

The 5 Steps of Problem Solving

Problem solving is a critical skill for success in business – in fact it’s often what you are hired and paid to do. This article explains the five problem solving steps and provides strategies on how to execute each one.
Defining Problem Solving
Before we talk about the stages of problem solving, it’s important to have a definition of what it is. Let’s look at the two roots of problem solving — problems and solutions.
Problem – a state of desire for reaching a definite goal from a present condition [1] Solution – the management of a problem in a way that successfully meets the goals set for treating it
[1] Problem solving on Wikipedia
One important call-out is the importance of having a goal. As defined above, the solution may not completely solve problem, but it does meet the goals you establish for treating it–you may not be able to completely resolve the problem (end world hunger), but you can have a goal to help it (reduce the number of starving children by 10%).
The Five Steps of Problem Solving
With that understanding of problem solving, let’s talk about the steps that can get you there. The five problem solving steps are shown in the chart below:
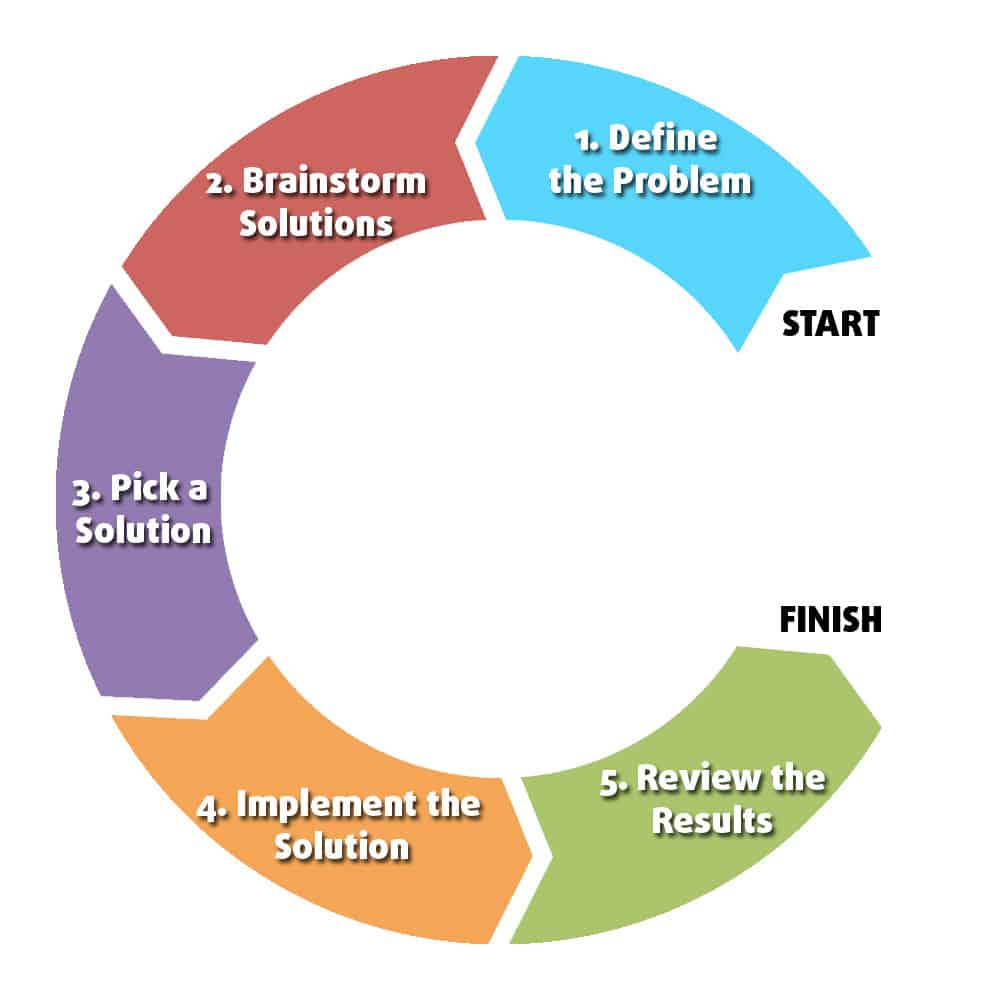
However this chart as is a little misleading. Not all problems follow these steps linearly, especially for very challenging problems. Instead, you’ll likely move back and forth between the steps as you continue to work on the problem, as shown below:
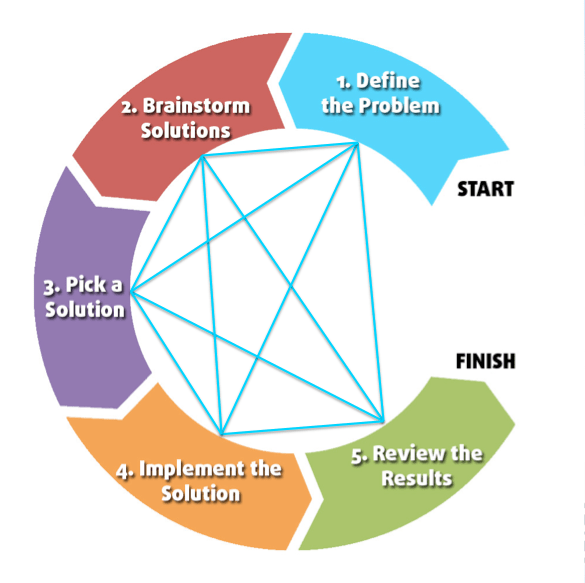
Let’s explore of these steps in more detail, understanding what it is and the inputs and outputs of each phase.
1. Define the Problem
aka What are you trying to solve? In addition to getting clear on what the problem is, defining the problem also establishes a goal for what you want to achieve.
Input: something is wrong or something could be improved. Output: a clear definition of the opportunity and a goal for fixing it.
2. Brainstorm Ideas
aka What are some ways to solve the problem? The goal is to create a list of possible solutions to choose from. The harder the problem, the more solutions you may need.
Input: a goal; research of the problem and possible solutions; imagination. Output: pick-list of possible solutions that would achieve the stated goal.
3. Decide on a Solution
aka What are you going to do? The ideal solution is effective (it will meet the goal), efficient (is affordable), and has the fewest side effects (limited consequences from implementation).
Input: pick-list of possible solutions; decision-making criteria. Output: decision of what solution you will implement.
4. Implement the Solution
aka What are you doing? The implementation of a solution requires planning and execution. It’s often iterative, where the focus should be on short implementation cycles with testing and feedback, not trying to get it “perfect” the first time.
Input: decision; planning; hard work. Output: resolution to the problem.
5. Review the Results
aka What did you do? To know you successfully solved the problem, it’s important to review what worked, what didn’t and what impact the solution had. It also helps you improve long-term problem solving skills and keeps you from re-inventing the wheel.
Input: resolutions; results of the implementation. Output: insights; case-studies; bullets on your resume.
Improving Problem Solving Skills
Once you understand the five steps of problem solving, you can build your skill level in each one. Often we’re naturally good at a couple of the phases and not as naturally good at others. Some people are great at generating ideas but struggle implementing them. Other people have great execution skills but can’t make decisions on which solutions to use. Knowing the different problem solving steps allows you to work on your weak areas, or team-up with someone who’s strengths complement yours.
Want to improve your problem solving skills? Want to perfect the art of problem solving? Check out our training programs or try these 20 problem solving activities to improve creativity .
THIS FREE 129 SECOND QUIZ WILL SHOW YOU
what is your humor persona?
Humor is a skill that can be learned. And when used correctly, it is a superpower that can be your greatest asset for building a happier, healthier and more productive life. See for yourself...
you might also be interested in...
Last Minute Team Building Idea – Improv Talent Show
Hosting a Improv talent show at work is a great team building event. Improv talent shows and Improv games are […]

Your Brain Is a Sheep In Wolf’s Clothing
Every now and then, I’ll go to a yoga class with Pretzel (my wife). On two different occasions, different yoga […]

The United States of Laughter
Today is the day! After 18 months of traveling and 12 months of writing, editing, re-writing, re-editing, re-writing etc, my […]
22 thoughts on “The 5 Steps of Problem Solving”
very helpful and informative training
Thank you for the information
YOU ARE AFOOL
I’m writing my 7th edition of Effective Security Management. I would like to use your circular graphic illustration in a new chapter on problem solving. You’re welcome to phone me at — with attribution.
Sure thing, shoot us an email at [email protected] .
i love your presentation. It’s very clear. I think I would use it in teaching my class problem solving procedures. Thank you
It is well defined steps, thank you.
these step can you email them to me so I can print them out these steps are very helpful
I like the content of this article, it is really helpful. I would like to know much on how PAID process (i.e. Problem statement, Analyze the problem, Identify likely causes, and Define the actual causes) works in Problem Solving.
very useful information on problem solving process.Thank you for the update.
Pingback: Let’s Look at Work Is Working with the Environment | #EnviroSociety
It makes sense that a business would want to have an effective problem solving strategy. Things could get bad if they can’t find solutions! I think one of the most important things about problem solving is communication.
Well in our school teacher teach us –
1) problem ldentification 2) structuring the problem 3) looking for possible solutions 4) lmplementation 5) monitoring or seeking feedback 6) decision making
Pleace write about it …
I teach Professional communication (Speech) and I find the 5 steps to problem solving as described here the best method. Your teacher actually uses 4 steps. The Feedback and decision making are follow up to the actual implementation and solving of the problem.
i know the steps of doing some guideline for problem solving
steps are very useful to solve my problem
The steps given are very effective. Thank you for the wonderful presentation of the cycle/steps/procedure and their connections.
I like the steps for problem solving
It is very useful for solving difficult problem i would reccomend it to a friend
this is very interesting because once u have learned you will always differentiate the right from the wrong.
I like the contents of the problem solving steps. informative.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Humor Persona - Template B2B
I make an effort to appreciate the humor of everyday life....
This question helps us further the advancement of humor research to make it more equitable.
Humor Persona - Main B2C

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 4 min read
The Problem-Solving Process
Looking at the basic problem-solving process to help keep you on the right track.
By the Mind Tools Content Team
Problem-solving is an important part of planning and decision-making. The process has much in common with the decision-making process, and in the case of complex decisions, can form part of the process itself.
We face and solve problems every day, in a variety of guises and of differing complexity. Some, such as the resolution of a serious complaint, require a significant amount of time, thought and investigation. Others, such as a printer running out of paper, are so quickly resolved they barely register as a problem at all.

Despite the everyday occurrence of problems, many people lack confidence when it comes to solving them, and as a result may chose to stay with the status quo rather than tackle the issue. Broken down into steps, however, the problem-solving process is very simple. While there are many tools and techniques available to help us solve problems, the outline process remains the same.
The main stages of problem-solving are outlined below, though not all are required for every problem that needs to be solved.
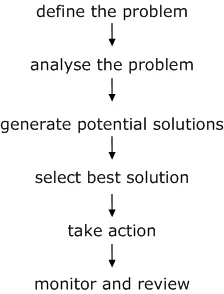
1. Define the Problem
Clarify the problem before trying to solve it. A common mistake with problem-solving is to react to what the problem appears to be, rather than what it actually is. Write down a simple statement of the problem, and then underline the key words. Be certain there are no hidden assumptions in the key words you have underlined. One way of doing this is to use a synonym to replace the key words. For example, ‘We need to encourage higher productivity ’ might become ‘We need to promote superior output ’ which has a different meaning.
2. Analyze the Problem
Ask yourself, and others, the following questions.
- Where is the problem occurring?
- When is it occurring?
- Why is it happening?
Be careful not to jump to ‘who is causing the problem?’. When stressed and faced with a problem it is all too easy to assign blame. This, however, can cause negative feeling and does not help to solve the problem. As an example, if an employee is underperforming, the root of the problem might lie in a number of areas, such as lack of training, workplace bullying or management style. To assign immediate blame to the employee would not therefore resolve the underlying issue.
Once the answers to the where, when and why have been determined, the following questions should also be asked:
- Where can further information be found?
- Is this information correct, up-to-date and unbiased?
- What does this information mean in terms of the available options?
3. Generate Potential Solutions
When generating potential solutions it can be a good idea to have a mixture of ‘right brain’ and ‘left brain’ thinkers. In other words, some people who think laterally and some who think logically. This provides a balance in terms of generating the widest possible variety of solutions while also being realistic about what can be achieved. There are many tools and techniques which can help produce solutions, including thinking about the problem from a number of different perspectives, and brainstorming, where a team or individual write as many possibilities as they can think of to encourage lateral thinking and generate a broad range of potential solutions.
4. Select Best Solution
When selecting the best solution, consider:
- Is this a long-term solution, or a ‘quick fix’?
- Is the solution achievable in terms of available resources and time?
- Are there any risks associated with the chosen solution?
- Could the solution, in itself, lead to other problems?
This stage in particular demonstrates why problem-solving and decision-making are so closely related.
5. Take Action
In order to implement the chosen solution effectively, consider the following:
- What will the situation look like when the problem is resolved?
- What needs to be done to implement the solution? Are there systems or processes that need to be adjusted?
- What will be the success indicators?
- What are the timescales for the implementation? Does the scale of the problem/implementation require a project plan?
- Who is responsible?
Once the answers to all the above questions are written down, they can form the basis of an action plan.
6. Monitor and Review
One of the most important factors in successful problem-solving is continual observation and feedback. Use the success indicators in the action plan to monitor progress on a regular basis. Is everything as expected? Is everything on schedule? Keep an eye on priorities and timelines to prevent them from slipping.
If the indicators are not being met, or if timescales are slipping, consider what can be done. Was the plan realistic? If so, are sufficient resources being made available? Are these resources targeting the correct part of the plan? Or does the plan need to be amended? Regular review and discussion of the action plan is important so small adjustments can be made on a regular basis to help keep everything on track.
Once all the indicators have been met and the problem has been resolved, consider what steps can now be taken to prevent this type of problem recurring? It may be that the chosen solution already prevents a recurrence, however if an interim or partial solution has been chosen it is important not to lose momentum.
Problems, by their very nature, will not always fit neatly into a structured problem-solving process. This process, therefore, is designed as a framework which can be adapted to individual needs and nature.
Join Mind Tools and get access to exclusive content.
This resource is only available to Mind Tools members.
Already a member? Please Login here

Team Management
Learn the key aspects of managing a team, from building and developing your team, to working with different types of teams, and troubleshooting common problems.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

SWOT Analysis

SMART Goals
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
How to stop procrastinating.
Overcoming the Habit of Delaying Important Tasks
What Is Time Management?
Working Smarter to Enhance Productivity
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Energizing yourself infographic.
Infographic Transcript
Infographic
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Overview of the Problem-Solving Mental Process
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
- Identify the Problem
- Define the Problem
- Form a Strategy
- Organize Information
- Allocate Resources
- Monitor Progress
- Evaluate the Results
Frequently Asked Questions
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue.
The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything they can about the issue and then using factual knowledge to come up with a solution. In other instances, creativity and insight are the best options.
It is not necessary to follow problem-solving steps sequentially, It is common to skip steps or even go back through steps multiple times until the desired solution is reached.
In order to correctly solve a problem, it is often important to follow a series of steps. Researchers sometimes refer to this as the problem-solving cycle. While this cycle is portrayed sequentially, people rarely follow a rigid series of steps to find a solution.
The following steps include developing strategies and organizing knowledge.
1. Identifying the Problem
While it may seem like an obvious step, identifying the problem is not always as simple as it sounds. In some cases, people might mistakenly identify the wrong source of a problem, which will make attempts to solve it inefficient or even useless.
Some strategies that you might use to figure out the source of a problem include :
- Asking questions about the problem
- Breaking the problem down into smaller pieces
- Looking at the problem from different perspectives
- Conducting research to figure out what relationships exist between different variables
2. Defining the Problem
After the problem has been identified, it is important to fully define the problem so that it can be solved. You can define a problem by operationally defining each aspect of the problem and setting goals for what aspects of the problem you will address
At this point, you should focus on figuring out which aspects of the problems are facts and which are opinions. State the problem clearly and identify the scope of the solution.
3. Forming a Strategy
After the problem has been identified, it is time to start brainstorming potential solutions. This step usually involves generating as many ideas as possible without judging their quality. Once several possibilities have been generated, they can be evaluated and narrowed down.
The next step is to develop a strategy to solve the problem. The approach used will vary depending upon the situation and the individual's unique preferences. Common problem-solving strategies include heuristics and algorithms.
- Heuristics are mental shortcuts that are often based on solutions that have worked in the past. They can work well if the problem is similar to something you have encountered before and are often the best choice if you need a fast solution.
- Algorithms are step-by-step strategies that are guaranteed to produce a correct result. While this approach is great for accuracy, it can also consume time and resources.
Heuristics are often best used when time is of the essence, while algorithms are a better choice when a decision needs to be as accurate as possible.
4. Organizing Information
Before coming up with a solution, you need to first organize the available information. What do you know about the problem? What do you not know? The more information that is available the better prepared you will be to come up with an accurate solution.
When approaching a problem, it is important to make sure that you have all the data you need. Making a decision without adequate information can lead to biased or inaccurate results.
5. Allocating Resources
Of course, we don't always have unlimited money, time, and other resources to solve a problem. Before you begin to solve a problem, you need to determine how high priority it is.
If it is an important problem, it is probably worth allocating more resources to solving it. If, however, it is a fairly unimportant problem, then you do not want to spend too much of your available resources on coming up with a solution.
At this stage, it is important to consider all of the factors that might affect the problem at hand. This includes looking at the available resources, deadlines that need to be met, and any possible risks involved in each solution. After careful evaluation, a decision can be made about which solution to pursue.
6. Monitoring Progress
After selecting a problem-solving strategy, it is time to put the plan into action and see if it works. This step might involve trying out different solutions to see which one is the most effective.
It is also important to monitor the situation after implementing a solution to ensure that the problem has been solved and that no new problems have arisen as a result of the proposed solution.
Effective problem-solvers tend to monitor their progress as they work towards a solution. If they are not making good progress toward reaching their goal, they will reevaluate their approach or look for new strategies .
7. Evaluating the Results
After a solution has been reached, it is important to evaluate the results to determine if it is the best possible solution to the problem. This evaluation might be immediate, such as checking the results of a math problem to ensure the answer is correct, or it can be delayed, such as evaluating the success of a therapy program after several months of treatment.
Once a problem has been solved, it is important to take some time to reflect on the process that was used and evaluate the results. This will help you to improve your problem-solving skills and become more efficient at solving future problems.
A Word From Verywell
It is important to remember that there are many different problem-solving processes with different steps, and this is just one example. Problem-solving in real-world situations requires a great deal of resourcefulness, flexibility, resilience, and continuous interaction with the environment.
Get Advice From The Verywell Mind Podcast
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares how you can stop dwelling in a negative mindset.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
You can become a better problem solving by:
- Practicing brainstorming and coming up with multiple potential solutions to problems
- Being open-minded and considering all possible options before making a decision
- Breaking down problems into smaller, more manageable pieces
- Asking for help when needed
- Researching different problem-solving techniques and trying out new ones
- Learning from mistakes and using them as opportunities to grow
It's important to communicate openly and honestly with your partner about what's going on. Try to see things from their perspective as well as your own. Work together to find a resolution that works for both of you. Be willing to compromise and accept that there may not be a perfect solution.
Take breaks if things are getting too heated, and come back to the problem when you feel calm and collected. Don't try to fix every problem on your own—consider asking a therapist or counselor for help and insight.
If you've tried everything and there doesn't seem to be a way to fix the problem, you may have to learn to accept it. This can be difficult, but try to focus on the positive aspects of your life and remember that every situation is temporary. Don't dwell on what's going wrong—instead, think about what's going right. Find support by talking to friends or family. Seek professional help if you're having trouble coping.
Davidson JE, Sternberg RJ, editors. The Psychology of Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press; 2003. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511615771
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. Published 2018 Jun 26. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu

The 5 steps of the solving problem process
August 17, 2023 by MindManager Blog
Whether you run a business, manage a team, or work in an industry where change is the norm, it may feel like something is always going wrong. Thankfully, becoming proficient in the problem solving process can alleviate a great deal of the stress that business issues can create.
Understanding the right way to solve problems not only takes the guesswork out of how to deal with difficult, unexpected, or complex situations, it can lead to more effective long-term solutions.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the 5 steps of problem solving, and help you explore a few examples of problem solving scenarios where you can see the problem solving process in action before putting it to work.
Understanding the problem solving process
When something isn’t working, it’s important to understand what’s at the root of the problem so you can fix it and prevent it from happening again. That’s why resolving difficult or complex issues works best when you apply proven business problem solving tools and techniques – from soft skills, to software.
The problem solving process typically includes:
- Pinpointing what’s broken by gathering data and consulting with team members.
- Figuring out why it’s not working by mapping out and troubleshooting the problem.
- Deciding on the most effective way to fix it by brainstorming and then implementing a solution.
While skills like active listening, collaboration, and leadership play an important role in problem solving, tools like visual mapping software make it easier to define and share problem solving objectives, play out various solutions, and even put the best fit to work.
Before you can take your first step toward solving a problem, you need to have a clear idea of what the issue is and the outcome you want to achieve by resolving it.
For example, if your company currently manufactures 50 widgets a day, but you’ve started processing orders for 75 widgets a day, you could simply say you have a production deficit.
However, the problem solving process will prove far more valuable if you define the start and end point by clarifying that production is running short by 25 widgets a day, and you need to increase daily production by 50%.
Once you know where you’re at and where you need to end up, these five steps will take you from Point A to Point B:
- Figure out what’s causing the problem . You may need to gather knowledge and evaluate input from different documents, departments, and personnel to isolate the factors that are contributing to your problem. Knowledge visualization software like MindManager can help.
- Come up with a few viable solutions . Since hitting on exactly the right solution – right away – can be tough, brainstorming with your team and mapping out various scenarios is the best way to move forward. If your first strategy doesn’t pan out, you’ll have others on tap you can turn to.
- Choose the best option . Decision-making skills, and software that lets you lay out process relationships, priorities, and criteria, are invaluable for selecting the most promising solution. Whether it’s you or someone higher up making that choice, it should include weighing costs, time commitments, and any implementation hurdles.
- Put your chosen solution to work . Before implementing your fix of choice, you should make key personnel aware of changes that might affect their daily workflow, and set up benchmarks that will make it easy to see if your solution is working.
- Evaluate your outcome . Now comes the moment of truth: did the solution you implemented solve your problem? Do your benchmarks show you achieved the outcome you wanted? If so, congratulations! If not, you’ll need to tweak your solution to meet your problem solving goal.
In practice, you might not hit a home-run with every solution you execute. But the beauty of a repeatable process like problem solving is that you can carry out steps 4 and 5 again by drawing from the brainstorm options you documented during step 2.
Examples of problem solving scenarios
The best way to get a sense of how the problem solving process works before you try it for yourself is to work through some simple scenarios.
Here are three examples of how you can apply business problem solving techniques to common workplace challenges.
Scenario #1: Manufacturing
Building on our original manufacturing example, you determine that your company is consistently short producing 25 widgets a day and needs to increase daily production by 50%.
Since you’d like to gather data and input from both your manufacturing and sales order departments, you schedule a brainstorming session to discover the root cause of the shortage.
After examining four key production areas – machines, materials, methods, and management – you determine the cause of the problem: the material used to manufacture your widgets can only be fed into your equipment once the machinery warms up to a specific temperature for the day.
Your team comes up with three possible solutions.
- Leave your machinery running 24 hours so it’s always at temperature.
- Invest in equipment that heats up faster.
- Find an alternate material for your widgets.
After weighing the expense of the first two solutions, and conducting some online research, you decide that switching to a comparable but less expensive material that can be worked at a lower temperature is your best option.
You implement your plan, monitor your widget quality and output over the following week, and declare your solution a success when daily production increases by 100%.
Scenario #2: Service Delivery
Business training is booming and you’ve had to onboard new staff over the past month. Now you learn that several clients have expressed concern about the quality of your recent training sessions.
After speaking with both clients and staff, you discover there are actually two distinct factors contributing to your quality problem:
- The additional conference room you’ve leased to accommodate your expanding training sessions has terrible acoustics
- The AV equipment you’ve purchased to accommodate your expanding workforce is on back-order – and your new hires have been making do without
You could look for a new conference room or re-schedule upcoming training sessions until after your new equipment arrives. But your team collaboratively determines that the best way to mitigate both issues at once is by temporarily renting the high-quality sound and visual system they need.
Using benchmarks that include several weeks of feedback from session attendees, and random session spot-checks you conduct personally, you conclude the solution has worked.
Scenario #3: Marketing
You’ve invested heavily in product marketing, but still can’t meet your sales goals. Specifically, you missed your revenue target by 30% last year and would like to meet that same target this year.
After collecting and examining reams of information from your sales and accounting departments, you sit down with your marketing team to figure out what’s hindering your success in the marketplace.
Determining that your product isn’t competitively priced, you map out two viable solutions.
- Hire a third-party specialist to conduct a detailed market analysis.
- Drop the price of your product to undercut competitors.
Since you’re in a hurry for results, you decide to immediately reduce the price of your product and market it accordingly.
When revenue figures for the following quarter show sales have declined even further – and marketing surveys show potential customers are doubting the quality of your product – you revert back to your original pricing, revisit your problem solving process, and implement the market analysis solution instead.
With the valuable information you gain, you finally arrive at just the right product price for your target market and sales begin to pick up. Although you miss your revenue target again this year, you meet it by the second quarter of the following year.
Kickstart your collaborative brainstorming sessions and try MindManager for free today !
Ready to take the next step?
MindManager helps boost collaboration and productivity among remote and hybrid teams to achieve better results, faster.
Why choose MindManager?
MindManager® helps individuals, teams, and enterprises bring greater clarity and structure to plans, projects, and processes. It provides visual productivity tools and mind mapping software to help take you and your organization to where you want to be.
Explore MindManager

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)
Join our FREE training and learn the 5 things you can do to become a top 1% facilitator
What is problem-solving and how to do it right steps, processes, exercises.
The better your problem-solving skills are, the better (and easier!) your life will be. Organized problem-solving is a killer career skill - learn all about it here.
Whether we’re trying to solve a technical problem at work, or trying to navigate around a roadblock that Google Maps doesn’t see – most people are problem-solving every single day .
But how effective are you at tackling the challenges in your life? Do you have a bullet-proof process you follow that ensures solid outcomes, or... Do you act on a whim of inspiration (or lack thereof) to resolve your pressing problems?
Here’s the thing: the better your problem-solving skills are - the better (and easier!) your life will be (both professionally and personally). Organized problem-solving is a killer career (and life!) skill, so if you want to learn how to do it in the most efficient way possible, you’ve come to the right place.
Read along to learn more about the steps, techniques and exercises of the problem-solving process.
- 1. Do you want a Career in UX?
- Learn the Principles of UX Design
- Master a UX Design Tool
What is Problem-Solving?
We’re faced with the reality of having to solve problems every day, both in our private and professional lives. So why do we even need to learn about problem-solving? Aren’t we versed in it well enough already?
Well, what separates problem-solving from dealing with the usual day-to-day issues is that it’s a distinct process that allows you to go beyond the standard approaches to solving a problem and allows you to come up with more effective and efficient solutions. Or in other words, problem-solving allows you to knock out those problems with less effort.
Just like with any other skill, there’s an efficient way to solve problems, and a non-efficient one. While it might be tempting to go for the quickest fix for your challenge without giving it much thought, it will only end up costing you more time down the road. Quick fixes are rarely (if ever!) effective and end up being massive time wasters.
What separates problem-solving from dealing with the usual day-to-day issues is that it’s a distinct process that allows you to go beyond the standard approaches to solving a problem and allows you to come up with more effective and efficient solutions.
On the other hand, following a systemized clear process for problem-solving allows you to shortcut inefficiencies and time-wasters, turn your challenges into opportunities, and tackle problems of any scope without the usual stress and hassle.
What is the process that you need to follow, then? We’re glad you asked...
The Five Stages of Problem-Solving
So what’s the best way to move through the problem-solving process? There’s a 5-step process that you can follow that will allow you to solve your challenges more efficiently and effectively. In short, you need to move through these 5 steps:
- Defining a problem
- Ideating on a solution
- Committing to a course of action
- Implementing your solution
- And finally – analyzing the results.

Let’s look at each of those stages in detail.
Step 1: Defining The Problem
The first step might sound obvious, but trust us, you don’t want to skip it! Clearly defining and framing your challenge will help you guide your efforts and make sure you’re focussing on the things that matter, instead of being distracted by a myriad of other options, problems and issues that come up.
For once, you have to make sure you’re trying to solve the root cause, and not trying to mend the symptoms of it. For instance, if you keep losing users during your app onboarding process, you might jump to the conclusion that you need to tweak the process itself: change the copy, the screens, or the sequence of steps.
But unless you have clear evidence that confirms your hypothesis, your challenge might have an entirely different root cause, e.g. in confusing marketing communication prior to the app download.
Clearly defining and framing your challenge will help you guide your efforts and make sure you’re focussing on the things that matter, all the while ensuring that you’re trying to solve the root cause, and not trying to mend the symptoms of it
That’s why it’s essential you take a close look at the entire problem, not just at a fraction of it.
There are several exercises that can help you get a broader, more holistic view of the problem, some of our all-time favorites include Expert Interviews, How Might We, or The Map. Check out the step-by-step instructions on how to run them (along with 5 more exercises for framing your challenge!) here.
When in doubt, map out your challenge, and always try to tackle the bottlenecks that are more upstream - it’s likely that solving them will solve a couple of other challenges down the flow.
You also have to be mindful of how you frame the challenge: resist the urge to include a pre-defined solution into your problem statement. Priming your solutions to a predestined outcome destroys the purpose of following a step-by-step process in the first place!
Steer clear of formulations like:
We need to change the onboarding process... or We need to improve ad copy to increase conversions.
Instead, opt for more neutral, problem-oriented statements that don’t include a solution suggestion in them:
The drop off rate during the onboarding process is too high or Our ad conversion rates are below the norm.
Pro tip: Reframing your challenge as a ‘How Might We’ statement is a great way to spark up new ideas, opening your problem to a broader set of solutions, and is just a great way to reframe your problem into a more positive statement (without implying the possible solution!)
For example, following the onboarding drop-off rate problem we mentioned earlier, instead of framing it as a problem, you could opt for:
How Might We decrease the drop-off rate during the onboarding process?
Find out more about the best exercises for problem framing here!
Now that you have a clear idea of what you’re trying to solve, it’s move on to the next phase of the problem-solving process.
Learn more about facilitation and workshopping in our FREE FACILITATION COMMUNITY
Step 2: ideating a solution.
Get ready to roll up your sleeves and challenge the status quo! This step of the problem-solving process is all about thinking outside of the box, challenging old assumptions, and thinking laterally.
This stage is the one that tends to cause the most overwhelm in teams because it requires just the right balance of creativity and critical thinking, which tends to cause a lot of friction.
Our best advice?
Let go of the pressure to produce a polished, thought-through solution at this stage. You can hash out the details at a later point. Our goal right now is to come up with a direction, a prototype if you may, of where we want to move towards.
Embrace the “quantity over quality” motto, and let your creative juices flow! Now, we’re not saying you should roll with sub-par ideas. But you shouldn’t get too fixated on feasibility and viability just yet .
Your main goal during this step is to spark ideas, kick off your thinking process in the right direction, venture out of the familiar territories and think outside the box.
For the ideation to be the most effective your team will have to feel safe to challenge the norm and wide-spread assumptions. So lay judgment by side, there is no space for “that’s the way it’s always been done” in this step.
For your ideation sessions to be as efficient as possible, we highly recommend to run them in a workshop setting: this helps reduce the usual drawbacks of open discussions in teams (i.e. groupthink & team politics!)
Our favorite exercises to run during this phase include Lightning Demos, Sketching, and variations of Brainstorming. We crafted an entire article on how to run and facilitate these exercises in a separate article, so check it out of you’re going to be running an ideation session anytime soon!
Step 3: Choosing the Best Strategy & Committing
It’s time to decide which of the ideas that you generated in the last step will be the one you’ll implement.
This step is arguably the hardest one to complete smoothly: groupthink, team politics, differences in opinions and communication styles all make it very hard to align a team on a common course of action.
If you want to avoid the usual pitfalls of team decision-making, we recommend you steer clear of open unstructured discussion. While it’s useful in some scenarios, it’s a poor choice for when you need to make a decision, because it tends to reward the loudest people in the room, rather than give way to the best ideas.
It’s crucial you not only commit to a course of action but get full buy-in from the team. If your team members don’t understand the reasons for a decision, or are not fully onboard, the implementation of your decision will be half-hearted, and that’s definitely not what you want!
To achieve that, opt for anonymized, multi-layered voting, and include guided exercises like Storyboarding to prioritize your ideas.
We’ve gathered the list of our top-rated decision-making exercises, along with step-by-step instructions on how to run them in this article!
As a bonus tip, we recommend you involve a facilitator throughout the entire process. They will help align the team, and guide them through prioritizing and de-prioritizing solutions, as well as defining the next steps.
Pro tip : If you’re not the ultimate decision maker on the issue you’re trying to solve, make sure they’re in the room when the call is being made! Having a Decider in the room ensures that the decisions you come to will actually get executed on after, instead of getting shut down by your superiors after.
Join our FREE community and connect with other Facilitators and Workshoppers
Step 4: implementing your solution.
Here’s a truth that might be hard to swallow: it doesn’t matter how innovative, creative, or original your idea is, if your execution is weak.
One of our favourite illustrations of how this works in practice comes from the book “ Anything you want ” by Derek Sivers. He reveals that ideas should be treated as multipliers of execution. What this means is that a mediocre, “so-so” idea could be worth millions if executed well, while a “brilliant” idea can completely flop with bad execution.
That’s why this step is crucial if you want to really master the problem-solving process.
What do we mean by execution? Everything that happens after the whiteboards are wiped clean and your team starts to action the outcomes of your sessions, be it prototyping, development, or promotion.
But don’t just take our word for it, look at the example of how execution affected Nintendo’s sales:
In the past few years, Nintendo has come up with 3 products: the Wii, the Wii U and the Switch. Check out their sales figures on the graph below - Wii is the clear-cut leader, followed by Switch, and finally Wii U lagging behind.

The Wii was unbelievably successful - it was a genuinely unique, “brilliant”-level idea and it had a “brilliant” execution (20x $10 million = $200 million). It is one of the fastest selling game consoles of all time and it completely took over the market.
The next product was called Wii U and it was a “great” concept but the execution was absolutely terrible. So even though this product was very interesting and innovative, the end result was 15x $1,000 = $15,000.
Finally, Nintendo took the Wii U concept and tried it again with the Switch. The idea was “so so” as it was already done before, but the execution was “brilliant”. So, 5x $10 million = $50 million! Much better.

Bottom line?
The same idea can either make no dent in the market and damage your share price OR become a market hit and increase your share price dramatically. The only difference between the two scenarios – execution.
So shift your focus from coming up with crazy, innovative, outlandish ideas that will disrupt the market, and concentrate on really nailing down your execution instead.
This is likely the least “workshoppy” step out of the entire problem-solving process because it requires less alignment and decision-making and more..well.. Execution!
But hey, we wouldn’t be called “Workshopper” if we didn't offer you at least one way to optimize and workshopify (yup, we’re making it a thing) your execution process.
Cue in….prototyping.
We’re huge fans of prototyping all big solutions (and testing them!) The main reason?
This saves us time AND money! Prototyping and testing your solutions (especially if they’re time and investment-demanding) is a great way to make sure you’re creating something that is actually needed.
The key with prototyping the right way is to keep it simple. Don’t invest too much time, or resources into it. The goal is to gather data for your future decisions, not to create a near-to-perfect mockup of your solution.
There are LOADS of prototyping forms and techniques, and if you’d like to learn more on the subject you should definitely check out our extensive prototyping guide.
Step 5: Analyzing the Results
You’re nearly done, woo! Now that you have defined the right problem to tackle, brainstormed the solutions, aligned your team on the course of action, and put your plan into action it’s time to take stock of your efforts.
Seek feedback from all involved parties, analyze the data you’ve gathered, look at the bottom line of your efforts, and take a hard look at your problem: did it get solved? And even more than that, did the process feel smoother, easier, and more efficient than it normally is?
Running a retrospective is a great way to highlight things that went well and that you should keep for your next round of problem.solving, as well as pinpoint inefficiencies that you can eliminate.
But which kind of retrospective should you run? There are loads of options, and it’s easy to feel overwhelmed by them all, so we gathered our favorite retrospective variations in this article.
And there you have it, you just completed the cycle of problem-solving. We highly recommend you follow through with all the steps, without leaving any out. They all complement and build on each other, and it’s the combination of all 5 of them that makes the process effective.
Now that you have the problem solving process down, you might be wondering…
Do I need any special skills in order to be able to move through that process?
And the answer is… sort of! More in this in the next section.
Problem-Solving Skills
While your skill set will need to adapt and change based on the challenges you’ll be working on, most efficient problem-solvers have a solid foundation of these key skills:
- Active listening. While you might be the expert in the area of your challenge, there’s not a single person on Earth that knows it all! Being open to others’ perspectives and practicing active listening will come in very handy during step 1 of the process, as you’re trying to define the scope and the exact angle of the problem you’re working on.
- Analytical approach. Your analytical skills will help you understand problems and effectively develop solutions. You will also need analytical skills during research to help distinguish between effective and ineffective solutions.
- Communication. Is there a single area of expertise that DOESN’T require strong communication skills? We honestly don’t think so! Just like with any other life area, clear communication can make or break your problem-solving process. Being able to clearly communicate why you need to solve this challenge to your team, as well as align your team on the course of action are crucial for the success of the process.
- Decision-making. Ultimately, you will need to make a decision about how to solve problems that arise. A process without outcomes–regardless of how well thought-out and elaborate–is useless! If you want your problem-solving huddles to be effective, you have to come to grips with prioritization techniques and decision-making frameworks.
- Facilitation. Problem-solving revolves around being able to guide a group or a team to a common decision, and facilitation skills are essential in making that happen. Knowing how to facilitate will make it easy to keep the group focussed on the challenge, shortcut circular discussions, and make sure you’re moving along to solving the problem instead of just treading waters with fruitless discussions.
Not checking every single skill of your list just yet? Not to worry, the next section will give you practical tools on how to level up and improve your problem-solving skills.
How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills
Just like with any other skill, problem-solving is not an innate talent that you either have or you don’t. There are concrete steps you can take to improve your skills.
Here are some things that will get you closer to mastering the problem-solving process:
- Practice, Practice, Practice
Practice makes perfect, and problem-solving skills are no exception! Seek opportunities to utilize and develop these skills any time you can.
If you don’t know where or how to start just yet, here’s a suggestion that will get you up and running in no time: run a quick problem-solving session on a challenge that has been bothering your team for a while now.
It doesn’t need to be the big strategic decision or the issue defining the future of the company. Something easy and manageable (like optimizing office space or improving team communication) will do.
As you start feeling more comfortable with the problem-solving techniques, you can start tackling bigger challenges. Before you know it, you’ll master the art of creative problem-solving!
- Use a tried and tested problem-solving workshop
Facilitation is one of the essential skills for problem-solving. But here’s the thing… Facilitation skills on their own won’t lead you to a solved challenge.
While being able to shortcut aimless discussions is a great skill, you have to make sure your problem-solving session has tangible outcomes. Using a tried and tested method, a workshop, is one of the easiest ways to do that.
Our best advice is to get started with a tried and tested problem-solving workshop like the Lightning Decision Jam . The LDJ has all the right ingredients for quick, effective problem solving that leads to tangible outcomes. Give it a go!
- Learn from your peers
You may have colleagues who are skilled problem solvers. Observing how those colleagues solve problems can help you improve your own skills.
If possible, ask one of your more experienced colleagues if you can observe their techniques. Ask them relevant questions and try to apply as many of the new found skills i your career as possible.
- Learn & Practice the best problem-solving exercises
Having a toolbox of problem-solving exercises to pull from that can fit any type of challenge will make you a more versatile problem-solver and will make solving challenges that much easier for you!
Once you get used to the groove of learning how to combine them into effective sessions or workshops, there’ll be no stopping you. What are some of the most effective problem-solving exercises? Glad you asked! We’ve gathered our favorite ones here, check it out!
And there you have it, you’re now fully equipped for running creative problem-sessions with confidence and ease! Whichever method or exercise you choose, remember to keep track of your wins, and learn as much as you can from your losses!
Anastasia Ushakova
Brand Strategist, Digital Marketer, and a Workshopper.

When Do You Need a Facilitator?
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Suspendisse varius enim in eros elementum tristique. Duis cursus.

The Ultimate Facilitation Glossary: 50 Facilitation Terms You Should Know (From A-Z)

How To Improve Team Collaboration
- The Art of Effective Problem Solving: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Learn Lean Sigma
- Problem Solving
Whether we realise it or not, problem solving skills are an important part of our daily lives. From resolving a minor annoyance at home to tackling complex business challenges at work, our ability to solve problems has a significant impact on our success and happiness. However, not everyone is naturally gifted at problem-solving, and even those who are can always improve their skills. In this blog post, we will go over the art of effective problem-solving step by step.
You will learn how to define a problem, gather information, assess alternatives, and implement a solution, all while honing your critical thinking and creative problem-solving skills. Whether you’re a seasoned problem solver or just getting started, this guide will arm you with the knowledge and tools you need to face any challenge with confidence. So let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Problem solving methodologies.
Individuals and organisations can use a variety of problem-solving methodologies to address complex challenges. 8D and A3 problem solving techniques are two popular methodologies in the Lean Six Sigma framework.
Methodology of 8D (Eight Discipline) Problem Solving:
The 8D problem solving methodology is a systematic, team-based approach to problem solving. It is a method that guides a team through eight distinct steps to solve a problem in a systematic and comprehensive manner.
The 8D process consists of the following steps:
- Form a team: Assemble a group of people who have the necessary expertise to work on the problem.
- Define the issue: Clearly identify and define the problem, including the root cause and the customer impact.
- Create a temporary containment plan: Put in place a plan to lessen the impact of the problem until a permanent solution can be found.
- Identify the root cause: To identify the underlying causes of the problem, use root cause analysis techniques such as Fishbone diagrams and Pareto charts.
- Create and test long-term corrective actions: Create and test a long-term solution to eliminate the root cause of the problem.
- Implement and validate the permanent solution: Implement and validate the permanent solution’s effectiveness.
- Prevent recurrence: Put in place measures to keep the problem from recurring.
- Recognize and reward the team: Recognize and reward the team for its efforts.
Download the 8D Problem Solving Template
A3 Problem Solving Method:
The A3 problem solving technique is a visual, team-based problem-solving approach that is frequently used in Lean Six Sigma projects. The A3 report is a one-page document that clearly and concisely outlines the problem, root cause analysis, and proposed solution.
The A3 problem-solving procedure consists of the following steps:
- Determine the issue: Define the issue clearly, including its impact on the customer.
- Perform root cause analysis: Identify the underlying causes of the problem using root cause analysis techniques.
- Create and implement a solution: Create and implement a solution that addresses the problem’s root cause.
- Monitor and improve the solution: Keep an eye on the solution’s effectiveness and make any necessary changes.
Subsequently, in the Lean Six Sigma framework, the 8D and A3 problem solving methodologies are two popular approaches to problem solving. Both methodologies provide a structured, team-based problem-solving approach that guides individuals through a comprehensive and systematic process of identifying, analysing, and resolving problems in an effective and efficient manner.
Step 1 – Define the Problem
The definition of the problem is the first step in effective problem solving. This may appear to be a simple task, but it is actually quite difficult. This is because problems are frequently complex and multi-layered, making it easy to confuse symptoms with the underlying cause. To avoid this pitfall, it is critical to thoroughly understand the problem.
To begin, ask yourself some clarifying questions:
- What exactly is the issue?
- What are the problem’s symptoms or consequences?
- Who or what is impacted by the issue?
- When and where does the issue arise?
Answering these questions will assist you in determining the scope of the problem. However, simply describing the problem is not always sufficient; you must also identify the root cause. The root cause is the underlying cause of the problem and is usually the key to resolving it permanently.
Try asking “why” questions to find the root cause:
- What causes the problem?
- Why does it continue?
- Why does it have the effects that it does?
By repeatedly asking “ why ,” you’ll eventually get to the bottom of the problem. This is an important step in the problem-solving process because it ensures that you’re dealing with the root cause rather than just the symptoms.
Once you have a firm grasp on the issue, it is time to divide it into smaller, more manageable chunks. This makes tackling the problem easier and reduces the risk of becoming overwhelmed. For example, if you’re attempting to solve a complex business problem, you might divide it into smaller components like market research, product development, and sales strategies.
To summarise step 1, defining the problem is an important first step in effective problem-solving. You will be able to identify the root cause and break it down into manageable parts if you take the time to thoroughly understand the problem. This will prepare you for the next step in the problem-solving process, which is gathering information and brainstorming ideas.
Step 2 – Gather Information and Brainstorm Ideas
Gathering information and brainstorming ideas is the next step in effective problem solving. This entails researching the problem and relevant information, collaborating with others, and coming up with a variety of potential solutions. This increases your chances of finding the best solution to the problem.
Begin by researching the problem and relevant information. This could include reading articles, conducting surveys, or consulting with experts. The goal is to collect as much information as possible in order to better understand the problem and possible solutions.
Next, work with others to gather a variety of perspectives. Brainstorming with others can be an excellent way to come up with new and creative ideas. Encourage everyone to share their thoughts and ideas when working in a group, and make an effort to actively listen to what others have to say. Be open to new and unconventional ideas and resist the urge to dismiss them too quickly.
Finally, use brainstorming to generate a wide range of potential solutions. This is the place where you can let your imagination run wild. At this stage, don’t worry about the feasibility or practicality of the solutions; instead, focus on generating as many ideas as possible. Write down everything that comes to mind, no matter how ridiculous or unusual it may appear. This can be done individually or in groups.
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the next step in the problem-solving process, which we’ll go over in greater detail in the following section.
Step 3 – Evaluate Options and Choose the Best Solution
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the third step in effective problem solving, and it entails weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, considering their feasibility and practicability, and selecting the solution that is most likely to solve the problem effectively.
To begin, weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each solution. This will assist you in determining the potential outcomes of each solution and deciding which is the best option. For example, a quick and easy solution may not be the most effective in the long run, whereas a more complex and time-consuming solution may be more effective in solving the problem in the long run.
Consider each solution’s feasibility and practicability. Consider the following:
- Can the solution be implemented within the available resources, time, and budget?
- What are the possible barriers to implementing the solution?
- Is the solution feasible in today’s political, economic, and social environment?
You’ll be able to tell which solutions are likely to succeed and which aren’t by assessing their feasibility and practicability.
Finally, choose the solution that is most likely to effectively solve the problem. This solution should be based on the criteria you’ve established, such as the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and your overall goals.
It is critical to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all solution to problems. What is effective for one person or situation may not be effective for another. This is why it is critical to consider a wide range of solutions and evaluate each one based on its ability to effectively solve the problem.
Step 4 – Implement and Monitor the Solution
When you’ve decided on the best solution, it’s time to put it into action. The fourth and final step in effective problem solving is to put the solution into action, monitor its progress, and make any necessary adjustments.
To begin, implement the solution. This may entail delegating tasks, developing a strategy, and allocating resources. Ascertain that everyone involved understands their role and responsibilities in the solution’s implementation.
Next, keep an eye on the solution’s progress. This may entail scheduling regular check-ins, tracking metrics, and soliciting feedback from others. You will be able to identify any potential roadblocks and make any necessary adjustments in a timely manner if you monitor the progress of the solution.
Finally, make any necessary modifications to the solution. This could entail changing the solution, altering the plan of action, or delegating different tasks. Be willing to make changes if they will improve the solution or help it solve the problem more effectively.
It’s important to remember that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to start from scratch. This is especially true if the initial solution does not effectively solve the problem. In these situations, it’s critical to be adaptable and flexible and to keep trying new solutions until you find the one that works best.
To summarise, effective problem solving is a critical skill that can assist individuals and organisations in overcoming challenges and achieving their objectives. Effective problem solving consists of four key steps: defining the problem, generating potential solutions, evaluating alternatives and selecting the best solution, and implementing the solution.
You can increase your chances of success in problem solving by following these steps and considering factors such as the pros and cons of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and making any necessary adjustments. Furthermore, keep in mind that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to go back to the beginning and restart. Maintain your adaptability and try new solutions until you find the one that works best for you.
- Novick, L.R. and Bassok, M., 2005. Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press.
Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.
Free Lean Six Sigma Templates
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.
5S Floor Marking Best Practices
In lean manufacturing, the 5S System is a foundational tool, involving the steps: Sort, Set…
How to Measure the ROI of Continuous Improvement Initiatives
When it comes to business, knowing the value you’re getting for your money is crucial,…
8D Problem-Solving: Common Mistakes to Avoid
In today’s competitive business landscape, effective problem-solving is the cornerstone of organizational success. The 8D…
The Evolution of 8D Problem-Solving: From Basics to Excellence
In a world where efficiency and effectiveness are more than just buzzwords, the need for…
8D: Tools and Techniques
Are you grappling with recurring problems in your organization and searching for a structured way…
How to Select the Right Lean Six Sigma Projects: A Comprehensive Guide
Going on a Lean Six Sigma journey is an invigorating experience filled with opportunities for…
Protect your data
This site uses cookies and related technologies for site operation, and analytics as described in our Privacy Policy . You may choose to consent to our use of these technologies, reject non-essential technologies, or further manage your preferences.
- Career Advice
- Five Steps To Create a...
Five Steps To Create a Problem-Solving Process (Plus Tips!)
8 min read · Updated on August 31, 2023

Conquering workplace challenges fuses strategy and art
Sometimes, it can seem that obstacles are as prevalent as opportunities. When you're good at solving problems, though, you have the power to navigate issues with relative ease. In fact, problem solving is more than a skill - it's a tool that you can use to fuel career growth and success.
As an effective problem solver, you use innovative thinking, demonstrate leadership, and build resilience and confidence. Often, the people you work with come to trust that you're the person to go to when there's a challenge. This could be just the stepping stone you need to move into a leadership role .
Of course, problems range in complexity depending on your industry. But by having a five-step problem-solving process in place, you can enhance both efficiency and effectiveness. In this article, we'll explore tips to help you master the skill, strategy, and art of problem solving.
Identify, analyze, resolve, execute, evaluate
What's the definition of problem solving? It's quite simple. You have to come up with solutions to challenges or issues.
The first step to fixing any problem is recognizing that there is one. Then the trick is to engage with each step of the problem-solving process to incorporate analytical thinking , adaptability, and collaboration skills to build a framework for addressing challenges and driving positive outcomes.
Step 1: Identify
Identifying the problem may be simple, or it could be a detailed cognitive process that breaks the issue into manageable components. Either way, what you do during the identify step of the problem-solving process sets the stage for the next steps in problem solving.
Step 2: Analyze
Consider underlying factors and devise strategies. Here's where the art part of your problem-solving strategy becomes important. As you gather details about the problem, employ critical thinking to uncover the root causes and potential implications.
Step 3: Resolve
Once you have a thorough understanding of the issue, it's time to get creative. Develop some reasonable solutions that are aligned with the capabilities of your team and the mission, vision, and values of your company. Your problem-solving method could involve any one of the following - or even a combination of several:
Encourage your team to learn new technologies
Reallocate some resources
Restructure organizational elements
Draft new operating procedures
Implement brainstorming sessions
Develop metrics
Step 4: Execute
After you've outlined the solutions and decided which ones you think will resolve the problem, it's time to put them into place. The execution phase is the bridge between theory and practice.
Translate the solutions into actionable steps that produce tangible results
Clearly communicate the actionable steps to the relevant stakeholders - your team, colleagues, or managers
Delegate tasks based on team member acumen
Empower those you delegate tasks to by fostering a sense of ownership
Track the progress of your solutions
Overcome challenges, including unforeseen obstacles and stakeholder resistance
Step 5: Evaluate
Just because you think you solved the problem doesn't mean you actually did. It's critical to double-check your work and make sure there are no hiccups. Here's a list of 10 evaluative questions you can work through, to ensure that your problem-solving solutions were impactful:
Did the solutions effectively address the root cause of the problem?
Do you see the desired results?
What impact can you see on your team or the company?
Has there been a noticeable enhancement in efficiency, productivity, or overall performance?
Have any unintended consequences or new challenges arisen as a result of the implemented solution?
Can the solution be sustained in the long term, or is it a short-term fix?
Have stakeholders, such as team members or customers, reported positive experiences or feedback?
Have the predefined performance metrics and goals been achieved or exceeded?
Are there any new aspects of the problem that emerged after implementing the solution?
Which aspects of the solution would you retain and which would you modify?
When you reflect on the outcome of your problem solving strategies, you not only validate the effectiveness of your approach but you can also find insights for continuous improvement and refinement for future endeavors.
Problem solving isn't just for leaders
Sometimes, it seems that only managers and senior executives can engage in effective workplace problem solving. That's simply not the case. It doesn't matter if you're a fresher who's just graduated college or someone with decades of experience, you can employ problem-solving techniques and become a master problem solver.
You've likely heard of hard skills and soft skills ; you may have even seen problem solving lumped in with other soft skills. There are three essential soft skills you'll need to be good at to solve workplace problems:
Analytical thinking
Adaptability, collaboration.
Let's start with a foundational problem-solving skill. Analytical thinking is something you'll use in every step of your five-step problem-solving process, from identifying the problem to coming up with and executing solutions and measuring the success of those solutions. Being able to analyze trends, anticipate shifts, and make informed decisions along the problem-solving path, you'll be assured of success.
A real-world example: Sally is a new graduate and has secured her first job. After a few days at work, she wants to start making a name for herself by identifying a dip in sales. She dissects the customer engagement data and finds there has been a shift in consumer preferences. She knows that a new targeted marketing strategy could re-engage customers and bring sales back up.
Toss aside any notions that the plans you set into place to solve a problem are set in stone. They're not! Being able to make course corrections to change outcomes is at the heart of being adaptable . This soft skill becomes more and more important every day because of how quickly things change in business. Technology advances, economic fluctuations come into play, and unforeseen global events can wreak havoc on the best-laid problem-solving solutions. Think about how adaptable people had to be a few years ago when Covid shut the world down – there were tons of never-before-faced problems that ultimately got solved.
A real-world example : John has been employed in the technology sector for a little over 20 years. He's achieved the coveted role of CTO and found himself overseeing a team that had to transition into remote work. Because he's kept up with emerging technologies and the latest trends, he sets up processes that allow his team to enjoy a seamless shift with minimal impact on productivity.
When you have a problem-solving project in front of you, you'll often have to get people involved to help you to execute the solutions you come up with. Effective communication , organizational synergy, and a harmonious fusion of experiences can lend fresh insights to problem solving.
A real-world example: Marcus is involved in a complex project involving supply chain optimization. He works with geographically-dispersed stakeholders of all levels and has become an expert at pooling together specialized knowledge to create holistic solutions.
How do great problem-solving skills affect your career goals?
Challenges in life and at work are inevitable; by aligning your problem-solving skills with your career goals, not only will you be able to overcome immediate challenges, but you'll also cultivate a powerful tool for your job search toolkit. When you're good at solving problems and can show that you're good at it through accomplishment statements on your resume, your career trajectory will likely be positively impacted. In fact, there are several success stories that prove the journey to excellence is marked by innovative problem solving. Here are just a few:
Elon Musk: Musk's SpaceX faced immense challenges in developing reusable rockets. His innovative, problem-solving approach led to breakthrough solutions, revolutionizing space travel.
Indra Nooyi: As the former CEO of PepsiCo, Nooyi tackled the declining demand for sugary beverages by diversifying the product portfolio and focusing on healthier options, showcasing adaptability and strategic problem solving.
Nelson Mandela: Mandela's ability to collaborate across racial divides and negotiate solutions was instrumental in ending apartheid in South Africa.
Grace Hopper: A computer science pioneer, Hopper's analytical thinking led to the development of the first compiler, revolutionizing programming.
An invaluable asset
As you progress in your career, your skill in resolving a problem will set you apart from the rest of the job-seeking crowd as an invaluable asset. Whether you're identifying opportunities for growth, addressing operational inefficiencies, or strategizing through crises, the ability to solve problems creatively and effectively can become one of the key drivers for the advancement of your career. Essentially, strong problem-solving skills empower you to overcome challenges, seize opportunities, and carve a path of consistent achievement in your professional journey.
TopResume can help you to showcase exceptional problem-solving skills on your resume. Why not submit yours for a free resume review today, to make sure that you're giving this skill the prominence it deserves?
Recommended reading:
How to List Problem Solving Skills on a Resume
Divergent Thinking: Should You Include This Skill on Your Resume?
Higher Order Thinking Explained
Related Articles:
Don't “Snowplow” Your Kids' Job Search — Set Them Up for Success Instead
What Kind of Job Candidate Are You?
Why December is the Best Time of Year to Look for a Job
See how your resume stacks up.
Career Advice Newsletter
Our experts gather the best career & resume tips weekly. Delivered weekly, always free.
Thanks! Career advice is on its way.
Share this article:
Let's stay in touch.
Subscribe today to get job tips and career advice that will come in handy.
Your information is secure. Please read our privacy policy for more information.

The Five-Step Problem-Solving Process
Sometimes when you’re faced with a complex problem, it’s best to pause and take a step back. A break from…

Sometimes when you’re faced with a complex problem, it’s best to pause and take a step back. A break from routine will help you think creatively and objectively. Doing too much at the same time increases the chances of burnout.
Solving problems is easier when you align your thoughts with your actions. If you’re in multiple places at once mentally, you’re more likely to get overwhelmed under pressure. So, a problem-solving process follows specific steps to make it approachable and straightforward. This includes breaking down complex problems, understanding what you want to achieve, and allocating responsibilities to different people to ease some of the pressure.
The problem-solving process will help you measure your progress against factors like budget, timelines and deliverables. The point is to get the key stakeholders on the same page about the ‘what’, ‘why’ and ‘how’ of the process. ( Xanax ) Let’s discuss the five-step problem-solving process that you can adopt.
Problems at a workplace need not necessarily be situations that have a negative impact, such as a product failure or a change in government policy. Making a decision to alter the way your team works may also be a problem. Launching new products, technological upgrades, customer feedback collection exercises—all of these are also “problems” that need to be “solved”.
Here are the steps of a problem-solving process:
1. Defining the Problem
The first step in the process is often overlooked. To define the problem is to understand what it is that you’re solving for. This is also where you outline and write down your purpose—what you want to achieve and why. Making sure you know what the problem is can make it easier to follow up with the remaining steps. This will also help you identify which part of the problem needs more attention than others.
2. Analyzing the Problem
Analyze why the problem occurred and go deeper to understand the existing situation. If it’s a product that has malfunctioned, assess factors like raw material, assembly line, and people involved to identify the problem areas. This will help you figure out if the problem will persist or recur. You can measure the solution against existing factors to assess its future viability.
3. Weighing the Options
Once you’ve figured out what the problem is and why it occurred, you can move on to generating multiple options as solutions. You can combine your existing knowledge with research and data to come up with viable and effective solutions. Thinking objectively and getting inputs from those involved in the process will broaden your perspective of the problem. You’ll be able to come up with better options if you’re open to ideas other than your own.
4. Implementing The Best Solution
Implementation will depend on the type of data at hand and other variables. Consider the big picture when you’re selecting the best option. Look at factors like how the solution will impact your budget, how soon you can implement it, and whether it can withstand setbacks or failures. If you need to make any tweaks or upgrades, make them happen in this stage.

5. Monitoring Progress
The problem-solving process doesn’t end at implementation. It requires constant monitoring to watch out for recurrences and relapses. It’s possible that something doesn’t work out as expected on implementation. To ensure the process functions smoothly, you can make changes as soon as you catch a miscalculation. Always stay on top of things by monitoring how far you’ve come and how much farther you have to go.
You can learn to solve any problem—big or small—with experience and patience. Adopt an impartial and analytical approach that has room for multiple perspectives. In the workplace, you’re often faced with situations like an unexpected system failure or a key employee quitting in the middle of a crucial project.
Problem-solving skills will help you face these situations head-on. Harappa Education’s Structuring Problems course will show you how to classify and categorize problems to discover effective solutions. Equipping yourself with the right knowledge will help you navigate work-related problems in a calm and competent manner.
Explore topics such as Problem Solving , the PICK Chart , How to Solve Problems & the Barriers to Problem Solving from our Harappa Diaries blog section and develop your skills.


- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
Top 5+ Steps to Effective Problem Solving Process
Gain a deep understanding of the problem-solving process through our comprehensive exploration. We introduce you to the basics in "Introduction to Problem-Solving Process," delve into its key aspects and uncover the "Benefits of Problem-Solving Process." This blog will provide a valuable foundation for enhancing your problem-solving skills.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Introduction to Management
- Introduction to Managing People
- Senior Management Training

In a business environment, coming across problems is a frequent phenomenon. Therefore, developing Problem Solving Process to solve these problems becomes essential. A systematic approach ensures a positive attitude in resolving them efficiently. The process can integrate unique attributes aligned with your strengths to assist in Problem Solving.
Thus, understanding how this Process works will enable you to create problem-solving methods suitable to your needs. Want to know how? Read this blog to understand Problem Solving Process in detail, the importance of developing processes and the significance of acquiring this fundamental skill.
Table of contents
1) What is a Problem Solving Process?
2) Steps of Problem Solving Process
3) Benefits of the Problem Solving Process
4) Creating your process for Problem Solving
5) Conclusion
What is a Problem Solving Process?
Problem Solving Process can be defined as an essential analytical skill that enables individuals to identify, analyse, and devise effective solutions to various challenges. It acts as a guiding framework, facilitating logical and systematic approaches to tackle complex issues. After analysing the root causes of problems and evaluating potential options, individuals can make informed decisions and optimise outcomes.
By focusing on critical thinking and creativity, Problem Solving process fosters adaptability and resilience in the face of adversity. From personal dilemmas to professional difficulties, mastering the Problem Solving Process empowers individuals to navigate through uncertainties and achieve success.

Steps of Problem Solving Process
Step 1: identify the problem .
Initiate the Problem Solving process by visualising the ideal scenario. Define the standard against which the current situation will be measured. Ask critical questions like, "If things were going perfectly, what would that look like?"
Further, determine the acceptable variation from the norm, considering factors like engineering precision or behavioural flexibility. Assess how much deviation is tolerable. This step sets the stage for a clear understanding of the problem's context and the criteria for an optimal outcome.
Step 2: Analyse the problem
Understand the problem's urgency by identifying its stage: emergent, mature, or crisis. An emergent problem allows time for corrective action without immediate threats. At the same time, a mature problem causes more than minor damage, necessitating quick intervention. A crisis demands immediate correction due to severe repercussions. Thus, evaluating the potential damage guides decision-making and makes sure an appropriate level of urgency is assigned to the problem.
Step 3: Describe the problem
Craft a concise problem statement in a clear yet short manner. This concise articulation serves as a focal point for the problem-solving effort. Further, distribute the statement to the team for consensus, ensuring everyone involved agrees on the root cause. The critical question to ask here is, "Is your premise correct?" Validating the accuracy of the premise ensures a shared comprehension of the problem.
Step 4: Look for root causes
This step involves a thorough investigation to uncover the underlying issues and come up with targeted solutions. Delve into the root causes of the problem by asking a series of questions: who, what, when, why, how, and where. You can use the 5Why method or Fishbone Diagram to explore the factors that led to a departure from the set standards. Also, assess the possibility of solving the problem permanently while aligning with effective leadership principles.
Step 5: Develop alternate solutions
This step emphasises the importance of exploring a range of possibilities before committing to a specific course of action. So, generate a list of diverse solutions beyond the initial perspective. Apply the One-third Plus One Rule for consensus-building, involving key stakeholders in the Decision-making Process. Further, rank solutions based on their efficiency, cost, and long-term value. Carefully select the most suitable solution, considering available resources and potential impacts.
Step 6: Implement the solution
Translate the chosen solution into action by creating an implementation plan. Outline responsibilities, timelines, and contingency measures to ensure a smooth execution. Moreover, clearly communicate team roles and track the solution's progress. This step involves strategic planning and coordination to bring the selected solution to completion. Also, anticipate potential deviations from the plan and establish mechanisms for prompt resolution.
Step 7: Measure the results
Evaluate the solution's effectiveness by measuring and tracking results. Answer critical questions about its success, learning opportunities, and applicability to future challenges. This step involves a systematic assessment of the outcomes against the desired objectives. Insights gained from this evaluation contribute to continuous improvement and the refinement of Problem-solving Skills. The focus is on deriving meaningful conclusions and utilising them for continuous enhancement.
Increase productivity and efficiency; sign up for our Management Training now!
Benefits of the Problem-Solving Process
Developing and implementing a Problem Solving Process brings significant benefits. Listed below are the benefits that develop during this Process:
Improves analysis
Individuals develop and refine their analytical skills as they engage in the Problem Solving journey. This involves systematically examining complex situations, breaking them into manageable components, and comprehensively evaluating each element.
Through analysis, individuals gain a deeper understanding of the underlying factors contributing to the problem, leading to more precise and informed Problem Solving and Decision Making. Moreover, Problem Solving encourages individuals to gather relevant data, conduct research, and consider various perspectives. This can help enhance the accuracy and depth of their analysis.
Improves risk management
Individuals and teams naturally encounter various challenges and uncertainties as they engage in Problem Solving activities. In response, they learn to identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks associated with different solutions.
This heightened risk management awareness allows for a more comprehensive evaluation of each proposed solution's possible consequences and likelihood of success. By carefully considering and addressing risks, decision-makers can make more informed and calculated choices, minimising potential adverse outcomes.
Promotes creative thinking
The Problem Solving Process serves as a catalyst for promoting creative thinking and unlocking innovative solutions to complex challenges. Individuals and teams engage in Problem Solving activities and are encouraged to explore various ideas and perspectives.
This fosters divergent thinking, allowing the generation of unconventional and imaginative solutions that may not be initially apparent. By challenging conventional norms and encouraging the exploration of alternative approaches, Problem Solving stimulates the creative faculties of the mind.
Improves time management
The Problem Solving Process significantly improves time management by instilling a structured approach to tackling challenges, promoting efficient decision-making, and cultivating a habit of prioritisation and productivity. Individuals and teams can better allocate time and resources as they break down complex problems into manageable steps.
Moreover, the Process encourages swift evaluation of potential solutions, ensuring timely progress. These skills become ingrained, enabling individuals and teams to meet deadlines and optimise productivity. By embracing this process, individuals can effectively manage time in various aspects of life and work.
Reduces bias
The Problem Solving Process offers the invaluable benefit of reducing bias in decision-making. As individuals and teams work through problem-solving activities, they are compelled to approach challenges systematically and objectively. This structured approach encourages considering various perspectives and examining evidence and data without preconceived notions or personal biases.
Learn how the strength of teamwork can help the business; sign up for our Team Development Course now!
Creating your process for Problem Solving
Below are the Problem Solving steps that can help you create a suitable process:
Evaluate Problem Solving approach
To create an effective Process for Problem Solving, it is crucial to evaluate the Problem Solving approach. Assess the success of previous solutions, identify areas for improvement, and gather feedback from team members. Further, adjust the Process based on insights gained, fostering continuous improvement and enhancing Problem Solving capabilities.
Identify your strengths
When creating a Problem Solving Process, it's essential to identify your strengths. Recognise the skills and expertise within your team and your talents. Leveraging these strengths will enable you to assign tasks effectively and collaborate efficiently. It will also help capitalise on your team's unique abilities to achieve successful Problem Solving outcomes.
Research strategies for Problem Solving
To create an effective Problem Solving Process, research feasible strategies is vital. Explore various Problem Solving Techniques, methodologies, and best practices. Consider their applicability to your specific challenges and team dynamics. A well-informed approach ensures you adopt the most suitable strategies to tackle problems efficiently and achieve desired outcomes.
Encourage feedback
While creating a Problem Solving Process, it is crucial to encourage feedback. Foster an open and supportive environment for team members to freely share their thoughts and experiences. Valuable insights from diverse perspectives empower continuous improvement, refine Problem Solving strategies, and enhance overall effectiveness in resolving challenges successfully.
Evaluate your process
When creating your Problem Solving Process, testing and revising are essential steps. Implement the strategy in real-life scenarios to evaluate its effectiveness. Seek feedback from team members and superiors to examine strengths and areas for improvement. Make necessary adjustments to refine and optimise the process for better Problem Solving outcomes.
Improve Problem Solving skills
To create an effective Problem Solving Process, prioritise improving Problem Solving skills. Encourage continuous learning through workshops, training, and skill-building exercises—practice solving diverse problems to gain experience and confidence. By investing in skill development, individuals and teams can enhance their Problem Solving capabilities and achieve better outcomes in challenging situations.
Conclusion
Developing a well-defined and adaptive Problem Solving Process is crucial for navigating the complexities of life and work successfully. By fostering creativity, promoting collaboration, and continuously refining strategies, individuals and teams can approach challenges confidently and with agility, ultimately leading to improved problem resolution and overall success.
Unlock your potential with Problem-Solving training; sign up for our Problem Solving Training now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Choosing the right Problem Solving tool hinges on the nature of issue. Mind mapping, a versatile visual tool, fosters idea generation by illustrating connections between concepts. The Fishbone diagram, on the other hand, systematically identifies potential problem causes. Starting with a horizontal line featuring the problem, branches extend like a fishbone, each representing a probable cause category. Subsequently, specific causes are brainstormed within each category.
The 7-diamond Problem Solving Process systematically addresses complex issues. The process unfolds through seven diamonds that include the following:
a) Diamond 1: Define the problem
b) Diamond 2: Gather data
c) Diamond 3: Analyse data
d) Diamond 4: Develop hypotheses
e) Diamond 5: Verify hypotheses
f) Diamond 6: Identify Root Cause
g) Diamond 7: Implement Solutions
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue , encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 31st May 2024
Fri 26th Jul 2024
Fri 27th Sep 2024
Fri 29th Nov 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel & Certification Course
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
Table of Contents
The problem-solving process, how to solve problems: 5 steps, train to solve problems with lean today, what is problem solving steps, techniques, & best practices explained.

Problem solving is the art of identifying problems and implementing the best possible solutions. Revisiting your problem-solving skills may be the missing piece to leveraging the performance of your business, achieving Lean success, or unlocking your professional potential.
Ask any colleague if they’re an effective problem-solver and their likely answer will be, “Of course! I solve problems every day.”
Problem solving is part of most job descriptions, sure. But not everyone can do it consistently.
Problem solving is the process of defining a problem, identifying its root cause, prioritizing and selecting potential solutions, and implementing the chosen solution.
There’s no one-size-fits-all problem-solving process. Often, it’s a unique methodology that aligns your short- and long-term objectives with the resources at your disposal. Nonetheless, many paradigms center problem solving as a pathway for achieving one’s goals faster and smarter.
One example is the Six Sigma framework , which emphasizes eliminating errors and refining the customer experience, thereby improving business outcomes. Developed originally by Motorola, the Six Sigma process identifies problems from the perspective of customer satisfaction and improving product delivery.
Lean management, a similar method, is about streamlining company processes over time so they become “leaner” while producing better outcomes.
Trendy business management lingo aside, both of these frameworks teach us that investing in your problem solving process for personal and professional arenas will bring better productivity.
1. Precisely Identify Problems
As obvious as it seems, identifying the problem is the first step in the problem-solving process. Pinpointing a problem at the beginning of the process will guide your research, collaboration, and solutions in the right direction.
At this stage, your task is to identify the scope and substance of the problem. Ask yourself a series of questions:
- What’s the problem?
- How many subsets of issues are underneath this problem?
- What subject areas, departments of work, or functions of business can best define this problem?
Although some problems are naturally large in scope, precision is key. Write out the problems as statements in planning sheets . Should information or feedback during a later step alter the scope of your problem, revise the statements.
Framing the problem at this stage will help you stay focused if distractions come up in later stages. Furthermore, how you frame a problem will aid your search for a solution. A strategy of building Lean success, for instance, will emphasize identifying and improving upon inefficient systems.
2. Collect Information and Plan
The second step is to collect information and plan the brainstorming process. This is another foundational step to road mapping your problem-solving process. Data, after all, is useful in identifying the scope and substance of your problems.
Collecting information on the exact details of the problem, however, is done to narrow the brainstorming portion to help you evaluate the outcomes later. Don’t overwhelm yourself with unnecessary information — use the problem statements that you identified in step one as a north star in your research process.
This stage should also include some planning. Ask yourself:
- What parties will ultimately decide a solution?
- Whose voices and ideas should be heard in the brainstorming process?
- What resources are at your disposal for implementing a solution?
Establish a plan and timeline for steps 3-5.
3. Brainstorm Solutions
Brainstorming solutions is the bread and butter of the problem-solving process. At this stage, focus on generating creative ideas. As long as the solution directly addresses the problem statements and achieves your goals, don’t immediately rule it out.
Moreover, solutions are rarely a one-step answer and are more like a roadmap with a set of actions. As you brainstorm ideas, map out these solutions visually and include any relevant factors such as costs involved, action steps, and involved parties.
With Lean success in mind, stay focused on solutions that minimize waste and improve the flow of business ecosystems.
Become a Quality Management Professional
- 10% Growth In Jobs Of Quality Managers Profiles By 2025
- 11% Revenue Growth For Organisations Improving Quality
Certified Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
- 4 hands-on projects to perfect the skills learnt
- 4 simulation test papers for self-assessment
Lean Six Sigma Expert
- IASSC® Lean Six Sigma Green Belt and Black Belt certification
- 13 Projects, 12 Simulation exams, 18 Case Studies & 114 PDUs
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Xueting Liu
Mechanical engineer student at sargents pty. ltd. ,.
A great training and proper exercise with step-by-step guide! I'll give a rating of 10 out of 10 for this training.
Abdus Salam
I have completed the Lean Six Sigma Expert Master’s Program from Simplilearn. And after the course, I could take up new projects and perform better. My average pay rate for a research position increased by 21%.
4. Decide and Implement
The most critical stage is selecting a solution. Easier said than done. Consider the criteria that has arisen in previous steps as you decide on a solution that meets your needs.
Once you select a course of action, implement it.
Practicing due diligence in earlier stages of the process will ensure that your chosen course of action has been evaluated from all angles. Often, efficient implementation requires us to act correctly and successfully the first time, rather than being hurried and sloppy. Further compilations will create more problems, bringing you back to step 1.
5. Evaluate
Exercise humility and evaluate your solution honestly. Did you achieve the results you hoped for? What would you do differently next time?
As some experts note, formulating feedback channels into your evaluation helps solidify future success. A framework like Lean success, for example, will use certain key performance indicators (KPIs) like quality, delivery success, reducing errors, and more. Establish metrics aligned with company goals to assess your solutions.
Master skills like measurement system analysis, lean principles, hypothesis testing, process analysis and DFSS tools with our Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Training Course . Sign-up today!
Become a quality expert with Simplilearn’s Lean Six Sigma Green Belt . This Lean Six Sigma certification program will help you gain key skills to excel in digital transformation projects while improving quality and ultimate business results.
In this course, you will learn about two critical operations management methodologies – Lean practices and Six Sigma to accelerate business improvement.
Our Quality Management Courses Duration And Fees
Explore our top Quality Management Courses and take the first step towards career success
Get Free Certifications with free video courses
Quality Management
Lean Management
Project Management
Learn from industry experts with free masterclasses, digital marketing.
The Top 10 AI Tools You Need to Master Marketing in 2024
Unlock Digital Marketing Career Success Secrets for 2024 with Purdue University
Your Gateway to Game-changing Digital Marketing Careers in 2024 with Purdue University
Recommended Reads
Introduction to Machine Learning: A Beginner's Guide
Webinar Wrap-up: Mastering Problem Solving: Career Tips for Digital Transformation Jobs
An Ultimate Guide That Helps You to Develop and Improve Problem Solving in Programming
Free eBook: 21 Resources to Find the Data You Need
ITIL Problem Workaround – A Leader’s Guide to Manage Problems
Your One-Stop Solution to Understand Coin Change Problem
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.

- Miles Anthony Smith
- Sep 12, 2022
- 12 min read
The Ultimate Problem-Solving Process Guide: 31 Steps and Resources
Updated: Jan 24, 2023
GOT CHALLENGES WITH YOUR PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS? ARE YOU FRUSTRATED?
prob·lem-solv·ing noun -the process of finding solutions to difficult or complex issues. It sounds so simple, doesn’t it? But in reality problem-solving is hard. It's almost always more complex than it seems. That's why problem-solving can be so frustrating sometimes. You can feel like you’re spinning your wheels, arguing in circles, or just failing to find answers that actually work. And when you've got a group working on a problem, it can get even muddier …differences of opinions, viewpoints colored by different backgrounds, history, life experiences, you name it. We’re all looking at life and work from different angles, and that often means disagreement. Sometimes sharp disagreement. That human element, figuring out how to take ourselves out of the equation and make solid, fact-based decisions , is precisely why there’s been so much written on problem-solving. Which creates its own set of problems. Whose method is best? How can you possibly sift through them all? Are we to have one person complete the entire problem-solving process by themselves or rely on a larger team to find answers to our most vexing challenges in the workplace ? Today, we’re going to make sense of it all. We’ll take a close look at nine top problem-solving methods. Then we’ll grab the best elements of all of them to give you a process that will have your team solving problems faster, with better results , and maybe with less sharp disagreement. Ready to dive in? Let’s go!
9 PROFITABLE PROBLEM-SOLVING TECHNIQUES AND METHODS
While there are loads of methods to choose from, we are going to focus on nine of the more common ones. You can use some of these problem-solving techniques reactively to solve a known issue or proactively to find more efficient or effective ways of performing tasks. If you want to explore other methods, check out this resource here . A helpful bit of advice here is to reassure people that you aren’t here to identify the person that caused the problem . You’re working to surface the issue, solve it and make sure it doesn’t happen again, regardless of the person working on the process. It can’t be understated how important it is to continually reassure people of this so that you get unfiltered access to information. Without this, people will often hide things to protect themselves . After all, nobody wants to look bad, do they? With that said, let’s get started...
1. CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING (CPS)
Alex Osborn coined the term “Creative Problem Solving” in the 1940s with this simple four-step process:
Clarify : Explore the vision, gather data, and formulate questions.
Ideate : This stage should use brainstorming to generate divergent thinking and ideas rather than the random ideas normally associated with brainstorming.
Develop : Formulate solutions as part of an overall plan.
Implement : Put the plan into practice and communicate it to all parties.
2. APPRECIATIVE INQUIRY

Source: http://www.davidcooperrider.com/ai-process/ This method seeks, first and foremost, to identify the strengths in people and organizations and play to that “positive core” rather than focus our energies on improving weaknesses . It starts with an “affirmative topic,” followed by the “positive core (strengths).” Then this method delves into the following stages:
Discovery (fact-finding)
Dream (visioning the future)
Design (strategic purpose)
Destiny (continuous improvement)
3. “FIVE WHYS” METHOD
This method simply suggests that we ask “Why” at least five times during our review of the problem and in search of a fix. This helps us dig deeper to find the the true reason for the problem, or the root cause. Now, this doesn’t mean we just keeping asking the same question five times. Once we get an answer to our first “why”, we ask why to that answer until we get to five “whys”.
Using the “five whys” is part of the “Analyze” phase of Six Sigma but can be used with or without the full Six Sigma process.
Review this simple Wikipedia example of the 5 Whys in action:
The vehicle will not start. (the problem)
Why? - The battery is dead. (First why)
Why? - The alternator is not functioning. (Second why)
Why? - The alternator belt has broken. (Third why)
Why? - The alternator belt was well beyond its useful service life and not replaced. (Fourth why)
Why? - The vehicle was not maintained according to the recommended service schedule. (Fifth why, a root cause)
4. LEAN SIX SIGMA (DMAIC METHOD)

While many people have at least heard of Lean or Six Sigma, do we know what it is? Like many problem-solving processes, it has five main steps to follow.
Define : Clearly laying out the problem and soliciting feedback from those who are customers of the process is necessary to starting off on the right foot.
Measure : Quantifying the current state of the problem is a key to measuring how well the fix performed once it was implemented.
Analyze : Finding out the root cause of the problem (see number 5 “Root Cause Analysis” below) is one of the hardest and least explored steps of Six Sigma.
Improve : Crafting, executing, and testing the solution for measureable improvement is key. What doesn’t get implemented and measured really won’t make a difference.
Control : Sustaining the fix through a monitoring plan will ensure things continue to stay on track rather than being a short-lived solution.
5. ROOT CAUSE ANALYSIS
Compared to other methods, you’ll more often find this technique in a reactive problem-solving mode, but it is helpful nonetheless. Put simply, it requires a persistent approach to finding the highest-level cause, since most reasons you’ll uncover for a problem don’t tell the whole story.
Most of the time, there are many factors that contributed to an issue. The main reason is often shrouded in either intentional or unintentional secrecy. Taking the time to drill down to the root of the issue is key to truly solving the problem.
6. DEMING-SHEWHART CYCLE: PLAN-DO-CHECK-ACT (PDCA)
Named for W. Edwards Deming and Walter A. Shewhart, this model follows a four-step process:
Plan: Establish goals and objectives at the outset to gain agreement. It’s best to start on a small scale in order to test results and get a quick win.
Do: This step is all about the implementation and execution of the solution.
Check: Study and compare actual to expected results. Chart this data to identify trends.
Act/Adjust: If the check phase showed different results, then adjust accordingly. If worse than expected, then try another fix. If the same or better than expected, then use that as the new baseline for future improvements.
7. 8D PROBLEM-SOLVING

While this is named “8D” for eight disciplines, there are actually nine , because the first is listed as step zero. Each of the disciplines represents a phase of this process. Its aim is to implement a quick fix in the short term while working on a more permanent solution with no recurring issues.
Prepare and Plan : Collecting initial information from the team and preparing your approach to the process is a necessary first step.
Form a Team : Select a cross-functional team of people, one leader to run meetings and the process, and one champion/sponsor who will be the final decision-maker.
Describe the Problem : Using inductive and deductive reasoning approaches, lay out the precise issue to be corrected.
Interim Containment Action : Determine if an interim solution needs to be implemented or if it can wait until the final fix is firmed up. If necessary, the interim action is usually removed once the permanent solution is ready for implementation.
Root Cause Analysis and Escape Point : Finding the root of the issue and where in the process it could’ve been found but was not will help identify where and why the issue happened.
Permanent Corrective Action : Incorporating key criteria into the solution, including requirements and wants, will help ensure buy-in from the team and your champion.
Implement and Validate the Permanent Corrective Action : Measuring results from the fix implemented validates it or sends the team back to the drawing board to identity a more robust solution.
Prevent Recurrence : Updating work procedure documents and regular communication about the changes are important to keep old habits in check.
Closure and Team Celebration : Taking time to praise the team for their efforts in resolving the problem acknowledges the part each person played and offers a way to move forward.
8. ARMY PROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS
The US Army has been solving problems for more than a couple of centuries , so why not take a look at the problem-solving process they’ve refined over many years? They recommend this five step process:
Identify the Problem : Take time to understand the situation and define a scope and limitations before moving forward.
Gather Information : Uncover facts, assumptions, and opinions about the problem, and challenge them to get to the truth.
Develop Screening and Evaluation Criteria :
Five screening items should be questioned. Is it feasible, acceptable, distinguishable, and complete?
Evaluation criteria should have these 5 elements: short title, definition, unit of measure, benchmark, and formula.
Generate, Analyze, and Compare Possible Solutions : Most fixes are analyzed, but do you compare yours to one another as a final vetting method?
Choose a Solution and Implement : Put the fix into practice and follow up to ensure it is being followed consistently and having the desired effect.
9. HURSON'S PRODUCTIVE THINKING MODEL

Tim Hurson introduced this model in 2007 with his book, Think Better. It consists of the following six actions.
Ask "What is going on?" : Define the impact of the problem and the aim of its solution.
Ask "What is success?" : Spell out the expected outcome, what should not be in fix, values to be considered, and how things will be evaluated.
Ask "What is the question?" : Tailor questions to the problem type. Valuable resources can be wasted asking questions that aren’t truly relevant to the issue.
Generate answers : Prioritize answers that are the most relevant to solutions, without excluding any suggestion to present to the decision-makers.
Forge the solution : Refine the raw list of prioritized fixes, looking for ways to combine them for a more powerful solution or eliminate fixes that don’t fit the evaluation criteria.
Align resources: Identify resources, team, and stakeholders needed to implement and maintain the solution.
STEAL THIS THOROUGH 8-STEP PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS

Now that we’ve reviewed a number of problem-solving methods, we’ve compiled the various steps into a straightforward, yet in-depth, s tep-by-step process to use the best of all methods.
1. DIG DEEP: IDENTIFY, DEFINE, AND CLARIFY THE ISSUE
“Elementary, my dear Watson,” you might say.
This is true, but we often forget the fundamentals before trying to solve a problem. So take some time to gain understanding of critical stakeholder’s viewpoints to clarify the problem and cement consensus behind what the issue really is.
Sometimes it feels like you’re on the same page, but minor misunderstandings mean you’re not really in full agreement.. It’s better to take the time to drill down on an issue before you get too far into solving a problem that may not be the exact problem . Which leads us to…
2. DIG DEEPER: ROOT CAUSE ANALYSIS

This part of the process involves identifying these three items :
What happened?
Why did it happen?
What process do we need to employ to significantly reduce the chances of it happening again ?
You’ll usually need to sort through a series of situations to find the primary cause. So be careful not to stop at the first cause you uncover . Dig further into the situation to expose the root of the issue. We don’t want to install a solution that only fixes a surface-level issue and not the root. T here are typically three types of causes :
Physical: Perhaps a part failed due to poor design or manufacturing.
Human error: A person either did something wrong or didn’t do what needed to be done.
Organizational: This one is mostly about a system, process, or policy that contributed to the error .
When searching for the root cause, it is important to ensure people that you aren’t there to assign blame to a person but rather identify the problem so a fix can prevent future issues.
3. PRODUCE A VARIETY OF SOLUTION OPTIONS
So far, you’ve approached the problem as a data scientist, searching for clues to the real issue. Now, it’s important to keep your eyes and ears open, in case you run across a fix suggested by one of those involved in the process failure. Because they are closest to the problem, they will often have an idea of how to fix things. In other cases, they may be too close, and unable to see how the process could change.
The bottom line is to solicit solution ideas from a variety of sources , both close to and far away from the process you’re trying to improve.
You just never know where the top fix might come from!
4. FULLY EVALUATE AND SELECT PLANNED FIX(ES)

Evaluating solutions to a defined problem can be tricky since each one will have cost, political, or other factors associated with it. Running each fix through a filter of cost and impact is a vital step toward identifying a solid solution and hopefully settling on the one with the highest impact and low or acceptable cost.
Categorizing each solution in one of these four categoriescan help teams sift through them:
High Cost/Low Impact: Implement these last, if at all, since t hey are expensive and won’t move the needle much .
Low Cost/Low Impact: These are cheap, but you won’t get much impact.
High Cost/High Impact: These can be used but should be second to the next category.
Low Cost/High Impact: Getting a solid “bang for your buck” is what these fixes are all about. Start with these first .
5. DOCUMENT THE FINAL SOLUTION AND WHAT SUCCESS LOOKS LIKE
Formalize a document that all interested parties (front-line staff, supervisors, leadership, etc.) agree to follow. This will go a long way towards making sure everyone fully understands what the new process looks like, as well as what success will look like .
While it might seem tedious, try to be overly descriptive in the explanation of the solution and how success will be achieved. This is usually necessary to gain full buy-in and commitment to continually following the solution. We often assume certain things that others may not know unless we are more explicit with our communications.
6. SUCCESSFULLY SELL AND EXECUTE THE FIX

Arriving at this stage in the process only to forget to consistently apply the solution would be a waste of time, yet many organizations fall down in the execution phase . Part of making sure that doesn’t happen is to communicate the fix and ask for questions multiple times until all parties have a solid grasp on what is now required of them.
One often-overlooked element of this is the politics involved in gaining approval for your solution. Knowing and anticipating objections of those in senior or key leadership positions is central to gaining buy-in before fix implementation.
7. RINSE AND REPEAT: EVALUATE, MONITOR, AND FOLLOW UP
Next, doing check-ins with the new process will ensure that the solution is working (or identity if further reforms are necessary) . You’ll also see if the measure of predefined success has been attained (or is making progress in that regard).
Without regularly monitoring the fix, you can only gauge the success or failure of the solution by speculation and hearsay. And without hard data to review, most people will tell their own version of the story.
8. COLLABORATIVE CONTINGENCIES, ITERATION, AND COURSE CORRECTION

Going into any problem-solving process, we should take note that we will not be done once the solution is implemented (or even if it seems to be working better at the moment). Any part of any process will always be subject to the need for future iterations and course corrections . To think otherwise would be either foolish or naive.
There might need to be slight, moderate, or wholesale changes to the solution previously implemented as new information is gained, new technologies are discovered, etc.
14 FRUITFUL RESOURCES AND EXERCISES FOR YOUR PROBLEM-SOLVING JOURNEY

Want to test your problem-solving skills?
Take a look at these twenty case study scenario exercises to see how well you can come up with solutions to these problems.
Still have a desire to discover more about solving problems?
Check out these 14 articles and books...
1. THE LEAN SIX SIGMA POCKET TOOLBOOK: A QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE TO NEARLY 100 TOOLS FOR IMPROVING QUALITY AND SPEED
This book is like a Bible for Lean Six Sigma , all in a pocket-sized package.
2. SOME SAGE PROBLEM SOLVING ADVICE

The American Society for Quality has a short article on how it’s important to focus on the problem before searching for a solution.
3. THE SECRET TO BETTER PROBLEM SOLVING: HARVARD BUSINESS REVIEW
Wondering if you are solving the right problems? Check out this Harvard Business Review article.
4. PROBLEM SOLVING 101 : A SIMPLE BOOK FOR SMART PEOPLE
Looking for a fun and easy problem-solving book that was written by a McKinsey consultant? Take a look!
5. THE BASICS OF CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING – CPS

If you want a deeper dive into the seven steps of Creative Problem Solving , see this article.
6. APPRECIATIVE INQUIRY : A POSITIVE REVOLUTION IN CHANGE
Appreciative Inquiry has been proven effective in organizations ranging from Roadway Express and British Airways to the United Nations and the United States Navy. Review this book to join the positive revolution.
7. PROBLEM SOLVING: NINE CASE STUDIES AND LESSONS LEARNED
The Seattle Police Department has put together nine case studies that you can practice solving . While they are about police work, they have practical application in the sleuthing of work-related problems.
8. ROOT CAUSE ANALYSIS : THE CORE OF PROBLEM SOLVING AND CORRECTIVE ACTION
Need a resource to delve further into Root Cause Analysis? Look no further than this book for answers to your most vexing questions .
9. SOLVING BUSINESS PROBLEMS : THE CASE OF POOR FRANK

This solid case study illustrates the complexities of solving problems in business.
10. THE 8-DISCIPLINES PROBLEM SOLVING METHODOLOGY
Learn all about the “8Ds” with this concise primer.
11. THE PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS THAT PREVENTS GROUPTHINK HBR
Need to reduce groupthink in your organization’s problem-solving process ? Check out this article from the Harvard Business Review.
12. THINK BETTER : AN INNOVATOR'S GUIDE TO PRODUCTIVE THINKING

Tim Hurson details his own Productive Thinking Model at great length in this book from the author.
13. 5 STEPS TO SOLVING THE PROBLEMS WITH YOUR PROBLEM SOLVING INC MAGAZINE
This simple five-step process will help you break down the problem, analyze it, prioritize solutions, and sell them internally.
14. CRITICAL THINKING : A BEGINNER'S GUIDE TO CRITICAL THINKING, BETTER DECISION MAKING, AND PROBLEM SOLVING!
LOOKING FOR ASSISTANCE WITH YOUR PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS?
There's a lot to take in here, but following some of these methods are sure to improve your problem-solving process. However, if you really want to take problem-solving to the next level, InitiativeOne can come alongside your team to help you solve problems much faster than you ever have before.
There are several parts to this leadership transformation process provided by InitiativeOne, including a personal profile assessment, cognitive learning, group sessions with real-world challenges, personal discovery, and a toolkit to empower leaders to perform at their best.
There are really only two things stopping good teams from being great. One is how they make decisions and two is how they solve problems. Contact us today to grow your team’s leadership performance by making decisions and solving problems more swiftly than ever before!
- Featured Post
Recent Posts
Does Your Leadership Deserve Two Thumbs Up?
3 Ways to Harness the Power of Inspiration
Leadership Self-Check
- Content Marketing
- Marketing Automation
- Productivity
- Recurring Income

Problem solving techniques (a 5 step process)
Problem-solving techniques (a 5 step process).
How do you go about solving a problem effectively?
There are five key steps in solving a problem
Defining the problem
You need to define the problem clearly BEFORE you jump into solution mode. One of the biggest obstacles to problem-solving is not getting clear on what exactly problem is. What are the boundaries of that problem? How did it arise? Which brings us to our next point
Understanding the context of the problem
What caused the problem to arise? When did it arise? What situation or event triggered the problem? Is it likely to happen again? What’s likely to trigger it next time?
Answering these questions gives you an important perspective and context. It helps you understand the problem in it’s wider context and how it impacts the business.
Generating alternatives
Having defined the problem and understood its context, you can now embark on creating a solution. But before you jump into solution mode you need to put all the solutions on the table. So you can assess which solution is likely to work best.
One common mistake is not to list the option of “Do nothing” as an alternative. You might not always decide to do nothing but it’s important to have that option on the table. In some cases doing nothing might be the best decision.
Evaluating and selecting alternatives
So now that you have all the options on the table, you can spend some time evaluating the options. If I chose option A how would that play out over the next few weeks? What’s likely to happen next? And then after that?
If I chose option B how would that play out?
It’s useful to ‘wander’ down the path of each alternative and follow it to its natural conclusion.
Implementing solutions
After having gone through all the previous steps (and only then) do you pick the best alternative and go about implementing that alternative.

RELATED ARTICLES
5 Steps to Make your Problem-Solving Process Easier
No matter what kind of job you have, the chances of a problem arising at some point is almost inevitable. If the problem isn’t taken care of immediately with proper action, it could potentially get worse. No one wants to be in a hostile work environment, so it’s crucial to be aware of how to properly solve an issue.
What is Problem Solving?
Before we can even begin to explain what problem-solving is, we need to define what a problem is. A problem is any type of disturbance from normality that is hindering progress. A problem can be time-consuming and energy wasting. They can be as little as a disagreement, to as big as a miscommunication that costs millions of dollars to fix.
One problem-solving technique is determining whether it prevents you from reaching your goal. No matter the issue’s size, it can be solved by identifying it, gathering possible solutions, choosing the best possible one, and implementing it. That’s commonly known as the problem-solving process. If a company neglects any problems in the workplace, they could potentially get worse and cause significant problems.
Problem-solving can be the difference between a business succeeding or failing. According to Forbes.com , some common barriers that will prevent companies from being successful problem-solvers include the inability to see a problem, lack of respect, and failure to include all parts involved with the problem, among others.
Problem-solvers need some specific skills, like being able to do research and make both rational and emotionally intelligent decisions. Risk management is another skill that’s imperative to making a successful decision. Your team should all be able to work together in the problem-solving process.
In fact, in 2013, the Association of American Colleges and Universities released a report claiming that 93 percent of employers agree, “a candidate’s demonstrated capacity to think critically, communicate clearly, and solve complex problems is more important than their undergraduate major.”
Here are a few more problem-solving skills:
- Team building
- Effective communication
- Active listening
- Brainstorming
There are many benefits to problem-solving in an organization. For one thing, it creates a hostility-free environment that encourages everyone to speak their mind when a problem occurs. Resolving problems together as a team can foster team building. Problem-solving can also empower a workforce and make its members more confident. If an entire organization can problem-solve efficiently, they can spend their time more wisely.
5 Steps to Better Problem-Solving
Step 1: identify the problem.
As obvious as it may sound, the first step in the problem-solving process is to identify the root of the issue. However, the problem isn’t always easily identifiable and might require some extra analysis to get the source. One way you can identify a problem is by using Toyota’s “Five Whys” technique . In the event of a problem, ask yourself the five whys:
By asking yourself these questions, you’ll discover where the problem is coming from. If that isn’t enough, here are three steps you can take to better identify a problem:
Explore the situation : Expand on the problem to try to get to the bottom of it. If an individual is the problem’s source, try putting yourself in their shoes.
Draft a problem statement : Reduce the problem into the simplest of terms and put it down on paper. This can help you gather and organize your thoughts.
Try to answer the question : “Why is this current situation a problem?” Once you’ve boiled it down to one source, you’ll be able to better assess the situation.
Let’s use a coffee shop as an example. Say the coffee shop has slowly been losing business in the last quarter, despite being very successful in the past few months. The owner wants to better understand why they’re suddenly losing business.
First, they explore the situation and look at all the possible reasons for why this is happening. They look at their employees, their daily routines, and training procedures. They also observe the local competition and the regional factors, like the fact that they’re located in a college town.
After looking at every single possible reason, the owner figures out what’s causing the problem and writes it down: It’s the summer and most of their student clientele are away for the summer. Finally, the owner answers the question, “Why is this current situation a problem?” Then after further evaluation, they realize the problem is a limited market and that they must expand to get more business.
Step 2: Generate Potential Solutions
The next step is to create a list of possible solutions. Start by brainstorming some potential answers, either individually or in a group setting. The latter is recommended, because when you have more input, you get more perspectives that can lead to unique solutions.
Here are some other methods to create solutions:
Means-End Analysis : An artificial intelligence analysis that finds the best possible way of attaining a goal.
Plan Do Study Act Model : Also known as the PDSA Model. This is the shorthand version of the problem-solving method, where you start with planning, test the theory, study the results, and act based upon observations . This process is done several times.
Root Cause Analysis : This method is used to get to the root of the problem. Its four steps are to identify the problem, establish a timeline, distinguish between root causes and other factors, and create a cause graph.
Lean Prioritization Method : This method is created within a two-by-two matrix, with the X and Y-axis ranging from low to high. The X-axis is labeled as “effort”, while the Y-axis is labeled “value.” Inside the matrix, label the four squares with:
- And time sinks
Evaluate the problems and situations and put them in the appropriate categories to figure out where to focus your attention.
Step 3: Choose One Solution
Once a list of possible solutions has been made, it’s time to put your decision-making skills to the test. To find the best solution for the problem, analyze every possible resolution and decide which is best for your situation.
Before making a decision, consider the potential solution’s efficacy, practicality, timeliness, resources, and cost. Narrow your choices down with the process of elimination and with a risk manager’s input. Like brainstorming, choosing a solution doesn’t have to be done alone.
Step 4: Implement the Solution You’ve Chosen
Now that you’ve chosen a solution, it’s time to implement it throughout the necessary departments, areas, or people. On average, it takes about 66 days for a new habit to become automatic, according to a study published in the European Journal of Social Psychology. In other words, change doesn’t happen overnight. To make a new change to any business, planning, patience, and persistence are all required.
Planning : Timing is everything. When a company implements a new strategy, they often take a lot of time to implement the new idea. Decide on clear goals, address any issues or possible obstacles, and create a plan. It’s also critical to practice proper communication skills across the entire organization so that everyone knows what’s expected.
Patience : Change is scary and not everyone is going to accept it, that’s why it’s important to stay patient throughout this process. Try implementing the plan little by little so that employees aren’t overwhelmed. Encourage each other and make sure everyone understands the intention behind this change, and that everyone is participating in making it possible.
Persistence : Continuous application and monitoring of these changes are crucial. Make sure all of your employees are practicing the changes every week so they become the norm.
Step 5: Evaluate Results
The final part of the problem-solving process is to analyze the results. This can be done after a couple of weeks, months, or years, depending on what you’re trying to achieve. It’s important to remember why this problem started in the first place and how it affected the company. Ask yourself any of the following questions to better evaluate results:
- Are any of our processes being interrupted by the previous problem?
- Have any new problems arisen since we started this process?
- Is there a possibility the issue can return?
- Is everyone aware of the original problem, the solution created, and why it was created?
- Do you need to change any policy, procedure, or personnel to avoid this from happening again?
Sometimes, it’s necessary to start the process completely over. To make the problem-solving process easier, it’s best to simplify the solution as much as possible. Try to focus on the solution rather than the problem. Be positive, open-minded, and willing to make the change. With enough practice, any problem can be solved.
Problems will always occur no matter what situation you’re in, so it’s important to know how to conquer them before they get out of hand. Do you want to learn more about the process of problem-solving and how you can apply it to fix your company’s issues?
You can learn about different strategies that will help alleviate any workplace problems in KnowledgeCity’s course on Problem Solving in 5 Easy Steps . Use this information to take control of any problems that crop up at work.

- About the author
- Latest posts

Thanks for this terrific article! I am a mentor to undergraduate students and I was researching problem solving philosophies, methodologies, and techniques. This was a perfect resource! I like the way that you provided practical examples and also provided various methodologies and systems for problem solving. I think that’s always good to provide people options as certain methodologies may be best geared for certain disciplines, industries, or situations.
I took special note of these key quotes:
“because the more input, the better, simply because different perspectives can lead to different solutions.”
“It’s important to remember why this problem started in the first place and how it was affecting the company.”
Thanks again for making this great information publicly available.
Clifford Thornton
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Join 80,000+ Fellow HR Professionals. Get expert recruiting and training tips straight to your inbox, and become a better HR manager.
New Designs for School 5 Steps to Teaching Students a Problem-Solving Routine

Jeff Heyck-Williams (He, His, Him) Director of the Two Rivers Learning Institute in Washington, DC

We’ve all had the experience of truly purposeful, authentic learning and know how valuable it is. Educators are taking the best of what we know about learning, student support, effective instruction, and interpersonal skill-building to completely reimagine schools so that students experience that kind of purposeful learning all day, every day.
Students can use the 5 steps in this simple routine to solve problems across the curriculum and throughout their lives.
When I visited a fifth-grade class recently, the students were tackling the following problem:
If there are nine people in a room and every person shakes hands exactly once with each of the other people, how many handshakes will there be? How can you prove your answer is correct using a model or numerical explanation?
There were students on the rug modeling people with Unifix cubes. There were kids at one table vigorously shaking each other’s hand. There were kids at another table writing out a diagram with numbers. At yet another table, students were working on creating a numeric expression. What was common across this class was that all of the students were productively grappling around the problem.
On a different day, I was out at recess with a group of kindergarteners who got into an argument over a vigorous game of tag. Several kids were arguing about who should be “it.” Many of them insisted that they hadn’t been tagged. They all agreed that they had a problem. With the assistance of the teacher they walked through a process of identifying what they knew about the problem and how best to solve it. They grappled with this very real problem to come to a solution that all could agree upon.
Then just last week, I had the pleasure of watching a culminating showcase of learning for our 8th graders. They presented to their families about their project exploring the role that genetics plays in our society. Tackling the problem of how we should or should not regulate gene research and editing in the human population, students explored both the history and scientific concerns about genetics and the ethics of gene editing. Each student developed arguments about how we as a country should proceed in the burgeoning field of human genetics which they took to Capitol Hill to share with legislators. Through the process students read complex text to build their knowledge, identified the underlying issues and questions, and developed unique solutions to this very real problem.
Problem-solving is at the heart of each of these scenarios, and an essential set of skills our students need to develop. They need the abilities to think critically and solve challenging problems without a roadmap to solutions. At Two Rivers Public Charter School in Washington, D.C., we have found that one of the most powerful ways to build these skills in students is through the use of a common set of steps for problem-solving. These steps, when used regularly, become a flexible cognitive routine for students to apply to problems across the curriculum and their lives.
The Problem-Solving Routine
At Two Rivers, we use a fairly simple routine for problem solving that has five basic steps. The power of this structure is that it becomes a routine that students are able to use regularly across multiple contexts. The first three steps are implemented before problem-solving. Students use one step during problem-solving. Finally, they finish with a reflective step after problem-solving.
Problem Solving from Two Rivers Public Charter School
Before Problem-Solving: The KWI
The three steps before problem solving: we call them the K-W-I.
The “K” stands for “know” and requires students to identify what they already know about a problem. The goal in this step of the routine is two-fold. First, the student needs to analyze the problem and identify what is happening within the context of the problem. For example, in the math problem above students identify that they know there are nine people and each person must shake hands with each other person. Second, the student needs to activate their background knowledge about that context or other similar problems. In the case of the handshake problem, students may recognize that this seems like a situation in which they will need to add or multiply.
The “W” stands for “what” a student needs to find out to solve the problem. At this point in the routine the student always must identify the core question that is being asked in a problem or task. However, it may also include other questions that help a student access and understand a problem more deeply. For example, in addition to identifying that they need to determine how many handshakes in the math problem, students may also identify that they need to determine how many handshakes each individual person has or how to organize their work to make sure that they count the handshakes correctly.
The “I” stands for “ideas” and refers to ideas that a student brings to the table to solve a problem effectively. In this portion of the routine, students list the strategies that they will use to solve a problem. In the example from the math class, this step involved all of the different ways that students tackled the problem from Unifix cubes to creating mathematical expressions.
This KWI routine before problem solving sets students up to actively engage in solving problems by ensuring they understand the problem and have some ideas about where to start in solving the problem. Two remaining steps are equally important during and after problem solving.
The power of teaching students to use this routine is that they develop a habit of mind to analyze and tackle problems wherever they find them.
During Problem-Solving: The Metacognitive Moment
The step that occurs during problem solving is a metacognitive moment. We ask students to deliberately pause in their problem-solving and answer the following questions: “Is the path I’m on to solve the problem working?” and “What might I do to either stay on a productive path or readjust my approach to get on a productive path?” At this point in the process, students may hear from other students that have had a breakthrough or they may go back to their KWI to determine if they need to reconsider what they know about the problem. By naming explicitly to students that part of problem-solving is monitoring our thinking and process, we help them become more thoughtful problem solvers.
After Problem-Solving: Evaluating Solutions
As a final step, after students solve the problem, they evaluate both their solutions and the process that they used to arrive at those solutions. They look back to determine if their solution accurately solved the problem, and when time permits they also consider if their path to a solution was efficient and how it compares to other students’ solutions.
The power of teaching students to use this routine is that they develop a habit of mind to analyze and tackle problems wherever they find them. This empowers students to be the problem solvers that we know they can become.
Jeff Heyck-Williams (He, His, Him)
Director of the two rivers learning institute.
Jeff Heyck-Williams is the director of the Two Rivers Learning Institute and a founder of Two Rivers Public Charter School. He has led work around creating school-wide cultures of mathematics, developing assessments of critical thinking and problem-solving, and supporting project-based learning.
Read More About New Designs for School

NGLC Invites Applications from New England High School Teams for Our Fall 2024 Learning Excursion
March 21, 2024

Bring Your Vision for Student Success to Life with NGLC and Bravely
March 13, 2024

How to Nurture Diverse and Inclusive Classrooms through Play
Rebecca Horrace, Playful Insights Consulting, and Laura Dattile, PlanToys USA
March 5, 2024
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Join us: Learn how to build a trusted AI strategy to support your company's intelligent transformation, featuring Forrester .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Register now .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Collaboration |
- Turn your team into skilled problem sol ...
Turn your team into skilled problem solvers with these problem-solving strategies

Picture this, you're handling your daily tasks at work and your boss calls you in and says, "We have a problem."
Unfortunately, we don't live in a world in which problems are instantly resolved with the snap of our fingers. Knowing how to effectively solve problems is an important professional skill to hone. If you have a problem that needs to be solved, what is the right process to use to ensure you get the most effective solution?
In this article we'll break down the problem-solving process and how you can find the most effective solutions for complex problems.
What is problem solving?
Problem solving is the process of finding a resolution for a specific issue or conflict. There are many possible solutions for solving a problem, which is why it's important to go through a problem-solving process to find the best solution. You could use a flathead screwdriver to unscrew a Phillips head screw, but there is a better tool for the situation. Utilizing common problem-solving techniques helps you find the best solution to fit the needs of the specific situation, much like using the right tools.
Decision-making tools for agile businesses
In this ebook, learn how to equip employees to make better decisions—so your business can pivot, adapt, and tackle challenges more effectively than your competition.

4 steps to better problem solving
While it might be tempting to dive into a problem head first, take the time to move step by step. Here’s how you can effectively break down the problem-solving process with your team:
1. Identify the problem that needs to be solved
One of the easiest ways to identify a problem is to ask questions. A good place to start is to ask journalistic questions, like:
Who : Who is involved with this problem? Who caused the problem? Who is most affected by this issue?
What: What is happening? What is the extent of the issue? What does this problem prevent from moving forward?
Where: Where did this problem take place? Does this problem affect anything else in the immediate area?
When: When did this problem happen? When does this problem take effect? Is this an urgent issue that needs to be solved within a certain timeframe?
Why: Why is it happening? Why does it impact workflows?
How: How did this problem occur? How is it affecting workflows and team members from being productive?
Asking journalistic questions can help you define a strong problem statement so you can highlight the current situation objectively, and create a plan around that situation.
Here’s an example of how a design team uses journalistic questions to identify their problem:
Overarching problem: Design requests are being missed
Who: Design team, digital marketing team, web development team
What: Design requests are forgotten, lost, or being created ad hoc.
Where: Email requests, design request spreadsheet
When: Missed requests on January 20th, January 31st, February 4th, February 6th
How : Email request was lost in inbox and the intake spreadsheet was not updated correctly. The digital marketing team had to delay launching ads for a few days while design requests were bottlenecked. Designers had to work extra hours to ensure all requests were completed.
In this example, there are many different aspects of this problem that can be solved. Using journalistic questions can help you identify different issues and who you should involve in the process.
2. Brainstorm multiple solutions
If at all possible, bring in a facilitator who doesn't have a major stake in the solution. Bringing an individual who has little-to-no stake in the matter can help keep your team on track and encourage good problem-solving skills.
Here are a few brainstorming techniques to encourage creative thinking:
Brainstorm alone before hand: Before you come together as a group, provide some context to your team on what exactly the issue is that you're brainstorming. This will give time for you and your teammates to have some ideas ready by the time you meet.
Say yes to everything (at first): When you first start brainstorming, don't say no to any ideas just yet—try to get as many ideas down as possible. Having as many ideas as possible ensures that you’ll get a variety of solutions. Save the trimming for the next step of the strategy.
Talk to team members one-on-one: Some people may be less comfortable sharing their ideas in a group setting. Discuss the issue with team members individually and encourage them to share their opinions without restrictions—you might find some more detailed insights than originally anticipated.
Break out of your routine: If you're used to brainstorming in a conference room or over Zoom calls, do something a little different! Take your brainstorming meeting to a coffee shop or have your Zoom call while you're taking a walk. Getting out of your routine can force your brain out of its usual rut and increase critical thinking.
3. Define the solution
After you brainstorm with team members to get their unique perspectives on a scenario, it's time to look at the different strategies and decide which option is the best solution for the problem at hand. When defining the solution, consider these main two questions: What is the desired outcome of this solution and who stands to benefit from this solution?
Set a deadline for when this decision needs to be made and update stakeholders accordingly. Sometimes there's too many people who need to make a decision. Use your best judgement based on the limitations provided to do great things fast.
4. Implement the solution
To implement your solution, start by working with the individuals who are as closest to the problem. This can help those most affected by the problem get unblocked. Then move farther out to those who are less affected, and so on and so forth. Some solutions are simple enough that you don’t need to work through multiple teams.
After you prioritize implementation with the right teams, assign out the ongoing work that needs to be completed by the rest of the team. This can prevent people from becoming overburdened during the implementation plan . Once your solution is in place, schedule check-ins to see how the solution is working and course-correct if necessary.
Implement common problem-solving strategies
There are a few ways to go about identifying problems (and solutions). Here are some strategies you can try, as well as common ways to apply them:
Trial and error
Trial and error problem solving doesn't usually require a whole team of people to solve. To use trial and error problem solving, identify the cause of the problem, and then rapidly test possible solutions to see if anything changes.
This problem-solving method is often used in tech support teams through troubleshooting.
The 5 whys problem-solving method helps get to the root cause of an issue. You start by asking once, “Why did this issue happen?” After answering the first why, ask again, “Why did that happen?” You'll do this five times until you can attribute the problem to a root cause.
This technique can help you dig in and find the human error that caused something to go wrong. More importantly, it also helps you and your team develop an actionable plan so that you can prevent the issue from happening again.
Here’s an example:
Problem: The email marketing campaign was accidentally sent to the wrong audience.
“Why did this happen?” Because the audience name was not updated in our email platform.
“Why were the audience names not changed?” Because the audience segment was not renamed after editing.
“Why was the audience segment not renamed?” Because everybody has an individual way of creating an audience segment.
“Why does everybody have an individual way of creating an audience segment?” Because there is no standardized process for creating audience segments.
“Why is there no standardized process for creating audience segments?” Because the team hasn't decided on a way to standardize the process as the team introduced new members.
In this example, we can see a few areas that could be optimized to prevent this mistake from happening again. When working through these questions, make sure that everyone who was involved in the situation is present so that you can co-create next steps to avoid the same problem.
A SWOT analysis
A SWOT analysis can help you highlight the strengths and weaknesses of a specific solution. SWOT stands for:
Strength: Why is this specific solution a good fit for this problem?
Weaknesses: What are the weak points of this solution? Is there anything that you can do to strengthen those weaknesses?
Opportunities: What other benefits could arise from implementing this solution?
Threats: Is there anything about this decision that can detrimentally impact your team?
As you identify specific solutions, you can highlight the different strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of each solution.
This particular problem-solving strategy is good to use when you're narrowing down the answers and need to compare and contrast the differences between different solutions.
Even more successful problem solving
After you’ve worked through a tough problem, don't forget to celebrate how far you've come. Not only is this important for your team of problem solvers to see their work in action, but this can also help you become a more efficient, effective , and flexible team. The more problems you tackle together, the more you’ll achieve.
Looking for a tool to help solve problems on your team? Track project implementation with a work management tool like Asana .
Related resources

Don’t let your digital tools sabotage the employee experience

12 tips for effective communication in the workplace

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
How Asana uses work management to drive product development
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Share Podcast

Do You Understand the Problem You’re Trying to Solve?
To solve tough problems at work, first ask these questions.
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
Problem solving skills are invaluable in any job. But all too often, we jump to find solutions to a problem without taking time to really understand the dilemma we face, according to Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg , an expert in innovation and the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
In this episode, you’ll learn how to reframe tough problems by asking questions that reveal all the factors and assumptions that contribute to the situation. You’ll also learn why searching for just one root cause can be misleading.
Key episode topics include: leadership, decision making and problem solving, power and influence, business management.
HBR On Leadership curates the best case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, to help you unlock the best in those around you. New episodes every week.
- Listen to the original HBR IdeaCast episode: The Secret to Better Problem Solving (2016)
- Find more episodes of HBR IdeaCast
- Discover 100 years of Harvard Business Review articles, case studies, podcasts, and more at HBR.org .
HANNAH BATES: Welcome to HBR on Leadership , case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, hand-selected to help you unlock the best in those around you.
Problem solving skills are invaluable in any job. But even the most experienced among us can fall into the trap of solving the wrong problem.
Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg says that all too often, we jump to find solutions to a problem – without taking time to really understand what we’re facing.
He’s an expert in innovation, and he’s the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
In this episode, you’ll learn how to reframe tough problems, by asking questions that reveal all the factors and assumptions that contribute to the situation. You’ll also learn why searching for one root cause can be misleading. And you’ll learn how to use experimentation and rapid prototyping as problem-solving tools.
This episode originally aired on HBR IdeaCast in December 2016. Here it is.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Welcome to the HBR IdeaCast from Harvard Business Review. I’m Sarah Green Carmichael.
Problem solving is popular. People put it on their resumes. Managers believe they excel at it. Companies count it as a key proficiency. We solve customers’ problems.
The problem is we often solve the wrong problems. Albert Einstein and Peter Drucker alike have discussed the difficulty of effective diagnosis. There are great frameworks for getting teams to attack true problems, but they’re often hard to do daily and on the fly. That’s where our guest comes in.
Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg is a consultant who helps companies and managers reframe their problems so they can come up with an effective solution faster. He asks the question “Are You Solving The Right Problems?” in the January-February 2017 issue of Harvard Business Review. Thomas, thank you so much for coming on the HBR IdeaCast .
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Thanks for inviting me.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, I thought maybe we could start by talking about the problem of talking about problem reframing. What is that exactly?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Basically, when people face a problem, they tend to jump into solution mode to rapidly, and very often that means that they don’t really understand, necessarily, the problem they’re trying to solve. And so, reframing is really a– at heart, it’s a method that helps you avoid that by taking a second to go in and ask two questions, basically saying, first of all, wait. What is the problem we’re trying to solve? And then crucially asking, is there a different way to think about what the problem actually is?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, I feel like so often when this comes up in meetings, you know, someone says that, and maybe they throw out the Einstein quote about you spend an hour of problem solving, you spend 55 minutes to find the problem. And then everyone else in the room kind of gets irritated. So, maybe just give us an example of maybe how this would work in practice in a way that would not, sort of, set people’s teeth on edge, like oh, here Sarah goes again, reframing the whole problem instead of just solving it.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I mean, you’re bringing up something that’s, I think is crucial, which is to create legitimacy for the method. So, one of the reasons why I put out the article is to give people a tool to say actually, this thing is still important, and we need to do it. But I think the really critical thing in order to make this work in a meeting is actually to learn how to do it fast, because if you have the idea that you need to spend 30 minutes in a meeting delving deeply into the problem, I mean, that’s going to be uphill for most problems. So, the critical thing here is really to try to make it a practice you can implement very, very rapidly.
There’s an example that I would suggest memorizing. This is the example that I use to explain very rapidly what it is. And it’s basically, I call it the slow elevator problem. You imagine that you are the owner of an office building, and that your tenants are complaining that the elevator’s slow.
Now, if you take that problem framing for granted, you’re going to start thinking creatively around how do we make the elevator faster. Do we install a new motor? Do we have to buy a new lift somewhere?
The thing is, though, if you ask people who actually work with facilities management, well, they’re going to have a different solution for you, which is put up a mirror next to the elevator. That’s what happens is, of course, that people go oh, I’m busy. I’m busy. I’m– oh, a mirror. Oh, that’s beautiful.
And then they forget time. What’s interesting about that example is that the idea with a mirror is actually a solution to a different problem than the one you first proposed. And so, the whole idea here is once you get good at using reframing, you can quickly identify other aspects of the problem that might be much better to try to solve than the original one you found. It’s not necessarily that the first one is wrong. It’s just that there might be better problems out there to attack that we can, means we can do things much faster, cheaper, or better.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, in that example, I can understand how A, it’s probably expensive to make the elevator faster, so it’s much cheaper just to put up a mirror. And B, maybe the real problem people are actually feeling, even though they’re not articulating it right, is like, I hate waiting for the elevator. But if you let them sort of fix their hair or check their teeth, they’re suddenly distracted and don’t notice.
But if you have, this is sort of a pedestrian example, but say you have a roommate or a spouse who doesn’t clean up the kitchen. Facing that problem and not having your elegant solution already there to highlight the contrast between the perceived problem and the real problem, how would you take a problem like that and attack it using this method so that you can see what some of the other options might be?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Right. So, I mean, let’s say it’s you who have that problem. I would go in and say, first of all, what would you say the problem is? Like, if you were to describe your view of the problem, what would that be?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: I hate cleaning the kitchen, and I want someone else to clean it up.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: OK. So, my first observation, you know, that somebody else might not necessarily be your spouse. So, already there, there’s an inbuilt assumption in your question around oh, it has to be my husband who does the cleaning. So, it might actually be worth, already there to say, is that really the only problem you have? That you hate cleaning the kitchen, and you want to avoid it? Or might there be something around, as well, getting a better relationship in terms of how you solve problems in general or establishing a better way to handle small problems when dealing with your spouse?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Or maybe, now that I’m thinking that, maybe the problem is that you just can’t find the stuff in the kitchen when you need to find it.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Right, and so that’s an example of a reframing, that actually why is it a problem that the kitchen is not clean? Is it only because you hate the act of cleaning, or does it actually mean that it just takes you a lot longer and gets a lot messier to actually use the kitchen, which is a different problem. The way you describe this problem now, is there anything that’s missing from that description?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: That is a really good question.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Other, basically asking other factors that we are not talking about right now, and I say those because people tend to, when given a problem, they tend to delve deeper into the detail. What often is missing is actually an element outside of the initial description of the problem that might be really relevant to what’s going on. Like, why does the kitchen get messy in the first place? Is it something about the way you use it or your cooking habits? Is it because the neighbor’s kids, kind of, use it all the time?
There might, very often, there might be issues that you’re not really thinking about when you first describe the problem that actually has a big effect on it.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: I think at this point it would be helpful to maybe get another business example, and I’m wondering if you could tell us the story of the dog adoption problem.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Yeah. This is a big problem in the US. If you work in the shelter industry, basically because dogs are so popular, more than 3 million dogs every year enter a shelter, and currently only about half of those actually find a new home and get adopted. And so, this is a problem that has persisted. It’s been, like, a structural problem for decades in this space. In the last three years, where people found new ways to address it.
So a woman called Lori Weise who runs a rescue organization in South LA, and she actually went in and challenged the very idea of what we were trying to do. She said, no, no. The problem we’re trying to solve is not about how to get more people to adopt dogs. It is about keeping the dogs with their first family so they never enter the shelter system in the first place.
In 2013, she started what’s called a Shelter Intervention Program that basically works like this. If a family comes and wants to hand over their dog, these are called owner surrenders. It’s about 30% of all dogs that come into a shelter. All they would do is go up and ask, if you could, would you like to keep your animal? And if they said yes, they would try to fix whatever helped them fix the problem, but that made them turn over this.
And sometimes that might be that they moved into a new building. The landlord required a deposit, and they simply didn’t have the money to put down a deposit. Or the dog might need a $10 rabies shot, but they didn’t know how to get access to a vet.
And so, by instigating that program, just in the first year, she took her, basically the amount of dollars they spent per animal they helped went from something like $85 down to around $60. Just an immediate impact, and her program now is being rolled out, is being supported by the ASPCA, which is one of the big animal welfare stations, and it’s being rolled out to various other places.
And I think what really struck me with that example was this was not dependent on having the internet. This was not, oh, we needed to have everybody mobile before we could come up with this. This, conceivably, we could have done 20 years ago. Only, it only happened when somebody, like in this case Lori, went in and actually rethought what the problem they were trying to solve was in the first place.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, what I also think is so interesting about that example is that when you talk about it, it doesn’t sound like the kind of thing that would have been thought of through other kinds of problem solving methods. There wasn’t necessarily an After Action Review or a 5 Whys exercise or a Six Sigma type intervention. I don’t want to throw those other methods under the bus, but how can you get such powerful results with such a very simple way of thinking about something?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: That was something that struck me as well. This, in a way, reframing and the idea of the problem diagnosis is important is something we’ve known for a long, long time. And we’ve actually have built some tools to help out. If you worked with us professionally, you are familiar with, like, Six Sigma, TRIZ, and so on. You mentioned 5 Whys. A root cause analysis is another one that a lot of people are familiar with.
Those are our good tools, and they’re definitely better than nothing. But what I notice when I work with the companies applying those was those tools tend to make you dig deeper into the first understanding of the problem we have. If it’s the elevator example, people start asking, well, is that the cable strength, or is the capacity of the elevator? That they kind of get caught by the details.
That, in a way, is a bad way to work on problems because it really assumes that there’s like a, you can almost hear it, a root cause. That you have to dig down and find the one true problem, and everything else was just symptoms. That’s a bad way to think about problems because problems tend to be multicausal.
There tend to be lots of causes or levers you can potentially press to address a problem. And if you think there’s only one, if that’s the right problem, that’s actually a dangerous way. And so I think that’s why, that this is a method I’ve worked with over the last five years, trying to basically refine how to make people better at this, and the key tends to be this thing about shifting out and saying, is there a totally different way of thinking about the problem versus getting too caught up in the mechanistic details of what happens.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: What about experimentation? Because that’s another method that’s become really popular with the rise of Lean Startup and lots of other innovation methodologies. Why wouldn’t it have worked to, say, experiment with many different types of fixing the dog adoption problem, and then just pick the one that works the best?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: You could say in the dog space, that’s what’s been going on. I mean, there is, in this industry and a lot of, it’s largely volunteer driven. People have experimented, and they found different ways of trying to cope. And that has definitely made the problem better. So, I wouldn’t say that experimentation is bad, quite the contrary. Rapid prototyping, quickly putting something out into the world and learning from it, that’s a fantastic way to learn more and to move forward.
My point is, though, that I feel we’ve come to rely too much on that. There’s like, if you look at the start up space, the wisdom is now just to put something quickly into the market, and then if it doesn’t work, pivot and just do more stuff. What reframing really is, I think of it as the cognitive counterpoint to prototyping. So, this is really a way of seeing very quickly, like not just working on the solution, but also working on our understanding of the problem and trying to see is there a different way to think about that.
If you only stick with experimentation, again, you tend to sometimes stay too much in the same space trying minute variations of something instead of taking a step back and saying, wait a minute. What is this telling us about what the real issue is?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, to go back to something that we touched on earlier, when we were talking about the completely hypothetical example of a spouse who does not clean the kitchen–
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Completely, completely hypothetical.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Yes. For the record, my husband is a great kitchen cleaner.
You started asking me some questions that I could see immediately were helping me rethink that problem. Is that kind of the key, just having a checklist of questions to ask yourself? How do you really start to put this into practice?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I think there are two steps in that. The first one is just to make yourself better at the method. Yes, you should kind of work with a checklist. In the article, I kind of outlined seven practices that you can use to do this.
But importantly, I would say you have to consider that as, basically, a set of training wheels. I think there’s a big, big danger in getting caught in a checklist. This is something I work with.
My co-author Paddy Miller, it’s one of his insights. That if you start giving people a checklist for things like this, they start following it. And that’s actually a problem, because what you really want them to do is start challenging their thinking.
So the way to handle this is to get some practice using it. Do use the checklist initially, but then try to step away from it and try to see if you can organically make– it’s almost a habit of mind. When you run into a colleague in the hallway and she has a problem and you have five minutes, like, delving in and just starting asking some of those questions and using your intuition to say, wait, how is she talking about this problem? And is there a question or two I can ask her about the problem that can help her rethink it?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Well, that is also just a very different approach, because I think in that situation, most of us can’t go 30 seconds without jumping in and offering solutions.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Very true. The drive toward solutions is very strong. And to be clear, I mean, there’s nothing wrong with that if the solutions work. So, many problems are just solved by oh, you know, oh, here’s the way to do that. Great.
But this is really a powerful method for those problems where either it’s something we’ve been banging our heads against tons of times without making progress, or when you need to come up with a really creative solution. When you’re facing a competitor with a much bigger budget, and you know, if you solve the same problem later, you’re not going to win. So, that basic idea of taking that approach to problems can often help you move forward in a different way than just like, oh, I have a solution.
I would say there’s also, there’s some interesting psychological stuff going on, right? Where you may have tried this, but if somebody tries to serve up a solution to a problem I have, I’m often resistant towards them. Kind if like, no, no, no, no, no, no. That solution is not going to work in my world. Whereas if you get them to discuss and analyze what the problem really is, you might actually dig something up.
Let’s go back to the kitchen example. One powerful question is just to say, what’s your own part in creating this problem? It’s very often, like, people, they describe problems as if it’s something that’s inflicted upon them from the external world, and they are innocent bystanders in that.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Right, or crazy customers with unreasonable demands.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Exactly, right. I don’t think I’ve ever met an agency or consultancy that didn’t, like, gossip about their customers. Oh, my god, they’re horrible. That, you know, classic thing, why don’t they want to take more risk? Well, risk is bad.
It’s their business that’s on the line, not the consultancy’s, right? So, absolutely, that’s one of the things when you step into a different mindset and kind of, wait. Oh yeah, maybe I actually am part of creating this problem in a sense, as well. That tends to open some new doors for you to move forward, in a way, with stuff that you may have been struggling with for years.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, we’ve surfaced a couple of questions that are useful. I’m curious to know, what are some of the other questions that you find yourself asking in these situations, given that you have made this sort of mental habit that you do? What are the questions that people seem to find really useful?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: One easy one is just to ask if there are any positive exceptions to the problem. So, was there day where your kitchen was actually spotlessly clean? And then asking, what was different about that day? Like, what happened there that didn’t happen the other days? That can very often point people towards a factor that they hadn’t considered previously.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: We got take-out.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: S,o that is your solution. Take-out from [INAUDIBLE]. That might have other problems.
Another good question, and this is a little bit more high level. It’s actually more making an observation about labeling how that person thinks about the problem. And what I mean with that is, we have problem categories in our head. So, if I say, let’s say that you describe a problem to me and say, well, we have a really great product and are, it’s much better than our previous product, but people aren’t buying it. I think we need to put more marketing dollars into this.
Now you can go in and say, that’s interesting. This sounds like you’re thinking of this as a communications problem. Is there a different way of thinking about that? Because you can almost tell how, when the second you say communications, there are some ideas about how do you solve a communications problem. Typically with more communication.
And what you might do is go in and suggest, well, have you considered that it might be, say, an incentive problem? Are there incentives on behalf of the purchasing manager at your clients that are obstructing you? Might there be incentive issues with your own sales force that makes them want to sell the old product instead of the new one?
So literally, just identifying what type of problem does this person think about, and is there different potential way of thinking about it? Might it be an emotional problem, a timing problem, an expectations management problem? Thinking about what label of what type of problem that person is kind of thinking as it of.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: That’s really interesting, too, because I think so many of us get requests for advice that we’re really not qualified to give. So, maybe the next time that happens, instead of muddying my way through, I will just ask some of those questions that we talked about instead.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: That sounds like a good idea.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, Thomas, this has really helped me reframe the way I think about a couple of problems in my own life, and I’m just wondering. I know you do this professionally, but is there a problem in your life that thinking this way has helped you solve?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I’ve, of course, I’ve been swallowing my own medicine on this, too, and I think I have, well, maybe two different examples, and in one case somebody else did the reframing for me. But in one case, when I was younger, I often kind of struggled a little bit. I mean, this is my teenage years, kind of hanging out with my parents. I thought they were pretty annoying people. That’s not really fair, because they’re quite wonderful, but that’s what life is when you’re a teenager.
And one of the things that struck me, suddenly, and this was kind of the positive exception was, there was actually an evening where we really had a good time, and there wasn’t a conflict. And the core thing was, I wasn’t just seeing them in their old house where I grew up. It was, actually, we were at a restaurant. And it suddenly struck me that so much of the sometimes, kind of, a little bit, you love them but they’re annoying kind of dynamic, is tied to the place, is tied to the setting you are in.
And of course, if– you know, I live abroad now, if I visit my parents and I stay in my old bedroom, you know, my mother comes in and wants to wake me up in the morning. Stuff like that, right? And it just struck me so, so clearly that it’s– when I change this setting, if I go out and have dinner with them at a different place, that the dynamic, just that dynamic disappears.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Well, Thomas, this has been really, really helpful. Thank you for talking with me today.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Thank you, Sarah.
HANNAH BATES: That was Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg in conversation with Sarah Green Carmichael on the HBR IdeaCast. He’s an expert in problem solving and innovation, and he’s the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
We’ll be back next Wednesday with another hand-picked conversation about leadership from the Harvard Business Review. If you found this episode helpful, share it with your friends and colleagues, and follow our show on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you get your podcasts. While you’re there, be sure to leave us a review.
We’re a production of Harvard Business Review. If you want more podcasts, articles, case studies, books, and videos like this, find it all at HBR dot org.
This episode was produced by Anne Saini, and me, Hannah Bates. Ian Fox is our editor. Music by Coma Media. Special thanks to Maureen Hoch, Adi Ignatius, Karen Player, Ramsey Khabbaz, Nicole Smith, Anne Bartholomew, and you – our listener.
See you next week.
- Subscribe On:
Latest in this series
This article is about leadership.
- Decision making and problem solving
- Power and influence
- Business management
Partner Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The implementation of a solution requires planning and execution. It's often iterative, where the focus should be on short implementation cycles with testing and feedback, not trying to get it "perfect" the first time. Input: decision; planning; hard work. Output: resolution to the problem. 5.
The Problem-Solving Process. Problem-solving is an important part of planning and decision-making. The process has much in common with the decision-making process, and in the case of complex decisions, can form part of the process itself. We face and solve problems every day, in a variety of guises and of differing complexity.
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue. The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything ...
The problem solving process typically includes: Pinpointing what's broken by gathering data and consulting with team members. Figuring out why it's not working by mapping out and troubleshooting the problem. Deciding on the most effective way to fix it by brainstorming and then implementing a solution. While skills like active listening ...
1. Define the problem. Diagnose the situation so that your focus is on the problem, not just its symptoms. Helpful problem-solving techniques include using flowcharts to identify the expected steps of a process and cause-and-effect diagrams to define and analyze root causes.. The sections below help explain key problem-solving steps.
Problem solving is the process of reviewing every element of an issue so you can get to a solution or fix it. Problem solving steps cover multiple aspects of a problem that you can bring together to find a solution. ... 5 Problem Solving Steps. No matter what the problem is, to solve it, you nearly always have to follow these problem solving ...
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
There's a 5-step process that you can follow that will allow you to solve your challenges more efficiently and effectively. In short, you need to move through these 5 steps: Defining a problem. Ideating on a solution. Committing to a course of action. Implementing your solution. And finally - analyzing the results.
When we do problem definition well in classic problem solving, we are demonstrating the kind of empathy, at the very beginning of our problem, that design thinking asks us to approach. When we ideate—and that's very similar to the disaggregation, prioritization, and work-planning steps—we do precisely the same thing, and often we use ...
Step 1 - Define the Problem. The definition of the problem is the first step in effective problem solving. This may appear to be a simple task, but it is actually quite difficult. This is because problems are frequently complex and multi-layered, making it easy to confuse symptoms with the underlying cause.
Step 1: Identify. Identifying the problem may be simple, or it could be a detailed cognitive process that breaks the issue into manageable components. Either way, what you do during the identify step of the problem-solving process sets the stage for the next steps in problem solving.
The Five-Step Problem-Solving Process. Problems at a workplace need not necessarily be situations that have a negative impact, such as a product failure or a change in government policy. Making a decision to alter the way your team works may also be a problem. Launching new products, technological upgrades, customer feedback collection ...
Related: 10 Ideation Techniques for Problem-Solving. 4. Ask for support and feedback. Another way to build your problem-solving strategy is by asking your team for feedback. You can get ideas from mentors or colleagues on how they solve problems, or you can ask for feedback on a draft of your problem-solving process.
In general, effective problem-solving strategies include the following steps: Define the problem. Come up with alternative solutions. Decide on a solution. Implement the solution. Problem-solving ...
Step 3: Describe the problem. Craft a concise problem statement in a clear yet short manner. This concise articulation serves as a focal point for the problem-solving effort. Further, distribute the statement to the team for consensus, ensuring everyone involved agrees on the root cause.
How to Solve Problems: 5 Steps. 1. Precisely Identify Problems. As obvious as it seems, identifying the problem is the first step in the problem-solving process. Pinpointing a problem at the beginning of the process will guide your research, collaboration, and solutions in the right direction. At this stage, your task is to identify the scope ...
It starts with an "affirmative topic," followed by the "positive core (strengths).". Then this method delves into the following stages: Discovery (fact-finding) Dream (visioning the future) Design (strategic purpose) Destiny (continuous improvement) 3. "FIVE WHYS" METHOD. The 5 Whys of Problem-Solving Method.
He sacrificed his personality in the process. In 2004 he finished his MBA (Masters In Business Administration) from the Australian Graduate School of Management and loved it! He scored a distinction (average) and got his personality back too! This blog post aims to lay out a 5-step process to problem-solving. Feel free to join the conversation!
Steps of the problem-solving process. Effective problem-solving involves five essential steps. One way to remember them is through the IDEAL model created in 1984 by psychology professors John D. Bransford and Barry S. Stein . The steps to solving problems in this model include: ...
The McKinsey guide to problem solving. Become a better problem solver with insights and advice from leaders around the world on topics including developing a problem-solving mindset, solving problems in uncertain times, problem solving with AI, and much more.
Step 1: Identify the Problem. As obvious as it may sound, the first step in the problem-solving process is to identify the root of the issue. However, the problem isn't always easily identifiable and might require some extra analysis to get the source. One way you can identify a problem is by using Toyota's "Five Whys" technique.
The three steps before problem solving: we call them the K-W-I. The "K" stands for "know" and requires students to identify what they already know about a problem. The goal in this step of the routine is two-fold. First, the student needs to analyze the problem and identify what is happening within the context of the problem.
4 steps to better problem solving. While it might be tempting to dive into a problem head first, take the time to move step by step. Here's how you can effectively break down the problem-solving process with your team: 1. Identify the problem that needs to be solved. One of the easiest ways to identify a problem is to ask questions.
To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve. In this episode, you'll learn how to reframe tough problems by asking questions that reveal all the factors and assumptions that ...