- Syllabus 2024-25
- CBSE Class X SQP 2023-24
- CBSE Class XII SQP 2023-24
- Class X SQP 2022-23
- Class XII SQP 2022-23
- Request Answers


Reported Speech: Practice Exercises in Interrogative Sentences
- Post last modified: 1 March 2023
- Post category: Grammar Exercises / School Grammar
Do practice converting Direct Speech Interrogative sentences into Indirect Speech. The exercises are based on both types of Questions – Starting with an Auxiliary Verb and the other type starting with a Q Word. Try to first attempt yourself then see the answers given in the last of every set of questions.
More exercises are added from time to time, so keep coming here 😊
Click here more English Grammar study materials
I – Interrogative Sentences – Yes/No Type (Questions starts with an auxiliary verb)
See some examples before attempting practice exercises.
Direct speech: “Are you the one who stole the money?”
Indirect speech: He asked if I was the one who had stolen the money.
Direct speech: “What are you doing here at this time?”
Indirect speech: She asked what I was doing there at that time.
Direct speech: “Have you ever been to Europe before?”
Indirect speech: He asked if I had ever been to Europe before.
Direct speech: “Who taught you how to play the guitar so well?”
Indirect speech: She asked me who had taught me how to play the guitar so well.
Direct speech: “Why did you leave your previous job?”
Indirect speech: He asked me why I had left my previous job.
Q. Change the following sentences into Indirect Speech.
1. “Are there any more files?” He asked. “Yes, sir,” said the peon.
2. The teacher said to Rena, “Did you break the window pane?” “No, sir,” said Reena, “I did not.”
3. “If you find my answers satisfactory, will you give me five rupees?” said the astrologer. “No,” replied the customer.
4. I said to him, “Do you want to go to Delhi?” He said, “No, sir.”
5. Rahul said to me, “Does Mohit still play?” I said, “Yes, sir.”
6. Malik said to her, “Has Sara invited you to dinner?”
7. I said to her, “Did you enjoy the film?” She said, “No, sir.”
8. Sachin said, “Sonam, do you see what I see?” Sonam said, “Yes.”
9. He said, “Do you not like it?” She said, “Yes.”
10. She said to me, “Shall we ever see each other again?” I said, “Perhaps, never.”
1. He asked the peon if there were any more files. The peon replied respectfully in the affirmative.
2. The teacher asked Reena if she had broken the window pane. Reena replied respectfully that she had not done it.
3. The astrologer asked the customer if he would give him five rupees if he found his answers satisfactory. The customer replied in negative.
4. I asked him if he wanted to go to Delhi and he replied respectfully in negative.
5. Rahul asked me if Mohit still played and I replied respectfully in positive.
6. Malik asked her if Sara had invited her to dinner.
7. I asked her if she had enjoyed the film. She replied respectfully in negative.
8. Sachin asked Sonam if she saw what he saw. She replied in affirmative.
9. He asked if she did not like that and she replied in affirmative.
10. She asked me if we would ever see each other again but I replied that we would perhaps never.
II – Interrogative Sentences – Q. Word Type (Question begins with a Q. Word)
Q. change the following sentences into indirect speech. .
1. He said to me, “Whom does she want to contact?”
2. They said to her, “Whose house are you purchasing?”
3. You said to him “Why are you making mischief?”
4. They said to us, “How have you solved this sum?”
5. We said to them, “Who has misguided you?”
6. They said to him, “Where have you been wandering since yesterday?”
7. She said to me, “Why were you hiding today?”
8. Raja said to us, “When do you expect to see me again?”
9. He said to her, “What shall I be offering you with tea?”
10. We said to them, “When shall we have paid you a visit?”
1. He asked me whom she wanted to contact.
2. They asked her whose house she was purchasing.
3. You asked him why he was making mischief.
4. They asked us how we had solved that sum.
5. We asked them who had misguided them.
6. They asked him where he had been wandering since the previous day.
7. She asked me why I had been hiding that day.
8. Raja asked us when we expected to see him again.
9. He asked her what he would be offering her with tea.
10. We asked them when we would have paid them a visit.
Miscellaneous Exercises on Interrogative Sentences
I. change the following sentences into indirect speech..
- “What is your name?” asked the teacher. Indirect speech:
- “Where did you go yesterday?” she asked me. Indirect speech:
- “Are you feeling better now?” he asked her. Indirect speech: .
- “Will you come with me?” he asked her. Indirect speech: .
- “Why did you break the vase?” he asked his son. Indirect speech:
- “What are you doing here?” asked John.
- “Have you finished your homework?” the teacher asked.
- “Why did you leave the party so early?” she asked
- “Are you going to the concert tonight?” Tom asked.
- “Where did you put my phone?” asked Sarah.
- The teacher asked me what my name was.
- She asked me where I had gone the previous day.
- He asked her if she was feeling better then
- He asked her if she would go with him
- He asked his son why he had broken the vase.
- John asked what I was doing there.
- The teacher asked if I had finished my homework.
- She asked why I had left the party so early.
- Tom asked if I was going to the concert that night.
- Sarah asked where I had put her phone.
Contact for Paid Online Session to understand more or clear your doubts
Contact Ajeet Sir on Telegram , WhatsApp , Email

want to share! Share this content
- Opens in a new window
You Might Also Like
Modals: class 10 practice exercises, rearranging words and phrases to form meaningful sentences english grammar, story writing class 10 english grammar, prepositions: rules and usage english grammar cbse/icse schools, this post has 5 comments.
N Yashvanth 8th C
Sarman Rathore Rath Hamirpur Uttar pradesh
Cool…!!
Hi Safa, we have added a few more questions. You can also see and attempt them.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Reported speech: indirect speech
Indirect speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech , the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
Indirect speech: reporting statements
Indirect reports of statements consist of a reporting clause and a that -clause. We often omit that , especially in informal situations:
The pilot commented that the weather had been extremely bad as the plane came in to land. (The pilot’s words were: ‘The weather was extremely bad as the plane came in to land.’ )
I told my wife I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday. ( that -clause without that ) (or I told my wife that I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday .)
Indirect speech: reporting questions
Reporting yes-no questions and alternative questions.
Indirect reports of yes-no questions and questions with or consist of a reporting clause and a reported clause introduced by if or whether . If is more common than whether . The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She asked if [S] [V] I was Scottish. (original yes-no question: ‘Are you Scottish?’ )
The waiter asked whether [S] we [V] wanted a table near the window. (original yes-no question: ‘Do you want a table near the window? )
He asked me if [S] [V] I had come by train or by bus. (original alternative question: ‘Did you come by train or by bus?’ )
Questions: yes-no questions ( Are you feeling cold? )
Reporting wh -questions
Indirect reports of wh -questions consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a wh -word ( who, what, when, where, why, how ). We don’t use a question mark:
He asked me what I wanted.
Not: He asked me what I wanted?
The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She wanted to know who [S] we [V] had invited to the party.
Not: … who had we invited …
Who , whom and what
In indirect questions with who, whom and what , the wh- word may be the subject or the object of the reported clause:
I asked them who came to meet them at the airport. ( who is the subject of came ; original question: ‘Who came to meet you at the airport?’ )
He wondered what the repairs would cost. ( what is the object of cost ; original question: ‘What will the repairs cost?’ )
She asked us what [S] we [V] were doing . (original question: ‘What are you doing?’ )
Not: She asked us what were we doing?
When , where , why and how
We also use statement word order (subject + verb) with when , where, why and how :
I asked her when [S] it [V] had happened (original question: ‘When did it happen?’ ).
Not: I asked her when had it happened?
I asked her where [S] the bus station [V] was . (original question: ‘Where is the bus station?’ )
Not: I asked her where was the bus station?
The teacher asked them how [S] they [V] wanted to do the activity . (original question: ‘How do you want to do the activity?’ )
Not: The teacher asked them how did they want to do the activity?
Questions: wh- questions
Indirect speech: reporting commands
Indirect reports of commands consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a to -infinitive:
The General ordered the troops to advance . (original command: ‘Advance!’ )
The chairperson told him to sit down and to stop interrupting . (original command: ‘Sit down and stop interrupting!’ )
We also use a to -infinitive clause in indirect reports with other verbs that mean wanting or getting people to do something, for example, advise, encourage, warn :
They advised me to wait till the following day. (original statement: ‘You should wait till the following day.’ )
The guard warned us not to enter the area. (original statement: ‘You must not enter the area.’ )
Verbs followed by a to -infinitive
Indirect speech: present simple reporting verb
We can use the reporting verb in the present simple in indirect speech if the original words are still true or relevant at the time of reporting, or if the report is of something someone often says or repeats:
Sheila says they’re closing the motorway tomorrow for repairs.
Henry tells me he’s thinking of getting married next year.
Rupert says dogs shouldn’t be allowed on the beach. (Rupert probably often repeats this statement.)
Newspaper headlines
We often use the present simple in newspaper headlines. It makes the reported speech more dramatic:
JUDGE TELLS REPORTER TO LEAVE COURTROOM
PRIME MINISTER SAYS FAMILIES ARE TOP PRIORITY IN TAX REFORM
Present simple ( I work )
Reported speech
Reported speech: direct speech
Indirect speech: past continuous reporting verb
In indirect speech, we can use the past continuous form of the reporting verb (usually say or tell ). This happens mostly in conversation, when the speaker wants to focus on the content of the report, usually because it is interesting news or important information, or because it is a new topic in the conversation:
Rory was telling me the big cinema in James Street is going to close down. Is that true?
Alex was saying that book sales have gone up a lot this year thanks to the Internet.
‘Backshift’ refers to the changes we make to the original verbs in indirect speech because time has passed between the moment of speaking and the time of the report.
In these examples, the present ( am ) has become the past ( was ), the future ( will ) has become the future-in-the-past ( would ) and the past ( happened ) has become the past perfect ( had happened ). The tenses have ‘shifted’ or ‘moved back’ in time.
The past perfect does not shift back; it stays the same:
Modal verbs
Some, but not all, modal verbs ‘shift back’ in time and change in indirect speech.
We can use a perfect form with have + - ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past:
He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: ‘The noise might be the postman delivering letters.’ )
He said he would have helped us if we’d needed a volunteer. (original statement: ‘I’ll help you if you need a volunteer’ or ‘I’d help you if you needed a volunteer.’ )
Used to and ought to do not change in indirect speech:
She said she used to live in Oxford. (original statement: ‘I used to live in Oxford.’ )
The guard warned us that we ought to leave immediately. (original statement: ‘You ought to leave immediately.’ )
No backshift
We don’t need to change the tense in indirect speech if what a person said is still true or relevant or has not happened yet. This often happens when someone talks about the future, or when someone uses the present simple, present continuous or present perfect in their original words:
He told me his brother works for an Italian company. (It is still true that his brother works for an Italian company.)
She said she ’s getting married next year. (For the speakers, the time at the moment of speaking is ‘this year’.)
He said he ’s finished painting the door. (He probably said it just a short time ago.)
She promised she ’ll help us. (The promise applies to the future.)
Indirect speech: changes to pronouns
Changes to personal pronouns in indirect reports depend on whether the person reporting the speech and the person(s) who said the original words are the same or different.
Indirect speech: changes to adverbs and demonstratives
We often change demonstratives ( this, that ) and adverbs of time and place ( now, here, today , etc.) because indirect speech happens at a later time than the original speech, and perhaps in a different place.
Typical changes to demonstratives, adverbs and adverbial expressions
Indirect speech: typical errors.
The word order in indirect reports of wh- questions is the same as statement word order (subject + verb), not question word order:
She always asks me where [S] [V] I am going .
Not: She always asks me where am I going .
We don’t use a question mark when reporting wh- questions:
I asked him what he was doing.
Not: I asked him what he was doing?

Word of the Day
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
a type of singing in which four, usually male, voices in close combination perform popular romantic songs, especially from the 1920s and 1930s

Alike and analogous (Talking about similarities, Part 1)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Transform the following from direct to reported speech: The teacher said to me, "Do your homework." The teacher said to me to do my homework. The teacher said to me do your homework. The teacher told me to do your homework. The teacher told me to do my homework.
Indirect speech is used to report something in our own words. in case of order, the pattern for converting direct speech to reported speech is verb + indirect object + to-clause. the indirect object is the person spoken to. verbs in case of order can be command, order, warn. hence, option b is the correct answer..
Easy Insightful Literature Notes
Transformation of Sentence: Direct & Indirect Speech
A direct speech can be transformed into an indirect speech and vice versa using a suitable reporting verb and a linker depending on the sentence. Let’s have an example first.
- Tina said to me, “Are you busy now?” [direct speech]
- Tina asked me whether I was busy then. [indirect speech]
Direct Speech
Indirect Speech
- Look, if the reporting verb in direct speech (said) is in past tense, the reporting verb in indirect speech (asked) would also be in past tense. ‘Whether’ is the linker added here as it is a ‘yes-no’ type question (Refer to list 1 below).
- ‘Are’ changes to ‘was’. As the reporting verb was in past tense, the verb in the reported speech will also be in past. (Refer to list 2 below)
- ‘Now’ has become ‘then’. Time and place expressions change if the reporting verb is in past tense. (Refer to list 3 below)
- The question mark (?) has changed to a full stop(.).
- Another important thing, the format of question (v + s + o) has changed to the format of a statement (s + v + o). In indirect speech the pattern always comes to subject + verb + object.
List of Reporting verbs and linkers (list 1)
Verbs of Reported speech (if the reporting verb is in past tense) (list 2) Direct speech → Indirect speech Am / is / are → was / were Was / were → had been Has / have → had Had → had had Shall / will → would Can → could May → might Must, should → must, should Verb1 → verb2 Verb2 → had + verb3
Change of time and place expressions in past tense (list 3) now → then ago → before today → that day yesterday → the previous day tomorrow → the next day last night → the previous night here → there this → that these → those
Narration change of Assertive sentence
- Robin said, “I went to Delhi yesterday.” – Robin said that he had gone to Delhi the previous day .
- She said to her husband, “I want to go with you.” – She told her husband that she wanted to go with him.
Narration change of Interrogative sentence
- He said to me, “Do you know English?” – He asked me whether I knew English.
- She said to me, “Did you go there?” – She wanted to know whether I had gone there.
- I said to him, “What are you doing?” – I asked him what he was doing.
- Rahul said to his mother, “How do you do all these things together?” – Rahul asked his mother how she did all those things together.
Narration change of Imperative sentence
- He said to me, “Go there right now.” – He ordered me to go there right then.
- My teacher said to me, “Obey your parents.” – My teacher asked me to obey my parents.
- She said to me, “Please don’t go there.” – She requested me not to go there.
- He said to her, “Let’s go home.” – He suggested her that they should go home.
- His mother said, “Let him eat whatever he likes.” – His mother suggested that he might be allowed to eat whatever he liked.
Narration change of Optative sentence
- He said to the boy, “May god bless you.” – He prayed that God might bless the boy.
- The girl said, “Had I the wings of a dove.” – The girl wished that she had the wings of a dove.
Narration change of Exclamatory sentence
- “How happy we are here!” said the children. – The children exclaimed in joy that they were very happy there.
- The children said, “How happy we were there!” – The children exclaimed in sorrow that they had been very happy there.
- He said to me, “Good bye!” – He bade me good bye.
- She said to me, “Good evening!”—She wished me good evening.
Narration change of Vocatives
- Teacher said, “ Robin , stand up.” – Teacher asked Robin to stand up.
- The Bishop said to the convict, “Always remember, my son , that the poor body is the temple of the living God.” – The Bishop addressed the convict as his son and advised him to always remember that the poor body is the temple of the living God.
Narration change of question tag
- He said to me, “You went to Kolkata, didn’t you?” – He asked me whether I had gone to Kolkata and assumed that I had.
- I said to him, “Tina didn’t tell a lie, did she?” – I asked him if Tina had told a lie and assumed that she had not.
We serve cookies on this site to offer, protect and improve our services. KNOW MORE OK
Onlymyenglish.com
Learn English
Direct and Indirect Speech
Table of Contents
What is Speech (Narration):
If we want to describe the speech of some other people with other people in our own words, that speech is called a Reported speech or Narration.
Types of Speech
In the English language, there are certain ways to express the spoken words between two people.
The speech has two main types, Direct speech , and Indirect speech , respectively.
These two ways of narration of spoken words are also called Direct and Indirect speech, also known as Direct and Indirect narrations.
Direct and indirect speech is majorly used in any conversations, scripts, or any biographies, etc. where one or more than one person converses with each other.
Direct speech:
It is also called straight speech or quoted speech, which is spoken or written directly in the text by the speaker, writer, or the first person, who is going to speak with anyone with him.
The spoken statements of the speaker normally come under the inverted commas notation, and a speaker who speaks these sentences may come like “he said/he said that.”
The speaker’s words or statements are mentioned in a single phrase pattern or direct discussion.
Indirect speech:
An Indirect speech is also called a reported speech, or secondary speech means the speech, which has spoken indirectly.
It is simply an overlook statement that is used to say about the incident that has happened in the past time.
The actual words of the speaker changed into the past tense and the sentence, and hence the reported speech of the direct speech does not come inside the inverted commas.
Reporting speech:
A person who is going to report the speech or a speech that comes in the first part of the direct speech is called a reporting speech.
- He says , “He cooks food”.
Reported speech:
Reported speech is a speech that is always in an inverted comma or quotation marks.
It is a second part of the direct speech sentence.
- He says, “He cooks food.”
Reporting verb:
The verb, which is used in a reporting speech to report something in a direct speech, is called a reporting verb.
- Zoya said , “I want to go there.”
Reported verb:
The verb which comes inside the reported speech is called reported verb, respectively.
- Zoya said, “I want to go there.”
As we start writing any direct and indirect conversation, we often use reported verbs like “say, tell, ask, inform, instruct, claim, suggest, enquire, etc.”
These reported verbs, whenever used in direct or indirect speech, change into the past simple form like said, told, asked, informed, instructed, claimed, suggested, enquired, etc.
But the verbs used in a speech between the inverted commas will remain as it is.
Examples of direct and indirect speech:
- Indirect speech: John said that she was looking so beautiful.
- Indirect : He said that he was not a culprit.
- Indirect : He said that she was working on that project.
- Indirect : The teacher asked if he completed his homework.
- Indirect : She says that she is an artist.
- Indirect : Sam told me that he was not coming with me.
- Indirect : He says that she is working on that project.

Some basic rules for converting direct speech into indirect speech:
Rule 1 : “no inverted commas.”.
The reported speech does not come into inverted commas or quotation in an indirect speech.
Example: Direct: He said, “I have completed my assignments yesterday.”
Indirect: He said that he had completed his assignments the previous day.
Rule 2: use of “that” conjunction
Using the conjunction word “that” in-between the reporting speech and reported speech in an indirect speech.
Example:
- He said, “I have completed my assignment yesterday.”
- He said that he had completed his assignment the previous day.
Rule 3: Change of tense
While writing a direct speech into an indirect speech, we have to change the tense of the reported speech because whatever we are writing in indirect speech has already happened in the past timing.
- If the tense of a reporting speech of direct speech is in the present tense or future tense , then the tense of the reported speech in indirect speech will not change. It may be in the present tense, past tense, or future tense, respectively.
- Indirect : He says that he is going to school. (no change in tense)
- Indirect : She says that she will not come with me. (no change in tense)
- Indirect : He says that he wrote a letter. (no change in tense)
If the tense of the reporting verb of direct speech is in the past tense, then the tense will change according to these criteria.
For the present tense:
Simple present tense will change into simple past tense..
Direct: He said, “They come to meet me.”
Indirect: He said that they came to meet him.
Present continuous tense will change into past continuous tense.
Direct: She said, “They are coming to meet me.”
Indirect: She said that they were coming to meet her.
Present perfect tense will change into past perfect tense.
Direct: He said, “They have come to meet me.”
Indirect: He said that they had come to meet him.
Present perfect continuous tense will change into past perfect continuous tense.
Direct: She said, “They have been coming to meet me.”
Indirect: She said that they had been coming to meet her.
For the past tense:
Simple past tense will change into the past perfect tense.
Direct: He said, “They came to meet me.”
Indirect: He said that they had come to meet him.
Past continuous tense will change into past perfect continuous tense.
Direct: She said, “They were coming to meet me.”
Indirect: She said that they had been coming to meet her.
Past perfect tense and past perfect continuous tense will remain the same.
Direct: He said, “They had come to meet me.”
Direct: She said, “They had been coming to meet me.”
For the future tense:
There are no changes in the future tense sentences; only shall/will may change into would, can change into could.
- Direct: She said, “Can you come tomorrow.”
Indirect: She said that could he come on the next day
- Direct: He said, “I will never forgive you.”
Indirect: He said that he would never forgive me.
Rule 4: Changing the pronoun
The pronoun used as an indirect subject speech sometimes needs to be changed accordingly in indirect speech as of the reported verb of the direct speech.
- The pronoun used for representing the first person in reported speech changes based on the subject of the reporting speech in a direct speech.
- The pronoun used for representing the second person in reported speech changes based on the report’s object in a direct speech.
- The pronoun used for representing the third person remains the same in the reported speech.
- Direct: He said, “ I am going to school.”
- Indirect: He said that he is going to school.
- Direct: She says, “ I will not come with you .”
- Indirect: She says that she will not come with me .
- Direct: They said, “ we are eating our tiffin box.”
- Indirect: They said that they were eating their tiffin box.
Rule 5: Changing the time
The mentioned time (not the timing) in a direct speech sentence will have to change in indirect speech like now becomes then, tomorrow becomes the next day, yesterday becomes the previous day, today becomes that day, later becomes soon.
- Direct: He told, “He is coming from Tokyo today .”
- Indirect: He told me that he was coming from Tokyo that day .
- Direct: She asked, “Will the parcel reach by tomorrow or not?”
- Indirect: She asked whether the parcel will reach by the next day or not.
- Direct: “The teacher has given some assignments yesterday ”, he reminds me.
- Indirect: He reminds me that the teacher had given some assignments on the previous day.
Conversion of statements from direct speech into Indirect speech:
Assertive sentences:.
Assertive sentences are simple statements that may be affirmative or negative.
If we are going to convert assertive sentences from direct speech into indirect speech, we have to replace “said” with “told” sometimes.
Here, the subject in direct speech refers to someone in his talk.
- Direct: He said to me, “she is working on this project.”
Indirect: He told me that she was working on that project.
- Direct: She said to me, “I’m going for a long drive.”
Indirect: She told me that she was going for a long drive.
Imperative sentences:
Imperative sentences are statements that deliver a command, order, request, appeal, or advice.
It depends on the speaker, how he delivers the message to the other person.
- Sit properly!
- Stand by my side!
- Come closer!
While converting these types of sentences cum statements from direct speech to indirect speech, we have to check the type of sentence, whether it is a command, order, request, or else.
- Direct: The teacher said to me, “Sit properly!”
Indirect: The teacher ordered me to sit properly.
- Direct: The Boss said to an office boy, “Bring one coffee for me.”
Indirect: The Boss commanded an office boy to bring a coffee for him.
Indirect: The teacher requested me to sit properly.
- Direct: The bartender said to me, “try this drink.”
Indirect: The bartender advised me to try that drink.
Interrogative sentences:
An interrogative sentence is a sentence which interrogates or ask questions.
Each interrogative sentence ends with an interrogative sign or a question mark sign “?”.
- What is your name?
- Can you do me a favor?
- Why are you laughing in the classroom?
While writing interrogative sentences from direct speech into indirect speech,
- the reporting verb “said” in the direct speech is changed into “asked” in the indirect speech because it asks the question to another person.
- If any reporting verb comes first in the reporting speech, then “If” is used despite “that.”
- In a reporting speech, if any wh-type question words are present, then no other words will be used, and the sentence ends with a full stop sign instead of a question mark.
- Indirect: He asked me what was my name.
- Indirect: She asked if he could do her a favor.
- Indirect: The teacher asked him why he was laughing in the classroom.
Exclamatory sentences:
Exclamatory sentences are those sentences that show emotions, feelings and ends with an exclamation mark!
- Congratulations! You have a baby girl.
- I am extremely sorry for your loss!
- Most welcome!
If any interjection comes in an exclamation sentence, then the exclamation sign removes in an indirect speech, and an exclamatory sentence gets converted into an assertive sentence.
The replacement of reporting verb “said” with exclaimed with (great wonder, sorrow, joy) exclaimed (joyfully, sorrowfully)
Replace with very or very great , if words like how or what comes at the beginning of the reported speech.
- Indirect: He exclaimed with joy that I had a baby girl.
- Indirect: She exclaimed with sorrow that she felt sorry for my loss.
- Indirect: They exclaimed with joy that most welcome.
You might also like

Phrase: Definition & Types

Use of ‘Will and Shall’

Future Continuous Tense: Definition, Examples, Formula & Rules

Using of Not only…But also Rules and Examples

Present Perfect Tense: Definition, Examples, Formula & Rules

Past Simple Tense: Definition, Examples, Rules & Formula

- Elementary School
- Reading & Speaking
- External Independent Testing
- Grammar Exercises
Reported Speech


Grammar Time: Reported Speech. Exercises
When we want to report what someone said, we use indirect or reported speech. Revise the rule and have practice doing these exercises.
Exam in Mind Level B1
Task 1. change the direct speech into reported speech. choose the past simple of ‘ask’, ‘say’ or ‘tell’:.
- “Don’t do it!” – She asked not to do it.
- “I’m leaving tomorrow.”
- “Please get me a cup of tea.”
- “She got married last year”.
- “Be quick!”
- “Could you explain number four, please?”
- “Where do you live?”
- “We went to the cinema and then to a Chinese restaurant.”
- “I’ll come and help you at twelve.”
- “What are you doing tomorrow?”
- “Don’t go!”
- “Do you work in London?”
- “Could you tell me where the post office is?”
- “Come here!”
- “I’ve never been to Wales.”
- “Have you ever seen ‘Lord of the Rings’?”
- “I don’t like mushrooms.”
- “Don’t be silly!”
- “Would you mind waiting a moment please?”
- “How often do you play sport?”
- Sarah complained, “My head is aching.”
- I wanted to know, “Where are you going?”
- Uncle David said, “Please take off your shoes when you come in.”
- Mom asked me, “Are you feeling well?”
- The teacher said, “Turn the music down!”
- Jasper said, “You can borrow the book for a few days.”
- Johnny admitted, “I haven’t brushed my teeth yet.”
- The policeman ordered, “Move your car out of the way!” – The policeman ordered us …
- Mary said, “I have just got back from New York.”
- John explained, “I am starting work for a new company next week.
- The teacher said, “Sardinia is an island that belongs to Italy.”
- He asked me, “Can you come to the meeting tomorrow?”
- The manager said to Cathy, “Please stand up!”
- Jerry asked me,”Did you see that car over there?”
- Mr Jackson said, “I wouldn’t go there if I were you.”
Task 2. Change the sentences to reported speech.
- He said, ” I found the money in the garden yesterday.”
- The policeman asked me , “What were you wearing last Sunday”?
- The teacher explained to us, “The moon takes 28 days to go around the earth.”
- Dad warned us , “Don’t touch the fresh paint!”
- He wanted to know, “Will you go to the concert next week?”
- Mary begged the teacher, “Please, give me another chance!”
- Mother asked me, “Did he lend you the money?”
- I was wondering, “Why does the earth move around the sun?”
- She said, “I’m sorry but I have to go now.”
- My mum complained, “I have been trying to phone you all day!”
- My friend told me , “I’ll have to go to the party without you.”
- Dad asked me , “Where have you been so long ?”
- Jane said , “I want to tell you about my trip to New York.”
- He asked us ,” Don’t make so much noise!”
- Robert said, ” You can stay at my place over the weekend.”
- Keith told the immigration officer, “This is my first visit to the United States.”
- My friend said, “I’m going to visit my parents next month.”
- The tourist guide warned us, “Don’t drink tap water in this city.”
- He asked me, “Are you starting work on Monday?”
- Elisabeth to her brother: “Don’t read my emails!”
- Jimmy complained, “I have already written this invitation twice.”
- The policeman wondered, “Why didn’t you stop at the traffic lights?”
- My sister told me, “I saw you at the supermarket yesterday.”
- The teacher said, “If I knew the answer, I would tell you.”
- My dad said, “You have to study harder for the next test.”
- The girl asked the shop assistant, “Can you shorten this dress for me?”
- He asked, “Do you live near the city, James?”
- The reporter asked, “Did you see the accident?”
- I advised Mike, “You should see a doctor”.
- The teacher told the students, “Speak up if you want to say something!”
Task 3. Change the sentences to reported speech.
- Mary said, “I will play a card game tomorrow.” – Mary informed me that …
- Sophie said, “I went to bed early last night.”
- The teacher said to Jenny, “You have to learn your grammar.”
- Jessica told the immigration officer,”This is my first trip to England.”
- He told me, “You are the most beautiful girl I have ever seen.”
- Marty said, “I’m going to visit my uncle next month.”
- Lara said, “I get on with my parents really fine.”
- Gloria explained, “I can’t come to the party because I’m going away for the weekend.”
- Mark said, “My friend found a new job in the music business.”
- Judy complained, “I have already written this essay four times.”
- Peter announced, “I will not give up until this factory is shut down.”
- Her boyfriend told her,” You have bought a wonderful dress.”
- Paul said, “I don’t like my new flat.”
- My father told Ben, “I am sure I saw you here last week.
- Betty said, “If I knew the answer, I would tell you the answer.”
- The landlady said to the student, “You must keep your room clean!”
- Mr Simmons told Harry, “Don’t smoke in my car!”
- He asked me, “Do you want to be famous?”
- My dad said, “Our aunt will stay for breakfast.”
- Sally said, “I can’t believe he is leaving me like this.”
- He wondered, “Where did Maud work?”
- Mom said, “I need to be at work early this morning.”
- Maria said, “Angela had worked at this company before I came here.”
- The woman complained,” The clock I bought yesterday doesn’t work.”
- He asked, “Were you followed by the police?”
- The chef advised us, “Cook the meat carefully.”
- He promised, “I’ll return the book tomorrow.”
- The teacher reminded us, “Don’t forget your homework”.
- Patricia said, “My mother will celebrate her birthday next week.”
- He warned me, “Don’t shout at me like that!”
Task 4. Change the sentences to reported speech.
- He said, “I will be there by noon.”
- The twins said, “We are five years old.”
- Mum said, “You will have to get up early for the trip tomorrow.”
- The teacher told her, “You speak English very well.”
- The doctor said, “Your mother will recover quickly.”
- My aunt said, “I am leaving early on Friday morning.”
- The boy said, “I have been to Australia before.”
- Herbert said, “We are going to live in Manchester.”
- Jennifer said, “I have already read that book.”
- Jim said, “I hope it won’t rain tomorrow.”
- My mum said,” You can go shopping later.”
- He said to me, “Where have you been?”
- My dad said, “Go to your room at once.” – My dad ordered me …
- Jimmy said, “I own a brand-new sports car.”
- John said, “I am writing a new novel”.
- My mother said, “Close you eye and open your hands.”
- I said to the host, “Can I have another piece of cake?”
- The teacher wondered, “Will she be safe if she goes alone?”
- She told me, “He has never written to me before.” – She explained that …
- The shop assistant asked me, “What size are your shoes?” – The shop assistant wanted to know …
- The administrator warned us, “Don’t walk on the grass”.
- My friend said to me, “Go to the doctor.” – My friend advised me …
Task 5. Change the sentences to reported speech.
- The hotel manager said, “Dinner is served between 7 and 9.
- My little brother said, “I didn’t steal the money.”
- Martha said, “Let’s go to the movies.” – Martha suggested …
- The headmaster said, “All students are taking part in the project.”
- Jamie said, “I’ll never forget your birthday again.”
- He asked me, “Can I take a photo?” – He wondered if …
- Joanne asked me, “Where did you buy that dress?”
- I wanted to know, “Where is the IT department?”
- Denny asked me, “When are you leaving?”
- Linda asked her teacher, “When will you give us the results?”
- Mom asked her, “How often do you look at your phone?” – Mom wanted to know …
- Ashley asked me, “Who are you going to the ball with?”
- He asked me, “How many people have you invited to the party?” – He wanted to know …
- John asked him, “Where should we put the new equipment?”
- I asked Dad, “Are you going to the U.S.?” – I wanted to know …
- Mom wanted to know, “When will you start behaving?”
- The stranger asked me, “Do you speak Chinese?”
- Mary wanted to know, ” What have you done with your hair?”
- I asked the teacher, “Can I go to the restroom?”
- Andy wanted to know, “Did your mom make the wedding dress?”
- Tessa asked me, “Have you ever driven a motor scooter?”
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Related posts.

Inversion after Negative Adverbials

Many Much A Lot Of

Quantifiers

Wishes and Regrets

despite and in spite of

Going to and Present Continuous

Must and Have to

Do and Make

Infinitive or -ing Form

Phrasal Verbs Part 2
Leave a comment cancel reply.
- Grammar Tests
- Grammar Exercisers
English Study Here
100 examples of direct and indirect speech.
100 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech in English, 100 Examples of reported speech in english;
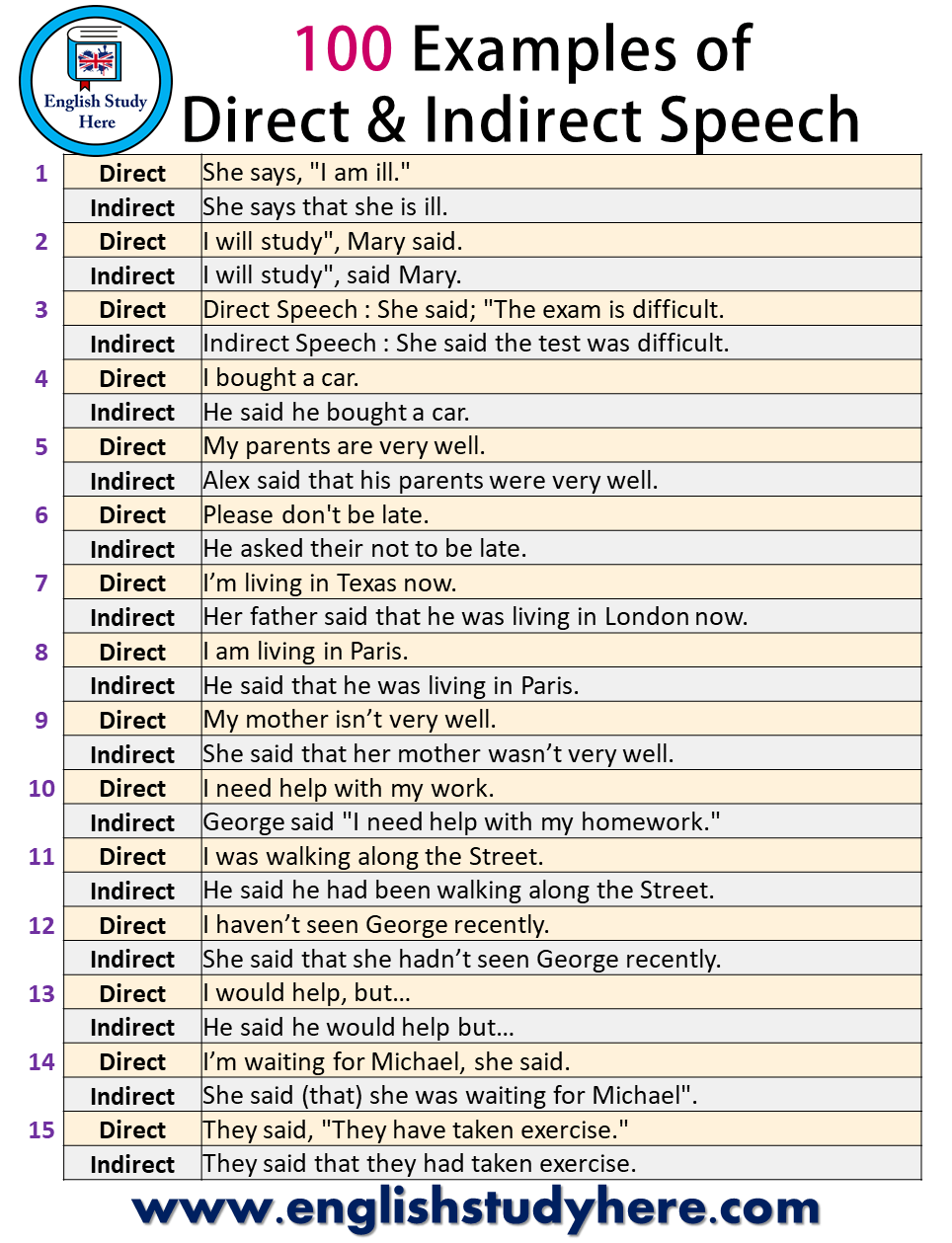
Related Posts

Present Perfect Continuous Tense in English

20 Examples of Prefixes

100 Abstract Nouns in English
About the author.
- B1-B2 grammar
Reported speech: questions

Do you know how to report a question that somebody asked? Test what you know with interactive exercises and read the explanation to help you.
Look at these examples to see how we can tell someone what another person asked.
direct speech: 'Do you work from home?' he said. indirect speech: He asked me if I worked from home. direct speech: 'Who did you see?' she asked. indirect speech: She asked me who I'd seen. direct speech: 'Could you write that down for me?' she asked. indirect speech: She asked me to write it down.
Try this exercise to test your grammar.
Grammar B1-B2: Reported speech 2: 1
Read the explanation to learn more.
Grammar explanation
A reported question is when we tell someone what another person asked. To do this, we can use direct speech or indirect speech.
direct speech: 'Do you like working in sales?' he asked. indirect speech: He asked me if I liked working in sales.
In indirect speech, we change the question structure (e.g. Do you like ) to a statement structure (e.g. I like ).
We also often make changes to the tenses and other words in the same way as for reported statements (e.g. have done → had done , today → that day ). You can learn about these changes on the Reported speech 1 – statements page.
Yes / no questions
In yes / no questions, we use if or whether to report the question. If is more common.
'Are you going to the Helsinki conference?' He asked me if I was going to the Helsinki conference. 'Have you finished the project yet?' She asked us whether we'd finished the project yet.
Questions with a question word
In what , where , why , who , when or how questions, we use the question word to report the question.
'What time does the train leave?' He asked me what time the train left. 'Where did he go?' She asked where he went.
Reporting verbs
The most common reporting verb for questions is ask , but we can also use verbs like enquire , want to know or wonder .
'Did you bring your passports?' She wanted to know if they'd brought their passports. 'When could you get this done by?' He wondered when we could get it done by.
Offers, requests and suggestions
If the question is making an offer, request or suggestion, we can use a specific verb pattern instead, for example offer + infinitive, ask + infinitive or suggest + ing.
'Would you like me to help you?' He offered to help me. 'Can you hold this for me, please?' She asked me to hold it. 'Why don't we check with Joel?' She suggested checking with Joel.
Do this exercise to test your grammar again.
Grammar B1-B2: Reported speech 2: 2
Language level
Hello, dear teachers and team!
Could you please help me with the following:
- She asked me "Does the Earth turn around the Sun?"
Does it have to be: "She asked me if the Earth TURNED around the Sun" ?
Do we have to change the question into the past form here as well?
2. She asked: "Was coffee originally green"?
Is "She asked me if the coffee HAD BEEN originally green" correct option? Can I leave WAS in an inderect speech here?
3. Is "She asked me if I knew if the Sun IS a star" or "She asked me if I knew if the Sun WAS / HAD BEEN a star" (if any) correct?
I'm very very grateful for your precious help and thank you very much for your answering this post in advance!!!
- Log in or register to post comments
Hello howtosay_.
1. She asked me "Does the Earth turn around the Sun?" Does it have to be: "She asked me if the Earth TURNED around the Sun" ?
No, you can use the present here as well. The verb for this context would be 'go' rather than 'turn':
She asked me if the earth goes around the sun.
She asked me if the earth went around the sun.
Do we have to change the question into the past form here as well? 2. She asked: "Was coffee originally green"? Is "She asked me if the coffee HAD BEEN originally green" correct option? Can I leave WAS in an inderect speech here?
You can use either 'had been' or 'was' here. The adverb 'originally' removes any ambiguity.
3. Is "She asked me if I knew if the Sun IS a star" or "She asked me if I knew if the Sun WAS / HAD BEEN a star" (if any) correct?
You can use 'is' or 'was' here but not 'had been' as that would suggest the sun is not a star any more.
The LearnEnglish Team
She offered me to encourage studying English. She asked us if we could give her a hand.
He said, "I wished she had gone."
How to change this sentence into indirect speech?
Hello bhutuljee,
'He said that he wished she had gone.'
Best wishes, Kirk LearnEnglish team
He said, "I wish she went."
How to change the above sentence into indirect speech?
Hi bhutuljee,
It would be: "He said that he wished she had gone."
LearnEnglish team
He said , "She wished John would succeed."
This is the third sentence you've asked us to transform in this way. While we try to offer as much help as we can, we are not a service for giving answers to questions which may be from tests or homework so we do limit these kinds of answers. Perhaps having read the information on the page above you can try to transform the sentence yourself and we will tell you if you have done it correctly or not.
Hi, I hope my comment finds you well and fine. 1- reported question of "where did he go?"
Isn't it: She asked where he had gone?
https://learnenglish.britishcouncil.org/grammar/b1-b2-grammar/reported-…
2- how can I report poilte questions with( can I, May I) For example: She asked me" Can I borrow some money?"
Your reply will be highly appreciated.
Online courses

Group and one-to-one classes with expert teachers.

Learn English in your own time, at your own pace.

One-to-one sessions focused on a personal plan.

Get the score you need with private and group classes.

- TENSES REVIEW
- FESTIVITIES
- READING IS FUN-TASTIC
- TV SERIES TO LEARN ENGLISH
Let’s practise the other introductory verbs. The verbs are given. Rewrite the following commands / requests / suggestions into reported speech in the past.
1) “Let’s go to the disco.” Tom – suggest
2) “Give me roasted meat with rice.” Mr Knight – order – the waiter
3) “Come on, Danny, write down your novel.” Angie - encourage
4) “Don’t meet these criminals, please!” Mum – beg - Allan
5) “Give me the salt, please” Brad - ask - Patrick
6) “Don’t touch this wire!” The electrician – warn – the children
7) “Remember to put the soup into the fridge.” Dad – remind - mum
8) “Take the second street on the right.” The officer – advise – the tourist
9) “Punish the wrong behaviour in the class.” Mr Hart - agree
10) “Tidy your room.” Mrs Taylor - tell – Susan
1) “Have your eyes tested.” The teacher to Liam
2) “Draw up the car immediately.” Captain Kingsley to the corporal
3) “Don’t let him do this crazy trick, please.” Don to Jim
4) “Hold my umbrella for a moment, please.” Mrs Marks to Mr Farley
5) “Give an award to the best student.” Mrs Simons
6) “Take the children to the museum.” Dad to mum
7) “Come on, girls, let’s show our courage.” The teacher
8) “Don’t sit on that fresh painted bench.” The park-keeper to Julian
9) “Don’t forget to post the letter to grandma.” Trina to Kevin
10) “Find a better place to play.” Mr Glum to the children
Use the following reporting verbs to report the following sentences:
advised, claimed, promised, refused, suggested
"I won't tell you where I've hidden it"
"Why don´t you go to Greece? It's beautiful"
"I won't lose it, I will bring it back tomorrow"
"It wasn't me. It was Pete!"
"You should report it to the police"
Told Said Advised Warned Suggested Asked Offered Ordered
1. "I'd go and see a doctor if I were you," Julie said to me. Julie me to go and see a doctor.
2. "Can you come and help me with this box?" John me to help him with the box.
3. "This is an exam Mr. Jenkins!! Shut up now!!!" The headmaster Mr. Jenkins to shut up.
4. "That road is very dangerous so just be very careful!" His mother him that the road was very dangerous and to be careful.
5. "Liverpool won the match last night." The journalist that Liverpool had won the match the previous night.
6. "Why don't we go and see that new film at the cinema." Bill going to see the new film at the cinema.
7. "I can come and look after the children tomorrow night." Jane to come and look after the children the following day.
8. "The lesson starts at six o'clock in the evening." The teacher us that the lesson started at six in the evening.

Reported speech answers
- PRESENT SIMPLE
- PRESENT PERFECT
- PERFECT TENSES
- REPORTED SPEECH
- PASSIVE VOICE
- REWRITING INTENSIFIERS
- MODAL VERBS
- ESO 3 DIVERSIFICACIÓN
- WEB ACTIVITIES
hola a todos
Esta página web ha sido creada con Jimdo. ¡Regístrate ahora gratis en https://es.jimdo.com !
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students

Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for Class 7 CBSE With Answers
When we use the exact words of the speaker, it is called direct speech. Indirect or Reported Speech refers to a sentence reporting what someone has said.
Basic English Grammar rules can be tricky. In this article, we’ll get you started with the basics of sentence structure, punctuation, parts of speech, and more.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for Class 7 CBSE With Answers PDF
When the exact words of the speaker are quoted, it is called direct speech. When the meaning of the words is reported without using the exact words, it is called indirect speech.
- Cam said, “The monster is coming.” (direct speech)
- Cam said that the monster was coming. (indirect speech)
Changing Tenses
When the reporting verb is in the past tense, we change tense as given below. The tense does not change in case of past perfect or past perfect continuous.
Exceptions 1. When the reporting verb is in the present tense or future time, the tenses in the reported verb remain unchanged. Example:
- Alam says, “I am feeling better.”
- Alam says that he is feeling better.
2. When reporting a universal truth or a moral principle or a natural fact, we may or may not change the present tense in the reported speech. Example:
- Deepti said, “The Pacific Ocean is the largest ocean in the world.”
- Deepti said that the Pacific Ocean is the largest ocean in the world.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises Solved Example With Answers for Class 7 CBSE
A. Complete the following reported speeches by filling in the blanks.
Question 1. Mary said, “Dipanwita is learning to play the piano.” Mary said that Dipanwita …………………………… (is learning/was learning) to play the piano. Answer: Mary said that Dipanwita was learning to play the piano.

Question 2. Kaustav said, “The next World Cup will take place in Russia.” Kaustav said …………………………… (that/which) the next World Cup …………………………… (will/would) take place in Russia. Answer: Kaustav said that the next World Cup would take place in Russia.

Question 3. Ms Paul said, “We should reduce our usage of oil and petrol.” Ms Paul said that we …………………………… (should reduce/had reduced) our usage of oil and petrol. Answer: Ms Paul said that we should reduce our usage of oil and petrol.
Question 4. The volunteer said, “The relief work in the flood-affected areas is going well.” The volunteer said that the relief work in the flood-affected areas …………………………… (had gone/was going) well. Answer: The volunteer said that the relief work in the flood-affected areas was going well.
Question 5. The newspapers report read, “There has been too much rain this year.” The newspapers …………………………… (report/reported) that there …………………………… (has been had been) too much rain this year. Answer: The newspapers reported that there had been too much rain this year.
Changing Pronouns And Possessive Adjectives
Changing Time And Place Words
Place, demonstrations, and time expressions:-Place, demonstrations, and time expressions change if the context of the reported statement (i.e. the location and/ or the period of time) is different from that of the direct speech.
In the following table, you will find the different changes of place, demonstrations, and time expressions.
B. Change these sentences to reported speech.
Question 1. Sharif said, “The books are here on this table.” Answer: Sharif said that the books were there on that table.
Question 2. Neelam said, “I am at the station now.” Answer: Neelam said that she was at the station then.
Question 3. Pragya said, “I bought these pens from the shop there.” Answer: Pragya said that she had bought those pens from the shop there.
Question 4. Her friends said, “We are going to the concert tonight.” Answer: Her friends said that they were going to the concert that night.
Question 5. I said, “Satya completed his graduation last year. This year, he will travel. Answer: I said that Satya had completed his graduation the previous year. That year, he would travel.
Reporting Questions
C. Kyle, a student from the Philippines, has enrolled in Shivani’s class. Shivani asks him the following questions. Report these questions.
Question 1. When did you and your parents move to India? Answer: Shivani asked Kyle when did he and his parents move to India.
Question 2. How long will you stay? Answer: She asked him how long would he stay.
Question 3. Are you enjoying your stay here? Answer: She also asked him if he was enjoying his stay there.
Question 4. Have you faced any difficulties while adjusting at school? Answer: Then, she asked him is he had faced any difficulties while adjusting at school.
Question 5. Do you miss your friends from the Philippines? Answer: At the end, whe asked him if he missed his friends from Philippines.
Reporting Requests And Commands
While reporting requests or commands, instructions or pieces of advice, we use the reporting verb which matches the meaning of the direct sentence, and the verb in the original direct speech is changed to its infinitive form. Example:
- Farzana asked, “Could you look after my dog when I am away?”
- Farzana requested me to look after her dog while she was away.
Reporting Wishes Or Exclamations
Those sentences, which express our feelings and emotions, are called exclamatory sentences. Mark of exclamation is used at the end of an exclamatory sentence.
For Examples:
- Hurray! We have won the match.
- Alas! He failed in the test.
- How beautiful that dog is!
- What a marvelous personality you are!
To change exclamatory sentences into Indirect Speech, follow the rules given below along with the above–mentioned rules: In case, there is an interjection i.e., alas, aha, hurray, aha, etc in the Reported Speech, then they are omitted along with a sign of exclamation. Reporting verb i.e. said is always replaced with exclaimed with joy, exclaimed with sorrow, exclaimed joyfully, exclaimed sorrowfully, or exclaimed with great wonder or sorrow.
D. Rewrite the following sentences in reported speech.
Question 1. Lalita said, “Wow! I have won the first prize!” Lalita exclaimed ……………………………………………………………………………… Answer: Lalita exclaimed that he had won the first prize.
Question 2. Hansa said to Kavya, “Happy journey!” Hansa wished Kavya. ……………………………………………………………………………… Answer: Hansa wished Kavya a happy journey.
Question 3. Dina said to me, “I solved the puzzle!” Dina exclaimed that ……………………………………………………………………………… Answer: Dina ‘exclaimed that she had solved the puzzle.
Question 4. My father (to me): May you have a successful career! My father wished me ……………………………………………………………………………… Answer: My father wished me a successful career.
Question 5. Child (to Mummy): Good night! The child wished his mother ……………………………………………………………………………… Answer: The child wished his mother a good night.
Question 6. Lalit said to Hansita, “Wish you a speedy recovery from illness!” Lalit wished Hansita ……………………………………………………………………………… Answer: Lalit wished Hansita a speedy recovery from illness.
Question 7. Ms. Quader said to the class, “Good luck for your exams!” Ms. Quader wished the class ……………………………………………………………………………… Answer: Ms. Quader wished the class good luck for their exams.
E. Change the following from indirect speech to direct speech.
Question 1. The gardener warned us to look out as there was a snake in the garden. The gardener said ……………………………………………………………………………… Answer: The gardener said, “Lookout! There is a snake in the garden.”
Question 2. My mother wished me a happy birthday. My mother said to me ……………………………………………………………………………… Answer: My mother said to me, “Happy birthday.”
Question 3. Kala exclaimed that she was very sorry for her mistake. Kala said to me ……………………………………………………………………………… Answer: Kala said to me, “I am sorry for my mistake.”
Question 4. Sugata cried out in pain that a thorn had pricked him. Sugata said ……………………………………………………………………………… Answer: Sugata said, “A thorn has pricked me!”
Question 5. Jatin wished me a lovely day. Jatin said to me ……………………………………………………………………………… Answer: Jatin said to me, “Have a lovely day.”
Converting Statements From Indirect Into Direct Speech
While changing indirect speech into direct speech, we use the reporting verb say or said. We make necessary changes to the tenses, personal pronouns and adjectives, and time and place words. We add inverted commas to the words spoken by the speaker. Examples:
- Meha said that she was in the library.
- Meha said, “I am in the library.”
- Amit told Rohan that the trip had been canceled.
- Amit said to Rohan, “The trip has/was/had been canceled.”
F. Fill in the missing words in the direct speech.
Question 1. Harry asked me if I had read that book. Harry ……………………………….. me, “Have you read this book?”. Answer: Harry asked me, “Have you read this book?”
Question 2. Soumya asked Tripti if she liked eggs. Soumya asked Tripti, “Do. ……………………………….. like eggs?” Answer: Soumya asked Tripti, “Do you like eggs?”
Question 3. Kinu asked Thimpu who would teach him English. Kinu asked Thimpu, “Who will teach ……………………………….. English?” Answer: Kinu asked Thimpu, “Who will teach me English?”!
Question 4. Charu asked why the laptop was not working. Charu asked, “Why ……………………………….. the laptop not working?” Answer: Charu asked, “Why is the laptop not working?”
Question 5. Sam asked who had let the dogs out. Sam asked, ……………………………….. the dogs out?” Answer: Sam asked, “Who let the dogs out?”

100+Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises and Answers

Improve your knowledge of Direct and Indirect Speech with our comprehensive set of Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises and Answers . Practice converting quotes to reported speech, understand the rules and techniques involved, and master the difference between direct and indirect speech. Sharpen your language skills and get a better grasp of the English language with our direct and indirect Speech exercises and answers.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises and answers are given in the following for practice. It’s important for students as well as for competitive Exams. For practice and easy comprehension, Direct and indirect speech Exercises and answers have been arranged according to different rules in the following.
With these Direct and indirect speech exercises with answers , the students will make themselves able to change Direct speech into indirect speech and indirect speech into direct speech with a Change of tenses, change of pronouns, and change of time and place words in different sentences .
Exercises on How to Change Tenses with Answers
Change the mode of narration from direct Speech to indirect speech .
(1) He said to me, “I can’t recall your name.” Ans: He told me that he could not recall my name.
(2) Poulami says, “I am fine.” Ans: Poulomi says that she is fine.
(3) He said, “I did it.” Ans: He said that he had done it.
(4) “I know her address,” said Gopi. Ans: Gopi said that he knew her address.
(5) Ram said, “The earth is round.” Ans: Ram said that the Earth is round.
(6) “We planted it ourselves,” said the grandfather. Ans: The Gran Father said that they had planted it themselves.
(7) Debu said, “I have been playing rugby.” Ans: Debu said that he had been playing rugby.
(8) Purbasha said to me,” I am afraid of ghosts.” Ans: Purbasha told me that she was afraid of ghosts.
People also like
Change the following mode of narration from direct Speech to indirect speech .
(1) The boys said, “It has been raining since morning. We cannot play today.” Ans: The boys said that it had been raining since morning so they could not play that day.
(2) Anjan’s mother said, “Your father has left for Mumbai.” Ans: Anjan’s mother said that my father had left for Mumbai.
(3) My teacher said, “Practice makes a man perfect.” Ans: My teacher said that practice makes a man perfect.
(4) He says, “I go to the temple every morning.” Ans: He says that he goes to the temple every morning.
(5) He said to me, “I will not get down from the bus.” Ans: He told me that he would not get off the bus.
(6) Rita says to Mita, “I will go with you.” Ans: Rita tells Mita that she will go with her.
(7) The boy said to his friend, “I went to school yesterday.” Ans: The boy told his friend that he had gone to school the previous day.
(8) You said, “I was right.” Ans: You said that you had been right.
(9) “I ‘ll go to the top,” said the young lady. Ans: The young lady said that she would go to the top.
(10) I ‘ve got my rules,” the conductor said to me. Ans: The conductor told me that he had got his rules.
Change of Pronouns Exercises and Answers
(1) He said to me, “ I have done the job.” Ans: He told me that he had done the job.
(2) Rohit said, “ I was absent yesterday.” Ans: Rohit said that he had been absent the previous day.
(3) The boy said, “ My father died two years ago.” Ans: The boy said that his father had died two years before.
(4) He said, “ My goal is to climb Mt Everest. “ Ans: He said that his goal was to climb Mount Everest.
(5) “ I shall certainly do nothing of this kind”, the woman. Ans: The woman said that she would certainly do nothing of that kind.
(6) The man said, “ I am exhausted.” Ans: The man said that he was exhausted.
(7) He said, “ I am washing my hands.” Ans: He said that he was washing his hands.
(8) Mother bird said to her little ones, “Today I will teach you how to fly.” Ans: Mother bird told her little ones that that day, she would teach them how to fly.
(9) Rita’s father says. “ I have done this for you. Ans: Rita’s father says that he had done that for her.
(10) Sumana said to her sister, “ I want to play with you.” Ans: Sumana told her sister that she wanted to play with her.
Change of Time & place for Direct Indirect Speech
Change the following sentences into indirect speech.
(1) The boy said to his father, “I had my tiffin in school yesterday. “ Ans: The boy told his father that he had had his tiffin in school the previous day .
(2) The captain informed, “The tournament was postponed last year. “ Ans: The captain informed us that the tournament was postponed the previous year .
(3) She said, “We have been living here for two years.” Ans: She said that they had been living there for two years.
(4) Arnab said to Ajit,” I am happy today .” Ans: Arna told Ajit that he was happy that day.
(5) My friend said to me, “We went to the zoo yesterday. “ Ans: My friend told me that they had gone to the zoo the previous day.
(6) The clerk said, “I’ll do the work now. “ Ans: Clark said that he would do the work then.
(7) Hiten said to Mihir, “I received this letter yesterday. “ Ans: Hiten told me that he had received that letter the previous day.
(8) Rajib said to me. “I shall go to the picture today. “ Ans: Rajiv told me that he would go to the picture that day.
(9) He said, “We are very happy here. “ Ans: He said that they were very happy there.
(10) The farmer said, “I’ll sow the seeds now. “ Ans: The farmer said that he will show the seats then.
(12) The man said to me, “I received your gift yesterday. “ Ans: The man told me that he had received my gift the previous day.
(15) I said to my friend, “You were present in the class yesterday. “ Ans: I told my friend that he had been present in the class the previous day.
Assertive Sentences Exercises with Answers
Change the following sentences converting the direct speeches into indirect speeches.
(1) The teacher said to the boy, “You have forgotten the lesson.” Ans: The teacher told the boy that he had forgotten the lesson.
(2) The boy said, “I shall go out and play.” Ans: The boy said that he would go out and play.
(3) He said, “I am happy to be here today.” Ans: He said that he was happy to be there that day.
(4) They said, “We shall play the game again tomorrow.” Ans: They said that they would play the game again the next day.
(5) The boy said, “Two and two make four.” Ans: The boy said that two and two make four.
Change the form of narration from indirect speech into direct speech.
(1) She told them that she had lost her books and theirs too. Ans : “I have lost my books and yours too”, she told them.
(2) The princess says that she has lost her way. Ans: The princess says, “I have lost my way.”
(3) They say that they must keep their locality clean. Ans: They say, “We must keep our locality clean.”
(4) The girl says that those books are theirs, but that one is hers. Ans: The girl says, “These books are theirs, but this one is mine.”
(5) The Happy prince said that he had led the dance in the Great Hall. Ans: The Happy Prince said, “I led the dance in the great hall.”
Interrogative Sentences Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises
Turn the following sentences from direct speech to indirect speech.
(1) Bulbuli said to her friend, “Will you come tomorrow?” Ans: Bulbuli asked her friend if she would on the next day.
(2) The policeman said to the stranger, “What are you looking for?” Ans: The police asked the stranger what he was looking for.
(3) Nikhil said to me, “Why do you look sad? Ans: Nikhil asked me why I looked sad.
(4) I said to her, “Did you take tea ?” Ans: I asked her if she had taken tea.
(5) The girl said to her mother, “Will you give me your bangles ?” Ans: The girl asked her mother if she would give her her bangles.
(6) Father said to me, “Why are you so upset?” Ans: Father asked me why I was so upset.
Change the following indirect speech into Direct speech.
(1) She asked me if I had called her. Ans: She said to me, “Did you call me ?”
(2) He asked me if I was writing a letter. Ans: He asked me, “Are you writing a letter ?”
(3) The man asked the child how he had got there. Ans: “How did you get here, child ?”, the man said.
(4) The police asked me if I could show my identity card. Ans: The police said to me, “Can you show your identity card ?”
(5) He asked us if we were attending the meeting that day. Ans: He said to us, “Are you attending the meeting today?”
(6) I asked her if she had taken medicine. Ans: I said to her, “Did you take medicine ?”
(7) Raja asked Dipu if he would go to school that day. Ans: Raja said to Dipu, “Will you go to school today?
Imperative Sentences Exercises with Answers
Change the following sentences from direct speech to indirect speech.
(1) The teacher said to the students, “Keep quiet.” Ans: The teachers ordered the students to keep quiet.
(2) My teacher said to me. “Do not neglect your studies.” Ans: My teacher advised me not to neglect my studies.
(3) The man said to his son, “Always try to be honest.” Ans: The man advised it’s on to always try to be honest.
(4) Mother said to Raju, “Do not run in the sun.” Ans: Mother ordered Raju not to run in the sun.
(5) The man said to me, “Brother, please help me.” Ans: Addressing as a brother, the man requested me to help him.
(6) The students said, “Please allow us to play in the field.” Ans: The students requested to allow them to play on the field.
(7) He said to me, “Please give me some money.” Ans: He requested me to give him some money.
Exercise 10
Change the following sentences from Indirect speech to Direct Speech of narration.
(1) He advised me not to waste my valuable time. Ans: He said to me, “Don’t waste your valuable time.”
(2) The grandson advised the children not to pluck flowers. Ans: The gardener said to the children, “Do not pluck flowers.”
(3) Tom forbade Sid to shake him. Ans: Tom said to Sid, “Don’t shake me.”
(4) The master ordered the servant to sort the door. Ans: The master said to the servant, “Shut the door.”
(5) The commander ordered the soldiers to stand at ease. Ans: The commander said to the soldiers, “Stand at ease.”
(6) Addressing as sethji, the vendor told him not to rob the poor. Ans: “Sethji, don’t rob the poor”, said the vendor.
(7) The doctor advised the patient to take proper vitamins to stay healthy. Ans: The doctor said to the patient, “Take proper vitamins to stay healthy.”
(8) The teacher ordered the students to do it then. Ans: The teacher said to the students, “Do it now.”
Direct and indirect speech Exercises Answers with “Let”
Exercise 11.
Change the following sentences from direct speech to indirect speech mode of narration.
(1) Rahim said, “Let us decide the matter together.” Ans: Rahim suggested that they should decide the matter together.
(2) The boy said to me, “Let us play cricket.” Ans: The boy proposed that they should play cricket.
(3) He said, “Let me go home.” Ans: He wished that he might go home.
(4) He said to me, “Let him say whatever he likes.” Ans: He wished me that he might say whatever he liked.
(5) He shouted, “Let me go out. Ans: He shouted at me to go out.
Exercise 12
Change the following sentences from indirect speech to direct speech mode of narration.
(1) She proposed that they should go to the cinema. Ans: She said, “Let us go to the cinema.”
(2) He suggested that they should drop the matter. Ans: He said, “Let us drop the matter”
(3) They suggested that they should make him give them their fears back. Ans: “Let’s make him give us our fares back,” they said.
(4) Shabnam proposed Chandni that they should go for a walk. Ans: “Let us go for a walk.” said Shabnam to Chandni.
(5) The leader suggested that they should hold a meeting the next day. Ans: The leader said, “Let’s hold a meeting tomorrow.”
Direct and indirect speech Exercises Answers of Optative Sentences
Exercise 13.
Change the following from Direct Speech to Indirect Speech.
(1) I said to him, “May you be happy.” Ans: I wished that he might be happy.
(2) Mother said to me, “May God bless you.” Ans: Mother prayed that God might bless me.
(3) He said, “May his soul rest in peace.” Ans: He prayed that his soul might rest in peace.
(4) The girl said, “Oh, had I the wings of a dove.” Ans: The girl wished that she could have the wings of a dove.
(5) I said to him, “May you live long.” Ans: I wished him that he might live long.
Exercise 14
Change the following from Indirect Speech to Direct Speech.
(1) Nilima wished me that I might recover soon. Ans: Nilima said to me, “May you recover soon.”
(2) Mother wished him that God might grant him a long life. Ans : Mother said to him, “May God grant you a long life.”
(3) The holy man wished that peace might prevail. Ans: The holy man said, “May peace prevail.”
(4) She wished that Mother Teresa might recover from illness soon. Ans: She said, “May Mother Teresa recover from illness soon.”
(5) He wished that he could bring his departed friend back to life. Ans: He said, “Oh, if I could bring my departed friend back to life.”
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises of Exclamatory Sentences
Exercise 15.
(1) The boys triumphantly said, “Hurrah! We have won the match.” Ans: The boys exclaimed in joy that they had won the match.
(2) The old man said to the girl, “May you be happy !” Ans: The old man wished the girl that she might be happy.
(3) He said, “What good news!” Ans: He exclaimed in joy that it was very good news.
(4) The children said, “How happy we were there!” Ans: The children gloomily said that they had been very happy there.
(5) He said to you. “May God bless you.” Ans: He wished you that God might bless you.
(6) My friend said to me. “What a fool you are!” Ans: My friend exclaimed in despair that she was a big fool.
Exercise 16
(1) Piyali exclaimed in sorrow that she had lost her phone. Ans: “Alas! I have lost my phone”, said Piyali.
(2) Mother wished Roy that his dreams might come true. Ans: Mother said to Roy, “May your dreams come true.”
(3) The girl exclaimed that she had been very sensible. Ans: How insensible I have been!”, said the girl.
(4) The girl exclaimed in sorrow that she had torn her frock. Ans: The girl said, “Oh dear! I have torn my frock.”
(5) She exclaimed in sorrow that she was undone. Ans: She said, “Alas! I am undone.”
(6) They wished me happy birthday. Ans: They said to me. “Happy birthday!”
(7) The students bade their teacher good morning. Ans: “Good morning, Madam!”, said the students to the teacher.
Practice Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises
A . Change the following into reported speech .
1. Rita says, “Kishore sang a song”.
2. The saint said, “Man is mortal”
3. You said, “we are learning our lesson’.
4. He said to me, “My father went to Mumbai last week.
5. I said to her, “Are you leaving tonight?”
6. He said to her, “Can you lend me your umbrella?”
7. She said, “I saw a tiger here’.
8. The principal said, “well done! my boys”.
9. She said, “Let them play.”
10. I said to Harsh, “Please help me.”
B. Change the direct speech into Indirect Speech
1. He asked me, “Where has he gone?”
2. The Prime Minister said, “National Integrity will be preserved at all costs.
3. She said, “My uncle came yesterday.”
4. Sheela said to us, “You must work hard.”
5. They said, “We trust in God.”
6. The officer said to him. “You will be dismissed if you do not attend the office in time.'”
7. He said to me “I am reading a book.”
8. He said, “Thanks for reminding me.’
9. She said,” Keep this room open.’
10. I said to him, “I went there on Tuesday.”
C. Choose the correct option .
1. I advised him ____________ it.
(a) to not do
(b) not to do
2. She told me ____________ careful.
(c) that be
3. She asked me if I ____________ my lunch.
(b) have eaten
(c) had eaten
4. She asked me ____________ going to the movies
(a) that I was
(b) if was I
(c) if I was
5. The dentist suggested ____________ get a new toothbrush.
(b) that I should
(c) me that I should
6. She said that no one ____________ me
(c) had called
7. He asked me ____________ to deserve such a cruel punishment.
(a) what had he done
(b) what he had done
(c) that he had done
8. He promised he ____________ do it by the end of the week.
9. She said that ____________ me before.
(a) she hadn’t met
(b) she did not meet
(c) she will not meet
10. I requested her____________ me.
(b) to help
(c) that help
D. Complete the sentences in reported speech.
1. The girl said that it ___________ to be there that evening.
(a) gave her great pleasure
(b) gives her great pleasure
(c) gives her great pleasure
2. The man said that he ___________ as soon as possible.
(a) must go
(b) had gone
(c) should be gone
3. She said that she ___________ to se any of them.
(a) does not want
(b) did not want
(c) had not wanted
4. The teacher says that if you work hard you ___________
(a) would pass
(b) will pass
5. He said that he ___________
(b) has won
(c) had won
6. He proposed that they ___________ for her return.
(a) shall wait
(b) will wait
(c) should wait
7. Alice exclaimed how clever ___________
(a) she was
(b) was she
(c) she has been
8. The young man asked which way she ___________
(a) has gone
(c) would go.
9. He asked me where ___________ going.
10. She requested them to wait there till she ___________
(a) returns
(b) returned
(c) will return
E. Complete the sentence in reported speech.
1. Ravi said, “I love this place”.
Ravi said _______________
2. “Do you like football?” He asked me.
He asked me_______________
3. “I can’t drive a lorry”, he said.
He said _______________
4. “Be nice to your brother”, he said
He asked me _______________
5. “Don’t be nasty, “he said
He urged me _______________
6. “Don’t waste your money “she said,
She told the boys _______________
7. “What have you decided to do? “she asked
him. She asked him _______________
8. “I always wake up early”. he said,
He said_______________
9. “You should revise your lessons’, he said,
He advised the students _______________
10. “Where have you been? “he asked me
He wanted to know _______________
F. Complete the sentence in reported speech.
1. She said, “I went to cinema yesterday,”
She said _______________
2. You said, “I will do this for him.”
You said _______________
3. He said, “I am writing a test tomorrow,
4. She said, “I am not hungry now”,
5. They said, “We have never been here before.”
They said _______________
6. They said, “We were in London last week.”
7. He said, “They won’t sleep.”
8. “Have you been shopping?” he asked us.
9. She said, “It is very quiet here.
10. “I don’t speak Italian”, she said.
She said_______________
Direct and Indirect Speech Answers Key
1. Rita says that Kishore sang a song.
2. The saint said that the man is mortal.
3. You said that you were learning your lesson.
4. He hold me that his father had gone to Mumbai the previous week.
5. I asked her if she was leaving that night.
6. He asked her if she could lend him her umbrella.
7. She said that she had seen a tiger there.
8. The principal exclaimed with applause that the boys had done well.
9. She suggested that they should be allowed to play.
10. I requested Harsh to help me.
1. He asked me where he had gone.
2. The Prime Minister declared that the National Integrity would be preserved at all costs.
3. She said that her uncle had come the previous day.
4. Sheela told us that we must work hard.
5. They said that they trusted in God.
6. The officer warned him that he would be dismissed
if he did not attend the office in time.
7. He told me that he was reading a book.
8. He thanked me for reminding him.
9. She ordered to keep that room open.
10. I told him that I had gone there on Tuesday.
1. (b) not to do
2. (b) to be
3. (c) had eaten
4. (c) if I was
5. (b) that I should
6. (c) had called
7. (b) what he had done
8. (b) would
9. (a) she hadn’t met
10. (b) to help
1. (a) gave her great pleasure.
2. (a) must go
3. (b) did not want
4. (b) will pass
5. (c) had won
6. (c) should wait
7. (a) she was
8. (b) had gone
9. (a) I was
10. (b) returned
1. that he loved that place
2. whether I liked football
3. that he couldn’t drive a lorry
4. to be nice to my brother
5. not to be nasty
6. not to waste their money
7. what he had decided to do
8. that he always wake up early
9. to revise their lessons
10. where I had been
1. that she had gone to cinema the previous day.
2. that you would do that for him.
3. that he will be writing a test the next day.
4. that she was not hungry then.
5. that they had never been there before.
6. that they had been in London the previous week.
7. that they wouldn’t sleep.
8. whether we had been shopping.
9. that it was very quiet there.
10. that she didn’t speak Italian.
FAQs on Direct and Indirect speech
Q: what’s the purpose of the indirect speech.
A: Indirect speech allows us to convey someone else’s words without quoting them verbatim. It’s useful for summarizing and paraphrasing.
Q: Are tense changes mandatory in indirect speech?
A: Yes, tense changes are often necessary to accurately reflect the timing of the original statement.
Q: Can reporting verbs be used interchangeably?
A: While reporting verbs can be interchangeable to some extent, their nuances can impact the meaning of the reported speech.
Q: Is it possible to transform any direct speech into indirect speech?
A: Yes, most direct speech can be converted into indirect speech, although some cases may require adjustments.
Q: How can I identify indirect speech in a sentence?
A: Look for keywords like “said,” “asked,” or other reporting verbs, as well as changes in pronouns, tenses, and time expressions.
Q: Why is mastering direct and indirect speech important?
A: Mastering these skills enhances communication clarity, adds variety to language use, and fosters effective expression.
Conclusion:
Direct and indirect speech exercises and answers are invaluable tools for effective communication. By honing this skill, you’ll not only convey information accurately but also showcase your language expertise. Remember that practice makes perfect, and the more you engage in these exercises, the more naturally you’ll incorporate them into your everyday language use.
Related posts:

Have an account?
Suggestions for you See more

Where Does Food Come From?
3rd - 6th , reported speech statements, university .

Reported Speech
10th - 12th grade.
10 questions

Introducing new Paper mode
No student devices needed. Know more
"Bring your books tomorrow,” The teacher said
The teacher told us to bring our books the following day
The teacher told us to brought our books the following day
The teacher said us to bring our books the following day
Have you done the homework?” The teacher said
The teacher asked that if we had done the homework
The teacher asked if we had done the homework
The teacher asked if we have done the homework
"Don’t ask questions in the exam,” The teacher said
The teacher told us not to asked questions in the exam
The teacher said that we didn't ask questions in the exam
The teacher told us not to ask questions in the exam
Do you study biology?” My teacher asked me
My teacher asked me if I had studied biology
My teacher asked me if I studied biology
My teacher asked me if I did study biology
Jane wants to go to the party next week,” Tom said __
Tom said Jane wanted to went to the party the following week
Tom said Jane wanted to go to the party the following week
Tom said Jane wanted to go to the party the previous week
“Where are you going to live?” My mum asked me
My mum asked me where I was going to live
My mum asked to me where I was going to live
My mum asked that where I was going to live
“Why did you immigrate to Spain?” She asked me
She asked me why had I immigrated to Spain
She asked me why I had immigrate to Spain
She asked me why I had immigrated to Spain
"I can come with you to the restaurant,” Bobby said
Bobby said he could came with me to the restaurant
Bobby said he could come with me to the restaurant
Bobby told he could come with me to the restaurant
“I will play chess when I learn” Peter said
Peter said that he would play chess when he learns
Peter said that he would play chess when he learnt
Peter told that he would play chess when he learnt
“You must go to bed now”, Dad said to me
Dad said to me I had to go to bed then
Dad said to me I had to go to bed later
Dad said to me I had to go to bed in the moment
Explore all questions with a free account

Continue with email
Continue with phone

- Trắc Nghiệm Trực Tuyến
- Phòng tự học
- Sách Ôn Thi Điểm 10
Bài tập áp dụng câu tường thuật (Reported Speech) có đáp án chi tiết

BÀI TẬP ÁP DỤNG
Exercise 1: Viết lại câu bằng cách chuyên từ câu trực tiếp sang câu gián tiếp
- Nam said: "I am told to be at school before 7 o'clock".
®....................................................................................................................................................................
- Thu said: "All the students will have a meeting next week".
- Phong said: “My parents are very proud of my good marks".
- The teacher said: "All the homework must be done carefully".
- Her father said to her: "You can go to the movie with your friend".
- "Do you enjoy reading?", Phong asked Peter.
- "Do your sister and brother go to the same school?", she asked Nam.
- "Are there any oranges in the fridge?", she asked her mom.
- "Were you reading this book at 8 o'clock last Sunday?", she asked Ba.
- "Will it rain tomorrow morning?", he asked his friend.
- "Where does your father work?" the teacher asked me.
- "How many people are there in your family?" she asked Lan.
- Tam's friend asked him: "How long will you stay in England?"
- The teacher said to Lien: "What's your hobby?"
- "How do you go to the airport?" his friend asked him.
- "I wish I hadn't gone to the party last night" she said.
- " The Earth moves around the Sun", my teacher said.
- Peter said: "I want to tell you the news. You must be surprised"
- The woman said: “When I was walking on the pavement, a strange man stopped and asked me the way to the nearest bank."
- "How many lessons are you going to learn next month?", he asked me.
Exercise 2: Chia dạng đúng của động từ trong ngoặc
- Jack asked his sister where she (go) the following day.
- The mother told her son (behave) so impolitely
- She asked why Mathew (look so embarrassed when he saw Carole.
- The boy admitted (not do) the homework.
- Our grandparents used to suggest (wear) sunglasses when we were out on bright sunny days.
- Robert offered (help) Carlo do the dishes.
- The captain ordered his men (abandon) the ship immediately.
- Jane criticized Frank for (disclose) their confidential report to the press.
- The team leader reminded us (tidy up) the final draft before submission.
- The kidnappers threatened (kill) our boy if we did not pay the ransom.
- Bill said that he never (be) to Russia and he thought he (go) there the next year.
- John apologized to his Mum for (break) his promise.
- Steve warned Mike (touch) the wires as it might be deadly.
- The police asked Mr John what he (do) the night before.
- The doctor strongly advised Jasmine (take) a few days' rest.
- Mary said if she (be) rich, she (travel) around the world.
- He said that English (be) very useful for my future job and I (must) master it
- He said they (play) games in the bedroom then.
- She said that I had better (go) home early.
Exercise 3: Viết lại câu bằng cách chuyển từ câu trực tiếp sang câu gián tiếp
- She said to him: "Give me another glass of wine".
®She told......................................................................................................................................................
- She said to me: "Bring me a book".
®She asked ....................................................................................................................................................
- The mother said to him: "Open the window please!".
®The mother told ..........................................................................................................................................
- The captain said to them: "Wait here until I come back".
®The captain asked ......................................................................................................................................
- "Do come and enjoy tea with my family" she said.
®She invited us .............................................................................................................................................
- "Why don't we come to visit our teacher today?" he said.
®He suggested...............................................................................................................................................
- "My advice to you is to do morning exercises" she said.
®She advised me ...........................................................................................................................................
- "I'm sorry I broke the glass", said Peter.
®Peter apologized ........................................................................................................................................
- "Why don't you put your luggage under the seat?" he asked,
®He suggested..............................................................................................................................................
- "It's true that I broke your old vase", she said in tears.
®She admitted ...............................................................................................................................................
- "Don't move or I'll shoot", said the bank robber to the clerk.
®The bank robber threatened ......................................................................................................................
- "Don't forget to phone the police", she told him.
®She reminded .............................................................................................................................................
- "Don't swim out too far, boys", said the coach.
®The coach warned.......................................................................................................................................
- Linh said, "If my father repairs the bike now, I will ride the bike to school."
®Linh said ....................................................................................................................................................
- "I would have passed the exam if I had tried my best” Binh said.
®Binh said ...................................................................................................................................................
Exercise 4: Chọn phương án đúng
- do you get B. did I get C. I got D. you got
- next day afternoon B. the afternoon followed
C. the following afternoon D. tomorrow afternoon
- I have been B. have I been C. had I be D. I had been
- what time I leave B. what time I will leave
C. what time I had left D. what time I left
- what does this word mean B. what that word means
C. what did this word mean D. what that word meant
- am B. was C. were D. have been
- yesterday B. two days ago C. the day before D. the next day
- if I were B. if were I C. if was I D. if I was
- that I saw B. had I seen C. if I had D. if had I seen
- if / had occupied B. whether / was occupied
C. if / has been occupied D. whether / occupied
- had any of us seen the accident happen
- if had any of us seen the accident happen
- whether any of us had seen the accident happen
- that if any of us had seen the accident happen
- what the matter was B. what was the matter
C. the matter was what D. what's the matter was
A. told me wake B. asked me to wake
C. said me to wake D. requested me waking
- if / and whether B. whether / or that C. if / or that D. whether / or whether
- what time is it B. what is the time C. what time it is D. it is what time
- why did he not resign B. why he did not resign
C. why he not resign D. why didn't he resign
- that why were his friends laughing B. why were his friends laughing
C. why his friends were laughing D. the reason why his friends laughing
- previous B. following C. before D. last
- asks B. wondered C. wanted to know D. asked
- why B. when C. where D. what
Luyện bài tập vận dụng tại đây!
TIẾNG ANH LỚP 12
CHUYÊN ĐỀ 1: NGỮ PHÁP
- A.1. THÌ ĐỘNG TỪ - VERB TENSES
- A.2. SỰ PHỐI HỢP THÌ – THE SEQUENCE OF TENSES
- A.3. SỰ HOÀ HỢP GIỮA CHỦ NGỮ VÀ ĐỘNG TỪ SUBJECT AND VERB AGREEMENTS
- A.4. ĐỘNG TỪ KHUYẾT THIẾU – MODAL VERBS
- A.5. CỤM ĐỘNG TỪ - PHRASAL VERBS
- A.6. THỨC GIẢ ĐỊNH - THE SUBJUNCTIVE MOOD
- A.7. DANH ĐỘNG TỪ (GERUND) VÀ ĐỘNG TỪ NGUYÊN MẪU (INFINITIVE VERB)
- A.8. CÂU HỎI ĐUÔI - TAG QUESTIONS
- A.9. SO SÁNH - COMPARISON
- A.10. TRẬT TỰ CỦA TÍNH TỪ - THE ORDERS OF THE ADJECTIVES
- A.11. MẠO TỪ - ARTICLES
- A.12. CẤU TẠO TỪ - WORD FORMS
- A.13. TỪ CHỈ SỐ LƯỢNG - EXPRESSIONS OF QUANTITY
- A.14. GIỚI TỪ - PREPOSITIONS
- A.15. LIÊN TỪ - CONJUNCTIONS
- A.16. CÂU BỊ ĐỘNG - PASSIVE VOICES
- A.17. CÂU ĐIỀU KIỆN - CONDITIONAL SENTENCES
- A.18. CÂU TƯỜNG THUẬT - REPORTED SPEECH
- A.19. ĐẢO NGỮ - INVERSIONS
- A.20. MỆNH ĐỀ QUAN HỆ - RELATIVE CLAUSES
- A.21. THÀNH NGỮ - IDIOMS
- A.22. CỤM TỪ CỐ ĐỊNH – COLLOCATIONS
- A.23. MỘT SỐ CẤU TRÚC THÔNG DỤNG
CHUYÊN ĐỀ 2: TỪ VỰNG (VOCABULARY)
- B.1. CHỦ ĐỀ 1: CULTURE IDENTITY
- B.2. CHỦ ĐỀ 2: EDUCATION
- B.3. CHỦ ĐỀ 3: URBANIZATION
- B.4. CHỦ ĐỀ 4: GLOBAL WARMING
- B.5. CHỦ ĐỀ 5: NATURAL IN DANGER
- B.6. CHỦ ĐỀ 6: ENERGY
- B.7. CHỦ ĐỀ 7: ENDANGERED SPECIES
- B.8. CHỦ ĐỀ 8: PRESERVATION
- B.9. CHỦ ĐỀ 9: VOLUNTEER WORK
- B.10. CHỦ ĐỀ 10: HEALTHY LIFESTYLE AND LONGEVITY
- B.11. CHỦ ĐỀ 11: LIFE STORIES
- B.12. CHỦ ĐỀ 12: FAMILY LIFE
- B.13. CHỦ ĐỀ 13: RELATIONSHIPS
- B.14. CHỦ ĐỀ 14: FILM AND MUSIC
- B.15. CHỦ ĐỀ 15: ENTERTAINMENT
- B.16. CHỦ ĐỀ 16: POPULATION
- B.17. CHỦ ĐỀ 17: GENDER EQUALITY
- B.18. CHỦ ĐỀ 18: ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
- B.19. CHỦ ĐỀ 19: WONDERS OF THE WORLD
- B.20. CHỦ ĐỀ 20: JOBS
- B.21. CHỦ ĐỀ 21: LIFE IN THE FUTURE
- B.22. CHỦ ĐỀ 22: INVENTIONS
- B.23. CHỦ ĐỀ 23: WAYS OF SOCIALIZING
- B.24. CHỦ ĐỀ 24: INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATIONS
- B.25. CHỦ ĐỀ 25: MASS MEDIA
- B.26. CHỦ ĐỀ 26: SPORTS
- B.27. CHỦ ĐỀ 27: NEW WAYS TO LEARN
- B.28. CHỦ ĐỀ 28: CELEBRATIONS
- B.29. CHỦ ĐỀ 29: SPACE CONQUEST
- B.30. CHỦ ĐỀ 30: SCIENCE
CHUYÊN ĐỀ 3: NGỮ ÂM
- C.1. PHÁT ÂM - PRONUNCIATION
- C.2. TRỌNG ÂM - STRESS
CHUYÊN ĐỀ 4: ĐỌC HIỂU
- D.1. KỸ NĂNG ĐỌC HIỂU
CHUYÊN ĐỀ 5: ĐỌC ĐIỀN TỪ
- E.1. 3 DẠNG CHÍNH TRONG ĐIỀN TỪ VÀO ĐOẠN VĂN
- E.2. CÁC LOẠI CÂU HỎI TRONG ĐIỀN TỪ VÀO ĐOẠN VĂN
CHUYÊN ĐỀ 6: ĐỒNG - TRÁI NGHĨA
- F.1. TABLE OF SYNONYMS/ RELATED WORDS AND ANTONYMS
CHUYÊN ĐỀ 7: TÌM LỖI SAI
- G.1. LỖI SAI NGỮ PHÁP CẤU TẠO TỪ VÀ TỪ LOẠI
- G.2. CẤU TRÚC SONG SONG
- G.3. CÂU CHỦ ĐỘNG - CÂU BỊ ĐỘNG
- G.4. MỆNH ĐỀ
Hãy viết chi tiết giúp Tự Học 365

100 Bài tập câu tường thuật có đáp án | Bài tập Reported Speech
Bài viết 100 Bài tập câu tường thuật có đáp án chi tiết giúp bạn có thêm nguồn bài tập tự luyện để nắm vững cách sử dụng câu tường thuật từ đó giúp bạn học tốt Ngữ pháp Tiếng Anh hơn.
Bài tập câu tường thuật (phần 1)
Bài tập câu tường thuật (phần 2), ngữ pháp câu tường thuật.
Bài 1: Yesterday you sent a friend of yours Steve. You hadn't seen him for a long time. Here are some of the things Steve said to you:
1. I'm living in London.
2. My father isn't very well.
3. Rachel and Mark are getting married next month.
4. My sister has had a baby.
5. I don't know what Frank is doing.
6. I saw Helen at a party in June and she semed fine.
7. I haven't seen Diane recently.
8. I'm not enjoying my job very much.
9. You can come and stay at my place if you're ever in London.
10. My car was stolen a few days ago.
11. I want to go on holiday but I can't afford it.
12. I'll tell Chris I saw you.
Later that day you tell another friend what Steve said. Use reported speech :
1. Steve said that he was living in London .
2. He said that .........................
3. He ...................................
4. ......................................
5. ......................................
6. ......................................
7. ......................................
8. ......................................
9. ......................................
10. ......................................
11. ......................................
12. ......................................
Đáp án & Hướng dẫn:
2. He said his father wasn't very well.
3. He said Rachle and Mark were getting married next month.
4. He sai his sister had had a baby.
5. He said he didn't know what Frank was doing.
6. He said he had seen Helen at a party.
7. He said he hadfn't seen Diane.
8. He said he wasn't enjoying his job very much.
9. He said I could come and stay at his place if I was ever in London.
10. He said his car had been stolen a few days ago.
11. He said he wanted to go on holiday but he couldn't afford it.
12. He said he'd tell.
Bài 2: Somebody says something to you which is the oppsite of what they said earlier. Complete the answers.
1. A: That restaurant is expensive
B: Is it? I thought you said it was cheap .
2. A: Sue is coming to the party tonight.
B: Is she? I thought you said she .....................
3. A: Sarah likes Paul.
B: Does she? Last week you said .......................
4. A: I know lots of people.
B: Do you? I thought you said ........................
5. A: Jane will be here next week.
B: Will she? But didn't you say .......................
6. A: I'm going out this evening.
B: Are you? But you said .............................
7. A: I can speak a little French.
B: Can you? But earlier you said ......................
8. A: I haven't been to the cinema for ages.
B: Haven't you? I thought you said ....................
Example answers:
2. she wasn't coming somewhere else/ ... she was staying at home.
3. she didn't like him
4. you didn't know anybody
5. she wouldn't be here
6. you were staying at hjome/ you weren't going out
7. you couldn't speak French
8. you went to the cinema last week
But later Sarah says something diffierent to you. What do you say?
2. But you said you didn't like fish
3. but you said you couldn't drive
4. But you said she had very well-paid job
5. But you sai you didn't have any brothers or sisters
6. But you said you had never been to the United States
7. But you said you were working tomorrow evening
8. but you said she was friend of yours.
Bài 2: Complete the sentences with say or tell . Use the only one word each time.
1. Ann said goodbye to me and left.
2. .... us about your holiday.Did you have a nice time?
3. Don't just stand there! .... something!
4. I wonder where Sue is. She .... she would be here at
8. o'clock.
5. Dan .... me that he was bored with his job
6. The doctor .... that I should rest for at least a week.
7. Don't .... anybody what I ..... It's a secret just between us.
8. Did she .... you what happened? No, she didn't .... anything to me.
9. Gary couldn't help me. He .... me to ask Caroline.
10. Fary couldn't help me. He .... to ask Caroline.
7. tell .... said
8. tell .... say
Bài 3: The following sentences are direct speech :
Don't wait for me if I'm late.
Mind your own business.
Don't worry Sue.
Please slow down.
Can you open your bag, please.
Could you get a newspaper.
Will you mary me?
Do you think you could give me a hand, Tom?
Now choose one of these to complete each of the sentences below. Use reported speech :
1. Bill was taking a long time to get ready, so I told him to hurry up .
2. Sarah was driving too fast, so I asked .............................
3. Sue was nervous about the situation. I told .......................
4. I couldn't move the piano alone, so I .............................
5. The customs officer looked at me suspiciously and ..................
6. Tom was going to the shop, so I ....................................
7. The man started asking me personal questions, so I .................
8. John was very much in love with Mary, so he ........................
9. I didn't want to delay Helen so I ..................................
2. he to slow down
3. her not to worry
4. asked Tom to give me a hand or ... to help me
5. asked me to open my bag
6. asked him to get a newspaper
7. told him to mind his own business
8. asked her to marry him
9. told her not to wait if I was late.
I. Khái niệm ( phân biệt câu trực tiếp và câu gián tiếp)
II. Các thành phần cần biến đổi từ câu trực tiếp sang câu gián tiếp
* Các đại từ: Ta cần thay đổi đại từ sao cho phù hợp với ngữ cảnh trong câu
* Thay đổi thì của câu:
* Thay đổi một số động từ khuyết thiếu:
* Thay đổi Đại từ
Các đại từ nhân xưng và đại sở hữu khi chuyển từ lời nói trực tiếp sang lời nói gián tiếp thay đổi như bảng sau:
* Các trạng từ chỉ nơi chốn, thời gian:
II. Các dạng câu trần thuật cơ bản
1. REPORTED SPEECH: STATEMENTS (Câu trần thuật)
Ta dùng động từ say hoặc tell để tường thuật:
Ex: He said, “I have just bought a computer today.”
He said that he had just bought a computer that day.
( Anh ấy nói: “ Tôi vừa mới mua một cái máy tính vào hôm nay”
-> Anh ấy nói rằng anh ấy vừa mới mua một cái máy tính ngày hôm nay)
Linda said, “There is someone at the door, Bill.”
Linda told Bill that there was someone at the door.
( Linda nói rằng : “ Có ai ở ngoài của kìa, Bill”
-> Linda nói với Bill rằng có ai ở ngoài cửa)
2. REPORTED SPEECH: QUESTIONS (Câu hỏi)
a. Yes-No questions: Khi đổi sang câu gián tiếp, ta cần thêm if hoặc whether trước chủ từ của câu hỏi được tường thuật:
Ex: He said to me, “Are you from Canada?”
He asked me if/whether I was from Canada.
( Anh ấy nói với tôi: “ Bạn đến từ Canada à?
-> Anh ấy hỏi tôi tôi đến từ Canada phải không. )
The man said to her, “Did Bill tell you my address?”
The man asked her if/whether Bill had told her his address.
( Người đàn ông nói với cô ấy: “ Bill đã nói chô biết địa chỉ của tôi à?”
-> Người đàn ông hỏi cô ấy có phài Bill cho cô ấy biết địa chỉ của anh ấy hay không)
The girl said, “Do you live near here, David?”
She asked David if/whether he lived near there.
(Cô gái hỏi: “ Cậu sống gần đây à, David?
-> Cô gái hỏi David có phải anh ấy sống gần đây hay không.)
b. Wh – Questions: Các câu hỏi bắt đầu bằng một từ để hỏi như: who, when, where, when, why, how…

-> He asked them where they were going.
( Anh ấy nói với họ: “ Các bạn đang đi đâu đấy?”
-> Anh ấy hỏi họ rằng họ đang đi đâu đấy.)
The teacher asked, “When do you do your homework, Tom?”
-> The teacher asked Tom when he did his homework.
( Cô giáo hỏi: “ Khi nào con làm bài tập về nhà, Tom?”
-> Cô giáo hỏi Tom khi nào anh ấy làm bài tập về nhà.)
3. REPORTED SPEECH: COMMANDS/ORDERS/REQUESTS (Câu mệnh lệnh/Câu đề nghị)
Ta dùng động từ ask hoặc tell để tường thuật:

- Dick said to Jim: “Please open the window.” ® Dick told Jim to open the window.
- Mother said, “Tim, go to bed early.” ® Mother told Tim to go to bed early.
- Father said to Liz: “Don’t come home late.” ® Father told Liz not to come home late.
* LƯU Ý: Các trường hợp KHÔNG thay đổi thì trong câu tường thuật:
a. Câu điều kiện loại 2 và 3
Nếu câu nói trực tiếp là câu điều kiện loại 2 và loại 3, ta chỉ thay đổi các đại từ, tình từ…mà không đổi thì trong câu.
Ex: “If I were older, I would retire.”, he said.
He said if he were older, he would retire.
“If I had heard the whole story, I would have acted differently”, he said
He said that if he had heard the whole story, he would have acted differently.
b. Câu trực tiếp diễn tả một chân lí, hay một thói quen ở hiện tại.
Nếu câu nói trực tiếp nói về một sự thật, một chân lí hay một thói quen thường xuyên lặp đi, lập lại ở hiện tại, khi đổi sang câu gián tiếp ta phải giữ nguyên thì của câu trực tiếp.
Ex 1: Trực tiếp: The teacher said, “The earth moves round the Sun”
Gián tiếp: The teacher said that The earth moves round the Sun.
Ex 2: Trực tiếp: My wife always drinks coffee for breakfast.
Gián tiếp: He said that his wife always drinks coffee for breakfast.
c. Động từ tường thuật ở thì hiện tại đơn, hiện tại tiếp diễn, hiện tại hoàn thành, tương lai.
Nếu động từ tường thuật ở thì hiện tại đơn, hiện tại tiếp diễn, hiện tại hoàn thành, tương lai, khi đổi sang câu gián tiếp, ta không thay đổi thì và các cum trạng từ và cụm từ chỉ thời gian và nơi chốn, mà chỉ thay đổi các đại từ hay tính từ…
Ex : He says/ He is saying/ He has said/ He will say, “The bus is coming.” → He says the bus is coming.
d. Không thay đổ thì của động từ trong câu gián tiếp nếu có thời gian xác định trong quá khứ.
Ex. She said, ‘‘I was born in 1980’’
She said that she was born in 1980
e. Các động từ khiếm khuyết: could, would, might, ought to, should thường không thay đổi trong câu tường thuật.
Ex. He said, ‘I might come’
He said that He might come’
- Khi tường thuật mệnh đề ước muốn: “wish’
Ex: He said; “I wish I had a lot of money”
® He wishes (that) he had a lot of money
- Khi tường thuật cấu trúc: “It’s (high/ about) time”
Ex: She said; “It’s about time you went to bed; children”
® She told her children that It’s about time they went to bed
Xem thêm bài tập ngữ pháp Tiếng Anh có đáp án chi tiết hay khác:
- Bài tập Câu hỏi & Cách đặt câu hỏi
- Bài tập Trợ động từ
- Bài tập Câu hỏi đuôi (Question Tag)
- Bài tập V + V-ing
- Bài tập V + To V
- Bài tập V + V-ing hay V + to

Loạt bài Bài tập ngữ pháp tiếng Anh của chúng tôi một phần dựa trên cuốn sách English Grammar In Use của tác giả Raymond Murphy .
Follow fanpage của team https://www.facebook.com/vietjackteam/ hoặc facebook cá nhân Nguyễn Thanh Tuyền https://www.facebook.com/tuyen.vietjack để tiếp tục theo dõi các loạt bài mới nhất về Ngữ pháp tiếng Anh, luyện thi TOEIC, Java,C,C++,Javascript,HTML,Python,Database,Mobile ... mới nhất của chúng tôi.
Bài tập Ngữ pháp tiếng Anh phổ biến tại vietjack.com:
Bài tập câu điều kiện trong tiếng Anh
Bài tập về câu bị động trong tiếng Anh
Bài tập mệnh đề quan hệ trong tiếng Anh
Bài tập về giới từ trong tiếng Anh
Bài tập về mạo từ trong tiếng Anh
- Soạn Văn 12
- Soạn Văn 12 (bản ngắn nhất)
- Văn mẫu lớp 12
- Giải bài tập Toán 12
- Giải BT Toán 12 nâng cao (250 bài)
- Bài tập trắc nghiệm Giải tích 12 (100 đề)
- Bài tập trắc nghiệm Hình học 12 (100 đề)
- Giải bài tập Vật lý 12
- Giải BT Vật Lí 12 nâng cao (360 bài)
- Chuyên đề: Lý thuyết - Bài tập Vật Lý 12 (có đáp án)
- Bài tập trắc nghiệm Vật Lí 12 (70 đề)
- Luyện thi đại học trắc nghiệm môn Lí (18 đề)
- Giải bài tập Hóa học 12
- Giải bài tập Hóa học 12 nâng cao
- Bài tập trắc nghiệm Hóa 12 (80 đề)
- Luyện thi đại học trắc nghiệm môn Hóa (18 đề)
- Giải bài tập Sinh học 12
- Giải bài tập Sinh 12 (ngắn nhất)
- Chuyên đề Sinh học 12
- Đề kiểm tra Sinh 12 (có đáp án)(hay nhất)
- Ôn thi đại học môn Sinh (theo chuyên đề)
- Luyện thi đại học trắc nghiệm môn Sinh (18 đề)
- Giải bài tập Địa Lí 12
- Giải bài tập Địa Lí 12 (ngắn nhất)
- Giải Tập bản đồ và bài tập thực hành Địa Lí 12
- Bài tập trắc nghiệm Địa Lí 12 (70 đề)
- Luyện thi đại học trắc nghiệm môn Địa (20 đề)
- Giải bài tập Tiếng anh 12
- Giải bài tập Tiếng anh 12 thí điểm
- Giải bài tập Lịch sử 12
- Giải tập bản đồ Lịch sử 12
- Bài tập trắc nghiệm Lịch Sử 12
- Luyện thi đại học trắc nghiệm môn Sử (20 đề)
- Giải bài tập Tin học 12
- Giải bài tập GDCD 12
- Giải bài tập GDCD 12 (ngắn nhất)
- Bài tập trắc nghiệm GDCD 12 (37 đề)
- Luyện thi đại học trắc nghiệm môn GDCD (20 đề)
- Giải bài tập Công nghệ 12
Học cùng VietJack

Trang web chia sẻ nội dung miễn phí dành cho người Việt.
Lớp 1-2-3 Lớp 4 Lớp 5 Lớp 6 Lớp 7 Lớp 8 Lớp 9 Lớp 10 Lớp 11 Lớp 12 Lập trình Tiếng Anh
Chính sách bảo mật
Hình thức thanh toán
Chính sách đổi trả khóa học
Chính sách hủy khóa học
Về chúng tôi
Liên hệ với chúng tôi
Tầng 2, số nhà 541 Vũ Tông Phan, Phường Khương Đình, Quận Thanh Xuân, Thành phố Hà Nội, Việt Nam
Phone: 084 283 45 85
Email: [email protected]

CÔNG TY TNHH ĐẦU TƯ VÀ DỊCH VỤ GIÁO DỤC VIETJACK
Người đại diện: Nguyễn Thanh Tuyền
Số giấy chứng nhận đăng ký kinh doanh: 0108307822, ngày cấp: 04/06/2018, nơi cấp: Sở Kế hoạch và Đầu tư thành phố Hà Nội.
Confirm Password *
By registering, you agree to the Terms of Service and Privacy Policy . *
Username or email *
Forgot Password
Lost your password? Please enter your email address. You will receive a link and will create a new password via email.
Sorry, you do not have permission to ask a question, You must login to ask a question.
Please briefly explain why you feel this question should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this answer should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this user should be reported.

English Notes
English notes latest questions, the teacher said, “do your homework.” change into indirect speech.
Indirect Speech: The teacher asked us to do our homework.
Explanation: While reporting imperative sentences we use reporting verbs like ask, request, beg, order, advise, wish etc to match the mood of the sentence.
Learn Narration
- Share on WhatsApp
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
- Select as best answer
You must login to add an answer.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The teacher asked the boys if they had done their homework. 2. The little girl asked the man if he would help her. 3. Janaki said that she had been reading that book. 4. Mother told the daughter to go and change her dresses. 5. Susie said that she had read that book before she gave it to me.
Tom told me 5. Teacher: "Do your homework." The teacher told me 6. Andrew: "Wash the dishes." Andrew told me 7. Jessica: "Write a letter." ... Emma said that her teacher was going to London the following / the next day. 33. Justin asked me what I was doing. 34. Mary asked me if I was reading that book then.
Indirect Speech: The teacher asked me if I had done my homework. Explanation: When the reporting verb is in the past (said) and the direct speech is in the present perfect tense, then the indirect (reported) speech will change into the past perfect tense. Present Perfect Tense > Past Perfect Tense. And if the sentence is interrogative, we use ...
3. You said to him "Why are you making mischief?" 4. They said to us, "How have you solved this sum?" 5. We said to them, "Who has misguided you?" 6. They said to him, "Where have you been wandering since yesterday?" 7. She said to me, "Why were you hiding today?" 8. Raja said to us, "When do you expect to see me again?" 9.
Reported speech: indirect speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Click here:point_up_2:to get an answer to your question :writing_hand:transform the following from direct to reported speechthe teacher said to me do your homework
He said to me, "Go there right now." - He ordered me to go there right then. My teacher said to me, "Obey your parents." - My teacher asked me to obey my parents. She said to me, "Please don't go there." - She requested me not to go there. He said to her, "Let's go home." - He suggested her that they should go home.
Direct: The teacher said, "Do you complete your homework?" Indirect: The teacher asked if he completed his homework. Direct: She says, "She is an artist." Indirect: She says that she is an artist. Direct: Sam told, "I'm not coming with you." Indirect: Sam told me that he was not coming with me.
The teacher told the students, "Speak up if you want to say something!". Task 3. Change the sentences to reported speech. Mary said, "I will play a card game tomorrow.". - Mary informed me that …. Sophie said, "I went to bed early last night.". The teacher said to Jenny, "You have to learn your grammar.".
George said "I need help with my homework." ... Tom said Mercedes was a good car. 76: Direct: I am a doctor he said. Indirect: He said he was a doctor. 77: ... I don't understand you. Indirect: Teacher said that he didn't understand me. 98: Direct: He said, "I will wash my teeth".
A reported question is when we tell someone what another person asked. To do this, we can use direct speech or indirect speech. direct speech: 'Do you like working in sales?' he asked. indirect speech: He asked me if I liked working in sales. In indirect speech, we change the question structure (e.g. Do you like) to a statement structure (e.g.
Tom told me to come at 8. 7) Teacher:"Do your homework!" The teacher told me to do my homework. 8) Doris:"Dance with me!" Doris told me to dance with her. 9) Sabine:"Meet Sandy at the station!" Sabine told me to meet Sandy at the station. 10) Victoria:"Check your e-mails!" Victoria told me to check my e-mails
The teacher asked the girl, "When do you have to be home?" ... "Do your homework again. There are a lot of mistakes." says the teacher to Kate. ... 17. Tom said to Carol, "Can I borrow your dictionary. Mine is at home." ...
1. I said to her, "When do you do your homework?" 1. I asked her when she did her homework. 2. We said to him, "Are you ill?" 2. We asked him if he was ill. 3. You said to me, "Have you read the article?" 3. You asked me if I had read the article. 4. He said to her, "Will you go to the Peshawar Radio Station?" 4.
Exercise 1. Change the mode of narration from direct Speech to indirect speech. (1) He said to me, "I can't recall your name.". Ans: He told me that he could not recall my name. (2) Poulami says, "I am fine.". Ans: Poulomi says that she is fine. (3) He said, "I did it.". Ans: He said that he had done it. (4) "I know her address ...
5. 'I am a humble servant ready to obey the orders,' said Madame Magloire to the Bishop. 6. Rob's father said to Mary, 'I hate to call Rob in the mornings.' 7. The teacher said to the boys, 'If you do your best, you will surely pass.' 8. 'Joseph, have you finished writing?' asked the teacher. 9. 'I have something to show you ...
1 Answer. Indirect Speech: Ram asked me if I had done my homework. Explanation: When the reporting verb is in the past (said) and the direct speech is in the past indefinite tense, then the indirect (reported) speech will change into the past perfect tense. Past Indefinite Tense > Past Perfect Tense. And if the sentence is interrogative, we use ...
The teacher asked if we have done the homework. 3. Multiple Choice. Edit. 30 seconds. 1 pt "Don't ask questions in the exam," The teacher said. The teacher told us not to asked questions in the exam. ... Tom said Jane wanted to went to the party the following week.
Câu trần thuật trong câu trực tiếp sẽ đổi tương lai đơn. "will" thành "would" trong câu gián tiếp và "next week ®the next/following week". 3. Luyện bài tập vận dụng tại đây! Báo lỗi. BÀI TẬP ÁP DỤNG Bài tập Exercise 1: Viết lại câu bằng cách chuyên từ câu trực tiếp sang câu ...
1 Answer. Zainab Shaikh. Added an answer on February 19, 2022 at 8:34 am. Indirect Speech: The teacher asked me what I was doing. Explanation: When the reporting verb is in the past (said) and the direct speech is in the present continuous tense, then the indirect (reported) speech will change into the past continuous tense.
The teacher asked, "When do you do your homework, Tom?"-> The teacher asked Tom when he did his homework. ( Cô giáo hỏi: " Khi nào con làm bài tập về nhà, Tom?"-> Cô giáo hỏi Tom khi nào anh ấy làm bài tập về nhà.) 3. REPORTED SPEECH: COMMANDS/ORDERS/REQUESTS (Câu mệnh lệnh/Câu đề nghị)
1 Answer. Indirect Speech: The teacher asked if I had done it correctly. Explanation: When the reporting verb is in the past (said) and the direct speech is in the present perfect tense, then the indirect (reported) speech will change into the past perfect tense. Present Perfect Tense > Past Perfect Tense. Note: While answering to "yes or no ...
1 Answer. Zainab Shaikh. Added an answer on February 14, 2022 at 10:22 pm. Indirect Speech: The teacher asked us to do our homework. Explanation: While reporting imperative sentences we use reporting verbs like ask, request, beg, order, advise, wish etc to match the mood of the sentence. Learn Narration. 0. Select as best answer.