Argumentative vs. Persuasive Essays: What’s the Difference?
The difference between an argumentative and persuasive essay isn’t always clear. If you’re struggling with either style for your next assignment, don’t worry. The following will clarify everything you need to know so you can write with confidence.
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!

First, we define the primary objectives of argumentative vs. persuasive writing. We then compare the best strategies for starting the writing process. In both cases, the key is knowing your audience, which we will discuss later in this article by Custom-Writing.org experts.
- 🎯 Primary Objectives
- 🎬 Starting Your Essay
- ✍️ Writing Technique
- 👁️ Point of View
- ❓ So, what’s the difference?

🔗 References
🎯 persuasive vs. argumentative writing: primary objectives.
Both argumentative and persuasive essays require you to present your point of view on a specific topic. However, your approach will differ between the two. The words “argumentative” and “persuasive” should help you recognize what you are expected to achieve. Let’s see how.
For the argumentative essay, it is sufficient to present your point of view and nothing more. That said, the information you present should come across as being reliable enough for the readers. They don’t need to agree with your take on the issue at hand. The reader need only acknowledge that your point of view is worth considering.
In a persuasive essay, however, your goal is to get the reader on your side. And so, in addition to presenting sensible information, you want the reader to share your opinion.
Here are some examples to show you the difference. For more examples try and use a thesis statement generator for persuasive essay and for argumentative one, and you’ll clearly see what sets them apart.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
Additionally, you can take a look at any example of term paper for college , which will clearly show you the differences between the types. Remember, though, that the more controversial your topic is, the more likely it is that the reader will disagree with you!
🎬 Argumentative vs. Persuasive Essay: How to Start
For either type of essay, the foundation is generally the same. Before even thinking about your introduction, settle on a topic that genuinely interests you. What follows will differ for argumentative and persuasive essays.
In the case of argumentative writing, it’s crucial to have all the information you need to build up a strong set of arguments and examples. Therefore, don’t forget to spend some time researching your topic in earnest. Once you have all the data, you can easily choose which side to take. Never force a paper to align with your personal opinion if you don’t have enough supporting evidence.
In the case of a persuasive essay, your job is to make sure you have a decent topic and identify which side to support. The starting point is a bit less complicated.
✍️ Persuasive vs. Argumentative Essays: Writing Technique
This is where things get interesting in the clash between persuasive and argumentative writing. For college-level writing, it’s never enough to follow a general essay outline . Getting that coveted higher mark requires that you know the unique yet subtle features of both writing styles.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!
Topical and relevant reasons are the backbone of any argumentative text. This is where preliminary research comes in. Having requisite evidence and facts from credible sources ensures the worthiness of your essay. That way, the reader can validate your point of view.
As with argumentative writing, persuasive essays should include some measure of supporting facts. What distinguishes persuasive writing is that you must also engage the reader on an emotional level. Moreover, there’s no need to present opposing opinions. Your goal is to make the reader take your side. All’s fair in love and war!
👁️ Persuasive vs. Argumentative Essays: Point of View
Let’s talk more about presenting different opinions. You were probably taught that an academic essay includes at least three arguments and an additional counterargument . Keep in mind, however, that this rule applies only to argumentative essays, in which you introduce three or more arguments with evidence to support your point of view. You then offset that point of view by including an opposing opinion. By doing so, you allow the reader to choose a side, even though the facts, as you’ve presented them, are in favor of your opinion. This is a logic-based approach.
In a persuasive essay, you’re not likely to entertain the opposition. Your conviction is the very essence of the essay. Your take on the issue in question must come across as the only sensible approach. If you’re feeling confident, you’re welcome to include a counterargument, but only if you decimate it right away!
👏 The Audience of Argumentative vs. Persuasive Essays
We’ve seen the differences and similarities between argumentative and persuasive writing and walked you through the technical aspects of both. But there’s one final piece of the puzzle to be considered: the question of your audience. This is the biggest difference of them all.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
When writing an argumentative essay, remember that you don’t need to convince anyone. There is no audience. You’re simply presenting the information you gathered without expecting anything in return (except maybe a pat on the back from your teacher).
Without an audience, there’s no one to persuade. This touches on another crucial element of the writing process : understanding what and how your readers think. This allows you to pick the best strategy to convince them to join your side.
❓ What’s the Difference between a Persuasive Essay and an Argumentative Essay?
The main difference between a persuasive essay and an argumentative essay comes down to your audience. For persuasive writing, it’s necessary to feel out your audience and wield that knowledge to prove the efficacy of your perspective. For argumentative writing, opt for a logical approach and just present the facts with no intent to persuade anyone.
Persuasive Essay Topics
- Cigarettes manufacturers must be banned .
- Unrestricted access to women’s health care is crucial for the welfare of future generations.
- College sports need to benefit student-athletes .
- Lowering TOEFL scores across university will benefit international students.
- American football promotes violence and jeopardize sportsmen’s health.
- Tattoos are fine art .
- Animal transplantation can reduce the problem of organs shortage.
- Smoking in public places should be banned to protect and improve public health.
- Job drug test has to be made obligatory.
- It is necessary to prohibit using cellphones while driving .
- Gun control legislation must be revised .
- Surveillance cameras have to be installed in all public places.
- Mandatory overtime for nurses must be made illegal.
- Marijuana should be legalized for medical use.
- Business should switch to remote work for an increased talent pool.
- Experimentation on animals has to be banned.
- It is crucial to limit clear cutting in rainforest .
- It is necessary to forbid guns in college campuses .
- Companies should prioritize the development of biometric security .
- Abortions should be legalized worldwide.
- Children should not have grades in school .
- Wearing face mask in public places should be mandatory.
- English language learners have to be immersed in English .
- Net neutrality should be supported.
- Body organs sale should not be allowed.
Argumentative Essay Topics
- Should celebrities be a positive role model ?
- Does the use of social media in nursing violate patients’ rights regarding privacy?
- Is it right to abolish capital punishment ?
- Is it ethical to use animals for research ?
- Should bullies be expelled from school?
- Is it fair to try juveniles as adults ?
- Do you think it wise to lower drinking age to 18 ?
- Will implementation of free higher education diminish economic disparities?
- Should the voluntary euthanasia be permitted?
- Is stem cells use ethical?
- Should schoolchildren study the evolution theory?
- Is container deposit legislation an urgent issue?
- Is marriage based on love more successful than arranged?
- Should the use of cell phones in public places be banned?
- Is it right for celebrities to be involved in political activism?
- Do you agree that health insurance has to cover art and music therapy ?
- Does the government have right to monitor its citizens using technology?
- Is it ethical to perform gene editing on human embryos ?
- Do you think online dating as serious as dating in person?
- Should vaccination of children be compulsory?
- Are the social media platforms a threat to human relationships?
- Are there limits to what should be questioned?
- Should modern society become vegan ?
- Do you think the cigarette smoking should be made illegal?
- Should illegal immigrants have full access to all social services?
- Argumentative Essays // Purdue Writing Lab
- Argumentative Essay Structure (University of Washington)
- Suggestions for Developing Argumentative Essays (UC Berkeley)
- Argumentative essay | Quick guide (article) | Khan Academy
- Writing a Persuasive Essay: Hamilton College
- Persuasion (UMN Libraries)
- Persuasive Writing – Georgetown Law
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

You don’t need to be a nerd to understand the general idea behind cause and effect essays. Let’s see! If you skip a meal, you get hungry. And if you write an essay about it, your goal is achieved! However, following multiple rules of academic writing can be a tough...
![the difference between argumentative and persuasive essays How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 101 Guide [+ Examples]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/young-writer-taking-notes-284x153.jpg)
An argumentative essay is a genre of academic writing that investigates different sides of a particular issue. Its central purpose is to inform the readers rather than expressively persuade them. Thus, it is crucial to differentiate between argumentative and persuasive essays. While composing an argumentative essay, the students have to...
![the difference between argumentative and persuasive essays How to Title an Essay: Guide with Creative Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/close-up-woman-making-greeting-card-new-year-christmas-2021-friends-family-scrap-booking-diy-writing-letter-with-best-wishes-design-her-homemade-card-holidays-celebration-284x153.jpg)
It’s not a secret that the reader notices an essay title first. No catchy hook or colorful examples attract more attention from a quick glance. Composing a creative title for your essay is essential if you strive to succeed, as it: Thus, how you name your paper is of the...

The conclusion is the last paragraph in your paper that draws the ideas and reasoning together. However, its purpose does not end there. A definite essay conclusion accomplishes several goals: Therefore, a conclusion usually consists of: Our experts prepared this guide, where you will find great tips on how to...
![the difference between argumentative and persuasive essays How to Write a Good Introduction: Examples & Tips [2024 Upd.]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/closeup-shot-woman-working-studying-from-home-with-red-coffee-cup-nearby-284x153.jpg)
A five-paragraph essay is one of the most common academic assignments a student may face. It has a well-defined structure: an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Writing an introduction can be the most challenging part of the entire piece. It aims to introduce the main ideas and present...

Exemplification essays, also called illustration essays, are one of the easiest papers to write. However, even the simplest tasks require experience and practice. It is a good idea to find and analyze free exemplification essay examples. You can also ask your teacher to give you some sample exemplification essays from...
![the difference between argumentative and persuasive essays How to Write about a Topic You Lack Interest in [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Frustrated-exhausted-young-woman-blogger-284x153.jpg)
During their school years, students may not always have the opportunity to select a topic for their essay or research paper. Instructors tend to assign one or offer a list of ideas that might not seem engaging. Moreover, even the topic that you choose yourself can sometimes end up being...

Sorry to disappoint you, but if you think that your high scores and grades would be enough to get accepted into the university of your dreams, you’re wrong… The best colleges worldwide, such as the Ivy League schools receive applications from thousands and thousands of talented students. You gotta stand...

Writing an essay is a task that everyone has to deal with. The first encounter most likely happens at primary school. Compositions in primary school are quite basic and only require a good imagination and somewhat decent writing skills. But… As time passes, essay writing becomes more and more complicated....

Often when you’re completing academic writing, especially essays, you need to use pronouns. In academic writing, the use of the word you is unacceptable. You can find yourself in a sticky situation, deciding upon gender-neutral pronouns in your academic writing. How can students deal with it? In most situations today,...

A divorce is a life-changing experience that affects spouses and their children (if there are any). Since divorce rates are relatively high in modern society, more and more people face this problem nowadays. When you are assigned to compose an argumentative essay about divorce, you should be as careful as...
![the difference between argumentative and persuasive essays How to Stop Corruption Essay: Guide & Topics [+4 Samples]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/close-up-two-hands-while-paying-money-284x153.jpeg)
Corruption is an abuse of power that was entrusted to a person or group of people for personal gain. It can appear in various settings and affect different social classes, leading to unemployment and other economic issues. This is why writing an essay on corruption can become a challenge. One...

Home » Language » Linguistic » Difference Between Argumentative and Persuasive Essay
Difference Between Argumentative and Persuasive Essay
Main difference – argumentative vs persuasive essay.
Persuasive essay and Argumentative essay are similar in nature and thus, often confused to be the same though there exists a difference between the two. In fact, Persuasive essay and Argumentative essay are two different types of essays, and the main difference between them is that the persuasive essay depends on opinions and emotions while an argumentative essay uses logic and reason. Let us first look at these two types of essays in detail and then move on to identify the differences between a persuasive essay and an argumentative essay.
What is an Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay is a piece of writing that attempts to convince the readers that the author’s idea is true . This is a genre of writing that is used to defend or prove a point. A writer should do a thorough research; gather accurate facts and figures before writing an argumentative essay. This is more like a debate written on paper. While writing an argumentative essay, a writer should be aware of both pros and cons of the argument, and should try to discredit the opposing view by using evidence .
What is a Persuasive Essay
A persuasive essay is a piece of writing that attempts to convince the readers to agree with author’s ideas. In this type of essay, the writer can use his own ideas, opinions and evoke the emotions in the reader in order to convince them to agree to his opinion . A writer of a persuasive essay needs to do research, gather evidence, but a clever writer can create a successful essay without knowing much. This is because; a persuasive writing appeals more to reader’s emotions rather than minds. In persuasive writing, the writer should have certain awareness about the audience . For example, opinions and ideas that could appeal to teenagers may not have the same effect on adults. First person narration and Second person narration (Ex: In my opinion, I believe, etc.,) are commonly used as the writer is addressing the audience directly.
As discussed before, argumentative essays are a genre of writing that attempts to convince the readers to accept the writer’s idea as true, by using statistics, facts and figures, etc. while persuasive essays are a genre of writing that attempts to convince the readers to agree with the writer, by using emotions, personal ideas, etc. In other words, an argumentative essay is based on logic and reasons while a persuasive essay is based on emotions and personal opinions. When it comes preparations, before writing an argumentative essay, the writer needs to do a thorough research on the subject but does not need to have the knowledge about the audience. On the other hand, the writer can write a persuasive essay even without doing much research, but he should have certain knowledge about the audience.

When we look at both types of essays in the perspective of the audience; an argumentative essay appeals to the minds of the readers whereas, a persuasive essay appeals to the hearts of the readers. Also, an argumentative essay acknowledges opposing views, but a persuasive essay may not acknowledge opposing views.
About the Author: Hasa
Hasanthi is a seasoned content writer and editor with over 8 years of experience. Armed with a BA degree in English and a knack for digital marketing, she explores her passions for literature, history, culture, and food through her engaging and informative writing.
You May Also Like These
Argumentative vs. Persuasive
What's the difference.
Argumentative and persuasive writing are both forms of communication that aim to convince the audience of a particular viewpoint or opinion. However, they differ in their approach and purpose. Argumentative writing focuses on presenting logical reasoning and evidence to support a claim, often engaging in a debate-like structure. It aims to persuade the reader by presenting a strong and well-reasoned argument. On the other hand, persuasive writing appeals to the emotions and values of the audience, using techniques such as storytelling and rhetoric to sway their opinion. It aims to convince the reader by appealing to their emotions and personal beliefs. While both forms of writing are effective in their own ways, argumentative writing relies more on facts and evidence, while persuasive writing relies on emotional appeal and personal connection.
Further Detail
Introduction.
When it comes to communication and expressing opinions, two common approaches are argumentative and persuasive. While both aim to convince others of a particular viewpoint, they differ in their strategies and techniques. In this article, we will explore the attributes of argumentative and persuasive communication styles, highlighting their similarities and differences.
Definition and Purpose
Argumentative communication involves presenting logical reasoning and evidence to support a specific claim or position. The primary goal is to engage in a rational debate, presenting facts and counterarguments to persuade the audience that the presented viewpoint is more valid than others. On the other hand, persuasive communication focuses on appealing to emotions, values, and beliefs to influence the audience's attitudes or behaviors. The purpose is to sway individuals by creating an emotional connection and tapping into their desires or fears.
Approach and Tone
In terms of approach, argumentative communication tends to be more formal and structured. It relies heavily on logical reasoning, critical thinking, and evidence-based support. The tone is often objective and impersonal, aiming to present a well-reasoned case. On the contrary, persuasive communication adopts a more personal and subjective tone. It often employs storytelling, rhetorical devices, and vivid language to evoke emotions and create a sense of connection with the audience.
Evidence and Support
Both argumentative and persuasive communication rely on evidence and support to strengthen their claims. However, the types of evidence used may differ. In argumentative communication, the focus is on empirical data, research findings, expert opinions, and logical deductions. The aim is to provide a solid foundation for the argument and counter any opposing viewpoints. In persuasive communication, anecdotal evidence, personal experiences, testimonials, and appeals to authority or popular opinion are often employed. The goal is to create relatability and establish credibility through emotional resonance.
Structure and Organization
Argumentative communication typically follows a clear and logical structure. It often begins with an introduction that presents the main claim, followed by body paragraphs that provide supporting evidence and counterarguments. Finally, a conclusion summarizes the main points and restates the claim. This structure helps the audience follow the line of reasoning and evaluate the presented arguments objectively. On the other hand, persuasive communication may adopt a more flexible structure. It often starts with an attention-grabbing introduction that captures the audience's interest. The body paragraphs focus on building an emotional connection and presenting persuasive techniques. The conclusion aims to leave a lasting impression and call the audience to action.
Audience Engagement
While both argumentative and persuasive communication aim to engage the audience, they do so in different ways. Argumentative communication relies on intellectual engagement, appealing to the audience's sense of reason and critical thinking. It encourages the audience to evaluate the presented evidence and make an informed decision. Persuasive communication, on the other hand, seeks to create an emotional bond with the audience. It aims to captivate their attention, trigger empathy, and tap into their values and desires. By establishing this emotional connection, persuasive communication can influence the audience's attitudes and behaviors more effectively.
Use in Different Contexts
Argumentative communication is often employed in academic settings, formal debates, and legal proceedings. Its emphasis on logical reasoning and evidence makes it suitable for situations where objectivity and rationality are valued. Persuasive communication, on the other hand, finds its place in advertising, marketing, political campaigns, and public speaking. Its ability to tap into emotions and create a personal connection makes it effective in influencing public opinion, consumer behavior, and decision-making processes.
While argumentative and persuasive communication share the goal of convincing others, they differ in their approach, tone, evidence, structure, and audience engagement. Argumentative communication relies on logical reasoning and evidence-based support, adopting a formal and structured approach. Persuasive communication, on the other hand, appeals to emotions and personal beliefs, using storytelling and vivid language to create a connection with the audience. Understanding the attributes of these communication styles can help individuals choose the most appropriate approach based on the context and desired outcome.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.
Argumentative Essay vs. Persuasive Essay: What's the Difference?
Key Differences
Comparison chart, approach to counterarguments, reliance on research, typical use, argumentative essay and persuasive essay definitions, argumentative essay, persuasive essay, do persuasive essays focus on emotional appeal, what is an argumentative essay, how does an argumentative essay handle counterarguments, is research important in argumentative essays, are persuasive essays less formal, what defines a persuasive essay, where are argumentative essays commonly used, can argumentative essays have a persuasive element, what is a key difference in structure between these essays, do persuasive essays always present counterarguments, can an argumentative essay change a reader's opinion, can both types of essays use statistical data, are persuasive essays biased, do persuasive essays require evidence, can a persuasive essay be subjective, what tone is typical in argumentative essays, is it necessary to pick a side in an argumentative essay, where would you typically find persuasive essays, are persuasive essays shorter than argumentative essays, can both essays be used in educational settings.

Trending Comparisons

Popular Comparisons

New Comparisons

At LanguageHumanities, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
Learn more...
What Is the Difference between an Argumentative and Persuasive Essay?
Argumentative and persuasive essays both aim to present a specific point of view, but they are different both in how they get their point across and why . The author of an argumentative essay will usually try to make his or her point through reason. This means identifying the opposing viewpoints andthen using facts, statistics, or other evidence to discredit them so that the reader ultimately concludes that the writer’s position is correct. The persuasive essay , on the other hand, more often uses passion and emotion in an attempt to sway the reader’s loyalties. Opposing views are often acknowledged here, but aren’t usually analyzed. As a result this sort of essay is often perceived to be essentially one-sided and is written based primarily on personal convictions. Argumentative papers are usually structured more like high-level analysis, with sections devoted to looking at key issues from multiple angles.
Argumentative Techniques
In most cases, the argumentative essay is one that objectively states an argument that it then backs up with facts, statistics, and expert evidence. Writers generally acknowledge counterclaims and opposing arguments from the very beginning, but make it their goal to discredit them by appealing to the reader’s reason . As such these sorts of papers often give an overview of all the main arguments or scholarship on a given topic, then build an argument about which is the best or the most correct.
There are a few different techniques writers of these sorts of papers can use, depending on their precise goal. Sometimes the point of the exposition is to demonstrate that the counterclaims are based on outdated information or incomplete research, or they might be discredited as factually inaccurate. The argumentative essay’s goal is to present a whole-cloth argument that will convince a reader because of its grounding in fact and logic.
The writer of this sort of paper knows that readers may not agree at the end of the argument, and in many cases convincing them isn’t really all that important. More essential is that the argument is logical and justifiable. Upon reading the reasons for the position, a reader should at the very least respect the writer’s position, even if he or she does not ultimately think the position is correct.
Passion and Persuasion
Persuasive essays, on the other hand, are usually designed to convince the reader, often by appealing to his or her emotions. Writers will often start out assuming that their readers are incorrect in their views and will then use the essay as a means of correcting or perfecting perceptions. In most cases it is an appeal that makes use of a traditional conceptions of right and wrong, and uses passion to draw the reader alongside the writer for what is more or less a shared walk.
This type of essay acknowledges opposing viewpoints, but doesn’t normally spend much time analyzing them. Instead, writers usually attempt to frame their own perspectives with more convincing language. Persuasive essays are often tailored to appeal to the personal interests, social convictions, and any known passions of the reader, and as such they’re often designed for a specific audience. This is in direct contrast to most argumentative essays, which tend to be written for almost anyone.
Writers of persuasive essays also rely more on human emotions than statistics when making their case. This type of writing focuses on empathetic and persuasive delivery and the writer might present anecdotal storytelling or share personal experience with which the reader can identify. The essay often presents the desired change of mind as a win-win rhetorical situation for both the writer and the reader.
Structural Differences
In most cases these essays are structured really differently, too. Writers with argumentative goals typically handle each issue or element in turn, analyzing it from all sides and then drawing a conclusion consistent with the paper’s thesis. Persuasive pieces, by contrast, more often raise and dismiss opposition at the outset, then spend the bulk of the body paragraphs emphasizing the writer’s position with different examples.
The ways in which the conclusions are presented often differ, too. An argumentative essay will usually end with a recap of all relevant facts and an assertion that the writer’s interpretation is the correct one. The persuasive writer will more often conclude by asking the reader to change his or her mind or “join the cause” presented in the paper.
Possible Places of Overlap
Argumentative and persuasive essays have a similar goal, which is to convince readers that the core assertion is correct or at least well-reasoned. The difference between proving a point and changing someone’s mind can be profound, but in certain aspects — identifying criticism, relating to the reader, and setting an authoritative tone, for instance — there can be similarities, too. A lot depends on the writer, the topic, and the intended audience.
AS FEATURED ON:

Related Articles
- What Is an Illustration Essay?
- What Are the Different Types of Essay Structures?
- What Is an Analytical Exposition?
- What Are Rhetorical Modes?
- What Is a Problem-Solution Essay?
- What Are the Different Types of Essay Formats?
- What Are the Different Types of Essays?
Discuss this Article
Post your comments.
- By: Rido Persuasive essays attempt to coax readers into the author's point of view.
- By: AlexOakenman An argumentative essay objectively states an argument that it backs up with facts.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to write an a+ argumentative essay.
Miscellaneous

You'll no doubt have to write a number of argumentative essays in both high school and college, but what, exactly, is an argumentative essay and how do you write the best one possible? Let's take a look.
A great argumentative essay always combines the same basic elements: approaching an argument from a rational perspective, researching sources, supporting your claims using facts rather than opinion, and articulating your reasoning into the most cogent and reasoned points. Argumentative essays are great building blocks for all sorts of research and rhetoric, so your teachers will expect you to master the technique before long.
But if this sounds daunting, never fear! We'll show how an argumentative essay differs from other kinds of papers, how to research and write them, how to pick an argumentative essay topic, and where to find example essays. So let's get started.
What Is an Argumentative Essay? How Is it Different from Other Kinds of Essays?
There are two basic requirements for any and all essays: to state a claim (a thesis statement) and to support that claim with evidence.
Though every essay is founded on these two ideas, there are several different types of essays, differentiated by the style of the writing, how the writer presents the thesis, and the types of evidence used to support the thesis statement.
Essays can be roughly divided into four different types:
#1: Argumentative #2: Persuasive #3: Expository #4: Analytical
So let's look at each type and what the differences are between them before we focus the rest of our time to argumentative essays.
Argumentative Essay
Argumentative essays are what this article is all about, so let's talk about them first.
An argumentative essay attempts to convince a reader to agree with a particular argument (the writer's thesis statement). The writer takes a firm stand one way or another on a topic and then uses hard evidence to support that stance.
An argumentative essay seeks to prove to the reader that one argument —the writer's argument— is the factually and logically correct one. This means that an argumentative essay must use only evidence-based support to back up a claim , rather than emotional or philosophical reasoning (which is often allowed in other types of essays). Thus, an argumentative essay has a burden of substantiated proof and sources , whereas some other types of essays (namely persuasive essays) do not.
You can write an argumentative essay on any topic, so long as there's room for argument. Generally, you can use the same topics for both a persuasive essay or an argumentative one, so long as you support the argumentative essay with hard evidence.
Example topics of an argumentative essay:
- "Should farmers be allowed to shoot wolves if those wolves injure or kill farm animals?"
- "Should the drinking age be lowered in the United States?"
- "Are alternatives to democracy effective and/or feasible to implement?"
The next three types of essays are not argumentative essays, but you may have written them in school. We're going to cover them so you know what not to do for your argumentative essay.
Persuasive Essay
Persuasive essays are similar to argumentative essays, so it can be easy to get them confused. But knowing what makes an argumentative essay different than a persuasive essay can often mean the difference between an excellent grade and an average one.
Persuasive essays seek to persuade a reader to agree with the point of view of the writer, whether that point of view is based on factual evidence or not. The writer has much more flexibility in the evidence they can use, with the ability to use moral, cultural, or opinion-based reasoning as well as factual reasoning to persuade the reader to agree the writer's side of a given issue.
Instead of being forced to use "pure" reason as one would in an argumentative essay, the writer of a persuasive essay can manipulate or appeal to the reader's emotions. So long as the writer attempts to steer the readers into agreeing with the thesis statement, the writer doesn't necessarily need hard evidence in favor of the argument.
Often, you can use the same topics for both a persuasive essay or an argumentative one—the difference is all in the approach and the evidence you present.
Example topics of a persuasive essay:
- "Should children be responsible for their parents' debts?"
- "Should cheating on a test be automatic grounds for expulsion?"
- "How much should sports leagues be held accountable for player injuries and the long-term consequences of those injuries?"
Expository Essay
An expository essay is typically a short essay in which the writer explains an idea, issue, or theme , or discusses the history of a person, place, or idea.
This is typically a fact-forward essay with little argument or opinion one way or the other.
Example topics of an expository essay:
- "The History of the Philadelphia Liberty Bell"
- "The Reasons I Always Wanted to be a Doctor"
- "The Meaning Behind the Colloquialism ‘People in Glass Houses Shouldn't Throw Stones'"
Analytical Essay
An analytical essay seeks to delve into the deeper meaning of a text or work of art, or unpack a complicated idea . These kinds of essays closely interpret a source and look into its meaning by analyzing it at both a macro and micro level.
This type of analysis can be augmented by historical context or other expert or widely-regarded opinions on the subject, but is mainly supported directly through the original source (the piece or art or text being analyzed) .
Example topics of an analytical essay:
- "Victory Gin in Place of Water: The Symbolism Behind Gin as the Only Potable Substance in George Orwell's 1984"
- "Amarna Period Art: The Meaning Behind the Shift from Rigid to Fluid Poses"
- "Adultery During WWII, as Told Through a Series of Letters to and from Soldiers"

There are many different types of essay and, over time, you'll be able to master them all.
A Typical Argumentative Essay Assignment
The average argumentative essay is between three to five pages, and will require at least three or four separate sources with which to back your claims . As for the essay topic , you'll most often be asked to write an argumentative essay in an English class on a "general" topic of your choice, ranging the gamut from science, to history, to literature.
But while the topics of an argumentative essay can span several different fields, the structure of an argumentative essay is always the same: you must support a claim—a claim that can reasonably have multiple sides—using multiple sources and using a standard essay format (which we'll talk about later on).
This is why many argumentative essay topics begin with the word "should," as in:
- "Should all students be required to learn chemistry in high school?"
- "Should children be required to learn a second language?"
- "Should schools or governments be allowed to ban books?"
These topics all have at least two sides of the argument: Yes or no. And you must support the side you choose with evidence as to why your side is the correct one.
But there are also plenty of other ways to frame an argumentative essay as well:
- "Does using social media do more to benefit or harm people?"
- "Does the legal status of artwork or its creators—graffiti and vandalism, pirated media, a creator who's in jail—have an impact on the art itself?"
- "Is or should anyone ever be ‘above the law?'"
Though these are worded differently than the first three, you're still essentially forced to pick between two sides of an issue: yes or no, for or against, benefit or detriment. Though your argument might not fall entirely into one side of the divide or another—for instance, you could claim that social media has positively impacted some aspects of modern life while being a detriment to others—your essay should still support one side of the argument above all. Your final stance would be that overall , social media is beneficial or overall , social media is harmful.
If your argument is one that is mostly text-based or backed by a single source (e.g., "How does Salinger show that Holden Caulfield is an unreliable narrator?" or "Does Gatsby personify the American Dream?"), then it's an analytical essay, rather than an argumentative essay. An argumentative essay will always be focused on more general topics so that you can use multiple sources to back up your claims.
Good Argumentative Essay Topics
So you know the basic idea behind an argumentative essay, but what topic should you write about?
Again, almost always, you'll be asked to write an argumentative essay on a free topic of your choice, or you'll be asked to select between a few given topics . If you're given complete free reign of topics, then it'll be up to you to find an essay topic that no only appeals to you, but that you can turn into an A+ argumentative essay.
What makes a "good" argumentative essay topic depends on both the subject matter and your personal interest —it can be hard to give your best effort on something that bores you to tears! But it can also be near impossible to write an argumentative essay on a topic that has no room for debate.
As we said earlier, a good argumentative essay topic will be one that has the potential to reasonably go in at least two directions—for or against, yes or no, and why . For example, it's pretty hard to write an argumentative essay on whether or not people should be allowed to murder one another—not a whole lot of debate there for most people!—but writing an essay for or against the death penalty has a lot more wiggle room for evidence and argument.
A good topic is also one that can be substantiated through hard evidence and relevant sources . So be sure to pick a topic that other people have studied (or at least studied elements of) so that you can use their data in your argument. For example, if you're arguing that it should be mandatory for all middle school children to play a sport, you might have to apply smaller scientific data points to the larger picture you're trying to justify. There are probably several studies you could cite on the benefits of physical activity and the positive effect structure and teamwork has on young minds, but there's probably no study you could use where a group of scientists put all middle-schoolers in one jurisdiction into a mandatory sports program (since that's probably never happened). So long as your evidence is relevant to your point and you can extrapolate from it to form a larger whole, you can use it as a part of your resource material.
And if you need ideas on where to get started, or just want to see sample argumentative essay topics, then check out these links for hundreds of potential argumentative essay topics.
101 Persuasive (or Argumentative) Essay and Speech Topics
301 Prompts for Argumentative Writing
Top 50 Ideas for Argumentative/Persuasive Essay Writing
[Note: some of these say "persuasive essay topics," but just remember that the same topic can often be used for both a persuasive essay and an argumentative essay; the difference is in your writing style and the evidence you use to support your claims.]

KO! Find that one argumentative essay topic you can absolutely conquer.
Argumentative Essay Format
Argumentative Essays are composed of four main elements:
- A position (your argument)
- Your reasons
- Supporting evidence for those reasons (from reliable sources)
- Counterargument(s) (possible opposing arguments and reasons why those arguments are incorrect)
If you're familiar with essay writing in general, then you're also probably familiar with the five paragraph essay structure . This structure is a simple tool to show how one outlines an essay and breaks it down into its component parts, although it can be expanded into as many paragraphs as you want beyond the core five.
The standard argumentative essay is often 3-5 pages, which will usually mean a lot more than five paragraphs, but your overall structure will look the same as a much shorter essay.
An argumentative essay at its simplest structure will look like:
Paragraph 1: Intro
- Set up the story/problem/issue
- Thesis/claim
Paragraph 2: Support
- Reason #1 claim is correct
- Supporting evidence with sources
Paragraph 3: Support
- Reason #2 claim is correct
Paragraph 4: Counterargument
- Explanation of argument for the other side
- Refutation of opposing argument with supporting evidence
Paragraph 5: Conclusion
- Re-state claim
- Sum up reasons and support of claim from the essay to prove claim is correct
Now let's unpack each of these paragraph types to see how they work (with examples!), what goes into them, and why.
Paragraph 1—Set Up and Claim
Your first task is to introduce the reader to the topic at hand so they'll be prepared for your claim. Give a little background information, set the scene, and give the reader some stakes so that they care about the issue you're going to discuss.
Next, you absolutely must have a position on an argument and make that position clear to the readers. It's not an argumentative essay unless you're arguing for a specific claim, and this claim will be your thesis statement.
Your thesis CANNOT be a mere statement of fact (e.g., "Washington DC is the capital of the United States"). Your thesis must instead be an opinion which can be backed up with evidence and has the potential to be argued against (e.g., "New York should be the capital of the United States").
Paragraphs 2 and 3—Your Evidence
These are your body paragraphs in which you give the reasons why your argument is the best one and back up this reasoning with concrete evidence .
The argument supporting the thesis of an argumentative essay should be one that can be supported by facts and evidence, rather than personal opinion or cultural or religious mores.
For example, if you're arguing that New York should be the new capital of the US, you would have to back up that fact by discussing the factual contrasts between New York and DC in terms of location, population, revenue, and laws. You would then have to talk about the precedents for what makes for a good capital city and why New York fits the bill more than DC does.
Your argument can't simply be that a lot of people think New York is the best city ever and that you agree.
In addition to using concrete evidence, you always want to keep the tone of your essay passionate, but impersonal . Even though you're writing your argument from a single opinion, don't use first person language—"I think," "I feel," "I believe,"—to present your claims. Doing so is repetitive, since by writing the essay you're already telling the audience what you feel, and using first person language weakens your writing voice.
For example,
"I think that Washington DC is no longer suited to be the capital city of the United States."
"Washington DC is no longer suited to be the capital city of the United States."
The second statement sounds far stronger and more analytical.
Paragraph 4—Argument for the Other Side and Refutation
Even without a counter argument, you can make a pretty persuasive claim, but a counterargument will round out your essay into one that is much more persuasive and substantial.
By anticipating an argument against your claim and taking the initiative to counter it, you're allowing yourself to get ahead of the game. This way, you show that you've given great thought to all sides of the issue before choosing your position, and you demonstrate in multiple ways how yours is the more reasoned and supported side.
Paragraph 5—Conclusion
This paragraph is where you re-state your argument and summarize why it's the best claim.
Briefly touch on your supporting evidence and voila! A finished argumentative essay.
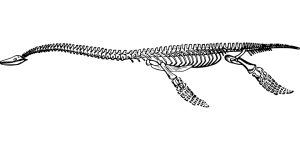
Your essay should have just as awesome a skeleton as this plesiosaur does. (In other words: a ridiculously awesome skeleton)
Argumentative Essay Example: 5-Paragraph Style
It always helps to have an example to learn from. I've written a full 5-paragraph argumentative essay here. Look at how I state my thesis in paragraph 1, give supporting evidence in paragraphs 2 and 3, address a counterargument in paragraph 4, and conclude in paragraph 5.
Topic: Is it possible to maintain conflicting loyalties?
Paragraph 1
It is almost impossible to go through life without encountering a situation where your loyalties to different people or causes come into conflict with each other. Maybe you have a loving relationship with your sister, but she disagrees with your decision to join the army, or you find yourself torn between your cultural beliefs and your scientific ones. These conflicting loyalties can often be maintained for a time, but as examples from both history and psychological theory illustrate, sooner or later, people have to make a choice between competing loyalties, as no one can maintain a conflicting loyalty or belief system forever.
The first two sentences set the scene and give some hypothetical examples and stakes for the reader to care about.
The third sentence finishes off the intro with the thesis statement, making very clear how the author stands on the issue ("people have to make a choice between competing loyalties, as no one can maintain a conflicting loyalty or belief system forever." )
Paragraphs 2 and 3
Psychological theory states that human beings are not equipped to maintain conflicting loyalties indefinitely and that attempting to do so leads to a state called "cognitive dissonance." Cognitive dissonance theory is the psychological idea that people undergo tremendous mental stress or anxiety when holding contradictory beliefs, values, or loyalties (Festinger, 1957). Even if human beings initially hold a conflicting loyalty, they will do their best to find a mental equilibrium by making a choice between those loyalties—stay stalwart to a belief system or change their beliefs. One of the earliest formal examples of cognitive dissonance theory comes from Leon Festinger's When Prophesy Fails . Members of an apocalyptic cult are told that the end of the world will occur on a specific date and that they alone will be spared the Earth's destruction. When that day comes and goes with no apocalypse, the cult members face a cognitive dissonance between what they see and what they've been led to believe (Festinger, 1956). Some choose to believe that the cult's beliefs are still correct, but that the Earth was simply spared from destruction by mercy, while others choose to believe that they were lied to and that the cult was fraudulent all along. Both beliefs cannot be correct at the same time, and so the cult members are forced to make their choice.
But even when conflicting loyalties can lead to potentially physical, rather than just mental, consequences, people will always make a choice to fall on one side or other of a dividing line. Take, for instance, Nicolaus Copernicus, a man born and raised in Catholic Poland (and educated in Catholic Italy). Though the Catholic church dictated specific scientific teachings, Copernicus' loyalty to his own observations and scientific evidence won out over his loyalty to his country's government and belief system. When he published his heliocentric model of the solar system--in opposition to the geocentric model that had been widely accepted for hundreds of years (Hannam, 2011)-- Copernicus was making a choice between his loyalties. In an attempt t o maintain his fealty both to the established system and to what he believed, h e sat on his findings for a number of years (Fantoli, 1994). But, ultimately, Copernicus made the choice to side with his beliefs and observations above all and published his work for the world to see (even though, in doing so, he risked both his reputation and personal freedoms).
These two paragraphs provide the reasons why the author supports the main argument and uses substantiated sources to back those reasons.
The paragraph on cognitive dissonance theory gives both broad supporting evidence and more narrow, detailed supporting evidence to show why the thesis statement is correct not just anecdotally but also scientifically and psychologically. First, we see why people in general have a difficult time accepting conflicting loyalties and desires and then how this applies to individuals through the example of the cult members from the Dr. Festinger's research.
The next paragraph continues to use more detailed examples from history to provide further evidence of why the thesis that people cannot indefinitely maintain conflicting loyalties is true.
Paragraph 4
Some will claim that it is possible to maintain conflicting beliefs or loyalties permanently, but this is often more a matter of people deluding themselves and still making a choice for one side or the other, rather than truly maintaining loyalty to both sides equally. For example, Lancelot du Lac typifies a person who claims to maintain a balanced loyalty between to two parties, but his attempt to do so fails (as all attempts to permanently maintain conflicting loyalties must). Lancelot tells himself and others that he is equally devoted to both King Arthur and his court and to being Queen Guinevere's knight (Malory, 2008). But he can neither be in two places at once to protect both the king and queen, nor can he help but let his romantic feelings for the queen to interfere with his duties to the king and the kingdom. Ultimately, he and Queen Guinevere give into their feelings for one another and Lancelot—though he denies it—chooses his loyalty to her over his loyalty to Arthur. This decision plunges the kingdom into a civil war, ages Lancelot prematurely, and ultimately leads to Camelot's ruin (Raabe, 1987). Though Lancelot claimed to have been loyal to both the king and the queen, this loyalty was ultimately in conflict, and he could not maintain it.
Here we have the acknowledgement of a potential counter-argument and the evidence as to why it isn't true.
The argument is that some people (or literary characters) have asserted that they give equal weight to their conflicting loyalties. The refutation is that, though some may claim to be able to maintain conflicting loyalties, they're either lying to others or deceiving themselves. The paragraph shows why this is true by providing an example of this in action.
Paragraph 5
Whether it be through literature or history, time and time again, people demonstrate the challenges of trying to manage conflicting loyalties and the inevitable consequences of doing so. Though belief systems are malleable and will often change over time, it is not possible to maintain two mutually exclusive loyalties or beliefs at once. In the end, people always make a choice, and loyalty for one party or one side of an issue will always trump loyalty to the other.
The concluding paragraph summarizes the essay, touches on the evidence presented, and re-states the thesis statement.
How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 8 Steps
Writing the best argumentative essay is all about the preparation, so let's talk steps:
#1: Preliminary Research
If you have the option to pick your own argumentative essay topic (which you most likely will), then choose one or two topics you find the most intriguing or that you have a vested interest in and do some preliminary research on both sides of the debate.
Do an open internet search just to see what the general chatter is on the topic and what the research trends are.
Did your preliminary reading influence you to pick a side or change your side? Without diving into all the scholarly articles at length, do you believe there's enough evidence to support your claim? Have there been scientific studies? Experiments? Does a noted scholar in the field agree with you? If not, you may need to pick another topic or side of the argument to support.
#2: Pick Your Side and Form Your Thesis
Now's the time to pick the side of the argument you feel you can support the best and summarize your main point into your thesis statement.
Your thesis will be the basis of your entire essay, so make sure you know which side you're on, that you've stated it clearly, and that you stick by your argument throughout the entire essay .
#3: Heavy-Duty Research Time
You've taken a gander at what the internet at large has to say on your argument, but now's the time to actually read those sources and take notes.
Check scholarly journals online at Google Scholar , the Directory of Open Access Journals , or JStor . You can also search individual university or school libraries and websites to see what kinds of academic articles you can access for free. Keep track of your important quotes and page numbers and put them somewhere that's easy to find later.
And don't forget to check your school or local libraries as well!
#4: Outline
Follow the five-paragraph outline structure from the previous section.
Fill in your topic, your reasons, and your supporting evidence into each of the categories.
Before you begin to flesh out the essay, take a look at what you've got. Is your thesis statement in the first paragraph? Is it clear? Is your argument logical? Does your supporting evidence support your reasoning?
By outlining your essay, you streamline your process and take care of any logic gaps before you dive headfirst into the writing. This will save you a lot of grief later on if you need to change your sources or your structure, so don't get too trigger-happy and skip this step.
Now that you've laid out exactly what you'll need for your essay and where, it's time to fill in all the gaps by writing it out.
Take it one step at a time and expand your ideas into complete sentences and substantiated claims. It may feel daunting to turn an outline into a complete draft, but just remember that you've already laid out all the groundwork; now you're just filling in the gaps.
If you have the time before deadline, give yourself a day or two (or even just an hour!) away from your essay . Looking it over with fresh eyes will allow you to see errors, both minor and major, that you likely would have missed had you tried to edit when it was still raw.
Take a first pass over the entire essay and try your best to ignore any minor spelling or grammar mistakes—you're just looking at the big picture right now. Does it make sense as a whole? Did the essay succeed in making an argument and backing that argument up logically? (Do you feel persuaded?)
If not, go back and make notes so that you can fix it for your final draft.
Once you've made your revisions to the overall structure, mark all your small errors and grammar problems so you can fix them in the next draft.
#7: Final Draft
Use the notes you made on the rough draft and go in and hack and smooth away until you're satisfied with the final result.
A checklist for your final draft:
- Formatting is correct according to your teacher's standards
- No errors in spelling, grammar, and punctuation
- Essay is the right length and size for the assignment
- The argument is present, consistent, and concise
- Each reason is supported by relevant evidence
- The essay makes sense overall
#8: Celebrate!
Once you've brought that final draft to a perfect polish and turned in your assignment, you're done! Go you!

Be prepared and ♪ you'll never go hungry again ♪, *cough*, or struggle with your argumentative essay-writing again. (Walt Disney Studios)
Good Examples of Argumentative Essays Online
Theory is all well and good, but examples are key. Just to get you started on what a fully-fleshed out argumentative essay looks like, let's see some examples in action.
Check out these two argumentative essay examples on the use of landmines and freons (and note the excellent use of concrete sources to back up their arguments!).
The Use of Landmines
A Shattered Sky
The Take-Aways: Keys to Writing an Argumentative Essay
At first, writing an argumentative essay may seem like a monstrous hurdle to overcome, but with the proper preparation and understanding, you'll be able to knock yours out of the park.
Remember the differences between a persuasive essay and an argumentative one, make sure your thesis is clear, and double-check that your supporting evidence is both relevant to your point and well-sourced . Pick your topic, do your research, make your outline, and fill in the gaps. Before you know it, you'll have yourself an A+ argumentative essay there, my friend.
What's Next?
Now you know the ins and outs of an argumentative essay, but how comfortable are you writing in other styles? Learn more about the four writing styles and when it makes sense to use each .
Understand how to make an argument, but still having trouble organizing your thoughts? Check out our guide to three popular essay formats and choose which one is right for you.
Ready to make your case, but not sure what to write about? We've created a list of 50 potential argumentative essay topics to spark your imagination.
Courtney scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT in high school and went on to graduate from Stanford University with a degree in Cultural and Social Anthropology. She is passionate about bringing education and the tools to succeed to students from all backgrounds and walks of life, as she believes open education is one of the great societal equalizers. She has years of tutoring experience and writes creative works in her free time.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!

Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

Difference Between Argumentative And Persuasive Essays
People often consider persuasive essays and argumentative essays synonymous with each other. They can’t be blamed for it as the nature of the two types, to an extent, is somewhat similar. When you develop a deeper understanding of the two types, you will be amazed that key points separate them apart.
- 1 Starting point
- 5 End Result
- 6 Viewpoint
Starting point
You can easily observe that perfect essay writers know the difference between Persuasive and argumentative essays. It is evident from the way they start each type. Argumentative essays require a lot of research. Before you begin writing this essay, you need to read a substantial amount of material and look for facts related to the topic. Once you have invested an adequate amount of time researching the subject and have collected several shreds of evidence, you will take a position based on a solid fact at the start of the essay. In the scenario of persuasive vs. argumentative, the reader can instantly detect the difference between the two the way a compelling essay starts. Unlike an argumentative essay, you don’t need to conduct a lot of research and spend quite a while finding facts about the topic. You can start with an opinion that you strongly believe in. From the start of the persuasive essay, the writer tries to convince the audience to have faith in his opinion. However, in argumentative essays, writers establish that their stance is better by referring to research or simply stating a fact at the start of the essay.
The difference between persuasive and argumentative types of writing can be understood by understanding the goals of writing behind both types. An argumentative essay aims to make the audience acknowledge that you have a stronger stance on a particular topic. You want your audience to know that your case is valid and should be considered more logical and acceptable. The goal is to put up a point in front of the audience using undeniable facts and references to research to show you have a stronger stance based on logic than the other opposing stance. However, in the context of argumentative vs. persuasive, the persuasive essay’s goal is not only to make your audience acknowledge that your case is stronger. The goal is to completely convince your audience to agree with your point of view. This is done by persuading the audience that your stance is the only one they should believe in. The success of persuasive and argumentative writers depends on how well they have written, keeping their goal of writing for the particular type.

Perhaps the best way to understand the persuasive vs. argumentative essay phenomenon is to investigate how significant the audience is for both types. As far as a persuasive essay is concerned, knowing your audience is very important. Because the intention is to persuade the audience by using emotional appeals and mentioning experiences the audience can relate to. As a writer, you will need to know about the mindset of our audience and the principles they believe in. You will also have to consider their background and the age group your audience belongs to. Writing for medical students will be different from writing for lawyers.
Similarly, you won’t be able to appeal to your audience from an older age group using the same ideals that you will use to convince youngsters. In comparison to the writer of an argumentative essay, the factor of the audience is not that significant. Irrespective of which age group and background your audience belongs to, argumentative writing aims to prove your stance by stating facts. These facts and pieces of evidence stand true no matter who your audience is. Therefore, having good awareness about your audience is not mandatory in argumentative writing.

A key difference between persuasive and argumentative essay is the purpose of writing. The purpose of argumentative writing is to focus on evidence to strengthen your argument. It requires good research skills as you need to collect pieces of evidence that are undeniable. On the other hand, the primary purpose of persuasive writing is not to focus solely on presenting undeniable facts. But the focus is more on consuming your energy in swaying away your audience using sentimental appeals and non-formal types of debate. In argumentative writing, the writer has a purpose to simply put the arguments in the form of facts in front of the audience. The writer is not bothered about whether the audience is completely convinced. However, in persuasive writing, the writers intentionally try to make the audience adopt the same point of view that the writers believe in.
One effective way of differentiating between persuasive writing and argumentative writing is by focusing on the intended result of these two types of writing. The ideal outcome for an argumentative essay is establishing the point that the writer has a much better argument based on facts. The reader gets to know the arguments from both sides, but ultimately the reader acknowledges that the writer has stronger arguments in comparison. While on the other hand, the ideal result for persuasive writing will be that audience believes the viewpoint of the writer to be completely true and the only thing that matters for them. It is clear by observing these two types of writing that they both are different.
To understand argumentative essays and the difference between them and persuasive essays, one needs to pay attention to the viewpoint both these types of writing have. In persuasive writing, only one side is presented, which is the writer’s side, and the writer tries his best to make the audience focus and believe on that side. The writer presents his viewpoint as the only sensible way to think. Whereas in argumentative essays, different perspectives are put forward, and the writers accept that other arguments exist, but their argument is stronger. Putting multiple perspectives allows them to counter their opposing views, giving them an impression of being fair-minded.
In an argumentative essay, the writer’s attitude is more authoritative as presenting facts and shreds of evidence with strong conviction. The idea is to share the argument in facts and let the audience know that you have a point worthy of consideration. The writer is least bothered about whether the audience agrees or not. While the approach is more aggressive in persuasive writing, the writers are very passionate about convincing their audience, and the writer uses more personal and emotional language.
The tone in an argumentative essay is a more authoritative one; the writers portray themselves as an authority on the matter, which is why more formal language is used to create a formal tone. Complex jargon is used in argumentative writing to have that authoritative effect. On the other hand, the tone is friendlier and relaxed, which appeals to readers’ emotions in persuasive writing.
The differences between argumentative and persuasive may seem subtle, but knowing the difference matters a lot if you want to be an expert on both types of writing. You will write clearly and more effectively once you know the difference, and you will get good grades in your academic studies.


Argumentative vs Persuasive Text: What’s the Difference?
A lot of people confuse the two or use the words interchangeably. The differences between persuasive and argumentative text are subtle but important. And knowing them will significantly impact our teaching of the two genres. So, argumentative vs. persuasive. What’s the difference?
Argumentative vs. Persuasive Text

The big thing that stands out here is that argumentative text supports the author’s claim with more factual evidence in an attempt to prove that the claim is valid, while persuasive text tends to appeal to the reader’s emotions in an attempt to get the reader to agree with the author’s opinion.
This difference is perhaps why the TEKS (the state standards in Texas) for writing include having the students write “opinion” pieces and the Common Core writing standards call for “opinion pieces,” leaving the word argumentative out of it altogether. To have the students write a true argumentative piece, research needs to be conducted first to gather evidence from credible sources. By contrast, our students can write opinion pieces by drawing from their own experiences and prior knowledge.
How important is it that our 3rd and 4th graders know the difference between the argumentative text and persuasive text?
I don’t really see the need to have our kids outline the differences between persuasive and argumentative texts. And I don’t think it’s worthwhile to practice distinguishing between them. They will get more detailed with it in later grades.
I do, however, think it’s important that we don’t confuse them by using the words interchangeably or teaching the two as the same thing. And let’s be sure to keep the differences between argumentative and persuasive texts in mind as we choose mentor texts.
If you’re wanting to highlight a difference for them, an easy way is to connect it to what they learned in second grade about persuasive. Say something like, “Last year you learned about persuasive text. This year, we’re going to learn about another genre that’s similar but gives a little more factual evidence.”
Need an Argumentative Passage?
I know it’s tough to find an argumentative text that’s appropriate for third grade. That’s why I’m excited to share this free high-interest argumentative passage about recess with you. Grab it and the response sheets that come with it below.

Pin It for Later:

More About Argumentative Text:

What Is An Argumentative Text? How to Teach It in 3rd Grade

Free Argumentative Text Passage for 3rd Grade

How to Teach Argumentative Text to 3rd Graders

Reading Comprehension Strategies That Will Help 3rd Graders Understand Argumentative Text

How to Introduce Argumentative Text to 3rd Graders

I help third and fourth grade RLA teachers like you create engaging and effective reading lessons without all the stress.

Categories:
Affiliate links:, need help teaching figurative language.

Let me help out.
Get my figurative language free interactive notbook, other free resources, ideas, and tips no spam, just things you can use in your classroom., leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
MORE FROM THE BLOG:

9 Argumentative Text Example Articles You Can Confidently Use with Your Third Graders
Searching for good argumentative text examples that are age appropriate for third graders takes forever. Here are 9 great argumentative articles you can confidently use with your third graders.

Empowering ELA Teachers: 3 Effective Strategies for Supporting ELL Students
FacebookPin14EmailPrint You may not have been expecting the number of English language learners you have in your elementary classroom. However,

How To Host an Incredible Back to School Night and Impress Your Parents
FacebookPin24EmailPrint Back to school night, meet the teacher night, open house, whatever you call it. It sets the tone for

8 Simple and Fun Icebreaker Games for Kids to Use During Back to School Season
FacebookPin18EmailPrint You likely have a thousand things to do to prepare for the first week of school and creating new,

Make STAAR Reading Review Fun with the Task Cards You Already Have
Facebook16Pin36EmailPrint You want to make STAAR Reading review fun, but you’re tired of spending every dollar you earn on your
FacebookPin4EmailPrint I love using videos to grab my students’ attention. I don’t usually use anything too long, a quick video
Copyright 2021 | Cultivating Critical Readers, LLC | All Rights Reserved
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Kinds of argumentative academic essays and their purposes
Published on November 5, 2014 by Shane Bryson . Revised on July 23, 2023.
Most of the time, when your supervisors and others talk about academic essays what they mean is essays that present well-reasoned points of view on various topics . This article explains some essential kinds of these essays—exegetical, discursive, expository, and argumentative—and outlines their key differences and similarities. We’ll call the group of them “persuasive essays,” since they all require you to persuade your reader in some way.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Kinds of persuasive academic essays, difference between persuasive academic essays and standard scientific articles, differences between kinds of persuasive academic essays, other interesting articles.
Exegetical essays persuade your reader to interpret a theory in a certain way and show your ability to understand and accurately explain difficult ideas.
Discursive essays persuade your reader to see the different sides of a debate in a certain way and present your ability to compare different approaches to a topic.
Expository essays persuade your reader that your opinion is the right one and that you are a competent critical thinker.
Argumentative essays persuade your reader to see something new in a field of research and to see that you have some authority in that field.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

One thing that separates a persuasive academic essay from a standard scientific article or an article in a newspaper is that the author’s point of view plays a more obvious role. Whereas a scientist is taught not to present the facts as she sees them but as anyone can see them, an essayist always presents information from a certain point of view (usually her own), even if she usually avoids referring to herself in the text.
The different kinds of persuasive academic essays are distinguished by the different things they do, but also by the prominence of the author’s point of view. The following tables presents the differences.
What all persuasive academic essays do
The first thing to notice is that, while essay assignments do sometimes ask for one or the other of these types of essay, often persuasive academic essays will need to mix these styles. For example, in order to properly situate her view in the current literature on a topic, the author of an argumentative essay will sometimes need to present a brief exegesis of someone else’s view. Many other combinations are possible, and the argumentative essay, especially, may draw on each of the other three styles.
Second, each of these academic essay forms is argumentative, even though we call only one of them “the argumentative essay.” In fact, you should keep in mind that, speaking loosely, people sometimes do refer to all of these as “argumentative essays.” This term is not entirely inaccurate, since they all require skillful treatment of argumentation, and they all require you to persuade your reader of something.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bryson, S. (2023, July 23). Kinds of argumentative academic essays and their purposes. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/kinds-argumentative-academic-essays-purposes/
Is this article helpful?
Shane Bryson
Shane finished his master's degree in English literature in 2013 and has been working as a writing tutor and editor since 2009. He began proofreading and editing essays with Scribbr in early summer, 2014.
Unlimited Academic AI-Proofreading
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- How it works
- Top Writers
- TOP Writers
Difference between an Argumentative and a Persuasive Essay
There are tens types of essays, which may be different or very alike. They are used to describe or research things, to support a certain point of view or to persuade the reader. In all of the cases, knowing main peculiarities of every type of an essay may greatly simplify your life and help to avoid low grades or even writing the assignment anew.
In this article, we will discuss two of the most popular essays among students of various academic levels: argumentative and persuasive ones. Their main difference lies in the whole point of the assignment, in its motivation.

A persuasive essay is a piece of writing, which aims to persuade the reader to buy a good or an item, to pay attention to a particular matter or support point of view of the writer. Claims of the author may not be backed with any evidence. There are no proofs, credible sources or facts. This is the key feature, which distinguishes a persuasive and an argumentative essay.
An argumentative essay also aims to persuade the audience but using proofs and evidence. Every fact is backed with relevant sources, academic works and other sorts of reliable data. An author should complete a profound research, collect information and work on the facts.
While a persuasive essay usually discusses only one side of the problem, an argumentative one is ready to listen to the arguments of both sides. Debates are very important and play a crucial part in the structure of an argumentative essay.

The difference to take into account
First thing you need to remember is that a persuasive essay is based on emotions. It doesn’t matter how much proof you have: you need to use vivid language , bright and emotional examples and try to engage the reader. On contrary, an argumentative essay is based on facts and objective approach, so you need to be honest and brief, when providing arguments on a topic.
When you work on a persuasive essay, you get to play with emotions and feelings of the audience, trying to make them support your point of view. When you deal with an argumentative paper, you need to convince the audience with facts and proofs. That is why the key difference is that a persuasive paper works with emotions and argumentative – with logics.
If you are assigned with an argumentative essay, you need to be ready to complete a thorough research, analyze multiple sources and distinguish facts to convince the reader. If you need to complete a persuasive essay, you don’t have to spend much time on a research. More important is how you are able to render your ideas to the audience.
However, the thing that is similar in both essays is the introduction and conclusions . They need to be persuasive enough, reaching the target audience and containing hooks and a thesis statement . Knowing these simple differences and similarities, you will easily write an argumentative or a persuasive essay in no time.

- Disclosure Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- CSEC ENGLISH A
- CSEC ENGLISH B
- Subject-Verb Agreement
- Equivalent Sentences
- [email protected]

The Difference between the Argumentative and Persuasive Essays

Argument and persuasion are two different concepts in English. An argumentative essay is a piece of writing that attempts to convince the readers that the author’s idea is true. This is a genre of writing that is used to defend or prove a point. A writer should do a through research; gather accurate facts and figures before writing an argumentative essay. This is more like a debate written on paper. While writing an argumentative essay, a writer should be aware of both pros and cons of the argument, and should try to discredit the opposing view by using evidence.
A persuasive essay is a piece of writing that attempts to convince the readers to agree with author’s ideas. In this type of essay, the writer can use his own ideas, opinions and evoke the emotions in the reader in order to convince them to agree to his opinion. A writer of a persuasive essay needs to do research, gather evidence, but a clever writer can create a successful essay without knowing much. This is because; a persuasive writing appeals more to readers’ emotions rather than minds. In persuasive writing, the writer should have certain awareness about the audience. For example, opinions and ideas that could appeal to teenagers may not have the same effect on adults. First person narration and second person narration ( Example: In my opinion, I believe, etc.) are commonly used as the writer is addressing the audience directly.
Looking at the purpose of both essays, argumentative essay attempts to convince the readers to accept the writer’s idea as true by using statistics, facts and figures, etc. Whereas persuasive essay attempts to convince the readers to agree with the writer, by using emotions, personal ideas, etc.
In addition, when it comes to audience, for persuasive essay, the writer needs an intended audience to address his request or need to. Who can give him what he wants? but for argumentative essay, the writer doesn’t need an intended audience. The writer is satisfied with simply “putting the truth out there.”
Also, argumentative essay acknowledges opposing views, and needs a thorough research before starting while persuasive essay may not acknowledge opposing views and can be written without doing much research.
Although both types of essays are not just descriptive, but prescriptive. On some level they both have a call to action. They both answer objections. They are both essays and follow a pretty typical structure in that regard.
In conclusion, argumentative essay appeals to the minds of the readers. On the other hand, persuasive essay appeals to the hearts of the readers.
One thought on “The Difference between the Argumentative and Persuasive Essays”
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Argumentative Essay vs. Persuasive Essay — What's the Difference?
Difference Between Argumentative Essay and Persuasive Essay
Table of contents, key differences, comparison chart, use of evidence, addressing counterarguments, compare with definitions, argumentative essay, persuasive essay, common curiosities, do argumentative essays address opposing views, how does a persuasive essay differ in intent, what's the primary purpose of an argumentative essay, is the tone of an argumentative essay generally assertive, which essay type is inherently biased, can an argumentative essay be subjective, is rhetoric more prominent in persuasive essays, can persuasive essays utilize emotional appeals, do persuasive essays need evidence, which essay type is more suitable for debates, which essay type emphasizes logical reasoning more, do both essay types require a clear thesis, can a persuasive essay include counterarguments, which essay hones the art of rhetoric more, are both essay types used in academic settings, share your discovery.

Author Spotlight
Popular Comparisons

Trending Comparisons

New Comparisons

Trending Terms

Breaking News
Column: Jack Smith’s latest push to get Donald Trump’s Jan. 6 trial moving before the election

- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
Special counsel Jack Smith’s latest brief to the Supreme Court on Donald Trump’s immunity claim strives to ensure that the justices’ decision puts the Jan. 6 trial back on track, ending the detour the former president has extracted from a weak argument.
The bulk of the brief Smith filed Monday is a methodical rejection of Trump’s far-fetched claims to immunity from prosecution for attempting to overturn the 2020 election. Smith and his Supreme Court specialist, Michael Dreeben, closely follow the D.C. Circuit Court of Appeals’ persuasive, bipartisan opinion contradicting Trump on all points.
In the last few pages, however, Smith argues for the particular exigency of this case, noting that “even if a former president has some immunity from federal criminal prosecution for official acts, this prosecution should proceed.”

Litman: How Jack Smith just called out Judge Aileen Cannon in the Trump classified records case
The special counsel suggested he could seek the 11th Circuit’s intervention if the judge continues to prevent the trial from taking place before the election.
April 3, 2024
Smith contends that Trump’s attempt to thwart the peaceful transfer of power is a paradigmatic example of conduct that can’t be immunized. He describes what’s alleged against the former president as “a private scheme with private actors to achieve a private end” — namely, staying in power by fraud.
In what may be the brief’s most consequential phrase, the special counsel insists that the case “should be remanded for trial” on the ground that whatever immunity the Constitution might provide a president, it can’t shield Trump from this prosecution.
That would be dramatically different from the order that typically concludes a Supreme Court opinion. The justices normally set out governing principles of law and leave it to the lower courts to apply them to the facts, ordering a case “remanded for proceeding consistent with this opinion.”

Litman: Without even ruling on Trump’s immunity claim, the Supreme Court handed him a huge victory
The justices will hear arguments in the federal Jan. 6 case, delaying the ex-president’s prosecution for months as his campaign to return to the White House proceeds.
Feb. 28, 2024
The practical difference between such a standard remand and Smith’s far more unusual proposed remand for trial may sound subtle. But it’s pivotal, as Smith and dozens of friend-of-the-court briefs recognize.
Smith’s suggestion is a preemptive strike against an opinion that would leave room for yet another trip up and down the federal court system before a trial can begin, an opening Trump would surely exploit for further delay.
The all but certain ultimate answer to Trump’s immunity claim is no: Under no plausible analysis will any court find that his conduct can’t be prosecuted. But if it takes even a relatively quick series of further appellate reviews to nail that point down, it will probably squander any remaining possibility that this crucial trial will occur before the election.
The reason that the nature of the remand is a distinct risk in the case has to do with the question the court crafted for argument during the 13 days it took to act on Trump’s petition for review. That extended period gave rise to speculation that some justice was writing a dissent. But it seems the justices were instead engaged in negotiating and formulating the question to be considered.
They settled on a somewhat convoluted construction asking “ whether and if so to what extent ” a former president enjoys immunity from criminal prosecution for potentially official acts. That strongly suggests that at least some of the justices are concerned that however weak Trump’s claim to immunity might be, presidential immunity might be required in some cases. They may have in mind an attempted prosecution of a president for, say, bombing an adversary during a war or refusing to crack down on unlawful immigration. And they may want to cover that ground in the court’s first ever consideration of criminal immunity even if it doesn’t apply to Trump.
Whatever room the justices leave for theoretical presidential immunity, you can be sure that Trump will aver in the trial court that it precisely describes his case. Presumably U.S. District Judge Tanya Chutkan and the D.C. Circuit would make quick work of it, but in the federal courts, quick work can take a couple of months.
Given the importance of the trial schedule, the key practical question is whether the court focuses solely on Trump’s case or endorses immunity in other instances. Smith’s gambit is a fallback that would let the court order the trial to proceed even if its opinion extends to broader principles of immunity.
The oral argument could also expose a fundamental divide among the justices about potential immunity unrelated to Trump’s conduct.That would suggest that the court will issue multiple opinions after engaging in a back-and-forth that would itself likely eat up several weeks.
The amicus briefs in the case divide along similar lines. The most prominent ones in Smith’s favor advise the court to simply affirm the D.C. Circuit’s rejection of Trump’s claim without venturing into possible instances of immunity that are not remotely presented here. The briefs on Trump’s side tend to argue for some immunity in some cases, a result that would likely give rise to a more complicated remand.
To date, the court has not seemed very sensitive to the political imperative of a verdict that gives voters a piece of critical information before the November election: whether one of the candidates is guilty of a scheme to subvert the last one. That is in stark contrast to the court’s obvious speed in deciding Trump’s eligibility for the Colorado ballot before the state’s primary. And the court has shown similar haste in politically supercharged cases before, among them Bush vs. Gore.
The justices’ apparent indifference to the need for speed and clarity in this case is a shame. If they continue merely proclaiming the law as usual, letting the political chips fall where — and, more importantly, when — they may, it will be an unnecessary boon to Trump and a loss for the country.
Harry Litman is the host of the “Talking Feds” podcast and the Talking San Diego speaker series. @harrylitman
More to Read

Judge rejects Trump’s request to delay hush-money trial until Supreme Court rules on immunity

Trump asks Supreme Court to dismiss case charging him with plotting to overturn 2020 election
March 19, 2024

Trump wants New York hush money trial delayed until Supreme Court rules on immunity claims
March 11, 2024
A cure for the common opinion
Get thought-provoking perspectives with our weekly newsletter.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.

Harry Litman, the senior legal affairs columnist for the Opinion page, is a former U.S. attorney and deputy assistant attorney general. He is the creator and host of the “Talking Feds” podcast ( @talkingfedspod ). Litman teaches constitutional and national security law at UCLA and UC San Diego and is a regular commentator on MSNBC, CNN and CBS News.
More From the Los Angeles Times

Opinion: L.A.’s Pershing Square is getting another makeover. Will this time finally be the charm?
April 11, 2024

Calmes: Trump 1.0 made some world leaders laugh. Trump 2.0 terrifies them

World & Nation
New York appeals court rejects Trump’s third request to delay Monday’s hush money trial
April 10, 2024
William Howell wrote Arizona’s 1864 abortion ban. He modeled it on California’s
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Help! Japan Airlines Downgraded Us From First Class and Skimped on the Refund.
A couple is bumped from ultraluxury to semi-luxury on a trans-Pacific flight and receives what they feel is only a pittance in compensation.

By Seth Kugel
Dear Tripped Up,
Last year, my husband and I splurged on round-trip first-class tickets on Japan Airlines from San Francisco to Tokyo for $13,474 each. We reserved them in February for an October flight through American Express Travel. On the same day, I also bought business class tickets for a couple who was traveling with us at $8,429 apiece. In September, Amex notified me that we had been downgraded to business class for the return flight. JAL’s conditions state that we would receive “the difference between the normal fare amount of original class of service and for the normal fare of lower class of service.” To me that means that since the difference between our first class seats and our friends’ business seats was $5,045 each, we should be refunded about half of that — around $2,522 per person — for the second leg. But we got only $941 each. I contested this with Amex Travel, but they rejected our claim. Can you help? Teri, San Francisco
I’ve been collecting stories from readers about downgrade disappointments recently, so I looked not only into yours but also stories from four other travelers — three of whom believe they were stiffed by British Airways and another by Avianca.
All three airlines I contacted delayed, obfuscated or otherwise dillydallied before getting me answers, but let’s start with your travel agent, American Express.
“We worked with the card member and merchant to the best of our ability to resolve the issue,” wrote Emily Vicker, a spokeswoman for Amex, in an emailed statement. “Card members wishing to pursue additional compensation requests need to do so directly with the airline.”
As you said to me, you did not follow up with Japan Airlines because an online link that Amex sent you led to a form that said it was only for those travelers who had booked with JAL directly; others should deal with their travel agent. Gary Leff, the writer behind the travel site View from the Wing , told me you should have ignored that. “Follow all avenues to advocate on behalf of yourself,” he said.
Could Amex have done more? It’s impossible to tell, and Japan Airlines, responding only to my third email, said that it “has verified that the amount applied was accurate and was based on the difference of the First Class fare originally purchased and the applicable Business Class fare with the same fare conditions as the original ticket for the sector involved.”
But that is just a restatement of the company’s terms and conditions . So I wrote back with a spruced-up version of your argument. Your original first class seats cost $13,474 round trip, so although the two legs may have varied somewhat in price, I simplified and said for each way, each ticket would cost $6,737. JAL refunded you $941 for each ticket, which means they consider the value of the business class seats you ended up in, on the return, to be $5,796.
But your friends’ business class seats were just $4,214 each. And every business class fare I can find for flights from Tokyo to San Francisco on the JAL site in recent days (except for last minute fares) is well under $5,000. Could they explain their calculations?
I did not hear back.
So I turned to Mr. Leff. He noted that simply knowing what another business class seat cost on the same flight does not mean that if you had bought four seats on that day rather than two, the third and fourth seat would have been the same price — airline pricing algorithms are notoriously complex and opaque. And there is no way to know if the leg back from Tokyo (the one you were downgraded for) was actually cheaper than the leg there, as your Amex invoice doesn’t give a breakdown.
But Mr. Leff still took your side, mostly. The $941 refund “strikes me as unreasonable,” he said, “especially given the not ironclad but very persuasive evidence of tickets bought on the same flight on the same day.”
Anyone who finds themselves in such a situation must realize, unfortunately, that it’s impossible to know exactly what their refund should be. “I don’t think there’s an organization beside the airline itself that has the data,” said Anton Radchenko, chief executive of AirAdvisor , a company that assists fliers in receiving compensation from airlines. But he added that in most cases, airlines do offer fair compensation.
Then he told me something I didn’t know — that flights starting in Britain or those operated by British carriers have set rates for downgrades depending on the length of the flight: a 30 percent refund if under 1,500 kilometers (around 932 miles), 50 percent between 1,500 and 3,500 kilometers, and 75 percent for longer flights. The European Union and Canada have similar rules.
Alas, such fixed reimbursement rates only work if you can get the airlines to refund you in the first place. All three British Airways customers faced, instead, a wall of customer service nonsense.
A British Airways spokeswoman, Catherine Wilson, apologized for the delays and said the airline aimed “to process refund requests as quickly as possible.” But even after my intervention, only two of the three got refunds — and for less than British regulations seem to demand.
In late 2021, Mark from San Diego and his wife were flying home on British Airways premium economy from Split, Croatia, via London and Dallas, but missed a connection. They were rebooked in economy on Virgin Atlantic and tried for two years to get reimbursed when finally, in December 2023, they were told they had agreed to the downgrade, which he denies. (It shouldn’t matter anyway, both Mr. Leff and Mr. Radchenko said.)
They finally received $746 from British Airways earlier this week. But the full cost of their original round-trip itinerary (two tickets from San Diego to Ljubljana, Slovenia, and back from Croatia) was $5,821, and it is unlikely that their refund could account for 75 percent of a premium economy trans-Atlantic flight. British Airways confirmed they calculated the difference in fare rather than using the parameters laid out by the British government and offered no explanation to me as to why.
A year later, Cynthia and her partner had a very similar situation, missing a British Airways premium economy connection in London on their way home to Los Angeles, ending up in economy. They had booked through a travel agent, who tried unsuccessfully to get a refund. Then Cynthia ran into a brick wall when she tried herself. She has still not received a refund.
In the third British Airways case, David of Carmel, N.Y., and his wife were booked to fly first class from London to New York when their flight was canceled. On their rebooked flight, they were downgraded to the equivalent of business class. Their initial request for a refund was rejected by someone who almost comically misread their complaint, responding that they were not entitled to compensation because their flight had arrived with only “18 minutes delay.” Subsequent calls to customer services led nowhere. And even after I got in touch with the airline, another representative wrote the couple with the coup d’absurdité: They were not entitled to a refund because “based on our research, your final flight was in First Class, hence there is no downgrade refund due for your booking.” (I can attest that their boarding passes say otherwise.)
British Airways did finally send the couple a refund, of $1,036, this past Saturday. But their original fare for first class (plus a short hop from Amsterdam to London on the return) was just under $10,000 for both, which presumably means the return flights from London to New York cost a total of close to $5,000. Again, British Airways said it calculated the difference in fares rather than the appropriate percentage of the original fare. I have advised David to look at Britain’s Civil Aviation Authority’s guidance on rejected claims.
The case with Avianca ended on a more positive note. Alan, of Riverside, Calif., and his wife were booked on a business class flight from Los Angeles to Buenos Aires via Bogotá this past February. But Avianca replaced that direct first leg, to Bogotá, with two legs — Los Angeles to San Salvador, El Salvador, and then on to Bogotá, with a three-hour layover. For these new flights, the couple was placed in economy, with no business-class lounge access, no free meals and no word about compensation.
Rolando Lamas, Avianca’s sales director for North America, Central America and the Caribbean explained in a statement that the airline suspended that direct Los Angeles-to-Bogotá flight in January and had offered most passengers either a full refund or compensation for the downgrade. But it had trouble communicating with a few passengers, including some who had booked through a third party, as was the case with Alan.
The airline has now offered Alan and his wife $580 each, and they have accepted.
Most of the time, airlines do refund fare differences promptly and accurately, but clearly there are holes in the system. If the airlines stymie any future refund requests, I suggest contacting a company like AirAdvisor or registering a complaint with the appropriate federal agency, like U.S. Department of Transportation . This process can be slow but often prods the airlines into action, said Mr. Leff. However, if the airline has done something as specifically absurd as reject your downgrade refund because your flight arrived almost on time, send me a copy so I can add it to my collection.
If you need advice about a best-laid travel plan that went awry, send an email to [email protected] .
Follow New York Times Travel on Instagram , Twitter and Facebook . And sign up for our weekly Travel Dispatch newsletter to receive expert tips on traveling smarter and inspiration for your next vacation.
Seth Kugel is the columnist for “ Tripped Up ,” an advice column that helps readers navigate the often confusing world of travel. More about Seth Kugel
Open Up Your World
Considering a trip, or just some armchair traveling here are some ideas..
52 Places: Why do we travel? For food, culture, adventure, natural beauty? Our 2024 list has all those elements, and more .
Mumbai: Spend 36 hours in this fast-changing Indian city by exploring ancient caves, catching a concert in a former textile mill and feasting on mangoes.
Kyoto: The Japanese city’s dry gardens offer spots for quiet contemplation in an increasingly overtouristed destination.
Iceland: The country markets itself as a destination to see the northern lights. But they can be elusive, as one writer recently found .
Texas: Canoeing the Rio Grande near Big Bend National Park can be magical. But as the river dries, it’s getting harder to find where a boat will actually float .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The main difference between a persuasive essay and an argumentative essay comes down to your audience. For persuasive writing, it's necessary to feel out your audience and wield that knowledge to prove the efficacy of your perspective. For argumentative writing, opt for a logical approach and just present the facts with no intent to persuade ...
Persuasive language. While both argumentative and persuasive writing aim to convince the reader, the main difference between the two is the approach. Argumentative writing uses logical arguments and evidence, while persuasive writing uses emotional appeals and persuasive language to influence the reader's beliefs and attitudes.
Persuasive essay and Argumentative essay are similar in nature and thus, often confused to be the same though there exists a difference between the two. In fact, Persuasive essay and Argumentative essay are two different types of essays, and the main difference between them is that the persuasive essay depends on opinions and emotions while an ...
Argumentative and persuasive writing are both forms of communication that aim to convince the audience of a particular viewpoint or opinion. However, they differ in their approach and purpose. Argumentative writing focuses on presenting logical reasoning and evidence to support a claim, often engaging in a debate-like structure.
Persuasive writing is highly personal and emotional. The argumentative writer is more detached, preferring to use a reasonable, respectful, and formal tone to present all sides of an argument. 6. Perspective. The persuasive writer believes and wants the reader to believe that their way of thinking is the best.
Persuasive writing tends to be somewhat aggressive in approach, but in most cases, it tends to be emotional, passionate, and personal. Argumentative vs Persuasive Essay. Let's take a closer look on argumentative vs persuasive essay below. Keep in mind that this guide focuses mostly on the differences between the two types of essays.
Audience of persuasive writing: Needs intended audience. Knowing what they think and believe, the writer "attacks" attempting to persuade them to his side. Attitude of persuasive writing: Persuasive writers want to gain another "vote" so they "go after" readers more aggressively. Persuasive writing is more personal, more passionate ...
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
In contrast, persuasive essays often use rhetorical devices to influence the reader's emotions and beliefs. 11. The tone of an argumentative essay is usually more formal and academic, focusing on facts and logical arguments. Persuasive essays may adopt a more passionate or personal tone to effectively sway the reader. 11.
Argumentative and persuasive essays have a similar goal, which is to convince readers that the core assertion is correct or at least well-reasoned. The difference between proving a point and changing someone's mind can be profound, but in certain aspects — identifying criticism, relating to the reader, and setting an authoritative tone, for ...
Persuasive and Argumentative Writing? Persuasive Writing Argumentative Writing Starting Point: Identify your topic and choose your side. Starting Point: Identify your topic, research your topic, and decide which side to support. Purpose: Get the reader to agree with your opinion. Purpose: Get the reader to recognize your side of the argument is ...
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
Remember the differences between a persuasive essay and an argumentative one, make sure your thesis is clear, and double-check that your supporting evidence is both relevant to your point and well-sourced. Pick your topic, do your research, make your outline, and fill in the gaps. Before you know it, you'll have yourself an A+ argumentative ...
The most pressing and important differences between argumentative and persuasive writing include the purpose of the piece, the tone in which the piece is written, and the end result of the piece in question. Different Purpose. An argumentative essay has a more formal purpose. Argumentative essays require a great deal of research to be
A key difference between persuasive and argumentative essay is the purpose of writing. The purpose of argumentative writing is to focus on evidence to strengthen your argument. It requires good research skills as you need to collect pieces of evidence that are undeniable. On the other hand, the primary purpose of persuasive writing is not to ...
In this video you will be introduced to argumentative writing, and explore the differences between argumentative and persuasive writing.
The big thing that stands out here is that argumentative text supports the author's claim with more factual evidence in an attempt to prove that the claim is valid, while persuasive text tends to appeal to the reader's emotions in an attempt to get the reader to agree with the author's opinion. This difference is perhaps why the TEKS (the ...
Expository essay. Purpose. Role of author. to present an original view on a topic. supports this view with good reasons. shows ability to invent and support an argumentative view. shows ability to think critically about this view. must show how the reasons provided establish your view as a convincing one.
The difference to take into account. First thing you need to remember is that a persuasive essay is based on emotions. It doesn't matter how much proof you have: you need to use vivid language, bright and emotional examples and try to engage the reader. On contrary, an argumentative essay is based on facts and objective approach, so you need ...
Are you confused about the difference between a persuasive essay and an argumentative essay? Look no further! This video will explore the key differences bet...
Looking at the purpose of both essays, argumentative essay attempts to convince the readers to accept the writer's idea as true by using statistics, facts and figures, etc. Whereas persuasive essay attempts to convince the readers to agree with the writer, by using emotions, personal ideas, etc. In addition, when it comes to audience, for ...
Argumentative Essay vs. Persuasive Essay: An argumentative essay delves into multiple perspectives on a topic, striving for a balanced overview. Conversely, a persuasive essay is inherently biased, as its primary goal is to persuade the reader to adopt a particular stance.
Second, follow these steps on how to write an argumentative essay: Brainstorm: research, free-write, and read samples to choose a debatable topic. Prepare: organize thoughts, craft a thesis, decide on arguments and evidence. Draft: outline an essay, start with an engaging introduction, delve into arguments, and conclude like a boss.
Abstract. Analyzing Two Categories of Academic Writing This research paper aims to clarify the difference between Argumentative and Persuasive academic writing. Furthermore, it also gives valuable ...
They were then shown an argument in support of that claim, constructed by either a human or an AI model, and asked to rate their stance on the original claim once again.⁴. We define the persuasiveness metric as the difference between the final and initial support scores, reflecting shifts towards greater or reduced support for the presented ...
The practical difference between such a standard remand and Smith's far more unusual proposed remand for trial may sound subtle. But it's pivotal, as Smith and dozens of friend-of-the-court ...
Your original first class seats cost $13,474 round trip, so although the two legs may have varied somewhat in price, I simplified and said for each way, each ticket would cost $6,737. JAL refunded ...