- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy

Eureka Math Grade 7 Module 3 Lesson 10 Answer Key
Engage ny eureka math 7th grade module 3 lesson 10 answer key, eureka math grade 7 module 3 lesson 10 example answer key.
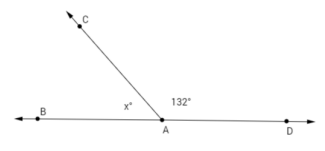
Write an equation for the angle relationship shown in the figure and solve for x. Then, find the measures of ∠BAC and confirm your answers by measuring the angle with a protractor. x + 132 = 180 x + 132 – 132 = 180 – 132 x = 48 m∠BAC = 48°
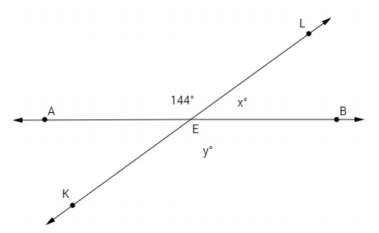
Write an equation for the angle relationship shown in the figure and solve for x and y. Find the measurements of ∠LEB and ∠KEB. Answer: y = 144°; m∠KEB = 144° (or vert. ∠s are = ) x + 144 = 180 x + 144 – 144 = 180 – 144 x = 36 m∠LEB = 36°
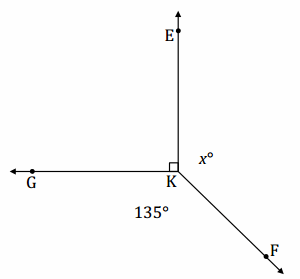
Write an equation for the angle relationship shown in the figure and solve for x. Find the measurement of ∠EKF and confirm your answers by measuring the angle with a protractor. Answer: x + 90 + 135 = 360 x + 225 = 360 x + 225 – 225 = 360 – 225 x = 135 m∠EKF = 135°
Label the diagram with expressions that describe this relationship. Write an equation that models the angle relationship and solve for x. Find the measurements of the acute and obtuse angles. Answer: 2x + 1x = 180 3x = 180 (\(\frac{1}{3}\))(3x) = (\(\frac{1}{3}\))(180) x = 60 Acute angle = 60° Obtuse angle = 2x° = 2(60°) = 120°
Eureka Math Grade 7 Module 3 Lesson 10 Opening Exercise Answer Key
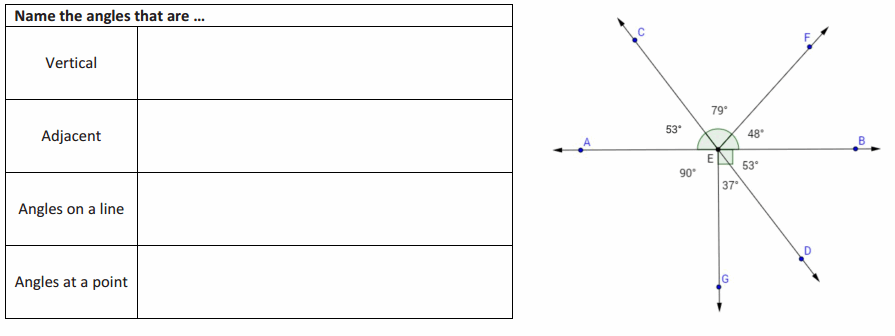
Eureka Math Grade 7 Module 3 Lesson 10 Exercise Answer Key
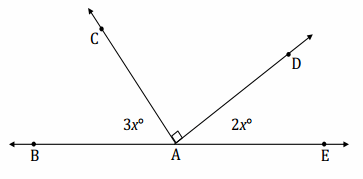
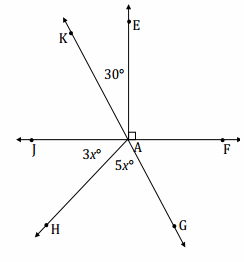
Find the measurements of ∠BAC and ∠DAE. Answer: 3x + 90 + 2x = 180 5x + 90 = 180 5x + 90 – 90 = 180 – 90 (\(\frac{1}{5}\))(5x) = (\(\frac{1}{5}\))(90) x = 18 m∠BAC = 3(18°) = 54° m∠DAE = 2(18°) = 36°
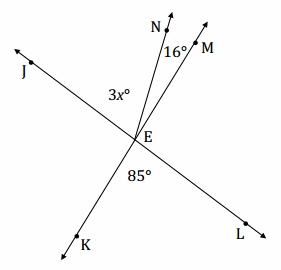
Write an equation for the angle relationship shown in the figure and solve for x. Answer: 3x + 16 = 85 3x + 16 – 16 = 85 – 16 3x = 69 (\(\frac{1}{3}\))3x = 69(\(\frac{1}{3}\)) x = 23
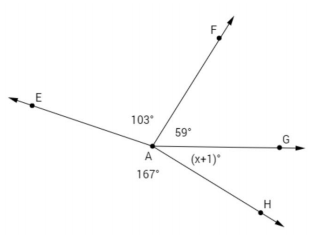
Find the measurement of ∠GAH. Answer: (x + 1) + 59 + 103 + 167 = 360 x + 1 + 59 + 103 + 167 = 360 x = 30 m∠GAH = (30 + 1)° = 31°
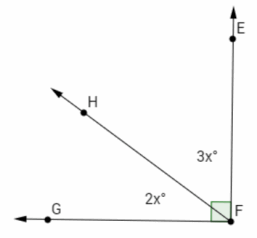
Find the measures of ∠GFH and ∠EFH. Answer: 2x + 3x = 90 5x = 90 (\(\frac{1}{5}\))(5x) = (\(\frac{1}{5}\))(90) x = 18 m∠GFH = 2(18°) = 36° m∠EFH = 3(18°) = 54°
Eureka Math Grade 7 Module 3 Lesson 10 Problem Set Answer Key
For each question, use angle relationships to write an equation in order to solve for each variable. Determine the indicated angles. You can check your answers by measuring each angle with a protractor.
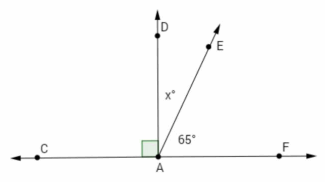
(65) + y = 90 65 – 65 + y = 90 – 65 y = 25
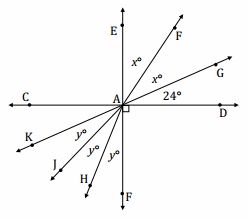
Question 9. The ratio of the measures of a pair of adjacent angles on a line is 4:5. a. Find the measures of the two angles. Answer: ∠1 = 4x, ∠2 = 5x 4x + 5x = 180 9x = 180 (\(\frac{1}{9}\))9x = (\(\frac{1}{9}\))180 x = 20 ∠1 = 4(20°) = 80° ∠2 = 5(20°) = 100°
Question 10. The ratio of the measures of three adjacent angles on a line is 3:4:5. a. Find the measures of the three angles. Answer: ∠1 = 3x, ∠2 = 4x, ∠3 = 5x 3x + 4x + 5x = 180 12x = 180 (\(\frac{1}{12}\))12x = (\(\frac{1}{12}\))180 x = 15 ∠1 = 3(15°) = 45° ∠2 = 4(15°) = 60° ∠3 = 5(15°) = 75°
Eureka Math Grade 7 Module 3 Lesson 10 Exit Ticket Answer Key
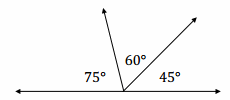
In a complete sentence, describe the relevant angle relationships in the following diagram. That is, describe the angle relationships you could use to determine the value of x. Answer: ∠KAE and ∠EAF are adjacent angles whose measurements are equal to ∠KAF; ∠KAF and ∠JAG are vertical angles and are of equal measurement.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
You are using an outdated browser and it's not supported. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
- LOGIN FOR PROGRAM PARTICIPANTS
- PROGRAM SUPPORT
Angle Problems and Solving Equations
Description.
Students use vertical angles, adjacent angles, angles on a line, and angles at a point in a multistep problem to write and solve simple equations
There may be cases when our downloadable resources contain hyperlinks to other websites. These hyperlinks lead to websites published or operated by third parties. UnboundEd and EngageNY are not responsible for the content, availability, or privacy policies of these websites.
- Grade 7 Mathematics Module 3, Topic B, Lesson 10: Student Version
- Grade 7 Mathematics Module 3, Topic B, Lesson 10: Teacher Version
Prerequisites
- CCSS Standard:
Related Guides and Multimedia
Our professional learning resources include teaching guides, videos, and podcasts that build educators' knowledge of content related to the standards and their application in the classroom.
There are no related guides or videos. To see all our guides, please visit the Enhance Instruction section here .
- AP Calculus
- AP Statistics
- Independent Study
Online Math Class
Mr. Math Blog
Thanks for your donation! Every little bit helps me help you! :-)
Problem Solving - Organize Data - Lesson 2.1
Use Picture Graphs - Lesson 2.2
Make Picture Graphs - Lesson 2.3
Use Bar Graphs - Lesson 2.4
Make a Bar Graph - Lesson 2.5
Solve Problems Using Data - Lesson 2.6
Use and Make Line Plots - Lesson 2.7
Number Patterns - Lesson 1.1
Round to Nearest Ten or Hundred - Lesson 1.2
Estimate Sums - Lesson 1.3
Mental Math Strategies for Addition - Lesson 1.4
Use Properties to Add - Lesson 1.5
Use the Break Apart Strategy to Add - Lesson 1.6
Use Place Value to Add - Lesson 1.7
Estimate Differences - Lesson 1.8
Mental Math Strategies for Subtraction - Lesson 1.9
Use Place Value to Subtract - Lesson 1.10
Combine Place Values to Subtract - Lesson 1.11
Describe Plane Shapes - Lesson 12.1
Describe Angles in Plane Shapes - Lesson 12.2
Identify Polygons - Lesson 12.3
Describe Sides of Polygons - Lesson 12.4
Classify Quadrilaterals - Lesson 12.5
Draw Quadrilaterals - Lesson 12.6
Describe Triangles - Lesson 12.7
Chapter 12 Performance Task Review For Test
Problem Solving - Compare Fractions - Lesson 9.1
Compare Fractions with the Same Denominator - Lesson 9.2
Compare Fractions with the Same Numerator - Lesson 9.3
Compare Fractions - Lesson 9.4
Compare and Order Fractions - Lesson 9.5
Model Equivalent Fractions - Lesson 9.6
Equivalent Fractions - Lesson 9.7
Divide by 2 - Lesson 7.1
Divide by 10 - Lesson 7.2
Divide by 5 - Lesson 7.3
Divide by 3 - Lesson 7.4
Divide by 4 - Lesson 7.5
Divide by 5 - Lesson 7.6
Mid-Chapter 7 Checkpoint on Division Facts and Strategies
Divide by 7 - Lesson 7.7
Divide by 8 - Lesson 7.8
Divide by 9 - Lesson 7.9
Problem Solving - Two-Step Problems - Lesson 7.10
Order of Operations - Lesson 7.11
Problem Solving - Model Division - Lesson 6.1
Size of Equal Groups - Lesson 6.2
Number of Equal Groups - Lesson 6.3
Model (Division) with Bar Model - Lesson 6.4
Relate Subtraction and Division - Lesson 6.5
Mid-Chapter 6 Checkpoint
Model (division) with Arrays - Lesson 6.6
Relate Multiplication and Division - Lesson 6.7
Write Related Facts - Lesson 6.8
Division Rules for 1 and 0 - Lesson 6.9
Chapter 6 Review for Test - Understanding Division
Multiply with 2 and 4 - Lesson 4.1
Multiply with 5 and 10 - Lesson 4.2
Multiply with 3 and 6 - Lesson 4.3
Distributive Property - Lesson 4.4
Multiply with 7 - Lesson 4.5
Associative Property of Multiplication - Lesson 4.6
Patterns on the Multiplication Table - Lesson 4.7
Multiply with 8 - Lesson 4.8
Multiply with 9 - Lesson 4.9
Review For Test on Chapter 4
Describe Patterns - Lesson 5.1
Find Unknown Factors - Lesson 5.2
Problem Solving: Using the Distributive Property - Lesson 5.3
Multiplication Strategies with Multiples of 10 - Lesson 5.4
Multiply Multiples of 10 by 1-Digit Numbers - Lesson 5.5
Chapter 5 Review on Multiplication Facts
Third Grade
Math
- Second Grade Math
- Third Grade Math
- Fourth Grade Math
- Fifth Grade Math
- Sixth Grade Math
- Sixth Grade Math (CA)
- Seventh Grade Math (CA)
- Eighth Grade Math (CA)
- Integrated Math 1
- Integrated Math 2
- Integrated Math 3
- PreCalculus
- AP Statistics Exam Prep
- Elementary Statistics
- ELM Practice
- Percents and Decimals
- Sixth Grade Math (Big Ideas)
Model Perimeter - Lesson 11.1
Find Perimeter - Lesson 11.2
Find Unknown Side Lengths - Lesson 11.3
Understanding Area - Lesson 11.4
Measure Area - Lesson 11.5
Use Area Models - Lesson 11.6
Problem Solving - Area of Rectangles - Lesson 11.7
Area of Combined Rectangles - Lesson 11.8
Same Perimeter - Different Area - Lesson 11.9
Same Area - Different Perimeter - Lesson 11.10
Chapter 11 Review for Test on Perimeter and Area
Please Donate, if you're a regular!
The donate link is below. Thanks so much!!
Count Equal Groups - Lesson 3.1
Relate Addition and Multiplication - Lesson 3.2
Skip Count on a Number Line - Lesson 3.3
Problem Solving - Model Multiplication - Lesson 3.4
Model with Arrays - Lesson 3.5
Commutative Property of Multiplication - Lesson 3.6
Multiply with 1 and 0 - Lesson 3.7
Time to the Minute - Lesson 10.1
A.M. and P.M. - Lesson 10.2
Measure Time Intervals - Lesson 10.3
Use Time Intervals - Lesson 10.4
Problem Solving - Time Intervals - Lesson 10.5
Measure Length - Lesson 10.6
Estimate and Measure Liquid Volume - Lesson 10.7
Estimate and Measure Mass - Lesson 10.8
Equal Parts of a Whole - Lesson 8.1
Equal Shares - Lesson 8.2
Unit Fractions of a Whole - Lesson 8.3
Fractions of a Whole - Lesson 8.4
Fractions on a Number Line - Lesson 8.5
Relate Fractions and Whole Numbers - Lesson 8.6
Fractions of a Group - Lesson 8.7
Find Part of Group Using Unit Fractions - Lesson 8.8
Problem Solving: Find the Whole Using Unit Fractions - Lesson 8.9
Copyright 2013. All rights reserved.

Problem Solving Activities: 7 Strategies
- Critical Thinking

Problem solving can be a daunting aspect of effective mathematics teaching, but it does not have to be! In this post, I share seven strategic ways to integrate problem solving into your everyday math program.
In the middle of our problem solving lesson, my district math coordinator stopped by for a surprise walkthrough.
I was so excited!
We were in the middle of what I thought was the most brilliant math lesson– teaching my students how to solve problem solving tasks using specific problem solving strategies.
It was a proud moment for me!
Each week, I presented a new problem solving strategy and the students completed problems that emphasized the strategy.
Genius right?
After observing my class, my district coordinator pulled me aside to chat. I was excited to talk to her about my brilliant plan, but she told me I should provide the tasks and let my students come up with ways to solve the problems. Then, as students shared their work, I could revoice the student’s strategies and give them an official name.
What a crushing blow! Just when I thought I did something special, I find out I did it all wrong.
I took some time to consider her advice. Once I acknowledged she was right, I was able to make BIG changes to the way I taught problem solving in the classroom.
When I Finally Saw the Light
To give my students an opportunity to engage in more authentic problem solving which would lead them to use a larger variety of problem solving strategies, I decided to vary the activities and the way I approached problem solving with my students.
Problem Solving Activities
Here are seven ways to strategically reinforce problem solving skills in your classroom.

Seasonal Problem Solving
Many teachers use word problems as problem solving tasks. Instead, try engaging your students with non-routine tasks that look like word problems but require more than the use of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division to complete. Seasonal problem solving tasks and daily challenges are a perfect way to celebrate the season and have a little fun too!
Cooperative Problem Solving Tasks
Go cooperative! If you’ve got a few extra minutes, have students work on problem solving tasks in small groups. After working through the task, students create a poster to help explain their solution process and then post their poster around the classroom. Students then complete a gallery walk of the posters in the classroom and provide feedback via sticky notes or during a math talk session.
Notice and Wonder
Before beginning a problem solving task, such as a seasonal problem solving task, conduct a Notice and Wonder session. To do this, ask students what they notice about the problem. Then, ask them what they wonder about the problem. This will give students an opportunity to highlight the unique characteristics and conditions of the problem as they try to make sense of it.
Want a better experience? Remove the stimulus, or question, and allow students to wonder about the problem. Try it! You’ll gain some great insight into how your students think about a problem.

Math Starters
Start your math block with a math starter, critical thinking activities designed to get your students thinking about math and provide opportunities to “sneak” in grade-level content and skills in a fun and engaging way. These tasks are quick, designed to take no more than five minutes, and provide a great way to turn-on your students’ brains. Read more about math starters here !
Create your own puzzle box! The puzzle box is a set of puzzles and math challenges I use as fast finisher tasks for my students when they finish an assignment or need an extra challenge. The box can be a file box, file crate, or even a wall chart. It includes a variety of activities so all students can find a challenge that suits their interests and ability level.
Calculators
Use calculators! For some reason, this tool is not one many students get to use frequently; however, it’s important students have a chance to practice using it in the classroom. After all, almost everyone has access to a calculator on their cell phones. There are also some standardized tests that allow students to use them, so it’s important for us to practice using calculators in the classroom. Plus, calculators can be fun learning tools all by themselves!
Three-Act Math Tasks
Use a three-act math task to engage students with a content-focused, real-world problem! These math tasks were created with math modeling in mind– students are presented with a scenario and then given clues and hints to help them solve the problem. There are several sites where you can find these awesome math tasks, including Dan Meyer’s Three-Act Math Tasks and Graham Fletcher’s 3-Acts Lessons .
Getting the Most from Each of the Problem Solving Activities
When students participate in problem solving activities, it is important to ask guiding, not leading, questions. This provides students with the support necessary to move forward in their thinking and it provides teachers with a more in-depth understanding of student thinking. Selecting an initial question and then analyzing a student’s response tells teachers where to go next.
Ready to jump in? Grab a free set of problem solving challenges like the ones pictured using the form below.
Which of the problem solving activities will you try first? Respond in the comments below.

Shametria Routt Banks
- Assessment Tools
- Content and Standards
- Differentiation
- Math & Literature
- Math & Technology
- Math Routines
- Math Stations
- Virtual Learning
- Writing in Math
You may also like...
2 Responses
This is a very cool site. I hope it takes off and is well received by teachers. I work in mathematical problem solving and help prepare pre-service teachers in mathematics.
Thank you, Scott! Best wishes to you and your pre-service teachers this year!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
©2024 The Routty Math Teacher. All Rights Reserved. Designed by Ashley Hughes.
Privacy overview.
Curriculum / Math / 7th Grade / Unit 1: Proportional Relationships / Lesson 10
Proportional Relationships
Lesson 10 of 18
Criteria for Success
Tips for teachers, anchor problems, problem set, target task, additional practice.
Make connections between the four representations of proportional relationships (Part 1).
Common Core Standards
Core standards.
The core standards covered in this lesson
Ratios and Proportional Relationships
7.RP.A.2 — Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities.
7.RP.A.2.A — Decide whether two quantities are in a proportional relationship, e.g., by testing for equivalent ratios in a table or graphing on a coordinate plane and observing whether the graph is a straight line through the origin.
7.RP.A.2.B — Identify the constant of proportionality (unit rate) in tables, graphs, equations, diagrams, and verbal descriptions of proportional relationships.
7.RP.A.2.C — Represent proportional relationships by equations. For example, if total cost t is proportional to the number n of items purchased at a constant price p, the relationship between the total cost and the number of items can be expressed as t = pn.
7.RP.A.2.D — Explain what a point (x, y) on the graph of a proportional relationship means in terms of the situation, with special attention to the points (0, 0) and (1, r) where r is the unit rate.
Foundational Standards
The foundational standards covered in this lesson
6.RP.A.3 — Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve real-world and mathematical problems, e.g., by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations.
The essential concepts students need to demonstrate or understand to achieve the lesson objective
- Identify the constant of proportionality in graphs, equations, and tables.
- Represent and analyze proportional relationships in graphs, equations, and tables.
Suggestions for teachers to help them teach this lesson
Lessons 10 and 11 pull together all the representations of proportional relationships – written description, table, graph, and equation – that students have been studying since the beginning of the unit. As needed, review any one representation that students may be stuck on, but continue to engage them in looking at multiple representations at a time in order to strengthen the connections between them.
Unlock features to optimize your prep time, plan engaging lessons, and monitor student progress.
Problems designed to teach key points of the lesson and guiding questions to help draw out student understanding
A scientist plants a seed in a laboratory and tracks the growth of the plant. The height of the plant in centimeters is proportional to the number of days since it was planted.

a. Explain what point B represents in context of the situation.
b. At what rate is the plant growing? Indicate this as a point on the graph.
c. Write an equation that represents the relationship between days and height.
d. If the plant continues to grow at this rate, how tall will it be after 12 days?
e. If the plant continues to grow at this rate, when will it be 6 cm tall?
Guiding Questions
Match each table to its equation.

i. $${y = {1 \over 2}x}$$
ii. $${y = {2 \over 3}x}$$
iii. $${y = 2x}$$
iv. $${y=3x}$$
The cost you pay for limes is proportional to the number of limes you buy. Four different stores sell limes for different amounts, as shown in the graphs, table, and equation below. Which store should you go to if you want to pay the least amount for limes? Explain your answer.

A set of suggested resources or problem types that teachers can turn into a problem set
Give your students more opportunities to practice the skills in this lesson with a downloadable problem set aligned to the daily objective.
A task that represents the peak thinking of the lesson - mastery will indicate whether or not objective was achieved
The width of a small book measures 6 inches, or approximately 15 centimeters. You know that the relationship between inches and centimeters is proportional, but you can’t remember the conversion rate between them.
Let $$y$$ represent the number of centimeters and $$x$$ represent the number of inches. Represent the relationship in the coordinate plane below, and then write an equation that approximates the relationship between inches and centimeters.

Student Response
An example response to the Target Task at the level of detail expected of the students.
The following resources include problems and activities aligned to the objective of the lesson that can be used for additional practice or to create your own problem set.
- MARS Summative Assessment Tasks for Middle School Buses
- SERP Poster Problems Drag Racer Dragonfly
- EngageNY Mathematics Grade 7 Mathematics > Module 1 > Topic B > Lesson 8 — Example 2, Exit Ticket, Problem Set 5-6
- MARS Formative Assessment Lessons for Grade 7 Representing: Road Race
Topic A: Representing Proportional Relationships in Tables, Equations, and Graphs
Solve ratio and rate problems using double number lines, tables, and unit rate.
7.RP.A.1 7.RP.A.2
Represent proportional relationships in tables, and define the constant of proportionality.
7.RP.A.2 7.RP.A.2.B
Determine the constant of proportionality in tables, and use it to find missing values.
7.RP.A.2.A 7.RP.A.2.B
Write equations for proportional relationships presented in tables.
7.RP.A.2.B 7.RP.A.2.C
Write equations for proportional relationships from word problems.
7.RP.A.2 7.RP.A.2.C
Represent proportional relationships in graphs.
7.RP.A.2 7.RP.A.2.A 7.RP.A.2.D
Interpret proportional relationships represented in graphs.
7.RP.A.2 7.RP.A.2.D
Create a free account to access thousands of lesson plans.
Already have an account? Sign In
Topic B: Non-Proportional Relationships
Compare proportional and non-proportional relationships.
Determine if relationships are proportional or non-proportional.
Topic C: Connecting Everything Together
7.RP.A.2 7.RP.A.2.A 7.RP.A.2.B 7.RP.A.2.C 7.RP.A.2.D
Make connections between the four representations of proportional relationships (Part 2).
Use different strategies to represent and recognize proportional relationships.
Topic D: Solving Ratio & Rate Problems with Fractions
Find the unit rate of ratios involving fractions.
Find the unit rate and use it to solve problems.
7.RP.A.1 7.RP.A.3
Solve ratio and rate problems by setting up a proportion.
Solve ratio and rate problems by setting up a proportion, including part-part-whole problems.
Solve multi-step ratio and rate problems using proportional reasoning, including fractional price increase and decrease, commissions, and fees.
Use proportional reasoning to solve real-world, multi-step problems.
7.RP.A.1 7.RP.A.2 7.RP.A.3
Request a Demo
See all of the features of Fishtank in action and begin the conversation about adoption.
Learn more about Fishtank Learning School Adoption.

Contact Information
School information, what courses are you interested in, are you interested in onboarding professional learning for your teachers and instructional leaders, any other information you would like to provide about your school.

Effective Instruction Made Easy
Access rigorous, relevant, and adaptable math lesson plans for free
Want a daily email of lesson plans that span all subjects and age groups?
Subjects all subjects all subjects the arts all the arts visual arts performing arts value of the arts back business & economics all business & economics global economics macroeconomics microeconomics personal finance business back design, engineering & technology all design, engineering & technology design engineering technology back health all health growth & development medical conditions consumer health public health nutrition physical fitness emotional health sex education back literature & language all literature & language literature linguistics writing/composition speaking back mathematics all mathematics algebra data analysis & probability geometry measurement numbers & operations back philosophy & religion all philosophy & religion philosophy religion back psychology all psychology history, approaches and methods biological bases of behavior consciousness, sensation and perception cognition and learning motivation and emotion developmental psychology personality psychological disorders and treatment social psychology back science & technology all science & technology earth and space science life sciences physical science environmental science nature of science back social studies all social studies anthropology area studies civics geography history media and journalism sociology back teaching & education all teaching & education education leadership education policy structure and function of schools teaching strategies back thinking & learning all thinking & learning attention and engagement memory critical thinking problem solving creativity collaboration information literacy organization and time management back, filter by none.
- Elementary/Primary
- Middle School/Lower Secondary
- High School/Upper Secondary
- College/University
- TED-Ed Animations
- TED Talk Lessons
- TED-Ed Best of Web
- Under 3 minutes
- Under 6 minutes
- Under 9 minutes
- Under 12 minutes
- Under 18 minutes
- Over 18 minutes
- Algerian Arabic
- Azerbaijani
- Cantonese (Hong Kong)
- Chinese (Hong Kong)
- Chinese (Singapore)
- Chinese (Taiwan)
- Chinese Simplified
- Chinese Traditional
- Chinese Traditional (Taiwan)
- Dutch (Belgium)
- Dutch (Netherlands)
- French (Canada)
- French (France)
- French (Switzerland)
- Kurdish (Central)
- Luxembourgish
- Persian (Afghanistan)
- Persian (Iran)
- Portuguese (Brazil)
- Portuguese (Portugal)
- Spanish (Argentina)
- Spanish (Latin America)
- Spanish (Mexico)
- Spanish (Spain)
- Spanish (United States)
- Western Frisian
sort by none
- Longest video
- Shortest video
- Most video views
- Least video views
- Most questions answered
- Least questions answered

This piece of paper could revolutionize human waste
Lesson duration 05:35
2,419,416 Views

Can you solve the magical maze riddle?
Lesson duration 04:51
306,628 Views

How to clear icy roads, with science
Lesson duration 06:13
191,101 Views

How to make smart decisions more easily
Lesson duration 05:16
1,023,296 Views

Can you solve a mystery before Sherlock Holmes?
Lesson duration 05:17
455,035 Views

Can you solve the secret assassin society riddle?
Lesson duration 05:01
648,600 Views

How to overcome your mistakes
Lesson duration 04:52
871,167 Views

What the fossil fuel industry doesn't want you to know - Al Gore
Lesson duration 25:45
734,460 Views

Can you solve the cursed dice riddle?
Lesson duration 04:31
647,223 Views

How the water you flush becomes the water you drink
Lesson duration 05:23
382,340 Views

The growing megafire crisis — and how to contain it - George T. Whitesides
Lesson duration 10:42
56,521 Views
Can you solve the time traveling car riddle?
Lesson duration 05:18
608,904 Views

4 epidemics that almost happened (but didn't)
Lesson duration 06:26
392,929 Views

The return of Mongolia's "wild" horses
Lesson duration 04:53
203,824 Views

Whatever happened to the hole in the ozone layer?
Lesson duration 05:13
512,599 Views

The most important century in human history
Lesson duration 05:20
336,221 Views

This one weird trick will get you infinite gold
Lesson duration 05:08
951,750 Views

How to quit your job — without ruining your career - Gala Jackson
102,445 Views

How to design climate-resilient buildings - Alyssa-Amor Gibbons
Lesson duration 14:12
42,726 Views

The case for free, universal basic services - Aaron Bastani
Lesson duration 19:09
79,824 Views

Can you steal the most powerful wand in the wizarding world?
747,874 Views

How college loans exploit students for profit - Sajay Samuel
Lesson duration 11:49
229,072 Views

What’s the smartest age?
1,529,952 Views

The 4 greatest threats to the survival of humanity
Lesson duration 05:24
483,845 Views

FREE K-12 standards-aligned STEM
curriculum for educators everywhere!
Find more at TeachEngineering.org .
- TeachEngineering
- Problem Solving
Lesson Problem Solving
Grade Level: 8 (6-8)
(two 40-minute class periods)
Lesson Dependency: The Energy Problem
Subject Areas: Physical Science, Science and Technology
- Print lesson and its associated curriculum
Curriculum in this Unit Units serve as guides to a particular content or subject area. Nested under units are lessons (in purple) and hands-on activities (in blue). Note that not all lessons and activities will exist under a unit, and instead may exist as "standalone" curriculum.
- Energy Forms and States Demonstrations
- Energy Conversions
- Watt Meters to Measure Energy Consumption
- Household Energy Audit
- Light vs. Heat Bulbs
- Efficiency of an Electromechanical System
- Efficiency of a Water Heating System
- Solving Energy Problems
- Energy Projects
TE Newsletter
Engineering connection, learning objectives, worksheets and attachments, more curriculum like this, introduction/motivation, associated activities, user comments & tips.

Scientists, engineers and ordinary people use problem solving each day to work out solutions to various problems. Using a systematic and iterative procedure to solve a problem is efficient and provides a logical flow of knowledge and progress.
- Students demonstrate an understanding of the Technological Method of Problem Solving.
- Students are able to apply the Technological Method of Problem Solving to a real-life problem.
Educational Standards Each TeachEngineering lesson or activity is correlated to one or more K-12 science, technology, engineering or math (STEM) educational standards. All 100,000+ K-12 STEM standards covered in TeachEngineering are collected, maintained and packaged by the Achievement Standards Network (ASN) , a project of D2L (www.achievementstandards.org). In the ASN, standards are hierarchically structured: first by source; e.g. , by state; within source by type; e.g. , science or mathematics; within type by subtype, then by grade, etc .
Ngss: next generation science standards - science.
View aligned curriculum
Do you agree with this alignment? Thanks for your feedback!
International Technology and Engineering Educators Association - Technology
State standards, national science education standards - science.
Scientists, engineers, and ordinary people use problem solving each day to work out solutions to various problems. Using a systematic and iterative procedure to solve a problem is efficient and provides a logical flow of knowledge and progress.
In this unit, we use what is called "The Technological Method of Problem Solving." This is a seven-step procedure that is highly iterative—you may go back and forth among the listed steps, and may not always follow them in order. Remember that in most engineering projects, more than one good answer exists. The goal is to get to the best solution for a given problem. Following the lesson conduct the associated activities Egg Drop and Solving Energy Problems for students to employ problem solving methods and techniques.
Lesson Background and Concepts for Teachers
The overall concept that is important in this lesson is: Using a standard method or procedure to solve problems makes the process easier and more effective.
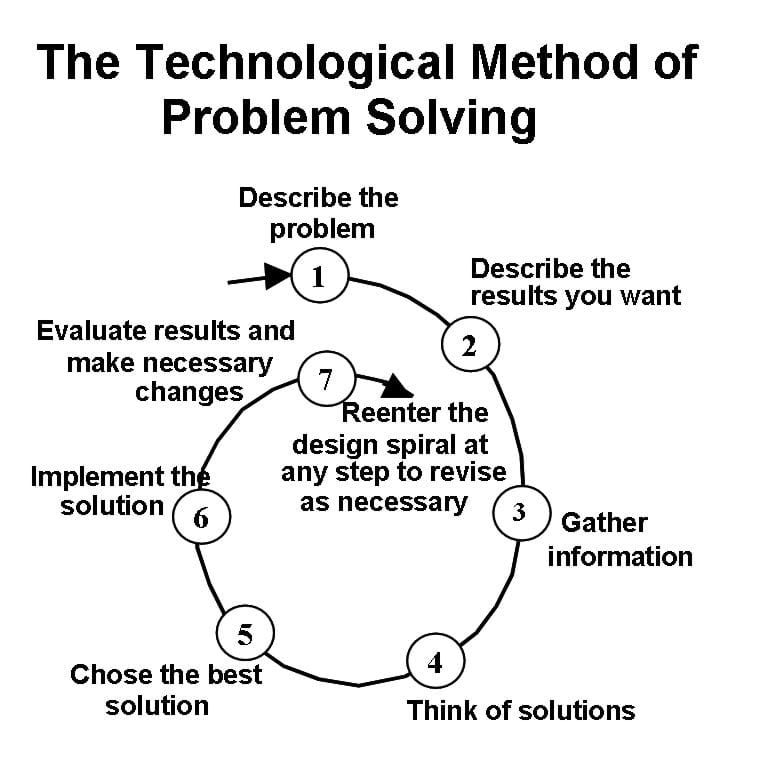
The specific process of problem solving used in this unit was adapted from an eighth-grade technology textbook written for New York State standard technology curriculum. The process is shown in Figure 1, with details included below. The spiral shape shows that this is an iterative, not linear, process. The process can skip ahead (for example, build a model early in the process to test a proof of concept) and go backwards (learn more about the problem or potential solutions if early ideas do not work well).
This process provides a reference that can be reiterated throughout the unit as students learn new material or ideas that are relevant to the completion of their unit projects.
Brainstorming about what we know about a problem or project and what we need to find out to move forward in a project is often a good starting point when faced with a new problem. This type of questioning provides a basis and relevance that is useful in other energy science and technology units. In this unit, the general problem that is addressed is the fact that Americans use a lot of energy, with the consequences that we have a dwindling supply of fossil fuels, and we are emitting a lot of carbon dioxide and other air pollutants. The specific project that students are assigned to address is an aspect of this problem that requires them to identify an action they can take in their own live to reduce their overall energy (or fossil fuel) consumption.
The Seven Steps of Problem Solving
1. Identify the problem
Clearly state the problem. (Short, sweet and to the point. This is the "big picture" problem, not the specific project you have been assigned.)
2. Establish what you want to achieve
- Completion of a specific project that will help to solve the overall problem.
- In one sentence answer the following question: How will I know I've completed this project?
- List criteria and constraints: Criteria are things you want the solution to have. Constraints are limitations, sometimes called specifications, or restrictions that should be part of the solution. They could be the type of materials, the size or weight the solution must meet, the specific tools or machines you have available, time you have to complete the task and cost of construction or materials.
3. Gather information and research
- Research is sometimes needed both to better understand the problem itself as well as possible solutions.
- Don't reinvent the wheel – looking at other solutions can lead to better solutions.
- Use past experiences.
4. Brainstorm possible solutions
List and/or sketch (as appropriate) as many solutions as you can think of.
5. Choose the best solution
Evaluate solution by: 1) Comparing possible solution against constraints and criteria 2) Making trade-offs to identify "best."
6. Implement the solution
- Develop plans that include (as required): drawings with measurements, details of construction, construction procedure.
- Define tasks and resources necessary for implementation.
- Implement actual plan as appropriate for your particular project.
7. Test and evaluate the solution
- Compare the solution against the criteria and constraints.
- Define how you might modify the solution for different or better results.
- Egg Drop - Use this demonstration or activity to introduce and use the problem solving method. Encourages creative design.
- Solving Energy Problems - Unit project is assigned and students begin with problem solving techniques to begin to address project. Mostly they learn that they do not know enough yet to solve the problem.
- Energy Projects - Students use what they learned about energy systems to create a project related to identifying and carrying out a personal change to reduce energy consumption.
The results of the problem solving activity provide a basis for the entire semester project. Collect and review the worksheets to make sure that students are started on the right track.
Learn the basics of the analysis of forces engineers perform at the truss joints to calculate the strength of a truss bridge known as the “method of joints.” Find the tensions and compressions to solve systems of linear equations where the size depends on the number of elements and nodes in the trus...

Through role playing and problem solving, this lesson sets the stage for a friendly competition between groups to design and build a shielding device to protect humans traveling in space. The instructor asks students—how might we design radiation shielding for space travel?
A process for technical problem solving is introduced and applied to a fun demonstration. Given the success with the demo, the iterative nature of the process can be illustrated.
The culminating energy project is introduced and the technical problem solving process is applied to get students started on the project. By the end of the class, students should have a good perspective on what they have already learned and what they still need to learn to complete the project.

Hacker, M, Barden B., Living with Technology , 2nd edition. Albany NY: Delmar Publishers, 1993.
Other Related Information
This lesson was originally published by the Clarkson University K-12 Project Based Learning Partnership Program and may be accessed at http://internal.clarkson.edu/highschool/k12/project/energysystems.html.
Contributors
Supporting program, acknowledgements.
This lesson was developed under National Science Foundation grants no. DUE 0428127 and DGE 0338216. However, these contents do not necessarily represent the policies of the National Science Foundation, and you should not assume endorsement by the federal government.
Last modified: August 16, 2023

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This lesson uses the strategy "Act It Out" to solve problems involving patterns.
10.7. Operations and Algebraic Thinking—. 4.OA.C.5. MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES. MP4, MP7, MP8. Unlock l t the Problem l. You can find patterns in fabric, pottery, rugs, and wall coverings. You can see patterns in shape, size, position, color, or number of figures. Sofia will use the pattern below to make a wallpaper border.
Problem Solving . Title: Go Math! Practice Book (TE), G5 Created Date: 3/29/2016 4:08:51 PM
Eureka Math Grade 7 Module 3 Lesson 10 Example Answer Key. Example 1. Estimate the measurement of x. ___. In a complete sentence, describe the angle relationship in the diagram. Answer: ∠BAC and ∠CAD are angles on a line and their measures have a sum of 180°. Write an equation for the angle relationship shown in the figure and solve for x.
11 cm 1.7 ft 3 6 m Example 1 (page 576) Quick Check 3 1 2(10)(10) 1 2bh 1 4 90 360 A B O 10 in. mAB 0 360 3 EXAMPLEEXAMPLE Area of sector Area of triangle Area of segment segment of a circle. Segment of a circle This pizza is cut into two segments. Practice and Problem Solving EXERCISES For more exercises, see Extra Skill, Word Problem, and ...
LESSON 10-7 Problem Solving Volume of Pyramids and Cones 1. A regular square pyramid has a base area of 196 meters and a lateral area of 448 square meters. What is the volume of the pyramid? Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 2. A paper cone for serving roasted almonds has a volume of 406 cubic centimeters. A smaller cone has half the ...
Lesson 10: Angle Problems and Solving Equations. Student Outcomes. Students use vertical and adjacent angles and angles on a line and angles at a point in a multi-step problem to write and solve simple equations for an unknown angle in a figure. Related Topics: More Lesson Plans for Grade 7 Common Core Math. Lesson Notes.
Curriculum / Math / 10th Grade / Unit 7: Circles / Lesson 10. Circles. Lesson 10 Math. Unit 7. 10th Grade. ... and activities aligned to the objective of the lesson that can be used for additional practice or to create your own problem set. ... MARS Formative Assessment Lessons for High School Solving Problems with Circles and Triangles ...
Use Algebraic Expressions - Lesson 7.6. Problem Solving - Combining Like Terms - Lesson 7.7. Generate Equivalent Expressions - Lesson 7.8. Identify Equivalent Expressions - Lesson 7.9. Thanks for your donation! Every little bit helps me help you! :-) Independent and Dependent Variables - Lesson 9.1.
Using If-Then Moves in Solving Equations (Continued) Previous Lesson. in this Series. ... adjacent angles, angles on a line, and angles at a point in a multistep problem to write and solve simple equations Downloads. ... Grade 7 Mathematics Module 3, Topic B, Lesson 10: Student Version; Grade 7 Mathematics Module 3, Topic B, Lesson 10: Student ...
Our resource for Ready Mathematics: Practice and Problem Solving Grade 7 includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems, you can take the guesswork out of studying and move forward with confidence. ...
Count Equal Groups - Lesson 3.1. Relate Addition and Multiplication - Lesson 3.2. Skip Count on a Number Line - Lesson 3.3. Problem Solving - Model Multiplication - Lesson 3.4. Model with Arrays - Lesson 3.5. Commutative Property of Multiplication - Lesson 3.6. Multiply with 1 and 0 - Lesson 3.7. Time to the Minute - Lesson 10.1.
Getting the Most from Each of the Problem Solving Activities. When students participate in problem solving activities, it is important to ask guiding, not leading, questions. This provides students with the support necessary to move forward in their thinking and it provides teachers with a more in-depth understanding of student thinking.
7.RP.A.2.A — Decide whether two quantities are in a proportional relationship, e.g., by testing for equivalent ratios in a table or graphing on a coordinate plane and observing whether the graph is a straight line through the origin. 7.RP.A.2.B — Identify the constant of proportionality (unit rate) in tables, graphs, equations, diagrams ...
How we can solve problems by using the information in a graph, table, or chart, comparing amounts to answer questions, writing number sentences (equations) f...
7. 1 8. The total of the probabilities for all possible events must be 1. 9. No; the range of functions can vary widely. A sum of 1 is only required for a probability function such as the one used here. 10. 9 16 11. 5 16 12. 3 16 13. 3 8 14. 5 8 15. 0 Problem Solving 1. 1 4 2. 3 3. 144 tiles 4. 17:1 5. B 6. J 7. A Reading Strategies 1. a. they ...
10. Connect students with change makers. Entrepreneurs all over the world are using the processes students use in GPS: The Series. Put your students in touch with them to bring concepts to life. GPS: The Series offers six videos called "The Putri Files", where GPS team leader Putri interviews these entrepreneurs.
This Go Math video covers the Essential Question: How can you use the strategy guess, check, and revise to solve problems with fractions? This is a CHALLENGI...
TED-Ed lessons on the subject Problem Solving. TED-Ed celebrates the ideas of teachers and students around the world. Discover hundreds of animated lessons, create customized lessons, and share your big ideas. ... Lesson duration 10:42 56,518 Views. 05:18. Mathematics Can you solve the time traveling car riddle? Lesson duration 05:18 ...
Introduction. (10 minutes) Bring students together in a circle, either seated or standing. Bring blocks with you to the circle. Show the student the blocks and ask them to watch you build a tall castle. After you build it, bring out two figurines that you would like to play with in the castle. Say out loud, "Hmm....there seems to be a problem.
1. Identify the problem. Clearly state the problem. (Short, sweet and to the point. This is the "big picture" problem, not the specific project you have been assigned.) 2. Establish what you want to achieve. Completion of a specific project that will help to solve the overall problem.
This lesson uses fraction rectangles and fraction pies to "Act Out" the problems when adding fractions.
Problem Solving • Multistep Fraction Problems 8 children COMMON CORE STANDARD—4.NF.B.3d Build fractions from unit fractions by applying and extending previous understandings of operations on whole numbers. Practice and Homework Lesson 7.10 4. WRITE Math Write a word problem that involves adding or subtracting two fractions.