TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024 Reading time · 4 min


# TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
The Python "TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment" occurs when we try to change the value of an item in a tuple.
To solve the error, convert the tuple to a list, change the item at the specific index and convert the list back to a tuple.
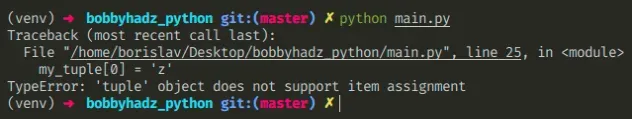
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
We tried to update an element in a tuple, but tuple objects are immutable which caused the error.
# Convert the tuple to a list to solve the error
We cannot assign a value to an individual item of a tuple.
Instead, we have to convert the tuple to a list.
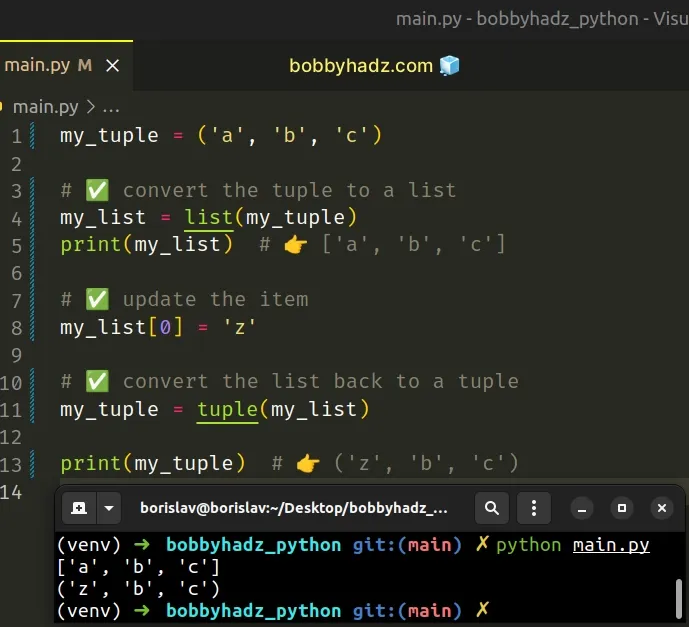
This is a three-step process:
- Use the list() class to convert the tuple to a list.
- Update the item at the specified index.
- Use the tuple() class to convert the list back to a tuple.
Once we have a list, we can update the item at the specified index and optionally convert the result back to a tuple.
Python indexes are zero-based, so the first item in a tuple has an index of 0 , and the last item has an index of -1 or len(my_tuple) - 1 .
# Constructing a new tuple with the updated element
Alternatively, you can construct a new tuple that contains the updated element at the specified index.
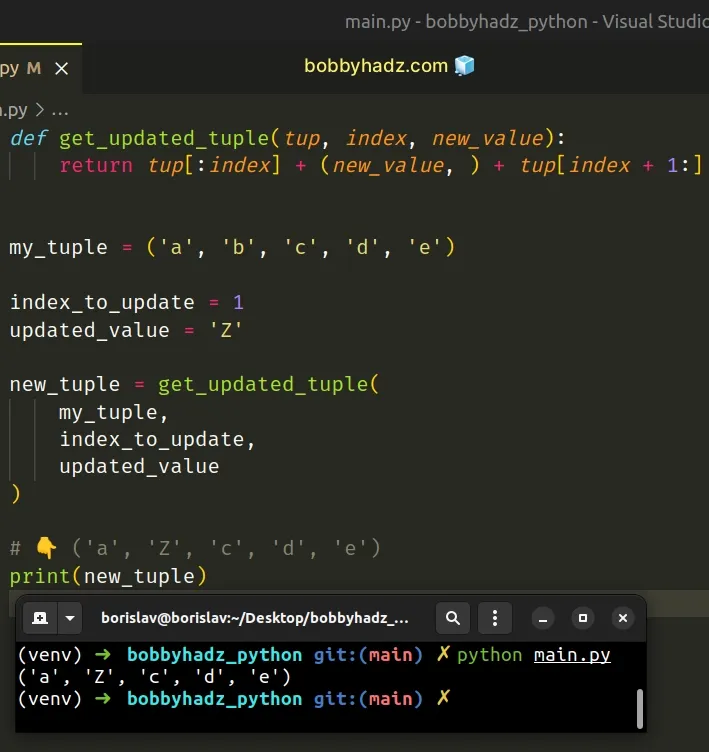
The get_updated_tuple function takes a tuple, an index and a new value and returns a new tuple with the updated value at the specified index.
The original tuple remains unchanged because tuples are immutable.
We updated the tuple element at index 1 , setting it to Z .
If you only have to do this once, you don't have to define a function.
The code sample achieves the same result without using a reusable function.
The values on the left and right-hand sides of the addition (+) operator have to all be tuples.
The syntax for tuple slicing is my_tuple[start:stop:step] .
The start index is inclusive and the stop index is exclusive (up to, but not including).
If the start index is omitted, it is considered to be 0 , if the stop index is omitted, the slice goes to the end of the tuple.
# Using a list instead of a tuple
Alternatively, you can declare a list from the beginning by wrapping the elements in square brackets (not parentheses).
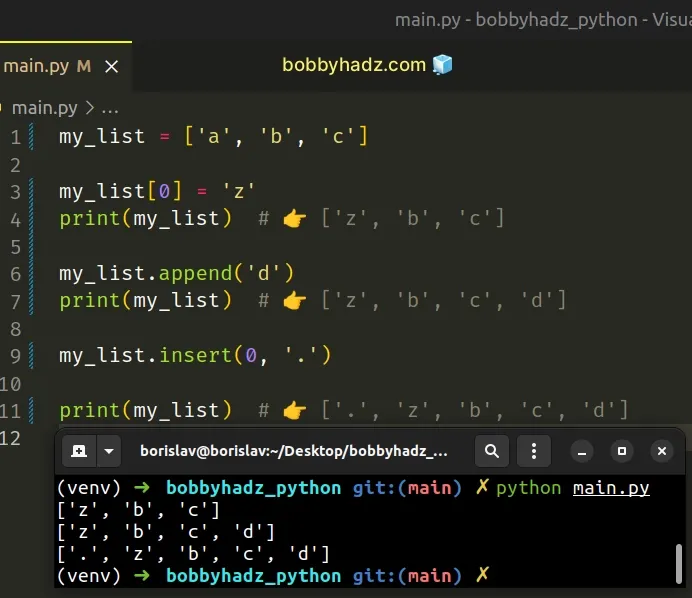
Declaring a list from the beginning is much more efficient if you have to change the values in the collection often.
Tuples are intended to store values that never change.
# How tuples are constructed in Python
In case you declared a tuple by mistake, tuples are constructed in multiple ways:
- Using a pair of parentheses () creates an empty tuple
- Using a trailing comma - a, or (a,)
- Separating items with commas - a, b or (a, b)
- Using the tuple() constructor
# Checking if the value is a tuple
You can also handle the error by checking if the value is a tuple before the assignment.
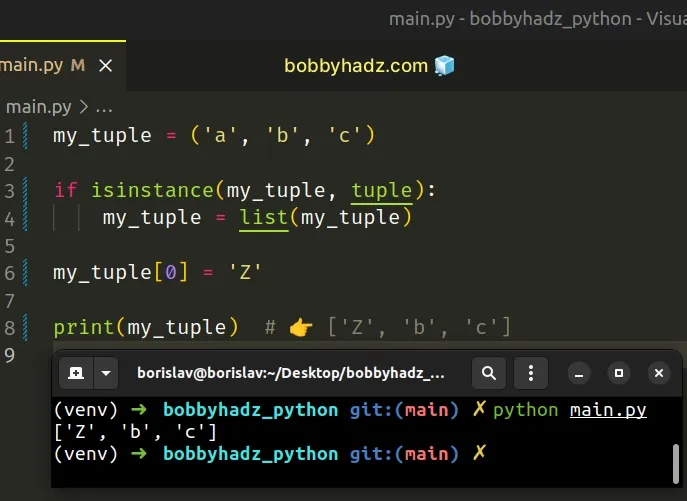
If the variable stores a tuple, we set it to a list to be able to update the value at the specified index.
The isinstance() function returns True if the passed-in object is an instance or a subclass of the passed-in class.
If you aren't sure what type a variable stores, use the built-in type() class.
The type class returns the type of an object.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to convert a Tuple to an Integer in Python
- How to convert a Tuple to JSON in Python
- Find Min and Max values in Tuple or List of Tuples in Python
- Get the Nth element of a Tuple or List of Tuples in Python
- Creating a Tuple or a Set from user Input in Python
- How to Iterate through a List of Tuples in Python
- Write a List of Tuples to a File in Python
- AttributeError: 'tuple' object has no attribute X in Python
- TypeError: 'tuple' object is not callable in Python [Fixed]

Borislav Hadzhiev
Web Developer

Copyright © 2024 Borislav Hadzhiev
Solve Python TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
by Nathan Sebhastian
Posted on Dec 26, 2022
Reading time: 2 minutes

In Python, tuples are immutable sequences that cannot be modified once they are created. This means that you cannot change, add, or delete elements from a tuple.
When you try to modify a tuple using the square brackets and the assignment operator, you will get the “TypeError: ’tuple’ object does not support item assignment” error.
Consider the example below:
The above code tries to change the first element of the tuple from “Orange” to “Mango”.
But since a tuple is immutable, Python will respond with the following error:
There are two solutions you can use to edit a tuple in Python.
Solution #1: Change the tuple to list first
When you need to modify the elements of a tuple, you can convert the tuple to a list first using the list() function.
Lists are mutable sequences that allow you to change, add, and delete elements.
Once you have made the changes to the list, you can convert it back to a tuple using the tuple() function:
By converting a tuple into a list, you can modify its elements. Once done, convert it back to a tuple.
Solution #2: Create a new tuple
When you only need to modify a single element of a tuple, you can create a new tuple with the modified element.
To access a range of elements from a tuple, you can use the slice operator.
For example, the following code creates a new tuple by adding a slice of elements from an existing tuple:
The code fruits[1:] means you are slicing the fruits tuple to return the second element to the last.
Creating a new tuple is more efficient than converting the entire tuple to a list and back as it requires only one line of code.
But this solution doesn’t work when you need a complex modification.
The Python TypeError: tuple object does not support item assignment issue occurs when you try to modify a tuple using the square brackets (i.e., [] ) and the assignment operator (i.e., = ).
A tuple is immutable, so you need a creative way to change, add, or remove its elements.
This tutorial shows you two easy solutions on how to change the tuple object element(s) and avoid the TypeError.
Thanks for reading. I hope this helps! 🙏
Take your skills to the next level ⚡️
I'm sending out an occasional email with the latest tutorials on programming, web development, and statistics. Drop your email in the box below and I'll send new stuff straight into your inbox!
Hello! This website is dedicated to help you learn tech and data science skills with its step-by-step, beginner-friendly tutorials. Learn statistics, JavaScript and other programming languages using clear examples written for people.
Learn more about this website
Connect with me on Twitter
Or LinkedIn
Type the keyword below and hit enter
Click to see all tutorials tagged with:
CodeFatherTech
Learn to Code. Shape Your Future

Tuple Object Does Not Support Item Assignment. Why?
Have you ever seen the error “tuple object does not support item assignment” when working with tuples in Python? In this article we will learn why this error occurs and how to solve it.
The error “tuple object does not support item assignment” is raised in Python when you try to modify an element of a tuple. This error occurs because tuples are immutable data types. It’s possible to avoid this error by converting tuples to lists or by using the tuple slicing operator.
Let’s go through few examples that will show you in which circumstances this error occurs and what to do about it.
Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Explanation of the Error “Tuple Object Does Not Support Item Assignment”
Define a tuple called cities as shown below:
If you had a list you would be able to update any elements in the list .
But, here is what happens if we try to update one element of a tuple:
Tuples are immutable and that’s why we see this error.
There is a workaround to this, we can:
- Convert the tuple into a list.
- Update any elements in the list.
- Convert the final list back to a tuple.
To convert the tuple into a list we will use the list() function :
Now, let’s update the element at index 1 in the same way we have tried to do before with the tuple:
You can see that the second element of the list has been updated.
Finally, let’s convert the list back to a tuple using the tuple() function :
Makes sense?
Avoid the “Tuple Object Does Not Support Item Assignment” Error with Slicing
The slicing operator also allows to avoid this error.
Let’s see how we can use slicing to create a tuple from our original tuple where only one element is updated.
We will use the following tuple and we will update the value of the element at index 2 to ‘Rome’.
Here is the result we want:
We can use slicing and concatenate the first two elements of the original tuple, the new value and the last two elements of the original tuple.
Here is the generic syntax of the slicing operator (in this case applied to a tuple).
This takes a slice of the tuple including the element at index n and excluding the element at index m .
Firstly, let’s see how to print the first two and last two elements of the tuple using slicing…
First two elements
We can also omit the first zero considering that the slice starts from the beginning of the tuple.
Last two elements
Notice that we have omitted index m considering that the slice includes up to the last element of the tuple.
Now we can create the new tuple starting from the original one using the following code:
(‘Rome’,) is a tuple with one element of type string.
Does “Tuple Object Does Not Support Item Assignment” Apply to a List inside a Tuple?
Let’s see what happens when one of the elements of a tuple is a list.
If we try to update the second element of the tuple we get the expected error:
If we try to assign a new list to the third element…
…once again we get back the error “‘ tuple’ object does not support item assignment “.
But if we append another number to the list inside the tuple, here is what happens:
The Python interpreter doesn’t raise any exceptions because the list is a mutable data type.
This concept is important for you to know when you work with data types in Python:
In Python, lists are mutable and tuples are immutable.
How to Solve This Error with a List of Tuples
Do we see this error also with a list of tuples?
Let’s say we have a list of tuples that is used in a game to store name and score for each user:
The user John has gained additional points and I want to update the points associated to his user:
When I try to update his points we get back the same error we have seen before when updating a tuple.
How can we get around this error?
Tuples are immutable but lists are mutable and we could use this concept to assign the new score to a new tuple in the list, at the same position of the original tuple in the list.
So, instead of updating the tuple at index 0 we will assign a new tuple to it.
Let’s see if it works…
It does work! Once again because a list is mutable .
And here is how we can make this code more generic?
Ok, this is a bit more generic because we didn’t have to provide the name of the user when updating his records.
This is just an example to show you how to address this TypeError , but in reality in this scenario I would prefer to use a dictionary instead.
It would allow us to access the details of each user from the name and to update the score without any issues.
Tuple Object Does Not Support Item Assignment Error With Values Returned by a Function
This error can also occur when a function returns multiple values and you try to directly modify the values returned by the function.
I create a function that returns two values: the number of users registered in our application and the number of users who have accessed our application in the last 30 days.
As you can see the two values are returned by the function as a tuple.
So, let’s assume there is a new registered user and because of that I try to update the value returned by the function directly.
I get the following error…
This can happen especially if I know that two values are returned by the function but I’m not aware that they are returned in a tuple.
Why Using Tuples If We Get This Error?
You might be thinking…
What is the point of using tuples if we get this error every time we try to update them?
Wouldn’t be a lot easier to always use lists instead?
We can see the fact that tuples are immutable as an added value for tuples when we have some data in our application that should never be modified.
Let’s say, for example, that our application integrates with an external system and it needs some configuration properties to connect to that system.
The tuple above contains two values: the API endpoint of the system we connect to and the port for their API.
We want to make sure this configuration is not modified by mistake in our application because it would break the integration with the external system.
So, if our code inadvertently updates one of the values, the following happens:
Remember, it’s not always good to have data structures you can update in your code whenever you want.
In this article we have seen when the error “tuple object does not support item assignment” occurs and how to avoid it.
You have learned how differently the tuple and list data types behave in Python and how you can use that in your programs.
If you have any questions feel free to post them in the comment below 🙂

Claudio Sabato is an IT expert with over 15 years of professional experience in Python programming, Linux Systems Administration, Bash programming, and IT Systems Design. He is a professional certified by the Linux Professional Institute .
With a Master’s degree in Computer Science, he has a strong foundation in Software Engineering and a passion for robotics with Raspberry Pi.
Related posts:
- Unhashable Type Python Error Explained: How To Fix It
- Python TypeError: Object is Not Callable. Why This Error?
- Python AttributeError: Fix This Built-in Exception
- Understand the “str object is not callable” Python Error and Fix It!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.

How to Solve Python TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment
by Suf | Programming , Python , Tips
Tuples are immutable objects, which means you cannot change them once created. If you try to change a tuple in place using the indexing operator [], you will raise the TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment.
To solve this error, you can convert the tuple to a list, perform an index assignment then convert the list back to a tuple.
This tutorial will go through how to solve this error and solve it with the help of code examples.
Table of contents
Typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment.
Let’s break up the error message to understand what the error means. TypeError occurs whenever you attempt to use an illegal operation for a specific data type.
The part 'tuple' object tells us that the error concerns an illegal operation for tuples.
The part does not support item assignment tells us that item assignment is the illegal operation we are attempting.
Tuples are immutable objects, which means we cannot change them once created. We have to convert the tuple to a list, a mutable data type suitable for item assignment.
Let’s look at an example of assigning items to a list. We will iterate over a list and check if each item is even. If the number is even, we will assign the square of that number in place at that index position.
Let’s run the code to see the result:
We can successfully do item assignments on a list.
Let’s see what happens when we try to change a tuple using item assignment:
We throw the TypeError because the tuple object is immutable.
To solve this error, we need to convert the tuple to a list then perform the item assignment. We will then convert the list back to a tuple. However, you can leave the object as a list if you do not need a tuple.
Let’s run the code to see the updated tuple:
Congratulations on reading to the end of this tutorial. The TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment occurs when you try to change a tuple in-place using the indexing operator [] . You cannot modify a tuple once you create it. To solve this error, you need to convert the tuple to a list, update it, then convert it back to a tuple.
For further reading on TypeErrors, go to the article:
- How to Solve Python TypeError: ‘str’ object does not support item assignment
To learn more about Python for data science and machine learning, go to the online courses page on Python for the most comprehensive courses available.
Have fun and happy researching!
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
Explore your training options in 10 minutes Get Started
- Graduate Stories
- Partner Spotlights
- Bootcamp Prep
- Bootcamp Admissions
- University Bootcamps
- Coding Tools
- Software Engineering
- Web Development
- Data Science
- Tech Guides
- Tech Resources
- Career Advice
- Online Learning
- Internships
- Apprenticeships
- Tech Salaries
- Associate Degree
- Bachelor's Degree
- Master's Degree
- University Admissions
- Best Schools
- Certifications
- Bootcamp Financing
- Higher Ed Financing
- Scholarships
- Financial Aid
- Best Coding Bootcamps
- Best Online Bootcamps
- Best Web Design Bootcamps
- Best Data Science Bootcamps
- Best Technology Sales Bootcamps
- Best Data Analytics Bootcamps
- Best Cybersecurity Bootcamps
- Best Digital Marketing Bootcamps
- Los Angeles
- San Francisco
- Browse All Locations
- Digital Marketing
- Machine Learning
- See All Subjects
- Bootcamps 101
- Full-Stack Development
- Career Changes
- View all Career Discussions
- Mobile App Development
- Cybersecurity
- Product Management
- UX/UI Design
- What is a Coding Bootcamp?
- Are Coding Bootcamps Worth It?
- How to Choose a Coding Bootcamp
- Best Online Coding Bootcamps and Courses
- Best Free Bootcamps and Coding Training
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Community College
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Self-Learning
- Bootcamps vs. Certifications: Compared
- What Is a Coding Bootcamp Job Guarantee?
- How to Pay for Coding Bootcamp
- Ultimate Guide to Coding Bootcamp Loans
- Best Coding Bootcamp Scholarships and Grants
- Education Stipends for Coding Bootcamps
- Get Your Coding Bootcamp Sponsored by Your Employer
- GI Bill and Coding Bootcamps
- Tech Intevriews
- Our Enterprise Solution
- Connect With Us
- Publication
- Reskill America
- Partner With Us
- Resource Center
- Bachelor’s Degree
- Master’s Degree
Python typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment Solution
Tuples are immutable objects . “Immutable” means you cannot change the values inside a tuple. You can only remove them. If you try to assign a new value to an item in a variable, you’ll encounter the “typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment” error.
In this guide, we discuss what this error means and why you may experience it. We’ll walk through an example of this error so you can learn how to solve it in your code.
Find your bootcamp match
Typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment.
While tuples and lists both store sequences of data, they have a few distinctions. Whereas you can change the values in a list, the values inside a tuple cannot be changed. Also, tuples are stored within parenthesis whereas lists are declared between square brackets.
Because you cannot change values in a tuple, item assignment does not work.
Consider the following code snippet:
This code snippet lets us change the first value in the “honor_roll” list to Holly. This works because lists are mutable. You can change their values. The same code does not work with data that is stored in a tuple.
An Example Scenario
Let’s build a program that tracks the courses offered by a high school. Students in their senior year are allowed to choose from a class but a few classes are being replaced.
Start by creating a collection of class names:
We’ve created a tuple that stores the names of each class being offered.
The science department has notified the school that psychology is no longer being offered due to a lack of numbers in the class. We’re going to replace psychology with philosophy as the philosophy class has just opened up a few spaces.
To do this, we use the assignment operator:
This code will replace the value at the index position 3 in our list of classes with “Philosophy”. Next, we print our list of classes to the console so that the user can see what classes are being actively offered:
Use a for loop to print out each class in our tuple to the console. Let’s run our code and see what happens:
Our code returns an error.
The Solution
We’ve tried to use the assignment operator to change a subject in our list. Tuples are immutable so we cannot change their values. This is why our code returns an error.
To solve this problem, we convert our “classes” tuple into a list . This will let us change the values in our sequence of class names.
Do this using the list() method:
We use the list() method to convert the value of “classes” to a list. We assign this new list to the variable “as_list”. Now that we have our list of classes stored as a list, we can change existing classes in the list.
Let’s run our code:
Our code successfully changes the “Psychology” class to “Philosophy”. Our code then prints out the list of classes to the console.
If we need to store our data as a tuple, we can always convert our list back to a tuple once we have changed the values we want to change. We can do this using the tuple() method:
This code converts “as_list” to a tuple and prints the value of our tuple to the console:
We could use this tuple later in our code if we needed our class names stored as a tuple.
The “typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment” error is raised when you try to change a value in a tuple using item assignment.
To solve this error, convert a tuple to a list before you change the values in a sequence. Optionally, you can then convert the list back to a tuple.
Now you’re ready to fix this error in your code like a pro !
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication .

"Career Karma entered my life when I needed it most and quickly helped me match with a bootcamp. Two months after graduating, I found my dream job that aligned with my values and goals in life!"
Venus, Software Engineer at Rockbot
What's Next?
Get matched with top bootcamps
Ask a question to our community, take our careers quiz.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

HatchJS.com
Cracking the Shell of Mystery
TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment: How to Fix
Have you ever tried to assign a value to a specific element of a tuple in Python, only to get an error message like “TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment”? If so, you’re not alone. This is a common error that can be confusing for beginners, but it’s actually pretty easy to understand once you know what’s going on.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what a tuple is, why you can’t assign values to individual elements of a tuple, and how you can work around this limitation. We’ll also provide some examples of how to use tuples effectively in your Python code.
So if you’re ready to learn more about tuples and how to avoid the “TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment” error, keep reading!
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | |—|—|—| | Error | `TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment` | An error that occurs when you try to assign a value to an item in a tuple. | | Cause | The cause of this error is that tuples are immutable, which means that you cannot change their values after they have been created. | | Solution | To fix this error, you can either convert the tuple to a list, or you can use a different data type, such as a dictionary or a set. |
A TypeError is a type of error that occurs when an operation is attempted on an object of an incorrect type. For example, trying to assign a value to an element of a tuple will result in a TypeError.
This error can be avoided by ensuring that the objects you are working with are of the correct type. For example, if you want to assign a value to an element of a tuple, you can use the `append()` method to add the value to the end of the tuple.
**What causes a TypeError?**
A TypeError can be caused by a number of things, including:
- Trying to use an operator that is not supported for the given type of object.
- Trying to access an element of an object that does not exist.
- Trying to assign a value to an object that is immutable.
**Trying to use an operator that is not supported for the given type of object**
One common cause of a TypeError is trying to use an operator that is not supported for the given type of object. For example, the `+` operator can be used to add two numbers together, but it cannot be used to add a string to a number.
python >>> 1 + ‘2’ TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for +: ‘int’ and ‘str’
To avoid this type of error, make sure that you are using the correct operators for the types of objects you are working with.
**Trying to access an element of an object that does not exist**
Another common cause of a TypeError is trying to access an element of an object that does not exist. For example, the following code will result in a TypeError because the `index` 0 does not exist in the `list` `my_list`:
python >>> my_list = [‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’] >>> my_list[0] ‘a’ >>> my_list[1] ‘b’ >>> my_list[2] ‘c’ >>> my_list[3] Traceback (most recent call last): File “ “, line 1, in IndexError: list index out of range
To avoid this type of error, make sure that you are checking the index of the element you are trying to access before you try to access it.
**Trying to assign a value to an object that is immutable**
Finally, a TypeError can also be caused by trying to assign a value to an object that is immutable. An immutable object is an object whose value cannot be changed after it has been created. For example, strings and numbers are immutable objects.
python >>> my_string = ‘hello’ >>> my_string[0] = ‘j’ Traceback (most recent call last): File “ “, line 1, in TypeError: ‘str’ object does not support item assignment
To avoid this type of error, make sure that you are not trying to assign a value to an immutable object.
A TypeError is a type of error that occurs when an operation is attempted on an object of an incorrect type. This error can be avoided by ensuring that the objects you are working with are of the correct type and that you are not trying to access elements of an object that do not exist or assign values to immutable objects.
Here are some additional tips for avoiding TypeErrors:
- Use the `type()` function to check the type of an object before you try to perform an operation on it.
- Use the `len()` function to check the length of a list or tuple before you try to access an element that is out of range.
- Use the `isinstance()` function to check whether an object is of a particular type.
By following these tips, you can help to avoid TypeErrors in your code.
What is a TypeError?
A TypeError occurs when you try to use an operator or function on an object that does not support it. For example, you cannot use the `+` operator to add two strings together, because strings are immutable.
How to fix a TypeError?
To fix a TypeError, you need to identify the cause of the error and correct it. This may involve:
- Using the correct operator for the given type of object.
- Checking that the object you are trying to access exists.
- Using a different type of object that is mutable.
Examples of TypeErrors
Here are some examples of TypeErrors:
>>> tuple = (1, 2, 3) >>> tuple[0] = 4 TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment
>>> list = [1, 2, 3] >>> list[0] = ‘4’ TypeError: can’t convert ‘int’ object to str implicitly
>>> dict = {‘a’: 1, ‘b’: 2} >>> dict[‘c’] = 3 KeyError: ‘c’
In the first example, we try to assign the value 4 to the first element of the tuple `tuple`. However, tuples are immutable, which means that their values cannot be changed. This results in a TypeError.
In the second example, we try to convert the integer 1 to a string and assign it to the first element of the list `list`. However, the `int` type cannot be converted to the `str` type implicitly. This results in a TypeError.
In the third example, we try to access the key `c` in the dictionary `dict`. However, the key `c` does not exist in the dictionary. This results in a KeyError.
TypeErrors can be avoided by using the correct operators and functions for the given type of object. It is also important to check that the object you are trying to access exists before trying to access it.
If you are still getting TypeErrors, you can try using a different type of object that is mutable. For example, if you are trying to add two strings together, you can use the `join()` method to join the two strings into one.
Here are some additional resources that you may find helpful:
- [Python TypeErrors](https://docs.python.org/3/library/exceptions.htmltypeerror)
- [How to Fix Python TypeErrors](https://www.w3schools.com/python/python_errors_typeerror.asp)
A: This error occurs when you try to assign a value to an item in a tuple. Tuples are immutable, which means that their values cannot be changed after they are created. Therefore, you cannot use the assignment operator (=) to assign a new value to an item in a tuple.
Q: How can I avoid this error? A: There are a few ways to avoid this error.
- Use a list instead of a tuple. Lists are mutable, which means that their values can be changed after they are created. Therefore, you can use the assignment operator (=) to assign new values to items in a list.
- Use the slice operator ([]) to access items in a tuple. The slice operator allows you to access a range of items in a tuple. This can be useful if you need to change multiple items in a tuple at once.
- Use the `tuple()` function to create a new tuple with the desired values. This can be useful if you need to create a tuple with the same values as an existing tuple, but with the ability to change the values later.
Q: Can I still use tuples if I need to be able to change their values? A: Yes, you can still use tuples if you need to be able to change their values. However, you will need to use a different data structure, such as a list or a dictionary.
Q: What are some other common errors related to tuples? A: Some other common errors related to tuples include:
- Trying to access an item in a tuple that does not exist. This will result in a `KeyError` exception.
- Trying to add an item to a tuple. This will result in a `TypeError` exception.
- Trying to delete an item from a tuple. This will result in a `TypeError` exception.
Q: Where can I learn more about tuples? A: You can learn more about tuples by reading the following resources:
- [The Python Tutorial: Tuples](https://docs.python.org/3/tutorial/datastructures.htmltuples)
- [Stack Overflow: Tuples](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/tuples)
We hope that this blog post has been helpful. If you have any other questions about tuples or this error, please feel free to leave a comment below.
Here are some key takeaways from this blog post:
- A tuple is a collection of immutable objects, while a list is a collection of mutable objects.
- When you try to assign a value to an element of a tuple, you will get a TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment.
- To get around this error, you can use list comprehension or the tuple() function.
- For more information on tuples, please see the Python documentation.
Author Profile


Latest entries
- December 26, 2023 Error Fixing User: Anonymous is not authorized to perform: execute-api:invoke on resource: How to fix this error
- December 26, 2023 How To Guides Valid Intents Must Be Provided for the Client: Why It’s Important and How to Do It
- December 26, 2023 Error Fixing How to Fix the The Root Filesystem Requires a Manual fsck Error
- December 26, 2023 Troubleshooting How to Fix the `sed unterminated s` Command
Similar Posts
Tensorflow attributeerror: module ‘tensorflow’ has no attribute ‘gfile’.
AttributeError: module ‘tensorflow’ has no attribute ‘gfile’ TensorFlow is a powerful open-source machine learning library that has been used to create state-of-the-art models in a wide variety of domains. However, TensorFlow can sometimes be difficult to use, and errors can be hard to debug. One common error that TensorFlow users may encounter is the `AttributeError:…
How to Fix UnicodeError: UTF-16 Stream Does Not Start with BOM
Have you ever encountered the dreaded UnicodeError: UTF-16 stream does not start with BOM? If so, you’re not alone. This error is a common one, and it can be a real pain to troubleshoot. But don’t worry, I’m here to help. In this article, I’ll explain what the UnicodeError: UTF-16 stream does not start with…
How to Fix the Could Not Resolve Dependency Error
Could Not Resolve Dependency: A Guide to Fixing This Error Have you ever been working on a project in your terminal when you get the dreaded error message “Could not resolve dependency”? This error can be a real pain, especially if you’re not sure what it means or how to fix it. In this guide,…
zsh: command not found: gulp How to Fix This Error
Zsh: Command Not Found: Gulp Gulp is a popular JavaScript task runner that can be used to automate tasks such as compiling Sass, minifying JavaScript, and testing your code. However, if you try to run gulp from the command line in zsh, you may receive the error message “zsh: command not found: gulp.” This error…
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘pycocotools’
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘pycocotools’ Have you ever tried to import the `pycocotools` module into your Python project, only to be met with the dreaded `ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘pycocotools’`? If so, you’re not alone. This error is a common one, and it can be caused by a variety of factors. In this article, we’ll…
How to Fix KeyError: ‘not found in axis’ in Python
KeyError: ‘not found in axis’ Have you ever encountered a KeyError when working with pandas dataframes? If so, you’re not alone. This error is a common one, and it can be caused by a number of different things. In this article, we’ll take a look at what causes KeyErrors in pandas, and we’ll learn how…
Python Tuple does not support item assignment
5 minute read
Introduction
In Python, tuples are immutable, meaning that their elements cannot be modified once they have been assigned. This means that attempting to assign a value to an element in a tuple will result in the following error:
TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment
This error can be frustrating, but there are a few ways to work around it and achieve the desired outcome. In this article, we will explore three different ways to fix this error and give an in-depth explanation of how each method works.
Error and Cause
When attempting to reassign an item in a tuple using the indexing operator, such as:
Python will raise a TypeError, indicating that the tuple object does not support item assignment. This is because, as previously mentioned, tuples are immutable , and their elements cannot be modified once they have been assigned.
Python’s tuple is a built-in data structure that can store multiple values in a single object. This makes it useful for situations where you need to store multiple related values together.
Tuples are defined by enclosing the values in parentheses and separating them with commas. For example, the following code creates a tuple with three integers:
This tuple object, as stated before, is immutable, which means that once it is created, its elements cannot be modified. This means that you cannot add, remove, or change the values of the elements in a tuple.
This is why when you try to reassign a value to an element in the tuple using the indexing operator, such as my_tuple[0] = 4, python will raise a TypeError, indicating that the tuple object does not support item assignment.
Fix 1: Convert Tuple to List
One way to fix this error is to convert the tuple to a list, make the desired changes, and then convert it back to a tuple.
In the above example, we first convert the tuple to a list using the built-in list() function. Once the tuple is converted to a list, we can use the indexing operator to reassign the value at index 0 to 4.
Since lists are mutable, this operation is allowed. Once the desired changes have been made, we convert the list back to a tuple using the built-in tuple() function. The original tuple object is now replaced by the new tuple object which has the desired value at index 0.
It’s important to note that the original tuple remains unchanged, and the new tuple is created with the modified values. This method is useful when you want to make changes to the tuple and need to keep the original tuple object intact.
Fix 2: Using Slicing
Another way to change the values in a tuple is by using slicing. You can create a new tuple with the desired values by slicing the original tuple and concatenating the new values.
In this example, we use slicing to create a new tuple. The my_tuple[:0] slice returns an empty tuple, the (4,) creates a new tuple with the value 4, and the my_tuple[1:] slice returns a new tuple with all elements of the original tuple except the first element.
We then concatenate these three tuples using the + operator to create a new tuple with the desired values.
It’s important to note that the original tuple remains unchanged, and the new tuple is created with the modified values.
This method is useful when you want to make changes to the tuple and need to keep the original tuple object intact.
It is also worth noting that this method is the most efficient one of the three, as it only uses slicing which has O(k) time complexity where k is the number of elements in the slice.
Fix 3: Creating a new Tuple
The last fix is creating a new tuple with the desired values.
This method works similarly to the previous method, but instead of using slicing and concatenation, we create a new tuple with the desired value and concatenate it with the rest of the elements of the original tuple using the + operator.
While tuples are immutable in Python, there are a few ways to work around the ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment error. By converting the tuple to a list, using slicing, or creating a new tuple, you can achieve the desired outcome.
We hope this article was useful.
You may also enjoy
Python’s Default dict explained
4 minute read
In this article, we will explain how to use default dicts in the Python programming language. Find examples and more
C++ Undefined reference to std::cout
3 minute read
How to fix the undefined reference to std::cout in the C++ programming language. This error is usually caused by a dependency problem in the gcc compiler.
C++ Length of an Array With Examples (3 easy ways)
In this article, we will use sizeof() operator, for loop method and the std::size function to determine the length of any C++ array. We will provide examples
C++ Convert Int to String
1 minute read
How to convert an int to a string in C++, we will be using the to_string, stringstream and sprintf functions from the std library. Easiest methods to convert

How to Solve ‘Tuple’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment (Python)
Here’s everything about TypeError: ‘Tuple’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in Python.
You’ll learn:
- The specifics of the tuple data type
- The difference between immutable and mutable data types
- How to change immutable data types
So if you want to understand this error in Python and how to solve it, then you’re in the right place.
Let’s jump right in!
- IndentationError: Unexpected Unindent in Python
- How to Solve ImportError: Attempted Relative Import With No Known Parent Package (Python)
- SyntaxError: Invalid Character in Identifier: How to Solve? (Python)
- 3 Ways to Solve Series Objects Are Mutable and Cannot be Hashed (Python)
- 9 Examples of Unexpected Character After Line Continuation Character (Python)
Mutable, or Immutable? That Is the Question
Data types in Python are mutable or immutable .
All data types that are numeric , for example, are immutable .
You can write something like this:
Have you changed the variable a ?
Not really: When you write a = 1 , you put the object 1 in memory and told the name a to refer to this literal.
Next, when you write a = a + 1 , Python evaluates the expression on the right:
Python takes the object referred by a (the 1 ) and then adds 1 to it.
You get a new object, a 2 . This object goes right into the memory and a references instead of object 1 .
The value of object 1 has not changed—it would be weird if 1 would out of a sudden a 2 , for example, wouldn’t it? So instead of overwriting an object ( 1 ), a new object ( 2 ) is created and assigned to the variable ( a ).
Mutable Data Types
More complex data types in Python are sequences such as:
- Byte Arrays
Sequences contain several values, which can be accessed by index.

However, some sequences are mutable (byte arrays, lists) , while others are immutable (tuples) .
You can create a tuple and access its elements like this:
Yet if you try to change one of the elements, you get an error:
Notice that the item in the tuple at index 2 is a list. You can change the list without changing the tuple:
The object stored in the tuple remains the same, but its contents have changed. But what if you still need to change the element in the tuple?
You can do this by converting the tuple to a list. Then you change the element, and then convert the list to a tuple again:
For large amounts of data, conversion operations can take quite a long time:
As you can see, for a list of 100 million float numbers, this operation takes about a second. This is not a long time for most tasks, but it is still worth considering if you are dealing with large amounts of data.
However, there is another way to “change” a tuple element—you can rebuild a tuple using slicing and concatenation:
Note that it is necessary to put a comma in parentheses to create a tuple of one element. If you use just parentheses, then (‘uno’) is not a tuple, but a string in parentheses .
Concatenating a string with a tuple is not possible:
Interestingly, you can use shorthand operators on a tuple, like this:
Or even like this:
3 Examples of TypeError: ‘Tuple’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in Python
Let’s look at some practical examples of when this error can occur. The simplest is when you initially enter the sequence incorrectly:
In this example, the name list1 refers to a tuple despite the list in the name. The name does not affect the type of variable. To fix this error, simply change the parentheses to square brackets in the constructor:
Perhaps you have a list with some values, such as the student’s name and grade point average:
Alice did a poor job this semester, and her GPA dropped to 90:
Unfortunately, you cannot just change the average score in such a list. You already know that you can convert a tuple to a list, or form a new tuple. For example, like this:
However, if you need to change values regularly, it makes sense to switch from a list of tuples to a dictionary. Dictionaries are a perfect fit for such tasks. You can do this easily with the dict() constructor:
Now you can change the average by student name:
#1 Real World Example of TypeError: ‘Tuple’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in Python
An interesting example of a novice programmer trying to enter values in a list from the keyboard using the eval() function:
This method is not very reliable by itself.
Even if the user enters the correct sequence separated by commas—for example, 3, 2, 4, 1 —it will be evaluated in a tuple.
Naturally, an attempt to assign a new value to a tuple element in the line list[i +1] = list[i] raises a TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment .
Here, you see another mistake—which, by the way, may even be invisible during program execution.
The my_sort function uses the list data type name as the argument name. This is not only the name of the data type, but also the list constructor.
Python will not throw an error while executing this code, but if you try to create a list using the constructor inside the my_sort function, you will have big problems.

In this case, to enter elements into the list, it would be more correct to read the entire string and then split it using the split() method. If you need integer values, you can also apply the map() function, then convert the resulting map object into a list:
The construction looks a little cumbersome, but it does its job. You can also enter list items through a list comprehension:
You can choose the design that you like best.
#2 Real World Example of TypeError: ‘Tuple’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in Python
Another example of when a TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment may occur is the use of various libraries.
If you have not studied the documentation well enough, you may not always clearly understand which data type will be returned in a given situation. In this example, the author tries to make the picture redder by adding 20 to the red color component:
This produces an error on the line pixel[0] = pixel[0] + 20 . How?
You are converting pixels to a list in line of code 3 . Indeed, if you check the type of the pixels variable, you get a list:
However, in the loop, you iterate over the pixels list elements, and they already have a different type. Check the type of the pixels list element with index 0 :
And this is a tuple!
So, you can solve this problem by converting lists to tuples inside a loop, for example.
However, in this case, you will need to slightly adjust the iterable value. This is because you will need the pixel color values and the index to write the new values into the original array.
For this, use the enumerate() function:
The program will work successfully with that version of a loop, and you will get a redder image at the output. It would be more correct to trim values above 255 , for example:
But if the program consists only of this transformation, then Python will already truncate the values when saving the image.
Here’s more Python support:
- 9 Examples of Unexpected Character After Line Continuation Character
- 3 Ways to Solve Series Objects Are Mutable and Cannot be Hashed
- How to Solve SyntaxError: Invalid Character in Identifier
- ImportError: Attempted Relative Import With No Known Parent Package
- IndentationError: Unexpected Unindent in Python (and 3 More)

Tech entrepreneur and founder of Tech Medic, who has become a prominent advocate for the Right to Repair movement. She has testified before the US Federal Trade Commission and been featured on CBS Sunday Morning, helping influence change within the tech industry.
View all posts
- Python Introduction
- Python Fundamentals
- Python Control Flow
- Python Data Structures
- Python Files
- Python Essentials
- Python Exercises
- Python Networking
- Python Programming
- Python Exceptions
- Interview Questions
'tuple' object does not support item assignment
The TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment is an error that arises when attempting to modify the value of an element within a tuple. Tuples, as immutable objects, exhibit the property of being unalterable after their initialization. Consequently, any effort to alter the contents of a tuple results in this error.
This inherent immutability ensures the integrity of the data contained within the tuple and facilitates the creation of data structures where data should remain fixed and constant throughout its lifecycle. Tuples in Python are immutable, meaning once they are created, you cannot change their elements.
Converting the tuple into a list
To resolve this particular error, a suitable approach involves converting the tuple into a list, as lists boast mutability, allowing the modification of their elements. By transforming the tuple into a list, the desired changes to the item can be performed seamlessly.
Once the necessary modifications are accomplished, the list can then be transformed back into a tuple, thus retaining the original immutability and ensuring the integrity of the data structure. This conversion process allows for a flexible and efficient means of addressing the issue without compromising the inherent properties of tuples.
This code will first create a tuple called tuple_data with the values 1, 2, and 3. Then, it will try to change the value of the first item in the tuple. This will raise an error because tuples are immutable objects.
Then, the code will convert the tuple to a list. Lists are mutable objects, so the value of the first item can be changed. The code then changes the value of the first item to 4. Finally, the code converts the list back to a tuple and prints the tuple.
Other Solutions:
Use a list instead of a tuple.
Lists in Python are mutable, so you can modify their elements after creation.
Create a new tuple with the modified elements
Since tuples are immutable, you can't change an element directly, but you can create a new tuple with the desired changes.
It is essential to bear in mind that tuples are typically employed to store data that is intended to remain unaltered throughout its existence, whereas lists are utilized for data that may require modification. The choice of data structure should align with the specific use case to ensure optimal performance and data integrity. Selecting the appropriate structure ensures that the data is appropriately managed, safeguarding its intended purpose and preventing unintended changes that could compromise its consistency.
- TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not subscriptable
- IndexError: string index out of range
- IndentationError: unexpected indent Error
- ValueError: too many values to unpack (expected 2)
- SyntaxError- EOL while scanning string literal
- TypeError: Can't convert 'int' object to str implicitly
- IndentationError: expected an indented block
- ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10
- IndexError: list index out of range : Python
- AttributeError: 'module' object has no attribute 'main'
- UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment
- TypeError: string indices must be integers
- FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory
- Fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory
- ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
- ImportError: No module named requests | Python
- TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not iterable
- SyntaxError: unexpected EOF while parsing | Python
- zsh: command not found: python
- Unicodeescape codec can't decode bytes in position 2-3
- The AttributeError: 'bytes' object has no attribute 'read'
- All Communities Products ArcGIS Pro ArcGIS Survey123 ArcGIS Online ArcGIS Enterprise Data Management Geoprocessing ArcGIS Web AppBuilder ArcGIS Experience Builder ArcGIS Dashboards ArcGIS CityEngine ArcGIS Spatial Analyst All Products Communities Industries Education Water Resources State & Local Government Transportation Gas and Pipeline Water Utilities Roads and Highways Telecommunications Natural Resources Electric Public Safety All Industries Communities Developers Python JavaScript Maps SDK Native Maps SDKs ArcGIS API for Python ArcObjects SDK ArcGIS Pro SDK Developers - General ArcGIS REST APIs and Services ArcGIS Online Developers File Geodatabase API Game Engine Maps SDKs All Developers Communities Worldwide Comunidad Esri Colombia - Ecuador - Panamá ArcGIS 開発者コミュニティ Czech GIS ArcNesia Esri India GeoDev Germany ArcGIS Content - Esri Nederland Esri Italia Community Comunidad GEOTEC Esri Ireland Používatelia ArcGIS All Worldwide Communities All Communities Developers User Groups Industries Services Community Resources Worldwide Events Learning ArcGIS Topics Networks GIS Life View All Communities
- ArcGIS Ideas
- Community Resources Community Help Documents Community Blog Community Feedback Member Introductions Community Ideas All Community Resources
- All Communities
- Error with UpdateCursor: Object does not support d...
- GeoNet, The Esri Community - STAGE
- ArcGIS AppStudio
- ArcGIS AppStudio Questions
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Printer Friendly Page
Error with UpdateCursor: Object does not support data assignment?
- Mark as New
- Report Inappropriate Content
Solved! Go to Solution.
- item assignment
- update cursor
- Previous Topic
View solution in original post
- Terms of Use
- Community Guidelines
- Community Resources
- Contact Community Team
- Trust Center
- Contact Esri

Typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment
One of the errors we encounter, when we try to change the value of tuple item, is Typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment .
This error can be fixed in either of the following approaches:
- Convert the tuple to a list and back to a tuple
- Use tuple concatenation to create a new tuple
- Use named tuples from the collections module
Furthermore in this guide, we will tackle why this error occurs, as well as practical example codes for better understanding.
Now let’s know this error…
What is Typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment?
The “TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment” occurs when we attempt to change the value of an item in a tuple.
To solve the error, convert the tuple to a list, change the item at the specific index, and convert the list back to a tuple.
Why Typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment?
The reason why we get a “Typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment” error in Python is that tuples are immutable objects, which means their content cannot be changed after creation.
Every time we try to modify or assign a value to an element within a tuple using the assignment operator…
Essentially we are trying to change the content of an immutable object, which is not possible in Python.
As a result, in a type error, telling you that tuples do not support item assignment.
Here is how this error occurs:
In this code when we try to update an element in a tuple, but tuple objects are immutable which caused an error.
Traceback (most recent call last): File “C:\Users\Windows\PycharmProjects\pythonProject1\main.py”, line 4, in my_tuple[0] = ‘c’ TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment
Now that we understand what is this error and why this error occurs, let’s proceed to solutions to this error.
How to fix Typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment
Technically, there are different ways to solve the “Typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment” error in Python.
Here are three possible solutions with example codes and their explanations.
Solution 1: Convert the tuple to a list and back to a tuple
One way to fix the error is to convert the tuple to a list, make the needed modifications, and then convert it back to a tuple.
Here is an example code:
(‘IT’, ‘SOURCECODERS!’, ‘WELCOME’)
Solution 2: Use tuple concatenation to create a new tuple
Another way to fix the error is to create a new tuple that contains the modified values of the original tuple.
In this example, we define a tuple called my_tuple containing three elements.
We then create a new tuple called new_tuple that contains the first and third elements of my_tuple and a modified value for the second element.
(‘IT’, ‘SOURCECODERS!’, ‘Howdy’)
Solution 3: Use named tuples from the collections module
A third way to fix the error is to use named tuples from the collections module.
Named tuples are similar to tuples, but they allow you to access their elements by name instead of index.
In this example, we define a named tuple called MyTuple with three named elements. We then create an instance of the named tuple called my_tuple with three values.
We modify the value of the second element using the _replace() method, which creates a new named tuple with the same values as the original one but with the specified element replaced.
MyTuple(Howdy=1, IT=’SOURCODERS’, SOURCECODE=3)
Note that using named tuples may be overkill for simple cases. However, they can be useful when you need to work with tuples that have a large number of elements.
Thus, when you need to keep track of the meaning of each element.
Anyhow, if you are finding solutions to some errors you might encounter we also have Typeerror: unhashable type: ‘slice’ .
In conclusion, Python error Typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment is able to fixed through converting the tuple to a list and back to a tuple , using tuple concatenation to create a new tuple, and using named tuples from the collections module .
Any of the approaches can fix the error depending on your error.
We hope this guide has helped you! 😊

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Arcpy TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment, field was defined as FLOAT. Ask Question Asked 5 years, 6 months ago. Modified 5 years, 6 months ago. ... Python - 'tuple' object does not support item assignment. 2. TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for +: 'float' and 'tuple' ...
You appear to be trying to update values in your data using a Search Cursor arcpy.da.SearchCursor() rather than an Update Cursor arcpy.da.UpdateCursor(). Try changing to an Update Cursor: #Calculating LOS for each point with arcpy.da.UpdateCursor(fc_Opt_Opp, field_names) as cursor: for row in cursor:
The function input reads a string and evaluates it as a Python expression.Thus, the comma-separated list becomes a tuple of values, these are passed to add_25(), and this function tries to assign to mylist[i] something.. And tuples are immutable, they do not support item assignment (on purpose).
Once we have a list, we can update the item at the specified index and optionally convert the result back to a tuple. Python indexes are zero-based, so the first item in a tuple has an index of 0, and the last item has an index of -1 or len(my_tuple) - 1. # Constructing a new tuple with the updated element Alternatively, you can construct a new tuple that contains the updated element at the ...
Solution #1: Change the tuple to list first. When you need to modify the elements of a tuple, you can convert the tuple to a list first using the list() function. Lists are mutable sequences that allow you to change, add, and delete elements. Once you have made the changes to the list, you can convert it back to a tuple using the tuple() function:
Does "Tuple Object Does Not Support Item Assignment" Apply to a List inside a Tuple? Let's see what happens when one of the elements of a tuple is a list. >>> values = (1, '2', [3])
To do so I am just iterating through each row using 'arcpy.da.SearchCursor'. #Import geoprocessing. import arcpy # Stack Exchange System. Stack Exchange network consists the 183 Q&A communities including Piles Overflow, the tallest, most trusted online community for developers for learn, ...
Tuples are immutable objects, which means you cannot change them once created. If you try to change a tuple in place using the indexing operator [], you will raise the TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment. To solve this error, you can convert the tuple to a list, perform an index assignment then…
TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment when swapping values. Ask Question Asked 12 years, 6 months ago. Modified 2 years, ... TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment Code: def my_sort(list): for index in range(1,len(list)): value=list[index] i=index-1 while i>=0: if value<list[i]: list[i+1] = list[i] list ...
typeerror: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment. While tuples and lists both store sequences of data, they have a few distinctions. Whereas you can change the values in a list, the values inside a tuple cannot be changed. Also, tuples are stored within parenthesis whereas lists are declared between square brackets.
When you try to assign a value to an element of a tuple, you will get a TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment. To get around this error, you can use list comprehension or the tuple() function.
Python will raise a TypeError, indicating that the tuple object does not support item assignment. This is because, as previously mentioned, tuples are immutable, and their elements cannot be modified once they have been assigned. Python's tuple is a built-in data structure that can store multiple values in a single object.
1 list1 = (1, 2, 3) ----> 2 list1[0] = 'one'. TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment. In this example, the name list1 refers to a tuple despite the list in the name. The name does not affect the type of variable. To fix this error, simply change the parentheses to square brackets in the constructor:
Once the necessary modifications are accomplished, the list can then be transformed back into a tuple, thus retaining the original immutability and ensuring the integrity of the data structure. This conversion process allows for a flexible and efficient means of addressing the issue without compromising the inherent properties of tuples.
When I run it, I get the following error: Traceback (most recent call last): File "<string>", line 19, in <module>. TypeError: 'da.UpdateCursor' object does not support item assignment. I'm not sure if it's a basic syntax issue (it's very possible) or I'm not thinking about it correctly. Any ideas are greatly appreciated.
In Python, we have a built-in data structure " tuple " which is similar to a Python list and stores elements in sequential order.The only difference between a Python list and a tuple is that the tuple is an immutable data structure, which means once a tuple object is defined, we can not change its elements.
报错问题. TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment异常. 报错原因. 在Python中,如果你看到错误消息 TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment,这意味着你试图修改一个元组(tuple)中的一个元素,但是元组是不可变的(immutable),也就是说,你不能修改元组中的元素。
You can not change tuple()s - they are immutable. You could create a new one. You could create a new one. Or you could use itertools.groupby to group your tuples together and do some selective output:
One of the errors we encounter, when we try to change the value of tuple item, is Typeerror: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment.
The function takes in a tuple from d.items() (as the parameter df) so the first (0th) element is the name and the next is the data frame. I have to do some manipulations on the data frame in the function, and I do so using df[1] without any issues.