
25 Thesis Statement Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
A thesis statement is needed in an essay or dissertation . There are multiple types of thesis statements – but generally we can divide them into expository and argumentative. An expository statement is a statement of fact (common in expository essays and process essays) while an argumentative statement is a statement of opinion (common in argumentative essays and dissertations). Below are examples of each.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples

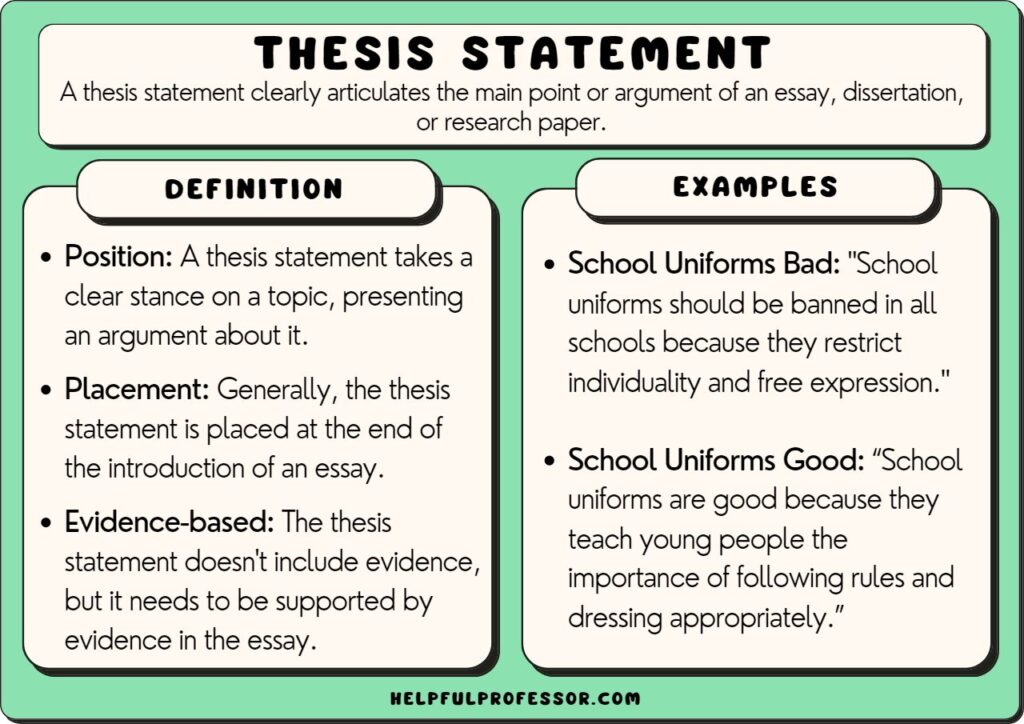
1. School Uniforms
“Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate
Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons

2. Nature vs Nurture
“This essay will explore how both genetic inheritance and environmental factors equally contribute to shaping human behavior and personality.”
Best For: Compare and Contrast Essay
Read More: Nature vs Nurture Debate

3. American Dream
“The American Dream, a symbol of opportunity and success, is increasingly elusive in today’s socio-economic landscape, revealing deeper inequalities in society.”
Best For: Persuasive Essay
Read More: What is the American Dream?

4. Social Media
“Social media has revolutionized communication and societal interactions, but it also presents significant challenges related to privacy, mental health, and misinformation.”
Best For: Expository Essay
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Social Media

5. Globalization
“Globalization has created a world more interconnected than ever before, yet it also amplifies economic disparities and cultural homogenization.”
Read More: Globalization Pros and Cons

6. Urbanization
“Urbanization drives economic growth and social development, but it also poses unique challenges in sustainability and quality of life.”
Read More: Learn about Urbanization

7. Immigration
“Immigration enriches receiving countries culturally and economically, outweighing any perceived social or economic burdens.”
Read More: Immigration Pros and Cons

8. Cultural Identity
“In a globalized world, maintaining distinct cultural identities is crucial for preserving cultural diversity and fostering global understanding, despite the challenges of assimilation and homogenization.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay
Read More: Learn about Cultural Identity

9. Technology
“Medical technologies in care institutions in Toronto has increased subjcetive outcomes for patients with chronic pain.”
Best For: Research Paper

10. Capitalism vs Socialism
“The debate between capitalism and socialism centers on balancing economic freedom and inequality, each presenting distinct approaches to resource distribution and social welfare.”

11. Cultural Heritage
“The preservation of cultural heritage is essential, not only for cultural identity but also for educating future generations, outweighing the arguments for modernization and commercialization.”
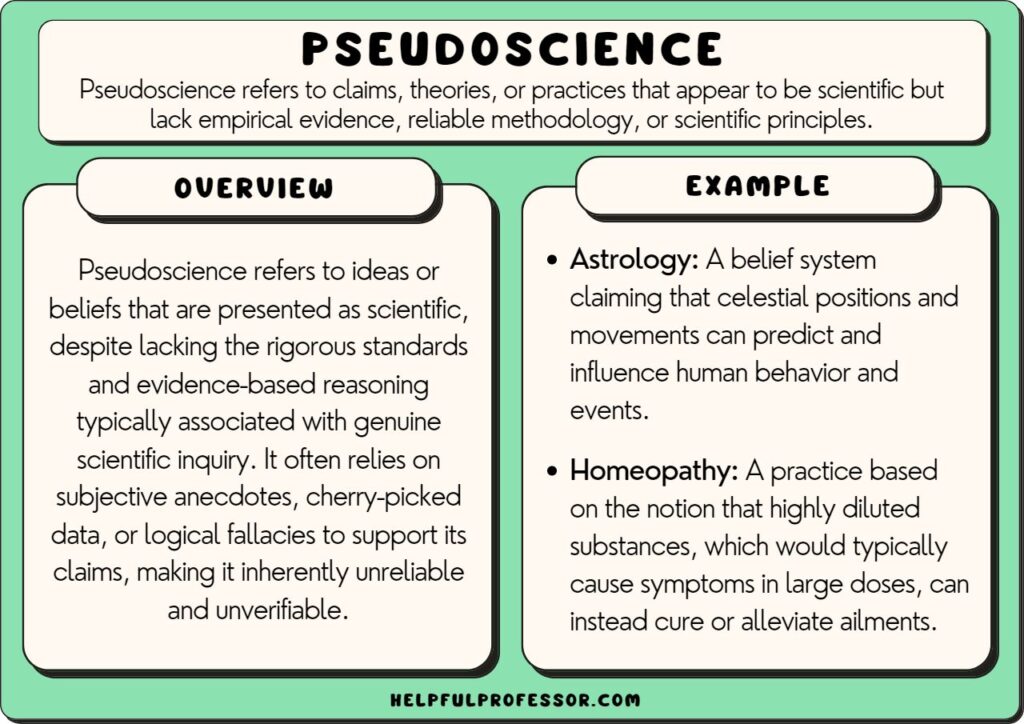
12. Pseudoscience
“Pseudoscience, characterized by a lack of empirical support, continues to influence public perception and decision-making, often at the expense of scientific credibility.”
Read More: Examples of Pseudoscience

13. Free Will
“The concept of free will is largely an illusion, with human behavior and decisions predominantly determined by biological and environmental factors.”
Read More: Do we have Free Will?

14. Gender Roles
“Traditional gender roles are outdated and harmful, restricting individual freedoms and perpetuating gender inequalities in modern society.”
Read More: What are Traditional Gender Roles?

15. Work-Life Ballance
“The trend to online and distance work in the 2020s led to improved subjective feelings of work-life balance but simultaneously increased self-reported loneliness.”
Read More: Work-Life Balance Examples
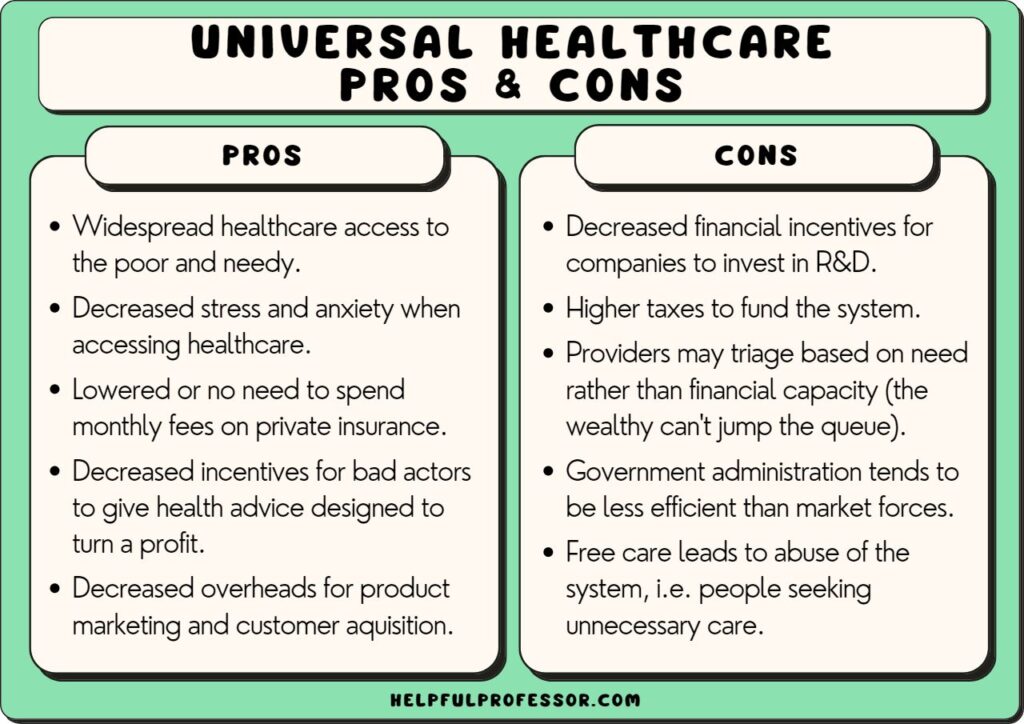
16. Universal Healthcare
“Universal healthcare is a fundamental human right and the most effective system for ensuring health equity and societal well-being, outweighing concerns about government involvement and costs.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Universal Healthcare

17. Minimum Wage
“The implementation of a fair minimum wage is vital for reducing economic inequality, yet it is often contentious due to its potential impact on businesses and employment rates.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Raising the Minimum Wage

18. Homework
“The homework provided throughout this semester has enabled me to achieve greater self-reflection, identify gaps in my knowledge, and reinforce those gaps through spaced repetition.”
Best For: Reflective Essay
Read More: Reasons Homework Should be Banned

19. Charter Schools
“Charter schools offer alternatives to traditional public education, promising innovation and choice but also raising questions about accountability and educational equity.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Charter Schools

20. Effects of the Internet
“The Internet has drastically reshaped human communication, access to information, and societal dynamics, generally with a net positive effect on society.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of the Internet

21. Affirmative Action
“Affirmative action is essential for rectifying historical injustices and achieving true meritocracy in education and employment, contrary to claims of reverse discrimination.”
Best For: Essay
Read More: Affirmative Action Pros and Cons

22. Soft Skills
“Soft skills, such as communication and empathy, are increasingly recognized as essential for success in the modern workforce, and therefore should be a strong focus at school and university level.”
Read More: Soft Skills Examples

23. Moral Panic
“Moral panic, often fueled by media and cultural anxieties, can lead to exaggerated societal responses that sometimes overlook rational analysis and evidence.”
Read More: Moral Panic Examples

24. Freedom of the Press
“Freedom of the press is critical for democracy and informed citizenship, yet it faces challenges from censorship, media bias, and the proliferation of misinformation.”
Read More: Freedom of the Press Examples

25. Mass Media
“Mass media shapes public opinion and cultural norms, but its concentration of ownership and commercial interests raise concerns about bias and the quality of information.”
Best For: Critical Analysis
Read More: Mass Media Examples
Checklist: How to use your Thesis Statement
✅ Position: If your statement is for an argumentative or persuasive essay, or a dissertation, ensure it takes a clear stance on the topic. ✅ Specificity: It addresses a specific aspect of the topic, providing focus for the essay. ✅ Conciseness: Typically, a thesis statement is one to two sentences long. It should be concise, clear, and easily identifiable. ✅ Direction: The thesis statement guides the direction of the essay, providing a roadmap for the argument, narrative, or explanation. ✅ Evidence-based: While the thesis statement itself doesn’t include evidence, it sets up an argument that can be supported with evidence in the body of the essay. ✅ Placement: Generally, the thesis statement is placed at the end of the introduction of an essay.
Try These AI Prompts – Thesis Statement Generator!
One way to brainstorm thesis statements is to get AI to brainstorm some for you! Try this AI prompt:
💡 AI PROMPT FOR EXPOSITORY THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTUCTIONS]. I want you to create an expository thesis statement that doesn’t argue a position, but demonstrates depth of knowledge about the topic.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR ARGUMENTATIVE THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTRUCTIONS]. I want you to create an argumentative thesis statement that clearly takes a position on this issue.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR COMPARE AND CONTRAST THESIS STATEMENT I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that remain objective.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Class Group Name Ideas (for School Students)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 19 Top Cognitive Psychology Theories (Explained)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 119 Bloom’s Taxonomy Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ All 6 Levels of Understanding (on Bloom’s Taxonomy)
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Summer Sale: Get 35% off The Successful Novel , only through July 9! Learn more »

If you’ve thought about putting your life to the page, you may have wondered how to write a memoir. We start the road to writing a memoir when we realize that a story in our lives demands to be told. As Maya Angelou once wrote, “There is no greater agony than bearing an untold story inside you.”
How to write a memoir? At first glance, it looks easy enough—easier, in any case, than writing fiction. After all, there is no need to make up a story or characters, and the protagonist is none other than you.
Still, memoir writing carries its own unique challenges, as well as unique possibilities that only come from telling your own true story. Let’s dive into how to write a memoir by looking closely at the craft of memoir writing, starting with a key question: exactly what is a memoir?
How to Write a Memoir: Contents
What is a Memoir?
- Memoir vs Autobiography
Memoir Examples
Short memoir examples.
- How to Write a Memoir: A Step-by-Step Guide
A memoir is a branch of creative nonfiction , a genre defined by the writer Lee Gutkind as “true stories, well told.” The etymology of the word “memoir,” which comes to us from the French, tells us of the human urge to put experience to paper, to remember. Indeed, a memoir is “ something written to be kept in mind .”
A memoir is defined by Lee Gutkind as “true stories, well told.”
For a piece of writing to be called a memoir, it has to be:
- Nonfictional
- Based on the raw material of your life and your memories
- Written from your personal perspective
At this point, memoirs are beginning to sound an awful lot like autobiographies. However, a quick comparison of Elizabeth Gilbert’s Eat, Pray, Love , and The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin , for example, tells us that memoirs and autobiographies could not be more distinct.
Next, let’s look at the characteristics of a memoir and what sets memoirs and autobiographies apart. Discussing memoir vs. autobiography will not only reveal crucial insights into the process of writing a memoir, but also help us to refine our answer to the question, “What is a memoir?”
Memoir vs. Autobiography
While both use personal life as writing material, there are five key differences between memoir and autobiography:
1. Structure
Since autobiographies tell the comprehensive story of one’s life, they are more or less chronological. writing a memoir, however, involves carefully curating a list of personal experiences to serve a larger idea or story, such as grief, coming-of-age, and self-discovery. As such, memoirs do not have to unfold in chronological order.
While autobiographies attempt to provide a comprehensive account, memoirs focus only on specific periods in the writer’s life. The difference between autobiographies and memoirs can be likened to that between a CV and a one-page resume, which includes only select experiences.
The difference between autobiographies and memoirs can be likened to that between a CV and a one-page resume, which includes only select experiences.
Autobiographies prioritize events; memoirs prioritize the writer’s personal experience of those events. Experience includes not just the event you might have undergone, but also your feelings, thoughts, and reflections. Memoir’s insistence on experience allows the writer to go beyond the expectations of formal writing. This means that memoirists can also use fiction-writing techniques , such as scene-setting and dialogue , to capture their stories with flair.
4. Philosophy
Another key difference between the two genres stems from the autobiography’s emphasis on facts and the memoir’s reliance on memory. Due to memory’s unreliability, memoirs ask the reader to focus less on facts and more on emotional truth. In addition, memoir writers often work the fallibility of memory into the narrative itself by directly questioning the accuracy of their own memories.
Memoirs ask the reader to focus less on facts and more on emotional truth.
5. Audience
While readers pick up autobiographies to learn about prominent individuals, they read memoirs to experience a story built around specific themes . Memoirs, as such, tend to be more relatable, personal, and intimate. Really, what this means is that memoirs can be written by anybody!
Ready to be inspired yet? Let’s now turn to some memoir examples that have received widespread recognition and captured our imaginations!
If you’re looking to lose yourself in a book, the following memoir examples are great places to begin:
- The Year of Magical Thinking , which chronicles Joan Didion’s year of mourning her husband’s death, is certainly one of the most powerful books on grief. Written in two short months, Didion’s prose is urgent yet lucid, compelling from the first page to the last. A few years later, the writer would publish Blue Nights , another devastating account of grief, only this time she would be mourning her daughter.
- Patti Smith’s Just Kids is a classic coming-of-age memoir that follows the author’s move to New York and her romance and friendship with the artist Robert Maplethorpe. In its pages, Smith captures the energy of downtown New York in the late sixties and seventies effortlessly.
- When Breath Becomes Air begins when Paul Kalanithi, a young neurosurgeon, is diagnosed with terminal cancer. Exquisite and poignant, this memoir grapples with some of the most difficult human experiences, including fatherhood, mortality, and the search for meaning.
- A memoir of relationship abuse, Carmen Maria Machado’s In the Dream House is candid and innovative in form. Machado writes about thorny and turbulent subjects with clarity, even wit. While intensely personal, In the Dream House is also one of most insightful pieces of cultural criticism.
- Twenty-five years after leaving for Canada, Michael Ondaatje returns to his native Sri Lanka to sort out his family’s past. The result is Running in the Family , the writer’s dazzling attempt to reconstruct fragments of experiences and family legends into a portrait of his parents’ and grandparents’ lives. (Importantly, Running in the Family was sold to readers as a fictional memoir; its explicit acknowledgement of fictionalization prevented it from encountering the kind of backlash that James Frey would receive for fabricating key facts in A Million Little Pieces , which he had sold as a memoir . )
- Of the many memoirs published in recent years, Tara Westover’s Educated is perhaps one of the most internationally-recognized. A story about the struggle for self-determination, Educated recounts the writer’s childhood in a survivalist family and her subsequent attempts to make a life for herself. All in all, powerful, thought-provoking, and near impossible to put down.
While book-length memoirs are engaging reads, the prospect of writing a whole book can be intimidating. Fortunately, there are plenty of short, essay-length memoir examples that are just as compelling.
While memoirists often write book-length works, you might also consider writing a memoir that’s essay-length. Here are some short memoir examples that tell complete, lived stories, in far fewer words:
- “ The Book of My Life ” offers a portrait of a professor that the writer, Aleksandar Hemon, once had as a child in communist Sarajevo. This memoir was collected into Hemon’s The Book of My Lives , a collection of essays about the writer’s personal history in wartime Yugoslavia and subsequent move to the US.
- “The first time I cheated on my husband, my mother had been dead for exactly one week.” So begins Cheryl Strayed’s “ The Love of My Life ,” an essay that the writer eventually expanded into the best-selling memoir, Wild: From Lost to Found on the Pacific Crest Trail .
- In “ What We Hunger For ,” Roxane Gay weaves personal experience and a discussion of The Hunger Games into a powerful meditation on strength, trauma, and hope. “What We Hunger For” can also be found in Gay’s essay collection, Bad Feminist .
- A humorous memoir structured around David Sedaris and his family’s memories of pets, “ The Youth in Asia ” is ultimately a story about grief, mortality and loss. This essay is excerpted from the memoir Me Talk Pretty One Day , and a recorded version can be found here .
So far, we’ve 1) answered the question “What is a memoir?” 2) discussed differences between memoirs vs. autobiographies, 3) taken a closer look at book- and essay-length memoir examples. Next, we’ll turn the question of how to write a memoir.
How to Write a Memoir: A-Step-by-Step Guide
1. how to write a memoir: generate memoir ideas.
how to start a memoir? As with anything, starting is the hardest. If you’ve yet to decide what to write about, check out the “ I Remember ” writing prompt. Inspired by Joe Brainard’s memoir I Remember , this prompt is a great way to generate a list of memories. From there, choose one memory that feels the most emotionally charged and begin writing your memoir. It’s that simple! If you’re in need of more prompts, our Facebook group is also a great resource.
2. How to Write a Memoir: Begin drafting
My most effective advice is to resist the urge to start from “the beginning.” Instead, begin with the event that you can’t stop thinking about, or with the detail that, for some reason, just sticks. The key to drafting is gaining momentum . Beginning with an emotionally charged event or detail gives us the drive we need to start writing.
3. How to Write a Memoir: Aim for a “ shitty first draft ”
Now that you have momentum, maintain it. Attempting to perfect your language as you draft makes it difficult to maintain our impulses to write. It can also create self-doubt and writers’ block. Remember that most, if not all, writers, no matter how famous, write shitty first drafts.
Attempting to perfect your language as you draft makes it difficult to maintain our impulses to write.
4. How to Write a Memoir: Set your draft aside
Once you have a first draft, set it aside and fight the urge to read it for at least a week. Stephen King recommends sticking first drafts in your drawer for at least six weeks. This period allows writers to develop the critical distance we need to revise and edit the draft that we’ve worked so hard to write.
5. How to Write a Memoir: Reread your draft
While reading your draft, note what works and what doesn’t, then make a revision plan. While rereading, ask yourself:
- What’s underdeveloped, and what’s superfluous.
- Does the structure work?
- What story are you telling?
6. How to Write a Memoir: Revise your memoir and repeat steps 4 & 5 until satisfied
Every piece of good writing is the product of a series of rigorous revisions. Depending on what kind of writer you are and how you define a draft,” you may need three, seven, or perhaps even ten drafts. There’s no “magic number” of drafts to aim for, so trust your intuition. Many writers say that a story is never, truly done; there only comes a point when they’re finished with it. If you find yourself stuck in the revision process, get a fresh pair of eyes to look at your writing.
7. How to Write a Memoir: Edit, edit, edit!
Once you’re satisfied with the story, begin to edit the finer things (e.g. language, metaphor , and details). Clean up your word choice and omit needless words , and check to make sure you haven’t made any of these common writing mistakes . Be sure to also know the difference between revising and editing —you’ll be doing both. Then, once your memoir is ready, send it out !
Learn How to Write a Memoir at Writers.com
Writing a memoir for the first time can be intimidating. But, keep in mind that anyone can learn how to write a memoir. Trust the value of your own experiences: it’s not about the stories you tell, but how you tell them. Most importantly, don’t give up!
Anyone can learn how to write a memoir.
If you’re looking for additional feedback, as well as additional instruction on how to write a memoir, check out our schedule of nonfiction classes . Now, get started writing your memoir!
32 Comments
Thank you for this website. It’s very engaging. I have been writing a memoir for over three years, somewhat haphazardly, based on the first half of my life and its encounters with ignorance (religious restrictions, alcohol, and inability to reach out for help). Three cities were involved: Boston as a youngster growing up and going to college, then Washington DC and Chicago North Shore as a married woman with four children. I am satisfied with some chapters and not with others. Editing exposes repetition and hopefully discards boring excess. Reaching for something better is always worth the struggle. I am 90, continue to be a recital pianist, a portrait painter, and a writer. Hubby has been dead for nine years. Together we lept a few of life’s chasms and I still miss him. But so far, my occupations keep my brain working fairly well, especially since I don’t smoke or drink (for the past 50 years).
Hi Mary Ellen,
It sounds like a fantastic life for a memoir! Thank you for sharing, and best of luck finishing your book. Let us know when it’s published!
Best, The writers.com Team
Hello Mary Ellen,
I am contacting you because your last name (Lavelle) is my middle name!
Being interested in genealogy I have learned that this was my great grandfathers wife’s name (Mary Lavelle), and that her family emigrated here about 1850 from County Mayo, Ireland. That is also where my fathers family came from.
Is your family background similar?
Hope to hear back from you.
Richard Lavelle Bourke
Hi Mary Ellen: Have you finished your memoir yet? I just came across your post and am seriously impressed that you are still writing. I discovered it again at age 77 and don’t know what I would do with myself if I couldn’t write. All the best to you!! Sharon [email protected]
I am up to my eyeballs with a research project and report for a non-profit. And some paid research for an international organization. But as today is my 90th birthday, it is time to retire and write a memoir.
So I would like to join a list to keep track of future courses related to memoir / creative non-fiction writing.
Hi Frederick,
Happy birthday! And happy retirement as well. I’ve added your name and email to our reminder list for memoir courses–when we post one on our calendar, we’ll send you an email.
We’ll be posting more memoir courses in the near future, likely for the months of January and February 2022. We hope to see you in one!
Very interesting and informative, I am writing memoirs from my long often adventurous and well travelled life, have had one very short story published. Your advice on several topics will be extremely helpful. I write under my schoolboy nickname Barnaby Rudge.
[…] How to Write a Memoir: Examples and a Step-by-Step Guide […]
I am writing my memoir from my memory when I was 5 years old and now having left my birthplace I left after graduation as a doctor I moved to UK where I have been living. In between I have spent 1 year in Canada during my training year as paediatrician. I also spent nearly 2 years with British Army in the hospital as paediatrician in Germany. I moved back to UK to work as specialist paediatrician in a very busy general hospital outside London for the next 22 years. Then I retired from NHS in 2012. I worked another 5 years in Canada until 2018. I am fully retired now
I have the whole convoluted story of my loss and horrid aftermath in my head (and heart) but have no clue WHERE, in my story to begin. In the middle of the tragedy? What led up to it? Where my life is now, post-loss, and then write back and forth? Any suggestions?
My friend Laura who referred me to this site said “Start”! I say to you “Start”!
Hi Dee, that has been a challenge for me.i dont know where to start?
What was the most painful? Embarrassing? Delicious? Unexpected? Who helped you? Who hurt you? Pick one story and let that lead you to others.
I really enjoyed this writing about memoir. I ve just finished my own about my journey out of my city then out of my country to Egypt to study, Never Say Can’t, God Can Do It. Infact memoir writing helps to live the life you are writing about again and to appreciate good people you came across during the journey. Many thanks for sharing what memoir is about.
I went to Egypt earlier this year. I aspire for my second book to document and tell the story of my travels of Africa, following the first – a memoir that led me to this post.
I am a survivor of gun violence, having witnessed my adult son being shot 13 times by police in 2014. I have struggled with writing my memoir because I have a grandson who was 18-months old at the time of the tragedy and was also present, as was his biological mother and other family members. We all struggle with PTSD because of this atrocity. My grandson’s biological mother was instrumental in what happened and I am struggling to write the story in such a way as to not cast blame – thus my dilemma in writing the memoir. My grandson was later adopted by a local family in an open adoption and is still a big part of my life. I have considered just writing it and waiting until my grandson is old enough to understand all the family dynamics that were involved. Any advice on how I might handle this challenge in writing would be much appreciated.
I decided to use a ghost writer, and I’m only part way in the process and it’s worth every penny!
Hi. I am 44 years old and have had a roller coaster life .. right as a young kid seeing his father struggle to financial hassles, facing legal battles at a young age and then health issues leading to a recent kidney transplant. I have been working on writing a memoir sharing my life story and titled it “A memoir of growth and gratitude” Is it a good idea to write a memoir and share my story with the world?
Thank you… this was very helpful. I’m writing about the troubling issues of my mental health, and how my life was seriously impacted by that. I am 68 years old.
[…] Writers.com: How to Write a Memoir […]
[…] Writers.com: “How to Write a Memoir” […]
I am so grateful that I found this site! I am inspired and encouraged to start my memoir because of the site’s content and the brave people that have posted in the comments.
Finding this site is going into my gratitude journey 🙂
We’re grateful you found us too, Nichol! 🙂
Firstly, I would like to thank you for all the info pertaining to memoirs. I believe am on the right track, am at the editing stage and really have to use an extra pair of eyes. I’m more motivated now to push it out and complete it. Thanks for the tips it was very helpful, I have a little more confidence it seeing the completion.
Well, I’m super excited to begin my memoir. It’s hard trying to rely on memories alone, but I’m going to give it a shot!
Thanks to everyone who posted comments, all of which have inspired me to get on it.
Best of luck to everyone! Jody V.
I was thrilled to find this material on How to Write A Memoir. When I briefly told someone about some of my past experiences and how I came to the United States in the company of my younger brother in a program with a curious name, I was encouraged by that person and others to write my life history.
Based on the name of that curious program through which our parents sent us to the United States so we could leave the place of our birth, and be away from potentially difficult situations in our country.
As I began to write my history I took as much time as possible to describe all the different steps that were taken. At this time – I have been working on this project for 5 years and am still moving ahead. The information I received through your material has further encouraged me to move along. I am very pleased to have found this important material. Thank you!
Wow! This is such an informative post packed with tangible guidance. I poured my heart into a book. I’ve been a professional creative for years to include as a writer, mainly in the ad game and content. No editor. I wasn’t trying to make it as an author. Looking back, I think it’s all the stuff I needed to say. Therapy. Which does not, in and of itself, make for a coherent book. The level of writing garnering praise, but the book itself was a hot mess. So, this is helpful. I really put myself out there, which I’ve done in many areas, but the crickets response really got to me this time. I bought “Educated” as you recommended. Do you have any blog posts on memoirs that have something to say to the world, finding that “something” to say? It feels like that’s theme, but perhaps something more granular. Thanks for this fantastic post. If I had the moola, I would sign up for a class. Your time is and effort is appreciated. Typos likely on comments! LOL
thanks. God bless
I am a member of the “Reprobates”, a group of seven retired Royal Air Force pilots and navigators which has stayed in intermittent touch since we first met in Germany in 1969. Four of the group (all of whom are in their late seventies or early eighties) play golf together quite frequently, and we all gather for reunions once or twice a year. About a year ago, one of the Reprobates suggested posterity might be glad to hear the stories told at these gatherings, and there have since been two professionally conducted recording sessions, one in London, and one in Tarifa, Spain. The instigator of these recordings forwarded your website to his fellow Reprobates by way of encouragement to put pen to paper. And, I, for one, have found it inspiring. It’s high time I made a start on my Memoirs, thank you.
Thank you for sharing this, Tim! Happy writing!
Hi, I’m Jo. I’m finally jumping in and writing the memoir that has been running alongside me for at least the last 5 years. I’m terrified, of what I’m not 100% sure. The story won’t leave me alone and right now is the time to start my first draft. I’m approaching half way through what nature may call natural life on Earth, mid-life sounds strange to say. It just feels like the right time to document the journey thus far – especially the last decade. It’s been a radical time for transformation, internally and externally. I’m afraid but your post and these comments have helped.
Good luck on your memoir, Jo! I’m excited to hear more.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 4, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
How to Write Memoir: Examples, Tips, and Ideas for School &College students

Everyone has the right to write his memoir; there is no need to become famous. If you want to write your memoirs quickly and successfully, our article will help you. It has all the helpful information for writing and practical examples and instructions on how to write an outline.
- ✔️ What Is a Memoir
✨ Memoir Examples and Ideas
- 🖊 ️ How to Write a Memoir
🔗 References
✔️ what is a memoir.
A memoir is a genre of non-fiction in which the author recounts specific historical events that they witnessed or participated in . This type of work can show either the author’s entire life as a biography or a particular event that they experienced.

Memoir Characteristics
Initially, the memoir genre acted as a subjective description of the past through the prism of the author’s life in it. An essential feature of memoirs is the claim for the authenticity of the reconstructed history and, accordingly, the documentary nature of the text, although, in reality, not all memoirs are truthful and accurate.
They have several stylistic features of memoir:
- Clear relevance to the history
- Factoriality
- Chronological narrative
Examples of memoirs can be diaries, notebooks, correspondence, memos, or travel notes.
You can get a better idea of what a memoir is in our free essays database.
Memoir vs. Autobiography
Despite the outward similarities between these types of literature, there is still a difference between memoir and autobiographical literature. They are entirely different genres that are independent and complete works.
| Criterion | Memoir | Autobiography |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | One period in the author’s life | Author’s entire life |
| The writer | Anyone | Protagonist |
| Reader Interest | Interested in a particular story | Learning about a specific person |
| Chronology | No strict chronological order | Strict chronological order |
| Emphasis on writing | Personal experience and the intrinsic | Facts and how the writer himself fits into the historical record |
| Moment of writing | Can be written anytime | Usually written later in life |
| Writing style | Free writing style | Formal style |
The best way to understand how to write this type of work is to see examples. That’s why we’ve given you examples of 100-word student memoirs below.
1. I dreamed of being an artist and becoming a doctor, and I don’t regret it. The dream of becoming a journalist has haunted me since my childhood. Back then, I was a very young boy, inspired by late-night TV shows and concerts. Those were glorious times when the well-known rock bands performed on stages, the real heroes. Wanting to become the darling of the audience, a hero like these guys, from time to time, I picked up a comb and sang into it in front of the mirror, impersonating the lead singer of one of them. Time passed, and fate had it so that now – 10 years later – I’m an emergency room doctor. You’d think my dream never came true. But it wasn’t. Over time, I realized that even though I do not have colossal fame and am not a hero to many teenagers, I did what I wanted – every day, I and my colleagues save lives. 2. Being sad for no reason frustrates me. For me, sadness can even be pleasant; justifying it in any way I can – I can imagine myself in that person’s shoes, listening to the sad music of the main character in a dramatic movie. I can look out the window as I cry and think, “This is so sad. I can’t even believe how sad this whole situation is.” Even reproducing my sadness can bring an entire theater audience to tears.” Feeling sorry for myself in times of sorrow intensifies it in me at such moments. 3. 1998 – This was the year my life changed. My friends and I went on a mountain trip, and as we were climbing rocks, I got oxygen deprivation at a certain altitude. Then my life was saved by people close to me. It was a moment after which I decided to live each year as if it were my last. It meant spending two years in New York City and focusing on loving life. It meant making new friends. It meant saying yes to many other things. It meant that my priorities were no longer the same as most.
If you would like to see more extensive examples of memoirs, the Fictional Memoir of Kerry Brodie and the Sociological Mini-Memoir on Personality Development would be remarkable for that.
6-word Memoir Examples
It is not necessary to write many paragraphs. Sometimes only 6 words are enough. There is a type of memoir of just one sentence. Mostly they are quotes from famous people, but no one forbids everyone to compose them. Here are some 6-word memoir examples:
- Unrehearsed, honest, unstoppable, and succeeding gradually
- Because of my big dreams, I’m always stressed.
- Every day is thinking of dreams , still thinking.
- The supremacy of reason over the dictatorship of emotion.
- Never let anyone steal your joy !
- Keep up the fight! Don’t give up .
- Loved his soul, not his money.
- A dream journey for all of us.
- At first glance, she was gentle.
- I was happy , and then I wasn’t.
- The right choice saves lives.
Memoir Prompts
To write a memoir, you must first choose a topic. Here are prompt ideas to help you:
- Write about your first love.
- Write how you survived the 2020 crisis.
- Write about the best trip of your life.
- Discuss friendship and what it means in your life.
- What are some of the things you regret that you didn’t do?
- Explain what you have too much of and what you have not had enough of in your life.
- Write about how you got into trouble.
- Tell me what aspect of your personality you are proud of.
- Write about what kind of music helped you cope with stress .
- Tell me how you felt when your father taught you to ride a bicycle .
- Tell about a situation in your life when you were insanely happy.
- Tell us about your most reckless purchase.
- Write about a goal that was easy for you to achieve.
- Discuss how you met your friends.
- Talk about a situation that is beyond your understanding.
Memoir Topics
What are some excellent memoir topics? Check out the list of memoir ideas:
- Hiking with friends in the mountains.
- How I survived Hurricane Katrina .
- Breathtaking Victoria Peak in Tokyo.
- Moving to another country left a mark on me.
- A man who saved my life.
- The problem of gun control and how it affected me.
- The lawsuits between Johnny Depp and Amber Heard led to a confrontation between my friends.
- The time when I lived in a house with a beautiful view of the mountains.
- A strange incident happened in my home in the middle of the night.
- Watching my favorite movie with my family.
- Fear of flying an airplane.
- Today I’m glad I made the right choice.
- My best friend at school.
- My car broke down in the middle of a mountain road.
- I didn’t get to be a designer .
- I never got to make up with my grandfather.
- A long trip to Europe.
- Switzerland won my heart.
- My favorite dish and memories associated with it.
- The war in Yugoslavia left a mark on me.
- How I found the courage to say “NO.”
- Surfing in Bali.
- The most horrible injury of my life.
- Winning a chess competition.
- Studying at Harvard .
- I didn’t help a man in trouble, and karma found me.
- Organizing the most massive event in town.
- Playing in the casino made me poor.
- The job that made me brave.
- The plane crash I survived.
🖊️ How to Write a Memoir
Now you can get out your pen and paper and start writing. Any work has specific rules and structure, and memoirs are no exception.
When you are writing a memoir, organizing all your memories makes sense. A peculiarity of this genre is that the author recalls their emotions and impressions as they write. They can negatively affect the work because they can mess up the structure and order. In addition, you may accidentally start telling stories that run parallel to the main story and “go astray.”
A well-written memoir synopsis will help you prevent this.
How to write a memoir outline?
Here are a few steps:
- Represent the main character . There will also necessarily be an antagonist in a person, situation, or circumstance. You need to “hook the reader’s interest in the first act. Examples of a successful hook will be below.
- Involve some drama, conflict, and critical events . All of your emotions need to be revealed, as do all of the events. In this part, your problems become more entangled and complex, as shown through scenes of actions and reactions that highlight your journey of change, transformation, and discovery of true or false.
- The drama, conflicts, and problems reach a climax , and the person (you) has completed the action, having had the experience. There are many endings in which the reader feels happy, sad, satisfied, with cause for reflection, etc. But the ending should always leave the reader feeling that the story is complete.
You can use this memoir outline template when writing your work:

Memoir Introduction
A memoir should reveal intense, exciting, and real-life discoveries from the first lines to the end of the first chapter. If you are just beginning to write your memoir, follow these writing tips on how to start:
- Engage. There’s nothing like a gripping hook to keep the reader engaged. Elizabeth Gilbert, for example, opens her bestseller Eat, Pray, Love with an intimate moment.
- Build credibility. From the beginning, tell your story as if you’re sharing a secret you’ve never told anyone. This approach makes the reader a confidant and builds trust from the start.
- Evoke emotion . Write your first pages from the heart. Use language that resonates with people on an emotional level. One of the best ways to evoke emotion in your reader is to talk about yourself.
- Lead the story with a laugh. Try leading with humor, whether you’re writing about your childhood or your memoir is about a darker story.
- Reveal a dramatic moment . Choose a dramatic moment to begin your memoir. You can revisit the event in more detail later, but it may interest the reader if you share a compelling glimpse of what is to come.
- Think like a fiction writer . A memoir is the true story of your life, but it should also include the structural elements of fiction. In your exposition, be sure to set the stage for the rest of the book by establishing yourself as the protagonist, laying out the source of the conflict, and highlighting the central theme.
- Keep it relevant. There are a million little details and life experiences that can be interesting on their own, but if they don’t support your story, you should exclude them.
- Chronology in the introduction is optional . Start writing the part of the story that inspires you the most, and then go back to your beginning after you finish your first draft. As you register, you will find the perfect start.
Memoir Hook Examples
As mentioned earlier, the memoir structure involves having a clear that draws the reader in the hook.
What’s it for?
First, the hook arouses the reader’s interest. Second, it reveals a situation, a feeling, an emotion, or all of these in a thesis statement. This gives the reader a chance to understand what the story will be about and get attention.
Effective hook characteristics:
- 1-2 sentences
- Brings emotions
- Goes beyond a memoir
You can see a great hook in a live example of a memoir, as well as in the examples below:
- At the Chess Olympiad then, everyone gave me a standing ovation.
- At that moment, I was one of the first to feel the fear of death.
- Broken knees and even my nose, but I still tried to pedal, getting on my bike time after time.
- I heard a scream. Something terrible had happened.
- The waterfall overshadowed all my memories with its beauty, even my first love.
- Few have spent their lives in Africa treating tigers.
- It’s about a historical event
- I was sure my parachute wouldn’t open
- The mass shooting at Columbine Middle School. I would have rather died than my friends.
- All the students were amazed to see an elderly professor doing somersaults, demonstrating the laws of physics.
Memoir Conclusion Examples
As you know, your story must have a beginning and an end. In the end, there needs to be a conclusion. Describe what you got out of your situation, how your life changed afterward, or what you gained or lost. You may want to jump back in time, perhaps many years in advance, to complete your story and summarize it for readers long after the “period” your memoir covers has ended.
And now, grab these memoir conclusion examples:
1. This journey along the river took all my energy. But it was nothing compared to the people I got to know. Billy, Miles, and Ashley seemed like strangers to me, but now we talk every day, and we see each other on weekends, reminiscing about our shared adventures on the Mississippi. 2. The moment the hurricane grabbed me and lifted me into the air, something changed in my mind. I thought I was about to die and was ready to accept it. But fate gave me a chance for salvation, and I took it. After that event, I became a different person; I rethought all the values in life and began to look at problems from another side. Although the trauma of that day still affects me, I’m happy with how my life has changed. 3. For a week after I had recovered from my serious injury, I had not heard from my unit in Afghanistan. The doctors told me not to get nervous, and no one gave me any information. Then on Wednesday, at 2 p.m., I heard the doorbell ring. It was Sean, the deputy squad leader, and a couple of other privates from our squad, safe and sound. A feeling of joy immediately filled me, and they broke into my house and started giving me a friendly hug and patting me on the back. All I could think about was how glad I was that they were in one piece, and the phrase kept rolling through my head, “We did it, Sean, we did it.”
These are just a few examples of the completion of a memoir. It’s enough to get the gist of a well-written.
As you can see, anyone can write a memoir, and it’s not as hard as it sounds. Now that you know how to write an outline, an introduction, and a conclusion, you have seen short memoir examples. You will write a fantastic memoir.
Don’t forget to share this article with your friends.
What Are the 5 Parts of a Memoir?
A memoir should contain 5 crucial elements: the truth, theme, first-person narration style, voice, and perception. The focused theme, demonstration of a specific event or experience, and conflict. The writing style of your memoir should be straightforward and spare. Supporting details will add charm to your memoir, and giving elements to your narrative will help the reader relive some of the emotions you experienced.
What Is the Purpose of a Memoir?
A memoir’s primary purpose is to recall an event from the past and present it to the reader in an exciting way. At the same time, it is necessary to conclude that it will be interesting for your audience.
What Is a Personal Memoir?
The essence of a personal memoir is that you write about what happened to you personally. Remember how you felt in those moments, and sincerely communicate that in your work. Only you can tell the story of your life that will make others more prosperous spiritually. A memoir about yourself examples is in the article.
How Many Words Should Be In a Memoir?
The standard size of a memoir is about 60,000 to 80,000 words. That’s about the size of the average novel. Can a memoir be smaller, like 40,000 words? Sure. Its main point is for the author to tell a story to the reader.
What Is the Difference Between Memoir and Biography?
These two genres are generally similar and are part of non-fiction. The critical difference is that while a memoir focuses explicitly on a particular incident or experience and attempts to highlight a point of view, a biography presents chronological events from a specific person’s life without emphasizing a specific experience. Also, unlike memoirs, which emphasize individual emotions, biography tends to be more general.
- The Personal Memoir: Purdue Writing Lab
- Audience Considerations for ESL Writers: Introduction: Purdue Writing Lab
- Making an Outline: USC Libraries
- Outline Components: Purdue Writing Lab
- Memoir | Definition, Examples, & Facts: Encyclopedia Britannica
- What Is a Memoir? – Definition & Examples: Study.com
- Six-Word Memoirs: UPENN
- Writing a Memoir: Dallas Baptist University
- Memoir: An Introduction: Oxford Scholarship
- Writing Memoir | Monmouth University
- Writing Lives: Autobiography in Fiction and Memoir – ANU
- Biography and Memoir | CUNY Graduate Center
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter X
- Share to LinkedIn
You might also like
Using scholarly articles as sources: a how-to guide, 30 google search tips & tricks for students, learning to write shorthand: the complete guide for students.
- Buy Custom Assignment
- Custom College Papers
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Research Papers
- Buy Custom Term Papers
- Cheap Custom Term Papers
- Custom Courseworks
- Custom Thesis Papers
- Custom Expository Essays
- Custom Plagiarism Check
- Cheap Custom Essay
- Custom Argumentative Essays
- Custom Case Study
- Custom Annotated Bibliography
- Custom Book Report
- How It Works
- +1 (888) 398 0091
- Essay Samples
- Essay Topics
- Research Topics
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Memoir Essay
October 12, 2023
What is a Memoir Essay?
A memoir essay is a form of autobiographical writing that focuses on a specific aspect of the author’s life. Unlike a traditional autobiography, which typically covers the author’s entire life, a memoir essay hones in on a particular event, time period, or theme. It is a deeply personal and reflective piece that allows the writer to delve into their memories, thoughts, and emotions surrounding their chosen subject.
In a memoir essay, the author aims to not only recount the events that took place but also provide insight into the impact and meaning of those experiences. It is a unique opportunity for self-discovery and exploration, while also offering readers a glimpse into the author’s world. The beauty of a memoir essay lies in its ability to weave together personal anecdotes, vivid descriptions, and introspective reflections to create a compelling narrative.
Writing a memoir essay can be both challenging and rewarding. It requires careful selection of memories, thoughtful introspection, and skillful storytelling. The process allows the writer to make sense of their past, gain a deeper understanding of themselves, and share their unique story with others.
Choosing a Topic for Your Memoir Essay
Selecting the right topic is crucial to write a good memoir essay. It sets the foundation for what you will explore and reveal in your personal narrative. When choosing a topic, it’s essential to reflect on your significant life experiences and consider what stories or themes hold the most meaning for you.
One approach is to think about moments or events that have had a profound impact on your life. Consider times of triumph or adversity, moments of exploration or self-discovery, relationships that have shaped you, or challenges you have overcome. These experiences can provide a rich foundation for your memoir essay.
Another option is to focus on a specific theme or aspect of your life. You might explore topics such as identity, family dynamics, cultural heritage, career milestones, or personal beliefs. By centering your essay around a theme, you can weave together various memories and reflections to create a cohesive narrative.
It’s also important to consider your target audience. Who do you want to connect with through your memoir essay? Understanding your audience’s interests and experiences can help you choose a topic that will resonate with them.
Ultimately, the topic should be one that excites you and allows for introspection and self-discovery. Choose a topic that ignites your passion and offers a story worth sharing.
Possible Memoir Essay Topics
- Childhood Memories
- Family Dynamics
- Life-altering Events
- Overcoming Societal Expectations
- Love and Loss
- Self-discovery and Transformation
- Lessons from Nature
- Journey from Darkness to Light
- Triumphing Over Adversities
- Life’s Defining Moments
Outlining the Structure of Your Memoir Essay
Writing a memoir essay allows you to share your personal experiences, reflections, and insights with others. However, before you start pouring your thoughts onto the page, it’s essential to outline the structure of your essay. This not only provides a clear roadmap for your writing but also helps you maintain a cohesive and engaging narrative.
First, consider the opening. Begin with a captivating introduction that hooks the reader and establishes the theme or central message of your memoir. This is your chance to grab their attention and set the tone for the rest of the essay.
Next, move on to the body paragraphs. Divide your essay into sections that chronologically or thematically explore different aspects of your life or experiences. Use vivid descriptions, anecdotes, and dialogue to bring your memories to life. It’s crucial to maintain a logical flow and transition smoothly between different ideas or events.
As you approach the conclusion, summarize the key points you’ve discussed and reflect on the significance of your experiences. What lessons have you learned? How have you grown or changed as a result? Wrap up your memoir essay by leaving the reader with a memorable takeaway or a thought-provoking question.
Remember, the structure of your memoir essay should support your storytelling and allow for a genuine and authentic exploration of your experiences. By outlining your essay’s structure, you’ll have a solid foundation to create a compelling and impactful memoir that resonates with your readers.
How to Write an Introduction for Your Memoir Essay
The introduction of your memoir essay sets the stage for your story and captivates your readers from the very beginning. It is your opportunity to grab their attention, establish the tone, and introduce the central theme of your memoir.
To create a compelling introduction, consider starting with a hook that intrigues your readers. This can be a surprising fact, a thought-provoking question, or a vivid description that immediately draws them in. Your goal is to make them curious and interested in what you have to say.
Next, provide a brief overview of what your memoir essay will explore. Give your readers a glimpse into the key experiences or aspects of your life that you will be sharing. However, avoid giving away too much detail. Leave room for anticipation and curiosity to keep them engaged.
Additionally, consider how you want to establish the tone of your memoir. Will it be reflective, humorous, or nostalgic? Choose your words and phrasing carefully to convey the right emotions and set the right atmosphere for your story.
Finally, end your introduction with a clear and concise thesis statement. This statement should express the central theme or message that your memoir will convey. It serves as a roadmap for your essay and guides your readers in understanding the purpose and significance of your memoir.
By crafting a strong and captivating introduction for your memoir essay, you will draw readers in and make them eager to dive into the rich and personal journey that awaits them.
Write the Main Body of Your Memoir Essay
When developing the main body of your memoir essay, it’s essential to structure your thoughts and experiences in a clear and engaging manner. Here are some tips to help you effectively organize and develop the main body of your essay:
- Chronological Structure: Consider organizing your memoir essay in chronological order, following the sequence of events as they occurred in your life. This allows for a natural flow and a clear timeline that helps readers understand your personal journey.
- Thematic Structure: Alternatively, you can focus on specific themes or lessons that emerged from your experiences. This approach allows for a more focused exploration of different aspects of your life, even if they did not occur in a linear order.
- Use Vivid Details: Use sensory details, descriptive language, and engaging storytelling techniques to bring your memories to life. Transport your readers to the settings, evoke emotions, and create a vivid picture of the events and people in your life.
- Show, Don’t Tell: Instead of simply stating facts, show your readers the experiences through engaging storytelling. Use dialogue, scenes, and anecdotes to make your memoir more dynamic and immersive.
- Reflections and Insights: Share your reflections on the events and experiences in your memoir. Offer deeper insights, lessons learned, and personal growth that came from these moments. Invite readers to reflect on their own lives and connect with your journey.
By organizing your main body in a logical and engaging manner, using vivid details, and offering thoughtful reflections, you can write a compelling memoir essay that captivates your readers and leaves a lasting impact.
Reflecting on Lessons Learned in Your Memoir Essay
One of the powerful aspects of a memoir essay is the opportunity to reflect on the lessons learned from your personal experiences. These reflections provide deeper insights and meaning to your story, leaving a lasting impact on your readers. Here are some tips for effectively reflecting on lessons learned in your memoir essay:
- Summarize Key Points: In the conclusion of your essay, summarize the key events and experiences you have shared throughout your memoir. Briefly remind readers of the significant moments that shaped your journey.
- Identify Core Themes: Reflect on the core themes and messages that emerged from your experiences. What did you learn about resilience, love, identity, or perseverance? Identify the overarching lessons that you want to convey.
- Offer Personal Insights: Share your personal insights and reflections on how these lessons have influenced your life. Were there specific turning points or moments of epiphany? How have these experiences shaped your beliefs, values, or actions?
- Connect to the Reader: Make your reflections relatable to your readers. Explore how the lessons you learned can resonate with their own lives and experiences. This allows them to connect with your story on a deeper level.
- Offer a Call to Action: Encourage readers to reflect on their own lives and consider how the lessons from your memoir can apply to their own journeys. Pose thought-provoking questions or suggest actions they can take to apply these insights.
By reflecting on the lessons learned in your memoir essay, you give your readers a chance to contemplate their own lives and find inspiration in your personal growth. These reflections add depth and impact to your storytelling, making your memoir essay truly memorable.
Crafting a Strong Conclusion for Your Memoir Essay
The conclusion of your memoir essay is your final opportunity to leave a lasting impression on your readers. It is where you tie together the threads of your story and offer a sense of closure and reflection. Here are some tips to help you craft a strong conclusion for your memoir essay:
- Summarize the Journey: Remind your readers of the key moments and experiences you shared throughout your essay. Briefly summarize the significant events and emotions that shaped your personal journey.
- Revisit the Central Theme: Reiterate the central theme or message of your memoir. Emphasize the lessons learned, personal growth, or insights gained from your experiences. This helps reinforce the purpose and impact of your story.
- Reflect on Transformation: Reflect on how you have transformed as a result of the events and experiences you shared. Share the growth, self-discovery, or newfound perspectives that have shaped your life.
- Leave a Lasting Impression: Use powerful and evocative language to leave a lasting impact on your readers. Craft a memorable phrase or thought that lingers in their minds even after they finish reading your essay.
- Offer a Call to Action or Reflection: Encourage your readers to take action or reflect on their own lives. Pose thought-provoking questions, suggest further exploration, or challenge them to apply the lessons from your memoir to their own experiences.
By crafting a strong conclusion, you ensure that your memoir essay resonates with your readers long after they have finished reading it. It leaves them with a sense of closure, inspiration, and a deeper understanding of the transformative power of personal storytelling.
Editing and Proofreading Your Memoir Essay
Editing and proofreading are crucial steps in the writing process that can greatly enhance the quality and impact of your memoir essay. Here are some tips to help you effectively edit and proofread your work:
- Take a Break: After completing your initial draft, take a break before starting the editing process. This allows you to approach your essay with fresh eyes and a clear mind.
- Review for Structure and Flow: Read through your essay to ensure it has a logical structure and flows smoothly. Check that your paragraphs and sections transition seamlessly, guiding readers through your story.
- Trim and Refine: Eliminate any unnecessary or repetitive information. Trim down long sentences and paragraphs to make your writing concise and impactful. Consider the pacing and ensure that each word contributes to the overall story.
- Check for Clarity and Consistency: Ensure that your ideas and thoughts are expressed clearly. Identify any confusing or vague passages and revise them to improve clarity. Check for consistency in tense, tone, and voice throughout your essay.
- Proofread for Errors: Carefully proofread your essay for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors. Pay attention to common mistakes such as subject-verb agreement, verb tenses, and punctuation marks. Consider using spell-checking tools or having someone else review your work for an objective perspective.
- Seek Feedback: Share your memoir essay with a trusted friend, family member, or writing partner. Their feedback can provide valuable insights and help you identify areas for improvement.
By dedicating time to edit and proofread your memoir essay, you ensure that it is polished, coherent, and error-free. These final touches enhance the reader’s experience and allow your story to shine.
Sociology Research Topics Ideas
Importance of Computer in Nursing Practice Essay
History Research Paper Topics For Students
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy. We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related emails.
Latest Articles
In today’s digital era, the fusion of artificial intelligence (AI) with academic writing has revolutionized how students approach essay composition....
Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) in education is changing how things are taught and learned in standard ways. With its ability...
The advancement of artificial intelligence has made it increasingly common for essays and articles to be written by AI. But...
I want to feel as happy, as your customers do, so I'd better order now
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However, you may visit "Cookie Settings" to provide a controlled consent.
- Paper writing help
- Buy an Essay
- Pay for essay
- Buy Research Paper
- Write My Research Paper
- Research Paper Help
- Custom Research Paper
- Custom Dissertation
- Dissertation Help
- Buy Dissertation
- Dissertation Writer
- Write my Dissertation
- How it works
How to Write a Memoir Essay to Remember

A memoir essay is one of the most exciting and introspective assignments you can receive in high school or college. If you were lucky enough to get to write this piece, but have no idea where to start, let me enlighten you. I’ll explain what it is, the thought process behind this essay type, and divulge three tips to make it perfect. Stay with me till the end, and I’ll share a memoir essay sample to inspire your writing.
What Is a Memoir Essay?
It is easy to guess that memoirs are nothing but memories on paper. They are akin to autobiography, but with an added twist. Where autobiographies are usually factual and a bit dry, memoir essays are rich with analysis, reflection, and even sidenotes. These make them a more pleasurable read, especially if you have the writing talent to make your piece captivating and exciting.
A memoir essay does not have to span your whole life, even if you are still in your twenties. It can tell about a particular period of your teenage years, your early childhood, or the gap year you took to travel abroad. The list of memoir essay ideas is endless, and you can choose the story you want to tell. However, be mindful of oversharing or divulging the facts you would rather stay unknown. You can also add a bit of creativity to your memoir by including vivid dreams you’ve had or your plans for the near future.
How to Write a Memoir Essay in 4 Easy Steps
Everyone’s writing process is different, but I find that these four stages are crucial to all assignments, memoir piece included:
Narrow Down the Storyline
There are dozens of memoir essay ideas available to you (I’ve already mentioned a couple). Periods of change, struggle, conflict are usually a safe bet, though you can also describe the most uneventful year of your life and fill the story with everyday rituals. You can narrow down your story to one month or scale it up to a decade of your life. Make sure the time period you choose tells one story. Otherwise, narrow it down further or split your essay into several parts, if the assignment allows it.
Outline the Story
Note all the important events you want to describe and leave enough room for reflections and analysis. Your story cannot simply contain the dry facts, or it will turn into an autobiography. Open the piece by introducing yourself, setting the time parameters of the story, and the thesis statement. Then go through the pivotal events and round up the outline with a conclusion that completes the story. You can also hint at the events that followed and leave the essay open-ended.
Write Your Tell-all
With an idea and outline ready, all you need to do is flesh out your story. Think of it as writing a diary or a journal, and the words will flow out of you onto the screen. If writing in chronological order is challenging, try starting with the most exciting part and extending the piece from there.
Get a Second Opinion
Never skip the post-writing routine of editing, proofreading, and formatting. Getting a second pair of eyes on your story is always a great idea, but if you don’t have that option, leave your memoirs essay for a while and come back to it in few days. Fresh eyes do wonders for finding unnecessary tangents and typos.
Three Quick Tips For Writing Memoir Essays
I’ve taken you through the paces, but now it’s time to step above the basics. When you follow the steps above, keep these three tips in mind, and your memoir essay will gain depth and the power to captivate the readers:
- Show, don’t tell. I know it’s old and beaten, but this advice works every time! Breathe life into your essay with the smell of the freshly mowed lawn, the sound of bacon sizzling in the kitchen, the taste of your mum’s rhubarb pie. Every detail makes your memoir essay more real for the reader, draws them in, and compels to read on.
- Research your history. Put on your Indiana Jones fedora and go digging into the old photo albums, diaries, letters. Talk to the people who were around you at the time you want to describe. They will share the perspective and details (cue tip #1) you might not remember. If nothing else, their stories might tickle your memory.
- Remain objective. When writing a personal memoir essay , you might be tempted to paint yourself a flawless hero beating all odds and overcoming insurmountable obstacles. Another extreme is showing yourself as a helpless victim of circumstance unable to change your destiny. Neither of these will make your story relatable. Instead, show your true colors, the struggles you’ve gone through, the problems you’ve had. Conflict makes for a captivating story.
Memoir Essay Example Worthy of Modelling
I am not a big fan of using other people’s work as a pattern to replicate in your writing. However, it is undoubtedly true that the more you read high-quality non-fiction pieces, the better your academic writing is likely to get. Your brain works as a recorder that consumes information before processing and replaying it. Therein lies the problem with reading one memoirs essay sample too many. You might not even notice your unconscious use of another’s style, phrases, or outline.
Another downside of reading samples is their low quality. Whenever you google a memoir essay example, you cannot know who has written it and what grade they have received (if they are a student). Relying on second-grade writing to guide your essay will never result in high grades.
If you want quality samples, look for personal memoir essay contests and winning entries. You can also check out non-fiction magazines that publish life stories. Even if the journal is published online, there is a higher chance of stumbling across quality writing there than on random blogs.

One last word of caution: do not get caught up in reading samples. It is yet another procrastination tactic your brain wants to embrace. Reading outstanding writing is easier than opening a blank file and filling it with your life story. However, professors don’t award points for reading, they expect on-time submissions. Set a maximum number of samples you read at three or five and move on to outlining and writing.
TRY OUR FREE APP
Write your book in Reedsy Studio. Try the beloved writing app for free today.
Craft your masterpiece in Reedsy Studio
Plan, write, edit, and format your book in our free app made for authors.

Guides • Perfecting your Craft
Last updated on Apr 14, 2023
How to Write a Memoir: Turn Your Personal Story Into a Successful Book
Writing a memoir can be a meaningful way to reflect on your life's journey and share your unique perspective with people around you. But creating a powerful (and marketable) book from your life's memories — one that can be enjoyed by readers across the world — is no easy task.
In this article, we'll explore the essential ingredients that make up an impactful and commercially viable memoir and provide you with tips to craft your own.
Here’s how to write a memoir in 6 steps:
1. Figure out who you’re writing for
2. narrow down your memoir’s focus, 3. distill the story into a logline , 4. choose the key moments to share, 5. don’t skimp on the details and dialogue, 6. portray yourself honestly.
Before you take on the challenge of writing a memoir, make sure you have a clear goal and direction by defining the following:
- What story you’re telling (if you’re telling “the story of your life,” then you may be looking at an autobiography , not a memoir),
- What the purpose of your memoir is,
- Which audience you’re writing it for.
Some authors write a memoir as a way to pass on some wisdom, to process certain parts of their lives, or just as a legacy piece for friends and family to look back on shared memories. Others have stronger literary ambitions, hoping to get a publishing deal through a literary agent, or publishing it yourself to reach a wide audience.
Whatever your motivation, we’d recommend approaching it as though you were to publish it. You’ll end up with a book that’s more polished, impactful, and accessible 一 even if it’ll only ever reach your Aunt Jasmine.
🔍 How do you know whether your book idea is marketable? Acclaimed ghostwriter Katy Weitz suggests researching memoir examples from several subcategories to determine whether there’s a readership for a story like yours.
Know your target reader
If you’re not sure where to start it doesn’t hurt to figure out your target audience 一 the age group, gender, and interests of the people you’re writing it for. A memoir targeted at business execs is a very different proposition from one written to appeal to Irish-American baseball fans.
If you want a little help in asking the right questions to define your audience, download our author market research checklist below.

FREE RESOURCE
Market Research Checklist
Find your ultimate target audience with our checklist.
Now that you know who you’re writing for, you need to clearly define which (yummy) slice of your life you want to share with them.
When writing a memoir, there's always the temptation to cover broad periods of your life, from that time in first grade when Mrs. Taylor laughed at your painting, to your third divorce, and everything in between. But remember, this is not a biography. You should try to choose specific experiences or aspects of your life that form a red thread or a central theme. The narrower the focus, the better your memoir will resonate with others.
For example, a memoir could be about the time you hiked the Appalachian Trail, became a Jiu-Jitsu master, or volunteered in a refugee camp. Naturally, anecdotes from other parts of your life may intertwine with your main narrative, but there needs to be a focused center to your book.
Not only will a narrower slice of life help you concentrate your efforts, it will also make it easier to shift the focus from your personal story to specific, relatable things you experienced , making it easier for readers to care and take something away from the book.

GET ACCOUNTABILITY
Meet writing coaches on Reedsy
Industry insiders can help you hone your craft, finish your draft, and get published.
A broader theme readers can relate to
Unless you’re a celebrity, you can’t expect people to just want to read your memoir 一 you have to give them a reason to carve time out of their busy schedule and sit with your book. People are drawn to stories that they can relate to or that teach them something about themselves and the world.
So, before you get to writing, identify the broader themes behind your personal experiences and center the book around them. For example, a story about hiking the Appalachian Trail could be a story about spiritual growth. A book about learning Jiu-Jitsu may be about building confidence and overcoming fear. A memoir about working with refugees could be about cultivating empathy and overcoming structural inequality.
These are themes that people from different ages, gender, and cultures can relate to. They will make your memoir much more universal. Figure out what readers can learn from your experiences, whether that’s something about resilience, trauma, parenting, self-discovery, or other, and center your book around that .
💡 Listen to 3-time memoir author Paul Bradley Carr explain the importance of nailing your memoir’s focus from the get-go in this advice-packed Reedsy Live.

At this point, you’re probably fired up and stretching your fingers to start writing. But there are a few more steps to take to ensure you’re set up for success.
Memory lane isn’t a straight path — it’s a winding road with many off-ramps and distractions. So before you start drafting, make a note of where you’re going by encapsulating your memoir in a sentence or two. Ask yourself: if I were to pitch it to a stranger on an elevator, how would I summarize it? The purpose of this exercise is to help you weave the main themes into a clear narrative arc, which is essential to turn your life into a captivating story.
Here are some example loglines from famous memoirs for inspiration:
| Memoir | Logline |
| by Andre Agassi | chronicles Agassi's journey from a much hated childhood tennis practice, to become one of the greatest players in the sport, exploring his struggles with identity, relationships, and purpose. |
| by Henry David Thoreau | documents Thoreau’s two-year experiment in simple living and self-sufficiency in a cabin near Walden Pond, exploring themes of solitude, self-reliance, and personal growth. |
| by Tara Westover | recounts Tara’s journey from struggling to pursue higher education due to her strict, religious parents, to earning a PhD from Cambridge University. It explores themes of family, education, and perseverance in the face of adversity. |
Take some time with your logline and whittle your story down to its purest form. If it helps, start by writing what you think the back cover blurb will be. Then boil it down further and further, until you can finally pitch it in just a few sentences.
The logline is the North Star that will guide you as you start to collect the moments of your life to include in the book.
Now that you have a direction and some central themes, it’s time to pick the best tales from your buffet of life experiences. It’s natural to look back at your life chronologically and select memories in a linear fashion, but really, what’s important is to pick the most meaningful moments, whether big or small, that propel your memoir forward.
For example, Trevor Noah’s Born a Crime is a collection of stories about growing up as a mixed-raced child in Apartheid South Africa. The book shares how Noah questioned his mother’s religious beliefs, spoke multiple languages to bridge cultural differences, made and sold CDs to escape poverty, and more. Each story is a different window into his world and how it shaped him, but all of them build on the book’s central themes of faith, identity, and resilience.
Look for moments of high emotion
When you’re mining your memory for stories, look for those with moments of high emotion and meaning. Whether it was a funny, sad, or embarrassing memory, the ones that shaped who you are and how you see the world tend to be the most emotionally charged.
To discern the gems from mediocre stories, consider working with a professional editor and take advantage of their editorial wisdom.

MEET EDITORS
Polish your book with expert help
Sign up, meet 1500+ experienced editors, and find your perfect match.
Now close your eyes, and dig deep into your memories to repaint your stories on the blank page as colorfully (and accurately) as possible.
To make your memoir deeply engaging, experiment with different storytelling techniques and use sensory details, actions, and dialogue, as opposed to explicitly stating what you did or how you felt. This falls into the classic writing advice of ‘Show, don’t tell.’
When revisiting your memories, be thorough in your research and try to collect as many details as possible:
- Read back your journal entries (if you kept one) to see how you felt in the moment.
- Get your hands on photos or videos from that period in your life (either digital or analog.)
- Interview your family members, friends, and other people relevant to your story.
- Revisit locations and settings from the past that you plan on writing about.
- Look up anything that can be verified or fact-checked (e.g. dates, social media posts, or world news.)
Once you've collected the raw material, organize these memories in a way that makes sense for you. Being systematic in your research will pay serious dividends when you actually start working on your manuscript.
You’re allowed some creative license with dialogue
One thing that is particularly important to get right is dialogue. Obviously, you don't have to write dialogue exactly as it happened — our memories are fallible after all. However, you do need to accurately capture the essence of what was said (and how). As long as you’re faithful to what happened (or at least honest about how you experienced it) you can take some liberties with the precise wording.
To write believable dialogue, take inspiration from your favorite writers, or take our free course below for tips.

FREE COURSE
How to Write Believable Dialogue
Master the art of dialogue in 10 five-minute lessons.
😱 Inevitably, when you write about other people there’s always a risk of portraying them in a way they don’t appreciate. As general advice, tell them you’re writing this story, or prepare to lose some relationships. And if you’re really pushing some boundaries, discuss it with your lawyer!
Next, it’s time to look inwards and flesh out a compelling and relatable protagonist: you!
The best memoirs read like novels, which means they hinge on the protagonist’s voice and personality 一 their quirks, values, and goals, and how they rise to life’s challenges. Just as in a novel, your memoir needs a relatable protagonist that undergoes some change.
It takes a good dose of courage to portray yourself as a multidimensional character 一 one with both strengths and weaknesses, one who sometimes wins and sometimes loses.
Do background work on yourself
To infuse a dose of humanity to your own character, you’ll have to do the background work as if you were a character in a novel. Take note of everything from your physical appearance, cultural background, psychological traits, and more. This exercise will help you bring to surface details about your personality that you’d otherwise look over, and depict a much more well-rounded protagonist. To facilitate the process, use our free character development template which will guide you with specific prompts and questions.

Reedsy’s Character Development Template
A story is only as strong as its characters. Fill this out to develop yours.
Define your character’s arc
Additionally, it's helpful to define your own character's arc 一 how you’ve matured through the life experiences highlighted in the memoir. There are specific steps you can follow to define your personal hero's journey , but among other questions, you’ll have to answer:
- What inciting incident set you on a journey?
- What were the obstacles you encountered?
- Which mentors helped you along the way?
- What were the lessons you needed to learn?
- How have you changed as a result?
These questions will help you strengthen your memoir’s narrative, hooking the readers in like the best novels do.
To give an example, Cheryl Strayed's journey in Wild begins after the death of her beloved mother and other family problems, which lead her on a path of self-destruction, culminating in a divorce and addiction to heroin. Having reached the bottom, she decides to hike the Pacific Crest Trail for three months in order to find herself. The path is filled with challenges 一 from her hiking inexperience, to losing her boots, to fellow hikers warning her that it's not safe to go on alone. Through resilience (and some help) she is able to overcome her physical and emotional challenges, find forgiveness and rediscover her inner strength.

Take inspiration from Wild and other memoirs, and deconstruct how your own experiences might fit into these all-important story elements.
You now have all the ingredients: a specific memoir topic that touches on universal themes (as summarized by your logline), a selection of vivid and relevant memories, and a multidimensional character with an interesting story arc. It’s time to put it all together by outlining the structure of your memoir, which is exactly what we’ll cover in our next post.
15 responses
CourtneySymons says:
11/01/2018 – 15:26
This was exactly the article I needed today! I've just begun a new career path as a ghostwriter and am finding it difficult to find learning resources (conferences, courses, books, networks of ghostwriters, etc.). If any readers have advice on where I should be looking or who I should be talking to, I would be forever grateful! Thanks so much!
M. Thomas Maxwell says:
11/01/2018 – 15:28
I had no intention of writing a book but encouraged by my grandson I embarked on a story telling venture that led to Grandfather's Journal, www.captaintommaxwell.com. It truly is a series of life stories shared with my grandson. Published by Westbow press in 2015 I used many Reedsy tips and am very pleased with the results.I have since encouraged others to consider doing the same. It took over a year and was a pleasant experience.
Don Karp says:
11/01/2018 – 16:06
As a self-published memoir writer, I read this with appreciation. I do not agree with all that's said here. For example, "2. Do Your Research." Of course certain events--those experienced publicly by a large number of people--need to be accurate. But even the word, "memoir," says it's about memory, not accuracy. This is one of the major differences from an autobiography which does require research. I looked up the dictionary definition and got confirmation on this. Perhaps you need to re-examine this and get it right?
↪️ Reedsy replied:
11/01/2018 – 17:00
I would agree that memoirs are indeed based on memory — and in some way that's why historians are often forced to question the reliability of memoirs as a primary source. I would say, however, that modern readers to expect memoirs to be as factually-correct as possible. Editors at publishers will go to great pains to ensure that — or face a public backlash. If you say anything in a memoir that can be disproved by a basic google search will seriously compromise your relationship with a reader. The other benefit with research is that it can do a lot to jog your memories. Unreliable recollections can often be set straight once you remind yourself of certain facts. Thanks for commenting!
↪️ Don Karp replied:
11/01/2018 – 17:28
Thanks for your response. This brings up two points for me. First, what is more powerful, a memory of an experience or the actual experience? Different people interpret the same experience differently. Second, what do you propose to do with the dictionary definition of "memoir?" Since the word is based on memory and not research, perhaps you can suggest some alternate word form?
↪️ The Red Lounge For Writers replied:
05/12/2018 – 08:14
I think looking at the idea of the 'voice of innocence' and the 'voice of experience' could really help with this distinction between fact and memory. As writers of memoir, we are expected to write what we remember. We can do this using the voice of innocence, and use the voice of experience to write about the factual context.
Stu Mountjoy says:
11/01/2018 – 21:48
A group I used to attend, on a Friday, started people off with the basic exercise of writing a story about one thing that happened to you, and I did one about a race at school. I am always impressed by the first page I read of Alan Alder's bio (actor in M*A*S*H TV series) - "Hi I'm Alan Alder, and when I was six, my mother tried to kill my father." - wow.
31/01/2018 – 10:15
Alda's a great writer — "Things I Overheard While Talking to Myself" is such a fantastic name for a memoir too.
Robbie Cheadle says:
31/01/2018 – 04:48
A very useful and interesting post on writing a memoir.
31/01/2018 – 10:14
I'm glad you like it Robbie :)
The Red Lounge For Writers says:
05/12/2018 – 08:10
All great advice. Memoir is probably my favourite genre to read, and some of my favourite books are memoirs. I'm of the opinion that everyone has a story to tell; it's just a matter of figuring out how to do it really well.
James Soil says:
15/07/2019 – 13:16
Thank you very much I just finished my Memoir titled Addicted it will be out this summer after reading this article I feel much better about it I pretty much did what the article says.
Izaura Nicolette says:
04/08/2019 – 04:50
Self-published Author, Izaura Nicolette. 'Within The Mountains: A Mormon Reform School Experience.' Published January, 2019. Seeking legit Publishing House or Agent. I still have not received any royalties due to publishers being fraudulent. I want to speak publicly about my memoir. Hundreds to thousands can back me up. This is a true story. I hold too close to my heart. Hoping to heal by sharing this experience, and opening door for many others.
Magzley says:
08/08/2019 – 02:14
Can I *breathe* life into my story instead?
Cassandra Janzen says:
20/12/2019 – 04:35
Very helpful, thank you!
Comments are currently closed.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.

The Ultimate FREE Book-Formatting App
Try Reedsy Studio: the free formatting app used by thousands of authors every day.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:
Join our mailing list and receive your free eBook. You'll also receive great tips on story editing, our best blogs, and learn how to use Fictionary software to make your story unforgettable.
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Blogs / Non-fiction / How to Write a Memoir: 10 Tips for Sharing Your Story
Perfect Your Storytelling
How to write a memoir: 10 tips for sharing your story.
What happens when a writer wants to tell a true story about themselves? They become the protagonist and fill the chapters with scenes from their own lives. They share their personal character arc and the life lessons it imparts. That is a memoir.
What is a Personal Memoir?
The term memoir comes from the French word “mémoire,” which means memory or remembrance, reflecting the personal and reflective nature of the genre.
Memoirs can cover a wide range of topics, from childhood memories to professional accomplishments, and they often include emotional and introspective insights from significant moments, relationships, and events.
Memoir vs. Autobiography
A memoir focuses on a small slice, an event or series of related events, sometimes bound by theme, that have occurred in the writer’s life. They deliver a message.
An autobiography is the whole pie. It’s a linear, usually chronological accounting of a person’s entire life, typically written by someone with fame or prominence. For example, someone who has a high profile within their realm or beyond like a movie star, a politician, an athlete, or even a criminal.
While we all like to think we’ve led interesting lives, it’s unlikely that interest would prevail beyond our circle of family and friends. But everyday people have tales that can and should be told.
What to Include in a Memoir
When deciding what to write about, consider the 5 W’s: Who/What/Why/Where/When.
Who Am I Writing About?
The obvious answer is you. Who makes up your cast of characters? Friends, enemies, lovers, relatives, co-workers, your favorite teacher from sixth grade, the cop who arrested you, or the doctor who treated your cancer?

What Statement Am I Making?
Being able to reduce your book’s point to a statement, belief, or argument gives you focus and helps you evaluate it for its potential resonance. If you’re looking for revenge by sharing someone’s dirty laundry, it’s best to rethink your strategy.
A story about bringing someone else down rarely wins over the hearts of your readers. But if you want to illuminate the biggest life lesson you gleaned from your experiences to help others, by all means, write about it.
Why Am I Writing?
From an external standpoint, your “why” may involve recognition, validation, and income. These are all valid reasons.
The internal “why” may be harder to pinpoint. It could range from wanting to share what you’ve learned, to spare people from suffering like you did, to telling a story that touches people and helps them understand their own lives better.
Providing knowledge, comfort, encouragement, and inspiration to others appeals to our human need of finding meaning in the things that happen to us.
External Reasons:
- Gain notoriety
- Document family history
- Capture memories
- Establish my writing presence
Internal Reasons:
- Tell a personal story
- Discover the meaning of life
- Share knowledge
- Provide inspiration
- Validate myself as a writer
- Get healing through telling my story
Where Did My Story Take Place?
Even if you grew up in Chicago, you can’t take for granted that everyone knows what it’s like to experience life in the Windy City.
A small town in Texas or a quaint village in the English countryside also require enough description for your reader to feel like they’re experiencing it with you, the beauty, the horror, and the quirks.
When Did This Happen?
Anchoring your story in a time frame is important for your reader. Whether you’re a child of the 70s or Generation Z, when your story takes place is important and you need to place your readers in that time. Were you a child, a college student, or about to retire?
Writing a memoir does not involve inventing a world or characters out of thin air. It should be based on truth. However, truth is the eye of the beholder.
Picture a crime scene. Police interview the witnesses. Each gives a different account. Why? They might be standing in different locations so what they could see varied from the others. Their perspectives may differ because one witness thinks the victim resembles the neighborhood bully from their childhood. Another thinks every stranger is a criminal. Their life experiences shape the way they view everyday occurrences.
As we recall the events of our life, many things can color our memories like trauma, illness, prejudices, and even the simple passage of time. What did our memory choose to keep and why? This doesn’t mean we are being untruthful, rather, it is simply our version of the truth that we’re telling. Don’t feel constrained by your perspective. Embrace it.
How to Start a Memoir
Write what comes to mind. You can decide later what you’ll keep and what you’ll cut. Try to keep it related to the specific event, situation, or experience. Many memoir writing coaches suggest simply tapping into memories and writing them down.
Some people like to write a long, detailed account of events while others jot down a few lines. Some like to produce snippets in chronological order while others write whatever comes to mind. What’s most important is to have enough content to choose from when forming your story. This doesn’t mean writing your life story. (Save that for when you’re making the talk show circuit celebrating your worldwide success.)
Once you’re ready to write your first draft, begin by writing a simple summation of your story, just like you would for a novel. Develop a one-sentence premise of your memoir. Remember, make it about one specific situation and what you learned from it.
If you’re having trouble, imagine writing a skeleton blurb for a novel. Who is the protagonist? You! What shook your world up? How did you respond? In what ways did your life change after going through this situation?
Different Types of Memoirs
Now that you’ve gotten started, decide what kind of story you’re telling. Here are the more common types of memoirs:
- Traditional Memoirs: These are retrospective, recounting significant life events and providing a comprehensive exploration of the author’s experiences and emotions.
- Childhood Memoirs: These transport readers back to the author’s formative years, capturing innocence, challenges, and the profound impact of early experiences, tapping into the universal human longing to understand one’s roots.
- Coming-of-Age Memoirs: These navigate the tumultuous waters of adolescence, exploring themes of self-discovery, forming one’s identity, and the trials of growing up.
- Transformative Journey Memoirs: These delve into pivotal moments or journeys that changed the author’s life, resulting in personal transformation through travel, self-discovery, or overcoming adversity.
- Historical Memoirs: These intertwine personal experiences with historical events. Using a backdrop of wars, revolutions, cultural shifts, or other significant periods, authors share their perspectives using a unique lens through which readers can understand historical events.
- Confessional Memoirs: These are deeply personal and often raw stories revealing intimate details, vulnerabilities, and struggles, inviting readers into their emotional landscapes.
- Educational Memoirs: These combine personal stories with lessons learned. Authors share wisdom and insights gained from their experiences, aiming to offer inspiration or guidance to others.
- Retrospective Memoirs: These look back on a specific time or event in the author’s life, offering reflections, insights, and a sense of newfound understanding and closure.
- Thematic Memoirs: These memoirs weave together different stories and events from the author’s life to illustrate a central theme, such as love, loss, or betrayal.
- Chronological Memoirs: These tell the story from start to finish, providing a linear narrative of the author’s journey for that portion of their life.
Within each of these types of memoirs, there is an external story and an internal story. The external story focuses on the events themselves, such as surviving war, abuse, or tragedy. The internal story reflects the growth of the character in response to those events.
What to Write a Memoir About
Consider these things when writing your memoir:
- Who is your book for: Having a target audience will help you focus on the message you want to share.
- Write with honesty and authenticity : Being vulnerable can make your story more relatable and compelling. Only you know what it was like to take your journey. Tell it with the emotion of the triumphs and challenges you experienced.
- Show, Don’t Tell : Though it might tempt you to merely lay out the events in a journalistic way, strive to show what happened with dialogue, vivid descriptions, and sensory details. Bring to life the people, places, and events as you experienced them.
- Character Development : Even if you are the only character in your story, you need to show who you are to your readers. Develop yourself and others in your memoir with depth, showing motivations, strengths, weaknesses, and growth.
- Prose : Pay attention to the craft of writing. Most memoirs are written from a first-person point of view in order to establish a connection with readers. It is possible to write from a third-person point of view, but it may create a more objective or detached perspective. It may be suitable if your story involves more than just you as the protagonist, such as siblings whose experiences are intertwined. You’ll also decide which tense to use. Be consistent. Watch your pacing and narrative flow.
What Is Good Memoir Structure?
While a memoir involves writing about personal events and recollections, the story still requires the same solid story structure as a novel.
It’s true that in a novel there can be three points of view—the author, the perspective from which the story is told, and the main character or protagonist who lives the story.
In memoirs, these three are one and the same. This presents a critical lesson: a memoirist must determine what they know and how they should reveal it to the reader.
Another important point to consider is that of truth. Remember that one person’s account may vary from another and yet remain truthful due to varying perceptions. You may not remember the exact words exchanged in a conversation, but the gist of the message should remain.
Memoir Writing Tips
Before getting to the structure, consider these tips:
- Narrow your focus: Remember, you’re not writing an autobiography. You’re focusing on one moment or series of moments around a theme.
- Write about more than the story: Yes, the focus is on an event or related events, but consider the other players—the characters, the time, and the setting. Share interesting facts about them in your writing to bring vivid details to life.
- Use fictional elements: While your memoir is a true story, you can and may need to embellish it, depending on how vivid your memory is. When focusing on other characters, locations, and dialogue, create intriguing details about them to evoke emotions in your readers. This will not compromise the integrity of your story; it will keep your reader mesmerized.
- Be careful with pacing: Determine the rhythm of your story. Some events may need more detailed exploration, while others can be summarized to maintain the flow.
- Have a narrative arc: Your memoir should have a clear beginning, middle, and end.
Memoir Structure
It makes sense to approach your memoir’s structure like that of a novel. It needs the following components:
- Opening Image: Start with a compelling hook or scene that establishes the setting, time, and key characters.
- Setup/Exposition: These scenes show what your ordinary world is like, setting the tone before changes come. It helps to establish what’s at stake for you.
- Inciting Incident: Introduce the main conflict that sets your story into motion. What happens that shakes up your world and causes you to react?
- Plot Point 1: At this stage, you know what your goal is, but you’re not thrilled about chasing it. Since you’re in reactionary mode, your actions may not be related to achieving the goal.
- Middle: The middle marks the point where you become proactive to the goal. This means you’ve learned the rules, and you can now make plans to go after the goal. No longer just accepting your fate, you’re finding the strength to deal with the obstacles in your path. How do you grapple with the challenges, make decisions, and demonstrate personal growth?
- Plot Point 2: It is the low point in your story where it seems all is lost. Have your efforts to reach your goal resulted in failure or brought more hardship? Were you lacking knowledge or had incorrect information that led you to make unwise choices?
- Climax: This is where you achieve (or fail to achieve) your story’s goal. The tension, conflict, and emotional upheaval reach their peak in this scene and offer your reader the payoff to the story’s promise. This is your moment of triumph, crisis, self-realization, or transformation.
- Resolution: Wrap up by reflecting on lessons learned, personal growth achieved, and the impact of the events on your life. You may offer insights or wisdom gained from your experiences.
Memoir Examples
Here are some highly regarded books which offer guidance on writing memoirs:
The Art of Memoir by Mary Karr
Mary Karr, a celebrated memoirist, shares her wisdom and experience in this book, offering theoretical insights and practical advice on crafting compelling memoirs while reflecting on her writing journey.
Writing the Memoir: From Truth to Art by Judith Barrington
This book provides a comprehensive guide to writing memoirs, covering topics such as memory, structure, voice, and revision.
Fearless Confessions: A Writer’s Guide to Memoir by Sue William Silverman
Sue William Silverman draws upon her own personal and professional experience to provide a practical guide for transforming life into words that matter.
The Memoir Project: A Thoroughly Non-Standardized Text for Writing & Life by Marion Roach Smith
This concise and engaging book emphasizes the importance of storytelling and personal voice in memoir writing.
Your Life As Story by Tristine Rainer
Tristine Rainer fills her book with examples from renowned writers and demonstrates techniques for crafting character portraits, remembering forgotten memories, unifying a story with thematic conflict, and employing fictional devices such as dialogue and humor.
Bird by Bird: Some Instructions on Writing and Life by Anne Lamott
A classic offering advice on writing and life, encouraging writers to take it one step at a time and to find humor in the process. It’s a valuable resource for writers of all genres.
Naked, Drunk, and Writing: Shed Your Inhibitions and Craft a Compelling Memoir or Personal Essay by Adair Lara
Lara guides writers through the process of writing their stories with authenticity and courage, helping them to craft a narrative that resonates with readers.
Great Memoirs to Read
If you want to be inspired, here are some critically acclaimed memoirs to read:
The Glass Castle by Jeannette Walls
Walls’ memoir chronicles her unconventional upbringing by deeply dysfunctional parents, exploring themes of resilience, family, and forgiveness.
Educated by Tara Westover
This memoir tells the story of Westover’s self-transformation from growing up in a strict, isolated household in rural Idaho to eventually pursuing higher education at Cambridge and Harvard.
The Liar’s Club by Mary Karr
Karr’s memoir offers a candid and often humorous account of her turbulent childhood in East Texas, marked by her dysfunctional family and her own struggles with addiction.
Crying in H Mart by Michelle Zauner
This memoir is a touching tale of growing up Korean-American, dealing with family bonds, cultural identity, and grief.
H is for Hawk by Helen MacDonald
Part memoir, part nature writing, MacDonald’s book explores her experience of grief and healing following her father’s death, intertwined with her journey of training a goshawk.
A Long Way Gone: Memoirs of a Boy Soldier
A testament to the resilience of the human spirit, Beah’s story of his transformation from an innocent child to a child soldier during Sierra Leone’s civil war recounts his harrowing experiences.
Drinking: A Love Story by Caroline Knapp
A powerful narrative of Knapp’s love affair with alcohol, her struggle with addiction, and her courageous path to recovery.
Eat, Pray, Love by Elizabeth Gilbert
Gilbert explores themes of spirituality, love, and the quest for inner peace on a year-long journey of self-discovery following a divorce.
Conclusion on Writing a Memoir
Writers are passionate about telling the stories they’ve created in their minds. Memoir writers have lived their stories and want to share their messages of hope and inspiration or perhaps experience a catharsis of their own. In any case, memoir is a valuable genre worth considering for any writer.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
Elaine Ambrose
Bestselling Author, Ventriloquist, & Humorist
How to Write the Introduction to Your Memoir
June 2, 2018 By Elaine Ambrose

If you want to write a memoir, begin with a powerful scene that provides a provocative glimpse into the story that follows. Here is the first paragraph of my upcoming memoir, Frozen Dinners – A Memoir of a Fractured Family.
“Irritated clouds of gray dust swirl behind my car and settle back onto the patches of scruffy sagebrush as I drive a back road into the village of Wendell, Idaho. I turn down 4 th Avenue and stop in front of an insignificant old house where my family lived before my father became rich. Decades of decay and neglect are exposed as cheap vinyl siding sags on the outside walls and dead vines hang on crooked trellises over weathered boards thirsty for paint. I stare at the window of my former bedroom and wonder if it’s still nailed shut.”
Those four sentences reveal several essential facts to the story through key words and phrases. The words “village of Wendell, Idaho” tell readers the location of my small hometown. The phrase “before my father became rich” adds an interesting element in the second sentence. The third sentence about “decades of decay” offers a glimpse into a memoir about loss and longing. By the fourth sentence, I intend to hook the reader with the words “wonder if it’s still nailed shut.”
Why was my childhood window nailed shut? Keep reading to learn the truth. Also, to emphasize immediacy, the first chapter is written in present tense. The remaining chapters are in past tense.

Everyone has a story, and you should consider writing yours. Your life’s history contains a series of pivotal scenes that incorporate all the senses and emotions. List the important memories and then review them for the basis of an outline for your memoir. Do certain times and events seem more compelling that others? What is the essence of your story? How do you begin?
My memoir first percolated in my mind more than twenty years ago, and I adjusted the intensity of my writing for several years, often jumping into the mess of words only to quit and relinquish everything to the back burner. How do I, as a humor writer, rip open the scars to inspect the pain of the past? I couldn’t finish it, so I sporadically wrote additional chapters for the manuscript while working on humorous books, including Menopause Sucks , Midlife Cabernet , and Midlife Happy Hour .
My mother’s death in 2014, followed three years later by the death of my younger brother George, convinced me to complete the book. The memoir will be released in the fall by Brown Books Publishing.
Write Your Memoir – Free Workshop in Boise

The Idaho Writers Guild offers a full schedule of free workshops for beginning and intermediate writers. I’ll be presenting a memoir writing class on Thursday, June 21 at the Library at Collister , 4724 W State Street in Boise. The workshop, titled “Your Memoir – How to Avoid Flirting with Fiction,” begins at 7:00 with a 90-minute interactive session followed by audience discussion. The event is free and open to the public. Intermediate writers are encouraged to attend.
The workshop will focus on how to outline a memoir and how to separate fact from fiction. Worksheets will emphasize the importance of an opening paragraph to set the stage for the rest of the story.
Reader Interactions
June 2, 2018 at 5:37 pm
Looking forward to reading it. Now, to get to work on mine…


18 Narrative and Memoir Essays
Narrative writing.

Human beings tell stories every day. We understand most of nature through stories. Though facts can be memorized, stories — the details, the description, the experience — make us believe.
Therefore, as we begin to study writing, we need to begin with the properties of the story. How do good storytellers make us believe? How can good writing draw a reader into a story? How can we harness the power of the story to make a point, even in a dry, academic context?
The purpose of narrative writing is to tell stories. This is a form we are familiar with, as any time we tell a story about an event or incident in our day, we are engaging in a form of narration. In terms of writing, narration is the act of describing a sequence of events. Sometimes this is the primary mode of an essay—writing a narrative essay about a particular event or experience, and sometimes this is a component used within an essay, much like other evidence is offered, to support a thesis. This chapter will discuss the basic components of narration, which can be applied either as a stand-alone essay or as a component within an essay.
Ultimately, narrative writing tries to relay a series of events in an emotionally engaging way. You want your audience to be moved by your story, which could mean through laughter, sympathy, fear, anger, and so on. The more clearly you tell your story, the more emotionally engaged your audience is likely to be.
| Sherlock Holmes, a creation of the writer Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, has become one of the most famous detectives of all time — though he never lived. Have you heard of him? Why do you think this story perseveres? How can stories permeate our culture so thoroughly? |
WHERE DO WE FIND NARRATIVE?
We talk about narrative writing in many ways. Books will introduce it as Narration, Narrative, and Storytelling. Narrative creeps into most of the other kinds of writing we learn about, too. Persuasive essays use short stories — often called anecdotes — to engage a reader’s attention and sympathy. Consider the difference between these two openings to the same essay:
| Statistics show that consistent seatbelt wearing is vital if passengers are to survive a moving vehicle accident. Though laws have been in place since the 1970s in most states mandating this behavior, some drivers and passengers resist because belts cause some discomfort. However, everyone should wear a seatbelt because they’ve been proven to save lives. |
| Timmy’s mother was in a hurry as they left the mall. He’d climbed into the backseat of their minivan and immediately started playing with his tablet, and his mother was in too much of a rush to fight him over putting on his seatbelt. They had to make it to his sister’s concert on time. The van rushed into traffic, and Timmy’s mother tried to beat a yellow light to make a left turn at the intersection — but someone else, coming from the other direction, had tried to do the same thing, and the car barreled into their van, connecting with the door beside Timmy with a sickening bang and crunch. |
Which opening makes you want to read more? The second one engages its readers with a story — and we’re hard-wired, as humans, to want to hear the end of a story.
Television plays on this characteristic all the time. Think of your favorite show and the maddening, brief preview that starts before the credits roll. It’s always a quick snippet that makes you stay tuned because the writers and producers know their audience will sit through several minutes of mindless commercials just to find out how the story will continue.
In our own writing, we can use stories in just the same way. We can draw our readers into our own experiences, even if they’ve never been through anything even similar to what we have, by telling our own stories.
HOW DO WE WRITE A NARRATIVE?
A narrative essay is a piece that tells one consistent, cohesive story. In academic writing, a narrative essay will also always convey a lesson, a moral, or a point that the writer wishes the reader to take.
When we say “moral,” some people think of after-school specials and having “good behavior” tips crammed down their throat. However, the most powerful lessons conveyed through writing are often done with great subtlety. True, the punishing pace of writing expected in a college course may not leave enough time to develop a nuanced story — no one is going to churn out War and Peace or even The Hobbit in ten weeks — but not every story has to have the moral stated clearly, in bold font, at the very beginning.
Think about it this way: When you were a kid, if your grandmother had sat you down and said, “Listen. We’re now going to have a thirty-minute conversation about how it’s really bad if you start smoking,” would you have listened? Probably not. If, however, your grandmother took you to visit your uncle Larry, who had terminal lung cancer, and then casually mentioned as you left that Larry had been smoking since he was your age — would you get the lesson? Would you remember it? Do you remember better the 200 lectures you had as a teenager about not being a bully, or do you remember the one time that you witnessed its effects firsthand?
In a narrative, we want to pull that same kind of trick on our readers: get our point across, but do it in a way that engages the imagination and attention. Use the power of the story.
The narrative relies on the same components that all good writing does: it needs detail, clear organization, and a central purpose (AKA our friends Development, Organization, and Unity).
NARRATIVE DEVELOPMENT: BRING THE DETAILS
Consider this passage from the very first Sherlock Holmes mystery, “A Study in Scarlet,” which describes a major character:
| His face was lean and haggard, and the brown parchment-like skin was drawn tightly over the projecting bones; his long, brown hair and beard were all flecked and dashed with white; his eyes were sunken in his head, and burned with an unnatural luster; while the hand which grasped his rifle was hardly more fleshy than that of a skeleton. As he stood, he leaned upon his weapon for support, and yet his tall figure and the massive framework of his bones suggested a wiry and vigorous constitution. His gaunt face, however, and his clothes, which hung so baggily over his shriveled limbs, proclaimed what it was that gave him that senile and decrepit appearance. The man was dying—dying from hunger and from thirst. |
The author includes detail upon detail to describe this gentleman. He could have simply said, “He was dying from hunger and from thirst,” which would tell us everything we need to know. Instead, he describes how these feelings have had an effect upon the man — he is gaunt , he’s starting to look like a skeleton, and he can barely stand without the support of his rifle.
Think of the best book you’ve ever read (or the best television show you’ve ever watched, or the movie you love), and you may be able to relate to this. Good description is the difference between hearing a game on the radio and watching it live in the stadium (or on a ginormous 3-D television). The very breath of life in a narrative will always be your ability to describe a scene.

This relies on the use of specific language. As you read through the revision section, you were encouraged to avoid phrases that your audience might find misleading. Consider this as you write a story. With every sentence, ask, “What does my audience know? What do they think?” If you say a car is “beautiful,” will your audience think of a 2018 Hybrid Honda Accord or of a 1966 Chevelle (pictured at right)? If there’s some doubt, change your words to reflect your meaning.
You may have heard the advice that asks you to “show, not tell” in writing. This is what we mean: be so descriptive in telling a story that the reader feels s/he is there beside you, seeing the swimming pool or the school’s front doors or the new car or the new child with his/her own eyes.
NARRATIVE ORGANIZATION
Narrative traditionally follows time order, or chronological order , throughout. This seems obvious when you think about it — we tell stories in time order, starting (usually) at the beginning and working through to the end.
In an essay, pieces of the story can be organized into timespans by paragraph. For instance, if I’m describing a particularly harrowing day at work, I might have a paragraph just for the morning, and then a paragraph about my terrible lunch break, and then a paragraph about my afternoon.
Narrative essays usually can’t cover more ground than a day or two. Instead of writing about your entire vacation experience, study abroad month, two years of work at the plant, or 18 years living at home, focus on one particular experience that took place over a day or two. That’s enough for a reader to digest in a few pages, and it will also give you a chance to really lay in details without feeling rushed.
Sometimes, we start stories out of order. Many popular movies and television shows do this regularly by showing a clip of something that happens later before starting the whole show. If you’ve ever seen an episode of NCIS, you’ll be familiar with this technique: they start each section of the show with a photo of the ending scene, then start an hour or two before that scene in the live-action. Shows often jump to “One Week Earlier” between commercial breaks.
Think of the emotional impact that has upon you as a viewer. Again, it’s a trick the writers pull with their story to drive you through the boring/silly/pointless/insulting commercials so that you’ll stay with them. We want to know how the characters get to that end.
You can manipulate your audience in this way, too, but be careful; giving away too much of the ending may sometimes make a reader simply put down what they’re reading. It’s safer (though not always better) to just start at the beginning and write things down as they happened. Particularly in a first draft, sticking to the natural story order will be a good way to make sure nothing gets missed.
Chronological order , the order in which events unfold from first to last, is the most common organizational structure for narratives. Stories typically have a beginning, a middle, and an end. Certain transitional words and phrases aid in keeping the reader oriented in the sequencing of a story. Some of these phrases are listed below.
Figure 5.2 Transition Words and Phrases for Expressing Time
| LOGICAL RELATIONSHIP
| TRANSITIONAL EXPRESSION
|
The following are the other basic components of a narrative:
• Plot . The events as they unfold in sequence.
• Characters . The people who inhabit the story and move it forward. Typically, each narrative has there are minor characters and main characters. The minor characters generally play supporting roles to the main character, or the protagonist.
• Conflict . The primary problem or obstacle that unfolds in the plot, which the protagonist must solve or overcome by the end of the narrative. The way in which the protagonist resolves the conflict of the plot results in the theme of the narrative.
• Theme . The ultimate message the narrative is trying to express; it can be either explicit or implicit.
Writing at Work
When interviewing candidates for jobs, employers often ask about conflicts or problems a potential employee had to overcome. They are asking for a compelling personal narrative. To prepare for this question in a job interview, write out a scenario using the narrative moved structure. This will allow you to troubleshoot rough spots as well as better understand your own personal history. Both processes will make your story better and your self-presentation better, too.
Narrative Anecdotes
An anecdote is a short, personal narrative about something specific. It is often used as a component in an essay, acting as evidence to support your thesis, as an example to demonstrate your point, and/or as a way to establish your credibility. It always has a point in telling it.
Elements of an Anecdote
1. Who, Where, When
Have you ever wondered why children’s stories begin something like this?
Once upon a time, in a galaxy far, far away, the teachers were revolting …
It is the start of a simple narrative. It also contains all the elements of a beginning to any narrative: when, where, and who. An anecdote, because it is short, will begin similarly:
One day, while I was sitting at a stop sign waiting for the light to change…
This little particle of an anecdote tells when, who, and where before the first sentence even ends.
Note : An anecdote sets up a particular incident; it does not tell about a long period of time.
2. What Happened (Sequence of Events)
Any narrative also includes a sequence of events. You should be able to read an anecdote and tell what happens first, what happens next, and so on. In the following anecdote, the bolded words suggest each event in the sequence.
Example Anecdote:
My first day of college I parked in the “South Forty,” which is what everyone called the huge parking lot on the edge of the campus. It was seven forty-five in the morning, hazy and cool. I walked across the parking lot, crossed a busy street, walked over a creek, through a “faculty” parking lot, crossed another street, and came to the first row of campus buildings. I walked between buildings, past the library and the student mall. I passed many quiet, nervous-looking students along the way. Many of them smiled at me. One trio of young girls was even chuckling softly among themselves when they all smiled and said “Hi” to me at once. By the time I got to my classroom, far on the other side of campus from the parking lot, I was smiling and boldly saying “Hi” to everyone, too, particularly the girls. Every single one of them smiled or responded with a “Hi” or made a friendly comment or even chuckled happily. It was my first day of college.
When I found the building I was looking for, a friend from high school appeared. She was in my first class! I smiled at her and said, “Hi!” She looked at me. She smiled. Then she laughed. She said, “Why are you wearing a sock on your shirt?” I looked down. A sock had come out of the dryer clinging to my shirt.
3. Implied Point
Most of us want to make sure that we “get the point across” to whatever story we are telling, assuming it has a point. To do this, we tend to explain what we are telling. It is sometimes very difficult to stop. However, stopping in a timely way allows the reader to draw his or her own conclusions.
Show, don’t tell
In the anecdote above, I am very tempted to tell the reader what I felt at the moment I realized that everyone was laughing AT me rather than just being friendly. For the ending, where the point is in this case, it is best to let the reader infer (draw conclusions, fill in the blanks) what happens implicitly rather than to state explicitly what the point is, or what the narrator felt, or anything else.
The more indirect you are about your object or place the better. In the anecdote above, it might be obvious that my object is a sock or my place is a parking lot. The point is, it is not an anecdote “about” a sock; it is referred to indirectly.
How do we show rather than tell? First, describe what you see (I don’t really see anything with “I was SO embarrassed…”) or what you smell, hear, or taste, but NOT what you feel. An easy way to check whether you are showing or telling is to go through your anecdote and underline the verbs. If the verbs are “be”-verbs (is, was, were, etc.) or verbs that describe actions we cannot see (“I thought…” “I believed…” “I imagined…” “it made me upset…” and so on) then you are probably telling. In the sentence above I used “walked,” “lecturing,” “ripped,” and “said.”
Most Common Question:
“What makes stories or anecdotes interesting and something I can relate to?”
Actually, it is a simple principle, even though it may not be obvious. We “relate” or “connect” most easily to situations we recognize and so fill in the blanks. If you “tell” me, for example, “I was SO embarrassed …” then you have not let me fill in MY embarrassment. On the other hand, if you “show” me a scene, it allows me to fit my own experience into it:
“I walked past the corner of the aluminum whiteboard tray while lecturing to a class. It ripped my pants. After a moment I said, ‘Class dismissed.’”
The writer of those statements, hopes the reader will fill in some similarly embarrassing moment without the writer clearly stating that this is what is supposed to be done. The connection, the act of “filling in,” is what people tend to refer to as “relating to.”
Interestingly, it does not even matter whether or not readers fill in what the writer intend for them to fill in; it is the act of filling in our own experiences that makes us “relate” to an incident. From a writer’s perspective, that means we should show rather than tell.
Second, resist the temptation to “explain.” Let the reader fill in the blanks! It is so much more personal when the reader participates by filling in.
Assignment 1
Write an anecdote that contains who, where, when, and what happens (a sequence of events). Think about an anecdote that involves , alludes to, or otherwise includes your object or place ; it does not have to be “about” your place. It also does not have to be “true” in the strict sense of the word; we will not be able to verify any believable details if they add to the effect of the anecdote. Type it out. Keep it simple and to the point.
What are ‘clichés’ and why can’t we use them?
Clichés are figurative phrases and expressions that you have probably heard a million times. For our purposes, there are two kinds of clichés: the ones that jump out at you and the ones that we use without thinking.
If you are paying attention, you will notice that the two sentences above contain at least 3 clichés. You might also notice that clichés are best suited to spoken language, because they are readily available and sometimes when we speak, we don’t have time to replace a common expression with a unique one. However, we DO have time to replace clichés while we are writing.
The problem with clichés in writing is that they are too general when we should be much more specific. They also tend to tell rather than show. In the first sentence above, we have most likely heard the phrase, “have probably heard a million times.” In speech, that expression works. In writing, it should be literal rather than figurative. The first sentence is better this way:
Clichés are figurative phrases and expressions that we have heard so many times that we all share some understanding of what they mean.
Not exactly what you thought when you read it at the beginning of this answer, is it? That is why being literal and specific in writing is better than figurative and vague as a rule.
Here is a re-write of the second sentence at the start of this answer:
For our purposes, there are two kinds of clichés: the ones that are obvious expressions (like “You can lead a horse to water …”) and the ones that are not part of expressions but seem to “go” easily into a group of words (like “we use without thinking”).
The second type is more difficult to identify and eradicate. Usually it is a group of words we have heard before that doesn’t add anything to a statement. For example, instead of “We watched the donuts roll down the street every night,” you might be tempted to add to it this way: “We watched the donuts roll down the street each and every night.” Avoid clichés in your writing.
To see more see more commonly used clichés and for guidance on how to rewrite them, see this handout (https://writingcenter.unc.edu/cliches/)from The University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, Writing Center.
Some Other Rhetorical Tips
- To create strong details, keep the human senses in mind. You want your reader to be immersed in the world that you create, so focus on details related to sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch as you describe people, places, and events in your narrative.
- Create tension by making the reader nervous about what is going to happen through sentence structure, tone, and voice.
- Add dialogue to show the immediacy and drama of the personal interactions (re-creating conversations as necessary to make your narrative work).
- Name specific objects to re-create the scene by selecting details that leave the readers with a dominant impression of how things were.
- Show people in action by describing precise movements and dialogue to convey the action of the scene.
External Links:
“ Sixty-nine Cents ” (https://tinyurl.com/ybjasq9c) by Gary Shteyngart: In “Sixty-nine Cents,” author Gary Shteyngart describes a coming-of-age experience as a first-generation Russian-Jewish immigrant in modern America.
Sherman Alexie grew up on the Spokane Reservation in Washington State. He chronicles his challenges in school, starting in first grade, in Indian Education (https://tinyurl.com/hlshngr).
Sandra Cisneros offers an example of a narrative essay in “ Only Daughter ” (https://tinyurl.com/yc4srod7) that captures her sense of her Chicana-Mexican heritage as the only daughter in a family of seven children. The essay is also available here (https://tinyurl.com/y7hzxhz6).
Annie Dilliard offers an example of a narrative essay in an excerpt, often entitled “ The Chase ” (https://tinyurl.com/ycsen7r4) from her autobiography An American Childhood , outlining a specific memorable event from her childhood. This essay is also available here (https://tinyurl.com/y7udsl88).
NARRATIVE UNITY
The final consideration in putting together a narrative essay should be unifying it around a single theme or lesson. As you draft, you may already have this lesson in mind: everyone should wear a seatbelt. However, remember that your reader needs to make up her own mind. Don’t insult a reader by beating them up with your lesson, and don’t leave them guessing about the meaning of your piece by leaving it out completely.
Many writers include a paragraph of reflection after telling a personal story in an essay that lets a reader know, directly, the significance that the story has on the writer’s life. This can be a good way to get a lesson across. Showing what you’ve learned or found important in an event will provide the reader with a clue about the overall meaning of the story.
You should use “I” in a personal, narrative essay . There are types of academic writing where “I” is inappropriate, but this is not one of those times. In fact, the best narratives will often be the most personal, the stories that avoid hiding behind “you” or “they” and instead boldly tell the writer’s own story.
NARRATIVE OUTLINES
The typical narrative essay follows an outline that should seem like common sense:
- Paragraph 1: Introduction
- Paragraph 2: Event #1
- Paragraph 3: Event #2
- Paragraph 4: Event #3
- Paragraph 5: Conclusion
This outline is flexible. Perhaps the first event in your story will take significant space to describe; it may need 2 paragraphs of its own. Maybe there are smaller events that happen within the larger events. Maybe for your piece, it makes sense to jump right into the story instead of spending an introduction paragraph to give some setup. What matters most is that a reader can easily follow the piece from beginning to end and that she will leave with a good understanding of what you wanted the reader to learn.
Student Sample Essay
My College Education
The first class I went to in college was philosophy, and it changed my life forever. Our first assignment was to write a short response paper to the Albert Camus essay “The Myth of Sisyphus.” I was extremely nervous about the assignment as well as college. However, through all the confusion in philosophy class, many of my questions about life were answered.
I entered college intending to earn a degree in engineering. I always liked the way mathematics had right and wrong answers. I understood the logic and was very good at it. So when I received my first philosophy assignment that asked me to write my interpretation of the Camus essay, I was instantly confused. What is the right way to do this assignment, I wondered? I was nervous about writing an incorrect interpretation and did not want to get my first assignment wrong. Even more troubling was that the professor refused to give us any guidelines on what he was looking for; he gave us total freedom. He simply said, “I want to see what you come up with.”
Full of anxiety, I first set out to read Camus’s essay several times to make sure I really knew what was it was about. I did my best to take careful notes. Yet even after I took all these notes and knew the essay inside and out, I still did not know the right answer. What was my interpretation? I could think of a million different ways to interpret the essay, but which one was my professor looking for? In math class, I was used to examples and explanations of solutions. This assignment gave me nothing; I was completely on my own to come up with my individual interpretation.
Next, when I sat down to write, the words just did not come to me. My notes and ideas were all present, but the words were lost. I decided to try every prewriting strategy I could find. I brainstormed, made idea maps, and even wrote an outline. Eventually, after a lot of stress, my ideas became more organized and the words fell on the page. I had my interpretation of “The Myth of Sisyphus,” and I had my main reasons for interpreting the essay. I remember being unsure of myself, wondering if what I was saying made sense, or if I was even on the right track. Through all the uncertainty, I continued writing the best I could. I finished the conclusion paragraph, had my spouse proofread it for errors, and turned it in the next day simply hoping for the best.
Then, a week or two later, came judgment day. The professor gave our papers back to us with grades and comments. I remember feeling simultaneously afraid and eager to get the paper back in my hands. It turned out, however, that I had nothing to worry about. The professor gave me an A on the paper, and his notes suggested that I wrote an effective essay overall. He wrote that my reading of the essay was very original and that my thoughts were well organized. My relief and newfound confidence upon reading his comments could not be overstated.
What I learned through this process extended well beyond how to write a college paper. I learned to be open to new challenges. I never expected to enjoy a philosophy class and always expected to be a math and science person. This class and assignment, however, gave me the self-confidence, critical-thinking skills, and courage to try a new career path. I left engineering and went on to study law and eventually became a lawyer. More important, that class and paper helped me understand education differently. Instead of seeing college as a direct stepping stone to a career, I learned to see college as a place to first learn and then seek a career or enhance an existing career. By giving me the space to express my own interpretation and to argue for my own values, my philosophy class taught me the importance of education for education’s sake. That realization continues to pay dividends every day.
Most People Don’t Understand Memoirs
In 2006, James Frey wrote a memoir about parts of his life when he was under the influence of drugs called A Million Little Pieces , and after Oprah had him on her show to discuss the book – it was featured in her popular book club, of course – she was told that he “lied” about certain parts. Well, he didn’t lie. Memoirs contain what we remember. What we remember isn’t always “fact.” What I always say is that if you have all of your family members report what happened at a family gathering – like a birthday party or Christmas – whose report would be correct? No ones! That’s what a memoir is. It’s still nonfiction because it’s what the person remembers, but it’s not false on purpose. If I remember that my sister responded to me in a snotty way one day and my other sister didn’t think so, no one is correct. It’s just my memory versus hers.
Now, typically, memoirs encompass just a chunk of someone’s life, like when James Frey wrote about his drug years, but sometimes, some famous person in their 70s (or older) will write his/her memoir. No matter what, it’s simply what they remember, and I suppose if someone’s on drugs or has an awful memory, the stories could appear to be false. But they aren’t. That’s why they say, “life is stranger than fiction.”
Memoirs are part of the nonfiction category of literature; they contain a lot of description and detail, and they are typically very, very personal in content.

The Bits and Pieces of Memoir
The memoir is a specific type of narrative. It is autobiographical in nature, but it is not meant to be as comprehensive as a biography (which tells the entire life story of a person). Instead, a memoir is usually only a specific “slice” of one’s life. The time span within a memoir is thus frequently limited to a single memorable event or moment, though it can also be used to tell about a longer series of events that make up a particular period of one’s life (as in Cameron Crowe’s film memoir Almost Famous ). It is narrative in structure, usually describing people and events that ultimately focuses on the emotional significance of the story to the one telling it. Generally, this emotional significance is the result of a resolution from the conflict within the story. Though a memoir is the retelling of a true account, it is not usually regarded as being completely true. After all, no one can faithfully recall every detail or bit of dialogue from an event that took place many years ago. Consequently, some creative license is granted by the reader to the memoirist recounting, say, a significant moment or events from his childhood some thirty years, or more, earlier. (However, the memoirist who assumes too much creative license without disclosing that fact is vulnerable to censure and public ridicule if his deception is found out, as what happened with James Frey and his memoir, A Million Little Pieces .)
Furthermore, names of people and places are often changed in a memoir to protect those who were either directly or indirectly involved in the lives and/or event(s) being described.
Why read memoirs?
To learn about other people’s lives and their thoughts about events that have occurred. Memoirs are a personalized look at history.
How to write memoirs?
Reflect n your life. write what you remember about events that matter to you from your unique point-of-view.
Dialogue is another way to bring life to your writing. Dialogue is conversation or people speaking in your story. An engaging dialogue goes beyond what is simply being said to include descriptions of non-verbal communication (facial expressions, body movement, changes in tone, and speed of speech) and characterization. The way people speak and interact while talking reveals much about them and the situation.
Writing a natural-sounding dialogue is not easy. Effective dialogue must serve more than one purpose – it should:
- Drive the plot forward,
- Reveal information about the characters, and
- Build tension or introduce conflict.
Sample Dialogue
“So, what was it really like?” I asked.
“I’ve told you. It was amazing.”
I shifted to my side so I could look at her. “You have to give me more than that,” I insisted, “and not the mom and dad version.”
Liv mirrored my move to her side and propped up her head with her arm. Her blue eyes searched my greens, looking for the right words. “I shouldn’t–”
We broke our gaze as we heard our mom call for us. Once again, I didn’t get the truth.
Basic Dialogue Rules
- “I want to go to the beach,” she said.
- He asked, “Where’s the champagne?”
- “That is,” Wesley said, “that neither you nor me is her boy.”
- Even if the speaker says only one word, with no accompanying attribution or action, it is a separate paragraph.
- Start a new paragraph when you wish to draw the reader’s attention to a different character, even if that character doesn’t actually speak.
- For internal dialogue, italics are appropriate.
Example Memoir
Chocolate Can Kill You
Just when you think your life could not get any better, the Great One Above throws you for a loop that causes you to think upon your life, yourself, and your “little” obsession with chocolate. I am somewhat ashamed of this story, but it taught me so much. I still remember Alisa’s face when I came crying into the Valley City gym, I can hear Dad’s echoing “Are you OKAY?” consistently in my mind as if it had been a childhood scolding, and I see the image of the snow coming at me at 70mph every time I drive on a highway now.
In 1997, the morning after Valentine’s Day, I took off to see my sister in Valley City. She was there because of a wrestling meet. She is one of their prized assistants and without her, they would never get to see how goofy they look in tights. It was a crisp morning, and I cannot remember if I filled the bronco’s tank, but I did purchase a Twix bar before heading out on I-94. I vaguely remember thinking, Gee a seat belt would be good, even though the roads were as clean as they could have been in a North Dakota February. On that ten-degree morning, I met up with no one on the highway.
I was just bee-bopping along the left side of the road, listening to the radio and singing aloud as if I was Mariah Carey. It was at this time that I chomped into my first Twix bar.
In an attempt at a different radio station or something or another, I dropped the last bar between my legs onto the floor of the black beastly bronco.
This is where I become a stupid human. I tried to recapture the chocolate bar thinking, or maybe not even thinking, It will only take me a second. Whoever has said that seconds count in any accident WAS RIGHT! All of a sudden, I look up to see that I am driving 70 mph into the median’s snowdrifts. I cranked the wheel, thinking I could just drive back onto the highway. I mumble a few swear words and realize I am going 70 MPH IN A VERY DEEP SNOWDRIFT! I take my foot off the accelerator and while the front end slows, the back end has accumulated too much energy or velocity (a good physics question) and begins to lift upwards. I close my eyes, cross my arms across my chest, and crouch back into my seat and start to feel the bronco as well as myself turn and twist and hover for what seemed an eternity in slow motion. I did not open my eyes once.
And then all of a sudden, the small jolted car lands- PLOP – ON ITS WHEELS! My chair has completely reclined, and I sit up seeing smoke coming from my engine. I forget how to work my car and instinctively get out as if to show God I am alive. I stand on top of the drift becoming taller than my boxy 4×4. There are small dents in the front where you would open the hood but that is the biggest damage I can see.
“Are you OKAY?” An old couple are parked and honking at me from the other side of the highway going towards Fargo. They tell me to come with them and turn off the engine. I grab my parka and make my way through the snow to sit down in the back seat of the long car and take in that old people smell. This is when I quietly cry.
“You did a flip! It’s amazing you walked away from it,” says the old man and I think to myself sarcastically to calm down, Yeah I tried to do that. I ask them to take me to Valley City trying not to sound three and a half. Another major thought echoes What will Dad say?
They turned around at the next available bridge which was a mile away and the lady told me the exit so I could give it to the people that will tow my little bruised bronco. They talked to themselves as I tried to think of what exactly happened, how glad I was to be alive, and how I felt about it. Once inside the gymnasium, I found Alisa’s eyes and she instantly frowned and looked scared.
“Did you and Jason fight?” No, I try to say but I am crying in front of a large crowd who all seem more interested in me now than the matches. I sit down beside her and say:
“I did a flip… the bronco… flipped … it did a 360.”
“The bronco did a WHAT! ARE YOU OKAY!” She panics. I go to call Dad as she tells her friends, and they also feel sympathetic and are quite amazed. I don’t know how I managed to remember my calling card number, but I reached Mom and Dad just waking up. Once again Dad frightens me with his voice and vows to be there as soon as possible and tells me to call the highway patrol.
I was the only accident that whole day on the highway, I think, so I looked pretty silly.
Mom and Dad showed up an hour later. Mom was half-awake, and Dad looked like he’d been chugging coffee left and right. They had seen the bronco being towed incorrectly towards Fargo, so Dad feared the transmission was screwed up again much less the rest of the car. We took off for Fargo and stopped at the spot seeing the tracks lead into the snow, then 25 feet of no tracks, and suddenly a large indentation where the bronco had sat down.
Once at the Mobile on I-29, Dad jumped into the bronco to try to start it. It revved right up. I shook my head and thought of the motto, Built Ford Tough. Only the alignment and steering was off from me trying to turn it back onto the road, and the steam I had seen was the radiator fluid splashing onto the hot engine.
We had to meet with a highway patrolman, so the bronco could get a sticker and photos could be taken. I also, fortunately for the taxpayers, had to pay a Care of Vehicle bill of thirty dollars which means that the government basically can fine someone for trashing his/her own vehicle. This pissed me off incredibly after a day like I had just had. My mom had to remind me though that at least it wasn’t a medical bill.
The highway patrolman reminds me how valuable it was that I had had a seat belt on because I would have for sure gone through the windshield with that type of event and all the tossing that I had endured. That does not make replaying this event in my memory any better. As if God was saying: “No, not yet.”
It’s a common joke to not let me eat while I am driving.
That day made me incredibly grateful for my life, and for the people who came to my aid, especially my parents for spending their whole Saturday with me. Whether we were trying to contact the highway patrolman, paying the tower and the ticket, or comforting me- they never complained. Who knew chocolate could lead to such a life-threatening, yet philosophical day?
Time to Write
Purpose: This assignment will demonstrate the understanding of how to write a memoir
Task: This assignment frames a single event for the memoir essay.
Write a Memoir Essay. This essay should clearly identify a significant event or series of closely tied events that convey the significance of that event or has somehow shaped your personal perspective. Remember that you are writing for an audience that doesn’t share your knowledge of the event(s), people, setting, etc. It is up to you to make your memoir come to life.
Key Features of a Memoir:
- Invoke the 5 senses
- Use narrative suspense
- use metaphor
- include significant details
- provide descriptive language
- use effective dialogue
- include transitions
Key Grading Considerations
- The rhetorical purpose is clear, focused, and appropriate to the audience and assignment.
- The purpose is focused on the memoir.
- Shows engagement with issues of story, language, rhetoric, or thinking deeply about a personal event.
- The theme relates to a personal experience but also illustrates more universal principles.
- Transitions
- Learning Point Thesis Statement
- Topic Sentences
- Some Narrative Elements that flow with the paper
- Clear introduction, event story, and conclusion
- Dialogue is used
- Descriptions and quotes to help visualize the event
- Correct, appropriate, and varied integration of textual examples, including in-text citations
- Limited errors in spelling, grammar, word order, word usage, sentence structure, and punctuation
- Good use of academic English
- Demonstrates cohesion and flow
- Uses the rules of dialogue
- Date format
Attributions
- Memoir Content Adapted from Excelsior Online Writing Lab (OWL). (2020). Excelsior College. Retrieved from https://owl.excelsior.edu/ licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-4.0 International License .
- Narrative Writing Content Adapted from BETTER WRITING FROM THE BEGINNING . (2020). Jenn Kepka. Retrieved from Better Writing from the Beginning licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-4.0 International License .
English 101: Journey Into Open Copyright © 2021 by Christine Jones is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
25 Thesis Statement Examples That Will Make Writing a Breeze

Understanding what makes a good thesis statement is one of the major keys to writing a great research paper or argumentative essay. The thesis statement is where you make a claim that will guide you through your entire paper. If you find yourself struggling to make sense of your paper or your topic, then it's likely due to a weak thesis statement.
Let's take a minute to first understand what makes a solid thesis statement, and what key components you need to write one of your own.

A thesis statement always goes at the beginning of the paper. It will typically be in the first couple of paragraphs of the paper so that it can introduce the body paragraphs, which are the supporting evidence for your thesis statement.
Your thesis statement should clearly identify an argument. You need to have a statement that is not only easy to understand, but one that is debatable. What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute . An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic.
Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's cuteness is derived from its floppy ears, small body, and playfulness." These are three things that can be debated on. Some people might think that the cutest thing about puppies is the fact that they follow you around or that they're really soft and fuzzy.
All cuteness aside, you want to make sure that your thesis statement is not only debatable, but that it also actually thoroughly answers the research question that was posed. You always want to make sure that your evidence is supporting a claim that you made (and not the other way around). This is why it's crucial to read and research about a topic first and come to a conclusion later. If you try to get your research to fit your thesis statement, then it may not work out as neatly as you think. As you learn more, you discover more (and the outcome may not be what you originally thought).
Additionally, your thesis statement shouldn't be too big or too grand. It'll be hard to cover everything in a thesis statement like, "The federal government should act now on climate change." The topic is just too large to actually say something new and meaningful. Instead, a more effective thesis statement might be, "Local governments can combat climate change by providing citizens with larger recycling bins and offering local classes about composting and conservation." This is easier to work with because it's a smaller idea, but you can also discuss the overall topic that you might be interested in, which is climate change.
So, now that we know what makes a good, solid thesis statement, you can start to write your own. If you find that you're getting stuck or you are the type of person who needs to look at examples before you start something, then check out our list of thesis statement examples below.
Thesis statement examples
A quick note that these thesis statements have not been fully researched. These are merely examples to show you what a thesis statement might look like and how you can implement your own ideas into one that you think of independently. As such, you should not use these thesis statements for your own research paper purposes. They are meant to be used as examples only.
- Vaccinations Because many children are unable to vaccinate due to illness, we must require that all healthy and able children be vaccinated in order to have herd immunity.
- Educational Resources for Low-Income Students Schools should provide educational resources for low-income students during the summers so that they don't forget what they've learned throughout the school year.
- School Uniforms School uniforms may be an upfront cost for families, but they eradicate the visual differences in income between students and provide a more egalitarian atmosphere at school.
- Populism The rise in populism on the 2016 political stage was in reaction to increasing globalization, the decline of manufacturing jobs, and the Syrian refugee crisis.
- Public Libraries Libraries are essential resources for communities and should be funded more heavily by local municipalities.
- Cyber Bullying With more and more teens using smartphones and social media, cyber bullying is on the rise. Cyber bullying puts a lot of stress on many teens, and can cause depression, anxiety, and even suicidal thoughts. Parents should limit the usage of smart phones, monitor their children's online activity, and report any cyber bullying to school officials in order to combat this problem.
- Medical Marijuana for Veterans Studies have shown that the use of medicinal marijuana has been helpful to veterans who suffer from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Medicinal marijuana prescriptions should be legal in all states and provided to these veterans. Additional medical or therapy services should also be researched and implemented in order to help them re-integrate back into civilian life.
- Work-Life Balance Corporations should provide more work from home opportunities and six-hour workdays so that office workers have a better work-life balance and are more likely to be productive when they are in the office.
- Teaching Youths about Consensual Sex Although sex education that includes a discussion of consensual sex would likely lead to less sexual assault, parents need to teach their children the meaning of consent from a young age with age appropriate lessons.
- Whether or Not to Attend University A degree from a university provides invaluable lessons on life and a future career, but not every high school student should be encouraged to attend a university directly after graduation. Some students may benefit from a trade school or a "gap year" where they can think more intensely about what it is they want to do for a career and how they can accomplish this.
- Studying Abroad Studying abroad is one of the most culturally valuable experiences you can have in college. It is the only way to get completely immersed in another language and learn how other cultures and countries are different from your own.
- Women's Body Image Magazines have done a lot in the last five years to include a more diverse group of models, but there is still a long way to go to promote a healthy woman's body image collectively as a culture.
- Cigarette Tax Heavily taxing and increasing the price of cigarettes is essentially a tax on the poorest Americans, and it doesn't deter them from purchasing. Instead, the state and federal governments should target those economically disenfranchised with early education about the dangers of smoking.
- Veganism A vegan diet, while a healthy and ethical way to consume food, indicates a position of privilege. It also limits you to other cultural food experiences if you travel around the world.
- University Athletes Should be Compensated University athletes should be compensated for their service to the university, as it is difficult for these students to procure and hold a job with busy academic and athletic schedules. Many student athletes on scholarship also come from low-income neighborhoods and it is a struggle to make ends meet when they are participating in athletics.
- Women in the Workforce Sheryl Sandberg makes a lot of interesting points in her best-selling book, Lean In , but she only addressed the very privileged working woman and failed to speak to those in lower-skilled, lower-wage jobs.
- Assisted Suicide Assisted suicide should be legal and doctors should have the ability to make sure their patients have the end-of-life care that they want to receive.
- Celebrity and Political Activism Although Taylor Swift's lyrics are indicative of a feminist perspective, she should be more politically active and vocal to use her position of power for the betterment of society.
- The Civil War The insistence from many Southerners that the South seceded from the Union for states' rights versus the fact that they seceded for the purposes of continuing slavery is a harmful myth that still affects race relations today.
- Blue Collar Workers Coal miners and other blue-collar workers whose jobs are slowly disappearing from the workforce should be re-trained in jobs in the technology sector or in renewable energy. A program to re-train these workers would not only improve local economies where jobs have been displaced, but would also lead to lower unemployment nationally.
- Diversity in the Workforce Having a diverse group of people in an office setting leads to richer ideas, more cooperation, and more empathy between people with different skin colors or backgrounds.
- Re-Imagining the Nuclear Family The nuclear family was traditionally defined as one mother, one father, and 2.5 children. This outdated depiction of family life doesn't quite fit with modern society. The definition of normal family life shouldn't be limited to two-parent households.
- Digital Literacy Skills With more information readily available than ever before, it's crucial that students are prepared to examine the material they're reading and determine whether or not it's a good source or if it has misleading information. Teaching students digital literacy and helping them to understand the difference between opinion or propaganda from legitimate, real information is integral.
- Beauty Pageants Beauty pageants are presented with the angle that they empower women. However, putting women in a swimsuit on a stage while simultaneously judging them on how well they answer an impossible question in a short period of time is cruel and purely for the amusement of men. Therefore, we should stop televising beauty pageants.
- Supporting More Women to Run for a Political Position In order to get more women into political positions, more women must run for office. There must be a grassroots effort to educate women on how to run for office, who among them should run, and support for a future candidate for getting started on a political career.
Still stuck? Need some help with your thesis statement?
If you are still uncertain about how to write a thesis statement or what a good thesis statement is, be sure to consult with your teacher or professor to make sure you're on the right track. It's always a good idea to check in and make sure that your thesis statement is making a solid argument and that it can be supported by your research.
After you're done writing, it's important to have someone take a second look at your paper so that you can ensure there are no mistakes or errors. It's difficult to spot your own mistakes, which is why it's always recommended to have someone help you with the revision process, whether that's a teacher, the writing center at school, or a professional editor such as one from ServiceScape .
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Need an academic editor before submitting your work?
Writing the Memoir (Moxley): Introduction
- Introduction
- Tips for Writing the Memoir
- Annotated Memoirs
- Describing a Person
- Describing a Place
- Sample Topics and Essays
Introduction to Writing the Memoir
Teaching and writing the memoir .
A memoir can be one of the most meaningful essays that a student can write and one of the most engaging essays for a teacher to read. The spirit generated by the memoir can create class fellowship less attainable through subjects requiring pure analysis, description, or narration. More than any other subject, a memoir demands that a student bring his sensibilities and experiences to school, and when that happens, it is virtually impossible for anyone to accept a mediocrity of passion. Students and teachers are likely to treat writing as an experience in itself, a means for writers to understand their lives and for teachers to understand their students’ worlds.
In Terrains of the Heart, Willie Morris writes,
If it is true that a writer's world is shaped by the experience of childhood and adolescence, then returning at long last to the scenes of those experiences, remembering them anew and living among their changing heartbeats, gives him, as Marshall Frady said, the primary pulses and shocks he cannot afford to lose. I have never denied the poverty, the smugness, the cruelty which have existed in my native state [ Mississippi ]. Meanness is everywhere, but here the meanness, and the nobility, have for me their own dramatic edge, for the fools are my fools, and the heroes are mine too.
As a young editor who left his native state for New York City, Willie Morris wrote prolifically about his hot Mississippi youth from the cold Northeast. His essays on home preserve a way of life in the Delta—a complicated history marked by romance and violence—while he lived in a New York far removed from this past. We sense when reading Willie Morris’s carefully crafted memories that he is coming to know himself through his writing and, in a broader sense, has resurrected a world that can help others understand their own lives.
To both student and teacher, this is what I hope teaching and writing the memoir will give you: a chance to investigate your past, your culture, and your lives in general, and in so doing, create a community of authors who delight in the struggle to write clearly, meaningfully, and correctly.
The Rationale
By clicking here , or by opening the above tab, Annotated Memoirs, you will go to a list of six types of essays, each of which is hyperlinked to a sample essay and a discussion of it.
Each sample annotated essay will have the following:
1. an introduction that comments on the type of essay and how it may generate good writing from young students;
2. a link to the essay so you can open or print it;
3. a discussion of the essay, called “The Craft of the Essay,” which explains the strategy in each paragraph or “part” of the essay so that the teacher and student can see how the memoir was crafted from the bare memory. This section should encourage teacher and student to scrutinize the essay together during a read-aloud session to determine how they think the memory was turned into memoir;
4. an “Assignment” section that gives the student some specific questions to answer that might help them see the further craft of the particular memoir.
Teaching Strategies
As with any assignment, the teaching strategy depends on the size of the class, the amount of time allotted for the assignment, how much it is weighted, and so forth.
Ideally, teaching the memoir should take 6-7 nights of homework. These nights could be spaced over the course of two-three weeks.
You could also make it a lighter assignment and cut it to 3-4 assignments, with only one rough draft, instead of the two I suggest.
Homework Assignment #1:
The teacher/class decides which category of memoir they will read together as a class to introduce the assignment. For example, you may choose from the Annotated Memoirs to read the Writing about Death and Mortality assignment and its sample annotated essay “Death of a Pig” by E. B. White. For this night’s homework, the students should print out the assignment and essay at home to bring to class as their text. They should read the essay, read the “Craft of the Essay” discussion, and then answer on paper the questions under the “Assignment” section.
In class the next day, read the essay aloud (or as much of it as possible), go over the “Craft of the Essay” and finish the day having the students explain their responses to the “Assignment.”
If there is any time left, you might get the students to discuss the topic, “Where does memory begin?” ( Click here for a passage from Willie Morris's Taps to get the ball rolling. )
Homework Assignment #2:
Open the Sample Topics and Essays tab to find numerous topics and sample essays. Decide whether everyone is going to write the same type of essay or whether the topic will be open to a variety of memoirs. Then read a few sample essays for the topic you choose.
Written homework is to sit for 40 minutes and do a “fast write,” in which the student writes about half of the first draft of the memory, paying no attention to grammar, style, syntax, or organization. This assignment is to get the student to write or type 2-3 pages of his memory with some, but minimal, revision (the revision should take place after the fast-write). Click on the tab, Tips for Writing the Memoir, for some help getting started after the fast-write.
In class the next day, students will read aloud what they have written. The object is to hear one or two inspiring accounts so that each student can “get the hang of the assignment.” The teacher should be pushing everyone to develop his “voice.” Again, see Tips for Writing the Memoir for a discussion of voice and other terms.
Homework Assignment #3:
Continue where the students left off in Assignment #2 and try to write 4-5 handwritten, or 3-4 typed, pages. If someone does not like what he/she did in Assignment #2, then start anew.
In class the next day, have the students read aloud their work. By the end of this day everyone should have read his/her essay at least once, either on this day or the day before. The teacher should keep track of who has read. Again, note how distinct the students’ written voices are, and who is putting in moments of self-reflection and not getting hung up on chronological retelling.
Homework Assignment #4:
By this time the students should know the focus of their essay (in other words, what wisdom, revelation, or general idea that their essay is revealing) and should begin “crafting,” or creatively organizing, the memory to become a memoir.
It is crucial that the student realize that facts are not solely important. Good memoirs are a blend of fact and creation; this concept will be tough to defend, but the writers of memoir have flexibility regarding the facts of the memory, since it is the “truth” of the memory they are creating; sometimes the facts are too confusing or pallid to have the needed color to make a memory vivid. For a memory to become memoir, it needs a larger-than-life appeal. ( Click here for some comments by Dorothy Gallagher on fact versus truth in memoir. )
To craft the essay, for homework (5-10 minutes) try having them draw a timeline of the way the memory works; in class the teacher can draw the timeline of other successful sample essays. They will see that many essays about a lost loved one starts at the funeral, flashes back to the life, and at the end returns to the funeral. Flashbacks are crucial to building characters, dead or alive
Also ask them to outline what they have written as best they can (10-15 minute assignment). Then, looking at their outlines, they may see a way to restructure the telling of the memory to get the most out of it.
The students should be encouraged to imitate the structure of essays that resemble the one they are writing.
With all this in mind, they should go back and begin writing a new draft for 30 minutes. In class the next day, have them report on what they’ve changed and have them read some first paragraphs aloud.
Homework Assignment #5:
Finish draft number 2. The students should be keeping track of their rough drafts, as their grade will be based as much on effort and process as on final product. By now the essays should have incorporated a number of ways to build character, place, and their focus: short dialogue, concrete descriptions, anecdotes, and moments of reflection.
Have each student read his or her first 3-4 sentences. Urge everyone to listen intently and decide which of these sentences should be the first one in the essay. Frequently, the first paragraph or two can be cut. It takes most writers about 100 or more words to get warmed up. Remind them of the Truman Capote Rule: “I believe more in the scissors than I do the pencil.”
Homework Assignment #6:
The final essay is due, approximately 4-5 typed pages. The student should turn in at least two verifiable rough drafts and the final draft. The teacher will have heard every student’s paper at least once and should have encouraged each student to drop by for 5-10 minutes during the last 4-5 days to discuss the progress of the memoir.
The process of this assignment should be weighted as heavily as the final product. I usually check that the student has written two drafts, contributed to class workshops, and has revised carefully by showing he has learned:
(1) to start strategically;
(2) to create the various characters through description, action, anecdote, and brief dialogue;
(3) to create place and atmosphere through concrete description, temperature, climate, and telling details;
(4) to build a strong focus through moments of self-reflection;
(5) to organize strategically, dividing his essay into many paragraphs, some short, some long;
(6) to unify his essay so that, although it may wander, it ultimately returns to some unifying point or image;
(7) to punctuate and write solid sentences that create a pleasing variety and rhythm.
- Willie Morris's "Taps"
- Comments by Dorothy Gallagher
- Next: Tips for Writing the Memoir >>
- Last Updated: Jan 18, 2024 11:10 AM
- URL: https://libguides.montgomerybell.edu/memoir
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Writing Guide
- Essay Writing
How to Write a Memoir Essay
- The seedier side of town
- A broken family home
- A tumultuous or abusive relationship
- Addiction or substance abuse
- The social service system
- In a position of power
- Fit or healthy
- Open to faith
Tips How to Write a Memoir Essay – Step by step
- Understand your theme, and stick to it: Remember that no one cares that you’ve ‘made something of yourself’, except for your mom and maybe a handful of other close friends and relatives who already know and love you.
- Find a Common Ground
- Pick your Anecdotes Carefully
- Write your Memoir like You Would Write a Novel
- Share your story, but don’t steamroll people
What is the difference between a Memoir vs. Autobiography
- less formal
- less inclusive
- focused more on emotional truth and how it has shaped the current life of the writer
- less strict to factual events
- Written by the subject, or with a collaborating writer
- A chronological account of the entire life of the subject
- Extremely fact based
Tips for Writing a Well-Written Memoir
- Don’t make it too much like an autobiography. Stick to your theme.
- Don’t include minutiae. (Small, insignificant details that no one cares about)
- Try not to gloat or brag.
- Don’t gloss over the truth. Yes, you can change identifying details so that you don’t expose the people you are writing about, but don’t outright lie.
- Try not to sound to ‘preachy’ or like you are far superior to those around you.
Some Remarkable Memoir Examples
- Mao’s Last Dancer by Li Cunxin
- Trafficked by Sophie Hayes
- On Writing by Stephen King
- Dancing to the Beat of the Drum by Pamela Nomvete
- The Girl from Foreign by Sadia Shepard
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account

Why Write a Memoir?
- Share this:
Guest post by Laura Waterman
If we write to gain an understanding of ourselves, memoir is the form in which such writing can take place.
In my memoir, Calling Wild Places Home , I devoted an essay to how making one phone call changed my life. This, at the time, I couldn’t have seen. I was much too wrapped up in my daily life to see how becoming a rock climber—and everything that came from that—evolved from a relatively casual decision to pick up the telephone and call to register for the Appalachian Mountain Club’s program for beginner rock climbers.
Memoir writing can be about those pivotal events that lead you into a greater understanding of your life.
But here’s the catch. Here’s the great thing about memoir. What made me make that call? Here’s where the real work begins. For me, I had recently returned from a months-long trip and found myself unable to pick up my old life in the city again. I was looking for a way out, though I was hardly aware of this. At that point, just getting out of the city on weekends sounded good to me. And then what happened? That’s how we memoirists start, as we say, “peeling the onion.”
In writing memoir we are given the chance to engage with ourselves at a deep level. We can take a “backward glance,” as Edith Wharton titled her autobiography. This great writer was not writing a memoir, but I’ll use her evocative phrase to serve as a stepping-off point for memoir writers. I’ve come to think of memoir writing as a “backward glance,” plus . For me the plus means this backward glance can become a scrutiny, a microscopic examination, an exercise in a form that has the power to change our lives. Writing memoir puts us on the path to focus on events that have, for better or worse, shaped us. Through writing memoir, we gain an understanding of the mechanics of how that shaping happened. We gain self-knowledge. We learn who we are.
Of course, we will never discover ourselves completely because we are always being changed by the daily experience of our living. We are like the onion: another fold is beneath the one just peeled. You can keep on peeling until a tiny invisible center is left. That could be peeled too, if you had the tools for it.
Memoir writing gives us those tools. The hardest part is to begin.
The interesting thing about this peeling—of the onion, of your own inner core of emotions and often tangled thoughts—is that with every layer peeled you gain. Memoir writing is pure gain. It’s highly personal. You are confronting your past. By doing so you risk evoking thoughts, or scenes, that can cause pain. But if you stick with it, the pain eases. It’s not gone. It’s just waiting for you to return, with pen and paper in hand, to keep peeling. It might feel never ending, but every revision gets you closer, deeper into an understanding.
Yes! That “backward glance plus ” can turn into hard work. Scary work. When we touch these memories they can burn our fingers. You shy back, pull away. You bury those pages in a deep dark drawer. But, ah! You can’t help yourself. Despite your stinging fingers you’re compelled to pick up your work again. You might battle back and forth, but at some point you get caught up in what you’re discovering. It feels true. And the other side of that is, you’ll know when it’s not true. You’ll feel yourself cringe, when you read over your work, if you’re lying to yourself. Or even if you’re just skimming the surface. And that is because you’re dealing with emotions, and emotions never lie. Memory cannot be trusted, but the emotions contained in the memory don’t change. Emotions can be complex and confusing, but they speak the truth. There is an emotional truth to events that we disregard at our peril, and it is the grist in the memoirist’s mill.
With my first memoir, Losing the Garden , I wrote five or six drafts that went no deeper than the first two or three peels of that onion. What made me find the courage to continue? The subject was my husband’s choice to take his own life. I was finding that to continue on with mine I needed to find out who I was, particularly why I morally supported his decision. Now I was on the right path—true and honest. It took a good half dozen more drafts.
This new memoir, Calling Wild Places Home , is another attempt at a scrutinizing “backward glance” from twenty plus years after my husband’s death. There is always more to discover. With the passage of time we learn about how past events can affect and change us. That’s the glory of writing memoir! We’ve hit our stride when we commit to the form that can not only bring healing but joy as well. Have I come to the end? Have I finished the job? Oh, no! We are always growing and changing. Our emotions, if we let them, will be our true guide, our lodestone.
We are writing to explain ourselves to ourselves. I believe that even if we choose not to publish our work, an act of sharing takes place: we have become more human—more ourselves—in the course of gaining self-understanding.
Laura Waterman is the author of Losing the Garden: The Story of a Marriage and Starvation Shore: A Novel . With her husband, Guy Waterman, she maintained the Franconia Ridge in the White Mountains of New Hampshire for almost two decades and was awarded the American Alpine Club's 2012 David R. Brower Award for outstanding service in mountain conservation. Together, she and Guy wrote numerous articles and books on the outdoors, including The Green Guide to Low-Impact Hiking and Camping ; Wilderness Ethics: Preserving the Spirit of Wildness ; Yankee Rock & Ice: A History of Climbing in the Northeastern United States ; and A Fine Kind of Madness: Mountain Adventures Tall and True . In 2019, SUNY Press published the thirtieth-anniversary edition of their book Forest and Crag: A History of Hiking, Trail Blazing, and Adventure in the Northeast Mountains . Laura lives in Vermont.
Books Mentioned In This Post

Calling Wild Places Home
A Memoir in Essays

Expanding the Public Service View

Growing North Fork Wine: A Terroirist Manifesto
- Essay Topic Generator
- Summary Generator
- Thesis Maker Academic
- Sentence Rephraser
- Read My Paper
- Hypothesis Generator
- Cover Page Generator
- Text Compactor
- Essay Scrambler
- Essay Plagiarism Checker
- Hook Generator
- AI Writing Checker
- Notes Maker
- Overnight Essay Writing
- Topic Ideas
- Writing Tips
- Essay Writing (by Genre)
- Essay Writing (by Topic)
Best Memoir Examples that Will Stir Your Imagination [UPD 2024]

If you are having a hard time writing your memoir, you should check out the memoir examples that we’ve prepared for you. These wonderful samples will show you what a truly good memoir is and what it might look like. We’ve also explained what a memoir is, chosen interesting tips, and provided a memoir essay structure for you.
📝 Memoir Definition
💡 memoir tips.
- 🖊️ Memoir Examples
- 📎 Memoir About Yourself
📜 Example of Memoir About Yourself
- 📋 One-Page Memoir
📚 Memoir Essay Structure
🔗 references.
A memoir is an account of your experiences related to events from your personal life or history that you witnessed.
A memoir is sometimes also called an autobiography, as the two terms share the same meaning to some extent.
But here’s the deal:
There is a slight difference between writing a memoir and writing an autobiography, and it is important to truly understand it in order to benefit most from reading an example of a memoir.
Let’s have a look at this difference!
Memoir VS Autobiography

Writing your memoirs is an excellent exercise and a good start for a beginning author.
You can learn from it different approaches to captivating readers, develop a skill to express emotions in the right way, and train your writing style .
And what is more pleasant:
After practicing this assignment for some time, you can know how to write a memoir book.If you want to read about other types of assignments, read the Overnight Essay blog . We can also help you to write your paper of any complexity.
A person who writes a memoir is a memoirist or… simply a student who has been assigned this task. No matter to which category you belong, the following memoir writing tips will help you write a killer memoir sample:
- choose an intriguing title (something like The Other Side of Me or A Day to Remember); it can help you a lot to interest the audience;
- express your personal opinions and impressions (use, for instance: to my mind, in my opinion, it seems, it turned out that, etc.);
- add a lot of sensory details (for example, instead of simply stating that a girl had an angry look on her face, you can specify that her face reddened and her teeth were clenched – these are valuable observations that can make your description more vivid);
- write about memories that are important to you – it’s impossible to write a good memoir without feeling a deep connection between yourself and the situation which you describe;
- be yourself when writing a memoir – you can hide your point of view in many academic writings , but this type of work requires you to be honest and show your personal traits;
- choose a proper tone and try to maintain it throughout your memoir essay – it’s an excellent exercise to develop your writing style;
- do research; even if you remember the situation, try to collect as much information as you can, including your friends’ commentaries, photos, blog posts – everything that can reveal more details;
- take care about your memoir idea – whether your writing is funny, well-structured, or creative and unusual, it means nothing if you don’t put a message in it.
The most famous memoir books are based on the principles listed above. Keeping to them, you can create a masterpiece or, at least, get an A at your college.
But that isn’t all we can offer you:
You can find even more truly good ideas for your memoir in this list of informative speech topics for college students .
🖊️ Memoir Examples to Your Attention
Finally, you can observe these memoir writing examples to know how to write one yourself.
Of course, you can use these memoir ideas, but reading these samples can also give you enough inspiration to develop your own paper from the very beginning.
Let’s check these memoir essay examples!
My Pursuit of Happiness
Actually, I started my pursuit of happiness as soon as I came into this world. My Mom says that I was an extremely capricious baby – I could cry out loud for a rather long period of time until all my demands were satisfied. A little terrorist, with large rainy eyes and a loud voice, I was! Later on, as I grew up, I preserved my willingness to do everything to get what I wanted, but I learned some new and more effective methods of achieving my goals.
I remember that when I was 4 years old, I wanted to have a dog. Absolutely nothing, even my allergy to dogs, could prevent me from making my dream come true…
Comment: The title is captivating – it sets the tone, but it does not reveal all the secrets. This example of a memoir contains some self-criticism. The author sounds truly sincere when s/he calls himself (herself) a terrorist.
A Revolution at School
The events of that sunny spring day turned out to change the course of history at our school. I am proud of being one of the revolutionaries who drove the change.
The problem was our school uniform, which was more or less bearable in winter but became a cause of students’ torture in spring because it was too hot.
This is why the girls from our class agreed to wear jeans instead of the uniform one day, to show our protest against the silly school rule of wearing the uniform even when it was too hot for it. We felt a bit scared before the beginning of the first lesson. Mrs. Stone, our Geography teacher, had to be the first to see our silent protest…
Comment: The author expresses his/her feelings and emotions about an important event at school. Note that this sample memoir focuses more on the event than on the author’s personality.
📎 Memoir about Yourself
A memoir about yourself or a personal memoir differs from just a personal essay. A memoir about yourself is a piece of writing in which a person reflects on important personal events. It is a place where the author analyzes and describes why certain events were so crucial.
But you might fairly ask: “What is the difference between a personal memoir and a personal essay?” Here is the answer!
To some extent, the personal memoir and the personal essay are pretty similar. However, there is one important difference! The essay can be a reflection on any events or just a description of anything personal. The memoir focuses on past and life-changing experiences.
In short, the personal memoir aims at answering the three questions:
- What event or events were important in the author’s life?
- Why were they so crucial?
- How they affected the author’s life?
We’ve created a great example of a personal memoir for you . Here you can see how you can structure your story and what it can be about. Let’s dive in!
The Life-Changing Morning
That morning the sky was especially grey, and the whole atmosphere did not dispose of something good. I woke up alone in my tiny flat in the middle of nowhere. It did not feel like something bad was happening or even going to happen shortly. However, the way I felt was hard to describe. I took my morning coffee and then heard a knock on the door. It was a postman with an envelope in his hand. I opened the letter and read it out loud. It said that I was invited to the University of Oxford to study journalism. My dream came true! I was filled with happiness, motivation, and a thirst to start my studies as soon as possible. I can still remember this special and life-changing moment.
Comment: First of all, the author chose the right, captivating title, which invites a reader to discover what had happened that morning. Secondly, the personal memoir focuses on the important event that changed a young person’s life. Thirdly, he reflects on how he felt when it happened.
📋 One-Page Memoir: What Is It About?
A memoir doesn’t have to be a thick book. It can be of any length and cover any important life events. Making your memoir relatively short means that you should focus on one particular event.
Besides, this event should be captivating and life-changing. It would be best to tell about the emotions you experienced and what they brought to your life. The text can be concise, for instance, only 1 page. However, it should be interesting enough to evoke a reader’s emotions in such a short time.
So, here is a few recommendations for your one-page memoir:
- Cover one event only.
- Choose the most captivating and life-changing event.
- Don’t forget to express your emotions.
- Mention why this event was crucial for your future life.
If your task is to create a memoir essay, you may be surprised because it doesn’t have any typical structure .
The way you do your memoir writing depends only on your style and preferences.
If you want to combine two different stories into one and underline the message by inferring it from both of them – do it.
If you want to tell a situation when you feel fear or anxiety, there is a nice place to put a flashback to make readers understand you better – then, do it as well.
Memoir writing structure is a field where you can apply creativity and originality.
What you must include are:
- the details of your memoir
- the message
- why this story matters to you
Other elements are free for you to add to your paper. Let your inner writer choose which of them do you need to make a memoir writing breath-taking.
So, after looking through these examples of memoirs, you have a pretty good idea of how to write your own papers in this genre. Good luck with your memoirs! We are certain that you will make them unforgettable!
- The Personal Memoir
- How to Write a Family Memoir
- Memoir Writing – UC San Diego
- How to Write a Memoir – The Guardian
- Memoir Writing Resources – Toledo Library
- How to Write a Memoir – Berkeley
- How to Write a Memoir: Be Yourself, Speak Freely, and Think Small – JStor
- Bibliography
- More Referencing guides Blog Automated transliteration Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Automated transliteration
- Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Referencing guides
27 Best Memoirs: Unforgettable Stories That Inspire
These autobiographies deliver poignant self-reflection, humor, and resilience.

We may earn commission from links on this page, but we only recommend products we back.
Whether it's an account of someone else's childhood adventures, professional triumphs, or personal struggles, these stories are meant to transport you — the reader — to new places and broaden your understanding of the human experience. The memoirs in this roundup resonate deeply and will leave you with a lasting impression you won't be able to unsee in the best possible way. We know you'll appreciate these selections. Memoirs or not, they represent some of the best books ever published .
From juicy tales from celebrities to acclaimed writers to renowned chefs and even lesser-known yet compelling voices, each book offers a unique lens on life. Check out the best memoirs below!
More Books: The Best Books from Reese Witherspoon’s Book Club • 19 Books About the Royal Family • The Juiciest Celebrity Memoirs
Anthony Bourdain "Kitchen Confidential: Adventures in the Kitchen Underbelly" (2000)

You’ve probably seen this book on several similar lists, but that’s because it’s endlessly interesting. Bourdain dishes on such a niche culture—that of high-octane kitchens in some of the world’s best restaurants—and doesn’t shy away from some of its ugliest qualities. He gets personal, too, with anecdotes both amusing and somber.
Michelle Obama "Becoming" (2018)

In Michelle Obama 's memoir, "Becoming," the former First Lady of the United States chronicles her journey from growing up on the South Side of Chicago to her time in the White House . Obama shares personal stories about her childhood, education, career, motherhood, and experience as a First Lady.
This powerful and inspiring read gives insights into her challenges and triumphs, including moments in history you might even remember. Her advocacy for education, health, and women's rights are major themes in her book and life. It is a must-read for those interested in personal growth, resilience, and the life of one of the most influential women in recent history.
Read more about Michelle Obama
Glennon Doyle "Untamed" (2020)

"Untamed" by Glennon Doyle is a memoir that chronicles the author's journey to find her true self. Doyle, a renowned speaker and activist, shares her experiences with personal struggles, including divorce and coming out. During the process, she learns to trust her inner voice. It's one of the best memoirs you can read because it challenges societal norms, encouraging readers to break free from expectations and live authentically just as Doyle did. With its powerful message of self-discovery and empowerment, "Untamed" is a compelling read for anyone looking to embrace their true identity and find liberation in their own lives.
Patric Gagne "Sociopath: A Memoir" (2024)

"Sociopath: A Memoir" by self-identified Patric Gagne takes a deep dive into the author's life as he navigates the complexities of living with antisocial personality disorder. Gagne, now a writer and mental health advocate, offers an unflinching look at her experiences. Throughout its chapters, she sheds light on the challenges and misunderstandings surrounding sociopathy.
With personal anecdotes and introspective insights, she aims to humanize the condition and foster empathy for others in the same position. For those interested in mental health, it's a crucial read and one of the best memoirs you can opt for, as it provides a rare, authentic perspective on a frequently stigmatized disorder of sociopathy.
Frank McCourt "Angela's Ashes: A Memoir" (1999)

"Angela's Ashes: A Memoir" is an evocative recount of Frank McCourt's impoverished childhood in Limerick, Ireland. The author narrates his early years with humor and resilience despite facing extreme poverty, his father's alcoholism, and the loss of siblings. This memoir vividly depicts the harsh realities of life in mid-20th-century Ireland.
You should read it for its poignant storytelling and its ability to find hope and humanity amidst adversity. McCourt's narrative is both heartbreaking and inspiring, making it a compelling read that highlights the strength of the human spirit.
Maya Angelou "I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings" (1969)

An American classic, Maya Angelou ’s debut memoir recounts the acclaimed author ’s childhood and adolescence from Arkansas to Missouri to California. She touches on themes of identity and self-acceptance and recounts the abhorrent racism she and her family experienced, as well as the sexual violence she suffered at the hands of her mother’s boyfriend. But there’s great joy here, too, especially when young Angelou learns to come out of her shell through her love of literature.
Read more about Maya Angelou
Sonali Deraniyagala "Wave by Sonali Deraniyagala" (2013)

Sri Lankan writer and economist Sonali Deraniyagala lost her parents, her husband, and her two young sons in the 2004 tsunami that devastated parts of Thailand, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, and India. In this relentless memoir, she explores the seemingly bottomless depths of grief and how our power to remember the past can be healing. Readers who love a resolution might look elsewhere, but they’d be missing out on some unflinching, courageous writing.
Joan Didion "The Year of Magical Thinking" (2005)

From acclaimed writer Joan Didion, The Year of Magical Thinking recounts the sudden death of her husband and the hospitalization of their daughter within days of each other. (Her daughter eventually died at 39, which Didion writes about in Blue Nights .) It’s an engrossing and vulnerable look into a year of experiencing and coping with tragedy—filled, of course, with the writer’s famously incisive prose.
Carrie Fisher "The Princess Diarist" (2016)

In her final book, actress and writer Carrie Fisher gives fans a peek behind the curtain of her time on set of the first Star Wars movie . She hilariously commentates on excerpts from her diary during that time, recalls her crush on Harrison Ford , and delves into how complicated it can be to navigate the world of celebrity—especially as the face of such an iconic character.
Read More about Carrie Fisher
Roxane Gay "Hunger: A Memoir of (My) Body" (2017)

Widely recommended as one of the best books of 2017, Hunger is Roxane Gay’s raw and powerful memoir about her own self-image and our society’s obsession with appearance. There’s a reason Gay is such a prolific writer today, whether you follow her musings on Twitter or her New York Times column; she is incredibly inquisitive and can make any reader question the status quo. Hunger is no exception.
Dave Holmes "Party of One: A Memoir in 21 Songs" (2017)

We all have songs that can conjure specific memories. Writer, comedian, and TV personality Dave Holmes takes that notion to heart in his memoir, where he writes about growing up Catholic and closeted in Missouri and how he “accidentally” became an MTV VJ. There’s a plethora of references to ʼ80s and ʼ90s music and self-deprecating humor that strikes the perfect balance.
Cathy Park Hong "Minor Feelings: An Asian American Reckoning" (2020)

There’s no shortage of powerful writing in this book by writer and poet Cathy Park Hong. Throughout the work—about America’s racialized consciousness—she expertly weaves many personal details of her life as the daughter of Korean immigrants with topics like intersectionality and artistic expression. There’s plenty of enlightening history, too, including on activist Yuri Kochiyama . Her writing demonstrates her self-awareness; she even challenges many of her own thoughts. It’s a fascinating, essential read.
Saeed Jones "How We Fight for Our Lives" (2019)

Saeed Jones, an award-winning poet, writes with such a distinct style in this searing memoir about coming of age as a young, black, gay man from the South. He writes about grief, about identity in a world that makes it hard to find one, and about acceptance. It’s a short read in length (at 192 pages) but leaves a memorable impression.
Jennette McCurdy "I’m Glad My Mom Died" (2022)

In what was arguably the most talked-about memoir of the past year, actor and writer/director Jennette McCurdy details what went on behind the scenes in her life before, during, and after making the hit Nickelodeon show iCarly . She bears it all—discussing her eating disorder and the toxic relationship she had with her mother—while using pitch perfect humor, in a memoir that’s hard to stomach at times. But it’s worth it to see how she ultimately takes back control of her life.
Chanel Miller "Know My Name" (2019)

You might remember Chanel Miller as Emily Doe. After being sexually assaulted by Brock Turner on the Stanford University campus in 2015, she wrote a victim impact statement under this name that reverberated around the world. In this profound memoir, she reclaims her real name and reveals the frustrating truths surrounding victimhood and the criminal justice system. But her writing also divulges her incredible strength—it’s a powerful read that this writer finished in one sitting.
Eric Ripert "32 Yolks: From My Mother’s Table to Working the Line" (2016)

Two memoirs on this list from acclaimed chefs? We couldn’t resist. For those who might’ve already enjoyed Bourdain’s Kitchen Confidential , might we suggest Eric Ripert’s 32 Yolks . Ripert is, as some will know, the famed French chef behind renowned New York City restaurant Le Bernardin. In this memoir, he chronicles his upbringing in a fractured family in the south of France and how food was always a great comfort. Equal parts fun, infuriating, and awe-inspiring, Ripert includes high-stakes stories from his days in culinary school and working the line at fine dining establishments in Paris.
Drew Barrymore "Wildflower" (2015)

Drew Barrymore's memoir "Wildflower" comprises of personal essays where the actress reflects on her unconventional upbringing , career in Hollywood, and her journey to becoming a successful actress and mother. Through candid and heartfelt stories, she shares the lessons learned from her tumultuous childhood , early fame, and struggles with addiction.
"Wildflower" is an inspiring read for its honesty and resilience, offering an intimate glimpse into her life and evolution into the grounded and joyous adult we see today on her own talk show.
Read more about Drew Barrymore
Sandra Tsing Loh "The Madwoman and the Roomba: My Year of Domestic Mayhem" (2020)

"The Madwoman and the Roomba: My Year of Domestic Mayhem" is a humorous memoir by award-winning columnist Sandra Tsing Loh. The book captures Loh's chaotic and relatable experiences managing household life, technology mishaps, and the everyday challenges of modern domesticity.
Through her witty anecdotes and sharp observations, she explores themes of middle age, parenting, and the absurdities of suburban life. You should read it for its laugh-out-loud humor and keen insights into the trials and tribulations of family and home management. It may even give you a comforting and comedic take on the universal struggles of domestic life if that's where you're at in life.
Roald Dahl "Boy and Going Solo" (1984)

"Boy and Going Solo” consist of two autobiographical works by renowned author Roald Dahl published in 1984 and 1986. "Boy" recounts Dahl's early childhood and school years in England, filled with vivid, often humorous tales of pranks and strict teachers. "Going Solo" continues his story into young adulthood, focusing on his adventures as a pilot in World War II.
These memoirs are rich with the storytelling flair that characterizes Dahl's fiction, offering insight into the experiences that shaped his creative imagination. You should read them for their engaging narrative, historical context, and to understand the formative years of one of the 20th century’s most beloved children's authors.
Read more about Roald Dahl
Jon Krakauer "Into Thin Air: A Personal Account of the Mt. Everest Disaster" (1997)

Writer Jon Krakauer’s infamous retelling of the 1996 Mount Everest expedition that left eight climbers in his party dead is a harrowing read. For those with zero mountaineering experience (like this writer), he makes it easy to visualize what conquering this mountain looks like. There’s also some fascinating insights on the commercialization of Everest. If you’re reading a recently printed version, there’s an interesting postscript that responds to the fairness of his account of events (which was questioned in fellow survivor Anatoli Boukreev’s book The Climb ).
Ysolt Usigan is a lifestyle writer and editor who has created share-worthy content for publishers like Shape , What To Expect , Cafe Mom , TODAY , CBS News , HuffPo , The Bump , Health , Ask Men , and BestGifts . A working mom of two, her editorial expertise in shopping, parenting, and home are rooted in her everyday life. Her passion is hunting for the best products and sharing them with the masses, so others don't have to waste time and money.
Watch Next .css-16toot1:after{background-color:#262626;color:#fff;margin-left:1.8rem;margin-top:1.25rem;width:1.5rem;height:0.063rem;content:'';display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;}

8 Revelations from Britney Spears' Memoir

Jada Pinkett Smith’s New Memoir Shocks In More Way

The Best Books About Philosophers

12 Best Prime Day Book Deals to Read Now

10 Best True Crime Books

The Best Memoirs by Musicians

The Best Celebrity-Narrated Books on Audible

The Best Books About Activists to Inspire You

The Best Books About Founding Fathers

The Best Books About Inventors

Best Books About Scientists
Do you need a thesis when writing a memoir?
When writing a memoir, a thesis statement is not a mandatory requirement. Unlike academic essays or research papers, memoirs are a form of autobiographical writing that focus on personal experiences, reflections, and storytelling rather than presenting an argument or making a specific claim.
In a memoir, the primary goal is thesis writing to share a significant or impactful aspect of your life and convey its emotional, cultural, or historical significance. The emphasis is on storytelling, self-reflection, and providing insights into your experiences. While a thesis statement is not a typical component of a memoir, you may still have a central theme or message that runs throughout your narrative.
lucascyrus00 ∙
A thesis should be included in any essay or piece of writing, although in a memoir the thesis does not have to be laid out in the manner which is tells the whole theme of the memoir.
Add your answer:
This wraps up a piece of writing and reminds readers of the thesis?
A conclusion wraps up a piece of writing and reminds readers of the thesis.
How does the thesis guide an essay?
The thesis is your main topic. It tells the reader what you will be writing about. Without a thesis the reader wouldn't know what your point was.
In an essay a thesis statement is important because it?
A thesis statement tells you or the reader what your essay or writing is about. Its just 1 or 2 sentences (the topic) about your essay/writing.
How do you write thesis statement about social media addiction?
Writing a thesis statement is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you write a thesis statement you have to have some ideas regarding your writing. Depending on your topic, you need to develop an argument , you have to collect and organize evidence, Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a "working thesis" that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way. A thesis statement gives a concise summary of the main point or claim of the essay, research paper, etc. A thesis statement is usually one sentence that appears at the beginning, though it may occur more than once.Be as clear and as specific as possible; avoid vague words.
What is a thesis paper?
Thesis paper is actually a document that is submitted during the academic life of a graduate student. It is a long paper having a definite structure. It contain title page, list of contents, list of tables, list of figures, result, conclusion. Care should be taken while writing thesis paper. Many students prefer online sources to complete their thesis paper. From there they can get good quality thesis paper. Thesis paper writing is very important for a student.
Top Categories


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Strong Thesis Statement Examples. 1. School Uniforms. "Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.". Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate. Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons.
7. How to Write a Memoir: Edit, edit, edit! Once you're satisfied with the story, begin to edit the finer things (e.g. language, metaphor, and details). Clean up your word choice and omit needless words, and check to make sure you haven't made any of these common writing mistakes.
A memoir can begin with the present and use a series of flashbacks to tell the story. **Regardless of organizational style, memoirs written for college courses should always include an introductory paragraph and thesis statement. Make the Memoir Interesting Use Detail The reader needs to visualize the details discussed in the essay.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Aug 23, 2021 • 3 min read. A memoir essay, as its name suggests, is an essay that comes from memory. Memoir writing is one of the oldest and most popular literary genres. The best memoirs not only tell a great story, but they also consider some of life's big questions through the prism of personal ...
Memoir Hook Examples . As mentioned earlier, the memoir structure involves having a clear that draws the reader in the hook. What's it for? First, the hook arouses the reader's interest. Second, it reveals a situation, a feeling, an emotion, or all of these in a thesis statement.
A memoir essay is a form of autobiographical writing that focuses on a specific aspect of the author's life. Unlike a traditional autobiography, which typically covers the author's entire life, a memoir essay hones in on a particular event, time period, or theme. ... Finally, end your introduction with a clear and concise thesis statement ...
Examples. Walden by Henry David Thoreau. In July of 1845, Henry David Thoreau walked into the woods and didn't come out for two years, two months, and two days. This is the seminal memoir that resulted. Into Thin Air: A Personal Account of the Mount Everest Disaster by Jon Krakauer.
Open the piece by introducing yourself, setting the time parameters of the story, and the thesis statement. Then go through the pivotal events and round up the outline with a conclusion that completes the story. You can also hint at the events that followed and leave the essay open-ended.
3. Distill the story into a logline. 4. Choose the key moments to share. 5. Don't skimp on the details and dialogue. 6. Portray yourself honestly. 🎒Turn your personal life stories into a successful memoir in 6 steps!
Narrow your focus: Remember, you're not writing an autobiography. You're focusing on one moment or series of moments around a theme. Write about more than the story: Yes, the focus is on an event or related events, but consider the other players—the characters, the time, and the setting.
If you want to write a memoir, begin with a powerful scene that provides a provocative glimpse into the story that follows. Here is the first paragraph of my upcoming memoir, Frozen Dinners - A Memoir of a Fractured Family. "Irritated clouds of gray dust swirl behind my car and settle back onto the patches of scruffy sagebrush as I drive a back road into the village of Wendell, Idaho.
An anecdote is a short, personal narrative about something specific. It is often used as a component in an essay, acting as evidence to support your thesis, as an example to demonstrate your point, and/or as a way to establish your credibility. It always has a point in telling it. Elements of an Anecdote. 1.
1 - Memoir examples of early life stories. Early life memoirs explore the foundational years that shape individuals, offering a deep dive into the experiences and influences that forge character, resilience, and perspective. These memoirs are a testament to the lasting impact of youth on personal growth and identity.
What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute. An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic. Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's ...
By clicking here, or by opening the above tab, Annotated Memoirs, you will go to a list of six types of essays, each of which is hyperlinked to a sample essay and a discussion of it. Each sample annotated essay will have the following: 1. an introduction that comments on the type of essay and how it may generate good writing from young students; 2.
This is important. Write your memoir in the same way that you would write a novel, your objective should be to show your story - not just tell it. Use dialogue, descriptions, tensions, conflicts and other literary devices to breathe life into your story. Don't focus so heavily into chronology, it isn't an autobiography so you don't need ...
1 - Start with a story. Begin your memoir with an anecdote. It should be something which connects to the rest of the memoir—if you're writing about your childhood in rural Kentucky, for example, the anecdote should be related to that. It should also connect to the themes you'll explore throughout your memoir.
A final example of a thesis statement for Night would be that Wiesel's story provides a powerful example of the strength and resilience of a father-son relationship in the face of ultimate horror ...
For me the plus means this backward glance can become a scrutiny, a microscopic examination, an exercise in a form that has the power to change our lives. Writing memoir puts us on the path to focus on events that have, for better or worse, shaped us. Through writing memoir, we gain an understanding of the mechanics of how that shaping happened.
Looking for great memoir examples? ⭐ It is the perfect place to get expert advice! 📝 Here, you can find memoir examples for students we've prepared for you! ... Thesis Statement: Formula, How-to Guide, & 18 Mind-blowing Examples [UPD 2024] May 30, 2024; 210 Argumentative Essay Topics on Religion, Music, Feminism, etc. Jun 24, 2024;
The following thesis is a memoir in essays. The narrative is a reflection of memory as a chaotic system. Each essay stands alone as a single memory but also is part of the larger story of the writer's life. The fragmentation of the story lends itself to what Roland Barthes called a readerly text.
"Untamed" by Glennon Doyle is a memoir that chronicles the author's journey to find her true self. Doyle, a renowned speaker and activist, shares her experiences with personal struggles, including ...
A thesis should be included in any essay or piece of writing, although in a memoir the thesis does not have to be laid out in the manner which is tells the whole theme of the memoir. When writing ...