
- Games & Quizzes
- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction & Top Questions

Development of the idea
Overall reaction of photosynthesis.
- Basic products of photosynthesis
- Evolution of the process
- Light intensity and temperature
- Carbon dioxide
- Internal factors
- Energy efficiency of photosynthesis
- Structural features
- Light absorption and energy transfer
- The pathway of electrons
- Evidence of two light reactions
- Photosystems I and II
- Quantum requirements
- The process of photosynthesis: the conversion of light energy to ATP
- Elucidation of the carbon pathway
- Carboxylation
- Isomerization/condensation/dismutation
- Phosphorylation
- Regulation of the cycle
- Products of carbon reduction
- Photorespiration
- Carbon fixation in C 4 plants
- Carbon fixation via crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM)
- Differences in carbon fixation pathways
- The molecular biology of photosynthesis

Why is photosynthesis important?
What is the basic formula for photosynthesis, which organisms can photosynthesize.

photosynthesis
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Khan Academy - Photosynthesis
- Biology LibreTexts - Photosynthesis
- University of Florida - Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences - Photosynthesis
- Milne Library - Inanimate Life - Photosynthesis
- National Center for Biotechnology Information - Chloroplasts and Photosynthesis
- Roger Williams University Pressbooks - Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology - Photosynthesis
- BCcampus Open Publishing - Concepts of Biology – 1st Canadian Edition - Overview of Photosynthesis
- photosynthesis - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
- photosynthesis - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)
- Table Of Contents

Photosynthesis is critical for the existence of the vast majority of life on Earth. It is the way in which virtually all energy in the biosphere becomes available to living things. As primary producers, photosynthetic organisms form the base of Earth’s food webs and are consumed directly or indirectly by all higher life-forms. Additionally, almost all the oxygen in the atmosphere is due to the process of photosynthesis. If photosynthesis ceased, there would soon be little food or other organic matter on Earth, most organisms would disappear, and Earth’s atmosphere would eventually become nearly devoid of gaseous oxygen.
The process of photosynthesis is commonly written as: 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 . This means that the reactants, six carbon dioxide molecules and six water molecules, are converted by light energy captured by chlorophyll (implied by the arrow) into a sugar molecule and six oxygen molecules, the products. The sugar is used by the organism, and the oxygen is released as a by-product.
The ability to photosynthesize is found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms. The most well-known examples are plants, as all but a very few parasitic or mycoheterotrophic species contain chlorophyll and produce their own food. Algae are the other dominant group of eukaryotic photosynthetic organisms. All algae, which include massive kelps and microscopic diatoms , are important primary producers. Cyanobacteria and certain sulfur bacteria are photosynthetic prokaryotes, in whom photosynthesis evolved. No animals are thought to be independently capable of photosynthesis, though the emerald green sea slug can temporarily incorporate algae chloroplasts in its body for food production.
Recent News
Trusted Britannica articles, summarized using artificial intelligence, to provide a quicker and simpler reading experience. This is a beta feature. Please verify important information in our full article.
This summary was created from our Britannica article using AI. Please verify important information in our full article.
photosynthesis , the process by which green plants and certain other organisms transform light energy into chemical energy . During photosynthesis in green plants, light energy is captured and used to convert water , carbon dioxide , and minerals into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds .
It would be impossible to overestimate the importance of photosynthesis in the maintenance of life on Earth . If photosynthesis ceased, there would soon be little food or other organic matter on Earth. Most organisms would disappear, and in time Earth’s atmosphere would become nearly devoid of gaseous oxygen. The only organisms able to exist under such conditions would be the chemosynthetic bacteria , which can utilize the chemical energy of certain inorganic compounds and thus are not dependent on the conversion of light energy.

Energy produced by photosynthesis carried out by plants millions of years ago is responsible for the fossil fuels (i.e., coal , oil , and gas ) that power industrial society . In past ages, green plants and small organisms that fed on plants increased faster than they were consumed, and their remains were deposited in Earth’s crust by sedimentation and other geological processes. There, protected from oxidation , these organic remains were slowly converted to fossil fuels. These fuels not only provide much of the energy used in factories, homes, and transportation but also serve as the raw material for plastics and other synthetic products. Unfortunately, modern civilization is using up in a few centuries the excess of photosynthetic production accumulated over millions of years. Consequently, the carbon dioxide that has been removed from the air to make carbohydrates in photosynthesis over millions of years is being returned at an incredibly rapid rate. The carbon dioxide concentration in Earth’s atmosphere is rising the fastest it ever has in Earth’s history, and this phenomenon is expected to have major implications on Earth’s climate .
Requirements for food, materials, and energy in a world where human population is rapidly growing have created a need to increase both the amount of photosynthesis and the efficiency of converting photosynthetic output into products useful to people. One response to those needs—the so-called Green Revolution , begun in the mid-20th century—achieved enormous improvements in agricultural yield through the use of chemical fertilizers , pest and plant- disease control, plant breeding , and mechanized tilling, harvesting, and crop processing. This effort limited severe famines to a few areas of the world despite rapid population growth , but it did not eliminate widespread malnutrition . Moreover, beginning in the early 1990s, the rate at which yields of major crops increased began to decline. This was especially true for rice in Asia. Rising costs associated with sustaining high rates of agricultural production, which required ever-increasing inputs of fertilizers and pesticides and constant development of new plant varieties, also became problematic for farmers in many countries.

A second agricultural revolution , based on plant genetic engineering , was forecast to lead to increases in plant productivity and thereby partially alleviate malnutrition. Since the 1970s, molecular biologists have possessed the means to alter a plant’s genetic material (deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA ) with the aim of achieving improvements in disease and drought resistance, product yield and quality, frost hardiness, and other desirable properties. However, such traits are inherently complex, and the process of making changes to crop plants through genetic engineering has turned out to be more complicated than anticipated. In the future such genetic engineering may result in improvements in the process of photosynthesis, but by the first decades of the 21st century, it had yet to demonstrate that it could dramatically increase crop yields.
Another intriguing area in the study of photosynthesis has been the discovery that certain animals are able to convert light energy into chemical energy. The emerald green sea slug ( Elysia chlorotica ), for example, acquires genes and chloroplasts from Vaucheria litorea , an alga it consumes, giving it a limited ability to produce chlorophyll . When enough chloroplasts are assimilated , the slug may forgo the ingestion of food. The pea aphid ( Acyrthosiphon pisum ) can harness light to manufacture the energy-rich compound adenosine triphosphate (ATP); this ability has been linked to the aphid’s manufacture of carotenoid pigments.
General characteristics
The study of photosynthesis began in 1771 with observations made by the English clergyman and scientist Joseph Priestley . Priestley had burned a candle in a closed container until the air within the container could no longer support combustion . He then placed a sprig of mint plant in the container and discovered that after several days the mint had produced some substance (later recognized as oxygen) that enabled the confined air to again support combustion. In 1779 the Dutch physician Jan Ingenhousz expanded upon Priestley’s work, showing that the plant had to be exposed to light if the combustible substance (i.e., oxygen) was to be restored. He also demonstrated that this process required the presence of the green tissues of the plant.
In 1782 it was demonstrated that the combustion-supporting gas (oxygen) was formed at the expense of another gas, or “fixed air,” which had been identified the year before as carbon dioxide. Gas-exchange experiments in 1804 showed that the gain in weight of a plant grown in a carefully weighed pot resulted from the uptake of carbon, which came entirely from absorbed carbon dioxide, and water taken up by plant roots; the balance is oxygen, released back to the atmosphere. Almost half a century passed before the concept of chemical energy had developed sufficiently to permit the discovery (in 1845) that light energy from the sun is stored as chemical energy in products formed during photosynthesis.

This equation is merely a summary statement, for the process of photosynthesis actually involves numerous reactions catalyzed by enzymes (organic catalysts ). These reactions occur in two stages: the “light” stage, consisting of photochemical (i.e., light-capturing) reactions; and the “dark” stage, comprising chemical reactions controlled by enzymes . During the first stage, the energy of light is absorbed and used to drive a series of electron transfers, resulting in the synthesis of ATP and the electron-donor-reduced nicotine adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH). During the dark stage, the ATP and NADPH formed in the light-capturing reactions are used to reduce carbon dioxide to organic carbon compounds. This assimilation of inorganic carbon into organic compounds is called carbon fixation.

Van Niel’s proposal was important because the popular (but incorrect) theory had been that oxygen was removed from carbon dioxide (rather than hydrogen from water, releasing oxygen) and that carbon then combined with water to form carbohydrate (rather than the hydrogen from water combining with CO 2 to form CH 2 O).
By 1940 chemists were using heavy isotopes to follow the reactions of photosynthesis. Water marked with an isotope of oxygen ( 18 O) was used in early experiments. Plants that photosynthesized in the presence of water containing H 2 18 O produced oxygen gas containing 18 O; those that photosynthesized in the presence of normal water produced normal oxygen gas. These results provided definitive support for van Niel’s theory that the oxygen gas produced during photosynthesis is derived from water.
- COVID-19 Tracker
- Biochemistry
- Anatomy & Physiology
- Microbiology
- Neuroscience
- Animal Kingdom
- NGSS High School
- Latest News
- Editors’ Picks
- Weekly Digest
- Quotes about Biology

Photosynthesis
Reviewed by: BD Editors
Photosynthesis Definition
Photosynthesis is the biochemical pathway which converts the energy of light into the bonds of glucose molecules. The process of photosynthesis occurs in two steps. In the first step, energy from light is stored in the bonds of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH). These two energy-storing cofactors are then used in the second step of photosynthesis to produce organic molecules by combining carbon molecules derived from carbon dioxide (CO 2 ). The second step of photosynthesis is known as the Calvin Cycle. These organic molecules can then be used by mitochondria to produce ATP, or they can be combined to form glucose, sucrose, and other carbohydrates. The chemical equation for the entire process can be seen below.
Photosynthesis Equation
Above is the overall reaction for photosynthesis. Using the energy from light and the hydrogens and electrons from water, the plant combines the carbons found in carbon dioxide into more complex molecules. While a 3-carbon molecule is the direct result of photosynthesis, glucose is simply two of these molecules combined and is often represented as the direct result of photosynthesis due to glucose being a foundational molecule in many cellular systems. You will also notice that 6 gaseous oxygen molecules are produced, as a by-produce. The plant can use this oxygen in its mitochondria during oxidative phosphorylation . While some of the oxygen is used for this purpose, a large portion is expelled into the atmosphere and allows us to breathe and undergo our own oxidative phosphorylation, on sugar molecules derived from plants. You will also notice that this equation shows water on both sides. That is because 12 water molecules are split during the light reactions, while 6 new molecules are produced during and after the Calvin cycle. While this is the general equation for the entire process, there are many individual reactions which contribute to this pathway.
Stages of Photosynthesis
The light reactions.
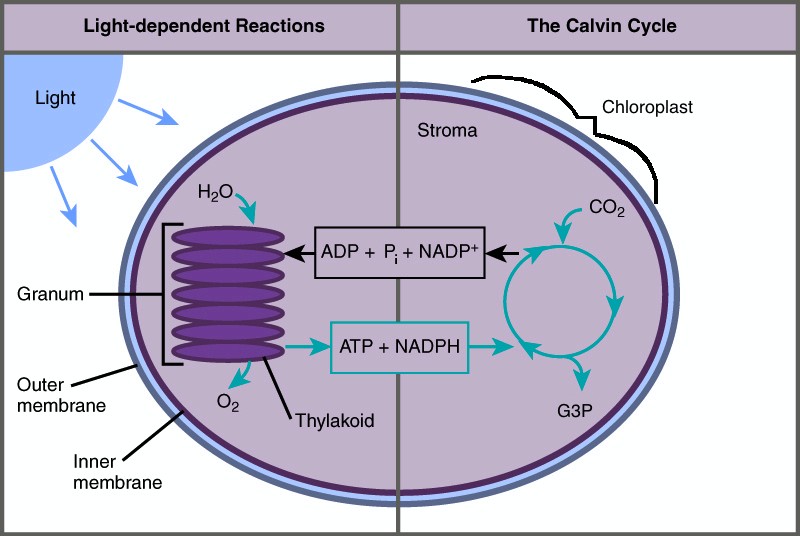
The light reactions happen in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts of plant cells. The thylakoids have densely packed protein and enzyme clusters known as photosystems . There are two of these systems, which work in conjunction with each other to remove electrons and hydrogens from water and transfer them to the cofactors ADP and NADP + . These photosystems were named in the order of which they were discovered, which is opposite of how electrons flow through them. As seen in the image below, electrons excited by light energy flow first through photosystem II (PSII), and then through photosystem I (PSI) as they create NADPH. ATP is created by the protein ATP synthase , which uses the build-up of hydrogen atoms to drive the addition of phosphate groups to ADP.

The entire system works as follows. A photosystem is comprised of various proteins that surround and connect a series of pigment molecules . Pigments are molecules that absorb various photons, allowing their electrons to become excited. Chlorophyll a is the main pigment used in these systems, and collects the final energy transfer before releasing an electron. Photosystem II starts this process of electrons by using the light energy to split a water molecule, which releases the hydrogen while siphoning off the electrons. The electrons are then passed through plastoquinone, an enzyme complex that releases more hydrogens into the thylakoid space . The electrons then flow through a cytochrome complex and plastocyanin to reach photosystem I. These three complexes form an electron transport chain , much like the one seen in mitochondria. Photosystem I then uses these electrons to drive the reduction of NADP + to NADPH. The additional ATP made during the light reactions comes from ATP synthase, which uses the large gradient of hydrogen molecules to drive the formation of ATP.
The Calvin Cycle
With its electron carriers NADPH and ATP all loaded up with electrons, the plant is now ready to create storable energy. This happens during the Calvin Cycle , which is very similar to the citric acid cycle seen in mitochondria. However, the citric acid cycle creates ATP other electron carriers from 3-carbon molecules, while the Calvin cycle produces these products with the use of NADPH and ATP. The cycle has 3 phases, as seen in the graphic below.

During the first phase, a carbon is added to a 5-carbon sugar, creating an unstable 6-carbon sugar. In phase two, this sugar is reduced into two stable 3-carbon sugar molecules. Some of these molecules can be used in other metabolic pathways, and are exported. The rest remain to continue cycling through the Calvin cycle. During the third phase, the five-carbon sugar is regenerated to start the process over again. The Calvin cycle occurs in the stroma of a chloroplast. While not considered part of the Calvin cycle, these products can be used to create a variety of sugars and structural molecules.
Products of Photosynthesis
The direct products of the light reactions and the Calvin cycle are 3-phosphoglycerate and G3P, two different forms of a 3-carbon sugar molecule. Two of these molecules combined equals one glucose molecule, the product seen in the photosynthesis equation. While this is the main food source for plants and animals, these 3-carbon skeletons can be combined into many different forms. A structural form worth note is cellulose , and extremely strong fibrous material made essentially of strings of glucose. Besides sugars and sugar-based molecules, oxygen is the other main product of photosynthesis. Oxygen created from photosynthesis fuels every respiring organism on the planet.
Lodish, H., Berk, A., Kaiser, C. A., Krieger, M., Scott, M. P., Bretscher, A., . . . Matsudaira, P. (2008). Molecular Cell Biology 6th. ed . New York: W.H. Freeman and Company. Nelson, D. L., & Cox, M. M. (2008). Principles of Biochemistry . New York: W.H. Freeman and Company.
Cite This Article
Subscribe to our newsletter, privacy policy, terms of service, scholarship, latest posts, white blood cell, t cell immunity, satellite cells, embryonic stem cells, popular topics, scientific method, mitochondria, adenosine triphosphate (atp), water cycle, homeostasis, amino acids.
5.1 Overview of Photosynthesis
Learning objectives.
- Summarize the process of photosynthesis
- Explain the relevance of photosynthesis to other living things
- Identify the reactants and products of photosynthesis
- Describe the main structures involved in photosynthesis
All living organisms on earth consist of one or more cells. Each cell runs on the chemical energy found mainly in carbohydrate molecules (food), and the majority of these molecules are produced by one process: photosynthesis. Through photosynthesis, certain organisms convert solar energy (sunlight) into chemical energy, which is then used to build carbohydrate molecules. The energy used to hold these molecules together is released when an organism breaks down food. Cells then use this energy to perform work, such as cellular respiration.
The energy that is harnessed from photosynthesis enters the ecosystems of our planet continuously and is transferred from one organism to another. Therefore, directly or indirectly, the process of photosynthesis provides most of the energy required by living things on earth.
Photosynthesis also results in the release of oxygen into the atmosphere. In short, to eat and breathe, humans depend almost entirely on the organisms that carry out photosynthesis.
Link to Learning
Click the following link to learn more about photosynthesis.
Solar Dependence and Food Production
Some organisms can carry out photosynthesis, whereas others cannot. An autotroph is an organism that can produce its own food. The Greek roots of the word autotroph mean “self” ( auto ) “feeder” ( troph ). Plants are the best-known autotrophs, but others exist, including certain types of bacteria and algae ( Figure 5.2 ). Oceanic algae contribute enormous quantities of food and oxygen to global food chains. Plants are also photoautotrophs , a type of autotroph that uses sunlight and carbon from carbon dioxide to synthesize chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates. All organisms carrying out photosynthesis require sunlight.
Heterotrophs are organisms incapable of photosynthesis that must therefore obtain energy and carbon from food by consuming other organisms. The Greek roots of the word heterotroph mean “other” ( hetero ) “feeder” ( troph ), meaning that their food comes from other organisms. Even if the food organism is another animal, this food traces its origins back to autotrophs and the process of photosynthesis. Humans are heterotrophs, as are all animals. Heterotrophs depend on autotrophs, either directly or indirectly. Deer and wolves are heterotrophs. A deer obtains energy by eating plants. A wolf eating a deer obtains energy that originally came from the plants eaten by that deer. The energy in the plant came from photosynthesis, and therefore it is the only autotroph in this example ( Figure 5.3 ). Using this reasoning, all food eaten by humans also links back to autotrophs that carry out photosynthesis.
Everyday Connection
Photosynthesis at the grocery store.
Major grocery stores in the United States are organized into departments, such as dairy, meats, produce, bread, cereals, and so forth. Each aisle contains hundreds, if not thousands, of different products for customers to buy and consume ( Figure 5.4 ).
Although there is a large variety, each item links back to photosynthesis. Meats and dairy products link to photosynthesis because the animals were fed plant-based foods. The breads, cereals, and pastas come largely from grains, which are the seeds of photosynthetic plants. What about desserts and drinks? All of these products contain sugar—the basic carbohydrate molecule produced directly from photosynthesis. The photosynthesis connection applies to every meal and every food a person consumes.
Main Structures and Summary of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis requires sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water as starting reactants ( Figure 5.5 ). After the process is complete, photosynthesis releases oxygen and produces carbohydrate molecules, most commonly glucose. These sugar molecules contain the energy that living things need to survive.
The complex reactions of photosynthesis can be summarized by the chemical equation shown in Figure 5.6 .
Although the equation looks simple, the many steps that take place during photosynthesis are actually quite complex, as in the way that the reaction summarizing cellular respiration represented many individual reactions. Before learning the details of how photoautotrophs turn sunlight into food, it is important to become familiar with the physical structures involved.
In plants, photosynthesis takes place primarily in leaves, which consist of many layers of cells and have differentiated top and bottom sides. The process of photosynthesis occurs not on the surface layers of the leaf, but rather in a middle layer called the mesophyll ( Figure 5.7 ). The gas exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen occurs through small, regulated openings called stomata .
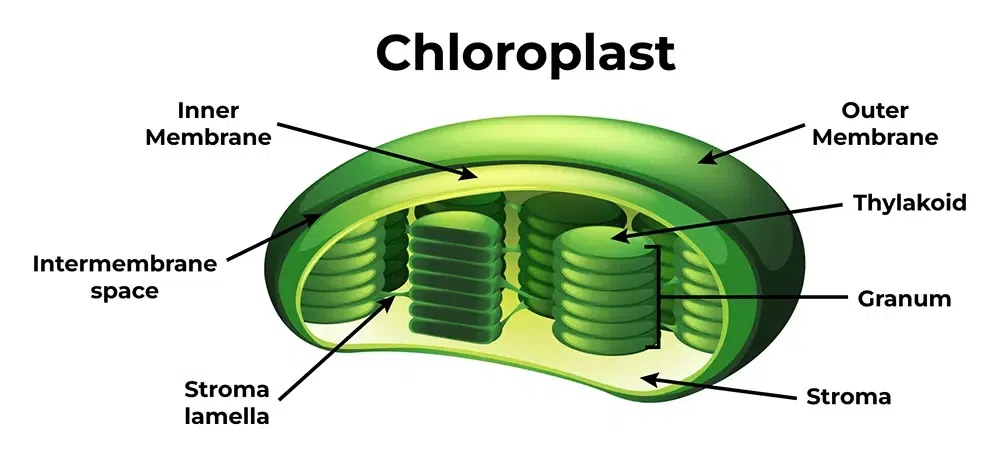
In all autotrophic eukaryotes, photosynthesis takes place inside an organelle called a chloroplast . In plants, chloroplast-containing cells exist in the mesophyll. Chloroplasts have a double (inner and outer) membrane. Within the chloroplast is a third membrane that forms stacked, disc-shaped structures called thylakoids . Embedded in the thylakoid membrane are molecules of chlorophyll , a pigment (a molecule that absorbs light) through which the entire process of photosynthesis begins. Chlorophyll is responsible for the green color of plants. The thylakoid membrane encloses an internal space called the thylakoid space. Other types of pigments are also involved in photosynthesis, but chlorophyll is by far the most important. As shown in Figure 5.7 , a stack of thylakoids is called a granum , and the space surrounding the granum is called stroma (not to be confused with stomata, the openings on the leaves).
Visual Connection
On a hot, dry day, plants close their stomata to conserve water. What impact will this have on photosynthesis?
The Two Parts of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis takes place in two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle. In the light-dependent reactions , which take place at the thylakoid membrane, chlorophyll absorbs energy from sunlight and then converts it into chemical energy with the use of water. The light-dependent reactions release oxygen from the hydrolysis of water as a byproduct. In the Calvin cycle, which takes place in the stroma, the chemical energy derived from the light-dependent reactions drives both the capture of carbon in carbon dioxide molecules and the subsequent assembly of sugar molecules. The two reactions use carrier molecules to transport the energy from one to the other. The carriers that move energy from the light-dependent reactions to the Calvin cycle reactions can be thought of as “full” because they bring energy. After the energy is released, the “empty” energy carriers return to the light-dependent reactions to obtain more energy. The two-stage, two-location photosynthesis process was discovered by Joan Mary Anderson, whose continuing work over the subsequent decades provided much of our understanding of the process, the membranes, and the chemicals involved.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/concepts-biology/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Concepts of Biology
- Publication date: Apr 25, 2013
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/concepts-biology/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/concepts-biology/pages/5-1-overview-of-photosynthesis
© Apr 26, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
This page has been archived and is no longer updated
Photosynthetic Cells
Cells get nutrients from their environment, but where do those nutrients come from? Virtually all organic material on Earth has been produced by cells that convert energy from the Sun into energy-containing macromolecules. This process, called photosynthesis, is essential to the global carbon cycle and organisms that conduct photosynthesis represent the lowest level in most food chains (Figure 1).
What Is Photosynthesis? Why Is it Important?
Most living things depend on photosynthetic cells to manufacture the complex organic molecules they require as a source of energy. Photosynthetic cells are quite diverse and include cells found in green plants, phytoplankton, and cyanobacteria. During the process of photosynthesis, cells use carbon dioxide and energy from the Sun to make sugar molecules and oxygen. These sugar molecules are the basis for more complex molecules made by the photosynthetic cell, such as glucose. Then, via respiration processes, cells use oxygen and glucose to synthesize energy-rich carrier molecules, such as ATP, and carbon dioxide is produced as a waste product. Therefore, the synthesis of glucose and its breakdown by cells are opposing processes.
However, photosynthesis doesn't just drive the carbon cycle — it also creates the oxygen necessary for respiring organisms. Interestingly, although green plants contribute much of the oxygen in the air we breathe, phytoplankton and cyanobacteria in the world's oceans are thought to produce between one-third and one-half of atmospheric oxygen on Earth.
What Cells and Organelles Are Involved in Photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll A is the major pigment used in photosynthesis, but there are several types of chlorophyll and numerous other pigments that respond to light, including red, brown, and blue pigments. These other pigments may help channel light energy to chlorophyll A or protect the cell from photo-damage. For example, the photosynthetic protists called dinoflagellates, which are responsible for the "red tides" that often prompt warnings against eating shellfish, contain a variety of light-sensitive pigments, including both chlorophyll and the red pigments responsible for their dramatic coloration.
What Are the Steps of Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis consists of both light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions . In plants, the so-called "light" reactions occur within the chloroplast thylakoids, where the aforementioned chlorophyll pigments reside. When light energy reaches the pigment molecules, it energizes the electrons within them, and these electrons are shunted to an electron transport chain in the thylakoid membrane. Every step in the electron transport chain then brings each electron to a lower energy state and harnesses its energy by producing ATP and NADPH. Meanwhile, each chlorophyll molecule replaces its lost electron with an electron from water; this process essentially splits water molecules to produce oxygen (Figure 5).
Once the light reactions have occurred, the light-independent or "dark" reactions take place in the chloroplast stroma. During this process, also known as carbon fixation, energy from the ATP and NADPH molecules generated by the light reactions drives a chemical pathway that uses the carbon in carbon dioxide (from the atmosphere) to build a three-carbon sugar called glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P). Cells then use G3P to build a wide variety of other sugars (such as glucose) and organic molecules. Many of these interconversions occur outside the chloroplast, following the transport of G3P from the stroma. The products of these reactions are then transported to other parts of the cell, including the mitochondria, where they are broken down to make more energy carrier molecules to satisfy the metabolic demands of the cell. In plants, some sugar molecules are stored as sucrose or starch.
This page appears in the following eBook
Topic rooms within Cell Biology

Within this Subject (25)
- Basic (25)
Other Topic Rooms
- Gene Inheritance and Transmission
- Gene Expression and Regulation
- Nucleic Acid Structure and Function
- Chromosomes and Cytogenetics
- Evolutionary Genetics
- Population and Quantitative Genetics
- Genes and Disease
- Genetics and Society
- Cell Origins and Metabolism
- Proteins and Gene Expression
- Subcellular Compartments
- Cell Communication
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
© 2014 Nature Education
- Press Room |
- Terms of Use |
- Privacy Notice |

Visual Browse

- Science Notes Posts
- Contact Science Notes
- Todd Helmenstine Biography
- Anne Helmenstine Biography
- Free Printable Periodic Tables (PDF and PNG)
- Periodic Table Wallpapers
- Interactive Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Posters
- Science Experiments for Kids
- How to Grow Crystals
- Chemistry Projects
- Fire and Flames Projects
- Holiday Science
- Chemistry Problems With Answers
- Physics Problems
- Unit Conversion Example Problems
- Chemistry Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Worksheets
- My Amazon Books
What Are the Products of Photosynthesis?

Photosynthesis is a set of chemical reactions that plants and other organisms use to make chemical energy in the form of sugar. Like any chemical reaction, photosynthesis has reactants and products . Overall, the reactants of photosynthesis are carbon dioxide and water, while the products of photosynthesis are oxygen and glucose (a sugar).
Here’s a closer look at the products of photosynthesis and the balanced equation for the reaction.
The reactants for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide and water, while the products are the sugar glucose and oxygen.
Balanced Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis actually involves many chemical reactions, but the net balanced equation is that six moles of carbon dioxide react with six moles of water to produce one mole of glucose and six moles of oxygen. Light from the Sun provides the activation energy for the reaction. Sometimes light is listed in the balanced equation as a reactant, but it’s usually omitted.
6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2
Carbon Dioxide + Water + Light → Glucose + Oxygen
Closer Look at the Products of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis occurs in a series of steps that are classified as light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions. Adding up the reactants and products of these reactions gives the overall equation for photosynthesis, but it’s good to know the inputs and outputs for each stage.
Light-Dependent Reactions

The light-dependent reactions or light reactions absorb certain wavelengths of light to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH). The light reactions occur in the chloroplast thylakoid membrane. The overall balanced equation for the light-dependent reactions is:
2 H 2 O + 2 NADP + + 3 ADP + 3 P i + light → 2 NADPH + 2 H + + 3 ATP + O 2
Light-Independent Reactions
While the light reactions use water, the light-independent reactions use carbon dioxide. The light-independent reactions are also called the dark reactions. These reactions do not require darkness, but they don’t depend on light to proceed. In plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, the dark reactions are called the Calvin cycle. Bacteria use different reactions, including the reverse Krebs cycle.
The overall balanced equation for the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle) in plants is:
3 CO 2 + 9 ATP + 6 NADPH + 6 H + → C 3 H 6 O 3 -phosphate + 9 ADP + 8 P i + 6 NADP + + 3 H 2 O
Finally, the three-carbon product from the Calvin cycle becomes glucose during the process of carbon fixation.
Other Products of Photosynthesis
Glucose is the direct product of photosynthesis, but plants turn most of the sugar into other compounds. These are indirect products. Linking glucose units forms starch and cellulose. Cellulose is a structural material. Plants store starch or link it to fructose (another sugar) to form sucrose (table sugar).
What Is Not a Product of Photosynthesis?
On an exam, you may need to identify which chemical is not a product of photosynthesis. For the overall process, choose any answer except “glucose” or “oxygen.” It’s good to know the overall reactants and products of the light reactions and dark reactions, in case you’re asked about them. The products of the light reactions are ATP , NADPH, protons, and oxygen. The products of the dark reactions are C 3 H 6 O 3 -phosphate, ADP, inorganic phosphate, NADP + , and water.
Where Does Photosynthesis Occur?
In addition to knowing the reactants and products of photosynthesis, you may need to know where photosynthesis occurs in different organisms.
- In plants, photosynthesis occurs in organelles called chloroplasts. Photosynthetic protists also contain chloroplasts. Leaves contain the highest concentration of chloroplasts in plants. Plants obtain carbon dioxide via diffusion through leaf stomata. Water comes from the roots and travels to the leaves via the xylem . Chlorophyll in chloroplasts absorbs solar energy. Oxygen from photosynthesis exits the plant via leaf stomata.
- Photosynthesis occurs in photosynthetic bacteria in the plasma membrane. Chlorophyll or related pigments are embedded in this membrane.
- Bidlack, J.E.; Stern, K.R.; Jansky, S. (2003). Introductory Plant Biology . New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-290941-8.
- Blankenship, R.E. (2014). Molecular Mechanisms of Photosynthesis (2nd ed.). John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-4051-8975-0.
- Reece J.B., et al. (2013). Campbell Biology . Benjamin Cummings. ISBN 978-0-321-77565-8.
Related Posts
What Are the Products of Photosynthesis?
Result of Photosynthesis in Plants
- Biochemistry
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Scientific Method
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
Photosynthesis is the name given to the set of chemical reactions performed by plants to convert energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of sugar. Specifically, plants use energy from sunlight to react carbon dioxide and water to produce sugar ( glucose ) and oxygen . Many reactions occur, but the overall chemical reaction for photosynthesis is:
- 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + light → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2
- Carbon Dioxide + Water + Light yields Glucose + Oxygen
In a plant, the carbon dioxide enters via leaf stomates by diffusion . Water is absorbed through the roots and is transported to leaves through the xylem. Solar energy is absorbed by chlorophyll in the leaves. The reactions of photosynthesis occur in the chloroplasts of plants. In photosynthetic bacteria, the process takes place where chlorophyll or a related pigment is embedded in the plasma membrane. The oxygen and water produced in photosynthesis exit through the stomata.
Key Takeaways
- In photosynthesis, energy from light is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
- For 6 carbon dioxide and 6 water molecules, 1 glucose molecule and 6 oxygen molecules are produced.
Actually, plants reserve very little of the glucose for immediate use. Glucose molecules are combined by dehydration synthesis to form cellulose, which is used as a structural material. Dehydration synthesis is also used to convert glucose to starch, which plants use to store energy.
Intermediate Products of Photosynthesis
The overall chemical equation is a summary of a series of chemical reactions. These reactions occur in two stages. The light reactions require light (as you might imagine), while the dark reactions are controlled by enzymes. They don't require darkness to occur -- they simply don't depend on light.
The light reactions absorb light and harness the energy to power electron transfers. Most photosynthetic organisms capture visible light, although there are some that use infrared light. Products of these reactions are adenosine triphosphate ( ATP ) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH). In plant cells, the light-dependent reactions occur in the chloroplast thylakoid membrane. The overall reaction for the light-dependent reactions is:
- 2 H 2 O + 2 NADP + + 3 ADP + 3 P i + light → 2 NADPH + 2 H + + 3 ATP + O 2
In the dark stage, ATP and NADPH ultimately reduce carbon dioxide and other molecules. Carbon dioxide from the air is "fixed" into a biologically usable form, glucose. In plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, the dark reactions are termed the Calvin cycle. Bacteria may use different reactions, including a reverse Krebs cycle . The overall reaction for the light-independent reaction of a plant (Calvin cycle) is:
- 3 CO 2 + 9 ATP + 6 NADPH + 6 H + → C 3 H 6 O 3 -phosphate + 9 ADP + 8 P i + 6 NADP + + 3 H 2 O
During carbon fixation, the three-carbon product of the Calvin cycle is converted into the final carbohydrate product.
Factors That Affect the Rate of Photosynthesis
Like any chemical reaction, the availability of the reactants determines the amount of products that can be made. Limiting the availability of carbon dioxide or water slows the production of glucose and oxygen. Also, the rate of the reactions is affected by temperature and the availability of minerals that may be needed in the intermediate reactions.
The overall health of the plant (or other photosynthetic organism) also plays a role. The rate of metabolic reactions is determined in part by the maturity of the organism and whether it's flowering or bearing fruit.
What Is Not a Product of Photosynthesis?
If you're asked about photosynthesis on a test, you may be asked to identify the products of the reaction. That's pretty easy, right? Another form of the question is to ask what is not a product of photosynthesis. Unfortunately, this won't be an open-ended question, which you could easily answer with "iron" or "a car" or "your mom." Usually this is a multiple choice question, listing molecules which are reactants or products of photosynthesis. The answer is any choice except glucose or oxygen. The question may also be phrased to answer what is not a product of the light reactions or the dark reactions. So, it's a good idea to know the overall reactants and products for the photosynthesis general equation, the light reactions, and the dark reactions.
- Bidlack, J.E.; Stern, K.R.; Jansky, S. (2003). Introductory Plant Biology . New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-290941-8.
- Blankenship, R.E. (2014). Molecular Mechanisms of Photosynthesis (2nd ed.). John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-4051-8975-0.
- Reece J.B., et al. (2013). Campbell Biology . Benjamin Cummings. ISBN 978-0-321-77565-8.
- Examples of Chemical Reactions in Everyday Life
- Photosynthesis Basics - Study Guide
- Photosynthesis Vocabulary Terms and Definitions
- The Photosynthesis Formula: Turning Sunlight into Energy
- Calvin Cycle Steps and Diagram
- 10 Fascinating Photosynthesis Facts
- Chloroplast Function in Photosynthesis
- Chlorophyll Definition and Role in Photosynthesis
- What Is the Primary Function of the Calvin Cycle?
- The Balanced Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis
- All About Photosynthetic Organisms
- Thylakoid Definition and Function
- Simple Chemical Reactions
- Chemosynthesis Definition and Examples
- An Introduction to Types of Respiration
- Understanding Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
ENCYCLOPEDIC ENTRY
Photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and energy in the form of sugar.

Loading ...
Learning materials, instructional links.
- Photosynthesis (Google doc)
Most life on Earth depends on photosynthesis .The process is carried out by plants, algae, and some types of bacteria, which capture energy from sunlight to produce oxygen (O 2 ) and chemical energy stored in glucose (a sugar). Herbivores then obtain this energy by eating plants, and carnivores obtain it by eating herbivores.
The process
During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and water (H 2 O) from the air and soil. Within the plant cell, the water is oxidized, meaning it loses electrons, while the carbon dioxide is reduced, meaning it gains electrons. This transforms the water into oxygen and the carbon dioxide into glucose. The plant then releases the oxygen back into the air, and stores energy within the glucose molecules.
Chlorophyll
Inside the plant cell are small organelles called chloroplasts , which store the energy of sunlight. Within the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast is a light-absorbing pigment called chlorophyll , which is responsible for giving the plant its green color. During photosynthesis , chlorophyll absorbs energy from blue- and red-light waves, and reflects green-light waves, making the plant appear green.
Light-dependent Reactions vs. Light-independent Reactions
While there are many steps behind the process of photosynthesis, it can be broken down into two major stages: light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions. The light-dependent reaction takes place within the thylakoid membrane and requires a steady stream of sunlight, hence the name light- dependent reaction. The chlorophyll absorbs energy from the light waves, which is converted into chemical energy in the form of the molecules ATP and NADPH . The light-independent stage, also known as the Calvin cycle , takes place in the stroma , the space between the thylakoid membranes and the chloroplast membranes, and does not require light, hence the name light- independent reaction. During this stage, energy from the ATP and NADPH molecules is used to assemble carbohydrate molecules, like glucose, from carbon dioxide.
C3 and C4 Photosynthesis
Not all forms of photosynthesis are created equal, however. There are different types of photosynthesis, including C3 photosynthesis and C4 photosynthesis. C3 photosynthesis is used by the majority of plants. It involves producing a three-carbon compound called 3-phosphoglyceric acid during the Calvin Cycle, which goes on to become glucose. C4 photosynthesis, on the other hand, produces a four-carbon intermediate compound, which splits into carbon dioxide and a three-carbon compound during the Calvin Cycle. A benefit of C4 photosynthesis is that by producing higher levels of carbon, it allows plants to thrive in environments without much light or water. The National Geographic Society is making this content available under a Creative Commons CC-BY-NC-SA license . The License excludes the National Geographic Logo (meaning the words National Geographic + the Yellow Border Logo) and any images that are included as part of each content piece. For clarity the Logo and images may not be removed, altered, or changed in any way.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
March 20, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
Sciencing_Icons_Science SCIENCE
Sciencing_icons_biology biology, sciencing_icons_cells cells, sciencing_icons_molecular molecular, sciencing_icons_microorganisms microorganisms, sciencing_icons_genetics genetics, sciencing_icons_human body human body, sciencing_icons_ecology ecology, sciencing_icons_chemistry chemistry, sciencing_icons_atomic & molecular structure atomic & molecular structure, sciencing_icons_bonds bonds, sciencing_icons_reactions reactions, sciencing_icons_stoichiometry stoichiometry, sciencing_icons_solutions solutions, sciencing_icons_acids & bases acids & bases, sciencing_icons_thermodynamics thermodynamics, sciencing_icons_organic chemistry organic chemistry, sciencing_icons_physics physics, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-physics fundamentals, sciencing_icons_electronics electronics, sciencing_icons_waves waves, sciencing_icons_energy energy, sciencing_icons_fluid fluid, sciencing_icons_astronomy astronomy, sciencing_icons_geology geology, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-geology fundamentals, sciencing_icons_minerals & rocks minerals & rocks, sciencing_icons_earth scructure earth structure, sciencing_icons_fossils fossils, sciencing_icons_natural disasters natural disasters, sciencing_icons_nature nature, sciencing_icons_ecosystems ecosystems, sciencing_icons_environment environment, sciencing_icons_insects insects, sciencing_icons_plants & mushrooms plants & mushrooms, sciencing_icons_animals animals, sciencing_icons_math math, sciencing_icons_arithmetic arithmetic, sciencing_icons_addition & subtraction addition & subtraction, sciencing_icons_multiplication & division multiplication & division, sciencing_icons_decimals decimals, sciencing_icons_fractions fractions, sciencing_icons_conversions conversions, sciencing_icons_algebra algebra, sciencing_icons_working with units working with units, sciencing_icons_equations & expressions equations & expressions, sciencing_icons_ratios & proportions ratios & proportions, sciencing_icons_inequalities inequalities, sciencing_icons_exponents & logarithms exponents & logarithms, sciencing_icons_factorization factorization, sciencing_icons_functions functions, sciencing_icons_linear equations linear equations, sciencing_icons_graphs graphs, sciencing_icons_quadratics quadratics, sciencing_icons_polynomials polynomials, sciencing_icons_geometry geometry, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-geometry fundamentals, sciencing_icons_cartesian cartesian, sciencing_icons_circles circles, sciencing_icons_solids solids, sciencing_icons_trigonometry trigonometry, sciencing_icons_probability-statistics probability & statistics, sciencing_icons_mean-median-mode mean/median/mode, sciencing_icons_independent-dependent variables independent/dependent variables, sciencing_icons_deviation deviation, sciencing_icons_correlation correlation, sciencing_icons_sampling sampling, sciencing_icons_distributions distributions, sciencing_icons_probability probability, sciencing_icons_calculus calculus, sciencing_icons_differentiation-integration differentiation/integration, sciencing_icons_application application, sciencing_icons_projects projects, sciencing_icons_news news.
- Share Tweet Email Print
- Home ⋅
- Science ⋅
- Nature ⋅
- Plants & Mushrooms
What Is Produced As a Result of Photosynthesis?

10 Facts on Photosynthesis
All living things consume energy in order to survive. Animals get their energy from the food they eat, but plants must absorb energy in a different way. Though plants use their roots to pull water and some nutrients from soil, the majority of plants' energy comes from the sun. Plants are able to convert sunlight into usable energy, in the form of glucose, due to the structure of their cells and a process called photosynthesis.
TL;DR (Too Long; Didn't Read)
Plants get most of the energy they need to survive via a two-stage process called photosynthesis. In the first stage, called the light-dependent reaction, sunlight is converted into two molecules. In the second stage, called the light-independent reaction, these molecules work together to form and synthesize glucose. Glucose is a sugar that plants use for energy.
How Photosynthesis Works
The cells of plants and animals differ slightly, in structure. For example, certain plant cells contain organelles called plastids, which help the cells store energy. Chloroplasts are plastids that contain the green pigment chlorophyll. This pigment is responsible for absorbing sunlight during the process of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is a two-stage process. The first stage of photosynthesis is called the light-dependent reaction because sunlight must be present in order for the reaction to occur. During this stage, chloroplasts absorb and trap sunlight, converting it into chemical energy. Specifically, the light is converted into two molecules to be used during the second stage of photosynthesis. These two molecules are nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
The second stage of photosynthesis is called the light-independent reaction because sunlight is not necessary for it to occur. In this stage, the two molecules formed during the light-dependent reaction work together to produce glucose. Hydrogen atoms from NADPH help to form the glucose, while ATP provides the energy necessary to synthesize it.
The Importance of Glucose
Glucose is a sugar that many plants, animals and fungi use for energy. In plants, glucose is produced as a result of photosynthesis. Plants need the energy glucose provides in order to grow and reproduce. Glucose is also required for the process of cellular respiration, in which plants convert carbon dioxide from the air into oxygen.
Because plants rely on sunlight to make glucose, inadequate sunlight can be a problem for plants that live in shady or cloudy areas. To deal with this problem, most plants store glucose inside their bodies to use when sunlight is scarce. Plants usually store glucose as starch. Starch granules can be found inside plant cells, in organelles called amyloplasts.
Without glucose, plants would not have the energy necessary to grow, reproduce or carry out cellular respiration. This means that without glucose, plant life could not exist on Earth.
Related Articles
How do plant cells obtain energy, how does a plant convert light energy to chemical energy, organelles involved in photosynthesis, what is glucose used for in a plant, what is the sun's role in photosynthesis, what is the role of pigments in photosynthesis, what is reduced & oxidized in photosynthesis, what is the relationship between co2 & oxygen in photosynthesis, how do plants store energy during photosynthesis, what happens in the light reaction of photosynthesis, two stages of photosynthesis, describe what a photosystem does for photosynthesis, how are photosynthesis & cellular respiration related, what part of plant can store extra food as sugar or..., importance of aerobic cellular respiration, what is the role of carotenoids in photosynthesis, how to compare the cells of plants, animals & unicellular..., where is starch stored in plant cells, what happens during stage one of photosynthesis.
- University of Illinois: Photosynthesis
- UCSB ScienceLine: How Are Respiration and Photosynthesis Related?
About the Author
Maria Cook is a freelance and fiction writer from Indianapolis, Indiana. She holds an MFA in Creative Writing from Butler University in Indianapolis. She has written about science as it relates to eco-friendly practices, conservation and the environment for Green Matters.
Find Your Next Great Science Fair Project! GO
- Bihar Board
James Dyson Award
Sanskriti university, srm university.
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- School Life
Photosynthesis: Definition, Reaction, Diagram and Process
Process of photosynthesis: understanding photosynthesis is simple yet complex when we dive deeper into the process. here, the basic to moderate information on photosynthesis is provided along with the definition, reaction, diagram and process..

Photosynthesis Simple Definition
Photosynthesis is the food-synthesising process in green plants . Some species of algae and certain bacteria also perform this process to make their food.
Raw Materials for Photosynthesis
The process of photosynthesis requires three main raw materials to synthesise energy in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate). Those three raw materials are; Carbon dioxide, Water, and Light.
Photosynthesis Reaction
The overall chemical reaction for photosynthesis can be simplified as:
6CO 2 +6H 2 O+light energy→C 6 H 12 O 6 +6O 2
Here, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and water (H 2 O) are converted into glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ) and oxygen (O 2 ) in the presence of light energy, usually from the sun.
Light Reaction of Photosynthesis
This is the first phase of photosynthesis that occurs in the presence of light and is thus called a light-dependent reaction. This reaction occurs in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts .
- Absorption of Light: Chlorophyll and other pigments absorb light energy.
- Water Splitting: Light energy is used to split water molecules into oxygen, protons, and electrons.
- Production of ATP and NADPH: The electrons travel through the electron transport chain, creating a proton gradient that helps produce ATP. Electrons are then used to reduce NADP+ to NADPH.
- End Result: Oxygen (released into the atmosphere), ATP, and NADPH (used in the Calvin cycle).
Dark Reaction of Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)
As the name suggests, this reaction can occur in the absence of light and is thus also named a light-independent reaction of photosynthesis. This reaction occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts . American biochemist Melvin Ellis Calvin discovered the dark reaction and thus, it is also called the Calvin Cycle or C3 cycle.
- Carbon Fixation: Carbon dioxide is attached to a five-carbon sugar, ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP), by the enzyme Rubisco, forming a six-carbon compound that immediately splits into two three-carbon molecules, 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA).
- Reduction Phase: ATP and NADPH are used to convert 3-PGA into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P), a three-carbon sugar.
- Regeneration of RuBP: Some G3P molecules are used to regenerate RuBP, enabling the cycle to continue.
- Synthesis of Glucose: The remaining G3P molecules are used to form glucose and other carbohydrates.
- Outputs: Glucose (which can be converted into other carbohydrates like starch and cellulose).
Location of Photosynthesis
- Chloroplasts are the main sites of photosynthesis in plant cells. These organelles contain pigments like chlorophyll that capture light energy and convert it into chemical energy.
- Within the chloroplasts, there are disc-like structures called thylakoids . Thylakoids are stacked in some regions to form structures called grana (singular: granum). The thylakoid membranes are the sites of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. These membranes contain chlorophyll and other pigments, as well as the proteins and enzymes necessary for the light reactions.
- The stroma is the fluid-filled space that surrounds the thylakoids inside the chloroplast. It is the site of the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle) of photosynthesis. The stroma contains enzymes that facilitate the conversion of carbon dioxide and other compounds into glucose.
Process of Photosynthesis
The process of photosynthesis follows certain steps to achieve its end products. Those steps are mentioned below:
>Light-Dependent Phase of Photosynthesis:
- Entry of gases like carbon dioxide into the leaf through stomata.
- Water gets absorbed through roots and reaches leaves through xylem tissue.
- Absorption of light energy that excites electrons, raising them to a higher energy level.
- The excited electrons from chlorophyll are passed through a series of proteins embedded in the thylakoid membrane, known as the electron transport chain.
- As electrons move through the ETC, their energy is used to pump protons into the thylakoid lumen, creating a proton gradient.
- The proton gradient created by the ETC drives the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) through a process called chemiosmosis, facilitated by the enzyme ATP synthase.
- At the end of the ETC, the electrons are transferred to NADP + along with a proton (H + ) to form NADPH.
- NADPH is an electron carrier that will be used in the Calvin cycle.
>Light-Independent Phase of Photosynthesis
- Carbon dioxide is attached to a five-carbon sugar called ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) by the enzyme Rubisco.
- This forms a six-carbon compound that immediately splits into two three-carbon molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA).
- ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions are used to convert 3-PGA into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P), a three-carbon sugar.
- ATP provides energy, while NADPH provides electrons for the reduction.
- Some molecules of G3P are used to regenerate RuBP, the five-carbon molecule needed to accept new carbon dioxide molecules.
- This step requires ATP and allows the cycle to continue.
- The remaining G3P molecules can be used to form glucose and other carbohydrates, which serve as energy sources for the plant and other organisms that consume it.
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
- Light Intensity: The rate of photosynthesis generally increases with increasing light intensity up to a certain point.
- Carbon Dioxide Concentration: An increase in carbon dioxide concentration typically enhances the rate of photosynthesis.
- Temperature: Photosynthesis requires an optimum temperature to occur. Its rates decrease at extreme hot or cold temperatures.
- Chlorophyll Content: Higher chlorophyll content increases the efficiency of light absorption.
- Light Quality: Red and blue light are most effective for photosynthesis.
- Nutrient Availability: Essential nutrients like nitrogen, magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus are crucial for the synthesis of chlorophyll, ATP, and other molecules involved in photosynthesis.
This is a complete guide on photosynthesis. For more such information on various other topics check the official page of Jagran Josh.
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus 2024-25
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2024-25
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus 2024-25
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2024-25
- Periodic Table of Elements
- Atomic Mass And Molecular Mass of Elements
- Atomic Number and Mass Number
- Benzene: Chemical Formula and Molecular Structure
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- Define Photosynthesis + Photosynthesis is the food-synthesising process in green plants.
- What are the raw materials of photosynthesis? + The process of photosynthesis requires three main raw materials to synthesise energy in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate). Those three raw materials are; Carbon Dioxide, Water, and Light.
- UGC NET Exam 2024 Cancelled
- UPSC Question Paper 2024
- UPSC Exam Analysis 2024
- UPSC Prelims Cut Off 2024
- Bihar BEd Admit Card 2024
- IAS Exam Last Minute Tips 2024
- NTA NET Admit Card 2024
- APSC SO Result 2024
- APSC SO Admit Card 2024
- UPSC CSE Admit Card 2024
Latest Education News
SIPRI Report 2024: भारत और पाक सहित जानें किस देश के पास कितने परमाणु हथियार?
What is NTA: Know Which Exams Does it Conduct, Why is it in News?
UGC NET Paper 1 Syllabus 2024: Check Topics, Pattern, PDF Download
You have 20/20 vision if you can find the snake in the grass in 6 seconds!
PSPCL Admit Card 2024 OUT at pspcl.in: Check Download Link Here
TNSTC Recruitment 2024: Apply Online for 688 Apprenticeship Vacancies
Only the most intelligent minds can spot the second man in the bar in 8 seconds!
TNPSC Group 2 Syllabus 2024: PDF Download for Important Topics, Check Exam Pattern
UGC NET 2024 Exam Cancelled: Decision Taken to Safeguard Students' Interest, Says Education Minister
Quiz on International Yoga Day 2024: Test Your Knowledge
Optical Illusion IQ Test: Spot The Cat To Prove You Are Among 1% With Sharpest Vision In 8 Seconds!
RBSE Class 10 Concept Of Information Technology II Syllabus 2024-25: Download Free PDF!
PRSU Result 2024 OUT at prsu.ac.in; Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet
UGC NET Previous Year Question Paper, Download PDF with Answer Key
SHS Bihar CHO Recruitment 2024; Notification OUT for 4500 Community Health Officer Posts, Check Eligibility
Madras High Court Recruitment 2024 Registration Reopens for 2329 Vacancies at mhc.tn.gov.in, Apply Online Here
KEAM Cut Off 2024: Kerala CEE Previous Year B.Tech Course-wise Closing Ranks at Kerala Government Engineering Colleges
Patna High Court Revokes Bihar Reservation Policy Increasing Reservation For ST, ST Backward Classes to 65%
CUET Answer Key 2024: Check NTA CUET UG Response Sheet and Answer Key Expected Release Date, Time at exams.nta.ac.in, Official Updates Here
SSC Selection Post Memory Based Questions: List of Questions Asked in SSC Phase 12 Exam

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2.5.3: The Light-Dependent Reactions of Photosynthesis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 97023

\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
- Explain how plants absorb energy from sunlight
- Describe short and long wavelengths of light
- Describe how and where photosynthesis takes place within a plant
How can light energy be used to make food? When a person turns on a lamp, electrical energy becomes light energy. Like all other forms of kinetic energy, light can travel, change form, and be harnessed to do work. In the case of photosynthesis, light energy is converted into chemical energy, which photoautotrophs use to build basic carbohydrate molecules (Figure 8.9). However, autotrophs only use a few specific wavelengths of sunlight.
What Is Light Energy?
The sun emits an enormous amount of electromagnetic radiation (solar energy in a spectrum from very short gamma rays to very long radio waves). Humans can see only a tiny fraction of this energy, which we refer to as “visible light.” The manner in which solar energy travels is described as waves. Scientists can determine the amount of energy of a wave by measuring its wavelength (shorter wavelengths are more powerful than longer wavelengths)—the distance between consecutive crest points of a wave. Therefore, a single wave is measured from two consecutive points, such as from crest to crest or from trough to trough (Figure 8.10).
Visible light constitutes only one of many types of electromagnetic radiation emitted from the sun and other stars. Scientists differentiate the various types of radiant energy from the sun within the electromagnetic spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of radiation (Figure 8.11). The difference between wavelengths relates to the amount of energy carried by them.
Each type of electromagnetic radiation travels at a particular wavelength. The longer the wavelength, the less energy it carries. Short, tight waves carry the most energy. This may seem illogical, but think of it in terms of a piece of moving heavy rope. It takes little effort by a person to move a rope in long, wide waves. To make a rope move in short, tight waves, a person would need to apply significantly more energy.
The electromagnetic spectrum (Figure 8.11) shows several types of electromagnetic radiation originating from the sun, including X-rays and ultraviolet (UV) rays. The higher-energy waves can penetrate tissues and damage cells and DNA, which explains why both X-rays and UV rays can be harmful to living organisms.
Absorption of Light
Light energy initiates the process of photosynthesis when pigments absorb specific wavelengths of visible light. Organic pigments, whether in the human retina or the chloroplast thylakoid, have a narrow range of energy levels that they can absorb. Energy levels lower than those represented by red light are insufficient to raise an orbital electron to an excited (quantum) state. Energy levels higher than those in blue light will physically tear the molecules apart, in a process called bleaching. Our retinal pigments can only “see” (absorb) wavelengths between 700 nm and 400 nm of light, a spectrum that is therefore called visible light. For the same reasons, plants, pigment molecules absorb only light in the wavelength range of 700 nm to 400 nm; plant physiologists refer to this range for plants as photosynthetically active radiation.
The visible light seen by humans as white light actually exists in a rainbow of colors. Certain objects, such as a prism or a drop of water, disperse white light to reveal the colors to the human eye. The visible light portion of the electromagnetic spectrum shows the rainbow of colors, with violet and blue having shorter wavelengths, and therefore higher energy. At the other end of the spectrum toward red, the wavelengths are longer and have lower energy (Figure 8.13).
Understanding Pigments
Different kinds of pigments exist, and each absorbs only specific wavelengths (colors) of visible light. Pigments reflect or transmit the wavelengths they cannot absorb, making them appear a mixture of the reflected or transmitted light colors.
Chlorophylls and carotenoids are the two major classes of photosynthetic pigments found in plants and algae; each class has multiple types of pigment molecules. There are five major chlorophylls: a , b , c and d and a related molecule found in prokaryotes called bacteriochlorophyll . Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b are found in higher plant chloroplasts and will be the focus of the following discussion.
With dozens of different forms, carotenoids are a much larger group of pigments. The carotenoids found in fruit—such as the red of tomato (lycopene), the yellow of corn seeds (zeaxanthin), or the orange of an orange peel (β-carotene)—are used as advertisements to attract seed dispersers. In photosynthesis, carotenoids function as photosynthetic pigments that are very efficient molecules for the disposal of excess energy. When a leaf is exposed to full sun, the light-dependent reactions are required to process an enormous amount of energy; if that energy is not handled properly, it can do significant damage. Therefore, many carotenoids reside in the thylakoid membrane, absorb excess energy, and safely dissipate that energy as heat.
Each type of pigment can be identified by the specific pattern of wavelengths it absorbs from visible light: This is termed the absorption spectrum . The graph in Figure 8.14 shows the absorption spectra for chlorophyll a , chlorophyll b , and a type of carotenoid pigment called β-carotene (which absorbs blue and green light). Notice how each pigment has a distinct set of peaks and troughs, revealing a highly specific pattern of absorption. Chlorophyll a absorbs wavelengths from either end of the visible spectrum (blue and red), but not green. Because green is reflected or transmitted, chlorophyll appears green. Carotenoids absorb in the short-wavelength blue region, and reflect the longer yellow, red, and orange wavelengths.
Many photosynthetic organisms have a mixture of pigments, and by using these pigments, the organism can absorb energy from a wider range of wavelengths. Not all photosynthetic organisms have full access to sunlight. Some organisms grow underwater where light intensity and quality decrease and change with depth. Other organisms grow in competition for light. Plants on the rainforest floor must be able to absorb any bit of light that comes through, because the taller trees absorb most of the sunlight and scatter the remaining solar radiation (Figure 8.15).
When studying a photosynthetic organism, scientists can determine the types of pigments present by generating absorption spectra. An instrument called a spectrophotometer can differentiate which wavelengths of light a substance can absorb. Spectrophotometers measure transmitted light and compute from it the absorption. By extracting pigments from leaves and placing these samples into a spectrophotometer, scientists can identify which wavelengths of light an organism can absorb. Additional methods for the identification of plant pigments include various types of chromatography that separate the pigments by their relative affinities to solid and mobile phases.
How Light-Dependent Reactions Work
The overall function of light-dependent reactions is to convert solar energy into chemical energy in the form of NADPH and ATP. This chemical energy supports the light-independent reactions and fuels the assembly of sugar molecules. The light-dependent reactions are depicted in Figure 8.16. Protein complexes and pigment molecules work together to produce NADPH and ATP. The numbering of the photosystems is derived from the order in which they were discovered, not in the order of the transfer of electrons.
The actual step that converts light energy into chemical energy takes place in a multiprotein complex called a photosystem , two types of which are found embedded in the thylakoid membrane: photosystem II (PSII) and photosystem I (PSI) (Figure 8.17). The two complexes differ on the basis of what they oxidize (that is, the source of the low-energy electron supply) and what they reduce (the place to which they deliver their energized electrons).
Both photosystems have the same basic structure; a number of antenna proteins to which the chlorophyll molecules are bound surround the reaction center where the photochemistry takes place. Each photosystem is serviced by the light-harvesting complex , which passes energy from sunlight to the reaction center; it consists of multiple antenna proteins that contain a mixture of 300 to 400 chlorophyll a and b molecules as well as other pigments like carotenoids. The absorption of a single photon or distinct quantity or “packet” of light by any of the chlorophylls pushes that molecule into an excited state. In short, the light energy has now been captured by biological molecules but is not stored in any useful form yet. The energy is transferred from chlorophyll to chlorophyll until eventually (after about a millionth of a second), it is delivered to the reaction center. Up to this point, only energy has been transferred between molecules, not electrons.
Visual Connection
What is the initial source of electrons for the chloroplast electron transport chain?
- carbon dioxide
The reaction center contains a pair of chlorophyll a molecules with a special property. Those two chlorophylls can undergo oxidation upon excitation; they can actually give up an electron in a process called a photoact . It is at this step in the reaction center during photosynthesis that light energy is converted into an excited electron. All of the subsequent steps involve getting that electron onto the energy carrier NADPH for delivery to the Calvin cycle where the electron is deposited onto carbon for long-term storage in the form of a carbohydrate. PSII and PSI are two major components of the photosynthetic electron transport chain , which also includes the cytochrome complex . The cytochrome complex, an enzyme composed of two protein complexes, transfers the electrons from the carrier molecule plastoquinone (Pq) to the protein plastocyanin (Pc), thus enabling both the transfer of protons across the thylakoid membrane and the transfer of electrons from PSII to PSI.
The reaction center of PSII (called P680 ) delivers its high-energy electrons, one at the time, to the primary electron acceptor , and through the electron transport chain (Pq to cytochrome complex to plastocyanine) to PSI. P680’s missing electron is replaced by extracting a low-energy electron from water; thus, water is “split” during this stage of photosynthesis, and PSII is re-reduced after every photoact. Splitting one H 2 O molecule releases two electrons, two hydrogen atoms, and one atom of oxygen. However, splitting two molecules is required to form one molecule of diatomic O 2 gas. About 10 percent of the oxygen is used by mitochondria in the leaf to support oxidative phosphorylation. The remainder escapes to the atmosphere where it is used by aerobic organisms to support respiration.
As electrons move through the proteins that reside between PSII and PSI, they lose energy. This energy is used to move hydrogen atoms from the stromal side of the membrane to the thylakoid lumen. Those hydrogen atoms, plus the ones produced by splitting water, accumulate in the thylakoid lumen and will be used synthesize ATP in a later step. Because the electrons have lost energy prior to their arrival at PSI, they must be re-energized by PSI, hence, another photon is absorbed by the PSI antenna. That energy is relayed to the PSI reaction center (called P700 ). P700 is oxidized and sends a high-energy electron to NADP + to form NADPH. Thus, PSII captures the energy to create proton gradients to make ATP, and PSI captures the energy to reduce NADP + into NADPH. The two photosystems work in concert, in part, to guarantee that the production of NADPH will roughly equal the production of ATP. Other mechanisms exist to fine-tune that ratio to exactly match the chloroplast’s constantly changing energy needs.
Generating an Energy Carrier: ATP
As in the intermembrane space of the mitochondria during cellular respiration, the buildup of hydrogen ions inside the thylakoid lumen creates a concentration gradient . The passive diffusion of hydrogen ions from high concentration (in the thylakoid lumen) to low concentration (in the stroma) is harnessed to create ATP, just as in the electron transport chain of cellular respiration. The ions build up energy because of diffusion and because they all have the same electrical charge, repelling each other.
To release this energy, hydrogen ions will rush through any opening, similar to water jetting through a hole in a dam. In the thylakoid, that opening is a passage through a specialized protein channel called the ATP synthase. The energy released by the hydrogen ion stream allows ATP synthase to attach a third phosphate group to ADP, which forms a molecule of ATP (Figure 8.17). The flow of hydrogen ions through ATP synthase is called chemiosmosis because the ions move from an area of high to an area of low concentration through a semi-permeable structure of the thylakoid.
Link to Learning
Visit this site and click through the animation to view the process of photosynthesis within a leaf.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
AP®︎/College Biology
Course: ap®︎/college biology > unit 3.
- Photosynthesis
- Intro to photosynthesis
- Breaking down photosynthesis stages
- Conceptual overview of light dependent reactions
The light-dependent reactions
- The Calvin cycle
- Photosynthesis evolution
- Photosynthesis review
Introduction
- Plants carry out a form of photosynthesis called oxygenic photosynthesis . In oxygenic photosynthesis, water molecules are split to provide a source of electrons for the electron transport chain, and oxygen gas is released as a byproduct. Plants organize their photosynthetic pigments into two separate complexes called photosystems (photosystems I and II), and they use chlorophylls as their reaction center pigments.
- Purple sulfur bacteria, in contrast, carry out anoxygenic photosynthesis , meaning that water is not used as an electron source and oxygen gas is not produced. Instead, these bacteria use hydrogen sulfide ( H 2 S ) as an electron source and produce elemental sulfur as a byproduct. In addition, purple sulfur bacteria have only one photosystem, and they use chlorophyll-like molecules called bacteriochlorophylls as reaction center pigments 1 , 2 , 3 .
Overview of the light-dependent reactions
- Light absorption in PSII. When light is absorbed by one of the many pigments in photosystem II, energy is passed inward from pigment to pigment until it reaches the reaction center. There, energy is transferred to P680, boosting an electron to a high energy level. The high-energy electron is passed to an acceptor molecule and replaced with an electron from water. This splitting of water releases the O 2 we breathe.
- ATP synthesis. The high-energy electron travels down an electron transport chain, losing energy as it goes. Some of the released energy drives pumping of H + ions from the stroma into the thylakoid interior, building a gradient. ( H + ions from the splitting of water also add to the gradient.) As H + ions flow down their gradient and into the stroma, they pass through ATP synthase, driving ATP production in a process known as chemiosmosis .
- Light absorption in PSI. The electron arrives at photosystem I and joins the P700 special pair of chlorophylls in the reaction center. When light energy is absorbed by pigments and passed inward to the reaction center, the electron in P700 is boosted to a very high energy level and transferred to an acceptor molecule. The special pair's missing electron is replaced by a new electron from PSII (arriving via the electron transport chain).
- NADPH formation. The high-energy electron travels down a short second leg of the electron transport chain. At the end of the chain, the electron is passed to NADP + (along with a second electron from the same pathway) to make NADPH.
What is a photosystem?
Photosystem i vs. photosystem ii.
- Special pairs. The chlorophyll a special pairs of the two photosystems absorb different wavelengths of light. The PSII special pair absorbs best at 680 nm, while the PSI special absorbs best at 700 nm. Because of this, the special pairs are called P680 and P700 , respectively.
- Primary acceptor . The special pair of each photosystem passes electrons to a different primary acceptor. The primary electron acceptor of PSII is pheophytin, an organic molecule that resembles chlorophyll, while the primary electron acceptor of PSI is a chlorophyll called A 0 7 , 8 .
- Source of electrons . Once an electron is lost, each photosystem is replenished by electrons from a different source. The PSII reaction center gets electrons from water, while the PSI reaction center is replenished by electrons that flow down an electron transport chain from PSII.
Photosystem II
Electron transport chains and photosystem i, some electrons flow cyclically, attribution:, works cited:.
- Lodish, H., Berk, A., Zipursky, S. L., Matsudaira, P., Baltimore, D., and Darnell, J. (2000). Molecular analysis of photosystems. In Molecular cell biology (4th ed., section 16.4). New York, NY: W. H. Freeman. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21484/ .
- Boundless. (2015, July 21). Anoxygenic photosynthetic bacteria. In Boundless microbiology . Retrieved from https://www.boundless.com/microbiology/textbooks/boundless-microbiology-textbook/microbial-evolution-phylogeny-and-diversity-8/nonproteobacteria-gram-negative-bacteria-105/anoxygenic-photosynthetic-bacteria-551-7338/ .
- Purple sulfur bacteria. (2015, July 16). Retrieved October 24, 2015 from Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Purple_sulfur_bacteria .
- Soda lake. (2015, September 26). Retrieved October 24, 2015 from Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Soda_lake .
- Gutierrez, R. Bio41 Week 7 Biochemistry Lectures 11 and 12. Bio41. 2009.
- Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., and Stryer, L. (2002). Accessory pigments funnel energy into reaction centers. In Biochemistry (5th ed., section 19.5). New York, NY: W. H. Freeman. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK22604/ .
- Pheophytin. (2015, February 11). Retrieved October 28, 2015 from Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pheophytin .
- Photosystem I. (2016, June 25). Retrieved from Wikipedia on July 22, 2016: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Photosystem_I .
- Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., and Stryer, L. (2002). Two photosystems generate a proton gradient and NADPH in oxygenic photosynthesis. In Biochemistry (5th ed., section 19.3). New York, NY: W. H. Freeman. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK22538/#_A2681_ .
- Joliot, P. and Johnson, G. N. (2011). Regulation of cyclic and linear electron flow in higher plants. PNAS, 108(32), 13317-13322. http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1110189108 .
- Johnson, Giles N. (2011). Physiology of PSI cyclic electron transport in higher plants. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - Bioenergetics , 1807 (8), 906-911. http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2010.11.009 .
- Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., and Stryer, L. (2002). A proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane drives ATP synthesis. In Biochemistry (5th ed., section 19.4). New York, NY: W. H. Freeman. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK22519/ .
- Takahashi, S., Milward, S. E., Fan, D.-Y., Chow, W. S., and Badger, M. R. (2008). How does cyclic electron flow alleviate photoinhibition in Arabidopsis? Plant Physiology , 149 (3), 1560-1567. http://dx.doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.134122 .
Additional references:
Want to join the conversation.
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Photosynthesis is a process by which plants produce glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water using light energy. Learn the formula, the light-dependent and light-independent stages, and the role of chlorophyll and the Calvin cycle.
In chemical terms, photosynthesis is a light-energized oxidation-reduction process. (Oxidation refers to the removal of electrons from a molecule; reduction refers to the gain of electrons by a molecule.) In plant photosynthesis, the energy of light is used to drive the oxidation of water (H 2 O), producing oxygen gas (O 2 ), hydrogen ions (H ...
Photosynthesis is the process in which light energy is converted to chemical energy in the form of sugars. In a process driven by light energy, glucose molecules (or other sugars) are constructed from water and carbon dioxide, and oxygen is released as a byproduct. The glucose molecules provide organisms with two crucial resources: energy and ...
Photosynthesis Equation. 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + Light -> C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 + 6 H 2 O. Above is the overall reaction for photosynthesis. Using the energy from light and the hydrogens and electrons from water, the plant combines the carbons found in carbon dioxide into more complex molecules. While a 3-carbon molecule is the direct result of ...
Photosynthesis is powered by energy from sunlight. This energy is used to rearrange atoms in carbon dioxide and water to make oxygen and sugars. Carbon dioxide and water are inputs of photosynthesis. These inputs come from the environment. Oxygen and sugars are outputs of photosynthesis. The oxygen is released into the environment.
Figure 8.1.6 8.1. 6: Photosynthesis takes place in two stages: light dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle. Light-dependent reactions, which take place in the thylakoid membrane, use light energy to make ATP and NADPH. The Calvin cycle, which takes place in the stroma, uses energy derived from these compounds to make GA3P from CO 2.
By the end of this section, you will be able to: ... Photosynthesis also results in the release of oxygen into the atmosphere. In short, to eat and breathe, humans depend almost entirely on the organisms that carry out photosynthesis. ... Photosynthesis takes place in two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle. ...
Photosynthesis is a vital process that converts light energy into chemical energy and produces organic molecules and oxygen for living things. In this article, you will learn how photosynthesis works in different ecosystems, how it affects the carbon cycle, and how it interacts with other biogeochemical cycles. Khan Academy is a free online platform that offers high-quality education for ...
The chloroplast is involved in both stages of photosynthesis. The light reactions take place in the thylakoid. There, water (H 2 O) is oxidized, and oxygen (O 2) is released. The electrons that ...
Photosynthesis is a set of chemical reactions that plants and other organisms use to make chemical energy in the form of sugar. Like any chemical reaction, photosynthesis has reactants and products. Overall, the reactants of photosynthesis are carbon dioxide and water, while the products of photosynthesis are oxygen and glucose (a sugar).
Photosynthesis is the name given to the set of chemical reactions performed by plants to convert energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of sugar. Specifically, plants use energy from sunlight to react carbon dioxide and water to produce sugar ( glucose) and oxygen. Many reactions occur, but the overall chemical reaction for ...
5.1: Overview of Photosynthesis. All living organisms on earth consist of one or more cells. Each cell runs on the chemical energy found mainly in carbohydrate molecules (food), and the majority of these molecules are produced by one process: photosynthesis. Through photosynthesis, certain organisms convert solar energy (sunlight) into chemical ...
Photosynthesis ( / ˌfoʊtəˈsɪnθəsɪs / FOH-tə-SINTH-ə-sis) [1] is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their activities.
The overall function of light-dependent reactions is to convert solar energy into chemical energy in the form of NADPH and ATP. This chemical energy supports the light-independent reactions and fuels the assembly of sugar molecules. The light-dependent reactions are depicted in Figure 8.2.7 8.2. 7.
Most life on Earth depends on photosynthesis.The process is carried out by plants, algae, and some types of bacteria, which capture energy from sunlight to produce oxygen (O 2) and chemical energy stored in glucose (a sugar). Herbivores then obtain this energy by eating plants, and carnivores obtain it by eating herbivores.. The process. During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide (CO ...
Meaning. Photosynthesis. The process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy to chemical energy in the form of sugars. Photoautotroph. An organism that produces its own food using light energy (like plants) ATP. Adenosine triphosphate, the primary energy carrier in living things. Chloroplast.
Photosynthesis is really important for the plant because it provides the plant with food: some of the glucose is used immediately, to give the plant energy in the process of respiration. some of ...
As a result, the rate of photosynthesis will be inhibited. The Two Parts of Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis takes place in two sequential stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light independent-reactions. ... Chlorophyll a absorbs wavelengths from either end of the visible spectrum (blue and red), but not from green. Because green is ...
The Importance of Glucose. Glucose is a sugar that many plants, animals and fungi use for energy. In plants, glucose is produced as a result of photosynthesis. Plants need the energy glucose provides in order to grow and reproduce. Glucose is also required for the process of cellular respiration, in which plants convert carbon dioxide from the ...
Carbon atoms end up in you, and in other life forms, thanks to the second stage of photosynthesis, known as the Calvin cycle (or the light-independent reactions). Overview of the Calvin cycle In plants, carbon dioxide ( CO 2 ) enters the interior of a leaf via pores called stomata and diffuses into the stroma of the chloroplast—the site ...
Photosynthesis is an important process in plants and one of the most important concepts to understand in Biology. ... End Result: Oxygen (released into the atmosphere), ... At the end of the ETC, ...
Answer: Photosynthesis is an activity performed by plants to produce glucose and oxygen as products. The main end product of photosynthesis is carbohydrates. It is a crucial process that succours in the preparation of food by plants in nature. The glucose produced by plants is reserved in the form of starch. Starch is the condensed […]
The overall function of light-dependent reactions is to convert solar energy into chemical energy in the form of NADPH and ATP. This chemical energy supports the light-independent reactions and fuels the assembly of sugar molecules. The light-dependent reactions are depicted in Figure 8.16.
The light-dependent reactions use light energy to make two molecules needed for the next stage of photosynthesis: the energy storage molecule ATP and the reduced electron carrier NADPH. In plants, the light reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes of organelles called chloroplasts.
During photosynthesis, the chloroplasts inside the leaves of oak trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and use it to make glucose or sugar, which provides energy for the tree. Melvin Calvin conducted an experiment using radioactive carbon to trace how plants use carbon dioxide atoms from the atmosphere during photosynthesis.