APA Title Page (Cover Page) Format, Example, & Templates
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
In APA Style (7th edition), the cover page, or title page, should include:
- A running head (professional papers only) and page number
- The title of the paper
- The name of the author(s)
- The institutional affiliation
- An author note; optional (professional papers only)
- A student paper should also include course information
Note : APA 7 provides slightly different directions for formatting the title pages of professional papers (e.g., those intended for scholarly publication) and student papers (e.g., those turned in for credit in a high school or college course).

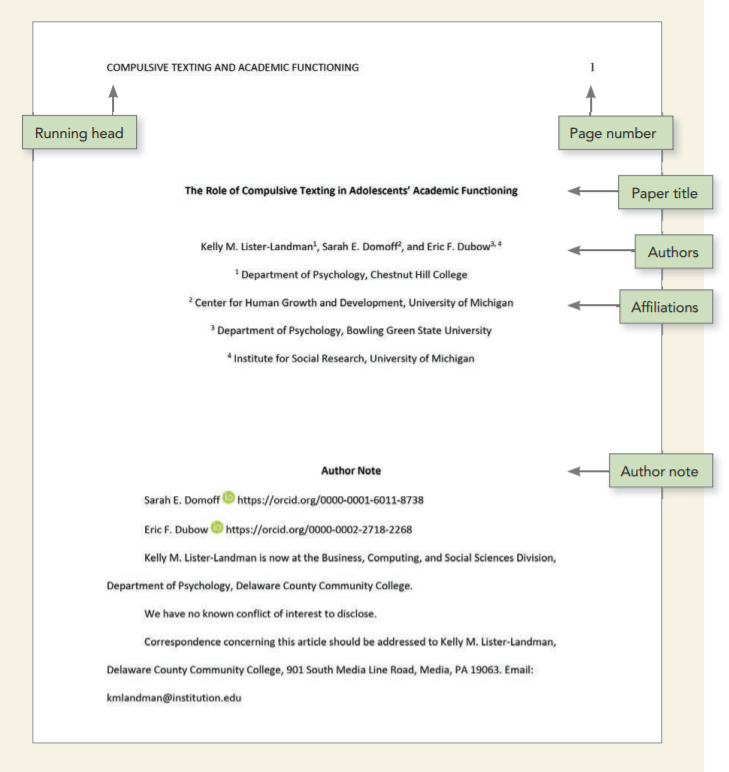
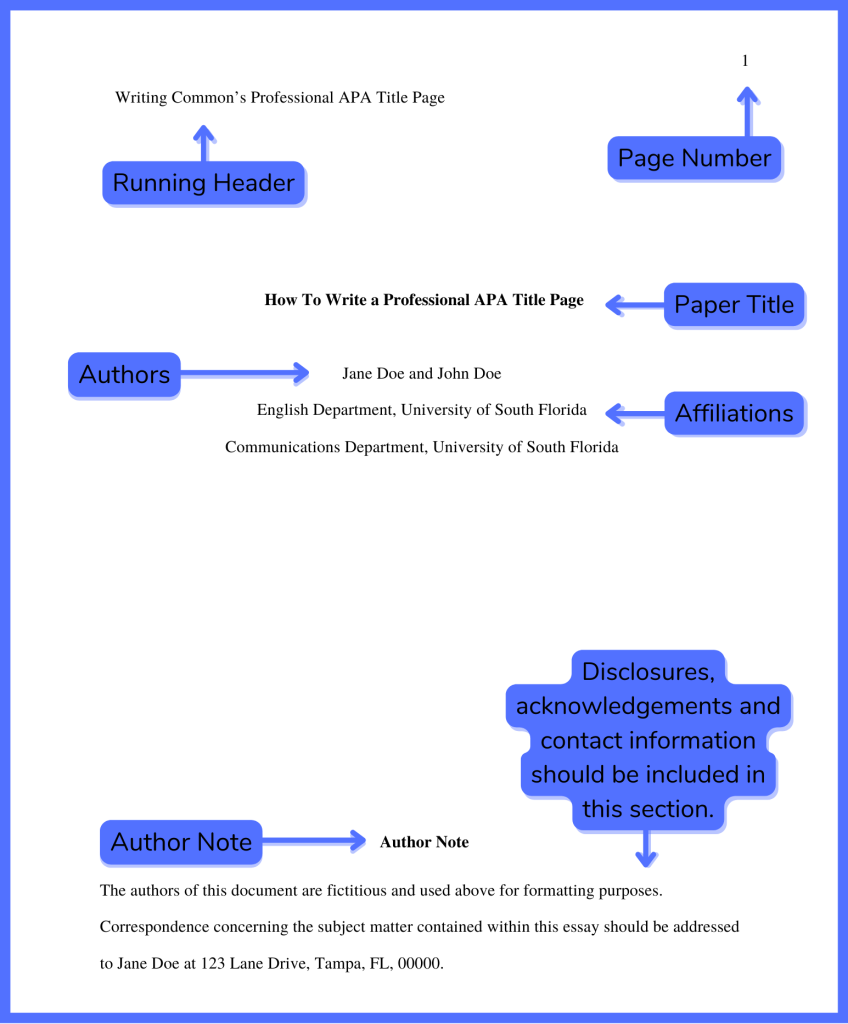
Professional paper APA title page
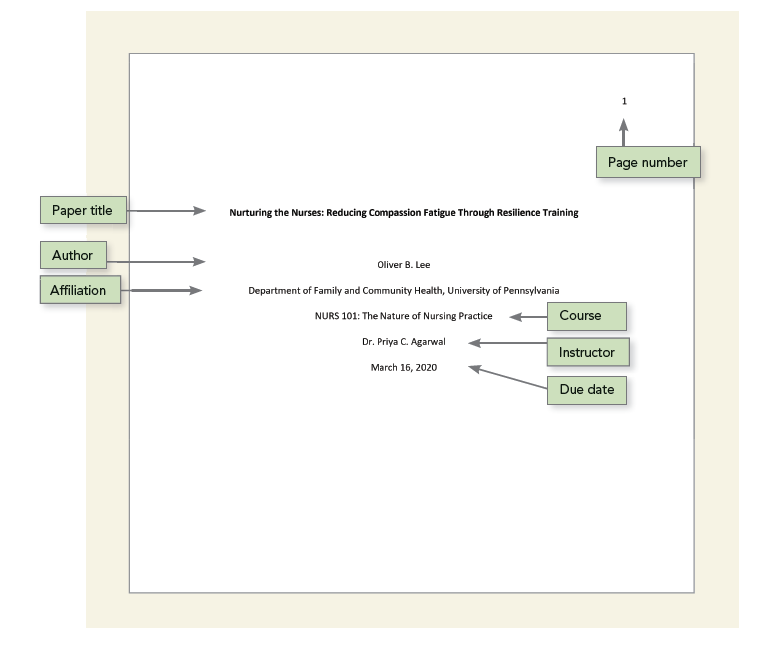
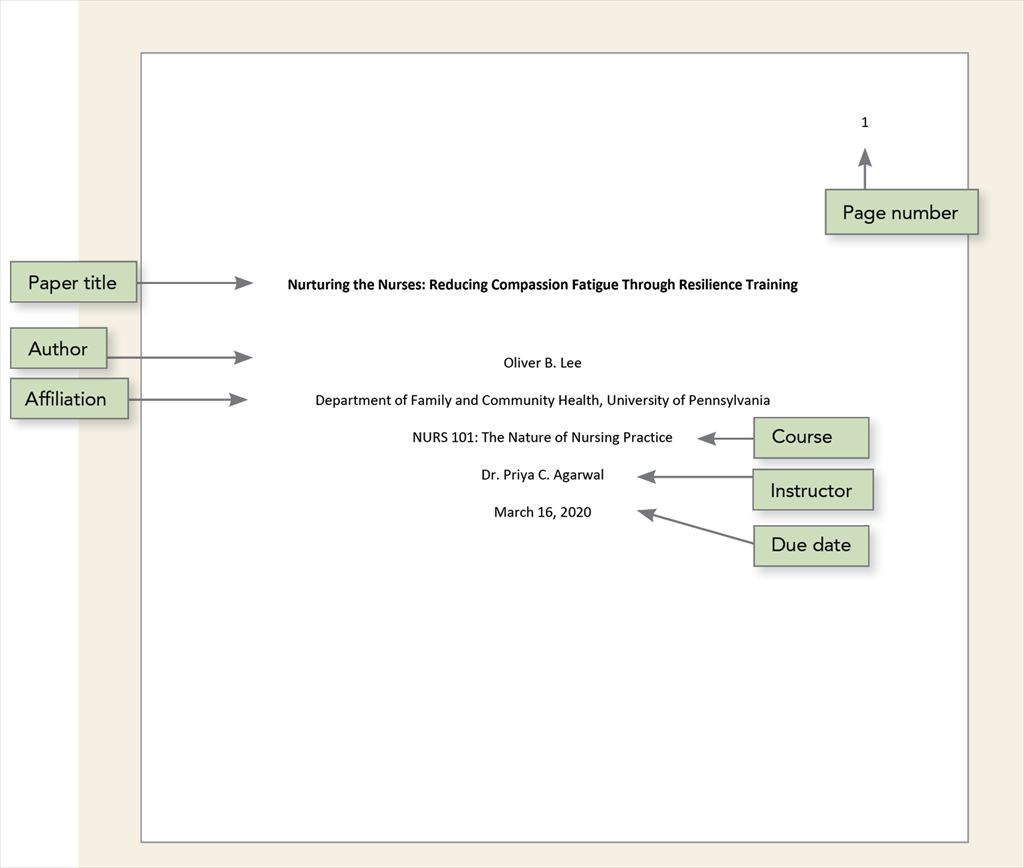
Student paper APA title page
Formatting an APA title page
Note : All text on the title page should be double-spaced and typed in either 12-point, Times New Roman font. In the 7th edition, APA increaded the flexibility regarding font options: which now include Calibri 11, Arial 11, Lucida Sans Unicode 10, Times New Roman 12, or Georgia 11. All words should be centered, and capitalize the first letter of important words.
Running Head
In the 7th edition of the APA style manual, running heads are only required for professional papers that are being submitted for publication (student papers do not require a running head, but still need a page number).
Your title page should contain a running head that is flush left at the top of the page and a page number that is flush right at the top of the page.
Place the running head in the page’s header:
- The running head is the abbreviated title of the paper (IN UPPERCASE LETTERS) aligned left on the page header of all pages, including the title page. APA (7th edition) guidelines require that running heads be a maximum of 50 characters (spaces count as characters).
- The “Running head:” label used in the APA sixth edition is no longer used.
- Place the page number in this same header, but align right, beginning with page number 1 on the title page.
- This header should be 1 inch from the top. Some instructors allow for 1/2 inch, too, but the default is 1 inch.
Paper Title
Position the title of the paper in the upper half of the page. The title should be centered and written in boldface, and important words should be capitalized.
The APA recommends that your title should be a maximum of 12 words and should not contain abbreviations or words that serve no purpose.
Author Name(s)
Institutional affiliation.
Position the school or university’s name below the author(s) name, centered.
A student paper should also include the course number and name, instructor name, and assignment due date.
Further Information
- APA Student Title Page Guide
- APA Referencing
- How to Write a Lab Report
- Essay Writing Guide for Psychology Students
- APA Style Citations & References
- Example of an APA Formatted Paper
Related Articles

Student Resources
How To Cite A YouTube Video In APA Style – With Examples

How to Write an Abstract APA Format

APA References Page Formatting and Example

How do I Cite a Source with Multiple Authors in APA Style?
How to Write a Psychology Essay

Lab Report Format: Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- The Complete Guide to APA Format in 2020
APA Title Page / Cover Page
- Headings and Subheadings
- Discussion Section
- Websites and Online Sources
- Journals and Periodicals
- Other Print Sources
- Other Non-Print Sources
- In-text Citations
- Footnotes and Endnotes
- Using MyBib Responsibly
- Miscellaneous Questions

Details to include
The title page (also known as the cover page) is the front page of your paper. It should contain:
- The running head , a header at the top of the page.
- The first page number .
- The title of the paper
- The institution for which you writing.
Running head
The running head should be in the top-left corner of the page in uppercase. It should include a shortened title of your paper. On the front page only, it should also be prepended with "Running head:".
First page number
The first page number -- generally page 1 -- should be in the top-right corner of the page. Both the page number and the running head should be a half inch from the top of the page.
The title of the paper can contain upper and lowercase letters, and ideally should be no more than 12 words in length. It should be direct, and should not contain abbreviations or other unnecessary words. It should not span longer than 2 lines. The first letter of each word should be uppercase, except for articles (a, an, the), and conjunctions (and, but, for, or, yet).
Underneath the title should be your name (or the author's name if you're not the author). It should be displayed as the first name , middle initial , and last name . Do not add titles (such as Dr.) to the beginning, or qualifications (such as PhD) to the end of an author's name.
Your institution
Finally, underneath the author's name, state the full name of the institution or school you're writing the paper for.
The font for all text on the title page should be Times New Roman, size 12pt, with double line-spacing.
A correct title page will look like the below image:

After completing your title page you will move on to writing an abstract of your paper.

APA Guide: 7th Edition
- Page Numbers
- Figures/Images
- Webpages and Other Online Content
- Legal Citations
- Writing Style
- Summary of Changes
Student Paper Example
- Student Paper Example This is a student paper example from the 7th Edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association.
Professional Paper Example
- Professional Paper Example This is a professional paper example from the 7th Edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association.
Student Title Page Elements
The title page includes the following elements: Page number, Paper title, Author, Author Affiliation, Course, Instructor, and Due Date . Remember, your instructor can include other requirements for your assignment. Refer to their instructions carefully.
Your title page and paper is double-spaced. Use 1-inch margins.
Acceptable Fonts:
- 11-point Calibri
- 11-point Arial
- 10-point Lucida Sans Unicode
- 12-point Times New Roman
- 11-point Georgia
- 10-point Computer Modern 1
- Should summarize the main idea in a succinct way .
- Include strong keywords so that readers can find your work in a database or by using a search engine.
- Avoid using abbreviations in a title.
- The title should be provided in title case . This means that all major words are capitalized.
- Be bolded, centered, and begin 3-4 lines down from the top margin of the paper.
- Put a double-spaced blank line between the title and the byline.
- The paper title also appears at the top of the first page of your paper.
Author Name(s) (Byline)
- Beneath the title, type the author's or authors' full name(s) .
- Do not use titles or degrees.
- Order the names of authors based on their contributions.
- Write all of the names on the same line.
- Center the names in a standard font.
- Smith and Doe
- Smith, Doe, and Jones
Author Affiliation
- Identify where you worked or studied when the body of work was completed.
- Include no more than two affiliations for each author.
- Example: College of Nursing and Health Innovation, University of Texas at Arlington
- Include the department or division.
- Include the name of the institution.
- Include the location of the institution.
- Example: Hematology/Oncology, Cook Children's Medical Center, Fort Worth, Texas, United States
- Include the location.
Locations should include the city, state, province, and country.
Course Name
- Put the course number and name below the Author Affiliation.
- Check with your instructor on the preferred name.
- Place the month, date, and year after the Instructor(s) name(s).
See the example title page below:

All content on this guide comes from the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association and from the APA Style Blog.
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association ( 7th ed.). https://doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000
American Psychological Association. (2020, October). Blog . https://apastyle.apa.org/blog
- << Previous: Page Numbers
- Next: Tables >>
- Last Updated: May 13, 2024 12:06 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uta.edu/apa
University of Texas Arlington Libraries 702 Planetarium Place · Arlington, TX 76019 · 817-272-3000
- Internet Privacy
- Accessibility
- Problems with a guide? Contact Us.
Table of Contents
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process, apa title page.
- © 2023 by Jennifer Janechek - IBM Quantum

What is an APA Title Page?
An APA Title Page refers to
- a Title Page for a longer document that is formatted according to the conventions prescribed by the American Psychological Association’s Publication Manual .
The title page is comprised of four elements and two optional elements:
Related Concepts: Archive; Scholarly Conversation; Organization
The Title Page appears at the top of the first page of an APA-styled paper.
Like the rest of the paper, the title page should be double-spaced and typed in Times New Roman, 12 pt. The margins are set at 1” on all sides.
Summary of Required & Optional Elements
- Page number
- Full title of paper
- Author byline (aka bio)
- Affiliated Institution(s) or Organization(s)
- Running head: The running head became optional in the 7th Edition of the Publication Manual.
- Author note
Required Components
- The full title of the paper is centered in the upper half of the page, and the first letter of each major word is capitalized. The paper’s title should be a maximum of 12 words and fill one or two lines; avoid using abbreviations and unnecessary words. Do not format the title with bold, italics, underlining, or quotation marks. The title should be centered in the upper portion of the page, centered, and written in boldface. Make sure to capitalize the major words of the title, such as The Silence of the Lambs . Keep your title as concise as possible! You’ll have plenty of time to be detailed in the body text.
- The author byline is comprised of the author(s)’ first name(s), middle initial(s), and last name(s); this line follows after the full title of the research paper. Note that two authors are separated by the word and, but more than two authors’ names are separated by commas. Do not include titles, degrees, or honorifics (Mr., Mrs., Mx., etc.).
- List the institutional affiliation of the author(s) involved with the research paper. Include the name of the college or university you attend, or the name of the organization(s) that provided support for your research.
Optional Components
- Running head (or shortened title) and label – Optional In accordance with APA 7th Edition updates, student papers typically no longer include a running head. If you are unsure about the need for a running head, be sure to consult with your professor. The running head and label is flush with the upper left-hand corner of the title page, while the page number is flush with the upper right-hand corner of the page. The label “Running head” should only appear on the title page; on all other pages, simply include the shortened title of the paper. All letters of the running head should be capitalized and should not exceed 50 characters, including punctuation, letters, and spaces. Example: EFFECTS OF NUTRITION ON MEMORY
- If you are a student, check to see whether your professor asked you to add any additional information in the Author note slot. Some professors require further information, including the date of submission, course number or title, or name of the professor. If your instructor requires you to include an author’s note, position it in the lower half of the title page. Follow your instructor’s directives regarding additional lines on the title page.
Example: APA Title Page of a Student Work
When creating the Title Page , professional and student papers have slightly different rules for APA. We’ll cover the rules that apply to both types first.
You’ll need to include the course number and name, the name of the professor, and the date your assignment is due. All of this should be done line by line beneath the name of your school.
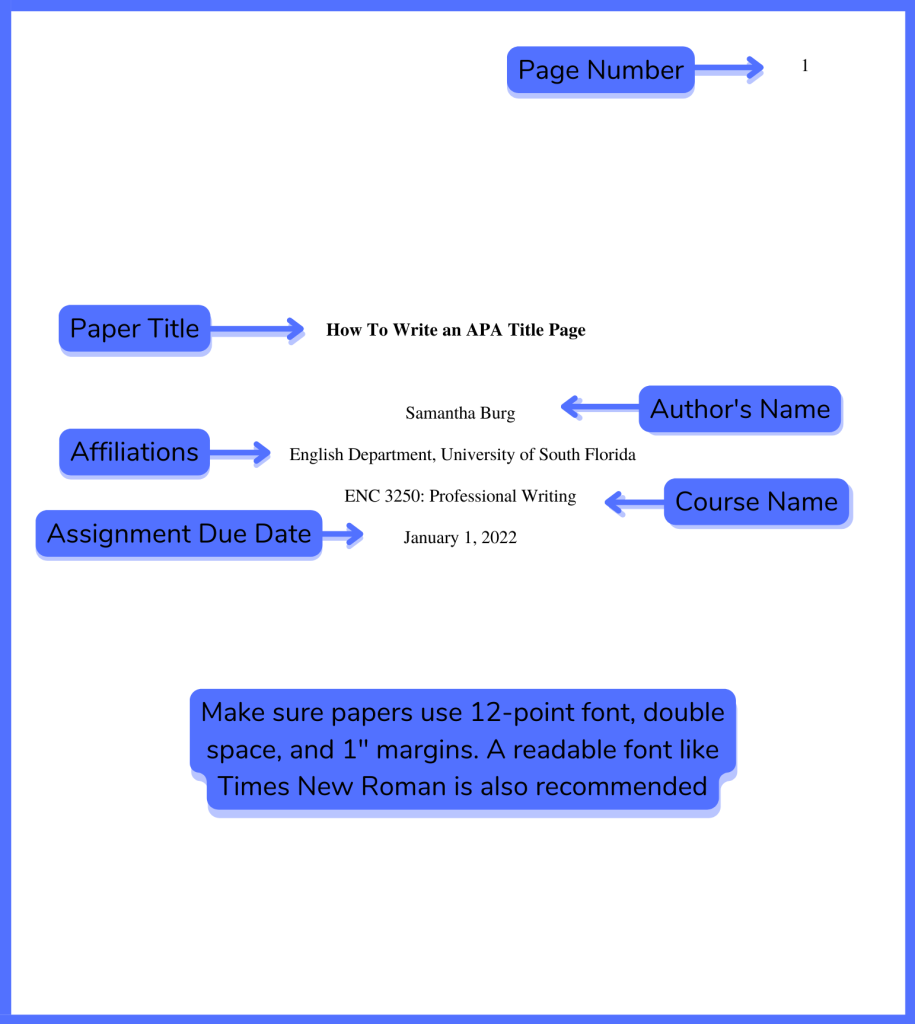
Image courtesy of the APA style guide
Example: APA Title Page of a Professional Work
You’ll need to include an author’s note underneath your institution on the bottom half of the page. There will be a couple of brief paragraphs to write for this note.
- The first paragraph should have the author’s name and symbol and URL for the ORCID iD. The ORCID iD can be excluded if you don’t have one.
- The second paragraph should include any changes in the institution or deaths of the authors.
- The third paragraph should include any disclosures, acknowledgments, or relevant information related to either.
- The fourth/final paragraph is where you’ll include the contact information for the author.
If any of these paragraphs are irrelevant, there is no need to include them. Simply skip to the next relevant one.
Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Recommended

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Structured Revision – How to Revise Your Work

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Research, Speech & Writing

Citation Guide – Learn How to Cite Sources in Academic and Professional Writing

Page Design – How to Design Messages for Maximum Impact
Suggested edits.
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

Title Page in Research Paper: Importance, Guidelines & Examples
Make your research paper stand out with an impressive title page. Learn how to craft the perfect title page in research paper in this guide.
The title page is a crucial component of a research paper, serving as the first point of contact between the reader and the study. It provides readers with a first impression, signaling the credibility and relevance of the work. Beyond conveying essential information, a well-designed title page adds visual appeal to the paper, contributing to its overall presentation. In this article, we will explore the importance of title pages in research papers, exploring how they capture attention, convey vital information, and enhance the overall quality of the study.
Overview of Title Page in Research Paper:
The title page in research paper is typically located at the beginning of the document and provides key information about the paper. The title page presents a professional and organized appearance, setting the tone for the entire research paper.
Purpose of a Title Page
The purpose of a title page in a research paper is to convey important details about the study. It includes the title of the paper, the author’s name, the institutional affiliation, and sometimes additional information such as the course name, instructor’s name, or submission date. The title page helps to identify and differentiate the research paper, making it easier for readers, instructors, and researchers to locate, reference, and cite the work accurately. Additionally, it establishes the credibility and professionalism of the study, demonstrating the author’s attention to detail and adherence to academic standards.
Creating a Title Page
To create a title page for a research paper, start by centering the title of your paper at the top of the page. Then, on separate lines, include your name, your affiliation (university or institution), and the date of submission. Optionally, you can also include the course name, instructor’s name, and any other relevant information specified by your institution or guidelines. Make sure to format the title page according to the required style guide (e.g., APA , MLA ) with consistent font, spacing, and alignment.
Elements of a Title Page
A title page is an essential component of a research paper, providing key information about the study and its authors. The elements commonly included on a title page are:
Title : Choose a concise and descriptive title that accurately reflects the main focus of your research. It should be informative, engaging, and capture the essence of your study.
Author’s Name : Include your full name as the author of the research paper. If there are multiple authors, list them in the order they contributed to the study.
Institutional Affiliation : Mention the name of the institution or organization with which you are affiliated. This could be your university, research institute, or academic department.
Course Information : If the research paper is being submitted for a course, include the course name and number.
Date : Indicate the date of submission or completion of the research paper.
Instructor : Include the instructor’s name below the author’s name, affiliation, and course (if the paper is being submitted for a course), using a centered format.
Page Number : Typically, the title page is counted as page 1, although it is often not numbered. Numbering usually starts on the second page, which is usually the abstract or introduction.
Formatting Guidelines for a Title Page
The formatting guidelines for a title page provide specific instructions on how to structure and present the elements of a title page in a research paper. These guidelines ensure consistency and uniformity in academic writing. They may vary depending on the required citation style, such as APA (American Psychological Association) or MLA (Modern Language Association).
APA Formatting Guidelines
The APA formatting guidelines provide a set of rules for formatting academic papers, including the title page. According to APA guidelines, the title page should include the title of the paper, the author’s name, institutional affiliation, and a running head. The running head is a shortened version of the paper’s title and appears at the top of each page. Additionally, APA guidelines specify the use of specific font size and type, margins, and alignment for the title page.
MLA Formatting Guidelines
The MLA formatting guidelines, commonly used in humanities and liberal arts disciplines, also provide instructions for creating a title page. According to MLA guidelines, the title page should include the title of the paper, the author’s name, the course name and number, the instructor’s name, and the due date. Unlike APA, MLA does not require a running head on the title page. MLA guidelines specify the use of specific font size and type, margins, and alignment for the title page.

Title Page Examples
Title page examples provide visual representations of how a title page should be formatted and organized in different contexts. These examples serve as valuable references for students and professionals to understand the layout and presentation of a title page in various academic or professional settings.
Student Version Example
A student version example of a title page demonstrates how a title page should be formatted for academic papers or assignments completed by students. It typically includes the paper’s title, the student’s name, the course name and number, the instructor’s name, and the date. This example is designed to meet the specific requirements and guidelines provided by the educational institution or instructor.
Professional Version Example
A professional version example of a title page showcases how a title page should be formatted for research papers, articles, or other professional documents. In addition to the title, it typically includes the author’s name, institutional affiliation, and any relevant professional credentials. This example follows the formatting guidelines of the specific citation style used in the professional field, such as APA or MLA, and may also include additional information such as the publication date or the name of the journal or conference.
6 Tips for Writing an Effective Title Page
Here are some tips for writing an effective title page:
1. Follow the formatting guidelines
Familiarize yourself with the specific formatting guidelines provided by your educational institution or the citation style you are using (such as APA or MLA). Adhere to these guidelines for font size, margins, spacing, and other formatting elements.
2. Use a clear and concise title
The title should accurately reflect the content of your paper or document in a concise and descriptive manner. Avoid using vague or ambiguous titles that may confuse readers.
3. Include relevant information
Include essential information such as the author’s name, the title of the work, the course or assignment name (if applicable), the instructor’s name, and the date of submission. Ensure that all required elements are included based on the guidelines provided.
4. Use consistent formatting
Maintain consistency in font style, size, and formatting throughout the title page. This helps create a professional and organized appearance.
5. Consider the placement of elements
Arrange the elements on the title page in a logical and visually appealing manner. Typically, the title is centered at the top, followed by the author’s name and other details.
6. Double-check for accuracy
Before finalizing your title page, review it carefully for any spelling or grammatical errors. Make sure all the information provided is accurate and up to date.
Communicate science visually with the best and free infographic maker
Mind the Graph platform offers scientists a valuable tool to communicate science visually through its exceptional and free infographic maker. With this platform, scientists can create stunning and informative infographics that effectively convey complex scientific concepts, data, and research findings in a visually appealing and accessible manner. Mind the Graph platform empowers scientists to transform their scientific content into captivating visual representations, enabling them to present their work with clarity, impact, and creativity.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Content tags

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
13.1 Formatting a Research Paper
Learning objectives.
- Identify the major components of a research paper written using American Psychological Association (APA) style.
- Apply general APA style and formatting conventions in a research paper.
In this chapter, you will learn how to use APA style , the documentation and formatting style followed by the American Psychological Association, as well as MLA style , from the Modern Language Association. There are a few major formatting styles used in academic texts, including AMA, Chicago, and Turabian:
- AMA (American Medical Association) for medicine, health, and biological sciences
- APA (American Psychological Association) for education, psychology, and the social sciences
- Chicago—a common style used in everyday publications like magazines, newspapers, and books
- MLA (Modern Language Association) for English, literature, arts, and humanities
- Turabian—another common style designed for its universal application across all subjects and disciplines
While all the formatting and citation styles have their own use and applications, in this chapter we focus our attention on the two styles you are most likely to use in your academic studies: APA and MLA.
If you find that the rules of proper source documentation are difficult to keep straight, you are not alone. Writing a good research paper is, in and of itself, a major intellectual challenge. Having to follow detailed citation and formatting guidelines as well may seem like just one more task to add to an already-too-long list of requirements.
Following these guidelines, however, serves several important purposes. First, it signals to your readers that your paper should be taken seriously as a student’s contribution to a given academic or professional field; it is the literary equivalent of wearing a tailored suit to a job interview. Second, it shows that you respect other people’s work enough to give them proper credit for it. Finally, it helps your reader find additional materials if he or she wishes to learn more about your topic.
Furthermore, producing a letter-perfect APA-style paper need not be burdensome. Yes, it requires careful attention to detail. However, you can simplify the process if you keep these broad guidelines in mind:
- Work ahead whenever you can. Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” includes tips for keeping track of your sources early in the research process, which will save time later on.
- Get it right the first time. Apply APA guidelines as you write, so you will not have much to correct during the editing stage. Again, putting in a little extra time early on can save time later.
- Use the resources available to you. In addition to the guidelines provided in this chapter, you may wish to consult the APA website at http://www.apa.org or the Purdue University Online Writing lab at http://owl.english.purdue.edu , which regularly updates its online style guidelines.
General Formatting Guidelines
This chapter provides detailed guidelines for using the citation and formatting conventions developed by the American Psychological Association, or APA. Writers in disciplines as diverse as astrophysics, biology, psychology, and education follow APA style. The major components of a paper written in APA style are listed in the following box.
These are the major components of an APA-style paper:
Body, which includes the following:
- Headings and, if necessary, subheadings to organize the content
- In-text citations of research sources
- References page
All these components must be saved in one document, not as separate documents.
The title page of your paper includes the following information:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Name of the institution with which the author is affiliated
- Header at the top of the page with the paper title (in capital letters) and the page number (If the title is lengthy, you may use a shortened form of it in the header.)
List the first three elements in the order given in the previous list, centered about one third of the way down from the top of the page. Use the headers and footers tool of your word-processing program to add the header, with the title text at the left and the page number in the upper-right corner. Your title page should look like the following example.

The next page of your paper provides an abstract , or brief summary of your findings. An abstract does not need to be provided in every paper, but an abstract should be used in papers that include a hypothesis. A good abstract is concise—about one hundred fifty to two hundred fifty words—and is written in an objective, impersonal style. Your writing voice will not be as apparent here as in the body of your paper. When writing the abstract, take a just-the-facts approach, and summarize your research question and your findings in a few sentences.
In Chapter 12 “Writing a Research Paper” , you read a paper written by a student named Jorge, who researched the effectiveness of low-carbohydrate diets. Read Jorge’s abstract. Note how it sums up the major ideas in his paper without going into excessive detail.

Write an abstract summarizing your paper. Briefly introduce the topic, state your findings, and sum up what conclusions you can draw from your research. Use the word count feature of your word-processing program to make sure your abstract does not exceed one hundred fifty words.
Depending on your field of study, you may sometimes write research papers that present extensive primary research, such as your own experiment or survey. In your abstract, summarize your research question and your findings, and briefly indicate how your study relates to prior research in the field.
Margins, Pagination, and Headings
APA style requirements also address specific formatting concerns, such as margins, pagination, and heading styles, within the body of the paper. Review the following APA guidelines.
Use these general guidelines to format the paper:
- Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch.
- Use double-spaced text throughout your paper.
- Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point).
- Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section. Page numbers appear flush right within your header.
- Section headings and subsection headings within the body of your paper use different types of formatting depending on the level of information you are presenting. Additional details from Jorge’s paper are provided.

Begin formatting the final draft of your paper according to APA guidelines. You may work with an existing document or set up a new document if you choose. Include the following:
- Your title page
- The abstract you created in Note 13.8 “Exercise 1”
- Correct headers and page numbers for your title page and abstract
APA style uses section headings to organize information, making it easy for the reader to follow the writer’s train of thought and to know immediately what major topics are covered. Depending on the length and complexity of the paper, its major sections may also be divided into subsections, sub-subsections, and so on. These smaller sections, in turn, use different heading styles to indicate different levels of information. In essence, you are using headings to create a hierarchy of information.
The following heading styles used in APA formatting are listed in order of greatest to least importance:
- Section headings use centered, boldface type. Headings use title case, with important words in the heading capitalized.
- Subsection headings use left-aligned, boldface type. Headings use title case.
- The third level uses left-aligned, indented, boldface type. Headings use a capital letter only for the first word, and they end in a period.
- The fourth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are boldfaced and italicized.
- The fifth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are italicized and not boldfaced.
Visually, the hierarchy of information is organized as indicated in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” .
Table 13.1 Section Headings
| Level of Information | Text Example |
|---|---|
| Level 1 | |
| Level 2 | |
| Level 3 | |
| Level 4 | |
| Level 5 |
A college research paper may not use all the heading levels shown in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” , but you are likely to encounter them in academic journal articles that use APA style. For a brief paper, you may find that level 1 headings suffice. Longer or more complex papers may need level 2 headings or other lower-level headings to organize information clearly. Use your outline to craft your major section headings and determine whether any subtopics are substantial enough to require additional levels of headings.
Working with the document you developed in Note 13.11 “Exercise 2” , begin setting up the heading structure of the final draft of your research paper according to APA guidelines. Include your title and at least two to three major section headings, and follow the formatting guidelines provided above. If your major sections should be broken into subsections, add those headings as well. Use your outline to help you.
Because Jorge used only level 1 headings, his Exercise 3 would look like the following:
| Level of Information | Text Example |
|---|---|
| Level 1 | |
| Level 1 | |
| Level 1 | |
| Level 1 |
Citation Guidelines
In-text citations.
Throughout the body of your paper, include a citation whenever you quote or paraphrase material from your research sources. As you learned in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , the purpose of citations is twofold: to give credit to others for their ideas and to allow your reader to follow up and learn more about the topic if desired. Your in-text citations provide basic information about your source; each source you cite will have a longer entry in the references section that provides more detailed information.
In-text citations must provide the name of the author or authors and the year the source was published. (When a given source does not list an individual author, you may provide the source title or the name of the organization that published the material instead.) When directly quoting a source, it is also required that you include the page number where the quote appears in your citation.
This information may be included within the sentence or in a parenthetical reference at the end of the sentence, as in these examples.
Epstein (2010) points out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Here, the writer names the source author when introducing the quote and provides the publication date in parentheses after the author’s name. The page number appears in parentheses after the closing quotation marks and before the period that ends the sentence.
Addiction researchers caution that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (Epstein, 2010, p. 137).
Here, the writer provides a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence that includes the author’s name, the year of publication, and the page number separated by commas. Again, the parenthetical citation is placed after the closing quotation marks and before the period at the end of the sentence.
As noted in the book Junk Food, Junk Science (Epstein, 2010, p. 137), “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive.”
Here, the writer chose to mention the source title in the sentence (an optional piece of information to include) and followed the title with a parenthetical citation. Note that the parenthetical citation is placed before the comma that signals the end of the introductory phrase.
David Epstein’s book Junk Food, Junk Science (2010) pointed out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Another variation is to introduce the author and the source title in your sentence and include the publication date and page number in parentheses within the sentence or at the end of the sentence. As long as you have included the essential information, you can choose the option that works best for that particular sentence and source.
Citing a book with a single author is usually a straightforward task. Of course, your research may require that you cite many other types of sources, such as books or articles with more than one author or sources with no individual author listed. You may also need to cite sources available in both print and online and nonprint sources, such as websites and personal interviews. Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.2 “Citing and Referencing Techniques” and Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provide extensive guidelines for citing a variety of source types.
Writing at Work
APA is just one of several different styles with its own guidelines for documentation, formatting, and language usage. Depending on your field of interest, you may be exposed to additional styles, such as the following:
- MLA style. Determined by the Modern Languages Association and used for papers in literature, languages, and other disciplines in the humanities.
- Chicago style. Outlined in the Chicago Manual of Style and sometimes used for papers in the humanities and the sciences; many professional organizations use this style for publications as well.
- Associated Press (AP) style. Used by professional journalists.
References List
The brief citations included in the body of your paper correspond to the more detailed citations provided at the end of the paper in the references section. In-text citations provide basic information—the author’s name, the publication date, and the page number if necessary—while the references section provides more extensive bibliographical information. Again, this information allows your reader to follow up on the sources you cited and do additional reading about the topic if desired.
The specific format of entries in the list of references varies slightly for different source types, but the entries generally include the following information:
- The name(s) of the author(s) or institution that wrote the source
- The year of publication and, where applicable, the exact date of publication
- The full title of the source
- For books, the city of publication
- For articles or essays, the name of the periodical or book in which the article or essay appears
- For magazine and journal articles, the volume number, issue number, and pages where the article appears
- For sources on the web, the URL where the source is located
The references page is double spaced and lists entries in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. If an entry continues for more than one line, the second line and each subsequent line are indented five spaces. Review the following example. ( Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provides extensive guidelines for formatting reference entries for different types of sources.)

In APA style, book and article titles are formatted in sentence case, not title case. Sentence case means that only the first word is capitalized, along with any proper nouns.
Key Takeaways
- Following proper citation and formatting guidelines helps writers ensure that their work will be taken seriously, give proper credit to other authors for their work, and provide valuable information to readers.
- Working ahead and taking care to cite sources correctly the first time are ways writers can save time during the editing stage of writing a research paper.
- APA papers usually include an abstract that concisely summarizes the paper.
- APA papers use a specific headings structure to provide a clear hierarchy of information.
- In APA papers, in-text citations usually include the name(s) of the author(s) and the year of publication.
- In-text citations correspond to entries in the references section, which provide detailed bibliographical information about a source.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
How to Make a Title Page for a Research Paper
- Post category: Uncategorized
- Reading time: 22 mins read
Imagine your research paper is a book in a vast library. Amidst thousands of others, what makes someone pick it up? The answer lies in the title page. This seemingly simple page announces the content and character of your research. Crafting a title page is about creating a compelling entrance to your scholarly journey.
In this guide, we’ll navigate through designing a research paper title page that meets academic standards and captures the purpose of your work, ensuring your research doesn’t just blend into the academic landscape but stands out, inviting, and informative.
What is a Research Paper Title?
The title page of a research paper serves as its initial page, prominently displaying the paper’s title or topic. This page previews the content of the research paper, setting the stage for the reader.
Adherence to specific citation and formatting style guidelines is crucial in structuring the title page. For instance, the title page must align with APA guidelines if you use APA format. This principle also applies to other styles, such as MLA, Harvard, and Chicago.
Key elements of the title page include the running head , research paper topic , page number, author’s name and number , and institutional affiliation . While there are several standard formatting styles like MLA, APA, and Chicago, the specific style to be used is typically dictated by the research paper’s instructions or rubric.
Creating a title page is straightforward, but attention to detail is important to ensure it is properly formatted, structured, and edited. Guidelines are often helpful for ensuring accuracy and adherence to the required academic standards.
Format and Features of a Title Page
The title page of a research paper serves as the face of your work and follows specific formatting guidelines that vary depending on the academic style guide (such as APA, MLA, or Chicago) being used. However, there are common elements and a general format that most title pages share. These include:
- Title of the Paper: Placed prominently at the top, the title should clearly and concisely reflect the paper’s content. It is usually typed in a larger font size than the rest of the text on the page.
- Author’s Name: This should appear below the title, indicating the paper’s authorship. In cases of multiple authors, their names are listed following the contribution or alphabetical order, depending on the guidelines followed.
- Affiliation: This refers to the institution or organization with which the author is associated. In academic papers, this usually includes the name of the university or college.
- Course Name and Number: Particularly relevant for academic assignments, this information helps in identifying the course for which the paper is written.
- Instructor’s Name: Including the name of the instructor or professor for whom the paper is being submitted is a common practice in academic papers.
- Submission Date: The paper is submission date is typically placed at the bottom of the title page.
- Running Head and Page Number: In certain styles, like APA, a running head (a shortened version of the title) and a page number are included in the title page’s header.
- Additional Information: Depending on the requirements, additional details like a student ID number, department, or university logo might be included.
The title page should have a clean, professional layout with centered text. Margins are usually set at 1 inch on all sides, and the title page is not adorned with images, decorative fonts, or colors unless specifically required by the guidelines or the nature of the paper warrants it. The goal is to present a clear, formal, and easily navigable title page that professionally represents the paper and its author.
Guide on How to Develop a Research Paper Title Page
Creating a title page for your research paper is a crucial step in presenting your academic work. Here’s a step-by-step process to help you develop a well-structured and properly formatted title page:
Answer Key Questions About Your Research Paper
Begin by reflecting on the ‘what,’ ‘why,’ and ‘how’ of your research. What is the main topic or problem you are addressing? Why is this research important or necessary? How did you approach the research? Understanding these elements is vital for formulating a title that accurately represents your study.
Identify Research Study Keywords
Keywords are the core terms that define your topic and are critical for making your paper searchable and accessible. These are the terms that a reader might use to find your work in databases and search engines. Think about the main concepts, theories, and methods involved in your research and list them as potential keywords.
Research Title Writing Using Keywords
Use the identified keywords to construct your title. A good title integrates these keywords in a way that is coherent and reflective of the paper’s content. This makes the title informative and ensures that your paper is easily discoverable in academic searches.
Create a Working Research Paper Title
Start with a draft title early in your research process. This initial title should capture the essence of your study. As your research progresses, revisit and refine this title. The evolution of your research might bring new insights that can lead to a more precise and effective title.
Remove Nonessential Words and Phrases
Review your title and eliminate unnecessary words or phrases. The goal is to keep the title concise without losing its intended meaning. Avoid jargon, acronyms, or any ambiguous terms unless they are well-known in your field and crucial to the title’s clarity.
Rules on Making the Best Research Paper Title
Creating an effective research paper title is an art that combines clarity, precision, and engagement. Here are some key rules to follow for crafting a title that stands out:
- Clarity is Key: Your title should clearly reflect your research’s main topic and scope. Avoid ambiguity and ensure that even non-experts in your field can understand the focus of your paper.
- Be Concise: A good title is brief yet informative. Aim to capture the essence of your research without unnecessary words. A concise title is easier to read and more impactful.
- Incorporate Relevant Keywords: Use specific keywords that define your research area. This improves the searchability of your paper in academic databases and makes it more accessible to the target audience.
- Avoid Jargon and Technical Terms: Unless necessary, steer clear of jargon and highly technical terms. These can alienate readers who are not specialists in your field.
- Make It Interesting: While maintaining academic professionalism, try to make your title engaging. A compelling title can spark interest and encourage more readers to delve into your paper.
- Reflect the Tone of Your Research: Ensure that your title correctly mirrors the nature of your research. For example, a serious, rigorous study should not have a frivolous title.
- No False Promises: Your title should accurately represent the content of your paper. Avoid misleading readers with a sensational or overpromising title your paper does not fulfill.
- Adhere to Formatting Guidelines: Follow the specific formatting rules of the style guide (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) required by your institution or publisher. This includes aspects like capitalization, punctuation, and font.
- Consider the Audience: Tailor your title to your intended audience’s expectations and knowledge level. A title for a specialized academic audience can be different from one intended for a general audience.
- Seek Feedback: Before finalizing, get feedback on your title from peers or mentors. They can provide insights on clarity, interest, and appropriateness.
APA Research Paper Cover Page Guide
When you’re preparing a research paper in APA format, the title page is an essential element that needs to be formatted correctly. Here’s a guide to help you set up your APA title page:
You need to include these four essential elements in the title page of your APA-style paper:
- Paper Title: Position your title in the center of the page. It should succinctly reflect the subject of your paper, including key variables or theoretical issues related to the topic. Aim for a title length of about 10-12 words.
- Author’s Name and Institutional Affiliation: Directly below the title, center your name and the name of the institution where the research was conducted. The institutional affiliation typically refers to the college or university associated with the research.
- Running Head: This is a shortened version of your title, limited to 50 characters (including spaces and punctuation). It appears at the top of each page of the paper, aligned to the left, followed by the page number.
- Page Number: The page number should be in the title page’s upper right-hand corner, following the running head. All subsequent pages of the paper should also have consecutive page numbering in the same location.
Research Paper APA Title Page Example
Here’s an example of how a title page for a research paper in APA format might look:

Research Paper Title Page MLA
In MLA (Modern Language Association) format, a separate title page is not typically required unless specifically requested by your instructor. Instead, the necessary information is included at the top of the document’s first page. Here’s how you would format it:
- University Name: At the top of the page, write the name of your university.
- Paper Title: Skip about one-third of the page down from the university name to place the title. The title should adhere to title capitalization standards: the first word and all major words are capitalized. Avoid underlining, italicizing, or placing quotation marks around the title. However, any in-text citations within the title should follow proper punctuation rules.
- Your Name: Skip a couple of lines after the title and write your full name (first and last names).
- Class, Professor’s Name, and Due Date: Skip another couple of lines and then write, on separate lines, the name of your class, your professor’s full name (including the appropriate title), and the due date. Names should be written accurately, and the date should be in European format: day, month, and year.
- Formatting of the Title Page: Double-space the title page and center-align all text. Ensure uniform formatting for each line and avoid using special formatting like underlining or highlighting.
- Formatting of the First Page (If a Separate Title Page is Not Required): If a separate title page is not used, the first page of your paper should include the title and your name. Remember to include your last name and page number in the header of each page.
The Correct MLA Format Title Page Example
While MLA style does not require a separate title page and instead includes necessary information on the first page of the document, if your instructor requests a separate title page, it would look like this:

Adding a Research Paper Subtitle
Subtitles in research papers can provide additional context, clarify the scope, or highlight specific aspects of the study. A subtitle is used to give more detail or a specific focus that complements the main title. It can narrow the topic, indicate a specific methodology or geographic region, or provide more clarity.
The subtitle should be placed directly below the main title. It’s typically separated from the title by a colon. Regarding formatting, the subtitle should be in the same font and size as the main title. While the main title is often capitalized (headline style), the subtitle can be in sentence case (only the first word and proper nouns capitalized), depending on your style guide.
Like the main title, the subtitle should be concise and clear. It should enhance the reader’s understanding of the paper’s content without being overly lengthy or complex. The subtitle should be directly aligned with the main title, both conceptually and visually. It should look like an integral part of the title, not an afterthought.
Adding a subtitle to a research paper should provide additional clarity or specific focus to the main title. Here’s how it might look:
Main Title: “Enhancing Patient Safety: Strategies for Reducing Medication Errors”
Subtitle: “A Comparative Analysis of Electronic versus Manual Prescription Methods”
Combined: “Enhancing Patient Safety: Strategies for Reducing Medication Errors: A Comparative Analysis of Electronic versus Manual Prescription Methods”
In this example:
- The main title, “Enhancing Patient Safety: Strategies for Reducing Medication Errors,” introduces the paper’s general topic, focusing on patient safety and medication errors.
- The subtitle, “A Comparative Analysis of Electronic versus Manual Prescription Methods,” provides specific details about the approach and scope of the research, indicating that the paper will compare electronic and manual prescription methods.
- Together, the title and subtitle give a comprehensive overview of the paper’s focus, guiding the reader’s expectations about the study’s content and methodological approach.
Research Paper Title Examples
Crafting the right title for a research paper is crucial, as it is the first point of engagement with the reader and sets the tone for the content. The following examples demonstrate how effective titles can convey the research’s scope, focus, and methodology, making them both informative and appealing.
- “Bridging the Gap: Innovative Approaches to Dementia Care in Geriatric Nursing”
- “The Impact of Telehealth Services on Chronic Disease Management in Rural Communities”
- “Exploring the Role of Nurse Practitioners in Primary Care: Patient Outcomes and Healthcare Efficiency”
- “Pediatric Pain Management: Evaluating the Effectiveness of Non-Pharmacological Interventions”
- “Maternal Health Disparities: Analyzing the Effects of Socioeconomic Status on Prenatal Care”
- “Infection Control in ICU: Strategies for Reducing Hospital-Acquired Infections”
- “Mental Health Nursing: Addressing the Challenges of Care in Adolescent Populations”
- “Advancing Palliative Care: The Role of Nursing in End-of-Life Decision Making”
- “The Efficacy of Continuing Education Programs in Nursing: A Comparative Study”
- “Technology in Nursing: The Impact of Electronic Health Records on Patient Safety and Care Quality”
Tips on Formulating a Good Research Paper Title
Here are essential tips and strategies to help you craft an effective and engaging title that accurately reflects the content and significance of your research.
- Ensure your title accurately represents the core idea or findings of your research. It should give a clear indication of what the reader can expect.
- Avoid overly complex or lengthy titles. Aim for a title that is to the point yet informative enough to convey the key aspects of your research.
- Incorporate relevant keywords that highlight the main topics or methods of your research. This aids in searchability and helps readers quickly understand the focus of your paper.
- Use language that is accessible to a broad audience. Technical terms and acronyms might confuse readers not specialized in your field.
- While maintaining academic appropriateness, choose an engaging title that catches the reader’s attention.
- A title that is too vague can be misleading or unhelpful. Including specific details like the study’s geographical location, time frame, or specific methodology can be beneficial.
- Ensure the tone of the title matches the tone of the paper. A serious study, for instance, demands a title that reflects its scholarly rigor.
- If you need to add more context or specify the focus of your research, consider using a subtitle. This can be especially useful for multidisciplinary studies.
- Don’t hesitate to ask colleagues, mentors, or peers for their opinions on your title. Sometimes, external perspectives can help refine and improve it.
- Your title might evolve as your research progresses. Be open to revising it as you gain more insights into your topic.
Writing a title page for your research paper with precision and adherence to academic guidelines is a skill that enhances the professionalism of your work. Applying these straightforward yet effective tips ensures that your research paper makes a strong, scholarly first impression, setting the stage for the valuable insights that follow. Remember, a well-composed title page is your first step towards presenting your research like a pro.
As a college or university student, you can apply these valuable tips to create an impressive and professional title page for your research paper. If time constraints or other commitments make it challenging to complete your research paper, our custom writing service is available to assist you.
You Might Also Like
Deliverable 07 – a model u.s. healthcare delivery system, nursing leadership discussion 2, reply to this post about limbic system.

A step-by-step guide for creating and formatting APA Style student papers
The start of the semester is the perfect time to learn how to create and format APA Style student papers. This article walks through the formatting steps needed to create an APA Style student paper, starting with a basic setup that applies to the entire paper (margins, font, line spacing, paragraph alignment and indentation, and page headers). It then covers formatting for the major sections of a student paper: the title page, the text, tables and figures, and the reference list. Finally, it concludes by describing how to organize student papers and ways to improve their quality and presentation.
The guidelines for student paper setup are described and shown using annotated diagrams in the Student Paper Setup Guide (PDF, 3.40MB) and the A Step-by-Step Guide to APA Style Student Papers webinar . Chapter 1 of the Concise Guide to APA Style and Chapter 2 of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association describe the elements, format, and organization for student papers. Tables and figures are covered in Chapter 7 of both books. Information on paper format and tables and figures and a full sample student paper are also available on the APA Style website.
Basic setup
The guidelines for basic setup apply to the entire paper. Perform these steps when you first open your document, and then you do not have to worry about them again while writing your paper. Because these are general aspects of paper formatting, they apply to all APA Style papers, student or professional. Students should always check with their assigning instructor or institution for specific guidelines for their papers, which may be different than or in addition to APA Style guidelines.
Seventh edition APA Style was designed with modern word-processing programs in mind. Most default settings in programs such as Academic Writer, Microsoft Word, and Google Docs already comply with APA Style. This means that, for most paper elements, you do not have to make any changes to the default settings of your word-processing program. However, you may need to make a few adjustments before you begin writing.
Use 1-in. margins on all sides of the page (top, bottom, left, and right). This is usually how papers are automatically set.
Use a legible font. The default font of your word-processing program is acceptable. Many sans serif and serif fonts can be used in APA Style, including 11-point Calibri, 11-point Arial, 12-point Times New Roman, and 11-point Georgia. You can also use other fonts described on the font page of the website.
Line spacing
Double-space the entire paper including the title page, block quotations, and the reference list. This is something you usually must set using the paragraph function of your word-processing program. But once you do, you will not have to change the spacing for the entirety of your paper–just double-space everything. Do not add blank lines before or after headings. Do not add extra spacing between paragraphs. For paper sections with different line spacing, see the line spacing page.
Paragraph alignment and indentation
Align all paragraphs of text in the body of your paper to the left margin. Leave the right margin ragged. Do not use full justification. Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5-in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. For paper sections with different alignment and indentation, see the paragraph alignment and indentation page.
Page numbers
Put a page number in the top right of every page header , including the title page, starting with page number 1. Use the automatic page-numbering function of your word-processing program to insert the page number in the top right corner; do not type the page numbers manually. The page number is the same font and font size as the text of your paper. Student papers do not require a running head on any page, unless specifically requested by the instructor.
Title page setup
Title page elements.
APA Style has two title page formats: student and professional (for details, see title page setup ). Unless instructed otherwise, students should use the student title page format and include the following elements, in the order listed, on the title page:
- Paper title.
- Name of each author (also known as the byline).
- Affiliation for each author.
- Course number and name.
- Instructor name.
- Assignment due date.
- Page number 1 in the top right corner of the page header.
The format for the byline depends on whether the paper has one author, two authors, or three or more authors.
- When the paper has one author, write the name on its own line (e.g., Jasmine C. Hernandez).
- When the paper has two authors, write the names on the same line and separate them with the word “and” (e.g., Upton J. Wang and Natalia Dominguez).
- When the paper has three or more authors, separate the names with commas and include “and” before the final author’s name (e.g., Malia Mohamed, Jaylen T. Brown, and Nia L. Ball).
Students have an academic affiliation, which identities where they studied when the paper was written. Because students working together on a paper are usually in the same class, they will have one shared affiliation. The affiliation consists of the name of the department and the name of the college or university, separated by a comma (e.g., Department of Psychology, George Mason University). The department is that of the course to which the paper is being submitted, which may be different than the department of the student’s major. Do not include the location unless it is part of the institution’s name.
Write the course number and name and the instructor name as shown on institutional materials (e.g., the syllabus). The course number and name are often separated by a colon (e.g., PST-4510: History and Systems Psychology). Write the assignment due date in the month, date, and year format used in your country (e.g., Sept. 10, 2020).
Title page line spacing
Double-space the whole title page. Place the paper title three or four lines down from the top of the page. Add an extra double-spaced blank like between the paper title and the byline. Then, list the other title page elements on separate lines, without extra lines in between.
Title page alignment
Center all title page elements (except the right-aligned page number in the header).
Title page font
Write the title page using the same font and font size as the rest of your paper. Bold the paper title. Use standard font (i.e., no bold, no italics) for all other title page elements.
Text elements
Repeat the paper title at the top of the first page of text. Begin the paper with an introduction to provide background on the topic, cite related studies, and contextualize the paper. Use descriptive headings to identify other sections as needed (e.g., Method, Results, Discussion for quantitative research papers). Sections and headings vary depending on the paper type and its complexity. Text can include tables and figures, block quotations, headings, and footnotes.
Text line spacing
Double-space all text, including headings and section labels, paragraphs of text, and block quotations.
Text alignment
Center the paper title on the first line of the text. Indent the first line of all paragraphs 0.5-in.
Left-align the text. Leave the right margin ragged.
Block quotation alignment
Indent the whole block quotation 0.5-in. from the left margin. Double-space the block quotation, the same as other body text. Find more information on the quotations page.
Use the same font throughout the entire paper. Write body text in standard (nonbold, nonitalic) font. Bold only headings and section labels. Use italics sparingly, for instance, to highlight a key term on first use (for more information, see the italics page).
Headings format
For detailed guidance on formatting headings, including headings in the introduction of a paper, see the headings page and the headings in sample papers .
- Alignment: Center Level 1 headings. Left-align Level 2 and Level 3 headings. Indent Level 4 and Level 5 headings like a regular paragraph.
- Font: Boldface all headings. Also italicize Level 3 and Level 5 headings. Create heading styles using your word-processing program (built into AcademicWriter, available for Word via the sample papers on the APA Style website).
Tables and figures setup
Tables and figures are only included in student papers if needed for the assignment. Tables and figures share the same elements and layout. See the website for sample tables and sample figures .
Table elements
Tables include the following four elements:
- Body (rows and columns)
- Note (optional if needed to explain elements in the table)
Figure elements
Figures include the following four elements:
- Image (chart, graph, etc.)
- Note (optional if needed to explain elements in the figure)
Table line spacing
Double-space the table number and title. Single-, 1.5-, or double-space the table body (adjust as needed for readability). Double-space the table note.
Figure line spacing
Double-space the figure number and title. The default settings for spacing in figure images is usually acceptable (but adjust the spacing as needed for readability). Double-space the figure note.
Table alignment
Left-align the table number and title. Center column headings. Left-align the table itself and left-align the leftmost (stub) column. Center data in the table body if it is short or left-align the data if it is long. Left-align the table note.
Figure alignment
Left-align the figure number and title. Left-align the whole figure image. The default alignment of the program in which you created your figure is usually acceptable for axis titles and data labels. Left-align the figure note.
Bold the table number. Italicize the table title. Use the same font and font size in the table body as the text of your paper. Italicize the word “Note” at the start of the table note. Write the note in the same font and font size as the text of your paper.
Figure font
Bold the figure number. Italicize the figure title. Use a sans serif font (e.g., Calibri, Arial) in the figure image in a size between 8 to 14 points. Italicize the word “Note” at the start of the figure note. Write the note in the same font and font size as the text of your paper.
Placement of tables and figures
There are two options for the placement of tables and figures in an APA Style paper. The first option is to place all tables and figures on separate pages after the reference list. The second option is to embed each table and figure within the text after its first callout. This guide describes options for the placement of tables and figures embedded in the text. If your instructor requires tables and figures to be placed at the end of the paper, see the table and figure guidelines and the sample professional paper .
Call out (mention) the table or figure in the text before embedding it (e.g., write “see Figure 1” or “Table 1 presents”). You can place the table or figure after the callout either at the bottom of the page, at the top of the next page, or by itself on the next page. Avoid placing tables and figures in the middle of the page.
Embedding at the bottom of the page
Include a callout to the table or figure in the text before that table or figure. Add a blank double-spaced line between the text and the table or figure at the bottom of the page.
Embedding at the top of the page
Include a callout to the table in the text on the previous page before that table or figure. The table or figure then appears at the top of the next page. Add a blank double-spaced line between the end of the table or figure and the text that follows.
Embedding on its own page
Embed long tables or large figures on their own page if needed. The text continues on the next page.
Reference list setup
Reference list elements.
The reference list consists of the “References” section label and the alphabetical list of references. View reference examples on the APA Style website. Consult Chapter 10 in both the Concise Guide and Publication Manual for even more examples.
Reference list line spacing
Start the reference list at the top of a new page after the text. Double-space the entire reference list (both within and between entries).
Reference list alignment
Center the “References” label. Apply a hanging indent of 0.5-in. to all reference list entries. Create the hanging indent using your word-processing program; do not manually hit the enter and tab keys.
Reference list font
Bold the “References” label at the top of the first page of references. Use italics within reference list entries on either the title (e.g., webpages, books, reports) or on the source (e.g., journal articles, edited book chapters).
Final checks
Check page order.
- Start each section on a new page.
- Arrange pages in the following order:
- Title page (page 1).
- Text (starts on page 2).
- Reference list (starts on a new page after the text).
Check headings
- Check that headings accurately reflect the content in each section.
- Start each main section with a Level 1 heading.
- Use Level 2 headings for subsections of the introduction.
- Use the same level of heading for sections of equal importance.
- Avoid having only one subsection within a section (have two or more, or none).
Check assignment instructions
- Remember that instructors’ guidelines supersede APA Style.
- Students should check their assignment guidelines or rubric for specific content to include in their papers and to make sure they are meeting assignment requirements.
Tips for better writing
- Ask for feedback on your paper from a classmate, writing center tutor, or instructor.
- Budget time to implement suggestions.
- Use spell-check and grammar-check to identify potential errors, and then manually check those flagged.
- Proofread the paper by reading it slowly and carefully aloud to yourself.
- Consult your university writing center if you need extra help.
About the author

Undergraduate student resources

Citation Style: APA 7th Edition: Title Page & Abstract
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- APA Style Guides
- Basic Formatting
- Title Page & Abstract
- The Main Body
- The References Page
- Reference Citation Examples
- Citation Generation Tools
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 7th Edition vs. 6th Edition
The Title Page
Your title page should follow all of the rules outlined in the Basic Formatting tab. In addition, it should be centered in the upper-half of the page. It must include the following information (and your instructor might prefer you to add more):
- The full title of your paper in title case
- Your name (First Last)
- Your institution (Keuka College)
- Your Instructor's Name with their preferred title (example: “Dr. Jill Smith,” or “J. Smith, PhD” or “Professor J. Smith”)
- Date assignment is due, with the month written out in full (example: November 10, 2019)
See the example below (click it to view a larger version):

The Abstract
An abstract is a brief summary of what your paper is all about. Your instructor may or may not require you to include an abstract, so ask them. If they do require an abstract, find out how long they would like it to be. Generally, an abstract is 150 to 250 words long. It is recommended that you write the abstract after you have written your paper. It's a good idea when you're first setting up your document, to include a placeholder page for the abstract on the 2nd page (after the title page).
Your abstract page should follow all of the rules outlined in the Basic Formatting tab. Left-align, but do not hit the tab key or indent in any way at the beginning of the abstract. The word "Abstract" should be bolded and centered at the top of the page.
See the example below (click it to view larger):

Reference Librarian

- << Previous: Basic Formatting
- Next: The Main Body >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 3:56 PM
- URL: https://libguides.keuka.edu/apa
APA Title Page Essentials: Creating a Stellar First Impression
Table of contents
- 1.0.1 Font Size
- 1.0.2 Font Style
- 1.0.3 Alignment
- 1.0.4 Spacing
- 2.1 Title of the Paper
- 2.2 Author’s Name
- 2.3 Running Head and Page Number
- 2.4 Institutional Affiliation
- 2.5 Course Information and Instructor Name
- 2.6 Due Date
- 2.7 Author Note
- 3 Finishing on a High Note
The formatting of an APA publication manual strictly requires a corresponding APA title page . The significance is that it highlights the APA style and sets it apart from other formatting standards. However, developing it is governed by strict laws. Hence, this article helps academic scholars know a proper APA title page format.
At the end of this content, you will:
- Understand how to create a title page in the 7th edition of the APA title format.
- Learn about the different formatting guidelines.
- Be able to choose a title and fill in its basic elements.
Follow closely to understand how to do the proper APA formatting in your next research paper.
APA Formatting Guidelines
Professional papers follow laid-down formats. The student title page has formatting guidelines that make it standard. Some people use writing services and may not be familiar with what has been done.
Here are the necessary factors to prioritize in your APA title format:
The generally acceptable font size is 12. While some may favor font size 11, that does not apply to the title page. You can consider it while writing the research content. Using a smaller or bigger font can poorly represent your hard work.
Times New Roman is the acceptable font style. Most academic materials instruct writers to employ font size 12 and Times New Roman rather than other styles and sizes.
It is advisable to align the text in the body of your work against the left margin, while the right one appears ragged. Even if you have writing services to help you write a research paper , you can cross-check the alignment and other formatting guidelines.
The double-spaced approach is the right format for an APA-style paper. This includes every part of the content. Remove extra space before and after paragraphs.
As a result, the next big question is, how do I choose a title?
There is always a topic to work with. The challenge could be that it doesn’t sound professional for an academic paper. A title should be concise yet informative about the entire research paper.
Here are some tips on how to choose the right title:
- Understand the topic sentence.
- Define the aim of the research.
- Create multiple titles for the same research.
- Select the most professional or seek your supervisor’s help.
Also, it is important to format the author names and institutional affiliations. If there are two authors, use ampersand (&) to separate their names. But, in the case of multiple authors, insert only the last name of the author. Follow it by “et al.” to imply other authors.
For institutional affiliations, identify where the author carried out their research. If there are multiple institutions, include dual affiliation. However, both institutions must have tangibly contributed to the research. If the affiliation changes at any point, ensure to include this in the author’s note.
Title Page Elements
An APA-style title page has major elements that you should follow.
Title of the Paper
You need a professional title page. Following the right formatting helps to achieve a good title and generally acceptable work.
Here are the major elements of APA-style papers:
- Page number.
- Paper title.
- Author (and their institution affiliation).
- Course instructor.
These are examples of the APA 7 title page:

Author’s Name
As stated earlier, including your name is necessary in your APA format title page. It acknowledges your effort and helps readers to trace your publication easily. For unpublished works, you can have the course number and name on the front page of your APA style manual.
Running Head and Page Number
The numbering of the pages in APA style papers (7th ed.) coincides with numbering in other formatting styles. The title page is also included in the list of numbered pages. Page numbering should appear in the upper-right corner of the header using Arabic numerals. The rule for running head in an APA research paper is that the short version of the title should not exceed 50 characters.
In the 7th edition of the APA style guide, the use of a running head on the title page (and subsequent pages) depends on the type of paper you are writing:
Student Papers: For most student papers, a running head is not required. Only a page number is included in the header, in the top right corner of each page.
Professional Papers: For professional manuscripts intended for publication (like journal articles), a running head is still required. It appears in the top header of each page, aligned to the left, and is a shortened version of the paper’s title.
Institutional Affiliation
Institutional affiliation is essential when working on any academic paper. It is mandatory if you want to publish your manual. Include relevant details like;
- Department.
- University Name.
- Author name(s).
Course Information and Instructor Name
Including the course information helps readers to know what your subject of discourse is about. Course information should be short. Sometimes, your course information may include your department and university. Whichever way, it shouldn’t exceed 50 characters.
The instructor’s name is essential because you acknowledge their supervisory role during your work. More than the experience your instructor offered during your research, adding their name adds more credibility to your entire work.
Due Date
The due date refers to the fulfillment of your research work. It can be your submission date. However, it helps a reader know the duration of your project and compare it with related papers.
Note the following rules when you want to write the due date:
- Include the month, day, and year based on your country’s format
See example below
“September 23, 2023”
“23 September 2023.”
Author Note
The author’s note should be at the bottom half of the APA title page. It should be below the title, authors, and affiliations. The author’s note details additional information about the author, data sharing, research paper types of study registration, conflicting statements, or any necessary disclaimer for the research paper.
Some notes include details about the funding or support they got during the research. It is necessary for a professional paper if you want to submit your work for publication.
Finishing on a High Note
Consistently, you will see the need to maintain proper APA format for your professional content. A title page plays a significant role in this. While your content is great, a perfect research paper contains basic information like the author’s name, institution affiliation, course information, due date, and author note.
Running head and page affiliation also help to complete your research paper. Being a great writer means following guidelines and proper formatting. Definitely, it will make you a good student, but it also takes you closer to having a published work. Take note that this content was based on the APA 7th edition.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Title Page in APA Format for a Psychology Research Paper
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
James Lacy, MLS, is a fact-checker and researcher.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/James-Lacy-1000-73de2239670146618c03f8b77f02f84e.jpg)
- Important Elements
- Choosing a Title
- Author’s Byline
- Formatting Guidelines
- Professional Papers
- Title Page Checklist
The title page is the first page of a psychology paper. APA format is used when writing lab reports and other types of psychology papers. Therefore, it's important to have a title page in proper APA format when submitting these writings.
Here we discuss how to write a title page for a psychology research paper. We also share the different guidelines based on whether the title page is for a student paper or if the paper is being prepared by a psychology professional.
Important Psychology Title Page Elements
A psychology paper's title page should contain certain key elements. Important elements to include are:
- Article title
- Author’s name
- Author's school or institutional affiliation
- Running head (not required for student papers)
- Course name
- Instructor's name
- Page number

Choosing a Psychology Paper Title
One of the most difficult tasks when writing a psychology paper is choosing a good title. Here are a few tips to help.
Be Specific
The paper's title should be as specific as possible. Work to craft a title that can stand alone and be fully explanatory without further elaboration. A reader browsing through paper titles in an online database should be able to quickly read the title and know exactly what the paper is about.
Page Title Examples
- An example of a good, specific title : Second-Order Beliefs and the Use of Self-Presentational Explanations for Behavior
- An example of a title that is too general : Cognitive Abilities and Social Understanding
Use Proper Structure
The best way to structure the title of a psychology paper is to look at the hypothesis and experimental variables . For example, it might be titled "The Effects of [Independent Variable] on [Dependent Variable]."
The official APA publication manual notes that a title should be brief, yet communicate the main topic and variables of interest. Avoid words that serve no real purpose or that do not communicate essential information. Some examples of such words and phrases include “An Experiment on…,” “A Study of…”, “method,” or “results.”
While there is no maximum length for titles, the APA recommends keeping the title concise while still including key terms.
How to Write a Title Page Byline
The next element of a psychology research paper title page is the byline, which lists the author’s name and institutional affiliation. Here's what to include for each.
Author's Name
The recommended format is first name, middle initial(s), and last name. Do not include titles or degrees, such as Dr. or PhD.
Students should include the name of the department followed by the name of their school. This should be centered on the page and appear after the author's name.
School Affiliation
The institutional affiliation is the location where the research was conducted, most often a college or university. In some cases, research may have been supported by more than one institution. In these instances, only include two affiliations if both schools offered substantial support to the research, and only list two affiliations for every author.
What should a person do if they are not affiliated with an academic institution where the research was conducted? In this instance, the APA suggests listing the author's city and state of residence in place of the academic affiliation.
Name and Affiliation Example
June Callaway
Department of Psychology, University of Ohio
PSYCH 101: Introduction to General Psychology
Dr. Ashana Lee
September 7, 2023
*Note: This information should be centered on the title page, not aligned to the left as it appears here.
Title Page Formatting Guidelines
There are additional formatting concerns to observe when drafting an APA format title page for a psychology paper:
- A running head should be included in the upper left-hand corner on all pages, including the title page. This is not required if it's a student paper.
- The running head should be no more than 50 characters , including letters, spacing between words, and punctuation.
- The running head should be in all uppercase letters and only include the title; it should not include the label "running head."
- All pages, including the title page, should also have a page number in the upper right-hand corner.
- The author's title, name, and institution should be double-spaced and centered on the page. Student papers should also include the assignment due date directly below the institution's information.
Formatting Professional Psychology Papers
The APA's guidelines are slightly different for papers intended for publication in professional psychology journals . In addition to the basic elements included in a title page, a professional paper should also include:
- A running head : The running head is a shortened version of the paper's title. It should appear on every page of the paper, along with the page number.
- Author affiliation : In the second paragraph, list any changes in author affiliation. For example, if one of the authors is now affiliated with a different university from where the research was conducted, the author's note might state that "Dr. [Last Name] is now at the Department of Psychology, University of Georgia."
- An author's note : This note includes the author's name, the symbol for the ORCID iD, and the URL for the ORCID iD. An ORCID iD is an alphanumeric code used to identify scientific and academic authors. If an author does not have an ORCID iD, their name should be omitted.
- Disclosures and acknowledgments : In the third paragraph, list any acknowledgments and disclosures, including possible conflicts of interest and sources of financial support.
- Contact information : In the fourth paragraph of the author's note, include the author's contact information.
Author's Note, Disclosure, and Contact Info
For an author's note, include the author's name followed by a link to their ORCID iD. The disclosure might be a simple sentence stating that there are no known conflicts of interest to disclose. Next, state that correspondence concerning the article should be addressed to the individual listed, then provide the mailing address and email contact for that individual.
Psychology Paper Title Page Checklist
Before turning in a psychology paper, it's helpful to use these questions as a checklist to ensure that the title page is correct:
- Does the title page contain a title, the author's name and institutional affiliation, a running head (not required on a student paper), and a page number?
- Is the title clear and specific, and does it accurately describe what the research paper is about?
- Is the running head in uppercase format and no longer than 50 characters in length?
- Is the title, author's name, and institutional affiliation centered on the page and double-spaced?
If all of these questions can be answered with a 'yes,' then the title page is properly formatted using APA format.
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, Seventh Edition (2020) .
American Psychological Association. Title page setup . APA Style.
American Psychological Association. Page header . APA Style.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example
Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example
Table of Contents

Research Paper Title
Research Paper Title is the name or heading that summarizes the main theme or topic of a research paper . It serves as the first point of contact between the reader and the paper, providing an initial impression of the content, purpose, and scope of the research . A well-crafted research paper title should be concise, informative, and engaging, accurately reflecting the key elements of the study while also capturing the reader’s attention and interest. The title should be clear and easy to understand, and it should accurately convey the main focus and scope of the research paper.
Examples of Research Paper Title
Here are some Good Examples of Research Paper Title:
- “Investigating the Relationship Between Sleep Duration and Academic Performance Among College Students”
- “The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Employment: A Systematic Review”
- “The Effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Interventions for Anxiety: A Meta-Analysis”
- “Exploring the Effects of Social Support on Mental Health in Patients with Chronic Illness”
- “Assessing the Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Depression: A Randomized Controlled Trial”
- “The Impact of Social Media Influencers on Consumer Behavior: A Systematic Review”
- “Investigating the Link Between Personality Traits and Leadership Effectiveness”
- “The Effect of Parental Incarceration on Child Development: A Longitudinal Study”
- “Exploring the Relationship Between Cultural Intelligence and Cross-Cultural Adaptation: A Meta-Analysis”
- “Assessing the Effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction for Chronic Pain Management”.
- “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health: A Meta-Analysis”
- “The Impact of Climate Change on Global Crop Yields: A Longitudinal Study”
- “Exploring the Relationship between Parental Involvement and Academic Achievement in Elementary School Students”
- “The Ethics of Genetic Editing: A Review of Current Research and Implications for Society”
- “Understanding the Role of Gender in Leadership: A Comparative Study of Male and Female CEOs”
- “The Effect of Exercise on Cognitive Function in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial”
- “The Impacts of COVID-19 on Mental Health: A Cross-Cultural Comparison”
- “Assessing the Effectiveness of Online Learning Platforms: A Case Study of Coursera”
- “Exploring the Link between Employee Engagement and Organizational Performance”
- “The Effects of Income Inequality on Social Mobility: A Comparative Analysis of OECD Countries”
- “Exploring the Relationship Between Social Media Use and Mental Health in Adolescents”
- “The Impact of Climate Change on Crop Yield: A Case Study of Maize Production in Sub-Saharan Africa”
- “Examining the Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Anxiety Disorders: A Meta-Analysis”
- “An Analysis of the Relationship Between Employee Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment”
- “Assessing the Impacts of Wilderness Areas on Local Economies: A Case Study of Yellowstone National Park”
- “The Role of Parental Involvement in Early Childhood Education: A Review of the Literature”
- “Investigating the Effects of Technology on Learning in Higher Education”
- “The Use of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Opportunities and Challenges”
- “A Study of the Relationship Between Personality Traits and Leadership Styles in Business Organizations”.
How to choose Research Paper Title
Choosing a research paper title is an important step in the research process. A good title can attract readers and convey the essence of your research in a concise and clear manner. Here are some tips on how to choose a research paper title:
- Be clear and concise: A good title should convey the main idea of your research in a clear and concise manner. Avoid using jargon or technical language that may be confusing to readers.
- Use keywords: Including keywords in your title can help readers find your paper when searching for related topics. Use specific, descriptive terms that accurately describe your research.
- Be descriptive: A descriptive title can help readers understand what your research is about. Use adjectives and adverbs to convey the main ideas of your research.
- Consider the audience : Think about the audience for your paper and choose a title that will appeal to them. If your paper is aimed at a specialized audience, you may want to use technical terms or jargon in your title.
- Avoid being too general or too specific : A title that is too general may not convey the specific focus of your research, while a title that is too specific may not be of interest to a broader audience. Strive for a title that accurately reflects the focus of your research without being too narrow or too broad.
- Make it interesting : A title that is interesting or provocative can capture the attention of readers and draw them into your research. Use humor, wordplay, or other creative techniques to make your title stand out.
- Seek feedback: Ask colleagues or advisors for feedback on your title. They may be able to offer suggestions or identify potential problems that you hadn’t considered.
Purpose of Research Paper Title
The research paper title serves several important purposes, including:
- Identifying the subject matter : The title of a research paper should clearly and accurately identify the topic or subject matter that the paper addresses. This helps readers quickly understand what the paper is about.
- Catching the reader’s attention : A well-crafted title can grab the reader’s attention and make them interested in reading the paper. This is particularly important in academic settings where there may be many papers on the same topic.
- Providing context: The title can provide important context for the research paper by indicating the specific area of study, the research methods used, or the key findings.
- Communicating the scope of the paper: A good title can give readers an idea of the scope and depth of the research paper. This can help them decide if the paper is relevant to their interests or research.
- Indicating the research question or hypothesis : The title can often indicate the research question or hypothesis that the paper addresses, which can help readers understand the focus of the research and the main argument or conclusion of the paper.
Advantages of Research Paper Title
The title of a research paper is an important component that can have several advantages, including:
- Capturing the reader’s attention : A well-crafted research paper title can grab the reader’s attention and encourage them to read further. A captivating title can also increase the visibility of the paper and attract more readers.
- Providing a clear indication of the paper’s focus: A well-written research paper title should clearly convey the main focus and purpose of the study. This helps potential readers quickly determine whether the paper is relevant to their interests.
- Improving discoverability: A descriptive title that includes relevant keywords can improve the discoverability of the research paper in search engines and academic databases, making it easier for other researchers to find and cite.
- Enhancing credibility : A clear and concise title can enhance the credibility of the research and the author. A title that accurately reflects the content of the paper can increase the confidence readers have in the research findings.
- Facilitating communication: A well-written research paper title can facilitate communication among researchers, enabling them to quickly and easily identify relevant studies and engage in discussions related to the topic.
- Making the paper easier to remember : An engaging and memorable research paper title can help readers remember the paper and its findings. This can be especially important in fields where researchers are constantly inundated with new information and need to quickly recall important studies.
- Setting expectations: A good research paper title can set expectations for the reader and help them understand what the paper will cover. This can be especially important for readers who are unfamiliar with the topic or the research area.
- Guiding research: A well-crafted research paper title can also guide future research by highlighting gaps in the current literature or suggesting new areas for investigation.
- Demonstrating creativity: A creative research paper title can demonstrate the author’s creativity and originality, which can be appealing to readers and other researchers.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Contribution – Thesis Guide

Significance of the Study – Examples and Writing...

APA Research Paper Format – Example, Sample and...

Appendices – Writing Guide, Types and Examples

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Chapter Summary & Overview – Writing Guide...
Steps on How to Make a Title Page for a Research Paper

Research Paper Title Page
A title page is the first thing that your instructor sees when looking at your document; therefore, it is essential for a student to invest in making it look consistent and professional. It is vital for students to learn how to format a title page of a research paper if they want to create an excellent first impression with the examiner. As you craft your title page, you should focus on reflecting what is in your paper. Here our professionals constructed a detailed guide for you to help with that title page.
What Is a Research Paper Title Page and How Do You Structure It?
A research paper title page is the first page of your research paper. It is essential to come up with a title page that gives the readers an overview of the research. It should also be structured in a way that gives it a professional outlook.
A title page should include a running head, research paper title, page number, student’s name, and student’s affiliations. There are three styles one can use to structure a title page in academic writing. Depending on the instructions given by the teacher, you can use APA, MLA or Chicago style to format your title page. Research paper title pages are easy and straightforward to make. With the help of a guideline, a student can draft a title page that meets the teacher’s instructions. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to develop a research paper title page:
- Start with the title page which is written a third way down on the document. The heading should be aligned at the center. Once you have written the title leave two spaces and write your name. Type your first name, middle initials, and last name.
- Write your full official names and do not include any title before or after your name. If the research paper, was a group effort, remember to include the name of the others. Separate each name with a comma.
- Include the name of your institution. Write the full name of your school. In case the paper was drafted by more than one individual from different institutions after the name of each writer, the name of their respective school should be typed.
- Type the name of the course and also the course code. The date of submission is optional; however, if you choose to include it, you should do so after writing the course title.
Basic Rules on How to Make a Research Paper Title Page
When writing a title page, there are some factors that one should keep in mind regardless of the formatting style you are using. If students want to obtain a well-written title page, they should adhere to the following rules:
- While formatting your work see to it that the entire text in the title page is aligned at the center. Also, keep your work double-spaced and the margin set at one inch on all sides.
- It is essential to keep your work well organized and readable. Therefore, ensure you use a clear and legible font. A preferable font to use is the News-Times Roman at 12 points.
- Use correct capitalization, except when writing short words like prepositions and conjunctions you can use lower case.
- When writing a research paper, numbering your work is a requirement, and that also includes the title page. Insert a running head on the right-hand top of the page and the page number of the left top of the page.
- Develop a brief and concise title that is relevant to the content in your research paper. Remove any extraneous words that do not add meaning to it. Craft an intriguing heading that will hook your readers to the research paper.
Employing these tips will assist any college student to write an impressive title page. Those who lack time to draft their papers can ask our custom writing service for help. Our company has extensive experience working on various academic tasks for students. With our team of experts, we see to it that clients get services that worth their money. We have a quality assurance department that guarantees to review all orders to ensure they meet customers’ standards before they are submitted. Order our writing service packages offered at student-friendly prices.
During our years in the writing industry, we have familiarized with different academic writing styles, and we can customize a title page as per your preference. Our research paper service has a strict confidentiality policy that assures customers to keep their information private.
Get an instant quote
- Essay Editor
Essay Format Tips from an English Teacher

Writing a solid and well-crafted essay is crucial for students and researchers, as it involves presenting arguments clearly and succinctly. Whether you are writing a paper for an assignment, a scientific journal, or a personal statement, understanding the correct essay format is pivotal. This meticulously collated guide covers key features of essay formatting and provides tips to refine your writing.
What is an Essay Format?
An essay format is a blueprint for shaping your written assignment, comprising the work’s headings, the title page, paragraphs, and references. Accurate structuring enhances readability and professionalism, thus adhering to academic standards. Instructors across disciplines may specify paper-formatting styles to apply, for instance, Chicago, APA, or MLA formatting, each with unique guidelines tailored to various academic fields.
The essay structure serves as the framework for effectively building and conveying ideas. It is the roadmap that leads the audience via the writer's reflection process, securing coherence, precision, and logical progression of supporting arguments.
Struggling to craft a refined and captivating essay? Want to know how to format an essay? Consider using Aithor's AI writing assistant. The AI Essay Generator is a revolutionary tool designed to streamline the writing procedure, offering assistance in editing, refining, and generating content. With its advanced algorithms, this tool assists in enhancing overall flow and consistency in your projects.
How to Format an Essay
Composing a well-structured piece is crucial for scholastic success and leaves a long-lasting impression on the audience. Structuring your text includes several key components to guarantee its clarity and coherence:
- Proper Heading: Start from the piece’s top left corner, typing your name, lecturer’s name, related course title, and current date. This heading provides essential facts about the essay's author and context.
- Margins: On the paper’s all four sides, set one-inch-long margins for consistency and compliance with educational standards.
- Spacing: Skip a line or double-space your writing unless specified otherwise. This enhances the composition’s clarity and allows room for annotations or feedback.
- Font & Size: Use a legible font, let’s say, 12-point sized Arial or Times New Roman. This provides uniformity and clarity all over your composition.
- Indentation: Leave a standard half an inch of space in the first line of each section to visually separate essay parts and improve the overall article structure.
Following these basic guidelines will guarantee an A-level presentation, increasing the readability and effectiveness of your piece.
How to Write an Essay: MLA Format vs. APA Format
Learning the essentials of correct essay formatting required by standard styles like MLA and APA is pivotal for scholastic success. While both are broadly used, they significantly differ in their arrangement and requirements. Knowing these distinctions ensures your assignment meets disciplinary standards and effectively communicates ideas.
MLA Format:
- Primarily utilized in the humanities area.
- Necessitates a Works Cited collection that catalogs alphabetically all academic materials used.
- Requires a text heading in the top left angle of the opening paper, and the project title centrally positioned on the succeeding line.
- For the in-text citations apply the ‘author-page’ format (e.g., (Smith 123)).
- Italicizes the work headings of larger pieces, for instance, literature and films.
- Typically, it is not obligatory to make a separate cover page for standard essays.
- Does not mandate inserting URLs for online resources in the Works Cited list.
APA Format:
- Generally employed in the space of social sciences.
- Demands a title page containing a so-called running head, a piece’s abstract, and a list of References.
- Uses the arrangement called ‘author-date’ for in-text references (e.g., (Smith, 2019, p. 123)).
- Italicizes the headings of larger essays but uses quotation marks for shorter pieces like articles.
- Demands a separate cover page containing a running head.
- Requires all URLs for online sources to be alphabetized in the list of References.
In summary, mastering both MLA and APA organizations is essential for educational settings. Comprehending their unique rules and adhering to their specific guidelines will ensure that your pieces are well-crafted and effectively convey your message to the audience.
How to Create a Title Page
Generating an effective title page is crucial for arranging an academic paper as it briefly introduces the content, sets the writing tone, and demonstrates crucial identification details. Yet, the particulars vary conditional on the assigned essay style format, with preferred MLA or APA organization styles requiring distinct approaches.
In MLA structure, the cover page is generally unnecessary for standard papers unless specified. If you decide to generate it, then center the composition’s title at the top of the opening page. Below it, indicate yours with the lecturer’s name, the discipline, current date, all centered.
In an APA-based organization, designing the title page is obligatory. Center the article’s or research’s heading at the top half of the opening page. Below that, put your name, and the educational institution's title, then in the header section, put a title’s shortened form. Additionally, set the page number correctly in the sheet’s top right corner.
Largely, MLA and APA differ in title sheet settings and layout. By sticking to the particular rules of each scholarly writing style, you can be confident that your notion is presented professionally and accurately mirrors educational standards.
The First Page of Your Essay
The opening page of the scholarly composition acts as the first encounter with your concept, offering a prospect to engage your audience and provide essential details about your subject matter and text organization style.
The MLA-based structure includes a left-aligned heading on the opening page. The proper heading for essay must contain your and the educator’s name, the related discipline with the current date. The composition’s title is adjusted centrally on the opening page, and the intro of your assignment is placed below without added introductory sections.
In contrast, APA organization begins with the document’s title aligned centrally at the page’s upper section. Under the title, indicate your name and indicate the educational institution. APA also entails a running head with a summarized title and page number located in the header. The intro paragraph commences below the title.
In essence, adhering to educational MLA or APA standards for the opening page of your written task is vital for establishing its content, tone, and format. By complying with the fixed procedures of each style, you can effortlessly generate an engaging and professional opening that effectively introduces your thoughts to the audience.
Introduction, Body, and Conclusion
As writers, we navigate a labyrinth of words, constructing compositions that captivate our readers' minds. The fundamental structure of paragraphs leads us through the maze of ideas, functioning as the backbone of our message. Here's how each section contributes:
Introduction
A solid intro is vital, establishing the setting and a captivating hook to engage the audience. Present your topic, add background data, and state your central idea, or thesis statement concisely.
Each body section must focus on a single aspect of your viewpoint, supported by illustrations and evidence. Use transitional phrases for smooth shifts, maintaining unity and clarity. Reinforce your points with facts and details to enhance credibility.
Recap your key points, reiterate the thesis, and offer a final perspective. Summarize the strongest arguments without introducing new details. The last paragraph provides closure and underlines your composition’s relevance.
Essay writing is akin to navigating a literary labyrinth, where structure guides comprehensibility and impact. A well-structured text that leaves a lasting impression is essential for academic accomplishment. By keeping to readability, organizing your thoughts reasonably, and supporting key arguments with evidence, your text becomes a powerful tool for conveying message and persuasion.
In-Text Citation
Scholarly essays require precise citation practices to demonstrate utilized sources and uphold the integrity of your ideas. Citing materials is needed for crediting them and promoting original writing.
- In MLA-based style, quotes typically indicate in parentheses the writer's surname and book’s page number, (e.g., Smith 23), making source identification easier.
- In contrast, the APA-focused formatting method indicates the author's surname with the book’s publication year, like (Smith, 2023), giving a brief reference to the literature’s publication date.
Adhering to the referencing rules leads to scholarly rigor and ethical integrity. Accurately citing used sources is a winning approach to increase the integrity of your points and demonstrate academic integrity.
Works Cited Page
In research, precise source citation is critical for demonstrating the integrity of your study and preventing plagiarism. A well-ordered Works Cited (in MLA) or References (in APA) list is a way to showcase the depth of your investigation and respect for any intellectual property.
Here’s how to format the bibliography list:
- MLA: Title it "Works Cited," alphabetize sources by listing all writers’ last names with indentation for clarity.
- APA: Title it "References," adding details about the author, book publication year, brief title, and literature to enhance credibility.
A meticulously curated Works Cited or References page heightens your proficiency, bolstering your composition’s overall reliability.
Utilizing Templates and Tools
Using templates and formatting-related tools can greatly simplify the process of crafting academic works. Word processing programs offer templates for MLA, APA, or Chicago styles to meet academic standards. Additionally, online tools and bibliography generators like Aithor AI streamline the creation of accurate citations with reference lists, saving your time and ensuring precision.
It's essential, however, to always review AI-generated content for accuracy and logic, as automated tools may occasionally introduce errors. For more comprehensive guidelines, consult authoritative sources such as Wikipedia's formatting guidelines, official academic style manuals, and scholarly publications.
Following the mentioned essay-formatting tips enables students, writers, and researchers to create clear, well-organized compositions that meet demanding academic standards. Proficient formatting not only enhances your readability and professionalism but also underscores your commitment to scholarly excellence.
By mastering specific style guidelines, organizing content efficiently, and employing correct citation practices, your pieces will resonate with clarity and flow. Upholding these standards ensures your assignment not only meets academic criteria but also communicates your notions effectively to readers.
Related articles
How to write essay thesis statement: a comprehensive analysis.
In academic writing, creating an impactful text that can deftly relay your opinion and persuade your audience is one of the key skills. That’s why it is essential to learn how to write a strong thesis statement. In this article, you will find all you need to know for creating a persuasive thesis statement. What is an essay thesis? In academic essays, a thesis is a part of the introduction that expresses the main idea and purpose of the essay. It aims to give the audience a brief overview of t ...
Types of Case Studies: a Comprehensive Guide
The art of writing involves multiple types of materials, which makes both writing and reading a pleasure that is informative and conducive to conveying knowledge and experience. However, when it comes to academic writing, there is a need to distinguish between the many types of materials based on their appropriateness to a certain kind of information. Each type of material with its own structure and manner of writing is best suited for certain types of topics. The latter can range from anything ...
Expository Essay Examples: Developing Skills in Informative Writing
Is your assignment to prepare a fine and well-structured expository essay but you don't know what point to start with? This material lends a helping hand to you. Here we discuss how to begin an expository essay, what parts should be in the text, and what linguistic means a person should use when creating a project mentioned above. We also introduce you a few tips on how to sharpen your skills in informative writing. So be ready to read and learn, the adventure to the land of expository papers ge ...
Diagnostic Essay Writing Guide and Outline Sample
Imagine stepping into a classroom on the first day and being asked to write an essay. This exercise, commonly referred to as a diagnostic essay, is a common tool used by instructors to gauge their students' writing proficiency. Interestingly, in a study exploring the effectiveness of evaluation papers, over 70% of participants reported that these tasks significantly improved their understanding of their writing strengths and challenges. This finding underscores the assessment assignment's role i ...
The Basics of Crafting an Outstanding Persuasive Essay Outline
When writing a persuasive essay, having a well-structured outline is critical to effectively presenting your argument and convincing your audience. An outline serves as a roadmap for your essay, organizing your thoughts and supporting evidence in a logical sequence that flows cohesively. In this guide, we will explore the essential components of a persuasive essay outline and provide tips on how to craft a compelling structure for your writing. Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned writer, ma ...
How to Conclude an Essay: A Guide for Academic Writing
Every essay requires a proper conclusion. It is particularly important in academic writing where texts can be several dozen pages long. A conclusion helps the audience remember the contents of your essay and retain important information. In this article, you will learn how to write a conclusion for an essay. Why the conclusion matters When writing essays, we always strive to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the topic. We do our research, present different perspectives, and provide examples ...
What is an Appendix in a Research Paper? | Aithor
What is an appendix in a research paper? An appendix is a supplementary section at the end of a research paper after the list of references. It contains more information that helps explain the main ideas in the paper. It's not needed in the main part because it would make the paper too long or go “off-topic." The appendix gives readers more details to help them understand the research better without making the main argument hard to follow. The length of an appendix can differ depending on what ...
How to Make an Essay Longer: 7 Useful Tips
Are you having trouble getting your essay to the right length? Do you look at your essay and think, "It's too short!" but don't know what to do? Don't worry, we've got some great ideas on how to make an essay longer without making it worse. Why is it Important to Make an Essay Longer? When you're writing an essay, it's important to make sure it's long enough. If your essay isn't as long as required, you might get a lower grade, even if the content of your essay is exceptional. By making your ...
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
- Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
Published on November 19, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on January 20, 2023.
The formatting of a research paper is different depending on which style guide you’re following. In addition to citations , APA, MLA, and Chicago provide format guidelines for things like font choices, page layout, format of headings and the format of the reference page.
Scribbr offers free Microsoft Word templates for the most common formats. Simply download and get started on your paper.
APA | MLA | Chicago author-date | Chicago notes & bibliography
- Generate an automatic table of contents
- Generate a list of tables and figures
- Ensure consistent paragraph formatting
- Insert page numbering
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Formatting an apa paper, formatting an mla paper, formatting a chicago paper, frequently asked questions about research paper formatting.
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in APA Style are as follows:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial.
- Set 1 inch page margins.
- Apply double line spacing.
- If submitting for publication, insert a APA running head on every page.
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch.
Watch the video below for a quick guide to setting up the format in Google Docs.
The image below shows how to format an APA Style title page for a student paper.
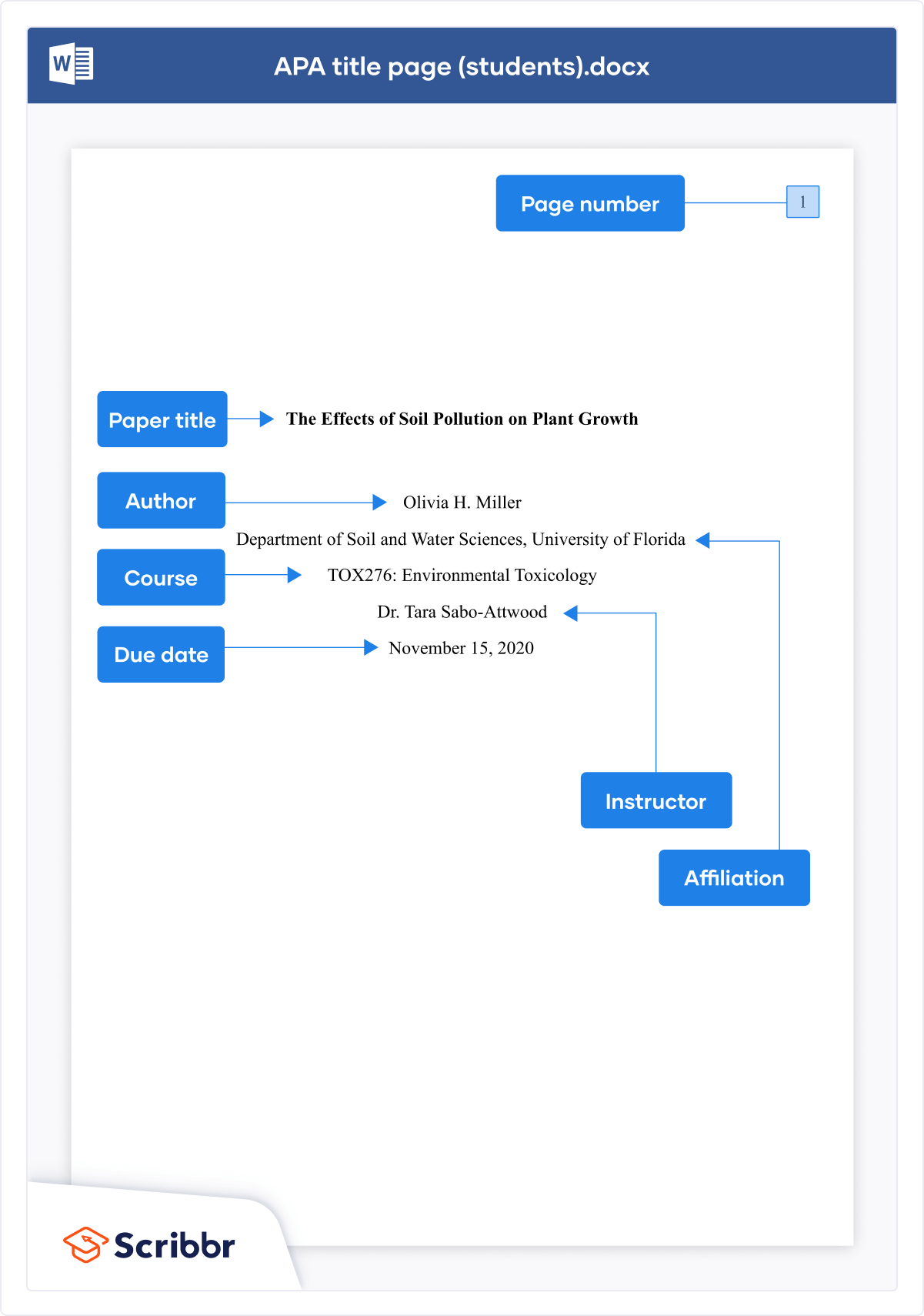
Running head
If you are submitting a paper for publication, APA requires you to include a running head on each page. The image below shows you how this should be formatted.
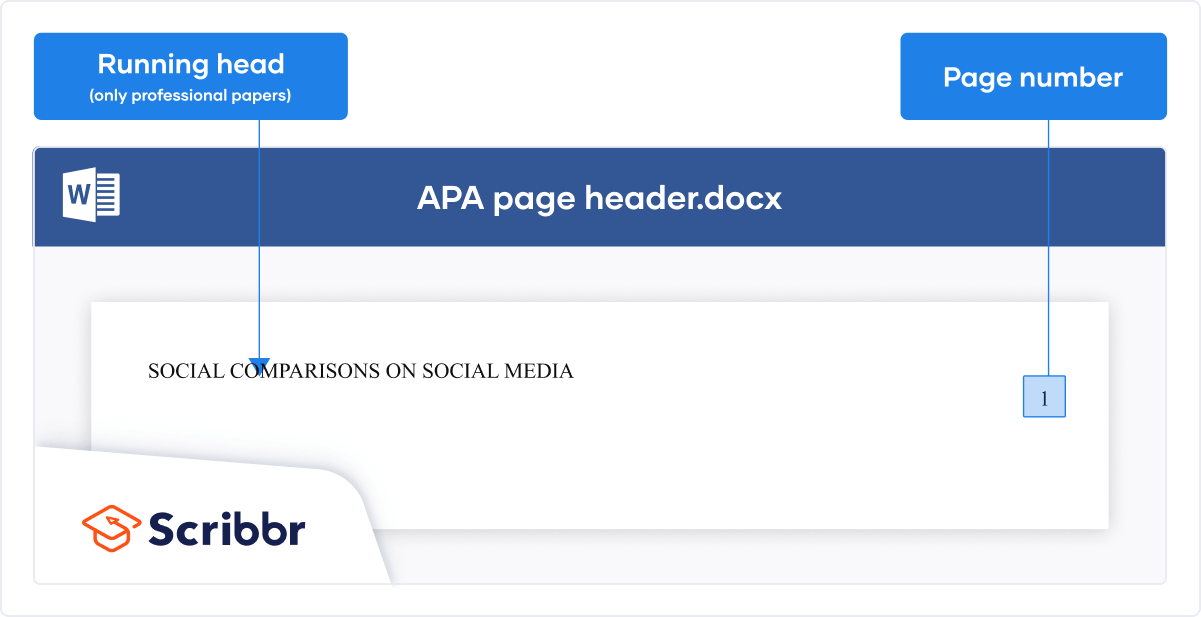
For student papers, no running head is required unless you have been instructed to include one.
APA provides guidelines for formatting up to five levels of heading within your paper. Level 1 headings are the most general, level 5 the most specific.
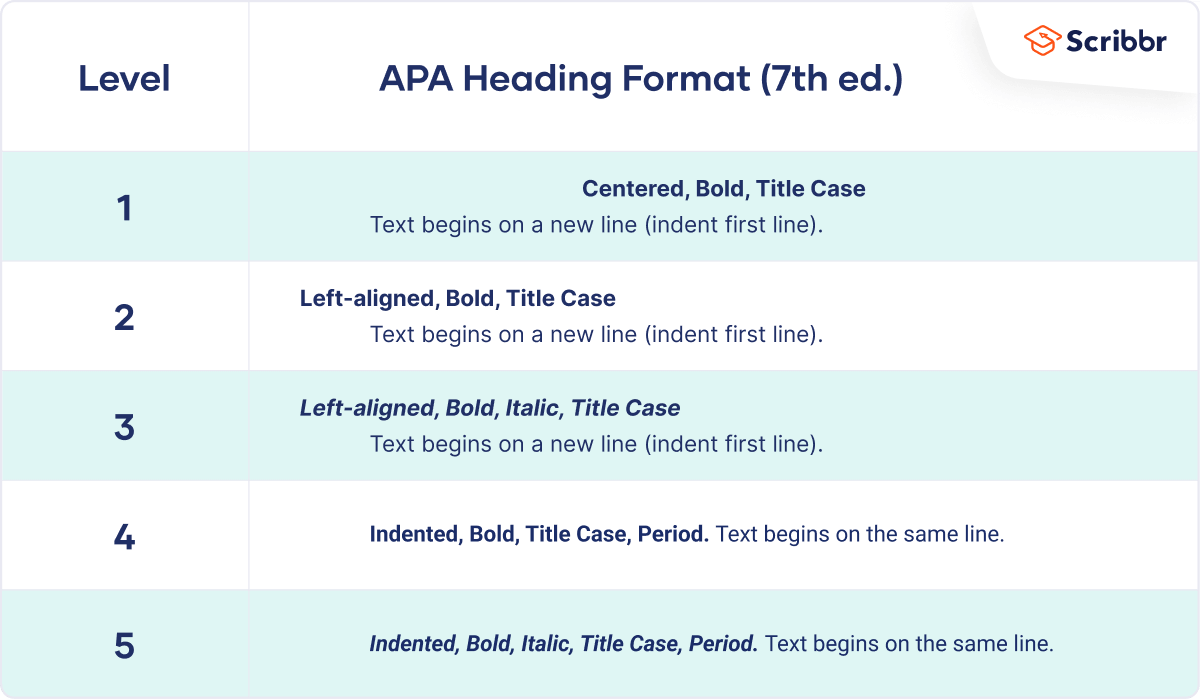
Reference page
APA Style citation requires (author-date) APA in-text citations throughout the text and an APA Style reference page at the end. The image below shows how the reference page should be formatted.
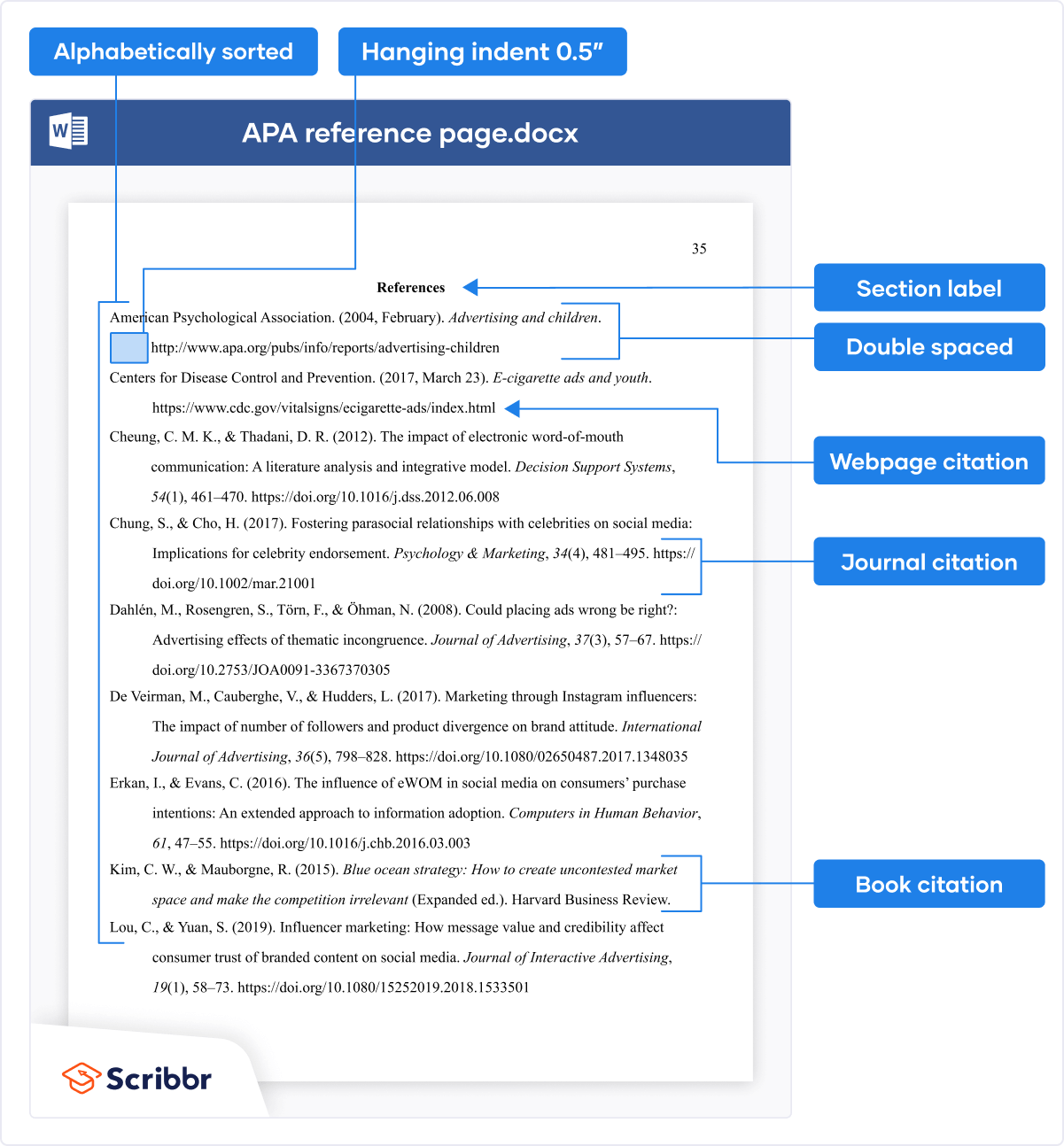
Note that the format of reference entries is different depending on the source type. You can easily create your citations and reference list using the free APA Citation Generator.
Generate APA citations for free
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

The main guidelines for writing an MLA style paper are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman.
- Use title case capitalization for headings .
Check out the video below to see how to set up the format in Google Docs.
On the first page of an MLA paper, a heading appears above your title, featuring some key information:
- Your full name
- Your instructor’s or supervisor’s name
- The course name or number
- The due date of the assignment
Page header
A header appears at the top of each page in your paper, including your surname and the page number.
Works Cited page
MLA in-text citations appear wherever you refer to a source in your text. The MLA Works Cited page appears at the end of your text, listing all the sources used. It is formatted as shown below.
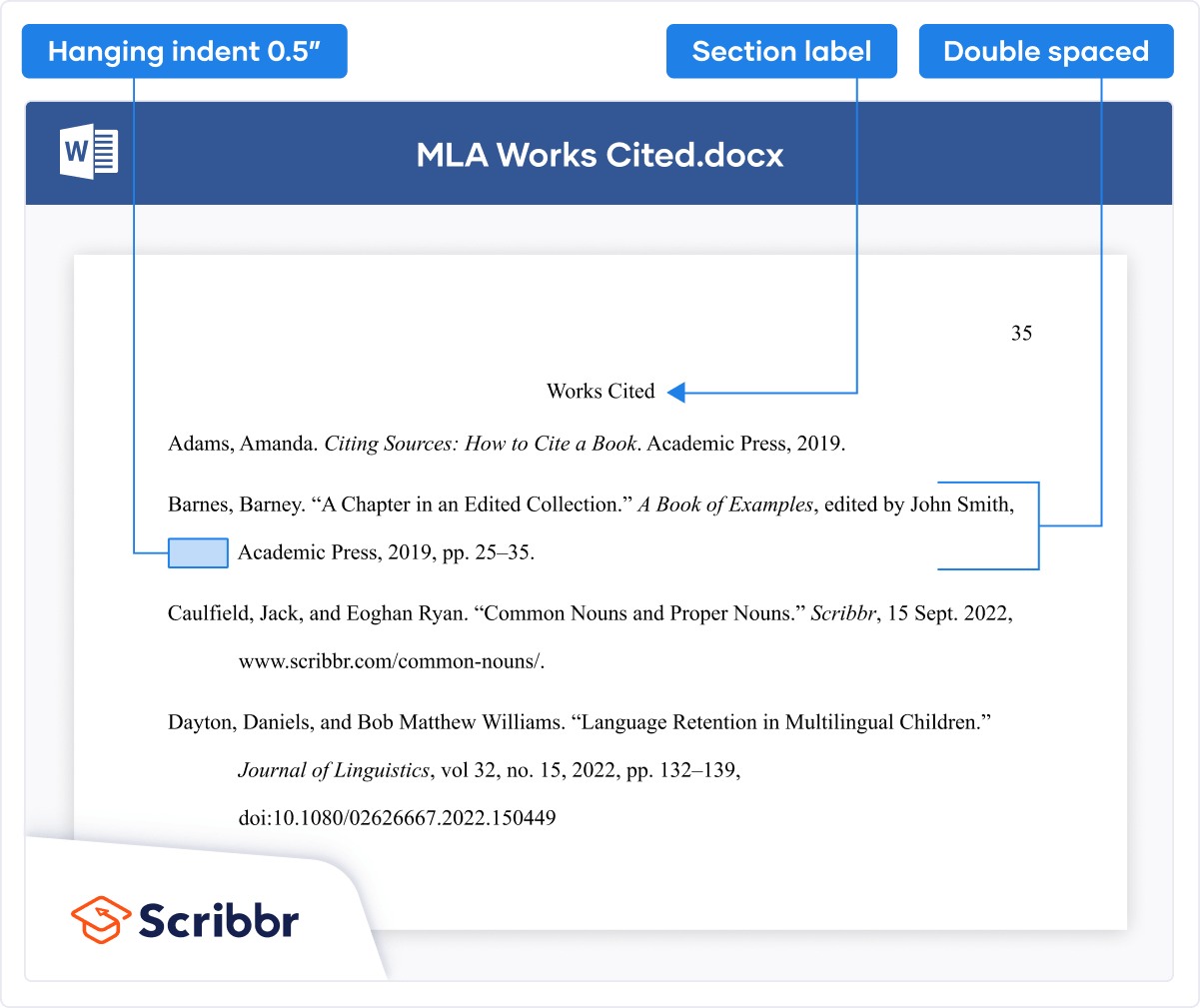
You can easily create your MLA citations and save your Works Cited list with the free MLA Citation Generator.
Generate MLA citations for free
The main guidelines for writing a paper in Chicago style (also known as Turabian style) are:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman.
- Use 1 inch margins or larger.
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center.
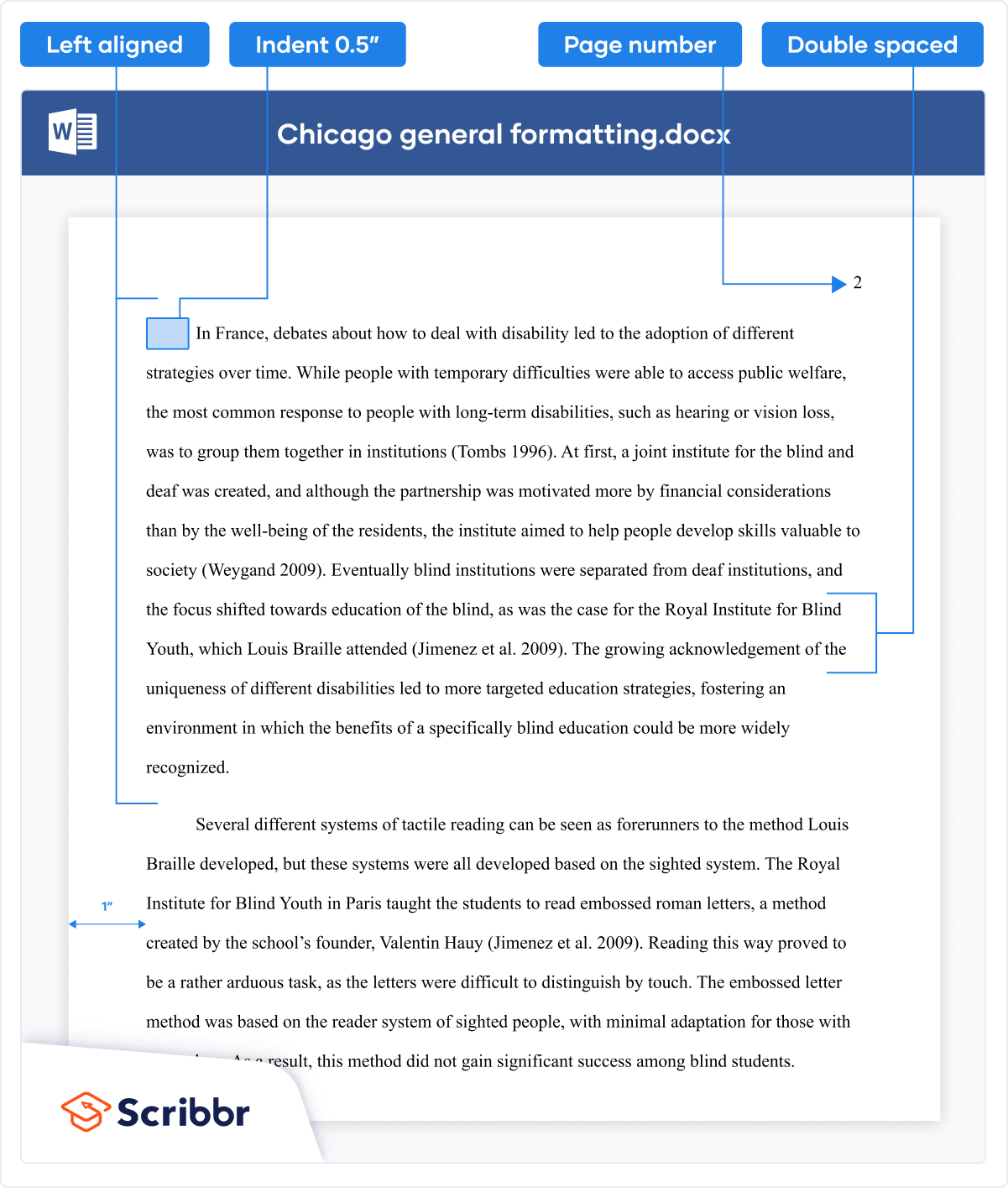
Chicago doesn’t require a title page , but if you want to include one, Turabian (based on Chicago) presents some guidelines. Lay out the title page as shown below.
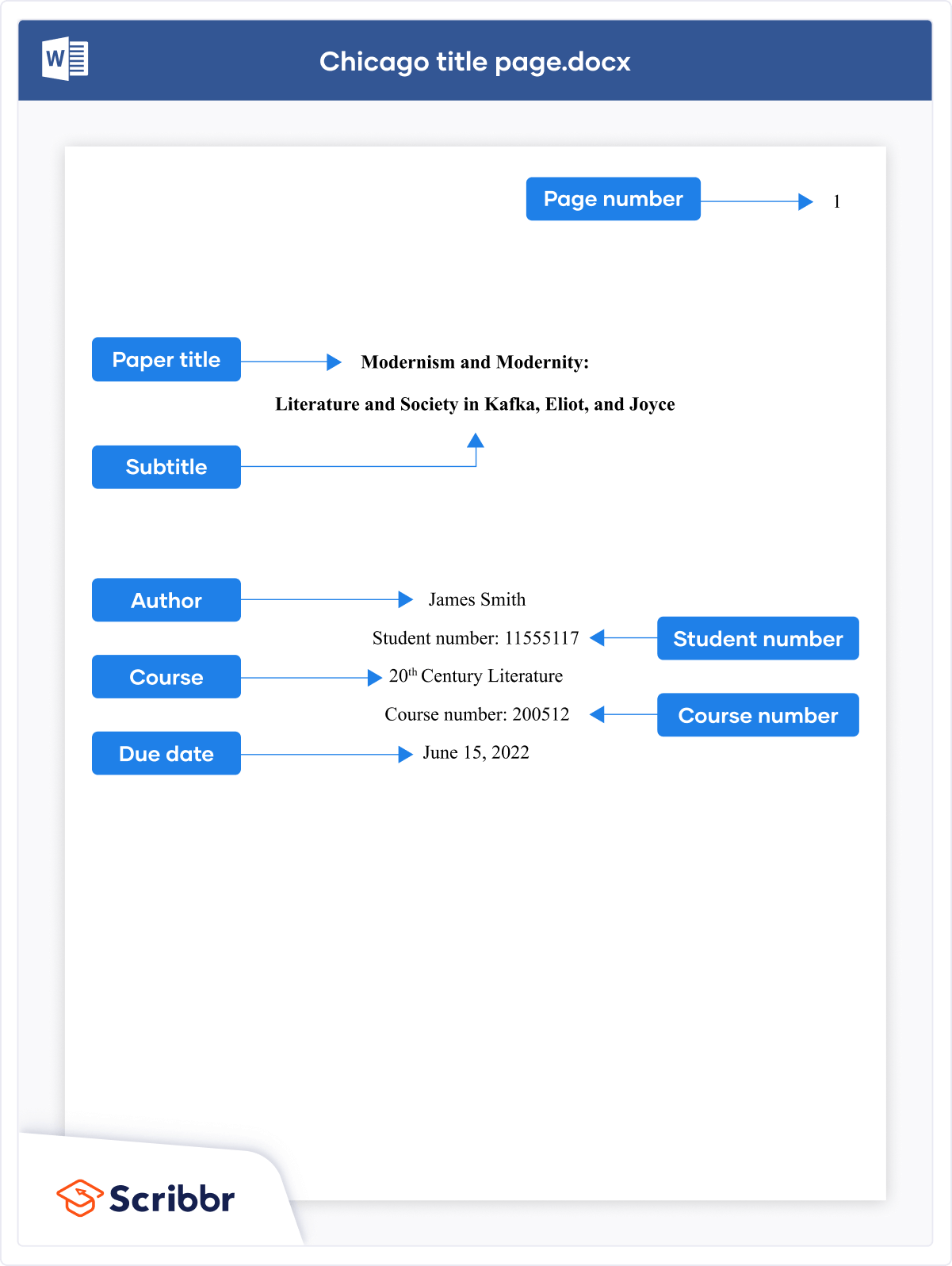
Bibliography or reference list
Chicago offers two citation styles : author-date citations plus a reference list, or footnote citations plus a bibliography. Choose one style or the other and use it consistently.
The reference list or bibliography appears at the end of the paper. Both styles present this page similarly in terms of formatting, as shown below.
To format a paper in APA Style , follow these guidelines:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial
- Set 1 inch page margins
- Apply double line spacing
- Include a title page
- If submitting for publication, insert a running head on every page
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch
- Apply APA heading styles
- Cite your sources with APA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a reference page at the end
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA style are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page
- Center the paper’s title
- Use title case capitalization for headings
- Cite your sources with MLA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a Works Cited page at the end
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in Chicago style are to:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Use 1 inch margins or larger
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center
- Cite your sources with author-date citations or Chicago footnotes
- Include a bibliography or reference list
To automatically generate accurate Chicago references, you can use Scribbr’s free Chicago reference generator .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, January 20). Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved June 26, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-format/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, apa format for academic papers and essays, mla format for academic papers and essays, chicago style format for papers | requirements & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

Research Title
Ai generator.

A research title is a succinct, informative phrase that encapsulates a study’s essence. It gives readers a clear indication of the research’s focus, scope, and significance. An effective research title is concise, specific, and engaging, incorporating key terms related to the primary subject matter. Crafting a well-thought-out research title is crucial as it influences first impressions and impacts the study’s visibility and accessibility. Additionally, a strong research title enhances the title page and ensures the research paper cover letter accurately reflects the study’s content.
What is Research Title?
A research title is a concise statement that clearly and precisely encapsulates the main topic, scope, and objective of a research study. It serves as the first point of contact for readers and should effectively communicate the essence of the research in a way that is both engaging and informative. A well-crafted research title is specific, descriptive, and reflective of the study’s core focus, helping to attract interest and provide a clear understanding of the research subject at a glance.
Research Title Format
A well-crafted research title follows a specific format to ensure clarity and precision. Here’s a structured approach:
[Main Topic]: [Specific Aspect or Focus]
Example: “The Impact of Social Media on Teen Mental Health: A Comprehensive Analysis of Behavioral Changes”
Examples of Research Titles

Here are some examples of well-crafted research titles across various fields:
- “The Effects of Bilingual Education on Cognitive Development in Early Childhood”
- “Assessing the Impact of Technology Integration on Student Engagement in High School Classrooms”
- “The Role of Genetics in the Development of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis”
- “Evaluating the Efficacy of Telemedicine in Managing Chronic Diseases During the COVID-19 Pandemic”
- “The Impact of Urbanization on Local Wildlife Populations: A Case Study of Central Park”
- “Assessing the Effectiveness of Renewable Energy Policies in Reducing Carbon Emissions”
- “The Influence of Social Media on Political Participation Among Millennials”
- “Exploring the Relationship Between Socioeconomic Status and Academic Achievement in Urban Schools”
- “Analyzing the Effects of Corporate Social Responsibility on Consumer Behavior”
- “The Role of Microfinance in Alleviating Poverty in Developing Countries”
- “The Development and Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Workforce Automation”
- “Assessing the Safety and Efficiency of Autonomous Vehicles in Urban Areas”
- “The Representation of Gender Roles in 21st Century Cinema”
- “Exploring the Influence of Renaissance Art on Modern Aesthetic Values”
- “The Impact of Childhood Trauma on Adult Relationships: A Longitudinal Study”
- “Exploring the Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Treating Anxiety Disorders”
- “The Effectiveness of Vaccination Campaigns in Reducing the Spread of Infectious Diseases: A Global Perspective”
- “Sustainable Farming Practices and Their Impact on Soil Health: A Comparative Study of Organic and Conventional Methods”
Research Titles for Students
- The Impact of Online Learning on Student Performance in High School
- Exploring the Relationship Between Sleep Patterns and Academic Achievement Among College Students
- The Effects of Extracurricular Activities on Student Social Skills Development
- The Influence of Peer Pressure on High School Students’ Academic Choices
- Assessing the Benefits of Early Childhood Education Programs on Later Academic Success
- The Role of Nutrition and Diet in Enhancing Student Concentration and Memory
- Examining the Effectiveness of Study Groups in Improving Academic Performance in University Settings
- The Impact of Part-Time Employment on High School Students’ Academic Achievement and Time Management
- Exploring the Relationship Between Physical Activity and Mental Health Among College Students
- The Effects of School Uniform Policies on Student Behavior and Academic Outcomes
Qualitative Research Titles
- Exploring Student Perceptions of Remote Learning During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- The Lived Experiences of First-Generation College Students: Challenges and Triumphs
- Understanding Teacher Attitudes Towards Inclusive Education in Mainstream Classrooms
- The Impact of Parental Involvement on Student Motivation and Academic Success
- Exploring the Cultural Adaptation Experiences of International Students in American Universities
- The Role of Peer Support in Coping with Academic Stress Among High School Students
- Investigating the Influence of School Climate on Teacher Job Satisfaction and Retention
- The Effects of Community-Based Learning on Student Engagement and Civic Responsibility
- Understanding the Barriers to STEM Education for Female Students in Rural Areas
- Exploring the Experiences of Students with Learning Disabilities in Higher Education
- The Impact of School Leadership Styles on Teacher Morale and Performance
- The Role of Mentorship Programs in Supporting Minority Students in STEM Fields
- Exploring the Emotional and Social Impacts of Bullying on Middle School Students
- The Influence of Extracurricular Activities on Identity Development in Adolescents
- Understanding the Perspectives of Parents on Bilingual Education Programs
Quantitative Research Titles
- The Impact of Class Size on Student Academic Achievement in Elementary Schools
- Analyzing the Correlation Between Homework Frequency and Student Performance in Mathematics
- The Effects of School Funding on Standardized Test Scores in Public Schools
- Assessing the Relationship Between Attendance Rates and Graduation Rates in High Schools
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Flipped Classrooms on Student Learning Outcomes
- The Influence of Parental Education Levels on Children’s Academic Success
- The Impact of Early Childhood Education on Literacy Rates in Primary School Students
- Comparing Academic Performance Between Students in Single-Sex and Coeducational Schools
- The Role of Technology in Enhancing Student Engagement in STEM Subjects
- Analyzing the Impact of Nutrition Programs on Student Health and Academic Performance
- The Relationship Between Physical Activity and Academic Achievement in High School Students
- Evaluating the Success of Mentorship Programs on College Retention Rates
- The Effects of Sleep Patterns on Academic Performance Among University Students
- Assessing the Impact of Socioeconomic Status on Access to Higher Education
- The Influence of Teacher Qualifications on Student Achievement in Science
Importance of a Research Title
A research title is a critical component of any research study or academic paper. It serves multiple important functions that contribute to the overall success and impact of the research. Here are key reasons why a research title is important:
1. First Impression
The research title is often the first element a reader encounters. A well-crafted title can create a strong first impression, attracting the reader’s attention and encouraging them to explore the study further.
2. Clarity and Focus
A good research title clearly and succinctly communicates the main topic and scope of the study. It helps the reader quickly understand what the research is about and what specific aspect is being addressed.
3. Guidance
The title provides guidance to the reader about the content and direction of the research. It sets expectations and helps readers decide if the paper is relevant to their interests or research needs.
4. Searchability
In the digital age, research titles are crucial for searchability. A precise and descriptive title improves the chances of the paper being found in online searches, databases, and academic journals, increasing its visibility and accessibility.
5. Academic and Professional Recognition
A well-formulated research title contributes to the academic and professional recognition of the work. It reflects the researcher’s ability to clearly define and articulate their study, which can enhance credibility and reputation within the academic community.
Characteristics of a Good Research Title
A good research title is essential for effectively communicating the main focus and scope of your study. Here are the key characteristics that make a research title effective:
- Clear and Understandable : The title should be easily understood by a broad audience, avoiding jargon or overly complex language.
- Direct : It should convey the main topic and scope of the research without ambiguity.
2. Conciseness
- Brevity : A good title is concise and to the point, typically no longer than 10-15 words.
- Essential Information : It includes only the most relevant information, omitting unnecessary words.
3. Specificity
- Focused : The title should clearly reflect the specific aspect or focus of the research.
- Detailed : It provides enough detail to give a clear sense of what the study entails.
4. Descriptiveness
- Informative : It accurately describes the content and scope of the study.
- Comprehensive : The title should give readers a good understanding of the research without needing to read the entire paper.
5. Keywords
- Relevant Keywords : Including key terms that are central to the research topic helps with searchability and indexing.
- SEO-Friendly : Using keywords that align with what potential readers might search for increases the paper’s visibility.
6. Engagement
- Interest : The title should be engaging and interesting, encouraging readers to want to learn more about the study.
- Appeal : It should appeal to the target audience, whether they are academics, practitioners, or the general public.
How to Write a Research Title?
A well-crafted research title is crucial as it provides the first impression of your study. It should be concise, informative, and engaging to capture the reader’s attention while conveying the essence of your research. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an effective research title.
1. Understand the Purpose of the Title
The title should:
- Summarize the main topic of the research.
- Indicate the scope and focus of the study.
- Reflect the methodology used (if applicable).
- Attract the target audience’s interest.
2. Identify the Key Components
To create a comprehensive title, identify the following components of your research:
- Main topic : The primary subject or focus.
- Variables : Key elements or factors studied.
- Population/sample : The group or sample studied.
- Methodology : The approach or techniques used in the research.
3. Be Clear and Specific
Avoid vague and ambiguous terms. Be precise in describing your research. For example, instead of “Study of Education Methods,” use “Effectiveness of Interactive Learning Techniques in High School Biology.”
4. Keep It Concise
A good title is typically between 10 to 15 words. It should be long enough to include essential information but short enough to be easily readable.
5. Use Descriptive Words
Use words that describe the content and aim of your research effectively. Descriptive words help in making the title informative and engaging. Examples include “effects,” “analysis,” “evaluation,” “comparison,” etc.
6. Avoid Jargon and Abbreviations
Ensure that your title is accessible to a broad audience by avoiding technical jargon and abbreviations that might not be widely understood.
7. Consider the Audience
Think about who will be reading your research. Tailor your title to meet the expectations and interests of your target audience, whether they are academic peers, professionals, or the general public.
8. Reflect the Type of Study
Indicate whether the research is a review, case study, experiment, or theoretical analysis. This helps set the context for the reader. For example, “A Case Study on Renewable Energy Adoption in Urban Areas.”
9. Include Keywords
Incorporate relevant keywords that reflect the main themes of your research. This not only helps in search engine optimization but also makes your research easily discoverable.
10. Revise and Refine
Review your title for clarity, conciseness, and accuracy. Ask for feedback from peers or mentors to ensure it effectively represents your research.
FAQ’s
How should a research title be structured.
A research title should be clear, concise, and informative, often including the main variables, methods, and context of the study.
What are the key elements of a good research title?
Key elements include relevance, clarity, specificity, and the inclusion of main keywords related to the research topic.
Can a research title be a question?
Yes, a research title can be a question if it effectively conveys the research’s focus and intrigues the reader.
How long should a research title be?
A research title should be brief but descriptive, typically between 10 to 15 words, avoiding unnecessary jargon or overly complex terms.
Should a research title include keywords?
Yes, including keywords helps in indexing and searching, making it easier for others to find your research.
Can a research title change during the research process?
Yes, it can be refined or adjusted as the research progresses to better reflect the study’s findings and scope.
Should the research title reflect the research methodology?
It can, especially if the methodology is central to the study’s uniqueness or understanding, but it’s not always necessary.
How specific should a research title be?
A research title should be specific enough to give a clear idea of the study’s focus but not so detailed that it becomes cumbersome.
What makes a research title catchy?
A catchy research title is engaging, piques curiosity, and uses intriguing language while still being clear and informative.
Can humor be used in a research title?
Humor can be used if appropriate for the subject matter and audience, but it should not compromise clarity or professionalism.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Browse Course Material
Course info.
- Prof. Elizabeth A. Wood
Departments
- Women's and Gender Studies
- Political Science
- Linguistics and Philosophy
As Taught In
- Gender Studies
- Women's Studies
Learning Resource Types
Feminist thought, final research paper.
Your research paper should address a topic in the field of what I call “big tent” feminism: e.g., gender, race, class, sexuality, disability, and/or structures of society. A strong paper will contain three basic elements: a motivating question/argument, a rough description of your methodology, and your findings. It should be roughly 10–15 pages double-spaced (roughly 2500–5000 words). The exact length is not as important as the clarity of argument, evidence, and conclusions.
Choosing a Topic
In my experience of finding topics, the best first step is to play. Noodle around in news articles. Try different combinations of words and phrases in Google or another broad search engine. If you add the word “news” to any topic, you will find stories and examples that might be off the beaten track. Then you can use Barton Plus and Google Scholar to find research and data about your topic. Or perhaps you will want to use other databases ( Nexis Uni , ProQuest , CQ Researcher , Statista ). A topic can be like the frame of your paper, the subject that you are going to home in on. Try to think what might be the boundaries of your topic—its beginning and end in time and space, the cast of characters, the subtopics or related topics you might bring in.
Question/Argument
Your question should speak to your interest and be sufficiently intriguing to draw in the reader. Ask yourself, “So what? Why should a busy person want to read my paper and learn about this topic?” Consider whether and how your argument adds new knowledge and insight that others have not addressed. One way to set up a good argument is to look at its opposite: Could someone say “no” to what I am arguing? Could they make a counterargument? You could say, for example, that most people believe x , but your evidence suggests y . Then you can ask why your y might be happening. By first setting up the opposite of what you want to argue, you can help prove to your reader the importance of your topic and findings, why it is something they should want to take note of and read. Be sure to try to state your argument by the end of your first paragraph.
Try also put your argument into your title. Don’t just call your paper “A Study of Y .” Instead you could say “The Misperception of Y in the Z Community” or “ Y Issue as the Tip of the Iceberg for Z ” or “ Y : The Problem Nobody Knows About but Everyone Should Be Thinking About.”
Once you’ve told the reader what you are going to argue, you’ll want to tell us how you came to your conclusions. What kinds of sources did you use? Are there benefits and/or limits to these sources?
Think about how you want to present your findings. What is the right order? Is it chronological (change over time)? Is it some kind of internal logic (say, from most obvious to least obvious answers to your burning question)? Is it some answers to a question that are actually wrong, while others turn out to be right? Can you organize it by subtopic and create corresponding subheadings?
Proofread, Proofread, Proofread
When you finish your paper, take time to read it over carefully to catch any mistakes or infelicities in word choice, grammar, logic, spelling, or punctuation. One good trick is to read your work out loud. Often you can hear when something isn’t working well when you read it out loud. Over the years I have often heard students say, “I knew that wasn’t the right word; but I couldn’t quite think of a better one.” If something isn’t quite the right word, take an extra moment to see if you can find the word you really want.
Try to avoid filler (e.g., “ x is an interesting topic”). Aim for strong verbs (" y issue calls for our attention because of a , b , and c ). If you can get rid of the verb “to be” as a connecting verb, you have already made your paper stronger (instead of “the house is big,” try for “the house has room for 4 people to sleep comfortably”).
Pay special attention to your first paragraph. Once you have finished a whole draft of your paper, go back and reread, rewrite the opening paragraph so your best points come first and draw the reader in. I often find that as I am writing, I gain new ideas. If that happens to you (I think it happens to almost all writers), be sure to go back and put your best ideas up front even if that means a bit of rewriting both there and throughout the paper.
Good luck, and enjoy your writing! We are happy to help at all stages of the research and writing.
Beginnings, Middles, and Ends: Some Writing Tips for Feminist Thought

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare
Training videos | Faqs

How to Write Catchy Research Paper Titles with Examples
Hey there, fellow researchers! Have you ever felt the struggle of coming up with the perfect title for your paper? You’re not alone. The title is like the headline of your favorite news article – it’s got to be catchy yet informative. Let’s dive into some tips and tricks to ensure your title stands out in the academic crowd.
1. Why is the Research Paper Title Important?
Every word in your title is crucial. It’s the first thing a reviewer or reader will see, and it can determine whether your paper gets read or skipped.
✖ Title is too long, wordy, and confusing An In-depth Examination into The Overall Chance of Becoming a World-Renowned Athlete vs Getting an Executive Position in a Fortune 500 Company ✖ Title is written for a small group of readers Examining Humor in Asian Nations as Expressed in Instagram Videos ✔ Title is short and to the point Autonomous Cars: The Ethical Dilemma
A great title is a concise summary of your research and a sneak peek into your work’s unique aspects and main findings. It’s a balance between being specific and informative without overwhelming the reader with details.
2. Rules for Writing Good Titles
Rules for writing great titles are like rules for good writing in general. Let’s look at some basic rules to follow while crafting a fitting title for your research paper.
2.1 Be Specific and Avoid Being Generic
A generic title is broad, vague, and lacks specificity about the research findings. It does not highlight the research’s unique factors or the study’s contribution.
✖ Generic title An Analysis of Healthcare Data Privacy ✔ Improved title Assessing the Effectiveness of Encryption Techniques in Protecting User Data Privacy in a Healthcare Organization _ Focus of research _ Context _ Aspect being studied
2.2 Highlight Your Main Findings and Unique Aspects
Craft the perfect title using three steps.
2.3 Make it Concise and Short
While a five-word short title may seem ideal, when trying to include the specificity of focus, method, and context, you are likelier to have an 8-12 word title. This length is perfect for journal articles.
✖ Not concise A Comprehensive Examination of the Use and Impact of AI-Driven Predictive Analytics for Improving Patient Outcomes in Healthcare Settings Including Hospitals, Labs, Physician’s Offices and Primary Care Facilities ✔ Concise AI-Driven Predictive Analytics in Healthcare: Improving Patient Outcomes
2.4 Attract Attention to Your Work
You want people to be able to find your research article easily through a Google search. Specificity is essential. Using vague adjectives like novel or unique to describe a method doesn’t mean anything, and these words are not likely to be entered into a search bar. Ask yourself, what would the person likely type into the search bar?
✖ Title with poor searchability A Novel Technique for Learning Science ✔ Title with good searchability AI Driven Exercises for Elementary Science Classes
3. Common Questions
Many questions arise when writing an article title. We will answer some of the most common questions, starting with writing mechanics.
3.1 Should Titles be Grammatically Correct?
You might wonder if using prepositions (for, in, of, for, by) in a title is okay. The answer is yes. It is often necessary for the title to make sense and be grammatically correct. Using articles (the, a, an) correctly is also essential. Let’s look at some examples.
Please remember, a countable singular noun (factor, cause, risk) must be preceded by an article. Are verbs acceptable in titles? Absolutely. Verbs make titles more dynamic.
Tip: Use the …ing form of verbs rather than vague nouns.
✖ Using abstract nouns The examination and categorization of educational software for high schools ✔ Replace abstract nouns with …ing form of verb Examining and categorizing educational software for high schools
Using verbs in the second example adds action words that depict the tasks performed in the study.
3.2 Can I Add Humor to My Title?
Humor can make a title more engaging and memorable, but it must be balanced with relevance to the research topic. The humor must not detract from the study’s credibility.
3.3 Can I Formulate My Paper Title as a Question?
Titles that ask questions are well-suited to abstracts submitted to conferences. Questioning titles are informal and catch the reader’s attention quickly. The question must be aligned with the primary focus of the research.
Rule: A title can end with a question mark. However, no other punctuation is required at the end of a title.
3.4 What is the Difference Between Conference and Journal Titles?
When you submit an abstract to a conference, you want it noticed so it will be accepted as a presentation. However, you also hope it will be published in the conference proceedings. You want to attract attention, but the title can’t be too witty as to lose professionalism. Two-part titles work well to blend fun and professionalism.
| |
3.5 When is a Two-Part Title a Good Idea
Two-part titles can pose a question in the first part to grab attention, with the second part providing a more academic description of the content. Two-part questions can also use the second part to explain the first part. Two-part questions must be specific, and the two parts must be connected.
✖ Poorly written two-part title : first and second parts don’t connect Advanced Algorithms in Machine Learning: Can They Really Improve Anything? ✔ Improved title Advanced Algorithms in Predictive Analytics: Are They Transforming Healthcare Outcomes?
The poorly written title does not strongly connect the first and second parts. “Can They Really Improve Anything?” isn’t specific enough to connect to the first part, which also lacks specificity.
Crafting an engaging and informative research article title is crucial for capturing attention and ensuring your work is read. You can create titles that stand out by being specific, highlighting unique findings, keeping titles concise, and ensuring grammatical correctness. Remember, a well-placed question or a bit of humor can enhance your title, but it must remain relevant and professional. Whether for journals or conferences, a well-crafted title can make a difference in the searchability and impact of your research. Happy titling!
If you have any questions, please drop a comment below, and we will answer as soon as possible. We also recommend you to refer to our other blogs on academic writing tools , academic writing resources , academic writing phrases , research paper examples and research paper writing tips which are relevant to the topic discussed in this blog.
Similar Posts

A New Academic Writing Technique and Tool for Foreign Non-native English Speaking PhD students
In this blog, we explain various writing difficulties faced by international students and introduce the concept of ‘imitative learning’.

Abstract Section Examples and Writing Tips
In this blog, we will go through many abstract examples and understand how to construct a good abstract for your research paper.

Introduction Paragraph Examples and Writing Tips
In this blog, we will go through a few introduction paragraph examples and understand how to construct a great introduction paragraph for your research paper.

Limitations in Research – A Simplified Guide with Examples
In this blog, we provide tips for presenting study limitations in your paper and provide some real-world examples.

Critical Literature Review : How to Critique a Research Article?
In this blog, we will look at how to use constructive language when critiquing other’s work in your research paper.

Results Section Examples and Writing Tips
In this blog, we will go through many results section examples and understand how to write a great results section for your paper.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- 10 Share Facebook
- 0 Share Twitter
- 0 Share LinkedIn
- 0 Share Email
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Title: burst image super-resolution with base frame selection.
Abstract: Burst image super-resolution has been a topic of active research in recent years due to its ability to obtain a high-resolution image by using complementary information between multiple frames in the burst. In this work, we explore using burst shots with non-uniform exposures to confront real-world practical scenarios by introducing a new benchmark dataset, dubbed Non-uniformly Exposed Burst Image (NEBI), that includes the burst frames at varying exposure times to obtain a broader range of irradiance and motion characteristics within a scene. As burst shots with non-uniform exposures exhibit varying levels of degradation, fusing information of the burst shots into the first frame as a base frame may not result in optimal image quality. To address this limitation, we propose a Frame Selection Network (FSN) for non-uniform scenarios. This network seamlessly integrates into existing super-resolution methods in a plug-and-play manner with low computational costs. The comparative analysis reveals the effectiveness of the nonuniform setting for the practical scenario and our FSN on synthetic-/real- NEBI datasets.
| Comments: | CVPR2024W NTIRE accepted |
| Subjects: | Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV) |
| Cite as: | [cs.CV] |
| (or [cs.CV] for this version) | |
| Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite |
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
- Skip to main content
- Skip to FDA Search
- Skip to in this section menu
- Skip to footer links

The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
- Search
- Menu
- Science & Research
- Scientific Meetings, Conferences, and Workshops
- FDA Omics Days 2024 - Precision in Practice: Regulatory Science, Best Practices, and Future Directions in Omics - 09/12/2024
Symposium | Mixed
Event Title FDA Omics Days 2024 - Precision in Practice: Regulatory Science, Best Practices, and Future Directions in Omics September 12, 2024

September 12, 2024
Where: FDA White Oak Campus Great Room and virtually via Zoom Webinar
On This Page: FDA Omics Days 2024
In the case of a government shutdown that exceeds past October 5, 2023, the event will be rescheduled for a yet-to-be-determined date. Questions can be sent to [email protected]
On this page:.
- September 12 th Agenda
Registration
View Recording 10/10 AM View Recording 10/10 PM
View Recording 10/11 AM View Recording 10/11 PM
View Posters
Poster Abstract Submission
Background:
At the FDA Omics Days 2024, the FDA Omics Working Group will be hosting speakers from industry, academia, and government to discuss topics important to the FDA. This event will include sessions on contemporary topics in the fields of precision medicine, multi-omics, and One Health.
Upon registration, further information will be sent to you that includes the link for the event. The meeting will be recorded and available after the event concludes.
Information for in-person attendees
- Getting to FDA
- Visitor Parking and Campus Map
- Public Meeting Information
- Non-FDA Participants: If you are a non-FDA participant, you will need to enter through Building 1 security screening and identify yourself as an FDA Omics Days presenter. You will then be directed to the Building 31, Great Room.
Poster Abstract Booklet
Additional details will be added closer to the event.
Thursday, September 12, 2024
Presenter bios and presentation titles
| Time | Topics |
|---|---|
| 9:00 am - 9:15 am ET | |
| 9:15 am - 10:00 am ET | |
| 10:00 am - 10:15 am ET | |
| 10:15 am - 11:45 am ET | |
| 11:45 am - 1:15 pm ET | |
| 1:15 pm - 2:45 pm ET | |
| 2:45 pm - 3:00 pm ET | |
| 3:00 pm - 4:30 pm ET |
Back to the top
Twitter: #FDAOmicsDay2023

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The professional title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation(s), author note, running head, and page number, as shown in the following example. ... the affiliation is the institution at which the research was conducted. Include both the name of any department and the name of the college, university, or ...
Formatting Rules. In APA Style (7th edition), the cover page, or title page, should include: A running head (professional papers only) and page number. The title of the paper. The name of the author (s) The institutional affiliation. An author note; optional (professional papers only) A student paper should also include course information.
Page header. For a student title page, the page header consists of just a page number in the top-right corner. There is no need for a running head (as was the case in APA 6th edition). A professional title page does have a running head. The running head is an abbreviated version of the paper title in all capital letters.
Title Page Content. student title page includes the following elements: title of the paper. author(s) ° include the full names of all authors of the paper; use the form first name, middle initial, last name (e.g., Betsy R. Klein) ° if two authors, separate with the word "and". (e.g., Ainsley E. Baum and Lucy K. Reid)
The title page of a research paper typically includes the following information: Title of the research paper. Author (s) of the paper (including their name (s), affiliation (s), and contact information) Date of submission or publication. Name of the academic institution or organization where the research was conducted (if applicable)
The title page (also known as the cover page) is the front page of your paper. It should contain: The running head, a header at the top of the page. The first page number. The title of the paper; Your name; The institution for which you writing. Running head. The running head should be in the top-left corner of the page in uppercase. It should ...
The title page includes the following elements: Page number, Paper title, Author, Author Affiliation, Course, Instructor, and Due Date. Remember, your instructor can include other requirements for your assignment. Refer to their instructions carefully. Your title page and paper is double-spaced. Use 1-inch margins.
Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5 in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. Page numbers: Put a page number in the top right corner of every page, including the title page or cover page, which is page 1. Student papers do not require a running head on any page.
MLA title page format. To create an MLA format title page, list the following on separate lines, left-aligned at the top of the page: Then leave a few blank lines and list the title of the paper, centered and in title case, halfway down the page. All text should be double-spaced and in the same font as the rest of the paper.
The title page (or cover page) of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper should contain all the key information about your document. It usually includes: Dissertation or thesis title. Your name. The type of document (e.g., dissertation, research paper) The department and institution. The degree program (e.g., Master of Arts)
The paper's title should be a maximum of 12 words and fill one or two lines; avoid using abbreviations and unnecessary words. Do not format the title with bold, italics, underlining, or quotation marks. The title should be centered in the upper portion of the page, centered, and written in boldface. Make sure to capitalize the major words of ...
10/31/2023. The title page is a crucial component of a research paper, serving as the first point of contact between the reader and the study. It provides readers with a first impression, signaling the credibility and relevance of the work. Beyond conveying essential information, a well-designed title page adds visual appeal to the paper ...
Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch. Use double-spaced text throughout your paper. Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point). Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section.
What is a Research Paper Title? The title page of a research paper serves as its initial page, prominently displaying the paper's title or topic. This page previews the content of the research paper, setting the stage for the reader. Adherence to specific citation and formatting style guidelines is crucial in structuring the title page.
Center all title page elements (except the right-aligned page number in the header). Title page font. Write the title page using the same font and font size as the rest of your paper. Bold the paper title. Use standard font (i.e., no bold, no italics) for all other title page elements. Text setup Text elements. Repeat the paper title at the top ...
The Title Page. Your title page should follow all of the rules outlined in the Basic Formatting tab. In addition, it should be centered in the upper-half of the page. It must include the following information (and your instructor might prefer you to add more): The full title of your paper in title case. Your name (First Last)
Title of the Paper . You need a professional title page. Following the right formatting helps to achieve a good title and generally acceptable work. Here are the major elements of APA-style papers: Page number. Paper title. Author (and their institution affiliation). Course instructor. Due Date. These are examples of the APA 7 title page ...
A running head: The running head is a shortened version of the paper's title. It should appear on every page of the paper, along with the page number. Author affiliation: In the second paragraph, list any changes in author affiliation.For example, if one of the authors is now affiliated with a different university from where the research was conducted, the author's note might state that "Dr.
Research Paper Title. Research Paper Title is the name or heading that summarizes the main theme or topic of a research paper.It serves as the first point of contact between the reader and the paper, providing an initial impression of the content, purpose, and scope of the research.A well-crafted research paper title should be concise, informative, and engaging, accurately reflecting the key ...
A research paper title page is the first page of your research paper. It is essential to come up with a title page that gives the readers an overview of the research. It should also be structured in a way that gives it a professional outlook. A title page should include a running head, research paper title, page number, student's name, and ...
If you decide to generate it, then center the composition's title at the top of the opening page. Below it, indicate yours with the lecturer's name, the discipline, current date, all centered. APA. In an APA-based organization, designing the title page is obligatory. Center the article's or research's heading at the top half of the ...
Formatting a Chicago paper. The main guidelines for writing a paper in Chicago style (also known as Turabian style) are: Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman. Use 1 inch margins or larger. Apply double line spacing. Indent every new paragraph ½ inch. Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center.
A research title is a critical component of any research study or academic paper. It serves multiple important functions that contribute to the overall success and impact of the research. Here are key reasons why a research title is important: 1. First Impression. The research title is often the first element a reader encounters.
Your research paper should address a topic in the field of what I call "big tent" feminism: e.g., gender, race, class, sexuality, disability, and/or structures of society. A strong paper will contain three basic elements: a motivating question/argument, a rough description of your methodology, and your findings.
There are two pages to the title and the following details use the California title as an example. Page 1 of the Title: The front page contains information on the vehicle and the current owner or seller. There are two key numbers listed typically near the top of the title. The title number is an 8-digit number associated with the title that is ...
The title of your paper should be catchy yet informative. Let's dive into some tips and tricks to ensure your title stands out in the academic crowd. ... Let's look at some basic rules to follow while crafting a fitting title for your research paper. 2.1 Be Specific and Avoid Being Generic. A generic title is broad, vague, and lacks ...
Burst image super-resolution has been a topic of active research in recent years due to its ability to obtain a high-resolution image by using complementary information between multiple frames in the burst. In this work, we explore using burst shots with non-uniform exposures to confront real-world practical scenarios by introducing a new benchmark dataset, dubbed Non-uniformly Exposed Burst ...
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.