Demystifying the Methodology Chapter: A Practical Guide for Social Science PhD Students
Hey there, fellow researchers! I'm Dr. Elizabeth Yardley, and today we're diving deep into the art of crafting your methodology chapter.
Writing this section doesn't have to be a labyrinthine journey. With each step, we'll not only explore what to include but, crucially, why you made the decisions you did. So, let's get into it!

1. Context: Setting the Stage
Let's set the stage – the context. Remind your reader of the aims and objectives of your research. What were you trying to achieve, and how did you set out to do this? In crafting this section, it's essential to link back to your aims and research questions. Why did you choose the specific research questions, and how do they align with your broader objectives?
For example:
The choice of ________ method aligns with my broader aim of __________.
2. Sampling: Picking Your Players
Now, let's talk about picking your players – your sample. Why did you choose this particular sample size and apply the inclusion/exclusion criteria that you did? How do these choices contribute to answering your research questions?
When determining my sample size, I considered __________ because it directly relates to my research question about __________.
The use of ________ sampling method was deemed appropriate because __________.
3. Data Collection: The Detective Work
The third heading, data collection, delves into the detective work – the techniques you used to gather information. Why did you opt for these specific data collection methods, and how do they connect to your research objectives?
My choice of data collection methods, including ________, was driven by the need to __________.
This aligns with my overarching goal of __________ as stated in my research aims.
4. Data Analysis: Making Sense of the Puzzle
After collecting your data, it's time to make sense of the puzzle. Why did you choose these particular data analysis methods? How do they contribute to answering your research questions and achieving your aims?
The selection of ________ for data analysis was appropriate because __________.
This choice supports my research objectives by __________.
5. Ethical Considerations: Playing Fair
Describe the ethical considerations guiding your research. Why did you take these specific measures, and how do they ensure the integrity of your study and respect the ethical principles guiding your research?
In addressing ethical considerations, I took steps such as __________ to uphold __________.
This is crucial because my research aims to __________, and these measures safeguard the well-being of my participants.
6. Changes and Reflections: Adapting on the Fly
Lastly, let's talk about adapting on the fly. Why did you make the changes you did during your research, and how do they align with your initial aims and research questions? Here we’re talking about reflexivity - when we flex and adapt our research approach in response to the circumstances in which we find ourselves.
During the research process, unexpected challenges arose, such as __________.
To stay true to my research goals of __________, I made adjustments like __________.
And there you have it – the blueprint for your methodology chapter. Always remember, each decision you make is a step toward answering your research questions and achieving your aims.
Step-by-step help with your methods chapter
If you want me to walk you through your methods chapter, from designing your study to writing it up, check out my PhD Survival Guide Part 7: The Methods Chapter. Click here to learn more.

Conquering Procrastination: The PhD Student's Guide to Productivity and Success
Academic conferences for introverts: 5 tips for surviving the conference as a phd student or early career researcher.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
- Table of Contents

Dissertation Methodology
In any research, the methodology chapter is one of the key components of your dissertation. It provides a detailed description of the methods you used to conduct your research and helps readers understand how you obtained your data and how you plan to analyze it. This section is crucial for replicating the study and validating its results.
Here are the basic elements that are typically included in a dissertation methodology:
- Introduction : This section should explain the importance and goals of your research .
- Research Design : Outline your research approach and why it’s appropriate for your study. You might be conducting an experimental research, a qualitative research, a quantitative research, or a mixed-methods research.
- Data Collection : This section should detail the methods you used to collect your data. Did you use surveys, interviews, observations, etc.? Why did you choose these methods? You should also include who your participants were, how you recruited them, and any ethical considerations.
- Data Analysis : Explain how you intend to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, thematic analysis, content analysis, etc., depending on the nature of your study.
- Reliability and Validity : Discuss how you’ve ensured the reliability and validity of your study. For instance, you could discuss measures taken to reduce bias, how you ensured that your measures accurately capture what they were intended to, or how you will handle any limitations in your study.
- Ethical Considerations : This is where you state how you have considered ethical issues related to your research, how you have protected the participants’ rights, and how you have complied with the relevant ethical guidelines.
- Limitations : Acknowledge any limitations of your methodology, including any biases and constraints that might have affected your study.
- Summary : Recap the key points of your methodology chapter, highlighting the overall approach and rationalization of your research.
Types of Dissertation Methodology
The type of methodology you choose for your dissertation will depend on the nature of your research question and the field you’re working in. Here are some of the most common types of methodologies used in dissertations:
Experimental Research
This involves creating an experiment that will test your hypothesis. You’ll need to design an experiment, manipulate variables, collect data, and analyze that data to draw conclusions. This is commonly used in fields like psychology, biology, and physics.
Survey Research
This type of research involves gathering data from a large number of participants using tools like questionnaires or surveys. It can be used to collect a large amount of data and is often used in fields like sociology, marketing, and public health.
Qualitative Research
This type of research is used to explore complex phenomena that can’t be easily quantified. Methods include interviews, focus groups, and observations. This methodology is common in fields like anthropology, sociology, and education.
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research uses numerical data to answer research questions. This can include statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. It’s common in fields like economics, psychology, and health sciences.
Case Study Research
This type of research involves in-depth investigation of a particular case, such as an individual, group, or event. This methodology is often used in psychology, social sciences, and business.
Mixed Methods Research
This combines qualitative and quantitative research methods in a single study. It’s used to answer more complex research questions and is becoming more popular in fields like social sciences, health sciences, and education.
Action Research
This type of research involves taking action and then reflecting upon the results. This cycle of action-reflection-action continues throughout the study. It’s often used in fields like education and organizational development.
Longitudinal Research
This type of research involves studying the same group of individuals over an extended period of time. This could involve surveys, observations, or experiments. It’s common in fields like psychology, sociology, and medicine.
Ethnographic Research
This type of research involves the in-depth study of people and cultures. Researchers immerse themselves in the culture they’re studying to collect data. This is often used in fields like anthropology and social sciences.
Structure of Dissertation Methodology
The structure of a dissertation methodology can vary depending on your field of study, the nature of your research, and the guidelines of your institution. However, a standard structure typically includes the following elements:
- Introduction : Briefly introduce your overall approach to the research. Explain what you plan to explore and why it’s important.
- Research Design/Approach : Describe your overall research design. This can be qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods. Explain the rationale behind your chosen design and why it is suitable for your research questions or hypotheses.
- Data Collection Methods : Detail the methods you used to collect your data. You should include what type of data you collected, how you collected it, and why you chose this method. If relevant, you can also include information about your sample population, such as how many people participated, how they were chosen, and any relevant demographic information.
- Data Analysis Methods : Explain how you plan to analyze your collected data. This will depend on the nature of your data. For example, if you collected quantitative data, you might discuss statistical analysis techniques. If you collected qualitative data, you might discuss coding strategies, thematic analysis, or narrative analysis.
- Reliability and Validity : Discuss how you’ve ensured the reliability and validity of your research. This might include steps you took to reduce bias or increase the accuracy of your measurements.
- Ethical Considerations : If relevant, discuss any ethical issues associated with your research. This might include how you obtained informed consent from participants, how you ensured participants’ privacy and confidentiality, or any potential conflicts of interest.
- Limitations : Acknowledge any limitations in your research methodology. This could include potential sources of bias, difficulties with data collection, or limitations in your analysis methods.
- Summary/Conclusion : Briefly summarize the key points of your methodology, emphasizing how it helps answer your research questions or hypotheses.
How to Write Dissertation Methodology
Writing a dissertation methodology requires you to be clear and precise about the way you’ve carried out your research. It’s an opportunity to convince your readers of the appropriateness and reliability of your approach to your research question. Here is a basic guideline on how to write your methodology section:
1. Introduction
Start your methodology section by restating your research question(s) or objective(s). This ensures your methodology directly ties into the aim of your research.
2. Approach
Identify your overall approach: qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods. Explain why you have chosen this approach.
- Qualitative methods are typically used for exploratory research and involve collecting non-numerical data. This might involve interviews, observations, or analysis of texts.
- Quantitative methods are used for research that relies on numerical data. This might involve surveys, experiments, or statistical analysis.
- Mixed methods use a combination of both qualitative and quantitative research methods.
3. Research Design
Describe the overall design of your research. This could involve explaining the type of study (e.g., case study, ethnography, experimental research, etc.), how you’ve defined and measured your variables, and any control measures you’ve implemented.
4. Data Collection
Explain in detail how you collected your data.
- If you’ve used qualitative methods, you might detail how you selected participants for interviews or focus groups, how you conducted observations, or how you analyzed existing texts.
- If you’ve used quantitative methods, you might detail how you designed your survey or experiment, how you collected responses, and how you ensured your data is reliable and valid.
5. Data Analysis
Describe how you analyzed your data.
- If you’re doing qualitative research, this might involve thematic analysis, discourse analysis, or grounded theory.
- If you’re doing quantitative research, you might be conducting statistical tests, regression analysis, or factor analysis.
Discuss any ethical issues related to your research. This might involve explaining how you obtained informed consent, how you’re protecting participants’ privacy, or how you’re managing any potential harms to participants.
7. Reliability and Validity
Discuss the steps you’ve taken to ensure the reliability and validity of your data.
- Reliability refers to the consistency of your measurements, and you might discuss how you’ve piloted your instruments or used standardized measures.
- Validity refers to the accuracy of your measurements, and you might discuss how you’ve ensured your measures reflect the concepts they’re supposed to measure.
8. Limitations
Every study has its limitations. Discuss the potential weaknesses of your chosen methods and explain any obstacles you faced in your research.
9. Conclusion
Summarize the key points of your methodology, emphasizing how it helps to address your research question or objective.
Example of Dissertation Methodology
An Example of Dissertation Methodology is as follows:
Chapter 3: Methodology
- Introduction
This chapter details the methodology adopted in this research. The study aimed to explore the relationship between stress and productivity in the workplace. A mixed-methods research design was used to collect and analyze data.
Research Design
This study adopted a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative surveys with qualitative interviews to provide a comprehensive understanding of the research problem. The rationale for this approach is that while quantitative data can provide a broad overview of the relationships between variables, qualitative data can provide deeper insights into the nuances of these relationships.
Data Collection Methods
Quantitative Data Collection : An online self-report questionnaire was used to collect data from participants. The questionnaire consisted of two standardized scales: the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) to measure stress levels and the Individual Work Productivity Questionnaire (IWPQ) to measure productivity. The sample consisted of 200 office workers randomly selected from various companies in the city.
Qualitative Data Collection : Semi-structured interviews were conducted with 20 participants chosen from the initial sample. The interview guide included questions about participants’ experiences with stress and how they perceived its impact on their productivity.
Data Analysis Methods
Quantitative Data Analysis : Descriptive and inferential statistics were used to analyze the survey data. Pearson’s correlation was used to examine the relationship between stress and productivity.
Qualitative Data Analysis : Interviews were transcribed and subjected to thematic analysis using NVivo software. This process allowed for identifying and analyzing patterns and themes regarding the impact of stress on productivity.
Reliability and Validity
To ensure reliability and validity, standardized measures with good psychometric properties were used. In qualitative data analysis, triangulation was employed by having two researchers independently analyze the data and then compare findings.
Ethical Considerations
All participants provided informed consent prior to their involvement in the study. They were informed about the purpose of the study, their rights as participants, and the confidentiality of their responses.
Limitations
The main limitation of this study is its reliance on self-report measures, which can be subject to biases such as social desirability bias. Moreover, the sample was drawn from a single city, which may limit the generalizability of the findings.
Where to Write Dissertation Methodology
In a dissertation or thesis, the Methodology section usually follows the Literature Review. This placement allows the Methodology to build upon the theoretical framework and existing research outlined in the Literature Review, and precedes the Results or Findings section. Here’s a basic outline of how most dissertations are structured:
- Acknowledgements
- Literature Review (or it may be interspersed throughout the dissertation)
- Methodology
- Results/Findings
- References/Bibliography
In the Methodology chapter, you will discuss the research design, data collection methods, data analysis methods, and any ethical considerations pertaining to your study. This allows your readers to understand how your research was conducted and how you arrived at your results.
Advantages of Dissertation Methodology
The dissertation methodology section plays an important role in a dissertation for several reasons. Here are some of the advantages of having a well-crafted methodology section in your dissertation:
- Clarifies Your Research Approach : The methodology section explains how you plan to tackle your research question, providing a clear plan for data collection and analysis.
- Enables Replication : A detailed methodology allows other researchers to replicate your study. Replication is an important aspect of scientific research because it provides validation of the study’s results.
- Demonstrates Rigor : A well-written methodology shows that you’ve thought critically about your research methods and have chosen the most appropriate ones for your research question. This adds credibility to your study.
- Enhances Transparency : Detailing your methods allows readers to understand the steps you took in your research. This increases the transparency of your study and allows readers to evaluate potential biases or limitations.
- Helps in Addressing Research Limitations : In your methodology section, you can acknowledge and explain the limitations of your research. This is important as it shows you understand that no research method is perfect and there are always potential weaknesses.
- Facilitates Peer Review : A detailed methodology helps peer reviewers assess the soundness of your research design. This is an important part of the publication process if you aim to publish your dissertation in a peer-reviewed journal.
- Establishes the Validity and Reliability : Your methodology section should also include a discussion of the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your measurements, which is crucial for establishing the overall quality of your research.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...

Dissertation – Format, Example and Template

Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences

Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and...

Sample PhD Research Methodology Chapter
1.0 introduction.
This chapter designs a comprehensive research methodology tailored to the aim and objectives of the study. Specifically, the research methodology chapter is responsible for explaining the philosophical underpinnings, as well as explaining their role in examining the selected research phenomenon. Second, the researcher’s philosophical orientation is explained and the rationale for the chosen methods is provided. Finally, this chapter defends the selected data collection instruments and analysis procedures, paying close attention to their advantages and limitations. Ethical issues and methodological limitations are covered in the end.
2.0 Ontological Perspective
The process of designing a research methodology starts with the branch of ontology, which is primarily concerned with what exists in the human world and what knowledge could be acquired about this world (Anfara & Mertz, 2014). With the help of ontology, researchers can recognise the extent to which the objects they are researching are ‘real’ and what ‘truth claims’ can be made about these objects (Chawla & Sodhi, 2011). The spectrum of ontological stances ranges from naïve realism to relativism; the former assumes that there is a single reality, which could be understood using appropriate research methods, whereas the latter implies that realities exist as multiple mental constructions that change depending on the subject and context in which they exist (Crotty, 2020).
This study follows a bounded relativist position, according to which there is one shared reality within a bounded group (Easterby-Smith et al., 2012). This choice has been made because organisational culture is a context-specific phenomenon, meaning each organisation has its own culture that is manifested in its values, artefacts, stories, and symbols (Kumar, 2014). The existing literature shows that organisational culture is something that is shared by all employees, suggesting there is a single reality within this group (Crotty, 2020). Although there may be outliers, organisational culture is often viewed as the glue that connects the employees of the same organisation and communicates the reality in which they exist.
3.0 Epistemological Perspective
Having identified how ‘things’ are, it is relevant to identify how the researcher creates knowledge by selecting and justifying an epistemological stance. The methodology literature distinguishes between three major epistemological positions, depending on the relationship between the object and the subject (Anfara & Mertz, 2014). Objectivism implies that meaning exists within an object and there is an objective reality that exists independently of the subject (Dew & Foreman, 2020). On the other end of the spectrum lies subjectivism, according to which it is the subject that creates meaning and imposes it on an object (Saunders & Lewis, 2014). Finally, constructionism is a more balanced epistemological position, where the interplay between the subject and the object creates meaning but the reality of the object is still constructed by the subject (Kumar, 2008).
Since the phenomenon of organisational culture exists independently from the researcher, this study is in keeping with the constructionist stance, which allows for generating a contextual understanding of organisational culture and its role in employees’ well-being perception in the selected company. On the one hand, each employee has their views, values, and beliefs, which inevitably affect their perception of well-being (Pruzan, 2016). This fact implies that multiple realities are likely to exist, which are shaped and formed by the company’s employees, as well as the meanings they attach to the world in general and their employer’s organisational culture, in particular (Dew & Foreman, 2020). Still, since the researcher attempts to establish the relationship between organisational culture and employees’ perceptions of well-being and achieve an adequate level of generalisation, the adoption of subjectivist epistemology seems counterproductive. In turn, objectivism fully excludes the possibility of the existence of multiple sources of meaning, which explains why this epistemology has not been adopted either (Chawla & Sodhi, 2011).
4.0 Theoretical Perspective
The next step in designing a comprehensive research methodology would be to have a look at the researcher’s philosophical orientation that guides their action (Creswell & Creswell, 2017). Per Singh and Nath (2010), all theoretical perspectives could be broadly divided into two groups, namely those that are applied to predict the phenomenon in question and those that help in getting a better understanding of this phenomenon. Since this study is focused on the establishment of the relationship between organisational culture and employees’ well-being perceptions, using more than one method to identify the valid and logical truth seems reasonable. Therefore, the theoretical perspective of post-positivism, according to which a valid belief could be properly identified only using multiple methods because all methods are imperfect, has been selected (Anfara & Mertz, 2014). The research design of this study, including its ontological and epistemological standpoints, is presented as follows.
Figure 1: Research Design
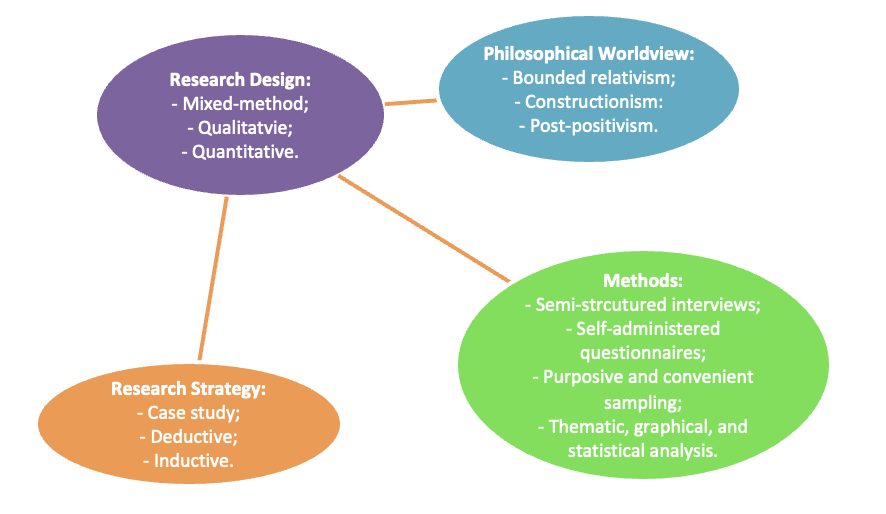
Source: Constructed for this study
Post-positivism can be viewed as a natural evolution of the positivist theoretical stance, primarily driven by the growing complexity of the social sciences, which requires examining social phenomena from multiple vantage points to make relevant and accurate predictions (Khan, 2011). As previously noted, employees’ values, attitudes, and beliefs, which form their realities and affect their perceptions of well-being in the organisational context, make this social phenomenon multifaceted and complex (Bryman & Bell, 2015). That is why using several methods is expected to help the researcher decipher this relationship and possibly extrapolate the produced findings to different contexts (Daniel & Sam, 2011). While post-positivism is less rigorous and ‘scientific’ as compared to positivism, some scholars argue that the social world is too complex to be explained by applying natural science methods. Interpretations of reality cannot be isolated from the cultural and social context, in which the research phenomenon is taking place (Easterby-Smith et al., 2012). Still, the application of natural science methods enables the researcher to identify certain patterns, allowing for examining the relationship between organisational culture and employees’ well-being perceptions in more detail.
5.0 Methodology
Based on the above explanation and justification, this doctoral project follows a mixed-method approach, which implies the collection and analysis of qualitative and quantitative data within the same study (Singh & Nath, 2010). A mixed-method research design enables the researcher to obtain data using multiple data collection instruments, adding to the breadth of this investigation and allowing for assessing the relationship between organisational culture and employees’ perceptions of well-being more comprehensively (Cohen et al., 2017). With that being stated, following a mono method can ensure a much higher level of detalisation as compared to a mixed-method approach (Howell, 2012). Still, within the organisational context, different truths are likely to exist among different stakeholder groups, which substantiates the need to examine and compare these truths in order to identify how they are similar or different (Daniel & Sam, 2011).
This project follows the research strategy of a case study, which enables the researcher to develop an in-depth description of the target organisation and its culture. One of the main advantages of this strategy is that it implies using multiple data collection techniques, which goes in keeping with the selected research design (Bryman & Bell, 2015). Although the case study strategy does not represent the world, it focuses on a single case in relation to the selected research problem and illustrates the contextualised case of the relationship between corporate culture and employee perceptions (Singh & Nath, 2010). Although some scholars believe that case studies have limited generalisation because they are primarily focused on a single object or case, it is still possible to compare the case study findings to existing theory and, hence, provide broader implications to similar contexts outside the selected case (Yin, 2014). Since this project not only draws on existing theory but also attempts to come up with a new theory linking organisational culture to employee well-being in the workplace, it incorporates certain aspects of both inductive and deductive approaches (Pruzan, 2016).
6.0 Data and Methods of Collection
Two primary data collection methods, namely self-administered questionnaires and semi-structured interviews have been selected for this study. The former method implies collecting primary quantitative data from individuals who self-report their perceptions of and attitudes towards the research phenomenon (Singh, 2010). In turn, in semi-structured interviews, a researcher asks questions within a predetermined thematic framework but the questions are not set in order or phrasing (Billups, 2019). Self-administered questionnaires have been selected because they not only enable the researcher to obtain a large amount of primary data in a short period. They also generate primary data that could easily be quantified and processed graphically and statistically, which goes in keeping with the post-positivist nature of this study (Saunders & Lewis, 2014). In turn, semi-structured interviews allow for generating highly detailed data that answers the ‘why’ and ‘how’ questions, leading to more comprehensive and detailed research findings (Cohen et al., 2017).
The decision to incorporate both self-administered questionnaires and semi-structured interviews in the research design allows for offsetting the drawbacks of each of these data collection instruments. For example, in questionnaire surveys, respondents’ answers are usually limited to a set of predefined, concise response options, which may not necessarily reflect how they feel about certain things (Novikov & Novikov, 2013). Concurrently, during interviews, interviewees can provide whatever responses they want, regardless of their length or content. At the same time, interviews are commonly considered a time-consuming data collection procedure (Carson et al., 2001). Due to this reason, as well as potential access issues, it is problematic to engage a relatively large number of individuals in interviews. Alternatively, questionnaires can be distributed among a sizeable population of social actors in a fraction of the time needed to conduct an interview (Daniel & Sam, 2011). Therefore, by utilising both self-administered questionnaires and semi-structured interviews, it is possible to make the most of these instruments while overcoming their drawbacks.
7.0 Sampling
For this study, two samples were drawn to approach the relationship between corporate culture and employees’ perceptions of well-being from different vantage points. First, judgemental sampling, a non-probability sampling technique where units to be sampled are selected by the researcher based on their professional judgement, was chosen to approach the most knowledgeable and experienced managers of the target company (Creswell & Creswell, 2017). While the researcher was not intended to cap the number of interviewees included in the sample, a total of 14 top managers agreed to participate. The selection of this sampling strategy is explained by its ability to ensure a deep focus on the researched phenomenon because the interviewees exist in the same context and share similar opinions and values. In turn, managers were selected because they are expected to have a more profound knowledge of the selected company’s organisational culture and its nuances than their subordinates. Interviews were conducted online using Zoom.
Second, the researcher followed the strategy of convenience sampling, which allows for collecting research data from the most easily accessed respondents, to draw a questionnaire survey sample (Gray, 2017). At this point, around 760 employees of the target multinational company were contacted via social media platforms and asked to participate. According to the existing methodology literature, the sample size plays a crucial role when it comes to data validity and reliability, which explains why the researcher intended to include as many employees in the sample as possible (Easterby-Smith et al., 2012). 549 questionnaires were returned to the researcher, out of which 32 were excluded due to missing values. Therefore, the questionnaire survey sample consisted of 517 participants. This sample size should be enough to ensure an adequate level of validity and reliability and make sure the produced findings are generalisable to a certain extent (Dew & Foreman, 2020). All questionnaires were distributed online using Google Forms.
8.0 Analysis Strategy
As previously noted, post-positivist studies tend to use multiple methods, which translates into employing several analysis instruments within the same research project (Novikov & Novikov, 2013). This study is not the exception to this rule. The primary data obtained using self-administered questionnaires was processed both graphically and statistically. This data was quantified by assigning a code (e.g., ‘1’, ‘2’, ‘3’, ‘4’, etc.) to each response and inserting the constructed set of raw data in Microsoft Excel, which was also used to design charts and graphs. The quantified data was then inserted into an SPSS spreadsheet to make it suitable for statistical analysis. Descriptive statistics and linear regression were used to analyse the primary quantitative data and establish the relationship between organisational culture and employees’ perceptions of well-being and test the Null Hypothesis and Hypothesis 1 presented in Chapter 2. In addition, the analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted to test Hypothesis 2 and identify whether those employees who belonged to an older generation perceived the role of organisational culture in their well-being differently than their young colleagues. The key methodological choices, including analysis methods, are presented as follows.
Figure 2: Methodological Choices
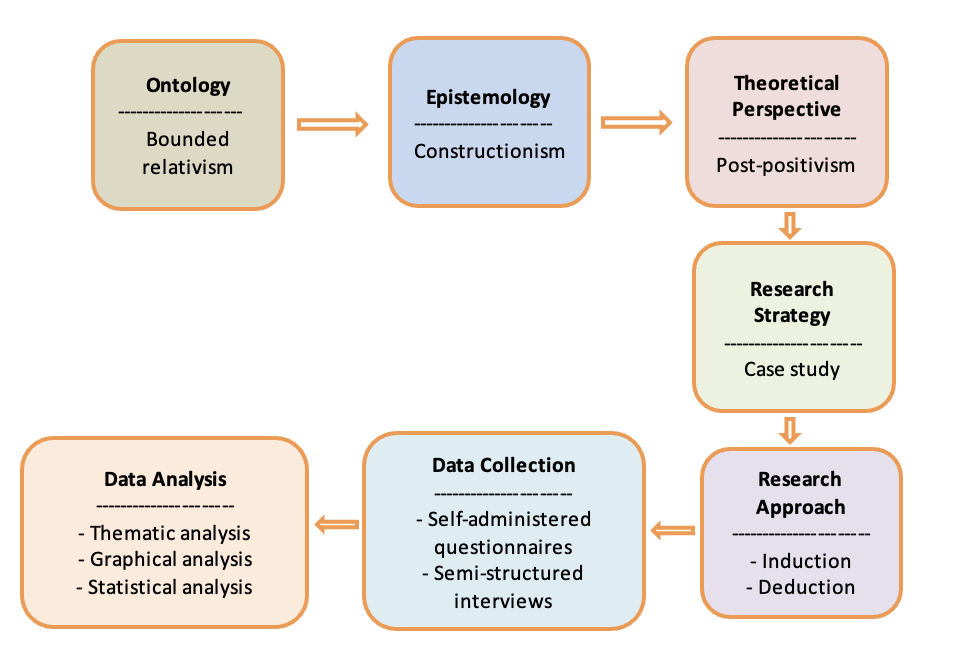
The researcher also used a content analysis technique to process the primary data generated by the interviewees. Unlike graphical or statistical analyses, the content analysis does not demonstrate cause-and-effect links between variables but rather enables the researcher to get a deeper understanding of interviewees’ perceptions, feelings, and lived experiences (Carson et al., 2001). The recorded interviews were first converted into text transcripts using word processing software. Afterwards, the transcribed data was processed by NVivo to create codes and nodes according to the main themes of this project, such as ‘organisational culture’, ‘employee well-being’, ‘work-life balance’, ‘employee recognition’, and ‘job satisfaction’. This software was also used to identify the frequency of the aforementioned themes and other tendencies in the interviewees’ responses.
9.0 Ethical Issues
Before obtaining primary data from the participants, they were provided with an information sheet that covered all the important aspects of this project, including its aim and objectives, anticipated outcomes, and research procedure (Saunders & Lewis, 2014). Informed consent was obtained from each potential interviewee and survey participant to make sure their participation was voluntary. They were explicitly communicated both verbally and in writing that they were able to withdraw from the data collection process at will. Moreover, this process was made fully anonymous to prevent the potential leakage of personal data and contribute to the participants’ intention to take part (Singh, 2010).
10.0 Methodological Limitations
Although the designed research methodology is characterised by a relatively high level of replicability, it could be argued that the adoption of bounded relativism does not add to the generalisability of the produced empirical outcomes (Daniel & Sam, 2011). The point is that the mental constructions of reality held by those managers and employees who participated in this project may not necessarily match one another, leading to multiple interpretations of how their well-being is affected by the employer’s organisational culture (Saunders & Lewis, 2014). Another limitation is that self-administered questionnaires significantly limit the researcher’s ability to decipher hidden meaning that exists in organisational practices and events, which makes this study biased towards making predictions rather than deepening our understanding of the research phenomenon (Novikov & Novikov, 2013).
11.0 Chapter Summary
Ontologically, this study is framed within bounded relativism, which implies that reality constructions exist within a boundary of a peculiar group. In turn, from an epistemological viewpoint, this project adopts constructionism and the post-positivist theoretical perspective. Since this study follows a mixed-method approach, the researcher obtained primary qualitative and quantitative data from 14 top managers and 517 employees of the target business entity by means of semi-structured interviews and self-administered questionnaires, respectively. The collected data was processed, thematically, graphically, and statistically using NVivo, Microsoft Excel, and SPSS.
Anfara, V., & Mertz, N. (2014). Theoretical Frameworks in Qualitative Research . SAGE.
Billups, F. (2019). Qualitative Data Collection Tools: Design, Development, and Applications . SAGE.
Bryman, A., & Bell, E. (2015). Business research methods . OUP.
Carson, D., Gilmore, A., Perry, C., & Gronhaug, K. (2001). Qualitative Marketing Research . SAGE.
Chawla, D., & Sodhi, N. (2011). Research Methodology: Concepts and Cases . Vicas Publishing House.
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2017). Research Methods in Education . Routledge.
Creswell, J., & Creswell, D. (2017). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . SAGE.
Crotty, M. (2020). The foundations of social research: Meaning and perspective in the research process . Routledge.
Daniel, S., & Sam, A. (2011). Research methodology . Gyan Publishing House.
Dew, J., & Foreman, M. (2020). How Do We Know?: An Introduction to Epistemology . InterVarsity Press.
Easterby-Smith, M., Thorpe, R., & Jackson, P. (2012). Management Research . SAGE.
Gray, D. (2017). Doing Research in the Real World . SAGE.
Howell, K. (2012). An introduction to the philosophy of methodology . SAGE.
Khan, J. (2011). Research methodology . APH Publishing.
Kumar, R. (2008). Research methodology . APH Publishing.
Kumar, R. (2014). Research Methodology: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners . SAGE.
Novikov, A., & Novikov, D. (2013). Research methodology: From philosophy of science to research design . CRC Press.
Pruzan, P. (2016). Research Methodology: The Aims, Practices and Ethics of Science . Springer.
Saunders, M., & Lewis, P. (2014). Doing Research in Business and Management: An Essential Guide to Planning Your Project . Pearson Education.
Singh, Y. (2010). Research methodology . APH Publishing.
Singh, Y., & Nath, R. (2010). Research methodology . APH Publishing.
Yin, R. (2014). Case study research: Design and methods . SAGE.

Library Guides
Dissertations 4: methodology: start.
- Introduction & Philosophy
- Methodology
The Methodology Chapter
The methodology chapter flows organically from the literature review. This means that at this stage you should have reviewed the literature in your field of study, analysed research that has been conducted and highlighted how it was conducted. In turn, this should reflect the foundation of your own project as you will have to link it to your chosen research method.
The methodology chapter also involves describing your method in detail and justifying the approach you are going to adopt, taking into consideration the limitations and ethical implications of your model. Your description should be detailed enough that someone reading your methodology can recreate your approach.
Therefore, the methodology requires you to:
- describe your methods
- demonstrate a clear connection between your research question (or hypothesis) and the means by which you will reach your conclusions
- present justification (strengths) and limitations (weaknesses) of your methods
What are Methods & Methodology?
Methods
In order to appreciate what methods are, let us remember what research is about. Research can be summarised into three points (Cottrell, 2014, p9):
A question
Methods of arriving at an answer
The answer
Thus, methods are the means to research and answer the research question, or test the hypothesis. Methods include techniques and procedures used to obtain and analyse data (Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, 2015, p4). Your methods can consist of primary and secondary sources, qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods, as illustrated in this guide.
Methodology
Methodology is sometimes used interchangeably with methods, or as the set of methods used in a research. More specifically, as the name would suggest, methodo-logy is the logos, the reasoning, on the methods. It is also referred to as the theory of how research should be undertaken (Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, 2015, p4). This is why you normally would have a methodology, rather than methods, chapter in a dissertation.
First Key Tip
We hope this guide will be helpful, but it is of fundamental importance that you also use a research methods book (or other authoritative source) for your discipline . The book will guide you on best methods for your research, give you practical guidance, and present critical insights and limitations of the methods.
- Next: Structure >>
- Last Updated: Sep 14, 2022 12:58 PM
- URL: https://libguides.westminster.ac.uk/methodology-for-dissertations
CONNECT WITH US
- Deutschland
- United Kingdom

- PhD Dissertations
- Master’s Dissertations
- Bachelor’s Dissertations
- Scientific Dissertations
- Medical Dissertations
- Bioscience Dissertations
- Social Sciences Dissertations
- Psychology Dissertations
- Humanities Dissertations
- Engineering Dissertations
- Economics Dissertations
- Service Overview
- Revisión en inglés
- Relecture en anglais
- Revisão em inglês
Manuscript Editing
- Research Paper Editing
- Lektorat Doktorarbeit
- Dissertation Proofreading
- Englisches Lektorat
- Journal Manuscript Editing
- Scientific Manuscript Editing Services
- Book Manuscript Editing
- PhD Thesis Proofreading Services
- Wissenschaftslektorat
- Korektura anglického textu
- Akademisches Lektorat
- Journal Article Editing
- Manuscript Editing Services
PhD Thesis Editing
- Medical Editing Sciences
- Proofreading Rates UK
- Medical Proofreading
- PhD Proofreading
- Academic Proofreading
- PhD Proofreaders
- Best Dissertation Proofreaders
- Masters Dissertation Proofreading
- Proofreading PhD Thesis Price
- PhD Dissertation Editing
- Lektorat Englisch Preise
- Lektorieren Englisch
- Wissenschaftliches Lektorat
- Thesis Proofreading Services
- PhD Thesis Proofreading
- Proofreading Thesis Cost
- Proofreading Thesis
- Thesis Editing Services
- Professional Thesis Editing
- PhD Thesis Editing Services
- Thesis Editing Cost
- Dissertation Proofreading Services
- Proofreading Dissertation
PhD Dissertation Proofreading
- Dissertation Proofreading Cost
- Dissertation Proofreader
- Correção de Artigos Científicos
- Correção de Trabalhos Academicos
- Serviços de Correção de Inglês
- Correção de Dissertação
- Correção de Textos Precos
- Revision en Ingles
- Revision de Textos en Ingles
- Revision de Tesis
- Revision Medica en Ingles
- Revision de Tesis Precio
- Revisão de Artigos Científicos
- Revisão de Trabalhos Academicos
- Serviços de Revisão de Inglês
- Revisão de Dissertação
- Revisão de Textos Precos
- Corrección de Textos en Ingles
- Corrección de Tesis
- Corrección de Tesis Precio
- Corrección Medica en Ingles
- Corrector ingles
- Choosing the right Journal
- Journal Editor’s Feedback
- Dealing with Rejection
- Quantitative Research Examples
- Number of scientific papers published per year
- Acknowledgements Example
- ISO, ANSI, CFR & Other
- Types of Peer Review
- Withdrawing a Paper
- What is a good h-index
- Appendix paper
- Cover Letter Templates
- Writing an Article
- How To Write the Findings
- Abbreviations: ‘Ibid.’ & ‘Id.’
- Sample letter to editor for publication
- Tables and figures in research paper
- Journal Metrics
- Revision Process of Journal Publishing
- JOURNAL GUIDELINES
Select Page
Writing the Methodology Chapter(s) for the Proposal
Posted by Rene Tetzner | Oct 12, 2021 | PhD Success | 0 |

3.3 Writing the Methodology Chapter(s) for the Proposal
The methodology used in a thesis is usually described in its own chapter (see Section 1.2.3 and Section 4.3), though, like the literature review, it can be blended with the introductory material, or the review of literature and description of methods can be combined, especially if reviewing the scholarship on a topic, problem or phenomenon is a main part of the methodology used. If two different types of methodology are used for comparative purposes or combined to produce more wide-ranging results, a chapter might be dedicated to each approach, but this is rare. Usually all methods are presented in a single chapter, which might simply be entitled ‘Methodology’ or feature a title more specific to the precise methods described. There are, of course, a great many different ways to pursue research of all kinds, and they are always increasing, with established methods undergoing alterations as scholars adjust and combine them, and new methods being developed to enable research that might not have been imagined only a few decades ago.
You may be planning to use quantitative methods focussing on prediction, explanation and statistical analysis, or you may be hoping to approach your research topic qualitatively, focussing on description and exploration via textual analysis; alternatively, you may wish to combine these two approaches to supplement the results of each with results of a different nature. You may intend to use tests, trials or experiments, or perhaps interviews, questionnaires and case studies; on the other hand, you may be planning to adopt a certain theoretical perspective (cultural historicism, for example, or deconstructionism) or hoping to rely on observation (in person and/or via audiovisual equipment and recordings) or intending to exercise your ability to transcribe, translate and interpret ancient languages and scripts.

The possibilities are virtually endless, and you may find it helpful as you design the methods you plan to use in your thesis to look back at your work in any research methodology classes you may have taken for ideas and techniques. Whatever research methods you might be considering for your thesis, the important point is that they will work effectively for investigating the topic, problem or phenomenon on which your thesis focuses, for answering any particular questions and testing any hypotheses you might have formulated regarding that topic and for meeting your aims and objectives. This is to say that your research methodology should arise from the topic, problem or phenomenon, not the other way around (unless perhaps the topic you are exploring is methodology). The design of your research may well affect the precise nature and wording of that topic, problem or phenomenon and what you can ask and discover about it, and you may have given a great deal of thought to your methodology before deciding upon exactly what you will investigate, but the methods you choose or devise should be determined by the requirements of researching the specific topic, problem or phenomenon you have chosen for your focus.
Once you have decided on the methods you will use, you need to describe them as clearly and precisely as you can, indicating the setting and subjects (texts, people, animals etc.) of your research, specifying the variables you are considering and the instruments you are using, and explaining in detail exactly how you plan to collect and analyse data at each stage of the research process, which may well involve a return to any research questions and hypotheses you introduced in your first chapter and a description of precisely how your procedures will answer and test them. You should also explain why your methodology is appropriate – indeed, the best methodology possible – and perhaps innovative for investigating the particular topic, problem or phenomenon, and this explanation will ideally involve a discussion of the strengths and weaknesses of various aspects of your design, the reliability and limitations of your instruments and procedures, and the use of controls and other rigorous methods for checking and guaranteeing the validity of your results. If you are using unusual or complex equipment in your research, you may want to include figures to illustrate it, and diagrams can be extremely effective for showing readers the procedural processes you will be following (for information on designing figures, see Section 4.4.1).

Your supervisor and the other members of your thesis committee will no doubt prove particularly helpful when you are refining your methodology: as more experienced researchers, they have already conducted studies of the magnitude you are just beginning and will very likely have practical knowledge of at least some of the methods and instruments you are planning to use, as well as an understanding of the vital differences that can arise between intentions, processes and results. There will almost certainly be adjustments to your first ideas as you write your methodology chapter and receive feedback from your committee members, and while this might seem distressing if you have already given your methods a lot of thought and feel rather attached to your approaches, remember that the proposal process is itself designed to iron out potential problems, clarify procedures and determine an effective working design.
There may well be further adjustments down the road, of course, but it is absolutely essential that you design and refine your research methods to such a degree at this point that you are able to begin constructive research immediately after the proposal process. Data collection and analysis take a great deal of time which you do not want to waste, so you need to be sure that you are moving in the right direction. You also want to be sure that your methodology does not raise any ethical issues that may hinder your progress or render your research unusable. Your thesis committee should be able to help you avoid or resolve problems of this kind, so if you are in doubt and the topic does not arise, do ask your supervisor (and perhaps other committee members) if they anticipate any problems, and check relevant university regulations and guidelines as well to be sure that you will be able to obtain any approval you may require.

Unlike the literature review, for which you will already have read a great deal, your methods (for the most part) will not yet be tried as you describe them in your methodology chapter for the proposal, so, with the exception of any pilot studies or trials you may already have conducted, you should discuss your methods as future events – ‘I will do this,’ ‘I plan to use,’ ‘I intend to investigate’ and so on. This approach may be appropriate for certain aspects of your introductory chapter as well, particularly when you are referring to what you will ultimately do in the thesis as opposed to what you are doing in the proposal, and may perhaps apply to parts of your literature review too: you may, for instance, only review some of many publications on a subject at the proposal stage, but be planning to add further reviews in the thesis itself. The careful use of verb tenses and other temporal indicators will make your writing, your plans for the future and your reports of what you have already done much clearer for your readers (see also Section 5.4.7).
Let us say, for instance, that you have already conducted one of the trials that you describe in your methodology chapter and have obtained results that begin to support one or more of your key hypotheses. This is the sort of progress that you certainly want your committee members to know about, so you need to describe it in a way that indicates that it has already been done – ‘I have completed,’ ‘I conducted,’ ‘I analysed’ and so on – just as you need to describe procedures still in the future as not yet done. Since most doctoral supervisors and committee members do not have the time to help you with your written English, if the careful use of tense (or any other aspect of the language) presents challenges for you, it may be a good idea to seek additional help from a qualified English proofreader, a friend or colleague whose English is more accomplished or the writing centre (if there is one) at your university. Finally, like a literature review, a chapter describing methodology usually closes with a brief summary, especially if the description of the methods has been long and complicated.
Tables and figures often are not needed in thesis proposals, but if you happen to make use of tables or figures while describing your methodology (or in any other part of your proposal), you will want to be sure that they are carefully designed and work effectively for your purposes, which are, generally speaking, to clarify the material you provide in the text. For further information on constructing tables and figures, see Section 1.3 and Section 4.4.1. If you do use tables and figures, you may also need to include in the proposal a list of each; if so, see Sections 1.1.8 and 1.1.9 and Section 4.6.2 for advice. Finally, if you use a large number of nonstandard abbreviations in your proposal chapters, you may need or choose to provide a list of abbreviations and their definitions, in which case, further information on abbreviations can be found in Section 6.3, and lists of abbreviations are also discussed in Section 1.1.7 and Section 4.6.2. For more general information on constructing lists, see Section 5.5.2.
Why PhD Success?
To Graduate Successfully
This article is part of a book called "PhD Success" which focuses on the writing process of a phd thesis, with its aim being to provide sound practices and principles for reporting and formatting in text the methods, results and discussion of even the most innovative and unique research in ways that are clear, correct, professional and persuasive.

The assumption of the book is that the doctoral candidate reading it is both eager to write and more than capable of doing so, but nonetheless requires information and guidance on exactly what he or she should be writing and how best to approach the task. The basic components of a doctoral thesis are outlined and described, as are the elements of complete and accurate scholarly references, and detailed descriptions of writing practices are clarified through the use of numerous examples.

The basic components of a doctoral thesis are outlined and described, as are the elements of complete and accurate scholarly references, and detailed descriptions of writing practices are clarified through the use of numerous examples. PhD Success provides guidance for students familiar with English and the procedures of English universities, but it also acknowledges that many theses in the English language are now written by candidates whose first language is not English, so it carefully explains the scholarly styles, conventions and standards expected of a successful doctoral thesis in the English language.
Individual chapters of this book address reflective and critical writing early in the thesis process; working successfully with thesis supervisors and benefiting from commentary and criticism; drafting and revising effective thesis chapters and developing an academic or scientific argument; writing and formatting a thesis in clear and correct scholarly English; citing, quoting and documenting sources thoroughly and accurately; and preparing for and excelling in thesis meetings and examinations.

Completing a doctoral thesis successfully requires long and penetrating thought, intellectual rigour and creativity, original research and sound methods (whether established or innovative), precision in recording detail and a wide-ranging thoroughness, as much perseverance and mental toughness as insight and brilliance, and, no matter how many helpful writing guides are consulted, a great deal of hard work over a significant period of time. Writing a thesis can be an enjoyable as well as a challenging experience, however, and even if it is not always so, the personal and professional rewards of achieving such an enormous goal are considerable, as all doctoral candidates no doubt realise, and will last a great deal longer than any problems that may be encountered during the process.

Interested in Proofreading your PhD Thesis? Get in Touch with us
If you are interested in proofreading your PhD thesis or dissertation, please explore our expert dissertation proofreading services.

Rene Tetzner
Rene Tetzner's blog posts dedicated to academic writing. Although the focus is on How To Write a Doctoral Thesis, many other important aspects of research-based writing, editing and publishing are addressed in helpful detail.
Related Posts

PhD Success – How To Write a Doctoral Thesis
October 1, 2021

Table of Contents – PhD Success
October 2, 2021

The Essential – Preliminary Matter
October 3, 2021

The Main Body of the Thesis
October 4, 2021
Writing The Methodology Chapter
5 Time-Saving Tips & Tools
By: David Phair (PhD) and Amy Murdock (PhD) | July 2022
The methodology chapter is a crucial part of your dissertation or thesis – it’s where you provide context and justification for your study’s design. This in turn demonstrates your understanding of research theory, which is what earns you marks .
Over the years, we’ve helped thousands of students navigate this tricky section of the research process. In this post, we’ll share 5 time-saving tips to help you effectively write up your research methodology chapter .
Overview: Writing The Methodology Chapter
- Develop a (rough) outline before you start writing
- Draw inspiration from similar studies in your topic area
- Justify every research design choice that you make
- Err on the side of too much detail , rather than too little
- Back up every design choice by referencing literature

1. Develop an outline before you start writing
The first thing to keep in mind when writing your methodology chapter (and the rest of your dissertation) is that it’s always a good idea to sketch out a rough outline of what you are going to write about before you start writing . This will ensure that you stay focused and have a clear structural logic – thereby making the writing process simpler and faster.
An easy method of finding a structure for this chapter is to use frameworks that already exist, such as Saunder’s “ research onion ” as an example. Alternatively, there are many free methodology chapter templates for you to use as a starting point, so don’t feel like you have to create a new one from scratch.
Next, you’ll want to consider what your research approach is , and how you can break it down from a top-down angle, i.e., from the philosophical down to the concrete/tactical level. For example, you’ll need to articulate the following:
- Are you using a positivist , interpretivist , or pragmatist approach ?
- Are you using inductive or deductive reasoning?
- Are you using a qualitative , quantitative, or mixed methods study?
Keep these questions front of mind to ensure that you have a clear, well-aligned line of argument that will maintain your chapter’s internal and external consistency.
Remember, it’s okay if you feel overwhelmed when you first start the methodology chapter. Nobody is born with an innate knowledge of how to do this, so be prepared for the learning curve associated with new research projects. It’s no small task to write up a dissertation or thesis, so be kind to yourself!

2. Take inspiration from other studies
Generally, there are plenty of existing journal articles that will share similar methodological approaches to your study. With any luck, there will also be existing dissertations and theses that adopt a similar methodological approach and topic. So, consider taking inspiration from these studies to help curate the contents of your methodology chapter.
Students often find it difficult to choose what content to include in the methodology chapter and what to leave for the appendix. By reviewing other studies with similar approaches, you will get a clearer sense of your discipline’s norms and characteristics . This will help you, especially in terms of deciding on the structure and depth of discussion.
While you can draw inspiration from other studies, remember that it’s vital to pay close attention to your university’s specific guidelines, so you can anticipate departmental expectations of this section’s layout and content (and make it easier to work with your supervisor). Doing this is also a great way to figure out how in-depth your discussion should be. For example, word-count guidelines can help you decide whether to include or omit certain information.
Need a helping hand?
3. Justify every design choice you make
The golden rule of the methodology chapter is that you need to justify each and every design choice that you make, no matter how small or inconsequential it may seem. We often see that students merely state what they did instead of why they did what they did – and this costs them marks.
Keep in mind that you need to illustrate the strength of your study’s methodological foundation. By discussing the “what”, “why” and “how” of your choices, you demonstrate your understanding of research design and simultaneously justify the relevancy and efficacy of your methodology – both of which will earn you marks.
It’s never an easy task to conduct research. So, it’s seldom the case that you’ll be able to use the very best possible methodology for your research (e.g. due to time or budgetary constraints ). That’s okay – but make sure that you explain and justify your use of an alternate methodology to help justify your approach.
Ultimately, if you don’t justify and explain the logic behind each of your choices, your marker will have to assume that you simply didn’t know any better . So, make sure that you justify every choice, especially when it is a subpar choice (due to a practical constraint, for example). You can see an example of how this is done here.

4. Err on the side of too much detail
We often see a tendency in students to mistakenly give more of an overview of their methodology instead of a step-by-step breakdown . Since the methodology chapter needs to be detailed enough for another researcher to replicate your study, your chapter should be particularly granular in terms of detail.
Whether you’re doing a qualitative or quantitative study, it’s crucial to convey rigor in your research. You can do this by being especially detailed when you discuss your data, so be absolutely clear about your:
- Sampling strategy
- Data collection method(s)
- Data preparation
- Analysis technique(s)
As you will likely face an extensive period of editing at your supervisor/reviewer’s direction, you’ll make it much easier for yourself if you have more information than you’d need. Some supervisors expect extensive detail around a certain aspect of your dissertation (like your research philosophy), while others may not expect it at all.
Remember, it’s quicker and easier to remove/ trim down information than it is to add information after the fact, so take the time to show your supervisor that you know what you’re talking about (methodologically) and you’re doing your best to be rigorous in your research.

5. Provide citations to support each design choice
Related to the issue of poor justification (tip #3), it’s important include high-quality academic citations to support the justification of your design choices. In other words, it’s not enough to simply explain why you chose a specific approach – you need to support each justification with reference to academic material.
Simply put, you should avoid thinking of your methodology chapter as a citation-less section in your dissertation. As with your literature review, your methods section must include citations for every decision you make, since you are building on prior research. You must show that you are making decisions based on methods that are proven to be effective, and not just because you “feel” that they are effective.
When considering the source of your citations, you should stick to peer-reviewed academic papers and journals and avoid using websites or blog posts (like us, hehe). Doing this will demonstrate that you are familiar with the literature and that you are factoring in what credible academics have to say about your methodology.
As a final tip, it’s always a good idea to cite as you go . If you leave this for the end, then you’ll end up spending a lot of precious time retracing your steps to find your citations and risk losing track of them entirely. So, be proactive and drop in those citations as you write up . You’ll thank yourself later!
Let’s Recap…
In this post, we covered 5 time-saving tips for writing up the methodology chapter:
- Look at similar studies in your topic area
- Justify every design choice that you make
- Back up every design choice by referencing methodology literature
If you’ve got any questions relating to the methodology chapter, feel free to drop a comment below. Alternatively, if you’re interested in getting 1-on-1 help with your thesis or dissertation, be sure to check out our private coaching service .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

What data analysis method can work best for my study. I am using a mixed method in the study. I am developing a framework to address the challenges faced by the taxi operators as entrepreneurs. I will need to analyse both using qualitative and quantitative.
How to find standard deviation for non numerical data
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Dissertation Planner - Writing the Methodology: Writing the methodology
- Learning from lectures
- Managing your time
- Effective reading
- Evaluating Information
- Critical thinking
- Presentation skills
- Studying online
- Writing home
- Maths and Statistics Support
- Problem solving
- Maths skills by discipline
- Introduction to research skills
- Primary research
- Research methods
- Managing data
- Research ethics
- Citing and referencing
- Searching the literature
- What is academic integrity?
- Referencing software
- Integrity Officer/Panel
- Intellectual property and copyright
- Digital skills home
What does a methodology chapter need to include? What's the best way to structure the chapter? What does validity in research mean?
- For answers to these questions, and further tips on writing this chapter of your dissertation, consult our Writing the Methodology guide .
- You can also watch our recorded webinar Writing the Dissertation: the Methods or Methodology to learn the difference between the methods and methodology, what's expected and practical ways of structuring the chapter in a clear and coherent way.
Working with primary research? Take a look at our webpage for guidance on different forms of Primary research .
Look at our Research methods webpage to help you identify the right methodology for your dissertation.
- Last Updated: Mar 13, 2024 3:14 PM
- URL: https://library.soton.ac.uk/sash/dissertation-planner/writing-methodology

How to plan, structure and write every chapter in your PhD
In this collection, we’ll walk you through each chapter of your thesis. You’ll learn what goes where and how it fits together.

The PhD Discussion Chapter: What It Is & How To Write It
Your PhD discussion chapter is your thesis's intellectual epicenter. Think of it as the scholarly equivalent of a courtroom closing argument, where you summarise the evidence and make your case. Perhaps that’s why it’s so tricky - the skills you need in your...

Everything you wanted to know about structuring your PhD but were too afraid to ask
Understanding how to structure your PhD is tough. It helps to break it down into four distinct sections. In this guide, we explain how.

How to find the thread that runs through your PhD thesis
You probably worry about finding the thread that runs through the PhD thesis. In this guide we walk you through what’s required.


How to edit a PhD thesis (without going mad)
Your thesis takes a lot of time to research, ideate, and write. Here’s how to properly edit a PhD thesis such that you impress your examiners and achieve even greater success.

The 9 most effective ways to achieve PhD success
Writing a PhD is physically, intellectually and emotionally daunting. You may spend each day doubting yourself, not sure if you’re making the right choices and unsure whether you’ve got what it takes. During my life, I’ve helped thousands of PhD students like...

How To Structure A PhD Thesis
Struggling to understand what goes where? Let us walk you through a non-nonsense guide that’ll teach you how to structure a PhD thesis.

The difference between empirical and discussion chapters (and how to write them)
There is a very important distinction that needs to be made between the empirical and discussion sections/chapters. It is a common misconception that the empirical chapters are the place for your analysis. Often this confuses the reader.

Five tips to improve your PhD thesis
Regardless of what stage of the writing process you are at, there are five overarching tips you need to keep in mind if you want to improve your PhD thesis.

What are you doing and how are you doing it? Articulating your aims and objectives.
How long does it take the person reading your thesis to understand what you’re doing and how you’re doing it? If the answer is anything other than ’in the the opening lines of the thesis’, keep reading.

Learn how to write a PhD proposal that will stand out from the rest
When stripped down to its basic components, the PhD proposal explains the what and the why of your research. What it will be about and why it will be important.

Easily understand how to write a PhD thesis introduction
Get the introduction right and the rest of your dissertation will follow. Mess it up and you’ll be struggling to catch up. The introduction is the place to factually recount what it is you will be discussing in the thesis. Learn more in this detailed guide.

Last impressions count – writing your PhD thesis conclusion
The conclusion is the last thing your examiner will read before they write their viva report. You need to make sure it stands out.

What is a dissertation abstract and how do I write one for my PhD?
Don’t underestimate how hard it is to write a PhD thesis abstract. When I wrote mine I though it’d be straightforward. Far from it. It’s tricky. You have to condense hundred of pages and years of work into a few hundred words.

Russian (dolls) to the rescue – how to structure an argument in your PhD
At the core of the PhD are arguments. Lots of them. Some more important and some very specific. When you understand how to structure an argument, your thesis reads clearly and logically. If you don’t the reader ends up confused and your thesis suffers.

Drowning in a sea of authors – How to be critical in a PhD literature review.
Don’t get lost in a sea of authors when you write your PhD literature review. Instead be critical. In this guide we explain how.

Wrestling an elephant into a cupboard: how to write a PhD literature review in nine easy steps
When I was writing my PhD I hated the literature review. I was scared of it. I thought it would be impossible to grapple. So much so that it used to keep me up at night. Now I know how easy it can be and I’m sharing my top tips with you today.

A Template To Help You Structure Your PhD’s Theoretical Framework Chapter
In this guide, I explain how to use the theory framework template. The focus is on the practical things to consider when you’re working with the template and how you can give your theory framework the rockstar treatment.

How To Structure A PhD With Our PhD Writing Template
Our PhD Writing Template allows you to visualise your PhD on one page. Here we explain how to fill it in and how it can help you structure each chapter.

Eureka! When I learnt how to write a theoretical framework
The theoretical framework is so important, but so misunderstood. Here we explain it is in simple terms: as a toolbox.
Explore Other PhD Knowledge Base Collections
Eight collections of free resources to help you along the phd journey.

Mastering your theory and literature review chapters

How to structure and write every chapter of the PhD

How to stay motivated and productive

Techniques to improve your writing and fluency

Advice on maintaining good mental health

Resources designed for non-native English speakers

Explore our back-catalogue of motivational advice
Each week we send out a short, motivational email to over 4,000 students. Here you can sign up and access the archive.

A free one-page PhD structure template

What Is a Dissertation Methodology?
How to choose your methodology, final thoughts, how to write your dissertation methodology.
Updated September 30, 2021

Due to the complexities of the different research methods, writing your dissertation methodology can often be the most challenging and time-consuming part of your postgraduate dissertation .
This article focuses on the importance of writing a good PhD or master's dissertation methodology – and how to achieve this.
A postgraduate dissertation (or thesis) is usually formed of several detailed sections, including:
Abstract – A summary of your research topic.
Introduction – Provides background information on your topic, putting it into context. You will also confirm the main focus of your study, explain why it will add value to your area of interest and specify your key objectives.
Literature Review – A critical review of literature that relates to your chosen research topic. You will also need to identify which gap in the literature your study aims to address.
Methodology – Focuses on the research methods used within your research.
Results – Used to report on your main findings and how these relate to your research question.
Conclusion – Used to confirm the answer to your main research question, reflect on the research process and offer recommendations on future research.
The dissertation methodology forms the skeleton of any research project. It provides the reader with a clear outline of the methods you decided to use when carrying out your research.
By studying your dissertation methodology, the reader will be able to assess your research in terms of its validity and reliability.
In line with the outline given above, the methodology chapter usually appears after the literature review . Your methodology should be closely linked to the research that you conducted as part of this review, as well as the questions you aim to answer through your research and analysis.
Taking the time to find out about the different types of research available to you will allow you to identify any potential drawbacks to the method you have chosen to use. You should then be able to make allowances or adjustments to address these when it comes to carrying out your research.

Choosing your methodology will largely depend on the discipline of the qualification you are studying for and the question your dissertation will seek to answer. In most cases, you will use quantitative or qualitative research methods, although some projects will benefit from using a combination of both.
Quantitative research methods are used to gather numerical information. This research method is particularly useful if you are seeking to count, categorise, measure or identify patterns in data. To collect quantitative data, you might choose to conduct experiments, tests or surveys.
Qualitative research methods are used to gather non-statistical data. Instead of using numbers to create charts or graphs, you will need to categorise the information according to identifiers. This research method is most useful if you are seeking to develop a hypothesis. To collect qualitative data, you might choose to conduct focus groups, interviews or observations.
What to Include in Your Dissertation Methodology
Below is a dissertation methodology example to show you what information to include:
You will need to reiterate your research topic or question and give an overview of how you plan to investigate this. If there were any ethical or philosophical considerations to be made, give details.
For example, you may have sought informed consent from the people taking part in interviews or surveys.
Outline of the Methods Chosen
Confirm whether you have chosen to use quantitative research, qualitative research or a combination of both.
When choosing between qualitative and quantitative research methods, you will need to carry out initial literature and textbook research to establish the standard research methods that are normally used within your chosen area of research.
If you are not sure where to start, you could visit the library at your college or university and ask one of the librarians to help you to identify the most relevant texts.
Explanation of the Methods Chosen
Explain your rationale for selecting your chosen research methods. You should also give an overview of why these were more appropriate than using another research method.
Think about where and when the research took place and who was involved. For example, this might include information on the venue used for interviews or focus groups, dates and timescales, and whether participants were part of a particular demographic group.
Here are some examples of the type of information you may wish to include:
Qualitative Research Methods
Personal observations – Where and when did you conduct the observations? Who did you observe? Were they part of a particular community or group? How long did each observation take? How did you record your findings – did you collect audio recordings, video footage or written observations?
Focus groups – Where and when did the focus group take place? Who was involved? How were they selected? How many people took part? Were the questions asked structured, unstructured or semi-structured? Remember to include a copy of the questions that were used as an appendix.
Interviews – Where and when did the interviews take place? Who took part? How did you select the participants? What type of questions did you ask? How did you record your findings? Remember to include a copy of the questions that were used as an appendix.
The researcher’s objective was to find out customer perceptions on improving the product range currently offered by Company Y. Semi-structured interviews were held with 15 returning customers from the key target demographic for Company Y (18- to 35-year-olds). For research purposes, a returning customer was defined as somebody who purchased products from Company Y at least two times per week during the past three months. The interviews were held in an office in the staff area of the retail premises. Each interview lasted approximately 25 minutes. Responses were recorded through note-taking as none of the respondents wished to give their consent to be filmed.
Quantitative Research Methods
Existing information or data – What were the sources of the material used? How did you select material? Did you only use data published within a particular time frame?
Experiments – What tools or equipment did you use? What techniques were required? Note that when conducting experiments, it is particularly important to provide enough information to allow another researcher to conduct the experiment and obtain the same results.
Surveys – Were respondents asked to answer multiple-choice questions or complete free-text fields? How many questions were used? How long were people given to answer all of the questions? What were the demographics of the participants? Remember to include a copy of the survey in the appendices.
The survey was made up of 10 multiple-choice questions and 5 questions to be rated using a 5-point Lickert scale. The objective was to have 250 customers of Company Z complete the survey at the Company Z HQ between 1st and 5th February 2019, between the hours of 12 p.m. and 5 p.m. For research purposes, a customer was defined as any person who had purchased a product from Company Z during 2018. Customers completing the survey were allowed a maximum of 10 minutes to answer all of the questions. 200 customers responded, however not all of the surveys were completed in full, so only 150 survey results were able to be used in the data analysis.
How Was the Data Analysed?
If you have chosen to use quantitative research methods, you will need to prepare the data before analysing it – for example, you will need to check for variables, missing data and outliers. If you have used computer software to aid with analysis, information on this should also be included.
For qualitative data, you will need to categorise and code the ideas and themes that are identified from the raw data. You may also need to use techniques such as narrative analysis or discourse analysis to interpret the meaning behind responses given.
What Materials and Equipment Were Used During the Research?
This could include anything from laboratory equipment used in a scientific experiment to computer software used to analyse the results.
Were There Any Hurdles or Difficulties Faced During the Research?
If so, what were they and how did you manage to overcome them? This could be anything from difficulties in finding participants, problems obtaining consent or a shortage of the required resources needed to conduct a scientific experiment.
This paragraph should be used to evaluate the research you have conducted and justify your reasons for choosing this approach.
You do not need to go into great detail, as you will present and discuss your results in-depth within your dissertation’s ‘Results’ section.
You will need to briefly explain whether your results were conclusive, whether there were any variables and whether your choice of methodology was effective in practice.

Tips for Writing Your Dissertation Methodology
The objective for the methodology is not only to describe the methods that you used for your research. You will also need to demonstrate why you chose to use them and how you applied them.
The key point is to show that your research was conducted meticulously.
Try to keep your writing style concise and clear; this will ensure that it is easy for the reader to understand and digest.
Here are five top tips to consider when writing your dissertation methodology:
1. Look at Other Methodology Sections
Ask your supervisor to provide you with a few different examples of previously written dissertations. Reading through methodologies that have been written by past students will give you a good idea of what your finished methodology section should look like.
2. Plan Your Structure
Whichever research methods you have chosen to use, your dissertation methodology should be a clearly structured, well written section that gives a strong and justified argument for your chosen research methods.
You may wish to use headings such as:
- Research methods
- Explanation of research methods chosen
- Data analysis and references
Once you have drafted an outline, ask your supervisor for advice on whether there is anything you have missed and whether your structure looks logical.
3. Consider Your Audience
When writing your methodology, have regard for the people who are likely to be reading it. For example, if you have chosen to use research methods that are commonly chosen within your area of research or discipline, there is no need to give a great deal of justification or background information.
If you decide to use a less popular approach, it is advisable to give much more detailed information on how and why you chose to use this method.
4. Remain Focused on Your Aims and Research Questions
Your dissertation methodology should give a clear indication as to why the research methods you have chosen are suitable for the aims of your research.
When writing your dissertation methodology, ensure that you link your research choices back to the overall aims and objectives of your dissertation. To help you to remain focused, it can be helpful to include a clear definition of the question you are aiming to answer at the start of your methodology section.
5. Refer to Any Obstacles or Difficulties That You Dealt With
If you faced any problems during the data collection or analysis phases, use the methodology section to talk about what you did to address these issues and minimise the impact.
Whether you are completing a PhD or master's degree, writing your thesis or dissertation methodology is often considered to be the most difficult and time-consuming part of completing your major research project.
The key to success when writing a methodology section is to have a clear structure. Remember, the purpose of the methodology section of your research project is to ensure that the reader has a full understanding of the methods you have chosen.
You should use your methodology section to provide clear justification as to why you have chosen a particular research method instead of other potential methods. Avoid referring to your personal opinions, thoughts or interests within your methodology; keep the information that you include factual and ensure that everything is backed up by appropriate academic references.
You might also be interested in these other Wikijob articles:

Or explore the Postgraduate / PHD sections.

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
How to Write the Methodology Chapter: The Complete Guide
by Antony W
April 20, 2022

In this lesson, you’ll learn how to write the methodology chapter of a thesis, dissertation, or a research paper, step-by-step. So if you’ve reached this section in your assignment and you simply no idea how to proceed, this article will point you in the right direction.
You’ll learn what the methodology chapter is about and how you can go about writing one by following a systematic approach guaranteed to help you complete the project faster.
By definition, the methodology chapter of a thesis, dissertation, or research paper is the section where you explain about the specific research design options used in your research. It’s in the methodology chapter that you explain the process you used to design your research and give a justification for the research design.
In other words, the methodology section should clearly demonstrate:
- Whether you conducted quantitative or qualitative research
- The approach you used to collect the data
- What your approach to analyzing the data was and
- The kind of sampling that you did
With that said, let’s get into more details on dealing with the methodology chapter of your research work.
What is the Methodology Chapter for a Research Paper and Dissertation?
In your methodology chapter, you’ll explain the conceptual foundations of your study as well as the specific research design decisions you’ve made. The purpose of this chapter is to explain how you designed your research.
There are two reasons why your research paper, thesis, and dissertation should have a methodology section:
- It shows that you understand the concept of research design theory, that you understand what you’re doing in research, and that the results you’ll present have a high degree of credibility.
- Because it outlines the steps you took to do and analyze your research, the methodology chapter is what sets your study apart from the others. It also allows you to identify and describe any methodological concerns or problems that you ran into, as well as explain how you dealt with them.
How to Write The Methodology Chapter – Step-by-Step
It’s worth mentioning that the methodology chapter’s specific format and contents will differ based on the study topic and the university. We strongly recommend that you check with your professor to find out what structure they would like you to use.
More often than not, they will allow you to use the standard structure for your paper, which should make the writing process easier for you. Ideally, the methodology chapter of your research paper, thesis, or dissertation should have the following sections:
- Introduction
- Research design
- Methodological limitation
- A concluding summary
Let’s look at each section in more details below:
The Introduction
The methodology chapter should contain a brief introduction of your dissertation or thesis. You should remind your readers about the emphasis of your study, particularly the research objectives.
Your research design must correspond with your research aims, objectives, and research questions, so include this up front to remind the reader what you intend to accomplish with your research design.
We strongly recommend that you explain how you’ve organized the chapter. Doing so will make it easy for the reader to have a clear roadmap of what to expect from reading the rest of the section of your methodology chapter.
Research Design
We like to refer to research design as the heart of the methodology chapter because it presents your research design in great depth to the reader. The information you provide here should be good enough to justify the design choices you made for your paper.
Here’s how to approach it:
1. Describe Your Methodological Approach
Start by explaining the research subject or problem you looked into. It could be that you wanted to methodically define something’s qualities, investigate a little-studied issue, or prove a cause-and-effect relationship. Whatever it is, write it down because it will guide your reader throughout the other section of the research design.
Some questions to think about when working on your methodological approach include:
- Did you require quantitative or qualitative data?
- Was it necessary for you to obtain primary data personally, or did you rely on secondary data gathered by others?
- Did you collect descriptive data by gathering observations without intervening, or did you collect experimental data by altering variables?
- Were there any ethical factors involved in your decision-making?
2. Explain Your Methods of Data Collection
Next step in research design is to explain the data collection method you used to gather information for your research project.
The following table is a summary of the data collection methods as used in research writing:
3. Explain Your Data Analysis Methods
The next step is to describe how you processed and analyzed the data.
- Quantitative analysis: Your analysis in quantitative research will be on numbers. You may include how you prepared the data for analysis, the computer software you used, and the statistical you employed.
- Qualitative analysis: Your analysis in qualitative research will be based on language, visuals, and observations (often involving some form of textual analysis).
4. Methodological Limitations
You can admit to the approach’s limits or flaws, but explain why the advantages exceeded the disadvantages. Explain why prior strategies were ineffective in achieving your goals, and how this strategy adds new information or insight.
Your methodology should be a well-structured, unambiguous document that argues for your approach rather than a collection of technical information and processes.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
- How it works

Chapter 3 – Dissertation Methodology (example)
Disclaimer: This is not a sample of our professional work. The paper has been produced by a student. You can view samples of our work here . Opinions, suggestions, recommendations and results in this piece are those of the author and should not be taken as our company views.
Type of Academic Paper – Dissertation Chapter
Academic Subject – Marketing
Word Count – 3017 words
Introduction
The current chapter presents developing the research methods needed to complete the experimentation portion of the current study. The chapter will discuss in detail the various stages of developing the methodology of the current study. This includes a detailed discussion of the philosophical background of the research method chosen. In addition to this, the chapter describes the data collection strategy, including the selection of research instrumentation and sampling. The chapter closes with a discussion on the analysis tools used to analyse the data collected.
Selecting an Appropriate Research Approach
Creswall (2013) stated that research approaches are plans and procedures that range from steps, including making broad assumptions to detailed methods of data collection, analysis, and interpretation. The several decisions involved in the process are used to decide which approach should be used in a specific study that is informed using philosophical assumptions brought to the study (Creswall 2013). Included in this are procedures of inquiry or research designs and specific research methods used for data collection, its analysis, and finally, its interpretation. However, Guetterman (2015); Lewis (2015); and Creswall (2013) argue that the selection of the specific research approach is based on the nature of the research problem, or the issue that is being addressed by any study, personal experiences of the researchers’, and even the audience for which the study is being developed for.
There are many ways to customise research approaches to develop an approach most suited for a particular study. However, the main three categories with which research approaches are organised include; qualitative, quantitative, and mixed research methods. Creswall (2013) comments that all three approaches are not considered so discrete or distinct from one another. Creswall (2013) states, “qualitative and quantitative approaches should not be viewed as rigid, distinct categories, polar opposite, or dichotomies” (p.32). Newmand and Benz (1998) pointed out that quantitative and qualitative approaches instead represent different ends on a continuum since a study “tends” to be more quantitative than qualitative or vice versa. Lastly, mixed methods research resides in the middle of the continuum as it can incorporate elements and characteristics of both quantitative and qualitative approaches. Lewis (2015) points out that the main distinction that is often cited between quantitative and qualitative research is that it is framed in terms of using numbers rather than words; or using closed-ended questions for quantitative hypotheses over open-ended questions for qualitative interview questions. Guetterman (2015) points out that a clearer way of viewing gradations of differences between the approaches is to examine the basic philosophical assumptions brought to the study, the kinds of research strategies used, and the particular methods implemented in conducting the strategies.
Underlying Philosophical Assumptions
An important component of defining the research approach involves philosophical assumptions that contribute to the broad research approach of planning or proposing to conduct research. It involves the intersection of philosophy, research designs and specific methods as illustrated in Fig. 1 below.
Figure 3.2-1- Research Onion (Source; Saunders and Tosey 2013)
Slife and Williams (1995) have argued that philosophical ideas have remained hidden within the research. However, they still play an influential role in the research practice, and it is for this reason that it is most identified. Various philosophical assumptions are used to construct or develop a study. Saunders et al. (2009) define research philosophy as a belief about how data about a phenomenon should be gathered, analysed and used. Saunders et al. (2009) identify common research philosophies such as positivism, realism, interpretivism, subjectivism, and pragmatism. Dumke (2002) believes that two views, positivism and phenomenology, mainly characterise research philosophy.
Positivism reflects acceptance in adopting the philosophical stance of natural scientists (Saunders, 2003). According to Remenyi et al. (1998), there is a greater preference in working with an “observable social reality” and that the outcome of such research can be “law-like” generalisations that are the same as those which are produced by physical and natural scientists. Gill and Johnson (1997) add that it will also emphasise a high structure methodology to allow for replication for other studies. Dumke (2002) agrees and explains
that a positivist philosophical assumption produces highly structured methodologies and allows for generalisation and quantification of objectives that can be evaluated by statistical methods. For this philosophical approach, the researcher is considered an objective observer who should not be impacted by or impact the subject of research.
On the other hand, more phenomenological approaches agree that the social world of business and management is too complex to develop theories and laws similar to natural sciences. Saunders et al. (2000) argue that this is the reason why reducing observations in the real world to simple laws and generalisations produces a sense of reality which is a bit superficial and doesn’t present the complexity of it.
The current study chooses positivistic assumptions due to the literature review’s discussion of the importance of Big Data in industrial domains and the need for measuring its success in the operations of the business. The current study aims to examine the impact that Big Data has on automobile companies’ operations. To identify a positive relationship between Big Data usage and beneficial business outcomes, the theory needs to be used to generate hypotheses that can later be tested of the relationship which would allow for explanations of laws that can later be assessed (Bryman and Bell, 2015).
Selecting Interpretive Research Approach
Interpretive research approaches are derived from the research philosophy that is adopted. According to Dumke (2002), the two main research approaches are deductive and inductive. The inductive approach is commonly referred to when theory is derived from observations. Thus, the research begins with specific observations and measures. It is then from detecting some pattern that a hypothesis is developed. Dumke (2002) argues that researchers who use an inductive approach usually work with qualitative data and apply various methods to gather specific information that places different views. From the philosophical assumptions discussed in the previous section, it is reasonable to use the deductive approach for the current study. It is also considered the most commonly used theory to establish a relationship between theory and research. The figure below illustrates the steps used for the process of deduction.
Data Collection
- confirmed or rejected
- Revision of theory
Based on what is known about a specific domain, the theoretical considerations encompassing it a hypothesis or hypotheses are deduced that will later be subjected to empirical enquiry (Daum, 2013). Through these hypotheses, concepts of the subject of interest will be translated into entities that are rational for a study. Researchers are then able to deduce their hypotheses and convert them into operational terms.
Hire an Expert Dissertation Chapter Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

Justifying the Use of Quantitative Research Method
Saunders (2003) notes that almost all research will involve some numerical data or even contain data quantified to help a researcher answer their research questions and meet the study’s objectives. However, quantitative data refers to all data that can be a product of all research strategies (Bryman and Bell, 2015; Guetterman, 2015; Lewis, 2015; Saunders, 2003). Based on the philosophical assumptions and interpretive research approach, a quantitative research method is the best suited for the current study. Haq (2014) explains that quantitative research is about collecting numerical data and then analysing it through statistical methods to explain a specific phenomenon. Mujis (2010) defends the use of quantitative research because, unlike qualitative research, which argues that there is no pre-existing reality, quantitative assumes that there is only a single reality about social conditions that researchers cannot influence in any way. Also, qualitative research is commonly used when there is little to no knowledge of a phenomenon, whereas quantitative research is used to find the cause and effect relationship between variables to either verify or nullify some theory or hypothesis (Creswall 2002; Feilzer 2010; Teddlie and Tashakkori 2012).
Selecting an Appropriate Research Strategy
There are many strategies available to implement in a study, as evidenced from Fig. 1. There are many mono-quantitative methods, such as telephone interviews, web-based surveys, postal surveys, and structured questionnaires (Haq 2014). Each instrument has its own pros and cons in terms of quality, time, and data cost. Brymand (2006); Driscoll et al. (2007); Edwards et al. (2002); and Newby et al. (2003) note that most researchers use structured questionnaires for data collection they are unable to control or influence respondents, which leads to low response rates but more accurate data obtained. Saunders and Tosey (2015) have argued that quantitative data is simpler to obtain and more concise to present. Therefore, the current study uses a survey-based questionnaire (See Appendix A).
Justifying the use of Survey Based Questionnaire
Surveys are considered the most traditional forms of research and are used in non-experimental descriptive designs that describe some reality. Survey-based questionnaires are often restricted to a representative sample of a potential group of the study’s interest. In this case, it is the executives currently working for automobile companies in the UK. The survey instrument is then chosen for its effectiveness at being practical and inexpensive (Kelley et al., 2003). Due to the philosophical assumptions, interpretive approach, and methodological approach, the survey design for the current study is considered the best instrument in line with these premises, besides being cost-effective.
Empirical Research Methodology
Research design.
This section describes how research is designed to use the techniques used for data collection, sampling strategy, and data analysis for a quantitative method. Before going into the strategies of data collection and analysis, a set of hypotheses were developed.
Hypotheses Development
The current study uses a quantitative research approach, making it essential to develop a set of hypotheses that will be used as a test standard for the mono-method quantitative design. The following are a set of hypotheses that have been developed from the examination of the literature review.
H1- The greater the company’s budget for Big Data initiatives (More than 1 million GBP), the greater its ability to monetise and generate new revenues.
H2- The greater the company’s budget for Big Data initiatives (More than 1 million GBP) the more decrease in expenses in found.
H3- The greatest impact of Big Data on a company is changing the way business is done.
H4- Big Data integrating with a company has resulted in competitive significance.
H5- The analytical abilities of a company allows for achieved measurable results.
H6- Investing in Big Data will lead to highly successful business results.
H7- A business’s operations function is fuelling Big Data initiatives and effecting change in operations.
H8- The implementation of Big Data in the company has positive impacts on business.
This section includes the sampling method used to collect the number of respondents needed to provide information, then analysed after collection.
Sampling Method
Collis (2009) explains that there are many kinds of sampling methods that can be used for creating a specific target sample from a population. This current study uses simple random sampling to acquire respondents with which the survey will be conducted. Simple random sampling is considered the most basic form of probability sampling. Under the method, elements are taken from the population at random, with all elements having an equal chance of being selected. According to () as of 2014, there are about thirty-five active British car manufacturers in the UK, each having an employee population of 150 or more. This is why the total population of employees in car manufacturers is estimated to be 5,250 employees. The sample, therefore, developed used the following equation;
2 × (1 − )
+( 2 × (1− ) ) 2
Where; N is the population size, e is the margin of error (as a decimal), z is confidence level (as a z-score), and p is percentage value (as a decimal). Thus, the sample size is with a normal distribution of 50%. With the above equation, a population of 5,250; with a 95% confidence level and 5% margin of error, the total sample size needed for the current equals 300. Therefore, N=300, which is the sample size of the current study.
The survey develops (see Appendix A) has a total of three sections, A, B, and C, with a total of 39 questions. Each section has its own set of questions to accomplish. The survey is a mix of closed-end questions that look to comprehend the respondents’ demographic makeup, the Big Data initiatives of the company, and the impact that Big Data was having on their company. The survey is designed to take no longer than twenty minutes. The survey was constructed on Survey Monkey.com, and an online survey provided website. The survey was left on the website for a duration of 40 days to ensure that the maximum number of respondents were able to answer the survey. The only way that the survey was allowed for a respondent is if they passed a security question as if they were working for an automobile company in the UK when taking the survey. Gupta et al. (2004) believe that web surveys are visual stimuli, and the respondent has complete control about whether or how each question is read and understood. That is why Dillman (2000) argued that web questionnaires are expected to resemble those taken through the mail/postal services closely.
Data Analysis
The collected data is then analysed through the Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) version 24 for descriptive analysis. The demographic section of the survey will be analysed using descriptive statistics. Further analysis of the data includes regression analysis. Simple regression analysis includes only one independent variable and one dependent variable. Farrar and Glauber (1967) assert that the purpose of regression analysis is to estimate the parameters of dependency, and it should not be used to determine the interdependency of a relationship.
Need a Dissertation Chapter On a Similar Topic?
Conclusions.
The chapter provides a descriptive and in-depth discussion of the methods involved in the current study’s research. The current study is looking towards a quantitative approach that considers positivism as its philosophical undertaking, using deductive reasoning for its interpretive approach, is a mono-quantitative method that involves the use of a survey instrument for data collection. The methodology chapter also provided the data analysis technique, which is descriptive statistics through frequency analysis and regression analysis.
Examples of results;
Question 8- Of these staff, are mostly working in or for your consumer-facing (B2C) businesses, your commercial or wholesale (B2B) businesses, or both?
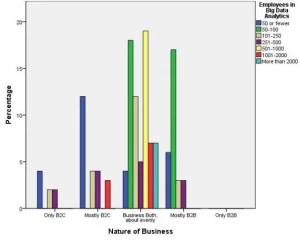
Based on the illustration, nineteen (19) respondents indicated that 501-1000 employees are dedicated to analytics for both B2B and B2C. The category of using Big Data analytics for both B2B and B2C comprises the most agreement of respondents with 72 of 132 indicated.
The figure above represents the respondents’ answers to their automobile company’s plan for measuring Big Data’s success. Of the 132 participants, 44.70 per cent responded that the company is planning on using quantitative metrics associated with business performance to analyse if Big Data is actually successful. Another, 30.30 per cent indicated that their company was planning on using qualitative metrics tied to business performance. Using business performance to analyse the success of Big Data is coherent to the results of the literature review that indicated previous studies of doing such. As an automobile company, they need to know the results of using Big Data analytics, and that is only by using business performance indicators regardless of being qualitative or quantitative.
Fig. 4.3-6 portrays the response of participants in regards to actually achieving measurable results from Big Data. According to 68.18 per cent of respondents, the company that they worked for did indeed show measurable results from their investments in Big Data. However, 31.82 per cent indicated that there was indeed no measurable result in investing in Big Data.
Bryman, A., Bell, E., 2015. Business Research Methods. Oxford University Press.
Daum, P., 2013. International Synergy Management: A Strategic Approach for Raising Efficiencies in the Cross-border Interaction Process. Anchor Academic Publishing (aap_verlag).
Dümke, R., 2002. Corporate Reputation and its Importance for Business Success: A European
Perspective and its Implication for Public Relations Consultancies. diplom.de.
Guetterman, T.C., 2015. Descriptions of Sampling Practices Within Five Approaches to Qualitative Research in Education and the Health Sciences. Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung /
Forum: Qualitative Social Research 16.
Haq, M., 2014. A Comparative Analysis of Qualitative and Quantitative Research Methods and a Justification for Adopting Mixed Methods in Social Research (PDF Download Available).
ResearchGate 1–22. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.1945.8640
Kelley, K., Clark, B., Brown, V., Sitzia, J., 2003. Good practice in the conduct and reporting of survey research. Int J Qual Health Care 15, 261–266. doi:10.1093/intqhc/mzg031
Lewis, S., 2015. Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing Among Five Approaches.
Health Promotion Practice 16, 473–475. doi:10.1177/1524839915580941
Saunders, M., 2003. Research Methods for Business Students. Pearson Education India.
Saunders, M.N.K., Tosey, P., 2015. Handbook of Research Methods on Human Resource
Development. Edward Elgar Publishing.
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this Dissertation Chapter and no longer wish to have it published on the www.ResearchProspect.com then please:
Request The Removal Of This Dissertation Chapter
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write methodology chapter of a dissertation.
To write the methodology chapter of a dissertation:
- Describe research design & approach.
- Explain data collection methods.
- Justify chosen methods.
- Address limitations.
- Analyse data.
- Ensure replicability.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Sample Research Methodology Chapter: Quantitative Research
The purpose of this chapter is to explain in detail the research methods and the methodology implemented for this study. The chapter will explain first of all the choice of research approach, then the research design, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of the research tools chosen. This will be followed by a discussion on their ability to produce valid results, meeting the aims and objectives set by this dissertation. The chapter then goes on to discuss the sample size and the sampling strategy applied by the author, and the data analysis methods which have been used. It concludes with a brief discussion on the ethical considerations and limitations posed by the research methodology, as well as problems encountered during the research.
Research Approach
Order custom essay Sample Research Methodology Chapter: Quantitative Research with free plagiarism report
This dissertation makes use of qualitative research strategy, where the research approach implemented has been that of interpretivism. Willis (2007) defines interpretivism as an approach which is implemented by the researcher in order to synthesize facts which are derived mainly from secondary sources, and which are qualitative in nature. He also observes that one characteristics of interpretivism is that these facts are abstract in nature, and governed by a variety of factors which are non-tangible and difficult to measure. These can be economic, social, or cultural factors. Therefore for the purposes of this research, the author chose the interpretivist approach, rather than the positivist and the pragmatist approaches, because abstract, non-quantifiable variables such as “”, “finding the arts in business and working with them to create a memorable experience”, comparing “traditional management” with “performing art management” and analysing whether performing techniques and their application into business can have positive influence on business practice were part of the objectives of the dissertation. These are all elements, which are not easily quantifiable (measureable), and between which different and complex connections were found to exist, therefore interpretivism was found to be most applicable.
Research Design
This research makes use of a qualitative research strategy in the sense that there will be no numeric data or quantitative data was produced (Bell, 2005; Sarantakos, 2013; Silverman, 2004). A qualitative research strategy is particularly applicable for the purposes of this research, where the connection between several different variables had to be established through interpretation. Also, the research makes use of triangulation because triangulation gives the opportunity to approach the research objectives from different viewpoints (Cohen and Manion, 2002; Altrichter et. al, 2008), obtaining a more nuanced view of the connections between the different variables. For this study, triangulation was very useful because the researcher aimed to find the intersection between two very different variables belonging to very distinct industries – the arts (performing arts in particular) and business. This necessitated questionnaires and interviews with the employees who have been recipients of the management with performing art model and with their managers as well.
The validity and the advantages and disadvantages of the tools used to implement the research strategy will be discussed next.
Research Methods
For the purposes of this research, the writer has decided to use a combination of two of the classic social sciences research tools – questionnaires and interviews (Winchester, 1999; Sarantakos, 2013; Silverman, 2004; Greenfield, 2002). The questionnaires will be distributed among managers from several companies which have used art elements as part of their management techniques, as well as among carefully selected employees of the same companies, who form part of the team of the same managers. As a complementary method, the writer conducted interviews with an equal number of representatives of each group. The advantages and disadvantages of each method are discussed below.
Questionnaires
Questionnaires were chosen for this research because they are a reliable and quick method to collect information from multiple respondents in an efficient and timely manner. This is especially important when it comes to large projects, with several complex objectives, where time is one of the major constraints (Greenfield, 2002; Silverman, 2004; Bell, 2005). This study was no exception and questionnaires were a quick and effective way for the researcher to reach multiple respondents within several weeks. A general disadvantage of the questionnaires however is their fixed and strict format, which eliminates the possibility for more in-depth or abstract observation (Bell, 2005; Sarantakos, 2013). Again, this study was not an exception from this rule, as the questionnaires provided linear and clear results, but many elements from the research were left uncovered.
In order to cover more abstract aspects of the research, the author chose as a complementary method structured interviews consisting of several questions, which were distributed among representatives of each participant group. Interviews are often used as complementary research method in the social sciences, because they give the opportunity for a more in-depth, open discussion, and more informal, free interaction between the interviewer and the interviewee (Potter, 2002; Winchester, 1999; Sarantakos, 2013). Despite being considered a disadvantage because it produces subjective results, the flexible format of the interviews was a major advantage for this study, as some nuances of the research such as exploring “emotions”, and “creating memorable experience” could not be properly captured with the questionnaire design. Of course the results from the interviews are not generalizable, because of the subjectivity of data obtained. On the other hand, their flexible format contributed for a deeper explanation and understanding of the connection between performing art and business performance, and if the researcher could have done the dissertation again, this would probably be chosen as the primary, not the secondary research method.
Other methods
Upon embarking on this research, the author initially considered focus groups and participant observation as possible research methods, due to the behavioural elements contained in this research.. However, because of time constraints and cost, these research methods were not opted for.
Initially the researcher also considered researching two groups of employees by comparison – one coming from an organisation where the performance management model is used, and another one, where this model is not used. They would be both given the same questionnaire. This approach was overruled however, because it does not reflect the interactive nature of the model being studied in which managers and business leaders play crucial role.
Sampling Strategy
For the purposes of this study, the writer had to examine two separate groups of participants. A method of stratified sampling has been used, as the relationships between different sub-groups had to be observed (Kirby et. al, 2000: 339). Furthermore, a particular group of the total population was invited to the interviews, forming a sub-group of the original population. Also, the participants were selected on the basis of specific criteria, such as company (organisation), where a particular type of model has been implemented.
The first group of participants consisted of managers from companies where the performance arts approached has been used. A total of 10 managers were involved in the study, and over 50 different managers from five different companies across the UK were contacted in order to reach the target group. The author tried to create as diverse a sample as possible, making sure there was an equal number of men and women represented, and more importantly thatthere were representatives of various industries: advertisingretail, finance, fashion and digital marketing. The other group of participants consisted of 30 employees, who were part of the teams of each one of the 10 managers. Not every team had the exact same number of people, as some teams were smaller and others larger. . However, the size of the teams was irrelevant to the purposes of this study as the participants had to complete individual questionnaires. All of the participants were approached via email, and the questionnaires were distributed via email, then completed by the participant and returned via email again. This took place in the course of four weeks. Five of the managers and five of the employees were invited for an interview, they were randomly selected from the questionnaire sample and the interviews took place took place over the phone/Skype and recorded then transcribed by the researcher. The interviews took place in the course of one month. The full transcripts of the interviews as well as the questionnaires are attached in the appendices.
Instrument Design
For the purposes of this research the writer designed two separate questionnaire scripts and two brief interview scripts.
The questionnaire for the managers from the companies consisted of twenty open questions, related to the business performance of their employees. The first part of the questionnaire consisted of demographic questions, related to age, gender, and questions related to the professional role of the participants, such as length of their experience in the company, exact position and responsibilities. The core questions were divided into groups for clarity, addressing the main objectives of the research, through the perspective of the managers. More importantly, these questions were designed to address the core competencies, established in the previous chapter to assess business performance by art performance – leadership, communication, team-building, emotion management, and creativity.
The questionnaire for the employees consists of the same number of questions, and again combines open and closed questions. Apart from the demographic questions, the rest of the questions are organised into groups, addressing the objectives through the prism of the employees, and addressing individual narratives on important concepts such as creativity, improvisation, and team-building within the organisation.
The interview scripts for both groups consist of six brief, but open questions.
The questions for the managers were designed to discuss in detail leadership as performance, and “business as show business”.
The questions for the employees were designed to reflect their experience as recipients of the performance bound management, and address specific components such as playing, rehearsing, performing in the workplace, with the purpose of team building and more effective task delivery/distribution.
The full scripts of the questionnaires and the interviews are available in the Appendices.
Most of the communication with the participants took place via email. Before that however, the author created a large database of companies, which met the research criteria using a simple google search. The author purposefully targeted smaller organisations, because the probability of being granted access to employees was higher, and the process – less time-consuming, which turned out to be the case. At first the writer contacted via the phone relevant people from each company, to make them acquainted with the purposes of the research and to ask for permission to conduct the research with representatives from their companies. For confidentiality, the job titles of the initial contacts are not disclosed, especially having in mind their job titles are not relevant to the research, as they are not direct participants in it. In some cases, the managers distributed the questionnaires to their employees, and in other cases the writer approached the employees directly via email. The questionnaires were distributed and completed in the course of four weeks. The interviews were conducted over the phone/Skype depending on the preferences of the participant. They were then recorded and transcribed by the researcher. The interviews were completed within four weeks.
Methods of Data Analysis
The analysis of the questionnaire results took place via thematic analysis. . Because of the small number of respondents and the diverse design and answer sets of the questions, and because of the qualitative research approach of the study, the author did not use any of the statistical software available such as SPSS or STRATA.
The results of the interviews were also analysed manually, where the author aimed to detect common words, phrases, and group or “cloud” them together, in order to be able to determine trends and tendencies in the answers of the respondents.
The results from the questionnaires were presented in the format of tables and charts. The major findings of this dissertation will be discussed in details in the next chapter.
Ethical Considerations
There were several types of ethical issues, which the researcher had to take into consideration for this project. The most important one was related with the informed consent of the participants. All of the participants (both managers and employees) were informed in advance about the purposes of this project, and gave their informed consent to participate in writing. Their identity as well as the names of the organisations they belong to has been kept in strict confidentiality, thus meeting the requirements of the code of ethics of the University.
In addition, the privacy and confidentiality policy of all of the companies had to be taken into consideration as well, as the companies have a very strict policy for access to their employees for research purposes. Therefore the researcher had to sign consent forms for confidentiality and privacy with the companies whose employees and managers agreed to participate in the study.
Consent forms are attached in the Appendices.
Finally, all the information collected in the course of this dissertation has been used only for the purposes of the study, and will be kept confidential.
Problems and Limitations
There were several problems and challenges which the researcher encountered while conducting the research for this dissertation.
The first challenge was recruiting a sufficient number of participants. The creation of the initial database of prospective companies took long time, and many times the requests of the researcher were turned down, because most of the companies rarely allow the opportunity for external research. Thus access to the participants and obtaining permission for the research was a major challenge.
Secondly the researcher was restricted by time and cost, which determined the choice of more efficient method, such as the questionnaire, instead of the more time consuming focus groups or participant observation.
In terms of the methodology chosen, there are several limitations which need to be mentioned. The first one is the fact that because of the small sample, the data collected and the findings made cannot be extrapolated on a broader scale. In other words, the generalizability of the results is questionable.
Another weakness of the methodology was related to the fact that the researcher used interpetivist approach, which was determined by the nature and the objectives of the research. In this sense the results and the achievements of this project can be deemed as biased, because the connections between the different variables have been determined not on the basis of empirical evidence, but on the basis of the analytical and judgemental skills of the researcher, in the context of a particular academic field.
This chapter has outlined and justified the research methodology implemented in this dissertation and its validity. Because of the nature of the research, the author opted for the qualitative strategy, bound by interpretivist approach. The key research tools were questionnaire, supplemented by interviews with two groups of participants – employees and managers. The participants were carefully targeted and recruited through stratified sampling technique. The results were analysed manually, due to the small sample of participants. The major results and findings of this dissertation are discussed in the following chapter.
Altrichter, H., Feldman, A., Posch, P. & Somekh, B. (2008). Teachers investigate their work; An introduction to action research across the professions. London: Routledge. p. 147. (2nd edition).
Bell, J. (2005) Doing Your Research Project, Berkshire: Open University Press/McGraw-Hill Education
Cohen, L.,& Manion, L. (2000). Research methods in education. London: Routledge. p. 254. (5th edition).
Greenfield, T. (2002) Research Methods for Postgraduates, London: Arnold
Kirby, M., Konbel., F., Barter, J., Hope, T., Kirton, D., Madry, N., Manning, P., Trigges, K. (2000) Sociology in Perspective, Oxford: Heinnemann
Potter, S. (2002) Doing Postgraduate Research, London: Sage
Sarantakos, S. (2013) Social Research, Basingstoke: Macmillan
Silverman, D., (2004). Qualitative Research: Theory, Method and Practice. 2nd ed. London: Sage Publication.
Willis, J. W., (2007). Foundations of Qualitative Research: Interpretive and Critical Approaches. London: Sage
Winchester, H. P. M. (1999) ‘Interviews and Questionnaires as Mixed Methods in Population Geography: The Case of Lone Fathers in Newcastle, Australia’, The Professional Geographer, 51: 1, 60 — 67 DOI: 10.1111/0033-0124.00145 URL: http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/0033-0124.00145
Cite this Page
Sample Research Methodology Chapter: Quantitative Research. (2019, Feb 26). Retrieved from https://phdessay.com/sample-research-methodology-chapter-quantitative-research/
Run a free check or have your essay done for you

More related essays
The use of both quantitative and qualitive research are a key factor in the development of theories in numerous areas of study. The use of research has proven to be.
Research is a key aspect for any scientist as they seek to produce knowledge and validate it through logical and imperial validity. Many times those that undertake a research project.
Quantitative research tools and methods provide emphasis on the objectives measurements. As well as statistical analysis of data collected through questionnaires and surveys. Primarily, quantitative research is geared towards gathering.
Identifying a need: In health and social care research is a very important factor in identifying the needs of groups of individuals, whether that research is through medical examination or through.
Jonathan Hoffsuemmer A serious problem seen by nurse practitioners that work in rural areas is teen pregnancy. A peer-reviewed research paper published by The Journal for Nurse Practitioners entitled “Who Will.
Empirical research in India in particular creates so many problems for the researchers. State the problems that are usually faced by such researchers. A research scholar has to work as a.
Descriptive studies help discover new meaning, describe what currently exists, and categorize the information. We will use desk research as well as field research; we will use both kinds of.
“The study of man contains a greater variety of intellectual styles than any other area of cultural endeavor. How different social scientists go about their work, and what they aim.
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy
Save time and let our verified experts help you.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
3 Methodology (In this unit I use the word Methodology as a general term to cover whatever you decide to include in the chapter where you discuss alternative methodological approaches, justify your chosen research method, and describe the process and participants in your study).
Do yourself a favour and start with the end in mind. Section 1 - Introduction. As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, the methodology chapter should have a brief introduction. In this section, you should remind your readers what the focus of your study is, especially the research aims. As we've discussed many times on the blog ...
Research Methodology Example. Detailed Walkthrough + Free Methodology Chapter Template. If you're working on a dissertation or thesis and are looking for an example of a research methodology chapter, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through a research methodology from a dissertation that earned full distinction ...
This template covers all the core components required in the research methodology chapter or section of a typical dissertation or thesis, including: The purpose of each section is explained in plain language, followed by an overview of the key elements that you need to cover. The template also includes practical examples to help you understand ...
survey methodology and includes a number of survey instruments. The pur-pose of the design was to correlate the scores of the personality tests listed below with the scores on responses to the short stories, as well as measure the interrelationship of the responses to the short stories. (p. 115) Describing Your Sample
If you want me to walk you through your methods chapter, from designing your study to writing it up, check out my PhD Survival Guide Part 7: The Methods Chapter. Click here to learn more. demystifying methodology chapter methods How to write a methodology chapter PhD methodology Methodology chapter examples methodology template social science ...
Guide contents. As part of the Writing the Dissertation series, this guide covers the most common conventions found in a methodology chapter, giving you the necessary knowledge, tips and guidance needed to impress your markers! The sections are organised as follows: Getting Started - Defines the methodology and its core characteristics.; Structure - Provides a detailed walk-through of common ...
Types of research methodology. 1. Qualitative research methodology. Qualitative research methodology is aimed at understanding concepts, thoughts, or experiences. This approach is descriptive and is often utilized to gather in-depth insights into people's attitudes, behaviors, or cultures. Qualitative research methodology involves methods ...
In any research, the methodology chapter is one of the key components of your dissertation. It provides a detailed description of the methods you used to conduct your research and helps readers understand how you obtained your data and how you plan to analyze it. This section is crucial for replicating the study and validating its results.
This chapter designs a comprehensive research methodology tailored to the aim and objectives of the study. Specifically, the research methodology chapter is responsible for explaining the philosophical underpinnings, as well as explaining their role in examining the selected research phenomenon. Second, the researcher's philosophical ...
3. Methodology 4. Findings 5. Analysis and synthesis 6. Conclusions and recommendations Chapter 1: Introduction This chapter makes a case for the signifi-cance of the problem, contextualizes the study, and provides an introduction to its basic components. It should be informative and able to stand alone as a document.
Methodology. Methodology is sometimes used interchangeably with methods, or as the set of methods used in a research. More specifically, as the name would suggest, methodo-logy is the logos, the reasoning, on the methods. It is also referred to as the theory of how research should be undertaken (Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, 2015, p4).
Score 93% Score 93%. 3.3 Writing the Methodology Chapter (s) for the Proposal. The methodology used in a thesis is usually described in its own chapter (see Section 1.2.3 and Section 4.3), though, like the literature review, it can be blended with the introductory material, or the review of literature and description of methods can be combined ...
Overview: Writing The Methodology Chapter. Develop a (rough) outline before you start writing. Draw inspiration from similar studies in your topic area. Justify every research design choice that you make. Err on the side of too much detail, rather than too little. Back up every design choice by referencing literature. 1.
For answers to these questions, and further tips on writing this chapter of your dissertation, consult our Writing the Methodology guide. You can also watch our recorded webinar Writing the Dissertation: the Methods or Methodology to learn the difference between the methods and methodology, what's expected and practical ways of structuring the ...
A Template To Help You Structure Your PhD's Theoretical Framework Chapter. In this guide, I explain how to use the theory framework template. The focus is on the practical things to consider when you're working with the template and how you can give your theory framework the rockstar treatment. Use our free tools, guides and templates to ...
The key point is to show that your research was conducted meticulously. Try to keep your writing style concise and clear; this will ensure that it is easy for the reader to understand and digest. Here are five top tips to consider when writing your dissertation methodology: 1. Look at Other Methodology Sections.
Dissertation Chapter 3 Sample. be be 1. Describe. quantitative, CHAPTER III: METHOD introduce the qualitative, the method of the chapter and mixed-methods). used (i.e. The purpose of this chapter is to introduce the research methodology for this. methodology the specific connects to it question(s). research.
Here's how to approach it: 1. Describe Your Methodological Approach. Start by explaining the research subject or problem you looked into. It could be that you wanted to methodically define something's qualities, investigate a little-studied issue, or prove a cause-and-effect relationship.
Dissertations are typically structured as follows: Chapter 1 Introduction (broad overview of the research) Chapter 2 Review of the literature (and conceptual framework) Chapter 3 Methodology Chapter 4 Results or Findings Chapter 5 Interpretations, Conclusions, and Recommendations References Appendices.
Introduction. The current chapter presents developing the research methods needed to complete the experimentation portion of the current study. The chapter will discuss in detail the various stages of developing the methodology of the current study. This includes a detailed discussion of the philosophical background of the research method chosen.
The purpose of this chapter is to explain in detail the research methods and the methodology implemented for this study. The chapter will explain first of all the choice of research approach, then the research design, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of the research tools chosen. This will be followed by a discussion on their ability ...