- Graduate School

How Long Does it Take to Get a PhD?: A Go-Getter’s Guide to Graduation
Featured Expert: Dr. Charlene Hoi, PhD

How long does it take to get a PhD? On average, PhD programs are 4 or 5 years long. The time it takes to get a PhD is slightly longer in the US, between 4-6 years, because these programs tend to be more structured. If you want to know how to get a PhD in Canada or Europe, you can expect it to take 3-5 years. However, there are PhD programs that take longer, such as part-time programs, or are extremely short, like online accelerated PhD programs. Ultimately, how long it takes to get a PhD is up to you. In this article, we’ll look at the average PhD program lengths, the typical PhD timeline, and tips on how to get your PhD finished faster.
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Listen to the blog!
Article Contents 13 min read
How long does it take to get a phd.
On average, it takes 4-5 years to complete a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) program. In the US, most PhD programs are between 4-6 years, while in Canada they are typically shorter, around 3-4 years.
Some students take longer than 6 years to complete their PhD, but in general the longest time it takes to get a PhD is capped at 8 years. If you’re enrolling in a part-time PhD program, for instance, your timeline will probably be extended to 6-8 years.
The shortest PhD programs out there are accelerated or sometimes online PhD programs. Some of these are only 1-2 years long, but there are comparatively fewer programs available, and they are only suitable for certain fields and careers which require less intensive research which defines most PhD programs.
One of the main reasons why it takes many years to get a PhD is because these programs are comprehensive and the requirements to graduate are extensive. Most have a set number of credit hours you need to complete, examinations to write, plus you’ll need to write your PhD thesis or dissertation, unless you pursue a PhD without dissertation .
There are certainly ways to shorten the PhD application timeline and time to graduate, which includes enrolling in a shorter program if possible, increasing your course load or the number of research hours you can dedicate per week, but generally a PhD will still take some time.
Even if you want to do a PhD without a master’s degree first, such as by applying to a direct entry PhD program, the program is still usually 4-5 years long.
We’ll take a look at the typical PhD timeline and how long it takes to get a PhD normally. After, we’ll cover some tips on how to get your PhD done faster or how you can avoid dragging things out.
In North America, the typical PhD program is divided into two stages. The first stage is where you complete all the required coursework, comprehensive exams and other academic requirements, depending on the program. The second stage is when you submit a proposal for original, independent research, get it approved and start working on your thesis or dissertation. Your PhD culminates with your thesis defense. Once your thesis has been approved, you’ll be eligible to graduate.
This timeline is somewhat flexible, as you might complete the first stage in 1 or 2 years but take longer to complete your dissertation. For the purpose of this general PhD schedule, we’ll assume your PhD program is a typical length of 4-6 years.
Application Stage
We’ve included the application stage of getting your PhD here first because the grad school application timeline can take several months to put together your application package and hear back about acceptance to a program. Secondly, because the application stage involves some critical steps you’ll need to complete in order to get your PhD.
1. Research proposal
To apply to a PhD program, you’ll most likely be required to submit a research proposal and be prepared to answer any research proposal questions your advisor will have. This is your “proposal” of what research question you will explore during your studies at a program, or an outline of what research topic you want to pursue. If you’re not sure how to write a research proposal, check out these Oxford PhD proposal samples or a Cambridge PhD proposal sample.
2. Application materials
The admission requirements for a PhD can vary from program to program, but here are the general components of a PhD application:
- Required prerequisite coursework
- Official transcripts (and minimum GPA)
- Graduate school statement of purpose
- CV for graduate school or research resume
- PhD motivation letter
Some programs may also ask you to submit additional essays, such as a letter of intent, research interest statement or grad school career goals statement .
Many PhD programs also invite you to a grad school interview to get to know you better. Be ready for common graduate school interview questions such as “ tell me about yourself ” and “ why do you want to do a PhD ?”
Writing a grad school statement of purpose? Check out these examples:
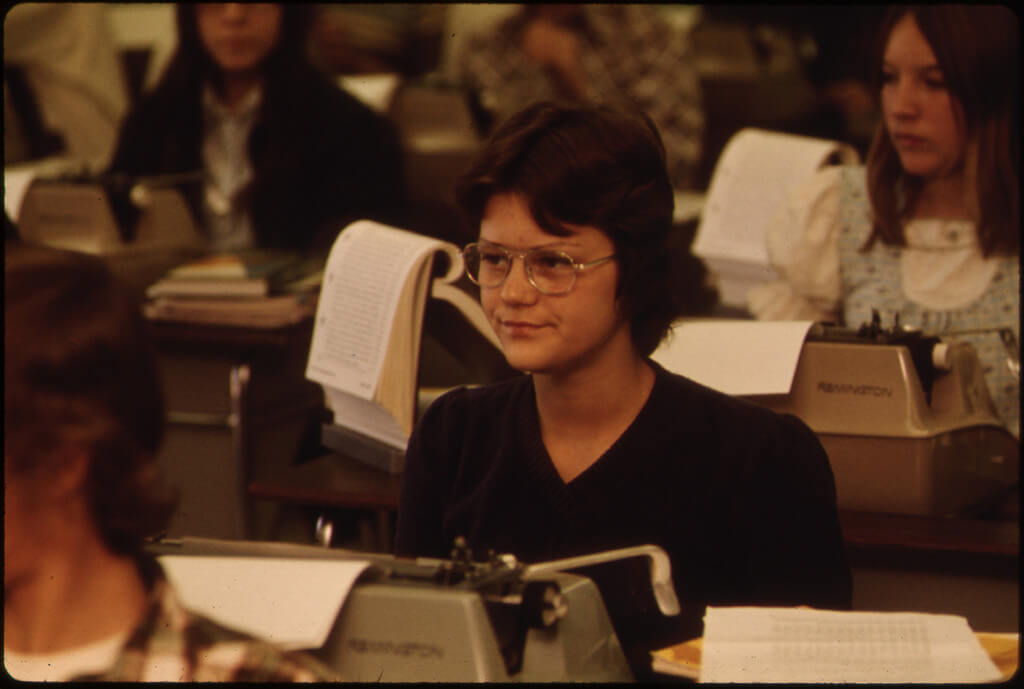
PhD Years 1-3: Coursework Stage
1. orientation.
Your PhD program will usually begin with your orientation, where you’ll learn about the program’s individual structure, requirements and expectations. You’ll also either choose or be assigned an academic advisor and schedule an initial meeting with them. Your advisor will be a member of the university faculty who will act as your support while you complete your research and write your thesis.
2. Coursework
The first year or two of your PhD will involve completing required advanced coursework in your field. You’ll attend lectures and seminars and you may participate in research projects with department faculty or fellow graduate students or even lab work, depending on your field.
3. Electives
Along with required coursework, you’ll have the chance to take elective courses that interest you or relate to your field. It’s important to choose electives that will enrich your program. Choose ones that really interest you, that might help inform your PhD research or that will help you fulfill your credit requirements.
4. Extracurriculars
PhD programs sometimes have extracurricular activities or additional requirements outside the classroom. This can include internships or a practicum you need to complete for credit, or you might be interested in attending academic conferences or relevant events to socialize and network you’re your colleagues in the field.
5. Comprehensive exams
The coursework stage of your PhD program will end with comprehensive exams , sometimes called qualifying or preliminary exams. These are your “final exams” to make sure that you completed the necessary PhD coursework and that you’re ready and qualified to take on your own independent research in the next phase.
1. Thesis proposal
You may recall that you submitted a research proposal as part of your PhD application, and this step of the process is similar. Your thesis proposal is just like your research proposal, but it’s a more refined and developed version. Throughout your coursework, your research question might have changed or you might have changed course a little bit. If you’re still thinking about your PhD topic , take the time to solidify it before you reach the thesis proposal stage.
Your research proposal might have been a first draft, while your thesis proposal is your official announcement of: this is what I propose to research in this PhD program.
Depending on your field and the program, you thesis research might involve a great deal of lab work, or data collection or fieldwork. Whatever the case, your thesis proposal is a complete outline of what you intend to do for this independent research project and the steps you’ll take.
2. Thesis approval
Once your proposal is written, you’ll submit it for approval. Your academic advisor, PhD supervisor or the PhD committee overseeing your program will review it and either approve it or make suggestions for changes. Once it’s been polished and finalized, you’ll be given the go ahead to start conducting your research.
3. PhD research
Your research alone will probably take you several semesters to complete. On top of the fieldwork, lab work or data collection and analysis you’ll be completing, you’ll be using this time to write and review. Writing your thesis or dissertation takes a fair number of hours to outline, draft, edit and complete. It also means hitting the books to complete a literature review of your research topic so you have a complete background understanding of your chosen topic and how it will inform your research.
Your research and the preparation of your thesis is really the biggest part of this second stage, and is probably the longest part of your PhD altogether.
4. Extra requirements
When you’re not deep in your research, you’ll be completing other requirements of your PhD program or additional duties that enrich your education. Some programs require you to dedicate some hours to teaching, whether it be leading seminars for undergraduate students or acting as a teaching assistant for university faculty.
You’ll also be strongly encouraged to publish as a graduate student , so you may be involved in the research projects of faculty members or other grad students when you’re not working on your dissertation.
5. Thesis submission and preparation for thesis defense
When you’re finished writing your thesis and you’re ready to submit it, it’s critical to know how to prepare for thesis defense . Because not only do you have to complete this original, new body of research work, you have to get the approval of your PhD committee to put it out into the world.
Your thesis defense is essentially the final presentation of your PhD.
6. Thesis defense
Your thesis defense is an oral presentation of your research project, but it also involves submitting your written document to be reviewed. Essentially, you’ll present the entirety of your thesis to the PhD supervising committee, including your findings and conclusions. From there, the committee will ask thesis defense questions . Your answers will defend your methodology and results to the committee, basically proving the value and validity of your work. While this is an evaluation of sorts, it is also your opportunity to share your original ideas and invite further research into your topic.
After your defense, the PhD committee will either approve your thesis or send it back to you with edits or changes to be made before it can be formally approved.
Graduation and Postdoc
Once your thesis has been approved, congratulations! You’ll be eligible for graduation and be awarded your degree. Now that you’ve finished this marathon, you can choose to pursue further studies or start looking for a job after grad school .
With a PhD, you have many different options for positions in your field. You might want to know how to find a job in academia or how to get a tenure track position at a university if you’re interested in teaching others. PhD graduates who decide to transition from academia to industry or who would rather work outside the realm of academia can find industry jobs after PhD that suit their skills and experiences.
Either way, you’ll need to prepare for how to find a postdoc position, explore what the career options are for you, decide what your career goals are and start sending out applications. Remember to prep your postdoc resume and get read for postdoc interview questions , since the job hunt will begin soon after you finish your PhD!
Is it possible to get your PhD done faster? What are some ways you can speed up the process and avoid taking 8 years to complete your graduate studies? Luckily, there are many key ways you can make your journey through grad school easier and speed things up a little, from the type of PhD program you choose to the habits and skills you cultivate during your program.
#1 Enroll in an accelerated program
The first way to guarantee it will take less time to get your PhD is to, of course, enroll in a shorter PhD program. Direct entry PhD programs allow you to enroll once you’ve completed your bachelor’s degree in exceptional circumstances. Note that these are not the easiest PhD programs to get into , as your academic record needs to be excellent, and you’ll likely need prior research experience and you may even need to have publications already. However, a direct entry PhD program is around 4-5 years, but it allows you to skip the 1-2 years it would take to earn a master’s degree.
You can also choose to enroll in an online or accelerated PhD program that is designed to be much shorter than the traditional PhD. Once again, though, these programs are not available to students in every field, so you may need to research whether there are any options for you.
#2 Choose the right mentor
One of the first things you can do to ensure your PhD is smooth sailing is to choose the right mentor or academic advisor. Many programs allow you to choose your advisor, while some assign one to you. Whatever the case, it’s important to establish a strong working relationship and clear expectations early on.
One of the first things you’ll do as a PhD student is meet with your advisor. Take the time to discuss with them what your expectations for the program are, ask questions and ask them what their expectations are of you. Your advisor is there to help you and advise you, and they have resources and connections you can use to your advantage. But they are also working with a busy schedule and might be advising more than one PhD student, too. A mutually respectful relationship with open communication will ensure fewer interpersonal hurdles down the road.
#3 Earn credit hours faster
One way you can shave some time off your PhD is by earning your credit hours faster and getting to the research and thesis-writing stage faster. This might mean you take on a full-time course load or ask your advisor for ways to earn extra credit, such as participating in research projects. Some PhD programs will give you course credit for previous graduate level coursework you might have completed during your master’s degree, or for certifications and professional education you completed outside of school.
#4 Keep your thesis focused
When you get started on your research, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed with the amount of work you need to complete, with the writing of your thesis on top of it all. One way to keep your research hyper-focused and on point is to keep your thesis topic narrow. If your subject is too broad, you’ll be spending way too much time in your research. Give yourself clear objectives and scope, and don’t deviate from your PhD proposal if you don’t have to.
There may be a million questions you want to explore within your PhD topic, but there will be other opportunities to explore them. Keep your focus narrow so you don’t spend years and years asking and answering research questions!
One of the best things you can do to get your PhD done faster and adjust to the experience of graduate school is to change your thinking. Adopt a growth mindset so that you’re open to new learning, willing to listen to constructive feedback on your proposal or thesis and willing to grow your skills. A PhD is an advanced program, and you’ll already be very skilled, but it is also an opportunity to learn and grow. There will be challenges for you, so be ready to meet and overcome them instead of letting them draw you back or slow you down.
#5 Develop your professional skills fast
A PhD is an opportunity to grow your professional skillset as much as it is an opportunity for you to contribute meaningfully to your field. If you haven’t already been working on skills such as communication, presenting or lecturing and writing, now is the time to start.
Strong writing skills will help you get your thesis finished and edited faster, as you’ll be more familiar with the process and understand what makes a strong document. It’s also a useful skill to learn how to write effective funding proposals or grant proposals. You may need to do so to secure funding for your research, but it’s a highly valuable skill in the workforce, too.
Good presentation skills will help you during your thesis defense or if you’re asked to present during a conference. They will also help you build confidence in your voice and ideas and make you a better communicator when you’re networking or job searching.
#6 Keep to your schedule
This is maybe the most important skill if you want to finish your PhD faster: make a detailed schedule and hold yourself accountable to it. If you like, you can plan out your entire PhD week by week from Day 1. Write down what your course schedule is, when you’ll do research and how many hours, when you’ll write and how many hours, what extracurriculars or personal activities will take up your time and so on.
A detailed schedule gives you an overview of your PhD and a timeline of when you’ll finish. It will keep you organized and accountable, so you can avoid procrastinating or avoidable speed bumps that might slow you down. It also helps you compartmentalize the many items on your to-do list so you don’t stress out about how much you need to accomplish.
When creating your schedule, especially during the research stage when there is no formal class schedule for you to adhere to, focus on deliverables. Set a date when you will submit a section of your thesis to your advisor, or when you will complete your literature review. Setting goals and clear outcomes will keep you on track and focused.
#7 Take initiative and be independent
The last tip to help you get your PhD done faster is to take initiative. Remember that a PhD is a largely independent endeavor. You’ll have the support of a committee or advisor, but you can’t rely on them to do the work for you or put everything on hold if they aren’t available when you need them. Be flexible and adaptable so you can keep working and moving forward, even if your schedule gets interrupted or needs to change to suit your situation.
It's also important to take the initiative in your learning. Take advantage of opportunities for growth, networking, and gaining experience where you can. Get the most out of your PhD program and use your experiences to fuel your end goal of completing your thesis.
On average, it takes 4-5 years to get a PhD. There are a few factors that can influence the time it takes to complete your PhD, from program length and structure to what country you are earning your PhD in, to your own personal work ethic and schedule.
PhD programs in the US are on average 4-6 years. In Canada and the UK, they are usually 3-5 years long. Part-time PhD programs may take up to 7-8 years to complete. Direct-entry PhD programs and dual master’s and PhD programs are typically 5 years long. If you’re enrolling in an online, hybrid or accelerated PhD program, the timeline is usually 2-3 years, but there are some extremely short 1-year PhD programs offered online for specific disciplines.
Yes, you can finish your PhD before the “normal” timeline. For example, if you complete your coursework early, if you finish writing your thesis faster than average and get it approved, or if you otherwise complete all your PhD program requirements before the anticipated finish date.
Yes, there are online PhDs available for certain fields and disciplines. These typically range from 2-3 years, although there are some traditional 4-year PhD programs offered online. There are also some “accelerated” online PhDs which last 12-18 months.
A PhD program is not necessarily shorter if you first complete a master’s degree, but having gone through a master’s program can better prepare you to finish your PhD faster. Some PhD programs accept credit hours from your master’s degree towards the coursework requirements for a PhD, and if you’ve previously written a master’s thesis or completed some research during your graduate studies, this will be an advantage. Since you’ll already be familiar with the process of writing a thesis and conducting your own research, you can avoid some stumbling blocks in your PhD program that might otherwise slow down your progress.
Yes, it is possible to get a PhD without first completing a master’s degree. There are direct entry PhD programs that allow students with a bachelor’s degree to enroll, so long as they meet the admission requirements and have exceptional academic records. Some online PhDs also waive the master’s degree requirement.
Yes, it is possible to complete a traditional PhD program in a shorter amount of time than anticipate. This usually means dedicating yourself to full-time study or taking on a larger course load and increased research hours. It takes significant work, but it can be done with the right schedule and commitment.
The fastest PhD programs are the short, 1-year accelerated programs. These programs have fewer credit hours to complete, and some have no dissertation requirement, only qualifying exams to finish. However, there are not many programs out there, and they are not available for every field of interest.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar:
How to make your grad school application stand out, (and avoid the top 5 mistakes that get most rejected).
Time Sensitive. Limited Spots Available:
We guarantee you'll get into grad school or you don't pay.
Swipe up to see a great offer!
How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD?
If you aspire to rise to the top of your field, then you may have your sights set on a PhD.

Earning a doctoral degree can be a years-long process, but choosing an accelerated doctoral online program may help you complete your program more quickly.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Whether you’re wanting to earn one of the highest paying doctoral degrees or you have a specific one in mind, this guide can help walk you through how long it takes to complete your PhD program.

For a traditional, campus-based PhD program, the average time to finish a PhD is 8 years. Fulfilling the program’s requirements will often demand a serious investment of your time.
Even still, some people are able to finish their programs in just 3 to 6 years. Multiple factors may influence the overall length of your program.
Required Credit Hours
Many PhD programs require you to earn 120 credit hours before entering the exam and dissertation phases.
Fortunately, there are PhD programs without such high credit-hour demands. For example, at some universities, you may earn a PhD with only 60 credit hours.
Full-Time vs. Part-Time Schedule
Enrolling in a doctoral program part-time may allow you to keep up with your regular job. You’ll have to decide whether you prefer the flexibility of part-time schooling or the faster schedule of full-time studies.
Final Project Requirements
Many PhD programs end with the completion of a dissertation. This assignment may take years to complete, so PhD students often end up in the all-but-dissertation (ABD) phase for quite some time.
University Scheduling
Some schools promote their ability to help you through the PhD process faster than normal. Accelerated class schedules with eight-week online courses may speed your studies along. Focused attention from dissertation advisors may help as well.
PhD Program Components

Before you enroll in a PhD program, it’s important to know some of the basic requirements:
Prerequisites
Most schools require you to already hold a master’s degree, but some offer bachelor’s-to-PhD programs.
Length to Completion
On average, it takes eight years to earn a PhD. Even still, completing doctoral coursework and a dissertation in three to four years is not unheard of.
Topic of Interest
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy, but that doesn’t mean you’ll be getting a philosophy degree. Your field of study will depend on your interests and the programs that your university offers. You may tailor your doctoral focus though your choice of a dissertation topic.
Steps to Completion
You’ll take advanced classes before sitting for comprehensive exams. After passing your exams, you’ll likely begin working on a dissertation. You must defend your dissertation before finishing your program.
Doctoral studies begin with a series of classes through which you may increase your knowledge of your field of study and learn about conducting research. These are advanced classes, so they should be more in-depth than the ones you took during your undergraduate and master’s programs.
The number of courses that you need to take can vary significantly. It’s not uncommon for PhD programs to require 120 credit hours of coursework. That amounts to about 40 classes.
At other schools, the requirements are lower. Your university’s program may involve just 60 credit hours or, possibly, even fewer. A less intense course load may significantly slash your time to completion.
Your university may require you to maintain a GPA above a minimum threshold. An unsatisfactory GPA may keep you from moving on to the next step of the PhD process.
Comprehensive Examinations
Universities often require students to demonstrate their readiness for a doctoral project before advancing to the next stage of their studies. Readiness is proven through comprehensive exams , which may also be known as:
- Preliminary examinations
- Major field examinations
- General examinations
Often, comprehensive exams take the form of written or oral tests. In other situations, faculty may assess students’ readiness on the basis of a portfolio evaluation or a written paper.
Dissertation and Defense

A dissertation, also known as a graduate thesis, is a body of work that presents original research in your field. This manuscript focuses on a unique idea and includes evidence to support your thesis. During your doctoral studies, there are classes designed to help prepare you for your dissertation work.
The dissertation process may take several years. Once your manuscript is complete, you must defend it to the doctoral program faculty. After your defense, you may need to do further work on your manuscript, or the committee may decide that your dissertation is complete.
Not all programs require a dissertation. Instead, there may be an alternative doctoral project. Although both dissertations and capstone projects are rigorous, projects can sometimes be completed within a shorter time frame.
Average Time to Complete PhD by Field of Study
Students in some disciplines usually take a lot more time to finish their doctoral work than students in other fields.
If you’re studying in the following scientific fields, you may be more likely to earn your on-campus degree in seven years or less:
- Physics — average of five years
- Psychology — average of five to seven years
On the other hand, if your field of study relates more to the humanities, your on-campus degree program may take longer:
- History — average of eight years
- English — average of eight years
- Education — average of 13 years
These are the traditional figures. There are ways to finish faster.
Why Does It Take So Long to Finish a Traditional PhD?

Some schools require doctoral students to take around 40 classes, which, in a traditional on-campus setting, may take years. After completing the coursework, you must write your dissertation and defend it. The dissertation process alone might take multiple years.
Doctoral programs online may help shorten the PhD process to three or four years. Fewer credit hours may be required, and the classes may be delivered in an accelerated format.
Schools with an emphasis on quick doctoral programs may also offer dissertation advisors to efficiently guide students through that phase. Alternatively, some universities allow students to complete capstone projects that don’t take as long as dissertations.
Getting a PhD Online vs. Campus

Online education has changed students’ options for earning a PhD. These days, aspiring students may choose whether to attend classes on a college campus or online.
Traditional programs may require you to relocate to the university’s campus and attend school full-time. On average, it takes just over eight years to complete those programs. The benefits of choosing an online school instead may include:
Faster Progress
Accelerated eight-week courses may allow you to finish your course load sooner. You may complete your entire program in just three or four years.
Multiple Start Dates
Online programs often let you join throughout the year, so you don’t have to put your studies on hold until the fall semester.
Flexibility
Not being required to move to campus or come to class at set times may allow you to work your studies around your schedule.
Equal Status
Online programs are just as rigorous as on-campus ones. As long as your university is accredited, your degree will be just as valuable as one from a traditional university setting.
Cost-Savings
Finishing your doctoral studies faster may mean that you pay less tuition.
How to Finish Your PhD in Less Time

Although you can’t earn a doctoral degree overnight, you shouldn’t have to spend the majority of your working years striving toward PhD-completion. The following tips for accelerating the PhD process may help you finish your studies more quickly than the average doctoral student.
1. Use What You Already Know
Every school requires a minimum number of credit hours that you must earn in the pursuit of your degree. To help you meet this threshold, some schools will allow you to transfer in credits from other doctoral programs. Universities may also give you credit for your professional experience. Reducing your class load may save you both time and money.
2. Look for Short Classes
Accelerated course schedules are one of the best ways to speed through the degree process. Every eight weeks, you’ll begin a new set of classes. Over the course of a year, there may be five different sessions during which you can take classes.
3. Work on Your Dissertation Throughout the Program
Traditionally, dissertation work begins once the classroom portion of your studies is over. Quick doctoral programs may allow you to begin the dissertation process while you’re still taking other classes. This approach, known as an embedded dissertation, may reduce the likelihood that you’ll drop out before finishing your final project. It might also speed up your doctoral timeline.
4. Ask for Help
A lack of support can lead some doctoral students to drop out. On the other hand, having a good support system can help you push through and finish your program more quickly. Build a team of family, friends, and academic mentors who can encourage you, guide you, and lend practical help when you’re feeling overwhelmed by school.
Why Get a PhD?
You may need to earn a doctoral degree to achieve your career goals . For example, if you want to become a clinical psychologist, this level of study is essential. Many scientific and research positions require doctoral studies. University faculty typically need to hold terminal degrees as well.
Even if a doctorate is not a requirement for your desired line of work, it may help you achieve greater success. You might be granted higher levels of responsibility, and you may earn more money. In some fields, those who hold PhDs make around 20% more than those with master’s degrees, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics .
Do You Have to Have a Master’s Degree to Get a PhD?
Many schools consider a master’s degree an essential prerequisite for PhD admission. If you don’t already have a master’s degree, a bachelor’s-to-doctorate program may allow you to earn a master’s and a PhD for less time and money than it would take to pursue them separately.
How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD After a Master’s?
You may be able to complete your doctoral program in three to four years if you opt for an accelerated online program. On average, traditional on-campus PhD programs take around eight years to complete.
How Hard Is It to Finish a PhD?
Doctoral studies are challenging. That shouldn’t come as a surprise; if doctorates were easy to acquire, nearly every college graduate would end up with a PhD behind his or her name.
Approximately 50% of students who begin a PhD program don’t end up finishing. Many quit within two years of starting. Another large portion gives up upon reaching the dissertation phase.
Although all PhD programs are challenging, the flexible nature of online programs may help you find success. Choosing a doctoral track that doesn’t require a dissertation may help as well.
What Is the Easiest PhD to Get?

All PhD programs are demanding, but you might have an easier time if you select a program that aligns with your interests and your career goals. The flexibility of online study may help your doctoral program seem less burdensome. In addition, capstone projects are sometimes easier than writing dissertations.
If earning a doctoral degree in a short time frame is important to you, then consider the many potential benefits that online programs have to offer. Within just a few years, you may be able to place the letters “PhD” at the end of your name.

Study a PhD: A Guide to PhD Degrees
Looking to undertake PhD studies? This guide will tell you everything you need to know about PhD studies.

Looking to undertake PhD studies? Is getting a PhD even worth it? This guide will tell you everything you need to know about getting a PhD.
In this guide, we'll cover:
- What is a PhD?
- What Types of PhD Are There?
- How Long Does It Take To Get A PhD?
What Are The Requirements To Study A PhD?
What are the benefits of getting a phd, what is the average salary of a phd graduate.
- How Much Does Earning a PhD Cost?
Can I Do a PhD Online?
Would you like to study a phd abroad.
Click here to start a search for your ideal PhD program!
What is a PhD/Doctorate degree?
A Doctor of Philosophy, more commonly known as a PhD, is the highest level of degree you can achieve in one field of study. It’s awarded by universities around the world for significant contributions to knowledge in various academic fields, or upon completing a PhD program.
Pursuing a PhD involves conducting in-depth original research in a certain field . The results of this research are then compiled into a thesis or dissertation . This usually culminates in an oral examination or defense , where the candidate must demonstrate comprehensive knowledge of their research area and defend their findings in front of a panel of academics in that subject field.
Different Types of PhDs
“PhD” is an umbrella term for different types of programs. These can be broadly divided into four categories:
- Traditional/Academic PhDs: Also known as a research doctorate, this involves a couple of years of original research on a specific topic. It usually focuses on a theoretical understanding of the topics, rather than practicing the knowledge in the professional setting. This is the most common type of PhD.
- Professional Doctorate: These are designed for professionals who want to apply their research to their professional practice. Examples include the Doctor of Education (EdD), Doctor of Psychology (PsyD), and Doctor of Business Administration (DBA). These degrees are often more practice-oriented compared to the traditional PhD.
- Higher Doctorates: These are awarded to people who contributed greatly to the research and knowledge body within their field and are thus given out later in that researcher’s life. You can’t apply for this type of doctorate like a regular PhD program.
- Honorary Doctorates: These are given out by universities at their discretion, and don’t require any specific academic achievement or publication. Just like Higher Doctorates, you can’t apply for this type of Doctorate.
What the breakdown above suggests is that you essentially have two options when it comes to pursuing a PhD – you can either opt for an academic route, or a professional/industry doctorate .

How Long Does It Take To Get a PhD?
On average, PhD programs last 5-7 years , but this number varies greatly depending on the country, the university, and the specific field of study.
For example:
- PhD programs in the UK tend to be on the shorter end of the spectrum, typically lasting 3-4 years .
- In the US, however, the average completion time for PhDs rounds out at 6 years .
Make sure to keep in mind that the time it takes to earn a PhD also depends on the pace of your study, the field of study, the requirements of your program, and your prior educational background.
You’ll need to do some preparation in order to successfully apply for a PhD. The general rule-of-thumb is to check the university’s website for the specific requirements of the program you’re interested in.
That said, there are some general requirements you’ll need to meet to pursue a PhD:
Academic Transcripts
You’ll be expected to submit transcripts of your Bachelor’s and Master’s studies , which have to show the courses you took and grades you received during your programs.
Some PhD programs in the UK, particularly in STEM fields, may allow you apply for a PhD with only a Bachelor’s degree. However, PhD programs in Arts and Humanities require a Master’s degree.
You may need to have to get your transcripts (and other documents) translated and stamped by a notary . For example, if you got your Bachelor’s and Master’s in Hungarian, but you’d like to study in Canada, you will need to get your transcripts translated into English.
Research Proposal
The majority of universities require students to submit a research proposal as a part of their PhD program application, unless if you’re applying for a pre-defined research project in science, technology, engineering, mathematics or medicine. Make sure if this exception applies to your program of interest.
A good research proposal includes the scope, significance and some details about the topic you plan on researching during your program.
Your research proposal will have varying significance depending on the country you’re planning on studying in.
Academic CV/Resume
The general practice is to include your education at the top of the CV, followed by work experience and then academic research.
Make sure to check the industry standard for CVs/Resumes in the country and field you want to study in . For example, U.S. Resume may differ from your home country’s standards – it will make you stand out above other candidates who didn’t take that time to research your study destination’s standards.
Note: While not adhering to the CV/Resume standards of the country/university won't immediately disqualify you as a candidate, it does show a certain lack of care and polish that other candidates might showcase in their own applications. The best way to describe is that details like this show your determination and proactiveness (because you're actively thinking about what could leave a better impression on the admission committee).

Motivation Letter/Statement of Purpose
Research the university and the faculty thoroughly .
To compose an effective motivation letter for your PhD application, it’s crucial to thoroughly research the university and the faculty you're interested in . This is something recruiters and admission committees are actively looking out for - they want to see that:
- You know what the university/faculty is about
- You're familiar with the projects the department you're interested in is involved in
- You care enough to learn about the professors, researchers, and other people at the department you're applying for
It's not only about looking good - this thorough approach shows dedication and leaves a positive first impression when it comes to your research skills and maturity.
Avoid clichés and communicate who you are
Faculty members and admission committees have likely sifted through countless formulaic letters and readily available templates from the internet, so your authenticity and genuine enthusiasm will set you apart .
Remember that no one expects you to be perfect - admission committees hire on potential, not perfection . Craft an interesting narrative unique to you, and articulate why that specific university and its PhD program align with your research interests and career aspirations. Don't forget to also explain why you are the right choice for them .
Bonus tip: If you have been involved in the process of securing funding for research in the past, make sure to mention that. This is especially important for institutions that don’t have internal funding, but it’s always a bonus no matter where you apply.
Letters of Recommendation and/or References
Some universities and programs require you to submit letters of recommendation and academic references from people who you’ve studied under or collaborated with in the past.
Make sure to give people you want recommendation letters from enough time to write a strong letter detailing why you’re the right choice for this.
Proof of Language Proficiency
You’ll need to prove that you can speak and write in the language you want to study in. This usually means taking a language proficiency test.
Here are some examples of certificates that are widely accepted for different languages:
* General German language test for all foreign higher education students. ** German language test for those who want to study at Vienna University. Lots of universities in German-speaking countries offer their own specialized German courses like this, and they're often free or very affordable.
Additional Requirements
If you're non-EU/EEA/Swiss citizen, you may be required to apply for an Academic Technology Approval Scheme (ATAS) certificate if you want to get a PhD in certain subjects in the UK. You can check if you need to apply for this clearance on the UK government website .
You may need to complete graduate entry tests to apply for a PhD in certain countries – most commonly in the US, Canada, Australia and India. These include but are not limited to:
- Graduate Record Examination (GRE)
- Graduate Management Admissions Test (GMAT)
- Law School Admission Test (LSAT)
- Medical College Admissions Test (MCAT)
- And various language tests.

A PhD can equip you with a variety of skills and a deep knowledge of your chosen field, but it also offers tangible benefits.
Laura Forsberg White , PhD and a Professor in Biostatistics at Boston University, in the KAS interview with her, listed the following as the key skills students acquire in graduate programs:
Hard Skills and a Deep Understanding of Your Field
A PhD allows you to delve deeply into your field of interest, exploring complex theories, methodologies, and concepts in a profound way. You will gain hard skills that can be applied in a variety of contexts within your area of specialization . This level of knowledge makes you a sought-after professional in academia, industry, or the public sector.
The example Prof. White gave was in her own field: students in Biostatistics and adjacent fields learn practical knowledge and skills in statistics, probability, critical analysis and more.
Research Skills and Collaboration
An essential part of many PhD programs is based around developing research plans, performing data collection and analysis, and presenting your findings . This cultivates strong research skills that are highly valuable both in academia and industry, in sectors such as finance, tech, consulting, and more, where data-driven decision-making is crucial.
What’s more, PhD programs involve lots of collaboration with other researchers, which matures you as an individual and teaches you various soft skills you’ll need to succeed in your future roles, such as proper communication, taking and receiving feedback, critical thinking, time management and resilience and perseverance .
Transferrable Skills
Aside from academic knowledge and research skills, a PhD program helps you develop a range of transferable skills. These include project management, leadership, team working, and communication skills . Such skills are highly valuable in a variety of professional contexts.
Many PhD programs also require students to undertake teaching or mentoring roles . This offers valuable experience if you aim to pursue a career in academia, giving you the chance to shape the minds of future generations and contribute to the growth and development of your field of study.
Career Advancement
If you decide to leave academia to pursue a career in the industry, a PhD can open up higher-level career opportunities, such as more prestigious roles, higher pay, and quicker promotions.
It's also worth noting that a PhD is often required for tenure-track positions in academia .
What’s more, during your PhD, you'll attend conferences, seminars, and other academic events. These platforms allow you to meet and collaborate with other professionals, academics, and experts in your field. Such networking can lead to fruitful collaborations, job offers, or research partnerships .
Contribution to Society
As a PhD researcher, your work could lead to significant breakthroughs or advancements in your field . Whether you're studying medical sciences to contribute to public health, or researching environmental science to advance sustainability efforts, your research can make a real difference in society and/or the overall body of knowledge of your chosen field.

When we consider pursuing higher education, one of the key factors that often drives our decisions is the potential impact it will have on our financial future. A PhD can provide the edge you need to not only secure high-paying roles but also garner respect and credibility in your chosen field .
The average salary of PhD graduates varies significantly across countries and fields:
United States
- Bachelor’s degree average: $70,000/year
- Master’s degree average: $82,000/year
Source: Payscale, 2023
United Kingdom
- Bachelor’s degree average: £33,000/year
- Master’s degree average: £35,000/year
- Bachelor’s degree average: €51,000/year
- Master’s degree average: €56,000/year
How Much Does Getting a PhD Cost?
A PhD can cost you nothing or a fortune, depending on the university and the country in which you want to study in. Most universities also have different tuition fee structures for domestic and international students.
Here’s a breakdown of the average tuition fees depending on the region and citizenship:
You can read a more detailed breakdown of the costs of getting a degree in various countries in our Country Guides .
For those of you worried about the costs of studying abroad, there are plenty of scholarships out there to help you find your studies. Take a look at our free Scholarship Directory for a list of 440+ scholarships in 37 countries around the world.

Yes, you can definitely complete PhD programs online . More and more of them are available every year, but it's important to remember that their quality varies widely depending on the field of study and the institution.
It would be good to check how long the online program you’re interested in has existed. PhD programs are collaborative by nature, and many majors aren’t a good fit for online studies.
Typically, PhD programs specifically designed for online instruction tend to be more effective compared to traditional programs that have been simply transferred to online learning platforms.
Need More Help With Your PhD Application?
Download our free PhD Application Documents handbook, which goes into detail on how to perfect your motivation letter, CV/resume, research proposal and more!

Keystone Team Author
The Keystone Team is comprised of experienced educators and advisors dedicated to providing valuable resources and advice to students all over the world.
Read related articles

How to Study Abroad Guide: What Can I Study Abroad?
February 2022 Master's Degree Bachelor's Degree Preparing to Study Abroad Associate's Degree PhD

Best Decision of My Life: Pursuing My PhD at Manchester Met
December 2020 Student Stories Study Abroad in the United Kingdom Why Study Abroad? PhD
- Search All Scholarships
- Exclusive Scholarships
- Easy Scholarships to Apply For
- No Essay Scholarships
- Scholarships for HS Juniors
- Scholarships for HS Seniors
- Scholarships for College Students
- Scholarships for Grad Students
- Scholarships for Women
- Scholarships for Black Students
- Scholarships
- Student Loans
- College Admissions
- Financial Aid
- Scholarship Winners
- Scholarship Providers
Student-centric advice and objective recommendations
Higher education has never been more confusing or expensive. Our goal is to help you navigate the very big decisions related to higher ed with objective information and expert advice. Each piece of content on the site is original, based on extensive research, and reviewed by multiple editors, including a subject matter expert. This ensures that all of our content is up-to-date, useful, accurate, and thorough.
Our reviews and recommendations are based on extensive research, testing, and feedback. We may receive commission from links on our website, but that doesn’t affect our editors’ opinions. Our marketing partners don’t review, approve or endorse our editorial content. It’s accurate to the best of our knowledge when posted. You can find a complete list of our partners here .
How Long Does It Take to Earn a PhD?

Cece Gilmore is a Content Writer at Scholarships360. Cece earned her undergraduate degree in Journalism and Mass Communications from Arizona State University. While at ASU, she was the education editor as well as a published staff reporter at Downtown Devil. Cece was also the co-host of her own radio show on Blaze Radio ASU.
Learn about our editorial policies

Cari Schultz is an Educational Review Board Advisor at Scholarships360, where she reviews content featured on the site. For over 20 years, Cari has worked in college admissions (Baldwin Wallace University, The Ohio State University, University of Kentucky) and as a college counselor (Columbus School for Girls).

Maria Geiger is Director of Content at Scholarships360. She is a former online educational technology instructor and adjunct writing instructor. In addition to education reform, Maria’s interests include viewpoint diversity, blended/flipped learning, digital communication, and integrating media/web tools into the curriculum to better facilitate student engagement. Maria earned both a B.A. and an M.A. in English Literature from Monmouth University, an M. Ed. in Education from Monmouth University, and a Virtual Online Teaching Certificate (VOLT) from the University of Pennsylvania.

How long is a PhD program? That might be one of the first questions you ask yourself If you are thinking of earning a PhD. You have probably heard a range of years, and that is because how long it takes to earn a PhD depends on a number of factors. Keep reading to learn more!!
What is a PhD?
PhD stands for a “Doctorate of Philosophy.” This is an academic degree that qualifies the degree holder to teach their chosen subject at university level or to work in a specialized position in their chosen field. In general, the PhD is the highest level of degree a student can achieve.
Also see: Top fully funded PhD programs
Why get a PhD?
A PhD is a serious commitment with a serious return on investment. Here is a list of professional and personal benefits for earning a PhD.
How long does it take to earn a PhD?
Earning a PhD usually takes between four and seven years to complete, depending on the type of PhD as well as the schools requirements, the students educational background, and personal progress. Students who take full-time classes can typically finish in four years. A typical PhD program requires anywhere from 60 to 120 semester credit hours .
Why earning a PhD takes years to earn
Assistantship obligations.
Teaching and research assistantships can be very beneficial for the experience they provide and the potential funding, but they can also be time consuming obligations for PhD students. Therefore, assistantships may affect the amount of time it takes to complete a PhD program.
Comprehensive examinations
Universities often require students to demonstrate their readiness in a PhD program through comprehensive exams. These comprehensive exams may be known as:
- Preliminary examinations
- Major field examinations
- Comprehensive exams or “Comps”
- General examinations
Dissertation
A dissertation is an in-depth research document that serves as the culmination of a doctoral program. It is an important document that demonstrates a student’s original research and contribution to their field of study.
The dissertation involves conducting extensive research, reviewing previous literature, analyzing data, and presenting your findings in a structured manner. Once the dissertation is completed, it is typically defended orally in front of a committee of faculty members who assess the quality and validity of the research.
Average PhD timeline
The specific of a PhD timeline carried by college and university. However, the following is a good overview of the average PhD program.
- Year 1: Take advanced courses
- Year 2: Take advanced courses and begin preparing for exams
- Year 3: Study, take and defend your comprehensive exams and begin researching your dissertation proposal
- Year 4: Begin working on your dissertation
- Year 5: Finish and defend your dissertation
Average PhD completion by focus
According to data from the National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics the average time in years from graduate school entry to doctorate it took students to receive their degree in 2020 in certain fields is listed below.
- Life sciences = 6.9 years
- Physical sciences and earth sciences = 6.3 years
- Mathematics and computer sciences = 7.0 years
- Psychology and social sciences = 7.9 years
- Engineering = 6.8 years
- Education = 12.0 years
- Humanities and arts = 9.6 years
- Other non-S&E fields = 9.3 years
Related : Top 10 PhD in Education programs
How to finish your PhD is less time
Look for accelerated classes.
Accelerated courses are an easy way to reduce the amount of time it takes to finish a PhD. Therefore, look into if your program offers any shorter courses.
Work on your dissertation throughout the program
Working on your dissertation little by little throughout the program will allow you to speed up your doctoral timeline. In addition, it may reduce the likelihood that you’ll drop out before finishing your final project.
Maintain regular communication with your advisor
Establish regular communication with your advisor or supervisor. Regular meetings can help you receive guidance, address any issues, and ensure you are heading in the right direction.
Seek feedback early and often
Share your work and progress with your advisor, peers, or other trusted individuals often. Then, you should incorporate suggestions and revisions as you go along. This will help you refine your work and avoid major revisions later.
Maintain a healthy school-life balance
While it is important to be dedicated to your PhD, it’s just as important to maintain a healthy work-life balance. Therefore, be sure to prioritize yourself! While finishing your PhD in less time is a great feat, it is important that you are not sacrificing your well-being while doing so.
Key Takeaways
- PhD stands for “doctorate of philosophy” and is generally the highest level of degree a student can earn
- There are many professional and personal benefits to earning a PhD which can lead to a serious return on investment
- A PhD program typically takes 4-7 years to complete. However, it can take longer or shorter depending on personal circumstances and field of study
- With planning and guidance from advisors, students can sometimes complete PhDs in less time
Start your scholarship search
- Vetted scholarships custom-matched to your profile
- Access exclusive scholarships only available to Scholarships360 members
Frequently asked questions about how long it takes to earn a PhD
Do i need to have a master’s degree to get a phd, what is the easiest phd to earn, can i finish my phd earlier than the estimated time frame, what happens if i don’t complete my phd within the expected timeframe, can i work while pursuing a phd, can i accelerate the process of earning a phd, scholarships360 recommended.

10 Tips for Successful College Applications

Coalition vs. Common App: What is the difference?

College Application Deadlines 2023-2024: What You Need to Know
Trending now.

How to Convert Your GPA to a 4.0 Scale

PSAT to SAT Score Conversion: Predict Your Score

What Are Public Ivy League Schools?
3 reasons to join scholarships360.
- Automatic entry to our $10,000 No-Essay Scholarship
- Personalized matching to thousands of vetted scholarships
- Quick apply for scholarships exclusive to our platform
By the way...Scholarships360 is 100% free!
- Skip to main content
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Apply Apply
- Follow Us

How Do You Get a PhD? A Guide to the PhD Timeline

Everyone who considers a doctoral degree knows a Ph.D. is a big commitment.
Not only will it require all your mental energy, focus, and persistence, but it will also require a significant investment of your time. Your particular area of research, your institution’s policies and procedures, and the standard expectations within your field all play a significant role in how long it takes to earn a PhD. The average PhD length is five or six years, while some students may take eight or nine years.
Regardless of how long a PhD program takes, there are some common stages of a PhD that all doctoral students share. These major and essential milestones shape the timeline for earning your doctorate . Read on as we take you through each step and explore the typical steps to a doctorate degree.

How Many Credit Hours for a PhD?
The number of hours that you need to complete your doctoral coursework might depend on several factors: do you already have a master’s degree? Will you earn one en route to the doctorate? Or do you even need one?
Different disciplines and research interests have their own PhD process, but even within your field of study, you may find that institutions have diverse pathways for obtaining that terminal degree. For most, coursework will take anywhere from two to three years to complete.
During this time, students can serve as graduate research or teaching assistants or could even lead their own courses as an instructor. In many degree programs, students develop their potential dissertation topics through their coursework and start to define what their research plans might look like in the next few years.
PhD Qualifying Exam and Comprehensive Exam
Many programs set up academic checkpoints to help keep students on track during their PhD journeys. The timing varies by program, but one of the most common – and possibly most stressful – forms of benchmarking is the PhD comprehensive exam or qualifying exam. Often administered around the end of the student’s coursework, these exams are your chance to demonstrate what you learned in your classes.
Testing is overseen by a committee of faculty from your department. Usually comprised of at least three members, your professors ask questions or assign writing prompts based on your experience in the program thus far. The format is generally a combination of written and oral exams designed to test your expertise in your discipline’s methodologies and significant content areas.
To better prepare yourself, research the number and kind of qualifying benchmarks the program will require in the university catalog before you begin your program. This will allow you and your advisor to effectively plan out the first few years of your degree and give you an idea of how you’ll be evaluated throughout your program.
Dissertation Prospectus and Defense
You may be required to complete and defend a dissertation prospectus before officially becoming a PhD candidate. A prospectus is a document outlining your dissertation plan, which includes an explanation of your research topic, a potential outline of your dissertation, the methodologies you intend to employ, the significance of your research question, and a bibliography including sources that form the foundation of your research.
Your prospectus allows your dissertation advisor to understand the scope of your project. It should be thorough enough that they can provide useful feedback to help shape your research plan. After some revisions, an approved prospectus is the green light to move into the next stage of your PhD.
Advancement to Candidacy
If you have heard the term ABD – “All But Dissertation” – then that means you are in the home stretch of your doctoral program!
Well, sort of…only your dissertation remains!
Dissertation Research and Writing
While you’ve made it through the coursework and qualifying exams, the dissertation is the culminating component of the doctoral degree. At this point, your approved research plan is ready to be set into motion. Depending on your discipline, this could be the stage where you travel extensively to conduct fieldwork, explore archives, or visit labs to collaborate on projects that relate to your dissertation work. For many students, the research phase can take a couple of years, but some may be able to complete it in one.
Writing your dissertation can be one of the most challenging parts of the whole PhD. process. Not only are you condensing years of research into a single cohesive document, but you are also formulating graphs, charts, and other textual references to help clarify your argument. Often, formatting can be a major challenge for many students.
In this stage, it’s most helpful to seek out resources to help you with the writing process. Many universities have dissertation writing workshops where you can learn best practices, as well as support groups where students meet regularly and help keep each other accountable. Most universities also offer competitive dissertation completion grants, supporting students with additional funding so they focus more of their time and effort on completing this undertaking.
Dissertation Defense
Everyone gets nervous about this major rite of passage. It can be difficult to take criticism over something you have poured your heart and soul into for years. Remember, though, that a good advisor will not let you defend if you’re not ready, and you literally wrote the book on your topic!
The dissertation defense is not intended to tear your work apart but rather is your opportunity to prove your expertise to your dissertation committee. Many defenses are open to observers, so you should attend a few in advance of your own, especially within your department, to get a sense of what it’s like.
First, you’ll present the main points of your thesis. Then the committee will ask questions so they can clearly understand your arguments. Finally, they’ll send you out of the room while they deliberate and decide if you pass or not. If all goes well, you’ll be addressed as “Doctor” the next time you walk into the room!
Get Started on Your PhD Journey Today
No matter what your particular timeline looks like as you work toward your doctorate, know that the faculty and other students within your program are frequently a huge source of support — which means you won't do this alone! Additionally, every school has resources to assist Ph.D. students, from libraries to writing centers to dedicated student support services.
If you are excited about beginning your Ph.D. journey, we invite you to request more information or reach out to one of our admissions professionals today. Best of luck as you begin this transformational experience!
learn more about
what it takes to apply to and succeed in a PhD program. Explore our resource — A Guide to Choosing, Applying for, and Thriving in a PhD Program!
hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(3974384, 'aeb4e03d-f8e9-4232-9726-8852204e83e1', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
Request more, information.
Complete the form to reach out to us for more information

Published On
More articles, recommended articles for you, 5 bad reasons not to get a phd.
Whether or not to pursue a PhD is worth it decision, and it’s not unusual to invest time and effort...
Why I Chose a Ph.D. In Civil Engineering: An International Student’s Story
Now, more than ever before, our society has placed increasing demands on the systems and structures...
Spotlight: University Ph.D. Fellow Sara Mosher
SMU is proud to award University Ph.D. Fellowships to some of our most outstanding applicants. Get...
Browse articles by topic
Subscribe to.
Frequently asked questions
How long does it take to get a phd.
This varies by country. In the United States, PhDs usually take between 5–7 years: 2 years of coursework followed by 3–5 years of independent research work to produce a dissertation.
In the rest of the world, students normally have a master’s degree before beginning the PhD, so they proceed directly to the research stage and complete a PhD in 3–5 years.
Frequently asked questions: Graduate school
In the US, most graduate school applications require you to include:
- Transcripts from previous educational institutions
- Standardized test scores (such as the GRE or MCAT)
- A graduate resume
- 2–3 letters of recommendation
- A statement of purpose
Some programs may ask you to write a personal statement in addition to, or instead of, a statement of purpose. You may also be asked to an interview .
Always carefully read the application instructions for the specific program you’re applying to.
Most medical school programs interview candidates, as do many (though not all) leading law and business schools.
In research programs, it depends—PhDs in business usually do, while those in economics normally do not, for example.
Some schools interview everyone, while others only interview their top candidates. Look at the websites of the schools you’re applying to for more information on whether they conduct interviews.
In addition to thinking about your answers for the most commonly asked grad school interview questions , you should reach out to former and current students to ask their advice on preparing and what sort of questions will be asked.
Look back through your resume and come up with anecdotes that you could use for common questions, particularly those that ask about obstacles that you overcame. If you’re applying for a research program, ensure that you can talk about the previous research experience you’ve had.
You should also read as much research in your field as possible. Research the faculty at the schools you’re applying to and read some of their papers. Come up with a few questions that you could ask them.
Graduate schools often ask questions about why you are interested in this particular program and what you will contribute.
Try to stay away from cliche answers like “this is a good program” or “I got good grades in undergrad” and focus instead on the unique strengths of the program or what you will bring to the table. Understand what the program is looking for and come up with anecdotes that demonstrate why you are a good fit for them.
Different types of programs may also focus on different questions:
- Research programs will often ask what topics you’d like to research and who you would like to work with, as well as specific questions about your research background.
- Medical schools are interested in your personal motivation, qualities such as integrity and empathy, and how you’d respond to common ethical dilemmas.
- Business schools will focus on your past work experience and future career prospects, and may be particularly interested in any experience you have managing or working with others.
Some students apply to graduate school straight from undergrad, but it’s also common to go back to school later in life. The ideal time to do so depends on various financial, personal, and career considerations . Graduate school is a big commitment, so you should apply at a time when you can devote your full attention to it.
Your career path may also determine when you should apply. In some career fields, you can easily progress without a graduate degree, while in others—such as medicine, business, and law—it’s virtually impossible to move up the career ladder without a specific graduate degree.
Most graduate school applications for American graduate programs are due in December or January for a September start.
Some types of programs, especially law school, are rolling applications, meaning that the earlier you apply, the earlier you’ll hear back. In this case, you should aim to apply as early as possible to maximize your chances.
Medical school follows a completely separate timeline with much earlier deadlines. If you’re applying for medical school, you should speak to advisors at your university for more information.
A good starting point to aim for is about 18 months before you would start the program, or 6–9 months before the applications are due.
In the first few months of the process, research programs and study for any standardized exams you might need.
You can then begin writing your personal statements and statements of purpose , as well as contacting people to write your letters of recommendation . Ensure that you give recommenders plenty of time to complete their letters (ideally around 2–4 months).
In the US, the graduate school application process is similar whether you’re applying for a master’s or a PhD . Both require letters of recommendation , a statement of purpose or personal statement , a resume or CV , and transcripts. Programs in the US and Canada usually also require a certain type of standardized test—often the GRE.
Outside the US, PhD programs usually also require applicants to write a research proposal , because students are expected to begin dissertation research in the first year of their PhD.
A master’s degree usually has a higher upfront cost, but it also allows you to start earning a higher salary more quickly. The exact cost depends on the country and the school: private universities usually cost more than public ones, and European degrees usually cost less than North American ones. There are limited possibilities for financial aid.
PhDs often waive tuition fees and offer a living stipend in exchange for a teaching or research assistantship. However, they take many years to complete, during which time you earn very little.
This depends on the country. In the United States, you can generally go directly to a PhD with only a bachelor’s degree, as a master’s program is included as part of the doctoral program.
Elsewhere, you generally need to graduate from a research-intensive master’s degree before continuing to the PhD.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
It’s best to ask in person if possible, so first reach out and request a meeting to discuss your graduate school plans.
Let the potential recommender know which programs you’re applying to, and ask if they feel they can provide a strong letter of recommendation . A lukewarm recommendation can be the kiss of death for an application, so make sure your letter writers are enthusiastic about recommending you and your work!
Always remember to remain polite. Your recommenders are doing you a favor by taking the time to write a letter in support of your graduate school goals.
This depends on the program that you are applying for. Generally, for professional programs like business and policy school, you should ask managers who can speak to your future leadership potential and ability to succeed in your chosen career path.
However, in other graduate programs, you should mostly ask your former professors or research supervisors to write your recommendation letters , unless you have worked in a job that corresponds closely with your chosen field (e.g., as a full-time research assistant).
Choose people who know your work well and can speak to your ability to succeed in the program that you are applying to.
Remember, it is far more important to choose someone who knows you well than someone well-known. You may have taken classes with more prominent professors, but if they haven’t worked closely with you, they probably can’t write you a strong letter.
The sections in your graduate school resume depend on two things: your experience, and the focus of the program you’re applying to.
Always start with your education. If you have more than one degree, list the most recent one first.
The title and order of the other sections depend on what you want to emphasize. You might include things like:
- Professional experience
- Voluntary and extracurricular activities
- Publications
- Awards and honors
- Skills and certifications
The resume should aim for a balance between two things: giving a snapshot of what you’ve done with your life so far, and showing that you’re a good candidate for graduate study.
A resume is typically shorter than a CV, giving only the most relevant professional and educational highlights.
An academic CV should give full details of your education and career, including lists of publications and presentations, certifications, memberships, grants, and research projects. Because it is more comprehensive, it’s acceptable for an academic CV to be many pages long.
Note that, outside of the US, resume and CV are often used interchangeably.
No, don’t include your high school courses and grades. The education section should only detail your college education.
If you want to discuss aspects of high school in your graduate school application, you can include this in your personal statement .
A resume for a graduate school application is typically no more than 1–2 pages long.
Note, however, that if you are asked to submit a CV (curriculum vitae), you should give comprehensive details of all your academic experience. An academic CV can be much longer than a normal resume.
Always carefully check the instructions and adhere to any length requirements for each application.
If you’re applying to multiple graduate school programs, you should tailor your personal statement to each application.
Some applications provide a prompt or question. In this case, you might have to write a new personal statement from scratch: the most important task is to respond to what you have been asked.
If there’s no prompt or guidelines, you can re-use the same idea for your personal statement – but change the details wherever relevant, making sure to emphasize why you’re applying to this specific program.
If the application also includes other essays, such as a statement of purpose , you might have to revise your personal statement to avoid repeating the same information.
The typical length of a personal statement for graduate school applications is between 500 and 1,000 words.
Different programs have different requirements, so always check if there’s a minimum or maximum length and stick to the guidelines. If there is no recommended word count, aim for no more than 1-2 pages.
A statement of purpose is usually more formal, focusing on your academic or professional goals. It shouldn’t include anything that isn’t directly relevant to the application.
A personal statement can often be more creative. It might tell a story that isn’t directly related to the application, but that shows something about your personality, values, and motivations.
However, both types of document have the same overall goal: to demonstrate your potential as a graduate student and s how why you’re a great match for the program.
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our team helps students graduate by offering:
- A world-class citation generator
- Plagiarism Checker software powered by Turnitin
- Innovative Citation Checker software
- Professional proofreading services
- Over 300 helpful articles about academic writing, citing sources, plagiarism, and more
Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents . We proofread:
- PhD dissertations
- Research proposals
- Personal statements
- Admission essays
- Motivation letters
- Reflection papers
- Journal articles
- Capstone projects
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker is powered by elements of Turnitin’s Similarity Checker , namely the plagiarism detection software and the Internet Archive and Premium Scholarly Publications content databases .
The add-on AI detector is powered by Scribbr’s proprietary software.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
How to get a PhD?
Interested in obtaining a phd learn more about the steps to earn a phd, careers with phd, list of colleges offering programs and more..
Updated by TCM Staff on 15th April 2021
How to get a PhD: Steps and Requirements Explained
15th April 2021
College Monk — How to Get a PhD
A PhD is a postgraduate doctoral degree awarded to those students who produce an original thesis and make a significant research contribution to their respective field.
PhDs are available for those in a variety of different fields, and it’s often considered the highest and most well-respected degree available. Earning a PhD truly establishes someone as an expert in their field and indicates the deepest level of knowledge on a particular subject.
What is a PhD?
PhD — technically short for Doctor of Philosophy — is a type of doctoral degree, often considered the highest-level degree one can earn.
A PhD is a type of research degree that requires students to do an extensive amount of research and produce an original work, known as a dissertation.
People often use their PhD as a launchpad to pursue a career in academia. But, it’s also a popular option for those pursuing a career in STEM.
Those with PhDs make up a fairly exclusive club. Data from the US Census Bureau shows that fewer than 5% of the population holds a doctorate. And it’s not surprising, considering it often takes up to eight years to achieve this coveted title and requires writing an original dissertation the length of a book.
A PhD is actually just one type of doctoral degree. PhDs are research-focused. The other type of doctorate is application-focused (also known as an applied doctorate).
Source: https://strathsltresearchers.wordpress.com
PhD admission requirements
Not just anyone can earn a PhD. Given how well-respected the title is, it takes a lot of work and very specific criteria to enter a doctoral program.
The most basic requirement that all PhD candidates must have is a bachelor’s degree from an accredited institution. You won’t be accepted without this. You also usually need a high GPA.
Another requirement is a statement of purpose. In this statement, doctoral candidates will describe why they’re seeking a PhD, what they’ve done so far to prepare themselves, and what goals they plan to accomplish later.
Finally, PhD applicants will need several letters of recommendation.
If you’re considering pursuing a PhD, it’s critical that you work to build relationships with professors and mentors who might recommend you. There’s a lot of competition, especially for the top PhD programs, and excellent recommendations will help you to stand out.
Keep in mind that the requirements might vary somewhat from one school to the next, so it’s important to do your research and decide ahead of time where you’ll apply.

Steps to obtain a PhD
Earning a PhD is no easy feat. It takes most students years to do so. Let’s look into the steps someone must take to get a PhD.
Step 1: Complete an undergraduate degree
Before you can take the next step toward your PhD, you’ll first have to receive a bachelor’s degree through an undergraduate program at a reputable university.
This education will provide the foundation for your more advanced coursework later. It’s important that you maintain a high GPA throughout your undergraduate years.
Step 2: Complete a master's program
Once you complete your bachelor’s degree, the next natural step is to pursue a master’s degree.
Graduate school requires that a student take the Graduate Record Examinations (GRE) or the Graduate Management Admissions Test (GMAT). A master’s degree typically takes about two years to achieve, and will be in a particular field of study.
While not technically required for a PhD, most people earn a master’s degree before earning their PhD.
Step 3: Apply for a PhD program
Once you complete your graduate program, it’s time to apply for your PhD program.
There are many doctoral programs to choose from, so it’s important that you research and find the best fit for your field of study.
During the application process, you’ll have to submit the following:
- A completed application
- Undergraduate and graduate transcripts
- Your GMAT or GRE scores
- Letters of recommendation
- A statement of purpose
Step 4: Complete your coursework
When you begin your PhD program, you’ll start by taking your coursework.
As is usually the case with undergraduate and graduate programs, you’ll likely have some required courses and some electives. Usually, students will prepare their own plan of study for the courses they’ll take over the next couple of years.
Step 5: Prepare a research proposal
A research proposal is a document that outlines what, exactly, a PhD student will focus on during their research.
A research proposal should include the major question or questions someone plans to answer with their dissertation, and how exactly they plan to arrive at that answer.
Even though the proposal won’t be a part of your final thesis, it plays a vital role in shaping your PhD.
Step 6: Complete a literature review
The literature review is the first thing you’ll do before starting your project report.
In this review, you’ll conduct an in-depth study of all the research in your field. During this phase, a doctoral student should critically assess the existing literature on their topic and find gaps they may be able to fill with their research.
Step 7: Research and collect results
Once a student has completed their literature review, they’ll do more first-hand research and perform experiments to help answer the questions they’re exploring for their dissertation.
Step 8: Produce a thesis and write a dissertation

Source: https://www.wikihow.com
Once you’ve completed your research and gathered sufficient results, it’s time to write your final thesis and dissertation.
Though the two terms are often used interchangeably, your thesis is the argument or conclusion you’ve arrived at, while your dissertation is where you demonstrate your thesis.
Your dissertation is the culmination of all the research you’ve done. Dissertations are original work and often focus on a newly developed theory. A dissertation is roughly the length of a book, and can often take years to produce.
Step 9: Viva Voce
Viva voce is a Latin phrase that means “with living voice” or “by word of mouth.” It’s also the final — and one of the most important — steps in the process of earning a PhD.
Unlike other degrees, where you take a final exam, a PhD candidate must defend their thesis before a panel of appointment examiners. It’s common for the examiners to ask many questions, and this process can often take several hours.
Once you successfully complete your viva voce, you’ll be awarded your doctorate and can add that coveted “Dr.” to your title.
Online colleges offering PhD programs
Many students choose to pursue a PhD through an online doctoral program for the flexibility and convenience it brings.
Here are a few popular online PhD programs:
What can you do with a PhD?
A PhD is the highest-degree that someone can earn. But after all those years of work, what exactly can you do with your degree?
One of the most common career paths for someone with a PhD is academia. Those with a doctorate degree often go on to teach at universities or spend their careers performing research, not all that different from what they did to earn the degree in the first place.
But academia isn’t the only option for PhD recipients, nor is it the most lucrative.
PhD students often study STEM fields — science, technology, engineering, and math. Those industries are thriving today more than ever, making it a great field for those holding a doctorate.

Source: https://www.jax.org
Some of the highest-paying PhD fields include:
- Information assurance
- Computer science
- Biochemistry and molecular biology
- Organic chemistry
Though academia and STEM may be the most common paths for PhD participants, they’re hardly the only ones. There are many options available to someone with a PhD. Other non-STEM fields include clinical psychology, market research, business development, linguistics, and intelligence.
A doctorate is the highest level of degree someone can achieve. There’s no doubt that it takes a considerable amount of work, and it takes most people years to achieve this recognition.
It’s important to understand these trade-offs before you get started. But once you earn your PhD, you will hold one of the most highly-respected titles in the academic field and have a lot of doors open to you.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. 1) How long does a PhD take?
A. According to CBS news on an average, an American Student takes 8.2 years to complete their Ph.D. This can change according to various courses and in various countries.
2. 2) What qualifications do I need?
A. In US Bachelors degree holders can also apply for Ph.D. For applying in a PhD program one should have completed 16 years of formal education. Qualification in the entrance test is also necessary.
3. 3) Can I take PhD as a part-time?
A. Yes, part-time PhD is possible, and it has a more flexible schedule with classes and degree completion. In some programs, a minimum one-year residency is required. But, part-time PhD will take more time, and managing a part-time PhD will be more challenging.
4. 4) What is M.Phil?
A. A M.Phil qualification is less advanced than that of a PhD. In this, the students are expected to master a content area and it can be mastered in two years. Moreover, the PhD dissertation takes more time than an M.Phil dissertation.
5. 5) What are Financial Aid options available for me?
A. For Ph.D. there are a lot of financial aid opportunities available in the form of Scholarship and loans. Eg: National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Program.

- How Long Does A PhD Take?
- Doing a PhD
Sometimes, just knowing how long a PhD takes can be enough to sway your decision on whether a research degree is for you. So with that in mind, exactly how long does a PhD take?
In the UK, a full-time PhD takes 3 to 4 years to finish whilst a part-time PhD takes twice as long at 6 to 7 years. Alongside these average durations, there are time limits on how long you can be enrolled on to a PhD programme. To discover these limits, the factors which most influence doctoral degree durations and how the UK durations compare to international PhDs, continue reading on.
How Long Does It Take to Get a Full-time PhD?
In the UK, a full-time PhD will typically take you 3 to 4 years. You will usually spend the first three years on the technical aspects of your doctorate. This includes undertaking independent research, designing your research methodology and collecting and analysing data. You will then spend an additional academic year on writing up your PhD thesis and sitting your viva.
How Long Does It Take to Get a Part-time PhD?
In the UK, a part-time PhD will typically take you 6 to 7 years; twice as long as doing a full-time PhD. The reason for this is that as a part-time PhD student, you would dedicate around 20 hours per week to your PhD as opposed to the typical 40 hours full-time students would put into their subject.
How Long Does a Distance Learning PhD Take?
Similarly, distance learning PhD’s take an average of 6 to 7 years to complete. This is because the vast majority of students who undertake a distance learning PhD do so because they can’t relocate closer to the university. Although these commitments will differ, they often mean the student isn’t able to dedicate 40 hours per week to their studies.
Students in STEM disciplines will often take longer to finish a distance learning doctorate degree than those in non-STEM disciplines. This because the progress of a STEM PhD student will be limited by how often they can access a laboratory for experiment work.
How Does Funding Impact a PhD’s Duration?
In reality, the actual time it will take you to complete your PhD degree will depend on your funding situation.
If you’re receiving funding , it will usually only cover you for 3.5 years if you’re studying full-time or for 7 years at half the stipend if you’re studying part-time. Although this could vary slightly, most PhD funding providers, e.g. Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC), follow this timescale as indicated on their ‘ length of PhD studentships’ page. Because of this, most students who obtain scholarships try to complete their PhD within the timeframe of their funding so they don’t incur additional fees which they need to cover themselves.
It’s also worth noting that some funded PhD positions have additional conditions attached to them as part of their eligibility requirements. For example, they may require teaching undergraduate students, hosting laboratory sessions or attend presentations and conferences. This will be especially true if you’re on a Graduate Teaching Assistantship (GTA). Although these shouldn’t add considerable time to the length of a PhD programme, they have the potential to do so if they aren’t managed properly.
As self-funded students cover their own annual tuition fees and other associated costs, how long they’ll spend to complete their PhD project will largely depend on their own personal financial situation. Because of this, most self-funded PhD students find it best to complete their PhD study in the shortest time-frame they can manage.
Are There Deadlines?
Yes – unfortunately, all good things must come to an end! Within the UK, the deadline for your PhD is defined as the last date which you must submit your final thesis by. This date is set by your university’s overall regulations and varies depending on the arrangements of your PhD, e.g. whether it’s full or part time. In the vast majority of cases, the adopted deadlines are four years for full-time PhDs and seven years for part-time PhDs from the date you were officially registered onto your programme, as shown below from the University of Leicester’s registration guidance page .

This time-frame may vary from university to university. For example, the University of Sheffield adopts an additional year for part-time PhDs as shown below.
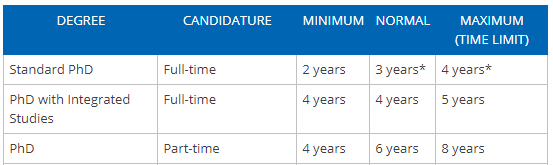
Can I Complete It Faster?
Although it’s possible to complete a full-time PhD in under 3 years, it’s a significant feat that’s rarely heard of. When these feats occur, they’re usually where the doctoral student already has extensive knowledge and experience in their field before undertaking their PhD.
Whilst it’s possible to complete a part-time PhD in under 6 years, it largely depends on your commitments outside your studies. For example, if you have a part-time career alongside your PhD, it’s unlikely that you’ll be able to commit the additional hours required to complete your doctorate a year faster.
However, if instead of a steady part-time job you take on occasional work as a freelancer, you’ll be able to set aside many more hours towards your doctoral degree.
Will Having only A Bachelor’s Degree or Being an International Student Limit My Rate of Progression?
Not at all. While there are benefits to having a Master’s degree such as an additional year of learning and greater research experience due to your fourth-year dissertation project, this doesn’t mean not having one would limit you. A PhD is very different to both Bachelor and Master degrees due to being heavily research-based, therefore, both types of students will have just as much to learn on their way to completing their doctorate.
Similarly, whether you’re an international student will bear no influence on the duration of your PhD.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
How Does This Compare to the Duration of EU and US PhDs?
PhD hosted by universities within the EU, such as those in France, Norway and Spain, have the same programme structure as those within the UK. As a result, there are no noticeable differences in the time to complete a doctorate between UK and EU institutions.
However, this is not the case in the US. Compared to PhDs conducted within the UK or EU, PhDs conducted within the US take considerably longer to obtain. According to a 2017 study conducted by the National Science Foundation, a US government agency which supports research and higher education, the average time to get a PhD within the US is 5.8 years. Besides this, the average completion time can further increase depending on the disciplines. For example, they found doctorates within the humanities and arts to take an average of 7.1 years to achieve.
The primary reason for this difference is the way PhD degrees are structured within the United States. As mentioned previously, PhDs conducted within UK and EU universities are essentially broken into two sections – one covering the analytical aspects and the other covering the writing up aspects. However, within the US, doctorate programmes comprise additional sections. PhD students are first required to undertake 2 to 3 years of courses, which cover a broad range of topics related to their schools’ discipline. This is then followed by coursework and several examinations, which only once passed can the PhD candidate then start working on their research project and dissertation.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD in Psychology?
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Ariel Skelley/Getty Images
- How Long Will It Take?
Before You Earn PhD in Psychology
Which type of degree should you get, can you finish your degree early.
Just how long does it take to get a PhD in psychology? The answer can vary depending on your program, educational background, and academic schedule. In general, most PhD psychology programs take anywhere from five to seven years to complete.
Learning more about what it takes to get a doctorate in psychology can help you better plan your educational and career journey.
At a Glance
Getting a PhD in psychology can take several years of graduate study. If you are thinking about becoming a psychologist, research your degree options to figure out what type of degree you need and how long it will take to enter your chosen profession. No matter what you decide, plan to spend anywhere from three to seven years in graduate school to earn a doctorate.
How Long Will It Take to Get a Doctorate Degree?
How long it takes to get a doctorate in psychology depends on various factors, including the type of degree you have selected, your educational background, and the individual doctorate program in which you have enrolled.
Most doctorate programs in psychology take between four to seven years to complete.
PhD in Psychology
Most PhD programs require at least five to seven years to complete. These programs often follow a scientist-practitioner model that trains professionals both in research and clinical practice.
In addition to regular coursework, you may also be expected to complete an internship or supervised residency. The program usually culminates in completing an original research project or dissertation.
PsyD Degree
Most PsyD programs require between four to six years to complete. A PsyD is a degree designed to train professionals to apply psychological knowledge to treating and helping people in real-world settings.
According to the American Psychological Association, PsyD programs focus more on applying psychological science, usually in the form of service.
Most EdD programs require between three to five years to complete. EdD programs are often focused on psychology, counseling, or counselor education. They explore topics that involve both education and psychology.
It is important to note that many applicants to EdD programs already hold a master's degree in a related field. This differs from applicants to PhD and PsyD programs, who often begin their program of study with a bachelor's degree.
Before you begin your academic journey, it is a good idea to look at just how long it will take you to complete your degree. The amount of time it will take can depend upon various factors, including:
- Your chosen specialty area
- The program you select
- The course load you can take each semester
A doctorate-level degree in psychology is required to work in many job areas, including as a licensed clinical psychologist or counseling psychologist. According to the American Psychological Association, a doctorate degree is also often required in fields such as school psychology or health psychology .
So how long does it take to get a PhD in Psychology ? First, it is essential to realize that the degree requirements can vary depending on the field that you decide to pursue. A PhD, or Doctor of Philosophy degree is not necessarily your only option. In some cases, you might want also to consider the PsyD (Doctor of Psychology) or the EdD (Doctor of Education) degree options.
The PhD, PsyD, and EdD are all great options, but don't let how long it takes to complete be the primary deciding factor. Before you decide to get a doctorate degree, start by deciding which type of degree is most suited to your professional goals.
If you want to conduct research:
A PhD in Psychology tends to focus on a research-based model of education. People with a PhD in Psychology are qualified for a wide range of teaching, research, and clinical positions in colleges, universities, hospitals, government offices, and private mental health practices.
If you want to treat mental health issues:
The PsyD degree option generally focuses on a practitioner-based model of education. Individuals with a PsyD degree can also teach or conduct psychology research, but they frequently work in applied settings to provide direct mental health services.
If you want to apply psychology to help students:
Finally, there is also a third doctorate option that you might also want to consider depending on your career goals. If you are interested in working as a school psychologist or in a related educational field, the EdD, or Doctor of Education, is a possible option.
Despite the years of work, earning your PhD, PsyD, or EdD can be well worth the effort. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics suggests that workers with a doctoral or education specialist degree in clinical, counseling, and school psychology will find the strongest job opportunities.
Generally, if you have a strong background in psychology and have completed all of the necessary prerequisites, you can finish your doctorate sooner than students who have not taken the prerequisite courses.
Carefully planning your degree can also help ensure you complete the program requirements quickly.
Be sure you have a clear idea of what you want to do with your psychology degree once you've completed it. Do you want to teach, or is research more appealing to you? Are you interested in seeing clients, or are you planning to combine your training in psychology with another field, such as law or medicine?
If you need help deciding, make an important with an academic advisor at your school. They can help you explore your options and answer any questions you may have.
What This Means For You
No matter the degree you decide to pursue, earning a doctorate in psychology requires a significant investment of time, money, and effort. Because of this, it is essential to carefully consider your goals before deciding on a graduate program. You should also think about whether you need a doctorate or if a master's might be more appropriate.
Gee DG, DeYoung KA, McLaughlin KA, et al. Training the next generation of clinical psychological scientists: A data-driven call to action . Annu Rev Clin Psychol . 2022;18:43-70. doi:10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-081219-092500
Loyola University. Can I get my Psy.D. without a Master's in Psychology?
American Psychological Association. Doctoral degrees in psychology: How are they different, or not so different ?
Franklin University. Is getting a Doctorate in Education worth it?
American Psychological Association. Frequently asked questions about graduate school .
Bureau of Labor Statistics. Psychologists . Occupational Outlook Handbook .
Carr, A. Clinical Psychology: An Introduction . London: Routledge; 2012.
Kuther, TL. The Psychology Major's Handbook . Boston, MA: Cengage Learning; 2016.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Crimson Careers
- For Employers
- Harvard College
- Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts & Sciences
- Harvard Extension School
- Premed / Pre-Health
- Families & Supporters
- Faculty & Staff
- Prospective Students
- First Generation / Low Income
- International Students
- Students of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Undocumented Students
- Explore Interests & Make Career Decisions
- Create a Resume/CV or Cover Letter
- Expand Your Network
- Engage with Employers
- Search for a Job
- Find an Internship
- January Experiences (College)
- Find & Apply for Summer Opportunities Funding
- Prepare for an Interview
- Negotiate an Offer
- Apply to Graduate or Professional School
- Access Resources
- AI for Professional Development and Exploration
- Arts & Entertainment
- Business & Entrepreneurship
- Climate, Sustainability, Environment, Energy
- Government, Int’l Relations, Education, Law, Nonprofits
- Life Sciences & Health
- Technology & Engineering
- Still Exploring
- Talk to an Advisor
How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree?
- Share This: Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on Facebook Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on LinkedIn Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on X
Earning a Ph.D. from a U.S. grad school typically requires nearly six years, federal statistics show.

(CAIAIMAGE/TOM MERTON/GETTY IMAGES)
A Ph.D. is most appropriate for someone who is a “lifelong learner.”
Students who have excelled within a specific academic discipline and who have a strong interest in that field may choose to pursue a Ph.D. degree. However, Ph.D. degree-holders urge prospective students to think carefully about whether they truly want or need a doctoral degree, since Ph.D. programs last for multiple years.
According to the Survey of Earned Doctorates, a census of recent research doctorate recipients who earned their degree from U.S. institutions, the median amount of time it took individuals who received their doctorates in 2017 to complete their program was 5.8 years. However, there are many types of programs that typically take longer than six years to complete, such as humanities and arts doctorates, where the median time for individuals to earn their degree was 7.1 years, according to the survey.
Some Ph.D. candidates begin doctoral programs after they have already obtained master’s degrees, which means the time spent in grad school is a combination of the time spent pursuing a master’s and the years invested in a doctorate. In order to receive a Ph.D. degree, a student must produce and successfully defend an original academic dissertation, which must be approved by a dissertation committtee. Writing and defending a dissertation is so difficult that many Ph.D. students drop out of their Ph.D. programs having done most of the work necessary for degree without completing the dissertation component. These Ph.D. program dropouts often use the phrase “ all but dissertation ” or the abbreviation “ABD” on their resumes.
According to a comprehensive study of Ph.D. completion rates published by The Council of Graduate Schools in 2008, only 56.6% of people who begin Ph.D. programs earn Ph.D. degrees.
Ian Curtis, a founding partner with H&C Education, an educational and admissions consulting firm, who is pursuing a Ph.D. degree in French at Yale University , says there are several steps involved in the process of obtaining a Ph.D. Students typically need to fulfill course requirements and pass comprehensive exams, Curtis warns. “Once these obligations have been completed, how long it takes you to write your dissertation depends on who you are, how you work, what field you’re in and what other responsibilities you have in life,” he wrote in an email. Though some Ph.D. students can write a dissertation in a single year, that is rare, and the dissertation writing process may last for several years, Curtis says.
[ READ: What Is a Doctorate or a Doctoral Degree? ]
Curtis adds that the level of support a Ph.D. student receives from an academic advisor or faculty mentor can be a key factor in determining the length of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. program. “Before you decide to enroll at a specific program, you’ll want to meet your future advisor,” Curtis advises. “Also, reach out to his or her current and former students to get a sense of what he or she is like to work with.”
Curtis also notes that if there is a gap between the amount of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. and the amount of time a student’s funding lasts, this can slow down the Ph.D. completion process. “Keep in mind that if you run out of funding at some point during your doctorate, you will need to find paid work, and this will leave you even less time to focus on writing your dissertation,” he says. “If one of the programs you’re looking at has a record of significantly longer – or shorter – times to competition, this is good information to take into consideration.”
Pierre Huguet, the CEO and co-founder of H&C Education, says prospective Ph.D. students should be aware that a Ph.D. is designed to prepare a person for a career as a scholar. “Most of the jobs available to Ph.D. students upon graduation are academic in nature and directly related to their fields of study: professor, researcher, etc.,” Huguet wrote in an email. “The truth is that more specialization can mean fewer job opportunities. Before starting a Ph.D., students should be sure that they want to pursue a career in academia, or in research. If not, they should make time during the Ph.D. to show recruiters that they’ve traveled beyond their labs and libraries to gain some professional hands-on experience.”
Jack Appleman, a business writing instructor, published author and Ph.D. candidate focusing on organizational communication with the University at Albany—SUNY , says Ph.D. programs require a level of commitment and focus that goes beyond what is necessary for a typical corporate job. A program with flexible course requirements that allow a student to customize his or her curriculum based on academic interests and personal obligations is ideal, he says.
[ READ: Ph.D. Programs Get a Lot More Practical. ]
Joan Kee, a professor at the University of Michigan with the university’s history of art department, says that the length of time required for a Ph.D. varies widely depending on what subject the Ph.D. focuses on. “Ph.D. program length is very discipline and even field-specific; for example, you can and are expected to finish a Ph.D, in economics in under five years, but that would be impossible in art history (or most of the humanities),” she wrote in an email.
Jean Marie Carey, who earned her Ph.D. degree in art history and German from the University of Otago in New Zealand, encourages prospective Ph.D. students to check whether their potential Ph.D. program has published a timeline of how long it takes a Ph.D. student to complete their program. She says it is also prudent to speak with Ph.D. graduates of the school and ask about their experience.
Bennett urges prospective Ph.D. students to visit the campuses of their target graduate programs since a Ph.D. program takes so much time that it is important to find a school that feels comfortable. She adds that aspiring Ph.D. students who prefer a collaborative learning environment should be wary of graduate programs that have a cut-throat and competitive atmosphere, since such students may not thrive in that type of setting.
[ READ: 4 Fields Where Doctorates Lead to Jobs. ]
Alumni of Ph.D. programs note that the process of obtaining a Ph.D. is arduous, regardless of the type of Ph.D. program. “A Ph.D. is a long commitment of your time, energy and financial resources, so it’ll be easier on you if you are passionate about research,” says Grace Lee, who has a Ph.D. in neuroscience and is the founder and CEO of Mastery Insights, an education and career coaching company, and the host of the Career Revisionist podcast.
“A Ph.D. isn’t about rehashing years of knowledge that is already out there, but rather it is about your ability to generate new knowledge. Your intellectual masterpiece (which is your dissertation) takes a lot of time, intellectual creativity and innovation to put together, so you have to be truly passionate about that,” Lee says.
Erin Skelly, a graduate admissions counselor at the IvyWise admissions consulting firm, says when a Ph.D. students struggles to complete his or her Ph.D. degree, it may have more to do with the student’s academic interests or personal circumstances than his or her program.
“The time to complete a Ph.D. can depend on a number of variables, but the specific discipline or school would only account for a year or two’s difference,” she wrote in an email. “When a student takes significantly longer to complete a Ph.D. (degree), it’s usually related to the student’s coursework and research – they need to take additional coursework to complete their comprehensive exams; they change the focus of their program or dissertation, requiring extra coursework or research; or their research doesn’t yield the results they hoped for, and they need to generate a new theory and conduct more research.”
Skelly warns that the average completion time of a Ph.D. program may be misleading in some cases, if the average is skewed based on one or two outliers. She suggests that instead of focusing on the duration of a particular Ph.D. program, prospective students should investigate the program’s attritition and graduation rates.
“It is worthwhile to look at the program requirements and the school’s proposed timeline for completion, and meet current students to get their input on how realistic these expectations for completion are,” Skelly says. “That can give you an honest idea of how long it will really take to complete the program.”
Searching for a grad school? Access our complete rankings of Best Graduate Schools.
What Is a Doctorate Degree?
A doctorate is usually the most advanced degree someone can get in an academic discipline, higher education experts say.
What Is a Doctorate?

Getty Images
It's unwise to apply to a doctoral program if you don't have a clear idea of how you might use a doctorate in your career.
In many academic disciplines, the most advanced degree one can earn is a doctorate. Doctorate degree-holders are typically regarded as authorities in their fields, and many note that a major reason for pursuing a doctorate is to increase professional credibility.
"If someone wants to be respected as an expert in their chosen field, and also wants to have a wider array of options in research, writing, publishing, teaching, administration, management, and/or private practice, a doctorate is most definitely worth considering," Don Martin, who has a Ph.D. in higher education administration , wrote in an email.
A doctoral degree is a graduate-level credential typically granted after multiple years of graduate school, with the time-to-degree varying depending on the type of doctoral program, experts say.
Earning a doctorate usually requires at least four years of effort and may entail eight years, depending on the complexity of a program's graduation requirements. It also typically requires a dissertation, a lengthy academic paper based on original research that must be vetted and approved by a panel of professors and later successfully defended before them for the doctorate to be granted.
Some jobs require a doctorate, such as certain college professor positions, says Eric Endlich, founder of Top College Consultants, an admissions consulting firm that helps neurodivergent students navigate undergraduate and graduate school admissions.
Endlich earned a Doctor of Philosophy degree, commonly known as a Ph.D., from Boston University in Massachusetts. He focused on psychology and notes that a doctoral degree is generally required to be a licensed psychologist.
"Since a Ph.D. is a research-focused degree, it can be advantageous to those seeking high-level research positions in scientific fields such as astrophysics or biotechnology," he says.
How Long it Takes to Get a Doctorate Degree
Martin, founder and CEO of Grad School Road Map, an organization that helps grad school applicants navigate the admissions process, says obtaining a doctorate is often a lengthy endeavor.
"Typically it can take between four and six years to complete any doctoral program," he says. "If comprehensive examinations and a dissertation are part of the graduation requirements, it may take a year or two longer. There is no standard amount of time – some students take seven to 10 years to finish."
Endlich says doctoral degree hopefuls should be aware that completing a dissertation may take a long time, especially if unexpected hurdles arise.
"My dissertation, for example, involved recruiting college students to complete questionnaires, and it took much longer than I anticipated to recruit enough subjects for my study," he says.
The standards for a dissertation, which include the proposal and research, are rigorous and usually involve a review and approval by a faculty committee, says Hala Madanat, vice president for research and innovation at San Diego State University in California.
"As part of dissertation requirements, some programs will require publication of the research in high-impact peer-reviewed journals," Madanat wrote in an email.
Types of Doctoral Degree Programs
According to professors and administrators of doctoral programs, there are two types of doctorates.
Doctor of Philosophy
A doctor of philosophy degree is designed to prepare people for research careers at a university or in industry, and teach students how to discover new knowledge within their academic discipline. Ph.D. degrees are offered in a wide range of academic subjects, including highly technical fields like biology , physics, math and engineering; social sciences like sociology and economics; and humanities disciplines like philosophy.
A Ph.D. is the most common degree type among tenure-track college and university faculty, who are typically expected to have a doctorate. But academia is not the only path for someone who pursues a Ph.D. It's common for individuals with biology doctorates to work as researchers in the pharmaceutical industry, and many government expert positions also require a Ph.D.
Professional or clinical doctorates
These are designed to give people the practical skills necessary to be influential leaders within a specific industry or employment setting, such as business, psychology , education or nursing . Examples of professional doctoral degrees include a Doctor of Business Administration degree, typically known as a DBA; a Doctor of Education degree, or Ed.D.; and a Doctor of Nursing Practice degree, or DNP.
A law degree, known as a juris doctor or J.D., as well as a Doctor of Medicine degree, or M.D., are also considered professional doctorates.
How to Get a Doctorate
Getting a doctorate is challenging. It ordinarily requires a series of rigorous classes in a field of study and then passage of a qualification exam in order to begin work on a dissertation, which is the final project.
Dissertations are difficult to write, says David Harpool, vice president of graduate and online programs at Newberry College in South Carolina. Some research indicates that only about half of doctoral students go on to finish their degree, and a main reason is that many never finish and successfully defend their dissertation
"Many of them are in programs that permit them to earn a master’s on the way to a doctorate," Harpool, who earned a Ph.D. from Saint Louis University in Missouri and a J.D. from the University of Missouri , wrote in an email. "The transition from mastering a discipline to creating new knowledge (or at least applying new knowledge in a different way), is difficult, even for outstanding students."
Learn about how M.D.-Ph.D. programs
There is a often a "huge shift in culture" at doctoral programs compared to undergraduate or master's level programs, says Angela Warfield, who earned a Ph.D. in English from the University of Iowa.
Doctoral professors and students have more of a collaborative relationship where they function as colleagues, she says. And there's pressure on each student to produce "significant and original research."
Many full-time doctoral students work for the school as researchers or teaching assistants throughout their program, so time management is crucial to avoid burnout. However, the dissertation "is by far the biggest battle," she says. The goal is to avoid an "ABD," she says, meaning "all but dissertation."
"In my writing group, we had two motivational slogans: 'ABD is not a degree,' and 'a good dissertation is a done dissertation,'" Warfield, now the principal consultant and founder of admissions consulting firm Compass Academics, wrote in an email.
How Are Doctorate Admissions Decisions Made?
Admissions standards for doctoral programs vary depending on the type of doctorate, experts say.
The quality of a candidate's research is a distinguishing factor in admissions decisions, Madanat says. Meanwhile, leaders of clinical and professional doctorate programs say that the quality of a prospective student's work experience matters most.
Doctoral programs typically expect students to have a strong undergraduate transcript , excellent letters of recommendation and, in some cases, high scores on the Graduate Record Examination , or GRE, Endlich says.
"The size of the programs may be relatively small, and universities need to be sure that applicants will be able to handle the demands of their programs," he says.
Because professional doctorates often require students to come up with effective solutions to systemic problems, eligibility for these doctorates is often restricted to applicants with extensive first-hand work experience with these problems, according to recipients of professional doctorates.
In contrast, it's common for Ph.D. students to begin their programs immediately after receiving an undergraduate degree. The admissions criteria at Ph.D. programs emphasize undergraduate grades, standardized test scores and research projects , and these programs don't necessarily require work experience.
Admissions decisions may also depend on available funding, says Madanat, who works with doctoral students to provide funding, workshops and faculty support to help their research.
Who Is a Good Fit for a Doctoral Program?
Doctoral degree hopefuls "should be interested in making a deep impact on their field, open-minded, eager to learn, curious, adaptable and self-motivated," Madanat says. "Doctoral programs are best suited for those whose goals are to transform and change the fields they are studying and want to make a difference in the way the world is."
Someone who loves to study a subject in great depth, can work alone or in teams, is highly motivated and wants to develop research skills may be a good candidate for a doctoral program, Endlich says.
Because of the tremendous effort and time investment involved in earning a doctorate, experts say it's foolish to apply to a doctoral program if it's unclear how you might use a doctorate in your career.
"The students are being trained with depth of knowledge in the discipline to prepare them for critical thinking beyond the current state of the field," Madanat says. "Students should consider the reasons that they are pursuing a doctoral degree and whether or not it aligns with their future professional goals, their family circumstances and finances."
Rachel D. Miller, a licensed marriage and family therapist who completed a Ph.D. degree in couples and family therapy at Adler University in Illinois in 2023, says pursuing a doctorate required her to make significant personal sacrifices because she had to take on large student loans and she needed to devote a lot of time and energy to her program. Miller says balancing work, home life and health issues with the demands of a Ph.D. program was difficult.
For some students, the financial component may be hard to overlook, Warfield notes.
"Student debt is no joke, and students pursuing graduate work are likely only compounding undergraduate debt," she says. "They need to really consider the payoff potential of the time and money sacrifice."
To offset costs, some programs are fully funded, waiving tuition and fees and providing an annual stipend. Some offer health insurance and other benefits. Students can also earn money by teaching at the university or through fellowships, but those adding more to their plate should possess strong time management skills, experts say.
"Graduate school, and higher education in general, can be brutal on your physical and mental health," Miller wrote in an email.
But Miller says the time and effort invested in her doctoral program paid off by allowing her to conduct meaningful research into the best way to provide therapy to children affected by high-conflict divorce and domestic violence. She now owns a therapy practice in Chicago.
Miller urges prospective doctoral students to reflect on whether getting a doctorate is necessary for them to achieve their dream job. "Really know yourself. Know your purpose for pursuing it, because that's what's going to help carry you through."
Searching for a grad school? Access our complete rankings of Best Graduate Schools.
30 Fully Funded Ph.D. Programs

Tags: graduate schools , education , students , academics
You May Also Like
Mba programs that lead to good jobs.
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 10, 2024

B-Schools With Racial Diversity
Sarah Wood April 10, 2024

Law Schools That Are Hardest to Get Into
Sarah Wood April 9, 2024

Ask Law School Admissions Officers This
Gabriel Kuris April 9, 2024

Grad School Housing Options
Anayat Durrani April 9, 2024

U.S. News Ranks Best Graduate Schools

MBA Scholarships
Sammy Allen April 4, 2024

Special Master's Programs and Med School
Renee Marinelli, M.D. April 2, 2024

15 Famous Fulbright Scholars
Cole Claybourn April 1, 2024

When to Expect Law School Decisions
Gabriel Kuris April 1, 2024

- Guide to Applying for Graduate School
The process of preparing for and applying to a PhD program can be overwhelming. The University of Pennsylvania has created this webpage to help prospective PhD students think through the process so you can put together a strong application.
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) is the highest degree one may obtain within a particular field of study. This ranges from studies in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (STEM) fields; Social Science fields such as Education, Economics, Political Science, and Sociology; as well as Humanities fields such as English, History, Music, Philosophy, and more. The PhD degree aims to prepare people to think critically, develop research, and produce scholarship that may be used for further research or implementation . The PhD historically prepared students to take on faculty roles in colleges and universities, and that is still the goal for many students pursuing the PhD. However, today the PhD is a sought-after degree in many other industries including pharmaceutical research, arts organizations and other nonprofits, publishing, government policy, big tech, finance, and more.
- Who can apply to a PhD program? PhD education is available to people from various educational, occupational, socioeconomic, and demographic backgrounds.
- Who should get a PhD? People interested in uncovering new ideas, solutions, or processes within a specific area of study through conducting independent research.
- Why is it important for diverse candidates to become PhD holders? Our world thrives on heterogeneous ideas and experiences, which is why it is indispensable to include students with diverse perspectives in our PhD programs. These students will generate important and original research.
Most PhD programs are fully funded, meaning that for a specific number of years, the program will pay for your tuition and fees and health insurance, as well as provide you with a stipend for living expenses . The structure of this funding varies by field. Below is an outline of general funding information as well as trends according to field of study.
- Teaching Assistantships or Research Assistantships: Part-time service that provides teaching and research training opportunities within your area of study.
- Funding packages provided through faculty research grants: Many STEM fields fund students through research grants awarded to faculty. In these cases, students perform research alongside the faculty.
- Fellowships: Internal or external merit-based funding. Some fellowships require an application while others are given via nomination. Educational institutions typically have a resource listing fellowship opportunities. Winning a competitive fellowship looks good on your resume.
- Grants: Requires an application with supporting materials of either your grades, scholarly work, and/or anticipated research. These are available through internal and external means. Grants greatly vary so be sure to always understand the requirements. Educational institutions typically have a resource listing grant opportunities. Winning a competitive grant looks good on your resume.
- Employment: For example, serving as a residential advisor, on-campus jobs, etc. Some PhD programs restrict additional employment, so be sure to check before applying for jobs.
- The funding opportunities described here often can be combined.
Choosing a school or program that provides the most potential funding may be a challenging decision. The value of the same amount of funding will differ depending on the cost of living in different geographic locations. Admitted applicants should investigate cost-of-living tools (available on the web) and be sure to understand how their funding will be structured. Ask questions when you are admitted, such as:
- Could you share more about your program’s funding mechanism?
- For how long is funding guaranteed? How does that compare to the average time-to-completion? Historically, what percentage of students have received funding beyond the guaranteed funding package?
- Does funding cover tuition, fees, books, health insurance?
- Does the funding rely on teaching, research, or other service? How much and for how long?
Choosing a program for your studies is a personal decision that should reflect not only your research interests, but your work style, and interests outside of the classroom. Here we have identified five key tips to consider when selecting schools.
- Ask about which programs are strong in your area of interest, which have high completion rates, and which have career outcomes that align with your goals.
- Explore the websites of the professional academic associations in the field(s) that interest you. Many will have a directory of doctoral programs and other resources for graduate students. For example, see the American Economic Association’s list of graduate programs and their preparing for graduate school page .
- Conduct a general internet search with terms related to your research interest.
- Determine your geographic and personal preferences. Does the area meet your community needs? Is it important that the university aligns with your sociopolitical values? Do you prefer a large city or a smaller/college town? Is there a particular region(s) that has better access to resources needed to conduct your research?
- Access your current or former university career center. These services are often still available for former students!
- As you narrow your choices, try to identify at least 3 faculty in the programs of interest with whom you’d like to study. Also note how many of them have tenure. If relevant, research which of those faculty are taking on advisees in your year of matriculation.
- Read articles from faculty with similar research interests.
- Note the number of awards, publications, and service activities of faculty.
- Identify research opportunities funded by both your program and university at large.
- Connect with current and former students in the program for informational interviews.
- Connect with campus Diversity Offices.
- Whenever possible, before submitting your applications, make an appointment to visit the campuses and department(s) that interest you.
- Use LinkedIn to see what graduates of your program are doing and how they are involved in their communities.
- Estimate your feasible cost of living by geographic location and compare to the funding package offered.
- Consider availability of health insurance, childcare, housing, transportation, and other fringe benefits.
- Connect with a local bank or your prospective university’s financial services office for budgeting, savings, and other financial wellness advice.
- Research the career outcomes for PhD graduates from the institutions that interest you in your specific field.
- Your First Year in a Ph.D. Program
- What Does Academic Success Mean and How to Achieve it? (STEM)
- Pathways to Science (STEM)
- 7 Advantages PhDs Have Over Other Job Candidates (Industry)
- During your undergraduate/master’s education, you should pursue coursework and/or research that will prepare you for the higher expectations of a PhD program; for example, taking a research methods course, pursuing a summer research experience, or conducting research with a professor at your home institution.
- Identify instructors who could write a letter of recommendation. Share with those instructors your interest in doctoral studies; faculty can be excellent resources for advice as well as recommendations!
- Experiences outside of higher education can also strengthen your PhD application. These may range from project management to volunteer work.
- Develop soft or hard skills. A soft skill that is most useful from the first day of your PhD program is networking. This is necessary not only for meeting other students but also to find collaborators with similar research interests and selecting faculty for your dissertation committee. Learning how to negotiate will also serve you well when approaching collaborative projects. Hard skills related to your field might include learning statistical analysis software, economic theory, a foreign language, or search engine optimization. In short, identify a few soft and hard skills that you can familiarize yourself with prior to your program’s start date.
- Finally, prepare by identifying leading researchers and practitioners in your field , exploring peer-reviewed literature and/or publications, and gain familiarity with research methods.
- Typically, PhD applications are due 10-12 months in advance of the program’s start date (i.e. apply in November to start the following September). A good rule of thumb is to begin your application process 6 months before the deadline.
- The availability of reduced application fees or fee waivers varies and sometimes depends on financial status and/or experiences (AmeriCorps, National Society of Black Engineers, attending certain conferences, etc.). If you are interested in a reduced fee or waiver, reach out to the program coordinator for details.
- Be sure to address all the specific questions/topics in the statement prompt.
- Clearly state why you want to pursue a PhD.
- Propose your research interest.
- Identify the faculty you’d like to study under.
- Discuss the unique qualities/experiences you offer to the program/school.
- Outline what you hope to do with your degree.
- Ask for recommendation letters early in the process, at least 2-4 weeks before the deadline. A good letter takes time to write!
- Provide recommenders with your resume, information about the program, your statement of purpose and/or information about your research interests and research goals.
- Consider your current/former instructors, supervisors, colleagues. These should be people who can speak to your work ethic, academic abilities, and research interests.
- Test scores (i.e. TOEFL, GRE, GMAT, etc.) may or may not be required.
- All transcripts including those for coursework completed abroad and transfer credits. Some programs require official transcripts, which take longer to procure.
- Resume/Curriculum Vitae (CV)
- Writing sample (field dependent): Include a graduate-level sample and update any statements, statistics, etc. as needed. It is highly encouraged that you edit your previous work.
- Diversity statement: Many institutions offer an optional short statement where students can expand on their diverse backgrounds and experiences that may contribute to the diversity interests/efforts of the school.
- Dress professionally, even if the interview is virtual. You don’t necessarily need to wear a suit but dress pants/skirt and a blouse/button down shirt would be appropriate.
- Develop an engaging elevator pitch, a 30-60 second summary of your research interests and what you hope to gain by becoming a student at that particular university. Practice your pitch with a career counselor, faculty advisor, or friends, and ask for honest feedback.
- Prepare 2-3 questions to ask during the interview. These could include questions about program expectations, the experience and success of their PhD students, and (academic/financial/mental health) support for PhD students.
- Some interview programs will include multiple activities including a social event. Be sure to maintain a professional attitude: do not drink too much and keep conversation on academic/professional topics.
- This is also your opportunity to decide whether this campus is a good fit for you.
- Academia Insider is a good resource.
Unlike undergraduate and master’s level education, coursework is just one component of the degree. A PhD comes with additional expectations: you must independently conduct scholarly research in your field of study, train in specific activities such as teaching or lab/field research, pass “milestone” requirements along the way, such as comprehensive exams, and complete the process by writing a dissertation. Furthermore, some fields require you to write multiple articles (number varies by field/program) for conference presentation and/or peer-reviewed publication.
There are other important elements as well:
- Student/Advisor relationship. This is one of the most valuable relationships you can have as a PhD student. Your faculty advisor not only assists you with learning how to approach your research topic, but also typically serves as the lead supervisor of your dissertation research and writing, and ideally mentors you throughout the PhD experience. The selection process of choosing your advisor varies so be sure to know what is expected of you as a student and what is expected of the faculty member. Whenever possible, it is important to align your personality and work style with that of your faculty advisor. Many universities publish expectations for the PhD student/faculty advisor relationship; AMP’ed is Penn’s guide.
- Other relationships: Your faculty advisor is far from the only important person during your PhD career. Other faculty members will also serve on your dissertation committee and be potential mentors. Students in your program can also provide good advice and guidance along the way.
- Coursework: Most programs have a number of required courses all students must take regardless of research interests. Once you have finished this requirement, the classes you choose should closely align with your research topic. Choose courses that will help you learn more about your dissertation topic and research methods. It is a good idea to discuss elective course selection with your advisor.
- The dissertation is a large-scale, written document that explores a narrow research topic of your choice. It is the final step before receiving your degree and must be presented and “defended” to your dissertation committee (made up of faculty members) for approval. Defending means that you have to answer in-depth questions about your topic. While this might sound daunting, the dissertation is simply a demonstration of all the knowledge and expertise you have acquired through your PhD education.
- Networking comes in many forms and includes connections with your fellow classmates, faculty members, and scholarly community. Formal networking events typically take place at academic conferences, where scholars and students present research. Increasing your academic circle will not only allow you to have study buddies, but offer you the opportunity to collaborate on articles or even gain employment. Your school’s career center can provide best practices for effective networking.
Explore graduate programs at the University of Pennsylvania and click on the programs that interest you to learn more about admissions and academic requirements.
Upcoming Penn recruitment events include:
- Fontaine Fellows Recruitment Dinner (by invitation only): every March
- IDDEAS@Wharton (Introduction to Diversity in Doctoral Education and Scholarship): April 18-19, 2024. Deadline to apply is January 31.
- DEEPenn STEM (Diversity Equity Engagement at Penn in STEM): October 11-13, 2024. Application opens in March 2024.
- DivE In Weekend (Diversity & Equity Initiative for Mind Research): Fall 2024
National conferences to explore:
- The Leadership Alliance supports students into research careers
- McNair Scholar Conferences
- SACNAS , the largest multidisciplinary and multicultural STEM diversity event in the U.S.
- ABRCMS , the annual biomedical research conference for minoritized scientists
- The PhD Project for students interested in business PhD programs

How Long Does it Take To Get A PhD? Doctorate Degree Timeline
Starting a PhD means you’re ready for a big academic adventure, full of tough challenges and exciting discoveries.
If you’re thinking about going for it, you’re probably wondering just how much time you’ll need to commit to this big goal.
For full-time PhD students, the journey typically take 3-6 years. However, if you’re juggling other commitments and opt for a part-time PhD, the timeline can extend to 7 years to complete, sometimes more.
This article breaks down what the PhD journey looks like, what can make it longer or shorter, and some tips on how to make it through.
If you’re curious about how long it’ll take to add ‘Dr.’ before your name, you’re in the right place. Let’s dive into the world of PhD timelines!
How Long Does It Take To Get A PhD?
The answer here isn’t straightforward, as it hinges on various factors, including:
- the discipline,
- the institution, and
- whether you’re a full-time or part-time student.
For full-time PhD students, the journey typically take 3-6 years. However, if you’re juggling other commitments and opt for a part-time PhD, the timeline can extend to 7 years to complete, sometimes more.

Distance learning PhD programs offer flexibility but similarly require a substantial time commitment, often mirroring the length of part-time studies.
The heart of a doctoral program is the dissertation, a rigorous research project that demands an in-depth exploration of your chosen field. This phase alone can take several months to years, significantly influencing the overall length of your PhD journey.
Beyond the dissertation, coursework, exams, and sometimes teaching responsibilities add layers to the doctoral experience.
The requirements for a PhD vary widely across disciplines and institutions. For instance, a doctorate in the sciences might involve extensive lab work, potentially extending the time to completion.
In contrast, a doctorate in the arts could hinge more on coursework and creative output, leading to variations in the timeline.
Does A Doctorate Degree Take Longer Than Masters?
A doctorate degree typically takes longer to complete than a master’s degree.
While a master’s program can often be completed in 1-2 years of full-time study, a doctoral program usually requires 4-6 years, depending on the:
- research complexity, and
- whether the student is enrolled full-time or part-time.
The doctoral journey is more than just additional coursework; it involves conducting original research, writing a comprehensive dissertation, and often teaching or engaging in professional development activities.
The dissertation phase, which requires students to contribute new knowledge to their field, is particularly time-consuming and can extend the duration of a PhD program significantly.
The time it takes to complete a doctorate can be influenced by your
- research topic,
- funding availability, and
- the level of support from advisors and faculty.
Master’s programs are typically more structured, with a clearer set of coursework requirements and a shorter thesis or capstone project, leading to a quicker path to graduation.

Why Does It Take So Long To Finish Doctoral Program?
Starting a doctoral program is a significant commitment, often taking longer than anticipated. If you wonder why it takes so long, here are a couple of reasons you can think about:
Extensive Coursework
Initially, you might think coursework in your PhD study is just a continuation of your previous studies.
Doctoral level courses are a different beast. They demand not just understanding but the ability to critically analyze and apply complex concepts.
Each course can feel like a mini research project, requiring more than just classroom attendance. This phase lays the foundation but is time-consuming.
The Dissertation
The heart of your doctoral journey is your dissertation. This isn’t just a long essay or an extended research paper. It’s an original contribution to your field, requiring:
- exhaustive research,
- experimentation, and
Some students find their research path straightforward, while others may hit unexpected roadblocks or need to pivot their focus, extending the time required.
Part-Time Study
Many PhD candidates choose a part-time path due to work, family, or other commitments. While this flexibility is crucial for many, it stretches the duration of the program.
What a full-time student might complete in 4-6 years, part-time students might take 7 years or more to finish.
Funding and Resources
Access to funding and resources can significantly impact the timeline. Some projects require extensive fieldwork, specialised equipment, or access to rare materials. Delays in funding or accessing necessary resources can stall progress.
If funding is an issue, consider applying for work outside of the university. You can also try your luck with the university, as a research or teaching assistant , or more.

Academic Publishing
As part of the doctoral process, many students are encouraged or required to publish their findings.
However, the process of submitting to academic journals, undergoing peer review, and possibly revising and resubmitting, is lengthy.
This step is crucial for the academic community but adds time to the doctoral timeline. If may help to start writing and publishing work earlier to ensure you have enough time to finish.
Faculty Supervision and Mentorship
The relationship with your advisor or supervisory committee is pivotal. These mentors gatekeep your studies, as they:
- guide your research,
- provide feedback, and
- approve your progress.
Scheduling conflicts, feedback loops, and the iterative nature of research can add semesters or even years to your timeline.
Personal Growth and Professional Development
Beyond the academic requirements, doctoral students often engage in teaching, attend conferences, and network within their academic community. These activities contribute to your professional development but also extend your time in the program.
Factors That Influence The Time To Get A PhD
The time it takes to complete PhD is influenced by a multitude of factors, each significant in its own right. Let’s delve deeper into these elements to understand the intricacies of the PhD voyage.
The Scope of Research :
The ambition of your research can significantly dictate the duration of your PhD. Some projects will need more time and commitment, especially if they:
- Demand extensive fieldwork,
- elaborate experiments, or
- groundbreaking theoretical developments.
Imagine embarking on a quest that not only seeks answers but also questions the very foundations of your field. Such endeavours are thrilling but inherently time-consuming, often extending the PhD journey beyond the typical timeframe.
Program Structure and Requirements
The architecture of a PhD program—its coursework, qualifying exams, and other prerequisites—lays the groundwork for your academic expedition.
Programs with a heavy load of initial coursework aim to equip you with a broad foundation, yet this can elongate the path to your actual dissertation work.
Mode of Study
The decision between full-time and part-time study is pivotal. A full-time commitment allows you to immerse yourself in research, ideally hastening progress.
Yet, life’s obligations may necessitate a part-time route, extending the journey but offering flexibility.
Distance learning, with its inherent flexibility, caters to those balancing diverse commitments, yet this mode, too, can stretch the timeline, particularly if it lacks the immediacy and intensity of on-campus engagement.
Quality of Supervision
The symbiotic relationship with your advisor is the compass guiding your research voyage. An advisor who is both a mentor and a critic, offering timely and constructive feedback, can expedite your journey.
Less engaged supervision may leave you adrift, prolonging the process as you navigate the academic waters largely on your own.
Worse still, if you are unlucky enough, you may end up with supervisors that not only does not help you, but actively attempt to make your study life difficult. These nightmare scenarios do exist, and you should be aware of them.
Financial Stability
The financial underpinnings of your PhD endeavor are more critical than often acknowledged. Consistent funding allows you to dedicate yourself fully to your research, free from financial distractions.
Conversely, the absence of stable support might necessitate part-time employment, diluting focus and extending the timeline.
Resource Availability
Access to specialized resources—be it state-of-the-art laboratories, rare archival collections, or cutting-edge software—can be the wind in your PhD sails.
Limited or delayed access to these essential tools, however, can stall progress, turning what could be a swift journey into a prolonged odyssey.
If you found yourself in a position without the right resources to complete your PhD, consider to propose your university to allow you to work with other universities with what you need. If this is not possible, you can always transfer university, although this would mean more work.
Publishing Requirements
The adage “publish or perish” holds particularly true in the realm of PhD studies. The process of getting your research published, from initial submission to eventual acceptance, is fraught with delays and revisions. Each publication cycle can add months to your timeline,
Yet these publications are crucial stepping stones towards establishing your academic credibility. In fact, some universities want you to publish papers to graduate.
Personal Life and Circumstances
The journey towards a PhD is not undertaken in academic isolation. Life, with its unforeseen challenges and responsibilities, continues.
Personal circumstances can impact your ability to devote time and energy to your studies, necessitating pauses or a reduction in research intensity.
These issues can range from situation such as:
- such as health issues,
- family commitments, or
- significant life events

Tips To Earn Your Doctoral Degree Fast
Earning a doctoral degree is a significant academic endeavor, often perceived as a marathon rather than a sprint. However, with strategic planning and focused effort, you can navigate this journey more swiftly than you might expect.
Here are some tips to help you earn your doctoral degree faster, drawing from the experiences and strategies of successful PhD candidates.
Choose Your Program Wisely
The structure of the PhD program you choose can greatly influence how long it takes to complete your degree. Programs that allow you to start your dissertation research early, even while completing your coursework, can save you a considerable amount of time.
Some program are designed to integrate dissertation work with coursework, enabling a more seamless transition into the research phase.
Opt for Full-Time Study If Possible
While part-time PhD programs offer flexibility for working professionals, full-time study allows for a more immersive research experience.
Dedicating all your working hours to your doctoral research can expedite the process, reducing the time it takes to get your PhD significantly.
Secure Adequate Funding
Financial stability is key to focusing fully on your research without the distraction of part-time work. Look for:
- scholarships,
- grants, and
- funding opportunities from your institution.
You can also try to secure funding from external sources like the National Science Foundation.
Secure funding not only supports your financial needs but also often comes with academic resources that can accelerate your research progress.
Develop a Strong Relationship with Your Advisor
Your advisor is your guide through the PhD process. A supportive advisor can provide invaluable feedback, help you navigate academic challenges, and keep you on track.
Regular meetings and clear communication with your advisor can help you refine your research direction and avoid time-consuming pitfalls.
Focus Your Research
A well-defined research question can provide a clear path forward. The more focused your research, the less likely you are to get bogged down in unmanageable amounts of data or tangential studies.
It’s about depth rather than breadth; delving deeply into a specific area can lead to significant contributions to your field and a quicker path to completion.

Take Advantage of Existing Research and Resources
Don’t reinvent the wheel. Building on existing research and utilizing available resources can save you time. This includes:
- leveraging datasets,
- using established methodologies, and c
- ollaborating with other researchers.
Access to resources like specialized labs or archives, as provided by your institution, can also streamline the research process.
Stay Organized and Manage Your Time Effectively
Good time management is crucial. Set realistic goals, create a timeline for your research and writing, and stick to it.
Tools like Gantt charts can help you visualize your PhD timeline, including key milestones like coursework completion, comprehensive exams, and dissertation chapters.
Get Your PhD Without Taking Too Much Time – Possible
The journey to obtaining a PhD is a unique blend of personal commitment, academic rigor, and research innovation.
While the timeline can vary widely, most candidates find themselves immersed in their studies and research for anywhere from 4 to 6 years. Exceptions can happen, and you may finish earlier or later.
Key factors like your field of study, the nature of your research, and your personal life circumstances play significant roles in shaping your individual journey.
Remember, earning a PhD is more than just a race to the finish line; it’s a profound journey of learning, discovery, and personal growth. Embrace the journey, stay focused, and the day you earn the title of ‘Doctor’ will be a milestone to remember.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

PhD Admissions
The PhD program in Psychology trains students for careers in research and teaching. In addition to a wide range of courses, the PhD program is characterized by close collaboration between students and their faculty advisors.
General Information
The Department of Psychology holistically reviews each candidate's complete application to assess the promise of a career in teaching and research. Consideration is based on various factors, including courses taken, grade point average, letters of recommendation, and the statement of purpose. Additionally, the Department of Psychology places considerable emphasis on research training, and admitted students have often been involved in independent research as undergraduate students or post-baccalaureate settings. Although there are no course requirements for admission, all applicants should have sufficient foundational knowledge and research experience to engage in graduate-level coursework and research.
We accept students with undergraduate degrees and those with both undergraduate and master's degrees. An undergraduate psychology major is not required; the Department welcomes applicants from other academic backgrounds.
Our application portal is now closed for the AY24-25 admissions cycle. Please consider applying during next year's AY25-26 admissions cycle, which opens on September 15, 2024.
How to Apply
Application and deadline.
Our 2025-26 Admissions application will open on September 15, 2024.
Applications will be due on November 30, 2024
The deadline for letters of recommendation will be November 30, 2024 .
Once an applicant submits the recommenders' information, the recommenders will receive an automated email with instructions for submitting the letter. Late letters should be sent directly to psych-admissions [at] stanford.edu (psych-admissions[at]stanford[dot]edu) . Staff will add them to the application file if the review process is still underway. Still, the faculty reviewers are not obligated to re-review files for materials submitted after the deadline.
The status of submitted applications can be viewed by logging in to the application portal .
The deadline to apply for the Stanford Psychology Ph.D. program is November 30, 2024 .
Applicants who are admitted to the program will matriculate in autumn 2025.
In addition to the information below, please review the Graduate Admissions website prior to starting your application. The Department of Psychology does not have rolling admissions. We admit for the Autumn term only.
Requirements
- U.S. Bachelor's degree or its foreign equivalent
- Statement of Purpose (submitted electronically as part of the graduate application). You will be able to specify three Psychology Department faculty members , in order of preference, with whom you would like to work.
- Three Letters of Recommendation (submitted electronically). A maximum of six letters will be accepted.
- Unofficial transcripts from all universities and colleges you have attended for at least one year must be uploaded to the graduate application. Applicants who reach the interview stage will be asked to provide official transcripts as well; Department staff will reach out to these applicants with instructions for submitting official transcripts. Please do not submit official transcripts with your initial application.
- Required for non-native English speakers: TOEFL (Test of English as a Foreign Language) scores, submitted by the Educational Testing Service (ETS) electronically to Stanford.
Application Fee
The fee to apply for graduate study at Stanford is $125. Fee waivers are available for some applicants. Please visit Graduate Admissions for information on applying for an Application Fee Waiver .
Application Review & Status Check
The Department of Psychology welcomes graduate applications from individuals with a broad range of life experiences, perspectives, and backgrounds who would contribute to our community of scholars. The review of applications is holistic and individualized, considering each applicant’s academic record and accomplishments, letters of recommendation, and admissions essays to understand how an applicant’s life experiences have shaped their past and potential contributions to their field.
To check the status or activity of your application, please log into your application account . You can also send reminders to recommenders who have not yet submitted their letter of recommendation.
Due to limited bandwidth, the Department of Psychology staff will not answer any phone or email queries about application status, including requests to confirm the receipt of official transcripts.
Our faculty will interview prospective students before making final admission decisions. Candidates who progress to the interview round will be informed in January. Interviews are generally conducted in February.
The Department of Psychology recognizes that the Supreme Court issued a ruling in June 2023 about the consideration of certain types of demographic information as part of an admission review. All applications submitted during upcoming application cycles will be reviewed in conformance with that decision.
- Diversity and Engagement in Psychology PhD Programs
- Vice Provost for Graduate Education
- Stanford IDEAL
- Graduate Application Fee Waiver Information
For More Information
Please see our list of Frequently Asked Questions and psych-admissions [at] stanford.edu (contact us) should you have additional questions.
Doctor of Philosophy in Education

Additional Information
- Download the Doctoral Viewbook
- Admissions & Aid
The Harvard Ph.D. in Education trains cutting-edge researchers who work across disciplines to generate knowledge and translate discoveries into transformative policy and practice.
Offered jointly by the Harvard Graduate School of Education and the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, the Ph.D. in Education provides you with full access to the extraordinary resources of Harvard University and prepares you to assume meaningful roles as university faculty, researchers, senior-level education leaders, and policymakers.
As a Ph.D. candidate, you will collaborate with scholars across all Harvard graduate schools on original interdisciplinary research. In the process, you will help forge new fields of inquiry that will impact the way we teach and learn. The program’s required coursework will develop your knowledge of education and your expertise in a range of quantitative and qualitative methods needed to conduct high-quality research. Guided by the goal of making a transformative impact on education research, policy, and practice, you will focus on independent research in various domains, including human development, learning and teaching, policy analysis and evaluation, institutions and society, and instructional practice.
Curriculum Information
The Ph.D. in Education requires five years of full-time study to complete. You will choose your individual coursework and design your original research in close consultation with your HGSE faculty adviser and dissertation committee. The requirements listed below include the three Ph.D. concentrations: Culture, Institutions, and Society; Education Policy and Program Evaluation; and Human Development, Learning and Teaching .
We invite you to review an example course list, which is provided in two formats — one as the full list by course number and one by broad course category . These lists are subject to modification.
Ph.D. Concentrations and Examples
Summary of Ph.D. Program
Doctoral Colloquia In year one and two you are required to attend. The colloquia convenes weekly and features presentations of work-in-progress and completed work by Harvard faculty, faculty and researchers from outside Harvard, and Harvard doctoral students. Ph.D. students present once in the colloquia over the course of their career.
Research Apprenticeship The Research Apprenticeship is designed to provide ongoing training and mentoring to develop your research skills throughout the entire program.
Teaching Fellowships The Teaching Fellowship is an opportunity to enhance students' teaching skills, promote learning consolidation, and provide opportunities to collaborate with faculty on pedagogical development.
Comprehensive Exams The Written Exam (year 2, spring) tests you on both general and concentration-specific knowledge. The Oral Exam (year 3, fall/winter) tests your command of your chosen field of study and your ability to design, develop, and implement an original research project.
Dissertation Based on your original research, the dissertation process consists of three parts: the Dissertation Proposal, the writing, and an oral defense before the members of your dissertation committee.
Culture, Institutions, and Society (CIS) Concentration
In CIS, you will examine the broader cultural, institutional, organizational, and social contexts relevant to education across the lifespan. What is the value and purpose of education? How do cultural, institutional, and social factors shape educational processes and outcomes? How effective are social movements and community action in education reform? How do we measure stratification and institutional inequality? In CIS, your work will be informed by theories and methods from sociology, history, political science, organizational behavior and management, philosophy, and anthropology. You can examine contexts as diverse as classrooms, families, neighborhoods, schools, colleges and universities, religious institutions, nonprofits, government agencies, and more.
Education Policy and Program Evaluation (EPPE) Concentration
In EPPE, you will research the design, implementation, and evaluation of education policy affecting early childhood, K–12, and postsecondary education in the U.S. and internationally. You will evaluate and assess individual programs and policies related to critical issues like access to education, teacher effectiveness, school finance, testing and accountability systems, school choice, financial aid, college enrollment and persistence, and more. Your work will be informed by theories and methods from economics, political science, public policy, and sociology, history, philosophy, and statistics. This concentration shares some themes with CIS, but your work with EPPE will focus on public policy and large-scale reforms.
Human Development, Learning and Teaching (HDLT) Concentration
In HDLT, you will work to advance the role of scientific research in education policy, reform, and practice. New discoveries in the science of learning and development — the integration of biological, cognitive, and social processes; the relationships between technology and learning; or the factors that influence individual variations in learning — are transforming the practice of teaching and learning in both formal and informal settings. Whether studying behavioral, cognitive, or social-emotional development in children or the design of learning technologies to maximize understanding, you will gain a strong background in human development, the science of learning, and sociocultural factors that explain variation in learning and developmental pathways. Your research will be informed by theories and methods from psychology, cognitive science, sociology and linguistics, philosophy, the biological sciences and mathematics, and organizational behavior.
Program Faculty
The most remarkable thing about the Ph.D. in Education is open access to faculty from all Harvard graduate and professional schools, including the Harvard Graduate School of Education, the Faculty of Arts and Sciences, the Harvard Kennedy School, the Harvard Law School, Harvard Medical School, and the Harvard School of Public Health. Learn about the full Ph.D. Faculty.

Jarvis R. Givens
Jarvis Givens studies the history of American education, African American history, and the relationship between race and power in schools.

Paul L. Harris
Paul Harris is interested in the early development of cognition, emotion, and imagination in children.

Meira Levinson
Meira Levinson is a normative political philosopher who works at the intersection of civic education, youth empowerment, racial justice, and educational ethics.

Luke W. Miratrix
Luke Miratrix is a statistician who explores how to best use modern statistical methods in applied social science contexts.

Eric Taylor
Eric Taylor studies the economics of education, with a particular interest in employer-employee interactions between schools and teachers hiring and firing decisions, job design, training, and performance evaluation.

Paola Uccelli
Paola Ucelli studies socio-cultural and individual differences in the language development of multilingual and monolingual students.

View Ph.D. Faculty
Dissertations.
The following is a complete listing of successful Ph.D. in Education dissertations to-date. Dissertations from November 2014 onward are publicly available in the Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard (DASH) , the online repository for Harvard scholarship.
- 2022 Graduate Dissertations (265 KB pdf)
- 2021 Graduate Dissertations (177 KB pdf)
- 2020 Graduate Dissertations (121 KB pdf)
- 2019 Graduate Dissertations (68.3 KB pdf)
Student Directory
An opt-in listing of current Ph.D. students with information about their interests, research, personal web pages, and contact information:
Doctor of Philosophy in Education Student Directory
Introduce Yourself
Tell us about yourself so that we can tailor our communication to best fit your interests and provide you with relevant information about our programs, events, and other opportunities to connect with us.
Program Highlights
Explore examples of the Doctor of Philosophy in Education experience and the impact its community is making on the field:

Lost in Translation
New comparative study from Ph.D. candidate Maya Alkateb-Chami finds strong correlation between low literacy outcomes for children and schools teaching in different language from home

Using E-Books to Get Young Readers Talking
New research shows how parents can help kids — and themselves — use e-books as a tool to improve early childhood development
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CORRESPONDENCE
- 02 April 2024
How can we make PhD training fit for the modern world? Broaden its philosophical foundations
- Ganesh Alagarasan 0
Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Tirupati, India.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
You have highlighted how PhD training assessment has stagnated, despite evolving educational methodologies (see Nature 613 , 414 (2023) and Nature 627 , 244; 2024 ). In particular, you note the mismatch between the current PhD journey and the multifaceted demands of modern research and societal challenges.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Nature 628 , 36 (2024)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-00969-x
Competing Interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Related Articles
See more letters to the editor
- Research management
- Scientific community

Ready or not, AI is coming to science education — and students have opinions
Career Feature 08 APR 24

After the genocide: what scientists are learning from Rwanda
News Feature 05 APR 24

The neuroscientist formerly known as Prince’s audio engineer
Career Feature 14 MAR 24
Brazil’s postgraduate funding model is about rectifying past inequalities
Correspondence 09 APR 24
Declining postdoc numbers threaten the future of US life science

How we landed job interviews for professorships straight out of our PhD programmes
Career Column 08 APR 24

How two PhD students overcame the odds to snag tenure-track jobs
Adopt universal standards for study adaptation to boost health, education and social-science research
Correspondence 02 APR 24
Group Leader at Católica Biomedical Research Centre and Assistant or Associate Professor at Católica
Group Leader + Assistant/Associate Professor, tenure-track position in Biological and Biomedical Sciences, Data Science, Engineering, related fields.
Portugal (PT)
Católica Biomedical Research Centre
Faculty Positions at SUSTech Department of Biomedical Engineering
We seek outstanding applicants for full-time tenure-track/tenured faculty positions. Positions are available for both junior and senior-level.
Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Southern University of Science and Technology (Biomedical Engineering)
Locum Associate or Senior Editor, Nature Cancer
To help us to build on the success of Nature Cancer we are seeking a motivated scientist with a strong background in any area of cancer research.
Berlin, Heidelberg or London - Hybrid working model
Springer Nature Ltd
Postdoctoral Research Fellows at Suzhou Institute of Systems Medicine (ISM)
ISM, based on this program, is implementing the reserve talent strategy with postdoctoral researchers.
Suzhou, Jiangsu, China
Suzhou Institute of Systems Medicine (ISM)
The Associate or Senior Editor will contribute to shaping the future of Nature Cancer journal.
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
9 things people get wrong about sociopaths, according to a sociopath
- Sociopaths are often depicted as unfeeling criminals and abusers.
- Dr. Patric Gagne, a psychologist and a diagnosed sociopath, wrote a memoir about her experiences.
- She described the many ways she felt misunderstood by others and struggled with finding help.

Diagnosed with sociopathic personality disorder in her 20s, Dr. Patric Gagne struggled to find resources to treat the symptoms she had all her life.
Since childhood, Gagne has felt starkly different from everyone else. She's wrestled with pervasive apathy, and violent urges that feel more calm than charged.
"Everyone else had access to hope," Gagne says in her new memoir, " Sociopath ." "Schizophrenics, alcoholics, bipolar depressives — there were treatment plans and support groups for all of them." Sociopaths in popular culture are "loathsome villains with few exceptions," like Hannibal Lecter in "The Silence of the Lambs" and Patrick Bateman in "American Psycho."
The lack of available care for sociopaths inspired Gagne to pursue a PhD in psychology, where she specialized in the relationship between sociopathy and anxiety. Eventually, she worked as a therapist, where she "earned a low-key reputation as 'the sociopath therapist,'" taking on clients with sociopathic tendencies.
Gagne's memoir cast light on a lot of misconceptions about sociopaths, from how they process emotions to how they form relationships.
1. Sociopaths do feel emotions, just not "social" ones
Sociopaths are often depicted in media as devoid of feelings entirely. But that's not true.
"Some feelings came naturally to me, like anger and happiness," Gagne writes. "But other emotions weren't so easy. Empathy and guilt, embarrassment and jealousy were like a language I couldn't speak or understand." She compares her emotional range to "a cheap set of crayons," where she can access primary colors but struggles with "more nuanced hues."
As an adult researching sociopathy and going to therapy, she learned that sociopaths — and even psychopaths — can feel basic emotions. But they don't experience "social emotions," such as shame, remorse, and even romantic love, because they feel a lack of attachment to people.
2. Anxiety drives violent or risky urges
In pop culture, sociopaths get a thrill out of hurting and manipulating others. But the driver of high-risk and harmful behavior is more complicated, Gagne argues.
She describes feeling a "pressure" and anxiety whenever she feels apathetic. "The nothingness, I'd started to notice, made my urge to do bad things more extreme," Gagne says.
Throughout the book, she tried to mitigate her violent or unlawful urges by committing smaller risky acts, like breaking into people's homes or temporarily stealing cars from drunk fraternity brothers.
Ultimately, she sees her past behavior as a "subconscious drive for feeling." Doing something dangerous didn't actively bring her joy as much as relieve tension and stress — similar, she said, to an OCD compulsion .
3. Unlike psychopaths, they can shows signs of change
"Sociopath" and "psychopath" are often used interchangeably, but there are some key differences . To make matters more confusing, they both fall under the term " antisocial personality disorder ," which Gagne finds unhelpful.
"While I could easily identify with most of the traits on the sociopathic and psychopathic checklists, I was only able to relate to about half of the antisocial ones," she says.
Gagne was diagnosed via a psychopath checklist , where scoring within a lower range indicates sociopathy more than psychopathy because the symptoms are not as extreme.
Related stories
While research on the diagnoses is still limited, Gagne says experts believe that, unlike psychopaths, sociopaths can feel anxiety and also show signs of learning right from wrong.
4. They're not devoid of healthy interests or hobbies
Sociopaths are often portrayed as stoic loners in media, with no hobbies other than committing crimes and hurting people.
In truth, they can have interests and hobbies just like anyone else. In the book, Gagne describes her passion for music (particularly jazz), her love for her childhood pet ferret, bonding with the kids she babysits, and becoming fascinated with psychology enough to turn it into a career.
5. They don't understand why some things are "wrong"
Throughout the book, Gagne explains how she finds it difficult to identify "bad" behavior.
"I may have been missing an emotional connection to the concepts of right and wrong, but I knew they existed," she says. Because she can't naturally feel fear, shame, guilt, or remorse, she wouldn't know when she was doing something that could make people uncomfortable or scared, like stealing or stalking.
Later in adulthood, she would try to pay people back when she felt she was doing something wrong. She'd bring flowers to the strangers' funerals she'd crash and fill up the cars she briefly stole with gas.
"One time someone left the stove on, so I turned it off," she said of a house she broke into. "It's my way of trying to balance the karma."
6. They may lie to avoid being judged
A common assumption is that sociopaths always lie for the fun of it, or for personal gain. In Gagne's case, she says she often lied about her feelings just to fit in. She felt claustrophobia whenever she realized she wasn't feeling the way she was "supposed" to, she says in the book.
When her pet ferret died, she felt sadness but couldn't authentically sob the way her sister did. Throughout her childhood, she didn't feel remorse or fear, and sharing that with others didn't help.
That made it hard for her to form genuine connections with others, because she feels like she has to perform or exaggerate emotions to make others comfortable.
7. They crave connection, too
Another big sociopath stereotype is that they're perfectly content being on their own. While Gagne always enjoyed solitude, she also felt loneliness from her inability to be honest about her disorder.
"No one could relate to me," she says. "Nobody wanted to spend time with me. Not the real me, anyway. I was utterly alone."
Over time, she learned how to be more honest, and found people who wouldn't judge her.
8. Treatment can improve their symptoms
In the book, Gagne mentions Dr. Ben Karpman, who theorized that sociopaths "are not hardwired to pursue an antisocial lifestyle and may be responsive to treatment."
Because of the lack of available treatment options, Gagne researched ways to help mitigate her symptoms. She found that cognitive behavioral therapy helped her unpack the feelings of anxiety that triggered unwanted actions. "It all boiled down to mindfulness," she writes.
Acceptance of being a sociopath also helped her, because she realized her anxiety often came from the pressure to fit in. She started to become more open about her diagnosis to reduce the feeling of always needing to hide from others.
9. They can maintain long, healthy relationships
Gagne got married to David, her childhood sweetheart. Together, they share two children, a dog, and a cat.
"I am a passionate mother and wife," she says in the book. "I am an engaging therapist. I am extremely charming and well-liked. I have lots of friends. I am a member of a country club. I throw parties for every occasion you can imagine."
She's been able to have lasting relationships with her friends and family because she sought treatment and answers, which is why she pursued her PhD and started publicly speaking about her experiences.
"I am a twenty-first-century sociopath," she says. "And I've written this book because I know I'm not alone."
Watch: I was assaulted by a Met Police officer at 14, I now train them. Here's how police racism works
- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Kee says funding for a humanities Ph.D. program typically only lasts five years, even though it is uncommon for someone to obtain a Ph.D. degree in a humanities field within that time frame ...
On average, it takes 4-5 years to complete a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) program in the US, between 4-6 years in Canada, and 3-5 years in Europe. The time it takes to get a PhD is slightly longer in the US, because these programs are more structured and have more requirements. Learn how to apply, write your thesis, and graduate faster with tips and examples.
Learn about the requirements, timeline, and factors that affect the length of a PhD program. Find out the average completion time by field and the benefits and costs of a doctorate degree.
Learn about the factors that affect the length of a PhD program, such as credit hours, schedule, dissertation and field of study. Compare online and campus-based options and find out how to speed up your studies.
How Long Does It Take To Get a PhD? On average, PhD programs last 5-7 years, but this number varies greatly depending on the country, the university, and the specific field of study. For example: PhD programs in the UK tend to be on the shorter end of the spectrum, typically lasting 3-4 years.
Learn about the factors that affect the duration of a PhD program, such as type, field, assistantships, exams, and dissertation. Find out the average PhD timeline, the benefits of earning a PhD, and how to finish it faster.
Learn how long it takes to get a PhD and what to expect along the way. From coursework to dissertation defense, discover the typical steps and challenges of earning a doctorate degree.
The length of a PhD varies by country and depends on the type of program, the research topic, and the institution. Learn more about the application process, the research stage, and the duration of a PhD from Scribbr's frequently asked questions.
Learn how to choose the right doctoral degree for your career goals and how online learning can help you complete it faster. Compare the differences between PhD and professional doctorate programs and the advantages of online education.
For example, it takes an average of 7.9 years to earn a doctorate in psychology and the social sciences compared to 6.3 years in physical and earth sciences. By contrast, humanities and arts doctorates can take significantly longer, with students finishing their degree in approximately 9.6 years. Meanwhile, students pursuing a doctoral degree ...
3 to 4 years. In the USA, a PhD takes four to six years. There are several reasons for this. While in the UK, you tend to apply for a specific project, in the US, your application is aimed at a certain department and your actual proposal takes shape in the first couple of years of PhD study. The US model involves a two-phase programme, wherein ...
In general, however, the typical annual tuition fee for a PhD in the US is between $12,000 and $45,000 per academic year. As with any doctoral degree, additional costs may include travel for collaborations, bench fees, accommodation and living expenses. A PhD in USA takes 5-6 years, costs between $12-45k per year and has a different structure ...
A PhD is a postgraduate doctoral degree that requires years of research, writing and exams. Learn the steps to earn a PhD, the requirements, the benefits and the careers with a PhD. Find out how long it takes to get a PhD and the online colleges offering programs.
Learn how long it takes to complete a full-time, part-time or distance learning PhD in the UK, EU and US. Find out the factors that influence PhD durations, the deadlines and the differences between UK and US PhDs.
The answer can vary depending on your program, educational background, and academic schedule. In general, most PhD psychology programs take anywhere from five to seven years to complete. Learning more about what it takes to get a doctorate in psychology can help you better plan your educational and career journey.
A Ph.D. typically takes between five to six years to complete but may take longer based on the program and the student. During the first half of a Ph.D. program, you usually complete coursework and exams. The latter half is for dissertation work, which can take between one to three years. If you conduct fieldwork or other hands-on scientific ...
The median time it takes to complete a Ph.D. from a U.S. grad school is 5.8 years, but the length of time varies by discipline and field. Learn how to choose a Ph.D. program, write a dissertation, and find funding and support from experts and alumni.
A doctoral degree is a graduate-level credential typically granted after multiple years of graduate school, with the time-to-degree varying depending on the type of doctoral program, experts say ...
Learn how to prepare and apply for a PhD program at the University of Pennsylvania. Find out about funding, choosing a program, preparing a competitive application, and what to expect in a PhD program.
The journey to obtaining a PhD is a unique blend of personal commitment, academic rigor, and research innovation. While the timeline can vary widely, most candidates find themselves immersed in their studies and research for anywhere from 4 to 6 years. Exceptions can happen, and you may finish earlier or later.
How long does it take to get a PhD in Psychology at Stanford? The PhD program is designed to be completed in five years of full-time study. Actual time will depend on students' prior background, progress, and research requirements. The minimum residency requirement for the PhD degree is 135 units of completed coursework and research units.
The deadline to apply for the Stanford Psychology Ph.D. program is November 30, 2024 . Applicants who are admitted to the program will matriculate in autumn 2025. In addition to the information below, please review the Graduate Admissions website prior to starting your application. The Department of Psychology does not have rolling admissions.
The Harvard Ph.D. in Education trains cutting-edge researchers who work across disciplines to generate knowledge and translate discoveries into transformative policy and practice. Offered jointly by the Harvard Graduate School of Education and the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, the Ph.D. in Education provides ...
Per-credit tuition rates for the programs in our guide ranged from $442 to $950. A 60-credit degree from NU totals about $26,500, while the 66-credit option at Capitol Tech costs more than $62,000 ...
02 April 2024. How can we make PhD training fit for the modern world? Broaden its philosophical foundations. By. Ganesh Alagarasan. You have highlighted how PhD training assessment has stagnated ...
But they don't experience "social emotions," such as shame, remorse, and even romantic love, because they feel a lack of attachment to people. Advertisement. 2. Anxiety drives violent or risky ...