Impact of online classes on the satisfaction and performance of students during the pandemic period of COVID 19
- Published: 21 April 2021
- Volume 26 , pages 6923–6947, ( 2021 )

Cite this article

- Ram Gopal 1 ,
- Varsha Singh 1 &
- Arun Aggarwal ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3986-188X 2
629k Accesses
241 Citations
25 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The aim of the study is to identify the factors affecting students’ satisfaction and performance regarding online classes during the pandemic period of COVID–19 and to establish the relationship between these variables. The study is quantitative in nature, and the data were collected from 544 respondents through online survey who were studying the business management (B.B.A or M.B.A) or hotel management courses in Indian universities. Structural equation modeling was used to analyze the proposed hypotheses. The results show that four independent factors used in the study viz. quality of instructor, course design, prompt feedback, and expectation of students positively impact students’ satisfaction and further student’s satisfaction positively impact students’ performance. For educational management, these four factors are essential to have a high level of satisfaction and performance for online courses. This study is being conducted during the epidemic period of COVID- 19 to check the effect of online teaching on students’ performance.
Explore related subjects
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Education and Educational Technology
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Coronavirus is a group of viruses that is the main root of diseases like cough, cold, sneezing, fever, and some respiratory symptoms (WHO, 2019 ). Coronavirus is a contagious disease, which is spreading very fast amongst the human beings. COVID-19 is a new sprain which was originated in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. Coronavirus circulates in animals, but some of these viruses can transmit between animals and humans (Perlman & Mclntosh, 2020 ). As of March 282,020, according to the MoHFW, a total of 909 confirmed COVID-19 cases (862 Indians and 47 foreign nationals) had been reported in India (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020 ). Officially, no vaccine or medicine is evaluated to cure the spread of COVID-19 (Yu et al., 2020 ). The influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on the education system leads to schools and colleges’ widespread closures worldwide. On March 24, India declared a country-wide lockdown of schools and colleges (NDTV, 2020 ) for preventing the transmission of the coronavirus amongst the students (Bayham & Fenichel, 2020 ). School closures in response to the COVID-19 pandemic have shed light on several issues affecting access to education. COVID-19 is soaring due to which the huge number of children, adults, and youths cannot attend schools and colleges (UNESCO, 2020 ). Lah and Botelho ( 2012 ) contended that the effect of school closing on students’ performance is hazy.
Similarly, school closing may also affect students because of disruption of teacher and students’ networks, leading to poor performance. Bridge ( 2020 ) reported that schools and colleges are moving towards educational technologies for student learning to avoid a strain during the pandemic season. Hence, the present study’s objective is to develop and test a conceptual model of student’s satisfaction pertaining to online teaching during COVID-19, where both students and teachers have no other option than to use the online platform uninterrupted learning and teaching.
UNESCO recommends distance learning programs and open educational applications during school closure caused by COVID-19 so that schools and teachers use to teach their pupils and bound the interruption of education. Therefore, many institutes go for the online classes (Shehzadi et al., 2020 ).
As a versatile platform for learning and teaching processes, the E-learning framework has been increasingly used (Salloum & Shaalan, 2018 ). E-learning is defined as a new paradigm of online learning based on information technology (Moore et al., 2011 ). In contrast to traditional learning academics, educators, and other practitioners are eager to know how e-learning can produce better outcomes and academic achievements. Only by analyzing student satisfaction and their performance can the answer be sought.
Many comparative studies have been carried out to prove the point to explore whether face-to-face or traditional teaching methods are more productive or whether online or hybrid learning is better (Lockman & Schirmer, 2020 ; Pei & Wu, 2019 ; González-Gómez et al., 2016 ; González-Gómez et al., 2016 ). Results of the studies show that the students perform much better in online learning than in traditional learning. Henriksen et al. ( 2020 ) highlighted the problems faced by educators while shifting from offline to online mode of teaching. In the past, several research studies had been carried out on online learning to explore student satisfaction, acceptance of e-learning, distance learning success factors, and learning efficiency (Sher, 2009 ; Lee, 2014 ; Yen et al., 2018 ). However, scant amount of literature is available on the factors that affect the students’ satisfaction and performance in online classes during the pandemic of Covid-19 (Rajabalee & Santally, 2020 ). In the present study, the authors proposed that course design, quality of the instructor, prompt feedback, and students’ expectations are the four prominent determinants of learning outcome and satisfaction of the students during online classes (Lee, 2014 ).
The Course Design refers to curriculum knowledge, program organization, instructional goals, and course structure (Wright, 2003 ). If well planned, course design increasing the satisfaction of pupils with the system (Almaiah & Alyoussef, 2019 ). Mtebe and Raisamo ( 2014 ) proposed that effective course design will help in improving the performance through learners knowledge and skills (Khan & Yildiz, 2020 ; Mohammed et al., 2020 ). However, if the course is not designed effectively then it might lead to low usage of e-learning platforms by the teachers and students (Almaiah & Almulhem, 2018 ). On the other hand, if the course is designed effectively then it will lead to higher acceptance of e-learning system by the students and their performance also increases (Mtebe & Raisamo, 2014 ). Hence, to prepare these courses for online learning, many instructors who are teaching blended courses for the first time are likely to require a complete overhaul of their courses (Bersin, 2004 ; Ho et al., 2006 ).
The second-factor, Instructor Quality, plays an essential role in affecting the students’ satisfaction in online classes. Instructor quality refers to a professional who understands the students’ educational needs, has unique teaching skills, and understands how to meet the students’ learning needs (Luekens et al., 2004 ). Marsh ( 1987 ) developed five instruments for measuring the instructor’s quality, in which the main method was Students’ Evaluation of Educational Quality (SEEQ), which delineated the instructor’s quality. SEEQ is considered one of the methods most commonly used and embraced unanimously (Grammatikopoulos et al., 2014 ). SEEQ was a very useful method of feedback by students to measure the instructor’s quality (Marsh, 1987 ).
The third factor that improves the student’s satisfaction level is prompt feedback (Kinicki et al., 2004 ). Feedback is defined as information given by lecturers and tutors about the performance of students. Within this context, feedback is a “consequence of performance” (Hattie & Timperley, 2007 , p. 81). In education, “prompt feedback can be described as knowing what you know and what you do not related to learning” (Simsek et al., 2017 , p.334). Christensen ( 2014 ) studied linking feedback to performance and introduced the positivity ratio concept, which is a mechanism that plays an important role in finding out the performance through feedback. It has been found that prompt feedback helps in developing a strong linkage between faculty and students which ultimately leads to better learning outcomes (Simsek et al., 2017 ; Chang, 2011 ).
The fourth factor is students’ expectation . Appleton-Knapp and Krentler ( 2006 ) measured the impact of student’s expectations on their performance. They pin pointed that the student expectation is important. When the expectations of the students are achieved then it lead to the higher satisfaction level of the student (Bates & Kaye, 2014 ). These findings were backed by previous research model “Student Satisfaction Index Model” (Zhang et al., 2008 ). However, when the expectations are students is not fulfilled then it might lead to lower leaning and satisfaction with the course. Student satisfaction is defined as students’ ability to compare the desired benefit with the observed effect of a particular product or service (Budur et al., 2019 ). Students’ whose grade expectation is high will show high satisfaction instead of those facing lower grade expectations.
The scrutiny of the literature show that although different researchers have examined the factors affecting student satisfaction but none of the study has examined the effect of course design, quality of the instructor, prompt feedback, and students’ expectations on students’ satisfaction with online classes during the pandemic period of Covid-19. Therefore, this study tries to explore the factors that affect students’ satisfaction and performance regarding online classes during the pandemic period of COVID–19. As the pandemic compelled educational institutions to move online with which they were not acquainted, including teachers and learners. The students were not mentally prepared for such a shift. Therefore, this research will be examined to understand what factors affect students and how students perceived these changes which are reflected through their satisfaction level.
This paper is structured as follows: The second section provides a description of theoretical framework and the linkage among different research variables and accordingly different research hypotheses were framed. The third section deals with the research methodology of the paper as per APA guideline. The outcomes and corresponding results of the empirical analysis are then discussed. Lastly, the paper concludes with a discussion and proposes implications for future studies.
2 Theoretical framework
Achievement goal theory (AGT) is commonly used to understand the student’s performance, and it is proposed by four scholars Carole Ames, Carol Dweck, Martin Maehr, and John Nicholls in the late 1970s (Elliot, 2005 ). Elliott & Dweck ( 1988 , p11) define that “an achievement goal involves a program of cognitive processes that have cognitive, affective and behavioral consequence”. This theory suggests that students’ motivation and achievement-related behaviors can be easily understood by the purpose and the reasons they adopted while they are engaged in the learning activities (Dweck & Leggett, 1988 ; Ames, 1992 ; Urdan, 1997 ). Some of the studies believe that there are four approaches to achieve a goal, i.e., mastery-approach, mastery avoidance, performance approach, and performance-avoidance (Pintrich, 1999 ; Elliot & McGregor, 2001 ; Schwinger & Stiensmeier-Pelster, 2011 , Hansen & Ringdal, 2018 ; Mouratidis et al., 2018 ). The environment also affects the performance of students (Ames & Archer, 1988 ). Traditionally, classroom teaching is an effective method to achieve the goal (Ames & Archer, 1988 ; Ames, 1992 ; Clayton et al., 2010 ) however in the modern era, the internet-based teaching is also one of the effective tools to deliver lectures, and web-based applications are becoming modern classrooms (Azlan et al., 2020 ). Hence, following section discuss about the relationship between different independent variables and dependent variables (Fig. 1 ).
Proposed Model
3 Hypotheses development
3.1 quality of the instructor and satisfaction of the students.
Quality of instructor with high fanaticism on student’s learning has a positive impact on their satisfaction. Quality of instructor is one of the most critical measures for student satisfaction, leading to the education process’s outcome (Munteanu et al., 2010 ; Arambewela & Hall, 2009 ; Ramsden, 1991 ). Suppose the teacher delivers the course effectively and influence the students to do better in their studies. In that case, this process leads to student satisfaction and enhances the learning process (Ladyshewsky, 2013 ). Furthermore, understanding the need of learner by the instructor also ensures student satisfaction (Kauffman, 2015 ). Hence the hypothesis that the quality of instructor significantly affects the satisfaction of the students was included in this study.
H1: The quality of the instructor positively affects the satisfaction of the students.
3.2 Course design and satisfaction of students
The course’s technological design is highly persuading the students’ learning and satisfaction through their course expectations (Liaw, 2008 ; Lin et al., 2008 ). Active course design indicates the students’ effective outcomes compared to the traditional design (Black & Kassaye, 2014 ). Learning style is essential for effective course design (Wooldridge, 1995 ). While creating an online course design, it is essential to keep in mind that we generate an experience for students with different learning styles. Similarly, (Jenkins, 2015 ) highlighted that the course design attributes could be developed and employed to enhance student success. Hence the hypothesis that the course design significantly affects students’ satisfaction was included in this study.
H2: Course design positively affects the satisfaction of students.
3.3 Prompt feedback and satisfaction of students
The emphasis in this study is to understand the influence of prompt feedback on satisfaction. Feedback gives the information about the students’ effective performance (Chang, 2011 ; Grebennikov & Shah, 2013 ; Simsek et al., 2017 ). Prompt feedback enhances student learning experience (Brownlee et al., 2009 ) and boosts satisfaction (O'donovan, 2017 ). Prompt feedback is the self-evaluation tool for the students (Rogers, 1992 ) by which they can improve their performance. Eraut ( 2006 ) highlighted the impact of feedback on future practice and student learning development. Good feedback practice is beneficial for student learning and teachers to improve students’ learning experience (Yorke, 2003 ). Hence the hypothesis that prompt feedback significantly affects satisfaction was included in this study.
H3: Prompt feedback of the students positively affects the satisfaction.
3.4 Expectations and satisfaction of students
Expectation is a crucial factor that directly influences the satisfaction of the student. Expectation Disconfirmation Theory (EDT) (Oliver, 1980 ) was utilized to determine the level of satisfaction based on their expectations (Schwarz & Zhu, 2015 ). Student’s expectation is the best way to improve their satisfaction (Brown et al., 2014 ). It is possible to recognize student expectations to progress satisfaction level (ICSB, 2015 ). Finally, the positive approach used in many online learning classes has been shown to place a high expectation on learners (Gold, 2011 ) and has led to successful outcomes. Hence the hypothesis that expectations of the student significantly affect the satisfaction was included in this study.
H4: Expectations of the students positively affects the satisfaction.
3.5 Satisfaction and performance of the students
Zeithaml ( 1988 ) describes that satisfaction is the outcome result of the performance of any educational institute. According to Kotler and Clarke ( 1986 ), satisfaction is the desired outcome of any aim that amuses any individual’s admiration. Quality interactions between instructor and students lead to student satisfaction (Malik et al., 2010 ; Martínez-Argüelles et al., 2016 ). Teaching quality and course material enhances the student satisfaction by successful outcomes (Sanderson, 1995 ). Satisfaction relates to the student performance in terms of motivation, learning, assurance, and retention (Biner et al., 1996 ). Mensink and King ( 2020 ) described that performance is the conclusion of student-teacher efforts, and it shows the interest of students in the studies. The critical element in education is students’ academic performance (Rono, 2013 ). Therefore, it is considered as center pole, and the entire education system rotates around the student’s performance. Narad and Abdullah ( 2016 ) concluded that the students’ academic performance determines academic institutions’ success and failure.
Singh et al. ( 2016 ) asserted that the student academic performance directly influences the country’s socio-economic development. Farooq et al. ( 2011 ) highlights the students’ academic performance is the primary concern of all faculties. Additionally, the main foundation of knowledge gaining and improvement of skills is student’s academic performance. According to Narad and Abdullah ( 2016 ), regular evaluation or examinations is essential over a specific period of time in assessing students’ academic performance for better outcomes. Hence the hypothesis that satisfaction significantly affects the performance of the students was included in this study.
H5: Students’ satisfaction positively affects the performance of the students.
3.6 Satisfaction as mediator
Sibanda et al. ( 2015 ) applied the goal theory to examine the factors persuading students’ academic performance that enlightens students’ significance connected to their satisfaction and academic achievement. According to this theory, students perform well if they know about factors that impact on their performance. Regarding the above variables, institutional factors that influence student satisfaction through performance include course design and quality of the instructor (DeBourgh, 2003 ; Lado et al., 2003 ), prompt feedback, and expectation (Fredericksen et al., 2000 ). Hence the hypothesis that quality of the instructor, course design, prompts feedback, and student expectations significantly affect the students’ performance through satisfaction was included in this study.
H6: Quality of the instructor, course design, prompt feedback, and student’ expectations affect the students’ performance through satisfaction.
H6a: Students’ satisfaction mediates the relationship between quality of the instructor and student’s performance.
H6b: Students’ satisfaction mediates the relationship between course design and student’s performance.
H6c: Students’ satisfaction mediates the relationship between prompt feedback and student’s performance.
H6d: Students’ satisfaction mediates the relationship between student’ expectations and student’s performance.
4.1 Participants
In this cross-sectional study, the data were collected from 544 respondents who were studying the management (B.B.A or M.B.A) and hotel management courses. The purposive sampling technique was used to collect the data. Descriptive statistics shows that 48.35% of the respondents were either MBA or BBA and rests of the respondents were hotel management students. The percentages of male students were (71%) and female students were (29%). The percentage of male students is almost double in comparison to females. The ages of the students varied from 18 to 35. The dominant group was those aged from 18 to 22, and which was the under graduation student group and their ratio was (94%), and another set of students were from the post-graduation course, which was (6%) only.
4.2 Materials
The research instrument consists of two sections. The first section is related to demographical variables such as discipline, gender, age group, and education level (under-graduate or post-graduate). The second section measures the six factors viz. instructor’s quality, course design, prompt feedback, student expectations, satisfaction, and performance. These attributes were taken from previous studies (Yin & Wang, 2015 ; Bangert, 2004 ; Chickering & Gamson, 1987 ; Wilson et al., 1997 ). The “instructor quality” was measured through the scale developed by Bangert ( 2004 ). The scale consists of seven items. The “course design” and “prompt feedback” items were adapted from the research work of Bangert ( 2004 ). The “course design” scale consists of six items. The “prompt feedback” scale consists of five items. The “students’ expectation” scale consists of five items. Four items were adapted from Bangert, 2004 and one item was taken from Wilson et al. ( 1997 ). Students’ satisfaction was measure with six items taken from Bangert ( 2004 ); Wilson et al. ( 1997 ); Yin and Wang ( 2015 ). The “students’ performance” was measured through the scale developed by Wilson et al. ( 1997 ). The scale consists of six items. These variables were accessed on a five-point likert scale, ranging from 1(strongly disagree) to 5(strongly agree). Only the students from India have taken part in the survey. A total of thirty-four questions were asked in the study to check the effect of the first four variables on students’ satisfaction and performance. For full details of the questionnaire, kindly refer Appendix Tables 6 .
The study used a descriptive research design. The factors “instructor quality, course design, prompt feedback and students’ expectation” were independent variables. The students’ satisfaction was mediator and students’ performance was the dependent variable in the current study.
4.4 Procedure
In this cross-sectional research the respondents were selected through judgment sampling. They were informed about the objective of the study and information gathering process. They were assured about the confidentiality of the data and no incentive was given to then for participating in this study. The information utilizes for this study was gathered through an online survey. The questionnaire was built through Google forms, and then it was circulated through the mails. Students’ were also asked to write the name of their college, and fifteen colleges across India have taken part to fill the data. The data were collected in the pandemic period of COVID-19 during the total lockdown in India. This was the best time to collect the data related to the current research topic because all the colleges across India were involved in online classes. Therefore, students have enough time to understand the instrument and respondent to the questionnaire in an effective manner. A total of 615 questionnaires were circulated, out of which the students returned 574. Thirty responses were not included due to the unengaged responses. Finally, 544 questionnaires were utilized in the present investigation. Male and female students both have taken part to fill the survey, different age groups, and various courses, i.e., under graduation and post-graduation students of management and hotel management students were the part of the sample.
5.1 Exploratory factor analysis (EFA)
To analyze the data, SPSS and AMOS software were used. First, to extract the distinct factors, an exploratory factor analysis (EFA) was performed using VARIMAX rotation on a sample of 544. Results of the exploratory analysis rendered six distinct factors. Factor one was named as the quality of instructor, and some of the items were “The instructor communicated effectively”, “The instructor was enthusiastic about online teaching” and “The instructor was concerned about student learning” etc. Factor two was labeled as course design, and the items were “The course was well organized”, “The course was designed to allow assignments to be completed across different learning environments.” and “The instructor facilitated the course effectively” etc. Factor three was labeled as prompt feedback of students, and some of the items were “The instructor responded promptly to my questions about the use of Webinar”, “The instructor responded promptly to my questions about general course requirements” etc. The fourth factor was Student’s Expectations, and the items were “The instructor provided models that clearly communicated expectations for weekly group assignments”, “The instructor used good examples to explain statistical concepts” etc. The fifth factor was students’ satisfaction, and the items were “The online classes were valuable”, “Overall, I am satisfied with the quality of this course” etc. The sixth factor was performance of the student, and the items were “The online classes has sharpened my analytic skills”, “Online classes really tries to get the best out of all its students” etc. These six factors explained 67.784% of the total variance. To validate the factors extracted through EFA, the researcher performed confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) through AMOS. Finally, structural equation modeling (SEM) was used to test the hypothesized relationships.
5.2 Measurement model
The results of Table 1 summarize the findings of EFA and CFA. Results of the table showed that EFA renders six distinct factors, and CFA validated these factors. Table 2 shows that the proposed measurement model achieved good convergent validity (Aggarwal et al., 2018a , b ). Results of the confirmatory factor analysis showed that the values of standardized factor loadings were statistically significant at the 0.05 level. Further, the results of the measurement model also showed acceptable model fit indices such that CMIN = 710.709; df = 480; CMIN/df = 1.481 p < .000; Incremental Fit Index (IFI) = 0.979; Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) = 0.976; Goodness of Fit index (GFI) = 0.928; Adjusted Goodness of Fit Index (AGFI) = 0.916; Comparative Fit Index (CFI) = 0.978; Root Mean Square Residual (RMR) = 0.042; Root Mean Squared Error of Approximation (RMSEA) = 0.030 is satisfactory.
The Average Variance Explained (AVE) according to the acceptable index should be higher than the value of squared correlations between the latent variables and all other variables. The discriminant validity is confirmed (Table 2 ) as the value of AVE’s square root is greater than the inter-construct correlations coefficient (Hair et al., 2006 ). Additionally, the discriminant validity existed when there was a low correlation between each variable measurement indicator with all other variables except with the one with which it must be theoretically associated (Aggarwal et al., 2018a , b ; Aggarwal et al., 2020 ). The results of Table 2 show that the measurement model achieved good discriminate validity.
5.3 Structural model
To test the proposed hypothesis, the researcher used the structural equation modeling technique. This is a multivariate statistical analysis technique, and it includes the amalgamation of factor analysis and multiple regression analysis. It is used to analyze the structural relationship between measured variables and latent constructs.
Table 3 represents the structural model’s model fitness indices where all variables put together when CMIN/DF is 2.479, and all the model fit values are within the particular range. That means the model has attained a good model fit. Furthermore, other fit indices as GFI = .982 and AGFI = 0.956 be all so supportive (Schumacker & Lomax, 1996 ; Marsh & Grayson, 1995 ; Kline, 2005 ).
Hence, the model fitted the data successfully. All co-variances among the variables and regression weights were statistically significant ( p < 0.001).
Table 4 represents the relationship between exogenous, mediator and endogenous variables viz—quality of instructor, prompt feedback, course design, students’ expectation, students’ satisfaction and students’ performance. The first four factors have a positive relationship with satisfaction, which further leads to students’ performance positively. Results show that the instructor’s quality has a positive relationship with the satisfaction of students for online classes (SE = 0.706, t-value = 24.196; p < 0.05). Hence, H1 was supported. The second factor is course design, which has a positive relationship with students’ satisfaction of students (SE = 0.064, t-value = 2.395; p < 0.05). Hence, H2 was supported. The third factor is Prompt feedback, and results show that feedback has a positive relationship with the satisfaction of the students (SE = 0.067, t-value = 2.520; p < 0.05). Hence, H3 was supported. The fourth factor is students’ expectations. The results show a positive relationship between students’ expectation and students’ satisfaction with online classes (SE = 0.149, t-value = 5.127; p < 0.05). Hence, H4 was supported. The results of SEM show that out of quality of instructor, prompt feedback, course design, and students’ expectation, the most influencing factor that affect the students’ satisfaction was instructor’s quality (SE = 0.706) followed by students’ expectation (SE =5.127), prompt feedback (SE = 2.520). The factor that least affects the students’ satisfaction was course design (2.395). The results of Table 4 finally depicts that students’ satisfaction has positive effect on students’ performance ((SE = 0.186, t-value = 2.800; p < 0.05). Hence H5 was supported.
Table 5 shows that students’ satisfaction partially mediates the positive relationship between the instructor’s quality and student performance. Hence, H6(a) was supported. Further, the mediation analysis results showed that satisfaction again partially mediates the positive relationship between course design and student’s performance. Hence, H6(b) was supported However, the mediation analysis results showed that satisfaction fully mediates the positive relationship between prompt feedback and student performance. Hence, H6(c) was supported. Finally, the results of the Table 5 showed that satisfaction partially mediates the positive relationship between expectations of the students and student’s performance. Hence, H6(d) was supported.
6 Discussion
In the present study, the authors evaluated the different factors directly linked with students’ satisfaction and performance with online classes during Covid-19. Due to the pandemic situation globally, all the colleges and universities were shifted to online mode by their respective governments. No one has the information that how long this pandemic will remain, and hence the teaching method was shifted to online mode. Even though some of the educators were not tech-savvy, they updated themselves to battle the unexpected circumstance (Pillai et al., 2021 ). The present study results will help the educators increase the student’s satisfaction and performance in online classes. The current research assists educators in understanding the different factors that are required for online teaching.
Comparing the current research with past studies, the past studies have examined the factors affecting the student’s satisfaction in the conventional schooling framework. However, the present study was conducted during India’s lockdown period to identify the prominent factors that derive the student’s satisfaction with online classes. The study also explored the direct linkage between student’s satisfaction and their performance. The present study’s findings indicated that instructor’s quality is the most prominent factor that affects the student’s satisfaction during online classes. This means that the instructor needs to be very efficient during the lectures. He needs to understand students’ psychology to deliver the course content prominently. If the teacher can deliver the course content properly, it affects the student’s satisfaction and performance. The teachers’ perspective is critical because their enthusiasm leads to a better online learning process quality.
The present study highlighted that the second most prominent factor affecting students’ satisfaction during online classes is the student’s expectations. Students might have some expectations during the classes. If the instructor understands that expectation and customizes his/her course design following the student’s expectations, then it is expected that the students will perform better in the examinations. The third factor that affects the student’s satisfaction is feedback. After delivering the course, appropriate feedback should be taken by the instructors to plan future courses. It also helps to make the future strategies (Tawafak et al., 2019 ). There must be a proper feedback system for improvement because feedback is the course content’s real image. The last factor that affects the student’s satisfaction is design. The course content needs to be designed in an effective manner so that students should easily understand it. If the instructor plans the course, so the students understand the content without any problems it effectively leads to satisfaction, and the student can perform better in the exams. In some situations, the course content is difficult to deliver in online teaching like the practical part i.e. recipes of dishes or practical demonstration in the lab. In such a situation, the instructor needs to be more creative in designing and delivering the course content so that it positively impacts the students’ overall satisfaction with online classes.
Overall, the students agreed that online teaching was valuable for them even though the online mode of classes was the first experience during the pandemic period of Covid-19 (Agarwal & Kaushik, 2020 ; Rajabalee & Santally, 2020 ). Some of the previous studies suggest that the technology-supported courses have a positive relationship with students’ performance (Cho & Schelzer, 2000 ; Harasim, 2000 ; Sigala, 2002 ). On the other hand, the demographic characteristic also plays a vital role in understanding the online course performance. According to APA Work Group of the Board of Educational Affairs ( 1997 ), the learner-centered principles suggest that students must be willing to invest the time required to complete individual course assignments. Online instructors must be enthusiastic about developing genuine instructional resources that actively connect learners and encourage them toward proficient performances. For better performance in studies, both teachers and students have equal responsibility. When the learner faces any problem to understand the concepts, he needs to make inquiries for the instructor’s solutions (Bangert, 2004 ). Thus, we can conclude that “instructor quality, student’s expectation, prompt feedback, and effective course design” significantly impact students’ online learning process.
7 Implications of the study
The results of this study have numerous significant practical implications for educators, students and researchers. It also contributes to the literature by demonstrating that multiple factors are responsible for student satisfaction and performance in the context of online classes during the period of the COVID-19 pandemic. This study was different from the previous studies (Baber, 2020 ; Ikhsan et al., 2019 ; Eom & Ashill, 2016 ). None of the studies had examined the effect of students’ satisfaction on their perceived academic performance. The previous empirical findings have highlighted the importance of examining the factors affecting student satisfaction (Maqableh & Jaradat, 2021 ; Yunusa & Umar, 2021 ). Still, none of the studies has examined the effect of course design, quality of instructor, prompt feedback, and students’ expectations on students’ satisfaction all together with online classes during the pandemic period. The present study tries to fill this research gap.
The first essential contribution of this study was the instructor’s facilitating role, and the competence he/she possesses affects the level of satisfaction of the students (Gray & DiLoreto, 2016 ). There was an extra obligation for instructors who taught online courses during the pandemic. They would have to adapt to a changing climate, polish their technical skills throughout the process, and foster new students’ technical knowledge in this environment. The present study’s findings indicate that instructor quality is a significant determinant of student satisfaction during online classes amid a pandemic. In higher education, the teacher’s standard referred to the instructor’s specific individual characteristics before entering the class (Darling-Hammond, 2010 ). These attributes include factors such as instructor content knowledge, pedagogical knowledge, inclination, and experience. More significantly, at that level, the amount of understanding could be given by those who have a significant amount of technical expertise in the areas they are teaching (Martin, 2021 ). Secondly, the present study results contribute to the profession of education by illustrating a realistic approach that can be used to recognize students’ expectations in their class effectively. The primary expectation of most students before joining a university is employment. Instructors have agreed that they should do more to fulfill students’ employment expectations (Gorgodze et al., 2020 ). The instructor can then use that to balance expectations to improve student satisfaction. Study results can be used to continually improve and build courses, as well as to make policy decisions to improve education programs. Thirdly, from result outcomes, online course design and instructors will delve deeper into how to structure online courses more efficiently, including design features that minimize adversely and maximize optimistic emotion, contributing to greater student satisfaction (Martin et al., 2018 ). The findings suggest that the course design has a substantial positive influence on the online class’s student performance. The findings indicate that the course design of online classes need to provide essential details like course content, educational goals, course structure, and course output in a consistent manner so that students would find the e-learning system beneficial for them; this situation will enable students to use the system and that leads to student performance (Almaiah & Alyoussef, 2019 ). Lastly, the results indicate that instructors respond to questions promptly and provide timely feedback on assignments to facilitate techniques that help students in online courses improve instructor participation, instructor interaction, understanding, and participation (Martin et al., 2018 ). Feedback can be beneficial for students to focus on the performance that enhances their learning.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Chitkara College of Hospitality Management, Chitkara University, Chandigarh, Punjab, India
Ram Gopal & Varsha Singh
Chitkara Business School, Chitkara University, Chandigarh, Punjab, India
Arun Aggarwal
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Arun Aggarwal .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval.
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Gopal, R., Singh, V. & Aggarwal, A. Impact of online classes on the satisfaction and performance of students during the pandemic period of COVID 19. Educ Inf Technol 26 , 6923–6947 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10523-1
Download citation
Received : 07 December 2020
Accepted : 22 March 2021
Published : 21 April 2021
Issue Date : November 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10523-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Quality of instructor
- Course design
- Instructor’s prompt feedback
- Expectations
- Student’s satisfaction
- Perceived performance
Advertisement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Open access
- Published: 16 September 2021
Online learning during COVID-19 produced equivalent or better student course performance as compared with pre-pandemic: empirical evidence from a school-wide comparative study
- Meixun Zheng 1 ,
- Daniel Bender 1 &
- Cindy Lyon 1
BMC Medical Education volume 21 , Article number: 495 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
215k Accesses
91 Citations
118 Altmetric
Metrics details
The COVID-19 pandemic forced dental schools to close their campuses and move didactic instruction online. The abrupt transition to online learning, however, has raised several issues that have not been resolved. While several studies have investigated dental students’ attitude towards online learning during the pandemic, mixed results have been reported. Additionally, little research has been conducted to identify and understand factors, especially pedagogical factors, that impacted students’ acceptance of online learning during campus closure. Furthermore, how online learning during the pandemic impacted students’ learning performance has not been empirically investigated. In March 2020, the dental school studied here moved didactic instruction online in response to government issued stay-at-home orders. This first-of-its-kind comparative study examined students’ perceived effectiveness of online courses during summer quarter 2020, explored pedagogical factors impacting their acceptance of online courses, and empirically evaluated the impact of online learning on students’ course performance, during the pandemic.
The study employed a quasi-experimental design. Participants were 482 pre-doctoral students in a U.S dental school. Students’ perceived effectiveness of online courses during the pandemic was assessed with a survey. Students’ course grades for online courses during summer quarter 2020 were compared with that of a control group who received face-to-face instruction for the same courses before the pandemic in summer quarter 2019.
Survey results revealed that most online courses were well accepted by the students, and 80 % of them wanted to continue with some online instruction post pandemic. Regression analyses revealed that students’ perceived engagement with faculty and classmates predicted their perceived effectiveness of the online course. More notably, Chi Square tests demonstrated that in 16 out of the 17 courses compared, the online cohort during summer quarter 2020 was equally or more likely to get an A course grade than the analogous face-to-face cohort during summer quarter 2019.
Conclusions
This is the first empirical study in dental education to demonstrate that online courses during the pandemic could achieve equivalent or better student course performance than the same pre-pandemic in-person courses. The findings fill in gaps in literature and may inform online learning design moving forward.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Research across disciplines has demonstrated that well-designed online learning can lead to students’ enhanced motivation, satisfaction, and learning [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ]. A report by the U.S. Department of Education [ 8 ], based on examinations of comparative studies of online and face-to-face versions of the same course from 1996 to 2008, concluded that online learning could produce learning outcomes equivalent to or better than face-to-face learning. The more recent systematic review by Pei and Wu [ 9 ] provided additional evidence that online learning is at least as effective as face-to-face learning for undergraduate medical students.
To take advantage of the opportunities presented by online learning, thought leaders in dental education in the U.S. have advocated for the adoption of online learning in the nation’s dental schools [ 10 , 11 , 12 ]. However, digital innovation has been a slow process in academic dentistry [ 13 , 14 , 15 ]. In March 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic brought unprecedented disruption to dental education by necessitating the need for online learning. In accordance with stay-at-home orders to prevent the spread of the virus, dental schools around the world closed their campuses and moved didactic instruction online.
The abrupt transition to online learning, however, has raised several concerns and question. First, while several studies have examined dental students’ online learning satisfaction during the pandemic, mixed results have been reported. Some studies have reported students’ positive attitude towards online learning [ 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 ]. Sadid-Zadeh et al. [ 18 ] found that 99 % of the surveyed dental students at University of Buffalo, in the U.S., were satisfied with live web-based lectures during the pandemic. Schlenz et al. [ 15 ] reported that students in a German dental school had a favorable attitude towards online learning and wanted to continue with online instruction in their future curriculum. Other studies, however, have reported students’ negative online learning experience during the pandemic [ 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 ]. For instance, dental students at Harvard University felt that learning during the pandemic had worsened and engagement had decreased [ 23 , 24 ]. In a study with medical and dental students in Pakistan, Abbasi et al. [ 21 ] found that 77 % of the students had negative perceptions about online learning and 84 % reported reduced student-instructor interactions.
In addition to these mixed results, little attention has been given to factors affecting students’ acceptance of online learning during the pandemic. With the likelihood that online learning will persist post pandemic [ 27 ], research in this area is warranted to inform online course design moving forward. In particular, prior research has demonstrated that one of the most important factors influencing students’ performance in any learning environment is a sense of belonging, the feeling of being connected with and supported by the instructor and classmates [ 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 ]. Unfortunately, this aspect of the classroom experience has suffered during school closure. While educational events can be held using a video conferencing system, virtual peer interaction on such platforms has been perceived by medical trainees to be not as easy and personal as physical interaction [ 32 ]. The pandemic highlights the need to examine instructional strategies most suited to the current situation to support students’ engagement with faculty and classmates.
Furthermore, there is considerable concern from the academic community about the quality of online learning. Pre-pandemic, some faculty and students were already skeptical about the value of online learning [ 33 ]. The longer the pandemic lasts, the more they may question the value of online education, asking: Can online learning during the pandemic produce learning outcomes that are similar to face-to-face learning before the pandemic? Despite the documented benefits of online learning prior to the pandemic, the actual impact of online learning during the pandemic on students’ academic performance is still unknown due to reasons outlined below.
On one hand, several factors beyond the technology used could influence the effectiveness of online learning, one of which is the teaching context [ 34 ]. The sudden transition to online learning has posed many challenges to faculty and students. Faculty may not have had adequate time to carefully design online courses to take full advantage of the possibilities of the online format. Some faculty may not have had prior online teaching experience and experienced a deeper learning curve when it came to adopting online teaching methods [ 35 ]. Students may have been at the risk of increased anxiety due to concerns about contracting the virus, on time graduation, finances, and employment [ 36 , 37 ], which may have negatively impacted learning performance [ 38 ]. Therefore, whether online learning during the pandemic could produce learning outcomes similar to those of online learning implemented during more normal times remains to be determined.
Most existing studies on online learning in dental education during the pandemic have only reported students’ satisfaction. The actual impact of the online format on academic performance has not been empirically investigated. The few studies that have examined students’ learning outcomes have only used students’ self-reported data from surveys and focus groups. According to Kaczmarek et al. [ 24 ], 50 % of the participating dental faculty at Harvard University perceived student learning to have worsened during the pandemic and 70 % of the students felt the same. Abbasi et al. [ 21 ] reported that 86 % of medical and dental students in a Pakistan college felt that they learned less online. While student opinions are important, research has demonstrated a poor correlation between students’ perceived learning and actual learning gains [ 39 ]. As we continue to navigate the “new normal” in teaching, students’ learning performance needs to be empirically evaluated to help institutions gauge the impact of this grand online learning experiment.
Research purposes
In March 2020, the University of the Pacific Arthur A. Dugoni School of Dentistry, in the U.S., moved didactic instruction online to ensure the continuity of education during building closure. This study examined students’ acceptance of online learning during the pandemic and its impacting factors, focusing on instructional practices pertaining to students’ engagement/interaction with faculty and classmates. Another purpose of this study was to empirically evaluate the impact of online learning during the pandemic on students’ actual course performance by comparing it with that of a pre-pandemic cohort. To understand the broader impact of the institutional-wide online learning effort, we examined all online courses offered in summer quarter 2020 (July to September) that had a didactic component.
This is the first empirical study in dental education to evaluate students’ learning performance during the pandemic. The study aimed to answer the following three questions.
How well was online learning accepted by students, during the summer quarter 2020 pandemic interruption?
How did instructional strategies, centered around students’ engagement with faculty and classmates, impact their acceptance of online learning?
How did online learning during summer quarter 2020 impact students’ course performance as compared with a previous analogous cohort who received face-to-face instruction in summer quarter 2019?
This study employed a quasi-experimental design. The study was approved by the university’s institutional review board (#2020-68).
Study context and participants
The study was conducted at the Arthur A. Dugoni School of Dentistry, University of the Pacific. The program runs on a quarter system. It offers a 3-year accelerated Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) program and a 2-year International Dental Studies (IDS) program for international dentists who have obtained a doctoral degree in dentistry from a country outside the U.S. and want to practice in the U.S. Students advance throughout the program in cohorts. IDS students take some courses together with their DDS peers. All three DDS classes (D1/DDS 2023, D2/DDS 2022, and D3/DDS 2021) and both IDS classes (I1/IDS 2022 and I2/IDS 2021) were invited to participate in the study. The number of students in each class was: D1 = 145, D2 = 143, D3 = 143, I1 = 26, and I2 = 25. This resulted in a total of 482 student participants.
During campus closure, faculty delivered remote instruction in various ways, including live online classes via Zoom @ [ 40 ], self-paced online modules on the school’s learning management system Canvas @ [ 41 ], or a combination of live and self-paced delivery. For self-paced modules, students studied assigned readings and/or viewings such as videos and pre-recorded slide presentations. Some faculty also developed self-paced online lessons with SoftChalk @ [ 42 ], a cloud-based platform that supports the inclusion of gamified learning by insertion of various mini learning activities. The SoftChalk lessons were integrated with Canvas @ [ 41 ] and faculty could monitor students’ progress. After students completed the pre-assigned online materials, some faculty held virtual office hours or live online discussion sessions for students to ask questions and discuss key concepts.
Data collection and analysis
Student survey.
Students’ perceived effectiveness of summer quarter 2020 online courses was evaluated by the school’s Office of Academic Affairs in lieu of the regular course evaluation process. A total of 19 courses for DDS students and 10 courses for IDS students were evaluated. An 8-question survey developed by the researchers (Additional file 1 ) was administered online in the last week of summer quarter 2020. Course directors invited student to take the survey during live online classes. The survey introduction stated that taking the survey was voluntary and that their anonymous responses would be reported in aggregated form for research purposes. Students were invited to continue with the survey if they chose to participate; otherwise, they could exit the survey. The number of students in each class who took the survey was as follows: D1 ( n = 142; 98 %), D2 ( n = 133; 93 %), D3 ( n = 61; 43 %), I1 ( n = 23; 88 %), and I2 ( n = 20; 80 %). This resulted in a total of 379 (79 %) respondents across all classes.
The survey questions were on a 4-point scale, ranging from Strongly Disagree (1 point), Disagree (2 points), Agree (3 points), and Strongly Agree (4 points). Students were asked to rate each online course by responding to four statements: “ I could fully engage with the instructor and classmates in this course”; “The online format of this course supported my learning”; “Overall this online course is effective.”, and “ I would have preferred face-to-face instruction for this course ”. For the first three survey questions, a higher mean score indicated a more positive attitude toward the online course. For the fourth question “ I would have preferred face-to-face instruction for this course ”, a higher mean score indicated that more students would have preferred face-to-face instruction for the course. Two additional survey questions asked students to select their preferred online delivery method for fully online courses during the pandemic from three given choices (synchronous online/live, asynchronous online/self-paced, and a combination of both), and to report whether they wanted to continue with some online instruction post pandemic. Finally, two open-ended questions at the end of the survey allowed students to comment on the aspects of online format that they found to be helpful and to provide suggestion for improvement. For the purpose of this study, we focused on the quantitative data from the Likert-scale questions.
Descriptive data such as the mean scores were reported for each course. Regression analyses were conducted to examine the relationship between instructional strategies focusing on students’ engagement with faculty and classmates, and their overall perceived effectiveness of the online course. The independent variable was student responses to the question “ I could fully engage with the instructor and classmates in this course ”, and the dependent variable was their answer to the question “ Overall, this online course is effective .”

Student course grades
Using Chi-square tests, student course grade distributions (A, B, C, D, and F) for summer quarter 2020 online courses were compared with that of a previous cohort who received face-to-face instruction for the same course in summer quarter 2019. Note that as a result of the school’s pre-doctoral curriculum redesign implemented in July 2019, not all courses offered in summer quarter 2020 were offered in the previous year in summer quarter 2019. In other words, some of the courses offered in summer quarter 2020 were new courses offered for the first time. Because these new courses did not have a previous face-to-face version to compare to, they were excluded from data analysis. For some other courses, while course content remained the same between 2019 and 2020, the sequence of course topics within the course had changed. These courses were also excluded from data analysis.
After excluding the aforementioned courses, it resulted in a total of 17 “comparable” courses that were included in data analysis (see the subsequent section). For these courses, the instructor, course content, and course goals were the same in both 2019 and 2020. The assessment methods and grading policies also remained the same through both years. For exams and quizzes, multiple choice questions were the dominating format for both years. While some exam questions in 2020 were different from 2019, faculty reported that the overall exam difficulty level was similar. The main difference in assessment was testing conditions. The 2019 cohort took computer-based exams in the physical classroom with faculty proctoring, and the 2020 cohort took exams at home with remote proctoring to ensure exam integrity. The remote proctoring software monitored the student during the exam through a web camera on their computer/laptop. The recorded video file flags suspicious activities for faculty review after exam completion.
Students’ perceived effectiveness of online learning
Table 1 summarized data on DDS students’ perceived effectiveness of each online course during summer quarter 2020. For the survey question “ Overall, this online course is effective ”, the majority of courses received a mean score that was approaching or over 3 points on the 4-point scale, suggesting that online learning was generally well accepted by students. Despite overall positive online course experiences, for many of the courses examined, there was an equal split in student responses to the question “ I would have preferred face-to-face instruction for this course .” Additionally, for students’ preferred online delivery method for fully online courses, about half of the students in each class preferred a combination of synchronous and asynchronous online learning (see Fig. 1 ). Finally, the majority of students wanted faculty to continue with some online instruction post pandemic: D1class (110; 78.60 %), D2 class (104; 80 %), and D3 class (49; 83.10 %).
While most online courses received favorable ratings, some variations did exist among courses. For D1 courses, “ Anatomy & Histology ” received lower ratings than others. This could be explained by its lab component, which didn’t lend itself as well to the online format. For D2 courses, several of them received lower ratings than others, especially for the survey question on students’ perceived engagement with faculty and classmates.
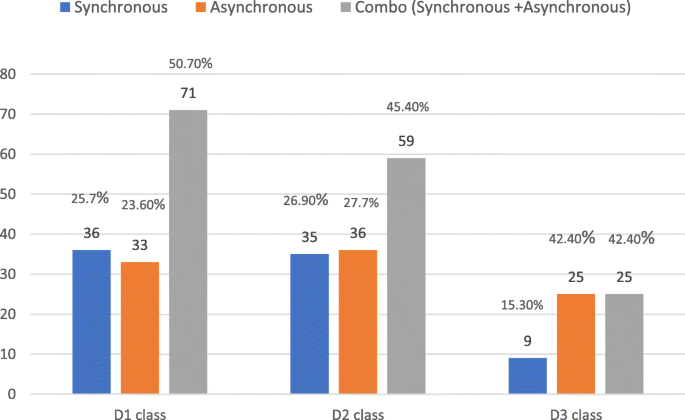
DDS students’ preferred online delivery method for fully online courses
Table 2 summarized IDS students’ perceived effectiveness of each online course during summer quarter 2020. For the survey question “ Overall, this online course is effective ”, all courses received a mean score that was approaching or over 3 points on a 4-point scale, suggesting that online learning was well accepted by students. For the survey question “ I would have preferred face-to-face instruction for this course ”, for most online courses examined, the percentage of students who would have preferred face-to-face instruction was similar to that of students who preferred online instruction for the course. Like their DDS peers, about half of the IDS students in each class also preferred a combination of synchronous and asynchronous online delivery for fully online courses (See Fig. 2 ). Finally, the majority of IDS students (I1, n = 18, 81.80 %; I2, n = 16, 84.20 %) wanted to continue with some online learning after the pandemic is over.
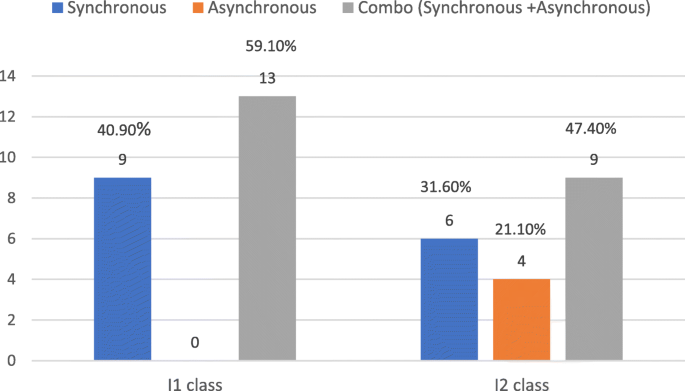
IDS students’ preferred online delivery method for fully online courses
Factors impacting students’ acceptance of online learning
For all 19 online courses taken by DDS students, regression analyses indicated that there was a significantly positive relationship between students’ perceived engagement with faculty and classmates and their perceived effectiveness of the course. P value was 0.00 across all courses. The ranges of effect size (r 2 ) were: D1 courses (0.26 to 0.50), D2 courses (0.39 to 0.650), and D3 courses (0.22 to 0.44), indicating moderate to high correlations across courses.
For 9 out of the 10 online courses taken by IDS students, there was a positive relationship between students’ perceived engagement with faculty and classmates and their perceived effectiveness of the course. P value was 0.00 across courses. The ranges of effect size were: I1 courses (0.35 to 0.77) and I2 courses (0.47 to 0.63), indicating consistently high correlations across courses. The only course in which students’ perceived engagement with faculty and classmates didn’t predict perceived effective of the course was “ Integrated Clinical Science III (ICS III) ”, which the I2 class took together with their D3 peers.
Impact of online learning on students’ course performance
Chi square test results (Table 3 ) indicated that in 4 out of the 17 courses compared, the online cohort during summer quarter 2020 was more likely to receive an A grade than the face-to-face cohort during summer quarter 2019. In 12 of the courses, the online cohort were equally likely to receive an A grade as the face-to-face cohort. In the remaining one course, the online cohort was less likely to receive an A grade than the face-to-face cohort.
Students’ acceptance of online learning during the pandemic
Survey results revealed that students had generally positive perceptions about online learning during the pandemic and the majority of them wanted to continue with some online learning post pandemic. Overall, our findings supported several other studies in dental [ 18 , 20 ], medical [ 43 , 44 ], and nursing [ 45 ] education that have also reported students’ positive attitudes towards online learning during the pandemic. In their written comments in the survey, students cited enhanced flexibility as one of the greatest benefits of online learning. Some students also commented that typing questions in the chat box during live online classes was less intimidating than speaking in class. Others explicitly stated that not having to commute to/from school provided more time for sleep, which helped with self-care and mental health. Our findings are in line with previous studies which have also demonstrated that online learning offered higher flexibility [ 46 , 47 ]. Meanwhile, consistent with findings of other researchers [ 19 , 21 , 46 ], our students felt difficulty engaging with faculty and classmates in several online courses.
There were some variations among individual courses in students’ acceptance of the online format. One factor that could partially account for the observed differences was instructional strategies. In particular, our regression analysis results demonstrated a positive correlation between students’ perceived engagement with faculty and classmates and their perceived overall effectiveness of the online course. Other aspects of course design might also have influenced students’ overall rating of the online course. For instance, some D2 students commented that the requirements of the course “ Integrated Case-based Seminars (ICS II) ” were not clear and that assessment did not align with lecture materials. It is important to remember that communicating course requirements clearly and aligning course content and assessment are principles that should be applied in any course, whether face-to-face or online. Our results highlighted the importance of providing faculty training on basic educational design principles and online learning design strategies. Furthermore, the nature of the course might also have impacted student ratings. For example, D1 course “ Anatomy and Histology ” had a lab component, which did not lend itself as well to the online format. Many students reported that it was difficult to see faculty’s live demonstration during Zoom lectures, which may have resulted in a lower student satisfaction rating.
As for students’ preferred online delivery method for fully online courses during the pandemic, about half of them preferred a combination of synchronous and asynchronous online learning. In light of this finding, as we continue with remote learning until public health directives allow a return to campus, we will encourage faculty to integrate these two online delivery modalities. Finally, in view of the result that over 80 % of the students wanted to continue with some online instruction after the pandemic, the school will advocate for blended learning in the post-pandemic world [ 48 ]. For future face-to-face courses on campus after the pandemic, faculty are encouraged to deliver some content online to reduce classroom seat time and make learning more flexible. Taken together, our findings not only add to the overall picture of the current situation but may inform learning design moving forward.
Role of online engagement and interaction
To reiterate, we found that students’ perceived engagement with faculty and classmates predicted their perceived overall effectiveness of the online course. This aligns with the larger literature on best practices in online learning design. Extensive research prior to the pandemic has confirmed that the effectiveness of online learning is determined by a number of factors beyond the tools used, including students’ interactions with the instructor and classmates [ 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 ]. Online students may feel isolated due to reduced or lack of interaction [ 53 , 54 ]. Therefore, in designing online learning experiences, it is important to remember that learning is a social process [ 55 ]. Faculty’s role is not only to transmit content but also to promote the different types of interactions that are an integral part of the online learning process [ 33 ]. The online teaching model in which faculty uploads materials online but teach it in the same way as in the physical classroom, without special effort to engage students, doesn’t make the best use of the online format. Putting the “sage on the screen” during a live class meeting on a video conferencing system is not different from “sage on the stage” in the physical classroom - both provide limited space for engagement. Such one-way monologue devalues the potentials that online learning presents.
In light of the critical role that social interaction plays in online learning, faculty are encouraged to use the interactive features of online learning platforms to provide clear channels for student-instructor and student-student interactions. In the open-ended comments, students highlighted several instructional strategies that they perceived to be helpful for learning. For live online classes, these included conducting breakout room activities, using the chat box to facilitate discussions, polling, and integrating gameplay with apps such as Kahoot! @ [ 56 ]. For self-paced classes, students appreciated that faculty held virtual office hours or subsequent live online discussion sessions to reinforce understanding of the pre-assigned materials.
Quality of online education during the pandemic
This study provided empirical evidence in dental education that it was possible to ensure the continuity of education without sacrificing the quality of education provided to students during forced migration to distance learning upon building closure. To reiterate, in all but one online course offered in summer quarter 2020, students were equally or more likely to get an A grade than the face-to-face cohort from summer quarter 2019. Even for courses that had less student support for the online format (e.g., the D1 course “ Anatomy and Histology ”), there was a significant increase in the number of students who earned an A grade in 2020 as compared with the previous year. The reduced capacity for technical training during the pandemic may have resulted in more study time for didactic content. Overall, our results resonate with several studies in health sciences education before the pandemic that the quality of learning is comparable in face-to-face and online formats [ 9 , 57 , 58 ]. For the only course ( Integrated Case-based Seminars ICS II) in which the online cohort had inferior performance than the face-to-face cohort, as mentioned earlier, students reported that assessment was not aligned with course materials and that course expectations were not clear. This might explain why students’ course performance was not as strong as expected.
Limitations
This study used a pre-existing control group from the previous year. There may have been individual differences between students in the online and the face-to-face cohorts, such as motivation, learning style, and prior knowledge, that could have impacted the observed outcomes. Additionally, even though course content and assessment methods were largely the same in 2019 and 2020, changes in other aspects of the course could have impacted students’ course performance. Some faculty may have been more compassionate with grading (e.g., more flexible with assignment deadlines) in summer quarter 2020 given the hardship students experienced during the pandemic. On the other hand, remote proctoring in summer quarter 2020 may have heightened some students’ exam anxiety knowing that they were being monitored through a webcam. The existence and magnitude of effect of these factors needs to be further investigated.
This present study only examined the correlation between students’ perceived online engagement and their perceived overall effectiveness of the online course. Other factors that might impact their acceptance of the online format need to be further researched in future studies. Another future direction is to examine how students’ perceived online engagement correlates with their actual course performance. Because the survey data collected for our present study are anonymous, we cannot match students’ perceived online engagement data with their course grades to run this additional analysis. It should also be noted that this study was focused on didactic online instruction. Future studies might examine how technical training was impacted during the COVID building closure. It was also out of the scope of this study to examine how student characteristics, especially high and low academic performance as reflected by individual grades, affects their online learning experience and performance. We plan to conduct a follow-up study to examine which group of students are most impacted by the online format. Finally, this study was conducted in a single dental school, and so the findings may not be generalizable to other schools and disciplines. Future studies could be conducted in another school or disciplines to compare results.
This study revealed that dental students had generally favorable attitudes towards online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic and that their perceived engagement with faculty and classmates predicted their acceptance of the online course. Most notably, this is the first study in dental education to demonstrate that online learning during the pandemic could achieve similar or better learning outcomes than face-to-face learning before the pandemic. Findings of our study could contribute significantly to the literature on online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic in health sciences education. The results could also inform future online learning design as we re-envision the future of online learning.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Bello G, Pennisi MA, Maviglia R, Maggiore SM, Bocci MG, Montini L, et al. Online vs live methods for teaching difficult airway management to anesthesiology residents. Intensive Care Med. 2005; 31 (4): 547–552.
Article Google Scholar
Ruiz JG, Mintzer MJ, Leipzig RM. The impact of e-learning in medical education. Acad Med. 2006; 81(3): 207–12.
Kavadella A, Tsiklakis K, Vougiouklakis G, Lionarakis A. Evaluation of a blended learning course for teaching oral radiology to undergraduate dental students. Eur J Dent Educ. 2012; 16(1): 88–95.
de Jong N, Verstegen DL, Tan FS, O’Connor SJ. A comparison of classroom and online asynchronous problem-based learning for students undertaking statistics training as part of a public health master’s degree. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2013; 18(2):245–64.
Hegeman JS. Using instructor-generated video lectures in online mathematics coursesimproves student learning. Online Learn. 2015;19(3):70–87.
Gaupp R, Körner M, Fabry G. Effects of a case-based interactive e-learning course on knowledge and attitudes about patient safety: a quasi-experimental study with third-year medical students. BMC Med Educ. 2016; 16(1):172.
Zheng M, Bender D, Reid L, Milani J. An interactive online approach to teaching evidence-based dentistry with Web 2.0 technology. J Dent Educ. 2017; 81(8): 995–1003.
Means B, Toyama Y, Murphy R, Bakia M, Jones K. Evaluation of evidence-based practices in online learning: A meta-analysis and review of online learning studies. U.S. Department of Education, Office of Planning, Evaluation and Policy Development. Washington D.C. 2009.
Google Scholar
Pei L, Wu H. Does online learning work better than offline learning in undergraduate medical education? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Med Educ Online. 2019; 24(1):1666538.
Andrews KG, Demps EL. Distance education in the U.S. and Canadian undergraduate dental curriculum. J Dent Educ. 2003; 67(4):427–38.
Kassebaum DK, Hendricson WD, Taft T, Haden NK. The dental curriculum at North American dental institutions in 2002–03: a survey of current structure, recent innovations, and planned changes. J Dent Educ. 2004; 68(9):914–931.
Haden NK, Hendricson WD, Kassebaum DK, Ranney RR, Weinstein G, Anderson EL, et al. Curriculum changes in dental education, 2003–09. J Dent Educ. 2010; 74(5):539–57.
DeBate RD, Cragun D, Severson HH, Shaw T, Christiansen S, Koerber A, et al. Factors for increasing adoption of e-courses among dental and dental hygiene faculty members. J Dent Educ. 2011; 75 (5): 589–597.
Saeed SG, Bain J, Khoo E, Siqueira WL. COVID-19: Finding silver linings for dental education. J Dent Educ. 2020; 84(10):1060–1063.
Schlenz MA, Schmidt A, Wöstmann B, Krämer N, Schulz-Weidner N. Students’ and lecturers’ perspective on the implementation of online learning in dental education due to SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19): a cross-sectional study. BMC Med Educ. 2020;20(1):1–7.
Donn J, Scott JA, Binnie V, Bell A. A pilot of a virtual Objective Structured Clinical Examination in dental education. A response to COVID-19. Eur J Dent Educ. 2020; https://doi.org/10.1111/eje.12624
Hung M, Licari FW, Hon ES, Lauren E, Su S, Birmingham WC, Wadsworth LL, Lassetter JH, Graff TC, Harman W, et al. In an era of uncertainty: impact of COVID-19 on dental education. J Dent Educ. 2020; 85 (2): 148–156.
Sadid-Zadeh R, Wee A, Li R, Somogyi‐Ganss E. Audience and presenter comparison of live web‐based lectures and traditional classroom lectures during the COVID‐19 pandemic. J Prosthodont. 2020. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/jopr.13301
Wang K, Zhang L, Ye L. A nationwide survey of online teaching strategies in dental education in China. J Dent Educ. 2020; 85 (2): 128–134.
Rad FA, Otaki F, Baqain Z, Zary N, Al-Halabi M. Rapid transition to distance learning due to COVID-19: Perceptions of postgraduate dental learners and instructors. PLoS One. 2021; 16(2): e0246584.
Abbasi S, Ayoob T, Malik A, Memon SI. Perceptions of students regarding E-learning during Covid-19 at a private medical college. Pak J Med Sci. 2020; 3 6 : 57–61.
Al-Azzam N, Elsalem L, Gombedza F. A cross-sectional study to determine factors affecting dental and medical students’ preference for virtual learning during the COVID-19 outbreak. Heliyon. 6(12). 2020. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05704
Chen E, Kaczmarek K, Ohyama H. Student perceptions of distance learning strategies during COVID-19. J Dent Educ. 2020. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/jdd.12339
Kaczmarek K, Chen E, Ohyama H. Distance learning in the COVID-19 era: Comparison of student and faculty perceptions. J Dent Educ. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1002/jdd.12469
Sarwar H, Akhtar H, Naeem MM, Khan JA, Waraich K, Shabbir S, et al. Self-reported effectiveness of e-learning classes during COVID-19 pandemic: A nation-wide survey of Pakistani undergraduate dentistry students. Eur J Dent. 2020; 14 (S01): S34-S43.
Al-Taweel FB, Abdulkareem AA, Gul SS, Alshami ML. Evaluation of technology‐based learning by dental students during the pandemic outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019. Eur J Dent Educ. 2021; 25(1): 183–190.
Elangovan S, Mahrous A, Marchini L. Disruptions during a pandemic: Gaps identified and lessons learned. J Dent Educ. 2020; 84 (11): 1270–1274.
Goodenow C. Classroom belonging among early adolescent students: Relationships to motivation and achievement. J Early Adolesc.1993; 13(1): 21–43.
Goodenow C. The psychological sense of school membership among adolescents: Scale development and educational correlates. Psychol Sch. 1993; 30(1): 79–90.
St-Amand J, Girard S, Smith J. Sense of belonging at school: Defining attributes, determinants, and sustaining strategies. IAFOR Journal of Education. 2017; 5(2):105–19.
Peacock S, Cowan J. Promoting sense of belonging in online learning communities of inquiry at accredited courses. Online Learn. 2019; 23(2): 67–81.
Chan GM, Kanneganti A, Yasin N, Ismail-Pratt I, Logan SJ. Well‐being, obstetrics and gynecology and COVID‐19: Leaving no trainee behind. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2020; 60(6): 983–986.
Hodges C, Moore S, Lockee B, Trust T, Bond A. The difference between emergency remote teaching and online learning. Educause Review. 2020; 2 7 , 1–12.
Means B, Bakia M, Murphy R. Learning online: What research tells us about whether, when and how. Routledge. 2014.
Iyer P, Aziz K, Ojcius DM. Impact of COVID-19 on dental education in the United States. J Dent Educ. 2020; 84(6): 718–722.
Machado RA, Bonan PRF, Perez DEDC, Martelli JÚnior H. 2020. COVID-19 pandemic and the impact on dental education: Discussing current and future perspectives. Braz Oral Res. 2020; 34: e083.
Wu DT, Wu KY, Nguyen TT, Tran SD. The impact of COVID-19 on dental education in North America-Where do we go next? Eur J Dent Educ. 2020; 24(4): 825–827.
de Oliveira Araújo FJ, de Lima LSA, Cidade PIM, Nobre CB, Neto MLR. Impact of Sars-Cov-2 and its reverberation in global higher education and mental health. Psychiatry Res. 2020; 288:112977. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2020.112977
Persky AM, Lee E, Schlesselman LS. Perception of learning versus performance as outcome measures of educational research. Am J Pharm Educ. 2020; 8 4 (7): ajpe7782.
Zoom @ . Zoom Video Communications , San Jose, CA, USA. https://zoom.us/
Canvas @ . Instructure, INC. Salt Lake City, UT, USA. https://www.instructure.com/canvas
SoftChalk @ . SoftChalk LLC . San Antonio, TX, USA. https://www.softchalkcloud.com/
Agarwal S, Kaushik JS. Student’s perception of online learning during COVID pandemic. Indian J Pediatr. 2020; 87: 554–554.
Khalil R, Mansour AE, Fadda WA, Almisnid K, Aldamegh M, Al-Nafeesah A, et al. The sudden transition to synchronized online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia: a qualitative study exploring medical students’ perspectives. BMC Med Educ. 2020; 20(1): 1–10.
Riley E, Capps N, Ward N, McCormack L, Staley J. Maintaining academic performance and student satisfaction during the remote transition of a nursing obstetrics course to online instruction. Online Learn. 2021; 25(1), 220–229.
Amir LR, Tanti I, Maharani DA, Wimardhani YS, Julia V, Sulijaya B, et al. Student perspective of classroom and distance learning during COVID-19 pandemic in the undergraduate dental study program Universitas Indonesia. BMC Med Educ. 2020; 20(1):1–8.
Dost S, Hossain A, Shehab M, Abdelwahed A, Al-Nusair L. Perceptions of medical students towards online teaching during the COVID-19 pandemic: a national cross-sectional survey of 2721 UK medical students. BMJ Open. 2020; 10(11).
Graham CR, Woodfield W, Harrison JB. A framework for institutional adoption and implementation of blended learning in higher education. Internet High Educ. 2013; 18 : 4–14.
Sing C, Khine M. An analysis of interaction and participation patterns in online community. J Educ Techno Soc. 2006; 9(1): 250–261.
Bernard RM, Abrami PC, Borokhovski E, Wade CA, Tamim RM, Surkes MA, et al. A meta-analysis of three types of interaction treatments in distance education. Rev Educ Res. 2009; 79(3): 1243–1289.
Fedynich L, Bradley KS, Bradley J. Graduate students’ perceptions of online learning. Res High Educ. 2015; 27.
Tanis CJ. The seven principles of online learning: Feedback from faculty and alumni on its importance for teaching and learning. Res Learn Technol. 2020; 28 . https://doi.org/10.25304/rlt.v28.2319
Dixson MD. Measuring student engagement in the online course: The Online Student Engagement scale (OSE). Online Learn. 2015; 19 (4).
Kwary DA, Fauzie S. Students’ achievement and opinions on the implementation of e-learning for phonetics and phonology lectures at Airlangga University. Educ Pesqui. 2018; 44 .
Vygotsky LS. Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes. Cambridge (MA): Harvard University Press. 1978.
Kahoot! @ . Oslo, Norway. https://kahoot.com/
Davis J, Chryssafidou E, Zamora J, Davies D, Khan K, Coomarasamy A. Computer-based teaching is as good as face to face lecture-based teaching of evidence-based medicine: a randomised controlled trial. BMC Med Educ. 2007; 7(1): 1–6.
Davis J, Crabb S, Rogers E, Zamora J, Khan K. Computer-based teaching is as good as face to face lecture-based teaching of evidence-based medicine: a randomized controlled trial. Med Teach. 2008; 30(3): 302–307.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Authors’ information
MZ is an Associate Professor of Learning Sciences and Senior Instructional Designer at School of Dentistry, University of the Pacific. She has a PhD in Education, with a specialty on learning sciences and technology. She has dedicated her entire career to conducting research on online learning, learning technology, and faculty development. Her research has resulted in several peer-reviewed publications in medical, dental, and educational technology journals. MZ has also presented regularly at national conferences.
DB is an Assistant Dean for Academic Affairs at School of Dentistry, University of the Pacific. He has an EdD degree in education, with a concentration on learning and instruction. Over the past decades, DB has been overseeing and delivering faculty pedagogical development programs to dental faculty. His research interest lies in educational leadership and instructional innovation. DB has co-authored several peer-reviewed publications in health sciences education and presented regularly at national conferences.
CL is Associate Dean of Oral Healthcare Education, School of Dentistry, University of the Pacific. She has a Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) degree and an EdD degree with a focus on educational leadership. Her professional interest lies in educational leadership, oral healthcare education innovation, and faculty development. CL has co-authored several publications in peer-reviewed journals in health sciences education and presented regularly at national conferences.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Office of Academic Affairs, Arthur A. Dugoni School of Dentistry, University of the Pacific, CA, San Francisco, USA
Meixun Zheng, Daniel Bender & Cindy Lyon
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
MZ analyzed the data and wrote the initial draft of the manuscript. DB and CL both provided assistance with research design, data collection, and reviewed and edited the manuscript. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Meixun Zheng .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study was approved by the institutional review board at University of the Pacific in the U.S. (#2020-68). Informed consent was obtained from all participants. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1:.
Survey of online courses during COVID-19 pandemic.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Zheng, M., Bender, D. & Lyon, C. Online learning during COVID-19 produced equivalent or better student course performance as compared with pre-pandemic: empirical evidence from a school-wide comparative study. BMC Med Educ 21 , 495 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-021-02909-z
Download citation
Received : 31 March 2021
Accepted : 26 August 2021
Published : 16 September 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-021-02909-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Dental education
- Online learning
- COVID-19 pandemic
- Instructional strategies
- Interaction
- Learning performance
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH METHODS IN ONLINE BUSINESS EDUCATION: A DISCIPLINARY REVIEW AND COMPARISON

This paper provides an assessment of methodological development of online and blended learning research in each of the primary business disciplines. We present a summary of variables examined and quantitative analytical techniques used by discipline and in multi-disciplinary studies from 157 articles in refereed journals published from 2000 through 2010. We found widely varying research activity and methodological variety across disciplines, with most of the studies published using samples from information systems, management, or multi-disciplinary settings. However, a discipline’s number of studies and methodological rigor were not necessarily correlated. For example, although a relatively small number of studies of economics courses were published, this discipline was comparatively innovative in their selection and operationalization of variables of interest. The paper concludes with recommendations both by discipline and collectively for improving this emerging stream’s research quality, with particular emphasis on how each of the disciplines might incorporate more of their native analytical tools and techniques into conducting research on online teaching and learning.
Related Papers
Ben Arbaugh
In this literature review, we examine and assess the state of research of online and blended learning in the business disciplines with the intent of assessing the state of the field and identifying opportunities for meaningful future research. We review research from business disciplines such as Accounting, Economics, Finance, Information Systems (IS), Management, Marketing, and Operations/Supply Chain Management. We found the volume and quality of research in online and blended business education has increased dramatically during the past decade. However, the rate of progress is somewhat uneven across disciplines. IS, Management, and multi-disciplinary studies have the highest volumes of research activity, with markedly less activity in Finance and Economics. Furthermore, scholars of online and blended business education predominantly publish in learning and education journals of the business disciplines rather than also publishing in journals that focus on technology-mediated learning, thereby missing an opportunity to inform scholars in other disciplines about their work. The most common research streams across disciplines were outcome comparison studies with classroom-based learning and studies examining potential predictors of course outcomes. Results from the comparison studies suggest generally that online courses are at least comparable to classroom-based courses in achieving desired learning outcomes, while there is divergence in findings of comparisons of other course aspects. Collectively, the range of untested conceptual frameworks, the lack of discipline-specific theories, and the relative absence of a critical mass of researchers focused on the topic suggest ample opportunities for business scholars seeking to enter this research community.
The Internet and Higher Education
Marianne Johnson , Bruce Niendorf , Ben Arbaugh
Prof. Sanjay Verma
The growth of online education has become a global phenomenon driven by emergence of new technologies, widespread adoption of the Internet, and intensifying demand for a skilled workforce for a digital economy. Online education is no longer a trend; it is slowly but surely becoming mainstream by 2025. This paper explores all efforts, accomplishments, issues, challenges, conclusions, and recommendations on this theme through meta-analysis of over 100 published papers since 2000. Through thorough content analysis, we provide useful recommendations for researchers and practitioners working in academia, industry, or government. We also propose a holistic model of interactions between diverse entities and stakeholders in the online tertiary business discipline education industry. This model will certainly be applicable with minor changes to other disciplines and other levels of education—primary and secondary. This model can be tested in piecemeal fashion by researchers using appropriate...
The International Journal of Management Education
Shailendra Palvia
Ben Arbaugh , Ashay Desai
This paper reviews studies of online and blended learning in management-oriented disciplines and management-related topics. The review shows that over the last decade, this emerging field has seen dramatic conceptual, methodological, and analytical advances. However, these advances have progressed within the particular disciplines at uneven rates. Studies examining courses in Organizational Behavior and Strategic Management have seen the most progress, with courses in Human Resources, Operations Management, and International Management receiving lesser attention. To date, studies of courses in Entrepreneurship are next to non-existent. Our review suggests that although several multi-course studies have been published, there is ample opportunity for research within the respective management disciplines. We also suggest topics and methodological issues requiring further study, including stronger delineations between online and blended management education; further examination of participant characteristics, particularly for instructors; and the influence of institutions located outside North America.
Ben Arbaugh , Alvin Hwang
This manuscript reviews and compares the use of multivariate statistical techniques in 85 studies of online and blended management education over the last decade relative to prescriptions for their use offered by both the organization studies and educational research communities. Although there is variation in the degree to which appropriate uses of the techniques have been employed, they appear to have been accepted and adopted at a much faster rate than typically is the case in organizational studies research. In fact, the nature of research samples to date indicates that the recent introduction of HLM techniques to this research stream may be premature. Other recommendations that emerge from the review include greater consideration of moderating effects, particularly of those that historically have been considered “control” variables, and reducing dependence upon EFA techniques for data reduction except when examining conceptual frameworks comprised of constructs borrowed from disparate fields. It is our hope that this review motivates further consideration of appropriate uses of these techniques in other areas of management education research.
Diane Fulton
The purpose of this research is to analyze the optimal pedagogical tools and methods for teaching quantitative disciplines in the newest delivery modes of blended and online education. This study will focus on a comprehensive literature review of quantitative disciplines in business and related areas. Which pedagogies are the same and which are different based on discipline? Practices, tools and approaches that are used and deemed effective in online learning will be overviewed and analyzed across disciplines in this exploratory research. The top rated skills and competencies for each quantitative discipline will be reviewed and summarized for similarities and differences. From this preliminary research, specific research proposals will be recommended for future research on quantitative discipline-specific best practices in the blended/online delivery of such courses.
Dr. Qaisar Abbas
Qaisar Abbas
Online education and its methods have been challenged by researchers since its widespread adoption. Over the past few decades, technology, globalization, and business model innovation have transformed business. Objectives of the study were to assess the effects of online learning on the performance of business students, explore the challenges that hinder online learning of business students and to provide strategies to improve online learning of business students. This study may help online course developers and teachers conceive, develop, and deploy online learning methods. Support staff who help establish curriculum, support services, and professional development may benefit from developing ways to satisfy students' requirements. There was a quantitative analysis carried out. The study used a survey to collect data, and its design was descriptive in nature. A survey consisting close ended questions related to various study variables were administered to a sample of 250 business students of Private universities in Islamabad Pakistan. Data collection was done through personal visits of the researcher. To evaluate the data, descriptive statistics are used, such as the mean, standard deviation and T-test. Study found the positive perceptions of academic performance and skills development which suggest that online learning can effectively contribute to students' educational outcomes. Furthermore, study identified challenges, such as technical issues and motivational barriers, underscore the need for targeted interventions to improve the online learning experience. Fostering interactive online content is recommended by the study, as it correlates positively with critical thinking and collaboration, key skills that contribute to academic success.
Journal of Eastern European and Central Asian research
Madina Duchshanova
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
College Teaching Methods & Styles Journal (CTMS)
Storm Russo
American Journal of Business Education (AJBE)
Harold Thiewes
Interactive Technology and Smart Education
Stewart Adam
The BRC Academy Journal of Business
Coral Snodgrass
Academia Letters
Dr. Milan Frankl
e-Service Journal
PATEL Taran
Alison Sheridan
International Journal of Education and Development using ICT
Balraj Kistow
Sarfraz sarfraz hussain
Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching
Christopher W. Harris
Lori Willoughby
Dorina Tila
The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning
John Grandzol
International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies (iJIM)
FAREED AWAE 15755
European Journal of Open, Distance and E-Learning
Anneleen Cosemans
The BRC academy journal of business
Manfred Borovcnik
International Journal on Integrating Technology in Education
GODFRED KOI-AKROFI
International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education (IJERE)
Kholid Haryono
Canadian Journal of Learning and Technology / La revue canadienne de l’apprentissage et de la technologie
Tess Miller
Journal of Systems and Information Technology
Brychan Thomas , Paul Jones , Amanda Jones , Gary Packham
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
Model for designing gamified experiences mediated by a virtual teaching and learning environment.

1. Introduction
2. background and related work in evea, 3. methodology, 4. mgtp model, 5. expert judgment as a first validation of the model, 5.1. application of expert judgment, 5.2. results and discussion, 6. conclusions, supplementary materials, author contributions, institutional review board statement, informed consent statement, data availability statement, acknowledgments, conflicts of interest.
- Merellano-Navarro, E.; Almonacid-Fierro, A.; Moreno-Doña, A.; Castro-Jaque, C. Buenos docentes universitarios: ¿Qué dicen los estudiantes? Educ. Pesqui. 2016 , 42 , 937–952. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Contreras, R.; Eguia, J.L. (Eds.) Gamificación en las Aulas Universitarias ; Instituto de la Comunicació Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain, 2016. [ Google Scholar ]
- Khaldi, A.; Bouzidi, R.; Nader, F. Gamification of e-learning in higher education: A systematic literature review. Smart Learn. Environ. 2023 , 10 , 10. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Cabalín, D.; Navarro, N.; Zamora, J.; Martín, S.S. Concepción de Estudiantes y Docentes del Buen Profesor Universitario: Facultad de Medicina de la Universidad de La Frontera. Int. J. Morphol. 2010 , 28 , 283–290. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Saleem, A.N.; Noori, N.M.; Ozdamli, F. Gamification Applications in E-learning: A Literature Review. Technol. Knowl. Learn. 2022 , 27 , 139–159. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kalogiannakis, M.; Papadakis, S.; Zourmpakis, A.I. Gamification in science education. A systematic review of the literature. Educ. Sci. 2021 , 11 , 22. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tuparov, G.; Keremedchiev, D.; Tuparova, D.; Stoyanova, M. Gamification and educational computer games in open-source learning management systems as a part of assessment. In Proceedings of the 2018 17th International Conference on Information Technology Based Higher Education and Training (ITHET), Olhao, Portugal, 26–28 April 2018; pp. 1–5. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Aguilos, V.; Fuchs, K. The Perceived Usefulness of Gamified E-Learning: A Study of Undergraduate Students with Implications for Higher Education. Front. Educ. 2022 , 7 , 945536. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ramírez-Montoya, M.S.; Valenzuela, J.R. Innovación Educativa: Tendencias Globales de Investigación e Implicaciones Prácticas ; Octaedro Publisher: Barcelona, Spain, 2019. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zahedi, L.; Batten, J.; Ross, M.; Potvin, G.; Damas, S.; Clarke, P.; Davis, D. Gamification in education: A mixed-methods study of gender on computer science students’ academic performance and identity development. J. Comput. High. Educ. 2021 , 33 , 441–474. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Deterding, S.; Dixon, D.; Khaled, R.; Nacke, L. From Game Design Elements to Gamefulness: Defining ‘Gamification’. In Proceedings of the MindTrek ’11 Proceedings of the 15th International Academic MindTrek Conference: Envisioning Future Media Environments, Tampere, Finland, 28–30 September 2011; pp. 28–30. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chans, G.M.; Castro, M.P. Gamification as a strategy to increase motivation and engagement in higher education chemistry students. Computers 2021 , 10 , 132. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Teixes, F. Gamificación: Fundamentos y Aplicaciones , 1st ed.; UOC: Barcelona, Spain, 2014. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hunicke, R.; LeBlanc, M.; Zubek, R. MDA: A Formal Approach to Game Design and Game Research. Proc. AAAI Workshop Chall. Game AI 2004 , 4 , 1722. [ Google Scholar ]
- Werbach, K.; Hunter, D. How Game Thinking Can Revolutionize Your Business ; Wharton Digital Press: Philadepphia, PA, USA, 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pomata, J.; Díaz, J. TIC y Gamificación en la Enseñanza de Español como Lengua Extranjera: Situación y Líneas de Actuación para las Universidades Japonesas. Cuadernos CANELA: Revista anual de Literatura, Pensamiento e Historia, Metodología de la Enseñanza del Español como Lengua Extranjera y Lingüística de la Confederación Académica Nipona, Española y Latinoamericana. 2017, pp. 79–101. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326698094_TIC_y_gamificacion_en_la_ensenanza_de_espanol_como_lengua_extranjera_situacion_y_lineas_de_actuacion_para_las_universidades_japonesas (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Teixes, F. Gamificación: Motivar Jugando ; Primera ed.; UOC: Barcelona, Spain, 2015. [ Google Scholar ]
- Garrison, R.; Anderson, T.; Archer, W. Critical inquiry in a text-based environment. Comput. Conf. High. Educ. 2000 , 16 , 6–12. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pardo, A.S. Formalización de un modelo de formación online basado en el factor humano y la presencia docente mediante un lenguaje de patrón. In Doctorado Formación en la Sociedad del Conocimiento ; Universidad de Salamanca: Salamanca, Spain, 2014. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mese, C.; Dursun, O.O. Effectiveness of gamification elements in blended learning environments. Turk. Online J. Distance Educ. 2019 , 20 , 119–142. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Papanikolaou, K.; Tzelepi, M.; Moundridou, M.; Petroulis, I. Employing Social Network Analysis to enhance community learning. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2020 , 12149 , 342–352. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tzelepi, M.; Makri, K.; Petroulis, I.; Moundridou, M.; Papanikolaou, K. Gamification in online discussions: How do game elements affect critical thinking? In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 20th International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT), Tartu, Estonia, 6–9 July 2020; pp. 92–94. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Antonaci, A.; Klemke, R.; Lataster, J.; Kreijns, K.; Specht, M. Gamification of MOOCs Adopting Social Presence and Sense of Community to Increase User’s Engagement: An Experimental Study. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Technology Enhanced Learning, Delft, The Netherlands, 16–19 September 2019; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11722. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Petroulis, I.; Tzelepi, M.; Papanikolaou, K. On the design of Gamification Elements in Moodle Courses. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference, GALA 2019, Athens, Greece, 27–29 November 2019; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11899. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Utomo, A.Y.; Santoso, H.B. Development of gamification-enriched pedagogical agent for e-learning system based on community of inquiry. In Proceedings of the CHIuXiD ’15: Proceedings of the International HCI and UX Conference in Indonesia, Bandung, Indonesia, 8–10 April 2015; pp. 1–9. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Utomo, A.Y.; Amriani, A.; Aji, A.F.; Wahidah, F.R.N.; Junus, K.M. Gamified E-learning Model Based on Community of Inquiry. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Advanced Computer Science and Information System, Jakarta, Indonesia, 18–19 October 2014; pp. 474–480. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Vera-Mora, G.; Sanz, C.; Baldassarri, S.; Coma, T. Entornos virtuales de enseñanza y aprendizaje gamificados a la luz del concepto de presencia: Revisión sistemática de literatura. Rev. Iberoam. Tecnol. Educ. Educ. Tecnol. 2023 , 33 , 25–35. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tzelepi, M.; Petroulis, I.; Papanikolaou, K. Investigating gamification and learning analytics tools for promoting and measuring communities of inquiry in moodle courses. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2020 , 1007 , 89–96. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pla, R. Una Concepción de la Pedagogía como Ciencia Desde el Enfoque Histórico Cultural. Material en Soporte Digital, Centro de Estudios e Investigación “José Martí”. UCP “Manuel Ascunce Domenech”. Ciego de Ávila. Estudio Sobre el discurso II. 2010, p. 79. Available online: https://profesorailianartiles.files.wordpress.com/2013/03/libro-de-pedagogc3ada.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Medrano, J. Universidad de Ingeniería y Tecnología—UTEC. Febrero. Available online: https://utec.edu.pe/ (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Garrison, D.; Anderson, T. El e-Learning en el Siglo XXI. Investigación Práctica , 1st ed.; Octaedro Publisher: Barcelona, Spain, 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Garrison, D.; Anderson, T.; Archer, W. Critical thinking, cognitive presence, and computer conferencing in distance education. Am. J. Distance 2001 , 15 , 7–23. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Alenezi, M. Digital Learning and Digital Institution in Higher Education. Educ. Sci. 2023 , 13 , 88. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- von Bertalanffy, L. General System Theory ; George Braziller, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [ Google Scholar ]
- Maslow, A.H. Motivation and Personality ; Harper & Row: New York, NY, USA, 1954. [ Google Scholar ]
- Leontev, A.N. Activity, Consciousness, and Personality ; Prentice-Hall Publisher: London, UK, 1978. [ Google Scholar ]
- Foncubierta, J.; Chema, R. Didáctica de la gamificación en la clase de español. Edinumen 2014 , 1–8. Available online: http://eleinternacional.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/Didactica_Gamificacion_ELE.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Richardson, J.C.; Cleveland-Innes, M.; Ice, P.; Swan, K.P.; Garrison, D.R. Using the Community of Inquiry Framework to Inform Effective Instructional Design. In The Next Generation of Distance Education: Unconstrained Learning ; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 1–266. ISBN 978-1-4614-1785-9. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tzavara, A.; Lavidas, K.; Komis, V.; Misirli, A.; Karalis, T.; Papadakis, S. Using Personal Learning Environments before, during and after the Pandemic: The Case of ‘e-Me’. Educ. Sci. 2023 , 13 , 87. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hernández-Nieto, R. Instrumentos de Recolección de Datos en Ciencias Sociales y Ciencias Biomédicas: Validez y Confiabilidad. In Diseño y Construcción ; Normas y Formatos: Mérida, Venezuela, 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cabero, J.; Llorente, M.d.C. La Aplicación del Juicio de Experto como Técnica de Evaluación de las Tecnologías de la Información y Comunicación (TIC) The expert’s judgment application as a technic evaluate Information and Communication Technology (ICT). Eduweb. Rev. Tecnol. Inf. Comun. Educ. 2013 , 7 , 11–22. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cabero, J.; Barroso, J. La utilización del juicio de experto para la evaluación de TIC: El coeficiente de competencia experta. Bordon. Rev. Pedagog. 2013 , 65 , 25–38. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Escobar-Pérez, J.; Cuervo-Martínez, Á. Validez de contenido y juicio de expertos: Una aproximación a su utilización. Av. Medición 2008 , 6 , 27–36. [ Google Scholar ]
- García, L.; Fernández, S.J. Procedimiento de aplicación del trabajo creativo en grupo de expertos. Ing. Energ. 2008 , 29 , 46–50. (In Spanish) [ Google Scholar ]
- Vygotskiĭ, L.S.; Kozulin, A. Thought and Language ; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986. [ Google Scholar ]
- Valencia-Arias, A.; Cartagena Rendón, C.; Palacios-Moya, L.; Benjumea-Arias, M.; Pelaez Cavero, J.B.; Moreno-López, G.; Gallegos-Ruiz, A.L. Model Proposal for Service Quality Assessment of Higher Education: Evidence from a Developing Country. Educ. Sci. 2023 , 13 , 83. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gutiérrez-Castillo, J.J.; Palacios-Rodríguez, A.; Martín-Párraga, L.; Serrano-Hidalgo, M. Development of Digital Teaching Competence: Pilot Experience and Validation through Expert Judgment. Educ. Sci. 2023 , 13 , 52. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Available online: https://www.revistadepedagogia.org/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=3452&context=rep (accessed on 10 March 2024).
Click here to enlarge figure
| Steps | Description |
|---|---|
| Technological–Pedagogical Gamification Model for a Virtual Teaching and Learning Environment (MGTP). | |
| Validate the content and reliability of the MGTP through the measurement instrument. | |
| Content Validity Coefficient (CVC) by Hernandez-Nieto [ ] | |
| Selection of experts in EVEA Pedagogy and Gamification through the biogram and Knowledge Quotient. | |
| The instrument consisted of four sections: . Analysis of Subsystem I . Analysis of Subsystem II . Analysis of Subsystem III . Opinion on the Adequacy of the MGTP | |
| Communication process and methodological follow-up of the expert judgment developed. | |
| E-mail sent to the experts for the development of the validation process by expert judgment. | |
| Communication process and methodological follow-up of the expert judgment developed. | |
| Procedure to calculate the CVC for each of the items and the general instrument and interpretation of the CVC, based on the scale of values established by Hernandez-Nieto [ ]. | |
| Verification of the concordance of the items for elimination, modification or approval. Review of considerations on comments or improvements suggested by experts. | |
| Procedure to calculate the reliability of the results obtained from the pilot test by means of a Cronbach’s Alpha Coefficient and a Test of Two Halves. | |
| Once the application and analysis of the results obtained have been completed, the experts are informed of the entire process. |
| The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
Share and Cite
Vera-Mora, G.; Sanz, C.V.; Coma-Roselló, T.; Baldassarri, S. Model for Designing Gamified Experiences Mediated by a Virtual Teaching and Learning Environment. Educ. Sci. 2024 , 14 , 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14080907
Vera-Mora G, Sanz CV, Coma-Roselló T, Baldassarri S. Model for Designing Gamified Experiences Mediated by a Virtual Teaching and Learning Environment. Education Sciences . 2024; 14(8):907. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14080907
Vera-Mora, Glenda, Cecilia V. Sanz, Teresa Coma-Roselló, and Sandra Baldassarri. 2024. "Model for Designing Gamified Experiences Mediated by a Virtual Teaching and Learning Environment" Education Sciences 14, no. 8: 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14080907
Article Metrics
Article access statistics, supplementary material.
ZIP-Document (ZIP, 1626 KiB)
Further Information
Mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals

IMAGES
COMMENTS
experienced an average decrease of 11.5 hours of work per week and a 21% decrease in weekly earnings, arnings for 52% of the sample, which again re ects s. variation in the e ects of COVID-19 across students. In terms of labor market expectations, on average, students foresee a 13 percentage points decrease in.
Online and face-to-face learning have been studied widely. Researchers had found that for online students they are usually older, have full or part-time work, requires commuting to the campus, have family obligations and have taken online courses before. Cleveland, Dutcher & Epps (2015) explained in their study that "online students
PDF | On Jan 1, 2009, Daniel Chen published Engaging online learners: A quantitative study of postsecondary student engagement in the online learning environment | Find, read and cite all the ...
OPEN ACCESS Research Article Gamification, Online Learning and Motivation: A Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis in Higher Education Milagros Torrado Cespón 1* 0000-0002-3213-8405 José María Díaz Lage 2 0000-0003-1865-3168 1 Universidad Internacional de La Rioja, La Rioja, SPAIN 2 Universidad Nacional de Educación a Distancia, Madrid, SPAIN
Distance learning has evolved over many generations into its newest form of what we commonly label as online learning. In this second-order meta-analysis, we analyze 19 first-order meta-analyses to examine the impact of distance learning and the special case of online learning on students' cognitive, affective and behavioral outcomes.
Quantitative research methods have undergone an online evolution both in content, in the data collected, but also in methodology and tools. The article is a scoping review that aims to trace the ...
Research examining the effectiveness of e-Learning has increased in recent years. This is primarily due to the increased possibilities for IT and learning as well as increased political and organisational attention to 'what works' in learning. Figure 1a shows the 761 papers relevant to this research, and Figure 1b shows 111
The relationship between learning strategies and academic success has been widely reported in the literature. The nature of student learning and the strategies students draw on when studying are ongoing areas of research for higher education institutions because 'equipping students with effective study strategies is vital to their educational success' (Miyatsu et al., 2018, p. 390).
This systematic analysis examines effectiveness research on online and blended learning from schools, particularly relevant during the Covid-19 pandemic, and also educational games, computer-supported cooperative learning (CSCL) and computer-assisted instruction (CAI), largely used in schools but with potential for outside school.
Tallent-Runnels et al. (2006) reviewed research late 1990's to early 2000's, Berge and Mrozowski (2001) reviewed research 1990 to 1999, and Zawacki-Richter et al. (2009) reviewed research in 2000-2008 on distance education and online learning. Table 1 shows the research themes from previous systematic reviews on online learning research.
Yi Yang Linda F. Cornelius Mississippi State University. Abstract. How to ensure the quality of online learning in institutions of higher education has been a growing concern during the past several years. While several studies have focused on the perceptions of faculty and administrators, there has been a paucity of research conducted on ...
10 years, research studies have expanded to include variations of online education. These include strictly online, hybrid courses, Web-assisted classroom settings, and the traditional higher education course offered only as face-to-face instruction (Carmel & Gold, 2007). Online education continues to proliferate at the same time the number of
Abstract This quantitative study aims to investigate the relationship between e-. education and reading comprehension skills acquisition. It also examines if the. previous relationship may impact ...
This quantitative study aims to investigate the relationship between e-education and reading comprehension skills acquisition. It also examines if the previous relationship may impact students' results in the exams. It also analyses the relationship between students' knowledge in ICT and their perception and acceptance of online education.
online classes could affect the academic performance of students. This paper seeks to study the. impact of online learning on the academic performance of university students and to determine. whether education systems should increase the amount of online learning for traditional in-class. subjects.
The aim of the study is to identify the factors affecting students' satisfaction and performance regarding online classes during the pandemic period of COVID-19 and to establish the relationship between these variables. The study is quantitative in nature, and the data were collected from 544 respondents through online survey who were studying the business management (B.B.A or M.B.A) or ...
Researchers wishing to request an accessible version of this PDF may complete this form. Recommended Citation Minkkinen, Mariah, "A Quantitative Study of an Online Learning Platform's Impact on High School Students' Engagement, Academic Achievement, and Student Satisfaction in a Mathematics Class" (2022). Dissertations, Theses, and Projects. 674.
Research across disciplines has demonstrated that well-designed online learning can lead to students' enhanced motivation, satisfaction, and learning [1,2,3,4,5,6,7].]. A report by the U.S. Department of Education [], based on examinations of comparative studies of online and face-to-face versions of the same course from 1996 to 2008, concluded that online learning could produce learning ...
the needs and learning styles of individual learners and instructional design. The 21st century has seen rapid pro-gress with such things as the Internet and online learning. The increased use of e-learning among educational in-stitutions has led to a change in higher education. Accord-ing to findings, there has been a rise of about 12-14 per-
sense of online learning. The altered learning environments created by web-based technologies, not only. eliminate barriers of time, space and arguably l earning styles, providing increased access ...
This paper provides an assessment of methodological development of online and blended learning research in each of the primary business disciplines. We present a summary of variables examined and quantitative analytical techniques used by discipline ... This paper reviews studies of online and blended learning in management-oriented disciplines ...
This research was a quantitative study using 4th grade participants from a Title 1 elementary school in Central Illinois. This study set out to determine whether one to one technology (1:1 ... learning in the classroom. The school district is working closely with local business for this 1:1 initiative to be district-wide in the near future. Due ...
The purpose of this study was to research the influence of professional learning communities (PLC) as perceived by New Jersey State-certified educators in three specific areas: content, process, and context of the reform's implementation. Perceptions of content are categorized within three areas: learning communities,
Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) face new challenges in regard to technological development in light of necessary pedagogical and didactic innovations in educational action. This article proposes a Technological-Pedagogical Gamification Model (MGTP) that guides the design of gamified educational practices in Virtual Teaching and Learning Environments (EVEAs). The MGTP proposal is based ...
learning, online learning experience s is also fitting to include as one of its aspects (Alia & Maqableh, 2021). Additionally, the im pacts of the learning experiences of the students could be