
- About / Contact
- Privacy Policy
- Alphabetical List of Companies
- Business Analysis Topics

Apple’s Stakeholders, CSR & ESG Strategy

Apple’s strategy for CSR (corporate social responsibility), ESG (environmental, social, and governance), sustainability, and business ethics addresses stakeholders grouped according to shared interests and their significance to the information technology business. Apple operates in markets for information technology, consumer electronics, and online services. This diversity of business operations creates challenges for corporate citizenship affecting brand image, as well as the satisfaction of business goals based on Apple’s mission statement and vision statement . Stakeholders expect the multinational technology company to take a leading role in influencing corporate social responsibility trends in the global market.
Corporate citizenship affects Apple’s financial performance, in terms of how customers perceive the desirability of the company’s products based on quality, as well as business policies for sustainability, environmental impact, and material sourcing relating to CSR and ESG. Employees’ perception of the information technology business also influences organizational resilience. The business strengths and weaknesses described in the SWOT analysis of Apple Inc. affect some corporate social responsibility challenges linked to stakeholders’ interests.
Apple’s Stakeholders and Programs for CSR and ESG
The interests of Apple’s stakeholders guide the company’s strategic management, sustainable green operations, and CSR and ESG decisions for minimal negative net impact on the environment, communities, and other stakeholders. Stakeholders expect the company’s information technology products to benefit society. Given these factors in corporate social responsibility, Apple’s stakeholders are as follows:
- Apple’s employees
- Governments
- Communities
Customers . In devising corporate social responsibility strategies, Apple prioritizes customers as one of its top stakeholder groups. This stakeholder group is composed of individual and organizational buyers of the company’s consumer electronics and online services. Customers are interested in the effectiveness, quality, and reasonable pricing of Apple products, such as iPhones, Macs, and iPads. In the CSR and ESG context, customers are stakeholders who seek appropriate pricing and quality in brick-and-mortar and e-commerce operations. Apple’s marketing mix (4P) involves high price points based on the premium pricing strategy. Considering the quality and aesthetics of the company’s information technologies, this pricing strategy suits the market and associated corporate citizenship objectives for quality and pricing of the business.
Customers as stakeholders also expect privacy and security in using Apple’s products. Privacy and security have always been core factors in the company’s product design and development. Addressing these concerns in product development and corporate social responsibility, Apple applies best practices and principles, such as security frameworks used in online services and computer systems design.
In addition, Apple’s corporate citizenship strategy includes environmental policies and programs for recycling and responsible sourcing to address customers’ interests in business sustainability. In this way, the company’s strategic planning for corporate social responsibility accounts for the information-technology sustainability expectations of the stakeholder group of customers.
Apple’s Employees . Employees are major stakeholders in the iPhone maker’s approach to corporate social responsibility. This stakeholder group’s interests include proper compensation and career development, which are linked to Apple’s organizational structure (corporate structure) and initiatives for addressing human resource management (HRM) issues in multinational business. The company’s HRM policies and programs satisfy this stakeholder group through compensation packages that are competitive and attractive in Silicon Valley and beyond.
Employees are also interested in a work environment that supports proper work-life balance, despite the technology company’s rigid human resource management requirements. This work-life balance aspect of corporate social responsibility is partly addressed through Apple’s organizational culture (corporate culture) . For example, the IT and consumer electronics company’s culture encourages excellent work performance, while supporting job flexibility and services for family-related matters, such as maternity needs. To partly satisfy this aspect of corporate citizenship, Apple’s human resource management also involves policies and strategies for preventing employee burnout, which can negatively affect this stakeholder group’s perception of the business and its CSR and ESG status.
Investors . Apple’s investors are stakeholders interested in maximizing the returns on their investments. The company addresses this ESG concern through excellent financial performance and business governance supported through profitable consumer electronics and online services. Apple’s competitive strategy and growth strategies ensure business competitiveness and profitability. Other strategies, policies, and programs touch on corporate citizenship challenges in the industry, as a way of enabling the information technology firm to maintain a desirable ESG and CSR status for its investors.
Even though investors are stakeholders focused on financial performance, Apple’s sustainability and environmental or ecological programs also matter. In corporate social responsibility, sustainable business practices make the iPhone company more attractive to customers and business partners. This factor contributes to Apple’s competitiveness against other information technology and consumer electronics firms, such as Google (Alphabet) , Samsung , Microsoft , and Sony , as well as companies that compete with Apple TV Plus video-streaming services, like Disney , Netflix , Amazon , and Facebook (Meta) . IBM and Intel , which have operations in computer technology, artificial intelligence, and related services, also influence Apple’s policies and programs for CSR, ESG, sustainability, and corporate citizenship. These companies challenge Apple’s dominance in the market and impose high standards in CSR, ESG, and corporate citizenship. Thus, satisfying the interests of investors as a stakeholder group involves initiatives and strategies for competitiveness and profitability, along with the satisfaction of corporate social responsibilities on a par with other multinational technology firms.
Governments . Governments are stakeholders that require Apple’s regulatory compliance. Different governments have different sets of regulations, policies, and programs that apply to the CSR and ESG of information technology and online service businesses. The PESTEL/PESTLE analysis of Apple Inc. shows that governments impose new laws and regulations, such as laws for reduced ecological impact and for enhanced information privacy and security. Thus, this stakeholder group shapes how information technology firms become sustainable corporate citizens through proper governance.
Apple maintains regulatory and legal compliance, but new laws or regulations occasionally challenge the company’s governance and business practices. For example, new and emerging right-to-repair regulations affect the company’s strategy of exclusivity in repairing and servicing its consumer electronics. Strategic responses to these challenges impact Apple’s performance for CSR and ESG goals.
Suppliers . This stakeholder group is interested in their profitability while doing business with Apple. Suppliers’ interests also include cooperation with the iPhone company, in terms of employment practices. Such cooperation is based on Apple’s corporate citizenship efforts through its Supplier Code of Conduct, which influences decisions in doing business with firms in the supply chain. Part of the technology company’s policy is to terminate business relations with suppliers that continue to fail or refuse to satisfy this Code of Conduct.
Apple’s CSR and ESG strategy imposes rules on this stakeholder group, while supporting mutually beneficial business relations with suppliers of consumer electronic components and other materials. This corporate social responsibility strategy helps manage the bargaining power of suppliers described in the Five Forces analysis of Apple Inc . To provide support for this stakeholder group, the company has approaches for streamlining suppliers’ operations. For example, Apple’s operations management approach to this area of corporate social responsibility involves information and communication technologies that inform about trends in supply requirements, to help suppliers optimize their operations and make them more efficient, green, and sustainable.
Communities . Communities are concerned with the socioeconomic and ecological impacts of Apple’s products. These stakeholders include people in neighborhoods and regions, and interest-based advocacy organizations, like non-government organizations for business ethics, sustainability, green operations, and environmental protection against electronic waste. In the corporate social responsibility context, communities require or expect socioeconomic and environmental benefits from Apple. The company’s Employee Giving program and Strengthen Local Communities (SLC) grant program directly address these CSR concerns. Through such philanthropic endeavors, Apple enhances its corporate citizenship status and makes its online services and consumer electronics more ethical, green, and desirable.
Does Apple’s CSR & ESG Performance Satisfy Stakeholder Interests?
The interests of stakeholders are addressed through Apple’s strategy for CSR and ESG goals. The company’s CSR initiatives maintain a balance between the financial objectives and purpose of the business, and the objectives of various groups that the technology business affects. Considering its programs and progress, Apple’s CSR and ESG strategy satisfies stakeholders’ interests. However, the technology business has opportunities for enhancing its CSR and ESG performance, such as in policies for suppliers’ employment practices. Improvements in this area can strengthen Apple’s corporate social responsibility and business ethics standing, while also helping suppliers strengthen their own sustainability and corporate citizenship efforts. Moreover, the company can improve the sustainability of products and related services to further minimize environmental impact, particularly in terms of e-waste.
- Across the globe, Apple and its teams find new ways to give .
- Apple Inc. – Environmental Social Governance .
- Apple Inc. – Form 10-K .
- Apple Inc. – Supplier Responsibility .
- Fatima, T., & Elbanna, S. (2023). Corporate social responsibility (CSR) implementation: A review and a research agenda towards an integrative framework. Journal of Business Ethics, 183 (1), 105-121.
- Hristov, I., & Appolloni, A. (2022). Stakeholders’ engagement in the business strategy as a key driver to increase companies’ performance: Evidence from managerial and stakeholders’ practices. Business Strategy and the Environment, 31 (4), 1488-1503.
- Homer, S. T. (2022). Perceived corporate citizenship: A scale development and validation study adopting a bottom-up approach. Quality & Quantity, 56 (3), 1435-1461.
- Onkila, T., & Sarna, B. (2022). A systematic literature review on employee relations with CSR: State of art and future research agenda. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 29 (2), 435-447.
- Park, J. G., Park, K., Noh, H., & Kim, Y. G. (2023). Characterization of CSR, ESG, and corporate citizenship through a text mining-based review of literature. Sustainability, 15 (5), 3892.
- U.S. Department of Commerce – International Trade Administration – Software and Information Technology Industry .
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency – Cleaning Up Electronic Waste (E-Waste) .
- Copyright by Panmore Institute - All rights reserved.
- This article may not be reproduced, distributed, or mirrored without written permission from Panmore Institute and its author/s.
- Educators, Researchers, and Students: You are permitted to quote or paraphrase parts of this article (not the entire article) for educational or research purposes, as long as the article is properly cited and referenced together with its URL/link.
Brought to you by:

Apple and Its Suppliers: Corporate Social Responsibility
By: Sun Hye Lee, Michael Mol, Kamel Mellahi
In a 2014 documentary, the multinational technology company Apple Inc. was implicated in alleged human rights violations at Pegatron, a large Chinese supplier that assembled Apple's iPhones. The…
- Length: 10 page(s)
- Publication Date: Mar 22, 2016
- Discipline: General Management
- Product #: W16147-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Teaching Note
- Educator Copy
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
In a 2014 documentary, the multinational technology company Apple Inc. was implicated in alleged human rights violations at Pegatron, a large Chinese supplier that assembled Apple's iPhones. The allegations followed similar, well-publicized violations in 2009 at another China-based Apple supplier. Although Apple had promised to improve its practices, doing so had clearly proven to be a difficult task. How should Apple respond to these new allegations? Should it evade the accusations and instead point to its existing efforts? Could it do more to protect workers? Should it rethink its offshoring and outsourcing strategy? Is it fair to blame Apple for the activities of its suppliers? Where does the blame fall?
Kamel Mellahi is affiliated with Warwick Business School.
Learning Objectives
The case is ideal for undergraduate, graduate, and executive courses. It is particularly well suited to ethics and corporate social responsibility (CSR) courses and is also suitable for courses in strategic management, international business, and operations management. After completion of the case, students will be able to understand: The trade-off between being profitable and doing well for society at large. The challenges of matching CSR practices to CSR expectations. The challenges of managing and monitoring outside suppliers. The hard realities of managing CSR across institutional boundaries. The complexity of managing CSR issues across multiple levels.
Mar 22, 2016
Discipline:
General Management
Ivey Publishing
W16147-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .

Apple Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Apple corporate social responsibility (CSR) programs and initiatives are led by Lisa Jackson, Vice President for Environment, Policy and Social Initiatives, reporting directly to CEO Tim Cook. More than 1 million people work in Apple supplier facilities and as such, the company’s operations have considerable implications on the society.
It has to be noted that “Steve Jobs wasn’t known for philanthropy. Some wondered if he made anonymous donations to charity, some criticized him for his lack of public giving, while others defended him” [1] .
However, with Tim Cook assuming Apple leadership in 2011, the focus on CSR aspect of the business has increased to a considerable extent. Tim Cook is a member of Paulson Institute’s CEO Council for Sustainable Urbanization, working with other CEOs of top Chinese and Western companies to advance sustainability in China.
Apple Supporting Local Communities
- In Oregon, USA, Apple partners with Bluestone Natural Farms to transform compostable materials generated onsite into rich organic material for use on the farm.
- The tech giant launched a 100-kilowatt rooftop solar project at an educational premise for disadvantaged children in Philippines.
- The company added 50-kilowatt solar power system and a 260-kilowatt-hour battery to supply clean electricity to off-grid fishing community in Thailand.
Apple Educating and Empowering Workers
- The multinational technology company provided training courses to about 4 million people since 2008.
- The tech giant has competitive employee benefits practices. For example, expectant mothers can take up to four weeks before a delivery and up to 14 weeks after a birth, while fathers and other non-birth parents are eligible for up to six weeks of parental leave.
- Apple suppliers paid back USD 32.2 million recruitment fees to their 36,599 employees since 2008.
- The iPhone maker taught employees organized 185,000 hours of inclusion and diversity training in 2021 [2]
- The company organized 80,000 hours of management education through Apple University in financial year 2021
Labour and Human Rights at Apple
- Apple enforces The Supplier Code of Conduct that is claimed to be the toughest in the electronics industry. Apple educated more than 19.4 million employees of its suppliers on their rights since 2008. [3]
- In 2018, Apple removed five mineral suppliers from is supply chain for failing to pass or not being willing to participate in human rights audits [4]
- The multinational technology company interviewed more than 52000 supplier employees about their workplace experience
Employee Health and Safety at Apple
- The multinational technology company has launched a group of health clinics called AC Wellness for its employees and their families.
- In 2019, Vietnam was included in employee health education program. The program is already in practice in China and India.
- In 2020, for the 2 nd time in a row the company was awarded
- Safer Chemicals, Healthy Families awarded Apple an A+ rating for eliminating toxic chemicals in production for the 2 nd time in a row in 2020.
Apple and Gender Equality and Minorities
- Tim Cook is the only openly gay CEO of a Fortune 500 company and he has been praised as a strong champion of workforce diversity
- The company maintains 1:1 pay equity for gender, race and ethnicity globally
- 47% of open leadership roles globally were filled by women in 2021 [5]
- 23% of open retail leadership roles in US were filled by Black candidates in 2021

Apple leadership diversity data for 2021 [6]
Energy Consumption by Apple
- Apple sources all of its facilities worldwide with 100% renewable energy
- 213 suppliers of the iPhone maker have committed to 100 percent renewable electricity for Apple production
- Apple is often praised for its environmental records that include decrease of total power consumption of Apple products by 57%, introduction of Mac mini as the world’s most energy-efficient desktop computer and exceeding ENERGY STAR guidelines
- Apple emerges as the only company that has been awarded with a Clean Energy Index of 100%, according to Greenpeace’s Clicking Clean Report.
Water Consumption by Apple
- Apple used more than 1,4 billions of gallons of water in fiscal year 2021. This include a small proportion of recycled water and temporary freshwater
- The multinational technology company saved 133 million gallons of freshwater in fiscal year 2021 due to efficiency projects implemented since 2017
- Alternative water sources primarily from recycled water sources accounted for 10% of Apple’s total corporate water usage
- Cooling systems in company’s date centres can reuse water up to 35 times
- Apple Park, a campus in Cupertino uses 75% recycled non-potable water. Apple campus in Austin, Texas, irrigates its drought-tolerant plants using a 600,000-gallon rainwater cistern.
Waste Reduction and Recycling by Apple
- Nearly 20% of materials in Apple products are made from recycled content
- As part of Apple’s Zero Waste Program more than 2 million metric tons of waste were redirected from landfill
- Apple offers recycling programs in 99 percent of the countries it operates and the company has diverted more than 508 million pounds of electronic waste from landfills since 2008.
- Supplier sites committed to achieving zero waste increased by 53% in 2019.
- In 2016 the company introduced Liam, a line of robots that can disassemble an iPhone every 11 seconds and sort its high-quality components so they can be recycled.
Carbon Emissions by Apple
- The first company ever to be valued at $1 trillion has been carbon neutral for its own operations since 2020 [7]
- The company has managed to reduce its carbon footprint 40% since its emissions peaked in 2015.
- The tech giant is committed to reach total carbon neutrality across its entire business, including the full life cycle of its products by 2030.
Apple and Sustainable Sourcing
- All the fibers Apple uses in product packaging are 100% responsible sourced
- All suppliers of tin, tantalum, tungsten, gold, and cobalt smelters and refiners participate in third-party audits
- The company partnered with The Conservation Fund to protect 36,000 acres of sustainable forest in North Carolina and Maine and more than 13,000 metric tons of wood was harvested responsibly.
- In 2022 plastics accounted for only 4% of company’s packaging
Apple Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Apple corporate social responsibility including Apple CSR issues. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on Apple. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Apple leadership, business strategy, organizational structure and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of Apple marketing strategy and its ecosystem.

[1] Apple Support for Charity (2015) Available at: https://macrumors.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/202084918-Apple-Support-for-Charity
[2] ESG Report (2022) Apple Inc.
[3] Supplier Responsibility (2020) Apple Inc. Available at: https://www.apple.com/supplier-responsibility/
[4] Zhou, M. (2019) “Apple ditches five mineral suppliers over failure to pass human rights audits” CNET, Available at: https://www.cnet.com/news/apple-ditches-five-mineral-suppliers-over-failure-to-pass-human-rights-audits/
[5] ESG Report (2022) Apple Inc.
[6] ESG Report (2022) Apple Inc.
[7] ESG Report (2022) Apple Inc.
The marketplace for case solutions.
Apple and Its Suppliers: Corporate Social Responsibility – Case Solution
In 2014, a documentary came out implicating Apple due to the alleged human rights violations by its suppliers which assemble its iPhones. This was after the 2009 scandal of another violation by another one of its suppliers. This case study looks into how Apple should respond to this new issue.
Sun Hye Lee, Michael Mol, Kamel Mellahi Harvard Business Review ( W16147-PDF-ENG ) March 22, 2016
Case questions answered:
Case study questions answered in the first solution:
- Identify the multiple levels of analysis at play for Apple as it addresses the Corporate Social Responsibility challenges in its supply chain.
- Is Apple responsible for the alleged human rights violations that occurred?
- Would onshoring, insourcing, or a combination of the two represent a suitable response to Apple’s problems?
- If Apple continues on the current path, what should it do differently?
- Is it reasonable for Apple to apply different ethical standards to different countries?
- Should firms such as Apple maximize their profits, or should they sacrifice some profits to do good?
- Have these CSR problems at Apple had a meaningful impact on the bottom line?
- What is the role of media, including social media, in shaping CSR expectations?
- Does Apple face an industry-specific issue, or do the same issues appear in other industries?
- If you were in the position of Jeff Williams, what, if anything, would you do differently?
Case study questions answered in the second solution:
- Is Apple responsible for the alleged human rights violations by its suppliers?
- Would onshoring, insourcing, or a combination of the two represent a suitable response to Apple’s problem?
- Have these corporate social responsibility problems at Apple had a meaningful impact on the bottom line?
- Does Apple face an industry-specific issue, or do the same issues appear in other industries? Do you know of any examples in electronics or other industries?
Not the questions you were looking for? Submit your own questions & get answers .
Apple and Its Suppliers: Corporate Social Responsibility Case Answers
You will receive access to two case study solutions the second is not yet visible in the preview., 1. identify the multiple levels of analysis at play for apple as it addresses the corporate social responsibility challenges in its supply chain..
Nowadays, Corporate Social Responsibility is the main topic everywhere. If any firm (including Apple, Inc.) wants to create the right image in society, it should contribute some of its profit and earnings to CSR (Lee & et al., 2016).
Many companies are donating some percentage of their revenue for the welfare of society and the environment. Moreover, Apple’s brand image was degraded when they violated the worker’s rights at one of Apple’s suppliers, Foxconn.
However, after they started contributing to CSR and applying some rules and regulations to preserve labor rights, this happened at one more distribution location, that was China (Lee & et al., 2016).
Instead of having a great brand image that invests in CSR, it still has many problems due to violations of laws in its supply chain. The four main reasons for CSR’s breach are lack of stakeholder engagement, lack of triple-bottom-line thinking, lack of transparency, and lack of CSR leader (Godelnik, 2012).
After analyzing it in detail, the company got to know that this problem is not at one level. The first level of challenges arises because Apple operates worldwide because they have different cultures, values, and rights. The second level of issues is due to the distinct goals of every company. The third level of challenges grows due to the relationship between supplier and buyer.
It’s then the responsibility and opinion of how much they want to give importance to Corporate Social Responsibility. Therefore, this depends on the stakeholders, which are customers, investors, employees, and suppliers’ employees (Thompson, 2017).
Apple can address the challenges of CSR by satisfying its stakeholders:
The main stakeholders of Apple are its customers. For CSR, Apple has designed its strategy to address the issue by giving preference to its customers and their desires.
Every customer or consumer always buys the right quality products that are available at reasonable prices in any company. In contrast, Apple is a prestigious brand and offers its products at high prices.
Also, almost all individuals want to buy Apple products. They do not care about the prices because Apple is satisfying their needs by providing products of high quality and also environment friendly (Thompson, 2017).
The Second most crucial stakeholder who helps Apple attain its corporate social responsibility goals is its employees. These are those individuals who work there and the company to achieve its goals and objectives.
If they are not satisfied with the management, they would do something wrong and do not do their jobs properly, and they might sometimes violate human rights.
Therefore, to satisfy them, the main reward is compensation and benefits. Apple tries to compensate its employees after some time to help them fulfill their CSR goals (Thompson, 2017).
Investors of any organization are their primary stakeholders, which is the same case for Apple. Therefore, in Apple, this stakeholder’s only want and objective is to get an excellent financial return on their investments. If they were satisfied, then they would be able to contribute more to their CSR efforts.
Moreover, Apple is an excellent, profitable company that has a superior profit margin. Therefore, this effort in CSR helps them to satisfy their investors (Thompson, 2017).
Supplier’s employees
Along with their employees, the employees working with their suppliers are also their stakeholders. But they are indirect stakeholders. Their want is ethical employment, compensation, and job security. Therefore, to successfully present Apple company as a company with a good reputation in CSR, they have to take care of their suppliers’ employees.
Moreover, Apple follows its code of conduct, according to which they can leave their suppliers if they do some evil things. Therefore, by addressing CSR goals, Apple can satisfy its stakeholders (Thompson, 2017).
Therefore, at last, if they want to remove the allegations of violation of CSR policies, then they have to satisfy their stakeholders first. Because if they follow the ethical code of conduct, they will automatically not face CSR challenges.
2. Is Apple responsible for the alleged human rights violations that occurred?
Apple’s supply chain is global in nature. Around 90% of Apple’s exclusive products, i.e., the iPhone, are manufactured in countries other than the USA. Semiconductors are manufactured in Germany and Taiwan, display panels in Korea, and chipsets in Europe. All these parts are ultimately assembled in China (Render, 2020).
Foxconn and Pegatron are Apple’s two key suppliers operating out of China, where, as per various media reports, many human rights violations occurred. These human rights violations included long working hours, low wage rates, poor labor practices and working conditions, use of the juvenile workforce, environmental pollution, and violation of women’s rights etc. (Lee, Mol, & Mellahi, 2016).
In my opinion, Apple is responsible for the alleged human rights violations as well due to the following reasons:
These suppliers are manufacturing on a contractual basis for Apple, so Apple can also be considered a principal employer (Moorhead, 2019). Hence, it is Apple’s duty to ensure that fair labor practices are followed by their suppliers.
Apple is a key buyer for these suppliers, i.e., 40% of Foxconn’s revenue comes from Apple (Oliver, 2013). Hence, Apple holds substantial power over its suppliers and can get better labor practices implemented by their suppliers.
Apple is known for forcing its suppliers to supply parts at a shallow margin, whereas its profit margin is very high, e.g., it pays a 0.8% margin to some of its suppliers, whereas its margin is more than 35%. To cut costs and increase their margins, the suppliers resort to these unfair trade practices. To counter this, Apple should ensure that while making their internal estimates for various purchases, they should ensure that enough margin is left for the suppliers so that they do not have to resort to unfair labor practices (Lu, 2020).
As part of their Corporate Social Responsibility, they should ensure that the supplier should declare that they will follow fair labor practices as part of their contract.
Apple believes in making processes simple; however, this principle has its limitations in the case of Supply Chain Management (Lu, 2020). They will have to maintain close coordination with all their suppliers to ensure that their suppliers’ labor practices are fair.
Apple is the world’s leading company in terms of valuation, cannot neglect its corporate social responsibility, and has to keep an eye on what labor practices are followed by its suppliers as Apple itself is indirectly responsible for that also.
Unlock Case Solution Now!
Get instant access to this case solution with a simple, one-time payment ($24.90).
After purchase:
- You'll be redirected to the full case solution.
- You will receive an access link to the solution via email.
Best decision to get my homework done faster! Michael MBA student, Boston
How do I get access?
Upon purchase, you are forwarded to the full solution and also receive access via email.
Is it safe to pay?
Yes! We use Paypal and Stripe as our secure payment providers of choice.
What is Casehero?
We are the marketplace for case solutions - created by students, for students.
Join us this Earth Day by recycling your Apple devices. Recycle for free

Environment
Apple 2030 a plan as innovative as our products., a detailed approach. from design to disassembly..

Design our products with recycled and renewable materials. 1
Our Approach
Recycled and renewable materials often carry a lighter footprint than mined materials. By sourcing more recycled and renewable content, we can help to one day end our reliance on mining.
Our Progress
22% of the materials we shipped in Apple products came from recycled and renewable sources. 2
Source all manufacturing electricity from clean energy.
Most of our carbon footprint comes from the electricity used to manufacture our products. So our suppliers are transitioning to electricity generated from solar, wind, and other renewable sources.
Over 320 of our suppliers have already committed to using 100% renewable electricity by 2030. *

Package and ship our products with less emissions.
We’re eliminating plastic from our packaging and making it more compact. 3 And we’re prioritizing low-carbon shipping methods such as ocean, rail, and electric vehicles.
More than 97% of our packaging is now fiber based. 4
Match 100% of our products’ energy use with clean electricity. 5
We’re investing in global renewable energy projects that help address the electricity our products use. And we’re making these products even more energy efficient.
We’re matching 100% of the expected electricity use for Apple Watch models by investing in projects like the IP Radian Solar project. 6
Maximize the materials we recover from recycled products.
We’re creating technologies, such as our disassembly robot Daisy, to recover critical materials so they can be recycled and reused. 7
In 2023, we recycled nearly 40,000 metric tons of electronic materials. 8
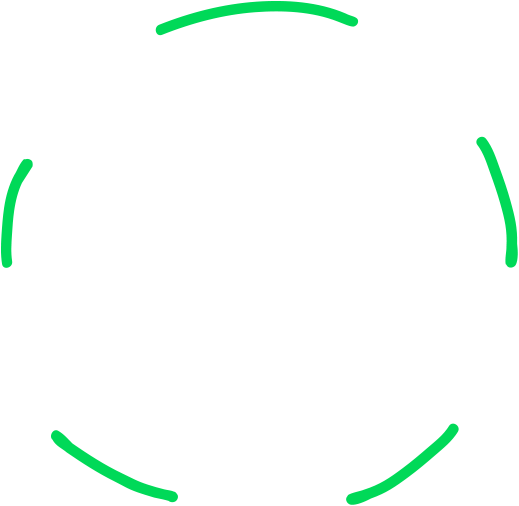

Our progress by the numbers.
We introduced our most significant product emissions reductions to date with the 2023 Apple Watch lineup. 9
Over 55% reduction in CO₂e emissions across our carbon footprint since 2015.
18.5M metric tons of CO₂e emissions avoided through our Supplier Clean Energy Program in 2023.
22% of materials shipped in our products came from recycled and renewable sources in 2023.
12.8M devices and accessories sent to new owners for reuse in 2023.
20% reduction in product transportation emissions compared to 2022.
The proof is in our products.
The same innovative thinking that goes into creating the products you love goes into our environmental initiatives. And as we design our products, we’re also using smarter chemistry to make sure they’re safer for everyone who assembles, uses, and recycles them.
MacBook Air 15‑inch (M3 chip)
MacBook Air is now halfway there.

Of all our products, MacBook Air leads the way in total recycled content. It’s made with 50% recycled materials, 10 including:
- 100% recycled cobalt in the battery 11 and MagSafe connector magnets.
- 100% recycled gold in the plating of multiple printed circuit boards.
- 100% recycled rare earth elements in all magnets.
Aluminum that goes around. And around. And around.

Moving toward low‑carbon shipping.
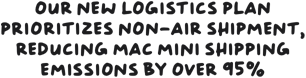
Apple Watch Series 9
A major step toward 2030.

Apple Watch is a milestone on our journey to 2030. 9 It shows that we can design, make, and ship great products with the planet in mind.
Apple Watch Series 9 is:
- designed with 30% recycled materials. 13
- made with 100% renewable electricity.
- shipped 50% or more without airplanes. 14
A best-case scenario.

Package and Ship
Good things come in small, 100% fiber‑based packages.

More recycled materials. From the outside in.

To reach our goal of making products with only recycled and renewable content, we’ve prioritized 15 materials — including cobalt, tungsten, and gold — based on their high environmental and social impacts. These 15 materials account for over 87% of the total mass of the products we ship.
In iPhone 15, we’re using:
- 100% recycled cobalt in the battery, a first for Apple. 11
- 100% recycled tungsten in the Taptic Engine, which creates your devices’ notification vibrations.
- 100% recycled gold in the wire of all cameras, the plating of multiple printed circuit boards, and the USB‑C connector.
Daisy gets the most out of your old iPhone.

A luxurious textile that’s lighter on the planet.

View all product innovations
Partnerships that do a world of good.
Doing right by the planet means doing right by the people who live on it — especially those most impacted by environmental risks. So we’re supporting partners and communities worldwide. Because we can achieve more together than we can alone.

Carbon removal. It’s in our nature.
As we continue to reduce our footprint, we’re also investing in high-quality, nature-based carbon removal projects to balance the emissions we can’t yet avoid.
Partnering with Goldman Sachs and Conservation International, we created a first-of-its-kind initiative called the Restore Fund. It aims to remove carbon emissions from the atmosphere by investing in projects that restore forests, wetlands, and grasslands — while offering a financial return. We expect to exceed our goal of removing 1 million metric tons of carbon dioxide from the air by 2025 from this first fund.
The Restore Fund has invested in three high-quality forestry managers. Our first project is in Paraguay through an investment in Arbaro Advisors. We’re supporting their efforts to develop sustainably certified working forests while creating opportunities for local communities. We’re also partnering with Symbiosis to help them grow native hardwood trees and restore biodiversity in Brazil’s Atlantic Forest. And with BTG Pactual Timberland Investment Group, we’re supporting their efforts to restore forests and protect natural ecosystems in Brazil.
In 2023, we announced an expansion of the Restore Fund with up to an additional $200 million committed to Climate Asset Management — a joint venture between HSBC and Pollination. And in 2024, we added another $80 million commitment from key manufacturing partners Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company and Murata Manufacturing.

Climate solutions that champion social change.
Communities of color are most impacted by environmental risks. And they’ve historically been denied the opportunity to be part of the solution.
As part of Apple’s Racial Equity and Justice Initiative (REJI), our Impact Accelerator program supports and champions Black-, Hispanic/Latinx-, and Indigenous-owned businesses at the cutting edge of green technology and clean energy.
In 2023, our third cohort featured 12 entrepreneurs committed to energy efficiency, water stewardship, and recycling innovation. And many of them focused on bringing clean energy and opportunities to underserved communities. By championing their growth, we can help dismantle systemic barriers and create change that promotes social and economic equity.
Learn more about Impact Accelerator

Conserving water like the earth depends on it.
Water is among the planet’s most precious resources. So to protect it, we’re going beyond our corporate footprint, across our supply chain, and into the communities and watersheds where we operate.
Our supply chain accounts for 99% of our total water footprint. Through our Clean Water Program, we help train our suppliers to better reuse and recycle water. Thanks to this partnership, our participating suppliers are now reusing and recycling water in their factories at an average rate of 42%, which reduces the amount of freshwater we withdraw by billions of gallons every year.
In addition, five of our data centers — in Prineville, Oregon; Reno, Nevada; Mesa, Arizona; Maiden, North Carolina; and Viborg, Denmark — as well as 20 of our supplier facilities, have achieved certification to the Alliance for Water Stewardship Standard for leading water management practices in their regions.

More renewable electricity. More readily available.
We’re actively working to democratize access to renewable electricity around the globe. Because clean energy benefits all of us, our communities, and the environment.
Our Power for Impact initiative gives local communities and organizations access to cost-effective energy while supporting their economic growth and championing social impact. Solar projects in 20 countries, including South Africa, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and the Philippines, help provide clean energy to the communities that need it most.
In 2018, we launched the China Clean Energy Fund to accelerate renewable progress in China. Together with our suppliers, we’ve invested in 1,000 megawatts of clean energy.
Additionally, through the RE100 initiative, we partner with the world’s most influential businesses that have committed to using 100% renewable electricity. And by forming groups like the Asia Clean Energy Coalition, we’re using our voice to support laws and policies that promote more renewable energy across Asia.
Help make Mother Nature proud.
There are many small actions you can take to make a big difference for the planet.
Trade in your device for credit. Or recycle it for free.
It’s good for you and the planet.
Learn more about Apple Trade In

Perform your own repairs with Apple parts, tools, and manuals.
Learn more about Self Service Repair
Charge your iPhone when your local grid is cleaner. 16
Learn more about Clean Energy Charging

View cleaner times to use electricity in your area. 17
Learn more about Grid Forecast
Designed with the earth in mind.
Learn more about the progress of your Apple devices with our product environmental reports.
iPhone 15 Pro and iPhone 15 Pro Max
iPhone 15 and iPhone 15 Plus
iPhone 14 and iPhone 14 Plus
iPhone SE (3rd generation)
iPad Pro 12.9‑inch (6th generation)
iPad Pro 11‑inch (4th generation)
iPad Air (5th generation)
iPad (10th generation)
iPad (9th generation)
iPad mini (6th generation)
Apple Watch
Apple Watch Ultra 2 — Carbon Neutral
Apple Watch Series 9 — Carbon Neutral
Apple Watch Series 9
Apple Watch SE — Carbon Neutral
Apple Watch Bands — Carbon Neutral
MacBook Pro 16-inch (M3 Pro or M3 Max chip)
MacBook Pro 14-inch (M3, M3 Pro, or M3 Max chip)
MacBook Air 13-inch and 15-inch (M3 chip)
MacBook Air 13-inch (M2 chip)
Studio Display
Pro Display XDR
Apple Vision Pro
HomePod (2nd generation)
HomePod mini
Apple TV 4K (3rd generation)
Archived reports
iPhone 14 Pro Max
iPhone 14 Pro
iPhone 13 Pro Max
iPhone 13 Pro
iPhone 13 mini
iPhone SE (2nd generation)
iPhone 12 Pro Max
iPhone 12 Pro
iPhone 12 mini
iPhone 11 Pro Max
View (2019 PDF)
iPhone 11 Pro
iPhone X S Max
View (2018 PDF)
View (2017 PDF)
iPhone 8 Plus
View (2016 PDF)
iPhone 7 Plus
iPhone SE (1st generation)
iPhone 6s Plus
View (2015 PDF)
View (2014 PDF)
View (2013 PDF)
View (2012 PDF)
View (2010 PDF)
View (2009 PDF)
iPad Pro 12.9-inch (5th generation)
iPad Pro 11-inch (3rd generation)
iPad Air (4th generation)
iPad (8th generation)
iPad Pro 12.9-inch (4th generation)
View (2020 PDF)
iPad Pro 11-inch (2nd generation)
iPad (7th generation)
iPad mini (5th generation)
iPad Air (3rd generation)
iPad Pro 12.9-inch (3rd generation)
iPad Pro 11-inch (1st generation)
iPad (6th generation)
iPad Pro 12.9-inch (2nd generation)
iPad (5th generation)
iPad Pro 10.5-inch
iPad Pro 9.7-inch
iPad Pro 12.9-inch
iPad mini 4
iPad mini 3
iPad mini 2
iPad (4th generation)
iPad (3rd generation)
View (2011 PDF)
Apple Watch Ultra (GPS + Cellular)
Apple Watch Series 8
Apple Watch Series 7 (GPS + Cellular, GPS)
View (2021 PDF)
Apple Watch Series 6 (GPS + Cellular, GPS)
Apple Watch SE (GPS + Cellular, GPS)
Apple Watch Series 5 (GPS + Cellular, GPS)
Apple Watch Series 4 (GPS + Cellular)
Apple Watch Series 4 (GPS)
Apple Watch Series 3 (GPS + Cellular)
Apple Watch Series 3 (GPS)
Apple Watch Series 2
Apple Watch Series 1
View (September 2015 PDF)
View (April 2015 PDF)
MacBook Air 15-inch (M2 chip)
View (2023 PDF)
MacBook Pro 16-inch (M2 Pro or M2 Max chip)
MacBook Pro 14-inch (M2 Pro or M2 Max chip)
MacBook Pro 13-inch (M2 chip)
View (2022 PDF)
MacBook Pro 16-inch
View (October 2021 PDF)
MacBook Pro 14-inch
MacBook Pro 13-inch
View (November 2020 PDF)
MacBook Air 13-inch (M1 chip)
MacBook Air 13-inch with Retina display
View (March 2020 PDF)
MacBook Pro 13-inch with Thunderbolt 3
View (May 2020 PDF)
View (July 2019 PDF)
MacBook Pro 15-inch with Thunderbolt 3
View (May 2019 PDF)
MacBook Air 13-inch
View (June 2017 PDF)
MacBook Pro 13-inch with Thunderbolt
MacBook Pro 15-inch with Thunderbolt
MacBook Pro 13-inch with Retina display
MacBook Pro 15-inch with Retina display
MacBook Air 11-inch
11-inch MacBook Air
13-inch MacBook Air
13-inch MacBook Pro
15-inch MacBook Pro
View (October 2011 PDF)
17-inch MacBook Pro
View (February 2011 PDF)
24-inch iMac
27-inch iMac with Retina 5K
21.5-inch iMac
21.5-inch iMac with Retina 4K
27-inch iMac with Retina 5K display
27-inch iMac
Mac mini with OS X Server
Mac mini with Lion Server
Mac mini with Snow Leopard Server
Apple Thunderbolt Display
27-inch Apple LED Cinema Display
24-inch Apple LED Cinema Display
View (2008 PDF)
View (January 2018 PDF)
Apple TV 4K (2nd generation)
Apple TV HD
Apple TV 4K
Apple TV (4th generation)
Apple TV (3rd generation)
iPod shuffle
iPod touch 32GB/64GB
iPod touch 16GB
iPod classic
View previous reports
An even closer look at our progress.
Learn more about our latest efforts to fight climate change and support equity.
2023 Progress Report
2022 Progress Report
2021 Progress Report
2020 Progress Report
2019 Progress Report
2018 Progress Report
2017 Progress Report
2016 Progress Report
2015 Progress Report
2014 Progress Report
2013 Progress Report
2012 Progress Report
2011 Progress Report
2010 Progress Report
2009 Progress Report
2008 Progress Report
Additional Reports and Resources
Circular economy.
Our aim is to make products using only recycled or renewable materials — so we prioritize, responsibly source, and recover materials.
- Learn how we prioritize materials with our Material Impact Profiles (PDF)
- Read our white paper on Apple’s Paper and Packaging Strategy (PDF)
- Read our Responsible Fiber Specification (PDF)
- Read our white paper on expanding access to service and repairs (PDF)
- Learn how to trade in or recycle your device
- Learn more about disassembly for professional recyclers
Smarter Chemistry
Apple has a rigorous program to ensure the safety of chemicals used in our products. Learn about Apple’s strict standards, detailed toxicological assessments, and methodology for assessing chemicals of concern.
- Read the Regulated Substances Specification (PDF)
- Read our white paper on Integrating Toxicological Assessments in Material Selection for Apple Products (PDF)
- Read our Protocol for Prioritizing Chemicals of Concern in the Electronics Industry (PDF)
- Read about Apple’s commitment to phasing out per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) (PDF)
Climate Change
Climate change is a defining issue of our time. View detailed updates on our progress.
- Read Apple’s 2023 CDP Climate Change response (PDF)
- Read our white paper on Apple’s Carbon Removal Strategy (PDF)
People and Environment in Our Supply Chain
We hold ourselves and our suppliers to the highest standards of labor and human rights, health and safety in the workplace, environmental practices, and the responsible sourcing of materials.
Visit the Supply Chain Innovation site
Frequently Asked Questions
Find answers to common questions about Apple and the environment.
Read the FAQs
More from Apple on the environment.
Our values lead the way., accessibility.
Our built-in accessibility features are designed to work the way you do.
We design every product and service to keep your data safe and secure.
Racial Equity and Justice Initiative
We’re addressing systemic racism by expanding opportunities for communities of color globally.
Supply Chain Innovation
We prioritize providing safe, respectful, supportive workplaces for everyone.
Inclusion and Diversity
We’re holding ourselves accountable for creating a culture where everyone belongs.
We empower students and educators to learn, create, and define their own success.
- The University of Warwick
Award-winning case study focuses on Apple's CSR
Share this article:

Sun Hye Lee and Kamel Mellahi won at the annual Case Centre Awards and Competitions for their case study on Apple.
The Warwick Business School academics joined Michael Mol, of Copenhagen Business School, to win the Strategy and General Management category at the 29th Case Centre Awards, which celebrates excellence in case writing and teaching at schools of business, management and government around the world.
The Case Centre is the independent home of the case method of teaching, a not-for-profit organisation and registered hold the world’s largest and most diverse collection of management cases, articles, book chapters and teaching materials, including the collections of leading business schools across the globe.
The Overall Winning Case, on Accor’s digital marketing, was co-authored by Jill Avery, of Harvard Business School, Chekitan S Dev, of Cornell SC Johnson College of Business, Cornell University and Peter O'Connor, of ESSEC Business School.
Outstanding Case Teacher was won by David Wood, the second time a member of Ivey Business School’s faculty has won this Competition.
Dr Lee and Professor Mellahi's case study, entitled Apple and its Suppliers: Corporate Social Responsibility, centres on a BBC documentary highlighting labour rights violations in Apple’s Chinese suppliers.
Pegatron was the second iPhone producer to have their methods scrutinised, with Apple’s Corporate Social Responsibility again called into question. Apple deploys a vast, global supply chain and it was proving difficult for the US company to maintain control.
Dr Lee, now a Lecturer in International Business at the School of Business and Economics, Loughborough University, said: “Winning this award is a great honour and the biggest possible encouragement to undertake more of this work. It was the first ever teaching case any of us had written, and it is an interesting form of creating new knowledge alongside research articles and other means.
“We think it is Apple’s relevance that makes the company so popular as a case subject. Lecture rooms of business schools nowadays are filled with students from different national and cultural backgrounds. For teachers like us, a big challenge is to find companies that will grab all these students’ attention.
“Apple is among the most profitable and biggest companies, but also highly admired. Students are likely to have experience with Apple products one way or another. This means a case on Apple leads to high student engagement.
“Our case, however, differs a lot from the others in that it discusses a darker side of Apple, namely the social responsibility problems they have experienced in relation to manufacturing operations of Apple suppliers in China.
“For our case, we only used publicly available sources. Apple continuously wishes to advertise its good deeds, while the media and industry experts also have much to say about the company, both positive and negative. And this was particularly useful for our case where we talk about these negative events.
“These would probably not have come out through interview methods, at least not from interviewing people inside Apple.”
This year’s Awards and Competitions saw a growing diversity of successful institutions from right across the globe including five first-time winning schools (Blavatnik School of Government, University of Oxford; Columbia Business School; Cornell SC Johnson College of Business; ESCP Europe; ISEG Lisbon School of Economics & Management), while there were 23 first-time individual faculty winners .
Richard McCracken, Director of The Case Centre, said: “Coming hot on the heels of the inaugural World Case Teaching Day , held on February 5, this year’s flagship Awards and Competitions show that over its 29-year history, standards of excellence in case writing and teaching have grown and spread right around the world to more institutions than ever before.
"Award-winning cases were taught in 103 schools in 34 countries. While many schools encourage faculty to prioritise journal-worthy research, the fact that ever more individual authors and teachers are now winning Case Awards and Competitions, bears testament to the widespread dedication of faculty to bring students around the world topical, relevant and innovative classroom materials. Our annual case ‘Oscars’ shine a proud annual light on these impactful achievements.”
For more on Dr Lee and Professor Mellahi's winning case study click here , while the full list of Case Centre Awards winners can be found here .
Related News
Strategy and Organisational Change How NASA fits into the new space race The new space race involves private companies and nation states, find out how NASA fits in.
Strategy and Organisational Change How to improve UK productivity The lack of UK productivity has dogged the country's economy for years, but Nigel Driffield lays out some policies that could finally produce productivity growth.
Strategy and Organisational Change World Book Day: Three novels business leaders need to read Christian Stadler argues that novels combine fun with function for business leaders and shares his top tips for World Book Day.
The CSR Strategy of Apple

Apple founder and former chief executive Steve Jobs did not believe in corporate social responsibility or CSR. He believed that companies should focus on making great products and that a CSR program could hurt the bottom line of a particular organization. However, despite these views, Apple stated a CSR strategy that revolved around environmental sustainability, responsible sourcing, and social impact. The strategy has evolved over the years and now includes more specific initiatives that are all aimed at producing a win-win situation for both the company and all of its relevant stakeholders.
A Look Into the CSR Strategy of Apple: Corporate Social Responsibility as a Critical Element of Its Business Strategy
The first comprehensive CSR strategy of Apple was described in 2004 in its first Corporate Responsibility Report which outlined its commitment to environmental sustainability, responsible sourcing, and social impact. Nevertheless, after Jobs stepped down and Tim Cook replaced him as chief executive in 2011, the company expanded its strategy with the creation of a department dedicated to developing further and implementing its CSR strategy.
Apple specifically appointed chemical engineer and former Environmental Protection Agency administrator Lisa Jackson in 2013 as its Vice President of Environmental Initiatives. She was promoted in 2015 and became the Vice President of Environment, Policy, and Social Initiatives. Her new role made her in charge of all the CSR strategy and CSR programs of Apple and her promotion marked a stronger commitment toward corporate social responsibility.
Noteworthy CSR Programs
Based on the role of Jackson, and in addition to its Corporate Responsibility Report and public pronouncements, the CSR programs of Apple are designed around environmental protection, adherence to legal and ethical standards, and promotion of social welfare. The following are some of the notable programs of the company:
• Apple Recycling Program: The company has a recycling program that assists customers in disposing of their old Apple products. Some older products can be traded for credits that can be used to purchase newer products. The program also includes the operations of collection centers and facilities for recovering and processing recyclable materials. The recovered materials are reintroduced to its supply chain and become production inputs for newer products. Apple has also redesigned its production processes and product design to improve the repairability and recyclability of its products.
• Other Environmental Initiatives: It has also launched numerous initiatives aimed at promoting sustainability by focusing on addressing climate change, sustainable use of resources, and smarter chemistry. These include maintaining carbon neutrality through the use of renewable electricity in its facilities, financial commitment to nature-based projects, a comprehensive waste strategy, and value chain emissions reduction.
• Ethics and Compliance: Apple has several compliance functions that are integrated into its operations. Its dedicated Business Conduct and Global Compliance team focuses on business conduct, political compliance, export and sanction compliance, health compliance, antitrust compliance, and anti-corruption compliance. It also holds an annual mandatory Business Compliance training to educate and reeducate its employees about its Business Conduct Policy.
• Supplier Responsibility: It also has various programs aimed at safeguarding the interest of its suppliers and their workers. The company requires its suppliers to observe adherence to labor rights and human rights. It does regular audits to ensure that its suppliers are compliant with its Apple Human Right Policy and Apple Supplier Code of Conduct. The company also runs the Apple Supplier Employee Development Fund to promote and protect the rights of employees and finance the Apple Education Hub which is responsible for implementing various skill-building and career enrichment programs.
• Apple and Education: The company has specific sales promotional activities and pricing strategy targeted toward educators and learners. It collaborates with different educational institutions to help in integrating its products and technologies with relevant curricula and courses. Apple also offers special discounts through its education pricing to these institutions and individual educators and learners.
• Product Red Involvement: Apple has also participated in the Product Red initiative that was introduced in 2006 to raise awareness and funds needed to eliminate HIV/AIDS and other infectious diseases. The company has launched special editions of iPhones based on the Product Red brand. A portion of earnings from the sales of these devices goes to The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria. Other multinational companies like Nike and Starbucks are also participants.
Purpose of the CSR Strategy
A closer look at the purpose behind its CSR strategy and all of its CSR programs would reveal that Apple promotes causes that can improve further its value chain. This is attuned to the established principles of corporate social responsibility. Proponents of the socioeconomic model of corporate social responsibility believe in the core principle of doing well by doing. This means that companies with well-designed CSR strategies and CSR programs create a win-win scenario that benefits themselves and their stakeholders.
Nevertheless, for its part, the CSR strategy of Apple benefits several areas of its value chain. Its Apple Recycling Program adds another layer of security to its supply chain while also reducing the bargaining power of its suppliers . Some of its environmental initiatives like its carbon neutral operations, comprehensive waste strategy, and smarter chemistry policy help in optimizing business processes and reducing long-term costs.
The commitment to ethics and compliance help in empowering its internal workforce while managing threats from possible regulatory scrutiny. Take note that compliance issues can cost Apple hundreds of millions of dollars. The various programs and initiatives aimed at promoting the interest or welfare of its suppliers and their employees also help in securing further its supply chain by reducing the possibilities of disruptions that can arise from legal compliance issues, workforce disempowerment, or supplier incompetence.
Both the education pricing scheme and the Product Red involvement reinforce some elements of its marketing mix . The education pricing scheme can be considered both a pricing strategy and a promotion strategy aimed at bringing in more people inside its product ecosystem . The development of iPhone models under the Product Red brand entices a targeted segment of the general target market while also promoting a positive corporate image.
The CSR strategy of Apple fundamentally centers on its goal of leaving the world better than it was found. Cook stated this in an internal memo sent to employees that announced the promotion of Jackson and her broader role. It is also interesting to note that this is one of the guiding principles utilized in the various facets and elements of its business strategy like its specific promotion strategy and public relations strategy . The company believes that its social impacts extend beyond its products and acknowledges the importance and benefits of advancing the interest of its stakeholders.
International Journal of Frontiers in Sociology , 2022, 4(7); doi: 10.25236/IJFS.2022.040710 .
Practical but Passive: Apple’s CSR Strategies on People and Planet
Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China
- Full-Text HTML
- Full-Text XML
- Full-Text Epub
- Download PDF
- Download: 19
The purpose of this research is to investigate existent Apple’s CSR strategies using third-party audits as focal means in resolving corporate social responsibilities (CSR) conflicts. Building on the reportage and statistics, this research provides original investigation into the passive CSR conflicts cycle of Apple’s CSR strategies on employers and environment. The significance of this study for Apple’s CSR strategies is threefold: (1) it indicates that Apple follows a conflict-solution driven CSR strategy, (2) it suggests that Apple embellishes the facts with asymmetric information between the company and the stakeholder, and (3) it discusses the potential improvement of an innovation-driven CSR integrated into its corporate strategic planning and daily decision making.
Corporate social responsibility; CSR strategy implementation; CSR conflict cycle
Cite This Paper
Han Bao. Practical but Passive: Apple’s CSR Strategies on People and Planet. International Journal of Frontiers in Sociology (2022), Vol. 4, Issue 7: 53-57. https://doi.org/10.25236/IJFS.2022.040710.
[1] Armstrong, M. Apple Earns $3,000 Per Second. Nov 23, 2021. https://www.statista.com/chart/26248/ tech-company-earnings-per-second/. Retrieved 25 Nov 2021.
[2] Assad, N. Apple puts India iPhone maker on probation for labor violations. Dec 30, 2021. https://pedfire.com/apple-puts-india-iphone-maker-on-probation-for-labor-violations. Retrieved 27 Dec 2021.
[3] Chow, L. Ever Wonder What's Happened to the More Than 570 million iPhones Sold Since 2007? Feb 24, 2016. https://www.ecowatch.com/ever-wonder-whats-happened-to-the-more-than-570-million-iphones-sold-s-1882178171.html. Retrieved 27 Dec 2021.
[4] Clark, E. Report Reveals Alleged Cases of Child Labour, Forced Labour, and Human Rights Violations. Sept 4, 2018. https://www.quality.org/Tech-on-Trial. Retrieved 26 Dec 2021.
[5] Deahl, D. Daisy is Apple’s new iPhone-recycling robot. Apr 19, 2018. https://www.theverge.com/ 2018/ 4/19/17258180/apple-daisy-iphone-recycling- robot. Retrieved 28 Dec 2021.
[6] Garcia, M. Four Case Studies on Corporate Social Responsibility: Do Conflicts Affect a Company’s Corporate Social Responsibility Policy? Nov 5, 2012. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/ 255724825. Retrieved 27 Nov 2021.
[7] Gomez, J. Developing Effective Transparency: A Case Study on Voluntary Disclosure and Social Responsibility at Apple Inc. Jan 1, 2014. https://repository.uchastings.edu/hastings_ international_comparative_law_review/vol37/iss2/3. Retrieved 28 Dec 2021.
[8] Hester, F. The E-Waste Problem: A Case Study of Apple. Jan 21, 2021. https://globuswarwick.com /2021/01/21/the-e-waste-problem-a-case-study-of-apple. Retrieved 28 Dec 2021.
[9] Hughes, A. Apple's Colossal E-Waste Timebomb. Feb 3, 2021. https://www.zdnet.com/article/apples-colossal-e-waste-timebomb. Retrieved 27 Nov 2021.
[10] Leahy, S. Each U.S. Family Trashes 400 iPhones’ Worth of E-Waste a Year. Dec 13, 2017. https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/e-waste-monitor-report-glut. Retrieved 30 Dec 2021.
[11] Paton, B. Corporate Social Responsibility: From Conflict Resolution to Conflict Anticipation. Nov 24, 2014. https://sites.miis.edu/reflections/2014/11/24/corporate-social-responsibility-from-conflict-resolution-to-conflict-anticipation. Retrieved 29 Dec 2021.
[12] Apple Factories Accused of Exploiting Chinese Workers. The Guardian. May 1, 2011. https://www. theguardian.com/technology/2011/apr/30/apple-chinese-factory-workers-suicides-humiliation. Retrieved 27 Dec 2021.
[13] Apple Secretive about “Polluting and Poisoning” Supply Chain, Says Report. The Guardian. Jan 20, 2011. https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2011/jan/20/apple-pollution-supply-chain. Retrieved 27 Dec 2021.
[14] Child labour uncovered in Apple's supply chain. The Guardian. Jan 25, 2013. https://www. theguardian.com/technology/2013/jan/25/apple-child-labour-supply. Retrieved 27 Dec 2021.
Case Study: Apple Inc. (China)
The electronics industry is one of the largest sectors in the global economy and some experts estimate that the sector employs more workers and create more revenue than any other industry in the world. The US consumer electronics industry alone is worth more than $211 billion, and technology and electronics companies top the list of Forbes’ ranking of the world’s most valuable brands. It is an industry that is both immensely profitable and harshly exploitative, and nowhere is this more evident than in the supply chain of Apple Inc. In 2017, the company was worth an estimated $170 billion, making it the world’s most valuable brand.

Foxconn, one of the Apple’s largest suppliers, installed nets after a spate of suicides at its factories in China. Credit: Jason Lee, Reuters.
Despite the vast sums of money at the top of Apple’s supply chain, the workers that make its products face a myriad of abuses: poverty wages, excessive and unpaid overtime well in excess of legal limits, long-term exposure to toxic chemicals without proper protective equipment, unsafe work environments including blocked and locked exits, intense psychological pressure, and the use of forced student labor. The long hours, extremely low pay, and high-pressure work environment led to a spate of suicides, beginning in 2010, by workers at Foxconn, one of Apple’s most important suppliers. In the span of a year, there were at least 18 attempted suicides, resulting in at least 14 deaths. (Foxconn’s shockingly cruel solution to this problem was to install nets around its buildings to prevent workers from jumping, demonstrating just how little the manufacturer and its customers cared about the conditions that workers faced). Between 2010 and 2012, another six workers were killed in explosions at iPad factories. According to reporting by the New York Times, Apple had been warned about the dangerous conditions inside at least one of the factories, but did nothing to prevent the deadly blast.
Amidst mounting pressure from consumers to address the problems in its supply chain, Apple joined the Fair Labor Association (FLA), a multi stakeholder initiative (MSI) that was originally founded to monitor conditions in the apparel industry but that has since expanded to other sectors, including footwear, sporting goods and agriculture. Although the FLA describes itself as an independent monitoring body, member companies play a significant role in the organization’s governance and its funding. As a result, the FLA has an abysmal track record when it comes to improving conditions in the supply chain of its member companies and Apple was no exception. Mere days after beginning its inspection of Apple’s largest supplier, Foxconn, the president of the FLA declared that the “facilities are first-class” and “Foxconn is really not a sweatshop.” Recall that Foxconn is the same supplier in which more than a dozen workers committed suicide just two years earlier, and where three workers had been killed in a factory explosion the prior year.
Six weeks after Apple announced that the FLA would be investigating its supply chain, the FLA published a report detailing a number of egregious abuses, many of which were also violations of Chinese law. It’s worth noting here that virtually all of these findings had previously been reported by independent investigators that Apple had simply chosen to ignore. Although Apple, Foxconn and the FLA publicly committed to fixing the violations, outside assessments showed little improvement. An independent evaluation of the FLA’s own reporting showed the following:
- Apple and its suppliers failed to implement changes to workers’ pay, including compensation for unpaid overtime and adoption of a wage that would cover workers’ basic needs. During the same time period, Apple reported earning nearly $50 billion in profits;
- Despite promises to the contrary, workers in Apple’s supply chain in China continued to work overtime hours in violation of legal limits;
- The promise to “establish a genuine voice for workers” was never fulfilled;
- Although Apple promised that “the FLA’s assessment will cover facilities where more than 90 percent of Apple products are assembled,” the FLA’s reporting covered less than 20% of workers in Apple’s supply chain; and
- Outside data demonstrated that serious labor rights abuses were continuing throughout the company’s supply chain.
It should come as no surprise that workers benefitted very little from Apple’s participation in the FLA. As is frequently the case with a brand’s decision to join an MSI, Apple approached the FLA not out of a genuine concern for the workers’ in its supply chain (Apple had known about egregious abuses at its factories for years), but out of a desire to repair the damage being done to its brand, the most valuable in the world. In exchange for its less-than-critical reporting, the FLA received a sizable fee. Unfortunately, this quid-pro-quo arrangement is all too common in the world of MSI’s, where, absent serious and meaningful changes to structure, governance, enforcement and funding, respect for workers’ rights will always be an afterthought instead of a reality.
In recent years, public attention has waned but workers continue to report serious human rights abuses in Apple’s supply chain. See, for example, the following reports: Apple still has miles to go despite the recent toxins ban , Apple making big profits but Chinese workers’ wages on the slide , and Blood and Sweat Behind the Screen of iPhones – Another Investigative Report on Apple’s Largest Display Screen Supplier .
Stay Connected
- ZIP / Postal Code
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
McCombs School of Business
- Español ( Spanish )
Videos Concepts Unwrapped View All 36 short illustrated videos explain behavioral ethics concepts and basic ethics principles. Concepts Unwrapped: Sports Edition View All 10 short videos introduce athletes to behavioral ethics concepts. Ethics Defined (Glossary) View All 58 animated videos - 1 to 2 minutes each - define key ethics terms and concepts. Ethics in Focus View All One-of-a-kind videos highlight the ethical aspects of current and historical subjects. Giving Voice To Values View All Eight short videos present the 7 principles of values-driven leadership from Gentile's Giving Voice to Values. In It To Win View All A documentary and six short videos reveal the behavioral ethics biases in super-lobbyist Jack Abramoff's story. Scandals Illustrated View All 30 videos - one minute each - introduce newsworthy scandals with ethical insights and case studies. Video Series
Case Study UT Star Icon
Apple Suppliers & Labor Practices
Is tech company Apple, Inc. ethically obligated to oversee the questionable working conditions of other companies further down their supply chain?

With its highly coveted line of consumer electronics, Apple has a cult following among loyal consumers. During the 2014 holiday season, 74.5 million iPhones were sold. Demand like this meant that Apple was in line to make over $52 billion in profits in 2015, the largest annual profit ever generated from a company’s operations. Despite its consistent financial performance year over year, Apple’s robust profit margin hides a more complicated set of business ethics. Similar to many products sold in the U.S., Apple does not manufacture most its goods domestically. Most of the component sourcing and factory production is done overseas in conditions that critics have argued are dangerous to workers and harmful to the environment.
For example, tin is a major component in Apple’s products and much of it is sourced in Indonesia. Although there are mines that source tin ethically, there are also many that do not. One study found workers—many of them children—working in unsafe conditions, digging tin out by hand in mines prone to landslides that could bury workers alive. About 70% of the tin used in electronic devices such as smartphones and tablets comes from these more dangerous, small-scale mines. An investigation by the BBC revealed how perilous these working conditions can be. In interviews with miners, a 12-year-old working at the bottom of a 70-foot cliff of sand said: “I worry about landslides. The earth slipping from up there to the bottom. It could happen.”
Apple defends its practices by saying it only has so much control over monitoring and regulating its component sources. The company justifies its sourcing practices by saying that it is a complex process, with tens of thousands of miners selling tin, many of them through middle-men. In a statement to the BBC, Apple said “the simplest course of action would be for Apple to unilaterally refuse any tin from Indonesian mines. That would be easy for us to do and would certainly shield us from criticism. But that would also be the lazy and cowardly path, since it would do nothing to improve the situation. We have chosen to stay engaged and attempt to drive changes on the ground.”
In an effort for greater transparency, Apple has released annual reports detailing their work with suppliers and labor practices. While more recent investigations have shown some improvements to suppliers’ working conditions, Apple continues to face criticism as consumer demand for iPhones and other products continues to grow.
Discussion Questions
1. Do you think Apple should be responsible for ethical lapses made by individuals further down its supply chain? Why or why not?
2. Should Apple continue to work with the suppliers in an effort to change practices, or should they stop working with every supplier, even the conscientious ones, to make sure no “bad apples” are getting through? Explain your reasoning.
3. Do you think consumers should be expected to take into account the ethical track record of companies when making purchases? Why or why not?
4. Can you think of other products or brands that rely on ethically questionable business practices? Do you think consumers are turned off by their track record or are they largely indifferent to it? Explain.
5. Would knowing that a product was produced under ethically questionable conditions affect your decision to purchase it? Explain with examples.
6. If you were part of a third-party regulating body, how would you deal with ethically questionable business practices of multinational corporations like Apple? Would you feel obligated to do something, or do you think the solution rests with the companies themselves? Explain your reasoning.
Related Videos

Ethical Fading
Ethical fading occurs when we are so focused on other aspects of a decision that its ethical dimensions fade from view.
Bibliography
Apple ‘failing to protect Chinese factory workers’ http://www.bbc.com/news/business-30532463
How Apple could make a $53 billion profit this year http://money.cnn.com/2015/07/17/technology/apple-earnings-2015/
Global Apple iPhone sales from 3rd quarter 2007 to 2nd quarter 2016 (in million units) http://www.statista.com/statistics/263401/global-apple-iphone-sales-since-3rd-quarter-2007/
Despite successes, labor violations still haunt Apple http://www.theverge.com/2015/2/12/8024895/apple-slave-labor-working-conditions-2015
Reports – Supplier Responsibility – Apple https://www.apple.com/supplier-responsibility/progress-report/
Stay Informed
Support our work.

Product details


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Apple's Corporate Social Responsibility Issues. Despite Apple's investment in CSR, the company continues to face a number of labor and human rights allegations regarding its Chinese subcontractors. According to recent reports, Apple has been accused of being too slow in cutting ties with Chinese supplies known for violating the company's ...
The interests of Apple's stakeholders guide the company's strategic management, sustainable green operations, and CSR and ESG decisions for minimal negative net impact on the environment, communities, and other stakeholders. Stakeholders expect the company's information technology products to benefit society.
Although Apple had promised to improve its practices, doing so had clearly proven to be a difficult task. ... The case is ideal for undergraduate, graduate, and executive courses. It is particularly well suited to ethics and corporate social responsibility (CSR) courses and is also suitable for courses in strategic management, international ...
By John Dudovskiy. July 11, 2023. Apple corporate social responsibility (CSR) programs and initiatives are led by Lisa Jackson, Vice President for Environment, Policy and Social Initiatives, reporting directly to CEO Tim Cook. More than 1 million people work in Apple supplier facilities and as such, the company's operations have considerable ...
at Apple supplier facilities A global supply chain means global responsibility At Apple, we care as much about how we make products as the products we make. The products and services that we create require resources from a global chain of suppliers and their employees who provide labour, goods and services to Apple.
Apple and Its Suppliers: Corporate Social Responsibility - Case Solution. In 2014, a documentary came out implicating Apple due to the alleged human rights violations by its suppliers which assemble its iPhones. This was after the 2009 scandal of another violation by another one of its suppliers. This case study looks into how Apple should ...
Environmental. Social. Governance. "We believe that business, at its best, serves the public good, empowers people around the world, and binds us together as never before.". We are committed to demonstrating that business can and should be a force for good. Achieving that takes innovation, collaboration, and a focus on serving others.
A BBC (British TV) documentary highlighted labour rights violations that continued to occur with Apple's Chinese suppliers. Pegatron was the second iPhone producer to have their methods scrutinised, with Apple's Corporate Social Responsibility again called into question.
search and case studies, it is found that Apple's supply chain sustainability success factors include. leadership a nd commitment, supplier selection and management, re source and energy ...
Apple's CSR Objectives Apple's corporate social responsibility objectives are focused on the three P's - people, planet and progress (Apple, 2018). Apple is one the biggest manufacturer of smartphone and electronic devices. At the root of their success is their supply chain. In 2005 Apple started the Apple supplier code.
Managing Corporate Legitimacy Through CSR Reporting: A Qualitative Case Study of Apple Inc.'s Supplier Responsibility Reports. @inproceedings{Mogensen2018ManagingCL, title={Managing Corporate Legitimacy Through CSR Reporting: A Qualitative Case Study of Apple Inc.'s Supplier Responsibility Reports.}, author={Bendik Granheim Mogensen}, year ...
profits. This paper examines the interaction between corporations, workers, and governments and. the challenges they face in balancing workers' rights and corporate performance through a case. study of Apple Inc., a company with an intricate supply chain that has recently come under fire.
More information is available in the product environmental reports for Apple Watch Series 9, Apple Watch SE, and Apple Watch Ultra 2. Daisy can disassemble 29 iPhone models — including various models between iPhone 5 and iPhone 14 Pro. One metric ton of main logic boards, cameras, and flexes recovered by Daisy avoids the mining of over 2000 ...
Social Responsibility: A Case study of Apple Incorporation . Joy Okundia . ... Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a theory that has become well-known and embraced by companies. In the ea rly
Award-winning case study focuses on Apple's CSR. Sun Hye Lee and Kamel Mellahi won at the annual Case Centre Awards and Competitions for their case study on Apple. The Warwick Business School academics joined Michael Mol, of Copenhagen Business School, to win the Strategy and General Management category at the 29th Case Centre Awards, which ...
Abstract. This paper critically analyzes the Corporate Social Responsibility policies practiced by Apple, Inc. and reflects upon how and why the CSR initiatives have evolved at Apple over the years. CSR demands an understanding in the field of business economics. However, one of the aspects of CSR places responsibility on corporations to ...
You will receive access to two case study solutions! The second is not yet visible in the preview. 1. Identify the multiple levels of analysis at play for Apple as it addresses the Corporate Social Responsibility challenges in its supply chain. Nowadays, Corporate Social Responsibility is the main topic everywhere.
However, despite these views, Apple stated a CSR strategy that revolved around environmental sustainability, responsible sourcing, and social impact. The strategy has evolved over the years and now includes more specific initiatives that are all aimed at producing a win-win situation for both the company and all of its relevant stakeholders.
This article studies four multinationals (Apple, Canon, Coca-Cola, Walmart) in relation to their CSR reporting. It will present a general outlook of the company's profile and its compliance with CSR standards. The article will focus on conflict situations concerning the social and environmental CSR practices of the four companies.
The significance of this study for Apple's CSR strategies is threefold: (1) it indicates that Apple follows a conflict-solution driven CSR strategy, (2) it suggests that Apple embellishes the facts with asymmetric information between the company and the stakeholder, and (3) it discusses the potential improvement of an innovation-driven CSR ...
This article studies four multinationals (Apple, Canon, Coca-Cola, Walmart) in relation to their CSR reporting. It will present a general outlook of the company's profile and its compliance with ...
In 2017, the company was worth an estimated $170 billion, making it the world's most valuable brand. Foxconn, one of the Apple's largest suppliers, installed nets after a spate of suicides at its factories in China. Credit: Jason Lee, Reuters. Despite the vast sums of money at the top of Apple's supply chain, the workers that make its ...
We have chosen to stay engaged and attempt to drive changes on the ground.". In an effort for greater transparency, Apple has released annual reports detailing their work with suppliers and labor practices. While more recent investigations have shown some improvements to suppliers' working conditions, Apple continues to face criticism as ...
Product details. Apple and Its Suppliers: Corporate Social Responsibility. Case. -. Reference no. 9B16MC040. Simplified Chinese language. Subject category: Strategy and General Management. Authors: Sun Hye Lee (Warwick Business School); Michael Mol (Copenhagen Business School); Kamel Mellahi (Warwick Business School) Published by: Ivey Publishing.