Invention Assignment Agreement
Create a high-quality document now!


Thank you for downloading!
How would you rate your free form.
Updated May 28, 2023
An invention assignment agreement is a new or unique device, process, or thing that is transferred from an inventor (assignor) to someone else (assignee). An invention that can be transferred will usually have a patent registered with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office .
How to Search for a Patent (3 steps)
Step 1 – go to the uspto website, step 2 – enter the patent information, step 3 – review the results.
Visit USPTO.gov and choose one of the following options:
- Quick Search
- Advanced Search ( recommended )
- Patent Number Search
Before 1976
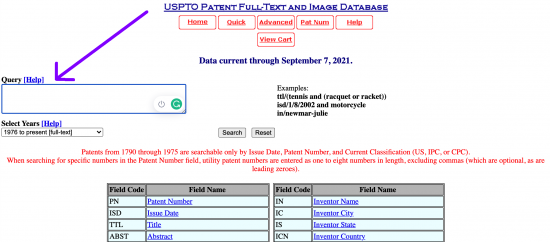
Use the Query box to conduct a general search for a patent. After entering, the result will load on the next page.
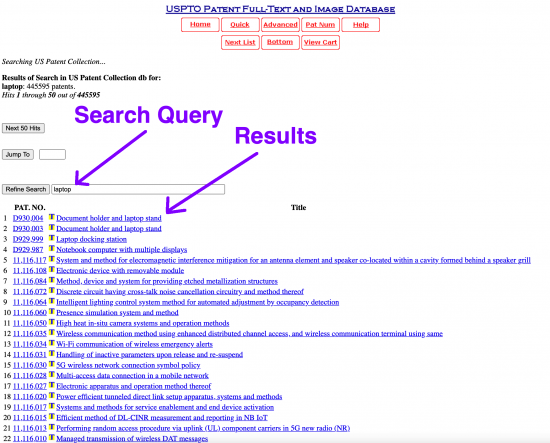
Use the results and view the Title and Patent Number . Choose a patent and view the public details that include:
- Inventor’s Names
- References Cited
- Description

What Is a Confidentiality and Invention Assignment Agreement?
A Confidentiality and Invention Assignment Agreement is a legally binding contract that establishes the terms and conditions for disclosing confidential information and assigning intellectual property rights, protecting valuable trade secrets and inventions from unauthorized use, disclosure, or misappropriation. This agreement outlines the parties' obligations and responsibilities, preventing misunderstandings and disputes, and enables businesses to share confidential information while maintaining confidentiality. By understanding the intricacies of this agreement, businesses can safeguard the protection of their intellectual property and foster trust in their relationships – a vital step in driving innovation and growth.
Table of Contents
Purpose of the Agreement
The purpose of this Confidentiality and Invention Assignment Agreement is to establish the terms and conditions under which confidential information will be disclosed and inventions will be assigned. This agreement provides contractual clarity, guaranteeing that all parties involved are aware of their obligations and responsibilities. By outlining the specific terms of confidentiality and invention assignment, businesses can protect their valuable intellectual property and trade secrets.
In today's competitive business landscape, safeguarding sensitive information is essential for maintaining a competitive edge. This agreement serves as a indispensable tool for business protection, enabling companies to share confidential information with employees, contractors, or partners while maintaining confidentiality. By assigning inventions and intellectual property rights, businesses can retain ownership and control over their innovations. This agreement provides a thorough framework for managing confidential information and intellectual property, thereby mitigating the risk of unauthorized disclosure or misappropriation.
Confidential Information Protection
To safeguard the confidentiality of sensitive information, this agreement outlines specific protocols for the protection of confidential information, including restrictions on disclosure, use, and reproduction. This is particularly vital for protecting trade secrets, which are valuable assets that can be compromised by information leaks. The agreement guarantees that all confidential information is handled with utmost care, and any unauthorized disclosure or use is strictly prohibited.
| Proprietary business information | Encryption, access restrictions | Legal action, financial penalties |
| Trade secrets | Secure storage, limited access | Loss of competitive advantage, reputational damage |
| Client data | Anonymization, secure transmission | Regulatory fines, loss of customer trust |
Invention Assignment Provisions
Invention assignment provisions are a critical component of a confidentiality and invention assignment agreement, as they dictate the terms under which intellectual property rights are transferred from the inventor to the assignee. The scope of assignment is a key consideration, as it defines the breadth of inventions and intellectual property that are subject to ownership transfer. The ownership rights provision, in particular, is crucial in establishing clear title to the assigned inventions and related intellectual property.
Ownership Rights
Upon creation, all intellectual property rights to any invention or discovery, whether or not patentable, shall vest exclusively in and be owned by the Company. This provision guarantees that the Company retains full control over all intellectual property developed by its employees, contractors, or agents. This includes, but is not limited to, patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets.
The ownership rights provision is a critical component of the invention assignment agreement, as it establishes the legal boundaries of intellectual property ownership. By vesting ownership exclusively in the Company, the agreement safeguards that the Company can fully exploit and protect its intellectual property rights.
Key aspects of ownership rights include:
- Exclusive ownership : The Company retains sole ownership of all intellectual property rights.
- Global applicability : The provision applies to all intellectual property developed globally.
- Comprehensive scope : The provision covers all types of intellectual property, including patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets.
Assignment Scope
The assignment scope provisions of this agreement delineate the specific circumstances under which the Company acquires ownership of intellectual property rights to inventions or discoveries made by its employees, contractors, or agents. These provisions establish clear boundaries, preventing scope creep and safeguarding that the Company's intellectual property rights are protected.
| Work-Related Inventions | Inventions developed during work hours or using company resources | Personal projects or hobbies |
| Contractual Obligations | Inventions developed under contractual agreements | Inventions developed outside of contract terms |
| Company Interests | Inventions related to the Company's business or operations | Inventions unrelated to the Company's business or operations |
The assignment scope provisions define the parameters of the Company's ownership rights, safeguarding that the Company's interests are protected while also respecting the intellectual property rights of its employees, contractors, and agents. By establishing clear assignment boundaries, the Company can prevent scope creep and safeguard that its intellectual property rights are protected.
Types of Protected Information
Company confidential information comprises trade secrets, business strategies, and technical know-how that provide a competitive advantage. This type of information is vital to a company's success and is often protected by confidentiality agreements.
The following types of information are commonly protected:
- Trade Secrets : Confidential manufacturing processes, formulas, or recipes that give a company a competitive edge. Examples include Coca-Cola's formula and Google's search algorithm.
- Intellectual Property : Patents, copyrights, and trademarks that are owned by the company, including software code, technical documentation, and creative works.
- Business Strategies : Confidential business plans, marketing strategies, and financial information that could be used by competitors to gain an unfair advantage.
Protecting this type of information is vital to maintaining a company's competitive advantage and preventing intellectual property theft. By understanding what types of information are protected, companies can take the necessary steps to safeguard their confidential information remains confidential.
Employee Obligations and Restrictions
Employees are bound by confidentiality obligations, which restrict their ability to disclose or use confidential information for personal gain or to the detriment of the company. This means that employees are prohibited from sharing trade secrets, proprietary information, or other confidential data with external parties or using it for personal benefit. In addition to confidentiality obligations, employees may also be subject to non-compete and non-solicitation clauses, which restrict their ability to engage in competitive activities or solicit clients or colleagues after leaving the company.
These restrictions can have a significant impact on an employee's career impact, work-life balance, and performance metrics. For instance, an employee may need to ponder exit strategies that do not involve competing with their former employer or soliciting former colleagues. Moreover, the restrictions may influence an employee's ability to shift to a new position or industry, which can affect their overall career trajectory. By understanding the scope of these obligations and restrictions, employees can better navigate their employment agreements and make informed decisions about their career paths.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
In the event of non-compliance with the confidentiality and invention assignment agreement, employees may face severe consequences. Failure to uphold their obligations can lead to legal ramifications, including lawsuits and court orders, which can lead to significant financial penalties. In addition, non-compliance can also lead to disciplinary actions, up to and including termination of employment, highlighting the importance of adhering to the agreement's terms.
Legal Ramifications
Failure to comply with the terms of the Confidentiality and Invention Assignment Agreement can lead to severe legal consequences, including but not limited to, damages, injunctive relief, and other legal remedies. Non-compliance can lead to costly legal battles, damaging an individual's or organization's reputation and financial stability.
The legal ramifications of non-compliance can be far-reaching, with court precedents setting a strong foundation for legal action against those who breach the terms of the agreement. In such cases, attorney fees can add up quickly, further exacerbating the financial burden of non-compliance.
Some key legal consequences of non-compliance include:
- Damages : Monetary compensation for losses incurred due to breach of contract.
- Injunctive Relief : Court-ordered restrictions to prevent further breaches of the agreement.
- Attorney Fees : The cost of legal representation, which can be substantial in complex cases.
It is crucial to understand the legal implications of non-compliance and take measures to guarantee adherence to the terms of the Confidentiality and Invention Assignment Agreement.
Financial Penalties
Non-compliance with the terms of the Confidentiality and Invention Assignment Agreement can lead to substantial financial penalties, which can have a debilitating impact on an individual's or organization's fiscal stability. In cases of breach, the agreement may stipulate breach fines, which can be substantial and crippling to one's financial health. These fines serve as a deterrent, encouraging parties to adhere to the agreement's terms and protect confidential information.
Penalty clauses are often incorporated into the agreement to outline the specific financial consequences of non-compliance. These clauses may include liquidated damages, which provide a predetermined amount of compensation in the event of a breach. The penalty clauses may also specify the method of calculation for damages, ensuring that the offending party is held accountable for their actions.
In addition to breach fines, non-compliance may also lead to other financial repercussions, such as legal fees, damages, and lost business opportunities. Therefore, it is essential for parties to understand the financial implications of non-compliance and to take necessary measures to ensure adherence to the agreement's terms. By doing so, individuals and organizations can mitigate the risk of financial penalties and protect their financial well-being.
Importance in Business Relationships
A well-drafted Confidentiality and Invention Assignment Agreement is crucial to fostering trust and protecting intellectual property in business relationships, as it clearly outlines the parties' obligations and responsibilities. This agreement plays a vital role in establishing a foundation of trust and cooperation between partners, investors, and employees. By outlining the terms of confidentiality and intellectual property ownership, parties can confidently share sensitive information, collaborate on projects, and drive innovation.
The importance of a Confidentiality and Invention Assignment Agreement in business relationships can be summarized as follows:
- Establishes Business Trust : A clear agreement helps build trust among partners, ensuring that sensitive information is protected and intellectual property is assigned correctly.
- Clarifies Partnership Dynamics : The agreement outlines the roles and responsibilities of each party, preventing misunderstandings and disputes.
- Protects Intellectual Property : By assigning ownership of intellectual property, the agreement safeguards innovative ideas and creations, ensuring that they are used for the intended purpose.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if an employee refuses to sign the agreement?.
If an employee refuses to sign a confidentiality and invention assignment agreement, employment implications may arise, including potential termination or limits on job responsibilities, while legal consequences could include disputes over intellectual property ownership and potential litigation.
Can Independent Contractors Be Required to Sign This Agreement?
Independent contractors, as freelance workers, can be required to sign a Confidentiality and Invention Assignment Agreement, thereby acknowledging their freelance obligations to protect intellectual property and maintain confidentiality.
Are Confidentiality Agreements Legally Enforceable in All Jurisdictions?
While confidentiality agreements are generally legally enforceable, jurisdictional variations in legal frameworks can impact their validity, with some jurisdictions imposing stricter requirements or limitations on their enforceability.
How Long Does Confidentiality Protection Typically Last?
Typically, confidentiality protection lasts for a specified period, usually 2-5 years, but can extend indefinitely under certain circumstances, adhering to industry standards and contractual time frames, which vary depending on jurisdiction and negotiation.
Can an Employer Waive the Confidentiality Requirement?
An employer may waive the confidentiality requirement through explicit waiver clauses in the agreement, potentially limiting employer liability, but careful drafting is vital to avoid unintended consequences and maintain contractual integrity.

(314) 454-9100
What You Need to Know About Invention Assignment Agreements

One way for a company to protect its intellectual property —such as trademarks, trade secrets and patents—is to require employees, consultants, independent contractors and even partners to sign what’s known as an “invention assignment agreement.” Do you think you might need one for your business? Read on.
What do invention assignment agreements do?
Invention assignment agreements are contracts that stipulate that anything the signee creates or develops on behalf of the company, is the property of the company. By signing an invention assignment agreement, the party relinquishes ownership rights to inventions and intellectual property he creates during his employment.
What is included in invention assignment agreements?
Specific terms vary, but usually these contracts include provisions regarding assignment of inventions, disclosure and a power of attorney. The assignment provision delineates the types of intellectual property the agreement covers. Depending on your needs, you may wish to make this part of the contract quite broad and include ideas (that are, or are not, implemented). The disclosure provision requires the signee to tell the company about inventions, developments, etc., she creates during the course of her employment. A power of attorney provision ensures that the business can proceed with registering ownership rights of the intellectual property even without the signee’s assistance or cooperation. Some agreements also include holdover clauses—which continue to apply after the signee’s employment ends—though courts are more skeptical of these, so they should be limited in time (six months to a year) and scope.
What kinds of businesses use invention assignment agreements?
While any business may benefit from these agreements, they are especially common in industries such as research and development, software and other engineering, technical fields and various creative pursuits.
Are invention assignment agreements enforceable?
While all states permit them, some jurisdictions do place restrictions on their enforcement , so legal advice on their formation and execution is essential. Do you want to protect your company’s intellectual property? Call us at (314) 454-9100 or send a message to discuss whether invention assignment agreements are the right solution for you.

About the Author
Pete Salsich III has been General Counsel for Coolfire Studios, LLC (an entertainment content creation studio), Coolfire Solutions, Inc. (a mobile software development studio focused on the military and commercial enterprise), and MedAware Solutions, Inc. (a mobile software platform company focused on the healthcare industry). Since joining AEGIS, Pete continues to serve in this capacity.
Select Categories
Schedule an appointment, related posts.

The Scourge of Counterfeit and Pirated Goods: A Call to Action

FTC’s Noncompete Ban: Navigating the Uncertain Landscape for Entrepreneurs and Small Businesses

The Misadventures in the Land of Legal Jargon: An Entrepreneur’s Guide to Estate Planning
Where we work, st. louis, mo, o’fallon, il.
807 West Highway 50 | Suite 1 O’Fallon, IL 62269 (618) 632-5544
Chicago, IL
233 South Wacker Drive, 44th Floor Chicago, IL 60606 (312) 329-0010
615 Channelside Drive, Suite 207 Tampa, FL 33602 (813) 999-0199
6870 W. 52nd Ave. Ste. 203 Arvada, CO 80002 (303) 228-1500
Cedar Rapids, IA
222 Third Ave SE, Suite 501, Office 6 Cedar Rapids, Iowa 52401 (319) 435-9793
GET IN TOUCH WITH AEGIS LAW
AEGIS Law has created an innovative approach to producing exceptional results. Contact us today to learn about what we can do for you.
© 2023 AEGIS LAW
- Find a Lawyer
- Ask a Lawyer
- Research the Law
- Law Schools
- Laws & Regs
- Newsletters
- Justia Connect
- Pro Membership
- Basic Membership
- Justia Lawyer Directory
- Platinum Placements
- Gold Placements
- Justia Elevate
- Justia Amplify
- PPC Management
- Google Business Profile
- Social Media
- Justia Onward Blog
Assignment of Inventions Contract Clauses (196)
Grouped into 5 collections of similar clauses from business contracts.
- Bankruptcy Lawyers
- Business Lawyers
- Criminal Lawyers
- Employment Lawyers
- Estate Planning Lawyers
- Family Lawyers
- Personal Injury Lawyers
- Estate Planning
- Personal Injury
- Business Formation
- Business Operations
- Intellectual Property
- International Trade
- Real Estate
- Financial Aid
- Course Outlines
- Law Journals
- US Constitution
- Regulations
- Supreme Court
- Circuit Courts
- District Courts
- Dockets & Filings
- State Constitutions
- State Codes
- State Case Law
- Legal Blogs
- Business Forms
- Product Recalls
- Justia Connect Membership
- Justia Premium Placements
- Justia Elevate (SEO, Websites)
- Justia Amplify (PPC, GBP)
- Testimonials
Invention Assignment Agreements – How to Avoid Pitfalls

Related Insights
Podcast episode 109: joanne molinaro, amanda beggs & kristin mcgaver sikora, fifth circuit rules sec exceeded its authority in adopting private fund advisers rule, cancer drugs: deals and licensing for antibody-drug conjugates.

How to Draft an Invention Assignment Agreement
Try our Legal AI - it's free while in beta 🚀

Genie's Legal AI can draft , risk-review and negotiate 1000s of legal documents
Note: Want to skip the guide and go straight to the free templates? No problem - scroll to the bottom. Also note: This is not legal advice.
Introduction
In the fast-paced world of technology, an invention assignment agreement is a key document for any inventor, entrepreneur or business owner. It provides legal protection and ensures that inventors receive a fair return on their inventions. But what exactly is an invention assignment agreement and why do entrepreneurs and business owners need one?
An invention assignment agreement is a legally binding contract that assigns ownership of an invention to another party, such as an employer or investor. The Agreement outlines the inventor’s rights and duties with regards to the use of their intellectual property while protecting them from theft or infringement by other parties. Furthermore, it clearly outlines payment terms, including any royalties or bonuses due to the inventor for their work. Having an Invention Assignment Agreement in place grants inventors peace of mind that their hard work will be rewarded fairly - something which can be invaluable when trying to succeed in the competitive technological landscape.
Business owners too should understand the importance of having a well-drafted Invention Assignment Agreement at hand as it can provide assurance that investments are adequately protected and secure from intellectual property theft. This can be crucial for entrepreneurs wanting to ensure long-term business success without facing costly legal disputes further down the line.
For anyone needing assistance creating an Invention Assignment Agreement, Genie AI offers a comprehensive resource to help you get started with drafting your own legally binding documents - all without paying a lawyer! Genie AI’s open source legal template library harnesses millions of data points to show you what constitutes market standard agreements; allowing users to customize high quality documents in minutes – saving both time and money! Our step-by-step guidance provides all the information needed on how to access our library today so you can get your project off to a strong start - all without needing a Genie AI account! So if you’re looking for reliable advice on how best tackle your next big venture - read on!
Definitions (feel free to skip)
Scope of Assignment – The range and limits of what is being assigned. Inventor – The person who creates or discovers something new. Assignee – The person or organization to whom something is assigned. Trade Secret – Information not generally known that gives a business an advantage over its competitors. Patent Application – A request to the government for permission to make, use, or sell an invention. Trademark – A distinctive word, phrase, symbol, or design used to identify a product or service. Copyright – A legal right that grants the creator of an original work exclusive rights to its use and distribution. Description of Invention – A detailed explanation of the features and functions of an invention. Rights of Assignment – The rights given to the assignee, such as the right to use, manufacture, reproduce, or sell the invention. Payment Terms – The amount and timing of payments made as part of the assignment. Confidentiality Clause – A clause that prohibits the assignee from disclosing any confidential information relating to the invention. Warranties – A guarantee that the inventor has the legal right to assign the invention to the assignee. Disclaimers – A statement that denies or limits a party’s legal responsibility. Legal Remedies – Ways of seeking legal enforcement of a contract, such as money damages or injunctive relief. Duration – The length of time that the agreement is in effect. Termination – The ending of the agreement. Notices – Written communication from one party to another. Dispute Resolution – The process of settling a disagreement between two parties. Governing Law – The set of laws that applies to a particular agreement. Jurisdiction – The authority of a court or other legal body to interpret and enforce the law. Sign and Date – To physically write one’s name and the date on a document to show agreement.
Define the scope of the assignment
Identify the inventor and assignee, draft a description of the invention, establish agreement on the assignment of rights to the assignee, set payment terms, include a confidentiality clause, include warranties and disclaimers, specify legal remedies, address duration and termination of the agreement, outline requirements for notices, including dispute resolution, clarify governing law and jurisdiction, sign and date the agreement, make copies of the agreement for each party, get started.
- Determine what invention is being assigned
- Identify who the inventor and assignee are
- Outline the scope of the assignment and what rights the assignee will be granted
- Specify the geographical area where the invention will be used
- Draft language for the assignment that includes the scope and rights of the assignee
- Review the language with both the inventor and assignee to make sure that everyone is in agreement
When you can check this off your list: When you have drafted the language for the assignment and both the inventor and assignee have reviewed and agreed to the language.
- Find out who the inventor is, and who the assignee (the person or company receiving the assignment) is
- Make sure the inventor and assignee are clearly identified in the agreement
- When the inventor and assignee have been clearly identified, you can move on to the next step of drafting a description of the invention.
- Include a detailed description of the invention, including relevant drawings, diagrams, and other relevant materials.
- Differentiate the invention from prior art if applicable.
- Identify the patent application number and filing date if the invention is already filed.
- If there is more than one inventor, make sure all inventors have agreed to the assignment.
- When the description is complete, you should have a clear understanding of the invention, who owns it and what is being assigned.
Once the description of the invention is complete, you can move on to the next step of establishing agreement on the assignment of rights to the assignee.
- Draft a clear agreement specifying the rights being assigned to the assignee
- Include details such as the scope of the rights, the geographic region and term of the assignment
- Make sure the assignee is aware that the invention must be kept confidential
- Include a clause which states that the assignee will not attempt to register the invention in any other country
- Add a clause that the assignor will defend any claims made against the assignee in relation to the invention
- Have both parties sign the agreement
You will know you are done with this step when you have completed the agreement, both parties have signed it, and the assignor and assignee have a copy of the agreement.
- Determine the payment method for the assignor in exchange for assigning the rights.
- Agree on a total sum for the payment or a payment plan.
- Include payment details in the agreement, such as the date of payment and any interest rates or fees.
- Have both the assignor and assignee sign off on the payment terms.
When this step is complete, the payment terms in the agreement should be agreed upon and documented in the agreement.
- Explain what a confidentiality clause is and why it’s important
- Identify the parties to the agreement, and include a definition and scope of confidential information
- Set out the duration of the confidentiality obligation
- Specify the permitted uses of confidential information
- Outline the remedies available to the parties in the event of a breach
- Include a clause permitting the parties to disclose confidential information to their advisors
- When complete, the confidentiality clause should provide a legally binding agreement between the parties that protects the confidential information disclosed
- When done, you can check this off your list and move on to the next step which is to include warranties and disclaimers.
- Include a clause in the agreement that states the assignor warrants that it owns the invention and has the right to assign it to the assignee
- Include a clause that the assignor has not previously assigned the invention to anyone else
- Include a clause that the assignor has not made any other agreement regarding the invention that would conflict with the assignment
- Include a disclaimer that the assignee is not receiving any implied warranties or guaranties with the assignment
- Include a clause that the assignor will indemnify the assignee in the event of any third-party claims
- Once you have included these warranties and disclaimers in the agreement, you can check this step off your list and move on to specifying legal remedies.
- Identify the legal remedies that each party would have if the other party breaches the agreement
- Consider what remedies are available in your jurisdiction and which are most appropriate for the situation
- Include remedies such as specific performance, liquidated damages, or other equitable relief
- Specify that the non-breaching party shall be able to seek all available remedies, including but not limited to damages and/or injunctive relief
- Indicate that the non-breaching party shall be entitled to recover all costs, including attorney fees, incurred in enforcing the agreement
- When complete, you can proceed to the next step, which is addressing duration and termination of the agreement.
- Determine the effective date of the agreement.
- Decide the duration of the agreement, including any applicable renewal options.
- Specify the circumstances under which the agreement can be terminated.
- Include provisions for either party to terminate the agreement with a certain amount of notice.
- Outline a timeline for any payments that need to be made upon termination.
Once you have determined the effective date, duration, termination, notice and payment requirements, you can check this step off your list and move on to the next step of outlining requirements for notices, including dispute resolution.
- Identify the parties to the agreement and their contact information
- Specify who will send and receive notices
- Outline the process for dispute resolution (e.g. arbitration, litigation)
- Establish a timeframe for notices to be sent and received
- Include language about compliance with applicable laws
- Include a clause that allows the parties to modify or amend the agreement
- Include a clause that allows the parties to assign their rights and obligations
- When complete, review the agreement and make sure it is legally sound
- When complete, sign and date the agreement
- When complete, get the agreement notarized, if required
- Identify the governing law of the agreement and the jurisdiction in which it will be interpreted and enforced
- Include the applicable state or country’s laws into the agreement
- Specify the court or other dispute resolution forum where any dispute or claim arising out of the agreement can be litigated
- Confirm that both parties agree to be bound by the governing law and jurisdiction chosen
- Once the governing law and jurisdiction is clarified, you can move on to the next step: signing and dating the agreement.
- Have both parties sign the agreement and include the date
- Make sure both parties include a witness to the agreement
- Have each party keep a copy of the signed agreement
- When done, you can check this off your list and move on to making copies of the agreement for each party.
- Ensure you have enough copies of the agreement for all parties
- Make sure to print out all copies of the agreement
- Make sure to provide copies for all parties to the agreement
- Once all parties to the agreement have a copy, you can check this off your list and move on to the next step.
Q: What are the differences between a US, UK and EU Invention Assignment Agreement?
Asked by Abigail on June 5th 2022. A: An Invention Assignment Agreement is an agreement between two parties, typically an employer and an employee, whereby the employee assigns all rights in any invention made during the course of their employment to the employer. The differences between US, UK and EU Invention Assignment Agreements mainly come down to the laws of the particular jurisdiction where the agreement is being used. US laws on invention assignment agreements are found in Title 35 of the United States Code, which covers patent law. In the UK, patent law is covered by The Patents Act 1977, while in the EU it is covered by Regulation (EU) No 1257/2012. Each jurisdiction will have different requirements for an Invention Assignment Agreement, so it is important to ensure that you are familiar with the laws of your jurisdiction when drafting an agreement.
Example dispute
Suing a company for breach of an invention assignment agreement.
- Plaintiff should be able to provide evidence of the invention assignment agreement between the parties, as well as any other relevant documents and communications.
- Plaintiff should be able to demonstrate that the terms of the agreement have been breached, e.g. by showing that the defendant has failed to pay royalties or has used the invention without permission.
- Plaintiff may be able to request an injunction against the defendant, requiring them to stop using the invention and/or pay back royalties.
- Plaintiff may be able to claim damages for any losses suffered as a result of the breach, for example, lost profits or other financial harm.
- Plaintiff may be able to negotiate a settlement including a payment from the defendant in exchange for dropping the suit.
Templates available (free to use)
Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreement Confidentiality And Invention Assignment Agreement Employee Invention Assignment Agreement Invention Assignment Agreement
Helpful? Want to know more? Message me on Linkedin
Links to get you started
Our Legal AI Assistant (free while in beta) Contract Template Library Legal Clause Library
Try the world's most advanced AI Legal Assistant, today

Navigating the CIIA Agreement: Essential Insights for Inventors and Employers
Short Answer:
A CIIA Agreement protects business innovation by having employees assign intellectual property to the employer, ensuring confidentiality. It’s vital for a secure, innovative environment, with its enforceability reliant on state laws, underscoring the need for legal counsel.
Introduction and Key Takeaways
As an attorney with over a decade of experience, including working with AM Law 200 firm Locke Lord LLP on Venture Capital, M & A, and private equity transactions, I understand the critical importance of protecting intellectual property in fostering innovation. A Confidential Information and Invention Assignment (CIIA) Agreement is crucial for businesses to secure their ideas and inventions. It ensures employees assign their intellectual creations to the employer, underpinning a culture of confidentiality and innovation. Compliance with state laws is key, highlighting the indispensable role of expert legal counsel in drafting enforceable agreements.
- A CIIA Agreement establishes a legal framework for determining the ownership of intellectual property created by employees, maintaining confidentiality, and assigning invention rights to the employer, all of which are essential for protecting a company’s ideas and sensitive information.
- The enforceability of a CIIA Agreement is subject to state law variations, highlighting the importance of compliance and the necessity for companies to seek legal counsel to ensure the agreement is robust and adheres to relevant regulations in different jurisdictions.
- Real-world case studies reveal the complexities and legal challenges related to CIIA Agreements and underscore the need for careful drafting, particularly of non-compete and non-solicitation clauses, to ensure their validity and enforceability.
Understanding the CIIA Agreement: Key Components and Objectives

A CIIA Agreement isn’t merely a standard contract, it acts as a crucial safeguard for businesses. Designed to delineate intellectual property rights, confidentiality obligations, and invention assignment terms between employers and employees, this agreement is an integral part of the employer-employee relationship. It provides a clear framework for intellectual property rights, ensuring that the creativity fostered within the company benefits the business itself.
Essentially, the CIIA Agreement forms the bedrock of a company’s protection strategy for its most valued asset – its ideas.
Intellectual Property Rights in CIIA Agreements
Intellectual property rights form the backbone of a CIIA Agreement. They vest the rights and ownership of inventions and confidential or proprietary information created by employees in the company. This underscores the importance for enterprises to have employees sign confidentiality and inventions assignment agreements, thereby securing these rights. Notably, these agreements also protect existing intellectual property and information, preventing unauthorized disclosure to third parties.
Resolving disputes over intellectual property can be a tricky business . Fortunately, a well-crafted CIIA Agreement includes measures to streamline this process. These include:
- Requiring employees to maintain the company’s confidential information in confidence
- Assigning ownership of any intellectual property created by the employee to the company
- Securing IP rights for the company to the employees’ inventions, including subject matter pertaining to the company’s objectives.
Confidentiality Requirements in CIIA Agreements

Confidentiality is a cornerstone of a successful business, and a CIIA Agreement provides a robust framework for the protection of sensitive information. Confidentiality requirements serve to safeguard the company’s trade secrets, proprietary information, and other sensitive data from unauthorized disclosure or misuse. Fundamentally, these requirements cultivate a culture of trust within the organization, ensuring confidence proprietary information acquired remains secure.
Defining what constitutes company’s confidential information is a critical aspect of a CIIA Agreement. Generally, confidential information includes all confidential knowledge, data, and information of the company, including inventions and confidential all trade secrets. Standard provisions regarding confidentiality mandate employees to maintain confidentiality, refrain from disclosing information to third parties without prior written consent, and specify procedures for the return or destruction of confidential information upon termination of the agreement. Violating confidentiality can lead to severe repercussions including financial damages, termination of employment, and potential legal action.
Invention Assignment Terms in CIIA Agreements
Invention assignment agreements form an integral part of a CIIA Agreement. They serve to grant the employer specific rights to inventions developed or conceived by the employee during their course of employment. The ‘integration’ clause, also known as the “entire agreement” clause, ensures that the invention assignment agreement is all-encompassing, preventing any informal supplementary oral or written agreement. It is crucial to have the invention assignment agreement signed by both parties to ensure its validity.
The transfer of rights from employees to employers is a pivotal aspect of the invention assignment terms. It specifies that any inventions developed during the employee’s tenure with the company are to be owned by the employer. Employees are obligated to reveal these inventions and transfer ownership rights to the employer, which may involve aiding the employer in securing patents.
However, enforcement of an invention assignment may not be possible in certain states if the invention was created during the employee’s working hours and without the use of employer resources. In such scenarios, it is the employee’s duty to demonstrate that the invention meets these criteria.
To avoid potential disputes regarding ownership of such inventions, employees are requested to list all prior invention owned they have created, including any such prior invention, before their employment.
Crafting an Effective CIIA Agreement: Best Practices
The creation of an effective CIIA Agreement demands meticulous planning and meticulous attention to detail. The agreement should:
- Clearly outline the types of intellectual property it covers
- Provide a comprehensive and balanced contract that accurately reflects the rights and responsibilities of both parties
- Manage potential exceptions effectively
- Incorporate non-compete clauses to safeguard the employer’s interests.
These best practices, coupled with legal guidance, can help to navigate the intricacies involved, ensuring a robust and enforceable CIIA Agreement.
Clarity on Ownership
Ensuring clarity on ownership in a CIIA Agreement is pivotal to avoid disputes and facilitate a smooth employer-employee relationship. This can be accomplished by incorporating suitable non-disclosure agreements, employee confidential/proprietary information, and invention assignment agreements. It’s also imperative to specifically delineate the types of intellectual property covered by the agreement and include comprehensive terms pertaining to IP ownership.
Incorporating a proprietary information and inventions assignment agreement (PIIA) can further aid in clarifying ownership issues within a CIIA Agreement. This agreement should explicitly outline the ownership of intellectual property generated by advisors, consultants, contractors, and employees while working for the company and delineate the categories of intellectual property it encompasses. Clearly specifying ownership rights in a CIIA Agreement ensures that the company possesses indisputable right, title, and interest in all inventions created by the individual during their employment.
Handling Exceptions
Dealing with exceptions effectively in a CIIA Agreement is instrumental to its success. Exceptions provide clarity and address specific circumstances where confidentiality obligations may not apply, thereby reducing uncertainties and potential financial exposure. Typical exclusions encompass scenarios such as:
- The agreement being overly restrictive or unclear, leading to potential oversight of inventions
- Absence of specific provisions in the agreement
- Limitations on invention assignment agreements only during the employee’s tenure
Detailing exceptions in a standardized manner helps to maintain clarity and consistency. Additionally, these exceptions play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with state laws by offering the flexibility to make necessary adjustments in cases where the agreement may contradict specific legal requirements.
Incorporating Non-Compete Clauses
Non-compete clauses in CIIA Agreements serve to prevent employees from participating in activities that could potentially place the company at a competitive disadvantage, thereby safeguarding confidential information. Typically, these clauses entail limitations on employees from engaging in work for competitors or initiating a competing business for a defined duration subsequent to their departure from the company.
Enhancing the enforceability of non-compete clauses involves:
- Careful drafting to guarantee their enforceability and compliance with state laws
- Engaging legal counsel to navigate the intricacies involved
- Ensuring clarity and reasonableness in scope and duration
- Clearly delineating the protected interests
- Providing consideration to the employee in exchange for agreeing to the non-compete
These steps can aid in enhancing the same legal force and enforceability, especially when dealing with such third party agreements.
Enforceability and Compliance: Navigating State Laws and Regulations
State laws govern the enforceability of CIIA agreements, and the disparities in these laws can present challenges for organizations operating across multiple locations. It’s critical to understand these variations and comply with the regulations in each state to ensure the enforceability of the CIIA Agreement. Regulations regarding Confidential Information and Invention Assignment (CIIA) Agreements vary from state to state, and include state statutory limitations and notice requirements.
Non-compliance with state laws when drafting a CIIA Agreement may result in its invalidation in certain states, impacting its enforceability. Furthermore, there may be monetary penalties, known as Stipulated Penalties, for the non-compliance. Hence, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of the specific regulations, which necessitates seeking guidance from employment counsel for the most precise and up-to-date legal counsel.
The Role of Legal Counsel in CIIA Agreements
Legal counsel holds a significant position in the formulation and enforcement of a CIIA Agreement. They ensure adherence to relevant laws, safeguard the interests of all parties, scrutinize and negotiate terms, and guarantee enforceability. Moreover, the review process by legal counsel involves ensuring that confidentiality provisions are in place, and comprehensively assessing the language of the agreement to clarify rights and obligations.
Counsel ensures enforceability by meticulously drafting clear terms that mandate employees to maintain the company’s confidential information in strict confidence and to abstain from using or disclosing it without authorization. They also provide invaluable guidance on compliance with state laws, offering guidance on compliance and aiding in safeguarding the rights and interests of all parties involved. In case of disputes, legal counsel collaborates with specialist employment and intellectual property law counsels to provide guidance on the proper transfer of IP rights and formulate resolution strategies.
Implementing and Managing CIIA Agreements in the Workplace
The implementation of CIIA Agreements in the workplace necessitates clear communication, mutual agreement, and appropriate acknowledgments from employees. Training also plays a pivotal role in the effective management of CIIA agreements within the workplace. A comprehensive employee training program that aligns with the requirements of the agreement can safeguard the company’s investment in its personnel.
Monitoring adherence to CIIA Agreements is equally important. This can be achieved by conducting annual reviews, performing audits, creating related policies and procedures, and implementing training and contract approval and monitoring processes. Additionally, companies can ensure that all employees are informed about the CIIA Agreement by implementing a mandate that requires employees to maintain the company’s confidential information with the utmost confidentiality and to refrain from using or disclosing it inappropriately.
Real-World Scenarios: Case Studies and Lessons Learned
Insights into the complexities of CIIA Agreements can be gleaned from real-world scenarios and case studies. Influential court rulings, such as Snepp v. United States, have set important precedents for government employment contracts. However, there have been cases where non-solicitation and non-compete clauses in CIIA Agreements were found to be unenforceable, often due to their excessive breadth or restrictiveness. Some key points to consider are:
- Real-world scenarios and case studies provide valuable insights into CIIA Agreements.
- Court rulings, like Snepp v. United States, have established important precedents.
- Non-solicitation and non-compete clauses can be unenforceable if they are too broad or restrictive.
Conflicts have arisen when companies seek to assert intellectual property rights over their employees’ inventions, leading to occasional employment disputes. Companies have effectively resolved these disputes by implementing clear terms in employment contracts and intellectual property assignment agreements, which diminish the probability of disputes and define the ownership of intellectual property rights.
Understanding, crafting, implementing, and managing CIIA Agreements is a complex task that requires careful consideration of various factors. From ensuring clarity on ownership and handling exceptions to incorporating non-compete clauses and navigating state laws and regulations, each step is crucial in safeguarding a company’s intellectual property and maintaining business confidentiality. However, with careful planning, legal guidance, and adherence to best practices, companies can create robust and enforceable CIIA Agreements that protect their interests and foster a secure environment for innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a ciiaa agreement.
A Ciiaa agreement is a legal document used to assign all intellectual property and proprietary rights created by an employee to the employer during the course of their employment.
What does executed a confidentiality and invention assignment agreement mean?
Executed a confidentiality and invention assignment agreement means that employees agree to assign intellectual property and proprietary rights created during their employment to the employer. This ensures protection of the employer’s interests in any inventions or confidential information.
What is an employee intellectual property assignment agreement?
An employee intellectual property assignment agreement is a contract that transfers ownership of intellectual property created by employees to the employer during their employment.
What is the purpose of a non-compete clause?
The purpose of a non-compete clause is to prevent employees from engaging in activities that could harm the company’s competitiveness. It aims to protect the company’s interests.
How does legal counsel contribute to a CIIA Agreement?
Legal counsel contributes to a CIIA Agreement by ensuring adherence to relevant laws, safeguarding the interests of all parties, scrutinizing and negotiating terms, and guaranteeing enforceability. This is crucial for a robust and legally sound agreement.

Legal Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for general informational purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. The content presented is not intended to be a substitute for professional legal, tax, or financial advice, nor should it be relied upon as such. Readers are encouraged to consult with their own attorney, CPA, and tax advisors to obtain specific guidance and advice tailored to their individual circumstances. No responsibility is assumed for any inaccuracies or errors in the information contained herein, and John Montague and Montague Law expressly disclaim any liability for any actions taken or not taken based on the information provided in this article.
Contact Info
Address: 5422 First Coast Highway Suite #125 Amelia Island, FL 32034
Phone: 904-234-5653
Table of Contents
Schedule a consultation.
" * " indicates required fields
More Articles

Coinbase vs SEC Showdown: Escalating Tensions and Critical Implications for Crypto Compliance
Coinbase vs SEC litigation continues; the SEC first filed charges in June 2023, alleging the exchange offered unregistered securities. In September, a federal court denied Coinbase’s request for dismissal and ruled that the case would proceed to trial. The outcome could shape US crypto regulation, impacting classification and compliance in the industry.

Choosing the Best Entertainment Contract Lawyer to Navigate Your Creative Future
An entertainment contract lawyer provides expertise spanning contract negotiation, intellectual property protection, and legal advice, ensuring fair and legally sound agreements. Such lawyers are indispensable for artists navigating entertainment law, offering protection against common pitfalls and advocating for their rights in various agreements

Specific Performance in Real Estate: How to Overcome Obstacles in 2024 and Achieve Victory
Short Answer: Specific performance in real estate enforces the actual

Invention Assignment Agreement
What Is an Invention Assignment Agreement?
Should you have new hires sign one, when to use an invention agreement.
- Employing workers to invent . If you are bringing on employees to invent, create or improve on behalf of your company, you’ll want them to sign an invention assignment agreement before they begin work.
- Employing independent contractors and freelancers . When you contract workers to create solutions that may require copyright or patent protection, consider getting a signed invention assignment agreement. These agreements are often rolled into other contracts and may come as less of a surprise to contract workers.
- Making a business case for safeguarding . If your business relies on innovations, inventions and branded solutions, you might want to make invention agreements part of your standard new-hire paperwork.
When Not to Use an Invention Agreement
- Employing workers as a stable asset . When you bring an employee on in a role not traditionally inventive, there’s no reason to burden the employment relationship with a legal document. Many great employees improve their work environment, processes and programs by incremental efforts.
- Collaborating with partners. Collaborating with other companies or brands entangles the inventive process a little more than traditional employment or contract work. In these cases, an invention agreement simply does not cover the scenario. You will need legal help to develop an appropriate contract.
- Not making a business case for safeguarding . If you have no intention of seeking patent protection for ideas or inventions, you should leave employees free of legal barriers if they want to safeguard their work.
Limitations of Invention Assignment Agreements
What to include in an employee invention agreement, 1. an assignment provision, 2. a disclosure provision, 3. a power of attorney provision.

Amanda Davis
Eddy’s HR Mavericks Encyclopedia

- Eddy Overview
- People Management
- Time Tracking
- Training Tracking
- HR Encyclopedia
- HR Mavericks Podcast
- Help Center
- Contact Support

Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreement
Jump to section, what is a confidential information and invention assignment agreement.
A confidential information and invention assignment agreement, also called invention assignment agreements and abbreviated to CIIAAs, is a legal contract that ensure that an employer has rights to any intellectual property created by an employee during their employment. Many states limit the scope of confidential information and invention assignment agreements to protect the employee and their intellectual property. For example, certain states may require that the product was created entirely on employer time using employer resources for the employer to have rights to the invention. Invention assignment agreements will usually include a nondisclosure agreement, a non-solicitation agreement, and, depending on state laws, a non-compete agreement. A CIIAA is a legally binding contract, so anyone asked to sign one for purposes of employment is encouraged to speak to an intellectual property attorney to learn their rights.
Common Sections in Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreements
Below is a list of common sections included in Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreements. These sections are linked to the below sample agreement for you to explore.
Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreement Sample
Reference : Security Exchange Commission - Edgar Database, EX-10.24 26 filename26.htm , Viewed November 9, 2021, View Source on SEC .
Who Helps With Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreements?
Lawyers with backgrounds working on confidential information and invention assignment agreements work with clients to help. Do you need help with a confidential information and invention assignment agreement?
Post a project in ContractsCounsel's marketplace to get free bids from lawyers to draft, review, or negotiate confidential information and invention assignment agreements. All lawyers are vetted by our team and peer reviewed by our customers for you to explore before hiring.
ContractsCounsel is not a law firm, and this post should not be considered and does not contain legal advice. To ensure the information and advice in this post are correct, sufficient, and appropriate for your situation, please consult a licensed attorney. Also, using or accessing ContractsCounsel's site does not create an attorney-client relationship between you and ContractsCounsel.
Meet some of our Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreement Lawyers
Oklahoma attorney focused on real estate transactions, quiet title lawsuits, estate planning, probates, business formations, and all contract matters.
International-savvy technology lawyer with 35years+ in Silicon Valley, Tokyo, Research Triangle, Silicon Forest. Outside & inside general counsel, legal infrastructure development, product exports, and domestic & international contracts for clients across North America, Europe, and Asia. Work with Founders to establish startup and continuous revenue, sourcing and partnering with investors to attract funding, define success strategy and direct high-performing teams, advising stakeholders and Boards of Directors to steer company growth.
Licensed to practice law in the states of Missouri and Kansas. Have been licensed to practice law for 44 years. Have been AV rated by Martindale Hubbel for almost 30 years.
Real estate and corporate attorney with over 30 years of experience in large and small firms and in house.
David Alexander advises clients on complex real estate transactions, including the acquisition, disposition, construction, financing and leasing of shopping centers, office buildings and industrial buildings throughout the U.S. An experienced real estate attorney, David reviews, drafts and negotiates all manner of retail, office and industrial real estate agreements, including purchase and sale agreements, construction contracts, leases and financing documentation.
Managing partner at Patel & Almeida and has over 22 years of experience assisting clients in the areas of intellectual property. business, employment, and nonprofit law.
Tiffanie W.
Tiffanie Wilson is a business transactions and personal injury lawyer. She helps clients realize their business goals by expertly drafting contracts, providing sound legal advice, and working for justice for injured clients.
Find the best lawyer for your project

Quick, user friendly and one of the better ways I've come across to get ahold of lawyers willing to take new clients.
How It Works
Post Your Project
Get Free Bids to Compare
Hire Your Lawyer
Employment lawyers by top cities
- Austin Employment Lawyers
- Boston Employment Lawyers
- Chicago Employment Lawyers
- Dallas Employment Lawyers
- Denver Employment Lawyers
- Houston Employment Lawyers
- Los Angeles Employment Lawyers
- New York Employment Lawyers
- Phoenix Employment Lawyers
- San Diego Employment Lawyers
- Tampa Employment Lawyers
Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreement lawyers by city
- Austin Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreement Lawyers
- Boston Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreement Lawyers
- Chicago Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreement Lawyers
- Dallas Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreement Lawyers
- Denver Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreement Lawyers
- Houston Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreement Lawyers
- Los Angeles Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreement Lawyers
- New York Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreement Lawyers
- Phoenix Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreement Lawyers
- San Diego Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreement Lawyers
- Tampa Confidential Information And Invention Assignment Agreement Lawyers
Contracts Counsel was incredibly helpful and easy to use. I submitted a project for a lawyer's help within a day I had received over 6 proposals from qualified lawyers. I submitted a bid that works best for my business and we went forward with the project.
I never knew how difficult it was to obtain representation or a lawyer, and ContractsCounsel was EXACTLY the type of service I was hoping for when I was in a pinch. Working with their service was efficient, effective and made me feel in control. Thank you so much and should I ever need attorney services down the road, I'll certainly be a repeat customer.
I got 5 bids within 24h of posting my project. I choose the person who provided the most detailed and relevant intro letter, highlighting their experience relevant to my project. I am very satisfied with the outcome and quality of the two agreements that were produced, they actually far exceed my expectations.
Want to speak to someone?
Get in touch below and we will schedule a time to connect!
Find lawyers and attorneys by city
Trending News

Related Practices & Jurisdictions
- Corporate & Business Organizations
- All Federal

Protecting your company’s intellectual property rights is essential during all stages of your company’s growth. One of the first steps you can take to protect your company’s intellectual property rights is to have all advisors, consultants, contractors and employees of your company enter into Proprietary Information and Inventions Assignment Agreements (“PIIAs”), also known as Confidential Information and Inventions Assignment Agreements.
In the rush of starting up a new business and bringing on your initial set of consultants and employees, it may be easy to overlook the importance of properly documenting the company’s relationship with these individuals related to ownership of intellectual property. However, as your company grows and attracts new investors, strategic partners and potential buyers, these other third parties will want you to be able to demonstrate that your company clearly owns its intellectual property and will ask if your advisors, consultants, contractors and employees have signed PIIAs.
The fact that an invention is created during the course of an individual’s employment with a company does not, in and of itself, give the company the right to all intellectual property related to such invention. In its Stanford v. Roche decision in 2011, the Supreme Court confirmed the general rule that the original inventor owns the inventions they make, unless the inventor makes an express assignment of those rights to another individual or entity.
In light of this, failure to have PIIAs in place represents a risk of potential intellectual property ownership disputes and can negatively impact your company’s ability to raise capital. Investors may also require you to go back to any current employees and have them sign a PIIA if it was not executed when the employee joined the company. Requiring an employee to sign such an agreement after he or she has already been with the company for some time can create a situation in which the employee has leverage to ask for something additional in return.
As indicated by its name, PIIAs address two main concerns: (1) confidential treatment of proprietary information and (2) ownership of inventions/intellectual property.
Confidentiality:
PIIAs typically require an individual to agree to keep all proprietary information confidential and to treat such information as the exclusive property of the Company. “Proprietary Information” includes information or material related to the company which has not been made generally available to the public, such as: (a) corporate plans, strategies, methods, or policies; (b) marketing information, including customer/prospective customer information; (c) financial information; (d) operational and technological information, including software, designs, procedures, formulas, discoveries, inventions, improvements, concepts and ideas; and (e) personnel information. Depending on your industry, there may be different types of information you may want your employees to keep strictly confidential and you should seek to tailor the definition of “Proprietary Information” in the PIIAs to fit your company’s circumstances.
Ownership of Inventions:
A PIIA should include an express assignment by the individual to the company of all right, title and interest in and to all “inventions”, including discoveries, designs, developments, methods, algorithms, formulae, techniques, trade secrets, know-how, software code and other works of authorship made or conceived by the individual (alone or with others) during the course of the individuals employment with the company and all patent, copyright, trademark, trade secret and other intellectual property rights and other proprietary rights therein.
It is important that the assignment of rights in the PIIA cover both an assignment of any current rights to such inventions and an agreement to assign such rights in the future when any additional inventions are made or conceived.
Carve-Outs:
Some employees may have preexisting inventions (which they created prior to joining your company) they want to specifically exclude from the assignment of intellectual property to the company. Thus, PIIAs often include a carve out provision which allows an employee to specifically exclude such preexisting inventions from the PIIA. When an employee seeks to carve out an invention from a PIIA you should seek advice from counsel to ensure there is a clear delineation between prior inventions and the type of intellectual property that may be produced by your company and that your company has any license or other applicable rights in place related to such preexisting inventions if they may be used by the employee in his or her work with the company.
Other Considerations:
Some states have placed statutory restrictions on the scope of PIIAs. In California, for example, PIIAs are not enforceable with respect to inventions developed by an individual entirely on his or her own time without using the employer’s equipment, supplies, facilities, or trade secret information except for those inventions that either: (1) relate at the time of conception or reduction to practice of the invention to the employer’s business, or actual or demonstrably anticipated research or development of the employer or (2) result from any work performed by the employee for the employer (California Labor Code, Section 2870).
PIIAs are also sometimes included as part of a larger employment related agreement and thus may also include non-solicitation and/or non-competition provisions, however such considerations are outside the scope of this article.
Similarly, some consulting agreements may also cover the terms of a PIIA, however you should be careful to ensure that the terms of any consulting agreement cover the full range of rights addressed in a standalone PIIA, to the extent applicable, if the consulting agreement will take the place of the PIIA.
Conclusion:
PIIAs are a critical tool for your company to protect its intellectual property and remain important throughout all stages of a company’s growth and thus should not be overlooked as part of the onboarding process with new employees or consultants. New companies should therefore seek to have a form PIIA in place that they can use with all new hires and consultants.
Current Legal Analysis
More from mintz, upcoming legal education events.

Sign Up for e-NewsBulletins
- Collections
Confidential Information and Inventions Assignment Agreements (CIIAA)
Also known as Proprietary Information and Inventions Assignment Agreements (or PIIAAs), Confidential Information and Inventions Assignment Agreements ensure that intellectual property and other proprietary rights created by employees during the course of their employment are assigned to the employer.
Effective CIIAAs assign intellectual property to the company and also contain nondisclosure, nonsoliciation, and (in some cases) noncompetition clauses (beware, though, that in some states, such as California, noncompetition clauses in these types of agreements are not enforceable and, accordingly, should not be included). Inventions or intellectual property created by the employee prior to beginning their employment are carved-out from the assignment by this type of agreement.
- Incorporation Package (Delaware)
- Form of Employee Confidential Information and Inventions Assignment Agreement (Singapore)
- Form of Employee Offer Letter (Singapore)
- PBC Incorporation Package (Delaware)
- Glossary: Inventions Assignment Agreement An inventions assignment agreement is a typical feature of an independent contractor or employee agreement where the worker agrees to assign any intellectual property arising from the worker's services to the company.
Want to receive the latest info from Cooley GO?
Sign up now
Give us feedback
Visit Cooley
Cooley LLP, Cooley (UK) LLP, and Cooley SG LLP. All rights reserved.
COOLEY® and the COOLEY LLP® logo are registered U.S. service marks of Cooley LLP.
COOLEY GO is a trademark of Cooley LLP.
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site.
By using our website, you agree to our use of cookies. Find out more information on how we use cookies and how you can change your settings in our cookie policy .
- Law of torts – Complete Reading Material
- Weekly Competition – Week 4 – September 2019
- Weekly Competition – Week 1 October 2019
- Weekly Competition – Week 2 – October 2019
- Weekly Competition – Week 3 – October 2019
- Weekly Competition – Week 4 – October 2019
- Weekly Competition – Week 5 October 2019
- Weekly Competition – Week 1 – November 2019
- Weekly Competition – Week 2 – November 2019
- Weekly Competition – Week 3 – November 2019
- Weekly Competition – Week 4 – November 2019
- Weekly Competition – Week 1 – December 2019
- Sign in / Join

Employee invention agreement
- Featured Student Assignments (LawSikho)
- Intellectual property
- Intellectual Property Rights
Role of employee invention agreements in safeguarding company IP

This article was written by Apoorv Tiwari , pursuing the Diploma in Advanced Contract Drafting, Negotiation, and Dispute Resolution Course from LawSikho , and edited by Koushik Chittella .
This article has been published by Shashwat Kaushik .
Table of Contents
Introduction
The ever-increasing scope of intellectual property rights is not an unknown phenomenon anymore. The importance of IP law and the protection of the same is the paramount reason for the success of any organisation. Without the implementation of IP law, a business can face setbacks in any form, be it financially or in reputation. The importance of intellectual property rights is very vast, from the protection of innovations to the preservation of competitive advantage.

Intellectual property Rights, such as copyrights, patents, and trademarks, protect a company’s innovations, inventions, and creative works from unauthorised use or exploitation by competitors. This protection encourages companies to invest resources in research, development, and innovation, knowing that their intellectual property will be safeguarded and they can reap the benefits of their investments. If there is no protection given to the creative mind about his creativity, he will lack motivation for further innovations. Thus, IP rights provide benefits to the inventor in many forms, be it monetary, social recognition, royalty, etc. Intellectual property rights allow companies to maintain a competitive edge in the marketplace by preventing competitors from replicating or imitating their products, services, or brands. By securing exclusive rights to their innovations and branding elements, companies can differentiate themselves from competitors and command higher prices for their unique offerings.
Employee invention agreements: meaning and use
It can very much happen in any business that an employee switches jobs and begins to work for a company that is a competitor of the previous employer. Since the employee knows every detail of his previous company, the same can be disclosed to the new employer, which can cause heavy losses to the company whose trade secret has been disclosed by its ex-employee. To combat the same situation, companies usually have to enter into employee invention agreements. This article seeks to shed light on the details regarding employee invention agreements.
Definition
An Employee Invention Agreement (EIA), also known as an Intellectual Property (IP) agreement or invention assignment agreement, is a legal contract between an employer and an employee regarding ownership and control of intellectual property created during the course of employment. Generally, in an employee invention agreement, the terms of the agreement are made in such a way that the work done by the employee during his course of employment shall exclusively belong to the employer and not to the employee.
Purpose of the EIA
The purpose of an EIA is to establish clear guidelines and obligations related to intellectual property rights, ensuring that inventions, innovations, and creative works developed by employees within the scope of their employment belong to the employer rather than the individual employee.
Key Components of the EIA
- Confidentiality Obligations : The agreement typically includes provisions requiring employees to maintain confidentiality regarding proprietary information and trade secrets of the employer. This helps prevent the unauthorised disclosure or misuse of sensitive company information, protecting the employer’s competitive advantage.
- Remedies for Breach : The EIA outlines the consequences of breach, including termination of employment, injunctive relief, and legal remedies for the unauthorised use or disclosure of confidential information. By specifying the potential consequences of non-compliance, the agreement encourages employees to adhere to its terms.
- Assignment of Rights : The assignment clause stipulates that the employee agrees to assign all rights, title, and interest in their inventions to the employer. This ensures that the employer has the legal authority to exploit, licence, or enforce intellectual property rights as needed.
- Ownership of Intellectual Property : The ownership clause specifies that any inventions or intellectual property developed by the employee during their employment belong to the employer. This clause ensures that the employer retains full control and ownership of the intellectual property.
Legal framework governing the EIA agreements
The legal framework governing the employee invention agreement differs from nation to nation as it should adhere to the law of the land where the agreement is made and executed, so it is pertinent for the business to make sure the agreement entered into should comply with the appropriate legislature; it can be a federal or state law or a union law. Also, the industry-specific rules and code of conduct determine the outline and content of the employee invention agreement. EIAs are generally governed by employment law, which regulates the relationship between employers and employees. Employment laws may address issues such as the rights and obligations of employers and employees, termination of employment, non-compete agreements, and confidentiality provisions. Some relevant legislation governing the employment laws in India include the Minimum Wages Act, 1948; the Factories Act, 1948 ; and many more.
Copyright Act, 1957
The Copyright Act, 1957 , prescribes certain provisions for a valid assignment of copyright developed in India. Under the Act, the deed of assignment of copyright must identify the work and specify the duration, territorial extent, and nature of the rights assigned to the assignee. If the duration is not specified, the term will be limited to five years from the date of assignment. Whereas, if the territory is not identified, the assignment will only be valid for the Indian territory. So, the deed must specify that it is a worldwide and perpetual assignment.
Further, if the assignee does not exercise his rights within a year from the date of assignment, the assigned rights will lapse, unless otherwise agreed upon by the parties. Hence, the deed must specify that the assignment won’t lapse even after a year of non-use. The assignment of copyright to future works will only take effect when the work comes into existence. To avoid future disagreement, the future work to be assigned should be identified in the deed and agreements at the time of the commencement of the project.
Intellectual property (IP) laws play a significant role in EIAs, as they govern the ownership, protection, and exploitation of intellectual property rights. Specific laws and regulations apply to determine the ownership, disclosure requirements, and enforcement mechanisms, depending on the type of intellectual property involved. In the case of Thomas v. Manorama , it was held that the employee is entitled to the ownership of works created by him after his employment is terminated by the employer, and in such a case, the previous employer has no copyright over the subsequent work so created.
Patent Act, 1970
Under the Patent Act, 1970 , patents are granted for inventions. It governs the requirements for patentability, the process of patent application and examination, and the rights and obligations of patent holders. EIAs often include provisions related to the assignment of patent rights to the employer and the employee’s obligation to assist in patent prosecution. In the course of their employment, the employee owns any invention created by them in the absence of a clause regarding assignment. Section 6 of the Patents Act, 1970 , provides for the persons who can apply for patents. They are:
- The first and true inventor.
- An assignee claiming rights.
- A deceased inventor’s legal heir. But there are no provisions vesting title in the favour of employers under the Patent Act, 1970.
Contract Act, 1872
EIAs are contractual agreements between employers and employees, and as such, they are subject to contract law principles. The Contract Act, 1872 , governs the formation, interpretation, and enforcement of agreements, including issues such as offer and acceptance, consideration, mutual assent, and contract remedies.
Benefits of an employee invention agreement
An employee invention agreement offers multiple benefits to both the employee and employer, as it builds trust and harmony between the two by ensuring the protection of IP rights while promoting innovation. It assures the employer about the protection of his IP rights and also the employee that the work created by him during his course of employment shall have the exclusive ownership of the employer and not him, owing to the very nature of EIA. This also helps in avoiding any future disputes. Here are several other benefits of an employee invention agreement:
- Protects the company’s intellectual property : EIAs protect a company’s intellectual property by ensuring that inventions, innovations, and other creative works developed by employees belong to the company. This protection prevents competitors from exploiting or misappropriating company-owned intellectual property, preserving the company’s competitive advantage and market position.
- Promotes innovation and creativity : By providing a framework for the protection and recognition of employee inventions, EIAs promote a culture of innovation and creativity within the company. Employees are encouraged to pursue new ideas and solutions, knowing that their contributions will be valued and protected by the company.
- Encourages disclosure of inventions : EIAs typically include provisions requiring employees to promptly disclose any inventions or innovations to the company. This encourages open communication and transparency between employees and management, facilitating the timely evaluation and protection of valuable intellectual property.
Challenges and considerations
Employee invention agreements are very essential for upholding intellectual property rights and supporting innovation in any business, yet they also come up with some challenges and considerations that both parties should have agreed to in the same consensus so as to avoid disputes arising in the future.
- Scope of employment : Determining the scope of employment covered by the EIA can be challenging, especially in roles where employees may engage in creative or innovative activities outside of their primary job duties. Employers must clearly define the scope of employment to ensure that the agreement covers all relevant activities and inventions developed by employees during their tenure.
- Acknowledgement of employee contribution : The scope and purpose of EIA itself can make an employee feel unmotivated to not contribute enough to the new innovations, so an employer should make enough efforts and try to recognise the efforts made by the employee to keep him in the loop and make him feel motivated for further innovations.
- International challenges : Employers with businesses in multiple nations may find it difficult to adhere to specific legal requirements or cultural practices that obviously differ from nation to nation. Therefore, an employer should always seek legal advice from the local legal advisor before entering into the EIA.
- Dispute Resolution Mechanisms : EIAs should include provisions for resolving disputes that may arise between employers and employees regarding intellectual property ownership, disclosure obligations, or breach of contract. Employers and employees should consider ADR mechanisms, such as arbitration or mediation, to resolve the conflicts cost effectively and efficiently.
- Confidentiality and Trade Secrets : EIAs often include confidentiality provisions requiring employees to maintain the confidentiality of proprietary information and trade secrets. Employers must take appropriate measures to ensure that the employees know their duties regarding non-disclosure and confidentiality to safeguard sensitive information.
Important case laws
Chidambaraiyer and others vs. p. s. renga iyer and others (1965).
In this case , it was held that when a person rests under an obligation to do something in the discharge of such obligation, he transfers a certain interest for valuable consideration. It was further held that in cases where an author created a work as part of their employment/ apprenticeship, the employer owns the copyright as the first owner by default under Section 17(c) of the Copyright Act. If an author creates a work independently, or if he creates a work under a contract for service, he will hold the copyright.

V.T. Thomas & Ors. vs. Malayala Manorama Co. Ltd. (1987)
In this case , an employee created a cartoon named Boban and Molly, which was created before the start of his employment at Manorama. Thus, the copyright is absolutely held by the author, that is, VT Thomas, and not the employer.
Charian P. Joseph vs. K. Prabhakaran Prabkaran Nair (1967)
It was held in this case that when the work is not a literary, dramatic, or artistic work made by the author in the course of employment by the proprietor or newspaper, magazine, or similar periodical, or in the case of a photograph taken or painted, or portrait drawn, or an engraving or cinematograph film made for valuable considerations at the instance of the person, but is the kind of work made in the course of the author’s employment under a contract of service or apprenticeship, the employer shall be the first owner of the copyright therein. But the provision would be applicable only when there is no agreement to the contrary.
University of London Press Ltd. vs. University Tutorial Press Ltd. (1916)
In this case , it was held that an employee is someone who follows the employer’s commands in the manner in which he shall work. The direct control of the employer, the independence of the person who renders services, and the place where the work is done determine whether there is a contract of service between the employee and employer.
Microsoft Corporation vs. Deepak Raval (2016)
In this case , Microsoft Corporation, a US-based company, sues for copyright infringement against defendants in India. Plaintiff’s software and hardware, including Microsoft Windows and Office, are protected under Indian law via international copyright conventions. Plaintiff seeks injunctions against copying, manufacturing, and selling unlicensed versions of their software and hardware. They also requested the delivery of infringing copies, accounts of profits, and damages. The Court grants injunctions and awards damages of Rs. 5 lakhs, limited to a higher estimate, acknowledging the defendant’s lack of knowledge.
Warner Bros. Entertainment Inc. and Mr. Santosh V.G. (2009):
This case involves a dispute over the distribution of films by the plaintiffs and their licencing agreements. Plaintiffs release films in the USA first, possibly on home video, before theatrical releases in other countries. Defendants argue for broader freedom of speech and expression in providing entertainment, citing their role as a film club promoting discussion and appreciation of cinema. They claim prominent members and societal value in their activities. The case raises issues of copyright infringement and the balance between commercial interests and fundamental rights to free expression.
Conclusion
Employee Invention Agreements (EIAs) play an important role in safeguarding intellectual property rights and fostering innovation. These agreements establish clear guidelines for ownership and control of inventions and creative works developed by employees during their tenure. By ensuring that intellectual property belongs to the employer, EIAs protect the company’s competitive advantage and promote a culture of innovation. However, challenges such as defining the scope of employment, acknowledging employee contributions, and navigating international legal requirements must be addressed to mitigate potential disputes. Overall, EIAs offer numerous benefits to both employers and employees, promoting trust, transparency, and the effective management of intellectual property assets.
- https://www.anaassociates.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/Who-owns-the-intellectual-property-developed-in-India.pdf
- https://legalserviceindia.com/articles/copy_owner.htm
- https://www.khaitanco.com/sites/default/files/2021-07/Intellectual%20property%20clause%20(employment)%20QAndA%20India.pdf
- http://library.sun.ac.za/SiteCollectionDocuments/judgmentscopyright/Judgments%20on%20Copyright%202019.pdf
- https://fastercapital.com/keyword/legal-regulatory-matters.html

RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Mohd. amin vs. vakil ahmad air (1952) , shabana bano vs. imran khan (2010) , rohtas bhankhar vs. union of india (2014) , leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
How to Pass the Advocate-on-Record (AoR) Exam and Establish Your Supreme Court Practice

Register now
Thank you for registering with us, you made the right choice.
Congratulations! You have successfully registered for the webinar. See you there.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

Suspended Counterparty Program
FHFA established the Suspended Counterparty Program to help address the risk to Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, and the Federal Home Loan Banks (“the regulated entities”) presented by individuals and entities with a history of fraud or other financial misconduct. Under this program, FHFA may issue orders suspending an individual or entity from doing business with the regulated entities.
FHFA maintains a list at this page of each person that is currently suspended under the Suspended Counterparty Program.
| Suspension Order | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YiHou Han | San Francisco | California | 03/26/2024 | Indefinite | |
| Alex A. Dadourian | Granada Hills | California | 02/08/2024 | Indefinite | |
| Tamara Dadyan | Encino | California | 01/10/2024 | Indefinite | |
| Richard Ayvazyan | Encino | California | 01/10/2024 | Indefinite | |
| Michael C. Jackson | Star | Idaho | 01/10/2024 | Indefinite |
This page was last updated on 03/26/2024
EU AI Act: first regulation on artificial intelligence
The use of artificial intelligence in the EU will be regulated by the AI Act, the world’s first comprehensive AI law. Find out how it will protect you.

As part of its digital strategy , the EU wants to regulate artificial intelligence (AI) to ensure better conditions for the development and use of this innovative technology. AI can create many benefits , such as better healthcare; safer and cleaner transport; more efficient manufacturing; and cheaper and more sustainable energy.
In April 2021, the European Commission proposed the first EU regulatory framework for AI. It says that AI systems that can be used in different applications are analysed and classified according to the risk they pose to users. The different risk levels will mean more or less regulation.
Learn more about what artificial intelligence is and how it is used
What Parliament wants in AI legislation
Parliament's priority is to make sure that AI systems used in the EU are safe, transparent, traceable, non-discriminatory and environmentally friendly. AI systems should be overseen by people, rather than by automation, to prevent harmful outcomes.
Parliament also wants to establish a technology-neutral, uniform definition for AI that could be applied to future AI systems.
Learn more about Parliament’s work on AI and its vision for AI’s future
AI Act: different rules for different risk levels
The new rules establish obligations for providers and users depending on the level of risk from artificial intelligence. While many AI systems pose minimal risk, they need to be assessed.
Unacceptable risk
Unacceptable risk AI systems are systems considered a threat to people and will be banned. They include:
- Cognitive behavioural manipulation of people or specific vulnerable groups: for example voice-activated toys that encourage dangerous behaviour in children
- Social scoring: classifying people based on behaviour, socio-economic status or personal characteristics
- Biometric identification and categorisation of people
- Real-time and remote biometric identification systems, such as facial recognition
Some exceptions may be allowed for law enforcement purposes. “Real-time” remote biometric identification systems will be allowed in a limited number of serious cases, while “post” remote biometric identification systems, where identification occurs after a significant delay, will be allowed to prosecute serious crimes and only after court approval.
AI systems that negatively affect safety or fundamental rights will be considered high risk and will be divided into two categories:
1) AI systems that are used in products falling under the EU’s product safety legislation . This includes toys, aviation, cars, medical devices and lifts.
2) AI systems falling into specific areas that will have to be registered in an EU database:
- Management and operation of critical infrastructure
- Education and vocational training
- Employment, worker management and access to self-employment
- Access to and enjoyment of essential private services and public services and benefits
- Law enforcement
- Migration, asylum and border control management
- Assistance in legal interpretation and application of the law.
All high-risk AI systems will be assessed before being put on the market and also throughout their lifecycle. People will have the right to file complaints about AI systems to designated national authorities.
Transparency requirements
Generative AI, like ChatGPT, will not be classified as high-risk, but will have to comply with transparency requirements and EU copyright law:
- Disclosing that the content was generated by AI
- Designing the model to prevent it from generating illegal content
- Publishing summaries of copyrighted data used for training
High-impact general-purpose AI models that might pose systemic risk, such as the more advanced AI model GPT-4, would have to undergo thorough evaluations and any serious incidents would have to be reported to the European Commission.
Content that is either generated or modified with the help of AI - images, audio or video files (for example deepfakes) - need to be clearly labelled as AI generated so that users are aware when they come across such content.
Supporting innovation
The law aims to offer start-ups and small and medium-sized enterprises opportunities to develop and train AI models before their release to the general public.
That is why it requires that national authorities provide companies with a testing environment that simulates conditions close to the real world.
The Parliament adopted the Artificial Intelligence Act in March 2024 . It will be fully applicable 24 months after entry into force, but some parts will be applicable sooner:
- The ban of AI systems posing unacceptable risks will apply six months after the entry into force
- Codes of practice will apply nine months after entry into force
- Rules on general-purpose AI systems that need to comply with transparency requirements will apply 12 months after the entry into force
High-risk systems will have more time to comply with the requirements as the obligations concerning them will become applicable 36 months after the entry into force.
More on the EU’s digital measures
- Cryptocurrency dangers and the benefits of EU legislation
- Fighting cybercrime: new EU cybersecurity laws explained
- Boosting data sharing in the EU: what are the benefits?
- EU Digital Markets Act and Digital Services Act
- Five ways the European Parliament wants to protect online gamers
- Artificial Intelligence Act
Share this article on:
- Sign up for mail updates
- PDF version

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Invention assignment agreement does not apply to any invention created on the employee's own (unpaid) time, without the use of company equipment, facilities, supplies, or information, unless it is related to the employer's business and R&D or is a result of the activities performed by the employee at work, except for those inventions that ...
An invention assignment agreement is a legal contract between an employer and a contractor or employee. It has become important as the world becomes increasingly digital. It is because intellectual property has become an invaluable asset for businesses. Protecting this asset is essential to ensure that companies retain their competitive edge.
An invention assignment agreement is a contract that gives the employer certain rights to inventions created or conceptualized by the employee during the employment relationship. Typically, this type of agreement requires the employee to disclose any such inventions to the employer, to "assign" (legally transfer) ownership rights in such ...
An invention assignment agreement is a new or unique device, process, or thing that is transferred from an inventor (assignor) to someone else (assignee). An invention that can be transferred will usually have a patent registered with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. How to Search for a Patent (3 steps)
An Invention Assignment Agreement is an agreement between an employer and employee where an employee agrees that anything created on behalf of the company (on the company's dime) will be owned by the company. Invention Assignment Agreements are s in technology companies and emerging start-ups but can also be used for a number of other business ...
An employee invention assignment agreement is a contract between an employer and employee that grants the employer certain rights to a worker's inventions. In other words, while an individual is employed with the company, they agree to relinquish their natural rights to their intellectual property and inventions to their employers. ...
June 2, 2024. Types of Contracts. A Confidentiality and Invention Assignment Agreement is a legally binding contract that establishes the terms and conditions for disclosing confidential information and assigning intellectual property rights, protecting valuable trade secrets and inventions from unauthorized use, disclosure, or misappropriation.
Invention assignment agreements are contracts that stipulate that anything the signee creates or develops on behalf of the company, is the property of the company. By signing an invention assignment agreement, the party relinquishes ownership rights to inventions and intellectual property he creates during his employment.
An invention agreement is a legal document that allows companies to retain the rights to intellectual property and creative works developed by employees. Find Lawyers ... and the provisions hereof requiring assignment of inventions to the Company do not apply to, any Invention which qualifies fully for exclusion under the provisions attached ...
Assignment of Inventions. 2.1Definitions. 2.2Excluded Inventions and Other Inventions. 2.3Assignment of Company Inventions. 2.4Unassigned or Nonassignable Inventions. 2.5Obligation to Keep Company Informed. 2.6Government or Third ... This Agreement does not apply to any Inventions made by you prior to your Employment or Service that are ...
Fact-Checked. In today's "information age," it is nearly universal practice for employers to require employees involved in research and development (R&D) or other technical work to sign so called "pre-invention assignment agreements" prior to employment. These assign to the employer ownership rights over any inventions created while employed.
Employee invention assignment agreements are one crucial tool for protecting intellectual property, but the laws governing them contain traps for the unwary. If the agreement is too narrow or ambiguous, it may allow inventions to slip away. Further, if the agreement fails to include certain provisions, it may be invalid in certain states.
An invention assignment agreement is a legally binding contract that assigns ownership of an invention to another party, such as an employer or investor. The Agreement outlines the inventor's rights and duties with regards to the use of their intellectual property while protecting them from theft or infringement by other parties. Furthermore ...
Invention assignment agreements form an integral part of a CIIA Agreement. They serve to grant the employer specific rights to inventions developed or conceived by the employee during their course of employment. The 'integration' clause, also known as the "entire agreement" clause, ensures that the invention assignment agreement is all ...
An invention assignment agreement is a contract in which an employee or independent contractor assigns intellectual property rights for their services to the company. These agreements typically appear in other employment documents such as confidentiality agreements or an independent contractor agreement. The types of work an invention ...
represent that there are no such Inventions at the time of signing this Agreement. (b) Use or Incorporation of Inventions. If in the course of the Relationship, I use or incorporate into a product, process or machine any Invention not covered by Section 4(d) of this Agreement in which I have an interest, I will promptly so inform the Company ...
Invention assignment agreements will usually include a nondisclosure agreement, a non-solicitation agreement, and, depending on state laws, a non-compete agreement. A CIIAA is a legally binding contract, so anyone asked to sign one for purposes of employment is encouraged to speak to an intellectual property attorney to learn their rights.
Related to Assignment of Inventions Agreement. Assignment of Inventions Subject to Sections 2.4, and 2.6, I hereby assign and agree to assign in the future (when any such Inventions or Proprietary Rights are first reduced to practice or first fixed in a tangible medium, as applicable) to the Company all my right, title and interest in and to any and all Inventions (and all Proprietary Rights ...
An inventions assignment agreement is a typical feature of an independent contractor or employee agreement where the worker agrees to assign any intellectual property rights arising from the worker's services to the company. Employees typically see these provisions in a Confidential Information and Invention Assignment Agreement (CIIAA) that ...
It is important that the assignment of rights in the PIIA cover both an assignment of any current rights to such inventions and an agreement to assign such rights in the future when any additional ...
Also known as Proprietary Information and Inventions Assignment Agreements (or PIIAAs), Confidential Information and Inventions Assignment Agreements ensure that intellectual property and other proprietary rights created by employees during the course of their employment are assigned to the employer. Effective CIIAAs assign intellectual ...
An Employee Invention Agreement (EIA), also known as an Intellectual Property (IP) agreement or invention assignment agreement, is a legal contract between an employer and an employee regarding ownership and control of intellectual property created during the course of employment. Generally, in an employee invention agreement, the terms of the ...
FHFA established the Suspended Counterparty Program to help address the risk to Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, and the Federal Home Loan Banks ("the regulated entities") presented by individuals and entities with a history of fraud or other financial misconduct. Under this program, FHFA may issue orders suspending an individual or entity from ...
The Parliament adopted the Artificial Intelligence Act in March 2024. It will be fully applicable 24 months after entry into force, but some parts will be applicable sooner: The ban of AI systems posing unacceptable risks will apply six months after the entry into force. Codes of practice will apply nine months after entry into force.