

Aligning human resources and business strategy
Reading time: about 7 min
You have to consider many factors when you create a go-to-market or business strategy. From brand messaging to product roadmaps to sales processes, effective business strategies also rely on the input of lots of people across many departments.
Few departments have a better bird’s-eye view of the entire organization than human resources. HR professionals can see both why a strategy exists and how it’s developed and implemented. Yet, too often, HR departments don’t have a seat at the strategy table. Let’s take a look at how HR can help shape business strategy and bring it to life.
Why HR should get involved with setting corporate strategy
Today, business moves faster than ever—it’s a platitude, but it’s still true. Technologies, industries, and consumers themselves continually evolve in a digitally-driven market, and companies continuously shift their strategic focus to keep pace.
This culture of change has a significant impact on people. Every business decision has a real-life impact, and HR departments are specially equipped to inform strategy and help employees navigate the resulting changes.
Consider these reasons why it’s so important for HR to align with business strategy:
- Move in lockstep with the rest of the company: Goals are always more achievable when there is universal buy-in and alignment across teams.
- Give HR initiatives a strategic focus: In today’s changing economy, there are countless ways to recruit, train, attract, invest in, and support employees. But it’s impossible to tackle every initiative all at once. Aligning with business strategy gives HR a strategic focus and helps prioritize goals.
- Secure the right talent: Good talent is always valuable, but companies may need to invest in different skill sets or roles at different times. Understanding the strategic goals of the business will help HR attract and retain the right talent at the right time.
What role human resources plays in strategic planning
So how does HR become part of the broader business decision-making process? How do HR departments move from a reactive, service-oriented function to a more executive-level, strategic one?
It starts with setting clear objectives for the department and strong values for the entire organization. Companies with documented values are less likely to ignore the real-life impact of any strategy shifts or big decisions. Consider these steps as you begin.
1. Align and set your HR goals
The main strategic role of HR is to create goals to help meet key business objectives. Goals may vary depending on the company’s strategic plan, but focusing on HR fundamentals is an excellent place to start. Here are some areas of HR most commonly affected by broader strategic business shifts.
Organizational structure
The way companies are organized largely depends on their current strategic objectives and growth stages. If a company is in a high-growth stage, it may have a sales-driven culture with more sales employees and sales executives in decision-making roles. Mature companies with a retention-focused strategy may hire more customer success roles.

See 7 types of organizational structures—along with pros and cons for each—to find one that fits your strategy.
Employee compensation
Maybe current business goals are more focused on employee retention or culture-building. Conversely, perhaps the company needs to cut costs. In either case, compensation structure may be an important consideration. When HR is aligned and informed on these goals, they can make strategic decisions to help the organization meet them.
Employee development
Depending on the business goals and immediate initiatives, it may be necessary to train employees on new skill sets. Some employees may resist additional roles and responsibilities, so the role of HR in these situations is to both evangelize additional training and ensure teams are developed to keep pace with shifting needs.
Performance reviews
Change management .
As a people-focused department, HR often has the best pulse on employee sentiment throughout the organization. HR departments can encourage employees to share their feedback on new business strategies or technology investments to ensure any changes or strategic shifts make sense from an operational perspective.
2. Formulate specific actions to hit those goals
Once you’ve aligned and set goals, it’s time to develop action plans to execute your HR strategic vision. Focus on developing and improving processes for recruiting, hiring, employee development, and performance reviews.
When you develop an action plan, you'll need to have a clear understanding of your organization’s current structure and identify any gaps or shortcomings in your processes. Where should you invest more in recruiting? If budgets are tight, what training or employee development programs could maximize the productivity and effectiveness of your existing talent? The ability to visualize where every player fits into the larger organization can help HR departments align employees to business strategy, maximize efficiency, and see data in context to drive better decisions. Org charts and related visuals can help HR departments optimize organizational structure at every level and make better decisions, such as:
- Assigning employees where their skills can make the most significant impact
- Making informed decisions about pay, equity, and performance
- Modeling current and future org structures to determine how best to scale your business

Does your organization needs to hire new talent to meet its strategic goals? See how to develop a staffing plan.
3. Track and measure performance
Historically, the role of HR has stayed in the “softer,” people-focused side of the business. However, people analytics are now the new HR, and HR departments are just as responsible for reporting on the performance of their initiatives as any other department.
With human resource alignment around data-driven goals, HR leaders can ensure that decision-making not only aligns with strategic business objectives but also helps drive those goals. HR leaders can analyze data from sales, marketing, and accounting to break down departmental silos and better align with overall business goals.
According to a Bersin by Deloitte study, data-driven HR teams are four times more likely to be respected by their business counterparts, which can result in more input in strategic decision-making. By combining departmental data and HR data and visualizing it all in a single workspace, HR departments can better align their decisions to business strategy. Consider the ways these types of people analytics can impact the broader business:
Employee analytics
Measure the performance of all the HR initiatives in terms of cost, time, performance, then use a dashboard to track recruiting times, onboarding speed, employee satisfaction, and employee salaries. This data-driven approach to people management helps HR departments evaluate pay disparities, track employee retention, identify trends, and see critical employee metrics that will provide quick insights for better decision-making.
All this gives you the chance to onboard new employees more efficiently, improve employee satisfaction, and reduce retention.
Talent analytics
Today, effective talent acquisition goes way beyond budget and headcount. HR departments can rely on algorithmic data to quickly sift through deep pools of qualified applicants to attract and retain top talent.
Today, effective talent acquisition goes way beyond budget and headcount. HR departments can rely on algorithmic data to quickly sift through deep pools of qualified applicants to attract and retain top talent. This allows you to identify and attract high-quality employees and improve your workforce planning.
Predictive analytics
Set up indicators to see when an employee is at risk of leaving the company. HR departments can use data to identify risk facts and predict employee churn and how this will affect the company. This leads to better retention and employee planning
Invest in better people planning
Modern human resources departments manage much more than hiring, onboarding, and benefits. Aligning HR with business strategy can boost employee satisfaction and performance, ensure teams are aligned to help the business achieve its strategic objectives and increase their influence and decision-making power across the organization.

Align teams, boost efficiency, and drive better decisions with Lucidchart.
About Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles
4 steps to strategic human resource planning.
Many CEOs believe that their employees are the most important factor in their company’s economic success, so if you want to succeed, find and keep the best talent. Learn how to develop your strategic human resource plan.
What does HR actually do? 11 key responsibilities
Everyone knows that HR is an important department in your organization, but few employees know why. Read our in-depth description of what the HR department does (or what they should be doing) to meet the needs of employees.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
By registering, you agree to our Terms of Service and you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Privacy Policy .
CUSTOMER SUCCESS STORY
Productive Serves Makerstreet as a Single Source of Truth
Makerstreet is an Amsterdam-based collective of agencies with over 300 employees in four offices.
Agency Valuation Calculator Report
See the 2023 Global Agency Valuations Report
Book a Demo
Try Productive
Comparisons
{{minutes}} min read
Human Resource Planning: Definition & Top Strategies
Lucija Bakić
April 4, 2024
Human resource planning is a key strategy for ensuring long-term business sustainability and resilience.
In this guide, we’ll explore the essentials of human resource planning (HRP), why it’s so important, and the best practices to start your human resource planning process. To learn more about the broader process of resource management, read our guide to business resource planning . Key Takeaways
- HRP is a process that ensures that companies have enough capacity to meet customer demands and business goals.
- The main steps of the process include analyzing current availability, forecasting future demand, identifying capacity gaps, and developing and monitoring HRP strategies.
- Some of the main challenges include ensuring the accuracy of your forecasting with reliable data, maintaining the balance between billable work and capacity building initiatives, and promoting collaboration and transparency.
- The right capacity planning solution can help you address the above with automation features, real-time data, and predictive analytics.
What Is Human Resource Planning (HRP)?
Human resource planning (HRP) is a process used to ensure that businesses have employees with the right skills, at the right time, and with the appropriate capacity to meet strategic goals. Some practical examples of HRP workflows for various businesses include:
- An e-commerce business forecasting the need for IT capacity increases according to seasonal trends and scaling their infrastructure and support team.
- A design agency identifying higher demand for digital media through benchmarking and developing strategies to upskill and reskill its employee pool.
- A law firm initiating a succession planning strategy for the impending employee retirements by developing internal leadership candidates and recruiting external talent.
Why Is HRP Important? Top 4 Benefits
According to research by the Work Institute, 78% of the reasons for voluntary turnover could have been prevented by the employer if identified and addressed on time. Human resource planning helps businesses increase employee engagement and drive various improvements by:
1. Maintaining a Qualified Workforce
HRP aligns talent capabilities with organizational goals through talent acquisition, training, and development initiatives. Ensuring you have a skilled workforce to meet future workforce requirements reduces the risk of inefficient workflows and supports daily business operations (learn more about the best operations strategy examples ). Investing in employee talent and skills can also help increase employee engagement and satisfaction.
2. Improving Risk and Change Management
HRP is a proactive approach that focuses on identifying issues before they occur. Analyzing trends and forecasting future needs helps businesses create contingency plans for various scenarios. This can include high-impact external changes, such as technological advancements, or internal disruptions, like leadership transitions.
Optimize Your Human Resource Planning
Productive is the all-in-one software for workload balancing, scenario planning, and financial management, tailored to businesses of all shapes and sizes.
Start Free Trial
Book a demo
3. Ensuring Your Business Is Competitive
HRP keeps businesses competitive by helping them attract the right talent and ensuring that current employees are skilled and engaged in the workplace. It helps companies adapt to changes quickly and efficiently, fostering the agility and proactiveness needed to stay ahead of industry trends and competitors.
4. Optimizing Workforce Costs
HRP optimizes business costs by providing balanced employee utilization so that your agency isn’t spending excess money on non-productive labor costs. It also ensures that your business can do more work with adequate supply. Finally, HRP reduces the chance of unexpected resource gaps through effective forecasting, minimizing the need for last-minute hiring or overtime work. You can also check our guide to the capacity management process to learn more.
ON DEMAND WEBINAR
Utilization and forecasting in crisis times.
Learn all about leading your agency through uncertain times by tracking your utilization rate with Productive and The Agency Collective.
The Main Steps of Human Resources Planning
The key steps of HRP include:
- Workforce analysis to determine your company’s current human resource capacity.
- Demand forecasting to future resource demand based on industry trends and internal needs.
- Gap analysis includes finding potential roadblocks in your HRP process and developing strategies to address them.
- Implementation and monitoring of your human resource strategies, usually by tracking key performance indicators.
Analyzing Current Availability
Workforce analysis involves a comprehensive evaluation of the current workforce’s size, skills, and capabilities. It assesses aspects such as:
- Employee productivity
- Job satisfaction
- Skill sets, including technical and soft skills
- Turnover rates
These metrics are used to identify your organization’s strengths and weaknesses. This is the foundation on which you’ll develop actionable steps to improve your HRP processes.
The utilization rate is the key metric for visualizing productivity — use Productive for real-time insights
Projecting Future Demand
Projecting future demand involves estimating the human resource requirements needed for an organization to meet its future goals. This forecast considers factors such as business growth, market expansion, technological advancements, and changes in operational processes. Three tools that are used in this process are:
- Ratio analysis , where historical data on the relationship between business metrics and workforce size is used to predict future staffing needs.
- Trend analysis , which examines patterns in the organization’s workforce data over time.
- Comparative analysis, whether by comparing internal resource planning practices across multiple projects or benchmarking your performance against competitors.
Another potential strategy is utilizing real-time data, such as forecasting charts that depict the impact of resource scheduling on agency analytics.
Productive’s forecasting charts let you predict your company’s revenue and profit margins
Gap Analysis
Gap analysis compares future human resource needs against the current workforce’s capabilities to identify discrepancies or gaps. A way to conduct gap analysis is to monitor where previous projects went wrong to pinpoint inefficiencies in your workflows, such as miscommunication or a deficit of specific skills. You can do this by checking estimated vs real completion times for various tasks — ERP solutions can deliver these insights with time tracking features. Then, by examining your upcoming projects or initiatives, you can identify and forecast potential areas where similar imbalances may occur.
Developing and Implementing Strategies
The final step is developing and implementing HR strategies to cover your company’s specific needs and requirements. These strategies may include:
- Creating a resource plan: A resource plan is an in-depth document that contains information on your employees, their availability, and their scheduled time. It helps businesses follow strategic objectives and monitor their ongoing processes.
Get an in-depth overview of your business resources and their availability
- Employee engagement and retention strategies: For example, drafting career development plans, introducing new benefits packages and competitive compensation, and promoting a healthy organizational mindset.
- Implementing modern software: Resource planning tools can support various steps of the HRP process, with features such as time off management, billable hours tracking, financial forecasting, real-time reporting, workflow automations, and more.
Best Practices for Effective HRP
Once you’ve pinpointed potential gaps and developed strategies to drive improvements, what are some best practices to ensure they stick?
Monitoring Your Progress
Whichever initiatives you decide to implement, monitoring them through capacity management metrics is necessary to assess their effectiveness. However, keep in mind that while business metrics are important, some benefits of HRP may be hard to quantify. This includes better work-life balance and improved working environment.
Regular Review
HRP can take a long time to provide results. Agility and flexibility are needed to make sure that your strategies can stay aligned with changing business needs and priorities. Regular review helps identify where your strategies have gone off track to implement timely changes.
Continuous Improvement
HRP is an ongoing process. As such, your strategies will need to evolve alongside your business goals and circumstances. Incremental improvements are always better than sudden, expansive changes — consistently seeking feedback and analyzing outcomes is a way to ensure your HRP strategies remain effective over time.
Types of HR Planning
There are different types or techniques associated with HR planning. Here are some common terms and how you can differentiate them:
Hard vs Soft HR Planning
- Hard HR Planning focuses on quantitative aspects of human resource management, such as headcount, costs, and labor allocation. This approach often involves in-depth data and forecasting for informed decision-making.
- Soft HR Planning considers qualitative factors of workforce management, such as engagement, development, and well-being. It’s less focused on data and more on fostering a committed and resilient workforce.
Short-Term vs Strategic HRP
- Short-term HRP is more of a reactive approach that addresses immediate staffing needs and focuses on resolving urgent issues. It typically spans a timeframe of up to one year.
- Strategic HRP is a long-term approach that aligns workforce planning with the organization’s future goals and strategies. It involves forecasting workforce requirements, sustainable talent management, and other proactive strategies for business success.
Employee Reskilling vs Upskilling
- Reskilling involves training employees in new skills and capabilities to help them transition to different roles within the company.
- Upskilling focuses on enhancing the current skills and competencies to improve performance, stay competitive, and meet job requirements.
To learn more, check out our article on the topic: what is capacity building and the best strategies for maintaining a skilled and satisfied workforce.
Future Trends in HR Planning
- Remote work is here to stay. According to survey results, 63% of professionals are willing to take a pay cut to work remotely (FlexJobs). If possible, consider including it as one of your benefits to drive a competitive advantage.
- In general, employee well-being initiatives are becoming more and more popular. This can include more flexible hours, hybrid or remote work, health insurance plans, as well as various fitness and wellness programs (learn more about workload management ).
- 72% of professionals agree that all forms of skill-based hiring are more effective than resumes. While the resume is still used to filter the pool of applicants, work-related tasks and technical questions have proven to be the more efficient and cost-effective way of hiring candidates (Test Gorilla).
- When it comes to daily workflows, 60% of professionals believe that automation helps them fight burnout and work-related stress. It allows for a more flexible work schedule, helps them be more organized at work, frees up their tasks for work they enjoy, and more (Zapier). Consider tools that can provide no-code automations to streamline day-to-day work.
The Challenges of Human Resource Planning
Now that we’ve gone through the main steps of the HRP, it’s time to address some of its main challenges:
- Accurate forecasting: Predicting future needs accurately can be a challenge in itself. Not only does it require having an in-depth understanding of your business circumstances, but it’s also sensitive to changes in market demand and economic conditions.
- Maintaining a flexible workforce: Maintaining a versatile and skilled workforce requires careful management of work hours. This ensures that profitability isn’t compromised, and at the same time, avoids situations where training is neglected entirely for billable work. This balance between billable vs non-billable time is crucial for sustainable organizational success.
- Aligning HR Strategy with Business Goals : Keeping track of the overarching business strategy in HRP can be hard, especially in large or rapidly evolving organizations. It requires transparent communication, cross-functional collaboration, and a deep understanding of the organization’s long-term objectives and the role of the workforce in achieving them.
The Solution: Utilizing Software for Enhanced HR Planning
A way to address these potential challenges is using tools with HR and resource management capabilities . Modern software provides a way to visualize and forecast employee hours, activities, and their impact on business financials for more informed decision-making. It also helps businesses view project progress in real time to streamline stakeholder collaboration.
Adapt your project management to your working preferences with Productive
An example of such a tool is Productive , with key HRP features including:
- Time tracking
- Resource scheduling
- Workload balancing
- Time off management
- Financial forecasting
Book a demo today to discover how Productive can help drive efficient human resource management. You can also check this article to learn more about the benefits of ERP systems.
What is meant by human resource planning?
Human resource planning (HRP) is the strategic process of ensuring your business has the correct number of skilled employees to meet company goals. It involves talent management, employee performance and data analysis, needs forecasting, and more.
What are the 5 steps in human resource planning?
The five main steps of human resource planning include identifying current organizational availability, demand forecasting, capacity gap analysis, strategy development and implementation, and results monitoring and analysis.
What are the 3 key areas of human resources planning?
The 3 key areas of human resource planning (HRP) include workforce forecasting, talent management, and gap analysis. Workforce forecasting involves analyzing current availability and predicting the future needs of the workforce. Talent management encompasses various strategies, from recruitment, training, and development to succession planning. Gap analysis involves pinpointing areas of improvement by identifying where capacity fell short of meeting demand (skills, quantity, time, etc.).
Why is human resources planning important?
Human resource planning (HRP) is important because it ensures that the workforce is aligned with the organization’s strategic goals. It helps businesses get the most out of their human resources, both by improving acquisition strategies, developing current talent, and increasing retention. HRP also supports organization agility, flexibility, and resilience by building a well-skilled and satisfied workforce.
Connect With Agency Peers
Access agency-related Slack channels, exchange business insights, and join in on members-only live sessions.
Content Specialist
Related articles
Agency workflows 101: the best process for agencies.
Agency Management
Capacity Management: Best Practices for Agency Growth
Project resource management: the ultimate guide.
Questions not answered yet? Our sales is here to help
+1 (415) 287-3073
Integrations
Automations
Permissions and User Access
Software Development
Marketing Agency
Business Consultancy
Design Studio
In-house Team
Customer Stories
End-to-end Agency Management
Agency Resource Management
Product Updates
Agency Valuation Calculator
The Bold Community
Building Productive
Brand Guidelines
Trust Center
© 2024 The Productive Company, Inc.
Privacy Policy
Terms & Conditions
We need your consent to continue
Necessary cookies
Cookies for the basic functionality of the Productive website.
Functional cookies
Cookies for additional functionality and increased website security.
Targeting cookies
Advertising and analytics service cookies that create day-to-day statistics and show ads on their site and on the advertiser’s partners websites.
Save changes
Manage cookies and help us deliver our services. By using our services, you agree to our use of cookies.
Try Productive for free
Free 14-day trial. No credit card required. Cancel any time.
Already using Productive? Sign in with an existing account

Enter your information to receive our Learning and Development Offerings Catalog

- Erin Aldridge
- February 16, 2023
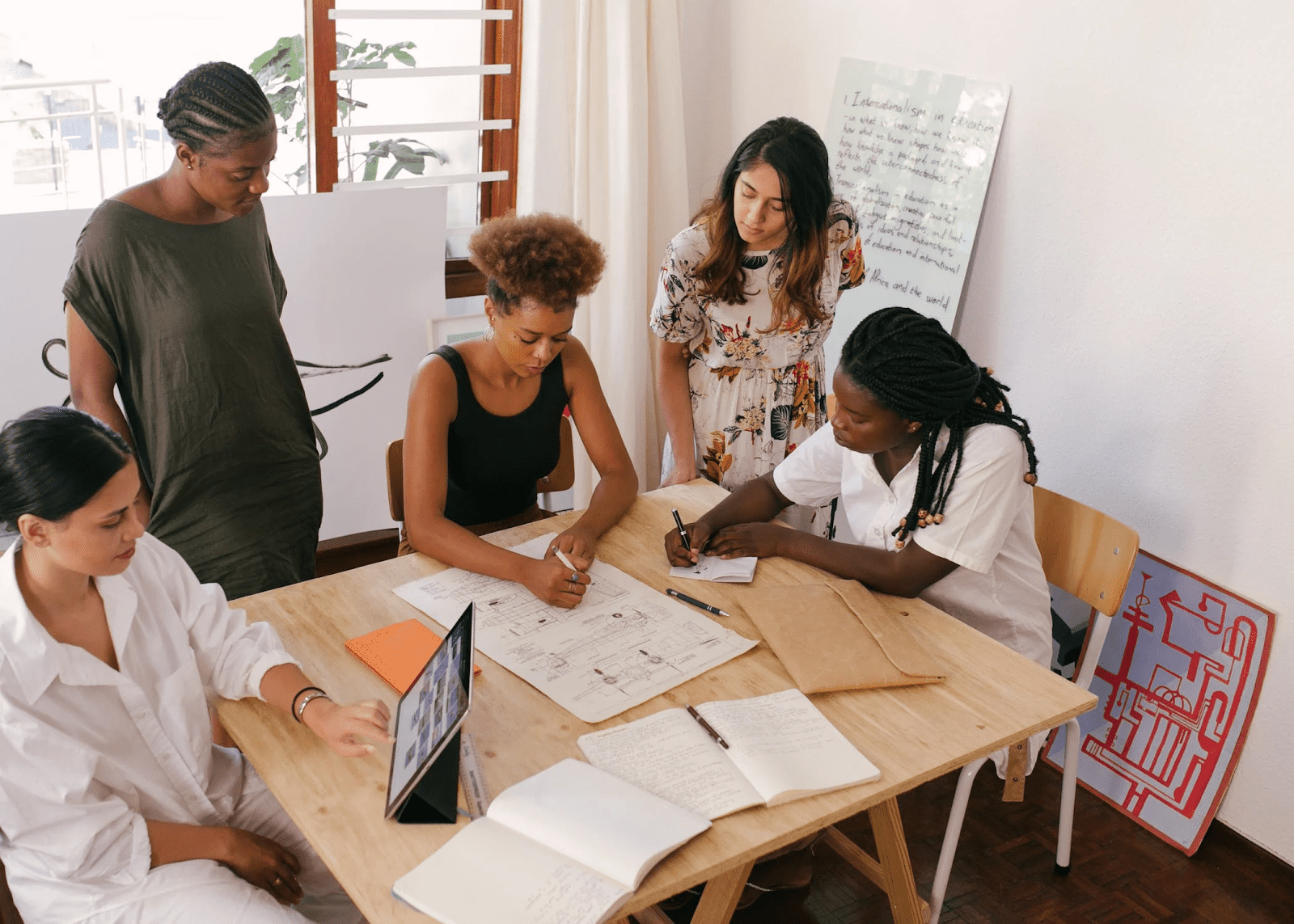
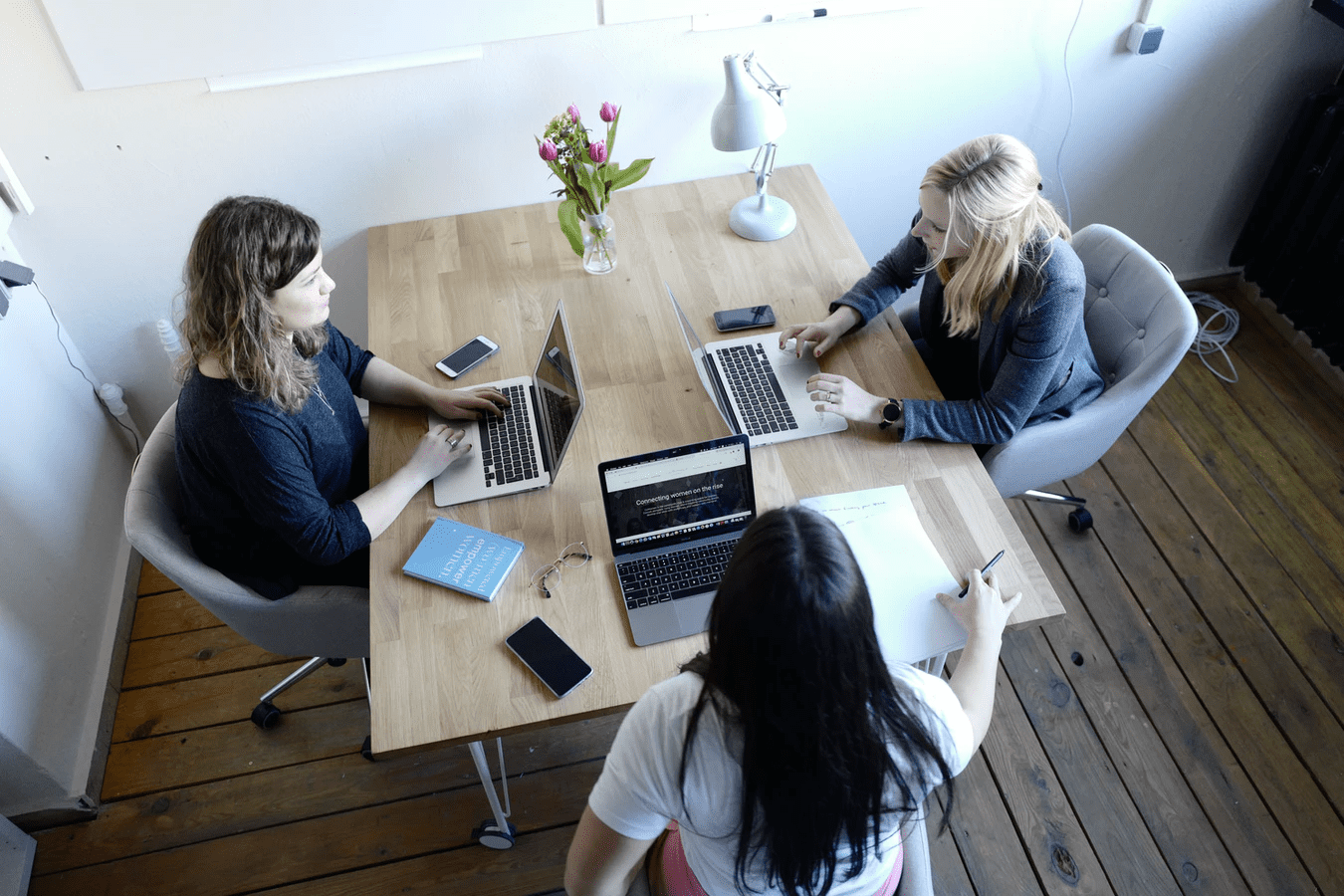
Align Human Resources (HR) with Business Strategy
A business strategy consists of clearly defined plans, actions, and goals that map how a business will use its products or services to compete in one or more markets. Compared to most business functions, Human Resources (HR) intersects with all other departments, making it a vital part of any good business strategy.
More businesses are giving HR a seat at the leadership table and tapping into workforce data to identify and reach critical business objectives. Companies that weave HR activities such as recruitment, retention, and training into their overall business strategy gain a competitive edge that sets them up for long-term success. This article will explain the role of human resources in strategic planning, provide examples demonstrating how to align human resources with business strategy, and more.

Discover the Top Training Trends for 2024
Stay ahead with the latest trends and strategies in corporate training.
On this page:
The Role of Human Resources in Strategic Planning
How to align hr strategy with business strategy, examples of aligning hr strategy with business strategy.
HR is often viewed as a day-to-day administrative business unit responsible for managing talent acquisition efforts, employee benefits, performance management, training and development , compensation, and more. Given the rapidly changing nature of business, HR can no longer operate in a silo. Technology is changing entire industries at a fantastic speed and altering labor markets in a way that has a real impact on people.
With this change comes opportunity, and it requires leveraging human resources as a long-term strategic partner in business. HR can communicate business goals to personnel and help them thrive amid subsequent organizational changes. Using HR to coordinate strategic initiatives directly improves a business’s ability to remain competitive.
Other benefits of aligning HR with the business strategy at large include:
- Improving communication between leaders and the rest of the business
- Helping maintain employee and business focus on strategic goals
- Augmenting productivity
- Promoting employee engagement and retention
Human Resources can no longer be viewed as just a service-oriented department but rather an essential partner in business decision-making. Whether defining business goals and forming strategic plans starts with the executive team, the HR team, or another department, HR will play an essential role in achieving success.
Dramatic changes to the workplace are already underway, from increasing remote work to rising healthcare costs. Executing a strategic plan requires understanding these challenges. Knowing the long-term business objectives allows the HR department to navigate these challenges in a way that contributes to the business.
To successfully align their efforts with business strategy, HR experts must complete the following:
- Understand the business strategy and how it impacts other departments
- Evaluate external and internal workforce conditions
- Plan and implement the HR strategy that includes key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Automate applicable tasks
- Measure and evaluate results

A typical HR team is responsible for a range of business operations that impact how all other business units operate. Here are a couple of examples demonstrating what it means to align HR initiatives with business strategy:
Example 1: Organizational Restructuring
A corporate restructure can take many forms, from moving to a hybrid work model to consolidating departments or choosing a new corporate headquarters. No matter what the organizational change is, it will impact all employees. The restructuring can make them fearful for job security, upend their work schedule, and require them to change teams.
HR should be looped into the goal of the restructuring and play a central role during the transition. If your business is moving towards remote work, HR can find the best technology and processes to help with the change. Are you opening an office in a new city? HR can find the best local talent and onboard them. Overall, aligning HR to the restructuring goal can help retain and recruit essential employees , ultimately preserving productivity and saving money.
Example 2: Employee Retention
In a competitive job market, employees can resign for many reasons. Better pay, flexible work options, and a better work/life balance are a few common reasons. Business leaders prioritizing employee retention should tap HR to execute a plan to stifle employee resignations. HR can run an employee satisfaction survey to determine why staff leave the company and recommend changes to address them.
Example 3: Social Responsibility
More companies are prioritizing social responsibility and looking to make it a central part of their corporate values. Baking social responsibility into a business’s DNA requires significant input from the Human Resources department. Depending on the specific goals the company wants to achieve, HR might introduce diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) training, organize volunteer dates with local charities, or establish a plan for integrating environmentally-friendly business practices.
Example 4: Crisis Management
Nearly every business received a wake-up call during the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Many had to significantly cut costs, including laying off employees, dealing a blow to morale and the bottom line. For businesses eager to be better prepared for potential crises, HR should take the lead by creating a business continuity plan (BCP) to mitigate disruptions in the case of disaster.
Keeping pace with the constant change affecting business requires using HR more strategically than ever. The core responsibilities of managing employee engagement, training, performance, and benefits will always be there. Aligning HR with the business strategy is essential for unlocking productivity, sustaining growth, achieving corporate objectives, and remaining competitive. Today’s HR function is more than just administrative cost-centers. It is a crucial partner that keeps the entire business working towards the same goals.
Receive our newsletter to stay on top of the latest posts
- Business Analysis
- Corporate Training
- Cybersecurity
- Data Analysis
- Digital Transformation
- Human Resources
- Learning & Development
- Project Management
- Technical Training
Related Blog Posts

- Uncategorized
The Critical Role of Soft Skills in Today’s Workplace: Addressing the Gap

Communication Training Programs for Employees: What They Are & Why They Matter

Real-Life Examples of the Skills Gap
Training and development.
Training Solutions Areas of Expertise Our Brands
Resources and Insights
Blog Webinars Resources
- (877) 243-6690
- [email protected]
- Mon - Fri | 8 AM - 6 PM EST
SHRM: alignment of HR function with business strategy
Strategic HR Review
ISSN : 1475-4398
Article publication date: 3 June 2014
Bagga, T. and Srivastava, S. (2014), "SHRM: alignment of HR function with business strategy", Strategic HR Review , Vol. 13 No. 4/5. https://doi.org/10.1108/SHR-03-2014-0023
Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Article Type: Strategic commentary From: Strategic HR Review, Volume 13, Issue 4/5
Thought leaders share their views on the HR profession and its direction for the future
Teena Bagga and Sanjay Srivastava
SHRM Connotation
Strategic human resource management (SHRM) is, indeed, one of the most momentous concepts in the field of business and management today. The idea of SHRM is to promote high performance workplaces and human capital management. SHRM can be defined as the linking of human resources (HR) with organisations’ strategic goals and objectives so as to improve business performance and develop organisational culture that nurture innovation, flexibility and competitive advantage. In an organisation, SHRM means accepting and involving the HR function as a strategic partner in the formulation and implementation of the company’s strategies through HR activities such as recruiting, selecting, training and rewarding personnel. It basically centers on HR programs with long-term objectives i.e. instead of focusing just on internal HR issues, the major focus is on addressing and solving problems that affect people management programs in the long run. Therefore, the primary goal of strategic HR is to increase employee productivity and to identify key HR areas where strategies can be implemented in the long run to improve the overall employee motivation along with productivity. Strategic orientation of human resource management (HRM) is important for all organisations irrespective of its size and domain. It simply requires the alignment of every HR function with business strategy. It establishes relationship between HRM and strategic management of the organization and facilitates the HRM to change its image as a “cost center” to that of a “strategic business partner”. Thus, the SHRM can be defined as the organisations action plan to align HRM with strategic business objectives so that the competitive advantage can be achieved through its skilled, committed and well-motivated workforce. This can only be possible if every HR function is strategically aligned.
Strategic human resource planning
Human resource planning (HRP) is a process of analyzing and identifying the need for and availability of HR so that the organisation can meet its objectives. The need for HRP is to reduce the significant lead time between recognition of job requirement and getting a qualified person to fill that need. This means HR is required to have an idea of the job market and how it can match to hiring needs as no organization can meet its goals without recruiting talented workers. Hiring, indeed, is an important aspect of HRP, as it provides the doorway for bringing in new employees and choosing individuals suited to the company’s culture and requirement. During hiring, the HR department looks for an applicant who specifically fits the job criteria or someone who is the most versatile individual. However, today HRP is viewed as a strategic operational process and its focus has shifted from traditional Hiring and Staffing to towards forecasting and succession planning that can handle different contingencies which intern impacts the success of business operations. Effective HRP can reduce turnover by keeping employees apprised of their career opportunities within the company. The success of HRP depends on how meticulously the HR department can integrate effective HRP with the organization’s business planning process. Strategic human resource planning (SHRP) is based on close working relationships between HR department and line managers. SHRM can be defined as a deliberate attempt of HR deployment to empower the organization to meet organizational goals, objectives and consistencies. Succession planning plays an important role in strategic alignment if HRP. Through succession planning organisations recruit skilled employees, develop their knowledge, skills, and abilities further, and prepare them for advancement or promotion into ever more challenging roles. This process ensures that employees are constantly developed fill each needed role. So, that a talent pipeline is maintained.
Strategic recruitment and selection
The core responsibility of recruitment and selection processes is “identifying the right pool of talent for establishing the right candidates”. Earlier, recruitment and selection was considered as traditional function with standard approach where the focus was on person–job fit. However, now, organisations are aiming at person–organisation fit and, therefore, applicants are selected against organizational characteristics rather than job-specific criteria. Today, choosing the correct employee is, indeed, essential to the development an effective SHRM system.
Strategic recruitment and selection (SR&S) can be defined as strategic integration of recruitment and selection with long-term business objectives so that strategic demands of the organisations can be translated into an appropriate recruitment and selection specification. In this, the alignment of candidate’s objective and business’s objective has become must. However, not all the job positions in the company are strategic and are not critical for the business operation. The strategic recruitment is focused only on the key job positions in the organization. It is focused on the hiring of the job positions needed for the accelerated growth of the business. The strategic recruitment can be a separate process from the usual recruitment process for the mass job positions.
Strategic training and development
Increasingly high performing organizations today are recognising the need to use best training and development practices to enhance their competitive advantage. Training and development is an essential element of every business if the value and potential of its people is to be harnessed and grown. By definition, training and development refers to the process to obtaining or transferring knowledge, skills and abilities needed to carry out a specific activity or task. Strategic positioning of training and development directly promotes organizational business goals and objectives. Key business challenges require that organisation thoughtfully gauge their market position and determine the talent, skills and knowledge to be successful. By adopting a strategic approach to training and development rather than an unplanned and ad hoc one, training and development initiatives become more targeted, measurable and effective. The strategic training and development (ST&D) is all about identifying, designing and delivering training programmes to employees to make them capable of delivering in accordance with business strategy. In addition, the evaluation of the outcomes to check the effectiveness of the training programme based on planning to determine whether the training was effective to its contribution to the business strategy.
Strategic performance management
Traditional performance management systems often fail to deliver desired business objectives because communications from the top are not always clearly understood further down the line, leading to a mismatch between corporate strategy and how it is translated into targets at a team or individual level. Then, if the business goals and strategy and the employee motivation and culture are not in harmony, results certainly suffer. This missing link can be complemented by the strategic performance management (SPM) approach. Top management must address how they actually want to manage performance? What targets must be met and by when? And how do they want managers and employees to work to achieve them? It is important not only to identify HR competencies in accordance with the business needs and develop selection and development practices to secure those competencies but also to evolve and implement a performance evaluation plan that links the performance of the employees to the strategic goals. It is certainly essential to have strategically linked compensation system to improve firm performance and to retain employees with required competencies. SPM creates this link between the strategy and culture of an organization and its ability to manage employees’ performance to have direct impact on business performance. SPM is actually about strategy implementation to deliver value by delivering the desired outcomes in accordance with business strategy. SPM link the individual’s objectives and performance management, driving the skill and capability requirements and ensure its alignment to the core values of the organisation.
Strategic compensation and reward management
The main objective of compensation policy is to give the right rewards for employee performances, their skills, competencies, their knowledge and experience to attract and retain them. It is again certainly an important motivator to reward the employees for their market worth and also for achievement of the desired organisational results. However, the traditional compensation and reward system alone cannot ensure the fulfilment of the business objectives. Strategic compensation and reward management (SCRM) facilitate the alignment of compensation and reward policy with business, which can be achieved by taking a data-driven approach so that the pay and benefits are allocated to only those positions and workers that produce the greatest return. One of the healthier ways to motivate employees and reward the stellar performers is to have variable pay rewards system based upon the individual and team performance to their contribution towards the achievement of organisations business objectives.
About the authors
Teena Bagga is an Assistant Professor and Sanjay Srivastava are both based at Amity Business School, Amity University, Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India. Teena Bagga can be contacted at: mailto:[email protected]
Related articles
All feedback is valuable.
Please share your general feedback
Report an issue or find answers to frequently asked questions
Contact Customer Support
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Human Resource Planning (HRP)
- Understanding HRP
What Is the Goal of Human Resource Planning (HRP)?
- Human Resource Planning FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Business Essentials
Human Resource Planning (HRP) Meaning, Process, and Examples
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
What Is Human Resource Planning (HRP)?
Human resource planning (HRP) is the continuous process of systematic planning to achieve optimum use of an organization's most valuable asset—quality employees. Human resources planning ensures the best fit between employees and jobs while avoiding manpower shortages or surpluses.
There are four key steps to the HRP process. They include analyzing present labor supply, forecasting labor demand, balancing projected labor demand with supply, and supporting organizational goals. HRP is an important investment for any business as it allows companies to remain both productive and profitable.
Key Takeaways
- Human resource planning (HRP) is a strategy used by a company to maintain a steady stream of skilled employees while avoiding employee shortages or surpluses.
- Having a good HRP strategy in place can mean productivity and profitability for a company.
- There are four general steps in the HRP process: identifying the current supply of employees, determining the future of the workforce, balancing between labor supply and demand, and developing plans that support the company's goals.
Michela Buttignol
What Is Human Resource Planning (HRP) Used For?
Human resource planning allows companies to plan ahead so they can maintain a steady supply of skilled employees. The process is used to help companies evaluate their needs and to plan ahead to meet those needs.
Human resource planning needs to be flexible enough to meet short-term staffing challenges while adapting to changing conditions in the business environment over the longer term. HRP starts by assessing and auditing the current capacity of human resources.
Here, identifying a company's skill set and targeting the skills a company needs enables it to strategically reach business goals and be equipped for future challenges. To remain competitive, businesses may need advanced skills or to upskill their employees as the market environment evolves and changes.
To retain employees and remain competitive, HRP often looks at organizational design, employee motivation, succession planning, and increasing return on investment overall.
Challenges of Human Resource Planning (HRP)
The challenges to HRP include forces that are always changing. These include employees getting sick, getting promoted, going on vacation, or leaving for another job. HRP ensures there is the best fit between workers and jobs, avoiding shortages and surpluses in the employee pool.
To help prevent future roadblocks and satisfy their objectives, HR managers have to make plans to do the following:
- Find and attract skilled employees.
- Select, train, and reward the best candidates.
- Cope with absences and deal with conflicts.
- Promote employees or let some of them go.
Investing in HRP is one of the most important decisions a company can make. After all, a company is only as good as its employees, and a high level of employee engagement can be essential for a company's success. If a company has the best employees and the best practices in place, it can mean the difference between sluggishness and productivity, helping to lead a company to profitability.
What Are the Four Steps to Human Resource Planning (HRP)?
There are four general, broad steps involved in the human resource planning process. Each step needs to be taken in sequence in order to arrive at the end goal, which is to develop a strategy that enables the company to successfully find and retain enough qualified employees to meet the company's needs.
Analyzing labor supply
The first step of human resource planning is to identify the company's current human resources supply. In this step, the HR department studies the strength of the organization based on the number of employees, their skills, qualifications, positions, benefits, and performance levels.
Forecasting labor demand
The second step requires the company to outline the future of its workforce. Here, the HR department can consider certain issues like promotions, retirements, layoffs, and transfers—anything that factors into the future needs of a company. The HR department can also look at external conditions impacting labor demand , such as new technology that might increase or decrease the need for workers.
Balancing labor demand with supply
The third step in the HRP process is forecasting the employment demand. HR creates a gap analysis that lays out specific needs to narrow the supply of the company's labor versus future demand. This analysis will often generate a series of questions, such as:
- Should employees learn new skills?
- Does the company need more managers?
- Do all employees play to their strengths in their current roles?
Developing and implementing a plan
The answers to questions from the gap analysis help HR determine how to proceed, which is the final phase of the HRP process. HR must now take practical steps to integrate its plan with the rest of the company. The department needs a budget , the ability to implement the plan, and a collaborative effort with all departments to execute that plan.
Common HR policies put in place after this fourth step may include policies regarding vacation, holidays, sick days, overtime compensation, and termination.
The goal of HR planning is to have the optimal number of staff to make the most money for the company. Because the goals and strategies of a company change over time, human resource planning must adapt accordingly. Additionally, as globalization increases, HR departments will face the need to implement new practices to accommodate government labor regulations that vary from country to country.
The increased use of remote workers by many corporations will also impact human resource planning and will require HR departments to use new methods and tools to recruit, train, and retain workers.
Why Is Human Resource Planning Important?
Human resource planning (HRP) allows a business to better maintain and target the right kind of talent to employ—having the right technical and soft skills to optimize their function within the company. It also allows managers to better train the workforce and help them develop the required skills.
What Is "Hard" vs. "Soft" Human Resource Planning?
Hard HRP evaluates various quantitative metrics to ensure that the right number of the right sort of people are available when needed by the company. Soft HRP focuses more on finding employees with the right corporate culture, motivation, and attitude. Often these are used in tandem.
What Are the Basic Steps in HRP?
HRP begins with an analysis of the available labor pool from which a company can draw. It then evaluates the firm's present and future demand for various types of labor and attempts to match that demand with the supply of job applicants.
Quality employees are a company's most valuable asset. Human resource planning involves the development of strategies to ensure that a business has an adequate supply of employees to meet its needs and can avoid either a surplus or a lack of workers.
There are four general steps in developing such a strategy: first, analyzing the company's current labor supply; second, determining the company's future labor needs; third, balancing the company's labor needs with its supply of employees; and fourth, developing and implementing the HR plan throughout the organization.
A solid HRP strategy can help a company be both productive and profitable.
International Journal of Business and Management Invention. " Human Resource Planning-An Analytical Study ," Page 64.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/erp-4196982-d232fedd39e64910bc29033d4db2e9ca.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
Sling is now Sling by Toast! Learn more
More Features

- Restaurants
- Get Started

Human Resource Planning: Definition, Objectives, And Steps
- Employee Management , Templates & Guides
Human resource planning is an essential part of every successful business. Unfortunately, many managers neglect this vital practice for other, easier tasks because they don’t understand what this type of planning requires.
Other times, managers may not understand how pivotal human resource planning is to their long-term corporate strategy and the ultimate success of their business.
That’s where Sling can help. In this article, we define human resource planning, outline its objectives, and provide a step-by-step guide to implementing this crucial practice in your business.
Table Of Contents
Human Resource Planning Defined
Human resource planning objectives, hrp vs. shrm, hrp and organizational strategy, steps in human resource planning, why human resource planning is important, challenges of human resource planning, scheduling and communication for effective hrp.
Human resource planning (or HRP for short) is the ongoing process of systematically planning ahead to optimize and maximize your business’s most valuable asset — high-quality employees .
When you incorporate HRP into every aspect of your strategy — functional , business , or organizational — you streamline the process of creating the best fit between available jobs and available employees. All while avoiding a shortage or surplus in your workforce.
As simple as that may sound, there’s more to human resource planning than setting up a system and implementing it in your organization.
The objectives of HRP are very specific and can mean the difference between success or stagnation. We’ll discuss those objectives in the next section.

As we mentioned earlier, human resource planning is about matching the right employees with the right jobs in your business.
You can do this while interviewing prospective employees, or even during the performance review of a long-time team member who is reaching out for more responsibility.
While matching employees to jobs is a big part of human resource planning, the goals of HRP don’t stop there. Other HRP objectives include:
- Adapting to rapid technology changes
- Powering product innovation
- Adjusting to a more globalized economy
- Preparing for generational and cultural shifts
- Anticipating job and skill changes
- Facilitating growth
- Improving business operations
- Mitigating risk
- Preventing talent shortage or surplus
- Complying with local, state, and federal regulations
- Implementing a successful onboarding process
As you can see, HRP is integral to the successful operation of your business and its growth over both the short- and long-term.
Because this process is connected to every aspect of your business , you may feel overwhelmed by the prospect of creating a new HRP strategy.
Don’t let this prevent you from implementing a system that can revolutionize the way your business operates — both now and in the future .
Keep in mind that human resource planning doesn’t have to address all of the objectives on this list from the moment it goes into effect. Start small and expand into different areas once you’ve addressed one or two objectives.
Later on in this article, we discuss a step-by-step method for producing a human resource planning strategy for your business.
But, first, let’s take a moment to discuss one of the most-confused aspects of human resource planning: how it differs from strategic human resource management.

Before we delve into the minutiae of human resources , let’s put the two relevant definitions side-by-side to see how they compare.
Human Resource Planning : HRP is the ongoing process of systematically planning ahead to optimize and maximize your business’s most valuable asset — high-quality employees.
Strategic Human Resource Management : SHRM is a holistic approach to assembling the best team for your business’s growth and success.
At first glance, it may appear that human resource planning is the same thing as strategic human resource management under a different name. They seem so similar because one is actually part of the other.
In this case, HRP is a small part of SHRM. Viewed from a different perspective, SHRM contains and governs HRP.
It’s very much like a set of nesting dolls: the smallest one (HRP) fits nicely into the next largest (SHRM), which, in turn, fits into the next largest, and so on.
For practical purposes, it helps to think about human resource planning as the frontline, boots-on-the-ground application, while strategic human resource management is the guiding principle behind those applications.
In other words, SHRM is the why to HRP’s what.
Another way to think about SHRM and HRP is to view your business as a large, complicated machine.
Human resource planning is one component (a gear, for example) that works with other similar components (e.g., production, logistics, shipping, management, etc.) to keep the machine running.
Strategic human resource management, on the other hand, takes a step back and analyzes the machine itself.
SHRM looks at the performance of each component (each department in your business), how they work together to make everything run smoothly, and what the business as a whole can do to improve.

Let’s return, for a moment, to the example of the nesting dolls mentioned earlier.
We established that human resource planning is the smallest doll and that strategic human resource management is the next largest doll. But what comes after that?
What’s the next largest doll in the series? Organizational strategy.
Organizational strategy , at its most basic, is a plan that specifies how your business will allocate resources to support infrastructure, production, marketing, inventory , and other business activities.
How does this affect human resource planning? Organizational strategy directs strategic human resource management directs human resource planning.
In many ways, the strategy side of your business mirrors the relationship between SHRM and HRP.
Organizational strategy is subdivided into three distinct categories: corporate strategy, business strategy, and functional strategy. Just like SHRM and HRP, each level is a part of the one above it.
Corporate level strategy is the main purpose of your business — it’s the destination toward which your business is moving.
Business level strategy is the bridge between corporate level strategy and much of the “boots-on-the-ground” activity that occurs in functional level strategy.
Functional level strategy is the specific actions and benchmarks you assign to departments and individuals that move your business toward the goals created by your corporate level strategy. They are a direct offshoot of your business level strategies.
With those categories in mind, we start to see the bigger picture of your business. SHRM is a component of your business level strategy, while HRP is a component of your functional level strategy.
Now that you understand the theory behind human resource planning, let’s focus our attention on the practice itself.

1) Analyze Organizational Strategy
Any successful workforce-management program — including human resource planning — is a direct offshoot of your business’s organizational strategy.
Therefore, you should always start your HRP process by analyzing the goals and plans of your organization. With those strategies in mind, you can then move on to crafting a general human resources mission statement.
From there, you can work your way through the various departments in your business to address issues such as:
- Recruitment
- Employee relations
When you have that information written down, you can craft a human resource plan to help your business reach and maintain its goals.
2) Inventory Current Human Resources
After analyzing your organizational strategy, it’s time to take stock of your business’s current human resources.
In the process, it’s beneficial to investigate such variables as:
- Total number of team members you employ
- Who works in what department
- Skills of each employee
- Performance reviews
- Team and individual potential
With that data in hand, you then make sure that your existing workforce is large enough and skilled enough to cover current demands before moving on to the next step in this guide.
3) Forecast The Future Of Your Workforce
Step three is all about planning, prediction, and preparing for the future.
Guided by your organizational strategy and your current employee data, do your best to forecast what the future of your workforce will look like. Be sure to incorporate any goals and plans into your forecast.
Examine variables such as:
- New product offerings
- New services
- A second (or third) location
- Labor costs
- Vendor and supplier relations
- Cost of goods sold
A forecast of this type, coupled with the workforce data from step two, gives you an accurate picture of where your business is right now and where you want it to be five, 10, even 15 years down the road.
4) Estimate Gaps
Armed with the information you’ve produced so far, you can now estimate whether or not there are any gaps in your human resource strategy.
Will you need more employees to get your business from the present to where you want it to be in the future? If so, how many? Will you need fewer employees? If so, how many?
Does your forecast call for a reallocation or redistribution of current team members? If so, how would you go about doing this?
Once you’ve estimated the gaps between your current and future workforce numbers, you can move on to step five, where all the planning and brainstorming comes to fruition.
5) Formulate An Action Plan
Formulating an action plan is where the rubber meets the road, so to speak.
Your action plan should take into account all the analysis that came before it — organizational strategies, current HR inventory, HR forecast, and gaps between present and future — to create a step-by-step system for taking your business from point A to point B.
The action plan will be different for every business. Some businesses may need to begin recruiting and training . Other businesses may need to promote or transition their existing workforce.
Still other businesses may need to develop a retirement program or a redeployment process to deal with surplus employees.
When crafting your plan, start with the theoretical — evolve from X to Y — and then move on to actionable steps that your HR department can take — hire and retain two new team members every year, for example — to transform the theory into reality.
With these steps in mind, you can implement a successful human resource planning system into your business, no matter how many employees you have.
As you go about implementing your business’s HRP, don’t neglect the foundation of all good employer/employee relations: scheduling and communication. We’ll discuss this topic at the end of the article.
6) Integrate With The Rest Of The Company

Now that you’ve got an action plan, your human resource planning efforts will start to yield results.
That said, the integration stage is the most difficult of the entire process, so be ready for some speed bumps.
Without proper preparation — and even with proper preparation, in some cases — both management and frontline employees may show resistance to the proposed changes.
In addition, all departments within your business work together in one way or another (even if it doesn’t at first appear so). This makes the integration phase challenging on many levels.
One of the best ways to integrate human resource planning into the rest of the company is to start with the recruitment , hiring , and training practices in your business.
Once you’ve brought in new, high-potential employees and have begun funneling them into the various departments, you can start to make other changes to accommodate these new hires.
Integrating slowly and pairing the changes with new employees who will further the goals and productivity of each department makes putting your new human resource planning into place much easier.
7) Monitor, Evaluate, And Adjust
The final step in human resource planning is to monitor the new practices, evaluate them for their effectiveness, and adjust as necessary.
In addition to monitoring each department and your business as a whole, it’s also beneficial to zoom in on how any changes made affect the individual employee.
To take the pulse of the front-line worker, include questions about your human resource planning during mid-year reviews and performance appraisals . You can even ask for their opinion when you have them complete an employee self-evaluation .
Monitoring and evaluating in this way will help you get a detailed view of how any new policies, procedures, and practices affect the men and women in the trenches.
Once you have all the information you need, you can then take steps to adjust your human resource planning accordingly.
For that, it’s best to return to the top of this list and start again at step one, incorporating what you learned from the previous run-through.
In essence, then, you can view this list as less of a straight line and more of a circle, with step seven leading directly back into step one. As such, your HRP should be in a constant state of development.

Your business can function without HRP, and, yes, it can be a challenge to get the plans in place, but the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks.
Among other things, HRP can help your business:
- Anticipate workforce needs in a changing market
- Plan for short-term and long-term growth
- Improve operations
- Facilitate staffing changes
- Avoid talent shortage
- Stay ahead of the technology curve
- Remain agile as the market evolves
- Maintain compliance with government laws and regulations
Human capital management is one of the most important parts of your business. HRP helps you maximize that potential.
As beneficial and powerful as human resource planning is, it is not without its drawbacks and challenges.
For one thing, HRP relies on forecasting, which is an imperfect art and is never — and can never be — 100% accurate.
Similarly, you can never account for the ambiguity in the market and the rapid change that could come out of nowhere.
There may be some error when you forecast the future of your workforce. That error will affect the other steps on this list for the good or the bad (depending on how accurate your forecast is).
Realistically, though, that can’t be helped and all you can do is give it your best shot. If you discover errors in your forecasting, you can always return to step one and start the process over with the new information.
Other challenges of the human resource planning process include:
- Resistant workforce
- Inefficient information systems
- Overall cost
- Time and effort
That said, when you are aware of these challenges going in, you can take steps to overcome them right away so that you can get to the benefits sooner.
Scheduling and communication are key components of an effective human resource planning process.
Your team’s schedule is the cornerstone on which you build their work experience. If the schedule doesn’t satisfy all parties — employees and management alike — your business suffers.
Similarly, clear communication with all your employees fosters a strong team and keeps everyone in the loop about employee performance, inventory, standard operating procedures , customer satisfaction , and your business as a whole.
In the 21st century, the best schedules are created and the best communication maintained with help from dedicated software like Sling .
Whether your business has one shift or three, offers flextime or a compressed workweek , or works a 9-to-5 work schedule or a 9/80 work schedule , Sling can help simplify the schedule-creation process.
And with advanced communication features built in, Sling is the only tool you’ll ever need to keep your employees informed about your business and connected with each other.
In fact, we developed the Sling app to streamline communication as well as make scheduling, tracking labor, finding substitutes, assigning tasks, and building employee engagement extremely simple.
There are so many ways Sling can help improve your human resource planning that we don’t have room to talk about them here. So instead of reading about it, why not try it out?
Sign up for a free account and see for yourself how Sling can help you implement the necessary strategies to make your team and your business successful.
For more free resources to help you manage your business better, organize and schedule your team, and track and calculate labor costs, visit GetSling.com today.
See Here For Last Updated Dates: Link
This content is for informational purposes and is not intended as legal, tax, HR, or any other professional advice. Please contact an attorney or other professional for specific advice.
Find the article useful? Share with others:
Related articles
Strategic Human Resource Management: What Is It And Why Is It Important?
Most businesses have some type of human resource management plan — even if it�...

Human Resource Management: What Is It And Why Is It Important?
Regardless of the size of your team, human resource management is crucial for th...

What Is a Human Resource Management System (HRMS)?
A human resource management system can help your business get ahead in the game....
Get started today
Schedule faster, communicate better, get things done.
Human Resource Planning (HRP): A Step-By-Step Guide

In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, having a plan in place for managing your human capital is key — and that’s where human resource planning (HRP) comes in. Human resource planning plays a critical role in making sure that your organization is well-equipped with the right talent at the right time.
Today, we’re walking through the intricacies of HRP so you can implement this practice in your organization.
What Is Human Resource Planning?
Human resource planning, or HRP, stands out as a strategic and methodical process designed to ensure that your organization fully leverages its human capital . It is not a one-time event but rather a continuous journey toward operational excellence and strategic alignment.
At its core, HRP aims to establish a seamless alignment between your employees and their respective roles, meticulously crafting a workforce that is both skilled and adequately sized to meet your organizational demands.
This proactive approach goes a long way in safeguarding your business against potential manpower shortages or surpluses, ensuring that you are well-prepared for the future.
Why Is HRP Important?
HRP is crucial for syncing your current workforce with your future needs. It entails a rigorous analysis of your existing staff, evaluating their skills, competencies, and performance.
This is where metrics come into play, providing a quantitative backbone to your workforce planning efforts. By leveraging data-driven insights, you can make informed decisions, ensuring that your team is not only talented but also aligned with your business objectives.
HRP doesn’t stop there, though — it’s a comprehensive approach that intertwines various facets of human resource management. Staffing, forecasting , performance management, and employee retention all fall under its umbrella. Each of these elements is crucial in building and maintaining a robust workforce.
In terms of staffing, HRP helps you decipher not just the number of employees you need, but also the types of skills and competencies they should possess. Forecasting, on the other hand, empowers your HR department to anticipate future demand, aligning your human resources with your company’s strategic direction.
Performance management is another vital cog in the HRP machine. It ensures that your employees are not just present but also productive and engaged. This, in turn, enhances employee retention, fostering a company culture that values growth, stability, and satisfaction.
HRP even plays a role in shaping your company culture . By aligning your human resources with your company’s needs and values, you create an environment where employees feel valued and aligned with the organization’s goals.
What Are the Advantages of Human Resource Planning?
At its core, human resource planning places the right talent in the right place at the right time, ensuring that your organization’s objectives align with your workforce’s capabilities. Now, let’s talk about the advantages of HRP and how it can lay the foundation for organizational success.
Ensures Effective Management of Current Employees
Strategic workforce alignment is at the heart of HRP. With effective human resource management, HR professionals can ensure that the current workforce is in sync with the company’s overarching goals.
This alignment can translate to better resource allocation, more informed decision-making, and enhanced overall performance.
Reveals Knowledge Gaps in the Workforce
The ever-evolving business landscape means organizations need to be adept at forecasting and adapting — and human resource planning plays a role here.
By examining current employees’ skill sets and comparing them with future needs, knowledge gaps can become more apparent. Addressing these gaps, whether through hiring new talent or upskilling existing employees, helps you ensure that your business stays competitive.
Balances HR Costs
Cost-effectiveness is crucial for the HR planning process. By anticipating future human resource needs, last-minute external recruitments — which often come with high costs — can be avoided.
Plus, recognizing surplus areas within your current workforce allows for internal reassignments to take place, cutting down on recruitment and onboarding expenses.
Keeps Companies Adaptable to Change
Change is constant, especially in today’s fast-paced business world, and human resource planning positions organizations to seamlessly navigate these changes.
From staying updated with industry trends to adapting to regulatory shifts, an HR department’s proactive planning ensures businesses remain resilient and agile. With Mosey , you can more effectively track, manage, and stay on top of changing regulations and requirements, making HR compliance a breeze.
Helps Secure Long-Term Growth
Another key component of HRP is succession planning. Identifying roles and preparing a talent pipeline ensures that your organization isn’t caught off-guard if leadership positions open up.
This planning not only opens the door to future leaders, but also ensures that institutional knowledge is retained, fueling your business’s long-term growth and stability.
Contributes to Organizational Goals
The nexus between human resource planning and organizational goals is undeniable. By streamlining the hiring process, ensuring employee satisfaction , and fostering employee retention, HRP contributes directly to the achievement of business objectives.
When employees see clear growth trajectories and development avenues, their commitment to the company’s vision intensifies, driving the organization closer to its goals.
What Are the Steps for Human Resource Planning?
HRP ensures that businesses are well-equipped, both in terms of the quantity and quality of their workforce, to meet their evolving goals and challenges. So, how can you actually navigate the intricacies of HRP? Here’s a step-by-step walkthrough of the essential phases that make up the human resource planning process.
Analyze Employee Skills and Performance
Human resource planning centers around an understanding of your company’s current workforce.
During this initial phase, the HR department dives into understanding the number of employees, their competencies, qualifications, positions, benefits, and performance levels. This skill inventory ensures that HR professionals have a clear picture of the strengths and areas for improvement in the present workforce.
Research Industry Trends and Forecasts
Effective human resource planning can also help you predict, and plan for, the future, so the next stage is to outline what your company will need in terms of human capital in the foreseeable future.
This forecasting phase requires the HR department to consider various factors, such as potential promotions, retirements, layoffs, and transfers. External conditions, like emerging technologies or industry shifts, can also have a significant impact on labor demand. Ensuring you stay ahead in terms of industry trends helps you align your staffing needs more effectively.
Conduct Demand Forecasting
Having a clear understanding of both the present workforce, potential employees, and future needs is vital to bridge the two through demand forecasting. This step in the HR planning process involves creating a gap analysis that points out discrepancies between the current workforce and future human resource demands.
This type of analysis leads to important questions like:
- Should current employees learn new skills?
- Is there a need for more managers?
- Are all employees fully utilizing their competencies in their present roles?
Answering these questions is key to crafting a strategic human resource plan that aligns with both the present and the future.
Determine Future Human Resource Needs
Once your demand forecasting has highlighted the shortages or surpluses in terms of competencies or number of employees, the next step is to determine the specific future human resource needs.
Whether it’s upskilling the current employees, succession planning for key roles, or identifying the need for new hires, this phase ensures that your business is poised for future growth without any HR hiccups.
Align HR Needs With Organizational Strategy
Human resource planning is intertwined with your broader business goals and strategies. Once your HR needs are identified, it’s important to make sure those needs align with your organizational goals.
This strategic planning phase ensures that every hiring process, training initiative, or retention effort contributes directly to your company’s overarching objectives.
Plan for Employee Development and Training
Once your future human resource needs are aligned with your company strategy, it’s time to implement plans for employee development. This might involve setting up training programs, workshops, or certifications to upskill current employees.
Ensuring your workforce is equipped with the right skills enhances employee satisfaction and retention and gives your business a competitive advantage.
Implement Plan for Forecasted HR Needs
The culmination of the human resource planning process is the implementation of your action plan. Taking cues from the gap analysis and strategic alignment, HR can now roll out a well-thought-out plan.
This could involve tweaking job descriptions, initiating new hiring processes, onboarding new employees, or even revisiting HR policies such as vacation, sick days, or overtime compensation. Collaboration with all departments is key here to ensure the successful execution of your plan, ensuring the HR strategies benefit the organization as a whole.
Support HRP Efforts With Mosey
From identifying when and where to open payroll accounts to managing workers’ compensation and paid family medical leave, Mosey simplifies the complex web of compliance and regulatory demands.
Why not explore how Mosey can streamline your HR processes and compliance management ? Our platform is designed to provide clarity, guidance, and ease, allowing you to focus on what matters most — nurturing and growing your most valuable asset, your employees. Try Mosey today .
Read more from Mosey:
- Compliance Automation: How It Works & Its Value
- Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC: Key Differences
- What Is a Foreign Corporation? FAQs Explained
- What Is a C Corporation (C Corp)?
- What Is Payroll? A Guide for Small Business Payroll
- What Is a Legal Entity? Definition & Examples
- What Is SUI? State Unemployment Insurance FAQs
Review your compliance risks, free.
Use our compliance checkup to learn more about what to do to be compliant in any state! It's free and takes less than five minutes.
Ready to get started?
Sign up now or schedule a free consultation to see how Mosey transforms business compliance.

Mosey has everything you need to get compliant in all 50 states in one, easy to use, platform.
Strategic Human Resources Management: Everything you Need to Know

Whats Inside?
What is strategic human resources management(shrm), the shift from administrative to strategic human resources management, the state of strategic hr, ai and strategic human resources management, strategic human resources management and organizational performance, strategic human resources management: what are the pillars, a step-by-step guide to developing an hr strategic plan, introduction to contemporary hr strategy formulation models.
Wright and McMahan defined SHRM as "the pattern of planned human resource deployments and activities intended to enable an organization to achieve its goals." This definition emphasizes the planned and systemic approach to managing human resources in alignment with the organization's strategic objectives. SHRM is viewed as an approach to making decisions on the intentions and plans of the organization concerning employment relationships, recruitment, training, development, and performance management. The strategic HR function aims to enhance and manage the organization's human capital for long-term strategic goals. Other scholars view it as an approach that builds HR strategies , enabling employees' knowledge and skills to contribute to the organization's achievement of its overall goals, thereby improving productivity and efficiency. In all this, HR can not be strategic without positively impacting the business.
Organizations increasingly recognize the importance of aligning their human resources practices with their strategic objectives to enhance performance and competitive advantage. According to a recent scholarly article , there has been a shift in the Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) literature to a stakeholder view, acknowledging the various stakeholders relevant to the HR function. Another study highlights the critical role of fit in SHRM, examining how high-commitment human resource practices and charismatic leadership can impact organizational outcomes.
Statistics show that a significant majority of CEOs, 89% to be precise, believe that HR should have a central role in business, according to data from Accenture. However, only 45% of these executives feel they successfully created the conditions for HR to lead business growth . These figures underscore the gap between the perceived importance of strategic HR and the actual implementation of practices that leverage HR for business success.
The perspectives of company boards on SHRM are also evolving. Boards are beginning to see the value of having HR expertise within their ranks, as this brings a unique perspective that is indispensable for managing the increasingly complex human capital landscape. An HR expert on the board can offer insights into culture, risk management, and ethical employment practices that are vital for the success and sustainability of the company.
Advertisment
The transition from administrative to strategic human resource management (SHRM) reflects a broader understanding of the value of human capital in achieving organizational goals. Historically, HR was predominantly concerned with administrative tasks such as hiring, payroll, and compliance. However, as organizations grew more complex, the need to align HR activities with business strategy became evident. Hendry and Pettigrew's study on " Patterns of strategic change in the development of human resource management " (1992) highlighted how the shift from personnel administration to HRM was uneven across organizations but was stimulated by the need to address more complex business challenges.
The shift to SHRM is largely driven by the recognition that human resources can be leveraged to create a competitive advantage and that HR practices need to be integrated with the strategic planning and execution of the company. Becker and Huselid's overview of SHRM in five leading firms (1999) noted that strategic HR management is essential in supporting significant organizational change and addressing human capital challenges central to strategic change.
Furthermore, the emergence of European transition economies necessitated a move from purely administrative HRM to more strategic and business-oriented practices. Zupan and Kaše (2005) built a conceptual model on the case of Slovenia , illustrating the need for strategic HRM in these evolving market economies and its role in organizational adaptation and competitiveness.
The transition to SHRM corresponds with the changing nature of work, globalization, and the increasing importance of knowledge-based economies. Organizations now view employees as strategic assets who can drive innovation and sustainable growth, and SHRM is designed to optimize the contribution of human capital to business success.
Strategic Human Resources Management (SHRM) is an evolving field that has gained prominence for its ability to align HR practices with the strategic direction of businesses. The state of SHRM today focuses on integrating human capital management with long-term organizational objectives, and the literature provides insights into its growing strategic importance.
A pivotal study by Schuler emphasized that SHRM is largely about integration and adaptation, ensuring human resources management is fully integrated with the strategy and strategic needs of the organization (Organizational Dynamics). This integration is crucial as businesses increasingly rely on human capital to gain competitive advantages in dynamic marketplaces.
Emerging SHRM Trends & Insights
The strategic human resource management (SHRM) landscape is reshaped by various innovations and trends emerging as critical in the 21st century. One of the primary shifts being acknowledged is the transition to creating more adaptable work environments, often called "The Great Rebalance." This involves a focus on re-skilling and upskilling employees and a strong emphasis on well-being to foster increased satisfaction and loyalty. A significant volume of work has gone into this area, especially work by Kess-Momoh et al ., who go deeper into into the evolution of SHRM in response to such challenges.
In the realm of analytics, HR is increasingly adopting a data-driven approach . Predictive analytics are being utilized to uncover hidden talent pools, anticipate workforce needs, and preemptively tackle potential skill shortages or attrition risks. This is echoed by Kar and Mahapatra's findings, which suggest that HR is beginning to arm itself with the tools and insights of a scientist.
The hybrid workplace is another area where SHRM plays a vital role, ensuring that remote or hybrid work models do not dilute company culture. Strategies are being developed to build deliberate connections, trust, and a sense of belonging for employees operating in a less centralized work environment.
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DE&I) are now seen as business imperatives, transitioning from compliance-based efforts to creating workplaces where every employee feels valued. SHRM professionals are crafting policies and systems that promote psychological safety and equitable opportunities for advancement, mentorship, and sponsorship, regardless of one's background.
These trends are statistics highlighting the growing focus on human-centric organizational design. Deloitte's 2023 Global Human Capital Trends Report reveals that 89% of companies are redesigning with a strong human focus, with 60% of respondents emphasizing "workforce capability" over cost reduction as critical to their mission.
Furthermore, CEOs increasingly prioritize the construction of adaptable organizations with a talent focus that surpasses investments in technology and customer-centricity to maximize returns. This is substantiated by the McKinsey Global Survey, indicating this shift towards talent.
Integrating AI in strategic human resources management (SHRM) is a transformative force with potential benefits in recruitment, performance management, employee engagement, and talent analytics. This transformation is driven by big data and AI technologies , which enhance the strategic development of HR. AI's ability to automate manual work allows HR professionals to focus on more strategic roles. However, using AI in HRM also presents challenges like bias, privacy issues, and transparency. Despite these challenges, AI has the potential to revolutionize HRM practices with applications in sentiment analysis, predictive analytics, intelligent decision support, and personalized employee experiences.
AI's predictive analytics capabilities will enable HR to make more informed decisions by analyzing large datasets to identify patterns, forecast trends, and provide insights. This can lead to better talent acquisition strategies, more effective workforce management, and improved employee retention efforts. AI can assist in identifying the best candidates for a job, predicting employee turnover, and suggesting optimal career paths for employees.
Another significant change is the personalization of the employee experience . AI-driven tools can deliver personalized learning and development programs, tailor benefits to individual employee needs, and provide targeted career advice. By leveraging AI, HR can create a more engaging and satisfying work environment for employees, which is increasingly important in attracting and retaining top talent.
A body of research consistently supports the positive relationship between strategic human resource management (SHRM) and company performance. This is evident in studies that have found a positive association between HRM practices and organizational performance and the significant impact of HRM bundles on business outcomes . This is further supported by a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies , which found a strong correlation between high-performance work practices and firm performance. The association between HRM practices and financial , market, and operational performance is also quantified, with the strongest association found with market performance.
A meta-analysis conducted by Combs et al. focused on high-performance work practices and their effects on organizational performance. The study synthesized findings from 92 studies and found that high-performance work practices are associated with a significant improvement in both financial (such as profit and return on assets) and non-financial (such as customer satisfaction and quality) organizational performance. The overall effect size reported was positive, with high-performance work practices showing a strong and positive impact on organizational outcomes.
Saridakis, Lai, and Cooper (2017) explored the relationship between HRM and firm performance through a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies . They examined the statistical association between various HRM practices and organizational performance. The study provided empirical support for the positive impact of HRM on firm performance over time, highlighting the importance of a strategic approach to HRM.
Tzabbar, Tzafrir, and Baruch performed a moderating meta-analysis to investigate the relationship between HRM practices and organizational performance . They found that training is independently related to organizational outcomes, which aligns with the universalistic perspective of SHRM.
Jiang, Lepak, Hu, and Baer conducted a meta-analysis that examined the relationship between SHRM and organizational performance, including 115 studies. They found that SHRM practices are positively associated with both financial performance (with an average correlation of r = .20) and non-financial performance (r = .21). Notably, the study also revealed that the relationship between SHRM and performance outcomes is stronger when SHRM practices are aligned with organizational strategy.
Huselid conducted a meta-analysis on the impact of HRM practices on turnover, productivity, and corporate financial performance. His study, which included 968 firms, found that a one-standard-deviation increase in HRM practices was associated with a 7.05% decrease in turnover, a $27,044 increase in sales per employee, and a $3,814 increase in market value per employee.
Crook, Todd, Combs, Woehr, and Ketchen conducted a meta-analysis to examine the relationship between human capital and firm performance. They included studies across various fields and found a significant positive correlation between human capital and organizational performance, with human capital being a crucial strategic asset for firms.
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) is integral to harnessing the value of human capital for corporate financial performance. The Harvard Law School study on "The Materiality of Human Capital to Corporate Financial Performance" presents compelling evidence that companies with robust human capital management (HCM) practices demonstrate superior financial outcomes. For example, businesses that emphasize employee development and engagement often see returns on these investments through increased productivity, leading to higher profit margins and return on assets. Labor-intensive industries, such as healthcare and technology, particularly benefit from effective HCM, with such practices potentially differentiating companies within these sectors. In these industries, the strategic management of human capital can result in a competitive edge, with some studies suggesting a correlation as high as 0.28 between comprehensive HCM practices and financial performance indicators like EBITDA margins.
Transparency and disclosure of HCM practices are becoming increasingly important to investors, as these practices are closely linked to both short-term and long-term financial performance. Effective SHRM contributes to a skilled and engaged workforce and mitigates risks associated with talent management. Consequently, companies that excel in reporting their HCM practices can attract more investors by showcasing their commitment to workforce development and the strategic alignment of HR practices with business goals. This transparency is not just about good governance; it also reflects on a company's ability to sustain and grow its financial performance. For instance, firms with favorable HCM practices have been shown to outperform their peers by as much as 16% to 19% on return on equity (ROE) and total shareholder return (TSR).
The strategic importance of SHRM in enhancing organizational performance is clear, and investors are taking notice. The quality of a company's HCM practices is increasingly factored into investment decisions, potentially influencing market value. Companies that report a one-standard-deviation increase in HCM practices can see a market value increase of up to $20,000 per employee. A study by Harvard Law School suggests that this increase in market value indicates the material impact that strategic human capital management can have on a firm's financial performance. As such, there is a growing call for standardized reporting of HCM practices, enabling investors and other stakeholders to make more informed decisions and recognize human capital's profound influence on an organization's success and sustainability.
Related: What are the 5 Steps of Strategic Human Resource Management?
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) is grounded in several foundational pillars that underpin its effectiveness in driving organizational success. A study by Bhatnagar and Sharma (2004) in the Indian Journal of Industrial Relations introduces the concept of strategic HRM dimensions, emphasizing the interlinkages between strategic HR roles and organizational performance. Similarly, Wood's research (1995) in the Human Resource Management Journal identifies the four quoted elements of human resource management as high commitment, a strategic and integrated approach to human resources, and line management responsibility for human resource outcomes, illuminating how these pillars are connected within the framework of SHRM .
A study by Martell and Carroll found that 115 subsidiaries of Fortune 500 companies had well-integrated HRM and strategic planning systems, illustrating how HRM issues were explicitly considered in strategic plans. Although no direct relationship was found between the integration level and short-term performance, the study suggests that time lags could influence this relationship. This underscores the importance of HRM executives as strategic partners in the planning process and highlights the need for organizations to integrate HRM and strategic planning while considering the temporal aspects of strategic outcomes.
Adding to the above insights, a Gartner report indicates that HR leaders are navigating unprecedented levels of disruption, with rapid shifts from planning to action and increasing imperatives. Priorities for HR leaders include enhancing leader and manager effectiveness, managing change, improving the employee experience, streamlining recruitment, and adapting to the future of work. This suggests an evolving landscape where SHRM must be agile and responsive to internal and external pressures, reinforcing the need for strategic adaptation and the continuous development of HR capabilities .
The pillars of SHRM are multifaceted and interconnected, encompassing a commitment to strategic integration, operational excellence, and a culture that values human capital. The integration of HRM into strategic planning is critical for long-term success, and the ability to adapt to rapidly changing demands and priorities is increasingly essential for HR leaders. These elements together form the bedrock of a strategic approach to HR that can steer organizations toward sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Step 1 - Understand the Business Strategy
In HR strategic planning, understanding the business strategy is paramount. It involves not just a superficial acknowledgment of company goals but a granular analysis of the business's direction and human capital's role in reaching those goals. HR must be intricately woven into the fabric of strategic business planning , acting as a key driver rather than a supporting act.
For XYZ Corp, with its focus on innovation in software solutions, this step would involve a detailed assessment of the specific skills and competencies required to achieve innovation goals. It would necessitate understanding the technological trends shaping the software industry, the competitive landscape, and the customer demands that drive the market. A strategic HR plan rooted in this understanding would align workforce planning, talent management, and organizational development directly with the need to foster an innovative culture.
Specifically, XYZ Corp's HR department might interview senior leaders to ensure a shared vision of the strategic direction. They may also perform a gap analysis to determine the current state of the workforce versus the desired state, identifying the specific roles and skills critical for future growth. This could involve analyzing the company's product pipeline, current innovation capabilities, and upcoming projects to forecast talent needs.
The HR team would then translate these insights into a strategic HR plan that includes targeted recruitment campaigns aimed at top tech talent, specialized training programs to upskill existing employees in emerging technologies, and creating an innovation lab where new ideas can be incubated. This approach ensures that HR initiatives are supportive of and integral to XYZ Corp's strategic objective to lead in software innovation.
This expanded focus on understanding the business strategy underscores HR's need to sit at the table during strategic discussions and decision-making processes. By doing so, HR can proactively address the human capital implications of business strategies and ensure that the organization has the talent to succeed in its objectives.
Step 2 - Conduct an Environmental Scan
Conducting an environmental scan is a comprehensive process encompassing a broad range of factors influencing the organization's ability to meet its strategic goals through its people. It's a critical diagnostic step that provides a macro and micro view of the forces in the internal and external environments. For XYZ Corp, this means examining the availability of software engineering talent and the quality, cost, and long-term sustainability of this talent pool.
Internally, XYZ Corp should assess its workforce demographics, compensation structures, job satisfaction levels, and employee turnover rates. This assessment might reveal potential issues such as high attrition among mid-level developers or a lack of critical skills that could hinder future product development. It should also review how well current HR programs and policies are working to meet existing needs and how they might be improved or scaled to support strategic objectives.
Externally, XYZ Corp must look at the broader labor market for technology talent, analyzing trends in the availability of skilled professionals, salary benchmarks, and the competitive landscape regarding how other software companies attract and retain their employees. They should also consider the impact of emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, on the demand for new skill sets.
Moreover, XYZ Corp must remain cognizant of regulatory and legal changes that could impact employment practices, such as shifts in labor laws, immigration policies affecting the global talent pool, and changes in work-related tax incentives. They should also evaluate economic indicators that could affect the supply and demand for labor, such as unemployment rates, economic growth forecasts, and educational trends in STEM fields.
This environmental scan should be an ongoing process, with XYZ Corp continuously gathering and analyzing data to stay ahead of trends. This could involve setting up a dedicated workforce analytics function to monitor these variables and provide actionable insights. By thoroughly understanding the internal and external environments, XYZ Corp's HR can make informed decisions about where to focus its efforts and how to structure its strategic HR initiatives for maximum impact.

Step 3- Perform a SWOT Analysis
A SWOT Analysis is a structured planning method used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to business competition or project planning. It provides a clear framework for analyzing the internal and external factors that can impact the success of HR strategies and, ultimately, the organization's objectives. For XYZ Corp, conducting a thorough SWOT Analysis means taking an introspective look at its HR capabilities and examining the broader market and industry trends.
Strengths are areas where XYZ Corp excels and can be leveraged as a competitive advantage. This could include a robust employee development program, a strong employer brand that attracts top talent, or an agile HR team adept at adopting new technologies. XYZ Corp should capitalize on these strengths to drive strategic initiatives, such as expanding their talent acquisition efforts to new regions known for producing high-quality tech talent.
Weaknesses are internal factors that detract from XYZ Corp's value proposition or hinder its ability to meet strategic objectives. A significant weakness might be the company's lack of diversity in technical roles, which could limit creativity and the development of products that appeal to a wider market. Addressing this weakness could involve implementing targeted recruitment campaigns and revising HR policies to promote inclusivity and equity in career progression.
There are opportunities for XYZ Corp to improve performance, increase profits, or enhance its competitive advantage. Opportunities may emerge from shifts in consumer preferences, technological advancements, or changes in the regulatory environment that allow XYZ Corp to tap into new labor markets or adopt remote working models to access a geographically diverse talent pool.
Threats include external factors beyond XYZ Corp's control that could potentially jeopardize the organization's performance. These might encompass competitive actions such as rival companies offering more compelling benefits packages, economic downturns leading to budget constraints, or new industry regulations that add complexity to HR operations. By identifying these threats, XYZ Corp can develop contingency plans, such as building a more flexible staffing model or investing in automation to reduce dependency on a volatile labor market.
In performing a SWOT Analysis, XYZ Corp gains a comprehensive picture of its strategic position and the environment in which it operates. This analysis should be conducted collaboratively with input from across the organization to ensure a full range of perspectives is considered. The insights gathered from the SWOT Analysis will inform the development of a strategic HR plan responsive to the current state and proactive in anticipating future challenges and opportunities.
Step 4- Define HR Strategic Objectives:
Defining HR strategic objectives is critical in ensuring that the human resource functions align with the organization's overarching goals. These objectives should bridge the business strategy and the actionable HR initiatives supporting it. They must be articulated, quantifiable, and directly linked to business outcomes to ensure that they are meaningful and have a demonstrable impact .
For XYZ Corp, setting an objective to increase the diversity of its technical workforce by 40% within three years is not just about numbers; it's about fostering an environment conducive to innovation and creativity. This objective acknowledges the benefits of diverse perspectives in driving innovation, which is essential for a software company looking to lead in a highly competitive market. Achieving this level of diversity may involve creating targeted recruitment campaigns, building partnerships with organizations that support underrepresented groups in tech, and developing internal programs to cultivate an inclusive culture.
Moreover, this objective must be broken down into smaller, actionable plans with clear metrics for success. For example, XYZ Corp could set quarterly recruitment diversity goals, track the retention rates of diverse hires, and measure employee sentiment on inclusiveness through regular surveys. These measurements would track progress against the objective and provide data to inform continuous improvement efforts.
The strategic objectives should also be achievable and realistic, considering the available resources and the market conditions. They must be relevant to the company's strategic direction, ensuring that HR efforts are not siloed but contribute to broader business goals. Finally, being time-bound means that there is a clear deadline for achieving these objectives, which creates a sense of urgency and allows for timely evaluation of the results.
In defining strategic objectives, XYZ Corp's HR team should involve stakeholders from across the organization to ensure buy-in and to gather diverse insights. This collaborative approach will help to ensure that the objectives are comprehensive and address the key areas of HR that will drive the company forward in achieving its business strategy.
Step 5- Develop HR Programs and Policies:
The development of HR programs and policies is where strategic objectives are operationalized into tangible actions. This step requires translating the broad goals set by HR into specific programs and policies that will systematically achieve these objectives. For XYZ Corp, this means creating structured initiatives that directly contribute to increasing diversity and fostering an inclusive environment.
When developing these programs, XYZ Corp must consider various elements, such as the target audience, the desired outcomes, and the metrics for measuring success. For example, a mentorship program could pair experienced employees with new hires from underrepresented groups, providing guidance, support, and opportunities for professional development. Such a program would require clear guidelines on the mentorship process, criteria for selecting mentors and mentees, and a structured timeline for the mentorship relationships.
Further, XYZ Corp should ensure that its policies reinforce the values of diversity and inclusion. This could involve revising existing policies to eliminate unconscious bias in hiring, promotion, and compensation practices. Additionally, the company could introduce new policies that support work-life balance, flexible working arrangements, and a zero-tolerance stance on discrimination and harassment. These policies should be communicated effectively to all employees and integrated into the company culture.
To ensure these programs and policies are effective, XYZ Corp must also consider how they will be implemented, who will be responsible for their execution, and how employees will be trained on new procedures. HR must work closely with other departments to integrate these initiatives into the company's daily operations.
XYZ Corp's HR department should also create a feedback loop where employees can share their experiences and suggestions for improvement. This feedback is invaluable for refining programs and ensuring they align with employee needs and business objectives.
By developing well-thought-out HR programs and structuring supportive policies, XYZ Corp can create a solid foundation for achieving its strategic goals. These initiatives will directly impact the company's ability to attract, retain, and develop a diverse and talented workforce, thus enhancing its competitiveness and capacity for innovation.
Step 6: Create an HR Scorecard
An HR Scorecard is essential for tracking and communicating the performance of HR initiatives against the strategic objectives. It provides a structured approach to measuring HR's contribution to business success (Walker and MacDonald, 2001). XYZ Corp's scorecard might include KPIs such as the number of diverse candidates hired, the retention rate of high-potential employees, or the satisfaction scores of participants in the mentorship program.
Step 7- Create an HR Scorecard:
The HR Scorecard is a strategic HR measurement system that links HR management with the organization's strategic goals. It operationalizes the concept of HR as a strategic partner by quantifying HR's effectiveness and efficiency in meeting the organization's strategic goals. For XYZ Corp, the HR Scorecard becomes a critical tool for ensuring that the HR department's contributions are visible and measurable.
In developing the HR Scorecard, XYZ Corp should identify key performance indicators (KPIs) aligning with the strategic HR objectives and broader business goals. These KPIs should be a balanced mix of leading indicators that predict future success and lagging indicators that reflect past outcomes.
For instance, to track progress toward the goal of increasing workforce diversity, KPIs might include:
- The percentage of diverse candidates in the recruitment pipeline.
- The rate of diverse hires against the total number of hires.
- The advancement rate of diverse employees within the organization.
By integrating these KPIs into an HR Scorecard, XYZ Corp can systematically review and communicate the value added by the HR department. The scorecard should be reviewed regularly, ideally as part of the strategic review process, to ensure that HR continues to align with and support the company's strategic direction. It also serves as a dashboard that allows senior leadership to make informed decisions based on current HR performance data.
Creating an HR Scorecard encourages accountability and continuous improvement within the HR department. It also elevates the role of HR by demonstrating how human capital strategies contribute to achieving strategic objectives and overall business success.
Step 8 - Communicate the Plan
Communication of the HR strategic plan is vital to ensure stakeholder buy-in and understanding. It involves clearly articulating the plan's components, expected outcomes, and the role of different stakeholders in its implementation. XYZ Corp could use a variety of communication channels to reach all levels of the organization and ensure that the HR strategic plan is understood and embraced.
Step 9 - Implement the Plan
Implementing the HR strategic plan requires careful planning, resource allocation, and project management to ensure that initiatives are rolled out effectively . XYZ Corp's HR department would need to prioritize initiatives, define clear roles and responsibilities, and establish timelines for executing each program.
Step 10 - Monitor Progress
Monitoring progress is about regularly reviewing the effectiveness of HR initiatives and their impact on the strategic objectives. It involves collecting and analyzing data to assess the success of the HR plan and making necessary adjustments. XYZ Corp should set up a system for continuously monitoring and evaluating its HR programs, using the data gathered to inform decision-making.
Step 11 -Adjust the Plan as Needed
Adjusting the HR strategic plan is an ongoing process that requires HR to be responsive to changes in the business environment, organizational needs, and the effectiveness of current HR initiatives. XYZ Corp must remain flexible and be prepared to update its HR strategy to adapt to new challenges and opportunities.
This detailed guide integrates evidence from scholarly sources to demonstrate the importance of each step in developing an HR Strategic Plan. By following these steps, organizations like XYZ Corp can ensure their HR strategies are effectively aligned with their business goals and can adapt to the dynamic business landscape.
In the realm of human resource management, the formulation of an HR strategy that is both reflective of and instrumental to the business strategy is paramount. To this end, various models have been developed to guide HR professionals in crafting strategies that support and drive business objectives. These models serve as blueprints for aligning HR practices with organizational goals and responding to the complexities of the modern business environment. Below, I share five such HR strategy formulation models and explore how they are applied in practice.
1. Integrative Model of HR Strategy Formulation
This model advocates for a seamless integration of HR strategy within the overall business strategy, considering both internal and external environmental factors. Additional insights can be found in works by Bamberger and others, which discuss the strategic approach to HR issues as part of formulating business strategy.
2. Knowledge Map-Driven Framework
This framework emphasizes using knowledge mapping to guide HR strategy formulation, particularly within knowledge-based organizations, to enhance innovation and learning.
3. Model of Formulating and Implementing HR Strategy
This comprehensive mode l is used for formulating and implementing HR strategies and offers examples of how the process is implemented within organizations.
In an era where the workforce is increasingly recognized as a pivotal element of competitive advantage, the concept of a human resources (HR) strategy has become a cornerstone of organizational success. A well-crafted HR strategy is not just a roadmap for managing a company's people; it is an integral part of the broader business strategy that ensures the organization's goals are met through effectively utilizing its human capital.
Throughout this article, we have explored various models and frameworks that guide the formulation and implementation of HR strategies. Each model offers unique insights into how HR can align with and propel business objectives, from the Integrative Model's harmonization of HR and business strategies to the Knowledge Map-Driven Framework's emphasis on leveraging intellectual assets for competitive advantage.
Ultimately, HR strategy is about more than just policies and practices; it's about creating a symbiotic relationship between an organization's people and its strategic aspirations. It's about ensuring the workforce is engaged, skilled, and motivated to fulfill their roles and drive the company toward its strategic vision.
As we conclude our exploration of what constitutes strategic human resources management, it is clear that the approaches to HR strategy formulation are as diverse as the organizations they serve. However, the common thread that ties these models together is their aim to integrate HR practices into the organization's strategic fabric, enabling it to navigate the complexities of the business world with agility and foresight.
A human resources strategy is a dynamic and evolving blueprint that must be continuously assessed and refined to meet the organization's and its workforce's needs. It is a critical component of an organization's overall strategy and a testament to the undeniable truth that the most valuable asset of any company is its people.
Related Articles
Notifications.
Sign up now to get updated on latest posts and relevant career opportunities
Filter by Keywords
People Management
Human resource planning (hrp): a guide for hr professionals.
March 21, 2024
In the business world of sameness, your employees are your true differentiator.
And that’s where HR teams come in—meticulously planning every step of the employee lifecycle to ensure your business’ success. Whether you’re a seasoned HR professional or a new member of an HR team, brush up on the must-haves for optimal human resource planning (HPR).
What Is Human Resource Planning?
Understanding human resource planning, steps to effective human resource planning, the role of hrp in boosting organizational performance, challenges of human resource planning, utilizing technology in human resource planning, future trends in human resource planning.
Companies need to ensure their human resource goals match their business goals. Businesses use human resource planning to evaluate their current workforce and predict its alignment with future needs.
In this process, you and the rest of your HR team identify skill requirements and formulate recruitment, training, management, and succession planning. Meticulously planning for future needs enables companies to optimize staffing levels while staying prepared for upcoming challenges and opportunities.
Human resource planning is often the unsung hero in a company’s strategic framework—the behind-the-scenes MVP deserves a closer look.
HR planning must align human resources with the broader organizational strategy and business goals to be effective. To do this, the HR planning process must be comprehensive, accurately assessing current employees and forecasting future needs so that any gaps can be filled at the appropriate time.
Different roles of human resource planning
Because a strategic human resource plan aligns with organizational goals, it encompasses everything from workforce planning to employee retention. To fully appreciate the benefits of HR planning, let’s zoom in and see the different hats it wears in a company.
The most obvious role human resource planning plays is in determining how many employees are necessary for the company to operate. To do this, HRP must also rely heavily on performance management, where past reviews are assessed to understand the current workforce’s strengths and weaknesses. Employee self-evaluations can be helpful in this regard.
Next, human resource planning plays a critical role in gap analysis. It lets companies know when and where they lack specific skills, not only for the present but also for future needs. Through this gap analysis, a business can more effectively plan for training current employees and hiring new employees.
“Hard” vs. “soft” human resource planning

There are two approaches to HRP: “Hard” and “soft.”
In “hard” human resource planning, a quantitative approach is taken. The focus is on workforce capabilities and resource planning. Supply forecasting and skills inventory data is used to predict future workforce requirements.
The sole mission is getting that sweet alignment between human resources and the business’s needs.
“Soft” human resource planning flips the script, prioritizing the qualitative side of the process. It’s all about company culture, employee satisfaction, and fine-tuning those essential soft skills.
Soft HRP aims to create a supportive work environment that fosters employee retention while aligning with organizational objectives. It’s accomplished through employee training programs, building skilled employees from within who can meet the organization’s strategy.

To understand the process more deeply, let’s break down the key steps of human resource planning and unlock its secrets.
Analyzing organizational objectives and plans
The HR planning process must align with the overall business strategy for human resource planning to be effective. The organization must carefully lay out its long-term goals so the human resource department has a roadmap.
HR professionals must work closely with department leads to understand the business objectives comprehensively. Only through this collaboration can the human resource plan strategically align with where the company wants to go.
Evaluating the current state of the workforce and uncovering gaps
The current workforce status must be assessed in the second step of the HR planning process. This involves a detailed analysis of their skills, capabilities, and performance, vividly showing the team’s strengths and areas for improvement.
HR teams use tools like performance management systems to build a comprehensive skills inventory. Try conducting employee self-evaluations to get a broader picture of where gaps may be.
The next steps hinge on how effectively the current employees align with the present and future needs of the business.
Forecasting future HR requirements
Once the HR manager knows the company’s future goals and the workforce’s current state, they can begin forecasting future HR requirements. They’ll use the data to predict the need for new employees.
This is a complex process—changes to the business environment, company culture, and market trends must all be considered to forecast future demand accurately. As markets shift, the pool of available quality employees changes, too. Supply forecasting helps HR human resource planners factor this in and initiate the hiring process at an optimal time.
Developing and implementing a plan
Now that we understand the the gaps between current staffing and future needs, let’s move on to developing and implementing a strategic HR plan.
The HR team should create talent strategies for recruiting and retaining new hires while developing the skills of existing employees to keep pace with changing business needs. Creating detailed job descriptions, refining the hiring process, and planning for benefits administration are vital during this step.
Monitoring, reviewing, and reassessing the plan
The final step is more of an ongoing HRP process. The team must continually monitor and reassess the needs of the company.
HR software and analytics tools help track the effectiveness of human resource planning over time. Continuously monitoring employee performance and the impact of training programs ensures that strategic human resource management stays aligned with the changing business environment.
A company’s performance depends heavily on how well-staffed it is. It isn’t just about the number of employees on the payroll but how well those employees meet the organization’s needs. The human resource planning process is the best way to ensure that alignment.
Strategic human resource planning effectively identifies the number of employees required, their needed skills, and the optimal hiring times to maximize the chances of securing qualified individuals when they’re needed.
HR professionals identify gaps in the ability of current employees as they go through the HRP process. These gaps degrade the overall performance of the business. A good human resource plan will weigh the ability to train the existing workforce to meet demand vs. the need to hire new employees.
Because HR managers must work closely with department heads for this alignment to occur, they’re always acutely aware of where performance issues are arising and can adapt the planning process to mitigate those problems.
Another area where HRP can boost a company’s performance is by facilitating organizational innovation. A business must have a skilled and dynamic employee pool to be innovative. With a well-developed HR plan, the company can identify potential employees who can fulfill those needs.

While the human resource planning process is vital to organizational management, it doesn’t come without challenges. Without a plan to overcome these challenges, they can derail the plan’s effectiveness. Strategic planning must anticipate the challenges an HR team will encounter during HRP, ranging from market fluctuations to internal workforce dynamics.
Business objective alignment
We’ve talked quite a bit about the need to balance a human resource strategy with the objectives of the business. This, essentially, is the core of HRP and one of the biggest challenges HR managers face when developing a plan. The ever-evolving market conditions and organizational priorities add a layer of complexity to the already challenging task of strategic human resource planning.
To counter this, HR departments must maintain a continuous approach to HRP and constantly consult with department heads to update the direction of the company and the needs of individual departments.
Accurate forecasting
A big part of human resource planning involves forecasting the demand for current employees and future talent. Business growth can be unpredictable, technological advancements can change needs rapidly, and economic changes can shift priorities.
Investing in HR software such as data analytics and forecasting tools will help HR plan more accurately for these changes. These tools used advanced machine learning and large amounts of data to create forecasts more accurately than humans alone can.
Maintaining balance
There’s a delicate balance to be maintained between the current workforce needs and future requirements. This planning process can be overwhelming, especially for small HR teams. Teams at larger companies may struggle to stay connected with the needs of frontline employees.
Smaller teams especially must rely on talent management software that will automate much of the work in predicting when new employees or skills will be needed. Larger companies must create and maintain a direct line of communication between HR and frontline employees so their concerns are always a part of the human resource planning process.
Integrating the planning processes
Human resource planning must not only consider the business’s goals but must be tightly integrated with the company’s overall planning process. This ensures that actions taken by HR aren’t just reactive but that a proactive approach to hiring and training employees is taken.
This requires a strategic approach to resource planning. HR managers should be a part of every discussion about the company’s future so they can provide input that shapes the company’s direction and receive input that shapes HR’s approach.

We’ve seen several instances where HR planning software will help teams better prepare for the business’s staffing needs. Technology has evolved rapidly in recent years, making it a vital part of strategic human resources planning. Chief among these advancements has been the growth of artificial intelligence , revolutionizing how companies manage their workforce through machine learning.
The rise of remote work has further driven the adoption of new technologies. An HR department must emphasize a flexible and dynamic human resource planning process with a dispersed workforce. Innovative tools and workforce planning software can help support these growing HR needs.
ClickUp is an all-in-one productivity platform. In addition to comprehensive project planning tools , the software has useful features for human resources planning. Its capabilities extend to various HR functions but also work well for every department in the company, making it ideally suited to keeping HR departments on the same page as other departments and the overall company direction.
As you can tell, it’s obvious how vital performance management is for strategic human resource planning. ClickUp provides a robust set of performance management tools, helping HR staff give and receive continuous feedback and set employee goals. By taking advantage of these features, your company can foster a constant learning and development culture that better prepares it for changing needs.
One of ClickUp’s biggest strengths is the extensive set of available templates. For nearly any productivity task your company needs to accomplish, a template shows you exactly how to put the software’s features to work on it.
ClickUp’s HR Standard Operating Procedures template is handy for identifying skill gaps and developing a plan to close them. To keep existing employees up-to-date and prepared for changing requirements, the ClickUp HR knowledge base template shines.
Technology has rapidly changed the landscape of human resources and shows no signs of slowing down. Changing attitudes and shifting priorities will also affect how strategic human resource planning evolves over the coming years.
Companies will no doubt find that artificial intelligence and data analytics tools will emerge that further refine processes and increase the accuracy of forecasts. As these tools improve the ability of an HR team to forecast staffing needs and identify skill gaps, smaller HR teams will be able to better compete with their larger counterparts.
We’re also seeing significant shifts in the way companies approach employment. More focus than ever is being placed on employee well-being and work-life balance. These priorities pay dividends by reducing burnout and improving productivity.
Human resources departments will increasingly shift from mere recruitment and training to working on building an inclusive and supportive workplace culture.
The trend of remote work and the gig economy will likely continue. The gig economy could provide opportunities for HR teams to rely on independent contractors for temporary surges in staffing requirements to keep the in-house staffing optimized during slow times but not overwhelmed during the busy ones.
Wrapping It Up

While many challenges are involved in keeping a company’s workforce as tightly tuned to its actual needs as possible, doing so provides the most efficient use of human resources and a substantial competitive advantage.
Thankfully, there are many tools available to help companies achieve this. Several free HR planning templates can help keep your staff organized and their processes streamlined. By combining this with effective employee management software , like ClickUp, even small teams can develop comprehensive human resource plans.
ClickUp is free to try. Sign up today to see how this powerful productivity tool can benefit your company.
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months

- Human Resource Planning (HRP)

Written by True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
Reviewed by subject matter experts.
Updated on July 12, 2023
Get Any Financial Question Answered
Table of contents, what is human resource planning (hrp).
Human Resource Planning (HRP) is the process of systematically analyzing and forecasting an organization's current and future human resource needs, and developing strategies to meet those needs.
This involves identifying the right number of employees with the appropriate skills, knowledge, and experience to effectively accomplish the organization's goals and objectives.
HRP is a crucial component of business planning and finance, as it ensures that an organization's workforce is aligned with its strategic direction and can adapt to changes in the business environment.
HRP directly impacts an organization's ability to achieve its goals and objectives by ensuring that the workforce is well-prepared, skilled, and motivated.
HRP also contributes to the financial health of a company by optimizing workforce productivity, minimizing costs associated with hiring and training, and reducing employee turnover.
Additionally, effective HRP enables businesses to respond more quickly and efficiently to changes in the external environment, such as technological advancements, economic fluctuations, and shifting market demands.
This adaptability is crucial for maintaining a competitive advantage and achieving long-term success.
The HRP Process
Environmental scanning.
The HRP process begins with environmental scanning, which involves collecting and analyzing information about the internal and external factors that may impact an organization's workforce.
This can include examining economic trends, technological advancements, demographic changes, industry competition, and government regulations, as well as assessing the company's internal strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis).
By conducting a thorough environmental scan, organizations can gain valuable insights into the factors that may affect their workforce and identify potential opportunities and challenges that need to be addressed through HRP.
Forecasting
Forecasting is a critical step in the HRP process, as it involves estimating the future demand for and supply of human resources within the organization.
This includes predicting the number of employees needed, the types of skills and competencies required, and the availability of internal and external talent to meet these needs.
Forecasting can be accomplished through various methods, such as trend analysis, regression analysis, or expert judgment.
Accurate forecasting is essential for developing effective HRP strategies and ensuring that the organization has the right people in the right roles at the right time.
Job Analysis
Job analysis is the process of collecting, analyzing, and documenting information about the tasks, duties, and responsibilities of each job within an organization.
This information is used to create detailed job descriptions and specifications, which are essential for HRP as they provide a clear understanding of the skills, knowledge, and abilities required for each role.
A thorough job analysis helps organizations identify the competencies needed to perform each job effectively and serves as a foundation for workforce planning, recruitment, training, performance management, and career development initiatives.
Supply Analysis
Supply analysis involves assessing the current workforce's skills, knowledge, and abilities to determine whether the organization has the necessary human resources to meet its strategic objectives.
This includes evaluating the number of employees, their skills and competencies, and their potential for growth and development.
By conducting a supply analysis, organizations can identify existing talent gaps and develop targeted strategies to address them, such as training and development programs, succession planning , or external recruitment.
Demand Analysis
Demand analysis focuses on estimating the organization's future human resource requirements based on its strategic goals and objectives.
This involves projecting the number of employees needed, the skills and competencies required, and the anticipated changes in workforce composition due to factors such as turnover, retirements, and promotions.
A comprehensive demand analysis enables organizations to develop targeted HRP strategies that align their workforce with their strategic direction and ensure they have the right people in place to achieve their goals.
Gap Analysis
Gap analysis is the process of comparing the organization's current human resource supply with its future demand to identify any discrepancies.
This includes evaluating the differences in the number of employees, skills, and competencies required to meet the organization's strategic objectives.
By conducting a gap analysis, organizations can determine whether they have a surplus or shortage of human resources and develop appropriate strategies to address these gaps.
This can include recruitment and hiring initiatives, training and development programs, or workforce restructuring efforts.
Action Planning
Action planning is the final step in the HRP process, which involves developing and implementing strategies to address the identified gaps between the current workforce supply and future demand.
This can include initiatives such as recruiting new employees, providing training and development opportunities for existing staff, implementing succession planning, or adjusting organizational structures to better align with strategic objectives.
Effective action planning requires ongoing monitoring and evaluation to ensure that the HRP strategies are achieving the desired results and that the organization remains well-prepared to respond to changes in its internal and external environment.
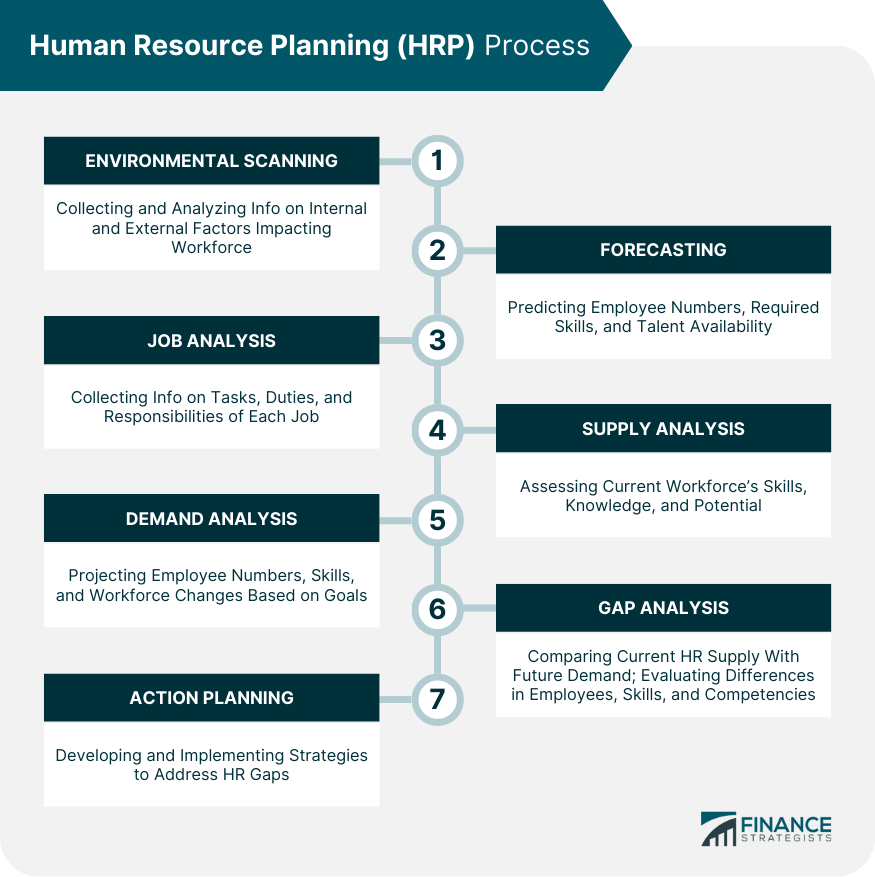
Benefits of HRP
Improved workforce productivity.
By ensuring that the organization has the right number of employees with the appropriate skills and competencies, HRP helps to optimize the use of human resources and enables employees to work more efficiently and effectively.
This increased productivity can lead to higher levels of employee engagement, job satisfaction, and overall organizational performance, ultimately contributing to the company's bottom line.
Cost Savings
HRP can result in significant cost savings for organizations by helping to minimize expenses associated with hiring, training, and retaining employees.
Through effective workforce planning, companies can reduce the costs of recruiting and onboarding new staff, as well as the expenses associated with high employee turnover, such as lost productivity and the need for additional training.
Additionally, HRP can help organizations identify opportunities for streamlining their workforce and eliminating redundancies, leading to further cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
Reduced Employee Turnover
Effective HRP can contribute to reduced employee turnover by ensuring that the organization has the right people in the right roles and that employees are provided with the necessary support and development opportunities to succeed in their positions.
By fostering a positive work environment and promoting employee engagement, HRP can help to improve job satisfaction and employee retention, ultimately reducing the costs associated with high turnover rates.
Increased Flexibility and Adaptability
HRP enables organizations to be more flexible and adaptable in the face of changing market conditions, technological advancements, and other external factors.
Through effective workforce planning, companies can quickly adjust their human resource strategies to respond to emerging trends and capitalize on new opportunities.
This increased agility is essential for maintaining a competitive advantage and ensuring long-term success in today's rapidly evolving business environment.
Better Risk Management
HRP plays a crucial role in risk management by helping organizations identify and address potential workforce-related risks, such as skill gaps, labor shortages, or an aging workforce.
By proactively addressing these risks through targeted HRP strategies, companies can mitigate potential negative impacts and ensure the continued success of their operations.
Challenges of HRP
Uncertainty.
Uncertainty is a significant challenge in HRP, as organizations must make predictions about future workforce needs based on a variety of factors, such as economic trends, technological advancements, and competitive pressures.
These factors are often unpredictable and subject to change, making it difficult for companies to accurately forecast their human resource requirements.
To address this challenge, organizations can leverage scenario planning techniques and continually update their HRP strategies as new information becomes available.
Resistance to Change
Employees may be reluctant to embrace new organizational structures, job roles, or training programs, which can impede the organization's ability to achieve its workforce planning goals.
To overcome this challenge, organizations should involve employees in the HRP process, clearly communicate the reasons for change, and provide adequate support and resources to help staff adapt to new roles and responsibilities.
Lack of Resources
The lack of resources, including time, funding, and personnel, can pose a significant challenge to implementing effective HRP strategies.
Organizations may struggle to allocate the necessary resources for workforce planning initiatives, particularly in times of financial constraints or competing priorities.
To address this challenge, organizations should prioritize HRP as a critical component of their overall business strategy and invest in the necessary resources to ensure its successful execution.
Inaccurate Forecasting
Inaccurate forecasting can undermine the effectiveness of HRP efforts by leading to imprecise estimates of future workforce needs. This can result in talent shortages or surpluses, which can negatively impact organizational performance and employee satisfaction.
To improve the accuracy of their forecasting efforts, organizations can leverage a variety of forecasting techniques, such as trend analysis, regression analysis, or expert judgment, and continually update their projections based on the latest available data.
Inadequate Data Analysis
Inadequate data analysis can hinder the effectiveness of HRP efforts by preventing organizations from identifying and addressing critical workforce gaps and opportunities.
This can result in suboptimal HRP strategies that fail to align the workforce with the organization's strategic objectives.
To overcome this challenge, organizations should invest in robust data collection and analysis tools, as well as develop the necessary skills and expertise within their HR teams to effectively analyze and interpret workforce data.
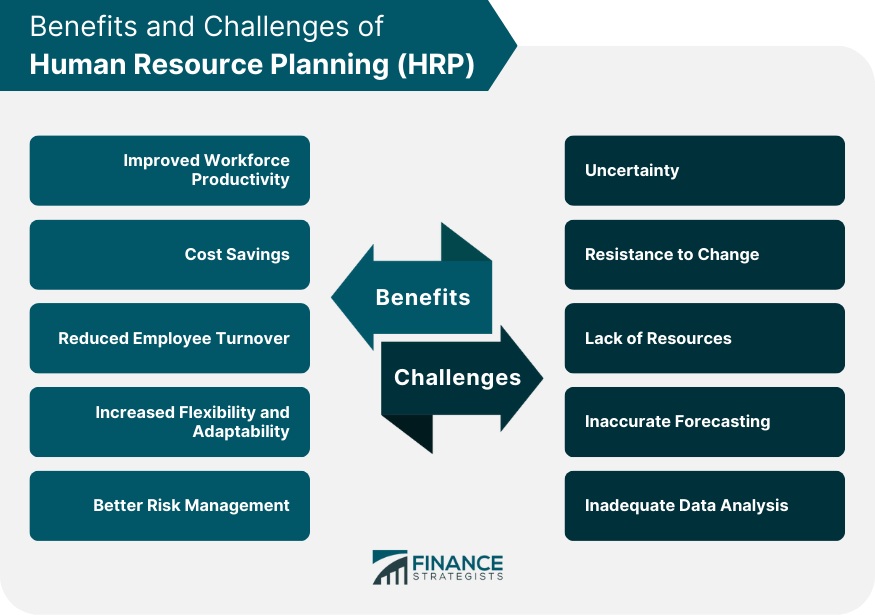
Best Practices in HRP
Involvement of top management.
Gaining the commitment and support of senior leaders is essential for the successful implementation of HRP initiatives, as it helps to ensure that workforce planning is prioritized and integrated into the organization's overall business strategy.
Collaboration Between HR and Other Departments
By working together, HR professionals and departmental leaders can share insights, resources, and expertise to develop and implement targeted HRP strategies that align the workforce with the organization's strategic objectives.
Use of Technology
Leveraging technology is a best practice in HRP, as it enables organizations to streamline and automate various aspects of the workforce planning process, such as data collection, analysis, and reporting.
By utilizing advanced HR software and analytics tools, companies can gain valuable insights into their workforce and make more informed decisions regarding their HRP strategies.
Regular Review and Update of HRP
Regular review and update of HRP strategies are essential for ensuring their ongoing effectiveness in the face of changing business conditions and workforce dynamics.
Organizations should continually monitor and evaluate their HRP efforts, making adjustments as needed based on new information, emerging trends, and shifting priorities.
Integration With Overall Business Strategy
Finally, HRP should be fully integrated with the organization's overall business strategy. This helps to ensure that workforce planning initiatives are aligned with the company's strategic objectives and that the organization has the necessary human resources to achieve its goals.
The Bottom Line
Human Resource Planning (HRP) is the systematic process of analyzing and forecasting an organization's current and future human resource needs and developing strategies to meet those needs.
It plays a critical role in aligning the workforce with the organization's strategic objectives and ensuring its long-term success.
The HRP process involves several key steps, including environmental scanning, forecasting, job analysis, supply analysis, demand analysis, gap analysis, and action planning.
Each of these steps plays a crucial role in identifying the organization's workforce needs and developing targeted strategies to address them.
To ensure the success of HRP initiatives, organizations should adhere to best practices, such as involving top management, fostering collaboration between HR and other departments, leveraging technology, regularly reviewing and updating HRP strategies, and integrating HRP with the overall business strategy.
By understanding and effectively implementing the HRP process, organizations can optimize their workforce, manage risks, and ensure their long-term success in today's competitive business environment.
Human Resource Planning (HRP) FAQs
What is human resource planning (hrp).
Human Resource Planning (HRP) is the process of forecasting future human resource needs and developing strategies to meet them.
Why is HRP important for business planning?
HRP helps businesses ensure that they have the right people with the right skills in the right positions at the right time to achieve their strategic objectives.
What is the HRP process?
The HRP process typically involves environmental scanning, forecasting, job analysis, supply and demand analysis, gap analysis, and action planning.
What are the benefits of HRP?
The benefits of HRP include improved productivity, cost savings, reduced employee turnover, increased flexibility, and better risk management.
What are some challenges associated with HRP?
Some challenges associated with HRP include uncertainty, resistance to change, lack of resources, inaccurate forecasting, and inadequate data analysis.
About the Author
True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide , a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University , where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon , Nasdaq and Forbes .
Related Topics
- Business Continuity Planning (BCP)
- Business Exit Strategies
- Business-to-Business (B2B)
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- Capital Planning
- Change-In-Control Agreements
- Corporate Giving Programs
- Corporate Philanthropy
- Cross-Purchase Agreements
- Crowdfunding Platforms
- Employee Retention and Compensation Planning
- Employee Volunteer Programs (EVPs)
- Endorsement & Sponsorship Management
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Entity-Purchase Agreements
- Equity Crowdfunding
- Family Business Continuity
- Family Business Governance
- Family Business Transition Planning
- Family Limited Partnerships (FLPs) and Buy-Sell Agreements
- Jumpstart Our Business Startups (JOBS) Act
- Request for Information (RFI)
- Request for Proposal (RFP)
- Revenue Sharing
- SEC Regulation D
- Sale of Business Contract
- Security Token Offerings (STOs)
- Shareholder Engagement and Proxy Voting
- Social Engagements
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
Meet top certified financial advisors near you, our recommended advisors.

Taylor Kovar, CFP®
WHY WE RECOMMEND:
Fee-Only Financial Advisor Show explanation
Certified financial planner™, 3x investopedia top 100 advisor, author of the 5 money personalities & keynote speaker.
IDEAL CLIENTS:
Business Owners, Executives & Medical Professionals
Strategic Planning, Alternative Investments, Stock Options & Wealth Preservation

Claudia Valladares
Bilingual in english / spanish, founder of wisedollarmom.com, quoted in gobanking rates, yahoo finance & forbes.
Retirees, Immigrants & Sudden Wealth / Inheritance
Retirement Planning, Personal finance, Goals-based Planning & Community Impact
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.
Fact Checked
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications.
They regularly contribute to top tier financial publications, such as The Wall Street Journal, U.S. News & World Report, Reuters, Morning Star, Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg, Marketwatch, Investopedia, TheStreet.com, Motley Fool, CNBC, and many others.
This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year.
We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources.
Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs.
How It Works
Step 1 of 3, ask any financial question.
Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Your information is kept secure and not shared unless you specify.

Step 2 of 3
Our team will connect you with a vetted, trusted professional.
Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise.

Step 3 of 3
Get your questions answered and book a free call if necessary.
A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.

Where Should We Send Your Answer?

Just a Few More Details
We need just a bit more info from you to direct your question to the right person.
Tell Us More About Yourself
Is there any other context you can provide.
Pro tip: Professionals are more likely to answer questions when background and context is given. The more details you provide, the faster and more thorough reply you'll receive.
What is your age?
Are you married, do you own your home.
- Owned outright
- Owned with a mortgage
Do you have any children under 18?
- Yes, 3 or more
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
- $50k - $250k
- $250k - $1m
Pro tip: A portfolio often becomes more complicated when it has more investable assets. Please answer this question to help us connect you with the right professional.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
- I would prefer remote (video call, etc.)
- I would prefer in-person
- I don't mind, either are fine
What's your zip code?
- I'm not in the U.S.
Submit to get your question answered.
A financial professional will be in touch to help you shortly.

Part 1: Tell Us More About Yourself
Do you own a business, which activity is most important to you during retirement.
- Giving back / charity
- Spending time with family and friends
- Pursuing hobbies
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
Part 3: confidence going into retirement, how comfortable are you with investing.
- Very comfortable
- Somewhat comfortable
- Not comfortable at all
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
- Very confident
- Somewhat confident
- Not confident / I don't have a plan
What is your risk tolerance?
How much are you saving for retirement each month.
- None currently
- Minimal: $50 - $200
- Steady Saver: $200 - $500
- Serious Planner: $500 - $1,000
- Aggressive Saver: $1,000+
How much will you need each month during retirement?
- Bare Necessities: $1,500 - $2,500
- Moderate Comfort: $2,500 - $3,500
- Comfortable Lifestyle: $3,500 - $5,500
- Affluent Living: $5,500 - $8,000
- Luxury Lifestyle: $8,000+
Part 4: Getting Your Retirement Ready
What is your current financial priority.
- Getting out of debt
- Growing my wealth
- Protecting my wealth
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have.
- Tax planning expertise
- Investment management expertise
- Estate planning expertise
- None of the above
Where should we send your answer?
Submit to get your retirement-readiness report., get in touch with, great the financial professional will get back to you soon., where should we send the downloadable file, great hit “submit” and an advisor will send you the guide shortly., create a free account and ask any financial question, learn at your own pace with our free courses.
Take self-paced courses to master the fundamentals of finance and connect with like-minded individuals.
Get Started
Hey, did we answer your financial question.
We want to make sure that all of our readers get their questions answered.
Great, Want to Test Your Knowledge of This Lesson?
Create an Account to Test Your Knowledge of This Topic and Thousands of Others.
Get Your Question Answered by a Financial Professional
Create a free account and submit your question. We'll make sure a financial professional gets back to you shortly.
To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
Great thank you for voting..
Relationship Between HR Strategies & Business
- Small Business
- Business Planning & Strategy
- Business Strategies
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
The Best Practices for Manager-Employee Relations
Top three recommendations for implementing an hr strategy in an organization, consequences of poor human resource planning.
- HR Strategies With Business Strategies
- Emerging Issues in HR
The personnel administration function of human resources has become outdated in the past 20 years. Today, human resources departments have a more defined, strategic role in organizations, and an HR strategy affects the bottom line. One of the challenges for HR leaders is convincing executive leadership teams that human capital is one of the most important resources in which the company can invest. This return on investment is an essential part of the argument for including HR as part of an overall business strategy.
HR Strategy Is Business Strategy
In an ideal world, there is not a line drawn in the sand between human resources strategy and business strategy. A successful business owner realizes the strong connection between the two. Developing human capital is important to the longevity and success of a business. In the past, personnel administration was merely the processing of payroll, benefits and applications. Human resources strategy today involves executive leadership teams conferring with human resources experts to develop complementary goals for human resources and the overall business.
HR Strategy and Business Productivity
The recruitment and selection process of your human resources department is paramount in building a productive workforce. Developing a human resource strategy for recruiting and selecting the best employees affects your organization's bottom line. Maintaining a workforce where employees enjoy high levels of job satisfaction and job security translates into a workforce that helps achieve business goals. According to HR experts, human capital, or human resources, is your most valuable resource.
Trends Affect HR and Business Strategy
In a study conducted by consulting giant Towers Watson, business executives are paying close attention to a trend toward blending human resources strategy and business strategy. According to the results of a 2010 Towers Watson study, "[W]e may be witnessing a tipping point — where HR technologies become the integrated engine for advancing the broader needs of the business, supporting far more than basic transactions, and advancing the HR and business agenda of the future. ... Human resources information systems are integral in the development of performance management, recruitment and selection.
Interaction Among Executive Leadership
The real test of a relationship between human resources and overall business strategy is the quality of the interaction between human resources executives and other company executives. Many times, human resources leaders who are denied access to the boardroom complain that organizations don't appreciate the value of human capital. The way to improve the relationship between HR and C-level executives is by demonstrating the return on investment (ROI) in human resources activities. This may involve explaining the connection between a reduction in employee turnover and an improvement in job satisfaction that improves the bottom line.
Considerations
A number of factors affect the relationship between human resources and business strategy. Executive leadership needs first to understand the benefits of aligning HR goals with overall business goals. Forward-thinking concepts may need to be approached carefully to avoid skepticism among old-school executives who still consider human resources as merely personnel administration. Building the relationship may also require the assistance of an HR consultant to map the strategy for effecting change in your organization.
- Entrepreneur: Four Steps to Building an HR Agenda for Growth
- Management.com: Integrating Human Resource Strategic Planning to Achieve Business Excellence
- U.S. Office of Personnel Management
- Society for Human Resource Management
- National Human Resources Association
- American Society for Training & Development
- U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission
Ruth Mayhew has been writing since the mid-1980s, and she has been an HR subject matter expert since 1995. Her work appears in "The Multi-Generational Workforce in the Health Care Industry," and she has been cited in numerous publications, including journals and textbooks that focus on human resources management practices. She holds a Master of Arts in sociology from the University of Missouri-Kansas City. Ruth resides in the nation's capital, Washington, D.C.
Related Articles
Differences between transactional hr & strategic hr, the main job of the hr function in an organization, the relationship of hr with business strategy, what is the hr business partner model, hr issues & solutions, the advantages of the human resource management strategy, what makes a human resource strategy successful, the skills needed for strategic human resource management, the disadvantages of an hr scorecard, most popular.
- 1 Differences Between Transactional HR & Strategic HR
- 2 The Main Job of the HR Function in an Organization
- 3 The Relationship of HR With Business Strategy
- 4 What Is the HR Business Partner Model?
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
Strategic Human Resource Management (2024 Guide)

Updated: Jun 8, 2024, 9:04am

Table of Contents
What is strategic human resources, why strategic human resources is important, 5 steps to strategic human resources, bottom line, frequently asked questions (faqs).
Strategic human resource management (SHRM) is a process that organizations use to manage their employees. It is a way to ensure that the organization’s HR are used in a way that supports the organization’s goals. Think of it as a bridge connecting human resources and the goals of the company. With SHRM, businesses can more effectively manage employee performance and development, as well as create programs and policies that support the company’s overall strategy.
Featured Partners
$40 per month + $6 per user

On OnPay's Website
SurePayroll
$29.99/mo plus $5 per employee

On SurePayroll's Website
$40 per month plus $6 per user

On Gusto's Website
$35/month plus $8 PEPM

On Rippling's Website
$50/month + $8/user

On Justworks' Website
The goal of SHRM is to create policies and programs that align with the company’s business strategy. The main difference between human resources and strategic human resources is that human resources focus on the day-to-day management of employees, while strategic human resources focus on how employees can achieve the company’s overall goals. This means that SHRM must first understand the company’s business goals and then create programs and policies that support those goals.
Some common examples of SHRM programs and policies include:
- Performance management: Creating systems to track and improve employee performance
- Training and development: Identifying employees’ development needs and providing training and resources to help them improve
- Compensation and benefits: Designing compensation and benefits programs that attract and retain employees
- Employee relations: Managing employee relations to create a positive work environment
These are just a few examples of the types of programs and policies that can be part of SHRM. The specific programs and policies will vary depending on the company’s goals and the needs of its employees.
SHRM is important because it helps businesses achieve their goals. By aligning HR programs and policies with the company’s business strategy, SHRM can help businesses improve employee performance, develop the workforce and create a positive work environment. SHRM can also help businesses save money by reducing turnover and improving productivity.
- Improve employee performance: SHRM can help businesses improve employee performance by creating systems to track and improve performance.
- Develop the workforce: SHRM can help businesses develop the workforce by identifying employees’ development needs and providing training and resources to help them improve.
- Create a positive work environment: SHRM can help businesses create a positive work environment by managing employee relations.
- Reduce turnover: SHRM can help businesses reduce turnover by designing compensation and benefits programs that attract and retain employees.
- Improve productivity: SHRM can help businesses improve productivity by improving employee performance and creating a positive work environment.
Now that you know what SHRM is and why it’s important, you may wonder how to get started. The process involves knowing the goals of your company, its abilities, future needs and resources. From there, you put your plan into action, then reassess and pivot if necessary.
Here are the five steps to strategic human resources plan:
1. Know your company’s goals and abilities
The first step to SHRM is understanding your company’s goals and abilities. When you know your company goals and can articulate them, you’ll have an easier time creating programs and policies that support those goals. You’ll also be able to more effectively measure the success of your SHRM programs and make changes as needed.
Consider the following questions:
- What are your company’s long-term goals?
- What are your company’s strengths and weaknesses?
- What resources does your company have now?
- What skills does your workforce currently have?
- Are there any gaps in talent or skills?
Answering these questions will help you understand your company’s goals and abilities, and how SHRM can help you achieve those goals.
2. Forecast future needs
Now that you have an idea of your company’s goals and abilities, you need to forecast future needs. In order to ensure your company’s future success, you need to predict how many employees with the required skills will be necessary and measure it against your company’s current workforce. This will help you determine what skills your company will need in the future and how to develop those skills in your workforce.
- What skills will your company need in the future?
- How many employees with those skills will you need?
- How does that compare to your current workforce?
By answering these questions, you will be able to comprehend what abilities your company will need in the future and how to cultivate a workforce with those required skills.
3. Determine the resources needed to achieve company goals
After you know your company’s goals and have forecasted future needs, you need to determine the resources needed to achieve those goals. This includes identifying the financial resources, human resources and physical resources required.
- What financial resources will you need to achieve your company’s goals?
- What human resources will you need to achieve your company’s goals?
- What physical resources will you need to achieve your company’s goals?
To determine these, you’ve got to conduct an audit of both your internal and external resources. This will give you a sense of what types of resources you have available to achieve your goals and where you may need to supplement.
For example, if you’re looking to expand your workforce, you may need to invest in recruiting programs. Or, after conducting a needs assessment, you may find that your current workforce doesn’t have the necessary skills to achieve your company’s goals, so you’ll need to invest in training programs.
Another example is if you’re looking to launch a new product. In this case, you’ll need to consider the financial resources required to develop and market the product, as well as the physical resources required to produce it. You’ve also got to consider talent and skill set when launching a new product. Do you have the right people in place to bring your product to market? And do they have the necessary skills to do so?
4. Execute your plan
Now that you’ve set your company’s goals, forecasted its future needs and gathered the resources required to achieve those goals, it’s time to put your SHRM plan into action. Most companies start by recruiting the right candidates, training and development and then performance management. However, this will vary depending on your company’s specific needs.
If you already have a large talent pool to choose from, you may be better off cultivating skills of current employees before recruiting outside talent. After you’ve satisfied that resource, you may find you still need to hire. If so, you’ll need to have clear expectations and skill requirements before recruiting.
Once you’ve hired talent, it’s imperative to have a proper onboarding process. This will help ensure that your new hires are set up for success and understand what’s expected of them. After you’ve brought new talent into the fold, you need to focus on development. This includes training programs as well as opportunities for professional growth. By offering these opportunities, you’ll be able to retain top talent and keep them engaged in their work.
Last but not least is performance management. This includes setting clear expectations, providing feedback and conducting performance reviews. Performance management is a key part of SHRM as it helps ensure that your workforce is meeting expectations and contributing to your company’s bottom line.
Here are a few things to keep in mind when executing your SHRM plan:
- Set realistic goals and timelines. Trying to accomplish too much in a short period of time can be overwhelming and lead to mistakes.
- Get buy-in from upper management. If those at the top aren’t on board with your SHRM plan, it’s going to be difficult to get everyone else on board.
- Communicate with your employees. Employees should be aware of the goals of the SHRM plan and how it will affect them. This will help get them on board and ensure that they’re working towards the same goals.
- Be prepared to adjust your plan. As with any plan, things may not go as expected. Be prepared to make adjustments to ensure that you’re still on track to achieve your company’s goals. We’ll discuss this in detail in the next section.
5. Assess and pivot
After you’ve executed your SHRM plan, it’s important to assess how things are going. This includes looking at what’s working and what’s not. Based on your assessment, you may need to make adjustments to your plan. For example, if you’re not seeing the results you want, you may need to change your recruiting strategy. Or, if you’re finding that your training programs aren’t effective, you may need to make changes to those as well.
It’s also important to keep in mind that your SHRM plan is not a one-time thing. As your company grows and changes, so too will your SHRM needs. As such, it’s important to revisit your SHRM plan on a regular basis to ensure that it’s still relevant and effective.
Strategic human resource management is a process that helps companies achieve their goals by better managing their workforce. By taking the time to develop a SHRM plan, companies can ensure that they have the right people in place to achieve their goals. While developing a SHRM plan can be time-consuming, the benefits outweigh the costs. Not only will a well-executed SHRM plan help you achieve your company’s goals, but it will also help you retain top talent and keep your employees engaged in their work.
What is strategic human resource management (SHRM)?
Strategic human resource management is a process that helps companies manage their workforce in a way that aligns with their company’s goals.
Why is SHRM important?
SHRM is important because it helps companies ensure that they have the right people in place to achieve their company’s goals. Additionally, SHRM can help companies retain top talent and keep their employees engaged in their work.
What's the difference between human resources and strategic human resource management?
The difference between human resources and strategic human resource management is that human resources focuses on the day-to-day management of employees while SHRM takes a more strategic approach.
- Best HR Software
- Best HCM Software
- Best HRIS Systems
- Best Employee Management Software
- Best Onboarding Software
- Best Talent Management Software
- Best HR Outsourcing Services
- Best Workforce Management Software
- Best Time And Attendance Software
- Best Employee Scheduling Software
- Best Employee Time Tracking Apps
- Best Free Time Tracking Apps
- Best Employee Training Software
- Best Employee Monitoring Software
- Best Enterprise Learning Management Systems
- Best Time Clock Software
- Best ERP Systems
- Zenefits Review
- Oracle HCM Review
- UKG Pro Review
- IntelliHR Review
- ADP Workforce Now Review
- ADP TotalSource Review
- SuccessFactors Review
- Connecteam Review
- What is Human Resources?
- Employee Benefits Guide
- What is Workforce Management?
- What is a PEO?
- What is Human Capital Management?
- HR Compliance Guide
- Onboarding Checklist
- Benefits Administration Guide
- What Is Employee Training?
- Employee Development Plan
- 30-60-90 Day Plan Guide
- How To Calculate Overtime
- What Is Outplacement?
- New Hire Orientation Checklist
- HR Analytics Guide
Next Up In Business
- Justworks Pricing
- Calendly Review
- 10 Management Styles Of Effective Leaders
- Contact Center Workforce Management
- What Is A Background Check?
- What Is Lattice Software?

Best Hawaii Registered Agent Services Of 2024
Best Arizona Registered Agent Services Of 2024

Free Mission Statement Template (With Examples)
How To Start A Print On Demand Business In 2024

HR For Small Businesses: The Ultimate Guide
How One Company Is Using AI To Transform Manufacturing
Katherine Haan is a small business owner with nearly two decades of experience helping other business owners increase their incomes.

- Process of Human Resource Planning
Table of Contents
Human Resource Planning (HRP) is the foundation of effective workforce management. It involves a systematic process that helps organizations align their human resource needs with their strategic goals. In this blog, we’ll walk you through the process of Human Resource Planning , highlighting each step to give you a comprehensive understanding of how it works.
Understanding the Process
HRP is a continuous process that involves several interconnected steps. These steps guide organizations in making informed decisions about their workforce, ensuring they have the right people with the right skills at the right time.
1. Environmental Analysis
The first step in the HRP process is environmental analysis . This involves examining both the internal and external factors that can impact the organization’s workforce needs. Internal factors include the company’s growth plans, technological advancements, and current employee skills. External factors encompass economic trends, labor market conditions, and regulatory changes.
Key Points:
- Internal and external factors analysis.
- Identifying growth plans and technological changes.
- Economic trends and labor market conditions.
2. Forecasting Future Needs
Once the environmental analysis is complete, the next step is forecasting future needs . This involves estimating the organization’s future demand for human resources based on projected business activities. Different methods, such as quantitative models and expert opinions, can be used to forecast staffing requirements accurately.
- Estimating future demand for human resources.
- Utilizing quantitative models and expert opinions.
- Ensuring accurate staffing predictions.
3. Inventory of Current Resources
After forecasting future needs, it’s essential to take stock of the current resources available within the organization. This includes evaluating the skills, competencies, and experience of existing employees. This step helps in identifying any gaps between the current workforce and the skills needed for future operations.
- Evaluating current employee skills and competencies.
- Identifying gaps in the existing workforce.
- Matching available resources with future requirements.
4. Gap Analysis
The gap analysis phase involves comparing the forecasted demand with the available supply of human resources. This step helps identify any shortages or surpluses in the workforce. If there’s a shortfall, the organization can take proactive measures such as recruitment, training, or outsourcing to bridge the gap.
- Comparing forecasted demand with available supply.
- Identifying workforce shortages or surpluses.
- Taking proactive measures to address gaps.
5. Developing Action Plans
Based on the gap analysis, organizations can then develop action plans to address workforce imbalances. These plans may involve strategies for recruitment, training and development, promotions, transfers, and succession planning. The aim is to ensure that the organization has the right people in the right positions at all times.
- Creating action plans to address imbalances.
- Strategies for recruitment, training, and promotions.
- Ensuring the right people in the right positions.
6. Monitoring and Evaluation
The final step is monitoring and evaluation . HRP is an ongoing process, and organizations need to continuously assess whether their strategies are effective. Regular monitoring allows for adjustments to be made in response to changing business conditions, ensuring that the workforce remains aligned with the organization’s goals.
- Ongoing monitoring and evaluation.
- Adjusting strategies based on changing conditions.
- Maintaining alignment with organizational goals.
The process of Human Resource Planning is a dynamic and systematic approach to managing an organization’s workforce. By analyzing the environment, forecasting future needs, evaluating current resources, conducting gap analyses, developing action plans, and continually monitoring and evaluating, organizations can ensure they have the right talent in place to achieve their strategic objectives.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 3.3 / 5. Vote count: 3
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you! 😔
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Human Resource Management
1. Concept and Evolution of HRM
- What is HRM?
- Evolution of HRM
- Objectives of HRM
- Importance of HR
- Scope of HRM
- Nature of HRM
- Components of HRM
2. Functions of HRM
- Functions of HRM
- Roles and responsibilities HR Managers
- Functions of HR Managers
- Emerging aspects of HRM function
- Challenges faced by HR Managers
3. Environment and HRM
- Organisational environment and HRM
- Strategic Human Resource Management
- International Human Resource Management
- HR analytics
- 4th Industrial Revolution and HRM
- Artificial intelligence and HRM
4. Human Resource Planning
- What is Human Resource Planning?
- Objectives, Benefits and Need of Human
- Resource Planning Determinants of Human Resource Planning
- Levels of Human Resource Planning
- Human Resource Demand Forecasting
- Human Resource Supply Forecasting
- Human Resource Gap Analysis
- Human Resource Plan Operative Formulation
- Responsibility of Human Resource Planning
- Problems in Human Resource Planning Process
- Guidelines for Effective Human Resource Planning
5. Job Analysis, Design and Evaluation
- Concept of Job Analysis
- Objectives of Job Analysis
- Importance of Job Analysis
- Aspects of job to be analysed
- Methods of Job Analysis
- Techniques to obtain data for Job Analysis
- Job Description and Job Specification
- Job Evaluation
6. Recruitment and Selection
- Recruitment Process
- Methods of Recruitment
- Selection Methods
- Selection Tests
- Physical Examination
- Reference Checks
7. Socialisation and Mobility
- Concept of Organizational Socialisation
- Individual and the Organization: The Process of Integration
- Self-concept and Organizational Socialisation
- Concept of Role and Organizational Socialisation
- Status and Socialisation
- Sociatisation Factors in Organizational Socialisation
- Separations
8. Performance Appraisal
- Concept of Performance Appraisal
- Goals of Performance Appraisal
- Objectives of Performance Appraisal
- The Performance Appraisal Process
- Benefits of Performance Appraisal
- Performance Appraisal Methods
- Performance Counselling
- Problems in Performance Appraisal
- Effective Performance Appraisal
- Potential Appraisal
9. Career Development
- Career Development
- Career Planning
- Career Stages and Career Anchors
- Career Development Strategy
- Process of Career Development
- Responsibility for Career Development
- Limitations of Career Planning
- Strategies for making career planning a success
- Succession Planning
10. Training and Development
- Defining Training
- Needs and Benefits of Training
- Organising Training System
- A Suggested Training System
- Evaluation of Training
- Some Issues in Training
- Making Training a Strategic Function
- Towards Learning Organisation
11. Compensation and Rewards Management
- Compensation Management
- Compensation Policies and Objectives
- Compensation Administration
- Compensation Determinants
- Compensation survey
- Compensation Structure
- Compensation Structure in India
- Executive Compensation
- Reward Systems
- Forms of Reward
- Employee Benefits
12. Employee Empowerment
- Empowerment
- Quality Circle
- Workers’ Participation in Management
- Workers’ Participation in Management in India
- Forms of Workers’ Participation in
- Management in Different Countries
- Evaluation of Workers’ Participation in Management
- Measures for Effective Workers’ Participation in Management
13. Grievance Handling and Discipline Management Procedures
- Dissatisfaction, Complaint and Grievance
- Forms of Grievance
- Causes of Grievance
- Effects of Grievance
- The Discovery of Grievance
- Grievance Handling Procedure
- Grievance Management in Indian Industry
- Concept and Meaning of Discipline
- Indiscipline
- Purpose and Objectives of Disciplinary Action
- Disciplinary Action Procedure
- Legal Provisions Relating to Discharge or Dismissal (Under Industrial Disputes Act, 1947)
14. Unions and Associations
- Definition of Trade Unions
- Formative Stages of Trade Unions
- Forms of Trade Unions
- Functions of Trade Unions
- Objective of Trade Unions
- Role of Trade Unions
- Classification of Trade Unions
- Theories of Trade Unionism
- Growth of Trade Union Movement and Membership In India
- Trade Union Act, 1926
- Recognition of Trade Union
- Rights of Recognised Unions
- Problems Confronting Unions and Measures to Strengthen Trade Union Movement in India
- White-Collar and Managerial Trade Unions
- Why White-Collar Workers’ Unions?
- Employers’ Association
Module 5: Workforce Planning
Why it matters: workforce planning, why learn about job analysis, job design, and employment forecasting.

Workforce planning may seem like a mundane series of tasks, but that is certainly not the case. This is where an organization’s vision and values, where their aspirations and operating realities are accurately embedded or are lost in translation. This is also a process that can either unleash human potential or squander it. Workforce management is simple in theory. Management consulting firm Korn Ferry describes workforce planning as “the practice of mapping an organization’s people strategy with its business strategy so they work in sync,” noting that when executed well it “helps to ensure that organizations have the right workforce, today and tomorrow, at the right cost.” [1]
There is also legal and equity factors to workforce planning. The process establishes a framework that either perpetuates or minimizes the probability of discrimination—that either moderates or increases exposure to legal action. Indeed, there are many points of failure in the workforce planning process and the effects are compounded by reliance on those findings for recruiting, selection, compensation and evaluation.
The significance of workforce planning is that it represents an approach to human resource management that is grounded in business strategy, legally and operationally valid and reflects market realities. Financial Express notes that “organizational success depends on having the right employees with the right competencies at the right time. Workforce planning provides managers the means of identifying the competencies needed in the workforce not only in the present, but also in the future and then selecting and developing that workforce. Finally, workforce planning allows organizations to address systematically issues that are driving workforce change.” [2]
In this module, we’ll discuss the workforce planning process broadly, including the relationship between business strategy and workforce planning, the process of workforce planning and job analysis, associated deliverables including workforce development plans and job descriptions and the concept of job design.
- " The Right Workforce, Today and Tomorrow ." Korn Ferry Institute. May 31, 2016. Accessed September 10, 2019. ↵
- " The Importance of Workforce Planning ." Financial Express. March 19, 2006. Accessed September 10, 2019. ↵
- Why It Matters: Workforce Planning. Authored by : Nina Burokas. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Untitled. Authored by : rawpixel. Provided by : pxhere. Located at : https://pxhere.com/en/photo/1557011 . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Align and set your HR goals. The main strategic role of HR is to create goals to help meet key business objectives. Goals may vary depending on the company's strategic plan, but focusing on HR fundamentals is an excellent place to start. Here are some areas of HR most commonly affected by broader strategic business shifts.
Align the workforce planning process with the organization's strategic plan and annual business plan to support achievement of long-term (strategic plan) and short-time (annual performance) goals and objectives. Current workforce analysis. Analyze current resources, including projections for training and development and turnover.
The Workplace Planning Process. Figure 5.2.1 5.2. 1: The Workplace Planning Process. Workplace planning is generally done based on a multi-year horizon (for example, 3-5 or 5-10 years) and consists of a six step process, as illustrated in Figure 1. The steps in the process are fleshed out based largely on the federal Office of Personnel ...
Ratio analysis, where historical data on the relationship between business metrics and workforce size is used to predict future staffing needs. ... Human resource planning (HRP) is important because it ensures that the workforce is aligned with the organization's strategic goals. It helps businesses get the most out of their human resources ...
Writer Bio. Human resource strategic planning is the process of forecasting a company's demand for people so the business has the right skills and competencies to meet its long-term business ...
Understand the business strategy and how it impacts other departments. Evaluate external and internal workforce conditions. Plan and implement the HR strategy that includes key performance indicators (KPIs) Automate applicable tasks. Measure and evaluate results. 5 Steps to Align HR with Business Strategy.
Strategic human resource planning (SHRP) is based on close working relationships between HR department and line managers. SHRM can be defined as a deliberate attempt of HR deployment to empower the organization to meet organizational goals, objectives and consistencies. Succession planning plays an important role in strategic alignment if HRP.
Human Resource Planning - HRP: Human resource planning, or HRP, is the ongoing, continuous process of systematic planning to achieve optimum use of an organization's most valuable asset — its ...
Human resource planning is one component (a gear, for example) that works with other similar components (e.g., production, logistics, shipping, management, etc.) to keep the machine running. Strategic human resource management, on the other hand, takes a step back and analyzes the machine itself.
Human resource planning, or HRP, stands out as a strategic and methodical process designed to ensure that your organization fully leverages its human capital. It is not a one-time event but rather a continuous journey toward operational excellence and strategic alignment. At its core, HRP aims to establish a seamless alignment between your ...
1. Anticipate future human resource needs in terms of quantity, quality, and skills. 2. Identify the factors that affect the organization's ability to achieve its goals. 3. Determine the best methods for forecasting demand for human resources and for selecting new employees. 4.
SHRM is viewed as an approach to making decisions on the intentions and plans of the organization concerning employment relationships, recruitment, training, development, and performance management. The strategic HR function aims to enhance and manage the organization's human capital for long-term strategic goals.
In "hard" human resource planning, a quantitative approach is taken. The focus is on workforce capabilities and resource planning. Supply forecasting and skills inventory data is used to predict future workforce requirements. The sole mission is getting that sweet alignment between human resources and the business's needs.
The Bottom Line. Human Resource Planning (HRP) is the systematic process of analyzing and forecasting an organization's current and future human resource needs and developing strategies to meet those needs. It plays a critical role in aligning the workforce with the organization's strategic objectives and ensuring its long-term success.
On a functional level, human resource management is responsible for developing human capital strategies that align with the organization's mission, goals and objectives. Human capital planning—often characterized as a roadmap—generally has a 3-5 year timeframe. Human Resource strategy sets the direction for all the key areas of HR ...
The real test of a relationship between human resources and overall business strategy is the quality of the interaction between human resources executives and other company executives. Many times ...
Strategic human resource management (SHRM) is a process that organizations use to manage their employees. It is a way to ensure that the organization's HR are used in a way that supports the ...
Human resource planning steps. Here are some of the steps you can take for effective human resource planning: 1. Analyze the company's current employees and their offerings. Analyzing a company's current offerings, staff skills and business goals are essential to planning. This helps you understand what you might need to improve or what works well.
This page titled 2.8: Why It Matters- Human Resource Strategy and Planning is shared under a CC BY 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Nina Burokas via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request.
Turning our attention to hypothesis 4, the different aspects of planning, compare the mean effect size of the relationship between human capital and the planning outcome (i.e. creating a business plan) (effect size = 0.059) against the relationship between human capital and the planning process (effect size = 0.154).
Naturally, this is when addressed up front in the HR business plan. Three Key Elements of HR in the Planning Process 1. Resource Planning. Once the business goals are set, it is people involved who will carry them out. So, having the right people in the right roles at the right time is key. A resource plan is the people equivalent of a ...
The process of Human Resource Planning is a dynamic and systematic approach to managing an organization's workforce. By analyzing the environment, forecasting future needs, evaluating current resources, conducting gap analyses, developing action plans, and continually monitoring and evaluating, organizations can ensure they have the right ...
Chapter 2 - Strategy and Human Resources Planning. What is the first step in the strategic planning process? a. putting together the human resource management team; b. executing the human resource plan. c. establishing the mission, vision, and values of the organization. d. aligning the human resource plan and the strategic plan. ANSWER: c
The significance of workforce planning is that it represents an approach to human resource management that is grounded in business strategy, legally and operationally valid and reflects market realities. Financial Express notes that "organizational success depends on having the right employees with the right competencies at the right time.