Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.

How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay (With Example)
November 27, 2023

Feeling intimidated by the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? We’re here to help demystify. Whether you’re cramming for the AP Lang exam right now or planning to take the test down the road, we’ve got crucial rubric information, helpful tips, and an essay example to prepare you for the big day. This post will cover 1) What is the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? 2) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Rubric 3) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis: Sample Prompt 4) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example 5)AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Why It Works
What is the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is one of three essays included in the written portion of the AP English Exam. The full AP English Exam is 3 hours and 15 minutes long, with the first 60 minutes dedicated to multiple-choice questions. Once you complete the multiple-choice section, you move on to three equally weighted essays that ask you to synthesize, analyze, and interpret texts and develop well-reasoned arguments. The three essays include:
Synthesis essay: You’ll review various pieces of evidence and then write an essay that synthesizes (aka combines and interprets) the evidence and presents a clear argument. Read our write up on How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis Essay here.
Argumentative essay: You’ll take a stance on a specific topic and argue your case.
Rhetorical essay: You’ll read a provided passage, then analyze the author’s rhetorical choices and develop an argument that explains why the author made those rhetorical choices.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Rubric
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is graded on just 3 rubric categories: Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication . At a glance, the rubric categories may seem vague, but AP exam graders are actually looking for very particular things in each category. We’ll break it down with dos and don’ts for each rubric category:
Thesis (0-1 point)
There’s nothing nebulous when it comes to grading AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay thesis. You either have one or you don’t. Including a thesis gets you one point closer to a high score and leaving it out means you miss out on one crucial point. So, what makes a thesis that counts?
- Make sure your thesis argues something about the author’s rhetorical choices. Making an argument means taking a risk and offering your own interpretation of the provided text. This is an argument that someone else might disagree with.
- A good test to see if you have a thesis that makes an argument. In your head, add the phrase “I think that…” to the beginning of your thesis. If what follows doesn’t logically flow after that phrase (aka if what follows isn’t something you and only you think), it’s likely you’re not making an argument.
- Avoid a thesis that merely restates the prompt.
- Avoid a thesis that summarizes the text but does not make an argument.
Evidence and Commentary (0-4 points)
This rubric category is graded on a scale of 0-4 where 4 is the highest grade. Per the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis rubric, to get a 4, you’ll want to:
- Include lots of specific evidence from the text. There is no set golden number of quotes to include, but you’ll want to make sure you’re incorporating more than a couple pieces of evidence that support your argument about the author’s rhetorical choices.
- Make sure you include more than one type of evidence, too. Let’s say you’re working on your essay and have gathered examples of alliteration to include as supporting evidence. That’s just one type of rhetorical choice, and it’s hard to make a credible argument if you’re only looking at one type of evidence. To fix that issue, reread the text again looking for patterns in word choice and syntax, meaningful figurative language and imagery, literary devices, and other rhetorical choices, looking for additional types of evidence to support your argument.
- After you include evidence, offer your own interpretation and explain how this evidence proves the point you make in your thesis.
- Don’t summarize or speak generally about the author and the text. Everything you write must be backed up with evidence.
- Don’t let quotes speak for themselves. After every piece of evidence you include, make sure to explain your interpretation. Also, connect the evidence to your overarching argument.
Sophistication (0-1 point)
In this case, sophistication isn’t about how many fancy vocabulary words or how many semicolons you use. According to College Board , one point can be awarded to AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essays that “demonstrate sophistication of thought and/or a complex understanding of the rhetorical situation” in any of these three ways:
- Explaining the significance or relevance of the writer’s rhetorical choices.
- Explaining the purpose or function of the passage’s complexities or tensions.
- Employing a style that is consistently vivid and persuasive.
Note that you don’t have to achieve all three to earn your sophistication point. A good way to think of this rubric category is to consider it a bonus point that you can earn for going above and beyond in depth of analysis or by writing an especially persuasive, clear, and well-structured essay. In order to earn this point, you’ll need to first do a good job with your thesis, evidence, and commentary.
- Focus on nailing an argumentative thesis and multiple types of evidence. Getting these fundamentals of your essay right will set you up for achieving depth of analysis.
- Explain how each piece of evidence connects to your thesis.
- Spend a minute outlining your essay before you begin to ensure your essay flows in a clear and cohesive way.
- Steer clear of generalizations about the author or text.
- Don’t include arguments you can’t prove with evidence from the text.
- Avoid complex sentences and fancy vocabulary words unless you use them often. Long, clunky sentences with imprecisely used words are hard to follow.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis: Sample Prompt
The sample prompt below is published online by College Board and is a real example from the 2021 AP Exam. The prompt provides background context, essay instructions, and the text you need to analyze. For sake of space, we’ve included the text as an image you can click to read. After the prompt, we provide a sample high scoring essay and then explain why this AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay example works.
Suggested time—40 minutes.
(This question counts as one-third of the total essay section score.)
On February 27, 2013, while in office, former president Barack Obama delivered the following address dedicating the Rosa Parks statue in the National Statuary Hall of the United States Capitol building. Rosa Parks was an African American civil rights activist who was arrested in 1955 for refusing to give up her seat on a segregated bus in Montgomery, Alabama. Read the passage carefully. Write an essay that analyzes the rhetorical choices Obama makes to convey his message.
In your response you should do the following:
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis that analyzes the writer’s rhetorical choices.
- Select and use evidence to support your line of reasoning.
- Explain how the evidence supports your line of reasoning.
- Demonstrate an understanding of the rhetorical situation.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating your argument.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
In his speech delivered in 2013 at the dedication of Rosa Park’s statue, President Barack Obama acknowledges everything that Parks’ activism made possible in the United States. Telling the story of Parks’ life and achievements, Obama highlights the fact that Parks was a regular person whose actions accomplished enormous change during the civil rights era. Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did.
Although it might be a surprising way to start to his dedication, Obama begins his speech by telling us who Parks was not: “Rosa Parks held no elected office. She possessed no fortune” he explains in lines 1-2. Later, when he tells the story of the bus driver who threatened to have Parks arrested when she refused to get off the bus, he explains that Parks “simply replied, ‘You may do that’” (lines 22-23). Right away, he establishes that Parks was a regular person who did not hold a seat of power. Her protest on the bus was not part of a larger plan, it was a simple response. By emphasizing that Parks was not powerful, wealthy, or loud spoken, he implies that Parks’ style of activism is an everyday practice that all of us can aspire to.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example (Continued)
Even though Obama portrays Parks as a demure person whose protest came “simply” and naturally, he shows the importance of her activism through long lists of ripple effects. When Parks challenged her arrest, Obama explains, Martin Luther King, Jr. stood with her and “so did thousands of Montgomery, Alabama commuters” (lines 27-28). They began a boycott that included “teachers and laborers, clergy and domestics, through rain and cold and sweltering heat, day after day, week after week, month after month, walking miles if they had to…” (lines 28-31). In this section of the speech, Obama’s sentences grow longer and he uses lists to show that Parks’ small action impacted and inspired many others to fight for change. Further, listing out how many days, weeks, and months the boycott lasted shows how Parks’ single act of protest sparked a much longer push for change.
To further illustrate Parks’ impact, Obama incorporates Biblical references that emphasize the importance of “that single moment on the bus” (lines 57-58). In lines 33-35, Obama explains that Parks and the other protestors are “driven by a solemn determination to affirm their God-given dignity” and he also compares their victory to the fall the “ancient walls of Jericho” (line 43). By of including these Biblical references, Obama suggests that Parks’ action on the bus did more than correct personal or political wrongs; it also corrected moral and spiritual wrongs. Although Parks had no political power or fortune, she was able to restore a moral balance in our world.
Toward the end of the speech, Obama states that change happens “not mainly through the exploits of the famous and the powerful, but through the countless acts of often anonymous courage and kindness” (lines 78-81). Through carefully chosen diction that portrays her as a quiet, regular person and through lists and Biblical references that highlight the huge impacts of her action, Obama illustrates exactly this point. He wants us to see that, just like Parks, the small and meek can change the world for the better.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Why It Works
We would give the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay above a score of 6 out of 6 because it fully satisfies the essay’s 3 rubric categories: Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication . Let’s break down what this student did:
The thesis of this essay appears in the last line of the first paragraph:
“ Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did .”
This student’s thesis works because they make a clear argument about Obama’s rhetorical choices. They 1) list the rhetorical choices that will be analyzed in the rest of the essay (the italicized text above) and 2) include an argument someone else might disagree with (the bolded text above).
Evidence and Commentary:
This student includes substantial evidence and commentary. Things they do right, per the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis rubric:
- They include lots of specific evidence from the text in the form of quotes.
- They incorporate 3 different types of evidence (diction, long lists, Biblical references).
- After including evidence, they offer an interpretation of what the evidence means and explain how the evidence contributes to their overarching argument (aka their thesis).
Sophistication
This essay achieves sophistication according to the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay rubric in a few key ways:
- This student provides an introduction that flows naturally into the topic their essay will discuss. Before they get to their thesis, they tell us that Obama portrays Parks as a “regular person” setting up their main argument: Obama wants all regular people to aspire to do good in the world just as Rosa Parks did.
- They organize evidence and commentary in a clear and cohesive way. Each body paragraph focuses on just one type of evidence.
- They explain how their evidence is significant. In the final sentence of each body paragraph, they draw a connection back to the overarching argument presented in the thesis.
- All their evidence supports the argument presented in their thesis. There is no extraneous evidence or misleading detail.
- They consider nuances in the text. Rather than taking the text at face value, they consider what Obama’s rhetorical choices imply and offer their own unique interpretation of those implications.
- In their final paragraph, they come full circle, reiterate their thesis, and explain what Obama’s rhetorical choices communicate to readers.
- Their sentences are clear and easy to read. There are no grammar errors or misused words.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay—More Resources
Looking for more tips to help your master your AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? Brush up on 20 Rhetorical Devices High School Students Should Know and read our Tips for Improving Reading Comprehension . If you’re ready to start studying for another part of the AP English Exam, find more expert tips in our How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis blog post.
Considering what other AP classes to take? Read up on the Hardest AP Classes .
- High School Success

Christina Wood
Christina Wood holds a BA in Literature & Writing from UC San Diego, an MFA in Creative Writing from Washington University in St. Louis, and is currently a Doctoral Candidate in English at the University of Georgia, where she teaches creative writing and first-year composition courses. Christina has published fiction and nonfiction in numerous publications, including The Paris Review , McSweeney’s , Granta , Virginia Quarterly Review , The Sewanee Review , Mississippi Review , and Puerto del Sol , among others. Her story “The Astronaut” won the 2018 Shirley Jackson Award for short fiction and received a “Distinguished Stories” mention in the 2019 Best American Short Stories anthology.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight

“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
I am a... Student Student Parent Counselor Educator Other First Name Last Name Email Address Zip Code Area of Interest Business Computer Science Engineering Fine/Performing Arts Humanities Mathematics STEM Pre-Med Psychology Social Studies/Sciences Submit
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay–Examples & Template
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
A rhetorical analysis essay is, as the name suggests, an analysis of someone else’s writing (or speech, or advert, or even cartoon) and how they use not only words but also rhetorical techniques to influence their audience in a certain way. A rhetorical analysis is less interested in what the author is saying and more in how they present it, what effect this has on their readers, whether they achieve their goals, and what approach they use to get there.
Its structure is similar to that of most essays: An Introduction presents your thesis, a Body analyzes the text you have chosen, breaks it down into sections and explains how arguments have been constructed and how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section sums up your evaluation.
Note that your personal opinion on the matter is not relevant for your analysis and that you don’t state anywhere in your essay whether you agree or disagree with the stance the author takes.
In the following, we will define the key rhetorical concepts you need to write a good rhetorical analysis and give you some practical tips on where to start.
Key Rhetorical Concepts
Your goal when writing a rhetorical analysis is to think about and then carefully describe how the author has designed their text so that it has the intended effect on their audience. To do that, you need to consider a number of key rhetorical strategies: Rhetorical appeals (“Ethos”, “Logos”, and “Pathos”), context, as well as claims, supports, and warrants.
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos were introduced by Aristotle, way back in the 4th century BC, as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience. They still represent the basis of any rhetorical analysis and are often referred to as the “rhetorical triangle”.
These and other rhetorical techniques can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify the concepts they are based on.
Rhetorical Appeals
Rhetorical appeal #1: ethos.
Ethos refers to the reputation or authority of the writer regarding the topic of their essay or speech and to how they use this to appeal to their audience. Just like we are more likely to buy a product from a brand or vendor we have confidence in than one we don’t know or have reason to distrust, Ethos-driven texts or speeches rely on the reputation of the author to persuade the reader or listener. When you analyze an essay, you should therefore look at how the writer establishes Ethos through rhetorical devices.
Does the author present themselves as an authority on their subject? If so, how?
Do they highlight how impeccable their own behavior is to make a moral argument?
Do they present themselves as an expert by listing their qualifications or experience to convince the reader of their opinion on something?
Rhetorical appeal #2: Pathos
The purpose of Pathos-driven rhetoric is to appeal to the reader’s emotions. A common example of pathos as a rhetorical means is adverts by charities that try to make you donate money to a “good cause”. To evoke the intended emotions in the reader, an author may use passionate language, tell personal stories, and employ vivid imagery so that the reader can imagine themselves in a certain situation and feel empathy with or anger towards others.
Rhetorical appeal #3: Logos
Logos, the “logical” appeal, uses reason to persuade. Reason and logic, supported by data, evidence, clearly defined methodology, and well-constructed arguments, are what most academic writing is based on. Emotions, those of the researcher/writer as well as those of the reader, should stay out of such academic texts, as should anyone’s reputation, beliefs, or personal opinions.
Text and Context
To analyze a piece of writing, a speech, an advertisement, or even a satirical drawing, you need to look beyond the piece of communication and take the context in which it was created and/or published into account.
Who is the person who wrote the text/drew the cartoon/designed the ad..? What audience are they trying to reach? Where was the piece published and what was happening there around that time?
A political speech, for example, can be powerful even when read decades later, but the historical context surrounding it is an important aspect of the effect it was intended to have.
Claims, Supports, and Warrants
To make any kind of argument, a writer needs to put forward specific claims, support them with data or evidence or even a moral or emotional appeal, and connect the dots logically so that the reader can follow along and agree with the points made.
The connections between statements, so-called “warrants”, follow logical reasoning but are not always clearly stated—the author simply assumes the reader understands the underlying logic, whether they present it “explicitly” or “implicitly”. Implicit warrants are commonly used in advertisements where seemingly happy people use certain products, wear certain clothes, accessories, or perfumes, or live certain lifestyles – with the connotation that, first, the product/perfume/lifestyle is what makes that person happy and, second, the reader wants to be as happy as the person in the ad. Some warrants are never clearly stated, and your job when writing a rhetorical analysis essay is therefore to identify them and bring them to light, to evaluate their validity, their effect on the reader, and the use of such means by the writer/creator.

What are the Five Rhetorical Situations?
A “rhetorical situation” refers to the circumstance behind a text or other piece of communication that arises from a given context. It explains why a rhetorical piece was created, what its purpose is, and how it was constructed to achieve its aims.
Rhetorical situations can be classified into the following five categories:
Asking such questions when you analyze a text will help you identify all the aspects that play a role in the effect it has on its audience, and will allow you to evaluate whether it achieved its aims or where it may have failed to do so.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Analyzing someone else’s work can seem like a big task, but as with every assignment or writing endeavor, you can break it down into smaller, well-defined steps that give you a practical structure to follow.
To give you an example of how the different parts of your text may look when it’s finished, we will provide you with some excerpts from this rhetorical analysis essay example (which even includes helpful comments) published on the Online Writing Lab website of Excelsior University in Albany, NY. The text that this essay analyzes is this article on why one should or shouldn’t buy an Ipad. If you want more examples so that you can build your own rhetorical analysis template, have a look at this essay on Nabokov’s Lolita and the one provided here about the “Shitty First Drafts” chapter of Anne Lamott’s writing instruction book “Bird by Bird”.
Analyzing the Text
When writing a rhetorical analysis, you don’t choose the concepts or key points you think are relevant or want to address. Rather, you carefully read the text several times asking yourself questions like those listed in the last section on rhetorical situations to identify how the text “works” and how it was written to achieve that effect.
Start with focusing on the author : What do you think was their purpose for writing the text? Do they make one principal claim and then elaborate on that? Or do they discuss different topics?
Then look at what audience they are talking to: Do they want to make a group of people take some action? Vote for someone? Donate money to a good cause? Who are these people? Is the text reaching this specific audience? Why or why not?
What tone is the author using to address their audience? Are they trying to evoke sympathy? Stir up anger? Are they writing from a personal perspective? Are they painting themselves as an authority on the topic? Are they using academic or informal language?
How does the author support their claims ? What kind of evidence are they presenting? Are they providing explicit or implicit warrants? Are these warrants valid or problematic? Is the provided evidence convincing?
Asking yourself such questions will help you identify what rhetorical devices a text uses and how well they are put together to achieve a certain aim. Remember, your own opinion and whether you agree with the author are not the point of a rhetorical analysis essay – your task is simply to take the text apart and evaluate it.
If you are still confused about how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, just follow the steps outlined below to write the different parts of your rhetorical analysis: As every other essay, it consists of an Introduction , a Body (the actual analysis), and a Conclusion .
Rhetorical Analysis Introduction
The Introduction section briefly presents the topic of the essay you are analyzing, the author, their main claims, a short summary of the work by you, and your thesis statement .
Tell the reader what the text you are going to analyze represents (e.g., historically) or why it is relevant (e.g., because it has become some kind of reference for how something is done). Describe what the author claims, asserts, or implies and what techniques they use to make their argument and persuade their audience. Finish off with your thesis statement that prepares the reader for what you are going to present in the next section – do you think that the author’s assumptions/claims/arguments were presented in a logical/appealing/powerful way and reached their audience as intended?
Have a look at an excerpt from the sample essay linked above to see what a rhetorical analysis introduction can look like. See how it introduces the author and article , the context in which it originally appeared , the main claims the author makes , and how this first paragraph ends in a clear thesis statement that the essay will then elaborate on in the following Body section:
Cory Doctorow ’s article on BoingBoing is an older review of the iPad , one of Apple’s most famous products. At the time of this article, however, the iPad was simply the latest Apple product to hit the market and was not yet so popular. Doctorow’s entire career has been entrenched in and around technology. He got his start as a CD-ROM programmer and is now a successful blogger and author. He is currently the co-editor of the BoingBoing blog on which this article was posted. One of his main points in this article comes from Doctorow’s passionate advocacy of free digital media sharing. He argues that the iPad is just another way for established technology companies to control our technological freedom and creativity . In “ Why I Won’t Buy an iPad (and Think You Shouldn’t, Either) ” published on Boing Boing in April of 2010, Cory Doctorow successfully uses his experience with technology, facts about the company Apple, and appeals to consumer needs to convince potential iPad buyers that Apple and its products, specifically the iPad, limit the digital rights of those who use them by controlling and mainstreaming the content that can be used and created on the device .
Doing the Rhetorical Analysis
The main part of your analysis is the Body , where you dissect the text in detail. Explain what methods the author uses to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience. Use Aristotle’s rhetorical triangle and the other key concepts we introduced above. Use quotations from the essay to demonstrate what you mean. Work out why the writer used a certain approach and evaluate (and again, demonstrate using the text itself) how successful they were. Evaluate the effect of each rhetorical technique you identify on the audience and judge whether the effect is in line with the author’s intentions.
To make it easy for the reader to follow your thought process, divide this part of your essay into paragraphs that each focus on one strategy or one concept , and make sure they are all necessary and contribute to the development of your argument(s).
One paragraph of this section of your essay could, for example, look like this:
One example of Doctorow’s position is his comparison of Apple’s iStore to Wal-Mart. This is an appeal to the consumer’s logic—or an appeal to logos. Doctorow wants the reader to take his comparison and consider how an all-powerful corporation like the iStore will affect them. An iPad will only allow for apps and programs purchased through the iStore to be run on it; therefore, a customer must not only purchase an iPad but also any programs he or she wishes to use. Customers cannot create their own programs or modify the hardware in any way.
As you can see, the author of this sample essay identifies and then explains to the reader how Doctorow uses the concept of Logos to appeal to his readers – not just by pointing out that he does it but by dissecting how it is done.
Rhetorical Analysis Conclusion
The conclusion section of your analysis should restate your main arguments and emphasize once more whether you think the author achieved their goal. Note that this is not the place to introduce new information—only rely on the points you have discussed in the body of your essay. End with a statement that sums up the impact the text has on its audience and maybe society as a whole:
Overall, Doctorow makes a good argument about why there are potentially many better things to drop a great deal of money on instead of the iPad. He gives some valuable information and facts that consumers should take into consideration before going out to purchase the new device. He clearly uses rhetorical tools to help make his case, and, overall, he is effective as a writer, even if, ultimately, he was ineffective in convincing the world not to buy an iPad .
Frequently Asked Questions about Rhetorical Analysis Essays
What is a rhetorical analysis essay.
A rhetorical analysis dissects a text or another piece of communication to work out and explain how it impacts its audience, how successfully it achieves its aims, and what rhetorical devices it uses to do that.
While argumentative essays usually take a stance on a certain topic and argue for it, a rhetorical analysis identifies how someone else constructs their arguments and supports their claims.
What is the correct rhetorical analysis essay format?
Like most other essays, a rhetorical analysis contains an Introduction that presents the thesis statement, a Body that analyzes the piece of communication, explains how arguments have been constructed, and illustrates how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section that summarizes the results of the analysis.
What is the “rhetorical triangle”?
The rhetorical triangle was introduced by Aristotle as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience: Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, Ethos to the writer’s status or authority, and Pathos to the reader’s emotions. Logos, Ethos, and Pathos can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify what specific concepts each is based on.
Let Wordvice help you write a flawless rhetorical analysis essay!
Whether you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay as an assignment or whether it is part of an application, our professional proofreading services feature professional editors are trained subject experts that make sure your text is in line with the required format, as well as help you improve the flow and expression of your writing. Let them be your second pair of eyes so that after receiving paper editing services or essay editing services from Wordvice, you can submit your manuscript or apply to the school of your dreams with confidence.
And check out our editing services for writers (including blog editing , script editing , and book editing ) to correct your important personal or business-related work.
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
What Is a Rhetorical Analysis and How to Write a Great One

Helly Douglas

Do you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay? Fear not! We’re here to explain exactly what rhetorical analysis means, how you should structure your essay, and give you some essential “dos and don’ts.”
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
How do you write a rhetorical analysis, what are the three rhetorical strategies, what are the five rhetorical situations, how to plan a rhetorical analysis essay, creating a rhetorical analysis essay, examples of great rhetorical analysis essays, final thoughts.
A rhetorical analysis essay studies how writers and speakers have used words to influence their audience. Think less about the words the author has used and more about the techniques they employ, their goals, and the effect this has on the audience.

In your analysis essay, you break a piece of text (including cartoons, adverts, and speeches) into sections and explain how each part works to persuade, inform, or entertain. You’ll explore the effectiveness of the techniques used, how the argument has been constructed, and give examples from the text.
A strong rhetorical analysis evaluates a text rather than just describes the techniques used. You don’t include whether you personally agree or disagree with the argument.
Structure a rhetorical analysis in the same way as most other types of academic essays . You’ll have an introduction to present your thesis, a main body where you analyze the text, which then leads to a conclusion.
Think about how the writer (also known as a rhetor) considers the situation that frames their communication:
- Topic: the overall purpose of the rhetoric
- Audience: this includes primary, secondary, and tertiary audiences
- Purpose: there are often more than one to consider
- Context and culture: the wider situation within which the rhetoric is placed
Back in the 4th century BC, Aristotle was talking about how language can be used as a means of persuasion. He described three principal forms —Ethos, Logos, and Pathos—often referred to as the Rhetorical Triangle . These persuasive techniques are still used today.
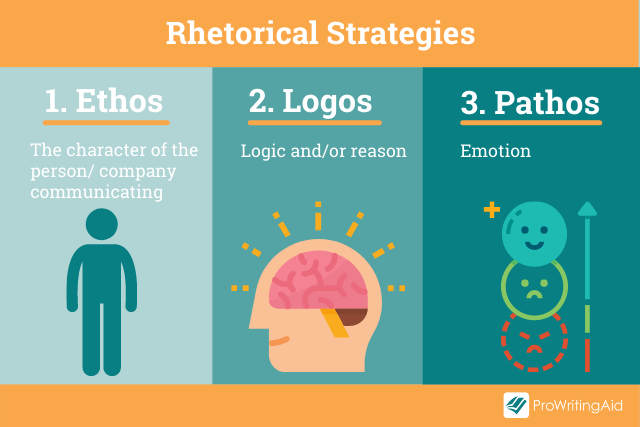
Rhetorical Strategy 1: Ethos
Are you more likely to buy a car from an established company that’s been an important part of your community for 50 years, or someone new who just started their business?
Reputation matters. Ethos explores how the character, disposition, and fundamental values of the author create appeal, along with their expertise and knowledge in the subject area.
Aristotle breaks ethos down into three further categories:
- Phronesis: skills and practical wisdom
- Arete: virtue
- Eunoia: goodwill towards the audience
Ethos-driven speeches and text rely on the reputation of the author. In your analysis, you can look at how the writer establishes ethos through both direct and indirect means.
Rhetorical Strategy 2: Pathos
Pathos-driven rhetoric hooks into our emotions. You’ll often see it used in advertisements, particularly by charities wanting you to donate money towards an appeal.
Common use of pathos includes:
- Vivid description so the reader can imagine themselves in the situation
- Personal stories to create feelings of empathy
- Emotional vocabulary that evokes a response
By using pathos to make the audience feel a particular emotion, the author can persuade them that the argument they’re making is compelling.
Rhetorical Strategy 3: Logos
Logos uses logic or reason. It’s commonly used in academic writing when arguments are created using evidence and reasoning rather than an emotional response. It’s constructed in a step-by-step approach that builds methodically to create a powerful effect upon the reader.
Rhetoric can use any one of these three techniques, but effective arguments often appeal to all three elements.
The rhetorical situation explains the circumstances behind and around a piece of rhetoric. It helps you think about why a text exists, its purpose, and how it’s carried out.
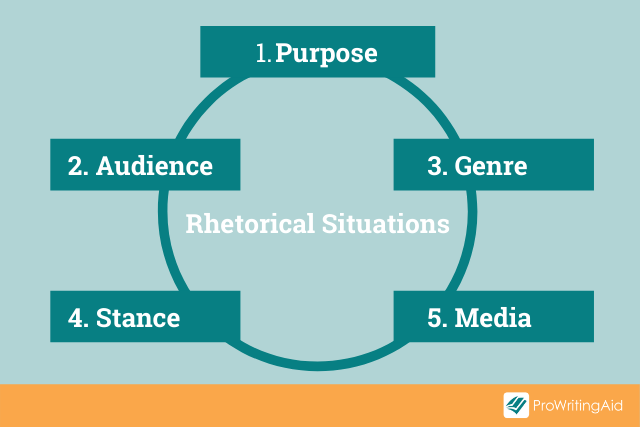
The rhetorical situations are:
- 1) Purpose: Why is this being written? (It could be trying to inform, persuade, instruct, or entertain.)
- 2) Audience: Which groups or individuals will read and take action (or have done so in the past)?
- 3) Genre: What type of writing is this?
- 4) Stance: What is the tone of the text? What position are they taking?
- 5) Media/Visuals: What means of communication are used?
Understanding and analyzing the rhetorical situation is essential for building a strong essay. Also think about any rhetoric restraints on the text, such as beliefs, attitudes, and traditions that could affect the author's decisions.
Before leaping into your essay, it’s worth taking time to explore the text at a deeper level and considering the rhetorical situations we looked at before. Throw away your assumptions and use these simple questions to help you unpick how and why the text is having an effect on the audience.

1: What is the Rhetorical Situation?
- Why is there a need or opportunity for persuasion?
- How do words and references help you identify the time and location?
- What are the rhetoric restraints?
- What historical occasions would lead to this text being created?
2: Who is the Author?
- How do they position themselves as an expert worth listening to?
- What is their ethos?
- Do they have a reputation that gives them authority?
- What is their intention?
- What values or customs do they have?
3: Who is it Written For?
- Who is the intended audience?
- How is this appealing to this particular audience?
- Who are the possible secondary and tertiary audiences?
4: What is the Central Idea?
- Can you summarize the key point of this rhetoric?
- What arguments are used?
- How has it developed a line of reasoning?
5: How is it Structured?
- What structure is used?
- How is the content arranged within the structure?
6: What Form is Used?
- Does this follow a specific literary genre?
- What type of style and tone is used, and why is this?
- Does the form used complement the content?
- What effect could this form have on the audience?
7: Is the Rhetoric Effective?
- Does the content fulfil the author’s intentions?
- Does the message effectively fit the audience, location, and time period?
Once you’ve fully explored the text, you’ll have a better understanding of the impact it’s having on the audience and feel more confident about writing your essay outline.
A great essay starts with an interesting topic. Choose carefully so you’re personally invested in the subject and familiar with it rather than just following trending topics. There are lots of great ideas on this blog post by My Perfect Words if you need some inspiration. Take some time to do background research to ensure your topic offers good analysis opportunities.

Remember to check the information given to you by your professor so you follow their preferred style guidelines. This outline example gives you a general idea of a format to follow, but there will likely be specific requests about layout and content in your course handbook. It’s always worth asking your institution if you’re unsure.
Make notes for each section of your essay before you write. This makes it easy for you to write a well-structured text that flows naturally to a conclusion. You will develop each note into a paragraph. Look at this example by College Essay for useful ideas about the structure.
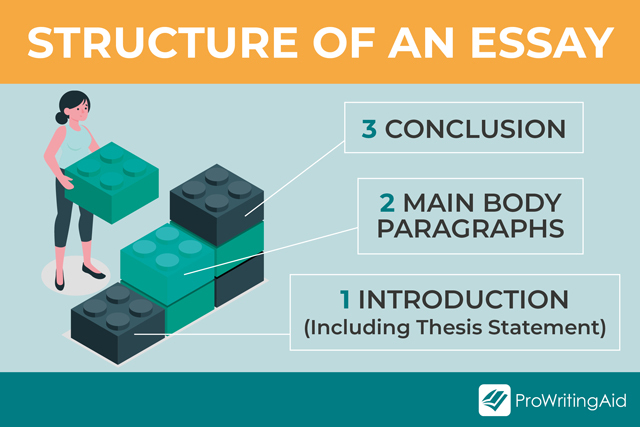
1: Introduction
This is a short, informative section that shows you understand the purpose of the text. It tempts the reader to find out more by mentioning what will come in the main body of your essay.
- Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses
- Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. “implies,” “asserts,” or “claims”
- Briefly summarize the text in your own words
- Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect
Create a thesis statement to come at the end of your introduction.
After your introduction, move on to your critical analysis. This is the principal part of your essay.
- Explain the methods used by the author to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience using Aristotle's rhetorical triangle
- Use quotations to prove the statements you make
- Explain why the writer used this approach and how successful it is
- Consider how it makes the audience feel and react
Make each strategy a new paragraph rather than cramming them together, and always use proper citations. Check back to your course handbook if you’re unsure which citation style is preferred.
3: Conclusion
Your conclusion should summarize the points you’ve made in the main body of your essay. While you will draw the points together, this is not the place to introduce new information you’ve not previously mentioned.
Use your last sentence to share a powerful concluding statement that talks about the impact the text has on the audience(s) and wider society. How have its strategies helped to shape history?
Before You Submit
Poor spelling and grammatical errors ruin a great essay. Use ProWritingAid to check through your finished essay before you submit. It will pick up all the minor errors you’ve missed and help you give your essay a final polish. Look at this useful ProWritingAid webinar for further ideas to help you significantly improve your essays. Sign up for a free trial today and start editing your essays!
You’ll find countless examples of rhetorical analysis online, but they range widely in quality. Your institution may have example essays they can share with you to show you exactly what they’re looking for.
The following links should give you a good starting point if you’re looking for ideas:
Pearson Canada has a range of good examples. Look at how embedded quotations are used to prove the points being made. The end questions help you unpick how successful each essay is.
Excelsior College has an excellent sample essay complete with useful comments highlighting the techniques used.
Brighton Online has a selection of interesting essays to look at. In this specific example, consider how wider reading has deepened the exploration of the text.

Writing a rhetorical analysis essay can seem daunting, but spending significant time deeply analyzing the text before you write will make it far more achievable and result in a better-quality essay overall.
It can take some time to write a good essay. Aim to complete it well before the deadline so you don’t feel rushed. Use ProWritingAid’s comprehensive checks to find any errors and make changes to improve readability. Then you’ll be ready to submit your finished essay, knowing it’s as good as you can possibly make it.
Try ProWritingAid's Editor for Yourself
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Helly Douglas is a UK writer and teacher, specialising in education, children, and parenting. She loves making the complex seem simple through blogs, articles, and curriculum content. You can check out her work at hellydouglas.com or connect on Twitter @hellydouglas. When she’s not writing, you will find her in a classroom, being a mum or battling against the wilderness of her garden—the garden is winning!
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
📕 Studying HQ
A comprehensive guide to rhetorical essays, carla johnson.
- June 14, 2023
- Essay Topics and Ideas , How to Guides
Rhetorical essays are an important part of academic writing because they require students to analyze and evaluate the ways that writers try to convince their readers. At its heart, a rhetorical essay looks at how a writer uses language, tone, and structure to get their point across. By learning how to write good rhetorical essays, students can learn how to think critically and become better communicators.
A rhetorical essay has more than one goal and is important for more than one reason. First, it helps students improve their analytical skills by letting them look at how writers try to convince their readers. Second, it helps students become better communicators by teaching them how to use language, tone, and structure in different ways. Lastly, it gives students a chance to work with complicated ideas and arguments and add to the academic discussion in their field.
This thorough guide will cover the most important parts of writing a rhetorical essay, such as planning, writing, and editing. We will also talk about how important it is for a rhetorical essay to have a clear and logical structure and give you tips on how to use rhetorical devices effectively. By the end of this guide, readers will know how to write effective and convincing rhetorical essays in a wide range of academic fields.
What You'll Learn
Understanding Rhetoric
Rhetoric is the art of persuading people with words. It means knowing how different parts of language, like tone, structure, and diction, can be used to persuade people. Rhetoric has a long and interesting history that goes back to ancient Greece and Rome, where it was seen as one of the most important parts of education and public life. One of the most important philosophers of all time, Aristotle, wrote a lot about rhetoric and how important it is in society.
The study of rhetoric is important because it gives people a way to think about how language can be used to persuade and change people. Rhetoric is often used in academic writing to analyze and evaluate the ways that writers use to get their point across. By learning how rhetoric works in writing, students can become better communicators and learn how to think critically .
Elements of a Rhetorical Essay
A rhetorical essay is composed of four key elements: the speaker, audience, purpose, and context. Each element plays an important role in the overall effectiveness of the essay .
The speaker is the person or thing in the essay that is giving the message. When analyzing a rhetorical essay, it is important to think about the background, beliefs, and values of the speaker, as well as their credibility. Knowing the speaker’s point of view can help the reader understand the essay’s purpose and setting better.
2. Audience
The group of people the speaker is talking to in the essay is called the audience. When analyzing a rhetorical essay, it is important to think about the audience’s background, beliefs, and values. Understanding the audience’s perspective can help readers better understand the strategies that the speaker is using to persuade them.
The purpose of a rhetorical essay is the reason why the speaker is delivering the message. It can be to inform , persuade, entertain, or any combination of these. It is important to consider the purpose of the essay when analyzing the strategies used by the speaker to achieve their goal.
A rhetorical essay’s context is its cultural, social, and political setting at the time it was written. It’s important to think about the essay’s setting to figure out how the people who read it might have felt about it. For example, an essay written during a time of social unrest might use different strategies than one written during a time of peace.
Real-world examples can help show why each part of a rhetorical essay is important. One powerful example of effective rhetoric is Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech. King gave this speech to the thousands of people who had gathered in Washington, D.C. The goal of the speech was to get people to join the civil rights movement, and it was given in the context of the fight for racial equality in the United States . By looking at each part of this speech, readers can learn more about the methods King used to get his point across and the effects it had on society.
To become a better communicator and improve your critical thinking skills , you need to know what goes into a rhetorical essay. By thinking about the speaker, audience, purpose, and setting of a rhetorical essay, readers can learn more about the ways writers try to convince their readers. Students can become more informed and involved citizens by studying rhetoric and adding to the academic conversation in their field of study.
How to Write a Rhetorical Essay
Writing a rhetorical essay requires careful analysis of a text and the use of effective writing strategies. Here is a step-by-step guide to writing a rhetorical essay:
1. Brainstorm and select a topic: Choose a topic that interests you and has a clear purpose. Consider the author’s intent, audience, and context of the text you will be analyzing.
2. Read and analyze the text: Read the text thoroughly and take notes on its key points, structure, and language. Identify the author’s use of rhetorical devices such as imagery, tone, and metaphor.
3. Develop a thesis statement: Based on your analysis, develop a thesis statement that summarizes the main argument of your essay.
4. Organize the essay: Create an outline that includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Use the four elements of a rhetorical essay (speaker, audience, purpose, and context) as a guide to structure your essay .
5. Write the introduction: Begin with a hook to grab the reader’s attention and provide background information on the text. End with a thesis statement that summarizes your argument.
6. Write the body paragraphs: Each body paragraph should focus on a specific rhetorical device or strategy used by the author. Use evidence from the text to support your analysis , and explain how the device contributes to the author’s overall purpose.
7. Write the conclusion: Summarize your main points and restate your thesis statement. End with a thought-provoking statement or call to action.
Tips for coming up with ideas and choosing a topic include picking a text with a clear purpose and audience, as well as thinking about your own interests and how the text relates to your life or field of study. When you’re trying to figure out what the text is about, it can help to mark up the text with notes about key points and rhetorical devices. Look for patterns in the language, like repetition, metaphor, or allusion, to figure out what kind of rhetorical device is being used.
To write a good rhetorical essay, you need to organize and structure the essay . Use the four parts of a rhetorical essay as a guide to organize the essay and make an outline with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The introduction should give background information about the text, grab the reader’s attention, and end with a thesis statement that sums up your argument.
In the body paragraphs, you should focus on specific types of rhetoric and use textual evidence to back up your analysis. The conclusion should summarize your main points and restate your thesis statement . It should end with a strong statement or a call to action.
Rhetorical Essay Examples
To better understand the use of rhetoric in writing, it can be helpful to examine examples of effective rhetorical essays. Here are ten inspiring examples of rhetorical essays:
1. Letter from Birmingham Jail” by Martin Luther King Jr.
2. “The Gettysburg Address” by Abraham Lincoln
3. A Modest Proposal” by Jonathan Swift
4. “Sinnersin the Hands of an Angry God” by Jonathan Edwards
5. Politics and the English Language” by George Orwell
6. “The Declaration of Independence” by Thomas Jefferson
7. “Why Women Still Can’t Have It All” by Anne-Marie Slaughter
8. “I, Too” by Langston Hughes
9. The Death of the Moth” by Virginia Woolf
10. The Souls of Black Folk” by W.E.B. Du Bois
Each of these examples shows how rhetoric can be used well in writing. For example, Martin Luther King Jr.’s “Letter from Birmingham Jail” makes a strong case for civil rights and peaceful protest by using strong images, repetition, and persuasive language. In his “Gettysburg Address,” Abraham Lincoln uses parallelism and imagery to honor the Civil War soldiers and promote the idea of a united country.
When looking at these examples, it’s important to figure out what rhetorical tools the authors used and how they fit into the essay as a whole. For example, in “Why Women Still Can’t Have It All,” by Anne-Marie Slaughter, she uses personal stories and statistics to show that working mothers need more help and a better balance between work and life. By looking at how rhetorical tools like pathos and logos are used, readers can get a better idea of how well the essay works .
A good way to learn how to use rhetoric in writing is to look at examples of good essays that use rhetoric. By looking at the main points and rhetorical devices in these essays , readers can learn more about how language can be used to persuade and sway an audience. It is important to identify the four parts of a rhetorical essay (speaker, audience, purpose, and context) and analyze how they contribute to the overall effectiveness of the essay . Students can learn the skills and knowledge they need to write their own effective and convincing rhetorical essays by looking at these examples and using them as guides.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, anyone who wants to improve their critical thinking , communication, and writing skills needs to learn how to write rhetorical essays. By understanding the main parts of a rhetorical essay, such as the speaker, the audience, the purpose, and the setting, as well as good writing techniques and the analysis of real-world examples , readers can become better communicators and more involved citizens.
To write a good rhetorical essay, you need to follow a step-by-step plan that includes coming up with ideas and choosing a topic , analyzing the text, coming up with a thesis statement, organizing and structuring the essay, and using good writing techniques. Also, it’s important not to make common mistakes like not addressing the four parts of a rhetorical essay, making claims that aren’t backed up, and not having a clear and logical structure.
By looking at examples of good rhetorical essays, readers can learn more about the power of language and the methods writers use to persuade and sway their audience. Letter from Birmingham Jail” by Martin Luther King Jr. and “Why Women Still Can’t Have It All” by Anne-Marie Slaughter are good examples of how imagery, repetition, and personal stories can be used to make a point.
To sum up, to be good at writing rhetorical essays, you need to be able to think critically and write well, and you also need to know what the main parts of a rhetorical essay are. By following the step-by-step instructions in this article and looking at real-world examples , readers can develop the skills they need to write effective and persuasive rhetorical essays that deal with complex ideas and add to academic discourse in their field of study.
1. What is a rhetorical essay?
A rhetorical essay is one that looks at and evaluates the ways that writers try to convince their readers. It means knowing how to use language, tone, structure, and other tools of rhetoric to get your point across.
2. How do I write a rhetorical essay?
To write a rhetorical essay, you should start by choosing a text to analyze and figuring out who the speaker, audience, purpose, and setting are. Look for rhetorical devices in the text, come up with a thesis statement, and put your essay together with an introduction , body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
3. What are some examples of rhetorical essays?
Examples of rhetorical essays include Martin Luther King Jr.’s “Letter from Birmingham Jail,” Abraham Lincoln’s “Gettysburg Address,” and Anne-Marie Slaughter’s “Why Women Still Can’t Have It All.”
4. How do I choose a topic for a rhetorical essay?
When choosing a topic for a rhetorical essay, consider the author’s intent, audience, and context of the text. Choose a topic that interests you and has a clear purpose.
5. What are some common mistakes to avoid when writing a rhetorical essay?
Common mistakes to avoid when writing a rhetorical essay include failing to address the four elements of a rhetorical essay, using unsupported assertions, and failing to provide a clear and logical structure.
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Have a subject expert write for you now, have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter, popular topics.
Business StudyingHq Essay Topics and Ideas How to Guides Samples
- Nursing Solutions
- Study Guides
- Free College Essay Examples
- Privacy Policy
- Writing Service
- Discounts / Offers
Study Hub:
- Studying Blog
- Topic Ideas
- How to Guides
- Business Studying
- Nursing Studying
- Literature and English Studying
Writing Tools
- Citation Generator
- Topic Generator
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Maker
- Research Title Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Summarizing Tool
- Terms and Conditions
- Confidentiality Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Refund and Revision Policy
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
Contact Us:
📞 +15512677917
2012-2024 © studyinghq.com. All rights reserved
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a rhetorical analysis


What is a rhetorical analysis?
What are the key concepts of a rhetorical analysis, rhetorical situation, claims, supports, and warrants.
- Step 1: Plan and prepare
- Step 2: Write your introduction
- Step 3: Write the body
- Step 4: Write your conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions about rhetorical analysis
Related articles.
Rhetoric is the art of persuasion and aims to study writers’ or speakers' techniques to inform, persuade, or motivate their audience. Thus, a rhetorical analysis aims to explore the goals and motivations of an author, the techniques they’ve used to reach their audience, and how successful these techniques were.
This will generally involve analyzing a specific text and considering the following aspects to connect the rhetorical situation to the text:
- Does the author successfully support the thesis or claims made in the text? Here, you’ll analyze whether the author holds to their argument consistently throughout the text or whether they wander off-topic at some point.
- Does the author use evidence effectively considering the text’s intended audience? Here, you’ll consider the evidence used by the author to support their claims and whether the evidence resonates with the intended audience.
- What rhetorical strategies the author uses to achieve their goals. Here, you’ll consider the word choices by the author and whether these word choices align with their agenda for the text.
- The tone of the piece. Here, you’ll consider the tone used by the author in writing the piece by looking at specific words and aspects that set the tone.
- Whether the author is objective or trying to convince the audience of a particular viewpoint. When it comes to objectivity, you’ll consider whether the author is objective or holds a particular viewpoint they want to convince the audience of. If they are, you’ll also consider whether their persuasion interferes with how the text is read and understood.
- Does the author correctly identify the intended audience? It’s important to consider whether the author correctly writes the text for the intended audience and what assumptions the author makes about the audience.
- Does the text make sense? Here, you’ll consider whether the author effectively reasons, based on the evidence, to arrive at the text’s conclusion.
- Does the author try to appeal to the audience’s emotions? You’ll need to consider whether the author uses any words, ideas, or techniques to appeal to the audience’s emotions.
- Can the author be believed? Finally, you’ll consider whether the audience will accept the arguments and ideas of the author and why.
Summing up, unlike summaries that focus on what an author said, a rhetorical analysis focuses on how it’s said, and it doesn’t rely on an analysis of whether the author was right or wrong but rather how they made their case to arrive at their conclusions.
Although rhetorical analysis is most used by academics as part of scholarly work, it can be used to analyze any text including speeches, novels, television shows or films, advertisements, or cartoons.
Now that we’ve seen what rhetorical analysis is, let’s consider some of its key concepts .
Any rhetorical analysis starts with the rhetorical situation which identifies the relationships between the different elements of the text. These elements include the audience, author or writer, the author’s purpose, the delivery method or medium, and the content:
- Audience: The audience is simply the readers of a specific piece of text or content or printed material. For speeches or other mediums like film and video, the audience would be the listeners or viewers. Depending on the specific piece of text or the author’s perception, the audience might be real, imagined, or invoked. With a real audience, the author writes to the people actually reading or listening to the content while, for an imaginary audience, the author writes to an audience they imagine would read the content. Similarly, for an invoked audience, the author writes explicitly to a specific audience.
- Author or writer: The author or writer, also commonly referred to as the rhetor in the context of rhetorical analysis, is the person or the group of persons who authored the text or content.
- The author’s purpose: The author’s purpose is the author’s reason for communicating to the audience. In other words, the author’s purpose encompasses what the author expects or intends to achieve with the text or content.
- Alphabetic text includes essays, editorials, articles, speeches, and other written pieces.
- Imaging includes website and magazine advertisements, TV commercials, and the like.
- Audio includes speeches, website advertisements, radio or tv commercials, or podcasts.
- Context: The context of the text or content considers the time, place, and circumstances surrounding the delivery of the text to its audience. With respect to context, it might often also be helpful to analyze the text in a different context to determine its impact on a different audience and in different circumstances.
An author will use claims, supports, and warrants to build the case around their argument, irrespective of whether the argument is logical and clearly defined or needs to be inferred by the audience:
- Claim: The claim is the main idea or opinion of an argument that the author must prove to the intended audience. In other words, the claim is the fact or facts the author wants to convince the audience of. Claims are usually explicitly stated but can, depending on the specific piece of content or text, be implied from the content. Although these claims could be anything and an argument may be based on a single or several claims, the key is that these claims should be debatable.
- Support: The supports are used by the author to back up the claims they make in their argument. These supports can include anything from fact-based, objective evidence to subjective emotional appeals and personal experiences used by the author to convince the audience of a specific claim. Either way, the stronger and more reliable the supports, the more likely the audience will be to accept the claim.
- Warrant: The warrants are the logic and assumptions that connect the supports to the claims. In other words, they’re the assumptions that make the initial claim possible. The warrant is often unstated, and the author assumes that the audience will be able to understand the connection between the claims and supports. In turn, this is based on the author’s assumption that they share a set of values and beliefs with the audience that will make them understand the connection mentioned above. Conversely, if the audience doesn’t share these beliefs and values with the author, the argument will not be that effective.
Appeals are used by authors to convince their audience and, as such, are an integral part of the rhetoric and are often referred to as the rhetorical triangle. As a result, an author may combine all three appeals to convince their audience:
- Ethos: Ethos represents the authority or credibility of the author. To be successful, the author needs to convince the audience of their authority or credibility through the language and delivery techniques they use. This will, for example, be the case where an author writing on a technical subject positions themselves as an expert or authority by referring to their qualifications or experience.
- Logos: Logos refers to the reasoned argument the author uses to persuade their audience. In other words, it refers to the reasons or evidence the author proffers in substantiation of their claims and can include facts, statistics, and other forms of evidence. For this reason, logos is also the dominant approach in academic writing where authors present and build up arguments using reasoning and evidence.
- Pathos: Through pathos, also referred to as the pathetic appeal, the author attempts to evoke the audience’s emotions through the use of, for instance, passionate language, vivid imagery, anger, sympathy, or any other emotional response.
To write a rhetorical analysis, you need to follow the steps below:
With a rhetorical analysis, you don’t choose concepts in advance and apply them to a specific text or piece of content. Rather, you’ll have to analyze the text to identify the separate components and plan and prepare your analysis accordingly.
Here, it might be helpful to use the SOAPSTone technique to identify the components of the work. SOAPSTone is a common acronym in analysis and represents the:
- Speaker . Here, you’ll identify the author or the narrator delivering the content to the audience.
- Occasion . With the occasion, you’ll identify when and where the story takes place and what the surrounding context is.
- Audience . Here, you’ll identify who the audience or intended audience is.
- Purpose . With the purpose, you’ll need to identify the reason behind the text or what the author wants to achieve with their writing.
- Subject . You’ll also need to identify the subject matter or topic of the text.
- Tone . The tone identifies the author’s feelings towards the subject matter or topic.
Apart from gathering the information and analyzing the components mentioned above, you’ll also need to examine the appeals the author uses in writing the text and attempting to persuade the audience of their argument. Moreover, you’ll need to identify elements like word choice, word order, repetition, analogies, and imagery the writer uses to get a reaction from the audience.
Once you’ve gathered the information and examined the appeals and strategies used by the author as mentioned above, you’ll need to answer some questions relating to the information you’ve collected from the text. The answers to these questions will help you determine the reasons for the choices the author made and how well these choices support the overall argument.
Here, some of the questions you’ll ask include:
- What was the author’s intention?
- Who was the intended audience?
- What is the author’s argument?
- What strategies does the author use to build their argument and why do they use those strategies?
- What appeals the author uses to convince and persuade the audience?
- What effect the text has on the audience?
Keep in mind that these are just some of the questions you’ll ask, and depending on the specific text, there might be others.
Once you’ve done your preparation, you can start writing the rhetorical analysis. It will start off with an introduction which is a clear and concise paragraph that shows you understand the purpose of the text and gives more information about the author and the relevance of the text.
The introduction also summarizes the text and the main ideas you’ll discuss in your analysis. Most importantly, however, is your thesis statement . This statement should be one sentence at the end of the introduction that summarizes your argument and tempts your audience to read on and find out more about it.
After your introduction, you can proceed with the body of your analysis. Here, you’ll write at least three paragraphs that explain the strategies and techniques used by the author to convince and persuade the audience, the reasons why the writer used this approach, and why it’s either successful or unsuccessful.
You can structure the body of your analysis in several ways. For example, you can deal with every strategy the author uses in a new paragraph, but you can also structure the body around the specific appeals the author used or chronologically.
No matter how you structure the body and your paragraphs, it’s important to remember that you support each one of your arguments with facts, data, examples, or quotes and that, at the end of every paragraph, you tie the topic back to your original thesis.
Finally, you’ll write the conclusion of your rhetorical analysis. Here, you’ll repeat your thesis statement and summarize the points you’ve made in the body of your analysis. Ultimately, the goal of the conclusion is to pull the points of your analysis together so you should be careful to not raise any new issues in your conclusion.
After you’ve finished your conclusion, you’ll end your analysis with a powerful concluding statement of why your argument matters and an invitation to conduct more research if needed.
A rhetorical analysis aims to explore the goals and motivations of an author, the techniques they’ve used to reach their audience, and how successful these techniques were. Although rhetorical analysis is most used by academics as part of scholarly work, it can be used to analyze any text including speeches, novels, television shows or films, advertisements, or cartoons.
The steps to write a rhetorical analysis include:
Your rhetorical analysis introduction is a clear and concise paragraph that shows you understand the purpose of the text and gives more information about the author and the relevance of the text. The introduction also summarizes the text and the main ideas you’ll discuss in your analysis.
Ethos represents the authority or credibility of the author. To be successful, the author needs to convince the audience of their authority or credibility through the language and delivery techniques they use. This will, for example, be the case where an author writing on a technical subject positions themselves as an expert or authority by referring to their qualifications or experience.
Appeals are used by authors to convince their audience and, as such, are an integral part of the rhetoric and are often referred to as the rhetorical triangle. The 3 types of appeals are ethos, logos, and pathos.


How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay
A rhetorical analysis essay requires you to write about an author’s writing. In other words, in a rhetorical analysis essay, you write about the way an author uses words to influence or persuade an audience to do or think something.
A rhetorical analysis essay explains how the parts of a text work together to persuade, entertain, or inform an audience.
When writing a rhetorical analysis, you are not writing a summary nor are you writing about whether or not you agree with the argument. Instead, you’re discussing how the author makes that argument and whether or not the approach used is successful.
In order to write a coherent and grade-winning rhetorical analysis essay, before you write, you need to make evident to yourself what you know about what you need to analyze (the text that you read and now have to analyze).

Rhetorical Analysis Essay
Rhetorical Analysis Essay - A Complete Guide With Examples

People also read
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics – 120+ Unique Ideas
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example - Free Samples
Crafting an Effective Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline - Free Samples!
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos - Structure, Usage & Examples
Are you a student faced with the daunting task of writing a rhetorical analysis essay? Does the thought of dissecting persuasive strategies, speeches, or texts send shivers down your spine?
You're not alone!
Rhetorical analysis can feel like deciphering an ancient code, with appeals like ethos, pathos, and logos.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll break down the art of rhetorical analysis into manageable steps. By the end of this blog, you'll be equipped with the skills and confidence to craft a compelling analysis that stands out.
Let's dive in together!

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
- 1. What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
- 2. How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
- 3. Writing Tips for Rhetorical Analysis Essay AP Language
- 4. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples
- 5. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
According to the rhetorical analysis essay definition:
“It is a type of academic writing that examines the techniques and strategies used by authors, speakers, or creators to persuade and influence their audience.”
It's a common assignment in high school and college courses, especially in English and communications classes where you use rhetorical devices.
But what exactly does it entail?
Breaking Down the Term: Rhetorical Analysis
Rhetorical: The art of effective communication through the use of language.
Analysis: Thorough examination, dissection, and evaluation of the elements within a text or communication, including words, phrases, structure, and style.
Unlike other types of essays , a rhetorical essay is based on the following information:
- The rhetorical situation is highlighted by the author in the original piece.
- Who is the author?
- The main goal of the analyzed text based on the original author’s intentions
- Does the main idea complete the author’s objectives?
So, a rhetorical analysis essay essentially involves analyzing how a piece of communication uses rhetorical techniques to achieve its persuasive goals.
This type of essay goes beyond summarizing or reviewing; it seeks to uncover the "how" and "why" behind the author's or speaker's persuasive power.
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
Before you move on to the writing section, it is vital to learn how to start a rhetorical analysis essay. Six elements are required to start a rhetorical analysis essay.

When the planning of your essay is strong, the writing process will become easier. Once you have taken all the required pre-writing steps, start writing your essay by taking the steps provided below:
Step 1: Understand the Prompt
This initial step is crucial. Carefully read and comprehend the assignment prompt or guidelines provided by your instructor.
For instance, if the prompt asks you to analyze a presidential speech, understand which speech is being referred to, the context, and any specific elements you should focus on.
Step 2: Determine the Rhetorical Strategy
The effectiveness of any communication, whether verbal or written, is based on persuading the audience. The strategies used to persuade the audience include; ethos, pathos, and logos , a rhetorical triangle.
- Ethos - ethical appeal convinces readers of the writer's credibility and moral argument.
- Pathos - Pathos, also known as pathetic appeal, is an appeal to emotion that can make readers feel pity or anger.
- Logos - This logical appeal is a strategy that uses logic to convince the intended audience.
Ethos, Pathos, And Logos Example | PDF
Step 3. Choose the Text
Once you understand the assignment, select a text for analysis.
Let's say you've been assigned to analyze Martin Luther King Jr.'s "I Have a Dream" speech. It's a famous speech that's rich in rhetorical elements.
Step 4. Pre-Writing Analysis
Before you begin writing, immerse yourself in the chosen text. Read it multiple times and take notes.
For instance, in "I Have a Dream," you might note King's passionate delivery, the use of historical references, and his appeal for racial equality.
Step 5. Create a Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement should be a concise summary of your main argument.
For example: "In 'I Have a Dream,' Martin Luther King Jr. employs powerful rhetorical strategies, including appeals to ethos, pathos, and logos, to call for racial justice and equality in America."
Step 6. Organize Your Essay
Plan your essay's structure.
Your rhetorical analysis essay introduction should introduce the text author and present your thesis. Body paragraphs should each focus on a specific rhetorical strategy or element supported by evidence from the text.
The conclusion should summarize your main points.
Step 7. Analyze Rhetorical Strategies
Analyzing rhetorical strategies in the body paragraphs of your rhetorical analysis essay is a critical part of the process. This is where you break down how the author or speaker uses specific techniques to persuade the audience.
For instance, when discussing ethos in King's speech, you might highlight his credentials as a civil rights leader, which enhances his credibility.
Step 8. Address Style and Language
Addressing the author's style and language is an important part of a rhetorical analysis essay. This step allows you to explore how the author's choices in the type of writing contribute to the overall persuasive effect of the text.
In King's speech, you can discuss his use of metaphors like "promissory note" and "content of their character," which evoke strong imagery.
Step 9. Provide Evidence
Back up your analysis with evidence from the text. Quote relevant passages, such as King's famous lines about his dream, to illustrate how he uses language to create emotional impact.
Step 10. Revise and Proofread
After drafting your essay, revise and proofread it for clarity, coherence, grammar, and punctuation. Make sure your ideas flow logically and that your analysis supports your thesis effectively.
Writing Tips for Rhetorical Analysis Essay AP Language
Writing a rhetorical analysis essay for Advanced Placement English Language and composition is mandatory. It is a course and examination offered in Advanced Placement Programs by the College Board.
There are some writing tips to make your rhetorical analysis essay for AP Lang perfect.
Follow the easy writing tips provided below to draft a compelling rhetorical analysis essay:
- Choose an interesting ap lang rhetorical analysis essay prompt for your essay.
- Read the original until the basic elements of the work are not clear. For example, speaker, occasion, audience, purpose, subject, and tone.
- When drafting a thesis statement for your rhetorical analysis essay, make sure the thesis matches your topic.
- Use accurate and appropriate language when drafting an essay.
- Keep in mind that the fundamental objective of this essay type is to analyze and not to prove the counter-argument.
- Keep your voice as well while explaining the ideas of the text.
- In the concluding section of the essay, only summarize the major points of the contents. Avoid introducing new ideas in the concluding paragraphs.
- Proofread your essay at least thrice to check if the content is error-free.
- Another tip is to take a professional’s help to draft a perfect essay.
You can refer to this example for a better understanding:
AP Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example (PDF)
Ap Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Rubric
The AP Language and Composition (AP Lang) rhetorical analysis essay is typically scored based on a rubric that evaluates various aspects of the essay.
While the specific rubric may vary slightly depending on the year and exam administration, the following is a general outline of key rhetorical concepts you can expect to be assessed in an AP Lang rhetorical analysis essay:
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples
It is essential to first go through examples and samples to see which structure and outline to follow when drafting.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Sample (PDF)
Rhetorical Analysis of Cory Doctorow’s (PDF)
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Ap Lang
Ap Rhetorical Analysis Essay Prompts
For your ease, give a read to our rhetorical analysis essay examples blog.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
To write a rhetorical analysis essay that is strong and effective, choosing a good topic is essential.
Selecting rhetorical analysis essay topics that are appropriate for the content is a time-consuming process.
- Martin Luther King Jr’s last speech
- A scene from Shakespeare’s play Romeo and Juliet
- “I Am Prepared to Die” by Nelson Mandela
- Pride and Prejudice
- Macbeth’s rhetorical analysis
- Rhetorical analysis of the movie “The fault in our stars”
- Analyze the poem "The Epic" by Alfred Lord Tennyson
- Analyze Joseph Stiglitz’s “The Price of Inequality”
- Mark Twain’s “Adventures of Huckleberry Finn"
- Harper Lee’s “To Kill a Mockingbird'
If you want more on rhetorical analysis essay topics , give a read to our blog!
In conclusion, writing a rhetorical analysis essay is not easy but with this descriptive guide, you can craft a well-structured analysis essay.
In addition to this, if you want professional assistance for your academic papers and academic essays, MyPerfectWords.com is the best essay writing service for your needs.
So why wait? Buy custom essay online with us and enjoy complimentary services at no extra cost!
Frequently Asked Questions
How many paragraphs does a rhetorical analysis essay have.
In your rhetorical analysis, you'll tackle the text directly by focusing on three areas in each paragraph. Each area should contribute to a larger argument that supports the main idea or thesis statement for this piece of work.
What is the purpose of rhetorical analysis?
The purpose of a rhetorical analysis is to understand HOW the author writes, rather than WHAT they wrote. To do this, you will look at how the author achieved their goal or purpose for writing.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

How to Write a Compelling Rhetorical Analysis Essay: Tips and Techniques
Understanding the rhetorical situation, identify the speaker, analyze the audience, determine the purpose, dissecting the argument, identify the claims, evaluate the evidence, recognize the appeals, analyzing rhetorical devices, figurative language, tone and diction, organization and structure, writing the essay, crafting an introduction, developing body paragraphs, concluding the analysis, proofreading and revising, check for clarity, ensure coherence, polish your style, additional resources, sample rhetorical analysis essays, recommended books, helpful websites.
Writing a rhetorical analysis essay can seem like a daunting task, but with the right approach and techniques, you'll be able to master it in no time. In this blog post, we'll explore the essential steps to creating a compelling rhetorical analysis essay, from understanding the rhetorical situation to polishing your final draft. Get ready to impress your audience with your analytical skills!
Before diving into the analysis, it's important to grasp the rhetorical situation of the piece you're examining. This involves identifying the speaker, analyzing the audience, and determining the purpose of the text. By doing so, you'll gain a deeper understanding of the context in which the author is communicating, which will ultimately strengthen your rhetorical analysis essay.
First, determine who the speaker or author of the text is. This is the person responsible for crafting the argument and presenting it to the audience. Keep in mind that the speaker's background, experiences, and beliefs can influence the way they convey their message. Consider the following aspects:
- Expertise : Is the speaker an expert in the subject matter?
- Reputation : How is the speaker perceived by the audience?
- Personal values : What beliefs or values might the speaker hold that could impact their argument?
Next, consider the audience the speaker is addressing. Understanding who the intended readers or listeners are will help you discern what strategies the speaker employs to persuade them. When analyzing the audience, think about:
- Demographics : What are the age, gender, and cultural background of the target audience?
- Knowledge : What does the audience likely know about the subject matter?
- Attitudes : How might the audience feel about the topic?
Lastly, identify the purpose of the text. Understanding the speaker's goal will help you see how their argument is structured and what techniques they use to achieve that goal. The purpose can be to inform, persuade, or entertain, among other possibilities. Ask yourself:
- What is the main message or argument the speaker wants to convey?
- How does the speaker want the audience to feel or react?
- What outcome does the speaker hope to achieve with their argument?
Now that you have a solid grasp of the rhetorical situation, you're well-prepared to start dissecting the argument and analyzing the various rhetorical devices at play in your rhetorical analysis essay.
With a clear understanding of the rhetorical situation, you're now ready to dive into the heart of the text and dissect the argument itself. This involves identifying the claims the speaker makes, evaluating the evidence they provide, and recognizing the appeals they use to persuade the audience. Let's break down these components to help you create a well-rounded rhetorical analysis essay.
Start by pinpointing the speaker's main claims or assertions in their argument. Claims are the building blocks of the argument and are used to support the overall thesis or purpose. As you read or listen, look for statements that:
- Assert a fact or belief : The speaker presents a statement as true or false.
- Propose a solution : The speaker suggests a course of action to address a problem.
- Express a value judgment : The speaker evaluates something as good or bad, ethical or unethical.
Next, assess the evidence the speaker uses to support their claims. Strong evidence is crucial to a persuasive argument, so evaluating its quality and relevance is a key part of your rhetorical analysis essay. Consider the following questions when examining the evidence:
- Is the evidence relevant and directly related to the claim?
- Does the evidence come from credible and reliable sources?
- Is the evidence sufficient to support the claim, or are there gaps in the argument?
In a rhetorical analysis essay, it's essential to identify the appeals the speaker uses to persuade the audience. There are three main types of appeals—ethos, pathos, and logos—that you should be able to recognize:
- Ethos : Appeals to credibility and trustworthiness, often demonstrated by the speaker's expertise or character.
- Pathos : Appeals to emotions and values, often using vivid language and personal anecdotes to evoke a specific feeling in the audience.
- Logos : Appeals to logic and reason, often using facts, statistics, and rational arguments to convince the audience of the validity of the claim.
By dissecting the argument and understanding its components, you can better analyze the effectiveness of the speaker's strategies in your rhetorical analysis essay.
Beyond the argument itself, a rhetorical analysis essay should also examine the specific rhetorical devices the speaker employs to make their message more persuasive. These devices include figurative language, tone and diction, and organization and structure. Let's explore each of these categories and their significance in the analysis.
Figurative language is a powerful tool speakers use to convey complex ideas and emotions in a more relatable way. Some common forms of figurative language include metaphors, similes, and personification. When analyzing figurative language, consider:
- What images or comparisons does the speaker use?
- How do these images help convey the message or evoke a specific emotion?
- Do the images contribute to the overall effectiveness of the argument?
The speaker's tone and diction—the words they choose and the way they express themselves—can greatly influence the audience's perception of their argument. In your rhetorical analysis essay, pay attention to:
- The tone of the speaker's voice : Is it formal or informal? Serious or humorous? Angry or empathetic?
- The choice of words : Are they simple or complex? Concrete or abstract? Do they evoke specific emotions or values?
- The impact of tone and diction : How do these elements contribute to the overall persuasiveness of the argument?
Lastly, the organization and structure of the text or speech can also play a significant role in the persuasiveness of the argument. When examining this aspect for your rhetorical analysis essay, consider:
- The overall structure : Does the speaker follow a clear and logical progression of ideas? Are there smooth transitions between points?
- The use of examples and anecdotes : Are they well-placed and relevant to the argument? Do they help illustrate the speaker's points effectively?
- The impact of organization and structure : How do these elements contribute to the clarity and persuasiveness of the argument?
By exploring these rhetorical devices, you can gain a deeper understanding of the speaker's strategies and better assess their effectiveness in your rhetorical analysis essay.
Now that you've analyzed the rhetorical situation, dissected the argument, and examined the rhetorical devices, it's time to put it all together and write your rhetorical analysis essay. This section will guide you through crafting an introduction, developing body paragraphs, and concluding the analysis.
The introduction sets the stage for your rhetorical analysis essay. To write an engaging and informative introduction:
- Introduce the text or speech : Mention the title, author or speaker, and the context in which it was delivered.
- Provide a brief summary : Give a concise overview of the main argument and key points.
- State your thesis : Present your central argument or analysis, focusing on the speaker's rhetorical strategies and their effectiveness.
Remember, the introduction should be interesting and engaging, but also clear and concise, to set the tone for the rest of your essay.
Body paragraphs are the heart of your rhetorical analysis essay, where you'll present the evidence and analysis to support your thesis. To create effective body paragraphs:
- Focus on one main idea per paragraph : Each paragraph should discuss a single rhetorical device or aspect of the argument.
- Provide evidence : Use specific examples from the text or speech to support your analysis.
- Analyze the evidence : Explain how the examples demonstrate the speaker's rhetorical strategies and their effectiveness.
- Transition smoothly : Use clear transitions between paragraphs to maintain a logical flow throughout your essay.
By following these guidelines, you can create well-structured and cohesive body paragraphs that effectively support your thesis.
The conclusion is your final opportunity to leave a lasting impression on your reader and wrap up your rhetorical analysis essay. To write a strong conclusion:
- Restate your thesis : Briefly rephrase your central argument, showing how you've proven it through your analysis.
- Summarize your main points : Recap the key aspects of the argument and the rhetorical devices you've discussed.
- End with a broader implication : Explain the overall significance of the speaker's rhetorical strategies, and how they contribute to the audience's understanding or reaction to the argument.
By crafting a compelling conclusion, you'll leave your reader with a clear understanding of the speaker's rhetorical techniques and their impact on the argument.
Once you've written your rhetorical analysis essay, it's important to proofread and revise it to ensure clarity, coherence, and polish. This section will provide you with some tips on how to improve your essay during the revision process.
Make sure your essay is easy to read and understand. To check for clarity:
- Read your essay out loud : This can help you catch awkward phrasing, confusing sentences, or repetitive wording.
- Ensure your thesis is clear and concise : Your thesis should be easily identifiable and clearly state your main argument.
- Explain rhetorical terms and concepts : If you've used specific rhetorical terms, make sure you've provided clear definitions or explanations for your reader.
By checking for clarity, you'll ensure that your essay is easy to follow and effectively communicates your analysis.
Your essay should have a logical flow and be well-organized. To ensure coherence:
- Use transitions between paragraphs : Connect your ideas with clear and smooth transitions to maintain a logical flow throughout your essay.
- Follow a logical structure : Organize your essay in a way that presents your analysis in a clear and accessible manner.
- Stay focused on your thesis : Make sure each paragraph relates back to your central argument and contributes to proving it.
By ensuring coherence, you'll create an essay that is easy to follow and maintains a strong connection between your analysis and your thesis.
Finally, make sure your essay is well-written and free of errors. To polish your style:
- Check for grammar and punctuation errors : Use a grammar checker or carefully proofread your essay to catch any mistakes.
- Vary your sentence structure : Use a mix of short and long sentences, as well as different sentence structures, for a more engaging and dynamic writing style.
- Choose precise and concise language : Use specific and clear wording to effectively convey your analysis.
By polishing your style, you'll create a professional and polished essay that showcases your rhetorical analysis skills and impresses your reader.
Beyond the tips and techniques provided in this blog, there are many additional resources available to help you further develop your rhetorical analysis essay writing skills. Let's explore some of these resources, including sample essays, books, and helpful websites.
Reading sample rhetorical analysis essays can be a great way to learn more about the structure, style, and techniques employed in this type of essay. Look for samples from reputable sources, such as:
- College writing centers : Many college and university writing centers offer sample essays to help students understand different types of assignments.
- Writing guidebooks : Books on essay writing often include sample essays, which can be a valuable resource for learning how to craft a rhetorical analysis essay.
- Online writing communities : Websites and forums dedicated to writing can be a treasure trove of sample essays and constructive feedback from other writers.
By reviewing sample essays, you can gain a better understanding of what makes a successful rhetorical analysis essay and improve your own writing in the process.
There are several books available that can help you learn more about rhetorical analysis and improve your essay writing skills. Some recommended titles include:
- "The Elements of Rhetoric" by Ryan Weber : This book provides a comprehensive overview of rhetorical concepts and techniques, making it an excellent resource for anyone looking to improve their rhetorical analysis essay writing.
- "Style: Lessons in Clarity and Grace" by Joseph M. Williams and Joseph Bizup : This book offers guidance on writing with clarity and style, which can be particularly useful when crafting a rhetorical analysis essay.
- "They Say / I Say: The Moves That Matter in Academic Writing" by Gerald Graff and Cathy Birkenstein : This book provides practical advice on effectively structuring your essay and making persuasive arguments, both of which are crucial skills for a successful rhetorical analysis essay.
By studying these books, you can deepen your understanding of rhetorical analysis and hone your essay writing skills.
There are numerous websites that offer helpful resources for improving your rhetorical analysis essay writing skills. Some examples include:
- OWL at Purdue : Purdue University's Online Writing Lab (OWL) offers a wealth of information on essay writing, including guides to rhetorical analysis, grammar, and style.
- The Writing Center at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill : This website offers a variety of resources, including guides on rhetorical analysis, essay organization, and style.
- Grammarly : While not specifically focused on rhetorical analysis, Grammarly offers a powerful grammar and style checker that can help you polish your essay and avoid common mistakes.
By taking advantage of these resources, you can continue to develop your rhetorical analysis essay writing skills and create compelling, high-quality essays.
If you're looking to gain valuable insights and tips on personal growth, don't miss the workshop ' Navigating Life VI ' by Rabih Salloum. This workshop will provide you with the tools and advice you need to navigate the complexities of life and achieve personal and professional success.

Live classes every day
Learn from industry-leading creators
Get useful feedback from experts and peers
Best deal of the year
* billed annually after the trial ends.
*Billed monthly after the trial ends.
Global Health and Education

2020 AP English Exam: How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay
In light of The College Board recently announcing that this year’s AP English Language and Composition exam will be only one question , a 45-minute rhetorical analysis essay, it would probably be a good idea to freshen up on your essay-writing skills. The benefits of doing this won’t stop once high-school ends- knowing how to write rhetorical analysis essays will also be extremely helpful for future college and professional endeavors where you might be required to examine a text or prepare a report on one. In this article you will learn the breakdown of every section of the rhetorical analysis essay, and what you should be including in order to earn a five this May.
2020 AP English Language and Composition Exam Changes: How to write a 45-minute rhetorical analysis essay?

Introduction
The first part of the rhetorical essay is the introduction. The introduction can be broken down into four simple parts, and because of this, if you feel that you are running short on time, don’t be afraid to actually wait until the end to write your introduction. This could possibly be beneficial since you’ll know exactly where the rest of your essay is going.
Before you start writing, make sure to thoroughly read through your text. Try to take note of the SPACECAT features: s peaker, p urpose, a udience, c ontext, e xigence, c hoices, a ppeals, and t one.
- Contextualization and Background Information
The beginning of your first paragraph will include naming the piece you are analyzing, then contextualizing it and including any relevant background information. This can include historical events that were taking place during the writing of this essay (for example, World War II, the Civil Rights Movement, a certain political campaign, etc.), the time period, the country, conflict, and anything else that could serve as the something affecting the purpose or exigence for the piece.
- Background information for the author
After you’ve finished contextualizing the piece itself, you will need to include pertinent information regarding the author, if you are aware of any. What has happened or is happening during their life that caused them to write this piece? If these events did not cause them to write this piece, how did it affect their argument? Are there any personal or political philosophies that they are subscribed to? How does the author themself affect the essay?
- Overview of the argument
In this section of your paragraph, you’ll give a brief overview of what the author is arguing. You don’t need to go into extreme detail, but you should outline their main points and the reason why they even bothered to write the essay in the first place. This is a very important step because if you do not understand the argument that the author is making, you are not going to be able to correctly write the paper. This is why your first read of the work is so important without taking the time to become familiar with the text, you’ll lose precious time re-reading and panicking because you aren’t sure what to write. It’s best if you make use of annotation and highlighting important information that you can quickly go back to later
The last portion of the first paragraph is the thesis. The thesis emphasizes the purpose of the writing- the why . Why is the author doing any of this? What’s the reason? Your thesis is basically the entire argument of your essay summed up into one sentence. Another thing that’s important to add in your thesis is the effectiveness of the author’s execution of their argument. Did they do a good job of getting their point across? Make sure to have evidence to back this point up later.

Body Paragraphs
The body of your essay will consist of at least two paragraphs analyzing the rhetorical choices made by the author throughout their work. Rhetorical devices are tactics used by the writer to emphasize their point and draw more people to their side, such as diction, appeals, imagery, etc. You can find a list of twenty different rhetorical strategies here . Unless stated otherwise, you should try and investigate a different rhetorical strategy in each paragraph.
- Topic Sentence
Each body paragraph will start with you introducing the topic. This can be through starting with a quote from the text that leads into an explanation of how it is an example of your chosen rhetorical device, or it can just simply be a statement about how the author used a certain device in the essay.
Another important aspect to look at is if the author used any appeals in their essay. The appeals are; ethos, appealing by establishing credibility; pathos, appealing to emotion; logos, appealing to logic; kairos, appealing to timeliness. Appeals are great characteristics of any argument and can be very powerful rhetorical choices to discuss in your essay.
Now you have to analyze the rhetorical device that you mentioned in your topic sentence. To do this, you should start by quoting passages from your text that show usage of the device, then elaborate on why that’s true and how it affects the delivery of the argument, as well as the argument itself. The analysis section will be the largest part of each body paragraph. Always be thinking about the argument that your author is making while doing your analysis.
- Connection to the Argument
To end your body paragraph, you should connect how the usage of this rhetorical choice connects to the overall purpose of the essay. Why is the author using this and why does it matter ? Who cares? Who should care- and for what purpose?

Contradiction
The contradiction paragraph is typically the last paragraph before your conclusion. In this section you will address the flaws in the author’s essay as well as in their argument. Be careful- do not share whether or not you agree with the author. This is not something that’s important in a rhetorical analysis essay. You are simply analyzing the techniques used by the author to get their point across- you are not making an argument about whether or not their point was right. Be sure to focus on the weaker parts of your author’s argument, find the holes in it. Try to focus on one or two things that stand out despite all of the rhetorical devices used by them. Adding a contradiction paragraph will show complexity in your essay and give depth to your writing.

You made it! You are now at the final paragraph of your rhetorical analysis essay. Luckily, you only have three things to accomplish before you can wrap everything up. This paragraph will be spent creating a miniature summary of everything you just wrote.
- Sum up your article
Now that you’ve spent so much time examining the author’s argument in tiny pieces, it’s time to bring it all together for the reader. Go back through the main points made throughout the essay and how they showcase the main points of the author. Don’t be afraid to re-mention how the rhetorical choices strengthen said main points.
- Present relevant conclusions
After you’ve summed up the main points made in the text , you should draw some major relevant conclusions from your essay. Talk about the bigger picture. If you had to sum up your entire essay in only three sentences, what would they be? Try to keep this in mind as you approach this part of your writing.
- Refer back to the main point
In the final sentences of your essay, you’ll want to both restate your thesis and leave a powerful ending sentence. When re-stating your thesis, try to make use of some rewording so that you aren’t just repeating the same sentence. It doesn’t have to be completely different, but it shouldn’t be a carbon copy of what you’ve already said before. Finally, end with a sentence that both compliments the flow of your last paragraph and leaves the reader with a good leeway into pondering about what they’ve just read, and to take with them as they begin formulating their final opinions on your essay.
Congratulations! You’ve officially finished writing your rhetorical analysis essay. This type of essay can be difficult at first, but once you get the hang of it you’ll be whipping them out in no time. If you’d like to see a sample of a full-length rhetorical analysis essay, you can click here . If you’d like to practice with prompts, the good news is that you can write a rhetorical analysis essay about basically anything. You can take out your favorite book and try and write about what you see in a random passage. What’s the argument behind your favorite book or essay?

Works Cited
“AP Exam Schedule 2020.” College Board. Accessed April 22, 2020.
https://apcoronavirusupdates.collegeboard.org/educators/taking-the-exams/ap-exam-schedule
“Examples of Rhetorical Devices.” Your Dictionary. Accessed April 21, 2020. https://examples.yourdictionary.com/examples-of-rhetorical-devices.html .
“Sample Rhetorical Analysis.” Excelsior Online Writing Lab. Excelsior College. Accessed April 21, 2020. https://owl.excelsior.edu/argument-and-critical-thinking/argument-analysis/argument-analysis-sample-rhetorical-analysis/
“SPACE CAT: New Rhetorical Analysis Acronym for AP Language.” The English Department. Teachers Pay Teachers. Accessed April 22, 2020.
https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/SPACE-CAT-New-Rhetorical-Analysis-Acronym-for-AP-Language-4712477
© Copyright 2020 Moosmosis – All rights reserved
All rights reserved. This essay or any portion thereof may not be reproduced or used in any manner whatsoever without the express written permission of the publisher.

Please Like our Facebook page to support! 🙂
Share this:.

- Share on Tumblr
Categories: Creative Writing , education , humanities , Literature
Tagged as: AP English , ap literature , english , learning , Literature , literature essay , literature high school , school , writing
Published by Elle Ward
Hi! I'm an aspiring journalist and writer. A picture may be worth a thousand words, but a novel can create a thousand pictures. View all posts by Elle Ward
7 replies »
Very thorough and excellent article, Elle! Helpful for many AP English literature and language students.
Like Liked by 1 person
Great article! 👍
Great information! Thanks
- Pingback: Romeo and Juliet Study Guide: Detailed Timeline Review, Summary of Events, and Quotes – Moosmosis
- Pingback: Literature 101: Literary and Poetry Terms Vocabulary Study Guide – 125 Most Common Literary Terms and Definitions – Moosmosis
- Pingback: Learning Languages 101: Top 5 Benefits and Top 5 Tips of Learning New Languages – Moosmosis
- Pingback: Running Into History: Eluid Kipchoge’s 1:59:40 Marathon – Moosmosis
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Thank you for visiting.
- 2,659,926 Lifelong Learners!
Join Moosmosis and our wonderful lifelong learning community today! Free lessons and student opportunities
Email Address:
Subscribe for Free!
Today’s Top Posts

Our Community
Choose a Language
Please Like to Support!
- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
Calculate for all schools
Your chance of acceptance, your chancing factors, extracurriculars, ap lang rhetorical analysis essay - how to ace it.
Hey guys! Currently prepping for the AP Lang exam, and I could use some advice on writing the rhetorical analysis essay. What's the best way to approach the text and analyze the author's choices effectively?
Hey there! Great to see you're prepping for the AP Lang exam. The rhetorical analysis essay can seem a bit challenging at first, but with practice and a solid strategy, you can ace it! Here are some tips for tackling this essay:
Start by reading the text carefully and taking notes on the author's use of rhetorical strategies, such as ethos, pathos, and logos. Jot down specific examples and make note of any patterns you notice. As you read, consider the author's purpose, audience, and context. What is the author trying to achieve, and how do their choices cater to their target audience and the specific context of the piece?
Make sure your thesis statement clearly and concisely provides an overview of the main points you'll be discussing in your essay. The body paragraphs should then explore each of these points in depth, using specific examples from the text to back up your claims.
In your analysis, focus on explaining the 'how' and 'why' - how the author uses a particular strategy, and why it's effective given the purpose, audience, and context.
Finally, don't forget to revise and proofread your essay before turning it in. This will help you catch any errors and ensure your writing is clear and well-organized. Best of luck on your exam!
About CollegeVine’s Expert FAQ
CollegeVine’s Q&A seeks to offer informed perspectives on commonly asked admissions questions. Every answer is refined and validated by our team of admissions experts to ensure it resonates with trusted knowledge in the field.
Module 1: An Overview of the Writing Process
Creating paragraphs.
A paragraph is a self-contained portion of your argument. Paragraphs will begin by making a claim that connects back to your thesis. The body of the paragraph will present the evidence, reasoning and conclusions that prove that claim. Usually, paragraphs will end by connecting their claim to the larger argument or by setting up the claim that the next paragraph will contain.
How Many Paragraphs Do You Need?
There is no set number for how many paragraphs a paper should have. You will need one for an introduction and one for a conclusion, but after that the number can vary. However, you will need one paragraph for every claim that makes up your argument.
Paragraphs should be used to develop one idea at a time rather than contain many different ideas and claims. If you have a lot of ideas and claims to address, you may be tempted to combine related claims into the same paragraph. Combining different points in the same paragraph cuts down on how much space you have to argue each point. This will divide your reader’s attention and make your argument less thorough.
By dedicating each paragraph to only one part of your argument, you will give the reader time to fully evaluate and understand each claim before going on to the next one. Think of paragraphs as a way of guiding your reader’s attention – by giving them a single topic, you force them to focus on it. When you direct their focus, they will have a much easier time following your argument.
Some writing manuals will direct you to have one paragraph for every point made in your thesis. The general idea behind this rule is a good one – you need to address every point, and you will need at least a paragraph for each. However, do not feel like you can only devote one paragraph to each point. If your argument is complex, you may need to have subsections for each of your main points. Each one of those supporting points should be its own paragraph.
Using Topic Sentences
Every paragraph of argument should begin with a topic sentence that tells the reader what the paragraph will prove. By providing the reader with expectations at the start of the paragraph, you help them understand where you are going and how the paragraph fits in with the overall structure of your argument. Topic sentences should always connect back to your thesis statement – if you cannot find a way to describe a paragraph in relation to your thesis, you probably do not need it for your argument.
Creating Good Paragraphs
If the thesis contains multiple points or assertions, each body paragraph should support or justify them, preferably in the order the assertions were originally stated in the thesis. Thus, the topic sentence for the first body paragraph will refer to the first point in the thesis sentence and the topic sentence for the second body paragraph will refer to the second point in the thesis sentence. Each body paragraph is something like a miniature essay in that they each need an introductory sentence that makes an important and interesting argument, and that they each need a good closing sentence in order to produce a smooth transition between one point and the next. Transitions from one argument to the next, as well as within paragraphs, are important to add coherence to your paper.
- Creating Paragraphs. Provided by : Boundless. Located at : https://www.boundless.com/writing/textbooks/boundless-writing-textbook/style-structure-grammar-5/sentence-building-28/creating-paragraphs-127-7913/? . Project : Boundless Writing. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How Many Paragraphs Should an Essay Have?

- 6-minute read
- 19th May 2023
You have an essay to write. You’ve researched the topic and crafted a strong thesis statement . Now it’s time to open the laptop and start tapping away on the keyboard. You know the required word count, but you’re unsure of one thing: How many paragraphs should you have in the essay? Gee, it would’ve been nice if your professor had specified that, huh?
No worries, friend, because in this post, we’ll provide a guide to how many paragraphs an essay should have . Generally, the number of paragraphs will depend on how many words and how many supporting details you need (more on that later). We’ll also explore the concept of paragraphs if you’re wondering what they’re all about. And remember, paragraphs serve a purpose. You can’t submit an essay without using them!
What Is a Paragraph?
You likely know what a paragraph is, but can you define it properly in plain English? Don’t feel bad if that question made you shake your head. Off the top of our heads, many of us can’t explain what a paragraph is .
A paragraph comprises at least five sentences about a particular topic. A paragraph must begin with a well-crafted topic sentence , which is then followed by ideas that support that sentence. To move the essay forward, the paragraph should flow well, and the sentences should be relevant.
Why Are Paragraphs Important?
Paragraphs expand on points you make about a topic, painting a vivid picture for the reader. Paragraphs break down information into chunks, which are easier to read than one giant, uninterrupted body of text. If your essay doesn’t use paragraphs, it likely won’t earn a good grade!
How Many Paragraphs Are in an Essay?
As mentioned, the number of paragraphs will depend on the word count and the quantity of supporting ideas required. However, if you have to write at least 1,000 words, you should aim for at least five paragraphs. Every essay should have an introduction and a conclusion. The reader needs to get a basic introduction to the topic and understand your thesis statement. They must also see key takeaway points at the end of the essay.
As a rule, a five-paragraph essay would look like this:
- Introduction (with thesis statement)
- Main idea 1 (with supporting details)
- Main idea 2 (with supporting details)
- Main idea 3 (with supporting details)
Your supporting details should include material (such as quotations or facts) from credible sources when writing the main idea paragraphs.
If you think your essay could benefit from having more than five paragraphs, add them! Just make sure they’re relevant to the topic.
Professors don’t care so much about the number of paragraphs; they want you to satisfy the minimum word requirement. Assignment rubrics rarely state the number of required paragraphs. It will be up to you to decide how many to write, and we urge you to research the assigned topic before writing the essay. Your main ideas from the research will generate most of the paragraphs.
When Should I Start a New Paragraph?
Surprisingly, some students aren’t aware that they should break up some of the paragraphs in their essays . You need to start new paragraphs to keep your reader engaged.
As well as starting a new paragraph after the introduction and another for the conclusion, you should do so when you’re introducing a new idea or presenting contrasting information.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Starting a paragraph often involves using transitional words or phrases to signal to the reader that you’re presenting a new idea. Failing to use these cues may cause confusion for the reader and undermine your essay’s coherence.
Let’s consider examples of transitional words and phrases in action in a conclusion. Note that the essay is about too much mobile device screen time and that transitional words and phrases can occur later in a paragraph too:
Thanks to “In conclusion” and “Additionally,” the reader clearly knows that they are now in the conclusion stage. They can also follow the logic and development of the essay more easily.
How Do I Know Whether I Have Enough Paragraphs?
While no magic number exists for how many paragraphs you need, you should know when you have enough to satisfy the requirements of the assignment. It helps if you can answer yes to the following questions:
- Does my essay have both an introduction and a conclusion?
- Have I provided enough main ideas with supporting details, including quotes and cited information?
- Does my essay develop the thesis statement?
- Does my essay adequately inform the reader about the topic?
- Have I provided at least one takeaway for the reader?
Conclusion
Professors aren’t necessarily looking for a specific number of paragraphs in an essay; it’s the word count that matters. You should see the word count as a guide for a suitable number of paragraphs. As a rule, five paragraphs should suffice for a 1,000-word essay. As long as you have an introduction and a conclusion and provide enough supporting details for the main ideas in your body paragraphs, you should be good to go.
Remember to start a new paragraph when introducing new ideas or presenting contrasting information. Your reader needs to be able to follow the essay throughout, and a single, unbroken block of text would be difficult to read. Transitional words and phrases help start new paragraphs, so don’t forget to use them!
As with any writing, we always recommend proofreading your essay after you’ve finished it. This step will help to detect typos, extra spacing, and grammatical errors. A second pair of eyes is always useful, so we recommend asking our proofreading experts to review your essay . They’ll correct your grammar, ensure perfect spelling, and offer suggestions to improve your essay. You can even submit a 500-word document for free!
1. What is a paragraph and what is its purpose?
A paragraph is a group of sentences that expand on a single idea. The purpose of a paragraph is to introduce an idea and then develop it with supporting details.
2. What are the benefits of paragraphs?
Paragraphs make your essay easy to read by providing structure and flow. They let you transition from one idea to another. New paragraphs allow you to tell your reader that you’ve covered one point and are moving on to the next.
3. How many paragraphs does a typical essay have?
An essay of at least 1,000 words usually has five paragraphs. It’s best to use the required word count as a guide to the number of paragraphs you’ll need.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Revised on July 23, 2023. A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience. A rhetorical analysis is structured similarly to other essays: an introduction presenting ...
Her story "The Astronaut" won the 2018 Shirley Jackson Award for short fiction and received a "Distinguished Stories" mention in the 2019 Best American Short Stories anthology. How to write the AP Lang rhetorical analysis essay. We look at a AP lang rhetorical analysis essay example and explore do's and don'ts.
2. Introducing Your Essay Topic. Introduce your essay by providing some context about the text you're analyzing. Give a brief overview of the author, intended audience, and purpose of the writing. You should also clearly state your thesis, which is your main point or argument about how and why the author uses rhetorical strategies.
Rhetorical appeal #2: Pathos. The purpose of Pathos-driven rhetoric is to appeal to the reader's emotions. A common example of pathos as a rhetorical means is adverts by charities that try to make you donate money to a "good cause". To evoke the intended emotions in the reader, an author may use passionate language, tell personal stories ...
Body Paragraph #1: Ethos. Describe how the speaker makes an appeal to ethos (the audience's sense of ethical responsibility) Use specific examples, referring to word choice, tone, anecdotes, and other devices. Body Paragraph #2: Pathos. Describe how the speaker makes an appeal to pathos (the audience's emotions)
Like all other essays, your rhetorical analysis essay will have an introduction with a thesis, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. WRITE - write your essay. Asher AP ELAC Name: _____ Step 3: Organizing and Writing Your Essay: Some of this is redundant, but this breaks down some of the steps from MAD TO WRITE even further. ...
Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses. Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. "implies," "asserts," or "claims". Briefly summarize the text in your own words. Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect.
Rhetorical Analysis. Rhetoric is the study of how writers and speakers use words to influence an audience. A rhetorical analysis is an essay that breaks a work of non-fiction into parts and then explains how the parts work together to create a certain effect—whether to persuade, entertain or inform. You can also conduct a rhetorical analysis ...
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay in 6 Steps. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Sep 2, 2021 • 3 min read. In a rhetorical analysis essay, a writer will examine the rhetoric and style of another author's work. If you want to write your own rhetorical analysis essay, we've developed a step-by-step guide to lead you through the ...
Use the four elements of a rhetorical essay (speaker, audience, purpose, and context) as a guide to structure your essay. 5. Write the introduction: Begin with a hook to grab the reader's attention and provide background information on the text. End with a thesis statement that summarizes your argument. 6.
How to write a rhetorical analysis. To write a rhetorical analysis, you need to follow the steps below: Step 1: Plan and prepare. With a rhetorical analysis, you don't choose concepts in advance and apply them to a specific text or piece of content. Rather, you'll have to analyze the text to identify the separate components and plan and ...
18.List three rhetorical devices used by the writer that you feel comfortable writing about and that provide you with ample material to use in your essay. In your list, name the device, include the quotation in which the device is used, and the page number or paragraph number. 19.Evaluate the text. Form an opinion.
rhetorical analysis essay. Below is one way that is a good, simple format to help you get started. You may find as you become more comfortable with analysis that you want to deviate from this format. That's fine as long as you are still focusing on numbers 1-3 from above. Introduction The introductory paragraph to an analysis essay is usually ...
Step 5. Create a Thesis Statement. Your thesis statement should be a concise summary of your main argument. For example: "In 'I Have a Dream,' Martin Luther King Jr. employs powerful rhetorical strategies, including appeals to ethos, pathos, and logos, to call for racial justice and equality in America." Step 6.
Rhetorical tools can sometimes be used for more than one appeal (e.g., a personal story on parenting may connect with an audience emotionally while also establishing the speaker's authority as an experienced parent). Consider how one tool might have multiple functions. Note: Be careful of analyzing the rhetorical tool word choice. It is ...
The introduction sets the stage for your rhetorical analysis essay. To write an engaging and informative introduction: Introduce the text or speech: Mention the title, author or speaker, and the context in which it was delivered. Provide a brief summary: Give a concise overview of the main argument and key points.
By Elle Ward on1 May 2020•( 7 Comments ) In light of The College Board recently announcing that this year's AP English Language and Composition exam will be only one question, a 45-minute rhetorical analysis essay, it would probably be a good idea to freshen up on your essay-writing skills. The benefits of doing this won't stop once high ...
The rhetorical analysis essay can seem a bit challenging at first, but with practice and a solid strategy, you can ace it! Here are some tips for tackling this essay: Start by reading the text carefully and taking notes on the author's use of rhetorical strategies, such as ethos, pathos, and logos. Jot down specific examples and make note of ...
Creating Paragraphs. A paragraph is a self-contained portion of your argument. Paragraphs will begin by making a claim that connects back to your thesis. The body of the paragraph will present the evidence, reasoning and conclusions that prove that claim. Usually, paragraphs will end by connecting their claim to the larger argument or by ...
As a rule, five paragraphs should suffice for a 1,000-word essay. As long as you have an introduction and a conclusion and provide enough supporting details for the main ideas in your body paragraphs, you should be good to go. Remember to start a new paragraph when introducing new ideas or presenting contrasting information.
The conclusion should reflect on your analysis, tie it back to the intro points, and take a more abstract view (i.e. relating your analysis to bigger ideas/concepts). You can do all of this in 3 sentences each, but you won't reach the level of sophistication you need to get high scores.
Two well-developed paragraphs can get a good score. Absolutely. The AP Lang test was only a rhetorical analysis essay when I took it in 2020 (because it was a shortened, virtual test due to the pandemic). I only wrote two body paragraphs, and I got a 5. So yes, you can certainly earn full credit with only two body paragraphs.
Length does not always equate to quality; try to make sure you just have enough material. I try to aim for either 3 body paragraphs with 2 pieces of evidence each or 2 body paragraphs with 3 pieces of evidence. The evidence doesn't have to be long, it could be a single word or one small detail. And make sure each piece of evidence has good ...