Essay Papers Writing Online
Your complete guide to writing an effective report essay to impress your readers.

Are you ready to take your academic writing prowess to the next level? Do you aspire to craft compelling and persuasive reports that leave a lasting impression on your readers? Look no further – we have all the insider tips and expert guidelines you need to succeed in writing a remarkable analytical essay!
Picture this: you have been assigned a report essay – a task that can seem overwhelming and intimidating at first. But fear not, for we are here to provide you with the essential tools and strategies to conquer this challenge with ease and finesse. So, grab your pen, gather your thoughts, and get ready to embark on a journey of analytical excellence!
In the realm of academic writing, a report essay requires a unique blend of critical thinking, meticulous research, and articulate writing skills. It is an opportunity for you to demonstrate your ability to analyze and interpret information, and to present your findings in a clear and concise manner. Throughout this guide, we will equip you with the knowledge and techniques necessary to deliver a report essay that captivates your audience and earns you the recognition you deserve.

Tips for Writing a Report Essay
When it comes to composing a report essay, there are several crucial aspects to consider that can enhance the quality and effectiveness of your writing. By following these tips, you can ensure that your report is well-organized, informative, and engaging to the reader.
- Choose a compelling topic: Select a subject that interests you and is relevant to your audience. A captivating topic will not only keep your readers engaged but will also make the writing process more enjoyable for you.
- Conduct thorough research: To provide valuable insights in your report essay, it is essential to gather reliable information. Utilize a variety of credible sources, such as books, academic journals, and reputable websites, to ensure a well-rounded perspective on the topic.
- Outline your essay: Before diving into the writing process, create an outline to organize your thoughts and ideas. This will help you establish a clear structure for your essay and ensure a logical flow of information.
- Use clear and concise language: Avoid unnecessary jargon or complex vocabulary that may confuse your readers. Instead, strive for clarity and simplicity in your writing. Explain concepts in a straightforward manner to ensure that your audience understands the information you are conveying.
- Provide evidence and examples: Back up your statements with evidence and examples to support your arguments and claims. This will add credibility to your report essay and demonstrate your research and understanding of the topic.
- Edit and revise: After completing the initial draft, take the time to edit and revise your essay. Look out for grammatical errors, logical inconsistencies, and areas that need improvement. Pay attention to the structure and flow of your writing to ensure a cohesive and coherent report.
- Cite your sources: Give credit to the authors and researchers whose work you have used in your report by providing proper citations. This not only acknowledges their contributions but also adds credibility and integrity to your essay.
By following these tips, you can enhance your report essay writing skills and produce a well-structured and informative piece of writing that engages and informs your readers.
Understanding the Purpose

In order to effectively write a report essay, it is essential to have a clear understanding of its purpose. This section will explore the main objectives and goals of writing a report essay, allowing you to approach the task with confidence and clarity.
Identifying the purpose:
The purpose of a report essay is to provide a comprehensive and well-researched account of a particular topic or subject. It aims to analyze, evaluate, and present information in a structured and organized manner. A report essay should be informative, objective, and credible, presenting facts and findings that are supported by evidence and research.
Informing and educating:
A key goal of a report essay is to inform and educate the reader. It should provide a clear understanding of the topic at hand, presenting relevant information and data in a concise and accessible way. The purpose is to ensure that readers gain knowledge and insights on the subject, enabling them to make informed decisions or form their own opinions.
Analyzing and evaluating:
In addition to presenting information, a report essay also aims to analyze and evaluate the data. This involves critically examining the evidence, assessing its strengths and weaknesses, and drawing conclusions based on logical reasoning and analysis. The purpose is to provide a balanced and objective perspective on the topic, allowing readers to understand its implications and significance.
Addressing a specific audience:
Another important aspect of understanding the purpose of a report essay is considering the target audience. Whether it is written for academic purposes, professional reasons, or a general audience, the tone and style of the essay may vary. The purpose is to effectively communicate with the intended readers, ensuring that the content is relevant and engaging.
Emphasizing clarity and organization:
Lastly, the purpose of a report essay is to emphasize clarity and organization. It should be well-structured, with a logical flow of ideas and information. The purpose is to ensure that readers can easily navigate through the essay, grasping the main points and arguments. Clear headings, subheadings, and a coherent paragraph structure can contribute to the overall effectiveness of the essay.
By understanding the purpose of a report essay, you can approach the writing process with a clear direction and focus. Keeping in mind the objectives discussed in this section will help you create a well-written and impactful report essay that reaches its intended audience.
Conducting Thorough Research
Immersion in the subject matter is the first key to successful research. To truly understand and convey the nuances of the topic, it is crucial to immerse oneself in it, allowing ideas and concepts to permeate one’s mind. Reading extensively, exploring various perspectives, and engaging with reliable sources creates a web of knowledge that forms the basis for the report essay.
Verification and validation are vital aspects of conducting thorough research. It is crucial to critically evaluate the sources of information, ensuring their credibility and reliability. Distinguishing between reputable scholarly articles, academic journals, reputable websites, and anecdotal sources is essential to present a balanced and accurate report. Additionally, cross-referencing information and verifying facts help to fortify the integrity of the essay’s content.
Unearthing the unconventional is another aspect of comprehensive research. Going beyond the usual sources and exploring alternative viewpoints can uncover valuable insights and add a unique perspective to the report. Seeking out lesser-known experts, delving into niche publications, and analyzing unconventional data can make the essay stand out and contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
Organizational prowess plays a crucial role in the research process. Creating an efficient system for storing and organizing gathered information is imperative to avoid the chaos of mismanaged data. Utilizing digital tools, such as note-taking apps or citation managers, can streamline the research process and enable easy retrieval of information during the writing stage.
Iteration and adaptation are essential components of thorough research. As new information is discovered and insights develop, it is crucial to iterate and adapt the research approach accordingly. Remaining open to new ideas and adjusting the research methodology ensures that the essay remains dynamic, robust, and relevant.
In conclusion, conducting thorough research is the cornerstone of writing a successful report essay. Through immersion, verification, exploration, organization, and adaptation, researchers can lay the groundwork for a well-informed and impactful piece of writing. By valuing the research process and committing to its intricacies, writers can elevate their essays to a realm of academic excellence.
Organizing Your Thoughts
When starting a writing project, it is essential to have a clear and organized plan in order to effectively convey your ideas. By structuring your thoughts in a logical and coherent manner, you can ensure that your report essay is engaging and easy to follow.
One effective way to organize your thoughts is by creating an outline. This involves breaking down the main points or arguments you want to make and arranging them in a hierarchical order. You can use bullet points or numbers to denote the different levels of importance or relevance. This visual representation of your ideas will serve as a roadmap for your report essay, guiding both you and your readers through the content.
Another method of organizing your thoughts is utilizing mind maps or concept maps. These tools allow you to visually connect related ideas and concepts, helping you to identify connections and patterns. Mind maps can be particularly useful when brainstorming or generating ideas, as they encourage free association and creativity.
In addition to these visual aids, it is essential to also consider the flow of your thoughts within the report essay itself. Each paragraph should have a clear topic sentence that introduces the main idea, followed by supporting details and evidence. Transitions between paragraphs should be smooth and logical, helping to guide the reader through the progression of your thoughts.
Furthermore, it is important to consider the overall structure of your report essay. Typically, an introduction should provide background information and a thesis statement, outlining the main argument or purpose of the essay. The body paragraphs should then present and support your main points or arguments, while a conclusion should summarize your findings and restate your thesis in a clear and concise manner.
In conclusion, organizing your thoughts is a crucial step in the writing process. By creating an outline, utilizing visual aids, ensuring flow within paragraphs, and considering the overall structure, you can effectively convey your ideas in a coherent and engaging manner. This organizational approach will not only make the writing process easier, but also enhance the clarity and effectiveness of your report essay.
Structuring Your Essay
Arranging the content of your essay is key to ensuring a cohesive and logical flow of ideas. A well-structured essay not only makes it easier for the reader to understand your arguments, but also demonstrates your ability to organize and communicate your thoughts effectively.
When structuring your essay, it is important to consider the overall framework, the arrangement of paragraphs, and the use of headings and subheadings to guide the reader. A clear and logical structure helps to keep your ideas organized and makes it easier for the reader to follow your line of reasoning.
One common approach to structuring an essay is the introduction-body-conclusion framework. In the introduction, you should provide a brief overview of your topic and present your thesis statement, which outlines the main argument or point of your essay. The body paragraphs should present the supporting evidence and arguments for your thesis, with each paragraph focusing on a specific idea or piece of evidence. Finally, the conclusion should summarize your main points and restate your thesis in a way that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
In addition to the overall structure, you can also enhance the clarity of your essay by using headings and subheadings. These help to break up the text and provide a clear hierarchy of ideas. Headings should be concise and descriptive, giving the reader an idea of what each section will cover. Subheadings can be used within each section to further divide the content and provide a more detailed breakdown of your arguments or evidence.
Another important aspect of structuring your essay is the arrangement and flow of paragraphs. Each paragraph should focus on a single main idea and be connected to the previous and following paragraphs through transitions. Transitions help to guide the reader from one idea to the next, creating a smooth and coherent progression of thoughts. Examples of transition words and phrases include “however,” “in contrast,” “on the other hand,” and “furthermore.”
In summary, structuring your essay is essential for organizing and effectively conveying your ideas. By following a clear framework, using headings and subheadings, and ensuring a logical flow of paragraphs, you can create a well-structured essay that engages the reader and supports your arguments effectively.
Editing and Proofreading Your Work
Perfecting your written work is just as important as the writing process itself. After you have completed your essay or report, it is crucial to spend time editing and proofreading your work to ensure it is clear, concise, and free of errors.
Editing involves reviewing and revising your work for clarity, organization, and overall coherence. This step allows you to enhance the flow of your ideas, structure your arguments effectively, and eliminate any unnecessary or repetitive information. Additionally, it gives you the opportunity to improve the overall readability and engagement of your work for your intended audience.
Proofreading, on the other hand, focuses on correcting grammatical, spelling, and punctuation errors. This stage involves meticulously checking your written piece for any mistakes and making necessary edits. By carefully proofreading your work, you can ensure that it is polished and professional, demonstrating your attention to detail and commitment to producing quality content.
When editing and proofreading, it is essential to take a step back and approach your work with a fresh perspective. Give yourself enough time between writing and editing to gain a new outlook and allow errors and inconsistencies to become more noticeable.
During the editing process, read through your work attentively and identify areas that need improvement. Look for clarity issues, awkward sentence structures, or illogical transitions. Consider the overall organization and coherence of your ideas and make any necessary adjustments to enhance the flow of your work.
When proofreading, pay close attention to grammar, spelling, and punctuation. Use spell check tools as a starting point, but be aware that they may not catch all errors and can sometimes even introduce new ones. Read your work aloud to identify any awkward phrasing or missing words. Consider seeking the assistance of a trusted friend or colleague to provide a fresh set of eyes and offer constructive feedback.
To ensure the utmost accuracy in your editing and proofreading, take advantage of the resources available to you. Use style guides and dictionaries to verify correct usage, spelling, and punctuation. Consult grammar reference books or reputable online sources to address specific grammar or usage questions.
By devoting time and attention to meticulously edit and proofread your work, you can elevate your essay or report to a higher level of professionalism and ensure that your message is communicated effectively to your readers.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.
How to Write a Report - Tips and Sample

What is a Report
A report is a written document that presents findings from an investigation, project, or study. It analyzes specific issues or data in detail. This type of writing is common in sciences, social sciences, and business, making it a valuable skill across different fields. Reports have a clear purpose and target audience. Like all academic writing, they emphasize clarity and brevity. Before starting, understand any guidelines in your brief and use headings to organize your report effectively.
Key parts of a report typically include:
- Detailed summaries of events or activities
- Analysis of their impact
- Evaluation of facts and data
- Predictions for future developments
- Recommendations for next steps
Reports differ from essays. While both use factual information, essays include personal opinions and arguments. Reports focus on facts, with interpretations mainly in the conclusion. They are highly structured, often with tables of contents, headings, and subheadings, which help readers quickly locate information. Essays, in contrast, are usually read straight through without needing to jump between sections.
Jobs that Use Written Reports
Many professions rely on written reports to communicate findings, make decisions, and guide future actions. Some of these jobs include:
- Scientists and Researchers : They use reports to document experiments, present research findings, and analyze data. These reports are crucial for advancing knowledge in their fields.
- Healthcare Professionals : Doctors, nurses, and medical researchers write reports to track patient progress, document clinical trials, and share medical research results.
- Business Analysts and Managers : They create reports to analyze market trends, assess financial performance, and propose business strategies. These reports help companies make informed decisions.
- Engineers and Technicians : Reports are used to document project progress, troubleshoot problems, and provide technical evaluations. They are essential for ensuring projects stay on track and meet specifications.
- Law Enforcement and Legal Professionals : Police officers, detectives, and lawyers write reports to document incidents, investigations, and legal proceedings. These reports are vital for building cases and ensuring justice.
- Academics and Educators : Professors, teachers, and educational researchers write reports to present research findings, assess educational methods, and evaluate student performance.
- Environmental Scientists and Conservationists : They use reports to document environmental studies, assess the impact of human activities on ecosystems, and propose conservation strategies.
- Journalists and Writers : They create investigative reports, feature stories, and analysis pieces to inform the public about current events, trends, and important issues.
- Government Officials and Policy Makers : They write reports to analyze policy impacts, assess program effectiveness, and provide recommendations for legislative actions.
- Financial Advisors and Accountants : Reports are used to analyze financial data, evaluate investment options, and provide clients with detailed financial assessments and plans.
Writing Reports Are Not Your Thing?
Our professional writers will get you any report type meeting your requirements in no time
Guide on How to Write a Report
Writing a report can seem challenging, but with clear steps, it becomes manageable. This section will simplify the process, helping you create well-structured and informative reports. Whether you need to write for work, school, or personal projects, following this guide will ensure your report is effective and easy to read. Let's start by breaking down the essential parts and understanding the purpose of each section.
If you want to save time, you can always buy essays online .
.webp)
Understand the Brief
Before you begin writing your report, you must first understand the brief. This step ensures that you know exactly what is required and expected. Here's how to do it:
- Read the Brief Carefully: Make sure you read the assignment or project brief thoroughly. Look for key details such as the purpose of the report, the target audience, and any specific requirements or guidelines.
- Identify the Main Objectives: Determine what the report aims to achieve. Is it to inform, analyze, recommend, or persuade? Knowing the objective helps shape your content and approach.
- Clarify Doubts: If anything is unclear, don't hesitate to ask for clarification. It's better to ask questions upfront than to guess and risk misunderstanding the task.
- Take Notes: Jot down important points from the brief. Highlight deadlines, required sections, and any specific data or information you need to include
Gather Information
Not every piece of information will fit in your report, so choose the ones that directly relate to your topic and support your main points. Finding all the information needed for your report will involve talking to people, reading articles and books, or looking at data like charts and graphs.
Once you have everything, take a moment to organize it. Is there information about the background, the main points, or any conclusions? Think of categories to group similar things together.
Meanwhile, If you want to further advance your writing skills, read our article about how to write a cover letter for essay .
Organize and Analyze Material
Now that you've sorted your information pieces, it's time to see how they fit together. Look for patterns and relationships between the information. Do some pieces contradict each other? Are there different perspectives on the same topic?
Once you see connections, group related pieces together. Think of headings or labels for each group that capture the main idea of that section. This will be the framework for your report's structure.
It is also important to not just describe the information but dig deeper. What does it all mean? Are there trends or underlying causes you can identify? Use your analysis to support your report's arguments or conclusions.
Write the First Draft
Now that you've gathered and organized your information, it's time to build your report. This is where you write your first draft. Start with a strong foundation:
- Grab your reader's attention and introduce the topic of your report. Briefly explain what you'll be covering and why it's important.
- In the body section, use organized information to build your case. Each paragraph should focus on one main point and use evidence from your research (facts, figures, quotes) to support it.
- Some reports may benefit from additional sections like a methodology (how you gathered information) or a limitations section (acknowledging any constraints of your study). Review your report's purpose and see if these sections are necessary.
This is a first draft, so focus on getting your ideas down on paper. Don't get bogged down in perfect grammar or style – you can polish that later. Just make sure you write in a clear way and use everyday language your target audience can understand. Don't be afraid to write freely and rearrange sections later. It's easier to work with a complete draft than a collection of disconnected thoughts.
Review and Redraft
Congratulations, you've conquered the first draft! Now comes the crucial stage of reviewing, editing, and redrafting. This is where you transform your rough draft into a polished and professional report.
Put your report aside for a day or two. This allows you to come back with fresh eyes and a more objective perspective. After, read your report aloud. Does it make sense? Does it flow smoothly from one point to the next? Are there any confusing sections that need clarification?
To edit with a keen eye, follow these tips:
- Grammar and mechanics: This is where you hunt down typos, grammatical errors, and punctuation mistakes. Use a spellchecker, but don't rely solely on it.
- Sentence structure and style: Can you improve the flow of your sentences? Are they concise and easy to understand? Avoid jargon and overly complex sentence structures.
- Strengthen your arguments: Review your evidence. Does it adequately support your claims? Are there any gaps that need to be filled?
- Conciseness is key: Look for opportunities to tighten your writing without sacrificing clarity. Eliminate unnecessary words and redundancy.
- Tailoring your tone: Is your report written in an appropriate tone for your audience? You might need to adjust the formality depending on whether you're writing for a manager, a client, or a scientific journal.
Report Structure Checklist
| Section 📝 | Description 📄 |
|---|---|
| Title Page | |
| Terms of Reference | |
| Summary | |
| Table of Contents | |
| Introduction | |
| Methodology | |
| Results | |
| Discussion | |
| Conclusion | |
| Appendices | |
| Bibliography |
Report Types
There are different types of report papers. Even though they are very formal, academic reports are only one of many people will come across in their lifetime. Some reports concentrate on the annual performance of a company, some on a project's progress, and others on scientific findings.
.webp)
Academic Reports
An academic report represents supported data and information about a particular subject. This could be a historical event, a book, or a scientific finding. The credibility of such academic writing is very important as it, in the future, could be used as a backup for dissertations, essays, and other academic work.
Students are often assigned to write reports to test their understanding of a topic. They also provide evidence of the student's ability to critically analyze and synthesize information. It also demonstrates the student's writing skills and ability to simply convey complex findings and ideas.
Project Reports
Every project has numerous stakeholders who like to keep an eye on how things are going. This can be challenging if the number of people who need to be kept in the loop is high. One way to ensure everyone is updated and on the same page is periodic project reports.
Project managers are often assigned to make a report for people that affect the project's fate. It is a detailed document that summarizes the work done during the project and the work that needs to be completed. It informs about deadlines and helps form coherent expectations. Previous reports can be used as a reference point as the project progresses.
Sales Reports
Sales reports are excellent ways to keep your team updated on your sales strategies. It provides significant information to stakeholders, including managers, investors, and executives, so they can make informed decisions about the direction of their business.
A sales report usually provides information about a company's sales performance over a precise period. These reports include information about the revenue generated, the total number of units sold, and other metrics that help the company define the success of sales performance.
Sales report preparation is a meticulous job. To communicate information engagingly, you can put together graphs showing various information, including engagement increase, profit margins, and more.
Business Reports
If you were assigned a business report, something tells us you are wondering how to write a report for work. Let us tell you that the strategy is not much different from writing an academic report. A Strong thesis statement, compelling storytelling, credible sources, and correct format are all that matter.
Business reports can take many forms, such as marketing reports, operational reports, market research reports, feasible studies, and more. The purpose of such report writing is to provide analysis and recommendations to support decision-making and help shape a company's future strategy.
Most business reports include charts, graphs, and other visual aids that help illustrate key points and make complex information easy to digest.
Scientific Reports
Scientific reports present the results of scientific research or investigation to a specific audience. Unlike book reports, a scientific report is always reviewed by other experts in the field for its accuracy, quality, and relevance.
If you are a scientist or a science student, you can't escape writing a lab report. You will need to provide background information on the research topic and explain the study's purpose. A scientific report includes a discussion part where the researcher interprets the results and significance of the study.
Whether you are assigned to write medical reports or make a report about new findings in the field of physics, your writing should always have an introduction, methodology, results, conclusion, and references. These are the foundation of a well-written report.
Annual Reports
An annual report is a comprehensive piece of writing that provides information about a company's performance over a year. In its nature, it might remind us of extended financial reports.
Annual reports represent types of longer reports. They usually include an overview of a company's activities, a financial summary, detailed product and service information, and market conditions. But it's not just a report of the company's performance in the sales market, but also an overview of its social responsibility programs and sustainability activities.
The format of annual report writing depends on the company's specific requirements, the needs of its stakeholder, and the regulation of the country it's based.
Student Research Report Sample
Here is a sample report that uses the format and tips we discussed in the article. Remember, this is just an example. Feel free to adjust the content to match your own research findings and analysis.
Meanwhile, if you need an expert to help with your physics homework, our physics helper is ready to take on the job!
The Bottom Line
By following the steps and tips outlined in this guide, you can create a clear, concise, and effective report. Remember to:
- Understand the brief thoroughly before you start.
- Use headings and subheadings to organize your report logically.
- Keep your writing clear, focusing on facts and analysis.
- Tailor your content to your audience and purpose.
- Proofread carefully to ensure clarity and accuracy.
And if you're short on time for other assignments, just say, ' write my argumentative essay ,' and our expert writers will gladly help you out.
Are You Looking for Help with Your Writing?
Our expert writers will provide top-notch assistance with any writing project
How to Write a Short Report?
What is the format of a report, what is the structure of a report.

Annie Lambert
specializes in creating authoritative content on marketing, business, and finance, with a versatile ability to handle any essay type and dissertations. With a Master’s degree in Business Administration and a passion for social issues, her writing not only educates but also inspires action. On EssayPro blog, Annie delivers detailed guides and thought-provoking discussions on pressing economic and social topics. When not writing, she’s a guest speaker at various business seminars.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
- Added new sections like defining reports, jobs that use reports, checklist, etc
- Added a new sample, FAQs and a checklist
- Updated writing guidelines
- REPORT WRITING TOP TIP Writing the report: where do I start? TOP TIP Understand the brief . (n.d.). https://www.ucc.ie/en/media/support/skillscentre/pdfx27sampbookmarks/ReportWriting.pdf
- EAP Writing Reports . (n.d.). Www.uefap.com. Retrieved June 26, 2024, from https://www.uefap.com/writing/genre/report.htm

How to Write a Report Essay (Plus Example) – PDF

Today, you’re going to learn how to write a report essay as part of your high school English Language course.
I will first show you the format or main features of a typical report essay. You can call it a report essay template. Then I will give you some tips to guide you any time you need to write a report essay.
At the end of it all, you will have a sample report essay which you may freely download and study.
Report Writing Format
INTRODUCTION
To write a good report essay, you need to have a conclusion. Make a quick summary of the key points you have been writing about in the body of the report.
YOUR NAME AND CREDENTIALS
Follow these guidelines to write a report essay you will be proud of.
Use names and pronouns
GRAMMATICAL NAME AND FUNCTIONS OF PRONOUNS
State your points clearly and be specific
Use simple language, active voice is better.
Use active voice for more sentences as you write a report essay. For instance, instead of “Mr Tomson was invited to the classroom.” (PASSIVE VOICE), write: “We invited Mr.Tomson to the classroom.” (ACTIVE VOICE).
Focus on relevant facts.
Write in brief paragraphs, report essay sample for high school.
QUESTION: There was a disagreement between your class and one of your teachers. As the class prefect, write a report to the head of your school on the incident.
A REPORT TO THE HEADMASTER ON A DISAGREEMENT BETWEEN MR. SAM TOMSON AND TECHNICAL 3B CLASS
On 18 th October 2020, Technical 3B class had English Language on the time table for the day. As the class prefect, I went and called Mr. Tomson. He came in with some books. He promptly announced to the class that he was going to use that book to teach the lesson. For that matter, every student must buy one so that the class could have effective studies and also to make the lesson easier for him and the class.
The book in question is No Sweetness Her e by Ama Ata Aidoo.
Mr. Tomson then said, “Today is the day you must pay for the books you bought because the owner of the books is this man. His name is Mr Sowah and he is here to take his money”.
Immediately, Mr Tomson got annoyed. He told John Dumelo he was a useless person. The whole class quickly rose to support John Dumelo because Mr. Tomson who was demanding that money was the same person who told the class that the books were sold on credit for two weeks.
The dispute became so serious that it got very close to a fight. Mr. Sowah (the owner of the books) eventually agreed that the students should pay the money in the stipulated two weeks’ time.
He, therefore, went away without teaching the English lesson for the day.
The next time it was time for English , we called Mr. Tomson for the lesson but he refused to show up. He said unless the class wrote an apology letter or brought someone to plead on their behalf, he would not step into the class for lessons. The class also said they had done nothing wrong to warrant their writing of an apology letter.
Sir, as the class prefect, I have to let you know about the situation just as you demanded. I hope this report would be given the much needed attention so that we can have our English Language lessons back. Thank you.
(CLASS PREFECT)
Did you find this information helpful? Then share it on your favourite social media platform for the benefit of others you care about. Thank you!
Image by Anja🤗#helpinghands #solidarity#stays healthy🙏 from Pixabay

Cegast Academy
Share this post.

Get Exclusive Updates & Offers

11 Unseen Prose Past Questions and Answers – PDF

WAEC Sample Comprehension Questions and Answers (Part 3)

Discuss the Theme of Domestic Violence in Second Class Citizen

Do Not Go Gentle into that Good Night Poem

Functions of the Security Council of the United Nations

Debate Speech: Religion Has Failed Our Society

One-Party System – Features, Advantages, and Disadvantages

Faceless: The Character and Role of Maa Tsuru
Leave a comment cancel reply.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Official Writing
- Report Writing
How to Write a Report
Last Updated: September 5, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA and by wikiHow staff writer, Amy Bobinger . Emily Listmann is a Private Tutor and Life Coach in Santa Cruz, California. In 2018, she founded Mindful & Well, a natural healing and wellness coaching service. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. Emily also received her Wellness Coach Certificate from Cornell University and completed the Mindfulness Training by Mindful Schools. There are 22 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 8,771,196 times.
When you’re assigned to write a report, it can seem like an intimidating process. Fortunately, if you pay close attention to the report prompt, choose a subject you like, and give yourself plenty of time to research your topic, you might actually find that it’s not so bad. After you gather your research and organize it into an outline, all that’s left is to write out your paragraphs and proofread your paper before you hand it in!
Easy Steps to Write a Report
- Choose an interesting topic and narrow it down to a specific idea.
- Take notes as you research your topic. Come up with a thesis, or main theme of your report, based on your research.
- Outline the main ideas you’ll cover in your report. Then, write the first draft.
Sample Reports

Selecting Your Topic

- The guidelines will also typically tell you the requirements for the structure and format of your report.
- If you have any questions about the assignment, speak up as soon as possible. That way, you don’t start working on the report, only to find out you have to start over because you misunderstood the report prompt.

- For instance, if your report is supposed to be on a historical figure, you might choose someone you find really interesting, like the first woman to be governor of a state in the U.S., or the man who invented Silly Putty.
- If your report is about information technology , you could gather information about the use of computers to store, retrieve, transmit, and manipulate data or information.
- Even if you don’t have the option to choose your topic, you can often find something in your research that you find interesting. If your assignment is to give a report on the historical events of the 1960s in America, for example, you could focus your report on the way popular music reflected the events that occurred during that time.
Tip: Always get approval from your teacher or boss on the topic you choose before you start working on the report!

- If you’re not sure what to write about at first, pick a larger topic, then narrow it down as you start researching.
- For instance, if you wanted to do your report on World Fairs, then you realize that there are way too many of them to talk about, you might choose one specific world fair, such as the Panama-Pacific International Exposition, to focus on.
- However, you wouldn’t necessarily want to narrow it down to something too specific, like “Food at the Panama-Pacific International Exposition,” since it could be hard to find sources on the subject without just listing a lot of recipes.
Researching the Report

- If you don’t have guidelines on how many sources to use, try to find 1-2 reputable sources for each page of the report.
- Sources can be divided into primary sources, like original written works, court records, and interviews, and secondary sources, like reference books and reviews.
- Databases, abstracts, and indexes are considered tertiary sources, and can be used to help you find primary and secondary sources for your report. [5] X Research source
- If you’re writing a business report , you may be given some supplementary materials, such as market research or sales reports, or you may need to compile this information yourself. [6] X Research source

- Librarians are an excellent resource when you're working on a report. They can help you find books, articles, and other credible sources.
- Often, a teacher will limit how many online sources you can use. If you find most of the information you need in the library, you can then use your online sources for details that you couldn’t find anywhere else.
Tip: Writing a report can take longer than you think! Don't put off your research until the last minute , or it will be obvious that you didn't put much effort into the assignment.

- Examples of authoritative online sources include government websites, articles written by known experts, and publications in peer-reviewed journals that have been published online.

- If you’re using a book as one of your sources, check the very back few pages. That’s often where an author will list the sources they used for their book.

- Remember to number each page of your notes, so you don’t get confused later about what information came from which source!
- Remember, you’ll need to cite any information that you use in your report; however, exactly how you do this will depend on the format that was assigned to you.

- For most reports, your thesis statement should not contain your own opinions. However, if you're writing a persuasive report, the thesis should contain an argument that you will have to prove in the body of the essay.
- An example of a straightforward report thesis (Thesis 1) would be: “The three main halls of the Panama-Pacific International Exposition were filled with modern creations of the day and were an excellent representation of the innovative spirit of the Progressive era.”
- A thesis for a persuasive report (Thesis 2) might say: “The Panama-Pacific International Exposition was intended as a celebration of the Progressive spirit, but actually harbored a deep racism and principle of white supremacy that most visitors chose to ignore or celebrate.”

- The purpose of an outline is to help you to visualize how your essay will look. You can create a straightforward list or make a concept map , depending on what makes the most sense to you.
- Try to organize the information from your notes so it flows together logically. For instance, it can be helpful to try to group together related items, like important events from a person’s childhood, education, and career, if you’re writing a biographical report.
- Example main ideas for Thesis 1: Exhibits at the Court of the Universe, Exhibits at the Court of the Four Seasons, Exhibits at the Court of Abundance.
Tip: It can help to create your outline on a computer in case you change your mind as you’re moving information around.
Writing the First Draft

- Try to follow any formatting instructions to the letter. If there aren't any, opt for something classic, like 12-point Times New Roman or Arial font, double-spaced lines, and 1 in (2.5 cm) margins all around.
- You'll usually need to include a bibliography at the end of the report that lists any sources you used. You may also need a title page , which should include the title of the report, your name, the date, and the person who requested the report.
- For some types of reports, you may also need to include a table of contents and an abstract or summary that briefly sums up what you’ve written. It’s typically easier to write these after you’ve finished your first draft. [14] X Research source

- Example Intro for Thesis 1: “The Panama-Pacific International Exposition (PPIE) of 1915 was intended to celebrate both the creation of the Panama Canal, and the technological advancements achieved at the turn of the century. The three main halls of the PPIE were filled with modern creations of the day and were an excellent representation of the innovative spirit of the Progressive era.”

- Typically, you should present the most important or compelling information first.
- Example topic sentence for Thesis 1: At the PPIE, the Court of the Universe was the heart of the exposition and represented the greatest achievements of man, as well as the meeting of the East and the West.
Tip: Assume that your reader knows little to nothing about the subject. Support your facts with plenty of details and include definitions if you use technical terms or jargon in the paper.

- Paraphrasing means restating the original author's ideas in your own words. On the other hand, a direct quote means using the exact words from the original source in quotation marks, with the author cited.
- For the topic sentence listed above about the Court of the Universe, the body paragraph should go on to list the different exhibits found at the exhibit, as well as proving how the Court represented the meeting of the East and West.
- Use your sources to support your topic, but don't plagiarize . Always restate the information in your own words. In most cases, you'll get in serious trouble if you just copy from your sources word-for-word. Also, be sure to cite each source as you use it, according to the formatting guidelines you were given. [18] X Research source

- Your commentary needs to be at least 1-2 sentences long. For a longer report, you may write more sentences for each piece of commentary.

- Avoid presenting any new information in the conclusion. You don’t want this to be a “Gotcha!” moment. Instead, it should be a strong summary of everything you’ve already told the reader.
Revising Your Report

- A good question to ask yourself is, “If I were someone reading this report for the first time, would I feel like I understood the topic after I finished reading?
Tip: If you have time before the deadline, set the report aside for a few days . Then, come back and read it again. This can help you catch errors you might otherwise have missed.

- Try reading the report to yourself out loud. Hearing the words can help you catch awkward language or run-on sentences you might not catch by reading it silently.

- This is a great trick to find spelling errors or grammatical mistakes that your eye would otherwise just scan over.

- Ask your helper questions like, “Do you understand what I am saying in my report?” “Is there anything you think I should take out or add?” And “Is there anything you would change?”

- If you have any questions about the assignment requirements, ask your instructor. It's important to know how they'll be grading your assignment.
Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libguides.reading.ac.uk/reports/writing-up
- ↑ https://emory.libanswers.com/faq/44525
- ↑ https://opentextbc.ca/writingforsuccess/chapter/chapter-7-sources-choosing-the-right-ones/
- ↑ https://libguides.merrimack.edu/research_help/Sources
- ↑ https://www.wgtn.ac.nz/__data/assets/pdf_file/0010/1779625/VBS-Report-Writing-Guide-2017.pdf
- ↑ https://www.library.illinois.edu/hpnl/tutorials/primary-sources/
- ↑ https://libguides.scu.edu.au/harvard/secondary-sources
- ↑ https://learningcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/taking-notes-while-reading/
- ↑ https://wts.indiana.edu/writing-guides/how-to-write-a-thesis-statement.html
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/outline
- ↑ https://ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub/engl250oer/chapter/10-4-table-of-contents/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/thesis-statements/
- ↑ https://www.yourdictionary.com/articles/report-writing-format
- ↑ https://www.monash.edu/student-academic-success/excel-at-writing/how-to-write/essay/how-to-build-an-essay
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/5-most-effective-methods-for-avoiding-plagiarism/
- ↑ https://wts.indiana.edu/writing-guides/using-evidence.html
- ↑ https://www.student.unsw.edu.au/writing-report
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/revising-drafts/
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/grammarpunct/proofreading/
- ↑ https://opentextbc.ca/writingforsuccess/chapter/chapter-12-peer-review-and-final-revisions/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

It can seem really hard to write a report, but it will be easier if you choose an original topic that you're passionate about. Once you've got your topic, do some research on it at the library and online, using reputable sources like encyclopedias, scholarly journals, and government websites. Use your research write a thesis statement that sums up the focus of your paper, then organize your notes into an outline that supports that thesis statement. Finally, expand that outline into paragraph form. Read on for tips from our Education co-author on how to format your report! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
NIYONSENGA J.
Did this article help you?
Bella McKinnon
Mar 10, 2018
Manasseh M.
Mar 20, 2023
Nov 27, 2018
Nazim Ullah
Apr 16, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
Report Writing Format, Tips, Samples and Examples
- December 11, 2023
- 8 minutes read
- Listen to this
- What is Report Writing? Learn how to write a report, format, topics, tips, common mistakes and Examples of Report Writing.
Report Writing: How to Write a Report (Format, Tips, Common Mistakes, Samples and Examples of Report Writing)
Struggling to write clear, concise reports that impress? Fear not! This blog is your one-stop guide to mastering report writing . Learn the essential format, uncover impactful tips, avoid common pitfalls, and get inspired by real-world examples.
Whether you’re a student, professional, or simply seeking to communicate effectively, this blog empowers you to craft compelling reports that leave a lasting impression.
Must Read: Notice Writing: How to write, Format, Examples
What is Report Writing ?
Report Writing – Writing reports is an organized method of communicating ideas, analysis, and conclusions to a target audience for a predetermined goal. It entails the methodical presentation of information, statistics, and suggestions, frequently drawn from study or inquiry.
Its main goal is to inform, convince, or suggest actions, which makes it a crucial ability in a variety of professional domains.
A well-written report usually has a concise conclusion, a well-thought-out analysis, a clear introduction, a thorough methodology, and a presentation of the findings.
It doesn’t matter what format is used as long as information is delivered in a logical manner, supports decision-making, and fosters understanding among stakeholders.
Must Read : Article Writing Format, Objective, Common Mistakes, and Samples
Format of Report Writing
Title Page:
- Title of the report.
- Author’s name.
- Date of submission.
- Any relevant institutional affiliations.
Abstract/Summary:
- A brief overview of the report’s key points.
- Summarizes the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions.
Table of Contents:
- Lists all sections and subsections with corresponding page numbers.
Introduction:
- Provides background information on the subject.
- Clearly states the purpose and objectives of the report.
Methodology:
- Details how the information was gathered or the experiment conducted.
- Includes any relevant procedures, tools, or techniques used.
Findings/Results:
- Presents the main outcomes, data, or observations.
- Often includes visual aids such as charts, graphs, or tables.
Discussion:
- Analyzes and interprets the results.
- Provides context and explanations for the findings.
Conclusion:
- Summarizes the key points.
- May include recommendations or implications.
Must Read: Directed Writing: Format, Benefits, Topics, Common Mistakes and Examples
Report Writing Examples – Solved Questions from previous papers
Example 1: historical event report.
Question : Write a report on the historical significance of the “ Battle of Willow Creek ” based on the research of Sarah Turner. Analyze the key events, outcomes, and the lasting impact on the region.
Solved Report:
Title: Historical Event Report – The “Battle of Willow Creek” by Sarah Turner
This report delves into the historical significance of the “Battle of Willow Creek” based on the research of Sarah Turner. Examining key events, outcomes, and the lasting impact on the region, it sheds light on a pivotal moment in our local history.
Sarah Turner’s extensive research on the “Battle of Willow Creek” provides a unique opportunity to explore a critical chapter in our local history. This report aims to unravel the intricacies of this historical event.
Key Events:
The Battle of Willow Creek unfolded on [date] between [opposing forces]. Sarah Turner’s research meticulously outlines the sequence of events leading to the conflict, including the political climate, disputes over resources, and the strategies employed by both sides.
Through Turner’s insights, we gain a nuanced understanding of the immediate outcomes of the battle, such as changes in territorial control and the impact on the local population. The report highlights the consequences that rippled through subsequent years.
Lasting Impact:
Sarah Turner’s research underscores the enduring impact of the Battle of Willow Creek on the region’s development, cultural identity, and socio-political landscape. The report examines how the event shaped the community we know today.
The “Battle of Willow Creek,” as explored by Sarah Turner, emerges as a significant historical event with far-reaching consequences. Understanding its intricacies enriches our appreciation of local history and its role in shaping our community.
Access the Learning Platform
Report Writing Samples
book review report.
Title: Book Review – “The Lost City” by Emily Rodriguez
“The Lost City” by Emily Rodriguez is an enthralling adventure novel that takes readers on a captivating journey through uncharted territories. The author weaves a tale of mystery, discovery, and self-realization that keeps the reader engaged from beginning to end.
Themes and Characters:
Rodriguez skillfully explores themes of resilience, friendship, and the pursuit of the unknown. The characters are well-developed, each contributing uniquely to the narrative. The protagonist’s transformation throughout the story adds depth to the overall theme of self-discovery.
Plot and Pacing:
The plot is intricately crafted, with twists and turns that maintain suspense and intrigue. Rodriguez’s ability to balance action scenes with moments of introspection contributes to the novel’s well-paced narrative.
Writing Style:
The author’s writing style is engaging and descriptive, allowing readers to vividly envision the settings and empathize with the characters. Dialogue flows naturally, enhancing the overall readability of the book.
“The Lost City” is a commendable work by Emily Rodriguez, showcasing her storytelling prowess and ability to create a captivating narrative. This novel is recommended for readers who enjoy adventure, mystery, and character-driven stories.
Boost your IGCSE Grades with 1-on-1 online tuition Book your Free Trial Today!
Report Writing Tips
Recognise your audience:
Take into account your target audience’s expectations and degree of knowledge. Adjust the content, tone, and language to the readers’ needs.
Precision and succinctness:
To communicate your point, use language that is simple and unambiguous. Steer clear of convoluted sentences or needless jargon that could confuse the reader.
Logical Structure:
Organize your report with a clear and logical structure, including sections like introduction, methodology, findings, discussion, and conclusion. Use headings and subheadings to improve readability.
Introduction with Purpose:
Clearly state the purpose, objectives, and scope of the report in the introduction. Provide context to help readers understand the importance of the information presented.
Methodology Details:
Clearly explain the methods or processes used to gather information. Include details that would allow others to replicate the study or experiment.
Presentation of Findings:
Give a well-organized and structured presentation of your findings. Employ graphics (tables, graphs, and charts) to support the text and improve comprehension.
Talk and Interpretation:
Examine the findings and talk about the ramifications. Explain the significance of the results and how they relate to the main goal.
Brief Conclusion:
Recap the main ideas in the conclusion. Indicate in detail any suggestions or actions that should be implemented in light of the results.
Specialist IGCSE Tutors, Revision Courses & Extensive Resources for Cambridge & Edexcel IGCSE Start your IGCSE Tuition Today!
Common mistakes for Report Writing
Insufficient defining:.
Error: Employing ambiguous or imprecise wording that could cause misunderstandings.
Impact: It’s possible that readers won’t grasp the content, which could cause misunderstandings and confusion.
Solution: Explain difficult concepts, use clear language, and express ideas clearly.
Inadequate Coordination:
Error: Not adhering to a coherent and systematic format for the report.
Impact: The report’s overall effectiveness may be lowered by readers finding it difficult to follow the information’s flow due to the report’s lack of structure.
Solution: Make sure the sections are arranged clearly and sequentially, each of which adds to the report’s overall coherence.
Inadequate Research:
Error: Conducting insufficient research or relying on incomplete data.
Impact: Inaccuracies in data or lack of comprehensive information can weaken the report’s credibility and reliability.
Solution: Thoroughly research the topic, use reliable sources, and gather comprehensive data to support your findings.
Inconsistent Formatting:
Error: Using inconsistent formatting for headings, fonts, or spacing throughout the report.
Impact: Inconsistent formatting can make the report look unprofessional and distract from the content.
Solution: Maintain a uniform format for headings, fonts, and spacing to enhance the visual appeal and professionalism of the report.
Unsubstantiated Conclusions:
Error: Drawing conclusions that are not adequately supported by the evidence or findings presented.
Impact: Unsubstantiated conclusions can undermine the report’s credibility and weaken the overall argument.
Solution: Ensure that your conclusions are directly derived from the results and are logically connected to your research objectives, providing sufficient evidence to support your claims.
To sum up, proficient report writing necessitates precision, organization, and clarity. Making impactful reports requires avoiding common errors like ambiguous wording, shoddy organization, inadequate research, inconsistent formatting, and conclusions that are not supported by evidence.
One can improve the caliber and legitimacy of their reports by following a logical format, carrying out extensive research, staying clear, and providing conclusions that are supported by evidence.
Aiming for linguistic accuracy and meticulousness guarantees that the desired meaning is communicated successfully, promoting a deeper comprehension of the topic among readers.
Pankaj Dhiman
See author's posts
Learn Anything, On Your Schedule
Designed for self-paced study, practice and revision
- Curated Study Resources
- 50000+ Practice Papers
- AI Exam Coach
- 200+ Topic Specific Videos
Join our community of 10,000+ students
Learn from the best teachers, an interactive learning platform, and a large library of engaging video sessions.
22 Changi Business Park Central 2, #02-08, Singapore, 486032,
All rights reserved ©2024 Tutopiya
Get Started
Learner guide
Tutor guide
IGCSE Tuition
IGCSE Revision & Exam Preparation
IB Revision & Exam Preparation
International AS & A-level Tuition
International AS & A-level Revision & Exam Preparation
Cambridge Lower Secondary Tuition
Cambridge Checkpoint Revision & Exam Preparation
Cambridge IGCSE Tuition
Edexcel IGCSE Tuition
Subjects & Curricula
IGCSE Maths Tuition
IGCSE Additional Math Tuition
IGCSE English Tuition
IGCSE English Literature Tuition
IGCSE Combined/Coordinated Science Tuition
IGCSE Physics Tuition
IGCSE Chemistry Tuition
IGCSE Biology Tuition
IGCSE Economics Tuition
IGCSE Business Studies Tuition
IGCSE Computer Science Tuition
A-level Maths Tuition
A-level Physics Tuition
A-level Biology Tuition
A-level Chemistry Tuition
A-level Economics Tuition
IB DP Maths Tuition
IB DP Physics Tuition
IB DP Chemistry Tuition
IB DP Biology Tuition
IB MYP Maths Tuition
IB MYP Science Tuition
IB MYP English Tuition
Cambridge Lower Secondary Maths Tuition
Cambridge Lower Secondary English Tuition
Cambridge Lower Secondary Science Tuition
Cambridge Primary Maths Tuition
Cambridge Primary English Tuition
Cambridge Primary Science Tuition
Privacy policy
Terms & Conditions
IGCSE Maths Resources
IGCSE English Language Resources
IGCSE English Literature Resources
IGCSE Physics Resources
IGCSE Chemistry Resources
IGCSE Biology Resources
IGCSE Economics Resources
IGCSE Business Studies Resources
IGCSE Computer Science Resources
IGCSE Additional Maths Resources
A-level Maths Resources
A-level Chemistry Resources
A-level Biology Resources
IB DP Maths Resources
IB DP Chemistry Resources
IB DP Biology Resources
Cambridge Lower Secondary Math Resources
Cambridge Lower Secondary English Resources
Cambridge Lower Secondary Science Resources
Fill out the form below and we will email you the webinar video.
- Design for Business
- Most Recent
- Presentations
- Infographics
- Data Visualizations
- Forms and Surveys
- Video & Animation
- Case Studies
- Digital Marketing
- Design Inspiration
- Visual Thinking
- Product Updates
- Visme Webinars
- Artificial Intelligence
Report Writing Format with Templates and Sample Report

Written by: Orana Velarde

If you’re probably wondering how to write a good report, you’re not alone. Many individuals face difficulties when it comes to report writing, as it requires a specific format and structure that can be confusing to navigate.
With so many types of reports - sales reports , marketing reports , school reports, social media reports and more, how do you know the best structure and organize your thoughts or data that would positively reflect your work?
It all lies in following the right report writing format. With the right format, you’ll be able to write your report with guidelines and make it easy to read and understand and make it easier for you to write as well.
Just as there are different types of reports, there are also different report formats and ways to deliver them. In this article, we’ll walk you through the best report writing formats, examples of reports, report layouts and templates for report writing.
Here's a short selection of 6 easy-to-edit report templates you can edit, share and download with Visme. View more templates below:

Table of Contents
6 types of reports, the ultimate report writing format, top report writing tips, how to write a report, sample report in standard report writing format, report writing format faqs.
- A report is unlike an essay, blog post or journalistic article. The main idea of a report is to present facts about a specific topic, situation, or event. It should always be in a clear and concise way.
- There are six main types of reports: annual reports, weekly reports, project reports, sales and marketing reports, research reports and academic reports.
- A report writing format includes a title, table of contents, summary, introduction, body, conclusion, recommendations and appendices.
- Top report writing tips include writing a report outline, creating the body of the report before the introduction or conclusion, sticking to facts, and keeping your appendix at a reasonable size.
- Visme offers not only hundreds of pre-made report templates but an initiative online report maker to provide you with everything you need to create high-quality reports for any niche, topic or industry.
There are six main types of reports you might encounter based on your goal or niche. In this section we’ll highlight and showcase what these reports are along with reports writing samples, each populated with a similar reporting writing format to what we'll cover further in this article.
1. Annual Reports
The first type of report we'll cover is an annual report . This type of company report format typically rounds up a business's year of progress and performance to let supervisors and team members know what they've accomplished.
It can include anything from website analytics to sales profits, depending on who the report is meant for.

2. Weekly Reports
One report that is helpful to provide your team is a weekly report based on your progress in various projects and goals. This can be a simple one-pager, or a more in-depth report with specific updates.

3. Project Reports
Keep clients and team members up-to-date on the status of various projects you're working on by providing them with a project report. This can include a timeline of your report progress and the deadline for each segment to keep everyone on the same page.

4. Sales/Marketing Reports
It's essential to keep your team updated on how your sales and/or marketing strategies are going. Put together graphs showing profit margins, increases in engagement and more.
These types of reports are also a great way to determine whether your strategies are working or if they need some tweaking in the future.

5. Research Report
Sometimes if you need to do some in-depth research, the best way to present that information is with a research report. Whether it's scientific findings, data and statistics from a study, etc., a research report is a great way to share your results.
For the visuals in your research report, Visme offers millions of free stock photos . But if you can’t find what you need, or are looking for something out of the box, try the Visme AI image generator . Prompt the AI tool to quickly create an image that matches your research, your brand and your report.

6. Academic Report
An academic report is one created for a class, often in a graduate or undergraduate university. This report format follows a formal writing style and dives into a topic related to the student's academic studies.

For more report examples you can learn from, check out our guide on Report Examples With Sample Templates .
Now we're getting to the good part — the ultimate report writing format. While this may vary based on the data and information you pull, it provides enough leeway for you to follow standard report formats.
Keep in mind that good report writing depends on first writing a report outline to start organizing the content in the best way possible.
A standard report format goes a little something like this:
- Title: A clear and concise report title.
- Table of Contents: A page dedicated to the contents of your report.
- Summary: An overview of your entire report — you'll need to wait until you've completed the full report to write this section.
- Introduction: Introduce your report topic and what readers will find throughout the pages.
- Body: The longest section of your report — compile all of your information and use data visualization to help present it.
- Conclusion: Different from the summary, this concludes the report body and summarizes all of your findings.
- Recommendations: A set of recommended goals or steps to complete with the information provided in this report.
- Appendices: A list of your sources used to compile the information in your report.
Each of these eight elements ensures that you leave no stone unturned and that your reader knows exactly what they're learning in your report and how you gathered this information.
Your next step is to get started with an outline. At each point of the outline, use one or two sentences to describe what will go in there. It doesn’t need to say much, just an idea for you to follow later. Input some design ideas for the overall design and report layout as well.
For example, in the Table of Contents section, simply add that you want it to only cover one page or slide, make a note if you’d like to add the pages for only the main sections or maybe also the subsections.
In the Appendices section, list all the links to the sources you used and add on as you do more research. Every source you reference in your report must be listed here.
The most important part of your outline is the Body section. In there, create an internal outline of sections and subsections that you can follow later when writing.

After you’ve drafted the outline, it’s time to put together all of the content into the report. The outline we provided above is the only report writing format you’ll ever need. You can add sections if needed but don’t take any away.
Let’s take a look at every section in detail.

Create your own Report with this easy-to-edit template! Edit and Download
The title of your report should be clear in its wording. It must say exactly what the report is about. Remember that this isn’t a novel. Include a subtitle if necessary, making sure the font size of each subtitle is smaller than the title.
In terms of design , your title can be designed as an inviting cover page. There needs to be a clear hierarchy in how the title looks.
On your title or cover page , be sure to include the following:
- Report title
- Report subtitle (if necessary)
- Author of the report
- Who the report is meant for
- Date the report was written
If you’re having trouble coming up with an interesting title or report content, you can get some help from the Visme AI Writer . Describe your report in the text prompt and ask the AI to write a few optional titles. If the first results aren’t to your liking, ask it to do some edits until you have just what you need.

Always leave the Table of Contents page until the end. After all, you can’t write a table of contents if you don’t know all of your page numbers yet.
However, if your Body outline already has each of your section and subsection titles defined, you can add those to the contents and leave the numbering for later.
Having a Table of Content pages makes it easy for your readers to find the information they're most interested in quickly and easily, improving overall readability. So you absolutely do not want to skip this step.

Likewise, the summary (also known as the abstract) of the report is best done after you’ve finished writing the report. You can draft a summary at the beginning to help guide your work, but you’ll definitely want to revisit it at the end. When you do, try using different paraphrasing techniques to ensure that you're not using repetitive phrases already present throughout the report.
A summary is a blurb of the entire report . It must include the purpose, the process and a snippet of the resolution. This should be no longer than a single paragraph or two.
Alternatively, if your report is data-heavy, the summary can also be a detail report where you share detailed data. Plus, you can add a hyperlink to further data analysis regarding what you’re reporting about.
Introduction

In the introduction, state what the report is about and why it has been created. Depending on the length of your report, the introduction format could range from one single paragraph to an entire page long.
For example, one paragraph is enough for a social media report introduction while an entire page would be more suitable for an annual report .
Take this time to introduce why your topic is so important, especially if it's a research report. You need to focus on why your readers should care about what you have uncovered.

The body of your report is where all the information is put together and will be the longest section of your report. This will likely span several (anywhere from 5-50) pages. Follow your initial outline to maintain consistent flow in the content creation. Write the body content as sections and subsections.
Furthermore, use bullet points and data visualization as visual cues . These will help your audience to better understand the content of your report.
Check out this video from Visme for some tips on visualizing all that data!

Close your report with a well-crafted conclusion . Formulate it as a brief summary of what was covered within the report, and be sure to include a mention to the recommendations section and the resources in the appendix.
This section should never bring new information to the table — instead, it should simply summarize all of the findings you've already mentioned into one concise final section.
Recommendations

Craft the recommendations section as a set of actionable steps with smart goals associated along with possible solutions. This section is irrelevant for school reports or book reports, but is essential for business reports or corporate settings.

This is the section where you list all your sources if it’s a research report. You should also add any links that are relevant to the report — or previous reports about the same topic.
You could even link an interactive version of the report you just created with Visme. Visme allows you to create interactive and animated documents that can be published to the web with a single click, offering a new dimension to your report.
A good rule of thumb when creating your appendices is to only add information that is relevant to the report or that you referenced when writing your report. Use reference annotations inside the report to link to the content in the appendix.
The report content used in this sample report design can be found here .
Following a report writing format is only a portion of the report writing process. When it comes to the content being placed in that context, it needs to be executed in a professional manner that will not only inform your reader but engage them from start to finish as well.
Here are some writing tips and best practices you should follow to complete your report in style.

Looking to create a stand-out visual report?
- Choose from dozens of professionally designed templates
- Create animated charts and creatively visualize stats and figures
- Customize anything to fit your brand image and content needs
Start With the Body of the Report
It's helpful to write the body of the report before the introduction or conclusion so you have a comprehensive overview of what key points should be covered in each section. This rule applies whether you're writing the report independently or as a team.
For the body of your report, you can assign specific sections to your team members and then appoint someone to write the conclusion and intro once it's complete.
Visme provides a space for team collaboration where you and your team members can work on your report simultaneously, adding comments, real-time updates and more. This feature helps to ensure everyone contributes and each section of your report is completed and well-rounded.
Use Visuals with Purpose
Don’t simply add visuals for the sake of adding them. Instead, by adding data visualization, you can condense complex information, pinpoint relationships and showcase values and risk. Not to mention a single chart can save you from adding unnecessary text to your report. Give each visual a strong purpose in your report.
Next to data visualization, you should also be mindful of what images you choose to include in your report, whether they’re used as a backdrop or illustration of the topic at hand. You can dive into Visme’s extensive library of royalty-free images, upload your own or create your own with Visme’s AI-powered Image Generator .
Tap into the infinite possibilities of AI image generation right inside your Visme editor. Available inside any project, old or new, just type in your prompts and generate creative and unique visuals for your report.
Write a Well Crafted Report
To ensure your report holds credibility, it must be error-free with proper spelling, grammar and tone. You should only use acronyms or jargon that are associated with your industry or profession, only if needed.
Try to use simple language and avoid adding unnecessary fluff. Lastly, before you send off your report, be sure to review it or ask for a colleague's opinion to ensure everything is in place.
You can send your report as a shareable link for a quick review or invite your colleague directly into your Visme project to decide if they can view, edit or comment on it. Make updates and share changes in real-time to streamline a faster editing process and have your report polished and ready to share with your audience.
Keep Your Appendix Short
Avoid creating a large appendix, as it can be intimidating or burdensome for the reader. It’s best only to add information or sources relevant to the report’s main points. One way to implement this tip is to review your appendix only after your report’s been completed, then do an extensive review to see what needs to stay or be removed until you're satisfied with the size of your appendix.
Use a Grammar Checker
If it’s accessible, ask an editor or writer to review your article. You can also use tools like Hemmingway, ProWritingAid or Grammarly . Even your best KPIs and ROIs won’t save you from bad grammar.
Writing a report may seem challenging, but anyone can do it with a proper plan, the right tools and some practice. You can sign up for Visme's AI Report Writer and follow these simple steps to write your own report.
Step 1: Define Your Objective
Before you put pen to paper, identify your reasons for writing the report. What do you want to accomplish with it? What is the purpose of your research, and why will it be important to others?
You might need to create a monthly , weekly , or annual report . Or, it could be a business report, including sales, marketing or social media reports .
No matter what type of report you are writing, the objective will guide you through the rest of the process.
Also, consider your target audience who will be reading it. For example, if you are writing a sales repor t for your team, it might be important to include data that shows their performance compared to the previous month, like the example below.

If you are writing a project status report like this, you must focus on showing the project's performance over a period of time.

In either case, your objective will help you determine what information is essential in your report and how much should be included.
Step 2: Conduct Research
Start by gathering relevant data and information from various sources, such as books, articles, interviews and online resources. Also, you can find data from your company's files, sheets, CRM or sales software and any other source you can.
As you explore different perspectives and evidence, you'll better understand the topic and be equipped to present a comprehensive analysis.
While researching, take notes and keep track of your sources for easy referencing later. In-depth research lays a solid foundation for a credible and insightful report.
Step 3: Prepare an Outline
Creating an outline provides a structured framework that guides your writing and keeps you focused. Start with the main headings like introduction, body and conclusion. Under each, add subheadings of key points or arguments you will cover.
An outline organizes your thoughts and lets you see where information fits best, ensuring a logical flow of ideas in your report. This planning tool ultimately makes the writing process easier and more efficient.
Step 4: Write the First Draft
After conducting research and preparing an outline, it's time to write your first draft. Start by stating your purpose in the introduction. Expand on your main points and provide necessary information and arguments in the body section.
Lastly, summarize and conclude your ideas. Don't focus on perfection in this stage; just get your thoughts down. It might look rough, but that's okay. This draft is your starting point, where you'll improve in the next revision and editing stages.
You can use Visme's AI writer to simplify the report writing process. It can help you prepare structured outlines, generate compelling report content and proofread text to ensure it's error-free. Just explain what you want to generate, and the AI writer will do the rest.
Step 5: Revise and Edit
This is one of the most important steps in this whole process. It involves reviewing the structure, flow and content of your report. Check your arguments, their logical presentation and if your evidence supports the claims.
Also, focus on editing the report by checking language, spelling, punctuation, style and formatting. You can use grammar checker tools like Grammarly and Hemmingway editor.
The more time you spend editing your report, the more clearly it conveys your message.
Step 6: Share the Report
Once your report is complete and you are satisfied with the results, it’s time to share it with your audience. You may need to share your report in various file formats and channels.
If you use Visme to write your report, you can download and share your report in many different ways:
- Download your report in various formats, including PDF, JPG, PNG and HTLM5.
- Publish it on social media or share it via email using a shareable link generated in the editor.
- Generate a code snippet in Visme to embed it anywhere online.
Click through the image below to use this customizable template to create your report. It follows the standard report writing format so you won’t get confused or miss a section.

Do you still have questions about good report writing and the best report writing formats? These FAQs will help.
What Are the Five Steps in Report Writing?
Writing a report effectively is best done by following a format and a set of guidelines. These are the five steps to follow to create a good report.
1. Understand your report’s purpose: Begin by having a clear understanding of the report's intent.
Whether it's an annual summary, weekly update, or research findings, knowing your report's purpose is crucial for effective writing. Compile and write the content with the purpose in mind as if it were a problem to be solved.
2. Follow the Right Report Writing Format: Adhere to a structured format, including a clear title, table of contents, summary, introduction, body, conclusion, recommendations, and appendices. This ensures clarity and coherence. Follow the format suggestions in this article to start off on the right foot.
3. Plan Your Writing: Create an outline to organize your thoughts and prioritize the body of the report. Stick to factual information, providing accuracy and reliability throughout. Be as detailed as possible in the outline; this will help build the report effectively.
4. Choose the Right Report Template: Utilize templates tailored to your report type, whether it's annual, weekly, project-related, sales/marketing, research, or academic. Templates streamline formatting and enhance professionalism. Visme has hundreds of report templates to choose from. Browse the gallery to find the perfect one.
5. Keep Your Audience in Mind: Tailor your report to meet your audience's needs. Whether it's supervisors, team members, clients, or peers, consider what information is most relevant and valuable to them. Make it easy for them to skim the report with clear headlines, titles and data visualizations.
How Do You Format a Report Nicely?
Formatting a report nicely involves attention to detail and adherence to specific guidelines. Here are some key characteristics that will ensure your report looks polished and professional:
1. Consistent Font and Size: Use a readable font like Arial or Verdana, and maintain consistency in font size throughout the report. Typically, a 12-point font is standard for most reports.
2. Clear Headings and Subheadings: Employ clear and descriptive headings and subheadings to organize your content. Use a consistent hierarchy, i.e., Heading 1, Heading 2, body text, etc, for a neat structure.
3. Adequate Margins: Ensure proper margins on all sides of the page (usually 1 inch or 2.54 cm) to provide white space and enhance readability.
4. Line Spacing: Use 1.5 or double spacing for the main text to prevent overcrowding and improve readability. Single spacing is acceptable for footnotes, references, and captions.
5. Page Numbers: Include page numbers, typically in the header or footer, to aid navigation. Ensure they are placed consistently and formatted appropriately.
6. Bullet Points and Numbering : When listing items or creating outlines, use bullet points or numbering for clarity. Maintain uniformity in style and indentation.
7. Tables and Figures: Format tables and figures consistently by providing clear labels and captions. Ensure they are properly aligned within the text.
8. Alignment: Align text and paragraphs consistently. Use left-justified text for most reports, as it's the easiest to read. Justify text only when necessary.
9. Page Breaks: Insert page breaks as needed to avoid awkward page transitions within sections or paragraphs.
10. Use of Color: If your report allows for color, use it sparingly and consistently. Ensure that text and background colors provide sufficient contrast for readability.
11. Proofreading and Editing: Always proofread and edit your report for grammar, spelling, and formatting errors. Consistency in formatting is essential for a polished look
12. Citations and References: If your report includes citations and references, follow a specific citation style guide (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago) consistently throughout the document.
13. Review for Accessibility: Consider accessibility guidelines, such as providing alternative text for images and using accessible color choices, to ensure all readers can access your report.
What Are the Five Qualities of a Good Report?
A well-crafted report possesses five key qualities that make it effective and valuable. Here they are:
1. Clarity and Conciseness: A good report is clear and concise. It presents information in a straightforward manner, avoiding unnecessary jargon or overly complex language. Readers should easily understand the content without confusion.
2. Relevance: Every piece of information in a good report is relevant to the report's purpose and objectives. Irrelevant or extraneous details are omitted, ensuring that the report focuses on what truly matters.
3. Structure and Organization: Reports are structured logically, with a clear beginning, middle, and end. They typically include sections like an introduction, body, and conclusion, ensuring a logical flow of information. Headings and subheadings help organize content effectively.
4. Accuracy and Reliability: Accurate and reliable data is a hallmark of a good report. Information presented should be based on thorough research, sound methodology, and credible sources. Any data or facts should be verifiable.
5. Actionable Recommendations: In many cases, a good report includes actionable recommendations or insights. After presenting the data and analysis, the report should offer practical suggestions or solutions that readers can implement or consider for decision-making.
Over to You
Hopefully, this post has helped you to better understand the best way to put together a report using a standard report format and layout. Following a standard report writing format is just what you need to create engaging, memorable reports . Follow the tips above and you’ll never make a boring report again.
Just how following a report writing format will help you create a better report, a Visme subscription will help you create a full suite of visual content.
Create stunning business reports faster using Visme

Trusted by leading brands
Recommended content for you:

Create Stunning Content!
Design visual brand experiences for your business whether you are a seasoned designer or a total novice.
About the Author
Orana is a multi-faceted creative. She is a content writer, artist, and designer. She travels the world with her family and is currently in Istanbul. Find out more about her work at oranavelarde.com
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Table of Contents

Research Report
Definition:
Research Report is a written document that presents the results of a research project or study, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions, in a clear and objective manner.
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the findings of the research to the intended audience, which could be other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public.
Components of Research Report
Components of Research Report are as follows:
Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the research report and provides a brief overview of the research question or problem being investigated. It should include a clear statement of the purpose of the study and its significance or relevance to the field of research. It may also provide background information or a literature review to help contextualize the research.
Literature Review
The literature review provides a critical analysis and synthesis of the existing research and scholarship relevant to the research question or problem. It should identify the gaps, inconsistencies, and contradictions in the literature and show how the current study addresses these issues. The literature review also establishes the theoretical framework or conceptual model that guides the research.
Methodology
The methodology section describes the research design, methods, and procedures used to collect and analyze data. It should include information on the sample or participants, data collection instruments, data collection procedures, and data analysis techniques. The methodology should be clear and detailed enough to allow other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the study in a clear and objective manner. It should provide a detailed description of the data and statistics used to answer the research question or test the hypothesis. Tables, graphs, and figures may be included to help visualize the data and illustrate the key findings.
The discussion section interprets the results of the study and explains their significance or relevance to the research question or problem. It should also compare the current findings with those of previous studies and identify the implications for future research or practice. The discussion should be based on the results presented in the previous section and should avoid speculation or unfounded conclusions.
The conclusion summarizes the key findings of the study and restates the main argument or thesis presented in the introduction. It should also provide a brief overview of the contributions of the study to the field of research and the implications for practice or policy.
The references section lists all the sources cited in the research report, following a specific citation style, such as APA or MLA.
The appendices section includes any additional material, such as data tables, figures, or instruments used in the study, that could not be included in the main text due to space limitations.
Types of Research Report
Types of Research Report are as follows:
Thesis is a type of research report. A thesis is a long-form research document that presents the findings and conclusions of an original research study conducted by a student as part of a graduate or postgraduate program. It is typically written by a student pursuing a higher degree, such as a Master’s or Doctoral degree, although it can also be written by researchers or scholars in other fields.
Research Paper
Research paper is a type of research report. A research paper is a document that presents the results of a research study or investigation. Research papers can be written in a variety of fields, including science, social science, humanities, and business. They typically follow a standard format that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion sections.
Technical Report
A technical report is a detailed report that provides information about a specific technical or scientific problem or project. Technical reports are often used in engineering, science, and other technical fields to document research and development work.
Progress Report
A progress report provides an update on the progress of a research project or program over a specific period of time. Progress reports are typically used to communicate the status of a project to stakeholders, funders, or project managers.
Feasibility Report
A feasibility report assesses the feasibility of a proposed project or plan, providing an analysis of the potential risks, benefits, and costs associated with the project. Feasibility reports are often used in business, engineering, and other fields to determine the viability of a project before it is undertaken.
Field Report
A field report documents observations and findings from fieldwork, which is research conducted in the natural environment or setting. Field reports are often used in anthropology, ecology, and other social and natural sciences.
Experimental Report
An experimental report documents the results of a scientific experiment, including the hypothesis, methods, results, and conclusions. Experimental reports are often used in biology, chemistry, and other sciences to communicate the results of laboratory experiments.
Case Study Report
A case study report provides an in-depth analysis of a specific case or situation, often used in psychology, social work, and other fields to document and understand complex cases or phenomena.
Literature Review Report
A literature review report synthesizes and summarizes existing research on a specific topic, providing an overview of the current state of knowledge on the subject. Literature review reports are often used in social sciences, education, and other fields to identify gaps in the literature and guide future research.
Research Report Example
Following is a Research Report Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance among High School Students
This study aims to investigate the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students. The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The findings indicate that there is a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students. The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers, as they highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities.
Introduction:
Social media has become an integral part of the lives of high school students. With the widespread use of social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and Snapchat, students can connect with friends, share photos and videos, and engage in discussions on a range of topics. While social media offers many benefits, concerns have been raised about its impact on academic performance. Many studies have found a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance among high school students (Kirschner & Karpinski, 2010; Paul, Baker, & Cochran, 2012).
Given the growing importance of social media in the lives of high school students, it is important to investigate its impact on academic performance. This study aims to address this gap by examining the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students.
Methodology:
The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The questionnaire was developed based on previous studies and was designed to measure the frequency and duration of social media use, as well as academic performance.
The participants were selected using a convenience sampling technique, and the survey questionnaire was distributed in the classroom during regular school hours. The data collected were analyzed using descriptive statistics and correlation analysis.
The findings indicate that the majority of high school students use social media platforms on a daily basis, with Facebook being the most popular platform. The results also show a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students.
Discussion:
The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. The negative correlation between social media use and academic performance suggests that strategies should be put in place to help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. For example, educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, this study provides evidence of the negative impact of social media on academic performance among high school students. The findings highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. Further research is needed to explore the specific mechanisms by which social media use affects academic performance and to develop effective strategies for addressing this issue.
Limitations:
One limitation of this study is the use of convenience sampling, which limits the generalizability of the findings to other populations. Future studies should use random sampling techniques to increase the representativeness of the sample. Another limitation is the use of self-reported measures, which may be subject to social desirability bias. Future studies could use objective measures of social media use and academic performance, such as tracking software and school records.
Implications:
The findings of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. Educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. For example, teachers could use social media platforms to share relevant educational resources and facilitate online discussions. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. They could also engage in open communication with their children to understand their social media use and its impact on their academic performance. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students. For example, schools could implement social media policies that restrict access during class time and encourage responsible use.
References:
- Kirschner, P. A., & Karpinski, A. C. (2010). Facebook® and academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(6), 1237-1245.
- Paul, J. A., Baker, H. M., & Cochran, J. D. (2012). Effect of online social networking on student academic performance. Journal of the Research Center for Educational Technology, 8(1), 1-19.
- Pantic, I. (2014). Online social networking and mental health. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 17(10), 652-657.
- Rosen, L. D., Carrier, L. M., & Cheever, N. A. (2013). Facebook and texting made me do it: Media-induced task-switching while studying. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(3), 948-958.
Note*: Above mention, Example is just a sample for the students’ guide. Do not directly copy and paste as your College or University assignment. Kindly do some research and Write your own.
Applications of Research Report
Research reports have many applications, including:
- Communicating research findings: The primary application of a research report is to communicate the results of a study to other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public. The report serves as a way to share new knowledge, insights, and discoveries with others in the field.
- Informing policy and practice : Research reports can inform policy and practice by providing evidence-based recommendations for decision-makers. For example, a research report on the effectiveness of a new drug could inform regulatory agencies in their decision-making process.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research in a particular area. Other researchers may use the findings and methodology of a report to develop new research questions or to build on existing research.
- Evaluating programs and interventions : Research reports can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and interventions in achieving their intended outcomes. For example, a research report on a new educational program could provide evidence of its impact on student performance.
- Demonstrating impact : Research reports can be used to demonstrate the impact of research funding or to evaluate the success of research projects. By presenting the findings and outcomes of a study, research reports can show the value of research to funders and stakeholders.
- Enhancing professional development : Research reports can be used to enhance professional development by providing a source of information and learning for researchers and practitioners in a particular field. For example, a research report on a new teaching methodology could provide insights and ideas for educators to incorporate into their own practice.
How to write Research Report
Here are some steps you can follow to write a research report:
- Identify the research question: The first step in writing a research report is to identify your research question. This will help you focus your research and organize your findings.
- Conduct research : Once you have identified your research question, you will need to conduct research to gather relevant data and information. This can involve conducting experiments, reviewing literature, or analyzing data.
- Organize your findings: Once you have gathered all of your data, you will need to organize your findings in a way that is clear and understandable. This can involve creating tables, graphs, or charts to illustrate your results.
- Write the report: Once you have organized your findings, you can begin writing the report. Start with an introduction that provides background information and explains the purpose of your research. Next, provide a detailed description of your research methods and findings. Finally, summarize your results and draw conclusions based on your findings.
- Proofread and edit: After you have written your report, be sure to proofread and edit it carefully. Check for grammar and spelling errors, and make sure that your report is well-organized and easy to read.
- Include a reference list: Be sure to include a list of references that you used in your research. This will give credit to your sources and allow readers to further explore the topic if they choose.
- Format your report: Finally, format your report according to the guidelines provided by your instructor or organization. This may include formatting requirements for headings, margins, fonts, and spacing.
Purpose of Research Report
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the results of a research study to a specific audience, such as peers in the same field, stakeholders, or the general public. The report provides a detailed description of the research methods, findings, and conclusions.
Some common purposes of a research report include:
- Sharing knowledge: A research report allows researchers to share their findings and knowledge with others in their field. This helps to advance the field and improve the understanding of a particular topic.
- Identifying trends: A research report can identify trends and patterns in data, which can help guide future research and inform decision-making.
- Addressing problems: A research report can provide insights into problems or issues and suggest solutions or recommendations for addressing them.
- Evaluating programs or interventions : A research report can evaluate the effectiveness of programs or interventions, which can inform decision-making about whether to continue, modify, or discontinue them.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies.
When to Write Research Report
A research report should be written after completing the research study. This includes collecting data, analyzing the results, and drawing conclusions based on the findings. Once the research is complete, the report should be written in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
In academic settings, research reports are often required as part of coursework or as part of a thesis or dissertation. In this case, the report should be written according to the guidelines provided by the instructor or institution.
In other settings, such as in industry or government, research reports may be required to inform decision-making or to comply with regulatory requirements. In these cases, the report should be written as soon as possible after the research is completed in order to inform decision-making in a timely manner.
Overall, the timing of when to write a research report depends on the purpose of the research, the expectations of the audience, and any regulatory requirements that need to be met. However, it is important to complete the report in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
Characteristics of Research Report
There are several characteristics of a research report that distinguish it from other types of writing. These characteristics include:
- Objective: A research report should be written in an objective and unbiased manner. It should present the facts and findings of the research study without any personal opinions or biases.
- Systematic: A research report should be written in a systematic manner. It should follow a clear and logical structure, and the information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand and follow.
- Detailed: A research report should be detailed and comprehensive. It should provide a thorough description of the research methods, results, and conclusions.
- Accurate : A research report should be accurate and based on sound research methods. The findings and conclusions should be supported by data and evidence.
- Organized: A research report should be well-organized. It should include headings and subheadings to help the reader navigate the report and understand the main points.
- Clear and concise: A research report should be written in clear and concise language. The information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand, and unnecessary jargon should be avoided.
- Citations and references: A research report should include citations and references to support the findings and conclusions. This helps to give credit to other researchers and to provide readers with the opportunity to further explore the topic.
Advantages of Research Report
Research reports have several advantages, including:
- Communicating research findings: Research reports allow researchers to communicate their findings to a wider audience, including other researchers, stakeholders, and the general public. This helps to disseminate knowledge and advance the understanding of a particular topic.
- Providing evidence for decision-making : Research reports can provide evidence to inform decision-making, such as in the case of policy-making, program planning, or product development. The findings and conclusions can help guide decisions and improve outcomes.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research on a particular topic. Other researchers can build on the findings and conclusions of the report, which can lead to further discoveries and advancements in the field.
- Demonstrating expertise: Research reports can demonstrate the expertise of the researchers and their ability to conduct rigorous and high-quality research. This can be important for securing funding, promotions, and other professional opportunities.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies. Producing a high-quality research report can help ensure compliance with these requirements.
Limitations of Research Report
Despite their advantages, research reports also have some limitations, including:
- Time-consuming: Conducting research and writing a report can be a time-consuming process, particularly for large-scale studies. This can limit the frequency and speed of producing research reports.
- Expensive: Conducting research and producing a report can be expensive, particularly for studies that require specialized equipment, personnel, or data. This can limit the scope and feasibility of some research studies.
- Limited generalizability: Research studies often focus on a specific population or context, which can limit the generalizability of the findings to other populations or contexts.
- Potential bias : Researchers may have biases or conflicts of interest that can influence the findings and conclusions of the research study. Additionally, participants may also have biases or may not be representative of the larger population, which can limit the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Accessibility: Research reports may be written in technical or academic language, which can limit their accessibility to a wider audience. Additionally, some research may be behind paywalls or require specialized access, which can limit the ability of others to read and use the findings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips


Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Research Contribution – Thesis Guide

Critical Analysis – Types, Examples and Writing...

Research Problem – Examples, Types and Guide

Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing...
How To Write A Report For A Formal Or Academic Occasion?

If you are immersed in academic, research, or the business world, it is likely that sooner or later (or even right now), you will have to face the task of report writing. Therefore, knowing how to write a report can save your life.
Here you can find a practical guide which will help you know the appropriate techniques needed in writing a report so that it will comply with standards. If you follow these steps to the letter, you will not only learn the art of making a report, but you will be the best at it.
What Is Report Writing?
Before getting into a subject and teaching you how to write a good paper , you need to know clearly what you are facing. Therefore, the first thing is to delve a bit into the concept and define it.
A formal report or report essay is a text written in prose form, exposing the results of an investigation, a business process, or the analysis of a particular topic.
This type of report is used as an expository tool in different areas such as business, scientific, literary, or even in the legal field.
A report paper aims to present the reader with an analysis of results in the framework of an investigation, with special emphasis on the conclusions and processes that led to a certain result.
In the business area, brief reports are used to account for progress in different processes within the company or to disclose timely information requested by external entities.
Types Of Reports
There are various types of reports from projects or business to lab reports, let’s take a look at these two generic types.
Business Or Project Report
Business report writing is an assignment which the writer or researcher is required to analyze a situation while using standard management theories to arrive at some recommendations for an improved result.
An example, within a business organization, can be when workers are evaluated or when another company is studied. In essence, we can have a report as a tool used in a research study or in a scientific field.
Academic Report
Another general type is an academic report. These could be book reports, movie reviews, research, and even lab reports.
Academic reports are different from other types with one of the reasons being that they must be written and structured according to a recommended style format such as APA or MLA.
Report Writing Format And Style
If your teacher or instructor doesn’t state otherwise, APA or AP is the best formatting style for writing academic and business reports or other journalistic writings.
Also, the best type of writing style used for producing reports is the formal type. To achieve this, you may want to steer clear of the active voice and use the passive voice more. The active voice sound subjective. Meanwhile, report writing is supposed to be objective and devoid of personal opinions and views.
Report Structure
To write an effective report, you must choose and maintain a certain structure. Check out the correct way to structure your paper.
Executive Summary
Executive summaries are frequently used more in business reports than academic ones. They are used in situations where the entire report is voluminous. Like a newspaper news article, the writer or researcher seeks to capture the entire gist in a few paragraphs before presenting the full paper.
The introduction is the presentation of your report where you must explain in brief words what the work is about. To make an effective introduction, you must answer these questions: what, how, where, and why. If you answer each of these questions and join them with logical connectors, you will surely have a great introduction.
Body Paragraphs
In developing the body paragraphs, you have to expose the subject in the most accurate way possible, explaining the results found through the use of clear arguments.
The body is dedicated to the analysis of the facts. Then, you move on to the synthesis, that is, to the phase which you interpret what happened and get the useful indications for the future.
Finally, you must finalize the text of the document with the conclusions. You take stock of all your work. The conclusion, as the name implies, is the synthesis of what is addressed in your report. Try to write brief conclusions that summarize the most relevant points of the topic addressed
The appendix cannot be mistaken for references, citations, or the bibliography. Appendices, in short, are added text which necessarily aren’t the main idea raised in the article, but are important in the making of the written report.
In principle, to write a report, you can use this standard structure:
- Introduction
- Presentation of the subject treated
- Motivations for choosing the topic
- Purpose of the work
- Phases and hours of work
- People involved in the work and their role
- Body paragraphs
- Presentation of the aspects examined
- Methods followed
- Work evaluation
- Possible difficulties encountered
- Final reflections on the evidence that emerged from the document
- Proposals for the future
Important Report Writing Tips
Before you begin a report, there are some talking points, tips and report writing skills such as fact gathering, persuasive writing technique , theoretical knowledge, etc. which you must observe or put into practice even before getting the report prompt. Check them out:
- Choose your goal well
It will seem trivial to start from here, but the result you want to obtain from your report is really the axis of everything. So, before writing a single line of the report, you should ask yourself: “What is the goal I want to achieve? What is the message I want to convey?
- Put yourself in the role of the recipient
This suggestion is not only valid when a report is written. More generally, it’s worth it for every time you sit down and write any kind of document. Putting yourself in the shoes of your recipient is essential: it helps you process the information contained in your report, to make it more understandable.
- Make a list of the things you need to write
Before writing your report, you should know what issues to touch. In summary: writing a report does not make sense if you do not know where you want to go and how. Take a sheet and write on it what are the topics of the project and the order it touches them. It is about choosing the topic to start from, the central topics and the concepts on which to build the end of the report.
- Search authorized sources
Writing a report means being as objective as possible. In fact, this type of document is an analysis of fact and not a creative history. Therefore, your sources must be reliable and objective. You must mention them in the text of your report: they should be based on truth.
- Be simple, clear and concrete
For your reader, you have an obligation to be extremely clear. Here are some tips on how to be more understandable and, consequently, on how to write a report that is more effective:
- Write short sentences
- Use simple language
- Avoid subordinates: force the reader and eliminate concentration
- Be clear, precise, concrete: avoid whirling words full of smoke
- Avoid a baroque or presumptuous style
- Avoid any technical jargon, unless the report is read by those who understand it
- Use tables and charts
Writing a report means exposing facts in a concrete way. And what is better to support facts than a graph or table? Therefore, use these elements to clarify and give even more concreteness to the things you write in your report.
- Insert photos and images
Images and photographs are much more intuitive than words. This also applies when you need to write a report. Therefore, in your reports, insert photographs or images to document, clarify, and exemplify.
- Format the report text
Writing a report also needs giving it a nice look. This means formatting your text appropriately. For example:
- Choose the most appropriate format for maximum readability, both in case the document is printed or read on a monitor.
- Highlight the most important words and concepts in bold.
- Use numbered and bulleted lists for item lists.
- Divide the text into blocks to avoid an unpleasant effect that makes the text look like a single wall.
- Choose an effective title: A very important point of writing a report is what title to give the document. The title must be absolutely clear, you must say what the report contains. You must not be lazy or use word games. Probably, the best time to choose the title is at the end of the report, when the work is finished, and everything is clear.
- Use summaries
If your report is long, it should be divided into chapters. In this case, the use of abstracts is recommended. A summary is a short text, a hundred or two hundred words maximum, which is placed at the beginning of each chapter and explains to the reader what you will find in that part of the report.
- Read the document carefully
Re-reading what is written is an important phase of writing a report. Verify especially that there are no errors in spelling, grammar, or syntax in the report. Also, verify that the sentences are logically linked to each other. In addition, the topic of each sentence should always be clearly expressed.
- Take care of your spelling. Any text loses its seriousness if it has spelling errors.
- Before you start writing your report, you can make summaries to find your main ideas.
- Create a template where you put in words and the things you should say. This will help you at the time of writing to develop your ideas.
- In case you include specific data of an investigation, book, press release, or other documents that have a copyright, you must quote properly and include a bibliography.
To be a successful report writer, you must to know the concept and the various types. Report writing has a definitive structure and style to follow, as already revealed in this article. Try to follow them correctly, and you’d be assured of a great report paper.
Don't waste time
Get a professional assistance from certified experts right now

Home / English Composition / Report Writing / Report Writing: Format, Topics, and Examples

Report Writing: Format, Topics, and Examples
Learn the essentials of report writing with this comprehensive guide. Explore the proper format, find inspiring topics, and discover real-world examples to enhance your report writing skills.
What is Report Writing?
A Report Writing is a written account that helps us to know about an event, situation, or occurrence in detail that has already taken place.
Report Writing is a narrative of Events described in an impartial approach. Rules and Format of Report Writing are necessary to know for English report writing. Examples of Report Writing help us in doing this easily.
The Power of Effective Report Writing
Report writing is a skill that transcends industries and disciplines, playing a vital role in conveying information, analyzing data, and making informed decisions.
Whether you are a student, a researcher, a business professional, or someone looking to improve your communication abilities, mastering the art of report writing is essential for success.
This article will provide you with insights into the format, topics, and real-world examples of report writing to help you become a proficient report writer.
Understanding the Format of a Report
A well-structured report not only facilitates easy comprehension but also leaves a lasting impact on the reader. Understanding the proper format is the foundation of creating an effective report. In crafting a comprehensive and impactful report, one must carefully consider and include the following crucial elements. :
1. Title Page
The title page should include the report’s title, the name of the author or organization, the date of submission, and any relevant affiliations.
2. Abstract or Executive Summary
The abstract or executive summary is a concise overview of the report’s main points, providing the reader with a snapshot of the entire report’s content.
3. Table of Contents
The table of contents outlines the report’s structure, listing the headings and subheadings with corresponding page numbers.
4. Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the report, providing context, stating the purpose, and highlighting the significance of the topic.
5. Methodology
In research-oriented reports, the methodology section explains the approach taken to gather data, conduct experiments, or perform studies.
6. Findings
The findings section presents the data collected or the results of the research in a clear and organized manner, often using tables, graphs, or charts.
7. Discussion
The discussion section interprets the findings, provides insights, and offers explanations for observed patterns or trends.
8. Conclusion
The conclusion summarizes the main points, draws conclusions based on the findings, and may include recommendations for future actions.
9. Recommendations
In reports with actionable outcomes, the recommendations section suggests specific steps or strategies based on the findings.
10. References
The references section lists all the sources cited in the report, ensuring proper acknowledgment of external work and adding credibility.
Writing Tips for an Effective Sample Report
Creating a compelling report requires not just proper structure but also excellent writing skills. Here are some valuable tips to enhance your report writing:
1. Know Your Audience
Understanding your target audience is crucial when writing a report. Tailor your language, tone, and content to suit the reader’s level of expertise and interest.
2. Use Clear and Concise Language
Keep your writing clear, straightforward, and to the point. Avoid jargon and unnecessary technical terms that may confuse readers.
3. Organize Information Logically
Present information in a logical sequence, ensuring that each section flows smoothly into the next. Use headings and subheadings to provide a clear structure.
4. Support Claims with Evidence
Back up your statements with credible evidence and data. This adds credibility to your report and strengthens your arguments.
5. Edit and Proofread Thoroughly
Always review your report for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. A well-edited report shows professionalism and attention to detail.
6. Seek Feedback
Before finalizing your report, seek feedback from colleagues or peers. Fresh perspectives can help identify areas of improvement.
Selecting Engaging Report Writing Topics
Choosing the right topic is essential for crafting a compelling report. Whether it’s for academic, business, or research purposes, an engaging topic will capture the reader’s interest and keep them invested in your report. Here are some inspiring report writing topics:
1. The Impact of Technology on Modern Workplace s
Explore how technology has transformed traditional workplaces, affecting productivity, communication, and employee satisfaction.
2. Environmental Sustainability in Urban Cities
Examine the efforts made by urban cities to promote environmental sustainability, including green initiatives and waste reduction strategies.
3. The Rise of E-Learning: A Comprehensive Analysis
Analyze the growth of e-learning platforms, their effectiveness in education, and their potential to revolutionize the traditional learning system.
4. Cybersecurity Threats and Mitigation Strategies for Businesses
Investigate the latest cybersecurity threats faced by businesses and outline effective strategies to safeguard sensitive data and prevent cyber attacks.
5. Mental Health in the Workplace: Strategies for Employee Well-Being
Discuss the importance of addressing mental health issues in the workplace and propose strategies to support employee well-being.
Real-World Examples of Impactful Reports
To gain a deeper understanding of report writing’s practical applications, let’s explore some real-world examples:
1. World Health Organization (WHO) – Global Health Report
The WHO publishes comprehensive reports on global health issues, providing data on disease outbreaks, vaccination rates, and healthcare access worldwide. These reports play a crucial role in shaping global health policies and initiatives.
2. McKinsey & Company – Industry Research Reports
Management consulting firm McKinsey & Company produces insightful industry research reports that analyze market trends, consumer behavior, and business strategies. These reports serve as valuable resources for executives and decision-makers.
3. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) – Climate Assessment Reports
The IPCC releases periodic reports on climate change, assessing its impacts, causes, and potential solutions. These reports are instrumental in guiding environmental policies and international climate agreements.
A Sample Report Writing Format on A Bank Robbery.
The following points will make it easy to write a report easily shown below.
( Heading) DARING BANK ROBBERY
( Who Reported ) By a Special Correspondent
Where, When, What: Kolkata, August 14 (Introduction): A daring (CART) robbery took place today at 3 p.m. at the United Bank of India, Gariahat Branch, Kolkata.
How, why, Casualty: According to the Branch Manager, three men armed with pistols overpowered the security staff and locked the gate from the inside. One of the miscreants (710) herded the customers and the staff into one corner of the bank and kept them silent at gunpoint. The other two miscreants snatched the keys from the Manager.
Condition: Then they unlocked the vault and bagged cash and jewelry worth Rs. 40 lacks. They came out of the bank hurling bombs, jumped into a black Maruti Van, and sped away.
Reaction & Measures Taken (Conclusion): The police arrived within half an hour. No one has been arrested yet. Investigations are on, as the Deputy Commissioner of Police told the media.
People may also like
| : |
Report Writing Types in English:
Basically, Report writing in English is of three types .
- General Report Writing: These reports give an account of a person’s experience of an event or an incident.
- Newspaper Report Writing: Newspaper reports are based on true incidents or accidents meant to express some information to the public.
- Business Report Writing: Business reports are made on orders based on observation, investigation, and analysis.
General Report Writing Examples
Example 1: Business Report – Market Analysis
Title: Market Analysis for XYZ Company’s Product Expansion
Executive Summary: The market analysis report assesses the potential of XYZ Company to expand its product line into a new market segment.
Introduction: This report aims to investigate the feasibility and potential challenges associated with XYZ Company’s entry into the youth-oriented consumer electronics market.
Methodology: Data was collected through a combination of surveys, focus groups, and secondary research from reputable industry reports.
Findings: The youth-oriented consumer electronics market is growing rapidly, with an annual growth rate of 12% over the past three years.
XYZ Company’s brand recognition is relatively low among the target audience.
The price sensitivity of the target market is a significant factor to consider.
- Analysis: The findings suggest that while there is a lucrative opportunity for XYZ Company to enter the market, it will require a focused marketing campaign and competitive pricing strategies to overcome initial brand awareness challenges.
- Discussion: By leveraging social media and influencers, XYZ Company can effectively reach the target audience and build brand loyalty. Additionally, offering a competitive pricing model will attract price-conscious customers.
- Recommendations:
- Collaborate with popular influencers to gain credibility and reach a wider audience.
Offer attractive introductory pricing and discounts to entice price-sensitive customers.
Conclusion: Entering the youth-oriented consumer electronics market presents a promising opportunity for XYZ Company. By implementing the recommended strategies, the company can capitalize on this potential growth and expand its product line successfully.
Remember that the specific format and content of a report may vary based on the requirements set by your institution, organization, or supervisor. Always check for any specific guidelines before starting your report writing.
Write a newspaper report on the “Annual Prize Distribution Ceremony in your school”
Annual Prize Distribution Ceremony in your school
By Staff Reporter
[City, Date]: The air was abuzz with excitement and anticipation as [Your School Name] hosted its grand Annual Prize Distribution Ceremony yesterday. The event, held in the school auditorium, was a momentous occasion that celebrated the academic excellence and achievements of the students.
Distinguished guests, parents, and faculty members graced the ceremony with their presence. The school principal, in his opening address, emphasized the significance of recognizing and applauding students’ efforts beyond academics.
The highlight of the event was the distribution of prizes to the meritorious students, acknowledging their outstanding performance in academics, sports, and extracurricular activities. The audience erupted with applause as the achievers walked up the stage to receive their awards.
The melodious music, vibrant dances, and thought-provoking skits captivated the audience.
The Annual Prize Distribution Ceremony concluded on a high note, leaving everyone inspired and motivated. It served as a testament to the school’s commitment to nurturing holistic development among its students.
[Your School Name] once again proved that it is not only a center of academic excellence but also a platform for nurturing well-rounded individuals.
By [Your Name]
Write a newspaper repot on “A terrible fire broke out in Kolkata”
Terrible fire breaks out in kolkata, causing extensive damage.
Kolkata, Date: A devastating fire broke out in a commercial area of Kolkata yesterday, causing widespread destruction and panic among residents and businesses. The incident occurred in the bustling market district, engulfing several multi-story buildings.
Eyewitnesses reported that the fire started in one of the shops due to an electrical short circuit and quickly spread to nearby establishments. Despite the immediate response from firefighters, the blaze proved challenging to control, as narrow streets hindered their access.
Local authorities and emergency services rushed to the scene, evacuating people from nearby buildings and providing medical assistance to those affected. Tragically, a few individuals sustained minor injuries in the process.
The fire caused extensive damage to properties, resulting in significant financial losses for business owners. The full extent of the damage is yet to be assessed.
Investigations into the incident are underway to determine the exact cause and potential safety lapses. As the city mourns the loss of properties and livelihoods, efforts are being made to extend relief and support to the affected residents.
1. Write a report for a newspaper about A Terrible Train Accident.
Odisha Train Accident / Coromandel Express Train Accident
Balasore, 3rd June 2023: At around 7 pm, 2nd June on Friday evening 10-12 coaches of the Shalimar-Chennai Coromandel Express derailed near Baleswar and fell on the opposite track. After some time, another train from Yeswanthpur to Howrah dashed into those derailed coaches resulting in the derailment of its 3-4 coaches. The train crash involving two passenger trains and a goods train in Odisha’s Balasore on Friday is said to be one of the deadliest rail accidents in India. More than 230 people have lost their lives in the accident and 900 have been injured. NDRF, ODRAF, and Fire Services are still working to cut the bogie and try to recover the living or the dead. Local people were seen helping the teams responsible for rescue and relief operations and they queued up to donate blood for the injured in Balasore. As a result, Local people became able to rescue 200-300 injured people A high-level committee has been declared to conduct an inquiry into the train accident. The Centre has announced an ex-gratia compensation of Rs 10 Lakh each to the kin of the deceased and Rs 2 Lakh to grievous and Rs 50,000 for minor injuries, Union Railways Minister Ashwini Vaishnav said.
2. Write a report for a newspaper about A Magic Show .
By Anik Dutta
On Friday, November 18: our school authority invited a magician to surprise the students of the school with a magic show. The magic show was a gift to the students from the school’s authoritative body as the school won the award for Best Disciplined School in Kolkata for the year 2015. The magic show was organized on the school’s open-air stage. The show went on for 2 hours, from 12 to 2 pm. The first magic shown by the great magician was pulling out of a rabbit from his hat which was absolutely empty when he wore it. The spectators were pleasantly surprised. He showed exciting magic tricks one after the other and ended the show with a message to the awestruck students, ‘Practice maths well, and you can do magic too as it is nothing but a game of calculation’. The show was immensely appreciated by all.
3. Write a report for a newspaper about Health Issues of the people of your District .
Health Issues of the People of Your District
By Ravi Yogi
On 20 May 2021: a health awareness campaign camp was organized in the Howrah district by the World Health Organisation. Some volunteers were chosen, who from then on, visit each house every month to remind people to get their children vaccinated. People now follow their instructions and keep their surroundings clean to avoid certain diseases. The volunteers distributed water purifiers at a cheap rate so that people could use them to get pure water. The mosquito-repellant sprays are used every month and mosquito nets are now used to keep mosquitoes away. If the volunteers arrange a blood donation camp every month it could help the people in need. Also, a free health checkup camp could be arranged for further health improvement of the people of the locality.
4. Write a report for a newspaper about the Annual sports Event of Your School .
Annual Sports Event of Your School
By Anwesha Das
The annual sports day of our school (St. Agnes H.S. School) was held on February 15 for the junior students at the school grounds. The event for the junior students started at 9:30 in the morning with a relay race. The next race they had was a tricycle race and the last one the junior students had was a treat to watch. The junior ones’ had to run wearing long gowns and they had to run the track without falling even once.
The juniors enjoyed the fun sporting events a lot, while the visitors’ race involving the parents remained the highlight of the day. At the end of the program Chief Guest Sourav Ganguly gave away the awards to the winners and the class teacher of each class distributed a box containing candies, a chocolate pastry, an orange, and two vanilla cream-filled wafer biscuits to every pupil of her class. The event turned out to be a joyful one with a smile on everyone’s face.
Newspaper Report Writing : Format, Topics, Examples
5. write a newspaper report on the first downpour of the season ..
FIRST DOWNPOUR OF THE SEASON
Kolkata, June 13: Today Kolkata experienced its first downpour during the season. The showers were brought about by a deep depression over the Gangetic West Bengal. There was incessant (WESO) rainfall accompanied by thunder and lightning. In Kolkata, it rained throughout the day with occasional breaks. The weather office at Alipore has recorded a rainfall of 20 cm. Many low-lying areas went underwater. Some of the major roads were waterlogged for several hours. There were traffic jams on many roads. The hand-pulled rickshaws had stopped. Train and air services were disrupted. There were cable faults in many parts of the city. Two persons were electrocuted. But they have not yet been identified, said the police officials.
6. As a Reporter for an English daily, write a report about A violent cyclonic storm .
A VIOLENT CYCLONIC STORM
By a Special Correspondent
Katak, August 12: A violent cyclonic storm ravaged the coastal areas of Odisha today. The cyclone started at about 6.45 p.m. It was said to have rushed at a speed of 80 km per hour. The worst-affected areas include Puri, Baleswar, and Paradip. The cyclone raised the sea to an alarming height. The high tidal waves submerged the low-lying coastal areas. It caused incalculable damage to life and property. More than 10,000 people were rendered homeless. Train services were totally disrupted. The State Government sent its rescue team along with central paramilitary forces to tackle the situation. A sum of Rs. 3 crores has been sanctioned for the relief and rehabilitation of the cyclone-hit people.
7. Write a report for a newspaper about A Serious Road Accident
A Serious Road Accident
Kolkata, January 18: As many as 20 persons including two women and a child were injured in an accident at about 8 pm, on M, G, Road yesterday. The accident took place when a speeding minibus, in a bid to overtake a private bus, skidded off the road. The vehicle carrying 45 passengers went straight into a shopping mall, after breaking the roadside railing, Persons inside the mall and the bus suffered serious injuries Local people started the rescue operation. The injured were taken to the nearest hospital. Locals got agitated and blocked the road causing the suspension of traffic for more than 3 hours. However, the police came and brought the situation under control.
8. Write a report within 100 words for an English daily about Cyclone hitting Coastal West Bengal .
Cyclone hits Coastal West Bengal
-By a Staff Reporter
Kolkata, June 12, 2013: A severe cyclone with a speed of 80 km. per hour hit the coastal areas of West Bengal yesterday evening at about 6-45 p.m. Caused by a deep depression in the Bay of Bengal, the cyclone ripped through the state resulting in huge damage to life and property. 60 persons have died and thousands have been rendered homeless. Train services have been disrupted leaving a number of people stranded. The state government has taken immediate steps to provide relief to the victims. More than 5000 people have been evacuated to temporary relief shelters. The Chief Minister has reviewed the situation and assured the people of all help.
9. Write a newspaper report on a road accident within 100 words .
BRAKE FAILURE BUS COLLIDES WITH A TRUCK
By a Staff Reporter
Kolkata, October 1, 2015: Yesterday at around 10:30 am an accident took place at Sinthi More when an Esplanade bound bus, of route no 78/1, suddenly collided with a truck. The report says the brake failure of the bus was the cause of this mishap. Five passengers were injured including a child and a woman. According to passengers, the ill-fated bus was moving at a great speed. Near Sinthi More the driver lost control and banged behind a truck. Local people rushed in, and took the injured to the nearest hospital where they were released after first aid. Traffic got disrupted. Cops reached the spot quickly, intervened, and normalcy was restored within an hour.
10. Write a report on a Railway accident.
A MAN DIED IN A RAILWAY ACCIDENT
By Kishore Ganguli
Kolkata, April 25: A man died after he had been hit by a Sealdah bound train close to Barrackpore station around 5.40 am today when the victim was returning home from a regular morning walk. According to an eyewitness, the man was trying to cross the tracks, got confused, and ended up on the track on which the train was coming on. Being hit on his head, he was hospitalized immediately. But the doctors declared him dead. The locals made a blockade on the railway tracks. The police came, dispersed the irate mob and the train service was restored. The railway authorities announced an exgratia payment of Rs 2 lakh to the next of kin of the deceased. The situation is tense till now.
FAQs about Report Writing
Q: what is the ideal length for a report.
Reports can vary in length depending on their purpose and complexity. However, a concise report of 10-20 pages is often preferred to keep the reader engaged.
Q: Can I use bullet points in my report?
Yes, using bullet points can enhance readability and make key information stand out. However, use them sparingly and only when appropriate.
Q: Should I include visuals in my report?
Yes, incorporating relevant visuals like graphs, charts, and images can make complex data easier to understand.
Q: Can I include my opinion in the report?
While reports should be objective and fact-based, there might be instances where your expert opinion is valuable. If so, clearly distinguish between facts and opinions.
Q: How can I make my executive summary compelling?
The executive summary should be concise yet informative. Highlight the most important findings and recommendations to pique the reader’s interest.
Q: Is it necessary to follow a specific report writing style?
Different organizations or fields may have their preferred report writing style. Always follow the guidelines provided by your institution or industry standards.
Q: What is the main purpose of a report?
A: The main purpose of a report is to present information, findings, and recommendations in a structured and organized manner.
A: Yes, bullet points can help present information concisely and improve readability.
Q: How long should an executive summary be?
A: An executive summary should be concise, typically ranging from one to two pages.
Q: Is it necessary to include visuals in a report?
A: Including visuals such as charts, graphs, and images can enhance the reader’s understanding of complex data.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid in report writing?
A: Common mistakes to avoid include using overly technical language, neglecting to cite sources properly, and lacking a clear structure.
Q: How can I make my report more engaging?
A: To make your report engaging, use real-life examples, incorporate visuals, and use a conversational tone when appropriate.
Related Posts:


Sample Essays
The breadth of Georgetown’s core curriculum means that students are required to write for a wide variety of academic disciplines. Below, we provide some student samples that exhibit the key features the most popular genres. When reading through these essays, we recommend paying attention to their
1. Structure (How many paragraphs are there? Does the author use headers?)
2. Argument (Is the author pointing out a problem, and/or proposing a solution?)
3. Content (Does the argument principally rely on facts, theory, or logic?) and
4. Style (Does the writer use first person? What is the relationship with the audience?)
Philosophy Paper
- Singer on the Moral Status of Animals
Theology Paper
- Problem of God
- Jewish Civilization
- Sacred Space and Time
- Phenolphthalein in Alkaline Solution
History Paper
- World History
Literature Review
Comparative Analysis
Policy Brief
- Vaccine Manufacturing
White Paper
Critical Analysis
- Ignatius Seminar
Sample Essays: Writing with MLA Style
Congratulations to the students whose essays were selected for the 2024 edition of Writing with MLA Style! Essays were selected as examples of excellent student writing that use MLA style for citing sources. Essays have been lightly edited.
If your institution subscribes to MLA Handbook Plus , you can access annotated versions of the essays published from 2022 to 2024.
Writing with MLA Style: 2024 Edition
The following essays were selected for the 2024 edition of Writing with MLA Style. The selection committee for high school submissions was composed of Lisa Karakaya, Hunter College High School; and Heather Smith, Dedham Public Schools. The selection committee for postsecondary submissions was composed of Rachel Ihara, Kingsborough Community College, City University of New York; Tarshia L. Stanley, Wagner College; and Joyce MacDonald, University of Kentucky.
High School Essays
Miguel Kumar (Ransom Everglades School)
“McCarthyism at the Movies: The Effects of Hollywood McCarthyism on the American Public”
Catherine Mao (Hunter College High School)
“ Beauty Is in the Eye of the Beholder, and the Beholder Is a White Man: The 1875 Page Act, Eugenics, and Beauty Standards for Chinese Women versus American Women ”
Undergraduate Essays
Rachelle Dumayas (California State University, Sacramento)
“Should Deaf Children Get Cochlear Implants?”
Holly Nelson (Johns Hopkins University)
“Creating Space? Representations of Black Characters in Regency Romance”
Chloe Wiitala (University of Minnesota, Duluth)
“ Reanimating Queer Perspectives through Camp: A Study of Frankenstein and Its Parodic Film Adaptations ”
Writing with MLA Style: 2023 Edition
The following essays were selected for the 2023 edition of Writing with MLA Style. The 2023 selection committee was composed of Ellen C. Carillo, University of Connecticut (chair); Rachel Ihara, Kingsborough Community College, City University of New York; and Tarshia L. Stanley, Wagner College.
Caroline Anderson (Pepperdine University)
“ L’Appel du Vide : Making Spaces for Sinful Exploration in The Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde ”
Hunter Daniels (University of South Carolina, Aiken)
“Biblical Legalism and Cultural Misogyny in The Tragedy of Mariam ”
Aspen English (Southern Utah University)
“Putting the ‘Comm’ in Comics: A Communication-Theory-Informed Reading of Graphic Narratives”
Raul Martin (Lamar University)
“The Book-Object Binary: Access and Sustainability in the Academic Library”
Grace Quasebarth (Salve Regina University)
“Finding a Voice: The Loss of Machismo Criticisms through Translation in Isabel Allende’s The House of the Spirits ”
Writing with MLA Style: 2022 Edition
The following essays were selected for the 2022 edition of Writing with MLA Style. The 2022 selection committee was composed of Ellen C. Carillo, University of Connecticut; Jessica Edwards, University of Delaware (chair); and Deborah H. Holdstein, Columbia College Chicago.
Kaile Chu (New York University, Shanghai)
“Miles Apart: An Investigation into Dedicated Online Communities’ Impact on Cultural Bias”
Sietse Hagen (University of Groningen)
“The Significance of Fiction in the Debate on Dehumanizing Media Portrayals of Refugees”
Klara Ismail (University of Exeter)
“Queering the Duchess: Exploring the Body of the Female Homosexual in John Webster’s The Duchess of Malfi ”
Yasmin Mendoza (Whittier College)
“Banning without Bans”
Niki Nassiri (Stony Brook University)
“Modern-Day US Institutions and Slavery in the Twenty-First Century”
Samantha Wilber (Palm Beach Atlantic University)
“‘Pero, tu no eres facil’: The Poet X as Multicultural Bildungsroman”
Writing with MLA Style: 2019 Edition
The following essays were selected for the 2019 edition of Writing with MLA Style. The 2019 selection committee was composed of Jessica Edwards, University of Delaware; Deborah H. Holdstein, Columbia College Chicago (chair); and Liana Silva, César E. Chavez High School, Houston, Texas.
Catherine Charlton (University of King’s College, Nova Scotia)
“‘Coal Is in My Blood’: Public and Private Representations of Community Identity in Springhill, Nova Scotia”
Alyiah Gonzales (California Polytechnic State University)
“Disrupting White Normativity in Langston Hughes’s ‘I, Too’ and Toni Morrison’s ‘Recitatif’”
Meg Matthias (Miami University, Ohio)
“Prescriptions of (Living) Historical Happiness: Gendered Performance and Racial Comfort in Reenactment”
Jennifer Nguyen (Chaminade University of Honolulu)
“The Vietnam War, the American War: Literature, Film, and Popular Memory”
Emily Schlepp (Northwest University)
“A Force of Love: A Deconstructionist Reading of Characters in Dickens’s Great Expectations ”

Assignment and Study Help
- Start your assignment
- Search for information
- Write your assignment
- Essay and report writing
- Revising and editing
- Copyright and plagiarism
- Groupwork/Teamwork
- Presenting and public speaking
- Resources Outside TAFE Queensland Library
- University of Canberra and FedUni Study Help
- Accessibility guide This link opens in a new window
- Learning support This link opens in a new window
- Referencing This link opens in a new window
- Student Software, PCs & Access This link opens in a new window
- Learning Skills Support This link opens in a new window
Essay and report layout
Introduction
- Essay layout
- Report layout
- Tips and Hints
Most assignments require either an essay or report. Essays and reports differ from one another in both their purpose and the information they contain.
The table below describes the differences between essays and reports.
| Essays | Reports |
| Present arguments and/or issues | Present information |
| Read carefully by your teacher/tutor | Can be scanned quickly by the reader |
| Use limited headings and/or lists | Use numbered headings and sub headings |
| Link ideas into paragraphs | Use dot points to emphasise points |
| Make limited use of tables, graphs and illustrations | Tables and graphs illustrate points more clearly |
| Abstracts are only required if essays are very long and one has been requested by your teacher/tutor | May require an executive summary or abstract |
| Seldom have recommendations | Recommendations often follow the conclusions in order to correct problems or situations discussed in the report |
| Seldom contain appendices | Contain appendices |
- Essay format example in PDF format
- Report format example in PDF
- Basic Report Format in Word format
Essay writing
While there are some basic steps for writing an essay, it is not always a straight forward process. You might like to work through the different stages a number of times. You may need to return to your reading and notetaking as you realise you are missing pieces of information.
General layout and presentation of an essay
The essay is generally organised into three broad sections - introduction, body, conclusion.
The introduction for the essay provides an overview of your assignment question and the arguments that you will make in this essay to answer it. The introduction captures the reader's interest and prepares the reader for what is to come The introduction is usually one paragraph in length.
The body of the essay uses ideas set out in the introduction, and expands on them to convince the reader of the argument or position of the author. The body is the largest section of the essay, with a number of paragraphs outlining a number of ideas or arguments related to the assignment question.
You should focus on one idea or argument in each paragraph. Each paragraph should logically follow on from the one that precedes it to make sure that the essay is presenting a clear and connected argument throughout. Paragraphs should be at least three sentences in length (mirroring the introduction, body and conclusion of an essay).
The conclusion bring together the ideas for the body of the assignment. It will sum up you ideas/arguments so the reader can understand in full the final position you are taking. The conclusion is only restating arguments that have been mad, and should not introduce new ideas or facts.
Your teacher will instruct you on margins, spacing, font and paragraph formatting for your assignments.
R eport writing
A report provides an account of research or an investigation. It clearly describes, in logical sequence the steps that have been followed. Reports can be any length and can be:
Informational - contain facts/figures, e.g. sales, production or accident reports. Analytical - written to solve problems/situations, contain recommendations.
Report structures include numbered sections and have:
Major headings in upper case letters. They can be underlined. Minor headings indented from the left margin and in lower case letters. They can be underlined also.
These headings distinguish major ideas from minor ones, help to organise your material and enable you to maintain a consistent layout throughout the report.
Remember: Write your report to get your message across - above all, your report should provide a clear and concise analysis of the work undertaken with no unfinished work apparent.
Example of a report format:
Cover page (Name of the report, your name, date, course name/no.)
Executive summary or abstract: short summary of the report containing all the most important information such as the purpose, methods, findings, any recommendations and conclusion. Write this summary after you have finished the rest of the report.
Table of contents : list of all headings and corresponding page numbers in the report
Body of report: 1. INTRODUCTION (an example of a major heading)
1.1 Aim of the report (an example of a minor heading) Describe the aim or scope of the report. 1.2 Authorisation Why the report was requested and by whom. 1.3 Sources of information List interviews, laboratory procedure manuals consulted and so on.
2. BACKGROUND INFORMATION
2.1 Information available A statement on the present situation.
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Summary of data 3.2 Explanation of tables and graphs 3.3 Analysis of data 3.4 Observation of results
4. CONCLUSION/S State what the results have proved or suggested. Do not introduce any new information at this stage of the report.
5. RECOMMENDATIONS (if required) It is recommended that: (action to be/not to be taken, or a choice can/cannot be made)
5.1 First recommendation 5.2 Second recommendation
Appendices Examples: Glossary, Survey results
Bibliography/Reference List
An essay usually consists of an introduction, the body, a conclusion and a reference list or bibliography. The assignment question will contain instruction or direction words.
Helpful Tips
- Use plain English: use familiar words rather than foreign phrases or scientific jargon.
- Don't use slang – try a dictionary or thesaurus to find a better word or term.
- Don’t use abbreviations such as “Aust”, “Qld”, “don’t” and “&” in essays.
- Be precise: use enough words to achieve clarity but avoid unnecessary words that can distract from the main point
- Acronyms: write the full name followed by the acronym in brackets, e.g. Department of Education, Training and Employment (DETE). “DETE” can then be used throughout the rest of the essay.
- Word length – stay on target to avoid writing too much or too little.
- You must include in-text referencing within the body of the assignment.
- The reference list, works cited list, or bibliography must be included at the end of the essay. Your teacher will determine which list is appropriate for your assignment.
- << Previous: Write your assignment
- Next: Revising and editing >>
- Last Updated: Aug 20, 2024 8:57 AM
- URL: https://library.tafeqld.edu.au/assignment_study_help
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an expository essay
How to Write an Expository Essay | Structure, Tips & Examples
Published on July 14, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
“Expository” means “intended to explain or describe something.” An expository essay provides a clear, focused explanation of a particular topic, process, or set of ideas. It doesn’t set out to prove a point, just to give a balanced view of its subject matter.
Expository essays are usually short assignments intended to test your composition skills or your understanding of a subject. They tend to involve less research and original arguments than argumentative essays .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When should you write an expository essay, how to approach an expository essay, introducing your essay, writing the body paragraphs, concluding your essay, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about expository essays.
In school and university, you might have to write expository essays as in-class exercises, exam questions, or coursework assignments.
Sometimes it won’t be directly stated that the assignment is an expository essay, but there are certain keywords that imply expository writing is required. Consider the prompts below.
The word “explain” here is the clue: An essay responding to this prompt should provide an explanation of this historical process—not necessarily an original argument about it.
Sometimes you’ll be asked to define a particular term or concept. This means more than just copying down the dictionary definition; you’ll be expected to explore different ideas surrounding the term, as this prompt emphasizes.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
An expository essay should take an objective approach: It isn’t about your personal opinions or experiences. Instead, your goal is to provide an informative and balanced explanation of your topic. Avoid using the first or second person (“I” or “you”).
The structure of your expository essay will vary according to the scope of your assignment and the demands of your topic. It’s worthwhile to plan out your structure before you start, using an essay outline .
A common structure for a short expository essay consists of five paragraphs: An introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Like all essays, an expository essay begins with an introduction . This serves to hook the reader’s interest, briefly introduce your topic, and provide a thesis statement summarizing what you’re going to say about it.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works.
In many ways, the invention of the printing press marked the end of the Middle Ages. The medieval period in Europe is often remembered as a time of intellectual and political stagnation. Prior to the Renaissance, the average person had very limited access to books and was unlikely to be literate. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century allowed for much less restricted circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation.
The body of your essay is where you cover your topic in depth. It often consists of three paragraphs, but may be more for a longer essay. This is where you present the details of the process, idea or topic you’re explaining.
It’s important to make sure each paragraph covers its own clearly defined topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Different topics (all related to the overall subject matter of the essay) should be presented in a logical order, with clear transitions between paragraphs.
Hover over different parts of the example paragraph below to see how a body paragraph is constructed.
The invention of the printing press in 1440 changed this situation dramatically. Johannes Gutenberg, who had worked as a goldsmith, used his knowledge of metals in the design of the press. He made his type from an alloy of lead, tin, and antimony, whose durability allowed for the reliable production of high-quality books. This new technology allowed texts to be reproduced and disseminated on a much larger scale than was previously possible. The Gutenberg Bible appeared in the 1450s, and a large number of printing presses sprang up across the continent in the following decades. Gutenberg’s invention rapidly transformed cultural production in Europe; among other things, it would lead to the Protestant Reformation.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The conclusion of an expository essay serves to summarize the topic under discussion. It should not present any new information or evidence, but should instead focus on reinforcing the points made so far. Essentially, your conclusion is there to round off the essay in an engaging way.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a conclusion works.
The invention of the printing press was important not only in terms of its immediate cultural and economic effects, but also in terms of its major impact on politics and religion across Europe. In the century following the invention of the printing press, the relatively stationary intellectual atmosphere of the Middle Ages gave way to the social upheavals of the Reformation and the Renaissance. A single technological innovation had contributed to the total reshaping of the continent.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An expository essay is a broad form that varies in length according to the scope of the assignment.
Expository essays are often assigned as a writing exercise or as part of an exam, in which case a five-paragraph essay of around 800 words may be appropriate.
You’ll usually be given guidelines regarding length; if you’re not sure, ask.
An expository essay is a common assignment in high-school and university composition classes. It might be assigned as coursework, in class, or as part of an exam.
Sometimes you might not be told explicitly to write an expository essay. Look out for prompts containing keywords like “explain” and “define.” An expository essay is usually the right response to these prompts.
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Expository Essay | Structure, Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/expository-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
4 Process Analysis Examples from Operational Excellence Expert Peter Evans
Kazyna turdibayeva september 10, 2024 business process management (bpm).
Table of Contents
Process analysis is one of those areas of business process management where everyone has their own view but you can never get enough actual case examples of processes that have been improved. Understanding the concept of a process analysis essay can also be beneficial, as it breaks down a complex process into clear, sequential steps, much like how business process analysis aims to improve operational efficiency.
To give you real business process analysis examples, we’ve asked operational excellence sherpa Peter Evans to share some of his favorite process analysis methods across his 30 years of experience analyzing and transforming business processes for some of the world’s greatest enterprise business operations in companies such as GE Capital, Virgin Media, and LEGO Group.
Before we hear Peter’s three classic case examples let’s cover some basic questions on business process analysis.
What exactly is business process analysis?
Business process analysis (or BPA) is a systematic approach to understanding, evaluating, and optimizing the processes within your organization. It involves analyzing processes to identify the current state of each process, finding areas for improvement, and implementing changes to maximize efficiency and effectiveness.
Definition of Process Analysis
Process analysis is a systematic method of examining how work is done in an organization. It involves breaking down a process into its component parts and studying each part to determine how it contributes to the overall outcome. This method can be applied to any process within an organization, from manufacturing and logistics to customer service and administrative tasks. By dissecting each step, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of their operations, identify inefficiencies, and implement improvements.
For instance, in a manufacturing setting, process analysis might involve examining the steps involved in producing a product, from raw material procurement to final assembly. By analyzing each step, manufacturers can identify bottlenecks, streamline workflows, and reduce production costs. Similarly, in a customer service context, process analysis can help organizations understand the flow of customer interactions, identify pain points, and enhance the overall customer experience.
In essence, process analysis is a powerful tool that can help organizations improve their operations, increase efficiency, and achieve their business goals. Whether you’re looking to optimize a complex process or simply understand how a particular task is performed, process analysis provides the insights needed to drive continuous improvement.
Is business process analysis the same as process mapping?
Process mapping is one key tool for analyzing business processes, but it’s not the only one. In this article, Peter will share with us three more specific examples of value stream mapping, root cause analysis, and workflow analysis.
A directive process analysis provides specific instructions for achieving a goal, such as a recipe for making waffles, whereas an informative process analysis focuses on describing a subject in detail.
For the sake of clarity let’s define business process analysis simply as the evaluation of the “ as is” state of any existing processes in order to map or model the “ to be” state of process improvement.
Why is process analysis important in business operations?
Business process analysis is crucial for organizations of all sizes because it helps uncover inefficiencies, bad business process design, and wasted work that can hinder growth and success. By analyzing your business processes, you can ensure they are aligned with your key objectives and create a roadmap to achieve your goals.
A clear process analysis essay structure is essential for maintaining reader engagement, as it breaks down the content into specific sections like introduction, materials needed, step-by-step instructions, and conclusion.
What are the key benefits of a comprehensive understanding of business process analysis?
Each business has its own goals and objectives. Some companies will be doing process analysis to automate processes, while some are simply looking to uncover inefficient business processes. Some are looking for cost savings, while others are looking to drive more sustainable continuous improvement.
A process analysis essay outline is crucial for presenting a process or task effectively, as it provides a structured framework that emphasizes clarity and organization.
Business process analysis can also provide different benefits to each organization depending on its own business targets, operational maturity level, and key performance indicators.
Broadly speaking, business process analysis looks to do three things:
- Improve efficiency . One of the main benefits of business process analysis is the increased efficiency it can bring to your organization. By streamlining processes and eliminating waste, you can save time, resources, and money, allowing you to focus on what really matters: growing your business.
- Increase agility . For many businesses, speed is money. Whether you measure lead time or throughput time, most business processes can be analyzed and streamlined to reduce the time of work. Through business process analysis, you can identify areas where your organization can be more agile and responsive to customer needs and changes in the market, ensuring you stay competitive and ahead of the curve.
- Reduce cost . Most businesses look to keep operational costs as low as possible, and for many businesses, the cost of manual tasks and complex processes quickly adds up. The reality is that sometimes business process analysts are tasked with simply reducing costs or finding ways to re-engineer the cost base of key business processes.
Industries and Functions
Process analysis is a versatile tool that can be applied across various industries and functions. Here are some examples of how different sectors can benefit from process analysis:
- Manufacturing : In the manufacturing industry, process analysis can help identify bottlenecks in the production process, streamline workflows, and improve overall efficiency. By analyzing each step of the production line, manufacturers can reduce waste, lower costs, and increase output.
- Healthcare : Healthcare organizations can use process analysis to streamline patient care processes, reduce wait times, and improve the quality of care. For example, analyzing the flow of patients through an emergency department can help identify inefficiencies and implement changes to enhance patient outcomes.
- Finance : Financial institutions can benefit from process analysis by identifying areas for improvement in transaction processing and customer service. By examining each step of a financial transaction, banks can reduce processing times, minimize errors, and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Retail : Retailers can use process analysis to optimize their supply chain and inventory management processes. By analyzing the flow of goods from suppliers to store shelves, retailers can reduce stockouts, minimize excess inventory, and improve overall efficiency.
- Customer Service : Process analysis can help organizations improve their customer service processes and reduce customer complaints. By examining the steps involved in handling customer inquiries and resolving issues, companies can identify areas for improvement and enhance the overall customer experience.
By applying process analysis to these and other industries, organizations can gain valuable insights into their operations, identify inefficiencies, and implement changes that drive continuous improvement.
Four real-world examples of business process analysis
If you’re looking for real examples of business process analysis, look no further.
We’ve asked our Operational Excellence expert Peter Evans to share examples from his experience of different kinds of business process analysis cases, the key challenges, and their outcomes. These include process analysis essay examples that demonstrate the breakdown of complex procedures into clear, manageable steps.
To start, let’s go through a value stream analysis case from Peter’s time in the aviation leasing industry.
1: Value stream mapping of core business processes
Value stream mapping involves analyzing the flow of materials or information within an organization to identify areas of waste and improve overall efficiency. This is akin to process analysis essays, which break down and explain various procedures or tasks into manageable steps. Value stream mapping can help organizations streamline their business processes and reduce costs.
Simplified value stream map diagram example
Peter’s case example: value stream mapping to diagnose finance close process
Peter shares a case from his time with GE Capital Aviation Services (GECAS) in the 1990s where he was challenged to shorten the amount of time it took to close accounting books.
“As a starting point, in GECAS, we saw about 13 or 14 days of work for us to close our books. The challenge came down to try and close in three days. The only real approach to that, is you either start with a completely blank piece of paper, which is very hard to do, or you start by mapping the process. Right from start to finish and understanding within that process where the big chunks of time and the big chunks of effort are.
In our case, we literally picked the process apart. So together with a team from finance, we had a look at all of those big chunks and then created charts just to show where those problems were. Our analysis uncovered a classic Pareto chart – where 80% of problems came from 20% of the work. By analyzing the full close process, we found the throughput time was impacted by things like manual journal entries and other garbage you have to wade through to get your books in balance.
Once we had the full process map, we evaluated where the true value came from and what we could do to decrease non-value-added work. Then, we systematically attacked inefficiencies and took out thousands and thousands of manual journal entries and accruals and all that other stuff that you have to do yourself to the point where you can close your books. The net effect of that project was that we were the first group within GECAS to get ourselves down to three days closing.”
Peter’s advice : “Value stream analysis helps you rethink why people work the way they do. Accounting is a good example of a function where there are all kinds of tasks where people will check things, and checkers will check the checking another time around. You map all those things in a value stream and analyze where is the value added of all these rounds of control. Often you find ways to get around manual work or identify ways to do things more efficiently.”
2: Root cause analysis to identify bottlenecks in an end-to-end process
Root cause analysis is a technique used to identify the underlying causes of problems within a business process. By finding the root challenges, organizations can address issues at their source and implement lasting improvements.
An informational process analysis essay is a type of essay that aims to inform the reader about a specific topic rather than giving instructions. It is important to differentiate between informative and directive process essays and to structure the content clearly to maintain reader engagement.
Simplified fishbone diagram example of root cause analysis
Peter’s case example: root cause analysis to optimize hospital capacity
Peter gives an example for analyzing root causes from the field of emergency healthcare services. More specifically, he recounts the analysis he has witnessed to analyze the flow of patients from triage in the accident and emergency (A&E) departments to other specialist units.
“The goal for the first-line emergency services like the A&E department is often to clear them out of there as soon as they possibly can, because they want to maintain capacity, they need the facility and the staff to be able to work with the next patient.
If you look along the client flow within a hospital, there’ll be intensive care wards, there’ll be other specialist areas where the patients can be sent for further care after A&E. What you often find in that scenario, is that people are not looking at the overall process, they’re only looking at their piece of a process. You actually find a massive disconnect within different hospital departments.
To understand the challenge, you can use root cause analysis. You go to the key stakeholders and ask questions like:
- why do we transfer patients like this?
- why can’t we get them into the next department?
- why don’t we have any beds ready?
In this case, one of the root causes may not be that the doctors are doing a bad job of signing off patients, but the process was designed so that they only did it in the afternoon or at a specific time during their shifts. These misalignments within processes between departments can be fixed and it can have a big impact on the big picture.”
Peter’s advice : “Root cause analysis is absolutely vital. The problem comes if you stop too early. Then you’re not solving a root cause, you’re solving a symptom. That can happen quite a lot. So, in my analysis, I’m dogged about really digging into things to the point where you can be satisfied from a data point of view and from a process point of view that you’ve really got to a root cause.”
3: Workflow analysis as part of business process analysis
Workflow analysis involves mapping out the current workflows within an organization to identify bottlenecks, redundancies, or other inefficiencies. This analytical approach is similar to writing a process essay, where each step is carefully examined and documented. This can help businesses optimize their processes and increase efficiency.
Simplified workflow diagram for accounts payable
Peter’s case example: analyzing accounts payable workflows in telecoms
Peter shares a case from his time working in the telecommunications industry with Virgin Media. in the 2000s where he was tasked to go and look at the shared services piece of finance operations with a target to identify operational efficiencies.
“We heard that the accounts payable process was very clunky and very manual at the time. Cycle times were very long and we didn’t have a great reputation for our ability to pay on time.
When we went to look at the place, we were very frustrated by what we saw. We looked at a number of things. One, how invoices were received and what we were doing about them. At the time, we were still manually sorting posts and we were making a terrible pig of that. It took hours when it should have taken minutes.
We then had a sorting process, which wasn’t very efficient and wasn’t really traceable. We then kind of put invoices into files and drawers and hoped that people would process them in the right order. All of those things are non-value adding from a point of view of our ability to pay our supplier on time.”
Once the key workflow challenges were identified, it was time to bring about process improvements.
“Basically from there, we took a number of approaches. We brought in one or two quick wins for getting the post sorted on a daily basis. We worked with the AP team slowly but surely to improve each aspect of the process. Changing workflows wasn’t easy. It included challenging a couple of the biggest naysayers in terms of what we were trying to do. We ran some very clear sessions for them, understanding their processes and getting to the point for them to realize perhaps their baby wasn’t as pretty as they’d like.”
Peter’s advice : “Workflow analysis is about chipping away at inefficiencies to really understand how processes work and moving them forward. You can’t stop with the analysis. Real improvement involves upskilling the actual people who do the work to recognize where waste is happening and systematically removing them.”
4. The Gemba Walk inspired by lean manufacturing
Let’s hear one more real case example where Peter recounts the case when he got to visit a production facility for the world-famous toy company, the LEGO Group. This case is an example of the “Gemba Walk” method, where you go and observe the actual place where work happens.
A memorable conversation from the factory shop floor
During his time working for the LEGO Group Peter Evans led continuous improvement initiatives that took him to different parts of the world to see how different business units functioned. One way Peter recommends starting and understanding processes is what lean coaches call a ‘Gemba Walk.’ In this method, you go to the place where work happens and you sit and watch what’s going around you.
“I was working mostly in the back office space, but I was really interested to see what work they’d done on the shop floor in manufacturing. While I was visiting our factory in Monterrey (Mexico) I once got permission to go down and sit in some of the morning huddles.”
Below is the way Peter remembers a conversation taking place between a team lead and the shift workers during a memorable morning huddle:
Team lead : Was there anything on safety to report?
Answer : Yes. We had an incident yesterday where somebody cut his hand on a machine.
Team lead: Ah, okay. Is the guy okay?
Answer: Yeah, we took him off. He’s got some stitches. He’s perfectly okay now and he’ll be alright again. Everything is fine.
Team lead: Why did that happen?
Answer: Well, on the machine, there’s a moving part, and that moving part over time was sharpening one of the rails and the man cut his hand on one of those sharp rails.
Team lead: Ok, why was the rail sharp?
Answer: It was sharp because of this […] issue with moving parts.
Team lead: What did you do to fix it?
Answer: Well, I replaced that rail.
Team lead: Okay. Do we have any other machines that are like that?
Answer: Actually, I went around and found 27 other machines that had the same problem or had the potential for the same problem.
Team lead: What did you do about it?
Answer: I changed them. I also put a process in place to check that rail on a daily basis to make sure that it’s safe and make sure it’s okay.
How the LEGO Group’s continuous improvement mindset can inspire process analysis
The conversation above shows how deeply the mindset of continuous improvement can be embedded in effective manufacturing operations. It wasn’t enough to analyze safety risks, employees took it as their responsibility to fix the problem beyond the initial scope of risk. This kind of behavior can be inspiring to observe during a walk on the shop floor, but it can also inspire a similar mindset across business operations.
Nurturing the continuous improvement mindset of business process analysts
In Peter’s experience, effective business process analysis is as much a mindset as a set of tools. Much like the example of shift workers in the LEGO Group factory, the people who hunger for continuous improvement are the ones who learn to adapt the tools and thrive the most in continuous process optimization.
Business process analysis is not always a case of health and safety, but the same mindset of continuous improvement can lead to the longest-lasting results in business operations. After 30 years of working in operational excellence, Peter Evans got the opportunity to train many colleagues as lean coaches and embed the culture of continuous analysis and improvement into different business functions.
“In Virgin Media, we had an effective method, where we’d first assess process capabilities and sign off our understanding. Then, we’d go through training to understand the methodologies and technologies that we recommended using. Finally, we’d assign a “lean coach” from within the working team to continue the journey. These lean coaches would drive against the plan, understand how to tackle the key challenges, and were trusted by the local managers and team. Today, 10 or 15 years later, some of these lean coaches we trained have learned so much by doing they are in very senior roles, driving improvements everywhere.”
Bottom line on business process analysis examples
In this article, Peter Evans shared four popular business process analysis methods: value stream mapping, root cause analysis, workflow analysis, and the Gemba Walk method.
There are hundreds of methods you can use for process analysis, from process mapping to Lean or Six Sigma methods and even process mining software. Instead of giving recommendations on one key tool, we saw from Peter’s real-world examples how analysis is often just one part of a bigger equation in the mission for process excellence and continuous improvement. On this journey, the enthusiasm and curiosity of your team are key to long-term results.
Selecting interesting and relevant process analysis essay topics is crucial for effective writing. Engaging topics that resonate with readers and highlight the step-by-step breakdown of everyday processes can enhance reader curiosity and improve the effectiveness of the essays.
Best practices for process analysis
To effectively conduct process analysis and achieve meaningful improvements, organizations should follow these best practices:
- Identify the particular process : Start by selecting the specific process to be analyzed and clearly define its boundaries. This ensures that the analysis is focused and relevant.
- Gather information : Collect detailed information about the process through process documentation, stakeholder interviews, and data collection methods. This provides a comprehensive understanding of how the process currently operates.
- Map out the process : Create a visual representation of the process using a process flowchart or process map. This helps to identify each step and understand the flow of work.
- Analyze each step : Examine each step in the process to identify areas for improvement. Look for bottlenecks, redundancies, and inefficiencies that may be hindering performance.
- Identify bottlenecks : Pinpoint areas where work is duplicated, unnecessary, or inefficient. These bottlenecks are often the key to unlocking significant improvements.
- Develop improvement strategies : Based on the analysis, develop strategies for improving the process. This may involve redesigning workflows, automating tasks, or implementing new technologies.
- Implement changes : Put the improvement strategies into action and monitor their effectiveness. This ensures that the changes lead to the desired outcomes.
- Continuous review and refinement : Process analysis is an ongoing effort. Continuously review and refine the process to ensure it remains efficient and effective over time.
By following these best practices, organizations can use process analysis to gain a comprehensive understanding of their business processes, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes that increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.

Related Content
Business Process Management (BPM)
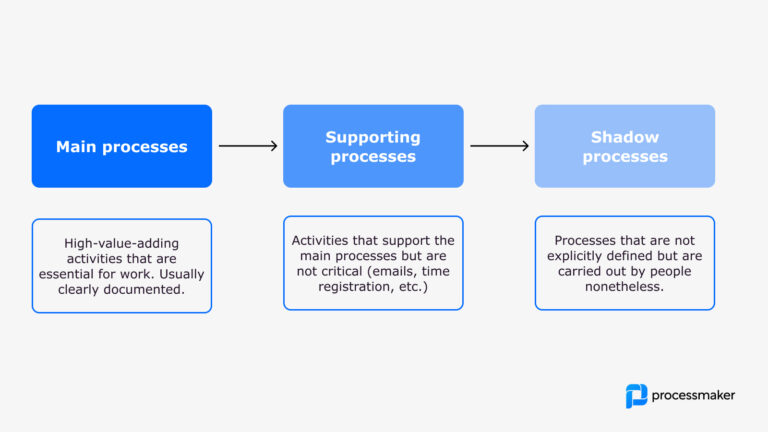
What are shadow processes and why do they matter in business?
Discover the concept of shadow processes—unwritten workflows that can disrupt the flow of your organization's...
September 10, 2024
How to create a process improvement plan in 4 simple steps?
How do you create a process improvement plan that increases efficiency, reduces costs, and enhances your processes? Learn ins and outs of process improvement in the next article....

BOAT: The Next Evolution or Just Another Term for BPM?
Gartner's introduction of Business Orchestration and Automation Technology (BOAT) seems to mark a significant moment in the landscape of enterprise automation. But is it really a groundbreaking...
September 05, 2024
Request a Demo
Discover how leading organizations utilize ProcessMaker to streamline their operations through process automation.

Evaluation Essay
Evaluation essay generator.

Creating an essay is a part of every student’s academic journey. There are different kinds of essays that can be a part of a student writing task. One of these essays is the evaluation essay. What can set apart an evaluation essay from various kinds of academic essays is that it can also be used in different undertakings within the corporate and professional environment. Evaluation essays are not limited to be used for educational purposes as it can also be beneficial in the fields of business, research and community development.
An evaluation essay contains an objective assessment that is written by an individual who should be fully-knowledgeable of what he or she is writing about. More so, this essay relays the sound judgement about a specific subject matter or topic of discussion. Each evaluation essay are based on evaluative writing that are commonly created in accordance to a set of criteria or value measurements. We have curated ten evaluation essays that you can refer to if you want to write your own evaluation essay.
Self-Evaluation Essay Sample

Size: 31 KB
Student Self-Evaluation Essay

Size: 121 KB
Things to Remember When Writing an Evaluation Essay
An evaluation essay should always be direct to the point and specific as it contains factual information that is essential to be known by the readers. To avoid common essay mistakes , some of the things that you should always remind yourself when writing an evaluation essay are listed below.
- When writing an evaluation essay, a writer must always be backed up by evidences so that he or she can support the evaluation being made. If you are writing an evaluation essay, you should always be objective with the content that you are presenting. Your opinion matters but you should make sure that it is based on reality. Evaluation essays work best if the readers can identify the sources that you have used to come up with the assessment that they are currently reading. If you will ensure that there is enough evidences to support you, then your evaluation essay can be more credible and relevant.
- Be specific with the kind of evaluation essay that you are creating. An evaluation essay can only be effective if you are aware of the purpose on why you are writing the document. Being able to present details, comments, and information that is directly related to the kind of evaluation essay that you are writing can help you create a highly-usable output. There are different kinds of evaluation essays and you should be aware that each of them have differences depending on the purpose of their creation. Come up with a highly-usable and effective evaluation essay by directly providing the needs of your readers.
- Always be clear when presenting your evaluation. Since the main purpose of an evaluation essay is to relay your viewpoint about a specific subject, you have to make sure that you will be precise and concise when delivering the message that you want your readers to be knowledgeable of. You have to explain how you were able to create the evaluation which includes the specification of the factors that you have considered within the entirety of the evaluation and writing process.
Humanities Project Evaluation Essay

Size: 331 KB
Printable Self-Evaluation Essay Example

Size: 128 KB
Purposes of an Evaluation Essay
There is a wide variety of evaluation essay examples that are specifically created for particular purposes. Evaluation essays can cover a lot of topics which is why it is used in a range of industries and processes. The different kinds of evaluation essays can be used for the following instances and activities:
- To create a book report or a review of a book’s content and how it has affected the reader
- To identify critical points of a written work may it be a poem, another essay or a research paper
- To create a literature or literary review to fully identify the content of a literary piece
- To give critique about an initial analysis or a full process
- To support the processes of employment regularization or employee promotion
- To assess and analyze the results of a reading activity
- To add value to a recommendation letter
- To analyze a research topic that can fully affect the entire research activity
- To evaluate the work performance of either a student or an employee
- To identify the strengths and weaknesses of an individual through a self-evaluation
With the different ways on how you can use an evaluation essay, it is safe to say that there are a lot of fields of expertise that can benefit from this document. When creating your own evaluation essay, you should always keep in mind that the content of your essay must be relevant to the message that you would like to disseminate or share to your target readers.
Thesis Paper Evaluation Essay Example

Size: 100 KB
Evaluation Essay Sample in PDF

Size: 282 KB
Qualitative Evaluation Essay Example

Size: 396 KB
Steps in Writing an Evaluation Essay
If you want to create an evaluation essay, you should be strategic when it comes to the presentation of information that can be helpful in the writing activity. Your evaluation essay can only be fully-maximized if there is an organized discussion of your evaluation as well as the facts that can support your thesis statement.
Here is an essay writing basic guide that you may follow when writing an evaluation essay:
- Be aware of your topic. The first thing that you need to do when writing an evaluation essay is to be knowledgeable about the topic that you will write about. As much as possible, research about the subject of discussion so you can easily identify the characteristics that you can evaluate and the criteria that you will use for evaluation.
- Make sure to have a set of criteria that can help you determine your evaluation. Once you are already aware of your topic, you can already set criteria that will serve as the basis for your evaluation. If you will properly identify the criteria that will best fit your needs for the specific evaluation, then you can make your evaluation essay stronger and more effective.
- Refer to samples and templates of evaluation essays. It will be helpful if you will look at different kinds of evaluation essay samples and templates. These documents can help you be more familiar with what an evaluation essay is and how the details present in this kind of essay should be arranged and presented.
- Create an evaluation essay draft. It will depend on you if you will use a template as your guide when writing an evaluation essay. You can also just browse through samples and start your evaluation essay from scratch. One thing that we highly suggest you should do is to make a draft or an outline of the discussion that you would like to have. This can help you ensure that all the necessary information will be placed in your final evaluation essay.
- Start writing the content of your evaluation essay. Through the help of the draft that you have created, write a thesis in the first paragraph of your essay. This is the part where you can discuss the topic that you will use for evaluation and the statement on whether you think positively or negatively of the subject. The way that you create a thesis statement will be based on the nature of operations or functions where the essay will be used.
- Incorporate evidences in your discussion so you can support your claims and/or opinions. After your thesis statement and discussion of important details, your next paragraphs should contain your opinions as well as the evidence that you have used as references. You can end your evaluation essay by having a firm statement of your conclusion.
Printable Self-Evaluation Essay Sample

Size: 13 KB
Self-Assessment Essay Example

Size: 29 KB
Simple Self-Evaluation Essay Example

Size: 51 KB
Evaluation Essay as an Important Written Document
An evaluation essay should be taken seriously especially in matters where its content can affect other people or even an entire community. Since an evaluation essay is not only a part of college essay examples as it can also be used in business and corporate processes, you have to understand the weight of its effectiveness. May it be a self-evaluation essay or a project evaluation essay, always keep in mind that you should put together all the evident facts and your statements in a professional and objective manner.
Whether it is a last minute essay writing or a thoughtfully planned evaluation essay composition, being aware of the items that we have discussed in this post can help you further improve the content and structure of an evaluation essay. It will also be easier for you to come up with an evaluation that can be trusted by your readers. Present all the details that you need to discuss in an organized and informative manner so you can come up with an evaluation essay that will truly work.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write an Evaluation Essay on the effectiveness of online learning platforms.
Discuss the quality of a school cafeteria's lunch options in an Evaluation Essay.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to Write a Report: A Guide to Report Formats ...
Emphasizing clarity and organization: Lastly, the purpose of a report essay is to emphasize clarity and organization. It should be well-structured, with a logical flow of ideas and information. The purpose is to ensure that readers can easily navigate through the essay, grasping the main points and arguments.
Ultimate Guide on How to Write a Report Tips and Sample
Report Essay Sample for High School . QUESTION: There was a disagreement between your class and one of your teachers. As the class prefect, write a report to the head of your school on the incident. A REPORT TO THE HEADMASTER ON A DISAGREEMENT BETWEEN MR. SAM TOMSON AND TECHNICAL 3B CLASS
How to Write a Report (with Pictures)
Report Writing Format, Tips, Samples and Examples
Report Writing Format with Templates and Sample ...
Thesis. Thesis is a type of research report. A thesis is a long-form research document that presents the findings and conclusions of an original research study conducted by a student as part of a graduate or postgraduate program. It is typically written by a student pursuing a higher degree, such as a Master's or Doctoral degree, although it ...
An example, within a business organization, can be when workers are evaluated or when another company is studied. In essence, we can have a report as a tool used in a research study or in a scientific field. Academic Report. Another general type is an academic report. These could be book reports, movie reviews, research, and even lab reports.
The Beginner's Guide to Writing an Essay | Steps & Examples
Report Writing - 18+ Examples, Format, How To ...
Example of a Great Essay | Explanations, Tips & Tricks
To gain a deeper understanding of report writing's practical applications, let's explore some real-world examples: 1. World Health Organization (WHO) - Global Health Report. The WHO publishes comprehensive reports on global health issues, providing data on disease outbreaks, vaccination rates, and healthcare access worldwide.
Below, we provide some student samples that exhibit the key features the most popular genres. When reading through these essays, we recommend paying attention to their. 1. Structure (How many paragraphs are there? Does the author use headers?) 2. Argument (Is the author pointing out a problem, and/or proposing a solution?) 3.
However, do not go into detail, even a general fact will do. 3. Keep It as Simple as Possible. Remember that this is a short report essay. Keep everything simple as possible. Having to explain in full detail may not be the right use for this kind of report essay.
Guide to Essay Writing: 5 Steps to Write an Outstanding ...
Sample Essays: Writing with MLA Style
Tips and Hints. Most assignments require either an essay or report. Essays and reports differ from one another in both their purpose and the information they contain. The table below describes the differences between essays and reports. Essays. Reports. Present arguments and/or issues. Present information. Read carefully by your teacher/tutor.
Make your Essay Structure Rock-Solid with These ...
How to Write an Expository Essay | Structure, Tips & ...
This is especially true when you are writing a narrative report essay on an event for school like Intramurals. You must be careful with how you may want to introduce the event and how you plan on writing it from there. 2. Draft Your Work. It is perfectly okay to start by drafting what you plan on writing.
How to Write an Informative Essay in 7 Steps
This is akin to process analysis essays, which break down and explain various procedures or tasks into manageable steps. Value stream mapping can help organizations streamline their business processes and reduce costs. Simplified value stream map diagram example. Peter's case example: value stream mapping to diagnose finance close process
There is a wide variety of evaluation essay examples that are specifically created for particular purposes. Evaluation essays can cover a lot of topics which is why it is used in a range of industries and processes. ... To create a book report or a review of a book's content and how it has affected the reader; To identify critical points of a ...
How to Write a Five-Paragraph Essay, With Outlines and ...