How to make a business plan
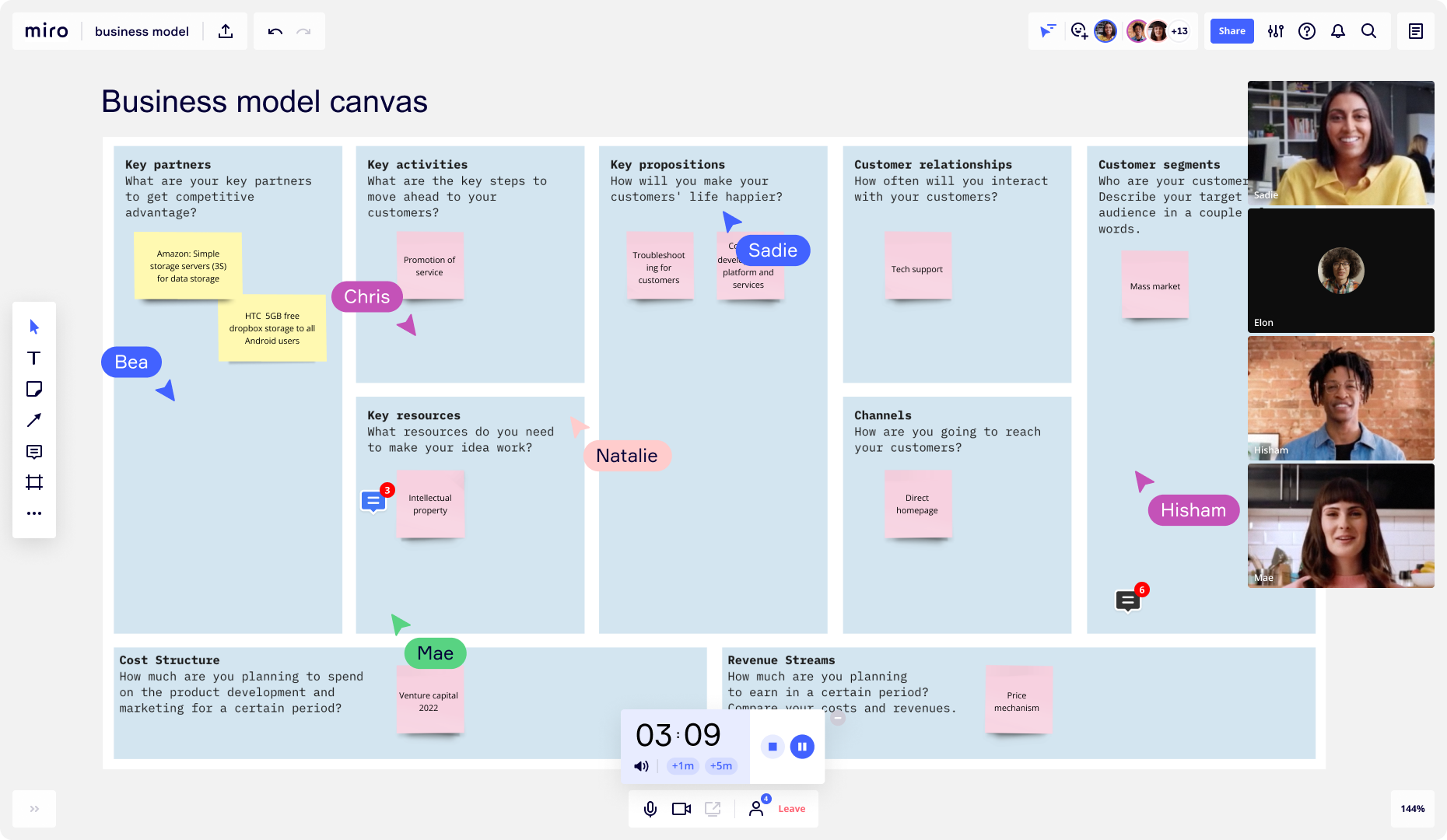

Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Business consultants
Entrepreneurs and Small Business
Accelerators and Incubators
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai pitch deck generator
Stratrgic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
Small Business Tools
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Strategic Planning
Business Planning Process: Create a Business Plan That Works

Free Business Startup Checklist
Radhika Agarwal
- December 15, 2023

If you are planning to start or grow your business, you might have heard about the importance of the business planning process countless times. And yes, it is necessary to have a plan. After all, it’ll be your roadmap to success.
But how would you go about it? Where will you start? And most importantly is there a tried and tested process that can make your job easier? What if we told you there is such a process?
And through this article, we’ll walk you through everything from what is business planning to the steps of the business planning process .
What is Business Planning?
Business planning is the process of giving structure to your business idea. It acts as a roadmap to your business journey, helps you get through obstacles, and maximizes opportunities.
It also helps you set realistic goals and pursue the same with a structured action plan.
Moreover, through a business plan, you can analyze your company’s strengths and weaknesses, and understand how that would impact your company while dealing with market competition and how your strengths would help you achieve your goal.
Above all, doing business with a well-written business plan increases your chances of success.
Steps of the Business Planning Process
Although there’s no sole right way to go about the process of planning your business, here’s a compilation of steps that’ll make your planning process faster and easier.
1. Carry out your research

The first step to creating a business plan is to do thorough research about the business and industry you are trying to get into. Tap into all the information you can get about your target audience, potential customer base, competitors, market and industry trends, cost of business, etc.
You can give a form to your research by asking yourself the following questions:
- What are your goals?
- Where does your business stand currently?
- What are the prevailing market trends?
- What strategies is your competitor following?
You can find your answers by conducting market surveys , talking to customers and industry experts, designing good questionnaires, reading articles, blogs, and news updates about your industry and related ones, and so on.
Also, it is a good practice to conduct a SWOT analysis for your company to understand how your company’s strengths and weaknesses would help you stand apart from your competitors based on the current market statistics.
2. Make a Framework

Once you’re done with your research the next step is to make a framework or a set of strategies for your business based on your research and business goals. You can either design strategies from scratch or reframe previously tried and tested successful strategies to fit your business goals.
But remember that you’ll have to tweak strategies to fit your unique competitive advantages and goals. Hence, strategies that are already being used can act as a good foundation, but it is essential to remember that you’ll have to expand upon them or improvise them for your business.
This step can be completed by taking a deep dive into your customer’s buying motivations and challenges that your product can help solve. Based on that, make a marketing plan, operations plan, and cost structure for your business at least for the first few years of your business.
3. Formulate your Financial Forecasts

No matter how tedious finances might seem, they are an integral part of any business. When you map out your finances it is essential to note down all the costs you’ll incur as you grow and run your business for the next five years and what would be your potential revenue, and if or not it would leave room for profit.
You can get your financial forecast by adding your financial assumptions to a financial system which will give you your cash flow statements and give you an idea of what amount of funds you’ll need to start and run your business for the first year.
This step is especially helpful if you want to acquire funding for your business. Nonetheless, it helps you prepare to deal with the financial aspects of your business.
A financial statement essentially provides details of a company’s expenses and profits. It also provides an overview of the company’s current financial stance, including its assets and liabilities.
Through this section try to write down and explain how you plan to use your investments and how would the same give a return.
4. Draft a Plan

As you’re done with creating business strategies and planning your finances, it is time to draft your business plan and compile everything into a single document. As you are done with all the technical aspects, this step should feel relatively easy.
But if you need help drafting a business plan and making it look presentable, you can subscribe to business plan software that comes with predesigned templates and tools to make your work easier .
5. Recheck and Improvise

Now as you’re done with writing your plan, it is a good idea to give it enough time to edit it. Check for any unclear sentences, irrelevant phrases, or confusing terms.
Take suggestions from your team members who are familiar with the functioning of your business. Finally, proofread for any grammar or punctuation errors. One of the most popular and useful pieces of editing advice is to put your work aside for a while and then look at it with fresh eyes to edit it better.
6. Create an Impressive Business Plan Presentation

Now, as you’re done with writing your business plan, it is time to create a presentation that leaves an excellent impression on your audience. Highlight all the important and relevant points.
Also, add references for your investors like your financial reports , resumes of your key team members, snippets of your marketing plan, and past sales reports to have a well-rounded presentation.
It is true that starting a business is intimidating. It includes a bunch of emotions, chaotic ideas, and a will to take risks. ( Risks are a part and parcel of starting a business, no matter how much you plan, but yes planning helps you prepare for it.) But in the end, all of us know that all of it is worth it if you have a profitable business in the end.
And business planning is something that takes you one step closer to your idea of success. Moreover, a plan keeps you going in the face of challenges and adversities, and helps you push yourself a little harder to achieve your dreams when things get tougher.
Above all, a business plan helps you take action and turn ideas into a real and functioning business. So, what are you waiting for? Go ahead and start planning !
And while you’re at it, to check out Upmetrics’s business planning software to make business planning easier and faster.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.

About the Author

Radhika is an economics graduate and likes to read about every subject and idea she comes across. Apart from that she can discuss her favorite books to lengths( to the point you\'ll start feeling a little annoyed) and spends most of her free time on Google word coach.
Related Articles

How to Write a Business Plan Complete Guide

17 Reasons Why do you Need a Business Plan?

How to Prepare a Financial Plan for Startup Business (w/ example)
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

How to Write a Business Plan in 2023 [Examples Included]

Table of contents
So you have come up with a business idea that will turn your company into a Forbes 500 enterprise? Sounds great!
However, you are going to need much more than an idea. You will need to do some comprehensive research, create operational standpoints, describe your product, define your goals, and pave out a road map for future growth.
In other words, you are going to need a business plan.
A business plan is a document that precisely explains how you are going to make your startup a success. Without it, your chances of attracting funding and investments significantly decrease.
Do you want to learn how to create a winning business plan that will take your company to the next level? We created a guide that will help you do just that.
Let’s dive in.
What Is a Business Plan?
Why and when do you need a business plan, types of business plans (what to include in each).
- How Do You Write a Business Plan?
Best Practices for Writing a Winning Business Plan
Business plan examples.
- Monitor the Performance of Your Business with Databox
A business plan is a comprehensive document that defines how a business will achieve its goals. It is essentially a road map for growth that includes operational standpoints from all the key departments such as marketing, financial, HR, and others.
Startups use business plans to describe who they are, what they plan to do, and how they plan to achieve it. This is an extremely valuable document for attracting investors.
However, they are valuable for the company members as well. A good business plan keeps executive teams on the same page regarding the strategies they should implement to achieve their set objectives.
Related : Reporting to Investors: 6 Best Practices to Help Increase Funding
While business plans are especially useful for startups, each business should include them. In the best-case scenario, this plan will be updated from time to time and reviewed whether the goals of the company have been met.
The main things that investors want to check out in the business plan are:
- Product-market fit – Have you researched the market demand for your products and services?
- Team efficiency – Does your startup have devoted professionals that will work on achieving your goals?
- Scalability – How probable is growth in sales volumes without proportional growth or fixed costs?
An organized business plan is essentially a blueprint of your goals and it showcases your abilities as an entrepreneur.
Related : Business Report: What is it & How to Write a Great One? (With Examples)
If you want to persuade venture capitalists and banking institutions to invest in your startup, you won’t be able to do it without a solid business plan. Following a clear business plan format is crucial, as it structures your plan in a way that is easily understandable and demonstrates your business’s potential.
A business plan is helpful in two ways – it allows you to focus on the specific goals you set for the future and it provides external parties with evidence that you have done your research in advance.
But don’t just take our word for it – here are some of the things that researchers from Bplans found out when they were analyzing the benefits of business plans with the University of Oregon.
- Companies that use business plans have recorded a 30% faster growth compared to those that didn’t use them.
- Getting investments and loans is twice as likely to happen with the help of business plans.
- There is a 129% increased chance for entrepreneurs to go past the ‘startup’ phase through business plans.
You should create a business plan before you decide to quit your regular job. It can help you realize whether you are ready or not.
Also, creating a business plan is helpful when:
- You want to attract investments or funding from external parties
- You want to find a new partner or co-founder
- You want to attract talented professionals to join your startup
- You need to change things up due to the slow growth
While creating a business plan is an important step, you first have to know how to differentiate all the different types. This will help you choose the one that is most suitable for your business.
Here are the most common types of business plans and what you should include in each.
One-Pager Business Plan
Startup business plan, internal business plan, strategic business plan, feasibility business plan.
The one-pager is a business plan that only includes the most important aspects of your business. It is essentially a simplified version of a traditional business plan.
When creating the one-pager business plan, your primary focus should be on making it easily understandable.
Since this business plan is rather short, you should avoid using lengthy paragraphs. Each section should be around 1-2 sentences long.
The things you should include in a one-pager business plan are:
- The problem – Describe a certain problem your customers have and support the claim with relevant data.
- The solution – How your products/services can solve the issue.
- Business model – Your plan on how to make money. Include production costs, selling costs, and the price of the product.
- Target market – Describe your ideal customer persona. Start with a broad audience and narrow it down by using TAM, SAM, and SOM models. This lets investors in on your thought process. To understand these models better, check out, for example, the importance of proper TAM evaluation for B2B startups .
- Competitive advantage – How are you different from your competitors?
- Management team – Include your business’s management structure.
- Financial summary – This part should revolve around the most significant financial metrics (profit, loss, cash flow, balance sheet, and sales forecast).
- Required funding – Define how much money you need to make your project a success.
PRO TIP: How Well Are Your Marketing KPIs Performing?
Like most marketers and marketing managers, you want to know how well your efforts are translating into results each month. How much traffic and new contact conversions do you get? How many new contacts do you get from organic sessions? How are your email campaigns performing? How well are your landing pages converting? You might have to scramble to put all of this together in a single report, but now you can have it all at your fingertips in a single Databox dashboard.
Our Marketing Overview Dashboard includes data from Google Analytics 4 and HubSpot Marketing with key performance metrics like:
- Sessions . The number of sessions can tell you how many times people are returning to your website. Obviously, the higher the better.
- New Contacts from Sessions . How well is your campaign driving new contacts and customers?
- Marketing Performance KPIs . Tracking the number of MQLs, SQLs, New Contacts and similar will help you identify how your marketing efforts contribute to sales.
- Email Performance . Measure the success of your email campaigns from HubSpot. Keep an eye on your most important email marketing metrics such as number of sent emails, number of opened emails, open rate, email click-through rate, and more.
- Blog Posts and Landing Pages . How many people have viewed your blog recently? How well are your landing pages performing?
Now you can benefit from the experience of our Google Analytics and HubSpot Marketing experts, who have put together a plug-and-play Databox template that contains all the essential metrics for monitoring your leads. It’s simple to implement and start using as a standalone dashboard or in marketing reports, and best of all, it’s free!
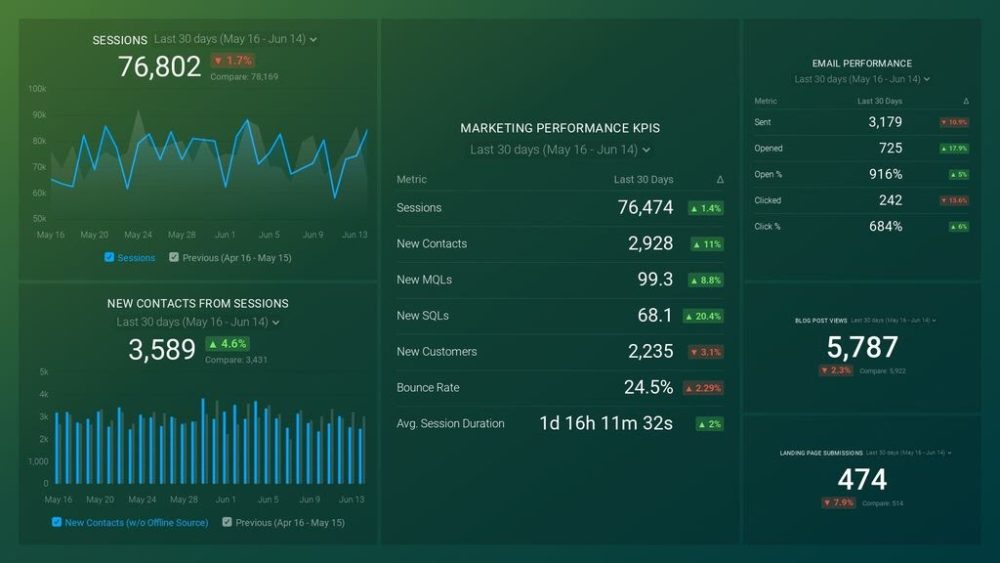
You can easily set it up in just a few clicks – no coding required.
To set up the dashboard, follow these 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Get the template
Step 2: Connect your HubSpot and Google Analytics 4 accounts with Databox.
Step 3: Watch your dashboard populate in seconds.
Related : Check out our comprehensive guide on writing a marketing plan report .
New businesses use startup business plans to outline their launching ideas and strategies to attract funding and investment opportunities. When creating startup business plans, you should primarily focus on the financial aspect and provide evidence that supports it (e.g. market research).
These are some of the main things that should be included:
- Vision statement – Explain your vision for the company and include the overall business goals you will try to achieve.
- Executive summary – A quick overview of what your company is about and what will make it successful. Make sure to include your products/services, basic leadership information, employees, and location.
- Company description – A detailed overview of your company. Talk about the problems you will solve and be specific about customers, organizations, and growth plans. This is the place where you should state your business’s main advantages.
- Market Analysis – Show investors that you have a good understanding of your industry and target market by providing a detailed market analysis. Try to point out certain trends, themes, or patterns that support your objective.
- Organization and management – This section explains the structure and the management hierarchy. Also, describe the legal structure of your business.
- Service or product line – Go into detail about the products and services you are going to sell. Explain the benefits they bring and share your intellectual property plans.
- Marketing and sales – Talk about your marketing strategy and describe how you plan to attract new customers.
- Financial projections – This section should be about convincing your readers why the business will be a financial success. Create a prospective financial outlook for the next few years and it includes forecasts.
An internal business plan is a document that specifically focuses on the activities within your company. While external business plans focus on attracting investors, internal business plans keep your team aligned on achieving goals.
Related : Internal vs. External Reporting: What Are the Differences?
This business plan can differentiate based on how specific you want it to be. For example, you can focus on a specific part of the business (e.g. financial department) or on the overall goals of the whole company.
Nonetheless, here are some things that should universally be included in all internal business plans:
- Mission statement – Focus on the practical, day-to-day activities that your employees can undertake to achieve overall objectives.
- Objectives – Provide specific goals that you want your company to achieve. Make the objectives clear and explain in which way they can be reached. Focus more on short-term objectives and set reasonable deadlines.
- Strategies – Talk about the general activities that will help your team reach the set objectives. Provide research that will describe how these strategies will be useful in the long term.
- Action plans – These plans revolve around particular activities from your strategy. For example, you could include a new product that you want to create or a more efficient marketing plan.
- Sustainability – This refers to the general probability of achieving the goals you set in the internal report. Sometimes, plans may seem overly ambitious and you are going to have to make amends with certain things.
A strategic business plan is the best way to gain a comprehensive outlook of your business. In this document, forecasts are examined even further and growth goals tend to be higher.
By creating a strategic business plan, you will have an easier time aligning your key stakeholders around the company’s priorities.
Here is a quick overview of what a strategic business plan should include:
- Executive summary – Since strategic business plans are generally lengthy, not all executives will have time to go through it. This is why you should include a quick overview of the plan through an executive summary, you can also create an executive summary template to make the step easily repeatable.
- Vision statement – Describe what you wish to achieve in the long term.
- Company overview – This refers to past achievements, current products/services, recent sales performances, and important KPIs.
- Core values – This section should provide an explanation of what drives the business to do what it does.
- Strategic analysis of internal and external environments – Talk about the current organizational structure, mission statements, and department challenges.
- Strategic objectives – Go into detail about the short-term objectives your team should reach in a specific period. Make sure the objectives are clear and understandable.
- Overall goals – This section should include operational goals, marketing goals, and financial goals.
A feasibility business plan is also known as a feasibility study. It essentially provides a foundation for what would be a full and comprehensive business plan. The primary focus of a feasibility plan is research.
The things you should include in a feasibility plan are:
- Product demand – Is there a high demand for your product? Would customers be interested in buying it?
- Market conditions – Determine the customer persona that would be interested in buying your products. Include demographic factors.
- Pricing – Compare your desired price with the current pricing of similar products. Which price would make your service profitable?
- Risks – Determine the risks of launching this new business.
- Success profitability – Is there a good way to overcome the risks and make your company profitable?
How Do You Write a Business Plan Report?
As we explained in the previous heading, there are a few different types of business plan. Depending on the audience you are referring to, the language you use in the plan should be adjusted accordingly.
Nonetheless, there are certain key elements that should be included in all business plans, the only thing that will vary is how detailed the sections will be.
Include these elements in your business plan.
Executive summary
Company description, market opportunity and analysis, competitive landscape, target audience, describe your product or service, develop a marketing and sales strategy, develop a logistics and operations plan, financial projections, explain your funding request, compile an appendix for official documents.
An executive summary is a quick overview of the document as a whole that allows investors and key stakeholders to quickly understand all the pain points from the report.
It is the best way to layout all the vital information about your business to bank officials and key stakeholders who don’t have the time to go through the whole business plan.
If you summarize the sections well, the potential investors will jump into the sections they are most interested in to acquire more details.
You should write the executive summary last since you will then have a better idea of what should be included.
A good executive summary answers these questions:
- Who are you?
- What do you sell?
- How profitable is it?
- How much money do you need?
This section of the business plan aims to introduce your company as a whole. The things you include in the company description can vary depending on if you are only starting a business or you already have a developed company.
The elements included in this section are:
- Structure and ownership – Talk about who the key shareholders in your company are and provide a full list of names. Also, mention details such as where the company is registered and what the legal structure looks like. In most countries, this is a legal requirement for AML regulations.
- History – This segment is if you already have an existing company. Use this section to show your credibility. Include company milestones, past difficulties, and a precise date for how long your company has been operating.
- Objectives – Describe the overall objectives of your company and how you plan to reach them.
Market analysis refers to creating your ideal customer persona and explaining why they would be interested in buying your products.
Market opportunities are the gaps that you found in the current industries and creating a way for your product to fill those gaps.
The most important step in this section is to create a target market (persona) through demographic factors such as location, income, gender, education, age, profession, and hobbies.
Make sure that your target market isn’t too broad since it can put off potential investors.
A good idea is to also include a detailed analysis of your competitors – talk about their products, strengths, and weaknesses.
Related : 12 Best Tools Marketers Use for Market Research
Although you may include a competitive analysis in the market analysis section, this segment should provide a more detailed overview.
Identify other companies that sell similar products to yours and create a list of their advantages and disadvantages. Learning about your competitors may seem overwhelming, but it’s an indispensable part of a good business plan.
Include a comparison landscape as well that defines the things that set you apart from the competitors. Describe the strengths of your product and show which problems it could solve.
Related : How to Do an SEO Competitive Analysis: A Step-by-Step Guide
Use the target audience section to fully describe the details of your ideal customer persona. Include both demographic and psychographic factors.
Ask yourself:
- What are the demographic characteristics of the people who will buy my product?
- What are their desires?
- What makes my product valuable to them?
Make sure to answer all of these questions to get in the mindset of your customers.
If you need more details on how to identify your target audience , check our full expert guide.
When talking about your products and services, be as precise as possible. Mention your target audience and the marketing channels you use for targeting this audience.
This section should reveal the benefits, life cycle, and production process of your products/services. Also, it is a good idea to include some pictures of your products if possible.
When describing your products, you should highlight:
- Unique features
- Intellectual property rights
- What makes the product beneficial
Marketing is the blood flow to your business’s body. Without a good marketing and sales strategy, the chances of your product succeeding are very slim.
It’s always best to already have a marketing plan in place before launching your business. By identifying the best marketing channels, you will show your investors that you researched this topic in detail.
Some of the things you should include are:
- Reach – Explain why a specific channel will be able to reach your target market
- Cost – Is the marketing strategy going to be cost-effective? How much money do you plan on spending on the strategy?
- Competition – Are your competitors already using this channel? If so, what will make your product stand out?
- Implementation – Who will be taking care of the implementation process? Is it a marketing expert? Which suppliers did you reach out to?
Related : 14 Reasons Sales And Marketing Alignment Is Crucial for Skyrocketing Company Growth
This section should explain the details of how exactly your company is going to operate.
These are the things you should include:
- Personnel plan – Define how many people you plan to employ and their roles. Also, if you plan on increasing your staff, you should explain what would be the cause of that.
- Key assets – This refers to assets that will be crucial for your company’s operation.
- Suppliers – Mention who your suppliers will be and what kind of relationship you have with them. Your investors will be interested in this part of the section since they want to be reassured that you are cooperating with respectable counterparties.
The financial projections section is one of the most important parts of your business plan. It includes a detailed overview of expected sales, revenue, profit, expenses, and all the other important financial metrics .
You should show your investors that your business will be profitable, stable, and that it has huge potential for cash generation.
Monthly numbers for the first year are crucial since this will be the most critical year of your company.
At the very least, you should provide:
- Funding needs
- Profit-and-loss statement forecast
- Balance sheet forecast
- Cash-flow statement forecast
Related : How to Write a Great Financial Report? Tips and Best Practices
When providing the funding request, be realistic. Explain why you need that exact amount of money and where it will be allocated.
Also, create both a best-case and worst-case scenario. New companies don’t have a history of generating profits which is why you will probably have to sell equity in the early years to raise enough capital.
This will be the final section of your business plan. Include any material or piece of information that investors can use to analyze the data in your report.
Things that could be helpful are:
- Local permits
- Legal documents
- Certifications that boost credibility
- Intellectual properties or patents
- Purchase orders and customer contracts
After reading the previous heading, you should have a clear idea of how to write a compelling business plan.
But, just to be sure, we prepared some additional information that can be very helpful.
Here are some of the best practices you should implement in your business plan according to the most successful companies.
Keep it brief
Make it understandable, be meticulous about money, design is important.
Generally, business plans will be around 10-20 pages long. Your main focus should be to cover the essentials that we talked about, but you don’t want to overdo it by including unnecessary and overwhelming information.
In business plan, less is more.
Create a good organizational outline of your sections. This will allow investors to easily navigate to the parts they are most interested in reading.
Avoid using jargon – everyone should be able to easily understand your business plan without having to Google certain terms.
Make a list of all the expenses your business incurs. Financial information should be maximally precise since it will directly impact the investor’s decision to fund your business idea.
After you wrap up your business plan, take a day off and read it again. Fix any typos or grammatical errors that you overlooked the first time.
Make sure to use a professional layout, printing, and branding of your business plan. This is an important first impression for the readers of the document.
Now you know what a business plan is, how you can write it, and some of the best practices you can use to make it even better.
But, if you are still having certain difficulties coming up with a great business plan, here are a few examples that may be helpful.
HubSpot’s One-Page Business Plan
Bplan’s free business plan template, small business administration free business plan template.
This One-Page Business Plan was created by HubSpot and it can be a great way to start off your business plan journey on the right foot.
You already have fields such as Implementation Timeline, Required Funding, and Company Description created so you will just need to provide your specific information.

This free business plan template highlights the financial points of the startup. If your primary focus will be your business’ financial plan and financial statements, you can use this template to save up some time.
It can also be useful for making sure everyone in your company understands the current financial health and what they can do to improve it.

If you need additional inspiration to kick start your own business plan, you can check out this free template by small business administration .
You just have to decide which type of plan you want to create and then review the format of how it should look like.
Monitor and Report on the Performance of Your Business with Databox
Tracking your company’s performance is an indispensable part of quality decision-making. It is crucial that you know how your business strategy is performing and whether it needs to be optimized in certain areas.
However, doing this manually will undoubtedly take a hefty amount of your valuable time. You will have to log into all of the different tools, copy-paste the data into your reports, and then analyze it. And this isn’t a one-time thing – you have to do it at least once a month.
Luckily, Databox can lend a helping hand.
By using customizable dashboards from Databox, you will be able to connect data from all your different tools into one comprehensive report. Not only that, but you can also visualize the most important metrics to make your presentation to shareholders immensely more impactful.
Did you spend a lot of time cutting and pasting? Say ‘no more’ to that. You will be able to use that time to better analyze your business performances and monitor any significant changes that occur.
Leave the grueling business reporting process in the past and sign up for a free trial with Databox.
Get practical strategies that drive consistent growth
12 Tips for Developing a Successful Data Analytics Strategy

What Is Data Reporting and How to Create Data Reports for Your Business

What Is KPI Reporting? KPI Report Examples, Tips, and Best Practices
Build your first dashboard in 5 minutes or less
Latest from our blog
- Playmaker Spotlight: Tory Ferrall, Director of Revenue Operations March 27, 2024
- New in Databox: Safeguard Your Data With Advanced Security Settings March 18, 2024
- Metrics & KPIs
- vs. Tableau
- vs. Looker Studio
- vs. Klipfolio
- vs. Power BI
- vs. Whatagraph
- vs. AgencyAnalytics
- Product & Engineering
- Inside Databox
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Talent Resources
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- API Documentation
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-14343635291-33bf053f368c43f6a792e94775285bbd.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Join us: Learn how to build a trusted AI strategy to support your company's intelligent transformation, featuring Forrester .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Register now .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Business strategy |
- What is business process management? A ...
What is business process management? A BPM guide

If outdated processes are holding you back, business process management (BPM) can help. In this article, learn how to streamline essential business processes so your company can get more done, faster.
What is business process management (BPM)?
Business process management, or BPM, is the practice of analyzing and improving business processes. A business process is a sequence of tasks or activities your business performs to achieve a specific organizational goal.
Why is this necessary? Over time, your business processes—which were likely built when you had fewer team members or before you used certain tools—may have become outdated, inefficient, or ineffective. BPM helps you analyze those processes and optimize them through tried-and-true process improvement practices. Oftentimes, this includes business process improvements like reducing bottlenecks, automating manual work, optimizing and streamlining inefficient processes, or re-orienting project goals around specific business outcomes.
Why is BPM important?
According to Gartner, a foremost authority in BPM research, the importance of business process management lies in its ability to synchronize people, systems, and information to achieve targeted business outcomes.
Here's how BPM helps both project managers and business process managers improve team and organizational process performance.
BPM systems streamline operational efficiency by improving business operations to become more efficient.
BPM enhances productivity by identifying and correcting inefficiencies, which leads to an increase in team productivity.
BPM drives innovation by aligning organizational processes and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Consider a software development team whose ad-hoc processes and frequent communication breakdowns caused delays in their project timelines. After adopting BPM systems, they established a clear workflow , assigned specific roles and responsibilities, and set measurable SMART goals . As a result, project completion rates improved significantly, and team collaboration became more efficient.
In essence, BPM helps project management professionals not only manage business process performance but also transform how teams achieve their goals.
3 types of business process management
BPM focuses on improving processes. But there are a lot of processes and use cases at your company, so there are additional types of BPM solutions to help you get to the bottom of these improvements.
You don’t necessarily need to use these terms, but understanding the three different types of BPM helps you know which one to use to improve your processes.
Human-centric BPM
Human-centric BPM caters to processes predominantly carried out by people. There are things that only people can do and often involve numerous approvals and tasks carried out by individuals. In this case, you can’t create perfect efficiency and effectiveness even if you try. So this type of BPM system works to unblock humans by integrating simple notifications, user-friendly interfaces, and effective tracking capabilities. All of which optimize people's understanding of the processes and provide them with real-time guidance.
Examples of human-centric business processes:
Hiring and onboarding. You can improve job postings, resume tracking, referrals—but there’s a uniquely human element to hiring a new employee. From that first phone screen to the onsite interview, improving hiring processes focuses on human-centric BPM.
Creative work. You can’t automate the creative process. This process requires a human component—the designers or copywriters—to provide the creative spark. In this case, human-centric BPM makes it easy to review and publish creative work, and to unblock creatives on your team for high-impact work.
Document-centric BPM
As the name suggests, document-centric business processes are those where a document is the main thing being created. Think of a legal document, blog post, or any document that goes through multiple rounds of revision.
Integration-centric BPM
Did you know the average knowledge worker switches between 10 tools up to 25 times per day ? Integration-centric BPM addresses that problem through digital transformation—adopting technology to use and integrate tools in one central platform. By enabling integrations between tools, you can create a central source of truth for all of your information. Instead of manually updating your tools or searching through apps for the data you need, integration-centric BPM makes it easy to find information and prevents things from falling through the cracks.
5 stages of the business process management lifecycle
Business process management helps you reduce inefficiencies and optimize business processes. To get started, follow these five steps of the BPM lifecycle:
Before optimizing your processes, you first need to understand what they are. The first step of BPM is Analyze—though it’s sometimes referred to as the Design step. During this step, take a look at your current business processes and map them end to end. At this point, you aren’t making any changes to your business processes; you’re simply understanding what they are.
For example, imagine you work at a small business. You want to improve the way you engage with your customers. To begin improving the customer experience through BPM, analyze what you currently do. How are tickets filed? Who responds? What happens when a team other than the customer service team needs to get involved? How quickly do you get back to customers? What’s their satisfaction rate? What’s the most recent NPS score? Do you use a CRM? Answering these questions helps paint a full picture of your customer experience process.
To help your team work more efficiently, you first need to understand a current process from start to finish. Then identify steps that can be cut or improved. Finally, train the team on the new process and roll it out, ideally via a template in Asana so the team can own future improvement.”
Now that you understand the process from start to finish, model what it should actually look like. Ideally, you’ve identified inefficiencies during the Analyze phase that you can trim, or places where work is being bottlenecked. Model the ideal process and flow of data, so you can begin to implement it in the next step.
To return to our example, one big blocker your team has is getting responses from people who aren’t on the customer service team, since they use a different tool. Your customer service members spend a lot of their time manually copying information from one tool to another. To streamline and automate these workflows, you decide to integrate your CRM with your work management tool . Now that you understand what you want the process to look like, model the behavior you want to see before implementing it.
3. Implement
During the Implement step—sometimes called the Execute step—put your model into action. As you do, establish metrics for success or failure, in order to evaluate whether this process is better than the one you already had in place.
Depending on the scope of the change, use a change management process to roll this out, especially if it’s a new technology or system your team isn’t familiar with. Luckily, we’ve got you covered—read our article on 6 steps to build a successful change management process .
To continue our example, you’ve modeled the ideal behavior between your work management and CRM tool. Now, you implement an integration-centric business process management model to do this. With effective integrations between your two tools, your customer service team can stop manually ferrying information from one tool to another and spend more time doing what they do best: serving your customers.
When you are beginning to implement new things and bring new things to your business, work with your leaders and your managers around change management of what's coming, how the organization will change, and what's required of everybody to be successful together. It’s much more than just flipping a switch or bringing in a new tool.”
Once you’ve implemented new processes, monitor them to see how well they’re doing. Have these new processes actually improved bottlenecks and inefficiencies? Are people using them? Sometimes, things that look good on paper—or even do well during a small test—don’t work during an organization-wide rollout. If that’s the case, pull back the rollout or consider pivoting to something else. By monitoring these processes, you can proactively identify any issues and jump on them if necessary.
For example, after rolling out a new integration between tools for your customer service team, monitor tool usage. Are people using the integration? Has the amount of manual work done by your customer team gone down? If not, host additional training and enablement sessions to encourage adoption.
5. Optimize
During the Optimize step—sometimes called Automate—continue to tweak and improve your business process. Even if the process you implemented worked perfectly, look for additional inefficiencies or manual processes to improve. This is also where business process automation comes into play. BPA is the process of automating business processes to make them more efficient and reduce manual work.
To return to our customer service example, you now want to automatically push updates between your two tools, instead of having the customer service team manually initiate the integration. Or, look for adjacent activities to automate. For example, create a rule to automatically send a customer feedback email after a ticket is closed, in order to gauge customer service efficacy and continue improving processes down the road.
BPM best practices
Effective BPM implementation can transform an organization's operational efficiency and align it with strategic objectives for optimal business value. Here are the top best practices essential for the success of any BPM initiative:
Engage diverse perspectives: Involving stakeholders from various departments, including the CIO and project management teams, ensures a broad range of insights. This diversity is key to re-engineering processes for improved performance.
Establish a BPM Center of Excellence (CoE): Create a central hub of BPM expertise, staffed with professionals skilled in Six Sigma and Agile methodologies. This CoE guides BPM projects to align with the organization’s strategic set of activities and business goals.
Manage expectations: Clearly define the project scope and objectives with all stakeholders to ensure that the BPM system is aligned with the business value it seeks to create. A well-defined scope prevents misinterpretations and sets a clear path for project success.
Integrate performance measurement: Incorporating clear performance metrics and KPIs is key. This enables the BPM process to be continuously monitored and improved, guaranteeing that it continuously generates business value and satisfies stakeholder expectations.
Benefits of business process management
Without a big picture view of your company processes, you have no way of knowing how efficient and effective those processes are. With BPM, you have a way to understand, analyze, and improve your business processes. When you model a business process, you outline your ideal process. Then, if it doesn’t currently look like that, you figure out why, and you improve it.
Remember, business process management isn’t a one-and-done process. Instead, it’s an ongoing effort to evaluate and improve your processes. As a result, you can drive meaningful process improvements, increased efficiency and effectiveness, and easier ways for team members to accomplish their goals faster and with less effort.
Maps and improves your processes
Automates processes where possible
Reduces waste
Eliminates bottlenecks
Cuts down on errors
Improves efficiency and effectiveness
Generates better services and products
Leads to better customer satisfaction
Streamlines inefficiencies
Ensures your business processes are clearly contributing to business outcomes
Business process management isn’t just effective for large, enterprise organizations—even small teams and small business users can benefit. If you have a business strategy with key business objectives, BPM helps you optimize processes and achieve those objectives.
What is business process management software?
BPM software is technology created to help you map and capture business processes. A BPM suite of tools helps your organization understand, monitor, and streamline business processes.
Business process management systems typically:
Map current, existing processes
Model ideal processes
Automate processes to achieve business goals with less manual work
Track ongoing work for continuous improvement of business processes
Business process management tools sometimes also:
Offer adaptive analytics dashboards to proactively identify business process opportunities.
Offer templates for specific business processes or workflows.
Offer BPM tools for A/B testing before you roll out business processes—especially for large changes that require change management.
Track new processes to ensure team members are using them correctly, and enforce change if they aren’t.
Types of BPM technologies
Business process management software makes use of various BPM technologies to help organizations manage their processes more effectively. By integrating tools for process design, execution, control, and analysis, it enables automation and optimization of workflows. Successful BPM implementation requires selecting the appropriate technology for your organization's unique requirements.
Process design
Process design technology focuses on the creation and modification of business processes. It involves tools that help in visually mapping out process flows, defining steps, and setting parameters for how a process should operate.
An e-commerce company may employ process design tools to revamp its order fulfillment system. The software helps visualize the entire order-to-delivery workflow, identifying bottlenecks and enabling the redesign of steps for faster processing and delivery.
Process mining
These tools analyze data from various business systems to discover, monitor, and improve real processes by extracting knowledge from event logs readily available in today's cloud-computing information systems.
A healthcare provider could use process mining tools to analyze patient flow through its facilities. The insights gained may lead to improved scheduling and resource allocation, which could significantly reduce wait times and enhance patient satisfaction.
Process performance
This type of BPM technology centers on monitoring and optimizing the performance of business processes. It involves tools that track key performance indicators (KPIs) and other metrics to evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of processes.
A manufacturing company might implement process performance tools to monitor production lines. These tools track the speed, quality, and downtime of each line, providing data that helps fine-tune operations for maximum efficiency and product quality.
Business process examples
Business process management plays a transformative role in various departments of an organization.
By looking at specific BPM examples, we see that it's more than just improving process performance. BPM aims to make organizations more agile, responsive, and strategically aligned. BPM, whether in sales, HR, or finance, can have a substantial impact on a company's success and competitiveness.
In sales, business process management can streamline the entire sales process, from lead generation to closing deals. It helps in managing customer data, tracking sales performance, and ensuring that sales activities align with business strategies.
Example: Consider a technology company implementing BPM to manage its sales pipeline . The BPM system automates lead tracking to ensure timely follow-ups. By analyzing sales data, the system identifies successful patterns and areas needing improvement. This allows the sales team to focus on strategies that yield the best results.
Human resources
BPM in human resources (HR) can automate and optimize various processes like recruitment, onboarding, employee performance management, and leave requests. This results in a more effective HR department, which enhances employee satisfaction and talent management.
Example: In a large retail corporation, business process management is used to streamline employee onboarding. The system automates document submissions and training schedules and integrates with payroll systems. This efficiency reduces the onboarding time, improves the new hire experience, and allows HR staff to focus on more strategic initiatives like employee engagement and retention.
In the finance department, BPM can be used to manage processes such as budgeting , invoicing, compliance, and financial reporting. It enhances accuracy, speeds up financial operations, and ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
Example: A manufacturing firm employs BPM for its budgeting process. The system allows for real-time budget tracking and variance analysis, enabling quick adjustments. This process ensures that the financial resources are optimally utilized, reducing waste and enhancing the company's ability to make data-driven financial decisions.
What type of process optimization is right for you?
There are a variety of process methodologies to help you optimize your business. Here’s how BPM stacks up:
Business process management vs. workflow management
Business process management focuses on the end-to-end business process. Instead of homing in on a specific workflow, BPM aims to improve efficiency and effectiveness across your organization.
Part of BPM is workflow management. A workflow is an end-to-end process that helps teams meet their goals by connecting the right people to the right data at the right time. Workflows organize data in an understandable and repeatable way by focusing on three things: planning, execution, and review. An effective workflow is a repeatable, sustainable business process.
Looking to improve a specific workflow? Learn how to create clear, repeatable workflows in 7 steps.
Business process management vs. project management office (PMO)
Business process management is a way to evaluate your entire process, model the ideal process, and then improve your work based on that process model.
A project management office (PMO) is also focused on improving business processes, but it goes about it in a slightly different way. Instead of tackling business processes, a PMO aligns your organization around project management best practices , defines how to execute core processes, and aligns strategic initiatives across the organization.
Looking for a PMO instead of BPM? Learn how to set and align project management conventions with a project management office.
Business process management vs. business process automation
BPM looks at your organization’s business practices holistically, then looks for ways to improve them. This often includes, but isn’t limited to, automating manual processes. Within BPM, this is referred to as business process automation (BPA).
Business process automation is critical because so many processes we do in our day-to-day lives are manual: duplicating work between tools, following up on the status of work, or even searching for information. However, you don’t need BPM in order to automate manual processes. Instead, look for any work management tool that offers workflow automation features. This type of no-code platform provides an intuitive user interface, so employees without technical expertise can still streamline manual processes.
What is robotic process automation (RPA)?
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a type of specialized business process automation. RPA helps your business build, deploy, and manage software robots that perform repetitive tasks—so your employees don’t have to. These robots can mimic all sorts of human-computer interactions, like copying and pasting or moving files from one location to another.
Business process management vs. task and project management
BPM helps you establish and align processes at the business level. When you implement business process management, you’re looking at your entire organization’s business processes and improving them.
Task and project management are slightly different. Task management is for individuals looking to improve their personal efficiency and effectiveness. With good task management software , you can gain clarity on your work and get your highest-impact work done.
As the name suggests, project management functions at the project level. Project management is a way for teams to organize, track, and execute work within a project. There are five phases of project management : project initiation, project planning, project execution, project performance, and project closure.
Related resources

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
How Asana uses work management to effectively manage goals

Beat thrash for good: 4 organizational planning challenges and solutions

How Asana uses work management to streamline project intake processes
Plan Smarter, Grow Faster:
25% Off Annual Plans! Save Now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
What Is a Business Plan? Definition and Planning Essentials Explained
Posted february 21, 2022 by kody wirth.

What is a business plan? It’s the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you’ll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance.
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It’s more than just a stack of paper and can be one of your most effective tools as a business owner.
Let’s explore the basics of business planning, the structure of a traditional plan, your planning options, and how you can use your plan to succeed.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and anyone else, better understand how your business will succeed.
Why do you need a business plan?
The primary purpose of a business plan is to help you understand the direction of your business and the steps it will take to get there. Having a solid business plan can help you grow up to 30% faster and according to our own 2021 Small Business research working on a business plan increases confidence regarding business health—even in the midst of a crisis.
These benefits are directly connected to how writing a business plan makes you more informed and better prepares you for entrepreneurship. It helps you reduce risk and avoid pursuing potentially poor ideas. You’ll also be able to more easily uncover your business’s potential. By regularly returning to your plan you can understand what parts of your strategy are working and those that are not.
That just scratches the surface for why having a plan is valuable. Check out our full write-up for fifteen more reasons why you need a business plan .
What can you do with your plan?
So what can you do with a business plan once you’ve created it? It can be all too easy to write a plan and just let it be. Here are just a few ways you can leverage your plan to benefit your business.
Test an idea
Writing a plan isn’t just for those that are ready to start a business. It’s just as valuable for those that have an idea and want to determine if it’s actually possible or not. By writing a plan to explore the validity of an idea, you are working through the process of understanding what it would take to be successful.
The market and competitive research alone can tell you a lot about your idea. Is the marketplace too crowded? Is the solution you have in mind not really needed? Add in the exploration of milestones, potential expenses, and the sales needed to attain profitability and you can paint a pretty clear picture of the potential of your business.
Document your strategy and goals
For those starting or managing a business understanding where you’re going and how you’re going to get there are vital. Writing your plan helps you do that. It ensures that you are considering all aspects of your business, know what milestones you need to hit, and can effectively make adjustments if that doesn’t happen.
With a plan in place, you’ll have an idea of where you want your business to go as well as how you’ve performed in the past. This alone better prepares you to take on challenges, review what you’ve done before, and make the right adjustments.
Pursue funding
Even if you do not intend to pursue funding right away, having a business plan will prepare you for it. It will ensure that you have all of the information necessary to submit a loan application and pitch to investors. So, rather than scrambling to gather documentation and write a cohesive plan once it’s relevant, you can instead keep your plan up-to-date and attempt to attain funding. Just add a use of funds report to your financial plan and you’ll be ready to go.
The benefits of having a plan don’t stop there. You can then use your business plan to help you manage the funding you receive. You’ll not only be able to easily track and forecast how you’ll use your funds but easily report on how it’s been used.
Better manage your business
A solid business plan isn’t meant to be something you do once and forget about. Instead, it should be a useful tool that you can regularly use to analyze performance, make strategic decisions, and anticipate future scenarios. It’s a document that you should regularly update and adjust as you go to better fit the actual state of your business.
Doing so makes it easier to understand what’s working and what’s not. It helps you understand if you’re truly reaching your goals or if you need to make further adjustments. Having your plan in place makes that process quicker, more informative, and leaves you with far more time to actually spend running your business.
What should your business plan include?
The content and structure of your business plan should include anything that will help you use it effectively. That being said, there are some key elements that you should cover and that investors will expect to see.
Executive summary
The executive summary is a simple overview of your business and your overall plan. It should serve as a standalone document that provides enough detail for anyone—including yourself, team members, or investors—to fully understand your business strategy. Make sure to cover the problem you’re solving, a description of your product or service, your target market, organizational structure, a financial summary, and any necessary funding requirements.
This will be the first part of your plan but it’s easiest to write it after you’ve created your full plan.
Products & Services
When describing your products or services, you need to start by outlining the problem you’re solving and why what you offer is valuable. This is where you’ll also address current competition in the market and any competitive advantages your products or services bring to the table. Lastly, be sure to outline the steps or milestones that you’ll need to hit to successfully launch your business. If you’ve already hit some initial milestones, like taking pre-orders or early funding, be sure to include it here to further prove the validity of your business.
Market analysis
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current market you’re entering or competing in. It helps you understand the overall state and potential of the industry, who your ideal customers are, the positioning of your competition, and how you intend to position your own business. This helps you better explore the long-term trends of the market, what challenges to expect, and how you will need to initially introduce and even price your products or services.
Check out our full guide for how to conduct a market analysis in just four easy steps .
Marketing & sales
Here you detail how you intend to reach your target market. This includes your sales activities, general pricing plan, and the beginnings of your marketing strategy. If you have any branding elements, sample marketing campaigns, or messaging available—this is the place to add it.
Additionally, it may be wise to include a SWOT analysis that demonstrates your business or specific product/service position. This will showcase how you intend to leverage sales and marketing channels to deal with competitive threats and take advantage of any opportunities.
Check out our full write-up to learn how to create a cohesive marketing strategy for your business.
Organization & management
This section addresses the legal structure of your business, your current team, and any gaps that need to be filled. Depending on your business type and longevity, you’ll also need to include your location, ownership information, and business history. Basically, add any information that helps explain your organizational structure and how you operate. This section is particularly important for pitching to investors but should be included even if attempted funding is not in your immediate future.
Financial projections
Possibly the most important piece of your plan, your financials section is vital for showcasing the viability of your business. It also helps you establish a baseline to measure against and makes it easier to make ongoing strategic decisions as your business grows. This may seem complex on the surface, but it can be far easier than you think.
Focus on building solid forecasts, keep your categories simple, and lean on assumptions. You can always return to this section to add more details and refine your financial statements as you operate.
Here are the statements you should include in your financial plan:
- Sales and revenue projections
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
The appendix is where you add additional detail, documentation, or extended notes that support the other sections of your plan. Don’t worry about adding this section at first and only add documentation that you think will be beneficial for anyone reading your plan.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. So, to get the most out of your plan, it’s best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you’ll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. We recommend only starting with this business plan format if you plan to immediately pursue funding and already have a solid handle on your business information.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear structure in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It’s faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations. This is really best for those exploring their business idea for the first time, but keep in mind that it can be difficult to actually validate your idea this way as well as adapt it into a full plan.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan. This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. It basically serves as a beefed-up pitch document and can be finished as quickly as the business model canvas.
By starting with a one-page plan, you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan. This plan type is useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Now, the option that we here at LivePlan recommend is the Lean Plan . This is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27-minutes . However, it’s even easier to convert into a full plan thanks to how heavily it’s tied to your financials. The overall goal of Lean Planning isn’t to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the Lean Planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and stable through times of crisis.
It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Try the LivePlan Method for Lean Business Planning
Now that you know the basics of business planning, it’s time to get started. Again we recommend leveraging a Lean Plan for a faster, easier, and far more useful planning process.
To get familiar with the Lean Plan format, you can download our free Lean Plan template . However, if you want to elevate your ability to create and use your lean plan even further, you may want to explore LivePlan.
It features step-by-step guidance that ensures you cover everything necessary while reducing the time spent on formatting and presenting. You’ll also gain access to financial forecasting tools that propel you through the process. Finally, it will transform your plan into a management tool that will help you easily compare your forecasts to your actual results.
Check out how LivePlan streamlines Lean Planning by downloading our Kickstart Your Business ebook .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Posted in Business Plan Writing
Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
- Business Profiles Menu arrow Industry IT & Services Food & Hospitality Education Nonprofit Other Industries Organization Type Enterprise SMB
- Key Features Menu arrow Features and tools GST Invoices Bulk Discounts Bulk Purchasing Account Security Compliance Tools Shipping & Delivery Business Analytics tools Business Pan Payment Methods Amazon Business App Three-way Matching Amazon Business Affiliate
- Shop by Category Menu arrow Category Selection Electronic Items Office Supplies Cleaning Products Hardware & MRO Supplies Pantry Products Medical Supplies Store Security Systems Mobile Accessories Packaging supplies Gym equipments Laptop accessories Wholesale beauty products Special Stores Corporate Gifting Store COVID-19 Supplies Store Distance Learning Store Hospitality Store AWS Store Event Stores Business Value Days EMI fest Stock-up Sale Great Indian Festival
Buying guides
- search Search
There was an error fetching results
- Check your spelling
- Broaden your search by using fewer or more general words
- Free shipping
- Customer success stories

Buy products with the GST invoice and save up to 28% more on all your B2B purchases. Filter the products according to GST Invoice and save on Bulk Purchases.

Bulk purchase for all your B2B needs online with Amazon Business. Order in Bulk, Get Wholesale Benefits and much more.

Get up to 20% cashback on business purchases
Special discounts only for Amazon Business customers on business orders. Don’t miss out!

Business Planning Process and Strategy - Steps & Plan
Starting a business is one thing, but sustaining it requires planning. Business planning strategies and processes are crucial to get ahead of the competition. A business growth plan and strategic development for sustainable growth is significant for business expansion.
Developing a business plan is essential to the strategic management planning process. It helps you to set goals, establish priorities, and develop strategies for achieving them. Business planning involves many critical steps, including market analysis, competitive research, financial forecasting, and risk assessment. With the proper business planning process and business planning strategy, you can build a roadmap for the future and take your business to the next level.
This blog will explain business planning and explore the steps involved in creating a successful business planning process, appropriate business strategy for growth, and a business growth plan. As we explain business planning, we will also discuss business strategic development and how to develop a business development plan that aligns with your goals and objectives.
If you're wondering how to grow a business or looking for ways to improve your business strategy for growth, register with Amazon Business . Amazon Business is a B2B marketplace that provides businesses of all sizes with a convenient way to purchase products and services online. Amazon Business has the best projectors for home & office use , the best Bluetooth speaker , the best water purifier for home & offices , and various other benefits for its users.
What is a Business Plan?

How to explain business planning? All businesses require a business planning strategy. A business planning strategy is the basic step while setting up a business. A business planning process is like a map of a company's success that includes the process of achieving the objectives.
An attempt to understand and explain business planning or business development plans involves systematically analyzing an organization's current state, defining its goals and objectives, and developing a business plan and strategy well-suited to the company's specific needs and circumstances.
For successful business strategic planning, it is essential to follow the steps outlined in the business plan steps. For new entrepreneurs, the business planning process in entrepreneurship is critical. It is also crucial to consider trademark registration . It helps prevent competitors from using similar marks or confusing consumers about the origin of products or services.
Objectives of a Business Plan
When it comes to the business planning process, an entrepreneur must be concerned about every aspect of the business and have clear goals. Any business planning strategy must include the following:

How to Prepare for a Business Plan?
Preliminary investigation.
Businesses must review the available business planning process and look for threats and opportunities to create a new business planning process and business planning strategy.
Business Planning Process
While working on the business planning process, determine the essential goals for your business and create a business planning strategy. Identify the company's strengths and weaknesses and lay down all necessary steps to initiate the proposed business.
Key Components of a Business Plan

Executive Summary
An executive summary is a brief business plan overview highlighting its key points and objectives. It serves as an introduction to the plan and gives a clear understanding of the business, its goals, and how it plans to achieve them. An executive summary serves as a quick snapshot of the entire business plan.
It has a critical role in the business planning process and business level strategy in strategic management. It helps business owners and managers focus on their business plan's essential elements. It helps them to articulate their objectives of business , strategies, and tactics concisely and compellingly.
Company Description
A company description in a business plan is a section that provides an overview of a business. It should include information about the nature of the business, its products or services, target market, competition, management team, and financial outlook. This section aims to give investors or potential partners a clear understanding of what the business does and what sets it apart from competitors.
Strategic management planning and business strategic development require a clear understanding of the company's objectives, which should be outlined in the company description. The objectives of the business should be aligned with the customer acquisition strategies to ensure a successful business process outsourcing.
Market Analysis
Market analysis is a crucial aspect of a business plan that involves researching and understanding the target market for a product or service. It includes identifying the needs of potential customers, analyzing competitors, and evaluating industry trends to create a strategy for market development.
Market analysis helps businesses understand their customers, their requirements, and how to reach them best. A company can develop a more effective market development and growth strategy by conducting a thorough market analysis.
Financial Plan
A financial plan is a detailed projection of a business's economic activities and outcomes over a specific period. It helps business owners plan and manage their finances effectively.
Financial planning is an essential component of strategic planning for small business growth and development. A sound financial plan is critical to overall planning and strategic management for any business.
Steps to a Successful Business Planning Process

Idea Generation
Idea generation is an important step in strategic management planning, integral to planning in business management. Generating new ideas involves several steps in the business planning process for creating a successful business development plan. Idea generation can be a powerful tool for planning in business management and can help in developing a business plan that aligns with the company's vision and mission.
Sources of New Ideas
For generating new ideas for the business planning process, businesses can obtain insights from various sources:
- Market research and development
- Competitors
- Vendors and retailers
These sources can provide a wealth of information to be analyzed and used to develop business plan steps, new ideas, or solutions to existing problems.
Methods of Generating New Ideas
- Data obtained through surveys and questionnaires
- Market research
- Group discussion and brainstorming activities
- Social media research
- Mind Mapping
- Adding value to existing products and services
2. Environmental Scanning
Several internal and external factors impact the success of every business planning process. An environmental scan helps to understand the factors that affect your business directly or indirectly.
External Environment
The external environment can be competitors, customers, suppliers, demographics, socio-political situations, or economic conditions.
Internal Environment
These are factors that exist within the business:
- Raw Material : Identify the availability, quality, and cost of raw materials needed for production.
- Production/ Operation : Assess the production processes, machinery, equipment needed, manufacturing capacity, and production costs.
- Finance : Analyze the financial resources available, including startup capital, cash flow, and potential funding sources.
- Market : Understand the target market, including their demographics, preferences, and buying habits.
- Human Resource : Evaluate the personnel needs, including their skills, knowledge, and experience, as well as their availability and cost.
3. Feasibility Analysis
Feasibility Analysis is one of the most important business plan steps in the business planning process. It analyzes different alternatives to achieving a successful business planning process. A feasibility analysis identifies the best and the worst scenarios in which the company can be.
The different variables included in a feasibility analysis are:
Market analysis provides data on the niche that the business wants to explore. Making the ideal business planning process and business planning strategy is critical.
Technical/ Operational Analysis
It analyzes the operational aspects required to carry on the business successfully. For instance, an idea discussed might have great potential. Still, it may not be feasible when it comes to operational costs. The primary parameters examined during the operational analysis are:
- Material Availability : Evaluate the availability, quality, and cost of raw materials needed for production.
- Plant Location : Assess the location's suitability, including access to raw materials, labor, transportation, and infrastructure.
- Choice of Technology : Analyze the production processes, machinery, equipment needed, manufacturing capacity, and production costs.
Financial Feasibility
The financial feasibility assesses the business's financial issues, including monthly operating expenses, forecasted income statements, cash flow, balance sheet, and capital expenditure.
Functional Plans
The top executives must ensure that functional business strategic planning and process sync with the business goals in a business planning process. Once the feasibility analysis gives the go-ahead, you can draft a business plan.
4. Project Report Preparation
Project report preparation is a critical part of every business planning process. Experts prepare the project report. This report acts as a plan of action that describes the goals and objectives of the business.
Project reports allow the business idea to shape and become a productive venture with a clear-cut business planning strategy. It tracks the progress of the business planning process and compares it with the original plan. It also identifies any risks or challenges and to take corrective action whenever necessary.
5. Plan Your Marketing Strategy
A well-planned marketing strategy and business development plan will help the business reach its target audience.
6. Evaluation, Control, and Review
All the strategies prepared for a business are open to modifications due to internal and external factors. The critical evaluation, control, and review activities include measuring performance based on the current strategy and taking corrective action to enhance or improve the business goal.
What is Business Strategy Planning?
The business planning strategy outlines the goals, objectives, and actions needed to achieve success in a business. It involves analyzing the company's current state, identifying areas for improvement, setting targets, and developing strategies to achieve them.
As part of the business planning process, it is essential to consider the competitive landscape and market trends and the strengths and weaknesses of the business.
In case you are curious about how to start an online business , register with Amazon Business and tap into Amazon's vast network of customers. Whether you are looking for the best laptops for students or the best printers for home & office use , Amazon has everything you need.
When it comes to the business planning process and planning in business management, having a solid strategy for market development is critical. By identifying and targeting new markets, businesses can expand their customer base and increase revenue. Strategic planning for small businesses is essential, as these businesses often have limited resources and must make every dollar count. Small companies can overcome challenges and succeed by focusing on planning and strategic management.
What does Strategic Planning Involve?
Business planning strategy involves analyzing the company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats and identifying the best methods for success.
For example, utilizing dropshipping business in India and GST tax invoice system can be highly beneficial. By taking advantage of these resources, businesses can simplify their operations.
Essentials of Strategy Planning
In planning and strategic management, it is essential to consider the unique challenges facing small businesses. Strategic planning for small businesses should prioritize flexibility and adaptability, as these businesses often operate in highly dynamic environments.
Past and Present Data Analysis
Past and present data analysis is essential for the business planning process and the business planning strategy. By examining historical data and current performance metrics, businesses can gain insights and identify opportunities for growth and development.
For example, past and present data analysis can help to make informed decisions about inventory management techniques and the purchasing process . By analyzing past sales data and inventory levels, businesses can determine which products are most popular among customers and ensure sufficient inventory to meet demand.
Insightful Analysis of Market Dynamics
Insightful analysis of market dynamics is an important component of the business planning process, particularly in the supply chain management process . By analyzing past demand and supply fluctuations, businesses can identify trends and patterns in the market and develop effective strategies for managing their supply chain.
In addition, insightful analysis of market dynamics is also essential when developing a business plan.
Following a Unique Approach to Planning
Following a unique approach to planning is critical to the business planning process, particularly in business strategic development. With a unique strategy, businesses can create a competitive advantage in the market.
Business level strategy in strategic management also plays a key role in following a unique approach to planning. Focusing on a specific market niche or target audience, businesses can tailor their strategy for market development to meet customers' needs.
Scenario Analysis Based on Relevant Inputs
Scenario analysis is an important aspect of the business planning process and is particularly relevant in business strategic development and business level strategy in strategic management. As businesses develop their strategies, they must consider a range of possible future scenarios and their potential impact on the company's value.
This process is also important in the business planning process in entrepreneurship, as entrepreneurs develop their business plans and strategies. By conducting scenario analysis, entrepreneurs can identify potential risks and opportunities and focus on developing a business plan and strategy to mitigate risk and capitalize on opportunities.
Risk Mitigation Measures to Minimize Loss
Risk mitigation measures are crucial in minimizing the losses a company may face due to unforeseen events. These measures help to identify and evaluate potential risks that could negatively impact the company.
Strategic management planning plays a crucial role in identifying potential risks and creating a risk mitigation plan in the business planning process. A risk management plan should be part of the business plan steps.
Business strategic planning should incorporate risk assessment and mitigation as a part of the overall planning process. A comprehensive understanding of potential risks is necessary for a successful business planning process in entrepreneurship.
BMGI's Approach to Strategy Planning
After working with different kinds of businesses, BMGI has developed a robust process for business strategy planning. It encompasses all the aspects required for the best business strategy planning.
For long-term goals, BMGI focuses on the following three aspects:
- Defining the strategy
- Establish how to implement the strategy
- Implementing the strategy and managing the changes
BMGI has a process in place for businesses to define how to implement their strategy as follows:
External Assessment
BMGI recommends the analysis of-
- Market and Customers
- Competition
- Probable Trends of the Future
- PESTEL (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, Legal)
Internal Assessment
Discover your business's SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) and compare them against various scenarios to determine your position.
The assessments mentioned above, along with the understanding of its impact, in the long run, enable businesses to plan their business strategy efficiently.
Impact Areas of Strategic Planning

While the impact areas of strategic planning may vary depending on the organization and industry, here are some common areas where business strategic planning can have an impact:
Organic Growth Strategy
Organic growth strategy focuses on growing the organization's existing business lines.
Business Unit Strategy
This growth route focuses on analyzing and implementing strategies for each business unit.

Corporate Strategy
Corporate strategy requires knowledge of the business level strategy in strategic management. In this strategy, the senior management steers the direction of the entire organization based on its core principles and values.
Emerging Markets Strategy
In this strategy, businesses look out for opportunities in places with the potential for promising growth. Entrepreneurs must have a solid business planning process to successfully enter and expand in new and emerging markets. A well-defined business planning process in entrepreneurship can be the difference between success and failure.
Sustainable Growth Strategy
The sustainable growth strategy is a critical component of the business planning process. This strategy involves taking meaningful steps toward the future while considering the unpredictable changes that may arise.
Measuring the Success of Your Business Plan and Strategy
Here are some key steps you can take to measure the success of your business plan and strategy:
Setting Measurable Goals and Objectives
It is essential to set measurable goals and objectives to measure the success of your business plan and strategy.
- Determine your business goals: First, you need to identify your goals with your business growth plan. It could be increasing revenue, expanding market share, or improving customer satisfaction.
- Define your objectives: Once you have identified your business goals, break them down into specific, measurable, and achievable objectives that are relevant and time-bound.
By setting measurable goals, you can track your progress over time and measure the success of your strategy.
Tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Here are some steps to follow to measure the success of your business plan and strategy by tracking KPIs:
- Identify the relevant KPIs: Once you have defined your objectives, identify the KPIs that are relevant to each objective.
- Set targets for each KPI: Once you have identified the KPIs, set targets for each one. These targets should be realistic and aligned with your business objectives.
- Track and analyze the KPIs: Once you have set targets for each KPI, start tracking them regularly.
Conducting Regular Performance Reviews
- Adjust your strategy: Based on your data analysis, adjust your business growth plan or planning in business management as necessary.
- Implement Business Process Outsourcing: Consider implementing business process outsourcing to help you achieve your strategic planning for small businesses. What is Business Process Outsourcing? It is a business practice where a company outsources non-core business functions or processes to a third-party provider.
- Review your performance against benchmarks regularly and adjust your strategy as necessary. This planning and strategic management process will help you stay on track and achieve your business goals.
Soliciting Customer Feedback
- Collect customer feedback: Collect customer feedback through surveys, focus groups, or social media platforms.
- Analyze the feedback: Once you have collected customer feedback, analyze it to identify areas for improvement.
- Implement changes: Use your collected feedback to change your business strategy.
- Measure the impact: Use the same KPIs you used to track your progress before to determine if the changes have positively or negatively impacted your business.
- Adjust your strategy: Based on the impact of your changes, adjust your business strategy as needed.
Examples of Successful Business Planning Process and Strategy
Toyota's US invasion in the '70s
Cars have had an enormous impact on Americans since the good old days. The three biggest American car companies ruled over the car market in the US. However, the Japanese car manufacturer, Toyota, did a market analysis and started selling cheaper and more efficient cars during the '70s.
The US car companies did not worry about Toyota at first. They thought Toyota must lose money exporting their vehicles to the US at such low prices. However, within a few years, Toyota started production in the US.
Toyota soon became the largest car company in the US. But what was their business strategy for growth?
Of course, Toyota was using the cost leadership strategy. However, Toyota's manufacturing process was so efficient that it cost them far less to produce cars than American companies. Besides, Toyota's supply chain management was their business strategy for growth, and it made a crucial difference in Toyota's survival. It was also a part of its business planning process.
The multi-billion-dollar idea began with the founders of Airbnb renting their mattresses to strangers. It was a business space no one had explored before.
They struggled to meet ends initially but saw potential in their idea. So, the founders created a website where people could rent their mattresses to travelers and strangers.
There were some scattered online bookings, but they needed to be more to be sustainable. The founders conducted an operational analysis and discovered the problem with poorly presented listings.
They visited all the nearby locations where people were renting out their mattresses. They moved things around to make them look more pleasing and clicked photos. After adding images to their website, the bookings started pouring in.
Then, they hired professional photographers to click photos of all the listings and their owners. The online orders kept skyrocketing. The founders of Airbnb analyzed data to discover the one problem keeping them from succeeding in their revolutionary idea. Airbnb is now valued at over 100 billion Dollars!
A clear understanding of the business planning process and a well-developed plan can help set the foundation for growth and profitability.
If you are a business owner, register with Amazon Business today! Whether you're looking for the Best Home Theater System to Consider , the Best Earphones with Mic , or the Best Vacuum Cleaners in India , Amazon Business has you covered. With access to millions of products, competitive pricing, fast shipping, and flexible payment options, it's the perfect platform for businesses of all sizes.
What questions should be asked in a business plan?
The vital questions to ask in a business plan are as follows:
- What makes you different?
- Who is your audience?
- How will you make profits?
- How will you promote your business?
- How will you get started?
What is the most important part of your business plan?
The executive summary is the most important part of your business plan. It contains the overview of your entire business plan and everything it encompasses.
How many years should a business plan cover?
It is recommended to have a business plan of at least one year to 3 years to address your business goals and possible objections.
How do you overcome lack of planning?
- Automate repetitive tasks such as data entry
- Set up a network between all your software so that your position is constantly getting updated
- Improve the communication between all the departments in your company
- Deploy cloud-based technologies for effectively sharing information
What are the barriers to planning?
Here is a list of things that become barriers to planning:
- Incompetent leaders
- Continuous distractions
- Limited resources for task completion
- Impractical expectations in senior management
How to define companies Vision and Mission?
A company's vision statement lists what an organization wants to represent in society. A mission statement lists the things a company does to achieve its vision.
What financial projections should I include in my business plan?
Common financial projections that most business plans consist of are sales forecast, profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, balance sheet, break-even analysis, and capital expenditure budget.
How do I revise and update my business plan as my business evolves?
To revise and update your business plan:
- Set aside time for review
- Analyze your financial performance and other key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Identify new opportunities for growth and challenges that may require adjustments to your business plan.
- Use the insights you have gained from your evaluation to update your business plan.
- Communicate changes with stakeholders
- Set new targets and milestones for your business.
How do I identify my target audience and develop a marketing strategy?
· Identify your target audience's demographics, preferences, behaviors, and needs through market research.
· Use the insights from your market research to create detailed profiles of your target audience.
· Determine your unique selling proposition (USP)
· Define your marketing goals.
· Choose your marketing channels.
· Tailor your marketing content to your target audience and communicate your USP.
· Test and refine your marketing strategy to optimize your results.
Who benefits from a good business strategy?
A good business strategy can benefit both the business and the consumers.
Product Updates
550+ Business Plan Examples to Launch Your Business

Need help writing your business plan? Explore over 550 industry-specific business plan examples for inspiration.
Find your business plan example

Accounting, Insurance & Compliance Business Plans
- View All 25

Children & Pets Business Plans
- Children's Education & Recreation
- View All 33

Cleaning, Repairs & Maintenance Business Plans
- Auto Detail & Repair
- Cleaning Products
- View All 39

Clothing & Fashion Brand Business Plans
- Clothing & Fashion Design
- View All 26

Construction, Architecture & Engineering Business Plans
- Architecture
- Construction
- View All 46

Consulting, Advertising & Marketing Business Plans
- Advertising
- View All 54

Education Business Plans
- Education Consulting
- Education Products
Business plan template: There's an easier way to get your business plan done.

Entertainment & Recreation Business Plans
- Entertainment
- Film & Television
- View All 60

Events Business Plans
- Event Planning
- View All 17

Farm & Agriculture Business Plans
- Agri-tourism
- Agriculture Consulting
- View All 16

Finance & Investing Business Plans
- Financial Planning
- View All 10

Fine Art & Crafts Business Plans

Fitness & Beauty Business Plans
- Salon & Spa
- View All 35

Food and Beverage Business Plans
- Bar & Brewery
- View All 77

Hotel & Lodging Business Plans
- Bed and Breakfast
Finish your plan faster with step-by-step guidance, financial wizards, and a proven format.

IT, Staffing & Customer Service Business Plans
- Administrative Services
- Customer Service
- View All 22

Manufacturing & Wholesale Business Plans
- Cleaning & Cosmetics Manufacturing
- View All 68

Medical & Health Business Plans
- Dental Practice
- Health Administration
- View All 41

Nonprofit Business Plans
- Co-op Nonprofit
- Food & Housing Nonprofit
- View All 13

Real Estate & Rentals Business Plans
- Equipment Rental

Retail & Ecommerce Business Plans
- Car Dealership
- View All 116

Technology Business Plans
- Apps & Software
- Communication Technology

Transportation, Travel & Logistics Business Plans
- Airline, Taxi & Shuttle
- View All 62
View all sample business plans
Example business plan format
Before you start exploring our library of business plan examples, it's worth taking the time to understand the traditional business plan format . You'll find that the plans in this library and most investor-approved business plans will include the following sections:
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally only one to two pages. You should also plan to write this section last after you've written your full business plan.
Your executive summary should include a summary of the problem you are solving, a description of your product or service, an overview of your target market, a brief description of your team, a summary of your financials, and your funding requirements (if you are raising money).
Products & services
The products & services chapter of your business plan is where the real meat of your plan lives. It includes information about the problem that you're solving, your solution, and any traction that proves that it truly meets the need you identified.
This is your chance to explain why you're in business and that people care about what you offer. It needs to go beyond a simple product or service description and get to the heart of why your business works and benefits your customers.
Market analysis
Conducting a market analysis ensures that you fully understand the market that you're entering and who you'll be selling to. This section is where you will showcase all of the information about your potential customers. You'll cover your target market as well as information about the growth of your market and your industry. Focus on outlining why the market you're entering is viable and creating a realistic persona for your ideal customer base.
Competition
Part of defining your opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage may be. To do this effectively you need to get to know your competitors just as well as your target customers. Every business will have competition, if you don't then you're either in a very young industry or there's a good reason no one is pursuing this specific venture.
To succeed, you want to be sure you know who your competitors are, how they operate, necessary financial benchmarks, and how you're business will be positioned. Start by identifying who your competitors are or will be during your market research. Then leverage competitive analysis tools like the competitive matrix and positioning map to solidify where your business stands in relation to the competition.
Marketing & sales
The marketing and sales plan section of your business plan details how you plan to reach your target market segments. You'll address how you plan on selling to those target markets, what your pricing plan is, and what types of activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success.
The operations section covers the day-to-day workflows for your business to deliver your product or service. What's included here fully depends on the type of business. Typically you can expect to add details on your business location, sourcing and fulfillment, use of technology, and any partnerships or agreements that are in place.
Milestones & metrics
The milestones section is where you lay out strategic milestones to reach your business goals.
A good milestone clearly lays out the parameters of the task at hand and sets expectations for its execution. You'll want to include a description of the task, a proposed due date, who is responsible, and eventually a budget that's attached. You don't need extensive project planning in this section, just key milestones that you want to hit and when you plan to hit them.
You should also discuss key metrics, which are the numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common data points worth tracking include conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, profit, etc.
Company & team
Use this section to describe your current team and who you need to hire. If you intend to pursue funding, you'll need to highlight the relevant experience of your team members. Basically, this is where you prove that this is the right team to successfully start and grow the business. You will also need to provide a quick overview of your legal structure and history if you're already up and running.
Financial projections
Your financial plan should include a sales and revenue forecast, profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, and a balance sheet. You may not have established financials of any kind at this stage. Not to worry, rather than getting all of the details ironed out, focus on making projections and strategic forecasts for your business. You can always update your financial statements as you begin operations and start bringing in actual accounting data.
Now, if you intend to pitch to investors or submit a loan application, you'll also need a "use of funds" report in this section. This outlines how you intend to leverage any funding for your business and how much you're looking to acquire. Like the rest of your financials, this can always be updated later on.
The appendix isn't a required element of your business plan. However, it is a useful place to add any charts, tables, definitions, legal notes, or other critical information that supports your plan. These are often lengthier or out-of-place information that simply didn't work naturally into the structure of your plan. You'll notice that in these business plan examples, the appendix mainly includes extended financial statements.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. To get the most out of your plan, it's best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you'll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or in any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It's faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan . This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business.
By starting with a one-page plan , you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You'll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan.
Growth planning
Growth planning is more than a specific type of business plan. It's a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, forecast, review, and refine based on your performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27 minutes . However, it's even easier to convert into a more detailed plan thanks to how heavily it's tied to your financials. The overall goal of growth planning isn't to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the growth planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and remain stable through times of crisis.
It's faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Download a free sample business plan template
Ready to start writing your own plan but aren't sure where to start? Download our free business plan template that's been updated for 2024.
This simple, modern, investor-approved business plan template is designed to make planning easy. It's a proven format that has helped over 1 million businesses write business plans for bank loans, funding pitches, business expansion, and even business sales. It includes additional instructions for how to write each section and is formatted to be SBA-lender approved. All you need to do is fill in the blanks.
How to use an example business plan to help you write your own

How do you know what elements need to be included in your business plan, especially if you've never written one before? Looking at examples can help you visualize what a full, traditional plan looks like, so you know what you're aiming for before you get started. Here's how to get the most out of a sample business plan.
Choose a business plan example from a similar type of company
You don't need to find an example business plan that's an exact fit for your business. Your business location, target market, and even your particular product or service may not match up exactly with the plans in our gallery. But, you don't need an exact match for it to be helpful. Instead, look for a plan that's related to the type of business you're starting.
For example, if you want to start a vegetarian restaurant, a plan for a steakhouse can be a great match. While the specifics of your actual startup will differ, the elements you'd want to include in your restaurant's business plan are likely to be very similar.
Use a business plan example as a guide
Every startup and small business is unique, so you'll want to avoid copying an example business plan word for word. It just won't be as helpful, since each business is unique. You want your plan to be a useful tool for starting a business —and getting funding if you need it.
One of the key benefits of writing a business plan is simply going through the process. When you sit down to write, you'll naturally think through important pieces, like your startup costs, your target market , and any market analysis or research you'll need to do to be successful.
You'll also look at where you stand among your competition (and everyone has competition), and lay out your goals and the milestones you'll need to meet. Looking at an example business plan's financials section can be helpful because you can see what should be included, but take them with a grain of salt. Don't assume that financial projections for a sample company will fit your own small business.
If you're looking for more resources to help you get started, our business planning guide is a good place to start. You can also download our free business plan template .
Think of business planning as a process, instead of a document
Think about business planning as something you do often , rather than a document you create once and never look at again. If you take the time to write a plan that really fits your own company, it will be a better, more useful tool to grow your business. It should also make it easier to share your vision and strategy so everyone on your team is on the same page.
Adjust your plan regularly to use it as a business management tool
Keep in mind that businesses that use their plan as a management tool to help run their business grow 30 percent faster than those businesses that don't. For that to be true for your company, you'll think of a part of your business planning process as tracking your actual results against your financial forecast on a regular basis.
If things are going well, your plan will help you think about how you can re-invest in your business. If you find that you're not meeting goals, you might need to adjust your budgets or your sales forecast. Either way, tracking your progress compared to your plan can help you adjust quickly when you identify challenges and opportunities—it's one of the most powerful things you can do to grow your business.
Prepare to pitch your business
If you're planning to pitch your business to investors or seek out any funding, you'll need a pitch deck to accompany your business plan. A pitch deck is designed to inform people about your business. You want your pitch deck to be short and easy to follow, so it's best to keep your presentation under 20 slides.
Your pitch deck and pitch presentation are likely some of the first things that an investor will see to learn more about your company. So, you need to be informative and pique their interest. Luckily, just like you can leverage an example business plan template to write your plan, we also have a gallery of over 50 pitch decks for you to reference.
With this gallery, you have the option to view specific industry pitches or get inspired by real-world pitch deck examples.
Ready to get started?
Now that you know how to use an example business plan to help you write a plan for your business, it's time to find the right one.
Use the search bar below to get started and find the right match for your business idea.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Operational planning: 5 steps to create a better business operational plan
Learn how to conduct operational planning to enhance collaboration, streamline workflows, and unlock peak productivity in all your company’s teams.

Webflow Enterprise gives your teams the power to build, ship, and manage sites collaboratively at scale.

Operational planning enhances collaboration and streamlines workflows to unlock peak efficiency.
Transforming a strategic vision into business success demands meticulous planning. It requires navigating unexpected obstacles, coordinating team activities with long-term goals, and implementing practical steps to realize organizational objectives.
Organizational planning plays a pivotal role in this context by translating high-level strategies into actionable day-to-day tasks.
But an operational plan is more than a structured to-do list — it’s a comprehensive framework that outlines roles, responsibilities, and timelines. By breaking down grand strategies into executable actions, operational planning ensures cohesive teamwork and transforms ambiguous business strategies into achievable realities.
What’s operational planning?
Operational planning is how companies organize day-to-day tasks to align with broader strategic goals. It’s a road map guiding teams through operational decisions about daily operations, ensuring every task contributes to the company’s long-term and high-level objectives. This typically involves setting short-term objectives, defining key activities, and establishing clear timelines.
In practice, operational planning often blends traditional and innovative methods to maximize efficiency. Conventional strategies like Gantt charts and flowcharts help leaders visualize data , tasks, and timelines to make complex projects more manageable. And digital tools like enterprise project management software introduce automation, real-time collaboration, and data analytics into the mix. These platforms enable agile plan adjustments and offer insights through predictive analytics.
By integrating these mixed methodologies, operational planning helps enterprises build a system that’s efficient and responsive to evolving business needs. It bridges the gap between meticulous organization and the agility needed in a fast-paced business environment.
Benefits of operational planning
Operational planning offers a structured approach to decision-making, but its advantages extend beyond planning. Here’s why it’s a crucial tool for achieving organizational goals.
Clarifies goals
Operational planning turns abstract ideas into concrete objectives. It encourages setting explicit goals with definitive timelines. This clarity benefits leadership and the entire team, ensuring everyone understands what needs doing, who’s doing it, and by when.
Enhances productivity
An operational plan enhances productivity by establishing timelines, outlining objectives, and allocating resources. This structure helps team members prioritize their work and manage their time efficiently because they have clear deadlines to guide them.
By defining precise objectives, the plan ensures every team member understands their specific tasks and expected outcomes, preventing unnecessary work and deviations from the plan. And knowing what resources are available helps team members prepare realistically for their taskwork.
Improves efficiency
A well-crafted operational plan boosts efficiency by optimizing workflows and streamlining organizational processes . By mapping out immediate and long-term objectives, the plan establishes a clear blueprint for task execution. As team members better understand their roles, task sequence, and the rationale behind each, they can execute them more seamlessly. This clarity and structure are also invaluable for onboarding new team members and allow them to integrate and understand the workflow with less friction.
Strategic planning vs. operational planning
Both plan types are distinct yet essential components of an organization’s overall planning process. Let’s break down the primary differences:
- A strategic plan defines your company’s “what,” outlines your business’s direction, and sets broad, long-term objectives. It’s a high-level overview that articulates your mission statement, establishes key business objectives, and outlines strategies for achieving them. This plan typically spans several years into the future and aligns the company’s efforts with its overarching vision.
- An operational plan focuses on the “how” by detailing how to execute the strategies and goals laid out in the strategic plan. This is where you get into the specifics — setting milestones, crafting a detailed road map, and establishing short-term, incremental goals that steer your company toward achieving strategic objectives. And at this point, you’ll focus on more immediate factors, like dealing with daily management and task implementation, that are necessary to achieve strategic organizational goals.
Types of operational plans
Departmental goals and needs vary significantly, and tailored operational plans ensure you optimally manage each area. While a sales department might need a plan focused on customer engagement and retention, an IT department might emphasize technology upgrades and cybersecurity . Combining various plan types — like a couple of those that follow — ensures optimal management and effectiveness in each area, aligning departmental activities with broader objectives.
Project operation plans
Project operation plans are indispensable documents for breaking projects into actionable milestones and assigning teams to relevant tasks. A well-developed project plan organizes tasks and anticipates resource requirements such as personnel, infrastructure, and time. By identifying these requirements early on, project operation plans provide planning foresight that helps avoid resource shortages and last-minute scrambles to ensure projects progress smoothly and stay on track.
Say you’re designing a website . Your project operation plan will outline key steps, such as user research , wireframing , user testing , and launch. Each step would have assigned teams, deadlines, and specific objectives, like establishing focus groups by a certain date and finalizing prototypes. The project manager would monitor progress to ensure resource availability and timeline adherence.
Enterprise operation plans
Enterprise operation plans translate broader strategic goals into smaller, manageable milestones. They involve assigning responsibility for these milestones to department directors to ensure accountability for each plan segment.
When creating an enterprise operational plan, it’s vital to identify resource gaps, dependencies, and other potential obstacles to ensure seamless execution. This lets you set realistic, achievable milestones and achieve smooth interdepartmental coordination. Involving directors from the start is also crucial because their insights can reveal critical aspects you might otherwise overlook.
Consider a web design agency planning to expand their service offerings to include mobile app development over the next year. The enterprise operational plan might include milestones such as hiring app developers, training current staff in responsive mobile design , and marketing these new services to potential leads. You might also ask the development head to oversee recruitment and training and involve the marketing director in developing strategies to promote the new services.
IT operation plans
IT departments confront unique challenges due to rapid cybersecurity threats and their critical role in every business sector. Unlike other departments focusing on sales and marketing, IT departments must ensure the organization’s technological structure is robust, secure, and current.
IT operation plans typically outline how the department will adapt to business changes, like scaling up for new hires, migrating from a legacy system to a new one, and safeguarding the organization against evolving cybersecurity threats.
If you’re preparing for a major server infrastructure upgrade, for instance, an IT operation plan will outline steps like evaluating current server and hosting capacities, selecting new hardware and infrastructure, and scheduling website migration to new servers. The plan would include specific timelines — such as completing server evaluations by the end of the first quarter and starting the migration in the second quarter — to ensure minimal downtime and a smooth transition for all hosted websites.

Discover how the right CMS can allow teams to efficiently scale rich, complex content – all without writing code.
Key elements of an operational plan
No matter the type you’re creating, most operational plans include the following core traits.
Operational plans should be clear and to the point. While comprehensive coverage is important, elaborating too much risks misinterpretation and becoming bogged down in the details. Focus on concise, direct explanations and allow the details to unfold during project execution.
Team buy-in is essential for success. Instead of leaving the executive team to dictate the plan exclusively, involve team members in its creation. A collaborative approach helps garner buy-in and fosters feelings of ownership and responsibility toward the plan’s objectives. This involvement translates to increased motivation and commitment because team members feel more likely to invest effort in a plan they helped shape.
Consistency
Consistency in operational plans is crucial for their effectiveness and for establishing organizational trust. It involves applying the same standards and procedures uniformly across all departments and teams. By consistently applying rules and policies, you ensure every organizational element operates under the same guidelines, enhancing fairness and reducing confusion. Consistent execution of your operational plan also streamlines progress and success tracking because the criteria and methods used for each remain uniform.
Specify the processes and methodologies each department should use. If the design team uses an agile, iterative process , for instance, implement similar practices in other departments like IT. This standardization enables smoother collaboration and operational harmony.
Key performance indicators
Every operational plan needs well-defined key performance indicators (KPIs) from the outset. These should include:
- Leading indicators provide early insights into your strategy’s effectiveness by signaling shifts and trends ahead of their full realization. By monitoring these indicators, you can gauge your strategy’s immediate impact and proactively adjust your approach. Indicator examples include customer satisfaction levels, changes in market share, and fluctuations in sales figures.
- Lagging indicators reflect the outcomes of your operational efforts by providing historical data on your plan’s efficacy after execution. Key lagging indicators include metrics like the time taken to complete projects, support ticket volumes, and total expenses incurred. Analyzing these metrics also helps identify improvement areas, like optimizing resource allocation, enhancing customer support processes, and streamlining operational workflows.
Constraints
Acknowledge any assumptions and constraints within your plan, such as technological limitations, tight deadlines, and regulatory requirements. Being upfront about these factors is essential for setting realistic expectations and guiding effective task execution. And it ensures everyone involved understands the framework they’re operating in.
Say you’re building an agency website in the European Union (EU). A critical constraint would be compliance with data protection regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). You must keep this constraint in mind as you develop your operational plan because it affects the technology and processes used for data handling and shapes your website’s design and functionality. For instance, you’ll likely need to integrate clear consent mechanisms for data collection, prominent user data management tools into the website’s layout, and GDPR-compliant technologies for data processing and storage.
The 5 steps of the operational planning process
Enterprises develop operational plans through five strategic steps, each essential for shaping an actionable and effective strategy. Let’s explore what this planning process looks like.
1. Set goals
Establish specific, immediate business goals that align with your strategic plan. This might include launching a redesigned website, increasing online sales by a specific percentage, or reducing digital marketing expenses.
Make these goals ambitious yet adaptable, allowing for flexible responses to unexpected challenges. This step lays the foundation for your operational strategy and aligns every subsequent action toward these well-defined objectives.
2. Allocate resources
After establishing your goals, evaluate your capacity to achieve them. Analyze your current resources and identify what additional expertise, technology, and budget you require. This step isn’t just about highlighting what’s missing — it’s about strategizing how to scale your business to accommodate these needs.
3. Define KPIs
Select KPIs that align closely with your operational goals and ensure they reflect key aspects of your strategy. These KPIs should include leading indicators, like website traffic and user engagement rates for predictive analytics, and lagging indicators, such as satisfaction scores post-launch, to evaluate past performance. Consistently apply these KPIs throughout your project to monitor progress and keep the team focused on core objectives.
Consider using digital analytic platforms like Google Analytics to track KPIs. These tools offer detailed insights into traffic and user behavior. And you can set up dashboards to visually represent these metrics to help spot trends and patterns without combing through data.
Suppose you notice rising bounce rates on a specific webpage — this might indicate user disinterest or navigational issues. In response, you might pivot to revise the page’s copy, restructure its visual hierarchy , or simplify the navigation structure to make it more engaging and user-friendly.
4. Prescribe processes
Develop clear and detailed plans for how your teams should execute tasks. This clarity guides them through each stage, reducing confusion, ensuring consistency, and enhancing productivity.
To communicate these procedures to your team, use tools like flowcharts. They simplify and clarify each operational plan phase and help ensure everyone understands their responsibilities.
For large-scale projects, consider using project management software like Asana, Trello, or Jira. These platforms offer features like task assignment, deadline tracking, and real-time communication, and they provide a centralized platform for monitoring progress and maintaining team alignment.
5. Determine milestones
Create a road map that outlines clear, measurable goals and specific objectives. This map transforms your operational plan into achievable targets, helping teams visualize where they’re headed and the benchmarks they need to hit. Host regular meetings when outlining your milestones — this consistent evaluation ensures everyone moves forward in sync, maintaining the necessary momentum to achieve the plan’s goals.
In a web development project, for example, these evaluations might reveal if certain phases, like design or development, have too few or surplus resources. Identifying these imbalances lets you efficiently reallocate resources to ensure each department has what it needs to meet its milestones effectively and on schedule.
Get started with Webflow
Operational planning thrives on agility, and Webflow has the tools you need to effectively navigate this dynamic environment. With Webflow, you can build flexible websites that keep pace with your operational goals and integrate with analytics and targeting tools for informed operational decision-making .
Learn how Webflow Enterprise can be a part of your operational strategy, and harness a visual-first design platform that lets you create and adapt web content in real time.
Loved by designers. Trusted by enterprises. Bring Webflow in-house at your company with advanced security, custom traffic scaling, guaranteed uptime, and much more.
Subscribe to Webflow Inspo
Get the best, coolest, and latest in design and no-code delivered to your inbox each week.
Related articles

The real cost of WordPress
We know what you’re thinking: WordPress is free! But as the saying goes: there’s no such thing as a free [website platform].

Designing landing pages in hours vs. days: an interview with Jamie Syke
Jamie Syke shares how Webflow has transformed his design process.

CSS grid: release 2.0
We’ve dramatically expanded what’s possible with grid in Webflow, and made some changes to how grid layout works.

How to build for those who prefer motion and for those who don't
Motion can make a beautiful website, but it can also cause harm. Learn how to account for accessibility while delivering award-winning experiences.

Looking for inspiration? Here are 5 stylish fashion website examples
From personal project portfolios to thriving ecommerce stores, find fun and fashionable design inspiration with these five fashion websites.

Webflow announces Winners of the 2021 Webflow Partner Awards
The Webflow Partner Awards celebrate our Partners and Experts who bring the most creative and technically impressive projects to life every day.
Get started for free
Try Webflow for as long as you like with our free Starter plan. Purchase a paid Site plan to publish, host, and unlock additional features.
Transforming the design process at
- Interactions
- Localization
- Figma to Webflow Labs
- DevLink Labs
- Feature index
- Accessibility
- Webflow vs WordPress
- Webflow vs Squarespace
- Webflow vs Shopify
- Webflow vs Contentful
- Webflow vs Sitecore
- Careers We're Hiring
- Webflow Shop
- Accessibility statement
- Terms of Service
- Privacy policy
- Cookie policy
- Cookie preferences
- Freelancers
- Global alliances
- Marketplace
- Libraries Beta
- Hire an Expert
- Made in Webflow
- Become an Expert
- Become a Template Designer
- Become an Affiliate
Quality Improvement Process: How to Plan and Measure It
Last Updated on March 21, 2024 by Owen McGab Enaohwo
Start your free 14-day trial of SweetProcess No credit card needed. Cancel anytime. Click Here To Try it for Free.
When a business takes that jump from small to more substantial, it can lose footing. Customers might complain that the product they used to love has lost the high quality they appreciated about it. The question becomes, how do you maintain quality while producing more?
Every business wants to present quality offers, but not everyone understands what it takes and how to have the best quality. And managers often get this wrong.
In this article, we will look at the quality improvement process, uncover the must-haves in a good QIP, and study the methods, tools, and steps to build a sound strategy.
SweetProcess is our software, and it’s built for teams to create and manage quality improvement documents and procedures in one place so they can focus on what drives real business growth. Without adding your credit card info, you can sign up for our 14-day free trial to see how it works.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
What Exactly Is a Quality Improvement Process?
Importance of quality improvement process in a business, key steps for planning an effective quality improvement process, enhance your company’s quality improvement process using sweetprocess, top quality improvement methodologies, common quality improvement tools, common challenges of quality improvement process, key ways to measure the quality improvement process, quality improvement process in healthcare, build an effective quality improvement process with sweetprocess.
Quality improvement process (QIP) is a journey to enhance and refine the overall quality of an organization’s products, services, and processes.
The main essence is to identify areas that need improvement, implement changes, and always monitor outcomes to ensure constant improvement. It’s driven by a commitment to meet or exceed customer expectations, comply with industry standards, and achieve organizational goals.
Let’s look in more detail at the importance and benefits of the quality improvement process.
Enhanced Brand Reputation
When a business regularly offers great products and services, it builds trust with customers, who become loyal and recommend the business to others. QIP helps to make sure that quality is maintained consistently.
Employee Engagement and Satisfaction
QIP ensures clear communication, setting expectations and reducing frustration. This clarity builds trust, enhances teamwork, and promotes collaboration. Investing in QIP not only improves products or services but also creates a workplace where employees feel valued and satisfied.
A motivated and happy team is key to delivering the quality customers expect. QIP is not just a process tool; it’s also a strategy for engaging employees, leading to overall business success.
Adaptability to Change
Change is constant, especially in a competitive market. The ability to adapt quickly can make or mar a brand. That’s where a strong QIP helps you build. It encourages you to stay vigilant, anticipating changes like shifts in customer behavior or new competitors. It promotes a culture of innovation by seeking better ways to operate.
Cost Reduction
Mistakes can be expensive, leading to rework, refunds, lost sales, and damage to your brand. QIP focuses on error prevention before they become complex issues and saves the costs of fixing mistakes. But it doesn’t stop there. QIP leads to long-term savings by promoting continuous learning and development . As you improve, you better understand processes, team capabilities, and customer needs, making informed decisions about technology, hiring, and market expansion.
Regulatory Compliance
QIP helps your business adhere to industry standards, regulations, and laws . It is a built-in guide, ensuring your business is on the right track. QIP prioritizes documenting every process and change, creating a reliable trail of evidence for compliance.
While it may seem like a lot of paperwork, this documentation serves as proof during audits or inspections, demonstrating that your business follows the rules.
Improved Productivity
Quality improvement process can transform your business into a productive powerhouse where you work smarter, not harder, and achieve more with less.
Let’s go over these ten important steps to plan a quality improvement process for your company.
Define Your Goals
Before you plan to improve your work, you must decide what you want to achieve. What are you trying to do with this improvement process? Do you want to spend less money, make customers happier, or get more work done?
Once you know your goals, you can start working toward them. Ensure your goals are specific, achievable, trackable, significant, and have a deadline.
Identify and Analyze the Current Situation
This step involves collecting information and looking at your current ways of doing things to find areas where you can improve. You can use tools like maps, charts, and checklists to write how things are done and find places where things might be slow or wasteful.
Once you know how things are, you can start thinking of ways to improve them. It’s important to include your team and others in this thinking process because they might have helpful ideas that you haven’t thought about.
Engage Stakeholders
Now that you’ve figured out where things can get better and chosen the right methods and tools, it’s time to involve the people that the changes will affect—your stakeholders.
Start by telling them about the goals and good things that will come from improving things. Explain how it will affect their work and answer questions they might have. Ask for their ideas and thoughts on how to make things better. This not only helps make sure the changes work well but also gets them more involved and feel responsible for the process.
Identify Improvement Opportunities
In order to improve your processes , you need to identify opportunities for improvement. It’s achievable by analyzing your current processes and looking for areas of waste, inefficiency, or error. You may also want to gather feedback from your stakeholders to identify problems or areas where they see room for improvement.
Keep in mind that quality improvement ideas can come from sources you least expect, so be open to suggestions from your team and stakeholders.
Set Measurable Goals
After figuring out what you want to achieve and where you can make things better, the next step is to make sure your goals are measurable. This means making sure your goals are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) .
For instance, if you want to reduce customer complaints, you could set a goal to decrease complaints by 20% in the next six months. This way, you have a specific target to aim at and a deadline to reach it.
Select Improvement Methodology and Tools
Choose from the various tools available, which could be lean, Six Sigma, or agile. Each method has its tools and techniques to find and fix problems, reduce mistakes, and boost employee productivity . However, when deciding on the method and tools, think about the business you have, how big your company is, and the QI project size.
Implement Strategy
This is where all your QI efforts in the previous steps come together. You’ll need to create a quality improvement project plan outlining the specific tasks and timelines for each part of the process.
Involve your team and stakeholders in the implementation, and ensure everyone has clear roles and responsibilities. Stay organized and take records during the implementation so you can spot any obstacles early on and make adjustments.
Monitor and Evaluate Progress
After you’ve put your quality improvement plan into action, it’s important to monitor your progress and ensure you’re on the right path to reaching your goals.
Schedule regular checks with your team and stakeholders to review the progress and pinpoint any issues or areas where you can improve. Be open-minded and be ready to change your approach when necessary.
Collect Feedback
While you’re making improvements to your QI process, it’s essential to hear from your team members. Their feedback can point out areas you can improve or your process might not work for them. You can collect feedback through surveys, interviews, or observations. You can also use data to track progress and spot places for improvement.
Standardize and Build a Culture of Continuous Improvement
You can do this through regular training, continuous iteration, and having a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) . However, getting feedback and monitoring the entire process without a platform that automates everything is stressful and time-consuming. You can also use SOP software , so you can automate the process and focus on growing your business.
Yes, you can use SweetProcess to enhance your quality improvement program. Let’s look at how our software can help you.
Document Your Process to Identify Opportunities for Improvement
SweetProcess can help you prevent scattered documents or misinformation in your quality improvement journey.
To do this, log in to SweetProcess, head to the drop-down ‘’More’’ button, and click on the “Processes” tab. After this, click on the “Create Process” button, enter a title for your process, then click “Continue.”
Then use the AI-suggested description or manually write a description of the steps to be followed to complete the process. This will help you easily spot bottlenecks later and make adjustments.
When choosing your description, always ensure that it’s simple, concise, and straight to the point. Once you’re okay with the output, click on the “Approve” button to save it.
As you can see in the image below, SweetProcess gives you the chance to know who edited or adjusted what and when exactly. Plus, you can trace each previous process version, so you can easily identify where to make adjustments.
Once you’re okay with the output, click on the “Approve” button to save it.
Leverage Reports and Analytics in SweetProcess to Make Data-Driven Decisions
SweetProcess also allows you to keep track of process data: every action, step, and task completion time is tracked, giving you a wealth of insights.
And you can use it to track changes and generate and analyze reports to see how improvements affect the quality of different procedures and processes.
As you can see in the image below, almost every important data you need is clearly shown: version history, the personnel who edited or approved a procedure, description of a process or procedure , toggles for approving requests, sign-off log, enable, disable, or preset review dates and number of times this can be done, check approval requests, and related tasks.
SweetProcess makes quality improvement a straightforward process, as it offers an easy-to-use platform that houses process steps. For instance, at Thimbleberry Financial , Amy Walls, president, and financial advisor, explained how documentation on SweetProcess helps them achieve this.
Their old process documentation on Microsoft Word worked until they started having high turnovers. The team couldn’t follow the process steps, and it led to chaos in their daily operations.
SweetProcess helped Amy and her team create documentation that allowed them to easily spot errors, inadequacies, and what were causing operational missteps; plus it helped enhance their overall service delivery.
“Once we started plugging things into SweetProcess, I found the team was finding, ‘Oh, these other documentations are missing so many steps,’ and we found part of the things that makes our processes and procedures more difficult…because we do the comprehensive plan and wealth management, there’s lots of crossover between things,” Amy explained.
Likewise, Tom, the quality assurance and sensory coordinator at Stone & Wood , was tasked with maintaining quality assurance and smooth operations.
Now, aside from being consistent with the taste and quality of its beer, it has to abide by the regulatory standards in its industry or risk being sanctioned. However, stepping up to the plate is a struggle because of the absence of an effective quality control system .
The binders and Microsoft Word documents the organization was working with were insufficient. Employees working with outdated procedures could alter the entire production, leaving the team with no option but to start afresh—a big waste of time and resources.
Tom took up the responsibility to resolve the problem. After trying several systems, he found the solution in SweetProcess.
In his words: “It gets a lot of use for onboarding new staff. We often get casual labor for a single day’s work. To do that, they have to go through safety induction, quality induction, and various other little documents, so we’ve actually put them all into SweetProcess. We can assign that process as a task to someone, and they can read through it at their own pace, tick it off, and then the manager can come back and see that they have done all of that. It’s working well for us in that regard.
“It really helps us a lot with standard requirements that are out there like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) where you have to demonstrate that your employees have been trained and show procedure documents, so it ticks all the boxes there,” he added.
SweetProcess is built to help teams create and manage quality improvement documents and procedures in one place so they can focus on what drives real business growth. Without adding your credit card info, you can sign up for our 14-day free trial to see how it works.
Now let’s look at some of the top quality improvement methodologies.
The PDCA, or Deming Cycle, stands for plan, do, check, and act. First, plan by setting goals. Do this by implementing changes and gathering data. In the check phase, observe the results and adjust accordingly. Finally, act by adopting and adjusting based on your analysis.
The PDCA cycle is a continuous loop for ongoing improvement that provides a structured framework to address challenges and enhance quality.
Six Sigma is a great way to make things better. It started in the 1980s at companies like Motorola and General Electric. The goal is to have an almost perfect process with very few mistakes. There are two major ways to use Six Sigma: DMAIC and DMADV.
- DMAIC (define, measure, analyze, improve, and control) is for fixing existing problems.
- DMADV (define, measure, analyze, design, and verify) is for making new things.
Kaizen is a Japanese word that means “change for the better.” It’s all about making slight adjustments regularly instead of improving everything all at once. And as time passes, many minor changes add up to make a big difference.
Total Quality Management
Total quality management (TQM) started in Japan after World War II and came to the United States in the 1980s. It’s known for being a way of thinking about quality that involves everyone and every process in a company, not just those on the manufacturing floor.
TQM relies on three main ideas to work on customer focus, continuous improvement , and teamwork. To meet and exceed what the customer wants, look for ways to get better and collaborate to ensure everyone on your team communicates regularly.
Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing is a way of making things better, and it comes from Japan, particularly from Toyota. The main idea is to do things efficiently and reduce any wasteful steps to make processes smoother and give customers what they truly want. By going this way, companies can work more efficiently, create less waste, and provide products or services that customers like.
Here are some common quality improvement tools.
Pareto Analysis
Pareto analysis is a helpful QI tool that helps us focus on the most significant things. It follows the 80/20 rule, where a small part (20%) causes most of the results (80%). You can use it by creating a chart to see what matters most.
For instance, in a business, you can use it to find and solve a few major problems causing most of the issues. It’s not only for finding problems; you can also use it to understand what’s going well.
Flowcharts are like maps for processes, simplifying complex procedures. They visually represent steps with symbols and arrows, making it easy to understand and improve the process.
Flowcharts can be simple or detailed and are versatile in various scenarios, from troubleshooting tech issues to event planning.
Voice of Customer Analysis
Next on our quality improvement tool list is voice of customer analysis (VOC). Forget lasers and holograms; this tool focuses on something even more powerful—customer feedback.
Think of it like understanding what guests want at a party. VOC involves gathering customer feedback through surveys, interviews, and social media to grasp their expectations and preferences. But it’s not just about collecting data; it’s also about analyzing it to find patterns and insights.
Process Maps
Process maps are visual representations of business processes, like a more specific version of flowcharts. They show steps, responsibilities, resources, and time. Use them for quality improvement—identify inefficiencies, waste, or errors in the existing process—and address them.
Process maps enhance communication, aiding coordination and collaboration. They also serve as effective training tools for new team members, boosting competence and confidence.
In the competitive business world, pursuing quality improvement is important for survival. Yet the journey isn’t always easy, and various challenges can arise. Here are some challenges to be ready for:
Lack of Continuous Improvement
Businesses should always try to get better. Doing something once and stopping can make things worse. Don’t settle for just okay — you might go backward if you don’t keep improving.
Improving only happens when a company encourages new ideas and takes risks. Employees should have the freedom to share ideas, which is why having a quality improvement tool is very important, as it helps you gather feedback and collaborate effectively with your team members.
Communication Gap
Operating in silos, where departments don’t share ideas, creates missed opportunities and friction. Listening is equally important, and having a platform for communicating ideas is key. Bridging the communication gap requires a conscious effort from all units to foster open dialogue, define communicating goals, promote collaboration, and encourage honest feedback.
Resistance to Change
Change in businesses, like upgrading to a new technology, often faces resistance because of the natural human inclination for stability. This resistance can manifest in various forms, such as employees’ hesitance about using quality improvement software or departments’ worries about losing power. That’s why open dialogue and a policy report that explains the reasons and benefits of such a transition are important.
Ineffective Documentation
Implementing quality improvement processes without effective documentation is like assembling furniture without simple instructions—frustrating and prone to errors.
Documentation serves as the blueprint, outlining standards, roles, procedures, and expected results. Inadequate or unclear documentation leads to confusion, assumptions, and errors and hinders the aim of the initiative.
Improving quality is a constant goal for all organizations. It’s about fixing mistakes and enhancing processes to meet customer expectations. Here are eight ways to measure the quality improvement process.
Defect Rate
In quality improvement, the defect rate shows how many mistakes there are in your system and points out where you can do better. It counts the number of messed-up items in a production process, trying to have as close to zero mistakes as possible.
To find the defect rate, you divide the number of messed-up items by the total produced, then multiply by 100 to get a percentage. What counts as a “defect” can be different depending on the industry and product, but it gives a simple way to keep track.
First Pass Yield
First pass yield (FPY) is a vital measure in making things better, checking how well a process works by seeing how many products or services are right the first time without fixing mistakes.
To calculate FPY, you divide the products without mistakes by the total made, then multiply by 100. This tells you how healthy the process is. If FPY is high, it means the process works well; if it’s low, there are problems causing mistakes.
Scrap and Rework Percent
Scrap and rework percent is an important measure in making things better, showing how much of what you produce ends up as waste or needs fixing. For example, if 15 out of 100 things you make are thrown away or require fixing, the scrap and rework percentage is 15%. To find it, count how many things are thrown away or fixed, then divide by the total made, then multiply by 100. A high percentage means more waste, fixing, costs, and maybe unhappy customers, telling you that you need to do better.
Cycle time simply shows how long it takes for a process or operation to be done from start to finish. It’s like using a stopwatch to see how well tasks are achieved. If the time is short, things are working well; if it’s long, there might be problems slowing things down.
Measuring cycle time is easy. Start the clock when the process begins and stop it when it’s done, then figure out the time in between. Doing this a few times gives an average time, which is a standard to compare against.
Customer Satisfaction Rate
The Customer satisfaction rate is a crucial external measure that shows how happy customers are with products, services, or their overall experience with a company. It’s figured out through surveys, finding the percentage of satisfied customers among those who respond to the survey. This gives insights into what customers think.
To calculate it, divide the number of satisfied customers by the total survey responses, then multiply by 100. For example, if 60 out of 80 people say they’re satisfied, the rate is 75%. But it’s not just about the numbers—it’s about using the feedback to improve things.
Compliance Rate
The compliance rate is an important measure that checks how well processes follow the rules. It shows the percentage of activities done according to the set standards. Not following these rules can lead to problems like fines, legal troubles, and harm to reputation.
Understanding why the compliance rate matters is key. It directly affects how things work inside a company, affecting product quality, efficiency, and overall performance. Having a high compliance rate is good, showing that things align with standards. But it’s not a one-time thing—you need to keep checking regularly to keep the rate high.
Equipment Downtime Rate
This metric keeps track of how often your equipment or machinery isn’t working correctly. It measures the percentage of time your equipment is out of service, whether because of breakdowns, maintenance, repairs, or any other reason.
Why does this matter? Imagine you’re in the middle of an important production, and suddenly your main machine stops working. This can lead to delays, missed deadlines, and increased costs. That’s why monitoring your equipment downtime rate is essential.
To measure it, think of it like a stopwatch. It starts when your equipment stops and starts when it’s back in action. Divide the total downtime by the planned production time, then multiply by 100 to get the equipment downtime rate.
For example, if you planned for 100 hours of production, but your machinery was down for 10 hours, your equipment downtime rate would be 10%.
A lower number is better. A high equipment downtime rate signals issues with machinery, maintenance, or spare parts. But don’t worry; a high rate is a call to action, prompting you to find and fix the root cause.
Return on Investment
In simple terms, ROI is like the financial payback you get from an investment. It helps you see the financial impact of your quality improvement efforts.
Why is ROI important? Quality improvement isn’t just about better processes; it’s also about making a profit. ROI measures if your investment in quality improvement is turning into dollars and cents.
Calculating ROI may sound complicated, but it’s quite simple. You subtract the cost of the investment from the gains, then divide by the cost of the investment. Multiply by 100, and you get your ROI percentage.
The healthcare quality improvement process is like a plan to make healthcare better. It includes finding what’s not working, setting goals to improve, making changes, and checking if it’s getting results.
For instance, if a hospital wants to reduce patient infections, they may first try a new way of sterilizing equipment in one unit. If it reduces infections, they can adopt the QI method in the entire hospital.
Having quality products and services involves sticking to a continuous quality improvement routine. But the journey to quality improvement is hard when you don’t have software to manage, automate, and streamline the whole process.
That’s why you need SweetProcess as a tool to help you every step of the way. You can sign up without a credit card for a 14-day FREE trial period so you can see how it works for yourself.
You also get to enjoy features like an AI process prompter, process documentation, drag-and-drop process maps, process version history, teammate feedback, progress tracker, alerts for team member tracking, assign tasks, process search bar, customizable process flow charts, cloud integration with CRM tools, and process activity reports. These tools allow you to organize the entire process and grow your company.
Related Posts:

Get Your Free Systemization Checklist

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Fix Your Company’s Culture of Overwork
- Malissa Clark

A three-step process will make everyone less stressed and more productive.
The new age of flexible of work has encouraged a culture of overwork, which is proving to be harmful to the mental health of employees. In her new book, Never Not Working , Malissa Clark offers a three-step process for organizations to reverse this unhealthy relationship: 1) Assess your company’s baseline level of overwork and its origins; 2) Plan for incremental change by targeting places where change will be most effective soonest; and 3) Execute a trial experiment, learn, and iterate.
Associate professor and head of the Healthy Work Lab at the University of Georgia, Malissa Clark, argues that in a post-pandemic work landscape that transcends buildings – and hours — the boundaries of professionalism and personal lives have been blurred. In her new book, Never Not Working: Why the Always-On Culture Is Bad for Business and How to Fix It (Harvard Business Review Press) , Clark explains the current epidemic of overwork, what it looks like at its worst, and how a generation of employees have unknowingly let their work consume them. This excerpt, which is lightly edited, outlines clear steps that organizations can take to correct a culture of overwork for the betterment of their employees.
- MC Malissa Clark is an associate professor of industrial and organizational psychology at the University of Georgia, where she leads the Healthy Work Lab. She is one of the world’s leading scholars on workaholism, overwork, burnout, and employee well-being. In addition to serving as an expert consultant to many organizations on these issues, Clark and her work have been featured in outlets including the New York Times, the BBC, Time, Glamour, The Atlantic, Huffington Post, and others.
Partner Center
- Getting Results.
- Newsletters
WEATHER ALERT
A rip current statement in effect for Coastal Volusia Region
The texas attorney general is investigating a key boeing supplier and asking about diversity.
David Koenig
Associated Press
DALLAS – The Texas attorney general has opened an investigation into a key Boeing supplier that is already facing scrutiny from federal regulators over quality of parts that it provides to the aircraft maker.
The office of Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton said it began looking into Spirit AeroSystems because of “apparent manufacturing defects” in parts that “have led to numerous concerning or dangerous incidents.”
Recommended Videos
In a statement Friday, a Spirit spokesman said, “While we do not comment on investigations, Spirit is wholly focused on providing the highest quality products to all our customers, to include the Boeing Company.”
Paxton asked the Wichita, Kansas-based supplier to turn over documents produced since the start of 2022 about communication with investors and Boeing about flaws in parts and corrective steps the company took.
The request goes into detail in seeking internal discussions around Spirit’s efforts to create a diverse workforce “and whether those commitments are unlawful or are compromising the company’s manufacturing processes.” Paxton asked for a breakdown of Spirit's workforce by race, sexual orientation and other factors, and whether the makeup has changed over time.
Since a Spirit-made door-plug panel blew off an Alaska Airlines Boeing 737 Max in January, some conservatives have tried to link aviation safety to diversity at manufacturers.
Paxton is a conservative Republican who this week agreed to pay $271,000 in restitution to victims and take 15 hours of training in legal ethics to settle felony charges of securities fraud . Paxton did not admit wrongdoing in the 9-year-old case.
The Federal Aviation Administration launched an investigation into Boeing Spirit after the Alaska Airlines incident. An FAA audit of manufacturing procedures in Spirit’s factory gave the company failing grades in seven of 13 areas.
Boeing is in talks to buy back Spirit , which it spun off nearly 20 years ago, as part of a plan to tighten oversight of manufacturing in its supply chain.
Copyright 2024 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Biden Approves $5.8 Billion in Additional Student Debt Cancellation
The incremental relief brings the canceled total to $143.6 billion for nearly four million Americans.

By Tara Siegel Bernard
The Biden administration continued its effort to extend student debt relief on Thursday, erasing an additional $5.8 billion in federal loans for nearly 78,000 borrowers, including teachers, firefighters and others who largely work in the public sector.
To date, the administration has canceled $143.6 billion in loans for nearly four million borrowers through various actions, fixes and federal relief programs. That’s the largest amount of student debt eliminated since the government began backing loans more than six decades ago, but it’s still far less than President Biden’s initial proposal, which would have canceled up to $400 billion in debt for 43 million borrowers but was blocked by the Supreme Court.
The latest debt erasures apply to government and nonprofit employees in the Public Service Loan Forgiveness program, which can eliminate their balance after 120 payments. The P.S.L.F. program, which was plagued with administrative and other problems, has improved in recent years after the administration made a series of fixes .
“For too long, our nation’s teachers, nurses, social workers, firefighters and other public servants faced logistical troubles and trap doors when they tried to access the debt relief they were entitled to under the law,” Education Secretary Miguel Cardona said.
Since those October 2021, more than 871,000 public service and nonprofit workers have received debt cancellation totaling $62.5 billion; before that, just 7,000 had reached forgiveness since the program was created more than 15 years ago.
Starting next week, borrowers who are set to receive the latest round of debt cancellation through the P.S.L.F. program will receive an email notification from Mr. Biden — a reminder of his administration’s work just eight months before the presidential election.
An additional 380,000 federal borrowers in the P.S.L.F program who are on track to have their loans forgiven in less than two years will receive emails from the president notifying them that they will be eligible for debt cancellation if they continue their public service work within that period.
Many of these borrowers have been helped by programs that tried to address past errors that may have failed to credit individuals for payments. As a result, many borrowers received account adjustments, or additional credits, pushing them closer to the repayment finish line.
Millions of borrowers with certain types of loans are still eligible for some of those adjustments, but they will need to apply to consolidate those loans by April 30 to qualify.
“There are a lot of people who need to consolidate by this deadline to benefit and potentially access life-changing student loan relief,” said Abby Shafroth, co-director of advocacy at the National Consumer Law Center. They include borrowers with privately held loans in the Federal Family and Education Loan , Perkins Loan and Health Education Assistance Loan programs, she added. (People with direct loans or loans held by the Education Department don’t need to do anything to have their payment counts adjusted; it happens automatically.)
Besides P.S.L.F., the administration has extended relief through a variety of other federal relief programs: About 935,500 borrowers were approved for $45.6 billion in debt cancellation through income-driven repayment plans, which base monthly payments on a borrower’s earnings and household size. After a set period of repayment, usually 20 years, any remaining debt is erased.
Another 1.3 million people had $22.5 billion wiped out through the federal borrower defense program, which provides relief to those defrauded by their schools.
The administration’s latest round of completed debt relief comes on the heels of its bungled rollout of the new Free Application for Federal Student Aid, or FAFSA, which was supposed to simplify the process. Instead, technical and other problems have created delays, leaving colleges without student financial information that they need to make aid offers. Students have been left in limbo, unable to make decisions on where they’ll attend college.
Tara Siegel Bernard writes about personal finance, from saving for college to paying for retirement and everything in between. More about Tara Siegel Bernard
What is pet dental insurance?
Coverage details, choosing the right dental insurance, benefits of pet dental insurance, how to get pet dental insurance, understanding pet dental insurance.
Affiliate links for the products on this page are from partners that compensate us (see our advertiser disclosure with our list of partners for more details). However, our opinions are our own. See how we rate insurance products to write unbiased product reviews.
- Pet insurance with pet dental coverage can be affordable while protecting your pet's health.
- The best pet insurance plans include coverage for periodontal disease.
- Scheduling regular pet dental cleanings can help you avoid lapses in coverage.
Just as brushing and flossing are essential for people, regular dental care is vital for pets, especially cats and dogs. The American Veterinary Medical Association recommends that pets get proper dental care annually (which can be part of their yearly physical).
"Dental health is an integral part of a pet's overall health and should be a key part of their preventive care routine," says Dr. Ari Zabell , a veterinarian with Banfield Pet Hospital.
Dental treatments for periodontal disease, broken teeth, or tumors can be costly. So, more pet owners are looking into pet dental insurance. If you shop carefully, pet dental insurance and other pet insurance protections for all your pet's needs can be open to you.
Some of the best pet insurers , like Embrace Pet Insurance offer comprehensive coverage to care for your pet's pearly whites. Read on to learn more about picking a plan and using it when the time comes.
In most cases, pet dental insurance can't be bought as a standalone policy, according to Dr. Brian Evans, clinical director at the online veterinary clinic, Dutch.
Zabell expands on this point, saying, "Dental insurance for pets is almost always part of a larger pet insurance plan." Pet dental is a natural part of the conversation after you answer the question of whether pet insurance is worth it with a yes.
Definition and scope of coverage
Pet insurance provides reimbursement for unforeseen or emergency care. Since dental pet insurance is typically a feature of your pet insurance policy, you'll receive coverage for dental care related to accidents and illnesses. The following are examples of dental conditions and treatments covered under a pet insurance policy:
- Periodontal disease
- Tooth abscesses
- Cancerous oral growths and tumors
- Fractured tooth
Your pet insurance coverage is based on a reimbursement model. You pay for services upfront then submit your claim to your insurance company for reimbursement. It might seem like a hassle as we're used to human medical providers taking care of the claims process for us. However, there is a silver lining. You won't need to worry about in-network vs. out-of-network providers for your pet's healthcare.
"Vets do not have a concern about which insurance plan you have as they are not a part of that process," Evans says.
Difference between dental insurance and wellness add-ons
Dental insurance comes with your standard accident and illness policy. Dental insurance is also available through a wellness plan at an additional fee.
Pet wellness plans cover the cost of preventative dental care, such as routine cleanings or checkups. In contrast, pet insurance policies cover medically necessary treatments and procedures like tooth extractions or root canals.
Depending on your insurance policy, pet dental insurance will cover emergency procedures and routine care. However, it excludes coverage for pre-existing conditions and certain types of pets.
Routine dental cleanings
Routine dental cleaning prevents severe dental illnesses in the long run. Wellness plans are typically purchased as add-ons to your regular insurance policy. These plans have their own premiums and coverage limits. Unlike your base policy, they generally don't require deductibles or co-pays.
Emergency dental procedures
Emergency dental procedures are covered under your base pet insurance policy. Some of these procedures and treatments include:
- Tooth extractions
- Root canals
- Prescription medicine
Exclusions and limitations
Most pet insurance plans won't cover pre-existing conditions. Since an astounding 80% of dogs have dental disease by the time they're three years old, getting coverage early is critical.
"The best way to ensure your pet's periodontal disease will not be considered pre-existing is to purchase the pet insurance while they still have their puppy teeth," Evans says.
Another exclusion to be aware of is your pet's breed and age. Insurance companies may deny coverage to certain breeds and older pets because they are more prone to health conditions. If your insurer doesn't restrict a high-risk pet, your insurance premiums will likely increase.
The right dental insurance policy offers coverage that aligns with your pet's needs at a price point comfortable for you. Comparing insurance providers can help you sift through the market and find a policy that meets your criteria.
Factors to consider
When choosing a pet insurance policy, you'll want to consider the following factors:
- Coverages: Know your pet's health needs and find a policy that covers them. The best pet dental insurance plans should cover periodontal disease, inflammation of the gums, and tissue around the teeth. This is the most common dental condition in cats and dogs.
- Premiums: The average cost of an accident-only pet insurance policy is $10.18 per month for cats and $16.70 for dogs. The average cost for a comprehensive policy is $32.25 per month for cats and $53.34 for dogs. But it varies widely based on your pet's type, breed, age, and where you live
- Deductible: The amount you need to pay toward your pet's care before the insurance kicks in. Usually, this is deducted from the first reimbursement.
- Reimbursement level: This is the percentage of the vet's invoice your insurer will cover. Usually, reimbursement levels range between 70% and 90% of the procedure costs.
- Coverage maximum: This max is the highest dollar amount your pet insurance will pay for a claim.
For the most comprehensive pet medical coverage, look for a pet insurance plan with unlimited coverage and a reimbursement rate of 80 to 90% (you pay 10-20% of your vet bills after the deductible).
"Some pet insurance companies will also say they cover dental cleanings but limit the reimbursement to a small portion of the actual cost," says Evans. "The entire dental cleaning procedure may cost $700, but the pet insurance will only reimburse you $150."
Comparing insurance providers
Shopping around for pet insurance helps you get the lowest price on the coverages you need. To compare insurance policies, get quotes for your pet from a few different insurance companies. Make sure each quote has a similar deductible, coinsurance, and policy limit for the most accurate apples-to-apples comparison.
Dental care insurance for your pet ensures that your pet's teeth are taken care of without the financial burden. Here are a few of its benefits:
Preventing costly dental problems
Preventative care is the best way to avoid complicated and costly dental problems as your pet ages. But routine cleaning isn't cheap. According to Spot, an examination, removal of plaque and tartar, and polishing cost between $150 to $350. Meanwhile, the monthly premium of a basic wellness policy can be as little as $9.95 for hundreds of dollars in coverage.
Enhancing overall pet health
Many pet owners avoid the vet or avoid certain treatments because they can get expensive. Whether you have a sizable emergency fund or wiggle room in your budget, every pet deserves quality healthcare. Pet insurance is a financial tool you can leverage to ensure your furry friend lives a long and healthy life.
Peace of mind for pet owners
Dental procedures come at a hefty price tag. According to Spot, a pet insurance company, a single tooth extraction will run you about $50 to $200. Extractions for multiple teeth can cost $1,000 or more. More complex procedures like a root canal or surgery for a fractured jaw can amount to thousands of dollars. Pet dental insurance allows you to pay only a fraction of that price.
You get pet dental insurance the same way you'd get a pet insurance policy or a wellness add-on.
- Step 1: Apply for a policy — After finding a policy that meets your pet's coverage needs and budget, fill out an application with the pet insurance company. The insurer will request personal information such as your location and contact information and your pet's details, such as their name, gender, and breed. This information will be used to assess your premiums.
- Step 2: Customize your coverages — Most insurance companies let you choose between an accident-only policy and an accident and illness policy. You may also have the option to add a wellness plan. Adjust factors such as deductibles, reimbursement rates, and coverage limits to your specific needs and financial situation.
- Step 3: Read the fine print — Review your policy's terms and conditions to understand any exclusions, limitations, waiting periods, or other important details that may apply.
- Step 4: Purchase your policy — At checkout, you'll have the option to pay an annual or monthly premium. Once you've made your decision, proceed by entering your payment details and confirming your payment to secure your coverage.
- Step 5: Provide requested documentation— Your insurer may ask for additional documentation, such as your pet's medical record or a physical exam to check for any pre-existing conditions.
How to file a pet dental insurance claim
After your pet has its teeth taken care of, you must pay the invoice from the veterinarian out-of-pocket. Next, submit the invoice and a pet insurance claim form to your insurer. You'll also need to provide your pet's medical records to prove the treatment wasn't for a pre-existing condition. After that, you'll get a check or direct deposit with the reimbursement. Usually, plans have a time limit for claims submissions.
Although pet dental insurance is relatively new, it can be a powerful tool for your pet's oral health.
"Pet dental health is one of the most important indicators of long-term health and should be a priority for your pet," Evans says. "Choose a pet insurance partner that will assist you in keeping your pet's mouth from being a source of chronic pain and inflammation."
Pet dental insurance covers emergency dental procedures like extractions, root canals, prescription medication, and more. Most wellness policies cover routine dental cleanings and checkups.
It depends. The standard pet insurance policy covers emergency dental procedures and treatments. If you want coverage for preventive dental care, you'll need to purchase a wellness policy.
The best way to choose pet dental insurance is to compare policies from multiple companies. Evaluate how each policy stacks up in terms of coverages, coverage limits, deductible amounts, reimbursement rates, and premiums.
Dental insurance helps manage the costs of dental care, which can be expensive, especially for emergency procedures. Additionally, routine dental care, which is covered by a wellness plan, prevents uncomfortable oral diseases like periodontal disease or tooth decay.
Start by researching insurance providers that offer dental coverage, either as part of their standard policies or as an add-on. Then, get a quote from the insurer through their website or by calling them. If you're happy with the price, review the terms carefully and finalize your policy. Your insurer may require updated medical records as well as a physical exam to check for pre-existing conditions, which are excluded from coverage.
Editorial Note: Any opinions, analyses, reviews, or recommendations expressed in this article are the author’s alone, and have not been reviewed, approved, or otherwise endorsed by any card issuer. Read our editorial standards .
Please note: While the offers mentioned above are accurate at the time of publication, they're subject to change at any time and may have changed, or may no longer be available.
**Enrollment required.

- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
The Better Business Planning Process. The business plan process includes 6 steps as follows: Do Your Research. Strategize. Calculate Your Financial Forecast. Draft Your Plan. Revise & Proofread. Nail the Business Plan Presentation. We've provided more detail for each of these key business plan steps below.
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process.
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Step 7: Financial Analysis and Projections. It doesn't matter if you include a request for funding in your plan, you will want to include a financial analysis here. You'll want to do two things here: Paint a picture of your business's performance in the past and show it will grow in the future.
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
1. Carry out your research. The first step to creating a business plan is to do thorough research about the business and industry you are trying to get into. Tap into all the information you can get about your target audience, potential customer base, competitors, market and industry trends, cost of business, etc.
Make sure to clearly state expectations and timelines for tasks, get involvement and input from managers in this process, and continue to track and measure goals. 6. Test and implement the process. Process definition and operation requires an interactive process that needs to be measured constantly.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page. The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions. A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
The things you should include in a one-pager business plan are: The problem - Describe a certain problem your customers have and support the claim with relevant data. The solution - How your products/services can solve the issue. Business model - Your plan on how to make money.
Strategic planning is a business process that helps you define and share the direction your company will take in the next three to five years. During the strategic planning process, stakeholders review and define the organization's mission and goals, conduct competitive assessments, and identify company goals and objectives. ...
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
The planning process is what uncovers those insights. Related Reading: 10 prompts to help you write a business plan with AI. How long should your business plan be? Thinking about a business plan strictly in terms of page length can risk overlooking more important factors, like the level of detail or clarity in the plan.
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
This section of your simple business plan template explores how to structure and operate your business. Details include the type of business organization your startup will take, roles and ...
Examples of human-centric business processes: Hiring and onboarding. You can improve job postings, resume tracking, referrals—but there's a uniquely human element to hiring a new employee. From that first phone screen to the onsite interview, improving hiring processes focuses on human-centric BPM. Creative work.
A business plan should be structured in a way that it contains all the important information that investors are looking for. Here are the main sections of a business plan: 1. Title Page. The title page captures the legal information of the business, which includes the registered business name, physical address, phone number, email address, date ...
The business planning process is a systematic approach to developing a strategic plan for a business. It involves analyzing the current business environment, setting goals and objectives, identifying strategies, creating an action plan, and regularly reviewing and adjusting the plan as needed.
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
Developing a business plan is essential to the strategic management planning process. It helps you to set goals, establish priorities, and develop strategies for achieving them. Business planning involves many critical steps, including market analysis, competitive research, financial forecasting, and risk assessment.
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea. The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template.
The 5 steps of the operational planning process. Enterprises develop operational plans through five strategic steps, each essential for shaping an actionable and effective strategy. Let's explore what this planning process looks like. 1. Set goals. Establish specific, immediate business goals that align with your strategic plan.
ROI measures if your investment in quality improvement is turning into dollars and cents. Calculating ROI may sound complicated, but it's quite simple. You subtract the cost of the investment from the gains, then divide by the cost of the investment. Multiply by 100, and you get your ROI percentage.
Step 4: Create an action plan. Once you've identified development opportunities, create an action plan. Break down your goals into smaller, manageable milestones and create a timeline and schedule for your development activities. Here's an example of how you can create an effective action plan: 1.
In her new book, Never Not Working, Malissa Clark offers a three-step process for organizations to reverse this unhealthy relationship: 1) Assess your company's baseline level of overwork and ...
The Texas attorney general says he's investigating a key Boeing supplier that is already under scrutiny by federal regulators over the quality of its work on Boeing planes.
For most organizations, their content supply chain - the end-to-end business process that every company needs to deliver the content required for marketing campaigns and personalized customer experiences - is a web of disconnected workflows, teams and systems that often break down. At the same time, the demand for content that is ...
Kristian Thacker for The New York Times. By Tara Siegel Bernard. March 21, 2024. The Biden administration continued its effort to extend student debt relief on Thursday, erasing an additional $5.8 ...
Premiums: The average cost of an accident-only pet insurance policy is $10.18 per month for cats and $16.70 for dogs. The average cost for a comprehensive policy is $32.25 per month for cats and ...