- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is Market Segmentation?
- How It Works
- Determining Your Market Segment
- Limitations
- Market Segmentation FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Marketing Essentials
Market Segmentation: Definition, Example, Types, Benefits
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/picture-53886-1440626964-5bfc2a89c9e77c005876da24.jpg)
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)
Market segmentation is a way of aggregating prospective buyers into groups or segments, based on demographics, geography, behavior, or psychographic factors in order to better understand and market to them.
Key Takeaways
- Market segmentation seeks to identify targeted groups of consumers to tailor products and branding in a way that is attractive to the group.
- Markets can be segmented in several ways such as geographically, demographically, or behaviorally.
- Market segmentation helps companies minimize risk by figuring out which products are the most likely to earn a share of a target market and the best ways to market and deliver those products to the market.
- With risk minimized and clarity about the marketing and delivery of a product heightened, a company can then focus its resources on efforts likely to be the most profitable.
- Market segmentation can also increase a company's demographic reach and may help the company discover products or services they hadn't previously considered.
Investopedia / Matthew Collins
Understanding Market Segmentation
Companies can generally use three criteria to identify different market segments:
- Homogeneity , or common needs within a segment
- Distinction , or being unique from other groups
- Reaction , or a similar response to the market
For example, an athletic footwear company might have market segments for basketball players and long-distance runners. As distinct groups, basketball players and long-distance runners respond to very different advertisements. Understanding these different market segments enables the athletic footwear company to market its branding appropriately.
Market segmentation is an extension of market research that seeks to identify targeted groups of consumers to tailor products and branding in a way that is attractive to the group. The objective of market segmentation is to minimize risk by determining which products have the best chances of gaining a share of a target market and determining the best way to deliver the products to the market. This allows the company to increase its overall efficiency by focusing limited resources on efforts that produce the best return on investment (ROI).
Market segmentation allows a company to increase its overall efficiency by focusing limited resources on efforts that produce the best return on investment (ROI).
Types of Market Segmentation
There are four primary types of market segmentation. However, one type can usually be split into an individual segment and an organization segment. Therefore, below are five common types of market segmentation.
Demographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation is one of the simple, common methods of market segmentation. It involves breaking the market into customer demographics as age, income, gender, race, education, or occupation. This market segmentation strategy assumes that individuals with similar demographics will have similar needs.
Example: The market segmentation strategy for a new video game console may reveal that most users are young males with disposable income.
Firmographic Segmentation
Firmographic segmentation is the same concept as demographic segmentation. However, instead of analyzing individuals, this strategy looks at organizations and looks at a company's number of employees, number of customers, number of offices, or annual revenue .
Example: A corporate software provider may approach a multinational firm with a more diverse, customizable suite while approaching smaller companies with a fixed fee, more simple product.
Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation is technically a subset of demographic segmentation. This approach groups customers by physical location, assuming that people within a given geographical area may have similar needs. This strategy is more useful for larger companies seeking to expand into different branches, offices, or locations.
Example: A clothing retailer may display more raingear in their Pacific Northwest locations compared to their Southwest locations.
Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation relies heavily on market data, consumer actions, and decision-making patterns of customers. This approach groups consumers based on how they have previously interacted with markets and products. This approach assumes that consumers prior spending habits are an indicator of what they may buy in the future, though spending habits may change over time or in response to global events.
Example: Millennial consumers traditionally buy more craft beer, while older generations are traditionally more likely to buy national brands.
Psychographic Segmentation
Often the most difficult market segmentation approach, psychographic segmentation strives to classify consumers based on their lifestyle, personality, opinions, and interests. This may be more difficult to achieve, as these traits (1) may change easily and (2) may not have readily available objective data. However, this approach may yield strongest market segment results as it groups individuals based on intrinsic motivators as opposed to external data points.
Example: A fitness apparel company may target individuals based on their interest in playing or watching a variety of sports.
Other less notable examples of types of segmentation include volume (i.e. how much a consumer spends), use-related (i.e. how loyal a customer is), or other customer traits (i.e. how innovative or risk-favorable a customer is).
How to Determine Your Market Segment
There's no single universally accepted way to perform market segmentation. To determine your market segments, it's common for companies to ask themselves the following questions along their market segmentation journey.
Phase I: Setting Expectations/Objectives
- What is the purpose or goal of performing market segmentation?
- What does the company hope to find out by performing marketing segmentation?
- Does the company have any expectations on what market segments may exist?
Phase 2: Identify Customer Segments
- What segments are the company's competitors selling to?
- What publicly available information (i.e. U.S. Census Bureau data) is relevant and available to our market?
- What data do we want to collect, and how can we collect it?
- Which of the five types of market segments do we want to segment by?
Phase 3: Evaluate Potential Segments
- What risks are there that our data is not representative of the true market segments?
- Why should we choose to cater to one type of customer over another?
- What is the long-term repercussion of choosing one market segment over another?
- What is the company's ideal customer profile, and which segments best overlap with this "perfect customer"?
Phase 4: Develop Segment Strategy
- How can the company test its assumptions on a sample test market?
- What defines a successful marketing segment strategy?
- How can the company measure whether the strategy is working?
Phase 5: Launch and Monitor
- Who are key stakeholders that can provide feedback after the market segmentation strategy has been unveiled?
- What barriers to execution exist, and how can they can be overcome?
- How should the launch of the marketing campaign be communicated internally?
Benefits of Market Segmentation
Marketing segmentation takes effort and resources to implement. However, successful marketing segmentation campaigns can increase the long-term profitability and health of a company. Several benefits of market segmentation include;
- Increased resource efficiency. Marketing segmentation allows management to focus on certain demographics or customers. Instead of trying to promote products to the entire market, marketing segmentation allows a focused, precise approach that often costs less compared to a broad reach approach.
- Stronger brand image. Marketing segment forces management to consider how it wants to be perceived by a specific group of people. Once the market segment is identified, management must then consider what message to craft. Because this message is directed at a target audience, a company's branding and messaging is more likely to be very intentional. This may also have an indirect effect of causing better customer experiences with the company.
- Greater potential for brand loyalty. Marketing segmentation increases the opportunity for consumers to build long-term relationships with a company. More direct, personal marketing approaches may resonate with customers and foster a sense of inclusion, community, and a sense of belonging. In addition, market segmentation increases the probability that you land the right client that fits your product line and demographic.
- Stronger market differentiation. Market segmentation gives a company the opportunity to pinpoint the exact message they way to convey to the market and to competitors. This can also help create product differentiation by communicating specifically how a company is different from its competitors. Instead of a broad approach to marketing, management crafts a specific image that is more likely to be memorable and specific.
- Better targeted digital advertising. Marketing segmentation enables a company to perform better targeted advertising strategies. This includes marketing plans that direct effort towards specific ages, locations, or habits via social media.
Market segmentation exists outside of business. There has been extensive research using market segmentation strategies to promote overcoming COVID-19 vaccination hesitancy and other health initiatives.
Limitations of Market Segmentation
The benefits above can't be achieved with some potential downsides. Here are some disadvantages to consider when considering implementing market segmentation strategies.
- Higher upfront marketing expenses. Marketing segmentation has the long-term goal of being efficient. However, to capture this efficiency, companies must often spend resources upfront to gain the insight, data, and research into their customer base and the broad markets.
- Increased product line complexity. Marketing segmentation takes a large market and attempts to break it into more specific, manageable pieces. This has the downside risk of creating an overly complex, fractionalized product line that focuses too deeply on catering to specific market segments. Instead of a company having a cohesive product line, a company's marketing mix may become too confusing and inconsistently communicate its overall brand.
- Greater risk of misassumptions. Market segmentation is rooted in the assumption that similar demographics will share common needs. This may not always be the case. By grouping a population together with the belief that they share common traits, a company may risk misidentifying the needs, values, or motivations within individuals of a given population.
- Higher reliance on reliable data. Market segmentation is only as strong as the underlying data that support the claims that are made. This means being mindful of what sources are used to pull in data. This also means being conscious of changing trends and when market segments may have shifted from prior studies.
Examples of Market Segmentation
Market segmentation is evident in the products, marketing, and advertising that people use every day. Auto manufacturers thrive on their ability to identify market segments correctly and create products and advertising campaigns that appeal to those segments.
Cereal producers market actively to three or four market segments at a time, pushing traditional brands that appeal to older consumers and healthy brands to health-conscious consumers, while building brand loyalty among the youngest consumers by tying their products to, say, popular children's movie themes.
A sports-shoe manufacturer might define several market segments that include elite athletes, frequent gym-goers, fashion-conscious women, and middle-aged men who want quality and comfort in their shoes. In all cases, the manufacturer's marketing intelligence about each segment enables it to develop and advertise products with a high appeal more efficiently than trying to appeal to the broader masses.
Market segmentation is a marketing strategy in which select groups of consumers are identified so that certain products or product lines can be presented to them in a way that appeals to their interests.
Why Is Market Segmentation Important?
Market segmentation realizes that not all customers have the same interests, purchasing power, or consumer needs. Instead of catering to all prospective clients broadly, market segmentation is important because it strives to make a company's marketing endeavors more strategic and refined. By developing specific plans for specific products with target audiences in mind, a company can increase its chances of generating sales and being more efficient with resources.
What Are the Types of Market Segmentation?
Types of segmentation include homogeneity, which looks at a segment's common needs, distinction, which looks at how the particular group stands apart from others, and reaction, or how certain groups respond to the market.
What Are Some Market Segmentation Strategies?
Strategies include targeting a group by location, by demographics—such as age or gender—by social class or lifestyle, or behaviorally—such as by use or response.
What Is an Example of Market Segmentation?
Upon analysis of its target audience and desired brand image, Crypto.com entered into an agreement with Matt Damon to promote their platform and cryptocurrency investing. With backdrops of space exploration and historical feats of innovation, Crypto.com's market segmentation targeted younger, bolder, more risk-accepting individuals.
Market segmentation is a process companies use to break their potential customers into different sections. This allows the company to allocate the appropriate resource to each individual segment which allows for more accurate targeting across a variety of marketing campaigns.
PubsOnline. " Millennials and the Takeoff of Craft Brands ."
Crypto.com. " Fortune Favors the Bold ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Term-Definitions_Target-market-49a03b58f6d54ddd88d46521f248fc8a.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
What is market segmentation? Definition, 5 types, and examples

Market segmentation is a vital component of any product marketing strategy. Without it, you may fail to address the diverse needs and pain points of your varied customers.
Market segmentation helps you develop products that cater to the specific needs of distinct segments within the total market. This enables you to more effectively solve customer problems. Moreover, market segmentation ensures a return on investment while guaranteeing profitability and market success.
Defining market segmentation
Market segmentation is a strategic approach that divides the total addressable market (TAM) into several smaller segments. Each segment consists of customers who share similar characteristics, such as demographics, pain points, needs, etc. Consequently, a single product or a similar set of products can satisfy all customers within a particular market segment.
Segmenting the market enables you to target customer segments with a highly personalized approach. This aligns with current industry trends that emphasize hyper-personalization across omnichannel customers.
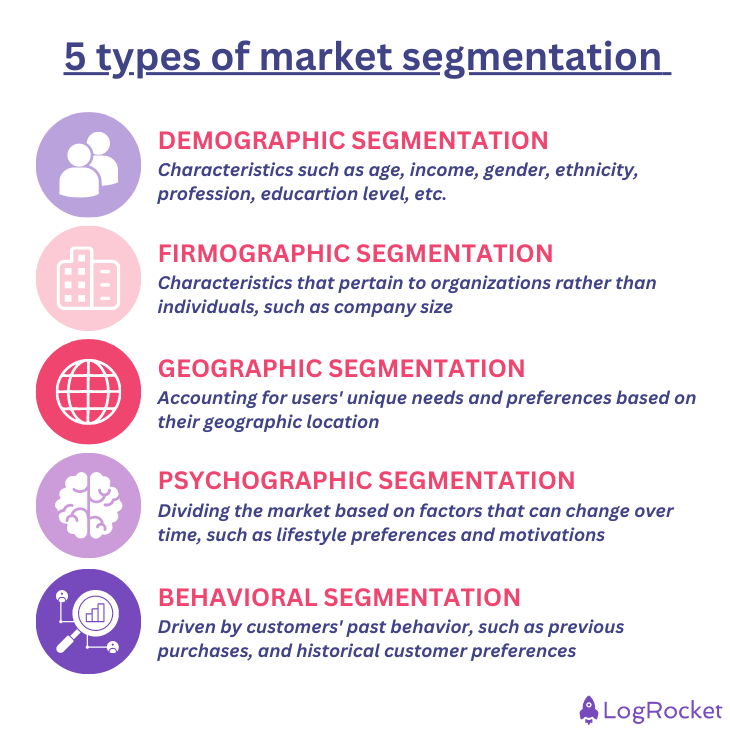
5 types of market segmentation
The five most common types of market segmentation are:
- Demographic segmentation
- Firmographic segmentation
- Geographic segmentation
- Psychographic segmentation
- Behavioral segmentation
1. Demographic segmentation
Demographic segmentation is perhaps the most common and straightforward method of segmenting the market. It considers demographic characteristics such as age, income, gender, ethnicity, profession, and level of education.
The assumption here is that individuals with similar demographic traits are likely to have shared preferences and are therefore likely to purchase the same products to meet their needs.
2. Firmographic segmentation
Firmographic segmentation applies an organizational perspective to demographic segmentation. In other words, it pertains to organizations rather than individuals.
For instance, the needs of a small firm will likely differ from those of a midsized organization or large corporation.
3. Geographic segmentation
Geographic segmentation is a subset of demographic segmentation. It pertains to people within a specific geographic area and takes into account their unique needs based on their location.
4. Psychographic segmentation
Psychographic segmentation is arguably the most challenging type of segmentation because it divides the market based on factors that can change or vary over time, such as lifestyle preferences, and motivations. However, this form of segmentation is gaining traction due to the industry’s shift towards hyper-personalization.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
When large internet companies gather customer data from online transactions, they use this information to make decisions about intrinsic preferences and spending habits, providing a comprehensive picture that allows for effective customer segmentation.
5. Behavioral segmentation
This type of segmentation is driven by customers’ past behavior. It projects market segments based on data collected from previous purchases and customer preferences over time, thereby predicting what they are likely to buy in the future.
Examples of market segmentation
To truly understand the power of market segmentation, let’s look at three companies that have effectively used this strategy to drive their success:
Apple’s demographic and psychographic segmentation
Apple, the tech giant behind the iPhone and iPad, has skillfully used both demographic and psychographic segmentation. The company targets customers based on age and income — typically younger, affluent consumers — as well as social class and occupation.
This understanding of their customer base allows Apple to focus on creating products with superior design and user experience, knowing that its target customers are willing to pay a premium for high-quality items.
Slack’s firmographic segmentation strategy
In the market of team collaboration tools, Slack stands out for its effective use of firmographic segmentation. The company targets businesses of all sizes, recognizing that a small startup’s needs will differ from those of a large corporation.
By segmenting its market in this way, Slack can offer tailored solutions — from Slack Free for smaller teams to Slack Enterprise Grid for larger organizations — that meet each segment’s unique needs.
Netflix’s mastery of behavioral segmentation
Streaming service Netflix provides an excellent example of behavioral segmentation. By collecting extensive data on users’ viewing habits — including what they watch, when they watch it, how often they watch it, and even when they pause or stop watching something — Netflix can segment its users based on these behaviors.
This approach not only allows Netflix to provide personalized content recommendations but also informs its decisions about which original series or films to produce.
Tips and best practices for effective market segmentation
- Adopt a data-driven approach — Relying on data for research and analysis allows you to quantify and define market segments accurately. This method leads to a more rationalized approach to market segmentation
- Define personas — Because market segmentation is based on user characteristics, defining user personas can help map these characteristics effectively. This process aids in creating a more precise segmentation
- Use established business models — Employing proven business models, such as Porter’s Five Forces , can provide insights into market conditions. Understanding factors such as market penetration and competition can lead to robust market segmentation
Market segmentation forms the bedrock of an effective marketing strategy. It ensures that the product is built for the right target customers, guarantees product profitability, fosters long-term customer retention, provides return on investment for marketing efforts, and supports an efficient business model.
Taking it one step further, market segmentation ensures that products are highly personalized and tailored for specific customer segments. Therefore, product and product marketing teams that adopt the market segmentation approach are best positioned to capitalize on the market for ensuring product success.
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #customer experience
- #market analysis

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.

Quality assurance (QA): Principles and process
Quality assurance (QA) is a proactive approach to ensure your products or services meet defined quality standards and customer requirements.

A guide to direct-to-consumer (DTC, D2C)
D2C enables you to reach out to your customers directly while controlling the entire brand purchase and after sales experience.

A guide to landing pages
You could say that a landing page is the modern equivalent of flyers, but not limited to their static, limited form.

Scaling up: How to not destroy your company culture
By rapidly changing the set of people who make up the company, you change your company’s DNA.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
A Step-by-step Guide to Segmenting a Market
How to segment a market.
Market segmentation, the selection of appropriate target markets, and the design of an appropriate and competitive positioning is critical to success in most marketplaces. This article walks through a step-by-step guide of the initial steps, from the defining the overall market where we are competing to the selection of a attractive target market.
Which Segmentation steps to complete?
Step one – define the market.
For instance, let’s assume that you are looking to segment the market for a firm that operates a chain of book stores. It would be too top-level and too awkward to define the market as all retailing consumers, as it is unlikely to lead to any meaningful segmentation.
Step Two – Create market segments
Demographic | Age group | Pre-teens, teens, young adults, older adults |
Behavioral | Shopping style | Enjoys shopping, functional, avoids |
Please note that we have used two top-level segmentation bases – of demographic and behavioral – and have selected a broad age group variable (from the demographic base), as well as shopping enjoyment/style (from the behavioral base).
As you can see, five different segments have been created by applying these segmentation variables. In the first stage, a broad demographic split has been used (to create children, young adults and older adults segment). The two adult segments then have a behavior variable applied to them (whether they enjoy shopping or just like to get in and out quickly).
Step Three – Evaluate the proposed market segments for viability
Now that we have developed some market segments we may be required to evaluate them to ensure that they are usable and logical. This would happen in a real-life firm, but it may not form part of your particular task if this is a student activity.
| Homogeneous | Segments should be similar in needs |
| Heterogeneous | Assumes that age groups vary in needs, which is likely in this market |
| Measurable | Market research data can be utilized |
| Substantial | Given the segments are relatively broad, they should be individually substantial |
| Accessible | Various merchandising techniques can be used to promote and reach each of these segments |
| Actionable/practical | The firm has the capabilities to market to each segment, if required |
| Responsive | Each market segment should respond better to a distinct marketing mix, rather than a generic offering |
Step Four – Construct segment profiles
Step Five – Evaluate the attractiveness of each segment
Step six – select target market/s.

Market Segmentation and Targeting
Identify potential customers, choose target customers, and create value
What are Market Segmentation and Targeting?
Market segmentation and targeting refer to the process of identifying a company’s potential customers, choosing the customers to pursue, and creating value for the targeted customers. It is achieved through the segmentation, targeting, and positioning (STP) process.

- Market segmentation and targeting help firms determine and acquire key customers.
- Consumers can be put into segments based on location, lifestyle, and demographics. Another way to segment consumers is by asking the who, what, and why questions.
- Segmentation and targeting influence a company’s strategy for pricing, communication, and customer management.
Overview of the STP Process
As mentioned earlier, STP stands for segmentation, targeting, and positioning.
Segmentation is the first step in the process. It groups customers with similar needs together and then determines the characteristics of those customers . For example, an automotive company can split customers into two categories: price-sensitive and price-insensitive. The price-sensitive category may be characterized as one with less disposable income.
The second step is targeting , in which the company selects the segment of customers they will focus on. Companies will determine this base on the attractiveness of the segment. Attractiveness depends on the size, profitability, intensity of competition, and ability of the firm to serve the customers in the segment.
The last step is positioning or creating a value proposition for the company that will appeal to the selected customer segment. After creating value, companies communicate the value to consumers through the design, distribution, and advertisement of the product. For example, the automotive company can create value for price-sensitive customers by marketing their cars as fuel-efficient and reliable.
How do Companies Segment Consumers?
The most common way to segment consumers is by looking at geography, demographics , psychographics, behavior, and benefits sought. Psychographics include the lifestyle, interests, opinions, and personality of the consumer.
Behavior is the loyalty, purchase occasion, and usage rate of the buyer, and benefits sought are the values the consumer is looking for, such as convenience, price, and status associated with the product.
Another way to segment consumers is by asking why, what, and who.
A more difficult but important thing for companies when segmenting consumers is understanding their behavior. This is the “why” question. By collecting information on a consumer’s past purchases, companies can make good predictions of future purchases. Therefore, this allows companies to target the right consumer.
The “what” that companies ask focuses on purchase behavior. Data that interests companies can be broken down into recency, frequency, and monetary value. These three things show when the last visit to the store was, how frequently customers shop in the store, and how much money they spend. They help companies determine the value and loyalty of customers.
Segmenting consumers by “who” is arguably the easiest way because the information is readily available. Information can include a person’s income, education, family size, and age. Firms hope that such features closely correlate to the needs of the consumer. For example, if a person is in their mid-40s and belongs to a large family, then the automobile company will likely advertise an SUV instead of a two-seater vehicle.
How Do Companies Target Customers?
Targeting is the process of evaluating the attractiveness of the consumer segments, as well as determining how to attract the consumers. A firm’s choice of consumer segment largely depends on the product and service they are offering. It also determines the marketing strategy the company will employ. Markets that are undifferentiated are suitable for mass marketing.
For example, large companies such as Microsoft will utilize the same design and similar ads for all customers. For other markets, one-to-one marketing is more appropriate. One example would be Dairy Queen, where the customers can design and create their own cake. Another example would be luxury stores such as Tiffany Co., which sends personalized letters as ads.
Three factors influence a company’s selection of segments. First of all, companies consider the characteristics of the segments. Characteristics include are how fast or slow a segment is growing and how profitable it is.
Secondly, the company considers its own competencies and resources to address the needs of the segments. For example, a large segment is attractive. However, a company may not be able to serve the whole segment because of a lack of resources.
Lastly, a company considers the competition in the segment, both current and in the future. A large and growing segment may be profitable but will attract a lot of competition, effectively reducing margins.
Segmentation and Targeting Strategy
Strategies are the process of creating product, pricing, communication, and customer management strategies. Product strategy aims to extract the most value out of customers. It is done by offering products at different price levels or by only making expensive products available first.
Pricing strategy involves appealing to either price-sensitive or price-insensitive segments. Communication strategy advertises using the appropriate ads and the right media to target the chosen consumer group.
For example, products for younger audiences will be advertised through digital channels as such a segment spends more time on Google and Facebook. Lastly, customer management strategies use a customer’s past purchase behavior to decide the best approach to promote products. They include offering upgrades, priority boarding for airplanes, or coupons. The strategy will also account for how frequently to promote the product.
Additional Resources
Thank you for reading CFI’s article on market segmentation and targeting. To keep learning and advancing your career, these CFI resources will be useful:
- Buyer Types
- Customer Profitability Analysis
- Cornering the Market
- Economic Moat
- See all management & strategy resources
- Share this article

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in
- What is PESTLE?
- Entrepreneurs
- Permissions
- Privacy Policy

Market Segmentation Analysis: Definition and Examples

Market segmentation analysis involves understanding your customers based on specific characteristics, both physical and behavioral.
Customers aren’t buying as often? Not enough people are engaging with your promotional posts on social media? Finding it difficult to retain new customers or keep current ones ?
You may have a market segmentation issue. Specifically, your customers aren’t feeling compelled to buy or interact with your offerings because their needs aren’t being met.
The best way to understand what your customers want requires market segmentation analysis.
In this article you’ll learn:
- What market segmentation analysis is
- The most popular and common market segmentation types
- Why any of this matters, and
- How to conduct market segmentation analysis yourself
Let’s begin with...
What is market segmentation analysis?
Market segmentation analysis is the study of customers, divided into smaller groups, to understand their specific characteristics like behavior, age, income, and personality. It’s easier for companies to advertise when they’re marketing a smaller segment of customers; this way, each campaign can be highly targeted and precise to the characteristics of each group. How a company should showcase a product or service depends on which group they’re targeting.

Why do businesses use market segmentation?
Leverage. It’s the main reason any company will use market segmentation when offering promotions, sales, and new products. When the company can hyper-focus on the details of segmented groups (rather than customers at mass), leveraging the benefits is easier than ever.
Market segmentation creates the perfect environment for engagement, customer retention, and acquisition. Because, when a company creates a campaign and sends to the masses, the responses will be hit or miss — with a higher chance of missing than hitting. This is because people want specific things at specific times, but only if the product, service, or promo ticks the right boxes.
Common types of market segmentation in the analysis?
There are actually many ways company’s can segment customer characteristics. But some are more popular (and common) than others. Here are five of the more viable options to consider for your market segmentation analysis.
Geographic segmentation. Segmenting customers by geography means understanding the environment where the customer lives. Needs change based on your physical environment; someone living in Japan may buy items to survive natural disasters like typhoons, tsunamis, and earthquakes. But people living inland, not surrounded by water or have ever experienced an earthquake, are less likely to worry about such dilemmas.
Understanding a customer’s surroundings allows companies to create new products based on location, but it can also shine a light on whether a company wishes to expand in the location too.
Demographic segmentation. Usually combined with geographic segmentation, demographic segmentation is one of the most popular segmentation types used by companies. This segmentation focuses on characteristics like age, gender, income, education, race, and more. It is arguably the most simple segmentation applicable in market segmentation analysis and determines how and what we buy, based on who we are as people. Although there are many segmentation variations, demographic (often combined with geographic) is often the first one conducted.
Psychographic segmentation. Psychographic segmentation focuses on the behavioral traits influencing customer buying habits. In this case, variables like personality, opinions, lifestyle, and values are tracked and measured. Compared to the other two segmentations on the list, psychographic traits can be harder to pin down. But it’s necessary for most industries, especially health and fitness. For instance, some people are gym-lovers and others aren’t; why? This is exactly the type of information psychographic segmentation uncovers.
Price segmentation. Price segmentation is another common segmentation used in market segmentation analysis. Although segmentation by demographic also mentions household income, price segmentation dives deeper. Personal income greatly impacts what people buy; someone with higher personal income can afford to splurge on luxury products, while someone who is working class is more likely to save extra income for a rainy day. This segmentation is popular for luxury brands, particularly automotive companies like BMW and Tesla .
Time segmentation. Less common than other segmentation types, time segmentation can still be effective. Physical stores have an open and close time, and their hours can impact sales. Some stay open all year round, while others choose “dead” days, like Sunday and Monday, to close because of slower sales traffic. Time segmentation also pertains to holiday sales and promotions, like Black Friday and Cyber Monday. These happen only once a year, and customers spend more since they expect the time-gated deals and sales.
How to conduct your own market segmentation analysis
Despite the many segmentation types, market segmentation analysis can be effective without being confusing. When getting started, make sure you have these four components:
1. Preliminary research
2. Segment your list
3. Create your study
4. Now, test!
I’ll explain more about each section below:
Preliminary research
This may be one of the longer points of your analysis, so be prepared. Preliminary research will require getting to know your customers in-depth. Talking with them directly is the best way to achieve this. You can talk in-person, on the phone, or (more commonly) through online surveys. The more information you have, the easier it’ll be to segment your audience.
Now that you have data about your customers, it’s time to segment them. You can choose based on the above segmentation types (price, time, psychographic, demographic, and geographic). I’d advise not to segment your customers into all of these segments; that’s when it gets messy and confusing. How can you do this effectively? By following the next step.
Create your study
When you’re creating your survey, be sure to ask a variety of questions related to the above segments. Then, take the answers and determine the best ways to segment your customers. For example, if the majority of your customers have high personal income, segmenting by price may be smart. If most are thrifty shoppers, the time segment may be optimal because of (holiday) discounts. If your customers seem to belong in more than one segment, that’s perfectly normal.
Now that you have your data and your customers segmented, it’s time to make sure the segmentation is useful. You can send out brief campaigns, discounts, or other marketing materials to see if it resonates with the customers in your segments. If it doesn’t, you may need to go through your data again and re-segment your customers.
Final Thoughts
Market segmentation analysis involves understanding your customers based on specific characteristics, both physical and behavioral. Companies use this analysis to create hyper-focused sales and promotions. By focusing on the smaller segments (and what they value most), it’ll be much easier to resonate with them. Customers are more likely to pay attention when an offering is tailored to their needs at the moment, rather than showcasing an abundance of benefits that don’t particularly matter to each individual. This analysis pairs well with descriptive research analysis for a greater understanding of customers.
Image by rawpixel
Integration of Cybersecurity in Market Analysis: How to Apply Different Methodologies to Identify Risks

Streamlining Your Business Analysis with a Master's in Lean Manufacturing
Technological factors affecting business to include in pestle analysis.
- Arts & Humanities
- Communications

Assignment 2: Topic 3-Market segmentation, targeting and positioning.
Related documents.

Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Market segmentation: What it is, Types & Examples

Market segmentation is the key to any long-term marketing plan that works.
To maximize your marketing budget, you should determine why your customers buy from you by dividing your market into subgroups. Then, you’ll be better able to meet their unique needs.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Research
Market segmentation techniques can help your business make more money because they can help you give customers more personalized experiences. Because of this, the best tools for personalization let you divide your audience into groups so you can:
- More email and text message leads
- Increase the number of sales on your website
- Improve average order values
- Increase the customer lifetime value
In this article, we will learn what market segmentation is and how it allows you to correctly direct your marketing efforts to the right audience to ensure the success of your business.
What is market segmentation?
Market segmentation is a process that consists of sectioning the target market into smaller groups that share similar characteristics, such as age, income, personality traits, behavior, interests, needs, or location.
Knowing your market segmentation will help you target your product, sales, and marketing methods. It can help your product development processes by guiding how you build product offers for various groups, such as males versus women or high-income versus low-income. These segments can be used to optimize products, marketing, advertising, and sales efforts.
Segmentation allows brands to create strategies for different types of consumers, depending on how they perceive the overall value of certain products and services. In this way, they can introduce a more personalized message with the certainty that it will be received successfully.
Types of market segmentation
Market segmentation is the process of breaking up a large market into smaller groups of customers with similar needs, traits, or ways of behaving. There are 4 types of market segmentation . Below, we describe each of them:
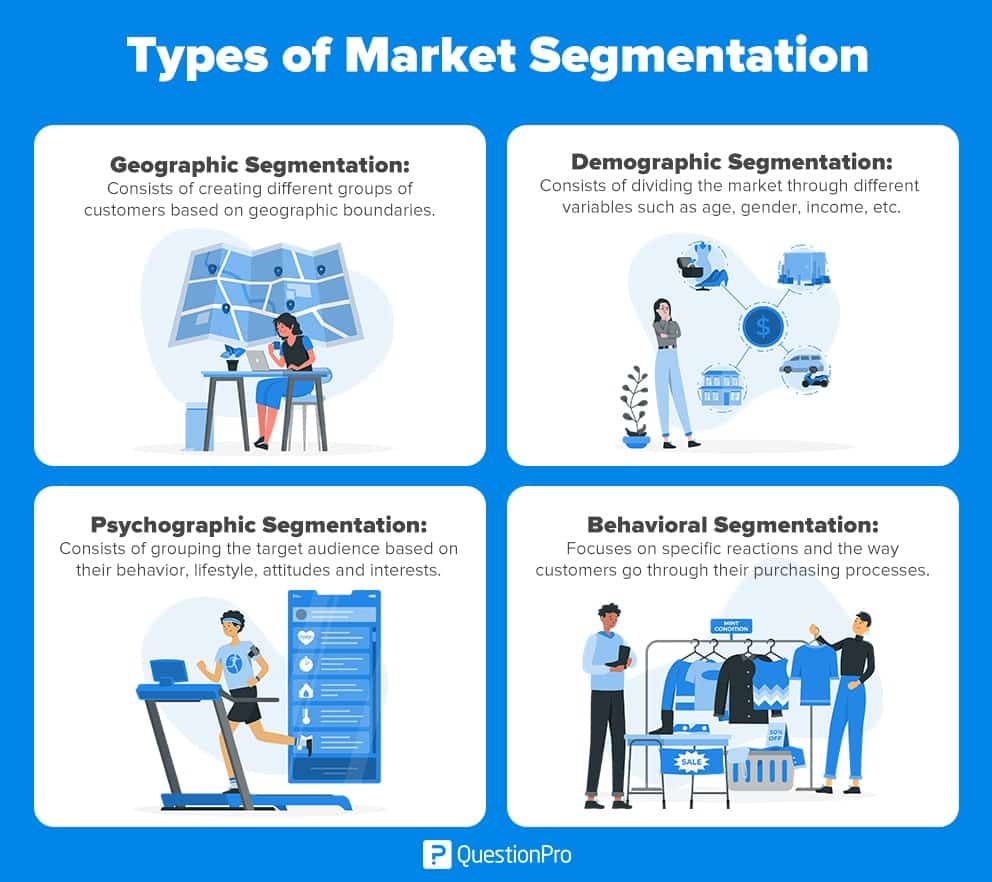
Geographic segmentation
Geographic segmentation consists of creating different groups of customers based on geographic boundaries.
A fast-food chain might change its menu items and specials based on what people in a certain area like. For example, they might have spicy food on the menu in places where spicy food is common.
The needs and interests of potential consumers vary according to their geographic location, climate, and region. So, geographic segmentation is valuable. Understanding geographic segmentation allows you to determine where to sell and advertise a brand and where to expand a business.
Demographic segmentation
Demographic segmentation divides the market through different variables. Demographic segmentation includes age, gender, nationality, education level, family size, occupation, income, etc.
A company that sells luxury cars might look for customers with a certain income, age, or job. For example, they might make ads for older, wealthy people who are likely to be interested in luxury cars.
Demographic segmentation is one of the most widely used forms of market segmentation since it is based on knowing how customers use your products and services and how much they are willing to pay for them. Surely demographic segmentation is very important.
Psychographic segmentation
Psychographic segmentation consists of grouping the target audience based on their behavior, lifestyle, attitudes, and interests.
A fitness brand might try to reach customers based on how they live and who they are. For example, they might go after people who like to be active and care about their health.
To understand the target audience, market research methods such as focus groups , surveys, interviews, and case studies can successfully compile psychographic segmentation conclusions.
Behavioral segmentation
Behavioral segmentation focuses on specific reactions, i.e. consumer behaviors , patterns, and how customers go through their decision-making and purchasing processes.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Targeting
An online store can target customers based on what they buy. For example, they might give discounts to people who buy from them often or send personalized suggestions based on what people have bought in the past.
The public’s attitudes towards your brand, how they use it, and their awareness are examples of behavioral segmentation. Collecting behavioral segmentation data is similar to how you would find psychographic data. This allows marketers to develop a more targeted approach.
Market segmentation objectives
There are different objectives for segmentation of market. Here we tell you what each of them is:
- Product: Creating successful products is one of the main objectives of organizations and one of the reasons why they conduct a market segment. This allows you to add the right features to your product and will also help you reduce costs to meet the needs of your target audience.
- Price: Another market segmentation objective is establishing the right price for your products. Identifying which is the public that will be willing to pay for it.
- Promotion: It helps you target each segment’s members and select them in different categories so that you can direct your strategies appropriately.
- Place: The ultimate goal of segmentation is to decide how you offer a product to each group of consumers and make it pleasant to them.
Strategies for market segmentation
A market segmentation strategy is a plan for dividing a market into different segments based on certain criteria, such as demographics, geography, psychographics, and behavior. Here are some steps that businesses can take to create a good strategy for it:
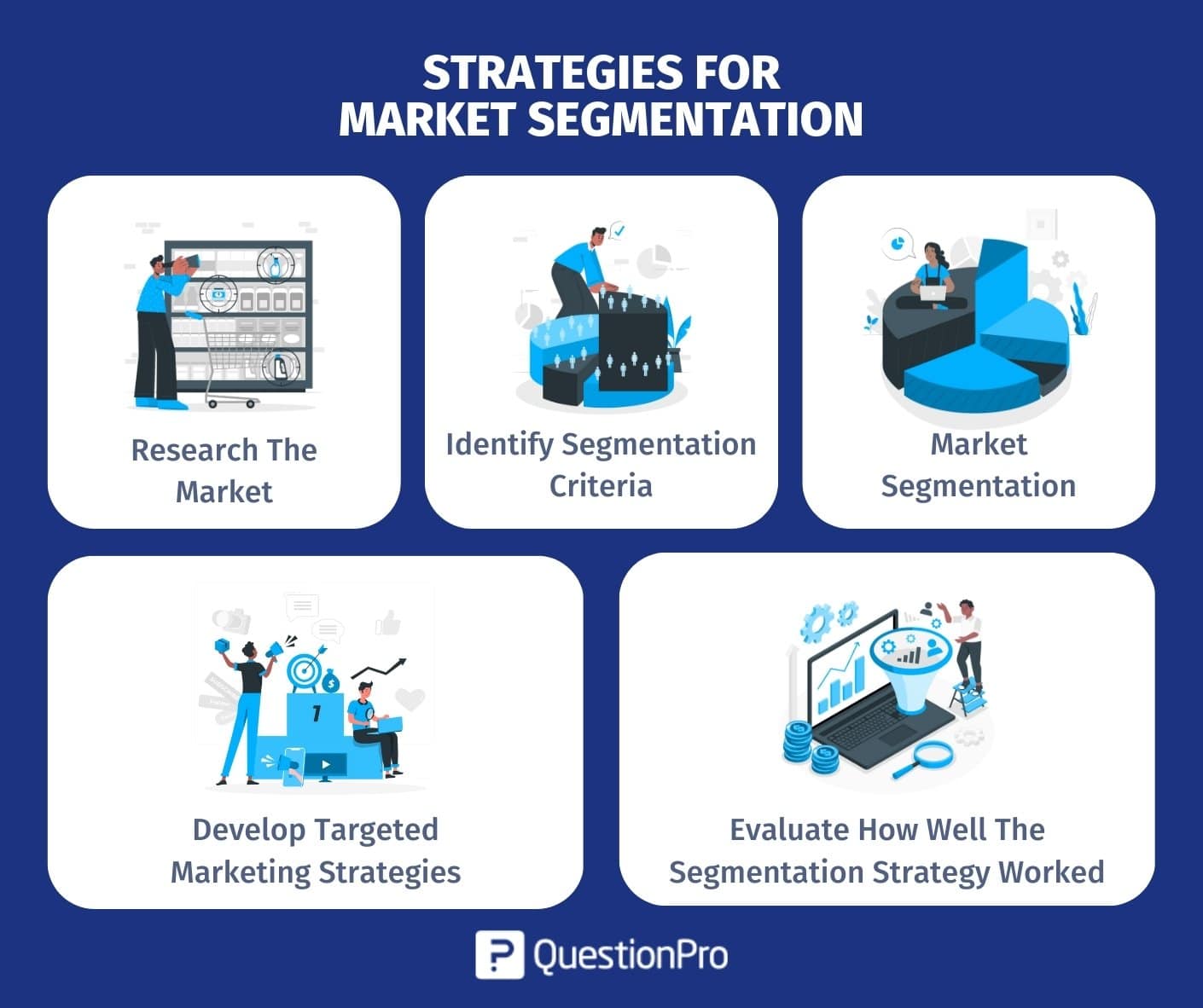
1. Research the market:
Before making a segmentation strategy, it’s important to research the different parts of the target market and their needs and preferences.
2. Identify segmentation criteria:
Based on the market segment, businesses can figure out which criteria for segmenting their target market are most important. This could include things like age, gender, income, and level of education, or it could include things like personality, lifestyle, and values.
3. Market segmentation:
Businesses can divide the market into different segments based on the criteria they have found. It’s important to ensure that each part is clear, measurable, and useful.
4. Develop targeted marketing strategies:
Businesses can make marketing plans for each segment when the market is divided into segments. This could mean making customized products and services, running targeted marketing campaigns, and adjusting pricing strategies to meet the needs and preferences of each segment.
5. Evaluate how well the segmentation strategy worked:
Businesses should keep an eye on the performance of all the customer segments and make changes as needed to ensure the segmentation strategy works. This could mean getting customer feedback, looking at sales data, and tracking how well marketing campaigns are working.
A market segmentation strategy can help businesses better understand their customers, create targeted marketing plans, increase customer satisfaction, improve product development, increase market share, increase profits, and gain a competitive advantage.
Steps to implement a market segmentation
In order to implement a strategy, you must not only know what market segmentation is. It is very important to know how to apply this method. That is why we have for you a guide that will help you:
Step: 1 – Define your market: At this point of the product segmentation , you should focus on discovering how big the market is, where your brand fits, and if your products have the capacity to solve what it promises.
Step: 2 – Segment your market: This step consists of choosing which of the types best suits your brand.
Step: 3 – Understand your market: Ask your customers the right questions, depending on the type you choose. You must know your target customer in detail. You can use online surveys to get their answers.
Step: 4 – Build your customer segments: After collecting responses, you need to perform data analysis to create dynamic segments unique to your brand.
Step: 5 – Test your strategy: Ensure you have correctly interpreted your survey data by testing it with your target audiences. This will help you to revisit your market segmentation strategies and make the necessary changes.
Step: 6 – Implement the strategies: Once the marketing plans have been tested and improved, put them into action on a larger scale.
Step: 7 – Evaluate the performance: Evaluate how well each segment and marketing strategy is doing and make changes as needed.
Step: 8 – Continue to improve: It is an ongoing process, so keep improving the segmentation criteria and marketing strategies based on customer feedback and changing market conditions.
By doing these things, businesses can effectively implement a market segmentation strategy and increase their chances of success in the marketplace.
Characteristics of good segmentation
Choosing the right segmentation type should ensure that the segments are relevant, accessible, measurable, profitable, and easy to use.
Different types of segmentation don’t meet these requirements in the same way. Sociodemographic criteria make it easier to get measurable segments than psychographic criteria.
Multi-criteria segmentations usually lead to a quantitative and objective description of the segment. In contrast, criteria can lead to a qualitative description of the segment that is richer and more relevant but harder to measure.
Advantages of market segmentation
Knowing what market segmentation is and the benefits it has for your organization will help you implement it correctly. Here are some of its advantages:
- Create stronger marketing messages: When you know who you are targeting, you can create strong, personalized messages that respond to the needs and wants of your target audience.
- Find the ideal marketing strategies: You may not know which is the right strategy to attract the ideal audience. It allows you to know the audience, create a plan that will work successfully, and determine better solutions and methods to reach them.
- Design-targeted advertising: Market segmentation allows you to target your advertising to the audience successfully and effectively, knowing their age, location, buying habits, interests, etc.
- Attract potential customers: By sending direct and clear marketing messages, you attract the right audience and are more likely to convert them into buyers.
- Differentiate your brand from the competition: By creating messages specific to your value proposition, you can stand out from the competition. Segmentation allows you to differentiate your brand by focusing on specific customer needs and characteristics.
- Identify your niche market: It helps you discover your niche market. Identify the niche with the broadest audience and whether it has needs that your brand can effectively address.
- Focus your efforts: This allows you to identify new marketing opportunities and avoid distractions that take you away from your target market.
- Create a customer connection: You can create effective strategies when you know what your customers want and need. This allows you to create strong bonds between your brand and the customer to create brand loyalty and customer satisfaction .
Disadvantages of market segmentation
Market segmentation can help a business in many ways but can also have some negative effects.
- Increased costs: If you want to target specific segments, you may need a bigger marketing budget to make customized products, create targeted advertising campaigns, and do a market segment.
- Overlooking potential customers: If you focus too much on specific segments, you might miss out on potential customers who don’t fit into your identified segments.
- Complexity: It can be a difficult process that requires detailed analysis and research. This can be hard for smaller businesses with fewer resources to do.
- Measuring effectiveness: It may be hard to know how effective a segmented marketing strategy is because it may not always be clear which segment is responsible for the success or failure of a campaign.
- Risk of stereotyping: There is a risk of stereotyping certain groups based on their demographic or psychological characteristics, which could lead to negative perceptions and backlash.
LEARN ABOUT: Perceived Value
Businesses need to consider the pros and cons of market segmentation to decide if it’s the right strategy for their products or services.
Market segmentation is a highly effective strategy for organizations because it lets them know which customers care about them and understand their needs enough to send a message ensuring brand success.
LEARN ABOUT: Average Order Value
Now that you know what it is, start your research today! Gather the information you need to learn more about your target audience using online surveys like QuestionPro Survey Software.
Contact us and we will help you collect the data you need.
How QuestionPro can help in market segmentation
QuestionPro is a platform for market research that offers a variety of tools to help businesses segment their markets. Here’s how QuestionPro can help:
- Doing a survey: QuestionPro has a powerful tool for doing surveys that businesses can use to make custom surveys to collect information from their target market. Businesses can use this tool to collect customer demographics, behaviors, preferences, and more information.
- Targeted sampling: QuestionPro offers various sample sources so businesses can ensure their surveys reach specific parts of their target market. This includes filters based on demographics, location targeting, and more.
- Advanced analytics: QuestionPro has advanced analytics tools that allow businesses to analyze their survey data in depth. This includes tools for dividing data by demographics, behaviors, and preferences and making charts and graphs to show the data.
- Automated reporting: QuestionPro has tools for automatic reporting that make it easy for businesses to create reports based on their survey data. This includes tools for making charts and graphs and for exporting data to Excel or other formats.
- Integration with other tools: QuestionPro works with a number of other tools and platforms, like Salesforce, Slack, and Zapier, which makes it easy to use survey data in other business processes.
QuestionPro is a powerful market research platform that can help businesses with market segmentation by giving them various tools for collecting, analyzing, and reporting on survey data.
LEARN ABOUT: Test Market Demand
FREE TRIAL LEARN MORE
Market segmentation divides customers into groups with similar traits. Marketers define their ICP through demographic, psychographic, geographic, and behavioral segmentation.
The four main types of market segmentation are: 1. Demographic 2. Psychographic 3. Geographic 4. Behavioral
Market segmentation lets organizations target specific consumer groups with their products, services, and marketing, improving efficiency and profitability.
Market segmentation helps companies target the most likely customers. Their marketing techniques are geared to these consumer segments’ demands, tastes, and behaviors.
MORE LIKE THIS

QuestionPro Thrive: A Space to Visualize & Share the Future of Technology
Jun 18, 2024

Relationship NPS Fails to Understand Customer Experiences — Tuesday CX

CX Platform: Top 13 CX Platforms to Drive Customer Success
Jun 17, 2024

How to Know Whether Your Employee Initiatives are Working
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.23: Assignment- Marketing Plan, Part I
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 47975
- Lumen Learning
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Student Instructions: Complete the following information about the organization and products and/or services you will focus on as you develop a complete marketing plan throughout the course. You may need to do research to get answers to the questions below. Be sure the organization and offering you select will 1) remain interesting to you for the duration of the course, and 2) have sufficient information available for you to conduct research and make informed recommendations in your marketing plan.
Company Profile
- Company Name:
- Major products and/or services (names, types):
- Products and/or services your marketing plan will focus on:
- Target customers:
- Distribution channel(s):
- Headquarters (city, state, country):
- Year founded:
- Number of employees:
- Annual revenue (estimated)
- Key competitors:
- Link to Web site:
- Link to Yahoo! Finance information page (for public companies):
Market Segmentation and Targeting
- What problem does your product or service solve?
- Describe the total market for your solution: Who are potential customers?
- What are the key segments within this market?
- Identify and briefly describe 1–3 segments that this company serves.
- Which segment does this marketing plan focus on, and why? Why do you believe this segment will offer growth and profit opportunities?
Situation and Company Analysis
Economic environment.
Discuss factors that affect your consumers’ purchasing power and spending patterns. What is the economic environment that you are operating in? Is it a growth, recovery or recession? Will it be easy to find staff? What is the current interest rate i.e. is it increasing or decreasing? What is consumer confidence like?
Technical Environment
The technological environment changes rapidly. You need to make sure that you are aware of trends in your industry and other industries could affect your business. New technologies create new markets and can influence you consumers and competitors. Industry environment What are the trends in your industry? Are there new entrants in the market? Has a substitute product been introduced? Are there changes in industry practices or new benchmarks to use?
Competitive Environment
How many competitors do you have? Who are the key competitors? What are the key selling points or competitive advantages of each one. What is your advantage over competitors? Is the market large enough to support you and competitors?
Political Environment
Consider the political environment for the areas that your business will trade and operate in. Is there a stable political system? Are there any licenses and regulations that you should be aware of? Do you need to win support to be able to operate?
SWOT Analysis
Instruction: Complete the table below with descriptive responses and explanation as you answer the questions below.
- Does the organization have a strong brand presence?
- What resources are available for marketing activities?
- Does the the company have unique products or services that satisfy the needs of their target market?
- What makes the company’s products or services unique?
- What value is brought to customers?
- Does the organization have a weak brand presence?
- Are resources insufficient for marketing activities?
- Does the company lack distinctive products or services?
- Do current products or services fail to satisfy the needs of customers?
- Do current products or services fail to bring value to customers?
Opportunities
- What is the unique opportunity that the company is trying to take advantage of?
- Does the target market have any unfulfilled needs that the company can satisfy?
- Are there emerging target markets with needs that the company can satisfy?
- Are there ways the company and its competitors can benefit by working together?
- Are there opportunities for collaborating with customers to build brand presence?
- Describe and analyze if market demand is increasing?
- Are there changes in the government regulations that will affect the company?
- Describe any emerging global issues that will affect the company?
- What are the tactics that competitors use to pursue customers?
- What are the strengths of the company’s biggest and or emerging competitors?
- In what ways are the competitors’ products or services superior to the company’s offerings?
- How are competitors likely to respond to any changes in the way the company markets?
- Is the company behind in adopting new technologies for marketing?
- Describe any ways in which international competitors are taking away market share?
- What do customers dislike about the company?
- Describe and analyze if market demand is decreasing?
Mission, Objectives, and Goals
State the mission or business purpose: what the organization wants to achieve, in market-oriented terms. (Example: Disney’s mission could be, “We create happiness by providing the finest in entertainment for people of all ages.)
List 1–3 objectives that move the organization a step closer to achieving the mission. (Example: A Disney objective could be, “To be the most popular theme park for international visitors.”)
Convert objectives into specific marketing goals that are easy to measure and evaluate. (Example: Our goal is to increase market share of international theme park visitors by 10% in the next two years.”)
Sample Grading Rubric
Company profile grading rubric.
| Criteria: Company Profile | Not Evident | Developing | Proficient | Exemplary | Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Professionalism | Many grammar and spelling mistakes, citations are missing or not all sources are cited, writing lacks logical organization. It may show some coherence but ideas lack unity. Serious errors and generally is an unorganized format and information. | Grammar and spelling mistakes, citations mistakes, some sources not cited, organization and readability is difficult to follow, fairly clear articulation of ideas, incorrect use of templates, etc. | Few grammar and spelling mistakes, few citations mistakes, all sources cited, fair organization and readability, fairly clear articulation of ideas, mostly correct use of templates, etc. | Proper grammar, spelling, citations, sources, good organization, readability, clear articulation of ideas, correct use of templates, etc. | |
| Thoroughness | Response doesn’t follow instructions; response is not researched or may state items directly from the source with little to no original thought, writing is confusing and difficult to follow; significantly falls short of or exceeds appropriate length; doesn’t address all prompts and assignment criteria; incomplete or missing analysis | Doesn’t follow all instructions; response is not researched and may be confusing or difficult to follow; significantly falls short of or exceeds appropriate length; doesn’t address all prompts and assignment criteria; incomplete analysis | Follows instructions; response is researched and articulate; may slightly fall short of or exceed appropriate length; addresses the majority of the prompts and assignment criteria; thoughtful analysis. | Follows instructions; response is well-researched and articulate; appropriate length; addresses all prompts and assignment criteria; thoughtful analysis. | |
| Progression | Does not incorporate feedback or suggestions from instructor and peers | Incorporates minimal feedback and suggestions from instructor and peers; demonstrates minimal continuous improvement | Incorporates much of the feedback and suggestions from instructor and peers; demonstrates continuous improvement | Incorporates feedback and suggestions from instructor and peers and makes an effort to improve the writing by editing it themselves; demonstrates continuous improvement and initiative in revising and improving work |
Total points possible for Company Profile Assignment: 10 pts.
Market Segmentation and Targeting Grading Rubric
| Criteria: Market Segmentation and Targeting | Not Evident | Developing | Proficient | Exemplary | Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Professionalism | Many grammar and spelling mistakes, citations are missing or not all sources are cited, writing lacks logical organization. It may show some coherence but ideas lack unity. Serious errors and generally is an unorganized format and information. | Grammar and spelling mistakes, citations mistakes, some sources not cited, organization and readability is difficult to follow, fairly clear articulation of ideas, incorrect use of templates, etc. | Few grammar and spelling mistakes, few citations mistakes, all sources cited, fair organization and readability, fairly clear articulation of ideas, mostly correct use of templates, etc. | Proper grammar, spelling, citations, sources, good organization, readability, clear articulation of ideas, correct use of templates, etc. | |
| Thoroughness | Response doesn’t follow instructions; response is not researched or may state items directly from the source with little to no original thought, writing is confusing and difficult to follow; significantly falls short of or exceeds appropriate length; doesn’t address all prompts and assignment criteria; incomplete or missing analysis | Doesn’t follow all instructions; response is not researched and may be confusing or difficult to follow; significantly falls short of or exceeds appropriate length; doesn’t address all prompts and assignment criteria; incomplete analysis | Follows instructions; response is researched and articulate; may slightly fall short of or exceed appropriate length; addresses the majority of the prompts and assignment criteria; thoughtful analysis. | Follows instructions; response is well-researched and articulate; appropriate length; addresses all prompts and assignment criteria; thoughtful analysis. | |
| Progression | Does not incorporate feedback or suggestions from instructor and peers | Incorporates minimal feedback and suggestions from instructor and peers; demonstrates minimal continuous improvement | Incorporates much of the feedback and suggestions from instructor and peers; demonstrates continuous improvement | Incorporates feedback and suggestions from instructor and peers and makes an effort to improve the writing by editing it themselves; demonstrates continuous improvement and initiative in revising and improving work |
Total points possible for Market Segmentation and Targeting Assignment: 10 pts.
Situation and Company Analysis Grading Rubric
| Criteria: Situation and Company Analysis | Not Evident | Developing | Proficient | Exemplary | Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Professionalism | Many grammar and spelling mistakes, citations are missing or not all sources are cited, writing lacks logical organization. It may show some coherence but ideas lack unity. Serious errors and generally is an unorganized format and information. | Grammar and spelling mistakes, citations mistakes, some sources not cited, organization and readability is difficult to follow, fairly clear articulation of ideas, incorrect use of templates, etc. | Few grammar and spelling mistakes, few citations mistakes, all sources cited, fair organization and readability, fairly clear articulation of ideas, mostly correct use of templates, etc. | Proper grammar, spelling, citations, sources, good organization, readability, clear articulation of ideas, correct use of templates, etc. | |
| Thoroughness | Response doesn’t follow instructions; response is not researched or may state items directly from the source with little to no original thought, writing is confusing and difficult to follow; significantly falls short of or exceeds appropriate length; doesn’t address all prompts and assignment criteria; incomplete or missing analysis | Doesn’t follow all instructions; response is not researched and may be confusing or difficult to follow; significantly falls short of or exceeds appropriate length; doesn’t address all prompts and assignment criteria; incomplete analysis | Follows instructions; response is researched and articulate; may slightly fall short of or exceed appropriate length; addresses the majority of the prompts and assignment criteria; thoughtful analysis. | Follows instructions; response is well-researched and articulate; appropriate length; addresses all prompts and assignment criteria; thoughtful analysis. | |
| Progression | Does not incorporate feedback or suggestions from instructor and peers | Incorporates minimal feedback and suggestions from instructor and peers; demonstrates minimal continuous improvement | Incorporates much of the feedback and suggestions from instructor and peers; demonstrates continuous improvement | Incorporates feedback and suggestions from instructor and peers and makes an effort to improve the writing by editing it themselves; demonstrates continuous improvement and initiative in revising and improving work |
Total points possible for Situation and Company Analysis Assignment: 50 pts.
Total points possible for Marketing Plan, Part 1 Assignment (Consists of Company Profile Assignment, Market Segmentation and Targeting Assignment, and Situation and Company Analysis Assignment combined): 100 pts.
Contributors and Attributions
- Assignment: Marketing Plan, Part I . Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- SWOT and Integrated Marketing Communications Templates. Authored by : Melissa Barker. License : CC BY: Attribution
Browse Course Material
Course info, instructors.
- William Aulet
- Howard Anderson
- Prof. Matt Marx
Departments
- Sloan School of Management
As Taught In
- Entrepreneurship
Learning Resource Types
New enterprises, lecture 6: how to do market segmentation.
Descriptions: Discussion of the process for performing market segmentation in a rigorous manner.
Instructor: Bill Aulet
- Download video
- Download transcript

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare
Module 5: Target Market/Segmentation
Assignment: target markets and segmentation.
Complete the following assignment in the discussion forum.
1. Read the following article from Inc. regarding defining your target market.
http://www.inc.com/guides/2010/06/defining-your-target-market.html
2. Assume you are the marketing manager for a new solar car that you are launching. Answer the following questions:
- What segmentation characteristics would you use for your target market?
- How would you define your target market? Be as specific and as detailed as possible.
- Discuss a time when you may have done market segmentation in your career?
- Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : http://lumenlearning.com . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Target Market Assignment. Authored by : John Russo. Provided by : Santa Ana College. Located at : http://sac.edu . Project : Project Kaleidoscope. License : CC BY: Attribution

Privacy Policy
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimise digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered straight to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Meet the operating system for experience management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
- Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Brand Experience
Market Segmentation
What is market segmentation?
The benefits of market segmentation, the basics of segmentation in marketing, types of market segmentation, how to get started with segmentation, market segmentation strategy, market segmentation use case examples, ensuring effective segments, common segmentation errors, qualtrics solutions for market segmentation, try qualtrics for free, market segmentation: definition, types and best practices.
21 min read Market segmentation helps your business efficiently target resources and messaging at specific groups of consumers. Here’s how it works.
At its core, market segmentation is the practice of dividing your target market into approachable groups . Market segmentation creates subsets of a market based on demographics, needs, priorities, common interests, and other psychographic or behavioural criteria used to better understand the target audience.
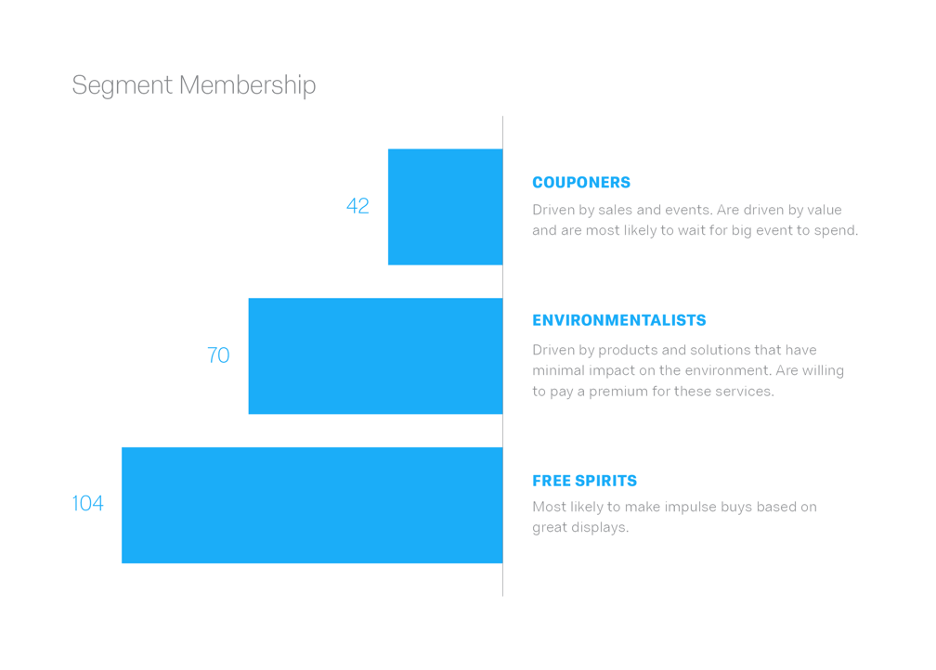
By understanding your market segments, you can leverage this targeting in product, sales, and marketing strategies . Market segments can power your product development cycles by informing how you create product offerings for different segments like men vs. women or high income vs. low income.
Read on to understand why segmentation is important for growth and the types of market segmentation to use to maximise the benefits for your business.
Free eBook: How to drive profits with customer segmentation
Companies who properly segment their market enjoy significant advantages. According to a study by Bain & Company , 81% of executives found that segmentation was crucial for growing profits. Bain also found that organisations with great market segmentation strategies enjoyed a 10% higher profit than companies whose segmentation wasn’t as effective over a 5-year period.
Other benefits include:
- Stronger marketing messages : You no longer have to be generic and vague – you can speak directly to a specific group of people in ways they can relate to, because you understand their characteristics, wants and needs.
- Targeted digital advertising : Market segmentation helps you understand and define your audience’s characteristics, so you can direct your marketing efforts to specific ages, locations, buying habits, interests etc.
- Developing effective marketing strategies : Knowing your target audience gives you a head start about what methods, tactics and solutions they will be most responsive to.
- Better response rates and lower acquisition costs : will result from creating your marketing communications both in ad messaging and advanced targeting on digital platforms like Facebook and Google using your segmentation
- Attracting the right customers : targeted, clear and direct messaging attracts the people you want to buy from you
- Increasing brand loyalty : when customers feel understood, uniquely well served and trusting, they are more likely to stick with your brand
- Differentiating your brand from the competition : More specific, personal messaging makes your brand stand out
- Identifying niche markets : segmentation can uncover not only underserved markets, but also new ways of serving existing markets – opportunities which can be used to grow your brand.
- Staying on message : As segmentation is so linear, it’s easy to stay on track with your marketing strategies, and not get distracted into less effective areas
- Driving growth : You can encourage customers to buy from you again , or trade up from a lower-priced product or service
- Enhanced profits : Different customers have different disposable incomes; prices can be set according to how much they are willing to spend . Knowing this can ensure you don’t over (or under) sell yourself.
- Product development : You’ll be able to design with the needs of your customers top of mind, and develop different products that cater to your different customer base areas.
Companies like American Express , Mercedes Benz , and Best Buy have all used segmentation strategies to increase sales, build better products, and engage better with their prospects and customers.
Understanding segmentation starts with learning about the various ways you can segment your market. There are four primary categories of segmentation, illustrated below.
| Classification based on individual attributes | Classification based on company or organisation attributes | Classification based on attitudes, aspirations, values, and other criteria | Classification based on behaviors like product usage, technology laggards, etc. | |
| Geography Gender Education Level Income Level | Industry Location Number of Employees Revenue | Lifestyle Personality Traits Values Opinions | Usage Rate Benefit Types Occasion Purchase Decision | |
| You are a smaller business or you are running your first project | You are a smaller business or you are running your first project | You want to target customers based on values or lifestyle | You want to target customers based on purchase behaviors | |
| Simpler | Simpler | More advanced | More advanced |
With segmentation and targeting, you want to understand how your market will respond in a given situation, like purchasing your products. In many cases, a predictive model may be incorporated into the study so that you can group individuals within identified segments based on specific answers to survey questions .
Demographic segmentation
Demographic segmentation sorts a market by elements such as age, education, household income, marital status, family size, race, gender, occupation, and nationality. The demographic approach is one of the simplest and most commonly used types of market segmentation because the products and services we buy, how we use those products, and how much we are willing to spend on them is most often based on demographic factors. It’s also seen as a simple method of predicting future behaviour, because target audiences with similar characteristics often behave in similar ways.
How to start demographic segmentation
Demographic segmentation is often the easiest because the information is the most readily available. You can send surveys directly to customers to determine their demographic data, or use readily available third party data such as government census data to gather further information.
Geographic segmentation
Geographic segmentation can be a subset of demographic segmentation, although it can also be a unique type of market segmentation in its own right. As its name suggests, it creates different target customer groups based on geographical boundaries. Because potential customers have needs, preferences, and interests that differ according to their geographies, understanding the climates and geographic regions of customer groups can help determine where to sell and advertise, as well as where to expand your business.
How to start geographic segmentation
Geographic segmentation data again can be solicited from customers through surveys or available third party market research data, or can be sourced from operational data such as IP addresses for website visitors.
Firmographic segmentation
Firmographic segmentation is similar to demographic segmentation, except that demographics look at individuals while firmographics look at organisations. Firmographic segmentation would consider things like company size, number of employees and would illustrate how addressing a small business would differ from addressing an enterprise corporation.
How to start firmographic segmentation
Firmographic segmentation data can be found in public listings for companies and information that the business makes available, as well as trade publications. Again, surveying existing and potential customers can help to build out this data.
Behavioural segmentation
Behavioral Segmentation divides markets by behaviours and decision-making patterns such as purchase, consumption, lifestyle, and usage. For instance, younger buyers may tend to purchase bottled body wash, while older consumer groups may lean towards soap bars. Segmenting markets based on purchase behaviours enables marketers to develop a more targeted approach, because you can focus on what you know they are looking for, and are therefore more likely to buy.
How to start behavioural segmentation
Of all the types of market segmentation, behavioural segmentation is likely best started with the information you have on an existing customer base. Though it can be bolstered by third party market research data, the information you already have on customer purchase and usage behaviour will be the best predictor of future behaviour.
Psychographic segmentation
Psychographic segmentation considers the psychological aspects of consumer behaviour by dividing markets according to lifestyle, personality traits, values, opinions, and interests of consumers. Large markets like the fitness market use psychographic segmentation when they sort their customers into categories of people who care about healthy living and exercise.
How to start psychographic segmentation
Psychographic segmentation relies on data provided by the consumers themselves. Though market research might provide insights on what particular segments are most likely to believe or prefer, psychographic segmentation is best completed with information direct from the source. You can use survey questions with a qualitative focus to help draw out insights in the customers’ own voice.
There are five primary steps to segmentation:
- Define your market : Is there a need for your products and services? Is the market large or small? Where does your brand sit in the current marketplace?
- Segment your market : Decide which of the five criteria (demographic/firmographic, psychographic, geographic or behaviour) you want to use to segment your market. You don’t need to stick to just one – in fact, most brands use a combination – so experiment with each one and find what works best.
- Understand your market : You do this by conducting preliminary research surveys, focus groups, polls , etc. Ask questions that relate to the segments you have chosen, and use a combination of quantitative (tickable/selectable boxes) and qualitative (open-ended for open text responses) questions.
- Create your customer segments : Analyse the responses from your research to highlight which customer segments are most relevant to your brand.
- Test your marketing strategy : Once you have interpreted your responses, test your findings on your target market, using conversion tracking to see how effective it is. And keep testing. If uptake is disappointing, relook at your segments or your research methods.
Why should market segmentation be considered a strategy? A strategy is a considered plan that takes you from point A to point B in an effective and useful way. Market segmentation is similar, as there will be times you need to revisit your market segments, such as:
In times of rapid change: A great example is how the Covid-19 pandemic forced a lot of businesses to rethink how they sell to customers. Businesses with physical stores looked at online ordering, while restaurant owners considered collections.
If your customers change, then your market segmentation should as well, so you can understand clearly what your new customers need and want from you.
On a yearly basis: Market segments can change year on year as customers are affected by external factors that could alter their behaviour and responses.
For example, natural disasters caused by global warming may impact whether a family chooses to stay living in an area prone to more of these events. On a larger scale, if your target customer segment moves away from one of your sales regions, you may want to consider re-focussing your sales activities in more populated areas.
At periodic times during the year: If you’ve explored your market and created market segments in the Spring, the same market segments may have different characteristics at a different time of the year.
For example, Winter has several holidays, with Christmas being a huge influence on families. This holiday impacts your market segments’ buying habits, how they’ll behave (spending more than normal at this time than any other) and where they will travel too (back home for the holidays). Knowing this information can help you predict and prepare for this period.
When considering updating your market segmentation strategy, consider these three areas:
- Acknowledge what has changed: Find out what has happened between one time period to another, and what have been the driving forces for that change. By understanding the reasons why your market is different, you can make key decisions on whether you want to change your approach or stay the course.
- Don’t wait to start planning: Businesses are always adapting to long-te r m trends , so refreshing market segmentation research puts you in a proactive place to tackle these changes head-on. When you have your market segments, a good idea is to consider the long-term complications or risks associated with each segment, and forward-plan some time to discuss problem-solving if those issues arise.
- Go from what to why : Why did those driving forces come about? Why are there risks with your target market? At Qualtrics, we partner with companies to understand the different aspects of the target markets that drive or slow success. You’ll have the internal data to understand what’s happening; we help unleash insight into why with advanced modelling techniques. This helps you get smart market segmentation that is predictive and actionable, making it easier for future research and long-term segment reporting.
Where can you use market segmentation in your business? We’ve collected some use case scenarios to help you see how market segmentation can be built in across several departments and activities:
Market and opportunity assessments
When your business wants to enter into a new market or look for growth opportunities, market segmentation can help you understand the sales potential. It can assist in breaking down your research, by aligning your findings to your target audience groups.
For example, When you’ve identified the threats and opportunities within a new market, you can apply your customer segment knowledge to the information to understand how target customers might respond to new ideas, products, or services.
Segmentation and targeting
If you have your entire market separated into different customer segments, then you have defined them by set criteria, like demographics, needs, priorities, common interests, or behaviour preferences .
With this information, you can target your products and services towards these market segments, making marketing messages and collateral that will resonate with the segment’s criteria.
Customer needs research
When you know a lot about your customers, you can understand where your business is connecting well with them and where there can be improvements.
Market segmentation can help with customer needs research (also known as habits and practices research) to deliver information about customer needs, preferences, and product or service usage. This helps you identify and understand gaps in your offerings that can be scheduled for development or follow-up.
Product development
If the product or service you’ve developed doesn’t solve the problem of your target audience or isn’t useful, then that product will have difficulty selling. When you know what each of your market segments cares about and how they live their lives, it’s easier to know what products will enrich or enhance their day to day.
Use market segmentation to understand your customers clearly, so that you can save time and money developing products and services that your customers will want to purchase.
Campaign optimisation
Marketing and content teams will value having detailed information on each segment, as this allows them to personalise their campaigns and strategies at scale. This may lead to variations in messaging that they know will connect with audiences better, making their campaign results more effective.
If the campaigns are combined with strong calls to action, the marketing campaigns will be a powerful tool that drives your target market segments towards your sales channels.
After you determine your segments, you want to ensure they’ll be useful. A good segmentation analysis should pass the following tests:
- Measurable : Measurable means that your segmentation variables are directly related to purchasing a product. You should be able to calculate or estimate how much your segment will spend on your product.For example, one of your segments may be those who are more likely to shop during a promotion or sale.
- Accessible : Understanding your customers and being able to reach them are two different things. Your segments’ characteristics and behaviour should help you identify the best way to meet them.For example, you may find that a key segment is resistant to technology and relies on newspaper or radio ads to hear about store promotions, while another segment is best reached on your mobile app. One of your segments might be a male retiree who is less likely to use a mobile app or read email, but responds well to printed ads.
- Substantial : The market segment must have the ability to purchase. For example, if you are a high-end retailer, your store visitors may want to purchase your goods but realistically can’t afford them. Make sure an identified segment is not just interested in you, but can be expected to purchase from you.In this instance, your market might include environmental enthusiasts who are willing to pay a premium for eco-friendly products, leisurely retirees who can afford your goods, and successful entrepreneurs who want to show off their wealth.
- Actionable : The market segment must produce the differential response when exposed to the market offering. This means that each of your segments must be different and unique from each other.Let’s say that your segmentation reveals that people who love their pets and people who care about the environment have the same purchasing habits. Rather than have two separate segments, you should consider grouping both together in a single segment.
Market segmentation is not an exact science. As you go through the process, you may realise that segmenting based on behaviours doesn’t give you actionable segments, but behavioural segmentation does. You’ll want to iterate on your findings to ensure you’ve found the best fit for the needs of your marketing, sales and product organisations.
We’ve outlined the do’s , so here are some of the dont’s :
- Avoid making your segments too small or specialised : Small segments may not be quantifiable or accurate, and can be distracting rather than insightful
- Don’t just focus on the segment rather than the money : Your strategy may have identified a large segment, but unless it has the buying power and wants or needs your product, it won’t deliver a return on investment
- Don’t be inflexible : Customers and circumstances change, so don’t let your segments become too entrenched – be prepared to let them evolve.
Market segmentation doesn’t need to be complicated to be effective. We would advise, though, to get automated from the beginning . Forget spreadsheets – choose market segmentation software to measure and streamline your marketing strategy; as you grow, the technology will scale with you.
Innovative features such as XM Directory allow you to build your own customer segments and start personalising experiences at scale based on the rich insights into your critical customer groups.
If you want to get a feel for your market segmentation upfront, before taking a step towards a streamlined and integrated system, trust us to take you through the research with our Market Segmentation Research service .
eBook: How to drive profits with customer segmentation
Related resources
Target market 11 min read, customer segmentation 17 min read, behavioural segmentation 19 min read, geographic segmentation 13 min read, demographic segmentation 14 min read, psychographic segmentation 11 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
- SI SWIMSUIT
- SI SPORTSBOOK
Daniel Vogelbach Hits Open Market After Being Released By Toronto Blue Jays
Sam connon | jun 19, 2024.

- Toronto Blue Jays
- Pittsburgh Pirates
- Milwaukee Brewers
- Seattle Mariners
The Toronto Blue Jays have released first baseman/designated hitter Daniel Vogelbach, according to the club's official transaction log.
Vogelbach was designated for assignment on Friday.
This marks just the latest major transaction for Toronto over the past week. On top of Vogelbach's departure, utility man Cavan Biggio got traded to the Los Angeles Dodgers , future Hall of Fame first baseman Joey Votto began his rehab assignment in the Florida Complex League, All-Star shortstop Bo Bichette was placed on the 10-day injured list and top prospect Orelvis Martinez was called up to make his MLB debut.
Before he got DFAd, Vogelbach was batting .186 with one home run, eight RBI, a .578 OPS and a -0.4 WAR. He had appeared in just 31 of Toronto's 68 games to that point, despite not suffering any injuries.
Toronto is now on the hook for Vogelbach's entire $2 million salary they guaranteed him this past offseason. He is now a free agent, able to sign with any team.
Vogelbach has been bouncing around ever since he made his lone All-Star appearance with the Seattle Mariners in 2019. That season, he hit 30 homers with 76 RBI, a .780 OPS and a 1.1 WAR.
The Blue Jays initially acquired Vogelbach in exchange for cash considerations in 2020, only to waive him and lose him to the Milwaukee Brewers a week later. Vogelbach stayed in Milwaukee for the 2021 season, then split 2022 between the Pittsburgh Pirates and New York Mets .
Vogelbach appeared in 104 games for the Mets in 2023, accounting for 13 home runs, 48 RBI and a 0.2 WAR, before getting non-tendered in November.
Over the course of nine MLB seasons, Vogelbach is a .219 hitter with a .745 OPS. He averages 22 home runs, 66 RBI and a 0.3 WAR per 162 games in his big league career.
Follow Fastball on FanNation on social media
Continue to follow our Fastball on FanNation coverage on social media by liking us on Facebook and by following us on Twitter @FastballFN .
You can also follow Sam Connon on Twitter @SamConnon .
Sam Connon is a Staff Writer for Fastball on the Sports Illustrated/FanNation networks. He previously covered UCLA Athletics for Sports Illustrated/FanNation's All Bruins, 247Sports' Bruin Report Online, Rivals' Bruin Blitz, the Bleav Podcast Network and the Daily Bruin, with his work as a sports columnist receiving awards from the College Media Association and Society of Professional Journalists. Connon also wrote for Sports Illustrated/FanNation's New England Patriots site, Patriots Country, and he was on the Patriots and Boston Red Sox beats at Prime Time Sports Talk.
Follow SamConnon

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
2 Geographic Segmentation. Geographic segmentation categorises a target audience by geography to allow consumers to be finest served by marketers in a specific region. This method of market segmentation is concentrated on the geographic regions within such as countries, states, towns, etc.
Market segmentation is a marketing term referring to the aggregating of prospective buyers into groups, or segments, that have common needs and respond similarly to a marketing action. Market ...
What is market segmentation? Market segmentation is the practice of dividing your target market into approachable groups.Market segmentation creates subsets of a market based on demographics, needs, priorities, common interests, and other psychographic or behavioral criteria used to better understand the target audience.. By understanding your market segments, you can leverage this targeting ...
The five most common types of market segmentation are: Demographic segmentation. Firmographic segmentation. Geographic segmentation. Psychographic segmentation. Behavioral segmentation. 1. Demographic segmentation. Demographic segmentation is perhaps the most common and straightforward method of segmenting the market.
This topic focuses on the basics of market segmentation and both cases require students to use data to identify market segments. The main case, The Fashion Channel: Market Segmentation, explores a cable TV network that methodically determines how to segment its potential audience.Students are asked to complete a quantitative assignment: calculating the bottom-line impact of various ...
The firm enacts the segmentation strategy through: (1) data collection, (2) applica-tion of models and frameworks and (3) resource. 223. allocation and differential action based on seg-ment (customer) value. The chapter concludes with a set of critical issues that provide the guide-lines for research agenda in this area.
Steps 1 to 3 cover the process of market segmentation only - where we decide on a market and then segment it into different groups of consumers with common needs or behaviors.. The further steps of 4 to 6 cover the steps of how to choose an attractive and viable target market. (Please note: There are actually nine steps of the full segmentation, targeting and positioning process, which are ...
The Advantages of Market Segmentation to the Organization. It's estimated that the average person sees an astounding 4,000-10,000 advertising messages each day. 3 That's why it's critical to target the right market. Most marketers have limited advertising budgets, so using one marketing message to reach a broad audience may garner a few new customers, but it's likely to come at a ...
Market segmentation is when a business splits potential customers into groups based on shared characteristics. These characteristics include location, age, income, credit rating, usage rates, or buying habits. Market segmentation can help inform and create a marketing plan that meets the needs of a target audience instead of creating a one-size ...
Market segmentation is the process of dividing your target market into clearly defined subgroups of consumers who have common characteristics and priorities. When you identify these segments, you can tailor your marketing strategy so you are better able to meet your customer's wants and needs. This approach enables you to focus your marketing ...
As mentioned earlier, STP stands for segmentation, targeting, and positioning. Segmentation is the first step in the process. It groups customers with similar needs together and then determines the characteristics of those customers. For example, an automotive company can split customers into two categories: price-sensitive and price-insensitive.
Assignment: Market Segmentation. Companies are expected to make decisions on what to offer to consumers in the form of services and/or products. This process can certainly be enhanced through the collection of data and the effective use of that data in strategic marketing planning. The VALS online survey is a tool used by companies to help them ...
Market segmentation analysis involves understanding your customers based on specific characteristics, both physical and behavioral. Companies use this analysis to create hyper-focused sales and promotions. By focusing on the smaller segments (and what they value most), it'll be much easier to resonate with them.
20/10/2014. Assignment 2: Topic 3 - Market segmentation, Targeting and Positioning. A. Market segmentation involves dividing the market into segments. Segmentation is. important when devising advertising campaigns to ensure that the advertisements hit the right. target audiences.
Market segmentation is a process that consists of sectioning the target market into smaller groups that share similar characteristics, such as age, income, personality traits, behavior, interests, needs, or location. Knowing your market segmentation will help you target your product, sales, and marketing methods.
10 pts. Total points possible for Situation and Company Analysis Assignment: 50 pts. Total points possible for Marketing Plan, Part 1 Assignment (Consists of Company Profile Assignment, Market Segmentation and Targeting Assignment, and Situation and Company Analysis Assignment combined): 100 pts.
Lecture 6: How to Do Market Segmentation Viewing videos requires an internet connection Descriptions: Discussion of the process for performing market segmentation in a rigorous manner.
2. Assume you are the marketing manager for a new solar car that you are launching. Answer the following questions: What segmentation characteristics would you use for your target market? How would you define your target market? Be as specific and as detailed as possible. Discuss a time when you may have done market segmentation in your career?
Geodemographic segmentation means segmenting a market by honing in on data on neighborhoods, ZIP codes, or census reports, under the assumption that consumers in particular cluster systems will behave similarly. This type of segmentation is especially valuable for highly directed, precise marketing. Over the years, several geodemographic ...
MRKT 310 WEEK 6 Assignment; MRKT310 Market Segmentation Memo; Assignment 1- Value Proposition Memo; Preview text. TO: Tiffany Morrow, Vice President of Marketing. FROM: Full Name, Marketing Analyst. DATE: 11 April 2023. SUBJECT: Amazon Smart Thermostat Market Segmentation Memorandum.
mkt420 - principles and practice of marketing group assignment: market segmentation, targeting and positioning a case study of nestlÉ (malaysia) berhad student name (student id) 1. zuriana binti zaini (2021255982) 2. norashida binti jari@bohari (2021646994) 3. nur kamaliah binti zamri (2021272638) 4. nor fatin atikah binti azman (2021287316) 5 ...
What is market segmentation? At its core, market segmentation is the practice of dividing your target market into approachable groups.Market segmentation creates subsets of a market based on demographics, needs, priorities, common interests, and other psychographic or behavioural criteria used to better understand the target audience. By understanding your market segments, you can leverage ...
This document discusses market segmentation, which involves dividing a market into distinct groups that have common needs, characteristics, or behaviors. The key points are: 1. Markets can be segmented based on geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavioral variables to better understand customer groups. 2. The benefits of segmentation include increased profitability, more tailored ...
To: Tiffany Morrow, Vice President of Marketing From: Marketing Analyst Date: February 8, 2022 Subject: Market Segmentation Memo I. Market Segment Analysis Disney Plus is an on-demand streaming service designed by The Walt Disney Company that offers content on-demand, allowing customers to decide what they want to watch and the time they will watch the shows and movies on the platform.
1.0 INTRODUCTION In advance of this assignment, we have learned about marketing segmentation, targeting, and positioning, as well as the marketing mix for the subject of Principles and Practice of Marketing. This assignment requires us to explain the company's market segmentation, targeting, and positioning in order to market their product.
The Toronto Blue Jays have released first baseman/designated hitter Daniel Vogelbach, according to the club's official transaction log. Vogelbach was designated for assignment on Friday. Before he ...