing instruction in scientific genres: Connecting knowledge production with writing to learn in science. Sci Educ . 1999;83:115–130.
[8] Gopen G & Swan J. The science of scientific writing. Am Sci . 1990;78:550–558. Available at: http://www.americanscientist.org/issues/pub/the-science-of-scientific-writing (accessed November 2016)
[9] Hulley S, Cummings S, Browner W et al . Designing clinical research. 3rd ed. Philadelphia (PA): Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2007.
[10] The Pharmaceutical Journal and Clinical Pharmacist. Author Guidance (2015). Available at: http://www.pharmaceutical-journal.com/for-authors-and-referees/article-types/#Practice_reports (accessed November 2016)
[11] Fisher JP, Jansen JA, Johnson PC et al . Guidelines for writing a research article for publication. Mary Ann Liebert Inc. Available at: https://www.liebertpub.com/media/pdf/English-Research-Article-Writing-Guide.pdf (accessed November 2016)
[12] Nature. Author Resources: How to write a paper. Available at: http://www.nature.com/authors/author_resources/how_write.html (accessed November 2016)
[13] Wiley Online Library. Resources for authors and reviewers: preparing your article. Available at: http://olabout.wiley.com/WileyCDA/Section/id-828006.html (accessed November 2016)
[14] SAGE Publications. Help readers find your article. Available at: http://www.uk.sagepub.com/journalgateway/findArticle.htm (accessed November 2016)
[15] Bem DJ. Writing the empirical journal article. In: MP Zanna & JM Darley (Eds.), The complete academic: a practical guide for the beginning social scientist (pp. 171–201). New York: Random House; 1987.
[16] Fathalla M & Fathalla M. A practical guide for health researchers. Available at: http://www.emro.who.int/dsaf/dsa237.pdf (accessed November 2016)
[17] Coghill A & Garson L (Eds.). Scientific Papers. In: A Coghill & L Garson (Eds.), The ACS Style Guide, 3 rd Edition (pp. 20–21). New York: Oxford University Press, 2006.
[18] The Scholarly Publishing and Academic Resources Institute. Available at: http://sparcopen.org/open-access/ (accessed November 2016).
[19] Elsevier. Understanding the publishing process: how to publish in scholarly journals. Available at: https://www.elsevier.com/__data/assets/pdf_file/0003/91173/Brochure_UPP_April2015.pdf (accessed November 2016).
[20] SciDevNet. How do I write a scientific paper? 2008. Available at: http://www.scidev.net/global/publishing/practical-guide/how-do-i-write-a-scientific-paper-.html (accessed November 2016)
[21] Moher D, Schultz KR & Altman DG. CONSORT GROUP (Consolidatied Standards of Reporting Trials). The CONSORT statement: Revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallelâ€group randomized controlled trials. Ann Intern Med . 2001;134:657–662. PMID: 11304106
[22] Bossuyt PM, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE et al . Towards complete and accurate reporting of studies of diagnostic accuracy: The STARD Initiative. Ann Int Med 2003;138:40–44. PMID: 12513043
[23] Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J et al . The PRISMA Group (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and metaâ€analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(6):e1000097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed1000097
[24] Devers KJ & Frankel RM. Getting qualitative research published. Educ Health 2001;14:109–117. doi: 10.1080/13576280010021888
[25] Van Way CW. Writing a scientific paper. Nutr Clin Pract 2007;22:636–640. PMID: 18042951
[26] Kishore V. When to use a survey in pharmacy practice research. The Pharmaceutical Journal 296(7886). doi: 10.1211/PJ.2016.20200700
[27] Perneger PV & Hudelson PM. Writing a research article: advice to beginners . Int J Qual Health Care 2004;16(3):191–192. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/mzh053
[28] World Association of Medical Editors. Professionalism Code of Conduct. 2016. Available at: http://www.wame.org/News/Details/16 (accessed November 2016)
[29] Royal Pharmaceutical Society. Map of Evidence. Available at: http://www.rpharms.com/support/map-of-evidence.asp (accessed November 2016)
You might also be interested in…

Working to improve our digital archive
The Pharmaceutical Journal is moving forward into a digital future

The launch of our new digital platform is just the beginning of our plans for the future of PJ
- (855) 776-7763
Training Maker
All Products
Qualaroo Insights
ProProfs.com
- Sign Up Free
Do you want a free Survey Software?
We have the #1 Online Survey Maker Software to get actionable user insights.
How To Write a Good Research Question: Guide with Definition, Tips & Examples

Sameer Bhatia
Founder and CEO - ProProfs
Review Board Member
Sameer Bhatia is the Founder and Chief Executive Officer of ProProfs.com. He believes that software should make you happy and is driven to create a 100-year company that delivers delightfully ... Read more
Sameer Bhatia is the Founder and Chief Executive Officer of ProProfs.com. He believes that software should make you happy and is driven to create a 100-year company that delivers delightfully smart software with awesome support. His favorite word is 'delight,' and he dislikes the term 'customer satisfaction,' as he believes that 'satisfaction' is a low bar and users must get nothing less than a delightful experience at ProProfs. Sameer holds a Masters in Computer Science from the University of Southern California (USC). He lives in Santa Monica with his wife & two daughters. Read less

Market Research Specialist
Emma David, a seasoned market research professional, specializes in employee engagement, survey administration, and data management. Her expertise in leveraging data for informed decisions has positively impacted several brands, enhancing their market position.

Research questions form the backbone of any study, guiding researchers in their search for knowledge and understanding. Framing relevant research questions is the first essential step for ensuring the research is effective and produces valuable insights.
In this blog, we’ll explore what research questions are, tips for crafting them, and a variety of research question examples across different fields to help you formulate a well-balanced research questionnaire.
Let’s begin.
What Is a Research Question?
A research question is a specific inquiry or problem statement guiding a research study, outlining the researcher’s intention to investigate. Think of it as a roadmap for your paper or thesis – it tells you exactly what you want to explore, giving your work a clear purpose.
A good research question not only helps you focus your writing but also guides your readers. It gives them a clear idea of what your research is about and what you aim to achieve. Before you start drafting your paper and even before you conduct your study, it’s important to write a concise statement of what you want to accomplish or discover.
This sets the stage for your research and ensures your work is focused and purposeful.
Why Are Research Questions Important?
Research questions are the cornerstone of any academic or scientific inquiry. They serve as a guide for the research process, helping to focus the study, define its goals, and structure its methodology.
Below are some of its most significant impacts, along with hypothetical examples to help you understand them better:
1. Guidance and Focus
Research questions provide a clear direction for the study, enabling researchers to narrow down the scope of their investigation to a manageable size. Research efforts can become scattered and unfocused without a well-defined question without a well-defined question, leading to wasted time and resources.
For example, consider a researcher interested in studying the effects of technology on education. A broad interest in technology and education could lead to an overwhelming range of topics to cover. However, by formulating a specific research question such as, “ How does the use of interactive digital textbooks in high school science classes affect students’ learning outcomes?” the researcher can focus their study on a specific aspect of technology in education, making the research more manageable and directed.
2. Defining the Research Objectives
A well-crafted research question helps to clearly define what the researcher aims to discover, examine, or analyze. This clarity is crucial for determining the study’s objectives and ensures that every step of the research process contributes toward achieving these goals.
For example, in a study aimed at understanding the impact of remote work on employee productivity, a research question such as “ Does remote work increase productivity among information technology professionals? ” directly sets the objective of the study to measure productivity levels among a specific group when working remotely.
3. Determining the Research Methodology
The research question influences the choice of methodology, including the design, data collection methods, and analysis techniques. It dictates whether the study should be qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods and guides the selection of tools and procedures for conducting the research.
For example, in a research question like “ What are the lived experiences of first-generation college students? ” a qualitative approach using interviews or focus groups might be chosen to gather deep, nuanced insights into students’ experiences. In contrast, a question such as “ What percentage of first-generation college students graduate within four years?” would require a quantitative approach, possibly utilizing existing educational data sets for analysis.
4. Enhancing Relevance and Contribution
A well-thought-out research question ensures that the study addresses a gap in the existing literature or solves a real-world problem. This relevance is crucial for the contribution of the research to the field, as it helps to advance knowledge, inform policy, or offer practical solutions.
For example, in a scenario where existing research has largely overlooked the environmental impacts of single-use plastics in urban waterways, a question like “ What are the effects of single-use plastic pollution on the biodiversity of urban waterways?” can fill this gap, contributing valuable new insights to environmental science and potentially influencing urban environmental policies.
5. Facilitating Data Interpretation and Analysis
Clear research questions help in structuring the analysis, guiding the interpretation of data, and framing the discussion of results. They ensure that the data collected is directly relevant to the questions posed, making it easier to draw meaningful conclusions.
For example, in a study asking, “ How do social media algorithms influence political polarization among users? ” the data analysis would specifically focus on the mechanisms of algorithmic content delivery and its effects on user behavior and political views. This focus makes it straightforward to interpret how algorithm-induced echo chambers might contribute to polarization.
Types of Research Questions
Understanding the different types of research questions is essential for researchers to effectively design and conduct studies that align with their research objectives and methodologies
These questions can be broadly categorized into three main types: quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-method research questions.
Let’s explore each type in-depth, along with some examples.
Type A: Quantitative Research Questions
Quantitative research involves the collection and analysis of numerical data to answer specific research questions or hypotheses. It focuses on quantifying relationships, patterns, and phenomena, often using statistical methods for analysis. Quantitative research questions are typically structured and aim to explore relationships between variables or assess the impact of interventions.
Quantitative research questions can again be subcategorized into three distinct types:
1. Descriptive Questions :
Descriptive questions aim to describe characteristics, behaviors, or phenomena within a population. These questions often start with words like “ how much ,” “ how many ,” or “ what is the frequency of .” They provide a snapshot of a particular situation or phenomenon.
Example: “ What is the average age of first-time homebuyers in the United States?”
2. Comparative Questions :
Comparative questions seek to compare two or more groups, conditions, or variables to identify differences or similarities. They often involve the use of statistical tests to determine the significance of observed differences or associations.
Example: “Is there a significant difference in academic performance between students who receive tutoring and those who do not?”
3. Relationship Questions:
Relationship questions explore the associations or correlations between variables. They aim to determine the strength and direction of relationships, allowing researchers to assess the predictive power of one variable on another.
Example: “What is the relationship between exercise frequency and levels of anxiety among adults?”
Type B: Qualitative Research Questions
Qualitative research involves the exploring and understanding of complex phenomena through an in-depth examination of individuals’ experiences, behaviors, and perspectives. It aims to uncover meaning, patterns, and underlying processes within a specific context, often through techniques such as interviews, observations, and content analysis.
Types of qualitative research questions:
1. Exploratory Questions:
Exploratory questions seek to understand a particular phenomenon or issue in depth. They aim to uncover new insights, perspectives, or dimensions that may not have been previously considered.
Example: “What are the experiences of LGBTQ+ individuals in accessing healthcare services in rural communities?”
2. Descriptive Questions:
Descriptive questions aim to provide a detailed description or portrayal of a phenomenon or social context. They focus on capturing the intricacies and nuances of a particular situation or setting.
Example: “What are the communication patterns within multicultural teams in a corporate setting?”
3. Explanatory Questions:
Explanatory questions delve into the underlying reasons, mechanisms, or processes that influence a phenomenon or behavior. They aim to uncover the ‘why’ behind observed patterns or relationships.
Example: “What factors contribute to employee turnover in the hospitality industry?”
Type C: Mixed-Methods Research Questions
Mixed-methods research integrates both quantitative and qualitative approaches within a single study, allowing researchers to gain a comprehensive understanding of a research problem. Mixed-method research questions are designed to address complex phenomena from multiple perspectives, combining the strengths of both quantitative and qualitative methodologies.
Types of Mixed-Methods Research Questions:
1. Sequential Questions:
Sequential questions involve the collection and analysis of quantitative and qualitative data in separate phases or stages. The findings from one phase inform the design and implementation of the subsequent phase.
Example: “Quantitatively, what are the prevalence rates of mental health disorders among adolescents? Qualitatively, what are the factors influencing help-seeking behaviors among adolescents with mental health concerns?”
2. Concurrent Questions:
Concurrent questions involve the simultaneous collection and analysis of quantitative and qualitative data. Researchers triangulate findings from both methods to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the research problem.
Example: “How do students’ academic performance (quantitative) correlate with their perceptions of school climate (qualitative)?”
3. Transformative Questions:
Transformative questions aim to use mixed-methods research to bring about social change or inform policy decisions. They seek to address complex societal issues by combining quantitative data on prevalence rates or trends with qualitative insights into lived experiences and perspectives.
Example: “What are the barriers to accessing healthcare services for underserved communities, and how can healthcare policies be redesigned to address these barriers effectively?”
Steps to Developing a Good Research Question
Developing a good research question is a crucial first step in any research endeavor. A well-crafted research question serves as the foundation for the entire study, guiding the researcher in formulating hypotheses, selecting appropriate methodologies, and conducting meaningful analyses.
Here are the steps to developing a good research question:
Identify a Broad Topic
Begin by identifying a broad area of interest or a topic that you would like to explore. This could stem from your academic discipline, professional interests, or personal curiosity. However, make sure to choose a topic that is both relevant and feasible for research within the constraints of your resources and expertise.
Conduct Preliminary Research
Before refining your research question, conduct preliminary research to familiarize yourself with existing literature and identify gaps, controversies, or unanswered questions within your chosen topic. This step will help you narrow down your focus and ensure that your research question contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
Narrow Down Your Focus
Based on your preliminary research, narrow down your focus to a specific aspect, problem, or issue within your chosen topic. Consider the scope of your study, the availability of resources, and the feasibility of addressing your research question within a reasonable timeframe. Narrowing down your focus will help you formulate a more precise and manageable research question.
Define Key Concepts and Variables
Clearly define the key concepts, variables, or constructs that are central to your research question. This includes identifying the main variables you will be investigating, as well as any relevant theoretical or conceptual frameworks that will guide your study. Clarifying these aspects will ensure that your research question is clear, specific, and focused.
Formulate Your Research Question
Based on your narrowed focus and defined key concepts, formulate your research question. A good research question is concise, specific, and clearly articulated. It should be phrased in a way that is open-ended and leads to further inquiry. Avoid vague or overly broad questions that are difficult to answer or lack clarity.
Consider the Type of Research
Consider whether your research question is best suited for quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods research. The type of research question will influence your choice of methodologies, data collection techniques, and analytical approaches. Tailor your research question to align with the goals and requirements of your chosen research paradigm.
Evaluate the Significance and Relevance
Evaluate the significance and relevance of your research question within the context of your academic discipline, field of study, or practical implications. Consider how your research question fills gaps in knowledge, addresses practical problems, or advances theoretical understanding. A good research question should be meaningful and contribute to the broader scholarly conversation.
Refine and Revise
Finally, refine and revise your research question based on feedback from colleagues, advisors, or peers. Consider whether the question is clear, feasible, and likely to yield meaningful results. Be open to making revisions as needed to ensure that your research question is well-constructed and aligned with the goals of your study.
Examples of Research Questions
Below are some example research questions from various fields to provide a glimpse into the diverse array of inquiries within each field.
1. Psychology Research Questions:
- How does childhood trauma influence the development of personality disorders in adulthood?
- What are the effects of mindfulness meditation on reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression?
- How does social media usage impact self-esteem among adolescents?
- What factors contribute to the formation and maintenance of romantic relationships in young adults?
- What are the cognitive mechanisms underlying decision-making processes in individuals with addiction?
- How does parenting style affect the development of resilience in children?
- What are the long-term effects of early childhood attachment patterns on adult romantic relationships?
- What role does genetics play in the predisposition to mental health disorders such as schizophrenia?
- How does exposure to violent media influence aggressive behavior in children?
- What are the psychological effects of social isolation on mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic?
2. Business Research Questions:
- What are the key factors influencing consumer purchasing behavior in the e-commerce industry?
- How does organizational culture impact employee job satisfaction and retention?
- What are the strategies for successful international market entry for small businesses?
- What are the effects of corporate social responsibility initiatives on brand reputation and consumer loyalty?
- How do leadership styles influence organizational innovation and performance?
- What are the challenges and opportunities for implementing sustainable business practices in emerging markets?
- What factors contribute to the success of startups in the technology sector?
- How do economic fluctuations affect consumer confidence and spending behavior?
- What are the impacts of globalization on supply chain management practices?
- What are the determinants of successful mergers and acquisitions in the corporate sector?
3. Education Research Questions:
- What teaching strategies are most effective for promoting student engagement in online learning environments?
- How does socioeconomic status impact academic achievement and educational attainment?
- What are the barriers to inclusive education for students with disabilities?
- What factors influence teacher job satisfaction and retention in urban schools?
- How does parental involvement affect student academic performance and school outcomes?
- What are the effects of early childhood education programs on later academic success?
- How do culturally responsive teaching practices impact student learning outcomes in diverse classrooms?
- What are the best practices for implementing technology integration in K-12 education?
- How do school leadership practices influence school climate and student outcomes?
- What interventions are most effective for addressing the achievement gap in STEM education?
4. Healthcare Research Questions:
- What are the factors influencing healthcare-seeking behavior among underserved populations?
- How does patient-provider communication affect patient satisfaction and treatment adherence?
- What are the barriers to implementing telemedicine services in rural communities?
- What interventions are effective for reducing hospital readmissions among elderly patients?
- How does access to healthcare services impact health disparities among marginalized communities?
- What are the effects of nurse staffing levels on patient outcomes in acute care settings?
- How do socioeconomic factors influence access to mental healthcare services?
- What are the best practices for managing chronic disease patients in primary care settings?
- What are the impacts of healthcare reform policies on healthcare delivery and patient outcomes?
- How does cultural competence training for healthcare providers affect patient trust and satisfaction?
5. Computer Science Research Questions:
- What are the security vulnerabilities of blockchain technology, and how can they be mitigated?
- How can machine learning algorithms be used to detect and prevent cyber-attacks?
- What are the privacy implications of data mining techniques in social media platforms?
- How can artificial intelligence be used to improve medical diagnosis and treatment?
- What are the challenges and opportunities for implementing edge computing in IoT systems?
- How can natural language processing techniques be applied to improve human-computer interaction?
- What are the impacts of algorithmic bias on fairness and equity in decision-making systems?
- How can quantum computing algorithms be optimized for solving complex computational problems?
- What are the ethical considerations surrounding the use of autonomous vehicles in transportation systems?
- How does the design of user interfaces influence user experience and usability in mobile applications?
Create a Compelling Research Question With the Given Examples
Understanding research questions is essential for any successful research endeavor. We’ve explored the various research questions – quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-methods – each with unique characteristics and purposes.
Through various examples, tips, and strategies, we’ve seen how research questions can be tailored to specific fields of study.
By following these guidelines, we are confident that your research questions will be well-designed, focused, and capable of yielding valuable insights.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some good research question examples.
Good research questions are clear, specific, relevant, and feasible. For example, “How does childhood trauma influence the development of personality disorders in adulthood?”
What are some examples of good and bad research questions?
Good research questions are focused and relevant, such as “What factors influence employee job satisfaction in the hospitality industry?” Bad research questions are vague or trivial, like “What is the favorite color of employees in the hospitality industry?”
Watch: How to Create a Survey Using ProProfs Survey Maker

About the author
Emma David is a seasoned market research professional with 8+ years of experience. Having kick-started her journey in research, she has developed rich expertise in employee engagement, survey creation and administration, and data management. Emma believes in the power of data to shape business performance positively. She continues to help brands and businesses make strategic decisions and improve their market standing through her understanding of research methodologies.
Popular Posts in This Category
Employee Surveys is Still the Best Way to Measure Engagement

Employee Engagement Surveys: Everything You Need To Know

10 Best Exit Interview Software to Look for in 2024

Conducting Gap Analysis: Steps, Tools and Examples

20 Website Survey Questions to Ask Your Customers in 2024

50+ Inspirational Customer Satisfaction Quotes From Experts
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Home › Resources › Giving Effective Feedback on Student Writing
Giving Effective Feedback on Student Writing
By Amanda Leary
Providing feedback is one of the most critical tasks of teaching. Well-balanced feedback, addressing both achievements and areas for improvement, can help students develop new skills, reinforce their learning, and boost their academic confidence. Ineffective feedback, however, can compound students’ low motivation and self-perception, hindering their development and learning (Wingate, 2010). Good feedback does much more than correct errors; it’s an opportunity to empower and affirm students as knowledge makers, to improve their self-awareness, and to develop strategies for improvement now and in their future work.
By focusing on providing quality, effective feedback, we can maximize its positive effects on learning—not only helping students become better writers, but better thinkers, with increased confidence and motivation to succeed. This doesn’t happen in a vacuum, however; feedback isn’t useful for students if they don’t understand or know how to incorporate it.
Deciding what and how much to comment on will depend on your particular disciplinary, class, and assignment context. The strategies below will help you determine what kind of feedback to give and when, as well as identify potential next steps for helping students actually use your feedback.
Preparing to Give Feedback
Before you ever read the first paper, there are a few key questions to ask yourself that can help save a lot of time and make your feedback more effective: 1) why are you giving feedback , and 2) what are you looking for? Let’s take these in turn.
Why are you giving feedback?
Depending on when in the writing process you’re providing students with feedback, your comments will serve different purposes. Just as assignments can be either formative or summative , so, too, can your feedback. Summative feedback addresses what students did well or poorly at one particular instance and is often used in evaluation to justify a grade, whereas formative feedback often answers, “What can I do to improve next time?” While formative feedback often aligns with formative assignments, such as drafts and other process work such as proposals and outlines, you can also provide formative feedback on final, summative assignments and vice versa. We often switch between these two types of feedback on a single assignment, so taking time to establish beforehand what the goal of giving feedback is will focus the kinds of comments you make. It might be helpful for students to use markers in your comments to clearly distinguish between “this time” and “next time” feedback.
Another way to distinguish the two is in your mindset toward the task of giving feedback: are you a coach or a grader? If you’re approaching student work with the sole purpose of attaching a grade, then your feedback is likely to be more summative—feeding back to the writing. The mindset of a reader, however, is more aligned with a developmental approach giving more formative feedback. Here, we might think more in terms of feeding forward —concentrating our attention on actionable steps students can take to continue to improve their writing.
What are you looking for?
Sometimes, the hardest part about giving feedback can be deciding where to start. We know good writing when we see it; however, articulating those features of good writing into clearly defined criteria for a successful assignment can help mitigate the feeling that you need to comment on every feature or correct every mistake you see. Providing these criteria to students in advance has demonstrable benefits for their learning and can improve the quality of their assignments (Brookhart, 2018). Criteria should be aligned with the goals you have for the assignment, the overall goals of your course, and targeted at students at the appropriate level (Hattie and Timperley, 2007).
As you’re developing your criteria, you may find it helpful to prioritize your higher-order and lower-order concerns . Higher-order concerns will be more closely aligned with your goals for the assignment. For example, if you are providing feedback on a seminar paper, your higher-order concerns may be related to how well students demonstrated their understanding of a particular set of readings through a clearly articulated thesis and synthesis of primary and secondary sources. Lower-order concerns, such as sentence structure and grammar, would not feature as heavily in your feedback except where they affect the readability of the writing. However, if teaching specific writing skills was the primary focus of your class, your higher-order concerns might include sentence structure or grammatical understanding. Knowing what your priorities are for students’ writing before you sit down with the first assignment will keep your feedback targeted to your high-priority criteria rather than noting every little detail, resulting in fewer comments—which can be overwhelming for both you and students.
Taking the time to identify why you’re giving feedback and what your priorities are for students’ writing keeps your comments focused and relevant to students.
While You’re Responding to Student Work
Whether formative or summative, your feedback should be specific , actionable , focused on patterns , and balanced . The following tips will help you not only save time commenting, but will also ensure your comments are useful to students:
- Be specific: Simply underlining, using exclamation marks, or the infamous “awkward” doesn’t tell students anything about how to revise their essay. Highlight strengths and weaknesses in reference to specific passages and examples and offer concrete, actionable suggestions for improvement.
- Focus on action: If students don’t understand your comments, they can’t use them (Chanock, 2000; Lea and Steirer, 2000). We may know what periodic and loose sentences are, or maybe we wrote our dissertation on that niche author that would really round out a students’ discussion of a topic. Writing “comma splice” or “what about the kinematics of root growth” in the margins without explaining what that is or why it matters for their writing (especially if it isn’t connected to what you’ve taught in class) isn’t actionable feedback.
- Look for patterns: There are likely to be several mistakes repeated within and across students’ writing. Keep a comment back of feedback addressing common mechanical mistakes; rather than re-writing the same comment on every paper, you can note the first instance with an explanatory comment that applies across students. Over time, you might also develop a repository of recurring comments on more structural or content-based patterns, such as thesis development, structure and organization, or use of quotes and evidence. Having stock language on hand that you can then tailor to a student’s particular essay can help save time. Where you see the same mistake being repeated across student work, you can include a more general comment about the issue with a note that more information will be provided in class.
- Balance praise and critique: The most effective feedback contains a balance of challenge and support (Lizzio and Wilson, 2008). This doesn’t mean, however, that we should feel compelled to use the “feedback sandwich”: placing critical feedback between moments of praise. Students can recognize and discount token positive comments (Hyland and Hyland, 2001), so rather than sandwiching feedback, give valid criticism while offering encouragement, genuine appreciation for student writing, and belief in students’ ability to succeed.
Applying Feedback
Giving feedback is just one part of the process; it is equally important for students to be active participants if learning is to happen (Winstone et al., 2017). Depending on the context of your course, you might facilitate student engagement with feedback in class or through assignments that promote reflection on the writing process:
- Use class time to address feedback that applies to many students’ work. Provide instruction or resources for how students can integrate that feedback into their writing with an opportunity to practice.
- Where time allows, incorporate writing days into your course calendar as a dedicated opportunity for students to work through your feedback as they revise their assignments.
- Try a reflective feedback journal as a space for students to reflect on their immediate reactions to your comments and how they plan to address them. This could be done in class or as part of an ongoing journal throughout the course.
- Incorporate peer review as a mechanism for understanding feedback and to empower students to further self-assess their own work (McConlogue, 2020; Huisman et al., 2019).
- Add a brief metacognitive cover letter or memo to final assignments that asks students to reflect on how they incorporated feedback from rough to final draft.
Integrating these strategies into your practice will not only save you time, but helps keep your feedback targeted, educative, and effective. Viewing feedback as a dialogic process that begins before you make your first comment and involves students as active recipients of that feedback is an important part of giving students comments they can—and actually want to—use.
Brookhart, Susan M. “Appropriate Criteria: Key to Effective Rubrics.” Frontiers in Education 3 (2018).
Chanock, Kate. “Comments on Essays: Do Students Understand What Tutors Write?” Teaching in Higher Education 5, no. 1 (2000): 95–105.
Hattie, John, and Helen Timperley. “The Power of Feedback.” Review of Educational Research 77, no. 1 (2007): 81–112.
Huisman, Bart, Nadira Saab, Paul van den Broek, and Jan van Driel. “The Impact of Formative Peer Feedback on Higher Education Students’ Academic Writing: a Meta-Analysis.” Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education 44, no. 6 (2019): 863–80.
Hyland, Fiona, and Ken Hyland. “Sugaring the Pill: Praise and Criticism in Written Feedback.” Journal of Second Language Writing 10, no. 3 (2001): 185–212.
Lea, M. R. and Steirer, B. (eds). Student Writing in Higher Education: New Contexts . Buckingham: Open University Press, 2000.
Lizzio, Alf, and Keithia Wilson. “Feedback on Assessment: Students’ Perceptions of Quality and Effectiveness.” Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education 33, no. 3 (2008): 263–75.
McConlogue, Teresa. Assessment and Feedback in Higher Education: A Guide for Teachers . UCL Press. 1st ed. London: UCL Press, 2020.
Wingate, Ursula. “The Impact of Formative Feedback on the Development of Academic Writing.” Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education 35, no. 5 (2010): 519–33.
Winstone, Naomi E., Robert A. Nash, James Rowntree, and Michael Parker. “‘It’d Be Useful, but I Wouldn’t Use It’: Barriers to University Students’ Feedback Seeking and Recipience.” Studies in Higher Education (Dorchester-on-Thames) 42, no. 11 (2017): 2026–41.
Send a Message

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
We've covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are: To choose a research question and review the literature. To plan your paper structure and draft an outline. To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing.
Choose a research paper topic. Conduct preliminary research. Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft.
Overall, while writing an article from scratch may appear a daunting task for many young researchers, the process can be largely facilitated by good groundwork when preparing your research project, and a systematic approach to the writing, following these simple guidelines for each section (see summary in Fig. 1). It is worth the effort of ...
The typical research paper is a highly codified rhetorical form [1, 2]. Knowledge of the rules—some explicit, others implied—goes a long way toward writing a paper that will get accepted in a peer-reviewed journal. Primacy of the research question. A good research paper addresses a specific research question.
Unlike essays, research papers usually divide the body into sections with separate headers to facilitate browsing and scanning. Use the divisions in your outline as a guide. Follow along your outline and go paragraph by paragraph. Because this is just the first draft, don't worry about getting each word perfect.
Assuming a student wants to publish their research article before the residency application is submitted, there are 3.5 years to excel in class and publish the best research possible. Many times, as class intensifies, the writing takes a backseat. This is really common. Then returning to writing can be challenging for a student without a plan.
This article presents a detailed guide for high school through graduate level instructors that leads students to write effective and well-organized scientific papers. Interesting research emerges from the ability to ask questions, define problems, design experiments, analyze and interpret data, and make critical connections.
Unlock the secrets to crafting an outstanding research paper with our step-by-step guide. From choosing a compelling topic to refining your thesis statement, our expert tips will help you navigate the intricacies of research paper writing. Elevate your academic prowess and ensure success in your endeavors with this essential resource.
All good writing starts with analytical reading. When you start reading a book or viewing a film, immediately make connections, stretch your imagination, ask questions, and anticipate conclusions. By becoming an active reader your mind will be analyzing the information simultaneously as you experience the journal article, book or film.
A clear format will ensure that your research paper is understood by your readers. Follow: 1. Context — your introduction. 2. Content — your results. 3. Conclusion — your discussion. Plan ...
By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers. 5. Write a thesis statement. A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction.
Definition: Research Paper is a written document that presents the author's original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue. It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
This article takes you through the first steps of the research process, helping you narrow down your ideas and build up a strong foundation for your research project. Table of contents. Step 1: Choose your topic. Step 2: Identify a problem. Step 3: Formulate research questions.
Then, writing the paper and getting it ready for submission may take me 3 to 6 months. I like separating the writing into three phases. The results and the methods go first, as this is where I write what was done and how, and what the outcomes were. In a second phase, I tackle the introduction and refine the results section with input from my ...
Upload your paper & get a free Expert Check. The pages in this section cover the following topic areas related to the process of writing a research paper: Genre - This section will provide an overview for understanding the difference between an analytical and argumentative research paper. Choosing a Topic - This section will guide the student ...
Copy your outline into a separate file and expand on each of the points, adding data and elaborating on the details. When you create the first draft, do not succumb to the temptation of editing. Do not slow down to choose a better word or better phrase; do not halt to improve your sentence structure.
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
groundbreaking research with leaders in the field. You get your Ph.D., and you're ready to open your own lab. That takes money, so you've got to write a funding application. Then you've got to be able to write up your research in academic articles that can be published to the scientific community that needs to know about your work.
Introduction. Undergraduate research (UR) is a high-impact practice that has been demonstrated to benefit student learning, persistence, and career preparation [1,2].Undergraduate research serves as a robust intervention for students from underrepresented groups who are at risk of dropping out of college [3,4].By engaging students during their early years of study, they develop a sense of ...
The process of publication of a scientific article consists of several important stages, summarized in Fig. 1.Prior to writing an article, it may take several months or even years to obtain results of research relevant enough to be published [1].This may look as the most demanding part of the process (and it usually is the case), but what follows should also be done with much care in order to ...
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
Once this is all completed, the article can be formally submitted (usually via email or an online submission system). Figure 2 provides a sample process for a manuscript once submitted to a journal for consideration for publication. Figure 2: Sample process for a submitted manuscript. Source: The Pharmaceutical Journal.
Research papers rely on other people's writing as a foundation to create new ideas, but you can't just use someone else's words. That's why paraphrasing is an essential writing technique for academic writing.. Paraphrasing rewrites another person's ideas, evidence, or opinions in your own words.With proper attribution, paraphrasing helps you expand on another's work and back up ...
This paragraph should both attract the reader's attention and give them the necessary information about the paper. In any academic paper, the introduction paragraph constitutes 10% of the paper's total word count. For example, if you are preparing a 3,000-word paper, your introduction paragraph should consist of approximately 300 words.
5. Facilitating Data Interpretation and Analysis. Clear research questions help in structuring the analysis, guiding the interpretation of data, and framing the discussion of results. They ensure that the data collected is directly relevant to the questions posed, making it easier to draw meaningful conclusions.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use" Title page
Providing feedback is one of the most critical tasks of teaching. Well-balanced feedback, addressing both achievements and areas for improvement, can help students develop new skills, reinforce their learning, and boost their academic confidence. Ineffective feedback, however, can compound students' low motivation and self-perception ...
Stock market data coverage from CNN. View US markets, world markets, after hours trading, quotes, and other important stock market activity.