- International Marketing Assignment
- Managing a Successful Business Project
- Unit 7 Business Law Assignment
- Innovation and Commercialisation Assignment
- Operations and Project Management Assignment
- Unit 6 Managing a Successful Business Project
- Download Free Samples
- Reviews 4.8*
- [email protected]
- Unit 37 Consumer Behavior and Insight Assignment Sample
- 54000+ Project Delivered
- 500+ Experts 24x7 Online Help
- No AI Generated Content
- Assignment Help

Unit 37 Consumer Behavior and Insight Assignment
Introduction, lo1- demonstrate the ability to map a path to purchase in a given category, including the decision-making process., p1- explain and analyse the stages of the consumer decision-making journey for a given product/service., p2- explain why it is important for marketers to map a path to purchase and understand consumer decision-making, m1- evaluate how marketers are responding to the decision-making process, applying relevant concepts and models., lo2- evaluate appropriate forms of research to understand influences on the decision-making process (b2c and b2b), p3- compare and contrast the key differences of the decision-making process in the context of b2c and b2b, providing specific examples., p4- evaluate the different approaches to market research and methods of research used for understanding the decision-making process in both b2c and b2b contexts., m2- provide a coherent and justified evaluation of how different factors influence decision-making and buying behaviour, supported by specific examples., lo3- evaluate how marketers influence the different stages of the decision-making process (b2c and b2b), p5- evaluate how marketers influence each stage of the decision-making process of b2c and b2b, giving specific examples, m3- critically evaluate how marketers influence each stage of the decision-making process of b2c and b2b with reference to relevant methods and models applied, d1- critically evaluate the application of appropriate theories, concepts, and models that influence and impact upon the decision-making process, supported by specific examples and contexts..
Consumers are the pivot for every business organisation around which every business activity revolves. Therefore, understanding and recognising the factors that affect their decisions regarding purchasing a product. In this report, five stages of consumer decision-making and factors that influence the ultimate decision have been discussed thoroughly in accordance with the online shopping giant- Amazon .In this case, the Prime membership option by Amazon has been studied. Apart from this, significance of mapping the consumer decision-making journey is elaborated with respect to the online shopping enterprises. In later section, a discussion on application of different models and theories to respond to the consumer decision making is done. Furthermore, the B2B and B2C approaches and their impact on consumer have been elucidated, and a comparison has been drawn between the two marketing approaches. Before concluding this report, an evaluation of different factors affecting the consumer decision-making process have been carried out.
Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking assignment help services.
The consumer decision-making process is a part of marketing studies which the marketers often brought into use in order to track or identify the whole process of decision-making of the customers from the beginning to end. Usually, it consists of five independent stages that are shown in the figure 1.
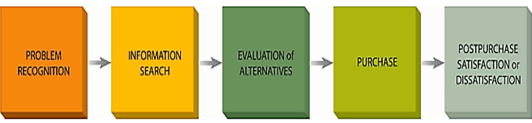
- Problem Recognition: This stage involves the identification of the customer’s desires or needs. The customer tries to identify the factor which is missing and make efforts to get back to feeling normal. In case of Amazon , the main problem that people used to face was delay in the delivery of their order. So, the giant of online shopping- Amazon identifies this problem and launched the Prime Membership Those who avail this service is given the benefit of delivery within 24 hours after placing the order.
- Information Search: This stage is always changing and the information is gathered from consumers through recommendations and prior experiences. In addition to this, the customer begins to give attention to risk management. A consumer might make a decision based on pros and cons list. Prime membership cost the consumer some extra amount but they are being benefitted with the fastest delivery than any other online shopping business.
- Evaluation of Alternative: In this stage, the consumer starts to ask questions in order to seek some alternatives of the product. This can be done by reading reviews or comparing the prices, and finally choosing a product that suits them the most. Amazon understands this, and recommend its consumers some alternatives of its own.
- Purchase: Here, the customer makes up his/her final decision regarding the purchasing of the product that they are interested in. The final decision is based on the assessment of emotions, experiences, marketing, or advertisement.
- Post Purchase Satisfaction (Reviews): The review stage is the most crucial stage as it can provide information about the satisfaction level of the customer. Feedback (both positive and negative) are studied and changes based on the analysis are made. Amazon specifically evaluates the feedbacks from the customer and try to change or improve its product quality.
The stages of purchase are ever-changing and it’s quite cyclic. Amazon understands that in today’s day and age, consumer are more into comparing, recommending, consuming, and make decisions regarding the purchase. In addition to this, social media and other review sites impact the decision-making decisions. They expect organisations to know their customer and their needs. Therefore, Amazon initiated the new trend of consumer journey mapping. These maps contain an overview of the consumer’s experience and how people behave with a particular brand (Wolny and Charoensuksai, 2014). The importance of mapping the purchase journey are given below:-
- It helps the marketer to develop some tailored experiences, thereby providing a better way of measuring the effectiveness of the campaign. For Amazon, the maps created from the viable data help in understanding the customer behaviour.
- It keeps its focus on developing long-term relationship with the customers by gathering data based on attitude, behaviour, demographic information, and perception of the people.
- It assists and triggers customer towards purchasing with the help of awareness campaign. In addition to this, mapping helps the marketers to understand the each stage of decision-making of customer, thereby making them attract people towards their brand.
- It helps the organisations to create a business plan in accordance with the desires of the customer. The quality of good journey map is that it helps in identification of those touch points that could assist in achieving the consumer-centric goals.
- It helps in understanding the buying stage and make the marketers to put more attention on that stage. By making use of customer insights in the identification of the areas that require high attention, mapping helps the organisation in meeting the need of customers (Trueblood, et.al, 2013).
- It assists in the identification of the gap in the objectives of business. It develops a framework for employees to work together in order to improvise the firm’s overall performance.
Customers in today’s time are like a fluid that can follow various steps to make a purchasing decision, and business must understand those critical paths taken by their customers. Amazon did not make it mandatory for everyone to pay the subscription fee of its prime membership service. Instead, it is keeping it as an option with some extra perks. Those customers who want to avail those benefits have to pay for the same (Simon Model). Different theories and models are being used by the marketers to understand, evaluate, and analyse the decision-making process of customers. Before moving further, first one should understand the customer behaviour. The Consumer Buying Behaviour in reference to the business environment can be defined as the process that makes the person look for, select, buy, consume, and dispose of goods or services. “Consumer behaviour” is the study of persons, groups, enterprises, or processes used by customers to choose, buy, use, and dispose of the goods to meet the desires of customers.
Decision-making Models are evaluated below:-
- Simon Model (1960): This model divides the decision-making process into three individual stages: 1) Intelligence activity 2) Design activity 3) Choice Activity. In his paper, Simon gave an argument that the process of decision-making is nothing more than a cognitive one which can be divided into simple steps.
- Nicosia Model (1966): This model talks about putting a focus on the communication process between the brand and customers. It makes use of event in some sort of sequence that is also called fields.
- Engel, Kollat& Blackwell model (1968): This consumer decision- making model consist of various components, such as input, analysing information, decision process, and identification of the variables affecting the decision-making. The decision-making process comprises five stages- 1) Recognition 2) Search 3) Alternative Evaluation 4) Purchase 5) Outcomes
- Mintzberg model (1976): The key theory of this model is that the decision of restructuring the project cost and project management is based upon the strategic decision process.
B2B and B2C are two major marketing approaches used for selling the products, they are not similar. B2B stands for Business to Business and is a variety of commercial transaction in which the buying and selling of the products are done between two business organisations. Business to Consumer (B2C) is a type of transaction where the business organisation sells its products and services directly to the end users (consumers). However, one should not consider the customer as the end user as it is very helpful for the organisation because for B2C to occur, several B2B transactions take place in the past.
The purchaser is sophisticated who understands the goods and services very well, and wants to purchase them in order to keep his/her company competitive and profitable. Talking about the B2C buyers, they are mostly seeking the best price and study the market and competition before making the purchase. Apart from this, another factor that does play a significant role is the trust of the buyer on the retail outlet or online business. It has been found that people still do not trust the online businesses and make purchases from the trusted outlets (Trainor, et.al, 2014). In this respect, B2C marketing should work in building trust and loyalty with their consumers.
B2B marketing is relationship-driven and focuses on the customer’s decision-making process. B2B marketing places quality as their key factor in business. B2B customer service plays a critical role as a bad service to a customer might waste all the marketing efforts of an organisation. Customer service takes place even before making the first sale and includes contacting the clients via, phone calls.
In B2B, mixed research approaches are quite common. The research methods can be qualitative or quantitative or ethnographic depending on the type of results the researcher seeks. The B2B marketing research is complicated and complex, therefore multiple approached are applied. Moreover, the B2B research methodologies are neutral. Tele-depth approach is one of the famous methods in qualitative Business to Business (B2B) as the businesses in this marketing make their most of the transactions by phone. Tele-depth interviews are often preferred as it provides a better top-notch quality data than face-to-face interviews (Karimi, 2013.). Apart from this, making use of the focus group does not serve the purpose of qualitative research as the businesses are geographically scattered and are in competition with each other.
In B2C research, the sample size is larger than the B2C, thereby making this research less skewed and more reliable. In addition to this, B2C research is customer-oriented rather than business-oriented in order to understand the perspective of the consumers while purchasing the product or services. Since B2C research focuses on building the relationship with the customers and loyal consumer base. Therefore, in B2C approaches incentives are given to participants in the form of cash, reward points, coupons, gift cards, etc (Hadjikhani and LaPlaca, 2013).
There are numerous factors affecting the consumer purchases, such as psychological, social, personal, etc. According to Amazon’s marketing manager, consumer behaviour is strongly derived from the factors, such as consumer’s social class and subculture. For example, needs of people living in Asian subcontinent differ from those living in Europe. Therefore, Amazon has to design its online marketing Assignment strategies to sell products according to the customer’s requirement.
Social factors comprise family, status, reference group. Here, the decisions of the consumer are influenced strongly by the opinion of other, changing lifestyles, and role. These factors reflect the changing shape of the market. Amazon is trying to match up with emerging lifestyle and is now offering products based on the social status of people (Lysonski and Durvasula, 2013).Apart from this, consumer’s attitude, perception, age, personality, etc., shape the brand image an Amazon has successfully match its marketing strategy in accordance with the aforementioned factors.
It is a well-known fact that an average customer go through a pre-defined decision-making process before making a purchase of the desired goods or services. This path involves some commonalities across organisations and target audience, but it is essential to understand a specific buying process. Understanding the decision making process is important to grow business. In this section, how marketers influence the consumer-decision making process has been evaluated.
There are numerous ways by which marketers can influence the consumer-decision making process in B2C that are elucidate in here.Identifying the target audience can help in influencing the consumer behaviour. For that purpose, marketers make use of both qualitative and quantitative market segment tools. These tools help in assessing the factors, such as geographic, demographic, age, location, etc. They also analyse the behavioural and psychographic influences. The organisations try to build the relationships with consumers based on experiences, knowledge, perceptions, and usage. This help the organisation in improving the brand loyalty, brand attributes, enhancing the usage rates and occasions.
Apart from this, companies are currently making use of niche marketing. It allows the organisation to amplify the marketing strategy rather than vanishing the investment in the general market. Niche market invented as a result of analysing the consumer behaviour in order to serve the under-served market.
There are numerous ways by which marketers can influence the consumer-decision making process in B2B that are explained here. The changing canvas of the commerce is affecting their choices. The business in current time is being operated online rather than offline modes. The seller’s behaviour and sophistication have been improved in the course of time. Buyers now have the option to return, exchange or replace their orders. Apart from that, the door-step services also helping the businesses in influencing the consumer behaviour. In addition, the technological changes have triggered the growth of the emerging market. Use of advance technology in the production of goods and services has led to higher efficiency and market in growth.
In this presentation, the marketer’s approaches to influence different stages of consumer buying process and business buying process have been explained. Firstly, the each stage of the B2B and B2C have been discussed, and then the factors affecting them have been mentioned. Based on these factors, the marketers approach have been explained.
Consumer behaviour tries to explain the buyer decision-making process and characteristics of a particular consumer, such as behavioural and demographics variables. Consumer behaviour in the field of management is a newly added topic and is very important in implementing and formulating most of the marketing strategies.Marketing starts with the customers’ requirements and ends with their satisfaction.
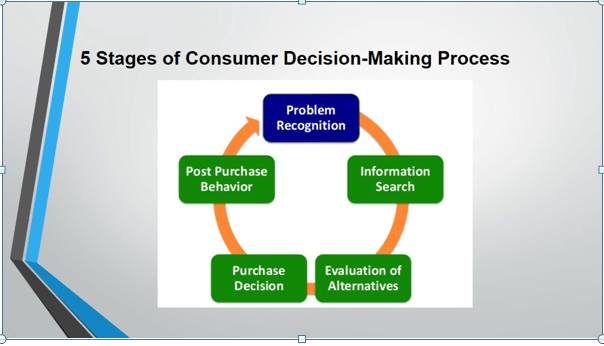
In B2C, there are five stages that are explained below:-
Problem Recognition: In this stage, the customer tries to figure out the problem or the missing factors (identify customer’s needs). Here, the fastest delivery is the need of the time and Amazon identifies it very well.
Information Search: In this stage, the consumer gathers information through recommendations and prior experiences. Reviews of Prime Membership are good, so taking the subscription is not a bad choice.
Evaluation of Alternative: In this stage, the customer look for some other options. This can be done by reading reviews or comparing the prices. Since no other online shopping brand offer the fastest delivery option so Amazon Prime Membership (Exclusive) is the only alternative.
Purchase: Here, final order is placed.
Post Purchase Satisfaction: Reviews are being given about the product quality.
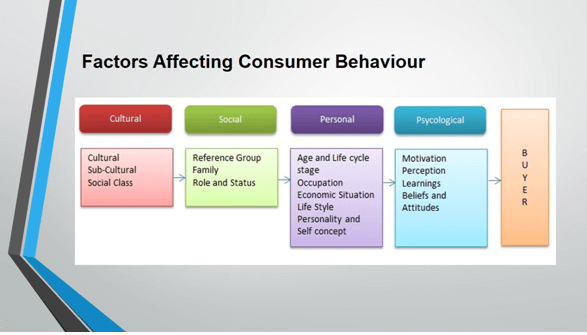
Psychological Factors: Motivation, attitude, biogenic needs, psychogenic needs, perception, past experience.
Cultural Factors: Demographic, religion, social class etc.
Social Factors: Family, reference group, roles and status.
Personal: Age, Occupation, Lifestyle, Self-concept.
All these factors affect the buyer’s choice of decision-making. So organisations must attend to them as soon as possible.
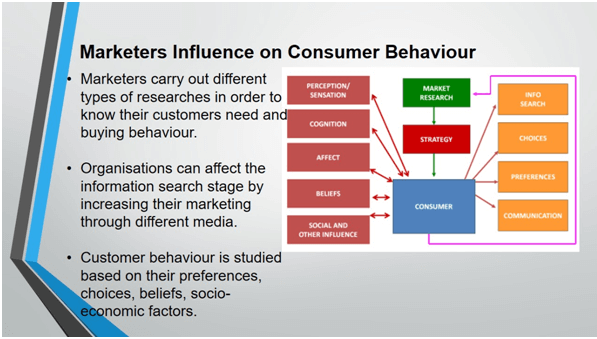
Marketers carry out different types of researches in order to know their customers need and buying behaviour. The behaviour depends on several factors, such as social factors, culture, demographic variables, age, gender, etc. The research can be qualitative and quantitative
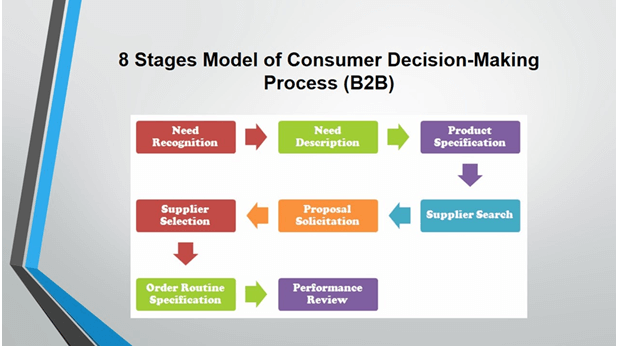
Need recognition: Organisationrecognises that by purchasing certain goods problems can be resolved.
Need Description: Organisation figures out the parameter about the goods that is required to be purchased
Product Specification: Products size, amount, etc., are noted down.
Supplier Search: The vendors that could meet the demand of the specified product is searched for.
Proposal Solicitation: The proposal is asked from the supplier (Request for Proposal (RPF)).
Supplier Selection: RPFs are reviewed and depending on the goals of the organization, the proposal is selected.
Order routine establishment: The quantities along with the time of delivery is set up here.
Post-purchase Evaluation: Routine surveys are done.
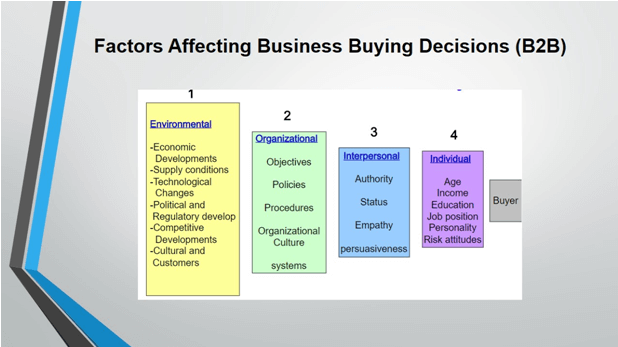
Environmental: Location, technological innovation, government regulations, industrial development, other cultural factors.
Organisational: Organisation’s structure, informal or formal interaction within the departments
Interpersonal and Individual: professional experience, personal goals, life-style, personality traitsattitudes and opinions,

It is the key mantra of business that the more time a business spend in understanding the each stage of decision-making process, the more solid its strategies are. Amazon understood its customer base and their need. Customers nowadays are not settling up with 24 hours delivery option. They want their products to be delivered within 5 to 6 hours of placing the order. Therefore, Amazon Prime Membership (Exclusive) offers the delivery-by-drone option that delivers the product within 6 hours of placement. Also, by increasing the payment options, it has simplified its ordering process.
In the report, it was noticed that how consumer behaviour is the driving force behind the launch of Amazon Prime Membership (Exclusive). It was also noticed that how controlling the factors affecting the buyers’ behaviour can help the business in flourishing. Also, a model of consumer decision-making was discussed in brief.
In an organisation, numerous approaches or models can be practiced in order to understand the consumer decision-making process. The area is undergoing many research and some new approaches may come in near future. The role of factors that influence the buying behaviour of consumers, such as ethics, social factors, age, gender, culture, etc., are considered in all the discussed model, but the social responsibility and altruism are highly ignored by the theories and models. The models discussed in the section 1 have undertaken the perplexing consumer choices and key factors that drives the behaviour. It is quite difficult to include all the factors together in one model, but there are some conceptual models that have been proposed and accepted by many researcher.
Here, it was figured out that customers’ decision-making process is one of the crucial factor organisations must consider to make their business going and growing. In the course of writing the report, different stages of consumer decision-making process were talked about with respect to the chosen organisation- Amazon. Furthermore, the models and theories organisation apply to understand the consumer’s behaviour and decision making had been talked about. In addition to this, organisations apply B2B and B2C approaches in order to gather information about the consumer’s interest and factors that affect their decision-making process. So, both of those approaches have been talked about and compared. In the end of the report, the impacts of different factors on customer’s choice-making had been evaluated briefly so as to justify how different factors affect the buying behaviour of consumer.
You Can Also Reach to our Other Assignment Help Services From the Popular category like Cheap Assignment Help and Assignment Help London .
- Ashman, R., Solomon, M.R. and Wolny, J., 2015. An old model for a new age: Consumer decision making in participatory digital culture. Journal of Customer Behaviour, 14(2), pp.127-146.
- Hadjikhani, A. and LaPlaca, P., 2013. Development of B2B marketing theory. Industrial Marketing Management , 42(3), pp.294-305.
- Jahromi, A.T., Stakhovych, S. and Ewing, M., 2014. Managing B2B customer churn, retention and profitability. Industrial Marketing Management , 43(7), pp.1258-1268.
- Karimi, S., 2013. A purchase decision-making process model of online consumers and its influential factors cross sector analysis [online].Available at: https://www.escholar.manchester.ac.uk/uk-ac-man-scw:189583. [Accessed 13 June, 2018].
- Lysonski, S. and Durvasula, S., 2013. Consumer decision making styles in retailing: evolution of mindsets and psychological impacts. Journal of Consumer Marketing , 30(1), pp.75-87.
- Professional Academy, 2015. Marketing theories – explaining the consumer decision making process [online]. Available at: https://www.professionalacademy.com/blogs-and-advice/marketing-theories---explaining-the-consumer-decision-making-process. [Accessed 13 June 2018].
- Shiau, W.L. and Luo, M.M., 2012. Factors affecting online group buying intention and satisfaction: A social exchange theory perspective. Computers in Human Behavior , 28(6), pp.2431-2444.
- Trainor, K.J., Andzulis, J.M., Rapp, A. and Agnihotri, R., 2014. Social media technology usage and customer relationship performance: A capabilities-based examination of social CRM. Journal of Business Research , 67(6), pp.1201-1208.
- Trueblood, J.S., Brown, S.D., Heathcote, A. and Busemeyer, J.R., 2013. Not just for consumers: Context effects are fundamental to decision making. Psychological science , 24(6), pp.901-908.
- Wolny, J. and Charoensuksai, N., 2014. Mapping customer journeys in multichannel decision-making. Journal of Direct, Data and Digital Marketing Practice , 15(4), pp.317-326.
- Kotler, P and Keller, K.l. (2012), marketing management, 13th Ed. New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall.
- Karimi S., (2013). A purchase decision making process model of online consumer and its influential factor a cross sector analysis. , PhD Thesis. Manchester Business School, faculty of humanities.
- Cole A. (2015). The implications of consumer behaviour for marketing , Anchor academic publishing.
- Solomon M.,Bamossy G.,Askegaard S., &K.Hogg M., (2016). Consumer Behaviour A european Perspective 3rd Ed. Prentice Hall Financial Times .

Get instant access to student account
Don't have an account? Sign Up
Already have an account? Sign In

- 500+ Experts 24*7 Online Help
offer valid for limited time only*
Hi! We're here to answer your questions! Send us message, and we'll reply via WhatsApp
Pleae enter your phone number and we'll contact you shortly via Whatsapp
We will contact with you as soon as possible on whatsapp.
We write, we don’t plagiarise! Every answer is different no matter how many orders we get for the same assignment. Your answer will be 100% plagiarism-free, custom written, unique and different from every other student.
I agree to receive phone calls from you at night in case of emergency
Please share your assignment brief and supporting material (if any) via email here at: [email protected] after completing this order process.
Important Note: Your order at Assignment Experts is protected by Consumer Law UK; also, we use 3rd party merchant support “PayPal” for all online transactions to provide you with the most protected online buying experience.
Custom-Written, AI & Plagiarism-Free with Passing "Guaranteed"

Unit 37: Consumer Behaviour and Insight
Assignment Title Consumer Behaviour and Insight
Purpose of this assessment
The assessment is designed to test students’ knowledge and understanding of the consumer’s decision-making processes, from needs recognition through research, the evaluation of alternatives, purchase and post-purchase evaluation. Is expected that students will be able to explore the underpinning theories and frameworks, and to relate these to real-world examples. An important part of marketing is to understand the processes behind how a consumer decides to purchase a product and service.
You have been appointed as the new marketing associate for a company of your choice. The marketing manager is in the process of compiling an annual marketing report for the London strategic business unit and needs you to provide an informative overview of the trends in consumer behaviour for your target market in the consumer sector.
The report will have to be based on one chosen organisation only. The organisation should trade in both B2C and B2B sectors.
The report must have three sections:
Section 1: Map of ‘Path to Purchase’ of the product/service
1. Evaluate (with a rationale of the selected product/service) the five different stages of the consumer’s decision-making process and analyse the factors that influence that process. Use a B2C context.
2. Evaluate the black box model of consumer behaviour. Explain how it influences marketing decisions.
3. Map out the consumer’s decision-making process for one product or service. Use B2C context for a chosen organisation.
Section 2: Research and Data in Consumer Behaviour
4. Compare the similarities and differences of the decision-making process (purchase decision-making) of B2C and B2B, with reference to the chosen organisation.
5. Evaluate the different market research methods that could be applied to a B2C and a B2B context. Use examples relevant to a chosen organisation.
6. Justify how market research can influence the stages of customer/consumer’s decisionmaking process, supported by examples. You can use both B2C and B2B contexts. Use relevant to a chosen organisation examples.
Section 3: Influence on the decision-making process
7. Evaluate a minimum of 2 factors that influence the decision-making process (you must include two of the following: personality, motivation, learning and perception, cultures and sub-cultures, using the appropriate theoretical models). Illustrate your evaluation using specific examples of promotional activities of your chosen company. This provides evidence for ALL LEARNING OUTCOMES Word count: 2000-2500 words. Students will not be penalised for exceeding this count.
Submission Format
Task 1: BUSINESS REPORT This should be written in a concise, formal business style using single spacing and font size 12. You are required to make use of headings, paragraphs, subsections and illustrations as appropriate and all work must be supported with research and referenced using the Harvard referencing system. Please also provide a bibliography using the Harvard referencing system. The recommended word limit is 2,000–2,500 words, although you will not be penalised for exceeding the total word limit.
Formative assignment
Discussion Forum Activity Watch the following video: https://www.ted.com/talks/reed_hastings_how_netflix_changed_entertainment_and_wh ere_it_s_headed/transcript During week five you will be asked to see the following video before coming to class. Then, as a group you are expected to conduct independent research and present a 500- word essay-type answer to the following questions:
1. What aspects of Netflix organisational culture strike you as unique?
2. Why is Netflix able to produce good quality entertainment that generate high viewership (e.g. Orange is the New Black)? How do they collect and utilise data to understand consumer behaviour?
3. Illustrate with examples how new technologies influence consumer behaviour, with specific reference to Netflix organic development from a small DVD rental company to a global streaming, content creating, and entertainment organisation. How do they differ from their main competitors? You will be given a total of 2 hours to answer the questions as a group, followed by a class discussion with your peers. After the class, you will need to submit your work in an online discussion forum where your lecturer give you feedback. Please note that non-submission of formative work will lead to a classification of an ATRISK student, which might jeopardise the submission of summative work and subsequent progression of your studies. Word count: 500 words maximum per post This formative task is designed to test understanding of LO1 and introduce students to concepts that related to LO2

The services provided by Assignment Experts UK are 100% original and custom written. We never use any paraphrasing tool, any software to generate content for e.g. Chat GPT and all other content writing tools. We ensure that the work produced by our writers is self-written and 100% plagiarism-free.
International House, 12 Constance Street, London, United Kingdom, E16 2DQ
UK Registered Company # 11483120
100% Pass Guarantee
Still not convinced.
We've produced some samples of what you can expect from our Academic Writing Service - these are created by our writers to show you the kind of high-quality work you'll receive. Take a look for yourself!
View Our Samples
Recent Uploads
Assignment 1: an investigation into the characteristics of high a ..., assignment 2: an investigation into the load flow analysis in 11 ..., 1. demonstrate a basic understanding of key skills used to assess ..., examine appropriate research methodologies and approaches as part ....
- Decoding Consumer Behavior in Microeconomics: Insights for Assignments
Decoding Consumer Behavior: Essential Insights for Microeconomics Homework

Microeconomics, as a pivotal branch of economics dedicated to scrutinizing the behavior of both individual consumers and firms, stands as an indispensable lens through which the intricate dynamics of market interactions come into focus. Positioned at the epicenter of this discipline is the nuanced exploration of consumer behavior – a complex interplay of decisions and preferences dictating how individuals allocate their finite resources within the marketplace. For students embarking on the journey of microeconomics homework, the cultivation of a profound comprehension of consumer behavior emerges as a non-negotiable imperative. This blog, therefore, sets out on the ambitious mission of furnishing a panoramic view of the intricacies involved in decoding consumer behavior, with the ultimate goal of equipping students with a repertoire of invaluable tools and perspectives that will undoubtedly fortify their prowess in navigating the intricacies of microeconomics homework. In essence, the study of consumer behavior becomes the linchpin, the very essence that unlocks a deeper understanding of economic principles, paving the way for more informed analyses and astute predictions in the microeconomic landscape, offering help with your microeconomics homework and ensuring proficiency in this essential aspect of economic analysis.

As students delve into this realm, they embark on a journey that transcends mere theoretical understanding, evolving into a practical grasp of how choices, preferences, and economic constraints converge to mold the consumer decision-making process. By unraveling the layers of utility, preferences, and budget constraints, students not only gain a theoretical foundation but are also armed with a powerful toolkit to decipher and analyze the multifaceted world of consumer choices. The narrative unfolds through a trajectory that moves beyond abstraction, delving into the tangible implications of economic decisions on the lives of individuals and the broader market equilibrium. In navigating the labyrinth of microeconomic homework, this blog elucidates not only the 'what' but also the 'why' behind consumer choices, enabling students to decipher patterns, predict trends, and offer nuanced insights that transcend the boundaries of conventional economic discourse. Ultimately, as students assimilate the comprehensive insights provided herein, they are poised to emerge not merely as passive observers of economic phenomena but as active participants equipped with the analytical acumen to decode and interpret the ever-evolving tapestry of consumer behavior – a skill set indispensable for success in the dynamic field of microeconomics.
Understanding the Basics
At its core, consumer behavior encapsulates the myriad actions and decisions undertaken by individuals within the marketplace as they navigate the process of purchasing goods and services. Microeconomics, as a discipline, occupies itself with an in-depth exploration of the multifaceted factors that sway and mold these decisions. This academic pursuit is instrumental for economists and students alike, providing a lens through which market trends can be scrutinized and predictions formulated. To unravel the intricate tapestry of consumer behavior, delving into key concepts is imperative. Utility, the measure of satisfaction or pleasure derived from the consumption of a good or service, serves as a foundational pillar. Preferences, shaped by individual tastes, cultural influences, and personal experiences, contribute to the diverse landscape of consumer choice. Furthermore, the budget constraints individuals face, dictated by income and the prevailing prices of commodities, intricately weave into the fabric of decision-making. These fundamental concepts - utility, preferences, and budget constraints - collectively form the cornerstone of comprehending consumer behavior. By grasping these essentials, economists and students acquire a robust toolkit for dissecting and understanding the motivations behind consumer choices, ultimately empowering them to navigate the intricate dynamics of microeconomics with precision and insight.
Utility: The Core of Consumer Decision-Making
At the heart of microeconomics lies the pivotal concept of utility, serving as the lodestar for consumer decision-making. Utility encapsulates the satisfaction or pleasure derived from the consumption of goods or services, constituting a fundamental factor in the choices individuals make. Consumers, in essence, strive to maximize their utility, aiming for the optimal balance between satisfaction and available resources. Microeconomics homework frequently task students with applying utility theory, emphasizing the critical need to comprehend how preferences and constraints intricately shape the process of utility maximization. This analytical skill becomes the linchpin for unraveling the complexities of consumer decisions and market dynamics.
Preferences: The Diverse Landscape of Consumer Choice
Diversity characterizes consumer preferences, reflecting the intricate interplay of taste, culture, and individual experiences. Microeconomics homework delve into the analysis of these preferences, recognizing their far-reaching impact on predicting consumer choices. To decipher the dynamic landscape of consumer choice, students delve into the exploration of how shifts in preferences reverberate through demand and supply. Indifference curves and budget lines emerge as indispensable tools, providing a visual framework to illustrate the nuanced dynamics inherent in consumer decision-making.
Budget Constraints: Navigating Scarcity
In the realm of consumer behavior, budget constraints loom large as individuals grapple with the limitations imposed by income and the prevailing prices of goods and services. Mastery of this aspect is imperative for students undertaking microeconomics homework. The budget constraint model, a stalwart in economic analysis, empowers students to dissect and understand how alterations in income and prices reverberate through consumer choices and influence market equilibrium. Thus, an adept understanding of budget constraints equips students with a lens to navigate the intricacies of scarcity within the realm of microeconomics.
Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
Beyond the foundational concepts of microeconomics, a myriad of factors intricately shape and influence consumer behavior, providing students with a multifaceted landscape to explore in their homework. These factors extend beyond the classical notions of utility, preferences, and budget constraints, delving into the nuanced realms of socio-economic dynamics, cultural influences, and psychological intricacies. Homework within the microeconomics domain often present students with the challenging task of unraveling the complexities associated with these influential factors and deciphering their profound implications for market dynamics. Socioeconomic factors, encompassing variables such as income distribution and employment levels, can significantly impact consumer decision-making, shaping patterns of demand and supply. Cultural influences, deeply ingrained in societal norms and values, play a pivotal role in steering consumer preferences, introducing a layer of diversity and dynamism to market interactions. Moreover, the burgeoning field of behavioral economics introduces psychological dimensions, exploring how cognitive biases, heuristics, and emotional factors contribute to the decision-making process. As students navigate these intricate dimensions, they are compelled to go beyond conventional economic models, employing interdisciplinary lenses to comprehend the multifaceted nature of consumer behavior. The synthesis of these factors not only broadens the scope of economic analysis but also equips students with a holistic understanding of the interconnected forces steering market dynamics. In essence, by exploring the factors influencing consumer behavior, students are challenged to elevate their analytical capabilities, providing them with the tools to dissect and interpret the ever-evolving tapestry of economic decision-making within the microeconomic landscape.
Income and Substitution Effects: Unraveling the Impact of Price Changes
In the intricate realm of microeconomics, the interplay of price changes and consumer behavior is illuminated through the examination of income and substitution effects. Price alterations can instigate both these effects, intricately shaping how individuals allocate their resources within the marketplace. An essential component of microeconomic analysis, students are tasked with comprehending the nuances of these effects as they hold a pivotal role in deciphering how consumers respond to market shifts. Understanding the differential impact of income and substitution effects provides students with a robust analytical framework, essential for unraveling the complexities inherent in the dynamic landscape of microeconomics.
Information Asymmetry: The Role of Knowledge in Decision-Making
In the intricate dance of market transactions, consumers don't always possess perfect information when making decisions. The concept of information asymmetry takes center stage, where varying levels of knowledge between buyers and sellers can significantly influence outcomes. Microeconomic homework often propel students into exploring this asymmetry and dissecting its effects on market dynamics. Rich grounds for analysis emerge as topics like adverse selection and moral hazard come into focus, providing students with a nuanced understanding of how information imbalances shape economic interactions and outcomes.
Behavioral Economics: The Psychology Behind Choices
In the evolving landscape of economic thought, behavioral economics has emerged as a prominent paradigm, shining a spotlight on the psychological underpinnings of decision-making. Recent years have witnessed the ascendancy of concepts such as bounded rationality and heuristics, offering alternative perspectives for students to incorporate into their microeconomic homework. This infusion of psychological insights enriches their analyses, providing a deeper understanding of the non-linear and sometimes irrational aspects inherent in consumer choices. As students delve into the psychology behind economic decisions, they gain a more holistic view, transcending traditional economic models and broadening the horizons of their microeconomic analyses.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
In the dynamic intersection between theory and reality, microeconomics homework serve as a bridge, compelling students to apply theoretical constructs to real-world scenarios. Beyond the confines of textbooks, the practical implications of economic principles come to life as students delve into case studies and scrutinize current market trends. The essence of microeconomics lies not just in understanding abstract concepts like utility, preferences, and budget constraints but in discerning how these theoretical frameworks manifest in the complexities of actual market dynamics. Homework, therefore, become more than academic exercises; they evolve into opportunities for students to navigate the intricate terrain of real-world economic scenarios. By immersing themselves in case studies, students gain a tangible appreciation for the multifaceted nature of consumer behavior, market equilibrium, and the broader economic landscape. Analyzing current market trends, they witness firsthand the applicability of theoretical models to the ebb and flow of supply and demand in the global marketplace. This practical engagement not only reinforces the theoretical foundation but also hones the analytical skills crucial for economic decision-making. Through this symbiotic relationship between theory and application, students are not merely consumers of economic knowledge but active participants in deciphering and shaping the economic realities they encounter. The ability to connect theory with practical insights becomes a cornerstone of their analytical toolkit, empowering them to confront and comprehend the ever-evolving challenges posed by the dynamic forces of microeconomics in the real world.
Consumer Surplus: Calculating Economic Welfare
An integral aspect of microeconomics involves unraveling the intricacies of consumer surplus, a metric that proves vital in evaluating the economic welfare of consumers. Microeconomic homework often task students with the responsibility of not only calculating but also interpreting consumer surplus within diverse market scenarios. This entails a comprehensive understanding of the benefits that consumers derive from their transactions in the marketplace. By delving into the nuances of consumer surplus, students acquire a tangible measure to gauge the economic well-being of individuals, offering a nuanced perspective on the efficiency and effectiveness of market interactions. Through such homework, students are not only computational analysts but also interpreters of the broader implications of economic transactions on consumer welfare.
Market Failures: Analyzing Externalities and Public Goods
The realm of consumer behavior invariably intersects with market failures, presenting students with a multifaceted landscape to explore within their microeconomic homework. Externalities and public goods stand out as prominent examples of market failures, demanding students to examine how consumer decisions contribute to or alleviate these inefficiencies. The analytical journey extends beyond mere observation, prompting students to craft policy recommendations aimed at achieving optimal outcomes. By scrutinizing the intricate dynamics of market failures, students become adept at recognizing the consequences of unregulated consumer behavior on societal welfare. The task of formulating policies to address market failures not only sharpens their analytical acumen but also positions them as potential contributors to the improvement of economic systems, fostering a deeper understanding of the pivotal role consumer choices play in shaping the efficiency and equity of market outcomes.
In the sphere of microeconomics homework, decoding consumer behavior is not merely a requisite skill but a gateway to unraveling the complexities of market interactions. A robust understanding of utility, preferences, and budget constraints empowers students to adeptly navigate the intricacies of consumer decisions. By delving into the factors influencing consumer behavior and applying these concepts to real-world scenarios, students elevate their analytical prowess, fostering excellence in microeconomics homework. As the economic landscape evolves, the ability to decode and analyze consumer behavior stands as a fundamental skill, essential for aspiring economists and students alike in navigating the dynamic intricacies of contemporary markets.
Post a comment...
Decoding consumer behavior in microeconomics: insights for assignments submit your homework, attached files.

- Why Choose Us
- Vision and Mission
- Hire Writers
- How it Works
- Managing Customer Experience
Consumer Behaviour and Insight
University: DOCKLANDS ACADEMY
- Unit No: 19
- Level: High school
- Pages: 9 / Words 2277
- Paper Type: Assignment
- Course Code:
- Downloads: 710
This assessment will cover the following questions:
- Intercontinental Hotel is the luxury hotel of United Kingdom . Identify the forces that influence hospitality consumer attitude and behaviour and its impact on the process of decision making.
- Differentiate between the Business to consumer(B2C) and Business to Business (B2B), with the help of specific example from the hospitality industry.
- Identify the various theories, approaches and methods that influences the decision-making process of the Intercontinental Hotel.
INTRODUCTION
CB also known as Consumer Behaviour refers to attitude and perception of customers or individual regarding the purchase of products, goods or services. If behaviour of the customers is good towards offerings of company, this means their business is performing well. Behaviour of consumers is associated with customer's actions in marketplace and reason behind those behaviours (Shih, and Ke, 2014). This assignment report is prepared in context with Holiday Inn, a America based hotel chain which is owned by Britain. This hotel is a subsidiary of Intercontinental hotel groups and headquartered in Buckinghamshire, UK. This hotel mainly serves in European, Middle East, Africa and Asia-Pacific region. This report is going to mention about different circumstances and their impact on the customer behaviour along with their attitudes. Changes in customer trends due to digital technology are discussed. Also, stages to customer decision-making and appropriate purchasing path will be explored. At last, role of marketers in impacting customer decision making is discussed.
P1 Describe Various Social, Personal, Cultural & Psychological Factors Which Impacts Attitude And Behaviour of Customers in Hospitality Sector
(Covered in PPT)
P2 Mention How Trends of Customers Are Changing Due to The Influence of Digitalisation of Technology
P3 define aspects for customer decision making process and present purchasing way for selected hospitality service.
Customer decision-making is a process where individuals take decision if they are interested in buying an offering of a firm or not. There exist multiple factors and stages which has a deep impact on CB (Shaw, McMaster and Newholm, 2016). Below are mentioned some stages related with customer's decision-making journey:
- Need Recognition : This is the foremost stage where consumers analyse as well as identify & acknowledge their needs according to their expectations.
- Searching and gathering informatio : After analysing their needs, clients will start collecting information about all those products and services which can serve their purpose though online, digital and traditional media (Petersen, Kushwaha and Kumar, 2015).
- Evaluation the alternatives : Here, screening of all alternatives will be done so that most desired service or product can be selected in terms of durability, time and cost.
- Actual Purchase of product : In this aspect, customer will purchase most suitable product so that their expectation can be fulfilled without any compromise.
- Post-purchase evaluation (PPE) : It is the final stage in which end user decide if purchasing product of service of a company is useful or not. If satisfaction level of customers is less they will not purchase the same product again in future.
Get Expert Help
We can help in getting your scores back on track. Get expert help from our writers.
There exist some stages which are followed by customers while mapping a purchasing path. These stages are discussed below:
- Pre purchase: Here, the customers will identify those hotels where they want to stay for their vacations or business purpose. To collect information about different hotels, internet and newspapers can be used.
- Purchase: After analysing all the hotels, customers will select a hotel such as Holiday Inn as their utmost choice so that all their needs can be fulfilled properly. Holiday inn is a four star hotel which offer standardised service to customers (Nagengast and et. al., 2014).
- Receive: Here, customers are using the chosen service or product. In case of Holiday Inn, at this stage customers will be staying there and demand services as per their choice and requirement.
- Post-purchase: In this stage, the consumers will identify if Holiday Inn is capable to provide expected services or not. If hotel has provided satisfactory service to customers then they will prefer repeat visits otherwise they will switch their preference to other hotel.
P4 Describe The Value For Marketers to Present a Purchasing Path And Acknowledging Decision Making of The End Users
Main goal of business firms is to make the satisfaction level of customer at higher scale so that sales and revenues are earned in appropriate manner. It is essential for business in Holiday Inn to map a path to purchase. Importance associated with this aspect is mentioned below:
- Increases ROI: Map to purchasing path benefits in acknowledging expectation and purchasing pattern of customers. By this, targeting customers in right manner is easy. This will helps Holiday Inn in earning high revenues and profits due to which ROI will also increase.
- Unifying consumer information: Mapping purchasing path helps Holiday Inn in arranging information and data of customers in systematic manner. By this, aligning needs of people in different sections is easy. By this, each customer can be given expected service without any compromise (Mortimer, Bougoure and FazalEHasan, 2015).
Also, mapping for purchasing path helps a company to understand different levels which are faced by customers at the time of product purchase. Some of these levels are discussed beneath:
- Extensive problem solving: Here, customers takes longest time to purchase products as they have no idea about the offerings of company.
- LPS (Limited Problem Solving): In this, customers already know about entities with offerings of a firm and other present alternatives. Here, Holiday inn need to put extra efforts to grab attention of Customers (Mihaela, 2015).
- Routine problem solving: In this level, customers purchases a product for large number of time and they don't require additional efforts from company.
Find Exactly What you Require
Take a look at our wide variety of dissertations and find the one that you need.
P5 Differentiate Decision Making Processes Associated With B2B and B2C, Including Hospitality Examples
B2B and B2C are two ways by which an organisation can perform commercial transactions. In B2B, a company tries to sell their offerings to another company whereas in B2C, an organisation tries to sell their maximised services and products to their customers. Comparison in B2B and B2C are stated below:
P6 Mention Various Methods to Conduct MR And Different Research Methods to Understand Decision Making
Organisation cannot perform their functions as well as operations in appropriate manner without MR. Market research is very essential for a company as it benefits them to identify and acknowledge the changing demands & requirements of customers in a proper way. There exist different approaches and methods to conduct research. In context with Holiday Inn, these approaches are listed below:
Market research for Business to Business: In this kind of research, a company perform research to analyse the needs of other organisations so that a business contract can be signed with them. In this context manager in Holiday Inn can use secondary resources to collect information about other companies. With the help of secondary research, all information about a firm can be acknowledged. In this context, different source to collect information are stated below:
- Government agencies: Collection of data via governmental agencies and officials is the best way to gather authentic information about another company. This source will help Holiday Inn in identifying trade and laws related information of different firms (Hofacker, Malthouse and Sultan, 2016).
- Internet: By using internet, official website of a company can be checked so that all important data about them can be attained properly. Also, internet will help manager of cornered hotel in analysing reputation of another organisations so that they can decide if wooing them for business is beneficial or not.
Market Research for Business to customers: In this research, response and expectations of customers towards the offerings of company is identified so that required changes can be carried out properly. Also, this research will help Holiday Inn in identifying the changing needs of customers so that they can be provided modern products (Gargiulo, Natale and Russo, 2015). In this context, primary research method is best as it helps in collecting latest information about customers without any ambiguity. Sources in this context are written below:
- Questionnaire: This will help the manager in acknowledging choice of customers from a group of alternatives. By this, preference of maximum customers can be given priority. This will help the hotel in retaining customers for long time.
- Interviews: In this method, marketing team of Holiday Inn will ask multiple questions to their customers via face to face meetings. By this, changing needs of customers can be identified and they can be provided with right products and services.
P7 Analyse How The Marketers Can Impact Various Aspects of Decision Making
In order to achieve expected success and growth, managing behaviour of customers is essential for every organisation. This is because customers are the major earning source for an organisation. In context with hospitality industry, a marketer is needed to evaluate every business stage so that clients can be provided right services and overall profits of organisation will rise. In case of Holiday Inn, the marketer plays an essential role as in influencing decisions of the customers by implementing innovative strategies on regular basis. Manager in Holiday Inn is already providing pick and drop facility to the clients at airports and other travelling stations so that they can have comfortable experience with the hotel. This strategy of marketers in Holiday Inn distinct the hotel from their rivals and helps them in gaining competitive advantage in marketplace (Gargiulo, Natale and Russo, 2015).
Also, customised menu is offered to customers during their stay which motivates the customers to have repeat visits. In this way, marketer in Holiday Inn impacts the decision-making of customers and divert it positively towards the concerned hotel. Hence, it can be said that Marketing manager of Holiday Inn is needed to adopt new strategies so that customised services can be offered to clients according to their requirements. By this, right customers can be targeted for the right product. Getting right product will allow the customers to think positive about the hotel. By this, DM of customers can also be affected positively and profit as well as revenue is gained by Holiday Inn.
Also Read :- Consumer Behaviour and Decision Making
As per this assignment, it has been concluded that it is necessary for a company to check the attitude and perception of customers towards their products on regular basis. Appropriate behaviour of clients will assure high sales and revenues to the concerned company. Different factors like cultural, social and psychological aspect influence the mind state of customers in high manner. Changing trends related with hospitality industry are highly skilled staff, technological advancement, high activeness of customers etc. Also, best approaches to carry out market research are qualitative and qualitative approach. Also, it is acknowledged that market research is essential for a firm as it assist in acknowledging the needs of end users appropriately.
To get more details about online assignment help connect with us

Avail The Benefit Today!
To View this & another 50000+ free
Share Your Requirements Now for Customized Solutions.
Delivered on-time or your money back
For Best Managing Customer Experience Assignment Help

- Zero Plagiarism
- 24*7 Live Support
- Unlimited Revisions
- Free Plagiarism Report
- Money-Back Guarantee
- No Privacy Infringement
To Make Your Work Original
Check your work against paraphrasing & get a free Plagiarism report!
Check your work against plagiarism & get a free Plagiarism report!
Quick and Simple Tool to Generate Dissertation Outline Instantly
Get citations & references in your document in the desired style!
Make your content free of errors in just a few clicks for free!
Generate plagiarism-free essays as per your topic’s requirement!
Generate a Compelling Thesis Statement and Impress Your Professor
INTRODUCTION Dock land academy is the academy which want to arrange the event for the students and customers. Academy has given the event to the restaurant Hazev and the employee of Hazev is to run in the planning and promotion of the event on the large scale. The report will include the digital
INTRODUCTION The consumer insight is comprises to utilized through the businesses to increase a deeper understanding of how their people feels and thinks. The organisation is Holiday inn which is situated in London. It is a British owned brand of hotels or a subsidiary of intercontinental hotels
INTRODUCTION Customer satisfaction is one of crucial element to measure the success of an enterprise. Thus, degree of satisfaction of product and services can be measured with help of repetitive customers. Customer satisfaction can be referred as term which works as to full fill the expectation of
INTRODUCTION Quality management ensures the productive service is consistency in the organisation. There are four components and elements which is required to be considered by the organisation. Such as quality control, quality assurance, quality improvement and most importantly quality planning.
TASK 1 1.1. Formulating and recording possible research project outline specifications Research Topic: “To ascertain the influence of technology on customer satisfaction in the context of travel and tourism sector: A study on Thomas Cook” Background of the study In the current times, travel
INTRODUCTION Literature review is the process of comparing and contrasting on articles, texts and journals written by senior researchers in an effective and efficient manner so that detailed understanding regarding the subject matter can be made. In this context, the researcher will conduct the
INTRODUCTION Comprehending in relation with the visitor attractions, it is being regarded as the natural location and features, man-made creations or objects that have some or the other special attention for travellers and the local residents. Different destinations have particular attractions
INTRODUCTION Travel and tourism industry is the major contributor to the economy of the nation. It enhances employment opportunities on the location and help to improve life standard of the local people. Current study will discuss overlap of visitor’s attraction in relation to type of
Introduction This assessment is based on visitor attraction management. In this report is to be focus on development understanding of visitors attraction, visitor types and impact on tourist motivation. This report is based on TUI group. The company basically located in United Kingdom and
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION 1.1 Title “Customer Satisfaction and Service Quality in retail sector in Copenhagen: A comparative study on Netto and Fakta.” 1.2 Introduction Companies around the world focus on gaining
Professional Assignment Writers
Choose a writer for your task among hundreds of professionals

Please rotate your device
We don't support landscape mode yet. Please go back to portrait mode for the best experience
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it. Know more
Calculate the Price
Professional Academic Help at Pocket-Friendly Prices!
Estimated Price
Limited Time Offer
Exclusive Library Membership + FREE Wallet Balance
1 Month Access !
5000 Student Samples
10,000 Answers by Experts
Get $300 Now
Consumer Behavior
Communicating the social change.
Students assume the role of a Communications Manager for a local government area, and to select the best communications campaign to persuade residents that a change to smaller waste bins is a positive change for the overall good. An activity that covers social marketing, communications, and perceptions.
Communicating the Social Change Review the Teaching Activity

Ethics of Text and Drive Campaigns
Students review a ‘text and drive’ campaign promoted by an apparent funeral home in Canada. It turned out to be a public service announcement, but was it effective and would your students have approved the communications approach?
Ethics of Text and Drive Campaigns Review the Teaching Activity
Choosing Social Media Platforms
In this activity, students will review a podcast episode on social media marketing and platforms, and explore the best platforms for different types of business and situations. A handy overview of the main social media players.
Choosing Social Media Platforms Review the Teaching Activity
Identifying Jobs to be Done for a Hotel Chain
Students analyze a series of online comments made by consumers, and using the Jobs to be Done (JTBD) framework, they will identify the functional, social, and emotional jobs that consumers expect the hotel chain to fulfill.
Identifying Jobs to be Done for a Hotel Chain Review the Teaching Activity
Functional, Social, Emotional Jobs in JTBD
In this activity, students apply the ‘Jobs to be Done’ (JTBD) framework to real-world products by drilling down to the functional, social, and emotional jobs these products are hired to do.
Functional, Social, Emotional Jobs in JTBD Review the Teaching Activity
Introduction to the Jobs to be Done (JTBD) Framework
This activity explores the ‘Jobs to be Done’ (JTBD) framework. Students review a detailed podcast script that gives an excellent introduction to JTBD. It covers the core concepts of JTBD, such as functional, social, and emotional jobs, and the role of JTBD in product development, customer experience, and brand storytelling. An ideal starting point for students to dive into JTBD.
Introduction to the Jobs to be Done (JTBD) Framework Review the Teaching Activity
Evaluating Sponsorship Opportunities
Students are faced with evaluating and selecting sponsorship opportunities from a list of five possibilities. Unfortunately, the company only has enough budget to choose either 2 or 3 of them. A good activity to understand the impact of sponsorships and to evaluate how effective they may be.
Evaluating Sponsorship Opportunities Review the Teaching Activity
Tapping into Customer Value
This activity involves analyzing market segments for Greenhills Shoes, a sustainable footwear company. Students will identify how to expand the brand without compromising its eco-friendly values, focusing on understanding brand positioning and the importance of sustainability in marketing.
Tapping into Customer Value Review the Teaching Activity
Do Tag-Lines Eventually Wear Out?
In this activity students will consider the value of a brand (Specsavers) utilizing a long-term tag-line. While tag-lines are often helpful for communicating positioning and guiding IMC campaigns, they may need to be refreshed at times to keep the brand modern and adaptive.
Do Tag-Lines Eventually Wear Out? Review the Teaching Activity
Risks of Shrinkflation
This activity looks at one of the more substantial risks of using shrinkflation, which is negative consumer backlash and media attention. It focuses on a real situation for KFC and includes customer comments.
Risks of Shrinkflation Review the Teaching Activity

Move fast, think slow: How financial services can strike a balance with GenAI

Take on Tomorrow @ the World Economic Forum in Davos: Energy demand

PwC’s Global Investor Survey 2023

Climate risk, resilience and adaptation

Business transformation

Sustainability assurance

The Leadership Agenda

AI Jobs Barometer

The s+b digital issue: Corporate “power changers”

The New Equation

PwC’s Global Annual Review

Committing to Net Zero

The Solvers Challenge
Loading Results
No Match Found
PwC’s Voice of the Consumer Survey 2024
Shrinking the consumer trust deficit

- 30 minute read
- May 15, 2024
Companies can strengthen the confidence consumers have in them by executing on six key imperatives.
Listen to the Voice of the Consumer Survey report, and hear insights from our experts.
Trust is crucial for consumers and for the companies that sell products and services to them: as shoppers confront a set of overlapping and often mutually reinforcing disruptions—financial, ecological and technological—they are prioritising reassurance and reliability from the brands they engage with.
That’s a signal finding of our inaugural Voice of the Consumer Survey, which builds on insights amassed over 15 years of consumer research by collecting the perspectives of more than 20,000 consumers across 31 countries and territories on a wide range of issues, including caring for the environment, attending to their health, being open about data, finding value for money and embracing AI.
The good news for leaders of consumer-facing businesses: global consumer markets are set to continue expanding. The global consumer class, comprised of those spending US$12 or more per day, reached 4 billion last year, and is projected to reach 5 billion people by 2031 . The bad news: there’s a widening gap between the trust that executives think consumers place in their companies and the trust that consumers actually have in them. In order to maintain and grow market share, companies must figure out how to build trust in several dimensions.
In interviews conducted alongside our quantitative survey, senior executives confirmed the importance of trust and reputation to their strategy and growth—and described a landscape of both challenges and enormous opportunities. ‘In an era of wide distrust, business is still one of the more trusted institutions,’ says Esi Eggleston Bracey, Unilever’s Chief Growth and Marketing Officer. ‘People trust brands they love and companies that use their data responsibly. Employees trust companies that support them, have responsible practices and treat them as people. And investors trust performance and solid, continuous returns.’
Six consumer trust imperatives
- Forge bonds with eco-conscious consumers by connecting their intentions to positive environmental impacts.
- Create and promote a product portfolio that reflects consumers’ desires for wellness, nutrition and more sustainable food production.
- Strike a balance with social media use, recognising its significance as a platform for sales and engagement, while being mindful of consumer concerns about its credibility.
- Safeguard personal data, while continuing to use it to offer personalised services and elevated customer experiences.
- Navigate conflicting priorities in an economy with rising prices, meeting customers’ expectations of value while managing price increases effectively.
- Incorporate and experiment with AI tools in business operations while maintaining a human element, especially in more complex and personal services.
Forge greater bonds with eco-conscious consumers
A staggering 85% of survey respondents report experiencing firsthand the disruptive effects of climate change in their daily lives. A smaller but still considerable number (46%) also say that they are buying more sustainable products as a way to reduce their personal impact on the environment.
This gap presents a chance for consumer markets companies to better connect with environmentally aware consumers. It also calls for a deeper understanding of consumer behaviour, including that of the 43% of all surveyed consumers who report making more considered purchases to reduce their overall consumption.
Across the board, consumers tell us they would be willing to pay 9.7% above average price for sustainably produced or sourced goods, in line with last year’s pulse survey results of 9.8%. They say the sustainability incentives that would have the greatest impact on their purchasing are mainly tangible attributes, including production methods that emphasise waste reduction and recycling (40%), eco-friendly packaging (38%), and making a positive impact on nature and water conservation (34%). Messaging that promotes a company’s social responsibility programmes or community engagements (20% and 17%, respectively) is seen as less influential.
In interviews, executives from a wide range of consumer markets companies—representing grocery, health, home decor and more—shared similar experiences of their customers’ eco-minded behaviour. The expectation that companies will do the right thing for the environment is now seen as table stakes. Thus, companies must achieve a delicate balance between consumer affordability and environmental impact. This may involve switching from high-performance plastic packaging to biodegradable options, or giving customers a choice of using more costly sustainable aviation fuels for product delivery. ‘If reusable packaging was less expensive, not more, that would be a game changer,’ says Bálint Lévai, CEO of the dietary supplements company BioTechUSA, which has experimented with a range of alternative packaging options, with limited consumer uptake.
Cost increases associated with sustainability are a fundamental challenge for consumer-facing companies. The 2024 edition of PwC’s Annual Global CEO Survey showed that two-thirds of companies have efforts underway to improve energy efficiency, but only about half are creating innovative climate-friendly products or services. Many are also facing tough decisions on costs. ‘For companies, there is a real focus on operational challenges and minimising impacts on product pricing. How do they create systems and supply chains to meet their climate commitments? Where do they source raw materials at appropriate prices? How do they drive needed efficiencies in new processes?’ asks David Chavern, President and CEO of the Consumer Brands Association, a US trade group for manufacturers of consumer packaged goods (CPG). ‘Ultimately, climate risk will be priced into inputs and processes, and the necessary next question will be how to also deliver the right price to the consumer.’
- Expand the impact of compliance and regulatory work, like the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) , by using non-financial information to find bottom-line benefits.
- Build more resilient, more efficient and less energy-intensive supply chains through network optimisation, integrated visibility and technological innovation.
- Discover efficiencies in operations such as truck loading, warehouse operations, routing, and waste and inventory reduction through machine learning, AI, and analytics.
- Embrace the opportunity for premiumisation through product differentiation valued by consumers (e.g., products that commit to doing no harm).
Create a product portfolio that reflects wellness, nutrition and sustainable food production
More than half of consumers (52%) express intentions to boost their intake of fresh fruits and vegetables, while a smaller but important group (22%) plan to reduce their red meat consumption. Despite these health-orientated preferences, only 19% of consumers consider the environmental implications of their food choices. This disconnect presents a significant opportunity for food producers, retailers and wholesalers to bridge the gap between consumer intent and sustainable practice.
The growing interest in plant-based diets hints at a rising awareness of the environmental burdens posed by traditional meat production, particularly beef, which is a known contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. Explicitly addressing these consumer concerns may help companies integrate plant-based options into mainstream shopping habits, while being mindful that the main motivations behind these shifts are consumers’ considerations of general health (57%) and product cost (52%) when they make food and dietary choices.
Feeding the globe
The ambition to adopt healthier and more sustainable diets cannot rest on consumers alone; producers and retailers must also step up. Global population numbers are expected to surge from 8.1 billion today to 9.7 billion by 2050 , and the dual challenge of feeding more mouths and reducing food production’s ecological footprint is becoming increasingly urgent. Although the business model of selling in larger quantities is necessary and lucrative, it will require innovation to reduce potential risks to long-term environmental and social sustainability.
Food companies can leverage the willingness of consumers to pay a premium for sustainably produced goods as a competitive advantage. Effective strategies might also include comprehensive food packaging and presentation that not only guides consumers towards environmentally friendly choices but also builds trust through transparency in product design and the communication of clear sustainability information at point of sale. For example, six in ten consumers in our survey agree that an independent sustainability score on food products would be helpful and that incentives on the pricing of foods nearing expiry would drive likelihood to purchase these items.
- Support consumers’ ability to eat a healthy diet through clear category signposting, packaging information, and other targeted communication and marketing efforts.
- Expand portfolio strategies to incorporate a greater number of alternative meat products and proteins.
- Cater to a growing demand for health and wellness products, such as weight-loss prescription drugs and other over-the-counter solutions.
- Innovate to meet a new generation of informed consumers who are focused on their health, offering products such as wearables that incorporate health-tracking features.
Strike a balance between engagement with social media and caution over its credibility concerns
Consumers have mixed feelings about social media. They increasingly use it as a place for purchases; 46% of consumers report directly buying products through social media, a significant rise from 21% in 2019. And they really like it as a place for discovery and reviews: 67% of consumers use social media channels to discover new brands, and 70% of consumers seek reviews to validate a company before making a purchase. But at the same time, consumers are questioning its safety and reliability, ranking social media their least trusted industry.
Striking the right balance on social media is crucial for companies. Brands need to create engaging and authentic content that resonates with their target audience, while also being mindful of the concerns that consumers have on trust. Data protection was the leading factor that influenced consumer trust—83% of respondents consider it a top priority. Other important factors are the quality of goods and services (79%), companies’ treatment of employees (77%), and product affordability (75%).
of consumers report purchasing products directly through social media—up from 21% in 2019.
Businesses are engaged in a delicate dance of expressing their purpose and values while also navigating the need for caution in their communications with consumers. ‘Companies today are trusted more than governments and media. That gives companies an opportunity to play a larger and purposeful role in society,’ says Ronald den Elzen, Chief Digital and Technology Officer at Heineken. ‘At the same time, we see many companies becoming more careful and restrictive in advertising, based on the polarisation we are seeing around the world.’
Advertising’s new frontier
‘Five years ago, we were spending half of what we spend now on digital advertising,’ says Kyle Artz, Vice President of China Strategy at Coca-Cola, one of the world’s largest advertisers, stressing the importance of directing this spend towards innovative consumer engagement. Through personalised approaches, user-generated content initiatives, gamification and more, companies are competing in the digital space to create relationships that go beyond mere brand awareness. The impact of personalised social media advertisements is evident, with seven in ten consumers reporting that it would influence their purchasing decisions, followed by the influence of retailer websites (66%), email (54%) and text messaging (38%).
Global social media ad spending alone is projected to reach US$220 billion this year, up from the US$207 billion forecast for 2023. This includes a strong focus on social media influencers, both widely recognisable celebrities and aspiring individuals, who are now an established channel—our survey found they have influenced 41% of consumers to make a purchase. ‘Influencers are playing a much bigger role than what they were playing even a year ago,’ says Nitish Gupta, Managing Director in Vietnam of the personal care brand Kimberly-Clark. ‘Across medical, beauty, baby and childcare, and personal care categories, when I look at the social commerce landscape, it’s a sea change.’
- Emulate front-running CPG companies by building social ecosystems targeted to specific generations (Gen Z, millennials, etc.) across various social media platforms (YouTube, Instagram, Snapchat, Twitch, etc.).
- Invest in marketing and advertising to build brands instead of pursuing more transactional trade promotion spend.
- Take a digital-first approach to investing in advertising channels such as text and email, in addition to social media.
Safeguard personal data, while using it to elevate customer experiences
A large majority of consumers (83%) say that protection of their personal data is one of the most crucial factors in companies’ ability to earn their trust. When asked specifically about privacy, a significant majority of consumers (80%) also demand assurances that their personal information won’t be shared. But only around half feel confident that they understand how their data is stored and shared, and 71% express concerns about the security of their personal data on social media.
The acquisition and use of first-person data for personalisation has also become crucial to maintaining a competitive advantage in the marketplace. ‘Consumers expect that brands today understand them better than ever before,’ says Tien Yue Chen, Executive Director of the Malaysia-based pewter home decor and luxury gifting company Royal Selangor. As Coca-Cola’s Artz tells us: ‘First-person data for personalisation and advanced insights is a point of consideration in nearly every decision we make.’ With competition for valuable data intensifying, and new regulations coming into force in the EU and several Asia-Pacific countries , it’s imperative for companies to implement robust data protection measures and enact a strategy that engages with consumers without compromising the ethical use of data.
Use it, don’t abuse it
Industry executives describe a developing social contract that involves consumers willingly sharing their personal information in exchange for valuable incentives such as promotions, exclusives and other perks. Indeed, nearly 50% of consumers say they are happy for their data to be used to offer them personalised services and experiences. ‘When our customers notice that their data is being used to provide them with better products or treatments, or to achieve efficiencies in obtaining their prescriptions, we can see that they feel much more confident in sharing their data with us, and this reinforces our reputation,’ says Patriciana Rodrigues, Chairwoman of Pague Menos, a Brazilian pharmacy chain.
This trend is especially evident in loyalty programmes, which are becoming the primary engine of customer data for many companies. Given that an overwhelming 93% of executives in the United States believe that establishing and nurturing trust has a direct and positive impact on financial performance , this exchange of data and incentive has the potential to create a virtuous circle between trust and revenue.
- Responsibly scale your data strategy to realise the full benefits for the company and your consumers, given that many CPG companies have already made their foundational investments in data, tech and AI use cases.
- Build AI-enabled digital tools for testing early-stage ideas and for digital prototyping in order to create efficiencies, such as the shortening of innovation cycles.
- Elevate your ‘power brands’ by using insights from consumer data to narrow or expand the focus of your brand portfolio.
Meet customers’ expectations of value while managing price increases effectively
Inflation ranks overwhelmingly as the number-one risk that consumers think could impact their country over the next year; 64% put the issue within their top three concerns. That’s more than 20 percentage points ahead of other major threats, including slow economic growth, climate change and health issues, and it was the top concern consistently around the globe—despite lower rates of inflation and, in some regions, signs of deflation.
A consistent observation came to light in our interviews with executives in a variety of consumer goods sectors. After consumers largely accepted the price increases of the covid era, they have shown little tolerance for continued rises, especially as they turn their attention to mounting non-discretionary spending: 62% expect the most significant increase in spending in the next six months to be on groceries.
Cost-effective pricing is emerging as an important and complex factor in gaining consumer trust. Governments and regulators, acting out of a sense of duty to consumers, have already started taking action against price increases that they see as outside reasonable bounds. And consumers are searching for better value for their money: 40% would consider switching from their preferred name brands to more affordable options, such as discount brands and generic products. ‘It’s important to remember that value doesn’t equal price,’ says Noel Keeley, CEO of the Irish food retailer and wholesaler Musgrave Group. ‘It’s not necessarily the cheapest, it’s the brand they feel they are getting the best value from.’
Given consumers’ and lawmakers’ reactions to price increases, companies need to make other moves to not only manage pricing but secure their finances and reassure investors. ‘Globally, investors are asking about how we are going to approach volume growth in the future,’ says Artz. ‘There is huge pressure on [consumer goods] companies that enjoyed price increases during covid but are now finding it increasingly challenging to deliver volume growth on top of pricing. So we have to be prudent and continue to monitor the right balance of volume and price at both a global and local level.’
Focus on the purchase journey
Brands and retailers must embrace a more flexible omnichannel strategy to meet consumers’ evolving expectations for a dynamic mix of online and offline experiences. Marketers should also take note that the distribution of consumers’ preferred shopping locations—either in-store or via remote channels—has remained consistent post-pandemic. Since 2022, preference for shopping in-store has hovered at around 42%, via smartphone at 34% and via PC at 23%.
For some companies, increasing resources to deliver a consistent and personalised experience, regardless of the platform or location, is a source of competitive advantage. ‘Our investment in customer-centricity, alongside delivering exceptional customer experience regardless of channel, has paid off in terms of an uplift in brand loyalty across our offerings,’ says Marc Giroux, COO of Food for Canadian grocery chain Metro Inc.
Consumers are seeking personal connection, particularly in their discovery of new brands; 55% of survey respondents say they choose to visit physical stores and engage with salespeople, compared with 49% who seek out recommendations from family and friends, and 46% who turn to online browsing. Indeed, many executives stressed the importance of empowering their sales staff through access to more personalised consumer data and offering consumers more meaningful in-store services and experiences.
Modest technological empowerment is also key to building consumer trust and satisfaction in the in-store experience. Nearly 40% of consumers indicated that the availability of mobile or contactless payment solutions would encourage them to shop in-store. Additionally, more than one-third of consumers expressed interest in smart tags that provide product details on smartphones, as well as self-checkout systems.
- Secure profitability (as prices normalise in the second half of 2024) by investing in consumer demand, restoring volume through marketing and advertising, and continuing cost-saving initiatives.
- Attract customers back into stores through targeted investments in talented staff and technology, to improve the shopping experience.
- Consider mergers and acquisitions as part of a disciplined capital allocation. Lagging brands may be ripe for pruning.
Incorporate AI while maintaining the human element
Companies face the challenge of responsibly aligning consumer sentiment towards emerging technology, like generative AI (GenAI ), with the technology’s current and potential capabilities. A substantial 80% of consumers express concerns about GenAI’s future developments. Although more than half of consumers trust GenAI for simpler tasks, such as aggregating product information or providing recommendations, consumers are less confident about its usage in higher-risk, more personal services such as healthcare. This means that companies must tread carefully in integrating technology that can reduce operating costs, addressing consumer concerns and maintaining ethical standards.
Unilever’s Eggleston Bracey, for example, notes that acceptance of AI among employees and consumers has grown significantly in the past 18 months. ‘I’m amazed at the receptivity towards AI from January 2023 to today,’ she told us. ‘Internally, we like to think of AI as an opportunity for Augmented Intelligence, the blend of artificial and human intelligence. Our responsible AI strategies dictate we always have a person in the loop.’
‘We’re also seeing more adoption as large language models have made AI so accessible, making it a lot less scary for people. People are identifying with it now because it’s making life easier.’
Take the percentage of consumers who trust AI to provide product recommendations: 50%. This number will continue to climb as familiarity with ChatGPT and other AI applications increases, and if consumers turn away from incumbent search engines and towards AI platforms. ‘AI search, with its propensity to “choose” products for consumers, will be a massive change for CPG companies,’ says Chavern of the Consumer Brands Association. ‘But that won’t be the only way that AI could turn marketing on its head. It is easy to see how it could be used for massively improved ad efficiency and content individualisation.’
Early-stage adoption
Today, adoption of machine learning and GenAI applications, such as LLMs (large language models) and text-to-image tools, varies among brands. Companies have used these tools for internal improvements such as supply chain optimisation, company information management and pricing strategies. Some brands have progressed further—and done so quickly—experimenting with consumer engagement and marketing personalisation through design-led tools in controlled environments or ‘sandbox’ settings. ‘Six months ago, we were just starting out in terms of our GenAI journey,’ says Kavindra Mishra, CEO of Shoppers Stop, a chain of department stores in 40 cities across India. ‘Now, we are using it to interact with more than 9 million loyalty customers, enabling us to personalise our engagement with them, and supercharging our understanding of their attitudes and behaviours.’
Despite high interest among respondents in the use of chatbots for providing detailed responses (42%) and to solve complex problems (44%), nearly half (49%) of consumers demand direct connection with a sales representative if the chatbot is unable to answer the consumer’s query effectively. This, again, highlights the crucial balance that companies need to strike between technological innovation and the human touch.
- Develop a responsible strategy for the regulatory landscape that will emerge around AI in the next few years.
- Scale successful machine learning, AI and digital use cases to optimise sales and demand planning.
- Explore the potential of AI tools to increase supply chain efficiency, from new product development to waste and inventory reduction.
- Test and learn with the producing capabilities of LLMs on ad campaign development and production.
Unlocking the trust premium
As global consumer markets continue to expand, companies must move beyond their own perceptions of customer trust and learn what their clients actually think. Senior executives recognise this, and though challenges exist, there are also significant opportunities for those companies that prioritise trust-building efforts rooted in brand building, responsible practices and solid performance. Trust is an increasingly valuable currency in consumer markets, so companies must commit to building and maintaining long-term integrity.
In January and February 2024, PwC surveyed 20,662 consumers across 31 countries and territories: Australia; Brazil; Canada; China; Czechia (Czech Republic); Egypt; France; Germany; Hong Kong, SAR; Hungary; India; Indonesia; Ireland; Malaysia; Mexico; the Netherlands; the Philippines; Poland; Qatar; Romania; Saudi Arabia; Singapore; Slovakia; South Africa; South Korea; Spain; Thailand; United Arab Emirates; Ukraine; the United States; and Vietnam. The respondents were at least 18 years old and were asked about a range of topics relating to consumer trends, including shopping behaviours, emerging technology and social media.
Interviews with industry executives took place in March and April 2024.
PwC Research , PwC’s global centre of excellence for market research and insight, conducted this survey.

Sabine Durand-Hayes , Global Consumer Markets Leader, is a partner with PwC France.

Myles Gooding , Global Consumer Markets Advisory Leader, is a partner with PwC Canada.

Brian Crane , Global Consumer Markets Assurance Leader, is a partner with PwC US.

Rakesh Mani , a specialist in the Southeast Asia Consumer Markets advisory practice, is a partner with PwC Malaysia.

Kelly Pedersen , a leading practitioner in global consumer markets transformation, is a principal with PwC US.
PwC’s 27th Annual Global CEO Survey: Thriving in an age of continuous reinvention
As existential threats converge, many companies are taking steps to reinvent themselves. Is it enough? And what will it take to succeed?
Consumer markets
PwC’s consumer markets practice provides support in areas such as disruption, the impacts of e-commerce, supply chain management, compliance and regulatory pressures, data analytics, and changing customer demands.

© 2017 - 2024 PwC. All rights reserved. PwC refers to the PwC network and/or one or more of its member firms, each of which is a separate legal entity. Please see www.pwc.com/structure for further details.
- Legal notices
- Cookie policy
- Legal disclaimer
- Terms and conditions

Opening Bell (Video)
Deciphering Inflation Impact: Consumer Behavior Analysis
Posted: May 22, 2024 | Last updated: May 22, 2024
Joining us at the New York Stock Exchange, Sarah Foster, a bank rate analyst, shared her insights on the consumer's response to the current economic climate. Despite inflation slowing in April for the first time this year, consumers remain wary, recalling prices at the onset of the pandemic. Bank rate's analysis of the Consumer Price Index (CPI) reveals that nearly all goods have become pricier since the pandemic began, with a general price level increase of about 21%. This translates to Americans spending an additional $200 monthly on the same $1,000 worth of goods and services as before. Interestingly, while consumers feel the economy might be in recession, the labor market boasts the lowest unemployment rates since the 1960s. In the banking sector, despite the Fed's potential rate cuts, high yield banks are increasing their yields, suggesting the expectation that high-interest rates may persist. This twist defies the usual trend where banks lower deposit rates in anticipation of Federal Reserve cuts, marking a significant shift in the economic landscape as we navigate 2024.
More for You
Zelensky calls out allies over worries that Russia could lose the war
The 30 best action movies of all time
Russia is about to hit an unprecedented new casualty milestone
Famous Christian symbols explained
Disease X: The next pandemic?
Putin’s Scare in Kharkiv Grows: Zelensky Signs New Law Allowing Prisoners to Join Military
Trump’s new media company has suffered huge losses
FC Barcelona and Atletico Madrid fans look away: the most overrated players in La Liga
Putin announces Russian nuclear weapon drills near Ukraine
The Rise and Fall of China’s Nicaragua Canal Megaproject
Best selling cars of all time, from each car maker
Lessons that people usually learn too late in life
Yahaya Bello’s alleged corruption is child’s play to ex-governors from South South – NACAT
10 Foods You Should Eat Before Drinking Alcohol
Malaysian-born Hock Tan tops US CEO pay chart with $162M earning
China: Spectacular Fire Performance
What will happen in Iran after the death of its president?

Russia Parades Captured Ukrainian Troops; Zelensky's Troops 'Voluntarily Surrender' In Kharkiv
Greatest supercars that never made it to production
Places in Europe where three countries meet

Consumer insight and Behaviour : Assignment
Added on 2021-01-02
About this Document
End of preview
Want to access all the pages? Upload your documents or become a member.
Customer Behaviour INTRODUCTION 1 TASK 11 Title Analysis of Stages of the Consumer Decision Making Process Journey lg ...
Understanding and analysing consumers decision-making lg ..., consumer behaviour and insight of coca-cola lg ..., consumer purchase behaviour of coca cola - report lg ..., consumer behaviour and insight essay lg ..., report on consumer behaviour of coco cola lg ....

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Table of Contents. Unit 37 Consumer Behavior and Insight Assignment. Introduction. LO1- Demonstrate the ability to map a path to purchase in a given category, including the decision-making process. P1- Explain and analyse the stages of the consumer decision-making journey for a given product/service. P2- Explain why it is important for ...
An assignment On B2C &B2B Consumer Decision-making Process. Assignment Part 1 - Assignment part 2. Module title: Consumer Behavior and Insight. Student Name:
Unit 37 Consumer Behaviour and Insight - Free download as Word Doc (.doc), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The document provides information about an assignment for a BTEC HND in Business unit on consumer behavior and insights. Students are asked to produce a research report analyzing the consumer decision-making process and how marketers can influence it.
INTRODUCTION Consumer behaviour is the vital element for the business organisation as this study how the individual , group or the association prefer, purchase and usage the items and services to fulfil their necessarily and demand.Consumer behaviour also mention to as activity which an individual client executes in the market. This assignment has been prepared to understand how the potential ...
INTRODUCTION Consumer behaviour and Insight refers to an acknowledgement of trends that fluctuated in interest and buying behaviour of consumers on timely basis. An organisation can achieve huge sustainability and profitability in competitive market only if their effective management is able to identify and interpret the trends in the market which makes easy for them to formulate an effective ...
Assignment Brief_HNBS 327 Consumer behaviour and Insight (1).pdf - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
INTRODUCTION Consumer behaviour is the study of an individual, group or organisation which signifies their behaviour or attitude towards buying, selecting, utilising product and services in order to satisfy their needs or wants in an effective manner. It is a continuous process which begins with pre purchase activity and ends with post purchase experience.
View Assignment Brief - Unit 37- Consumer Behaviour _ Insights V 1.2.pdf from BUSINESS 40532 at University of Ulster. ... Consumer Behaviour & Insights 5 J/508/0596 Student Name/ID Number Unit Assessor IV Name Dhaya Bennet V.S. Nofa F Issue Date Formative Submission Final Submission Submitted on 07-Oct-2021 06-Nov-2021 16-Nov-2021 Assignment ...
Executive summary This assignment is created to enhance the reader's knowledge and provide an understanding of the steps, factors involved in the consumer's decision-making processes with various types of examples absorbed by the present day to day examples. Various examples and scenarios which are involved in the steps from the needs recognition through research, the evaluation of ...
Unit 37: Consumer Behaviour and Insight. Assignment Title Consumer Behaviour and Insight . Purpose of this assessment. The assessment is designed to test students' knowledge and understanding of the consumer's decision-making processes, from needs recognition through research, the evaluation of alternatives, purchase and post-purchase ...
Conclusion. In the sphere of microeconomics homework, decoding consumer behavior is not merely a requisite skill but a gateway to unraveling the complexities of market interactions. A robust understanding of utility, preferences, and budget constraints empowers students to adeptly navigate the intricacies of consumer decisions.
Consumer behavior is an essential area of study for various fields, including marketing, business, psychology, and sociology, among others. Understanding consumer behavior is necessary for learning because it provides insights into how individuals make decisions about purchasing goods and services. In turn, this understanding helps businesses ...
This assessment will cover the following questions: Intercontinental Hotel is the luxury hotel of United Kingdom.Identify the forces that influence hospitality consumer attitude and behaviour and its impact on the process of decision making.
INTRODUCTION Consumer behaviour is explained as the activity which is conducted by organisation to study and know about the behaviour of consumer within marketplace. This process is conducted from initial stage to final purchase (Consumer Behaviour, 2018).In this assignment there will be detail examine about the behaviour of consumer towards any of the product.
BTEC Assignment Brief Qualification Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher National Diploma in Business Unit or Component number and title Unit 37: Consumer Behaviour and Insight (J/508/0596) Learning aim(s) This unit is designed to enhance students' knowledge and understanding of the consumer's decision-making processes, from needs recognition through research, the evaluation of alternatives ...
Explore consumer decision-making, behavior stages, and influencing factors in this BTEC Level 4 & 5 assignment. Dive into the world of consumer insights.. Explore more Assignments, projects and assessments.
Consumer Behavior, Digital Marketing, Discussion Exercises, Member Activities, Promotion. In this activity, students will review a podcast episode on social media marketing and platforms, and explore the best platforms for different types of business and situations. A handy overview of the main social media players. Review the Teaching Activity.
Course Code & Title: ABDT3503 CONSUMER INSIGHT & BEHAVIOUR. Declaration. I/We confirm that I/we have read and shall comply with all the terms and conditions of TAR University College's plagiarism policy. I/We declare that this assignment is free from all forms of plagiarism and for all intents and purposes is my/our own properly derived work ...
This assignment on consumer behaviour and insight. This method is also helpful for learn about the customer's behaviours and for enhancing the growth of company Ask a question from expert
Base: 20,662 (all respondents) Source: PwC's Voice of the Consumer Survey 2024. Striking the right balance on social media is crucial for companies. Brands need to create engaging and authentic content that resonates with their target audience, while also being mindful of the concerns that consumers have on trust.
Executive summary This assignment is created to enhance the reader's knowledge and provide an understanding of the steps, factors involved in the consumer's decision-making processes with various types of examples absorbed by the present day to day examples. Various examples and scenarios which are involved in the steps from the needs recognition through research, the evaluation of ...
Adapting to Consumer Behavior. The Role of Omnichannel in Supply Chain. 14.05.2023. Episode 14. The word omnichannel only came into existence in 2011. Since then, going omnichannel has become the only way for businesses to survive and thrive. Consumer buying preferences have changed drastically over the past few years.
INTRODUCTION Consumer behaviour is affiliated to the study of individuals, a group of people and organisations and how they choose their products and services in order to meet the consumers demand and needs. The main motive of consumer behaviour study by the business organisations to ascertain that how customers feel about different alternatives brand, how customer influenced from ...
Bank rate's analysis of the Consumer Price Index (CPI) reveals that nearly all goods have become pricier since the pandemic began, with a general price level increase of about 21%. This translates ...
Unit 37 - Consumer Behaviour and Insight: Credit Value: 15: Unit Level: 5: Academic Year: 2020-21: Cohort: September 2019: Assessor: Mohammad Islam: Assignment Title: Consumer Behaviour and Insight: Issue Date: ... • The assignment should be submitted in a MS Word© format, or equivalent. • Please read the assignment brief carefully.
Consumer behaviour and insight assignment. Stages of consumer decision making journey. Differences in the decision making process of B2C and B2B. Ask a question from expert. Ask now. Study. Writing. Homework Help. Blog; ... Added on 2021-01-02. Consumer insight and Behaviour : Assignment