

How to Write a Research Paper Introduction (with Examples)

Table of Contents
The research paper introduction section, along with the Title and Abstract, can be considered the face of any research paper. The following article is intended to guide you in organizing and writing the research paper introduction for a quality academic article or dissertation.
The research paper introduction aims to present the topic to the reader. A study will only be accepted for publishing if you can ascertain that the available literature cannot answer your research question. So it is important to ensure that you have read important studies on that particular topic, especially those within the last five to ten years, and that they are properly referenced in this section. 1
What should be included in the research paper introduction is decided by what you want to tell readers about the reason behind the research and how you plan to fill the knowledge gap. The best research paper introduction provides a systemic review of existing work and demonstrates additional work that needs to be done. It needs to be brief, captivating, and well-referenced; a well-drafted research paper introduction will help the researcher win half the battle.
The introduction for a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your research topic
- Capture reader interest
- Summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Define your specific research problem and problem statement
- Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper. Some research paper introduction examples are only half a page while others are a few pages long. In many cases, the introduction will be shorter than all of the other sections of your paper; its length depends on the size of your paper as a whole.
What is the introduction for a research paper?
The introduction in a research paper is placed at the beginning to guide the reader from a broad subject area to the specific topic that your research addresses. They present the following information to the reader
- Scope: The topic covered in the research paper
- Context: Background of your topic
- Importance: Why your research matters in that particular area of research and the industry problem that can be targeted
Why is the introduction important in a research paper?
The research paper introduction conveys a lot of information and can be considered an essential roadmap for the rest of your paper. A good introduction for a research paper is important for the following reasons:
- It stimulates your reader’s interest: A good introduction section can make your readers want to read your paper by capturing their interest. It informs the reader what they are going to learn and helps determine if the topic is of interest to them.
- It helps the reader understand the research background: Without a clear introduction, your readers may feel confused and even struggle when reading your paper. A good research paper introduction will prepare them for the in-depth research to come. It provides you the opportunity to engage with the readers and demonstrate your knowledge and authority on the specific topic.
- It explains why your research paper is worth reading: Your introduction can convey a lot of information to your readers. It introduces the topic, why the topic is important, and how you plan to proceed with your research.
- It helps guide the reader through the rest of the paper: The research paper introduction gives the reader a sense of the nature of the information that will support your arguments and the general organization of the paragraphs that will follow.
What are the parts of introduction in the research?
A good research paper introduction section should comprise three main elements: 2
- What is known: This sets the stage for your research. It informs the readers of what is known on the subject.
- What is lacking: This is aimed at justifying the reason for carrying out your research. This could involve investigating a new concept or method or building upon previous research.
- What you aim to do: This part briefly states the objectives of your research and its major contributions. Your detailed hypothesis will also form a part of this section.
Check out how Peace Alemede uses Paperpal to write her research paper

Peace Alemede, Student, University of Ilorin
Paperpal has been an excellent and beneficial tool for editing my research work. With the help of Paperpal, I am now able to write and produce results at a much faster rate. For instance, I recently used Paperpal to edit a research article that is currently being considered for publication. The tool allowed me to align the language of my paragraph ideas to a more academic setting, thereby saving me both time and resources. As a result, my work was deemed accurate for use. I highly recommend this tool to anyone in need of efficient and effective research paper editing. Peace Alemede, Student, University of Ilorin, Nigeria
Start Writing for Free
How to write a research paper introduction?
The first step in writing the research paper introduction is to inform the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening statement. The second step involves establishing the kinds of research that have been done and ending with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to address.
Finally, the research paper introduction clarifies how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses. If your research involved testing hypotheses, these should be stated along with your research question. The hypothesis should be presented in the past tense since it will have been tested by the time you are writing the research paper introduction.
The following key points, with examples, can guide you when writing the research paper introduction section:
1. Introduce the research topic:
- Highlight the importance of the research field or topic
- Describe the background of the topic
- Present an overview of current research on the topic
Example: The inclusion of experiential and competency-based learning has benefitted electronics engineering education. Industry partnerships provide an excellent alternative for students wanting to engage in solving real-world challenges. Industry-academia participation has grown in recent years due to the need for skilled engineers with practical training and specialized expertise. However, from the educational perspective, many activities are needed to incorporate sustainable development goals into the university curricula and consolidate learning innovation in universities.
2. Determine a research niche:
- Reveal a gap in existing research or oppose an existing assumption
- Formulate the research question
Example: There have been plausible efforts to integrate educational activities in higher education electronics engineering programs. However, very few studies have considered using educational research methods for performance evaluation of competency-based higher engineering education, with a focus on technical and or transversal skills. To remedy the current need for evaluating competencies in STEM fields and providing sustainable development goals in engineering education, in this study, a comparison was drawn between study groups without and with industry partners.
3. Place your research within the research niche:
- State the purpose of your study
- Highlight the key characteristics of your study
- Describe important results
- Highlight the novelty of the study.
- Offer a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
Example: The study evaluates the main competency needed in the applied electronics course, which is a fundamental core subject for many electronics engineering undergraduate programs. We compared two groups, without and with an industrial partner, that offered real-world projects to solve during the semester. This comparison can help determine significant differences in both groups in terms of developing subject competency and achieving sustainable development goals.
Write a Research Paper Introduction in Minutes with Paperpal
Paperpal is a generative AI-powered academic writing assistant. It’s trained on millions of published scholarly articles and over 20 years of STM experience. Paperpal helps authors write better and faster with:
- Real-time writing suggestions
- In-depth checks for language and grammar correction
- Paraphrasing to add variety, ensure academic tone, and trim text to meet journal limits
With Paperpal, create a research paper introduction effortlessly. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll walk you through how Paperpal transforms your initial ideas into a polished and publication-ready introduction.

How to use Paperpal to write the Introduction section
Step 1: Sign up on Paperpal and click on the Copilot feature, under this choose Outlines > Research Article > Introduction
Step 2: Add your unstructured notes or initial draft, whether in English or another language, to Paperpal, which is to be used as the base for your content.
Step 3: Fill in the specifics, such as your field of study, brief description or details you want to include, which will help the AI generate the outline for your Introduction.
Step 4: Use this outline and sentence suggestions to develop your content, adding citations where needed and modifying it to align with your specific research focus.
Step 5: Turn to Paperpal’s granular language checks to refine your content, tailor it to reflect your personal writing style, and ensure it effectively conveys your message.
You can use the same process to develop each section of your article, and finally your research paper in half the time and without any of the stress.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the introduction in research papers.
The purpose of the research paper introduction is to introduce the reader to the problem definition, justify the need for the study, and describe the main theme of the study. The aim is to gain the reader’s attention by providing them with necessary background information and establishing the main purpose and direction of the research.
How long should the research paper introduction be?
The length of the research paper introduction can vary across journals and disciplines. While there are no strict word limits for writing the research paper introduction, an ideal length would be one page, with a maximum of 400 words over 1-4 paragraphs. Generally, it is one of the shorter sections of the paper as the reader is assumed to have at least a reasonable knowledge about the topic. 2
For example, for a study evaluating the role of building design in ensuring fire safety, there is no need to discuss definitions and nature of fire in the introduction; you could start by commenting upon the existing practices for fire safety and how your study will add to the existing knowledge and practice.
What should be included in the research paper introduction?
When deciding what to include in the research paper introduction, the rest of the paper should also be considered. The aim is to introduce the reader smoothly to the topic and facilitate an easy read without much dependency on external sources. 3
Below is a list of elements you can include to prepare a research paper introduction outline and follow it when you are writing the research paper introduction.
- Topic introduction: This can include key definitions and a brief history of the topic.
- Research context and background: Offer the readers some general information and then narrow it down to specific aspects.
- Details of the research you conducted: A brief literature review can be included to support your arguments or line of thought.
- Rationale for the study: This establishes the relevance of your study and establishes its importance.
- Importance of your research: The main contributions are highlighted to help establish the novelty of your study
- Research hypothesis: Introduce your research question and propose an expected outcome. Organization of the paper: Include a short paragraph of 3-4 sentences that highlights your plan for the entire paper
Should I include citations in the introduction for a research paper?
Cite only works that are most relevant to your topic; as a general rule, you can include one to three. Note that readers want to see evidence of original thinking. So it is better to avoid using too many references as it does not leave much room for your personal standpoint to shine through.
Citations in your research paper introduction support the key points, and the number of citations depend on the subject matter and the point discussed. If the research paper introduction is too long or overflowing with citations, it is better to cite a few review articles rather than the individual articles summarized in the review.
A good point to remember when citing research papers in the introduction section is to include at least one-third of the references in the introduction.
Should I provide a literature review in the research paper introduction?
The literature review plays a significant role in the research paper introduction section. A good literature review accomplishes the following:
- Introduces the topic
- Establishes the study’s significance
- Provides an overview of the relevant literature
- Provides context for the study using literature
- Identifies knowledge gaps
However, remember to avoid making the following mistakes when writing a research paper introduction:
- Do not use studies from the literature review to aggressively support your research
- Avoid direct quoting
- Do not allow literature review to be the focus of this section. Instead, the literature review should only aid in setting a foundation for the manuscript.
Key points to remember
Remember the following key points for writing a good research paper introduction: 4
- Avoid stuffing too much general information: Avoid including what an average reader would know and include only that information related to the problem being addressed in the research paper introduction. For example, when describing a comparative study of non-traditional methods for mechanical design optimization, information related to the traditional methods and differences between traditional and non-traditional methods would not be relevant. In this case, the introduction for the research paper should begin with the state-of-the-art non-traditional methods and methods to evaluate the efficiency of newly developed algorithms.
- Avoid packing too many references: Cite only the required works in your research paper introduction. The other works can be included in the discussion section to strengthen your findings.
- Avoid extensive criticism of previous studies: Avoid being overly critical of earlier studies while setting the rationale for your study. A better place for this would be the Discussion section, where you can highlight the advantages of your method.
- Avoid describing conclusions of the study: When writing a research paper introduction remember not to include the findings of your study. The aim is to let the readers know what question is being answered. The actual answer should only be given in the Results and Discussion section.
To summarize, the research paper introduction section should be brief yet informative. It should convince the reader the need to conduct the study and motivate him to read further. If you’re feeling stuck or unsure, choose trusted AI academic writing assistants like Paperpal to effortlessly craft your research paper introduction and other sections of your research article.
- Jawaid, S. A., & Jawaid, M. (2019). How to write introduction and discussion. Saudi Journal of Anaesthesia, 13(Suppl 1), S18.
- Dewan, P., & Gupta, P. (2016). Writing the title, abstract and introduction: Looks matter!. Indian pediatrics, 53, 235-241.
- Cetin, S., & Hackam, D. J. (2005). An approach to the writing of a scientific Manuscript1. Journal of Surgical Research, 128(2), 165-167.
- Bavdekar, S. B. (2015). Writing introduction: Laying the foundations of a research paper. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, 63(7), 44-6.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
- 6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Practice vs. Practise: Learn the Difference
Academic paraphrasing: why paperpal’s rewrite should be your first choice , you may also like, how to cite in apa format (7th edition):..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements, how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples.

Research Blog
How to write a research paper introduction (with examples).

I hope you enjoy reading this blog post.
If you would like to learn more about research, check out this Research Course .
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on crafting the perfect introduction for your research paper. In this blog, we’ll explore the crucial elements of a strong introduction, highlight common pitfalls to avoid, and provide practical tips to effectively set the stage for your study’s objectives and significance.
Table of Contents
Lack of a clear thesis statement, lack of clear objectives and scope, failure to establish the research significance, insufficient background information, inadequate literature review, ignoring the research gap, overly technical language, poor organization and flow, neglecting the audience, the importance of a good introduction.
A strong introduction sets the tone for the entire paper, guiding the reader through the research journey. It provides context, establishes relevance, and ensures the reader understands the importance of the study.
Starting a research project is exciting, but getting the introduction right is key. It’s like opening the door to your study and inviting readers in. However, there are some common missteps that can trip you up along the way.
Find the U.S. Research Position of your dreams!
Common mistakes to avoid.
A thesis statement is the central argument or claim that guides the entire research paper. It is a concise summary of the main point or claim of the paper and is typically found at the end of the introduction. A clear thesis statement helps to focus the research, provide direction, and inform the reader of the paper’s purpose. Expert reviewers may even skip the rest of the introduction (as they are well versed in the topic) and focus only on your thesis statement, so it’s vital to make sure it is perfect!
When a research introduction lacks a clear thesis statement, several issues can arise:
- Ambiguity : Without a clear thesis, the reader may be confused about the paper’s purpose and the main argument. Do not talk in vague terms. Whenever possible, use terminology established in recent literature. Narrow down the key aspects of the association that you are investigating (the study sample, the outcome and predictor measures) as much as possible.
- Lack of Focus : The paper can become unfocused and meander through unrelated topics, making it difficult for the reader to follow the argument. Do not try to have more than 1-2 main aims in a paper. Even if you have done supplementary analysis, it is better to say so in the discussion. As a rule of thumb, try to answer one major question only!
- Weak Argumentation : A well-defined thesis provides a strong foundation for building arguments. Without it, the arguments may appear weak and unsupported.
Let's be more practical:
1- In this paper, I will discuss climate change.
- Problem: This statement is too broad and vague. It does not provide a clear direction or specific argument.
2- This paper argues that climate change, measured by global average temperature change, is primarily driven by human activities, such as deforestation and the burning of fossil fuels, and proposes policy measures to mitigate its impact.(1)
- Strengths: – Specificity : It clearly states that the paper will focus on human activities as the main drivers of climate change. – Argument : It presents a specific claim that the paper will argue. – Direction : It hints at the structure of the paper by mentioning policy measures.
If you would like to learn more about introductions and other aspects of clinical research, check out the Medical Research Course from the Match Guy here .
Powerful Tips:
- Be Specific : Clearly define the main argument or claim. Avoid vague or broad statements.
- Be Concise : Keep the thesis statement concise, ideally one to two sentences.
- Provide Direction : Indicate the structure of the paper by hinting at the main points that will be discussed.
- Revise as Needed : Be prepared to revise the thesis statement as your research progresses and your understanding deepens.
Transform research ideas into published papers!
A clear statement of objectives and scope is crucial in a research paper introduction because it outlines what the study aims to achieve and defines the boundaries within which the research will be conducted.
Example of Lacking Clear Objectives and Scope: This paper examines the impacts of climate change on agriculture.
- Problem : This statement is too broad and vague. It does not specify what aspects of climate change or agriculture will be studied, nor does it define the geographical or temporal scope.
Example with Clear Objectives and Scope: This study aims to investigate the effects of rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns on crop yields in the Midwest United States from 2000 to 2010. The objectives are to (1) assess the impact of temperature changes on corn and soybean yields, (2) analyze how variations in precipitation affect crop growth, and (3) identify adaptive strategies employed by farmers in the region.(2)
Powerful tips:
- Be Specific : Clearly state what the study aims to achieve and avoid vague or broad statements.
- Identify Key Areas : Outline the main areas or aspects that the research will focus on.
- Set Boundaries : Define the geographical, temporal, and conceptual boundaries of the research.
- List Objectives : Clearly articulate specific research objectives or questions that the study will address.
- Stay Realistic : Ensure that the objectives and scope are achievable within the constraints of the research project.
- Make it flow : Make sure you are not repeating the same concepts as the thesis statement, as these two sections are often presented back-to-back in the final paragraph of the introduction! Remember: the thesis statement is your hypothesis or question, and your objectives are ‘how’ you are going to test your thesis.
Master medical statistics and boost your productivity!
This mistake can result in the research appearing trivial or irrelevant, diminishing its potential impact. When the significance of the research is not well-established, readers may struggle to understand the value of the study and why they should care about it.
Example of Failure to Establish Research Significance: This study investigates the effects of social media usage on sleep patterns among teenagers.
- Problem : The significance of studying social media’s impact on sleep patterns is not explained. The reader may wonder why this research is important or what implications it has.
Example with Established Research Significance: This study investigates the effects of social media usage on sleep patterns among teenagers. Understanding this relationship is crucial because insufficient sleep is linked to numerous health issues, including decreased academic performance, heightened stress levels, and increased risk of mental health problems. With the pervasive use of social media among adolescents, identifying how it impacts sleep can inform strategies for promoting healthier habits and improving overall well-being in this vulnerable age group.(3)
- Link to Broader Issues : Connect the research topic to broader issues or trends that highlight its relevance and importance.
- Explain Practical Implications : Discuss the potential practical applications or benefits of the research findings.
- Address Gaps in Knowledge : Identify gaps in the existing literature that the research aims to fill.
- Highlight Potential Impact : Emphasize the potential impact of the research on the field, society, or specific populations.
- Use Concrete Examples : Provide concrete examples or scenarios to illustrate the significance of the research.
Feeling swamped by the complexities of Systematic Reviews?
Insufficient background information in the introduction of a research paper refers to failing to provide enough context for the reader to understand the research problem and its significance. Background information sets the stage for the research by offering necessary details about the topic, relevant theories, previous studies, and key terms.
This may lead to:
- Reader Confusion : Without adequate context, readers may struggle to understand the research question, its importance, and how it fits into the broader field of study.
- Weak Justification : Insufficient background can undermine the rationale for the research, making it difficult to justify why the study is necessary or valuable.
- Misinterpretation : Lack of context can lead to misinterpretation of the research objectives, methods, and findings.
Example of Insufficient Background Information: In recent years, many researchers have studied the effects of social media on teenagers. This paper explores the relationship between social media use and anxiety among teenagers.
- Problem : This introduction lacks specific details about the previous research, the theoretical framework, and key terms. It does not provide enough context for the reader to understand why the study is important.
Example of Adequate Background Information: Social media platforms have become an integral part of teenagers’ daily lives, with studies showing that 95% of teens have access to a smartphone and 45% are online almost constantly. Previous research has linked excessive social media use to various mental health issues, including anxiety and depression. However, the mechanisms underlying this relationship remain unclear. This paper explores the impact of social media use on anxiety levels among teenagers, focusing on the roles of social comparison and cyberbullying.(4)
If you would like to learn more about manuscript writing, check out the Comprehensive Research Course from the Match Guy here .
- Review Relevant Literature : Summarize key studies and theories related to your topic.
- Provide Context : Explain the broader context of your research problem.
- Define Key Terms : Ensure that any specialized terms or concepts are clearly defined.
- Identify the Research Gap : Highlight what is not yet known or understood about your topic.
- Be Concise : Provide enough information to set the stage without overwhelming the reader with details.
Getting No Replies from Institutions? Don't Stress!
This mistake can occur when the literature review is too brief, lacks depth, omits key studies, or fails to critically analyze previous work. An inadequate literature review can undermine the foundation of the research by failing to provide the necessary context and justification for the study.
Inadequate Literature Review: There has been some research on the relationship between exercise and mental health. This paper will investigate this relationship further.
- Problem : This review is too general and does not provide sufficient detail about the existing research or how it informs the current study.
Example with Adequate Literature Review: Research has consistently shown that regular physical activity has positive effects on mental health. For example, a study by Gujral et al. (2019) demonstrated that aerobic exercise can significantly reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. Similarly, Smith and Lee (2020) found that strength training also contributes to improved mood and reduced stress levels. However, much of the existing research has focused on adult populations, with relatively few studies examining these effects in adolescents. Additionally, the specific types of exercise that are most beneficial for different mental health outcomes have not been thoroughly investigated. This study aims to explore the effects of various types of exercise on the mental health of high school students, thereby addressing these gaps in the literature.(5-6)
- Be Comprehensive : Review a broad range of studies related to the research topic to provide a thorough context.
- Be Specific : Cite specific studies, including their methodologies, findings, and relevance to the current research.
- Be Critical : Analyze and evaluate the existing research, identifying strengths, weaknesses, and gaps.
- Be Structured : Organize the literature review logically, grouping studies by themes or findings to create a coherent narrative.
- Be Relevant : Focus on the most relevant studies that directly relate to the research question and objectives.
Unlock your research potential with our dynamic course designed for medical students! Built by an experienced researcher with 150+ publications and 3000+ citations!
Ignoring the research gap in a research paper introduction means failing to identify and articulate what specific aspect of the topic has not been explored or adequately addressed in existing literature. The research gap is a critical component because it justifies the necessity and originality of the study. Without highlighting this gap, the research may appear redundant or lacking in significance.
How huge is this mistake?
- Lack of Justification : The study may not appear necessary or relevant, diminishing its perceived value.
- Redundancy : The research may seem to duplicate existing studies, offering no new insights or contributions to the field. Even if you are using methodology similar to previous studies, it is important to note why you are doing so e.g., few studies have used that specific methodology, and you would like to validate it in your sample population!
- Reader Disinterest : Readers may lose interest if they do not see the unique contribution or purpose of the research.
Example of Ignoring the Research Gap: Many studies have examined the effects of exercise on mental health. This paper looks at the relationship between physical activity and depression.
- Problem : This introduction does not specify what aspect of the relationship between physical activity and depression has not been studied, failing to highlight the unique contribution of the research.
Example of Identifying the Research Gap: Numerous studies have demonstrated the general benefits of physical activity on mental health, particularly its role in alleviating symptoms of depression. However, there is limited research on how different types of exercise (e.g., aerobic vs. anaerobic) specifically impact depression levels among various age groups. This study investigates the differential effects of aerobic and anaerobic exercise on depression in young adults, aiming to fill this gap in the literature.(6)
- Conduct a Thorough Literature Review : Understand the current state of research in your field to identify what has been studied and where gaps exist.
- Be Specific : Clearly articulate what specific aspect has not been covered in existing studies.
- Link to Your Study : Explain how your research will address this gap and contribute to the field.
- Use Evidence : Support your identification of the gap with references to previous studies.
- Emphasize Significance : Highlight why filling this gap is important for advancing knowledge or practical applications.
Do Statistical Analysis on your own with confidence in 2 weeks!
Overly technical language refers to the excessive use of jargon, complex terms, and highly specialized language that may be difficult for readers, especially those not familiar with the field, to understand. While technical language is sometimes necessary in academic writing, overusing it in the introduction can create several problems:
- Reader Alienation : Readers may find the text intimidating or inaccessible, leading to disengagement.
- Lack of Clarity : The main points and significance of the research can become obscured by complex terminology.
- Reduced Impact : The research may fail to communicate its importance effectively if readers struggle to understand the introduction.
Example of Overly Technical Language: The present study examines the metacognitive strategies employed by individuals in the domain of second language acquisition, specifically focusing on the interaction between declarative and procedural memory systems in the process of syntactic parsing.
- Problem : This sentence is loaded with jargon (“metacognitive strategies,” “second language acquisition,” “declarative and procedural memory systems,” “syntactic parsing”), which can be overwhelming and confusing for readers not familiar with these terms.
Example with Simplified Language: This study looks at the thinking strategies people use when learning a second language. It focuses on how different types of memory, such as the knowledge of facts and the skills for doing things, help in understanding sentence structures.(7)
- Know Your Audience : Tailor the language to the intended audience, ensuring it is accessible to both specialists and non-specialists.
- Define Term s: When technical terms are necessary, provide clear definitions or explanations.
- Use Analogies : Simplify complex concepts using analogies or examples that are easy to understand.
- Avoid Jargon : Limit the use of jargon and specialized terms, especially in the introduction.
- Seek Feedback : Ask peers or non-experts to read the introduction and provide feedback on clarity and accessibility.
Curious about delving into research but unsure where to begin?
Poor organization and flow in a research paper introduction refer to a lack of logical structure and coherence that makes the introduction difficult to follow. This can occur when ideas are presented in a haphazard manner, transitions between sections are weak or non-existent, and the overall narrative is disjointed. A well-organized introduction should smoothly guide the reader from the general context to the specific objectives of the study.
Example of Poor Organization and Flow: “Climate change affects agriculture in various ways. Many studies have looked at the impact on crop yields. This paper will discuss the economic implications of these changes. Climate models predict increased variability in weather patterns, which will affect water availability. Researchers have found that higher temperatures reduce the growing season for many crops.”
- Problem : The ideas are presented in a scattered manner without clear connections. The mention of economic implications seems out of place, and there are abrupt shifts between topics.
Example with Good Organization and Flow: Climate change poses significant challenges to agriculture by altering weather patterns, impacting crop yields, and affecting water availability. Numerous studies have shown that increased temperatures can shorten the growing season for many crops, leading to reduced yields. Additionally, climate models predict increased variability in weather patterns, which complicates water management for farmers. These changes not only affect food production but also have substantial economic implications for agricultural communities. This paper will examine the economic impacts of climate-induced changes in agriculture, focusing on crop yield variability and water resource management.(1)
- Create an Outline : Before writing, outline the main points you want to cover in the introduction.
- Think in terms of an inverted triangle : Begin broadly to introduce basic concepts related to your topic. As you progress through the introduction, you can introduce more and more specific topics until you have enough information to justify your thesis statement
- Use Transitional Phrases : Employ transitional phrases and sentences to connect ideas and sections smoothly.
- Follow a Logical Sequence : Present information in a logical order, moving from general context to specific objectives.
- Maintain Focus : Stay focused on the main topic and avoid introducing unrelated ideas.
- Revise for Coherence : Review and revise the introduction to ensure that it flows well and that each part contributes to the overall narrative.

Advisor UNLIMITED Access
We get how stressful the residency match process is, so we're here for you - communicate with your personal advisor ANYTIME you need!

Personal Statement Editing
Our editing includes not only language but also context, structure, and content advising.

ERAS Application Editing
The editing goes beyond language and grammar corrections to structure, design, and content based on your personal story and achievement.

- Interview Preparation
The best way to learn something is to do it. That’s why we divide our interview preparation sessions into two parts. Mock Interview + Feedback
Neglecting the audience refers to failing to consider the background, knowledge level, and interests of the intended readers when writing the introduction of a research paper. This mistake can manifest in several ways, such as using overly technical language for a general audience, providing insufficient background information for readers unfamiliar with the topic, or failing to engage the readers’ interest.
Example of Neglecting the Audience: For experts in genomic sequencing, this study explores the epigenetic modifications resulting from CRISPR-Cas9 interventions, focusing on the methylation patterns and histone modifications observed in gene-edited cells.
- Problem : This introduction assumes a high level of expertise in genomic sequencing and epigenetics, which may alienate readers without this background.
Example with Audience Consideration: CRISPR-Cas9 is a groundbreaking tool in genetic research that allows scientists to edit DNA with precision. However, altering genes can lead to unexpected changes in how genes are expressed, known as epigenetic modifications. This study investigates these changes by looking at specific markers on DNA, such as methylation patterns, and how they affect gene activity in cells that have been edited using CRISPR-Cas9. Our goal is to understand the broader implications of gene editing on cellular functions, which is crucial for advancing medical research and treatments.(8)
- Identify the Audience : Determine who the intended readers are (e.g., experts, students, general public) and tailor the language and content accordingly. Read papers from the journals you are considering for submission. Professional editors curate the language used in these papers and are a great starting point to identify the level of expertise of your audience!
- Simplify Language : Use clear and straightforward language, avoiding jargon and technical terms unless they are necessary and well-explained.
- Provide Background Information : Include sufficient background information to help readers understand the context and significance of the research.
- Engage the Reader : Start with an engaging introduction that highlights the relevance and importance of the research topic.
- Anticipate Questions : Consider what questions or concerns the audience might have and address them in the introduction
USMLE Tutoring
By following these guidelines and avoiding common pitfalls, you can create an introduction that not only grabs the attention of your readers but also sets the stage for a compelling and impactful research paper.
Final Tips:
- Revise and refine your introduction multiple times to ensure clarity and coherence.
- Seek feedback from peers, mentors, or advisors to identify areas for improvement.
- Keep your audience in mind and tailor your language and content to their needs and interests.
- Stay focused on your research objectives and ensure that every part of your introduction contributes to achieving them.
- Be confident in the significance of your research and its potential impact on your field or community.
Let your introduction be more than just words on a page. It’s a doorway to understanding. To help you along, we’ve created a practical course on writing and publishing research projects. It’s 100% risk-free, with a money-back guarantee if you’re not satisfied. Try it out now by clicking here .
Wishing you success on your research journey!
Marina Ramzy Mourid, Hamza Ibad, MBBS
Dr. Ibad graduated from the Aga Khan University Medical College and completed a post-doctoral research fellowship at Johns Hopkins in the Department of Radiology (Musculoskeletal Division). Dr. Ibad’s research and clinical interests include deep-learning applications for automated image interpretation, osteoarthritis, and sarcopenia-related health outcomes.

The Pathways for ECFMG Certification for MATCH 2025

2025 ERAS Application Updates

General Surgery Residency Personal Statement Examples

Emergency Medicine Residency Personal Statement Examples
About thematchguy, become a researcher in the united states, interested in learning more about literature search with examples from published literature, the comprehensive research course, the systematic review course, the medical statistics course, how to find research positions in the us.
1. Abbass K, Qasim MZ, Song H, Murshed M, Mahmood H, Younis I. A review of the global climate change impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2022;29(28):42539-42559. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-19718-6
2. Cai X, Wang D, Laurent R. Impact of climate change on crop yield: a case study of rainfed corn in central illinois. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology. 2009;48(9):1868-1881. doi:10.1175/2009JAMC1880.1
3. Van Den Eijnden RJJM, Geurts SM, Ter Bogt TFM, Van Der Rijst VG, Koning IM. Social media use and adolescents’ sleep: a longitudinal study on the protective role of parental rules regarding internet use before sleep. IJERPH. 2021;18(3):1346. doi:10.3390/ijerph18031346
4. Schmitt, M. (2021). Effects of social media and technology on adolescents: What the evidence is showing and what we can do about it. Journal of Family and Consumer Sciences Education, 38(1), 51-59.
5. Gujral S, Aizenstein H, Reynolds CF, Butters MA, Erickson KI. Exercise effects on depression: Possible neural mechanisms. General Hospital Psychiatry. 2017;49:2-10. doi:10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2017.04.012
6. Smith PJ, Merwin RM. The role of exercise in management of mental health disorders: an integrative review. Annu Rev Med. 2021;72(1):45-62. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-060619-022943
7. Sun Q, Zhang LJ. Understanding learners’ metacognitive experiences in learning to write in English as a foreign language: A structural equation modeling approach. Front Psychol. 2022;13:986301. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2022.986301
8. Kolanu ND. Crispr–cas9 gene editing: curing genetic diseases by inherited epigenetic modifications. Glob Med Genet. 2024;11(01):113-122. doi:10.1055/s-0044-1785234
How can we help you?
Leave your message here and we will get in touch with you as soon as possible.

Quick Links
- Our Reviews
- Our Podcast
- Residency Advising
- Personal Statement
- Match®Application Package
- P.O. Box 40388 Pittsburgh, PA 15201
- [email protected]
- + 1 412-295-8358
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
WhatsApp Us

Join Over 20,000 Readers
Ertugrul Portakal
Apr 12, 2024
Writing a Research Paper Introduction (with 3 Examples)
Nail your research paper's introduction! Learn to captivate and inform readers from the start—our guide shows how!
%20(3).png)
TABLE OF CONTENTS
A catchy and informative introduction is essential in academic writing, especially if you want your readers to have background information about your paper. However, writing an interesting and informative introduction can sometimes be a time-consuming and tiring process. If you don't know where to start when crafting an introduction, no need to worry - we've got you covered!
In this article, we will explain step by step what an introduction is in academic writing and how to write it!
Ready? Let's start!
- An introduction is a paragraph that provides information about your entire paper and aims to attract and inform the reader.
- Before writing an introduction or even starting your paper, you need to research academic sources.
- The first one or two sentences of an introduction paragraph should be a hook to attract the reader's attention.
- Afterwards, you need to prepare the reader for your argument by giving background information about your topic.
- Finally, you should state your argument about your topic with a thesis statement.
- If you are writing a longer paper, you can inform your readers about the map of your paper.
- If you are looking for an AI assistant to support you throughout your writing process, TextCortex is designed for you with its advanced features.
What is an Introduction in a research paper?
In any academic writing, including essays and research papers, an introduction is the first paragraph that the reader will encounter. This paragraph should both attract the reader's attention and give them the necessary information about the paper. In any academic paper, the introduction paragraph constitutes 10% of the paper's total word count. For example, if you are preparing a 3,000-word paper, your introduction paragraph should consist of approximately 300 words. You should also write sentences within these 300 words that will attract the reader's attention and provide them with information about the paper.
Importance of an Introduction Paragraph
The biggest function of an introduction paragraph is to prepare the reader for the author's thesis statement. A traditional introduction paragraph begins with a few sentences or questions that will catch the reader's attention. After attracting the reader's attention, necessary background information on the subject is given. Finally, the author explains to the readers what the whole paper is about by stating the thesis. A thesis statement is the final sentence that summarizes the main points of your paper and conveys your claim.
First Things First: Preliminary Research
When working on any academic writing type, it is essential to start by researching your topic thoroughly before beginning to type. What sets academic writing apart from other writing types is the requirement for it to be written using accurate information from reliable sources.
Researching academic sources can be a time-consuming and unnecessary process. One has to read through hundreds of pages, review dozens of articles and verify the accuracy of each source. However, if you're looking to reduce your workload and maximize efficiency by automating repetitive tasks such as literature review, ZenoChat is the perfect solution for you. With its web search feature, ZenoChat can use the entire internet as a data source. Additionally, by activating the "scholar" option of the ZenoChat web search feature, you can ensure that it only uses academic sources when generating output.
How to Create an Introduction for Academic Writing?
Creating an introduction paragraph that is interesting, informative, and conveys your thesis is an easier process than it seems. As long as you have sufficient information about your topic and an outline , you can write engaging introductions by following a few simple steps. Let's take a closer look at how to write an introduction for academic writing.
1-) Start with a Catchy Hook
Your first sentence is one of the factors that most influence a reader's decision to read your paper. This sentence determines the tone of your paper and attracts the reader's attention. For this reason, we recommend that you start your introduction paragraph with a strong and catchy hook sentence.
- Avoid long and complex sentences
- Use clear and concise sentences
- Write a sentence that will spark the reader's curiosity
- You can ask questions that will encourage the reader to read the remaining paragraph
- Avoid fact or overly broad sentences
- Avoid using dictionary definitions as your hook
2-) Give Background Information
After writing a strong hook sentence, you need to provide basic information about your topic so that the reader can understand what they will learn about when they read your paper. In this section, you can benefit from opinions that support or oppose your argument. Additionally, this section should refer to the body paragraphs of your writing.
- You can write a background information sentence for each body paragraph.
- The information here should be concise and compact
- Avoid talking about your evidence and results unless necessary.
3-) State Your Thesis
After attracting the reader's attention and providing background information, it is time to present your approach and argument towards the topic with a thesis statement. A thesis statement usually comprises one or two sentences and communicates the paper's argument to the reader. A well-written thesis statement should express your stance on the topic.
- Avoid merely stating a fact
- Claim your argument
4-) Tell Reader About Your Paper
Although you need to move on to body paragraphs after the thesis statement in short papers, it will be useful to add a few sentences that will guide the reader in your longer papers. This way, your readers can better understand which arguments they will encounter on which pages and the course of your paper. That leads the reader to clearly understand and follow your content.
Let’s Wrap it Up
Writing an interesting and informative introduction is usually a long process that requires a lot of rewriting. You may need to rewrite a sentence dozens of times so that your words and sentences clearly describe your paper and argument. Fortunately, you can generate state-of-the-art introductions using AI tools and use them with a little editing.
When it comes to text generation, paraphrasing, and grammar & spelling checking, TextCortex is the way to go with its advanced LLMs and customization options. With TextCortex, you can generate all writing types, including introduction, from scratch, rewrite your existing texts, change their tone of voice, or fix their grammar. TextCortex is available as a web application and browser extension. The TextCortex browser extension is integrated with 30,000+ websites and apps. So, you can complete your AI-driven writing tasks anywhere and anytime.
Let's examine a few sample introductions generated by TextCortex.
Example Introduction #1
“Should social media platforms be banned from collecting their users' data?”

Example Introduction #2
“Do electric vehicles decrease overall emissions?”

Example Introduction #3
“Is graffiti an act of vandalism or the creation of art?”

Interested in adopting AI across your organization?
Teams using TextCortex save 3 work days a month per employee and achieve up to 28x ROI.
Did you like this article? Explore a few more related posts.
%20(6).png)
How to Create a Strong Thesis?
%20(5).png)
Top 3 AI Tools That Write Essays (Free & Paid)
%20(4).png)
5 Main Essay Types & Guide with Examples
Questions answers..
TextCortex is a powerful AI-powered writing tool that can help you reduce your writing time, handle big tasks, and create high-quality content without errors. With its customizable platform, personalized intelligence experience, advanced writing and research capabilities, and error-free content, TextCortex is the perfect tool for creative professionals who want to be a creative force in their industry.
Our AI copilot learned how to write from more than 3 billion sentences and has the ability to create unique content. However, fact-checking is something which still requires a human approval.
TextCortex supports more than 25 languages including English, Dutch, German, Ukranian, Romanian, Spanish, Portuguese, French, Italian.
Yes, TextCortex is completely free to use with many of its core features. When you sign up, you receive 100 free creations. Then you will receive 20 recurring creations every day on the free plan.
Yes, we have a Text Generation API, please talk to us directly to implement it. You can reach out to us at [email protected]
Account sharing is not allowed. If you have a need for more than 5 seats for an account, you can directly contact us at [email protected]
Yes, TextCortex offers 14-day free trial for users to try out all features extensively with higher number of generations. But keep in mind that you can already try everything with the free plan. There is no feature that is locked behind a premium plan.
Overall, TextCortex AI has over 1000 five-star reviews on reputable review sites such as G2, Trustpilot and Capterra.
TextCortex learns and adapts to your unique writing style and knowledge, making it easier for you to write high-quality & personalized content.
Your premium features will be available until the end of your subscription date, then your account plan will be set to Free plan.
General Questions
Your ai copilot is ready to collaborate with you..
Connect your knowledge, customize the style and start collaborating with your AI copilot.
Instant insights, infinite possibilities
How to write an effective introduction for your research paper
Last updated
20 January 2024
Reviewed by
However, the introduction is a vital element of your research paper . It helps the reader decide whether your paper is worth their time. As such, it's worth taking your time to get it right.
In this article, we'll tell you everything you need to know about writing an effective introduction for your research paper.
- The importance of an introduction in research papers
The primary purpose of an introduction is to provide an overview of your paper. This lets readers gauge whether they want to continue reading or not. The introduction should provide a meaningful roadmap of your research to help them make this decision. It should let readers know whether the information they're interested in is likely to be found in the pages that follow.
Aside from providing readers with information about the content of your paper, the introduction also sets the tone. It shows readers the style of language they can expect, which can further help them to decide how far to read.
When you take into account both of these roles that an introduction plays, it becomes clear that crafting an engaging introduction is the best way to get your paper read more widely. First impressions count, and the introduction provides that impression to readers.
- The optimum length for a research paper introduction
While there's no magic formula to determine exactly how long a research paper introduction should be, there are a few guidelines. Some variables that impact the ideal introduction length include:
Field of study
Complexity of the topic
Specific requirements of the course or publication
A commonly recommended length of a research paper introduction is around 10% of the total paper’s length. So, a ten-page paper has a one-page introduction. If the topic is complex, it may require more background to craft a compelling intro. Humanities papers tend to have longer introductions than those of the hard sciences.
The best way to craft an introduction of the right length is to focus on clarity and conciseness. Tell the reader only what is necessary to set up your research. An introduction edited down with this goal in mind should end up at an acceptable length.
- Evaluating successful research paper introductions
A good way to gauge how to create a great introduction is by looking at examples from across your field. The most influential and well-regarded papers should provide some insights into what makes a good introduction.
Dissecting examples: what works and why
We can make some general assumptions by looking at common elements of a good introduction, regardless of the field of research.
A common structure is to start with a broad context, and then narrow that down to specific research questions or hypotheses. This creates a funnel that establishes the scope and relevance.
The most effective introductions are careful about the assumptions they make regarding reader knowledge. By clearly defining key terms and concepts instead of assuming the reader is familiar with them, these introductions set a more solid foundation for understanding.
To pull in the reader and make that all-important good first impression, excellent research paper introductions will often incorporate a compelling narrative or some striking fact that grabs the reader's attention.
Finally, good introductions provide clear citations from past research to back up the claims they're making. In the case of argumentative papers or essays (those that take a stance on a topic or issue), a strong thesis statement compels the reader to continue reading.
Common pitfalls to avoid in research paper introductions
You can also learn what not to do by looking at other research papers. Many authors have made mistakes you can learn from.
We've talked about the need to be clear and concise. Many introductions fail at this; they're verbose, vague, or otherwise fail to convey the research problem or hypothesis efficiently. This often comes in the form of an overemphasis on background information, which obscures the main research focus.
Ensure your introduction provides the proper emphasis and excitement around your research and its significance. Otherwise, fewer people will want to read more about it.
- Crafting a compelling introduction for a research paper
Let’s take a look at the steps required to craft an introduction that pulls readers in and compels them to learn more about your research.
Step 1: Capturing interest and setting the scene
To capture the reader's interest immediately, begin your introduction with a compelling question, a surprising fact, a provocative quote, or some other mechanism that will hook readers and pull them further into the paper.
As they continue reading, the introduction should contextualize your research within the current field, showing readers its relevance and importance. Clarify any essential terms that will help them better understand what you're saying. This keeps the fundamentals of your research accessible to all readers from all backgrounds.
Step 2: Building a solid foundation with background information
Including background information in your introduction serves two major purposes:
It helps to clarify the topic for the reader
It establishes the depth of your research
The approach you take when conveying this information depends on the type of paper.
For argumentative papers, you'll want to develop engaging background narratives. These should provide context for the argument you'll be presenting.
For empirical papers, highlighting past research is the key. Often, there will be some questions that weren't answered in those past papers. If your paper is focused on those areas, those papers make ideal candidates for you to discuss and critique in your introduction.
Step 3: Pinpointing the research challenge
To capture the attention of the reader, you need to explain what research challenges you'll be discussing.
For argumentative papers, this involves articulating why the argument you'll be making is important. What is its relevance to current discussions or problems? What is the potential impact of people accepting or rejecting your argument?
For empirical papers, explain how your research is addressing a gap in existing knowledge. What new insights or contributions will your research bring to your field?
Step 4: Clarifying your research aims and objectives
We mentioned earlier that the introduction to a research paper can serve as a roadmap for what's within. We've also frequently discussed the need for clarity. This step addresses both of these.
When writing an argumentative paper, craft a thesis statement with impact. Clearly articulate what your position is and the main points you intend to present. This will map out for the reader exactly what they'll get from reading the rest.
For empirical papers, focus on formulating precise research questions and hypotheses. Directly link them to the gaps or issues you've identified in existing research to show the reader the precise direction your research paper will take.
Step 5: Sketching the blueprint of your study
Continue building a roadmap for your readers by designing a structured outline for the paper. Guide the reader through your research journey, explaining what the different sections will contain and their relationship to one another.
This outline should flow seamlessly as you move from section to section. Creating this outline early can also help guide the creation of the paper itself, resulting in a final product that's better organized. In doing so, you'll craft a paper where each section flows intuitively from the next.
Step 6: Integrating your research question
To avoid letting your research question get lost in background information or clarifications, craft your introduction in such a way that the research question resonates throughout. The research question should clearly address a gap in existing knowledge or offer a new perspective on an existing problem.
Tell users your research question explicitly but also remember to frequently come back to it. When providing context or clarification, point out how it relates to the research question. This keeps your focus where it needs to be and prevents the topic of the paper from becoming under-emphasized.
Step 7: Establishing the scope and limitations
So far, we've talked mostly about what's in the paper and how to convey that information to readers. The opposite is also important. Information that's outside the scope of your paper should be made clear to the reader in the introduction so their expectations for what is to follow are set appropriately.
Similarly, be honest and upfront about the limitations of the study. Any constraints in methodology, data, or how far your findings can be generalized should be fully communicated in the introduction.
Step 8: Concluding the introduction with a promise
The final few lines of the introduction are your last chance to convince people to continue reading the rest of the paper. Here is where you should make it very clear what benefit they'll get from doing so. What topics will be covered? What questions will be answered? Make it clear what they will get for continuing.
By providing a quick recap of the key points contained in the introduction in its final lines and properly setting the stage for what follows in the rest of the paper, you refocus the reader's attention on the topic of your research and guide them to read more.
- Research paper introduction best practices
Following the steps above will give you a compelling introduction that hits on all the key points an introduction should have. Some more tips and tricks can make an introduction even more polished.
As you follow the steps above, keep the following tips in mind.
Set the right tone and style
Like every piece of writing, a research paper should be written for the audience. That is to say, it should match the tone and style that your academic discipline and target audience expect. This is typically a formal and academic tone, though the degree of formality varies by field.
Kno w the audience
The perfect introduction balances clarity with conciseness. The amount of clarification required for a given topic depends greatly on the target audience. Knowing who will be reading your paper will guide you in determining how much background information is required.
Adopt the CARS (create a research space) model
The CARS model is a helpful tool for structuring introductions. This structure has three parts. The beginning of the introduction establishes the general research area. Next, relevant literature is reviewed and critiqued. The final section outlines the purpose of your study as it relates to the previous parts.
Master the art of funneling
The CARS method is one example of a well-funneled introduction. These start broadly and then slowly narrow down to your specific research problem. It provides a nice narrative flow that provides the right information at the right time. If you stray from the CARS model, try to retain this same type of funneling.
Incorporate narrative element
People read research papers largely to be informed. But to inform the reader, you have to hold their attention. A narrative style, particularly in the introduction, is a great way to do that. This can be a compelling story, an intriguing question, or a description of a real-world problem.
Write the introduction last
By writing the introduction after the rest of the paper, you'll have a better idea of what your research entails and how the paper is structured. This prevents the common problem of writing something in the introduction and then forgetting to include it in the paper. It also means anything particularly exciting in the paper isn’t neglected in the intro.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 22 August 2024
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
Get creative with full-sentence rewrites
Polish your papers with one click, avoid unintentional plagiarism.
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Research Paper Introduction in 4 Steps
Published on July 2, 2024 by Hannah Skaggs . Revised on September 11, 2024.
Having a hard time learning how to write a research paper introduction? Follow these four steps:
- Draw readers in.
- Zoom in on your topic and its importance.
- Explain how you’ll add new knowledge.
- Tell readers what they’ll find in your paper.
To understand why a great introduction matters, imagine a friend inviting you to lunch with another friend of hers. You show up at the restaurant and find them waiting for you at the table. You sit down, and her friend says, “So I wanna tell you about my major goal in life.”
Pretty awkward, right? You don’t even know this guy’s name yet, and he’s already diving into the heavy stuff. You’d probably prefer to have your friend introduce him, then spend some time learning about his background and personality before you get into deeper conversation.
Research paper readers need this kind of warmup, too. A good introduction, or intro, lives up to its name—it introduces readers to the topic. It prepares them to care about and understand your research, and it’s more convincing.
Free Grammar Checker
Table of contents
Steps to write a research paper introduction, tips for writing a research paper introduction, tools for writing a research paper introduction, frequently asked questions about how to write a research paper.
By following the steps below, you can learn how to write an introduction for a research paper that helps readers “shake hands” with your topic. In each step, thinking about the answers to key questions can help you reach your readers.
1. Get your readers’ attention
To speak to your readers effectively, you need to know who they are. Consider who is likely to read the paper and the extent of their knowledge on the topic. Then begin your introduction with a sentence or two that will capture their interest.
For instance, you might begin with an interesting quote or an example of a situation that illustrates your argument (as we did above). Or you could start by simply stating a fact that most people aren’t aware of, which may be a better approach in scientific fields. Whichever method you choose, remember that this is academic writing —keep your phrasing formal and don’t sensationalize.
Key questions:
- Who is your audience?
- What will your paper talk about?
- What will grab your audience’s interest in the topic?
2. Explain why your topic matters
Just as you’d like to understand where a new acquaintance is coming from as you get to know them, your readers want to understand the background of your research. Once you’ve got their attention, explain why they should care.
You can give background for your research by discussing previous research on the topic. While this part should be shorter than a literature review , it can explore some of the same kinds of connections and themes. Make sure the sources you cite relate to the argument you’re making or the problem you want to solve. The information you provide here should lay a factual foundation for your research.
- Why should readers care about your topic?
- What do readers need to know to understand your research?
- What have other researchers said about the topic?
- What is the field’s overall view of the topic?
3. Lay out your argument and plan
After showing your reader the existing knowledge on the topic, you can turn to how your paper will contribute new knowledge. Tying your research to previous research is the most important aspect of this step.
Explain what knowledge is missing from the existing research and how you plan to uncover that knowledge. This is the most common place for the thesis statement, which succinctly tells readers the purpose and main idea of your paper (though it could also appear at the end of Step 4).
- How does your research relate to the studies you described in Step 2?
- What question are you aiming to answer , or what problem are you looking to solve?
- What methods will you use to answer that question or solve that problem?
4. Define your direction
Besides introducing your readers to the topic and your related findings or argument, you’re introducing them to your research process and the paper itself. This means you need to help them understand how the paper is organized and where it’s going. Add a sentence, or a few sentences, describing the sections of your paper in order or the main ideas it will cover.
While longer papers typically need to include this step, shorter ones, such as a five-paragraph essay , can usually skip it. In these cases, the thesis statement outlines the paper’s structure.
- What goal will each section of your paper accomplish?
- What should readers take away from your paper?
As you go through the steps above, keep in mind the principles of quality academic writing. Specifically, understanding how to organize and summarize will empower you to complete each step with excellence.
Keep it smooth
A good flow helps readers follow your logic. As you progress from Step 1 to Step 4, the information you give should grow more and more specific. It’s similar to how, when you meet a person, you learn basics like their name and appearance first. Then you learn about their background and more specific details, like their political views.
To make your introduction flow, start with an outline. The outline functions like a skeleton. It provides a structure for the details that make up your introduction like muscles and other tissues. It helps you make sure you don’t miss any important elements. Then, as you flesh out the details, use transition words and phrases between them to show how they relate to each other.
Keep it brief
How long should a research paper introduction be? It depends on the overall length of your paper, but the intro is typically one of the shortest sections. For example, in a short paper like an essay, you can complete each of the steps above in just a sentence or two. But in a longer one, such as a dissertation , each step may take a couple of paragraphs.
In a sense, the intro is a summary of the rest of the paper, and summarizing is all about prioritizing. As business guru Karen Martin said, “When everything is a priority, nothing is a priority.”
Martin was talking about deciding which tasks are more urgent in a business, but the same principle applies to summarizing. You must decide which ideas are the most fundamental and leave the rest out. Think about it: when you’re first meeting someone, they don’t give you an exhaustive list of all their traits. They introduce themselves with just a few of their most prominent ones.
Besides narrowing your focus, another way to keep your introduction short is to write concisely. Plain, direct language helps hold the reader’s attention, but wordy sentences will make them nod off and lose interest.
Since the introduction of a research paper is basically a summary, you may find it helpful to write it last, after you’ve finished the rest of your paper. If you write it first, there’s a good chance you’ll have to change some of its main points later. This can happen because the other sections of your paper, which your intro is based on, may evolve while you’re writing them.
Of course, you should always go back and take a second or even third look at every section of your research paper to check for errors and other necessary changes. But if you write your intro last, editing it is likely to take much less time.
Now that we’ve introduced you to the basics of writing a research paper introduction, we’d like to introduce you to QuillBot. At every step of writing your intro, it can help you upgrade your writing skills:
- Cite sources using the Citation Generator .
- Avoid plagiarism using the Plagiarism Checker .
- Reword statements from previous research (but still cite them) using the Paraphraser .
- Write spectacular and concise thesis statements (or even your whole introduction section!) using the Summarizer .
A research paper introduction starts by acquainting readers with the topic generally. Then it explores the background of the research. Finally, it explains the specific purpose of the research and its contribution.
Quotes , anecdotes, and interesting facts are all effective hooks to begin the introduction of a research paper. Which one you choose depends on the subject of your paper and your field of study.
Is this article helpful?

Hannah Skaggs

Peer Recognized
Make a name in academia
How to Write a Research Paper: the LEAP approach (+cheat sheet)
In this article I will show you how to write a research paper using the four LEAP writing steps. The LEAP academic writing approach is a step-by-step method for turning research results into a published paper .
The LEAP writing approach has been the cornerstone of the 70 + research papers that I have authored and the 3700+ citations these paper have accumulated within 9 years since the completion of my PhD. I hope the LEAP approach will help you just as much as it has helped me to make an real, tangible impact with my research.
What is the LEAP research paper writing approach?
I designed the LEAP writing approach not only for merely writing the papers. My goal with the writing system was to show young scientists how to first think about research results and then how to efficiently write each section of the research paper.
In other words, you will see how to write a research paper by first analyzing the results and then building a logical, persuasive arguments. In this way, instead of being afraid of writing research paper, you will be able to rely on the paper writing process to help you with what is the most demanding task in getting published – thinking.
The four research paper writing steps according to the LEAP approach:

I will show each of these steps in detail. And you will be able to download the LEAP cheat sheet for using with every paper you write.
But before I tell you how to efficiently write a research paper, I want to show you what is the problem with the way scientists typically write a research paper and why the LEAP approach is more efficient.
How scientists typically write a research paper (and why it isn’t efficient)
Writing a research paper can be tough, especially for a young scientist. Your reasoning needs to be persuasive and thorough enough to convince readers of your arguments. The description has to be derived from research evidence, from prior art, and from your own judgment. This is a tough feat to accomplish.
The figure below shows the sequence of the different parts of a typical research paper. Depending on the scientific journal, some sections might be merged or nonexistent, but the general outline of a research paper will remain very similar.

Here is the problem: Most people make the mistake of writing in this same sequence.
While the structure of scientific articles is designed to help the reader follow the research, it does little to help the scientist write the paper. This is because the layout of research articles starts with the broad (introduction) and narrows down to the specifics (results). See in the figure below how the research paper is structured in terms of the breath of information that each section entails.
How to write a research paper according to the LEAP approach
For a scientist, it is much easier to start writing a research paper with laying out the facts in the narrow sections (i.e. results), step back to describe them (i.e. write the discussion), and step back again to explain the broader picture in the introduction.
For example, it might feel intimidating to start writing a research paper by explaining your research’s global significance in the introduction, while it is easy to plot the figures in the results. When plotting the results, there is not much room for wiggle: the results are what they are.
Starting to write a research papers from the results is also more fun because you finally get to see and understand the complete picture of the research that you have worked on.
Most importantly, following the LEAP approach will help you first make sense of the results yourself and then clearly communicate them to the readers. That is because the sequence of writing allows you to slowly understand the meaning of the results and then develop arguments for presenting to your readers.
I have personally been able to write and submit a research article in three short days using this method.
Step 1: Lay Out the Facts

You have worked long hours on a research project that has produced results and are no doubt curious to determine what they exactly mean. There is no better way to do this than by preparing figures, graphics and tables. This is what the first LEAP step is focused on – diving into the results.
How to p repare charts and tables for a research paper
Your first task is to try out different ways of visually demonstrating the research results. In many fields, the central items of a journal paper will be charts that are based on the data generated during research. In other fields, these might be conceptual diagrams, microscopy images, schematics and a number of other types of scientific graphics which should visually communicate the research study and its results to the readers. If you have reasonably small number of data points, data tables might be useful as well.
Tips for preparing charts and tables
- Try multiple chart types but in the finished paper only use the one that best conveys the message you want to present to the readers
- Follow the eight chart design progressions for selecting and refining a data chart for your paper: https://peerrecognized.com/chart-progressions
- Prepare scientific graphics and visualizations for your paper using the scientific graphic design cheat sheet: https://peerrecognized.com/tools-for-creating-scientific-illustrations/
How to describe the results of your research
Now that you have your data charts, graphics and tables laid out in front of you – describe what you see in them. Seek to answer the question: What have I found? Your statements should progress in a logical sequence and be backed by the visual information. Since, at this point, you are simply explaining what everyone should be able to see for themselves, you can use a declarative tone: The figure X demonstrates that…
Tips for describing the research results :
- Answer the question: “ What have I found? “
- Use declarative tone since you are simply describing observations
Step 2: Explain the results

The core aspect of your research paper is not actually the results; it is the explanation of their meaning. In the second LEAP step, you will do some heavy lifting by guiding the readers through the results using logic backed by previous scientific research.
How to define the Message of a research paper
To define the central message of your research paper, imagine how you would explain your research to a colleague in 20 seconds . If you succeed in effectively communicating your paper’s message, a reader should be able to recount your findings in a similarly concise way even a year after reading it. This clarity will increase the chances that someone uses the knowledge you generated, which in turn raises the likelihood of citations to your research paper.
Tips for defining the paper’s central message :
- Write the paper’s core message in a single sentence or two bullet points
- Write the core message in the header of the research paper manuscript
How to write the Discussion section of a research paper
In the discussion section you have to demonstrate why your research paper is worthy of publishing. In other words, you must now answer the all-important So what? question . How well you do so will ultimately define the success of your research paper.
Here are three steps to get started with writing the discussion section:
- Write bullet points of the things that convey the central message of the research article (these may evolve into subheadings later on).
- Make a list with the arguments or observations that support each idea.
- Finally, expand on each point to make full sentences and paragraphs.
Tips for writing the discussion section:
- What is the meaning of the results?
- Was the hypothesis confirmed?
- Write bullet points that support the core message
- List logical arguments for each bullet point, group them into sections
- Instead of repeating research timeline, use a presentation sequence that best supports your logic
- Convert arguments to full paragraphs; be confident but do not overhype
- Refer to both supportive and contradicting research papers for maximum credibility
How to write the Conclusions of a research paper
Since some readers might just skim through your research paper and turn directly to the conclusions, it is a good idea to make conclusion a standalone piece. In the first few sentences of the conclusions, briefly summarize the methodology and try to avoid using abbreviations (if you do, explain what they mean).
After this introduction, summarize the findings from the discussion section. Either paragraph style or bullet-point style conclusions can be used. I prefer the bullet-point style because it clearly separates the different conclusions and provides an easy-to-digest overview for the casual browser. It also forces me to be more succinct.
Tips for writing the conclusion section :
- Summarize the key findings, starting with the most important one
- Make conclusions standalone (short summary, avoid abbreviations)
- Add an optional take-home message and suggest future research in the last paragraph
How to refine the Objective of a research paper
The objective is a short, clear statement defining the paper’s research goals. It can be included either in the final paragraph of the introduction, or as a separate subsection after the introduction. Avoid writing long paragraphs with in-depth reasoning, references, and explanation of methodology since these belong in other sections. The paper’s objective can often be written in a single crisp sentence.
Tips for writing the objective section :
- The objective should ask the question that is answered by the central message of the research paper
- The research objective should be clear long before writing a paper. At this point, you are simply refining it to make sure it is addressed in the body of the paper.
How to write the Methodology section of your research paper
When writing the methodology section, aim for a depth of explanation that will allow readers to reproduce the study . This means that if you are using a novel method, you will have to describe it thoroughly. If, on the other hand, you applied a standardized method, or used an approach from another paper, it will be enough to briefly describe it with reference to the detailed original source.
Remember to also detail the research population, mention how you ensured representative sampling, and elaborate on what statistical methods you used to analyze the results.
Tips for writing the methodology section :
- Include enough detail to allow reproducing the research
- Provide references if the methods are known
- Create a methodology flow chart to add clarity
- Describe the research population, sampling methodology, statistical methods for result analysis
- Describe what methodology, test methods, materials, and sample groups were used in the research.
Step 3: Advertize the research
Step 3 of the LEAP writing approach is designed to entice the casual browser into reading your research paper. This advertising can be done with an informative title, an intriguing abstract, as well as a thorough explanation of the underlying need for doing the research within the introduction.

How to write the Introduction of a research paper
The introduction section should leave no doubt in the mind of the reader that what you are doing is important and that this work could push scientific knowledge forward. To do this convincingly, you will need to have a good knowledge of what is state-of-the-art in your field. You also need be able to see the bigger picture in order to demonstrate the potential impacts of your research work.
Think of the introduction as a funnel, going from wide to narrow, as shown in the figure below:
- Start with a brief context to explain what do we already know,
- Follow with the motivation for the research study and explain why should we care about it,
- Explain the research gap you are going to bridge within this research paper,
- Describe the approach you will take to solve the problem.
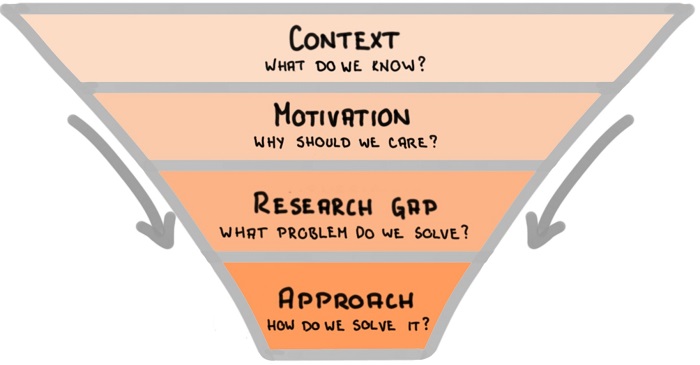
Tips for writing the introduction section :
- Follow the Context – Motivation – Research gap – Approach funnel for writing the introduction
- Explain how others tried and how you plan to solve the research problem
- Do a thorough literature review before writing the introduction
- Start writing the introduction by using your own words, then add references from the literature

How to prepare the Abstract of a research paper
The abstract acts as your paper’s elevator pitch and is therefore best written only after the main text is finished. In this one short paragraph you must convince someone to take on the time-consuming task of reading your whole research article. So, make the paper easy to read, intriguing, and self-explanatory; avoid jargon and abbreviations.
How to structure the abstract of a research paper:
- The abstract is a single paragraph that follows this structure:
- Problem: why did we research this
- Methodology: typically starts with the words “Here we…” that signal the start of own contribution.
- Results: what we found from the research.
- Conclusions: show why are the findings important
How to compose a research paper Title
The title is the ultimate summary of a research paper. It must therefore entice someone looking for information to click on a link to it and continue reading the article. A title is also used for indexing purposes in scientific databases, so a representative and optimized title will play large role in determining if your research paper appears in search results at all.
Tips for coming up with a research paper title:
- Capture curiosity of potential readers using a clear and descriptive title
- Include broad terms that are often searched
- Add details that uniquely identify the researched subject of your research paper
- Avoid jargon and abbreviations
- Use keywords as title extension (instead of duplicating the words) to increase the chance of appearing in search results
How to prepare Highlights and Graphical Abstract
Highlights are three to five short bullet-point style statements that convey the core findings of the research paper. Notice that the focus is on the findings, not on the process of getting there.
A graphical abstract placed next to the textual abstract visually summarizes the entire research paper in a single, easy-to-follow figure. I show how to create a graphical abstract in my book Research Data Visualization and Scientific Graphics.
Tips for preparing highlights and graphical abstract:
- In highlights show core findings of the research paper (instead of what you did in the study).
- In graphical abstract show take-home message or methodology of the research paper. Learn more about creating a graphical abstract in this article.
Step 4: Prepare for submission

Sometimes it seems that nuclear fusion will stop on the star closest to us (read: the sun will stop to shine) before a submitted manuscript is published in a scientific journal. The publication process routinely takes a long time, and after submitting the manuscript you have very little control over what happens. To increase the chances of a quick publication, you must do your homework before submitting the manuscript. In the fourth LEAP step, you make sure that your research paper is published in the most appropriate journal as quickly and painlessly as possible.
How to select a scientific Journal for your research paper
The best way to find a journal for your research paper is it to review which journals you used while preparing your manuscript. This source listing should provide some assurance that your own research paper, once published, will be among similar articles and, thus, among your field’s trusted sources.
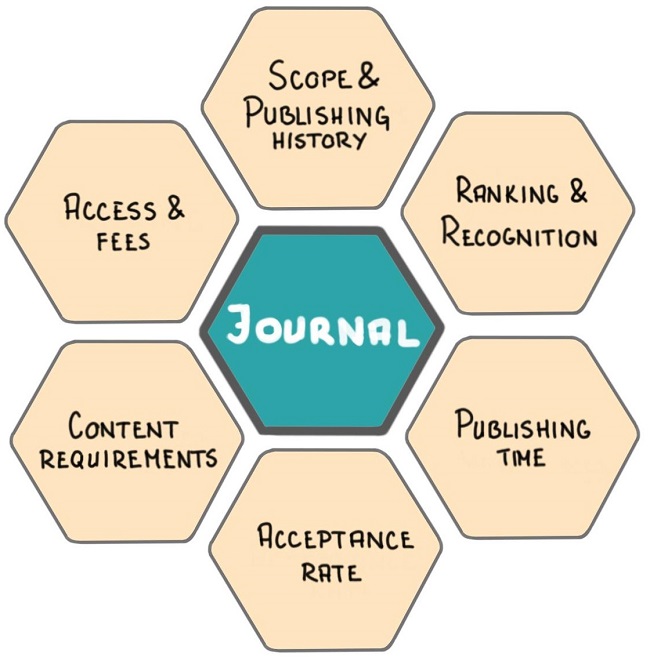
After this initial selection of hand-full of scientific journals, consider the following six parameters for selecting the most appropriate journal for your research paper (read this article to review each step in detail):
- Scope and publishing history
- Ranking and Recognition
- Publishing time
- Acceptance rate
- Content requirements
- Access and Fees
How to select a journal for your research paper:
- Use the six parameters to select the most appropriate scientific journal for your research paper
- Use the following tools for journal selection: https://peerrecognized.com/journals
- Follow the journal’s “Authors guide” formatting requirements
How to Edit you manuscript
No one can write a finished research paper on their first attempt. Before submitting, make sure to take a break from your work for a couple of days, or even weeks. Try not to think about the manuscript during this time. Once it has faded from your memory, it is time to return and edit. The pause will allow you to read the manuscript from a fresh perspective and make edits as necessary.
I have summarized the most useful research paper editing tools in this article.
Tips for editing a research paper:
- Take time away from the research paper to forget about it; then returning to edit,
- Start by editing the content: structure, headings, paragraphs, logic, figures
- Continue by editing the grammar and language; perform a thorough language check using academic writing tools
- Read the entire paper out loud and correct what sounds weird
How to write a compelling Cover Letter for your paper
Begin the cover letter by stating the paper’s title and the type of paper you are submitting (review paper, research paper, short communication). Next, concisely explain why your study was performed, what was done, and what the key findings are. State why the results are important and what impact they might have in the field. Make sure you mention how your approach and findings relate to the scope of the journal in order to show why the article would be of interest to the journal’s readers.
I wrote a separate article that explains what to include in a cover letter here. You can also download a cover letter template from the article.
Tips for writing a cover letter:
- Explain how the findings of your research relate to journal’s scope
- Tell what impact the research results will have
- Show why the research paper will interest the journal’s audience
- Add any legal statements as required in journal’s guide for authors
How to Answer the Reviewers
Reviewers will often ask for new experiments, extended discussion, additional details on the experimental setup, and so forth. In principle, your primary winning tactic will be to agree with the reviewers and follow their suggestions whenever possible. After all, you must earn their blessing in order to get your paper published.
Be sure to answer each review query and stick to the point. In the response to the reviewers document write exactly where in the paper you have made any changes. In the paper itself, highlight the changes using a different color. This way the reviewers are less likely to re-read the entire article and suggest new edits.
In cases when you don’t agree with the reviewers, it makes sense to answer more thoroughly. Reviewers are scientifically minded people and so, with enough logical and supported argument, they will eventually be willing to see things your way.
Tips for answering the reviewers:
- Agree with most review comments, but if you don’t, thoroughly explain why
- Highlight changes in the manuscript
- Do not take the comments personally and cool down before answering
The LEAP research paper writing cheat sheet
Imagine that you are back in grad school and preparing to take an exam on the topic: “How to write a research paper”. As an exemplary student, you would, most naturally, create a cheat sheet summarizing the subject… Well, I did it for you.
This one-page summary of the LEAP research paper writing technique will remind you of the key research paper writing steps. Print it out and stick it to a wall in your office so that you can review it whenever you are writing a new research paper.

Now that we have gone through the four LEAP research paper writing steps, I hope you have a good idea of how to write a research paper. It can be an enjoyable process and once you get the hang of it, the four LEAP writing steps should even help you think about and interpret the research results. This process should enable you to write a well-structured, concise, and compelling research paper.
Have fund with writing your next research paper. I hope it will turn out great!
Learn writing papers that get cited
The LEAP writing approach is a blueprint for writing research papers. But to be efficient and write papers that get cited, you need more than that.
My name is Martins Zaumanis and in my interactive course Research Paper Writing Masterclass I will show you how to visualize your research results, frame a message that convinces your readers, and write each section of the paper. Step-by-step.
And of course – you will learn to respond the infamous Reviewer No.2.

Hey! My name is Martins Zaumanis and I am a materials scientist in Switzerland ( Google Scholar ). As the first person in my family with a PhD, I have first-hand experience of the challenges starting scientists face in academia. With this blog, I want to help young researchers succeed in academia. I call the blog “Peer Recognized”, because peer recognition is what lifts academic careers and pushes science forward.
Besides this blog, I have written the Peer Recognized book series and created the Peer Recognized Academy offering interactive online courses.
Related articles:
One comment
- Pingback: Research Paper Outline with Key Sentence Skeleton (+Paper Template)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
I want to join the Peer Recognized newsletter!
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Copyright © 2024 Martins Zaumanis
Contacts: [email protected]
Privacy Policy
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper

How to write an introduction for a research paper? Eventually (and with practice) all writers will develop their own strategy for writing the perfect introduction for a research paper. Once you are comfortable with writing, you will probably find your own, but coming up with a good strategy can be tough for beginning writers.
The Purpose of an Introduction
Your opening paragraphs, phrases for introducing thesis statements, research paper introduction examples, using the introduction to map out your research paper.

Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
- First write your thesis.Your thesis should state the main idea in specific terms.
- After you have a working thesis, tackle the body of your paper before you write the rest of the introduction. Each paragraph in the body should explore one specific topic that proves, or summarizes your thesis. Writing is a thinking process. Once you have worked your way through that process by writing the body of the paper, you will have an intimate understanding of how you are supporting your thesis. After you have written the body paragraphs, go back and rewrite your thesis to make it more specific and to connect it to the topics you addressed in the body paragraph.
- Revise your introduction several times, saving each revision. Be sure your introduction previews the topics you are presenting in your paper. One way of doing this is to use keywords from the topic sentences in each paragraph to introduce, or preview, the topics in your introduction.This “preview” will give your reader a context for understanding how you will make your case.
- Experiment by taking different approaches to your thesis with every revision you make. Play with the language in the introduction. Strike a new tone. Go back and compare versions. Then pick the one that works most effectively with the body of your research paper.
- Do not try to pack everything you want to say into your introduction. Just as your introduction should not be too short, it should also not be too long. Your introduction should be about the same length as any other paragraph in your research paper. Let the content—what you have to say—dictate the length.
The first page of your research paper should draw the reader into the text. It is the paper’s most important page and, alas, often the worst written. There are two culprits here and effective ways to cope with both of them.
First, the writer is usually straining too hard to say something terribly BIG and IMPORTANT about the thesis topic. The goal is worthy, but the aim is unrealistically high. The result is often a muddle of vague platitudes rather than a crisp, compelling introduction to the thesis. Want a familiar example? Listen to most graduation speakers. Their goal couldn’t be loftier: to say what education means and to tell an entire football stadium how to live the rest of their lives. The results are usually an avalanche of clichés and sodden prose.
The second culprit is bad timing. The opening and concluding paragraphs are usually written late in the game, after the rest of the thesis is finished and polished. There’s nothing wrong with writing these sections last. It’s usually the right approach since you need to know exactly what you are saying in the substantive middle sections of the thesis before you can introduce them effectively or draw together your findings. But having waited to write the opening and closing sections, you need to review and edit them several times to catch up. Otherwise, you’ll putting the most jagged prose in the most tender spots. Edit and polish your opening paragraphs with extra care. They should draw readers into the paper.
After you’ve done some extra polishing, I suggest a simple test for the introductory section. As an experiment, chop off the first few paragraphs. Let the paper begin on, say, paragraph 2 or even page 2. If you don’t lose much, or actually gain in clarity and pace, then you’ve got a problem.
There are two solutions. One is to start at this new spot, further into the text. After all, that’s where you finally gain traction on your subject. That works best in some cases, and we occasionally suggest it. The alternative, of course, is to write a new opening that doesn’t flop around, saying nothing.
What makes a good opening? Actually, they come in several flavors. One is an intriguing story about your topic. Another is a brief, compelling quote. When you run across them during your reading, set them aside for later use. Don’t be deterred from using them because they “don’t seem academic enough.” They’re fine as long as the rest of the paper doesn’t sound like you did your research in People magazine. The third, and most common, way to begin is by stating your main questions, followed by a brief comment about why they matter.
Whichever opening you choose, it should engage your readers and coax them to continue. Having done that, you should give them a general overview of the project—the main issues you will cover, the material you will use, and your thesis statement (that is, your basic approach to the topic). Finally, at the end of the introductory section, give your readers a brief road map, showing how the paper will unfold. How you do that depends on your topic but here are some general suggestions for phrase choice that may help:
- This analysis will provide …
- This paper analyzes the relationship between …
- This paper presents an analysis of …
- This paper will argue that …
- This topic supports the argument that…
- Research supports the opinion that …
- This paper supports the opinion that …
- An interpretation of the facts indicates …
- The results of this experiment show …
- The results of this research show …
Comparisons/Contrasts
- A comparison will show that …
- By contrasting the results,we see that …
- This paper examines the advantages and disadvantages of …
Definitions/Classifications
- This paper will provide a guide for categorizing the following:…
- This paper provides a definition of …
- This paper explores the meaning of …
- This paper will discuss the implications of …
- A discussion of this topic reveals …
- The following discussion will focus on …
Description
- This report describes…
- This report will illustrate…
- This paper provides an illustration of …
Process/Experimentation
- This paper will identify the reasons behind…
- The results of the experiment show …
- The process revealed that …
- This paper theorizes…
- This paper presents the theory that …
- In theory, this indicates that …
Quotes, anecdotes, questions, examples, and broad statements—all of them can used successfully to write an introduction for a research paper. It’s instructive to see them in action, in the hands of skilled academic writers.
Let’s begin with David M. Kennedy’s superb history, Freedom from Fear: The American People in Depression and War, 1929–1945 . Kennedy begins each chapter with a quote, followed by his text. The quote above chapter 1 shows President Hoover speaking in 1928 about America’s golden future. The text below it begins with the stock market collapse of 1929. It is a riveting account of just how wrong Hoover was. The text about the Depression is stronger because it contrasts so starkly with the optimistic quotation.
“We in America today are nearer the final triumph over poverty than ever before in the history of any land.”—Herbert Hoover, August 11, 1928 Like an earthquake, the stock market crash of October 1929 cracked startlingly across the United States, the herald of a crisis that was to shake the American way of life to its foundations. The events of the ensuing decade opened a fissure across the landscape of American history no less gaping than that opened by the volley on Lexington Common in April 1775 or by the bombardment of Sumter on another April four score and six years later. The ratcheting ticker machines in the autumn of 1929 did not merely record avalanching stock prices. In time they came also to symbolize the end of an era. (David M. Kennedy, Freedom from Fear: The American People in Depression and War, 1929–1945 . New York: Oxford University Press, 1999, p. 10)
Kennedy has exciting, wrenching material to work with. John Mueller faces the exact opposite problem. In Retreat from Doomsday: The Obsolescence of Major War , he is trying to explain why Great Powers have suddenly stopped fighting each other. For centuries they made war on each other with devastating regularity, killing millions in the process. But now, Mueller thinks, they have not just paused; they have stopped permanently. He is literally trying to explain why “nothing is happening now.” That may be an exciting topic intellectually, it may have great practical significance, but “nothing happened” is not a very promising subject for an exciting opening paragraph. Mueller manages to make it exciting and, at the same time, shows why it matters so much. Here’s his opening, aptly entitled “History’s Greatest Nonevent”:
On May 15, 1984, the major countries of the developed world had managed to remain at peace with each other for the longest continuous stretch of time since the days of the Roman Empire. If a significant battle in a war had been fought on that day, the press would have bristled with it. As usual, however, a landmark crossing in the history of peace caused no stir: the most prominent story in the New York Times that day concerned the saga of a manicurist, a machinist, and a cleaning woman who had just won a big Lotto contest. This book seeks to develop an explanation for what is probably the greatest nonevent in human history. (John Mueller, Retreat from Doomsday: The Obsolescence of Major War . New York: Basic Books, 1989, p. 3)
In the space of a few sentences, Mueller sets up his puzzle and reveals its profound human significance. At the same time, he shows just how easy it is to miss this milestone in the buzz of daily events. Notice how concretely he does that. He doesn’t just say that the New York Times ignored this record setting peace. He offers telling details about what they covered instead: “a manicurist, a machinist, and a cleaning woman who had just won a big Lotto contest.” Likewise, David Kennedy immediately entangles us in concrete events: the stunning stock market crash of 1929. These are powerful openings that capture readers’ interests, establish puzzles, and launch narratives.
Sociologist James Coleman begins in a completely different way, by posing the basic questions he will study. His ambitious book, Foundations of Social Theory , develops a comprehensive theory of social life, so it is entirely appropriate for him to begin with some major questions. But he could just as easily have begun with a compelling story or anecdote. He includes many of them elsewhere in his book. His choice for the opening, though, is to state his major themes plainly and frame them as a paradox. Sociologists, he says, are interested in aggregate behavior—how people act in groups, organizations, or large numbers—yet they mostly examine individuals:
A central problem in social science is that of accounting for the function of some kind of social system. Yet in most social research, observations are not made on the system as a whole, but on some part of it. In fact, the natural unit of observation is the individual person… This has led to a widening gap between theory and research… (James S. Coleman, Foundations of Social Theory . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1990, pp. 1–2)
After expanding on this point, Coleman explains that he will not try to remedy the problem by looking solely at groups or aggregate-level data. That’s a false solution, he says, because aggregates don’t act; individuals do. So the real problem is to show the links between individual actions and aggregate outcomes, between the micro and the macro.
The major problem for explanations of system behavior based on actions and orientations at a level below that of the system [in this case, on individual-level actions] is that of moving from the lower level to the system level. This has been called the micro-to-macro problem, and it is pervasive throughout the social sciences. (Coleman, Foundations of Social Theory , p. 6)
Explaining how to deal with this “micro-to-macro problem” is the central issue of Coleman’s book, and he announces it at the beginning.
Coleman’s theory-driven opening stands at the opposite end of the spectrum from engaging stories or anecdotes, which are designed to lure the reader into the narrative and ease the path to a more analytic treatment later in the text. Take, for example, the opening sentences of Robert L. Herbert’s sweeping study Impressionism: Art, Leisure, and Parisian Society : “When Henry Tuckerman came to Paris in 1867, one of the thousands of Americans attracted there by the huge international exposition, he was bowled over by the extraordinary changes since his previous visit twenty years before.” (Robert L. Herbert, Impressionism: Art, Leisure, and Parisian Society . New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 1988, p. 1.) Herbert fills in the evocative details to set the stage for his analysis of the emerging Impressionist art movement and its connection to Parisian society and leisure in this period.
David Bromwich writes about Wordsworth, a poet so familiar to students of English literature that it is hard to see him afresh, before his great achievements, when he was just a young outsider starting to write. To draw us into Wordsworth’s early work, Bromwich wants us to set aside our entrenched images of the famous mature poet and see him as he was in the 1790s, as a beginning writer on the margins of society. He accomplishes this ambitious task in the opening sentences of Disowned by Memory: Wordsworth’s Poetry of the 1790s :
Wordsworth turned to poetry after the revolution to remind himself that he was still a human being. It was a curious solution, to a difficulty many would not have felt. The whole interest of his predicament is that he did feel it. Yet Wordsworth is now so established an eminence—his name so firmly fixed with readers as a moralist of self-trust emanating from complete self-security—that it may seem perverse to imagine him as a criminal seeking expiation. Still, that is a picture we get from The Borderers and, at a longer distance, from “Tintern Abbey.” (David Bromwich, Disowned by Memory: Wordsworth’s Poetry of the 1790s . Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1998, p. 1)
That’s a wonderful opening! Look at how much Bromwich accomplishes in just a few words. He not only prepares the way for analyzing Wordsworth’s early poetry; he juxtaposes the anguished young man who wrote it to the self-confident, distinguished figure he became—the eminent man we can’t help remembering as we read his early poetry.
Let us highlight a couple of other points in this passage because they illustrate some intelligent writing choices. First, look at the odd comma in this sentence: “It was a curious solution, to a difficulty many would not have felt.” Any standard grammar book would say that comma is wrong and should be omitted. Why did Bromwich insert it? Because he’s a fine writer, thinking of his sentence rhythm and the point he wants to make. The comma does exactly what it should. It makes us pause, breaking the sentence into two parts, each with an interesting point. One is that Wordsworth felt a difficulty others would not have; the other is that he solved it in a distinctive way. It would be easy for readers to glide over this double message, so Bromwich has inserted a speed bump to slow us down. Most of the time, you should follow grammatical rules, like those about commas, but you should bend them when it serves a good purpose. That’s what the writer does here.
The second small point is the phrase “after the revolution” in the first sentence: “Wordsworth turned to poetry after the revolution to remind himself that he was still a human being.” Why doesn’t Bromwich say “after the French Revolution”? Because he has judged his book’s audience. He is writing for specialists who already know which revolution is reverberating through English life in the 1790s. It is the French Revolution, not the earlier loss of the American colonies. If Bromwich were writing for a much broader audience—say, the New York Times Book Review—he would probably insert the extra word to avoid confusion.
The message “Know your audience” applies to all writers. Don’t talk down to them by assuming they can’t get dressed in the morning. Don’t strut around showing off your book learnin’ by tossing in arcane facts and esoteric language for its own sake. Neither will win over readers.
Bromwich, Herbert, and Coleman open their works in different ways, but their choices work well for their different texts. Your task is to decide what kind of opening will work best for yours. Don’t let that happen by default, by grabbing the first idea you happen upon. Consider a couple of different ways of opening your thesis and then choose the one you prefer. Give yourself some options, think them over, then make an informed choice.
Whether you begin with a story, puzzle, or broad statement, the next part of the introduction should pose your main questions and establish your argument. This is your thesis statement—your viewpoint along with the supporting reasons and evidence. It should be articulated plainly so readers understand full well what your paper is about and what it will argue.
After that, give your readers a road map of what’s to come. That’s normally done at the end of the introductory section (or, in a book, at the end of the introductory chapter). Here’s John J. Mearsheimer presenting such a road map in The Tragedy of Great Power Politics . He not only tells us the order of upcoming chapters, he explains why he’s chosen that order and which chapters are most important:
The Plan of the Book The rest of the chapters in this book are concerned mainly with answering the six big questions about power which I identified earlier. Chapter 2, which is probably the most important chapter in the book, lays out my theory of why states compete for power and why they pursue hegemony. In Chapters 3 and 4, I define power and explain how to measure it. I do this in order to lay the groundwork for testing my theory… (John J. Mearsheimer, The Tragedy of Great Power Politics . New York: W. W. Norton, 2001, p. 27)
As this excerpt makes clear, Mearsheimer has already laid out his “six big questions” in the introduction. Now he’s showing us the path ahead, the path to answering those questions.
At the end of the introduction, give your readers a road map of what’s to come. Tell them what the upcoming sections will be and why they are arranged in this particular order.
After having written your introduction it’s time to move to the biggest part: body of a research paper.
Back to How To Write A Research Paper .
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER


Creating A Research Space or CARS
Introduction, what is the cars model, why is this important.
- Guide License
- Move 1: Establishing a Territory
- Move 2: Establishing a Niche
- Move 3: Occupying the Niche
- Tips for Using the CARS Model
Paul V. Galvin Library

email: [email protected]
Chat with us:
Make a research appointment:, search our faq:.
This guide presents a detailed explanation of the CARS model, a framework that can help you organize your academic writing. It is useful for students and researchers writing introductions for all types of papers, including theses, dissertations, and grant proposals.
The CARS model simplifies writing introductions or proposals by helping you:
- Explain why your research is important
- Show how your work fits with existing research
- Describe the purpose of your paper or proposal
The following sections of this guide will explain each part of the CARS model, accompanied by examples to help you apply it to your writing. This model has proven valuable for many researchers and students, helping them produce clear, strong introductions that adhere to academic standards and emphasize the significance of their work. We hope it will help you, too.
CARS stands for "Creating a Research Space." It's a framework developed by linguist John Swales that helps you introduce your research in a way that captures your readers' attention and clearly shows your work's place in academic conversation. Think of it as a roadmap for your introduction, guiding you through three essential moves:
- Establishing a Territory
- Establishing a Niche
- Occupying the Niche
Each of these moves has specific steps, which we'll explore in detail. By the end of this guide, you'll have a clear understanding of how to apply the CARS model to your own writing, helping you craft introductions that are both engaging and academically sound.
It's also important to understand what the CARS model is not. Unlike formatting guides or grammar rules, CARS focuses on organizing your introduction's content. It doesn't teach basic writing skills or provide downloadable templates. Instead, it helps you articulate why your research matters, how it fits within existing work, and what you accomplished or hope to accomplish. By following this model, you'll create a compelling narrative for your research, setting the stage for the detailed work that follows.
A well-crafted introduction is essential because:
- It frames your research by providing context and relevance, helping readers understand why your work matters.
- It forms the foundation for your study, setting clear expectations for what follows.
- It enhances the quality and reception of your writing by presenting your ideas in a structured, logical manner.
- It improves your work's overall coherence and impact by establishing a clear direction from the outset.
Yet many people find crafting effective introductions to be the most difficult part of academic writing.
Understanding and using the CARS model is a proven method for crafting effective introductions. It ensures that all the essential elements listed above are effectively communicated.
Moreover, a strong introduction encourages other researchers who find your paper to continue reading your work. This increased engagement can lead to several benefits:
- Higher likelihood of your full study being read and understood
- Increased potential for your work to be cited by other researchers
- Greater visibility of your research within the academic community
- Potential for broader impact in your field of study
What this means is that by writing a compelling introduction to your paper, you're not just improving that one paper—you're potentially enhancing your contribution to the advancement of knowledge in your field and boosting your academic profile.
- Next: Move 1: Establishing a Territory >>
- Last Updated: Sep 27, 2024 9:30 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.iit.edu/cars
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Interpretation – Process, Methods and...

Research Results Section – Writing Guide and...

How to Publish a Research Paper – Step by Step...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Techniques – Methods, Types and Examples

Table of Contents – Types, Formats, Examples
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 4. The Introduction
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The introduction leads the reader from a general subject area to a particular topic of inquiry. It establishes the scope, context, and significance of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the research problem supported by a hypothesis or a set of questions, explaining briefly the methodological approach used to examine the research problem, highlighting the potential outcomes your study can reveal, and outlining the remaining structure and organization of the paper.
Key Elements of the Research Proposal. Prepared under the direction of the Superintendent and by the 2010 Curriculum Design and Writing Team. Baltimore County Public Schools.
Importance of a Good Introduction
Think of the introduction as a mental road map that must answer for the reader these four questions:
- What was I studying?
- Why was this topic important to investigate?
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study?
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding?
According to Reyes, there are three overarching goals of a good introduction: 1) ensure that you summarize prior studies about the topic in a manner that lays a foundation for understanding the research problem; 2) explain how your study specifically addresses gaps in the literature, insufficient consideration of the topic, or other deficiency in the literature; and, 3) note the broader theoretical, empirical, and/or policy contributions and implications of your research.
A well-written introduction is important because, quite simply, you never get a second chance to make a good first impression. The opening paragraphs of your paper will provide your readers with their initial impressions about the logic of your argument, your writing style, the overall quality of your research, and, ultimately, the validity of your findings and conclusions. A vague, disorganized, or error-filled introduction will create a negative impression, whereas, a concise, engaging, and well-written introduction will lead your readers to think highly of your analytical skills, your writing style, and your research approach. All introductions should conclude with a brief paragraph that describes the organization of the rest of the paper.
Hirano, Eliana. “Research Article Introductions in English for Specific Purposes: A Comparison between Brazilian, Portuguese, and English.” English for Specific Purposes 28 (October 2009): 240-250; Samraj, B. “Introductions in Research Articles: Variations Across Disciplines.” English for Specific Purposes 21 (2002): 1–17; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide. Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70; Reyes, Victoria. Demystifying the Journal Article. Inside Higher Education.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Structure and Approach
The introduction is the broad beginning of the paper that answers three important questions for the reader:
- What is this?
- Why should I read it?
- What do you want me to think about / consider doing / react to?
Think of the structure of the introduction as an inverted triangle of information that lays a foundation for understanding the research problem. Organize the information so as to present the more general aspects of the topic early in the introduction, then narrow your analysis to more specific topical information that provides context, finally arriving at your research problem and the rationale for studying it [often written as a series of key questions to be addressed or framed as a hypothesis or set of assumptions to be tested] and, whenever possible, a description of the potential outcomes your study can reveal.
These are general phases associated with writing an introduction: 1. Establish an area to research by:
- Highlighting the importance of the topic, and/or
- Making general statements about the topic, and/or
- Presenting an overview on current research on the subject.
2. Identify a research niche by:
- Opposing an existing assumption, and/or
- Revealing a gap in existing research, and/or
- Formulating a research question or problem, and/or
- Continuing a disciplinary tradition.
3. Place your research within the research niche by:
- Stating the intent of your study,
- Outlining the key characteristics of your study,
- Describing important results, and
- Giving a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
NOTE: It is often useful to review the introduction late in the writing process. This is appropriate because outcomes are unknown until you've completed the study. After you complete writing the body of the paper, go back and review introductory descriptions of the structure of the paper, the method of data gathering, the reporting and analysis of results, and the conclusion. Reviewing and, if necessary, rewriting the introduction ensures that it correctly matches the overall structure of your final paper.
II. Delimitations of the Study
Delimitations refer to those characteristics that limit the scope and define the conceptual boundaries of your research . This is determined by the conscious exclusionary and inclusionary decisions you make about how to investigate the research problem. In other words, not only should you tell the reader what it is you are studying and why, but you must also acknowledge why you rejected alternative approaches that could have been used to examine the topic.
Obviously, the first limiting step was the choice of research problem itself. However, implicit are other, related problems that could have been chosen but were rejected. These should be noted in the conclusion of your introduction. For example, a delimitating statement could read, "Although many factors can be understood to impact the likelihood young people will vote, this study will focus on socioeconomic factors related to the need to work full-time while in school." The point is not to document every possible delimiting factor, but to highlight why previously researched issues related to the topic were not addressed.
Examples of delimitating choices would be:
- The key aims and objectives of your study,
- The research questions that you address,
- The variables of interest [i.e., the various factors and features of the phenomenon being studied],
- The method(s) of investigation,
- The time period your study covers, and
- Any relevant alternative theoretical frameworks that could have been adopted.
Review each of these decisions. Not only do you clearly establish what you intend to accomplish in your research, but you should also include a declaration of what the study does not intend to cover. In the latter case, your exclusionary decisions should be based upon criteria understood as, "not interesting"; "not directly relevant"; “too problematic because..."; "not feasible," and the like. Make this reasoning explicit!
NOTE: Delimitations refer to the initial choices made about the broader, overall design of your study and should not be confused with documenting the limitations of your study discovered after the research has been completed.
ANOTHER NOTE: Do not view delimitating statements as admitting to an inherent failing or shortcoming in your research. They are an accepted element of academic writing intended to keep the reader focused on the research problem by explicitly defining the conceptual boundaries and scope of your study. It addresses any critical questions in the reader's mind of, "Why the hell didn't the author examine this?"
III. The Narrative Flow
Issues to keep in mind that will help the narrative flow in your introduction :
- Your introduction should clearly identify the subject area of interest . A simple strategy to follow is to use key words from your title in the first few sentences of the introduction. This will help focus the introduction on the topic at the appropriate level and ensures that you get to the subject matter quickly without losing focus, or discussing information that is too general.
- Establish context by providing a brief and balanced review of the pertinent published literature that is available on the subject. The key is to summarize for the reader what is known about the specific research problem before you did your analysis. This part of your introduction should not represent a comprehensive literature review--that comes next. It consists of a general review of the important, foundational research literature [with citations] that establishes a foundation for understanding key elements of the research problem. See the drop-down menu under this tab for " Background Information " regarding types of contexts.
- Clearly state the hypothesis that you investigated . When you are first learning to write in this format it is okay, and actually preferable, to use a past statement like, "The purpose of this study was to...." or "We investigated three possible mechanisms to explain the...."
- Why did you choose this kind of research study or design? Provide a clear statement of the rationale for your approach to the problem studied. This will usually follow your statement of purpose in the last paragraph of the introduction.
IV. Engaging the Reader
A research problem in the social sciences can come across as dry and uninteresting to anyone unfamiliar with the topic . Therefore, one of the goals of your introduction is to make readers want to read your paper. Here are several strategies you can use to grab the reader's attention:
- Open with a compelling story . Almost all research problems in the social sciences, no matter how obscure or esoteric , are really about the lives of people. Telling a story that humanizes an issue can help illuminate the significance of the problem and help the reader empathize with those affected by the condition being studied.
- Include a strong quotation or a vivid, perhaps unexpected, anecdote . During your review of the literature, make note of any quotes or anecdotes that grab your attention because they can used in your introduction to highlight the research problem in a captivating way.
- Pose a provocative or thought-provoking question . Your research problem should be framed by a set of questions to be addressed or hypotheses to be tested. However, a provocative question can be presented in the beginning of your introduction that challenges an existing assumption or compels the reader to consider an alternative viewpoint that helps establish the significance of your study.
- Describe a puzzling scenario or incongruity . This involves highlighting an interesting quandary concerning the research problem or describing contradictory findings from prior studies about a topic. Posing what is essentially an unresolved intellectual riddle about the problem can engage the reader's interest in the study.
- Cite a stirring example or case study that illustrates why the research problem is important . Draw upon the findings of others to demonstrate the significance of the problem and to describe how your study builds upon or offers alternatives ways of investigating this prior research.
NOTE: It is important that you choose only one of the suggested strategies for engaging your readers. This avoids giving an impression that your paper is more flash than substance and does not distract from the substance of your study.
Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Introduction. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Introductions. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Introductions, Body Paragraphs, and Conclusions for an Argument Paper. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide . Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70; Resources for Writers: Introduction Strategies. Program in Writing and Humanistic Studies. Massachusetts Institute of Technology; Sharpling, Gerald. Writing an Introduction. Centre for Applied Linguistics, University of Warwick; Samraj, B. “Introductions in Research Articles: Variations Across Disciplines.” English for Specific Purposes 21 (2002): 1–17; Swales, John and Christine B. Feak. Academic Writing for Graduate Students: Essential Skills and Tasks . 2nd edition. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press, 2004 ; Writing Your Introduction. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University.
Writing Tip
Avoid the "Dictionary" Introduction
Giving the dictionary definition of words related to the research problem may appear appropriate because it is important to define specific terminology that readers may be unfamiliar with. However, anyone can look a word up in the dictionary and a general dictionary is not a particularly authoritative source because it doesn't take into account the context of your topic and doesn't offer particularly detailed information. Also, placed in the context of a particular discipline, a term or concept may have a different meaning than what is found in a general dictionary. If you feel that you must seek out an authoritative definition, use a subject specific dictionary or encyclopedia [e.g., if you are a sociology student, search for dictionaries of sociology]. A good database for obtaining definitive definitions of concepts or terms is Credo Reference .
Saba, Robert. The College Research Paper. Florida International University; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
Another Writing Tip
When Do I Begin?
A common question asked at the start of any paper is, "Where should I begin?" An equally important question to ask yourself is, "When do I begin?" Research problems in the social sciences rarely rest in isolation from history. Therefore, it is important to lay a foundation for understanding the historical context underpinning the research problem. However, this information should be brief and succinct and begin at a point in time that illustrates the study's overall importance. For example, a study that investigates coffee cultivation and export in West Africa as a key stimulus for local economic growth needs to describe the beginning of exporting coffee in the region and establishing why economic growth is important. You do not need to give a long historical explanation about coffee exports in Africa. If a research problem requires a substantial exploration of the historical context, do this in the literature review section. In your introduction, make note of this as part of the "roadmap" [see below] that you use to describe the organization of your paper.
Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide . Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Always End with a Roadmap
The final paragraph or sentences of your introduction should forecast your main arguments and conclusions and provide a brief description of the rest of the paper [the "roadmap"] that let's the reader know where you are going and what to expect. A roadmap is important because it helps the reader place the research problem within the context of their own perspectives about the topic. In addition, concluding your introduction with an explicit roadmap tells the reader that you have a clear understanding of the structural purpose of your paper. In this way, the roadmap acts as a type of promise to yourself and to your readers that you will follow a consistent and coherent approach to addressing the topic of inquiry. Refer to it often to help keep your writing focused and organized.
Cassuto, Leonard. “On the Dissertation: How to Write the Introduction.” The Chronicle of Higher Education , May 28, 2018; Radich, Michael. A Student's Guide to Writing in East Asian Studies . (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Writing n. d.), pp. 35-37.
- << Previous: Executive Summary
- Next: The C.A.R.S. Model >>
- Last Updated: Sep 27, 2024 1:09 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Writing a scientific paper.
- Writing a lab report
What is a "good" introduction?
Citing sources in the introduction, "introduction checklist" from: how to write a good scientific paper. chris a. mack. spie. 2018..
- LITERATURE CITED
- Bibliography of guides to scientific writing and presenting
- Peer Review
- Presentations
- Lab Report Writing Guides on the Web
This is where you describe briefly and clearly why you are writing the paper. The introduction supplies sufficient background information for the reader to understand and evaluate the experiment you did. It also supplies a rationale for the study.
- Present the problem and the proposed solution
- Presents nature and scope of the problem investigated
- Reviews the pertinent literature to orient the reader
- States the method of the experiment
- State the principle results of the experiment
It is important to cite sources in the introduction section of your paper as evidence of the claims you are making. There are ways of citing sources in the text so that the reader can find the full reference in the literature cited section at the end of the paper, yet the flow of the reading is not badly interrupted. Below are some example of how this can be done: "Smith (1983) found that N-fixing plants could be infected by several different species of Rhizobium." "Walnut trees are known to be allelopathic (Smith 1949, Bond et al. 1955, Jones and Green 1963)." "Although the presence of Rhizobium normally increases the growth of legumes (Nguyen 1987), the opposite effect has been observed (Washington 1999)." Note that articles by one or two authors are always cited in the text using their last names. However, if there are more than two authors, the last name of the 1st author is given followed by the abbreviation et al. which is Latin for "and others".
From: https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/guides/imrad-reports-introductions
- Indicate the field of the work, why this field is important, and what has already been done (with proper citations).
- Indicate a gap, raise a research question, or challenge prior work in this territory.
- Outline the purpose and announce the present research, clearly indicating what is novel and why it is significant.
- Avoid: repeating the abstract; providing unnecessary background information; exaggerating the importance of the work; claiming novelty without a proper literature search.
- << Previous: ABSTRACT
- Next: METHODS >>
- Last Updated: Sep 27, 2024 12:38 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/scientificwriting
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
The PMC website is updating on October 15, 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Int J Med Educ
- PMC10693955
The importance of crafting a good introduction to scholarly research: strategies for creating an effective and impactful opening statement
Mohsen tavakol.
1 Medical Education Centre, School of Medicine, The University of Nottingham, UK
David O'Brien
Introduction.
The introduction section is arguably one of the most critical elements of a written piece of research work, often setting the tone for the remainder of any dissertation or research article. The primary purpose of an introduction is to provide the reader with a clear understanding of the research question, in addition to the scope, rationale, aims and objectives of the study. This ensures the reader can more easily comprehend the context of the research, which will consequently help them better interpret and evaluate the study results. One could liken an introduction to a trailer for a movie, where the plot of the film (the research topic) is introduced by setting the scene (outlining the significance of the topic) and enticing you to watch the full movie (understanding the research and its importance).
Despite this, our experience suggests that students frequently pay insufficient attention to the introduction section of their dissertation or omit elements which we consider essential to address. This editorial aims to help researchers appreciate the importance of a comprehensive dissertation introduction in medical education research and learn how to effectively manage this key section of their work. Although it focuses purely on the introduction section of a written research submission, readers interested in learning more about the other primary steps of the research process are encouraged to read AMEE Guide No. 90 1 , 2 textbooks on research methods and both consult and seek constructive feedback from colleagues with expertise in research methods and writing for publication.
Here we aim to provide the reader with a simple structure of how best to construct the introduction for a dissertation and recommend that this should typically include the following essential components and principles.
Background to the research topic
The purpose of providing background information in an introduction is to supply the context and other essential information concerning the research topic, and thus allow the reader to understand the significance of the specific research question and where it sits within the broader field of study. This aids the reader to better understand how the research question contributes to the existing body of knowledge and why it is, necessary to investigate this specific aspect further. For example, suppose the study concerns the effectiveness of simulation-based training in medical education. In this case, the broader field of the study may include relevant areas such as medical simulation, medical education research, health care education, standardised patients, simulation-based training, and curriculum development based on simulation training. After providing the reader with an understanding of the context and relevance of the topic of interest, the researcher must then establish a theoretical or conceptual framework. This underpins the study topic in order that the reader can understand how any research questions and objectives are formulated. It is important to distinguish between these two frameworks. A theoretical framework describes the rationale for applying a particular theory to provide support and structure for the topic being studied. In the absence of an applicable theory, a conceptual framework substantiates the significance of a particular problem, context or phenomenon within a specific area of the study by illustrating its relevance and connection to research topic. 3 A conceptual framework highlights the importance of a research topic by showing how it relates to the larger body of knowledge in a particular field. Here is an example to demonstrate the use of a theoretical framework in a research context.
When considering Social Cognitive Theory (SCT), one of the key constructs is self-efficacy, as described by Albert Bandura, 4 and refers to the belief that a person has it within their own ability to accomplish a specific task successfully. This is not related to what a person does, but more how they perceive their ability to use these skills. So, based on this construct of self-efficacy, a researcher may formulate a research hypothesis; that examiners with higher self-efficacy in OSCEs will demonstrate improved performance in subsequent exams compared to those with lower self-efficacy. Now the researcher is in a position to identify the fundamental concepts of the research, i.e., self-efficacy (personal factors), examiner performance (behavioural factors) and examination conditions and examiner scaffolding support (environmental factors). Identifying key concepts helps the researcher find the relationship between these, and develop appropriate research questions, e.g., 1) How does an examiner's self-efficacy in OSCEs affect their ability to assess students in subsequent exams? 2) How does the support provided to examiners and exam conditions influence the link between self-efficacy and examiner performance in OSCEs? 3) Do examiners with high self-efficacy provide fairer scores than those with low self-efficacy in OSCEs? By having a theoretical framework, researchers can establish a foundation for their research and provide a clear picture of the relationship between the key concepts involved in the study. Researchers must also provide any conceptual and operational definitions for key concepts or variables that will be used in the study. Clearly defining key concepts and variables in the background section of a dissertation can also help establish the significance of the research question and its relevance to the broader field of study. As the name implies, a conceptual definition refers to a variable's meaning in a conceptual, abstract, or theoretical sense. Conceptual definitions are often used to describe concepts which cannot be directly measured, such as active learning, rote learning, inter-professional learning, inter-professional education, or constructs such as clinical performance. Conversely, operational definitions define the steps researchers must take in order to collect data to measure a phenomenon or concept. 5 For example, clinical performance can be considered a conceptual construct but may also be defined operationally as the ability of students to pass 12 out of 16 stations of an OSCE. The researcher having already pre-specified specific the criteria for classifying students as pass/fail in order to determine the ability of students to perform clinically. This operational definition provides a clear method for evaluating and measuring student ability, which can then be used to give feedback and guide further learning or to establish clear expectations for students and provide a basis for evaluating and assessing their performance. In general, it can be beneficial for medical education programs to define aspects such as clinical performance operationally in this way in rather than conceptually, especially if there is a need to ensure that students meet a required standard of competence and are prepared for the demands of real-world clinical practice. These definitions can also then be used to establish the methods and criteria by which the variables of the study will subsequently be measured or altered.
Citing the existing literature to support the research aim
A literature review is the process of critically evaluating existing research and utilising it to inform and guide the research proposal under investigation. Taking this approach enables researchers to ensure that their research is not only grounded in, but also contributes meaningfully to, any existing knowledge as a whole. Critically reviewing the literature provides evidence and justification for any research and is essential when formulating a hypothesis, question, or study objectives. In addition, and perhaps most importantly, it helps identify any gaps or inconsistencies in the existing knowledge base. Determining the knowledge gap is critical in justifying the necessity for our research and advancing knowledge. A comprehensive literature review also helps establish the theoretical or conceptual frameworks to ground any subsequent research, providing researchers with guidance and direction on how best to conduct their future studies. Understanding from the literature what has worked previously and what may pose challenges or limitations assists researchers when exploring the best methods and techniques for answering new research questions. To clarify, consider a hypothetical study in which researchers wish to examine the effectiveness of a specific educational intervention in medical students to improve patient safety. Based on the existing literature, let's assume that researchers learned that most studies had only focused on short-term outcomes rather than long-term ones. The long-term effects of any intervention in medical students on patient safety therefore remain uncertain. Researchers may therefore wish to consider conducting longitudinal studies months after interventions have been carried out, rather than simply repeating research based on short-term outcomes, in order to address the current knowledge gap. A review of existing literature may highlight hitherto previously unconsidered logistical difficulties in conducting longitudinal studies in this area that the researcher may need to be aware of.
Stating the significance of the research
More than simply reporting the existing research, one of the key objectives in any literature review is to summarise and synthesise existing research on the intended topic in order to analyse the significance of the research in question. In this process, diverse ideas can be merged to form fresh new perspectives. Any gaps, limitations, or controversies in medical education can be identified, and potential future benefits and implications of the proposed research explained to the reader. Based on any potential impact or perceived importance, the introduction provides an excellent opportunity for the researcher to affirm the significance of the research study and why it should be conducted.
By way of an example, the significance of a study concerning feedback given to examiners for Objective Structured Clinical Examinations (OSCEs) is used to illustrate this point further. The potential significance of this research lies in improving the validity and reliability of OSCE scores in medical education. As a result of reviewing different types of feedback given to examiners, the research may assist in identifying the most effective strategies for improving the quality of OSCEs in medical education. By providing new insights into how feedback can improve the reliability and validity of OSCE results, the research could also contribute to the broader knowledge of assessment in general. This may result in the development of more accurate and robust medical education assessments, which in turn may potentially enhance delivery of healthcare and improve patient outcomes and safety. It may also address the current challenges and gaps in medical education assessment by providing evidence-based approaches for improving OSCE quality.
Formulating Research Questions and Objectives
Researchers formulate research questions and objectives based on the topic they are seeking to address. As noted previously, these will have already been derived as a result of a comprehensive literature review of any existing knowledge and based on a theoretical or conceptual framework. Furthermore, in medical education, the literature review provides researchers with the opportunity to formulate new research questions or research objectives to address any gaps or limitations in the existing literature and add something new to the current body of knowledge. Research questions and objectives should be stated clearly, being both specific, and measurable. These should then guide the subsequent selection of appropriate research methods, data collection and any subsequent analytical process. Clear, focused, and rigorous research questions and objectives will ensure the study is well-designed and make a valuable contribution to the existing body of knowledge.
Qualitative research questions should be open-ended and exploratory rather than focused on a specific hypothesis or proposition. It is common for qualitative studies to focus on understanding how and why certain phenomena occur, rather than simply describing what has occurred. These should be formulated to elicit rich, detailed, and context-specific data that can provide insights into the experiences, perspectives, and meanings of the participants. In contrast, quantitative research questions are more specific and are designed to test a particular hypothesis or relationship. In medical education, it is imperative to emphasise the importance of both qualitative and quantitative research questions when it comes to generating new knowledge. Combining both quantitative and qualitative research methods (mixed methods) can be particularly powerful in providing a more comprehensive understanding of any phenomena under study. Assume again that we are examining the effectiveness of feedback on the performance of medical students and adopt a mixed-methods approach using a combination of qualitative and quantitative research methods. A quantitative research question may be, what is the impact of feedback on the performance of medical students as measured by OSCE mark? How the experience of receiving feedback on performance contributes to the future professional development of medical students is a more qualitative research question. This combination of quantitative and qualitative research questions will provide an in depth understanding of the effectiveness of feedback on medical student performance. It is important to note that in qualitative research methods particularly, there can be a wide variety of research question types. For example, grounded theory researchers may ask so-called "process questions", such as 'how do students interpret and use the feedback they are given?' Phenomenologists, on the other hand, are concerned with lived experience of research subjects and frequently ask questions looking to understand the "meaning" of any such experience, often aiming to attribute feelings to this experience, for example, ‘how do students feel when they receive feedback?’ Ethnographers look to understand how culture contributes to an experience, and may ask more "descriptive questions" 5 for example, ‘how does the culture within a specific medical school affect students receiving feedback on their performance?’
For ease of reference, the key points we recommended are considered in any dissertation introduction are summarised below:
1. Set the context for the research
2. Establish a theoretical or conceptual framework to support your study
3. Define key variables both conceptually and theoretically
4. Critically appraise relevant papers during the literature review
5. Review previous studies to identify and define the knowledge gap by assessing what has already been studied and what areas remain unexplored
6. Clearly articulate the rationale behind your study, emphasising its importance in the intended field
7. Clearly define your research objectives, questions, and hypotheses
Conclusions
Whilst crafting a research introduction may seem a challenging and time-consuming task, it is well worth the effort to convey your research clearly and engage potential readers. Providing sufficient background information on the research topic, conducting a comprehensive review of the existing research, determining the knowledge gap, understanding any limitations or controversies in the topic of interest, before then exploring any theoretical or conceptual frameworks to develop the research concepts, research questions and methodology are fundamental steps. Articulating any conceptual and operational definitions of key concepts and clearly defining any key terms, including explanations of how these will be used in the study is also paramount to a good introduction. It is essential to clearly present the rationale behind the research and why this is significant, clarifying what it adds to the existing body of knowledge in medical education and exploring any potential future implications. Lastly, it is vital to ensure that any research questions are clearly stated and are open-ended and exploratory in the case of qualitative studies, or specific and measurable in the case of quantitative studies.
We feel that observing these basic principles and adhering to these few simple steps will hopefully set the stage for a highly successful piece of research and will certainly go some way to achieving a favourable editorial outcome for possible subsequent publication of the work.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
BibGuru Blog
Be more productive in school
- Citation Styles
How to write an introduction for a research paper

Writing an introduction for a research paper can be one of the hardest parts of the writing process. How do you get started? In this post, we discuss the components of an introduction and explore strategies for writing one successfully.
What is an introduction?
The introduction to a research paper provides background information or context on the topic. It also includes the thesis statement and signposts that let the reader know what you will cover in the rest of the paper.
Depending on the type of research paper that you’re writing, you may also include a brief state of the field in your introduction. You might also put that in a separate section, called a literature review. Before you tackle writing your introduction, be sure to consult the assignment guidelines for your paper.
How to write an introduction
An introduction provides an overview of your topic and any background information that your readers need to know in order to understand the context. It generally concludes with an explicit statement of your position on the topic, which is known as your thesis statement.
The opening section
Many papers begin with a hook: a short anecdote or scenario that draws the reader in and gives a hint of what the paper will cover. A hook allows you to capture your reader’s attention and provides an anchor for the context that you will provide in the bulk of the introduction.
Most of your introduction should be taken up with background information, but this doesn’t mean that you should fill your opening section with overly general statements. Instead, provide key pieces of information (like statistics) that a reader would need to know in order to understand your main argument.
The thesis statement
Towards the end of the introduction, you should state your thesis, preferably in the form of "I argue that..." or "This paper argues that..." or a similar phrase. Although it’s called a “thesis statement,” your thesis can be more than one sentence.
Finally, an introduction contains a brief outline or "signposts" of what the rest of the article will cover (also known as forecasting statements). You can use language like, “in what follows,” or “in the rest of the paper,” to signal that you are describing what you’ll do in the remainder of the paper.
Tips for writing an introduction
1. don’t rely on generalizations.
An introduction is not simply filler. It has a very specific function in a research paper: to provide context that leads up to a thesis statement.
You may be tempted to start your paper with generalizations like, “many people believe that...” or, “in our society...,” or a general dictionary definition, because you’re not sure what kind of context to provide. Instead, use specific facts like statistics or historical anecdotes to open your paper.
2. State your thesis directly
Once you’ve provided the appropriate, and specific, background information on your topic, you can move on to stating your thesis. As a rule of thumb, state your thesis as directly as possible. Use phrases like “I argue that..” to indicate that you are laying out your main argument.
3. Include signposts
A strong introduction includes clear signposts that outline what you will cover in the rest of the paper. You can signal this by using words like, “in what follows,” and by describing the steps that you will take to build your argument.
4. Situate your argument within the scholarly conversation
Some types of research papers require a separate literature review in which you explore what others have written about your topic.
Even if you’re not required to have a formal literature review, you should still include at least a paragraph in which you engage with the scholarly debate on your chosen subject. Be sure to include direct quotes from your sources . You can use BibGuru’s citation generator to create accurate in-text citations for your quotes.
This section can come directly before your thesis statement or directly after it. In the former case, your state of the field will function as additional context for your thesis.
Frequently Asked Questions about how to write an introduction for a research paper
A good introduction provides specific background information on your topic, sets up your thesis statement, and includes signposts for what you’ll cover in the rest of the paper.
An introduction should include context, a thesis statement, and signposts.
Do not include generalizations, apologies for not being an expert, or dictionary definitions in your introduction.
The length of your introduction depends on the overall length of your paper. For instance, an introduction for an 8-10 page paper will likely be anywhere from 1-3 pages.
You can choose to start an introduction with a hook, an important statistic, an historical anecdote, or another specific piece of background information.

Make your life easier with our productivity and writing resources.
For students and teachers.
Starting Your Research Paper: Writing an Introductory Paragraph
- Choosing Your Topic
- Define Keywords
- Planning Your Paper
- Writing an Introductory Paragraph
The Dreaded Introductory Paragraph
Writing the introductory paragraph can be a frustrating and slow process -- but it doesn't have to be. If you planned your paper out, then most of the introductory paragraph is already written. Now you just need a beginning and an end.
| for writing thesis statements. |
Here's an introductory paragraph for a paper I wrote. I started the paper with a factoid, then presented each main point of my paper and then ended with my thesis statement.
Breakdown:
| 1st Sentence | I lead with a quick factoid about comics. | |
| 2nd & 3rd | These sentences define graphic novels and gives a brief history. This is also how the body of my paper starts. | |
| 4rd Sentence | This sentence introduces the current issue. See how I gave the history first and now give the current issue? That's flow. | |
| 5th Sentence | Since I was pro-graphic novels, I gave the opposing (con) side first. Remember if you're picking a side, you give the other side first and then your side. | |
| 6th Sentence | Now I can give my pro-graphic novel argument. | |
| 7th Sentence | This further expands my pro-graphic novel argument. | |
| 8th Sentence | This is my thesis statement. |
- << Previous: Planning Your Paper
- Last Updated: Feb 12, 2024 12:16 PM
- URL: https://libguides.astate.edu/papers

We Trust in Human Precision
20,000+ Professional Language Experts Ready to Help. Expertise in a variety of Niches.
API Solutions
- API Pricing
- Cost estimate
- Customer loyalty program
- Educational Discount
- Non-Profit Discount
- Green Initiative Discount1
Value-Driven Pricing
Unmatched expertise at affordable rates tailored for your needs. Our services empower you to boost your productivity.
- Special Discounts
- Enterprise transcription solutions
- Enterprise translation solutions
- Transcription/Caption API
- AI Transcription Proofreading API
Trusted by Global Leaders
GoTranscript is the chosen service for top media organizations, universities, and Fortune 50 companies.
GoTranscript
One of the Largest Online Transcription and Translation Agencies in the World. Founded in 2005.
Speaker 1: After the title page and abstract, the reader's first true interaction with your research paper is the introduction. Your introduction will establish the foundation upon which your readers approach your work, and if you use the tips we discuss in this video, these readers should be able to logically apply the rules set in your introduction to all parts of your paper, all the way through the conclusion. What exactly is the purpose of the introduction? Think about your paper as a chronological story. It will begin at point A, the introduction, and move in time towards point B, the discussion and conclusion. Since your introduction includes content about the gaps in knowledge that your study aims to fill, the results you elaborate on in your discussion section should therefore be somewhat familiar to the reader, as you have already touched upon them in the introduction section. The introduction must answer two main questions. Why was this particular study needed to fill the gaps in knowledge? And why does this particular gap need filling? Imagine our entire plane of knowledge as an incomplete puzzle. The pieces snapped together are what is established, or what is known. The missing piece is the gap in knowledge, or what is currently unknown. This is what your study will be helping to explain. So the context you provide in the introduction must first identify that there is a knowledge gap in what it is, it must explain why it needs to be filled, and then briefly summarize how this study intends to fill that gap and why. The introduction is one of the most compact parts of the research paper, since it is not very long but needs to essentially give a complete overview of the context in which your study is taking place, and your specific reasons for doing the study. Most tend to be around 10% of the total length of your paper. The introduction consists of background information about a topic being studied, the rationale for undertaking the study, or for filling the gap with this particular information, key references to preliminary work or closely related papers appearing elsewhere, a clarification of important terms, definitions, or abbreviations to be used in the paper, and a review of related studies in which you give a brief but incisive analysis of work that heavily concerns your study. It could be a very similar study or one that supports the findings of your new study. So how should you structure your introduction? As you can see in this figure, your introduction should start broadly and then narrow until it reaches your hypothesis. The first thing you want to do is state your area of research and then immediately show what is already known. This is also known as background information. Then move on to what is unknown, the problem or gap you want to resolve. Finally, you should discuss how you will resolve this problem using a clear hypothesis. In step one, you will show what is already known. Start with a strong statement that reflects your research subject area and ask questions or post statements to frame the problems your study explores. You can ask general questions here to guide your readers to the problem and show them what we already know. For instance, what do we know about breathing capability of bottlenose dolphins? Use keywords from your title, the exact language of your study that is, to zero in on the problem at hand and show the relevance of your work. Avoid stating background information that is too broad in nature. You don't need to state too many obvious facts that your readers would know. If you are writing about bottlenose dolphins, for instance, you probably don't need to explain to them that mammals breathe oxygen. At the beginning of the introduction, you should also be sure to cite all of the sources that you use for background information and support. Only provide the necessary background information. Don't focus extensively on background, but use it to set up the context for doing this study. You should also review only relevant, up-to-date primary literature that supports your explanation of our current base of knowledge. In the second part of your introduction, you should answer the question, what is the knowledge gap? Here you will highlight areas where too little information is available. Explain how and why we should fill in that gap. What does this missing information do to impede our understanding of a process or system? And you should identify what logical next steps can be developed based on existing research. By showing you have examined current data and devised a method to find new applications and make new inferences, you're showing your peers that you are aware of the direction your research is moving in, and you're showing confidence in your decision to pursue this paper study. In the last part of your introduction, you will show how your study fills in the knowledge gap. This is where you state your purpose and give a clear hypothesis or objective of the study. The hypothesis is a very short 1-2 sentence supposition or explanation of what will happen in your study. This is quite often written as an if-then format. If X and Y are present, then Z will occur. Here you should also try to answer the question, if we fill this gap, what useful information will the readers gain? Many researchers have difficulty when it comes to deciding when to write their introduction. It is important to consider the order you draft your research paper, for as you recall, everything else in the research paper must flow from the introduction. Therefore, because it is one of the most difficult sections to nail down, consider writing the introduction second to last, after the materials and methods, results, and discussion section, and just before the conclusion. This will ensure you effectively lay a groundwork for the rest of your paper, and you can use the research you have already compiled to ensure that everything in your introduction is pertinent and accurate. In addition to content and organization, writers of research papers should also be aware of grammar and style issues that directly affect the readability and strength of their printed work. Here are some guidelines for writing the introduction section. Try and write in the active voice when possible. This will shorten your sentences and enhance the impact of your information. Always strive for concise sentences. This will allow you to get in all of the necessary information in this compact introduction section. Use stronger verbs when possible. This also impacts sentence length and strength of writing. Be careful not to overuse first-person pronouns such as I and we, and always organize your thoughts from the broad to the specific, as we have seen in our model. A strong introduction will encourage readers to read your entire research paper and help get your work published in scientific journals. For more information and tips on manuscript writing and journal submissions, visit the resources page at wordvice.com.


Organizing Academic Research Papers: 4. The Introduction
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
The introduction serves the purpose of leading the reader from a general subject area to a particular field of research. It establishes the context of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the hypothesis, question, or research problem, briefly explaining your rationale, methodological approach, highlighting the potential outcomes your study can reveal, and describing the remaining structure of the paper.
Key Elements of the Research Proposal. Prepared under the direction of the Superintendent and by the 2010 Curriculum Design and Writing Team. Baltimore County Public Schools.
Importance of a Good Introduction
Think of the introduction as a mental road map that must answer for the reader these four questions:
- What was I studying?
- Why was this topic important to investigate?
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study?
- How will this study advance our knowledge?
A well-written introduction is important because, quite simply, you never get a second chance to make a good first impression. The opening paragraph of your paper will provide your readers with their initial impressions about the logic of your argument, your writing style, the overall quality of your research, and, ultimately, the validity of your findings and conclusions. A vague, disorganized, or error-filled introduction will create a negative impression, whereas, a concise, engaging, and well-written introduction will start your readers off thinking highly of your analytical skills, your writing style, and your research approach.
Introductions . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Structure and Approach
The introduction is the broad beginning of the paper that answers three important questions for the reader:
- What is this?
- Why am I reading it?
- What do you want me to think about / consider doing / react to?
Think of the structure of the introduction as an inverted triangle of information. Organize the information so as to present the more general aspects of the topic early in the introduction, then narrow toward the more specific topical information that provides context, finally arriving at your statement of purpose and rationale and, whenever possible, the potential outcomes your study can reveal.
These are general phases associated with writing an introduction:
- Highlighting the importance of the topic, and/or
- Making general statements about the topic, and/or
- Presenting an overview on current research on the subject.
- Opposing an existing assumption, and/or
- Revealing a gap in existing research, and/or
- Formulating a research question or problem, and/or
- Continuing a disciplinary tradition.
- Stating the intent of your study,
- Outlining the key characteristics of your study,
- Describing important results, and
- Giving a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
NOTE: Even though the introduction is the first main section of a research paper, it is often useful to finish the introduction very late in the writing process because the structure of the paper, the reporting and analysis of results, and the conclusion will have been completed and it ensures that your introduction matches the overall structure of your paper.
II. Delimitations of the Study
Delimitations refer to those characteristics that limit the scope and define the conceptual boundaries of your study . This is determined by the conscious exclusionary and inclusionary decisions you make about how to investigate the research problem. In other words, not only should you tell the reader what it is you are studying and why, but you must also acknowledge why you rejected alternative approaches that could have been used to examine the research problem.
Obviously, the first limiting step was the choice of research problem itself. However, implicit are other, related problems that could have been chosen but were rejected. These should be noted in the conclusion of your introduction.
Examples of delimitating choices would be:
- The key aims and objectives of your study,
- The research questions that you address,
- The variables of interest [i.e., the various factors and features of the phenomenon being studied],
- The method(s) of investigation, and
- Any relevant alternative theoretical frameworks that could have been adopted.
Review each of these decisions. You need to not only clearly establish what you intend to accomplish, but to also include a declaration of what the study does not intend to cover. In the latter case, your exclusionary decisions should be based upon criteria stated as, "not interesting"; "not directly relevant"; “too problematic because..."; "not feasible," and the like. Make this reasoning explicit!
NOTE: Delimitations refer to the initial choices made about the broader, overall design of your study and should not be confused with documenting the limitations of your study discovered after the research has been completed.
III. The Narrative Flow
Issues to keep in mind that will help the narrative flow in your introduction :
- Your introduction should clearly identify the subject area of interest . A simple strategy to follow is to use key words from your title in the first few sentences of the introduction. This will help focus the introduction on the topic at the appropriate level and ensures that you get to the primary subject matter quickly without losing focus, or discussing information that is too general.
- Establish context by providing a brief and balanced review of the pertinent published literature that is available on the subject. The key is to summarize for the reader what is known about the specific research problem before you did your analysis. This part of your introduction should not represent a comprehensive literature review but consists of a general review of the important, foundational research literature (with citations) that lays a foundation for understanding key elements of the research problem. See the drop-down tab for "Background Information" for types of contexts.
- Clearly state the hypothesis that you investigated . When you are first learning to write in this format it is okay, and actually preferable, to use a past statement like, "The purpose of this study was to...." or "We investigated three possible mechanisms to explain the...."
- Why did you choose this kind of research study or design? Provide a clear statement of the rationale for your approach to the problem studied. This will usually follow your statement of purpose in the last paragraph of the introduction.
IV. Engaging the Reader
The overarching goal of your introduction is to make your readers want to read your paper. The introduction should grab your reader's attention. Strategies for doing this can be to:
- Open with a compelling story,
- Include a strong quotation or a vivid, perhaps unexpected anecdote,
- Pose a provocative or thought-provoking question,
- Describe a puzzling scenario or incongruity, or
- Cite a stirring example or case study that illustrates why the research problem is important.
NOTE: Only choose one strategy for engaging your readers; avoid giving an impression that your paper is more flash than substance.
Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions . University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Introduction . The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Introductions . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Introductions . The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Introductions, Body Paragraphs, and Conclusions for an Argument Paper. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Resources for Writers: Introduction Strategies . Program in Writing and Humanistic Studies. Massachusetts Institute of Technology; Sharpling, Gerald. Writing an Introduction . Centre for Applied Linguistics, University of Warwick; Writing Your Introduction. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University.
Writing Tip
Avoid the "Dictionary" Introduction
Giving the dictionary definition of words related to the research problem may appear appropriate because it is important to define specific words or phrases with which readers may be unfamiliar. However, anyone can look a word up in the dictionary and a general dictionary is not a particularly authoritative source. It doesn't take into account the context of your topic and doesn't offer particularly detailed information. Also, placed in the context of a particular discipline, a term may have a different meaning than what is found in a general dictionary. If you feel that you must seek out an authoritative definition, try to find one that is from subject specific dictionaries or encyclopedias [e.g., if you are a sociology student, search for dictionaries of sociology].
Saba, Robert. The College Research Paper . Florida International University; Introductions . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
Another Writing Tip
When Do I Begin?
A common question asked at the start of any paper is, "where should I begin?" An equally important question to ask yourself is, "When do I begin?" Research problems in the social sciences rarely rest in isolation from the history of the issue being investigated. It is, therefore, important to lay a foundation for understanding the historical context underpinning the research problem. However, this information should be brief and succinct and begin at a point in time that best informs the reader of study's overall importance. For example, a study about coffee cultivation and export in West Africa as a key stimulus for local economic growth needs to describe the beginning of exporting coffee in the region and establishing why economic growth is important. You do not need to give a long historical explanation about coffee exportation in Africa. If a research problem demands a substantial exploration of historical context, do this in the literature review section; note in the introduction as part of your "roadmap" [see below] that you covering this in the literature review.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Always End with a Roadmap
The final paragraph or sentences of your introduction should forecast your main arguments and conclusions and provide a description of the rest of the paper [a "roadmap"] that let's the reader know where you are going and what to expect.
- << Previous: Executive Summary
- Next: Background Information >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON
Welcome to 2024! Happy New Year!

Research Writing ~ How to Write a Research Paper
- Choosing A Topic
- Critical Thinking
- Domain Names
- Starting Your Research
- Writing Tips
- Parts of the Paper
- Edit & Rewrite
- Citations This link opens in a new window
Papers should have a beginning, a middle, and an end. Your introductory paragraph should grab the reader's attention, state your main idea and how you will support it. The body of the paper should expand on what you have stated in the introduction. Finally, the conclusion restates the paper's thesis and should explain what you have learned, giving a wrap up of your main ideas.
1. The Title The title should be specific and indicate the theme of the research and what ideas it addresses. Use keywords that help explain your paper's topic to the reader. Try to avoid abbreviations and jargon. Think about keywords that people would use to search for your paper and include them in your title.
2. The Abstract The abstract is used by readers to get a quick overview of your paper. Typically, they are about 200 words in length (120 words minimum to 250 words maximum). The abstract should introduce the topic and thesis, and should provide a general statement about what you have found in your research. The abstract allows you to mention each major aspect of you topic and helps readers decide whether they want to read the rest of the paper. Because it is a summary of the entire research paper, it is often written last.
3. The Introduction The introduction should be designed to attract the reader's attention and explain the focus of the research. You will introduce your overview of the topic, your main points of information, and why this subject is important. You can introduce the current understanding and background information about the topic. Toward the end of the introduction, you add your thesis statement, and explain how you will provide information to support your research questions. This provides the purpose, focus, and structure for the rest of the paper.
4. Thesis Statement Most papers will have a thesis statement or main idea and supporting facts/ideas/arguments. State your main idea (something of interest or something to be proven or argued for or against) as your thesis statement, and then provide supporting facts and arguments. A thesis statement is a declarative sentence that asserts the position a paper will be taking. It also points toward the paper's development. This statement should be both specific and arguable. Generally, the thesis statement will be placed at the end of the first paragraph of your paper. The remainder of your paper will support this thesis.
Students often learn to write a thesis as a first step in the writing process, but often, after research, a writers viewpoint may change. Therefore a thesis statement may be one of the final steps in writing.
Examples of thesis statements from Purdue OWL. . .
5. The Literature Review The purpose of the literature review is to describe past important research and how it specifically relates to the research thesis. It should be a synthesis of the previous literature and the new idea being researched. The review should examine the major theories related to the topic to date and their contributors. It should include all relevant findings from credible sources, such as academic books and peer-reviewed journal articles. You will want to:
- Explain how the literature helps the researcher understand the topic.
- Try to show connections and any disparities between the literature.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
More about writing a literature review. . . from The Writing Center at UNC-Chapel Hill More about summarizing. . . from the Center for Writing Studies at the University of Illinois-Urbana Champaign
6. The Discussion The purpose of the discussion is to interpret and describe what you have learned from your research. Make the reader understand why your topic is important. The discussion should always demonstrate what you have learned from your readings (and viewings) and how that learning has made the topic evolve, especially from the short description of main points in the introduction. Explain any new understanding or insights you have had after reading your articles and/or books. Paragraphs should use transitioning sentences to develop how one paragraph idea leads to the next. The discussion will always connect to the introduction, your thesis statement, and the literature you reviewed, but it does not simply repeat or rearrange the introduction. You want to:
- Demonstrate critical thinking, not just reporting back facts that you gathered.
- If possible, tell how the topic has evolved over the past and give it's implications for the future.
- Fully explain your main ideas with supporting information.
- Explain why your thesis is correct giving arguments to counter points.
7. The Conclusion A concluding paragraph is a brief summary of your main ideas and restates the paper's main thesis, giving the reader the sense that the stated goal of the paper has been accomplished. What have you learned by doing this research that you didn't know before? What conclusions have you drawn? You may also want to suggest further areas of study, improvement of research possibilities, etc. to demonstrate your critical thinking regarding your research.
- << Previous: Writing Tips
- Next: Edit & Rewrite >>
- Last Updated: Feb 1, 2024 4:06 PM
- URL: https://library.hccc.edu/research_paper
Gabert Library

NHC Library

- Database A-Z
- Research Guides
- Citation Help
- Ask a Librarian
- Library Instruction
- Academic Liaisons
- Library Staff Login
Frequently asked questions
What should i include in a research paper introduction.
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Frequently asked questions: Writing a research paper
A research project is an academic, scientific, or professional undertaking to answer a research question . Research projects can take many forms, such as qualitative or quantitative , descriptive , longitudinal , experimental , or correlational . What kind of research approach you choose will depend on your topic.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them.
In general, they should be:
- Focused and researchable
- Answerable using credible sources
- Complex and arguable
- Feasible and specific
- Relevant and original
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly

A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
Your research objectives indicate how you’ll try to address your research problem and should be specific:
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarize the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in Chicago style are to:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Use 1 inch margins or larger
- Apply double line spacing
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch
- Include a title page
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center
- Cite your sources with author-date citations or Chicago footnotes
- Include a bibliography or reference list
To automatically generate accurate Chicago references, you can use Scribbr’s free Chicago reference generator .
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA style are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Set 1 inch page margins
- Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page
- Center the paper’s title
- Use title case capitalization for headings
- Cite your sources with MLA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a Works Cited page at the end
To format a paper in APA Style , follow these guidelines:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial
- If submitting for publication, insert a running head on every page
- Apply APA heading styles
- Cite your sources with APA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a reference page at the end
No, it’s not appropriate to present new arguments or evidence in the conclusion . While you might be tempted to save a striking argument for last, research papers follow a more formal structure than this.
All your findings and arguments should be presented in the body of the text (more specifically in the results and discussion sections if you are following a scientific structure). The conclusion is meant to summarize and reflect on the evidence and arguments you have already presented, not introduce new ones.
The conclusion of a research paper has several key elements you should make sure to include:
- A restatement of the research problem
- A summary of your key arguments and/or findings
- A short discussion of the implications of your research
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our team helps students graduate by offering:
- A world-class citation generator
- Plagiarism Checker software powered by Turnitin
- Innovative Citation Checker software
- Professional proofreading services
- Over 300 helpful articles about academic writing, citing sources, plagiarism, and more
Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents . We proofread:
- PhD dissertations
- Research proposals
- Personal statements
- Admission essays
- Motivation letters
- Reflection papers
- Journal articles
- Capstone projects
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker is powered by elements of Turnitin’s Similarity Checker , namely the plagiarism detection software and the Internet Archive and Premium Scholarly Publications content databases .
The add-on AI detector is powered by Scribbr’s proprietary software.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
- Economics & Finance
- Foreign Policy
- Domestic Policy
- Health & Science
- All Publications
Nearshoring’s Environmental and Social Impacts and the Need for Trade Reform

Table of Contents

Ivonne Cruz
Share this publication.
- Print This Publication
Ivonne Cruz, “Nearshoring’s Environmental and Social Impacts and the Need for Trade Reform,” Rice University’s Baker Institute for Public Policy, September 26, 2024, https://doi.org/10.25613/W98N-4339 .
Introduction
Mexico is once again at the center of attention for companies seeking to relocate production back to North America — a phenomenon known as nearshoring. If this trend continues, it is expected to generate a surge in localized regional trade, driven by the influx of manufacturing plants moving to the U.S.-Mexico border. This shift could accelerate development in local economies and increase the pace of major infrastructure projects. In this context, both the United States and Mexico must craft effective transboundary policies to encourage responsible business practices that protect local communities and the fragile border environment from negative impacts caused by increased trade and economic activity.
Companies may argue that their operations already follow sustainable practices — such as optimizing proximity, reducing transportation waste, and increasing efficiency with streamlined supply chain arrangements. However, past and current trade policies have disproportionately impacted local communities and enabled environmental injustices in the region since the inception of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) in 1994. Thus, several questions remain unanswered:
- How will border communities cope with a new wave of environmental burdens, including pollution, deforestation, waste management, and water scarcity as nearshoring companies establish themselves in the region and across Mexico?
- How can the environmental and social risks of nearshoring be prevented or mitigated preemptively, especially when few regulatory means are available under current transboundary policy frameworks? What new policies could help address these risks?
- How can transboundary policies integrate an environmental justice perspective to address international trade impacts experienced by vulnerable communities?
- Why are there no regulatory mechanisms in place to prevent and mitigate past environmental and social impacts in the border region? And why are there no policies that aim to achieve sustainability and socioeconomic goals for both countries in the context of trade liberalization?
This report examines the environmental and social impacts of potential nearshoring activities along the U.S.-Mexico border. It highlights some of the concerns that must be addressed in the coming years, including climate change, water scarcity, poor air quality, waste management, land use, biodiversity, environmental justice, human rights, and labor issues. Lastly, it identifies potential policy opportunities to address the significant implications of neglecting social and environmental vulnerabilities in host communities experiencing rapid economic development along the U.S.-Mexico border.
Environmental and Social Impacts of Nearshoring
Nearshoring presents several opportunities, such as job creation and reskilling, technology transfer, social entrepreneurship and partnerships, community engagement, corporate sustainability, and cultural exchange. However, it also presents complex challenges due to increased industrial activities, including environmental and social impacts on host ecosystems and local communities. These challenges are not new. The borderlands area, often referred to as a “third country,” has a long history of industrial integration and complex environmental issues. [1] This region experiences “double exposure” as it benefits from industrial integration while also suffering from profound environmental changes exacerbated by increased economic activity. [2] These challenges include climate vulnerabilities, contentious transboundary watersheds, and cultural and social interdependencies. [3]
From the 1970s to the 1990s, the border area became one of the most polluted areas in Mexico due to loosely enforced environmental laws and the growth of foreign-owned factories — known as “maquiladoras” — across Mexico’s northern states. [4] Key concerns such as air pollution, water quality, toxic waste dumping, and public health threats led to ongoing binational environmental disputes and widespread social protests. [5] Civic upheaval also resulted from inadequate green or clean production processes, insufficient oversight of waste management, and the lack of effective policies to enforce basic environmental standards among assembly businesses in Mexican border cities. [6] Consequently, this unregulated industrial activity has led and continues to lead to widespread environmental and social burdens on border populations, further straining their already fragile ecosystems and problematic social dynamics.
In summary, while nearshoring offers key regional advantages — such as minimizing supply chain disruptions through production proximity, optimizing logistical operations, reskilling workers, and enabling easier communication with key markets — these benefits come with inherent environmental and social impacts. [7] These impacts are particularly significant in a region experiencing rapid infrastructure expansion, demographic stress, and persistent social inequalities in the context of a changing climate.
The Border’s Environmental and Social Problems
Emissions and air quality.
Climate change, characterized by rising temperatures and increasingly extreme weather patterns, calls for the examination of risks and vulnerabilities jeopardizing the health and well-being of populations already disproportionately affected by human economic activities. This issue is particularly urgent at the U.S.-Mexico border, an area highly susceptible to climate variability. Droughts and floods are expected to occur more frequently due to climatic factors. The Mexican border states, especially along the Rio Grande, are particularly vulnerable to droughts, as evidenced by decades of low precipitation rates. [8]
In addition to these climate stressors, increased manufacturing processes and infrastructure development in urban areas along the border will further impact the livelihoods of already vulnerable communities, where alternating flooding and droughts are likely to become the norm. [9] The combined effects of preexisting health and social disparities, climate change, and nearshoring-related growth are expected to exacerbate environmental and social inequities, affecting the overall health and well-being of these communities.
Air pollution is another critical concern along the border, where communities are already exposed to extremely high levels of air pollutants, including high concentrations of carbon monoxide from factories’ byproducts and excessive traffic caused by exponential growth in the density of commercial and noncommercial vehicles. [10] Nearshoring activities will likely add to this, potentially worsening air quality and increasing emissions. To address these challenges, it is critical to revise environmental policy parameters on both sides of the border and pursue bilateral action to secure the right to clean air for all communities.
Reducing emissions must be a priority for both existing and new companies in the region. These companies should aim to enhance competitiveness while simultaneously mitigating air pollution. The region could benefit from adopting collaborative strategies similar to climate-related trade policies in other parts of the world, such as the European Union, which has developed stringent environmental and regulatory measures to curb carbon emissions in pursuit of net-zero goals. [11]
Water-Related Vulnerability
Water scarcity is a major challenge in northern Mexico. The Water Stress Index shows that Mexico already ranks among the 50 most water-stressed nations on earth. [12] According to data from the Water Stress Index, Monterrey (Nuevo León), Chihuahua (Chihuahua), and Tijuana (Baja California) fall within the highest risk category, and this stress could grow further “by 2040, according to data covering ‘business as usual’ emissions and socioeconomic pathways.” [13] Industry analysts consider that nearshoring activity in Mexico will add to water-related vulnerabilities due to the following:
- 70% of the national territory faces water scarcity.
- Approximately 50% of the country’s basins are “overexploited.”
- One in three Mexicans lacks access to drinking water at home.
- Water demand is projected to surpass supply by 30% by 2030. [14]
Moreover, climate variability is not considered under current water treaties and international institutions that coordinate water exchanges between the two countries. Yet, climatic changes will continue affecting the timing of these water exchanges. For example, temperature and low amounts of rainfall will affect border cities’ and farmers’ water storage and use, as few governance mechanisms exist to assist in organizing binational activities in prolonged drought periods. Additionally, despite recent investments to preserve some of the most important reservoirs to keep water consumption at its best capacity, aging water infrastructure remains a persistent issue along with the continuing diplomatic conflict over Mexico’s checkered compliance with an 80-year-old treaty over cross-border flows of the Rio Grande and Colorado Rivers. [15] Altogether, the future of water in Mexico remains uncertain.
Nearshoring activities will demand additional water resources. Industry developers and U.S.-Mexico policymakers must consider present and imminent water-related vulnerabilities by allocating resources to consolidate a binational water plan. Both countries’ governance related to water exchanges need to contemplate integrated management protocols, data collection and usage, and the implementation of innovative water technologies to enhance hydraulic efficiency and water reuse, among others.
Hazardous and Toxic Waste
Manufacturing produces dangerous by-products. In response, the Repatriation Rule of the La Paz Agreement — a pact signed in 1983 between the U.S. and Mexico containing environmental regulatory requirements for maquiladoras to follow — states that “any hazardous waste generated by maquiladoras must be repatriated to the maquiladora’s country of origin, which is wherever the maquiladora’s parent company is located.” [16] However, as U.S companies in Mexico and other facilities find it expensive or unfeasible to build on-site treatment facilities to dispose of toxic waste, they fail to comply with requirements for hazardous waste disposal and wastewater treatment. This problem has generated a toxic waste crisis in Mexico where companies have prioritized profits over both the public and environment while jeopardizing public health. [17]
Even though the Repatriation Rule permits the recycling of hazardous waste in Mexico, facilities available to do so are scarce, leaving manufacturing plants little to no choice but to dump their waste illegally. Despite environmental provisions for toxic waste disposal available during the NAFTA years, tracking the amount of waste disposed by the expansion of the maquiladora industry in the last 10 years has been difficult, especially as annual hazardous waste generation has increased significantly. [18]
Mexican environmental law offers a variety of stringent regulations addressing the maquiladora regime through several articles and standard norms under the General Law of Ecological Balance and Environmental Protection (LGEEPA). [19] This law provides environmental regulations to hold industry accountable for the costs associated with the prevention and control of economic activities that pollute, and to those responsible for it. Some areas include obligations regarding waste and toxic petrochemical waste, highly risky activities, and emission to the atmosphere, to mention a few. [20] Yet, the problem of toxic waste in Mexico persists because of the country’s historic inability to enforce these laws and to implement environmental policies and properly monitor industry wrongdoings due to chronically underfunded and understaffed Mexican state and federal regulatory agencies, such as Procuraduría Federal de Protección al Ambiente (PROFEPA), Comisión Nacional Forestal, la Comisión Nacional de Áreas Naturales Protegidas, and their regional subsidiaries.
Moreover, corruption and bribery have also been constant factors contributing to this lack of enforcement in addition to powerful interest groups that protect maquiladoras’ management and economic assets by leaving toxic waste control unabated. Recent reports revealed that illegal dumpling happens often in border areas, such as Tijuana and Matamoros, denoting an existent pressing issue that is exacerbating environmental injustices for the border communities and, in the process, harming people’s health and regional ecosystems. [21] Once again, nearshoring without appropriate rules and stronger enforcement will only intensify the problem of toxic waste disposal.
Land Use, Habitat Loss, and Biodiversity
The U.S.-Mexico border is particularly rich in ecosystem diversity, despite being largely desertic. As many of these ecosystems are fragile, negative impacts from economic activity threaten their survival; these activities infringe on native species and exacerbate wildfire outbreaks, often caused by prolonged drought because of the region’s water-related vulnerabilities. [22] As such, the urban sprawl of both maquiladoras and housing have been some of the main causes of the border region’s animal habitat and biodiversity loss over the last few decades.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) reported that 6,500 animal and plant species on the U.S-Mexico border have been affected by economic activity, with 235 of these considered under risk and endangered on the Mexican side and 148 species threatened under the U.S. Endangered Species Act. [23] Land use change and habitat fragmentation caused by the U.S. border fence exacerbates biodiversity and environmental loss, along with threatened wetland systems where native species’ habitats are highly sensitive to increasing water scarcity. [24]
Additionally, the border fence already prevents dozens of species from moving freely and migrating naturally for reproduction. [25] Biodiversity loss in the border region includes rare species of cacti, birds, and other unique species of mammals — such as the American antelope, mule deer, lynx, mountain lions, and jaguars — losing habitat spaces due to damaging human activity and border militarization and poor oversight of these doings. Altogether, these features continuously affect public lands and contribute to ecosystem destruction. [26]
Nearshoring-related trade and infrastructure development will further stress both regions’ biodiversity and the lands where Indigenous peoples in the U.S. and Mexico live; protected wild and domestic plants will also suffer. [27] Bioactive components from the native plants, fungi, and microorganisms from soils that are potential economic assets will be in danger of extinction if the Convention on Biological Diversity and its latest 2022 regulations on extraction are not implemented soon. [28]
Socioeconomic Issues
Along with the environmental issues outlined above, it is important to acknowledge the connection between the environmental and the social and their relation to economic activities, especially as nearshoring materializes. There is an intrinsic correlation between the impacts of biophysical factors and social and cultural dynamics. In this regard, several studies have identified the border as a highly socially vulnerable hot spot due to “intersecting processes of rapid growth, domestic and international migration, economic intensification and globalization, and intensive climate change.” [29]
The very characteristics and assets that make the region optimal for trade and supply chain development — a potential nearshoring paradise — also make it vulnerable not only to environmental but also to social harms. Rapid growth and urbanization generated by the maquiladora industry and increased trade have created high rates of poverty because of uneven economic development. The environmental, social, economic, and cultural interdependency reflects a distinctive “institutional asymmetry and governance fragmentation” on the border, as this imbalance is partly the result of poorly managed transborder cooperation. [30]
There are, to be sure, binational institutions and frameworks that have been created to overcome many of these complex transboundary challenges, but they are overwhelmed by these economic dynamics and their consequences. Yet, the surge of nearshoring activities could represent a new opportunity to introduce better rules, regulations, and policies around the environmental and social impacts of industrialization, before the snowballing of consequences undermines the anticipated opportunity that nearshoring promises to bring.
Environmental Justice Communities
Climate impacts are uniformly distributed across populations and space. However, locally, climate change interacts with socioeconomic disparities, strongly impacting the ecosystems, human health, and social well-being of the most vulnerable. Climate change thus behaves like an intervening — or magnifying — variable of impacts, compounding these negative effects. Ethnicity, for example, is a factor correlated to exposure to climate risk and higher climate vulnerability. [31] Low-income status as well represents higher exposure to climate risk, due to socioeconomic aspects that shape people’s living options, such as:
- Limited housing choices and labor opportunities.
- Lack of affordable utility costs and transportation.
- Significant exposure to urban heat, diminished air quality, and industrial by-products. [32]
Problems of environmental justice are related to various social issues, such as inequality, poverty, and a population’s inability to have appropriate means to protect themselves from externalities of industrial output and environmental damages resulting from these activities. The U.S.-Mexico border, however, faces more environmental justice challenges unique to its region, “such as the historical legacy … the challenges of cross-border movements of people and pollutants, economic competition pressures of jurisdictional boundaries for environmental regulation and enforcement, and the problems of accountability of corporate polluters, governments, and international institutions to border communities.” [33]
These are a series of issues that have remained unresolved and have been exacerbated in the last two decades. The International Roundtable on Environmental Justice at the U.S.-Mexico Border in the early 2000s made a significant effort to promote awareness on environmental justice issues at the border. It provided recommendations to the EPA on the need for a more comprehensive approach to the right to a healthy and sustainable environment as an urgent matter in the wake of potential new industrial activity growth and offered ways to improve current efforts. Best known as the U.S-Mexico Border Roundtable, it “included representatives and members of communities of color; Indigenous peoples; women; labor, environmental justice and environmental protection advocates and activists; affected communities and grassroots groups; the private sector; the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and other U.S. federal agencies; and Mexican government officials.” [34]
The U.S.-Mexico Roundtable in the early 2000s made a significant effort to promote some awareness on environmental justice issues and communities at the border, and especially focused on the need for a more comprehensive approach to the right to a healthy and sustainable environment as an urgent matter in the wake of the potential new industrial activity growth.
Despite these efforts and even involvement from Indigenous people and other communities of the border, the problem persists since environmental provisions within the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) serve only as performative means. [35] They exist with little meaningful action and do not constitute effective protection — that is not enough. For instance, the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC) has the mandate to monitor the impact of trade on the environment and make recommendations to the U.S., Mexico, and Canada. [36] However, compliance of these recommendations is only voluntary. Another good example of this performative means of the provisions in USMCA’s Chapter 24: “Environment,” which alludes to the little regional effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and nationally determined contributions (NDCs), when there is still huge investment in fossil fuels in both U.S and Mexico administrations. [37] Additionally, an energy bill passed in Mexico in 2021 hinders private investment from promoting greener energy markets and renewable energy production sources by reducing economic competition and protections for companies. [38]
Environmental vulnerability and adaptation are intrinsic components of economic, infrastructure, and development initiatives, and the USMCA, nearshoring actions, and other economic development efforts need to bare into consideration that the region’s communities will bear the weight of these activities, ones that will only be exacerbated by climate change.
Nearshoring is likely to aggravate Indigenous peoples and local communities’ vulnerability to disruptions to their ecosystems and ecosystem services. [39] Therefore, maintaining environmental value in the region through effective, equitable resource governance will be key to the sustainability of tribal cultures and practices and local communities. Currently, numerous Indigenous tribes and nations reside along the U.S.-Mexico border with strong transborder ties, relying heavily on natural resources from the water and lands that contribute to a multicultural landscape, one that is not easily adaptable to the changing environment predicted to take place in the next few years.
Increasing social inequalities exacerbated by climate change, economic development and new trade dynamics require more collaborative and inclusive approaches to ensure:
- Adequate protection of noncitizens and Indigenous peoples in the U.S and Mexico under environmental, health, and safety laws and regulations across the border.
- The enforcement of environmental laws and regulations against industrial developments settling across international borders. [40]
Fair Employment and Labor
One of the main risks of being part of the supply chain of developed regions is being a builder of a final product, which does not necessarily lead to the generation of new knowledge, more profits, or further scientific or technological development. [41] This is currently the position in which Mexico finds itself — this is no longer adequate. Reskilling and investing in innovation, supporting technological development and transfer, improving economic conditions, and creating long-lasting jobs are game-changing opportunities in nearshoring initiatives. Labor dynamics respond to a twofold challenge that entail how industrial activity catalyzes income, growth, and training and how these economic benefits become translated into social well-being. Labor is a sector responsible for protecting equality and maintaining fair conditions for those people bringing economic benefits to shareholders; however, this section is also susceptible to human rights violations.
As companies bring more jobs to Mexico, labor rights safeguards must be part of the deal, since maquiladora wages have been historically below the threshold of survival and food insecurity remains constant struggle. [42] Lower wages under NAFTA served as the greatest incentive for companies to outsource manufacturing to the border and central Mexican regions. However, part of the USMCA’s new provisions include the eradication of protection contracts; in the past, these protection contracts put company interests over worker rights and affected women much more as they previously represented a majority of the workforce in the region — many of whom are victims of human rights violations and labor abuses that have not been fully resolved. [43]
Environmental Trade Provisions: Current Models and Needed Improvements
Even though there are new environmental provisions for trade in the U.S. and Mexico, there is room for improvement as the USMCA will be renegotiated during 2025 and approved in 2026. Further elements must be incorporated into the USMCA and other agreements as part of a framework the recognizes and addresses environmental and social concerns through the following:
- Environmental law principles that apply to both national and binational levels.
- Provisions that govern environmental lawmaking and policy-making, demanding the participation of civil society in the adoption of tougher environmental measures.
- Provisions that focus on public assistance and social investment.
- Provisions that refer to environmental institutions, and even some that involve “so-called environmental exceptions that permit countries to limit trade to conserve natural resources.” [44]
These are common practices in other regions, such as Europe, and could implemented for the North American region in these new stages of nearshoring. It will be key to push for industry policies promoting the expansion of trade undertakings to other areas, such as South America and even Central America, not only to open new venues of economic growth but also to reduce the natural resources stress, particularly for water, which is ever scarcer in the northern Mexican states.
Since the signing of the 1983 La Paz Agreement on cooperation for the protection of the environment and public health in the border area, the U.S. EPA and Mexico’s Secretariat for Environment and Natural Resources (Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales, SEMARNAT) have implemented a series of bilateral programs to support this treaty, including the Border 2020 and 2025 Programs which succeed in establishing certain guiding principles and leveraging some government agencies to improve environmental governance in the region. However, the lack of political will, efficient accountability bodies, and sufficient funding to address Border 2020 and 2025 Programs’ objectives fall so short that it is hard to prioritize and showcase success stories and exhibit them as examples of good practices to overcome the vast challenges that the region will face in the next decade. Whether these efforts have been enough or efficient is certainly questionable, but as both countries enter a new wave of international trade opportunities, the responsibility to address the economic developments’ intrinsic environmental and social consequences must follow as well.
Part of the new dispositions of the USMCA was the creation of an Agreement on Environmental Cooperation and an adjacent Environment Committee responsible for overseeing the implementation of the agreement’s Chapter 24: “Environment.” [45] This chapter details amplified areas of collaboration on environmental trade-related issues, although not to a very large extent despite the inclusion of several multilateral environmental agreements (MEAs), excluding the Paris Agreement. The USMCA’s institutional scaffolding can help balance the opportunities of nearshoring with the need to ensure and support development while addressing social and environmental issues by recognizing:
- The intrinsic need to integrate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) frameworks and decarbonization strategies into nearshoring operations in the wake of corporate sustainability.
- The political obligation to address the exacerbated environmental degradation and industrial contamination along the U.S.-Mexico border, which nearshoring activities will worsen in already disadvantaged communities.
There is, indeed, transboundary environmental and social governance architecture available:
- Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC).
- U.S.-Mexico Border Environmental Program: Border 2025.
- Border Environmental Cooperation Commission (BECC).
- International Boundary and Water Commission (IBWC) / Comisión Internacional de Límites y Aguas (CILA).
- National Environmental Justice Advisory Council (NEJAC).
- Good Neighbor Environmental Board.
- North American Development Bank (NADBank)
The challenge remains for governments and the private sector to work synchronically to redefine trade guidelines in the region and consider possible solutions to all the above-mentioned challenges through some of the following policy suggestions.
Trade Policy Recommendations
- Emissions reduction and climate action: USMCA’s Chapter 24 highlights the protection of the environment, alluding to the prevention of a danger to human life or health through the following: 1) the control and abatement of dangerous emissions, 2) hazardous waste management, and 3) the protection or conservation of wild and endangered species including their habitat. The latter must include an amendment and a regional strategy on emissions reduction and climate action. Such a strategy is currently nonexistent. Additionally, entities such as the Border 2025 Binational Environmental Program, EPA’s and SEMARNAT’s U.S.-Mexico Border Environmental Program: Border 2025 and BECC must continue their efforts to develop partnerships to standardize information sharing and data collection. These institutions are also consolidating their own funds to foster cooperation and more effective air pollution control policies in the region, aiming to protect health risks in vulnerable demographic groups — children, pregnant women, and people with preexisting cardiac or respiratory conditions — which is becoming a social impact concern on trade policy. [46]
- Water scarcity: Water challenges will certainly not be easy to fix. Important efforts from institutions, such as the North American Development Bank, IBWC/CILA, academia, and private sector entities, are working on developing binational water conservation partnerships to support the ecological health and fair extraction of groundwater in the border region to attend much of the upcoming water needs in an already highly water-stressed region. The renegotiation of the 1944 Water Treaty — which covers the redistribution of the border region’s water supply from Mexico to the U.S. — must become a priority issue where new climate scenarios must be considered, including the adoption of new technologies, the upgrading of irrigation systems and predictability models, and environmental and climate diplomacy. [47]
- Waste disposal and pollution: Corruption and ineffective governance play a key role in failing to oversee compliance rules on waste disposal and pollution as well as biodiversity conservation and habitat protection. On waste issues, Border 2025 suggests a series of action items to improve disposal operations, waste stream identification, strategies to reduce illegal dumping and landfill management. [48] However, circularity and innovation technology will be key to include in the Border 2025’s Binational Consultative Mechanism: an objective regarding hazardous waste storage, treatment, and disposal that also aims toward finding common ground to develop sustainable materials sourcing and management and enhance resource efficiency practices. [49] Continuing to strengthen the prevention of international pollution arbitrage efforts is also important to combat the “illegal trade of regulated chemicals, products and substances (such as pesticides, ozone-depleting substances (ODS), HFCs, hazardous waste, and non-compliant engines.)” [50]
- Biodiversity loss and habitat conservation: There is an intrinsic need for the new administrations of Mexico and the U.S. to incorporate sanctions relative to biodiversity loss as addressed by other international frameworks, such as the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) or the Pelly Amendment, which certifies “nations for ‘diminish[ing] the effectiveness’ of any wildlife treaty,” meaning the U.S. could embargo any product from a nation failing to comply, including Mexico. [51] Additionally, corporations are taking steps toward the integration of natural capital accounting and scenario planning through new frameworks predicting the interplay between climate and nature-related financial risks. [52] The private sector and governments are integrating the value of natural capital into corporate and infrastructure planning and drafting policies for the latter to prioritize trade and investment purposes and new infrastructure development projects, representing an opportunity to increase companies’ sustainability reporting efforts. [53] It remains uncertain, however, if corporate responsibility strategies would implement environmental remediation programs and other social investment plans.
- Socioeconomic issues: Socioeconomic disparities will remain a looming concern if they are not incorporated into new trade agreements and organizations and if stakeholders are not held accountable to integrate social and environmental agendas as regulated by some of the many MEAs mentioned. Commitment and cooperation are necessary to reduce the negative environmental — and then social — impacts of transnational commerce and to understand the need for connected environmental and trade policies. [54] The U.S.-Mexico border region might be in a difficult place to undertake this complex task. For many of these policies, research has proven that regulating local environmental challenges, such as water, air, and soil quality, generates more cost benefits than regulating global common goods, such as climate, which are oftentimes perceived to have a lower regulatory cost. [55] For example, protecting “freshwater and air quality are typically characterized by low regulatory costs.” Regional entities can implement accountability measures, resulting in collective benefits, such as public health, that are extensively valued. Furthermore, civil society, local governments, and businesses will advocate and respond with actions to protect the long-term benefits of regulatory action. However, policymakers may find measures to mitigate climate change to be less attractive due to the costly investments required to generate benefits from “regulating global common resources, such as the atmosphere.” [56] This is when regional entities come into play to mobilize actors, such as nonprofits, businesses and local authorities, in uplifting environmental protections and social cohesion. The role of most international and transboundary committees, such as the NEJAC and Good Neighbor Environmental Board, will be crucial to advocate for border communities and their livelihoods by endorsing the labor protections for these vulnerable communities. Additionally, the private sector must abide by international human rights and corporate performance standards, such as the International Finance Corporation’s (IFC) “Performance Standards on Environmental and Social Sustainability” and U.N.’s “Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights” to reduce their environmental impacts and embrace their responsibility for protecting third parties from environmental and, thus, social harm. [57]
- Labor: Many of these economic-environmental frameworks push for better labor standards, support human rights observation and compliance, maintain the safety of critical supply chains and workforces, and increase workers’ productivity and retention. The new USMCA dispositions on labor entail more fair wages, better working conditions, and possibilities for freedom of association. [58] The USMCA’s resource for the “Facility -Specific Rapid Response Labor Mechanism” will demand firms in Mexico and the United States to pay tariffs and other penalties for failing to ensure worker rights, which has already created some discontent with the private sector. [59] A new regulatory framework in Mexico and the USMCA’s revised labor law in 2019 favor higher ethical standards for multinational corporations — including permitting Mexican works to unionize — and are supervised by the U.S. Department of Labor ‘s undersecretary for international labor affairs, which is a significant change from 20 years ago. This revision will hopefully remain untouched or will even be expanded in the review and revision process mandated by the accord by 2026. [60]
The region is moving toward an extended localized trade hub with an economic agenda that claims to include, at least rhetorically, “prosperity through economic integration and free trade,” and the eradication of poverty and inequality by guaranteeing sustainability through preserving natural environments for future generations. [61] In this sense, nearshoring on the U.S.-Mexico border should align its goals to mitigate the negative externalities of trade more aggressively and comprehensively.
The U.S.-Mexico borderlands share a common history, cultural and economic linkages, as well as natural resources that are fundamental for its subsistence and well-being. New instruments are available to plan infrastructure development and natural resource management to promote sustainable development and fair growth. Environmental and social health must play a key role in nearshoring through the design of better trade agreements and equitable governance approaches. This is no longer a choice — but a responsibility — of stakeholders, governments, industry, and consumers. Only under this understanding will nearshoring be a powerful means for sustainable resource management and long-lasting growth for local and global communities.
[1] Gloria Anzaldúa, Borderlands/La Frontera: The New Mestiza (Aunt Lute Books, 1987), 3.
[2] Robin M. Leichenko and Karen L. O’Brien, Environmental Change and Globalization: Double Exposures (Oxford University Press, 2008).
[3] Margaret Wilder et al., “Climate Change and U.S.- Mexico Border Communities,” in Assessment of Climate Change in the Southwest United States: A Report Prepared for the National Climate Assessment , ed. Gregg Garfin, Angela Jardine, Robert Merideth, Mary Black, and Sarah LeRoy (Island Press, 2013), 340–84, 341, https://doi.org/10.5822/978-1-61091-484-0 . To access more information about this report, see https://swccar.arizona.edu/ .
[4] Per Stromberg, The Mexican Maquila Industry and the Environment; An Overview of the Issues , Serie Estudios y Perspectivas 12 (U.N. Publications, 2002), https://hdl.handle.net/11362/4887 .
[5] Public Citizen’s Global Trade Watch, NAFTA’s Broken Promises: The Border Betrayed: U.S.-Mexico Border Environment and Health Decline in NAFTA’s First Two Years (Public Citizen Publications, January 1996), https://www.citizen.org/wp-content/uploads/naftas_broken_promises_-_the_border_betrayed.pdf ; Lori Saldaa, “The Downside of the Border Boom,” Los Angeles Times , August 22, 1996, https://www.latimes.com/archives/la-xpm-1996-08-22-me-36482-story.html ; and Steve Sawicki, “The Maquiladoras: Back Door Pollution,” E — the Environmental Magazine 9, no. 4 (July–August 1998).
[6] Clara Brandi and Jean-Frédéric Morin, Trade and the Environment: Drivers and Effects of Environmental Provisions in Trade Agreements , Elements in Earth System Governance (Cambridge University Press, 2023), https://doi.org/10.1017/9781009461825 ; Ronald B. Mitchell, “Problem Structure, Institutional Design, and the Relative Effectiveness of International Environmental Agreements,” Global Environmental Politics 6, no. 3 (August 2006), 72–89, https://doi.org/10.1162/glep.2006 .
[7] Indira Romero and Jesús Antonio López Cabrera, “Nearshoring in Mexico: Seizing Opportunities and Facing Challenges” (Houston: Rice University’s Baker Institute for Public Policy, July 16, 2024), https://doi.org/10.25613/QAPE-AA23 .
[8] National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration and National Integrated Drought Information System, “Rio Grande Region Watershed Drought Information,” National Integrated Drought Information System, accessed August 2024, https://www.drought.gov/watersheds/rio-grande .
[9] Wilder et al.
[10] The Hunt Institute for Global Competitiveness, “Our Border Environment: Water and Air Pollution,” Atlantic Council, February 2023, https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Our_Border_Environment_Water_-and_-Air_Pollution.pdf .
[11] Inu Manak and Scott Lincicome, “In Biden’s Steel Tariff Deal with Europe, Trump’s Trade Policy Lives On,” Cato Institute, November 2, 2021, https://www.cato.org/blog/bidens-steel-tariff-deal-europe-trumps-trade-policy-lives .
[12] Jess Middleton, “Mexico’s Nearshoring Potential Undermined by Climate and Security Risks,” Verisk Maplecroft, December 20, 2023, https://www.maplecroft.com/capabilities/geopolitical-and-country-risk/insights/mexicos-nearshoring-potential-undermined-by-climate-and-security-risks/ .
[13] Middleton.
[14] “¿La Escasez de Agua en México es una Amenaza para el Nearshoring?” (Is Water Scarcity in Mexico a Threat to Nearshoring?), Incotex, March 12, 2024, https://grupoincotex.com/blog/escasez-de-agua-en-mexico-amenaza-para-nearshoring/ .
[15] Scott Dance, “A Water War Is Brewing between the U.S. and Mexico. Here’s Why.,” Washington Post , May 16, 2024, https://www.washingtonpost.com/climate-environment/2024/05/16/texas-mexico-water-shortage-treaty-dispute/ .
[16] “La Paz Agreement,” U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), accessed August 2024, annex 3, art. 11, https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-09/documents/lapazagreement.pdf ; Keari Platt, “An Electronics Eco-Labeling System for Reducing Toxic Wastewater Runoff in the Tijuana River Estuary,” Hastings Environmental Law J ournal 29, no. 1 (Winter 2023): 47–80, 57. Additionally, the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) relies on the La Paz Agreement for disposition of maquiladora-generated hazardous waste.
[17] Platt, 63.
[18] Platt, 65.
[19] “Reglamento de la ley General del Equilibrio Ecológico y la Protección al Ambiente en Materia de Residuos Peligrosos” (Regulation of the General Law of Ecological Balance and Environmental Protection in the Matter of Hazardous Waste), Government of Mexico, https://www.diputados.gob.mx/LeyesBiblio/regley/Reg_LGEEPA_MRP.pdf .
[20] Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales ( SEMARNAT) and Procuraduría Federal de Protección al Ambiente (PROFEPA), “Derechos y Obligaciones de la Industria,” 2021, https://bit.ly/3TIdmCW .
[21] Daniel Trotta, “With Sewage Gushing into Sea, US and Mexican Border Towns Plead for Help” Reuters , last modified July 18, 2024, https://www.reuters.com/business/environment/with-sewage-gushing-into-sea-us-mexican-border-towns-plead-help-2024-07-17/ ; Geo-Logic Associates, Investigation of Illegal Tire Dumping Sites along the Southern California-Mexico Border,” California Department of Resources Recycling and Recovery, March 15, 2023, https://www2.calrecycle.ca.gov/Publications/Details/1724 .
[22] Good Neighbor Environmental Board (GNE), EPA, last modified September 4, 2024, https://www.epa.gov/faca/gneb .
[23] Border 2012: U.S.-Mexico Environmental Program, State of the Border Region Indicators Report 2010 , SEMARNAT and EPA, May 2011, 14–5, https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/documents/border-2012_indicator-rpt_eng.pdf .
[24] New models that evaluate biodiversity loss in the region should be developed and updated. Theodore J. Bohn et al., “Land and Water Use Changes in the US-Mexico Border Region, 1992–2011,” Environmental Research Letters 13, no. 11 (October 2018): 1–8, https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aae53e .
[25] Robert Peters et al., “Nature Divided, Scientists United: US-Mexico Border Wall Threatens Biodiversity and Binational Conservation,” BioScience 68, no. 10 (October 2018): 740–3, https://doi.org/10.1093/biosci/biy063 ; Fred Pearce, “Fenced In: How the Global Rise of Border Walls Is Stifling Wildlife,” YaleEnvironment360 , November 16, 2022, https://e360.yale.edu/features/border-walls-animals-climate-change .
[26] Center for Biological Diversity, “Borderlands and Boundary Waters," https://bit.ly/4eCSowW .
[27] Julie Watson, “Botanists Are Scouring the US-Mexico Border to Document a Forgotten Ecosystem Split by a Giant Wall,” Associated Press, May 19, 2024, https://apnews.com/article/border-native-plants-biodiversity-un-wall-mexico-98f9aa8e737f697f8443470aeab53db9 .
[28] See the meeting notes for COP-15, “Conference of the Parties,” Convention on Biological Diversity, 2022, https://www.cbd.int/cop .
[29] Wilder et al., 355.
[30] Wilder et al., 352.
[31] Wilder et al., 355.
[32] Wilder et al., 355.
[33] National Environmental Justice Advisory Council (NEJAC), “Executive Summary,” in Unheard Voices from the Border: A Report on Environmental Justice in the U.S.-Mexico Border Region from the Past to the Future , EPA, May 2003, https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-02/documents/nejac-ej-border-report.pdf .
[34] NEJAC, 18.
[35] Scott Vaughan, “USMCA Versus NAFTA on the Environment,” International Institute for Sustainable Development, October 3, 2018, https://www.iisd.org/articles/usmca-nafta-environment .
[36] Commission on Environmental Cooperation, “Agreement on Environmental Cooperation,” http://www.cec.org/about/agreement-on-environmental-cooperation/ .
[37] USMCA, ch. 24, https://ustr.gov/sites/default/files/IssueAreas/Environment/USMCA_Environment_Chapter_24.pdf .
[38] Manak and Alfredo Carrillo Obregon, “Mexico’s Electricity Bill Rolls Back Energy Reforms and Threatens Relations with Trading Partners,” Cato Institute, April 7, 2021, https://www.cato.org/blog/mexicos-electricity-bill-rolls-back-energy-reforms-threatens-relations-trading-partners .
[39] Wilder et al.
[40] NEJAC, 10.
[41] Asael Villanueva, “¿Qué es el Nearshoring? ¿ Cómo Afecta a México?” (What Is Nearshoring? How It Affects Mexico?), TecScience, February 7, 2024, https://tecscience.tec.mx/es/negocios-innovacion/nearshoring/ .
[42] Carlos Salas, “The Impact of NAFTA on Wages and Incomes in Mexico,” in NAFTA at Seven , by Salas, Bruce Campbell, and Robert E. Scott, Economic Policy Institute, April 26, 2001, https://www.epi.org/publication/briefingpapers_nafta01_mx/ .
[43] Most maquiladora employees are women willing to work for cheaper wages, long shifts and poor working conditions suffering oftentimes sexual abuses (Mia Alemán, “Maquiladoras, Human Rights, and the Impact of Globalization on the US-Mexico Border,” Foreign Affairs Review , June 16, 2022, https://jhufar.com/2022/06/16/maquiladoras-human-rights-and-the-impact-of-globalization-on-the-us-mexico-border/ ).
[44] Brandi and Morin, 18.
[45] USMCA, ch. 24.
[46] U.S.-Mexico Border Program, “Policy Workgroups,” EPA, last modified March 4, 2024, https://www.epa.gov/usmexicoborder/policy-workgroups .
[47] International Boundary and Water Commission (IBWC), “Minute No. 325,” October 21, 2020, https://www.ibwc.gov/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Min325.pdf .
[48] EPA and SEMARNAT, Border 2025: United States-Mexico Environmental Program Report , June 2021, 20, https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2021-05/documents/final_us_mx_border_2025_final_may_6.pdf .
[49] EPA and SEMARNAT, 19 and 22.
[50] EPA, “U.S-Mexico-Canada Agreement Factsheet,” May 2024, https://ustr.gov/sites/default/files/EPA%20USMCA%20Factsheet%20May%202024.pdf .
[51] Natural Resource Defense Council, “United States Finds Mexico Is Undermining Wildlife Treaty, May Impose Embargo,” May 26, 2023, https://www.nrdc.org/press-releases/united-states-finds-mexico-undermining-wildlife-treaty-may-impose-embargo .
[52] For example, see Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), https://www.fsb-tcfd.org/ ; and Task Force on Nature-Related Disclosures (TNFD), https://tnfd.global/about/ .
[53] Convention on Biological Diversity, “Mainstreaming of Biodiversity in the Infrastructure Sector,” United Nations Environment Program (UNEP), May 18, 2018, https://www.cbd.int/doc/c/8298/46cb/5db39f803634f17b7abf45d2/sbi-02-04-add5-en.pdf .
[54] United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), “Promoting Trade for Sustainable Development,” May 24, 2004, https://unctad.org/system/files/official-document/tdxibp10_en.pdf .
[55] Mitchell.
[56] Brandi and Morin, 51.
[57] The International Finance Corporation (IFC) “Performance Standards on Environmental and Social Sustainability” provided companies with guidance on how to recognize socio-environmental risks and effects and how to avoid wrongdoings and operate in a sustainable way including stakeholder engagement and disclosure obligations along the project life cycle (IFC, “Performance Standards on Environmental and Social Sustainability,” January 1, 2012, https://www.ifc.org/content/dam/ifc/doc/2010/2012-ifc-performance-standards-en.pdf ). U.N. Working Group on Business and Human Rights, “The UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights: An Introduction,” accessed August 2024, https://bit.ly/3zxZAvy .
[58] USMCA, ch. 23: “Labor,” https://ustr.gov/sites/default/files/files/agreements/FTA/USMCA/Text/23-Labor.pdf .
[59] USMCA, ch. 31, annex A: “Facility-Specific Rapid-Response Labor Mechanism,” https://ustr.gov/issue-areas/enforcement/dispute-settlement-proceedings/fta-dispute-settlement/usmca/chapter-31-annex-facility-specific-rapid-response-labor-mechanism . In terms of these provisions generating frustration the private sector, such is the case for Tridonex, a Philadelphia-based, auto-part company with a plant stationed in Matamoros, Mexico, as hundreds of its workers sought to be allowed to switch unions to which in return, the company retaliated against the workers supporting this initiative (Daina Beth Solomon, “Insight: In Mexico Autos Town, Labor Rights Falter Despite U.S. Trade Deal,” Reuters , May 3, 2021, https://www.reuters.com/world/americas/mexico-autos-town-labor-rights-falter-despite-us-trade-deal-2021-05-03/ ).
[60] “Trade Economist Thea Lee Named U.S. Labor Dept. International Chief,” Reuters , May 10, 2021, https://www.reuters.com/world/americas/trade-economist-thea-lee-named-us-labor-dept-international-chief-2021-05-10/ .
[61] Mindähi C. Bastida Muñoz, “Americas Sustainability Issues: Biodiversity, Indigenous Knowledge and Intellectual Property Rights,” paper presented at Commission for Environmental Cooperation’s Second North American Symposium on Assessing the Environmental Effects of Trade, March 2003, http://www.cec.org/files/documents/publications/2190-americas-sustainability-issues-biodiversity-indigenous-knowledge-and-intellectual-en.pdf .
This material may be quoted or reproduced without prior permission, provided appropriate credit is given to the author and Rice University’s Baker Institute for Public Policy. The views expressed herein are those of the individual author(s), and do not necessarily represent the views of Rice University’s Baker Institute for Public Policy.
Related Research

Common Ground Is Needed to Rebuild US-Mexico Security Cooperation

Nearshoring Raises Questions About Environmental and Social Impacts in the Borderlands

Leverage Immigration To Address US Labor Shortages

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The introduction to a research paper presents your topic, provides background, and details your research problem.
The introduction of a research paper provides an overview of the study's purpose, scope, and significance. Read this article to understand what is a research paper introduction, its importance and how to write a research paper introduction with examples.
In this blog, we'll discuss how to write an introduction for a research paper and the crucial elements of a strong introduction.
Research paper introduction is the first section of a research paper that provides an overview of the study, its purpose, and the research question (s) or hypothesis (es) being investigated. It typically includes background information about the topic, a review of previous research in the field, and a statement of the research objectives.
A good research paper introduction includes: Scientific research papers with original data should also include the methodology, a literature review, and possibly a research question or hypothesis. How do you write an introduction for a research paper? There are a few important guidelines to remember when writing a research paper.
Let's start! An introduction is a paragraph that provides information about your entire paper and aims to attract and inform the reader. Before writing an introduction or even starting your paper, you need to research academic sources. The first one or two sentences of an introduction paragraph should be a hook to attract the reader's attention.
Learn to craft a compelling introduction for your research paper with our expert tips. Discover how to engage readers and set the stage for your study.
How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples Published on February 4, 2019 by Shona McCombes. Revised on July 23, 2023. A good introduction paragraph is an essential part of any academic essay. It sets up your argument and tells the reader what to expect. The main goals of an introduction are to: Catch your reader's attention. Give background on your topic. Present your thesis ...
Research paper readers need this kind of warmup, too. A good introduction, or intro, lives up to its name—it introduces readers to the topic. It prepares them to care about and understand your research, and it's more convincing. AI tools can be useful resources to help you plan the structure of your research paper.
The 4-step approach to writing the Introduction section. As a rule of thumb, this section accounts for about 10% of the total word count of the body of a typical research paper, or about 400 words spread over three paragraphs in a 4000-word paper.1 With that, let us now understand how to write the Introduction section step-by-step: 1.
What is the LEAP research paper writing approach? I designed the LEAP writing approach not only for merely writing the papers. My goal with the writing system was to show young scientists how to first think about research results and then how to efficiently write each section of the research paper. In other words, you will see how to write a research paper by first analyzing the results and ...
Beginning your paper with an introductory paragraph serves two purposes. It grabs your readers' attention, and it contains your thesis statement—the main idea of your entire paper. When you wrote your outline, you drafted a rough thesis statement. Now build it into a paragraph that makes your readers want to know what you have to say. Here are some tips for perfecting your introduction:
CARS stands for "Creating a Research Space." It's a framework developed by linguist John Swales that helps you introduce your research in a way that captures your readers' attention and clearly shows your work's place in academic conversation. Think of it as a roadmap for your introduction, guiding you through three essential moves:
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research.
Offers detailed guidance on how to develop, organize, and write a college-level research paper in the social and behavioral sciences.
Discussion of how to understand and write different sections of a scientific paper. Discussions of how to write Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Data, and Discussion.
The introduction section is arguably one of the most critical elements of a written piece of research work, often setting the tone for the remainder of any dissertation or research article. The primary purpose of an introduction is to provide the reader with a clear understanding of the research question, in addition to the scope, rationale, aims and objectives of the study. This ensures the ...
How to Write a Research Paper | A Beginner's Guide A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research. Research papers are similar to academic essays, but they are usually longer and more detailed assignments, designed to assess not only your writing skills but also your skills in scholarly research ...
The hardest part about writing a research paper is getting started. Learn how to write a solid introduction for a research paper in this blog post.
Writing the introductory paragraph can be a frustrating and slow process -- but it doesn't have to be. If you planned your paper out, then most of the introductory paragraph is already written. Now you just need a beginning and an end.
Writing a research paper introduction is an essential skill for students. An introduction to a research paper provides readers and potential stakeholders with necessary background information on a topic. It also builds up to a paper's main point, or thesis. Know that for a longer report, your introduction might be more than one paragraph (see sample below).
The introduction is one of the most compact parts of the research paper, since it is not very long but needs to essentially give a complete overview of the context in which your study is taking place, and your specific reasons for doing the study. Most tend to be around 10% of the total length of your paper.
The introduction serves the purpose of leading the reader from a general subject area to a particular field of research. It establishes the context of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the hypothesis, question, or research problem, briefly explaining your rationale ...
Toward the end of the introduction, you add your thesis statement, and explain how you will provide information to support your research questions. This provides the purpose, focus, and structure for the rest of the paper.
A Closer Look at Common Formats. Books - Usually a substantial amount of information, published at one time and requiring great effort on the part of the author and a publisher.. Magazines/Journals - Published frequently, containing lots of articles related to some general or specific professional research interest; edited.. Newspapers - Each is usually a daily publication of events of ...
1. Introduction. Globally, there were approximately 20 million new cancer cases in 2022 and 9.7 million cancer deaths [Citation 1, Citation 2].In the USA alone, there were more than 1.9 million new cancer cases in 2022 [Citation 3] and more than 600,000 people died from the disease [Citation 4].As life expectancy and the number of older patients living with cancer increase, the number of ...
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements: A hook to catch the reader's interest. Relevant background on the topic. Details of your research problem. and your problem statement. A thesis statement or research question. Sometimes an overview of the paper. Frequently asked questions: Writing a research paper.
This paper derives from High Spirits: Young Women's Pleasure in the NTE, a doctoral thesis completed in 2020, which introduced a serious consideration of pleasure into research on young women's alcohol use in the UK's NTE. The research was exploratory given the relative lack of work in this field; in terms of a research question, 'what ...
As Mexico becomes a desirable site for nearshoring, damaging environmental and social impacts on the border region may be exacerbated under the economic growth. A new report by research scholar Ivonne Cruz dissects the relationship between nearshoring's ecological and socioeconomic risks and offers trade policy recommendations to support sustainable economic development, mitigate potential ...