- Collections
- Special days
- World War I

Free - World War I PPT Presentation And Google Slides Themes

World War I Presentation Slides
Features of the templates:.
- 100% customizable slides and easy to download
- Slides are available in different nodes & colors.
- The slides contained 16:9 and 4:3 formats.
- Easy to change the slide colors quickly.
- Well-crafted Template with an instant download facility.
- Crisp and elegant font style.
- The best Template with attractive nodes.
- July Month Special Days
- World War 1
- First World War
- I World War
- Google Slides
-594.webp)
661+ Templates

Valentines day
69+ Templates

39+ Templates

349+ Templates

111+ Templates

Black Friday
67+ Templates

474+ Templates

160+ Templates

Cyber Monday
42+ Templates
You May Also Like These PowerPoint Templates


- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
World War I.
Published by Suzanne Landry Modified over 5 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "World War I."— Presentation transcript:

WW I Overview (It’s going to be on the TEST!). The countries in Europe The central powers Germany, Austria-Hungary, Turkey (Ottoman Empire) The.

Causes of WWI What are the MAIN causes of World War I?

Causes of World War One Militarism Role of Military on Government Decisions Arms Race Glorification of War Conscription Germany- 8.5 million Russia- 4.5.

CH 23: War and Revolution Our Lady of Lourdes Social Studies Department I.

The Great War Learning Targets 1.I can identify the four main causes of World War I 2.I can define Nationalism and Militarism 3.I can Identify.

Main Causes of World War I (Ch. 13, Sec. 1)
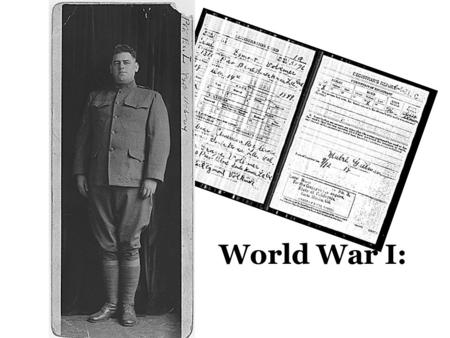
World War I:. Vocabulary ConscriptionMilitary draft PropagandaThe spread of ideas used to influence public opinion for or against a cause “Total war”entire.
Causes Leaders Dates America’s Entry Alliances & Sides Grab Bag

Causes of World War I ANIMAL.

Causes of WW1. The main players Kaiser Wilhelm II of Germany.

World War I War to end all wars 1914 – World War I Began on July 28, 1914 Ended on November 11, 1918 United States joined in April 1917.

WORLD WAR 1 THE GREAT WAR. “Some damned thing in the Balkans” The great powers – Russia, France, Britain, Germany, Austria-Hungary Kaiser Wilhelm provoked.

World War I. What is a “world war”? A world war is a war affecting the majority of the world's major nations. World wars usually span multiple continents,

World War I: Causes of WWI

2 pt 3 pt 4 pt 5pt 1 pt 2 pt 3 pt 4 pt 5 pt 1 pt 2pt 3 pt 4pt 5 pt 1pt 2pt 3 pt 4 pt 5 pt 1 pt 2 pt 3 pt 4pt 5 pt 1pt WWI Terms People, Places, Dates Dates,

Chapter 19.1 “The War to End all Wars”. THE GREAT WAR.

World War I, The Great War Causes of the War Nationalism- pride in and loyalty to one’s ethnic group Imperialism- race for colonies around.

WWI: Before, During & After. Extreme Nationalism.

World War I, The Great War
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Ohio State navigation bar
- BuckeyeLink
- Search Ohio State
The First World War in Global Context
German Troops Firing from a Trench, 1915
Introduction
- Teacher created lesson plans on the topic
- A bibliography of historical works on World War I
- Links to quality websites related to the history of the Great War
Lesson Plans
Analyzing primary sources, powerpoint presentations.
- Causes of World War I
- World War I: Total War
- The United States Enters World War I
- The US Homefront During World War I
- National Security vs. Liberty: The US Homefront
- The US and World War I: Social Change
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

61 templates

el salvador
34 templates

17 templates

16 templates

49 templates

american history
85 templates
World War I and Its Impact - History - 11th Grade
It seems that you like this template, world war i and its impact - history - 11th grade presentation, free google slides theme, powerpoint template, and canva presentation template.
Did you know that people used to call WWI "the Great War"? There was no way they would know that there would be a second one later, so that explains it. But there are other more important things to explain and teach about WWI, like its impact in Europe. That's a task for history teachers, and we want to help making education easier, so here's our editable template to facilitate the lessons! It's a very visual template, with lots of images generated by Wepik's AI Image Generator . We've even added some of the prompts you may use to have better results in order to replace those who look anachronistic (it's a template, after all!).
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 39 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides, Canva, and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?

Register for free and start downloading now
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

Create your presentation Create personalized presentation content
Writing tone, number of slides.

Register for free and start editing online

World War I -…

World War I – American Perspective PowerPoint & Google Slides | US History
Description, additional information.
- Reviews (0)
Check out this engaging PowerPoint (or Google Slides) presentation on World War I from the American perspective. It will help your students learn about the alliance system that started World War I, some major battles (e.g. Battle of Verdun, Battle of the Marne), reasons for the United States joining the war, and much more! In addition to the PPT, a primary source activity on the 1918 Flu Pandemic is included.
Content in PPT includes:
- Causes of World War I
- Alliance System
- Assassinated Archduke Franz Ferdinand
- Mexican Revolution
- American neutrality
- Central Power and Allied Powers
- Schlieffen Plan
- First Battle of the Marne
- Trench Warfare
- Christmas truce
- Battles of Isonzo
- Battle of Verdun
- Sussex Pledge
- U-Boat warfare
- Zimmerman Telegram
- U.S. joining the war
- 92nd and 93rd Divisions
- Committee on Public Information
- Sacrifices at home
- Russian Revolution
- Spring Offensive
- Second Battle of the Marne
- Hundred Days Offensive
- Battle of St. Mihiel
- Meuse River–Argonne Forest Offensive
- Aviation in World War I
- 1918 Flu Pandemic (Spanish Flu)
- Fourteen Points
- League of Nations
- Great Migration
- Red Summer of 1919
- Tulsa Race Massacre
- and much more!
Files in this download include:
- Editable PPT (Google Slides option available)
- Primary Source PDF (Google Drive option available)
- Student Study Guide Notes (print or load to LMS)
- Editable Word Document version
- Fillable PDF version
- PDF version
- Teacher Guide PDF (print one copy for you)
If you are a busy social studies teacher that expects the best for your students and want to feel confident in front of the class, this PPT is perfect because it is professionally designed, useful, and enjoyable for the students.
Zero to minimal preparation necessary. Just print the Teacher Guide Sheet for you (if you deem it necessary), then print the Student Study Guide Notes and primary source for students. If you want to save time (and paper), you could simply upload these files to your Learning Management System (LMS) and students could use the files on their devices.
To make the lesson more interactive, one slide directs the students to read a primary source on the 1918 Flu Pandemic. Students can work in groups, read the primary source, answer the questions (which can be found on their Student Study Guide Notes), then you can have a class discussion.
The design is professional and with the right amount of words on each slide (i.e. NO death by PowerPoint). The content is very detailed in the notes, so if you are busy, you could simply open the slides in front of the class and read the notes (it is suggested you review the slides before class though).
Furthermore, it includes a teacher guide sheet that you can print and use when presenting. The information in the guide sheet and PPT notes include additional information that is not on the slides (in other words, it will make you look smart!). This way, you can add interesting little comments or data to each slide. You can either print the whole guide sheet, or just the pages you need help with.
You can make changes to the PPT, if you deem it necessary. This presentation can be used in Microsoft PowerPoint or Google Slides (if you want to use Google Slides, just click the link which is found in the first slide).
This PPT follows standard American history textbooks.
How to use this presentation:
- Present the PowerPoint (or Google Slides) in the classroom; one slide includes an interactive primary source activity for students to complete
- Present and discuss – while presenting, get students involved and create discussion questions that get students thinking like a historian and comparing historical events to current events
- Students fill out the Student Study Guide Notes while you are presenting
| Grade Level | 8th, 9th, 10th |
|---|---|
| Resource Types | Full Units, Homeschool, PowerPoints, Google Slides |
There are no reviews yet.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Related products

- American History
Industrial America PowerPoint & Google Slides | Primary Source
- Add to cart

Cold War PowerPoint & Google Slides | American History


“Corrupt Bargain” Investigation – Primary Source Activities
- Privacy and Cookie Policy
- ANCIENT HISTORY
- Our Free Lesson Plans and Classroom Activities
- Archaeology
- Early Humans
- Mesopotamia
- Free Use Clipart
- AMERICAN HISTORY
- Native Americans
- New World Explorers
- 13 Colonies
- Revolutionary War
- Creating a New Nation and US Constitution
- Western Expansion
- The Civil War
- Industrial Revolution
- Roaring 20s
- Great Depression
- WORLD HISTORY
- African Kingdoms
- Middle Ages
- Renaissance Reformation and More
- Age of Exploration
- HOLIDAYS Around the World
- FAQ, About Us, Contact
- Show More Show Less
- World History
- Powerpoints
World War I Free Presentations in PowerPoint format
Free use powerpoints.
The Great War, World War I free use powerpoints for the classroom
World War I for Kids
Games about WW1
Military Games
For Teachers
World War 1 Lesson Plans

WORLD WAR 1
Jul 28, 2014
1.64k likes | 3.29k Views
WORLD WAR 1. CAUSES, PRACTICES & EFFECTS OF WAR. The World before World War I. The War was also known as THE FIRST WORLD WAR, THE GREAT WAR and famously “ THE WAR TO END ALL WARS” It was a global military conflict that took place mainly in Europe between 1914 & 1918.
Share Presentation
- serbian general staff
- only french
- black hand secret society
- economic market
- european divide

Presentation Transcript
WORLD WAR 1 CAUSES, PRACTICES & EFFECTS OF WAR
The World before World War I The War was also known as THE FIRST WORLD WAR, THE GREAT WAR and famously “ THE WAR TO END ALL WARS” • It was a global military conflict that took place mainly in Europe between 1914 & 1918. It was a total War which left great devastation, millions dead and shaped the modern world. World War I created a decisive break with the old world order that had emerged after the Napoleonic Wars , which was modified by the mid-19th century’s nationalistic revolutions. The results of World War I would be important factors in the development of world war II; 21 years later.
Long-term Causes: Why did the war break out? • Napoleon Bonaparte and the Rise of Nationalist Sentiment • Colonial Expansion • Anglo-German Naval Race • Tension in the Balkans • Ascension of Kaiser Wilhelm II • Web of alliances
Serb Nationalism: Napoleon Bonaparte and the Rise of Nationalist Sentiment • Nationalism means being a strong supporter of the rights and interests of one's country. The Congress of Vienna, held after Napoleon's exile to Elba, aimed to sort out problems in Europe. • Delegates from Britain, Austria, Prussia and Russia (the winning allies) decided upon a new Europe that left both Germany and Italy as divided states. • Strong nationalist elements led to the Re-unification of Italy in 1861 and Germany in 1871. • The settlement at the end of the Franco-Prussian war left France angry at the loss of Alsace-Lorraine to Germany and keen to regain their lost territory. • Large areas of both Austria-Hungary and Serbia were home to differing nationalist groups, all of whom wanted freedom from the states in which they lived.
The French Revolution resulted in chaos and the ascent of Napoleon to power. Napoleon's armies marched all over Europe, bringing not only French control, but French ideas. • The rise of ideas of nationalism, devotion and love for one's common people and ethnicity, increased in popularity during the Napoleonic Wars. • Napoleon encouraged the spread of nationalism, which he saw in his troops, to better the French war machine. • The French people began to feel pride in their culture and ethnicity. The world watched nationalism for the first time and saw the power the French gained from it. • Following the Napoleonic Wars, all of Europe was sharing these ideas
Europe in 1914 • By 1914 Europe was divided as a continent in power struggling forces for the top place in the world economic market. • At the start of the Great War in 1914, Germany was a relatively young power, only coming into existence following a series of wars in 1871. Germany's Chancellor, Otto von Bismarck, had shepherd the country into the 20th century with the adage that Germany must always be in a majority of three in any dispute among the five great European powers. His aim was to maintain peaceful ties with Russian. • When Kaiser Wilhelm II came to power, he quickly retired Bismarck, and upset the Chancellor's delicate balance of power by refusing to renew Germany's friendship with Russia. Germany soon found itself in a minority of two. Its only European ally was the weakest of the European powers, Austria-Hungary.
Otto Van Bismark His Strategies towards building a better Germany.
Kaiser Wilhelm II
Imperialism andColonial Expansion • Imperialism is when a country takes over new lands or countries and makes them subject to their rule. • By 1900 the British Empire extended over five continents and France had control of large areas of Africa. With the rise of industrialism countries needed new markets. • The amount of lands 'owned' by Britain and France increased the rivalry with Germany who had entered the scramble to acquire colonies late and only had small areas of Africa. Note the contrast in the map below.
Imperialist rivalry had grown more intense with the "new imperialism" of the late 19th and early 20th cent. • The great powers had come into conflict over spheres of influence in China and over territories in Africa, and the Easter question , created by the decline of the Ottoman Empire, had produced several disturbing controversies. Particularly unsettling was the policy of Germany. • It embarked late but aggressively on colonial expansion under Emperor William II came into conflict with France over Morocco , and seemed to threaten Great Britain by its rapid naval expansion.
Militarism • Militarism means that the army and military forces are given a high profile by the government. The growing European divide had led to an arms race (competition between nations to have the most powerful weapons) between the main countries. • The armies of both France and Germany had more than doubled between 1870 and 1914 and there was fierce competition between Britain and Germany for mastery of the seas. • The British had introduced the 'Dreadnought', an effective battleship, in 1906. The Germans soon followed suit introducing their own battleships. • The German, Von Schlieffen also drew up a plan of action that involved attacking France through Belgium if Russia made an attack on Germany. The map below shows how the plan was to work.
Alliances • An alliance is an agreement made between two or more countries to give each other help if it is needed. When an alliance is signed, those countries become known as Allies. • A number of alliances had been signed by countries between the years 1879 and 1914. These were important because they meant that some countries had no option but to declare war if one of their allies. declared war first
Formation of the Triple Alliance • In 1879 Germany and Austria- Hungray agreed to form a Dual Alliance. • This became the Triple Alliance when in 1882 it was expanded to include Italy, The three countries agreed to support each other if attacked by either France or Russia. It was renewed at five-yearly intervals. • The formation of the Triple Entente in 1907 by Britain, France and Russia reinforced the need for the alliance.
Formation of the Triple Entente • In 1882 Germany, Austria Hungary and Italy formed the Triple Alliance. The three countries agreed to support each other if attacked by either France or Russia. • France felt threatened by this alliance. Britain was also concerned by the growth in the Germany Navy and in 1904 the two countries signed the Entente Cordiale (friendly understanding). The objective of the alliance was to encourage co-operation against the perceived threat of Germany. • Three years later, Russia who feared the growth in the Germany Army, joined Britain & France to form the Triple Entente. • The Russian government was also concerned about the possibility of Austria Hungary increasing the size of its empire. It therefore made promises to help Serbia if it was attacked by members of the Triple Alliance
Arms races • The naval arms race that developed between Britain and Germany was intensified by the 1906 launch of HMS Dreadnought, a revolutionary warship that rendered all previous battleships obsolete. (Britain maintained a large lead over Germany in all categories of warship.) It has pointed out that both nations believed in thesis that command of the sea was vital to a great nation. • Davis Stephoson described the armaments race as "a self-reinforcing cycle of heightened military preparedness", while other Historians, viewed the shipbuilding rivalry as part of a general movement towards war. However, Niall Fergueson argues that Britain’s ability to maintain an overall advantage signifies that change within this realm was insignificant and therefore not a factor in the movement towards war..
The naval strength of the powers in 1914
Crisis • Moroccan Crisis In 1904 Morocco had been given to France by Britain, but the Moroccans wanted their independence. In 1905, Germany announced her support for Moroccan independence. War was narrowly avoided by a conference which allowed France to retain possession of Morocco. However, in 1911, the Germans were again protesting against French possession of Morocco. Britain supported France and Germany was persuaded to back down for part of French Congo.
Bosnian Crisis • In 1908, Austria-Hungary took over the former Turkish province of Bosnia. • This angered Serbians who felt the province should be theirs. Serbia threatened Austria-Hungary with war, Russia, allied to Serbia, mobilised its forces. Germany, allied to Austria-Hungary mobilised its forces and prepared to threaten Russia. War was avoided when Russia backed down. • There was, however, war in the Balkans between 1911 and 1912 when the Balkan states drove Turkey out of the area. The states then fought each other over which area should belong to which state. • Austria-Hungary then intervened and forced Serbia to give up some of its acquisitions. Tension between Serbia and Austria-Hungary was high.
The Black Hand • In May 1911, ten men in Serbia formed the Black Hand Secret Society. Early members included Colonel Dragutin Dimitrijevic, the chief of the Intelligence Department of the Serbian General Staff, Major Voja Tankosic and Milan Ciganovic. • The main objective of the Black Hand was the creation, by means of violence, of a Greater Serbia. Its stated aim was: "To realize the national ideal, the unification of all Serbs. This organisation prefers terrorist action to cultural activities; it will therefore remain secret."
By 1914 there were around 2,500 members of the Black Hand. The group was mainly made up of junior army officers but also included lawyers, journalists and university professors. • Three senior members of the Black Hand group, Dragutin Dimitrijevic, Milan Ciganovic, and Major Voja Tankosic, decided that Archduke Franz Ferdinand should be assassinated. Dimitrijevic was concerned about the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, Ferdinand's plans to grant concessions to the South Slavs. • Dimitrijevic feared that if this happened, an independent Serbian state would be more difficult to achieve.
The People chosen for the task • Gavrilo Princip, Nedjelko Cabrinovic and Trifko Grabez from Serbia to assassinate him.
QUESTIONS • What is meant by the term alliance? • Which countries were allied by the Triple Alliance? • Which countries were allied by the Triple Entente? • Why was Germany annoyed by Imperialism? • Which armies had increased in size between 1870 and 1914? • Describe the Schlieffen Plan. • Why were the two crises important factors?
Which countries were bound to each other by which alliance? • How did imperialism contribute towards Germany’s increasing anger with Britain and France? • Why was nationalism an important factor? • Describe the part played by Germany in increasing European militarism. • What links were there between the two crises and: Alliances Imperialism Militarism Nationalism
The Background to the Assasination • Archduke Franz-Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary wanted to marry the beautiful Countess Sophie von Chotkowa und Wognin (Sophie Chotek). • Emperor Franz Josef forbade the marriage; Franz Ferdinand was heir of a noble royal family. He was supposed to marry royalty. Sophie was only a commoner. • The two eloped and married secretly, anyway, on 28 June 1900. Then they returned to face the music. Franz Josef ruled that they could not be seen together in public, since an Archduke could not appear with a mere Countess as his consort. • She was raised by Franz Josef to Princess of Hohenberg when she married Franz Ferdinand in 1900, and to Duchess of Hohenberg in 1907. But Franz Josef disliked Sophie, and she was continually insulted and slighted in Vienna. • Franz Ferdinand was hurt by the ban on public appearances, until he found a loophole: as Field Marshall of the army he could appear with his wife (for a Field Marshall could be seen with a commoner as his consort). It was this that led Franz Ferdinand to go to more and more army reviews, and was to lead to his death.
In 1914, Austria-Hungary was a world power, but its rulers were afraid. • They feared nationalism. • Many different races lived in the Austrian Empire; fifteen different languages were spoken within its borders. • If nationalism caught on in Austria-Hungary, the Empire would fall apart.
The small nation-states in the south-east of Europe (`the Balkans') were very nationalistic. Serbia was the worst. • In Serbia, there was a group called Union or Death (nicknamed the `Black Hand'). It was the Balkan equivalent of the IRA. It was dedicated to uniting all Serbs. • Many Serbs lived in the Austrian province of Bosnia, and after 1908 the Black Hand waged a terrorist war there, with bombings, shootings and poisonings. • The Austrian Army wanted to destroy the Black Hand by attacking Serbia.
Assassination at Sarajevo • On 28 June 1914, the Archduke Franz-Ferdinand and his wife visited Sarajevo, the capital of Bosnia, to review these troops. • It was a sunny Sunday morning. It was the Archduke's wedding anniversary. But the Archduke could not have chosen a worse day to go to Sarajevo. • It was also Serbia's National Day - the anniversary of the battle, in 1389, when Serbia had been conquered by the Turkish Ottoman Empire, yet at which a Serb hero, Milos Obilic, had assassinated the Ottoman Sultan. The day was inextricably linked with Serbian nationalism, and with the assassination of foreign rulers. • Waiting for Franz Ferdinand, lined up along the Appel Quay, Sarajevo's main road, were six young men. They were armed with pistols and bombs supplied by the Black Hand. They were going to try to murder Franz Ferdinand
Austrian spies in Serbia had reported that there was going to be an assassination attempt. Panic, the Prime Minister of Serbia, had also told the Austrian government that there was going to be trouble. • Franz Ferdinand ignored these warnings. Only 120 policeman were on duty in Sarajevo, and they were so excited that they forgot to watch the crowds, and looked at the procession instead. • Franz Ferdinand was dressed in the ceremonial uniform of an Austrian cavalry general, with a blue tunic, a high collar with three stars, and a hat adorned with pale-green feathers. • He wore black trousers with red stripes down the sides and around his waist a Bauchband, a gold-braided ribbon with tassels.
To reach the Town Hall the procession had to drive along the Appel Quay. The six conspirators had posted themselves along the route; the Appel Quay was `a regular avenue of assassins.' As the procession moved along the Appel Quay there were a few shouts of Zivio! ('Long may he live!'). • At 10.10 am, as the procession drew near the Cumuria Bridge.
Near the Cumuria bridge: • 1st Mehmed Mehmedbasic: told a friend that he could not get a clear opportunity; told Albertini in 1937 that a policeman had approached him just as he was to throw the bomb. • 2nd Vaso Cubrilovic: told investigation that felt sorry for the Duchess; told Albertini that he was badly placed. • 3rd Nedeljko Cabrinovic: threw a bomb. Wearing a long black coat and a black hat, he asked a policeman to tell him which car the Archduke was in; seconds later he had knocked the cap off a hand grenade against a metal lamp-post and aimed it at the Archduke seated in the open car. Franz Ferdinand later claimed that he had knocked away the bomb with his hand; witnesses at the trial, however, all agreed that the bomb had bounced off the folded-back hood of the Archduke's car. It blew up the car behind, killing two officers and injuring about twenty people. Cabrinovic swallowed poison, but it failed to work. After stopping to see what had happened, Franz Ferdinand's car sped to the Town Hall. • 4th (landward side) Cvetko Popovic: told a friend that could not sec which was Franz Ferdinand because he was short-sighted; told the trial the lost his nerve.
After attending the official reception at the City Hall, Franz Ferdinand asked about the members of his party that had been wounded by the bomb. • When the archduke was told they were badly injured in hospital, he insisted on being taken to see them. A member of the archduke's staff, Baron Morsey, suggested this might be dangerous, but Oskar Potiorek, who was responsible for the safety of the royal party, replied, "Do you think Sarajevo is full of assassins?“ • However, Potiorek did accept it would be better if Duchess Sophie remained behind in the City Hall. When Baron Morsey told Sophie about the revised plans, she refused to stay arguing: "As long as the Archduke shows himself in public today I will not leave him." • In order to avoid the city centre, General Oskar Potiorek decided that the royal car should travel straight along the Appel Quay to the Sarajevo Hospital. However, Potiorek forgot to tell the driver, Franz Urban, about this decision. On the way to the hospital, Urban took a right turn into Franz Joseph Street.
One of the conspirators, Gavrilo Princip, was standing on the corner at the time. Oskar Potiorek immediately realised the driver had taken the wrong route and shouted "What is this? This is the wrong way! We're supposed to take the Appel Quay!". • The driver put his foot on the brake, and began to back up. In doing so he moved slowly past the waiting Gavrilo Princip. • The assassin stepped forward, drew his gun, and at a distance of about five feet, fired several times into the car. Franz Ferdinand was hit in the neck and Sophie von Chotkovato in the abdomen. • Princip's bullet had pierced the archduke's jugular vein but before losing consciousness, he pleaded "Sophie dear! Sophie dear! Don't die! Stay alive for our children!“ • Franz Urban drove the royal couple to Konak, the governor's residence, but although both were still alive when they arrived, they died from their wounds soon afterwards.
Nedjelko Cabrinovic, statement in court (23rd October, 1914) • We did not hate Austria, but the Austrians had done nothing, since the occupation, to solve the problems that faced Bosnia and Herzegovina. Nine-tenths of our people are farmers who suffer, who live in misery, who have no schools, who are deprived of any culture. • We sympathized with them in their distress. We thought that only people of noble character were capable of committing political assassinations. We heard it said that he (Archduke Franz Ferdinand) was an enemy of the Slavs. Nobody directly told us "kill him"; but in this environment, we arrived at the idea ourselves. • I would like to add something else. Although Princip is playing the hero, and although we all wanted to appear as heroes, we still have profound regrets. In the first place, we did not know that they late Franz Ferdinand was a father. We were greatly touched by the words he addressed to his wife: "Sophie, stay alive for our children." We are anything you want, except criminals. • In my name and in the name of my comrades, I ask the children of the late successor to the throne to forgive us. As for you, punish us according to your understanding. We are not criminals. We are honest people, animated by noble sentiments; we are idealists; we wanted to do good; we have loved our people; and we shall die for our ideals.
July Crisis and the declarations of war • After the assassination of the Arckduke Franz Ferdinand on June 28, Austria-Hungary waited for 3 weeks before deciding on a course of action. • This wait was due to a large part of the army being on leave to help in gathering the harvest, which practically denied Austria the possibility of military action at the time. • On July 23, assured by unconditional ('carte blanche') support of the Germans should war break out, it sent an ULTIMATUM to Serbia containing many demands, among them that Austrian agents would be allowed to take part in the investigation, and in general holding Serbia responsible for the assassination. • The Serbian government accepted all the terms, except that of the participation of the Austrian agents in the inquiry, which it saw as a violation of its sovereignty. Emboldened by last minute Russian support, Serbia rejected the ultimatum. • Austria-Hungary, in turn, rejected the Serbian reply on July 26. Breaking diplomatic relations, the Austro-Hungarian Empire declared war on Serbia on July 28, proceeding to bombard Belgrade on July 29. On July 30 Austria-Hungary and Russia both ordered general mobilization of their armies.
The Germans, having pledged their support to Austria-Hungary, sent Russia an ultimatum to stop mobilization within 12 hours on July 31. • On August 1, with the ultimatum expired, the German ambassador to Russia formally declared war. On August 2 Germany occupied Luxembourg, as a preliminary step to the invasion of Belgium and the Schlieffen Plan (i.e. Germany had planned to attack France first according to the plan, and then Russia, which had already gone wrong) the same day yet another ultimatum was delivered to Belgium, requesting free passage for the German army on the way to France. • The Belgians refused. At the very last moment, the Kaiser Wilhelm II asked Moltke, the German Chief of General Staff, to cancel the invasion of France in the hope this would keep Britain out of the war. • Moltke, horrified by the prospect of the utter ruin of the Schlieffen Plan, refused on the grounds that it would be impossible to change the rail schedule- "once settled, it cannot be altered". • On August 3 Germany declared war on France, and on August 4 invaded Belgium. This act, violating Belgian neutrality to which Germany, France, and Britain were all committed to guarantee, gave Britain, which up to that point had yet to choose a side in the conflict, a reason to declare war on Germany on August 4.
Opening hostilities • Some of the first hostilities of the war occurred in Africa and in the Pacific Ocean, in the colonies and territories of the European powers. • On August 1914 a combined French and British Empire forces invaded the German protectorate of Togoland in West Africa. Shortly thereafter, on August 10, German forces based in South West Africa attacked South Africa, part of the British Empire. • Another British Dominion, New Zealand, occupied German Samoa (later Western Samoa) on 30 August; on September 11 the Australian Naval & Military Expeditionary Force landed on the island of Neu Pommern (later New Britain), which formed part of German New Guinea. • Within a few months, the Entente forces had driven out or had accepted the surrender of all German forces in the Pacific. Sporadic and fierce fighting, however, continued in Africa for the remainder of the war.
In Europe, the Central Powers — the German Empire and the Austro-Hungarian Empire - suffered from mutual miscommunication and lack of intelligence regarding the intentions of each other's army. • Germany had originally guaranteed to support Austria-Hungary's invasion of Serbia, but practical interpretation of this idea differed. • Austro-Hungarian leaders believed Germany would cover her northern flank against Russia. Germany, however, had planned for Austria-Hungary to focus the majority of its troops on Russia while Germany dealt with France on the Western Front. • This confusion forced the Austro-Hungarian Army to split its troop concentrations. Somewhat more than half went to fight the Russians on their border, a somewhat smaller force was allocated to invade and conquer Serbia.
Serbian Campaign {WWI} • The Serbian army fought a defensive battle against the invading Austrian army (called the Battle of Cer) starting on 12 August. • The Serbians occupied defensive positions on the south side of the Drina and Save rivers. • Over the next two weeks Austrian attacks were thrown back with heavy losses. • This marked the first major Allied victory of the war. Austrian expectations of a swift victory over Serbia were not realized and as a result, Austria had to keep a very sizable force on the Serbian front, weakening their armies which faced Russia.
The German war plan to deal with the Franco-Russian alliance (called the Schlieffen plan) involved delivering a knock-out blow to the French and then turning to deal with the more slowly mobilized Russian army. Rather than invading eastern France directly, German planners deemed it prudent to attack France from the north. • To do so, the German army had to march through Belgium. Germany demanded free passage from the Belgian government, promising to treat Belgium as Germany's firm ally if permission was granted. • The Belgian government's refusal to come to terms at zero-hour was an unpleasant surprise but the German army chose to follow through with its plan just the same. After entering Belgian territory, it soon encountered resistance at a fortified Liege. • Although the army as a whole continued to make rapid progress into France, it was Britain's decision to declare war on Germany and honor a dated protection pact with Belgium that left the German government in disbelief and seriously hindered the military's plans. • Britain sent an army to France (the British Expenitionary Force or BEF) which advanced into Belgium and slowed the Germans. The first British soldier killed in the war was John Parr, on 21st August 1914, near Mons.
- More by User

World War 1
First World War (WW1) was a global military conflict which involved the majority of the world's great powers.
6.56k views • 39 slides

“The War to End All Wars”. World War 1. WW1. “Only the dead have seen the end of war.” George Santayana. Discussion Questions. Is the concept of “a war to end all wars” possible? Is war inevitable (unavoidable)? Why or why not? What causes war?
919 views • 68 slides

World War 1. Year 1914. Index. 1. General information about World War 1 2. The year 1914 3. Schlieffen Plan 4. Important battles 5. The Christmas Truce 6. Analysis of the year 7. Sources. World War 1. The Great War, from August 1914 to November 11,1918
376 views • 15 slides

WORLD WAR 1. By Eoin b And Calum. This is the solders going over the top. Random facts. World War 1 began on July 28, 1914 and lasted until November 11, 1918.
372 views • 6 slides
World War 1. Canada – The War at Home. Government Policy. War Measures Act: August, 1914 – This law granted government sweeping powers to suspend the legal and political rights of Canadian citizens.
170 views • 9 slides

World War 1.
484 views • 32 slides

World War 1. Megan , Heather , and Troy . Weapons. Poison gases Machine Guns Zeppelin Tank. Planes Torpedoes Rifle. Trench Warfare. Miles of trenches snaked through Western Europe from 1914-1918 Each side had their own trenches filled with soldiers, trench life was horrible.
257 views • 9 slides

World war 1
World war 1. Random facts.
139 views • 8 slides

World War 1. The beginning of World W ar 1. World War 1 started July 28, 1914 and ended November 11, 1918. They used poisonous gases, which were mustard and horrible chlorine gas .It would drown the person in their own liquid that their own bodies would produce. .
454 views • 13 slides

World War 1. The War to end all Wars!!. The Spark. The Assassin . Causes . Imperialism- colonization was nearly done around the world and the losers were jealous of the winners. Militarism- the rise in power of the military leaders led to buildups in weapons and personnel.
433 views • 27 slides

World War 1. Tension in the Balkans. Imperialism. Why would Britain feel threatened by the rise of a German Empire?. What is the message behind this cartoon? Where has the cartoon been produced?.
391 views • 12 slides

By : Baylie Glass and Helen Tran. World War 1. Time Period. The war started in 1914 and ended in 1918. In 1914 Austria-Hungary’s Archduke Francis Ferdinand and his wife were shot by a person from Serbia. By 1914 nations all over Europe had new technology. Location of WW1.
312 views • 10 slides

World War 1. The Great War. World War I devastated Europe’s economies, and the social and political orders. People were overwhelmed by the destruction, casualties and size of the battles. More disturbing because it followed an age of progress.
555 views • 36 slides

World War 1. The Causes . The four main causes began in the 1800s. The Period of Time. 1914-1918. The late 1800s to the early 1900s was a time of great hope in Europe. The Causes.
358 views • 15 slides

World War 1. Heather Nguyen - May 2012 - French 2, 3B. Timeline. Archduke Ferdinand and his wife Sophie are shot and assasinated at Sarajevo by members of the Black Hand. T he First Battle of Ypres happens, and the British lose a huge amount of soldiers. Italy joins the war. June 28, 1914.
489 views • 7 slides

World War 1. Nichole Rodriguez 3B http://www.historyonthenet.com/WW1/WW1_timeline.htm . World War 1 TimeLine. Germany declared war on France. Japan Declared war on Germany. Assassination of Franz Ferdinand. June 28,1914. Aug 1, 1914 . Aug , 1914. Aug 3,1914. Aug 4, 1914. Aug 13, 1914.
731 views • 8 slides

World War 1. Causes of the First World War. Several factors led to the war : 1. France and Germany butted heads over control of Alsace-Lorraine, a piece of land located on the border of the two countries ( 1871 ) . Russia's efforts to control the Balkans, so they can gain access
535 views • 12 slides

World War 1. KWL Chart. You must list 3 things you know about WWI 3 things you want to know about WWI 7 things you learned in the unit ( this will be take up with your test). World War 1 ( Introduction). World War 1 Essential Questions.
743 views • 54 slides
World War 1. Canadian Battles – The Somme CCH2P / D. The Somme, 1916. July 1 – November 18, 1916 A British offensive led by British General Haig A series of out-dated poorly planned battles along the Somme River lasting 5 months. The Somme. The Somme, 1916. The Somme.
235 views • 7 slides

World War 1. 1914-1918. Why did Congress reject the League of Nations?. Background Information European Allies were furious with Germany after WWI and wanted a treaty that punished Germany and made them pay for the damage of the war.
480 views • 27 slides

3.28k views • 216 slides

World war 1. by ISABELLA RATCLIFF. POPPIES. Poppies are a kind of flower,they are red and delicate flower. They help us remember the ones who died in ww1 and ww2. poppies are a beautiful flower. Anzac biscuits .
195 views • 4 slides

WW1 • World War One Free Presentation Template for Powerpoint (PPT) and Google Slides
Google slides theme and powerpoint template.
All the key moments about the First World War in one presentation. Download free WW1 Free Presentation Template by Slidecore to present all the milestones of this conflict. It features stunning stock footage , real content, and a timeline that summarizes key points. Available for Google Slides and PowerPoint (PPT).
Use as Google Slides theme

Buy Me a Coffee
It is not necessary, but you can donate to help me continue creating amazing free templates! :D
Support us!
Tutorials and Tips
- How To Reduce Your PowerPoint File Size Optimizing The Images
- How To Convert A PowerPoint To Google Slides (Steps)
Description
Additional information.
What you ill find in the template:
- Real content about World War One, key moments and dates.
- Animated timeline that shows the highlights about the conflict.
- Extra slides with beautiful covers you can adapt easily.
- 39 slides crafted in a 16:9 layout.
- Elegant red and black colors and stunning typography .
- Black and White images of real stock footage and real content .
- + 90 basic icon pack included.
- Download this document as many times as you want in Power Point or open it in Google Slides.
- Big shout-out to Unsplash and Pixabay that provided us with the free resources of this presentation. Special thanks to the source article from Britannica.com used for this presentation.
Not exactly what you are looking for? No problem, you can continue exploring more free presentations here.
| Color | Black, Red |
|---|
Related products

Malek • App Presentation Powerpoint Template

Solis • Animated Solar System Free Presentation Template for Powerpoint and Google Slides

Venu – Nutrition & Health Free Template

Pointer – SEO Strategy Plan Free Presentation Template
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
© 2024 Slidecore Templates.
- Health & Medical
- Miscellaneous
Privacy Overview
- Preferences

World War 1 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

World War 1
World war 1 1914-1918 the war to end all wars the great war causes of wwi nationalism a strong sense of believing in ones own country to where your ... – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- The War to End all Wars
- The Great War
- Nationalism a strong sense of believing in ones own country to where your own country is better than any other
- Alliance systems countries form a huge alliance with each other in order to intimidate other countries from attack them
- The Triple Alliance-Germany, Austria, Hungary, and Italy
- The Triple Entente- France, Great Britain, and Russia
- Balkan crisis in 1908 Austria-Hungary annexed Bosnia nationalists there angry about it
- Militarism glorification of the military Many countries were preparing for war even before they had anyone to fight
- June 28, 1914, Archduke Francis Ferdinand, heir to the Austrian throne, was Assassinated during a visit to a rival country
- He was shot by a Serbian terrorist, member of the Black Hand
- Hungary had imperial control over Serbia (Serbia was key in controlling the Balkans
- Serbian (Balkan) nationalists didnt like it so to show it they assassinated the archduke
- Alliance system goes into effect
- Russia declares war on Austria-Hungary
- Germany declares war on Russia
- France declares war on Germany
- Great Britain declares war on Germany because GB had allied with France and Germany had attacked neutral Belgium
- Germany makes the first move because they are still angry over the
- decisions in the Congress of Vienna
- - in the agreement European monarchs took territory away from Germany
- Germany hoped for a quick victory by use of its well thought out plan called the Schlieffen Plan
- France responded and stopped the German troops by building trenches all the way to the English Channel
- This line becomes known as the Western Front
- This form of warfare (Trench Warfare) becomes the chief way of fighting during WWI and leads to stalemate
- Troops advanced from trench to trench, across No Mans Land, then retreat back to their former trenches
- Troops spent years living in the trenches full of human death, feces, and rats
- There was nothing to eat except for what supply lines brought troops - soldiers even ate rats, b/c vegetation had been bombed
- Maxim Machine Gun
- Gas- Mustard, Chlorine
- Estimated totals of causalities of Gas attacks
- German-Fatal-9,000.Non Fatal-200,000
- British-Fatal-8109.Non Fatal-188,706
- Tanks- British Mark I T
- Slow, but created a fear factor
- Submarine U-Boat , unterseeboot invented by Germany and used to stop US, British supply convoys and troops ships
- Airplane- Used at first for reconnaissance, surveillance.
- During the last year of the war, planes used for dog fighting to control the skies
- Red Baron German Manferd Von Riechtoven
- Shot down 80 allied planes before he was shot down
- A German U-Boat sank the Lusitania, U.S. ship, killing 126 passengers
- Public opinion sways in favor of kicking German butt
- The final peace settlement of Paris ended with five separate peace treaties with the 5 defeated nations of the war
- Versailles near Paris, France in June 1918.
- The Germans considered it a harsh treaty
- article 231 War Guilt clause said Germany was responsible for starting the war.
- The other articles in the treaty required Germany to pay reparations for the war to the Allied Nations for ALL the damage the nations had suffered during the war
- - How can a war torn country, now 30 billion in debt, pay it back?
- This Treaty will be one of the chief reasons Germany will be thrown into World War 2
- Triple Alliance
- Triple Entente
- Nationalism
- Alliance System
- Balkan Crisis
- Schlieffen Plan
- Western Front
- Trench Warfare
- No Mans Land
- New Technology
- Reconnaissance
- Treaty of Versailles
- Reparations
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.

- Create an Account

Educational Resources

Lesson Plans

And Still, They Served
And Still, They Served: Black Servicewomen in World War II examines the critical roles that Black servicewomen play in the U.S. Armed Forces during World War II.

One Small Step For Women
Explore the contributions of servicewomen in support roles during the Space Race through the collection of Pearl Tucker, the Mother of aerospace nursing. Students will analyze primary sources and use critical thinking and discussion to explore various aspects of the Space Race, including the role of aerospace nurses, and consider the costs and viability of the space program.

Service & Suffrage
Examine the role of American servicewomen in World War I in the fight for women’s suffrage in the United States.
And Still, They Served: Black Servicewomen in World War II
Nearly 9,000 African American women served throughout the United States and in England under racially segregated and discriminatory conditions. Black servicewomen trained in all-Black units and were permitted only to compose a certain enlistment quota. They served largely in support roles and in positions of menial and manual labor. They were barred from the same advancement opportunities given to white women and almost entirely prohibited from serving overseas. And still, they served.
Grades 6-12
1-2 Class Periods
Meets standards of learning in history and social studies for Common Core, Virginia and the National Council for the Social Studies Standards.
This lesson plan, resource packet and presentation resource was created in part with the Military Women’s Memorial exhibit: The Color of Freedom.
Lesson Plan
Resource Packet

Presentations

Presentation to Print
Powerpoint Presentation

One Small Step For Women: American Servicewomen in the Space Race
This program examines the contributions of American servicewomen to the Space Race. From the late 1950s through the 1960s, the United States engaged in the Space Race against the Soviet Union, each trying to become the first country to put a man on the moon. The US and Soviet Union believed that having such capabilities would demonstrate a technological advantage over the other. NASA formed in 1958 to oversee aeronautical and space programs. President John F. Kennedy cemented America’s determination to win the Space Race in a 1962 speech in which he vowed to go to the moon by the end of the decade, demonstrating the importance of the Space Race to foreign policy.
Early American astronauts were all men who had a military background. NASA decided not to allow women to become astronauts during this period. Although they were excluded from spaceflight, women contributed to the Space Race in supporting roles, including aerospace nursing.
1 class period
Meets standards of learning in history and social studies for Common Core, Virginia and the National Council for the Social Studies Standards.

Service & Suffrage: How Women’s World War I Service Won Them the Vote
This program examines the role of American servicewomen in World War I in the fight for women’s suffrage.
The women’s suffrage movement was nearly a century-long struggle that faced factionalism and opposition. The movement ended in a victory with the passage of the 19th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution in 1920, which gave women the right to vote nationwide.
Women who served in the military during World War I demonstrated that they, like American men, were willing to sacrifice for their country, and could perform important work independently. Women’s wartime contributions, including in and alongside the U.S. Military, advanced the arguments for women’s suffrage based on civic participation to include military service. Other suffragists continuously picketed the White House, ensuring the issues were not forgotten. President Woodrow Wilson, beleaguered by protestors and swayed by women’s service, finally put his support behind the women’s suffrage movement, paving the way for the passage of the 19th Amendment.
Grades 9-12
1 Class Period
Meets standards of learning in history and social studies for Common Core, Virginia and the National Council for the Social Studies Standards.

Digital Presentation
Request A Tour – Coming in the Future
Visiting the Memorial? We will be offering free overview tours of the Military Women’s Memorial. Take a journey through HERstory – women’s service to our nation, from the American Revolution through today. Learn about the Military Women’s Memorial – the history, mission, and our future.
Time: 30 to 45 minutes
When: During regular operating hours
Minimum notice: Availability is limited and will require 2 weeks minimum advance notice to schedule a tour.
To request: Coming soon
Online Exhibits

MEMORIAL AVE & SCHLEY DR ARLINGTON, VA 22203
Hours of Operation
MON – SAT 9:00am – 5:00pm
SUN 12:00pm – 5:00pm
We'd love to hear from you! PHONE: (703) 533-1155
Connect With Us

IMAGES
COMMENTS
1. Blockades. Lusitania torpedoed, sinking with 1200 passengers and crew (including 128 Americans) Was eventually found to be carrying 4200 cases of ammunition.
World War I. World War I. Death, Destruction, Displacement and. the Triumph of the Nation-State. A Century of Conflict Russian wars 1806-1812 Greek War of Independence 1821 Turko-Russian War 1828-1829 Second Turko-Russian War 1877-1878 The Balkan Wars 1912-1913 The First World War 1914-1917 The War of Independence 1917-1922 The theater of war ...
The War to End All Wars. World War 1 ended on November 1, 1918. The Allied powers (Triple Entente) were victorious giving Great Britain, France, Italy, and the United States were setting punishments for the Central Powers (Triple Alliance).
World War I Presentation Slides. World War I, which took place from 1914 to 1918, was a monumental global conflict involving major world powers. It was characterized by trench warfare, technological advancements, and immense human suffering. The war had far-reaching consequences, leading to political and territorial changes, the collapse of ...
Presentation on theme: "World War I."— Presentation transcript: 1 World War I. 2 What is a "world war"? 3 A world war is a war affecting the majority of the world's major nations. World wars usually span multiple continents, and are very bloody and destructive. Total war is a military conflict in which nations mobilize all available ...
This First World War curriculum is aimed at getting students to think beyond causes, major battles and ramifications of the conflict. The textbook and lecture should lay out a political, diplomatic, and military overview before or while teachers implement pieces of this curriculum. Since the First World War marks such a dividing line in modern ...
Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups. Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon's extension for customizing your slides. Designed to be used in Google Slides, Canva, and Microsoft PowerPoint. 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens. Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of ...
World War One 1914-1918. War Mania: people thought war was a very good idea at the time. Imperialism: European Countries competed over controlling land. Nationalism: every country thought that it was the best country. Also Serbians (and other people) wanted to be free from the Austro-Hungarian Empire's influence.
Description. Check out this engaging PowerPoint (or Google Slides) presentation on World War I from the American perspective. It will help your students learn about the alliance system that started World War I, some major battles (e.g. Battle of Verdun, Battle of the Marne), reasons for the United States joining the war, and much more!
Learn about the causes, events and consequences of World War I in this PowerPoint presentation created by Saint Louis Public Schools. This resource provides an introduction and overview of the global conflict that shaped the 20th century. Find out how the war affected the United States and the world.
Free Use Powerpoints. The Great War, World War I free use powerpoints for the classroom. For Kids. World War I for Kids. Games about WW1. Military Games
1.64k likes | 3.28k Views. WORLD WAR 1. CAUSES, PRACTICES & EFFECTS OF WAR. The World before World War I. The War was also known as THE FIRST WORLD WAR, THE GREAT WAR and famously " THE WAR TO END ALL WARS" It was a global military conflict that took place mainly in Europe between 1914 & 1918. Download Presentation. serbian general staff.
Description. World War 1 PowerPoint with video clips and presenter notes covers the atmosphere in Europe leading up the the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, World War I, and finishes with the Treaty of Versailles and how it led to WWII. This 25 slide WWI PowerPoint/ is packed with beautiful graphics, engaging video clips and presenter ...
Download free WW1 Free Presentation Template by Slidecore to present all the milestones of this conflict. It features stunning stock footage, real content, and a timeline that summarizes key points. Available for Google Slides and PowerPoint (PPT). What you ill find in the template: Real content about World War One, key moments and dates.
This World History PowerPoint bundle includes presentations, Google Slides, guided notes worksheets, and flipped classroom videos to cover World History from the French Revolution through to the Modern World. Each PowerPoint file includes a Guided Notes worksheet that students use to follow along wi. 20. Products. $55.50 $74.96 Save $19.46.
In this complete World War I unit guided notes and PowerPoint bundle, you receive a jam-packed 45-page PowerPoint presentation and 6 pages of guided notes for instruction on World War I, the theories of nationalism, militarism, the Web of Alliances, the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, the...
About This Presentation. Title: World War 1. Description: World War 1 1914-1918 The War to End all Wars The Great War Causes of WWI Nationalism a strong sense of believing in ones own country to where your ... - PowerPoint PPT presentation. Number of Views: 3434. Avg rating:3.0/5.0. Slides: 16.
Women who served in the military during World War I demonstrated that they, like American men, were willing to sacrifice for their country, and could perform important work independently. Women's wartime contributions, including in and alongside the U.S. Military, advanced the arguments for women's suffrage based on civic participation to ...
This pack includes PowerPoint and Guided Notes sets for Settling the West & Frontier Wars, the Gilded Age and Populism, Industrialization, Imperialism and Progressivism, U.S. in WWI, the. 13. Products. $110.00 $130.35 Save $20.35. View Bundle.