Common Sense Media
Movie & TV reviews for parents
- For Parents
- For Educators
- Our Work and Impact

Or browse by category:
- Get the app
- Movie Reviews
- Best Movie Lists
- Best Movies on Netflix, Disney+, and More
Common Sense Selections for Movies

50 Modern Movies All Kids Should Watch Before They're 12

- Best TV Lists
- Best TV Shows on Netflix, Disney+, and More
- Common Sense Selections for TV
- Video Reviews of TV Shows

Best Kids' Shows on Disney+

Best Kids' TV Shows on Netflix
- Book Reviews
- Best Book Lists
- Common Sense Selections for Books

8 Tips for Getting Kids Hooked on Books

- 50 Books All Kids Should Read Before They're 12
- Game Reviews
- Best Game Lists
Common Sense Selections for Games
- Video Reviews of Games

Nintendo Switch Games for Family Fun

- Podcast Reviews
- Best Podcast Lists
Common Sense Selections for Podcasts

Parents' Guide to Podcasts

- App Reviews
- Best App Lists

Social Networking for Teens

Gun-Free Action Game Apps

Reviews for AI Apps and Tools
- YouTube Channel Reviews
- YouTube Kids Channels by Topic

Parents' Ultimate Guide to YouTube Kids

YouTube Kids Channels for Gamers
- Preschoolers (2-4)
- Little Kids (5-7)
- Big Kids (8-9)
- Pre-Teens (10-12)
- Teens (13+)
- Screen Time
- Social Media
- Online Safety
- Identity and Community

Explaining the News to Our Kids
- Family Tech Planners
- Digital Skills
- All Articles
- Latino Culture
- Black Voices
- Asian Stories
- Native Narratives
- LGBTQ+ Pride
- Best of Diverse Representation List

Celebrating Black History Month

Movies and TV Shows with Arab Leads

Celebrate Hip-Hop's 50th Anniversary
"best of" lists.
Get age-appropriate ideas and inspiration for every interest:
- Best Movies for Kids
- Best TV for Kids
- Best Streaming Picks for Kids
- Best Games for Kids
- Best Apps for Kids
- Best Books for Kids
- Best Podcasts for Kids
- Best Websites for Kids
- Best for Character Development for Kids
- Best for Diversity for Kids
- Best for Learning for Kids
The Best Book-Report Books for Middle Schoolers
No need to dread a book report! When kids find titles that are engaging, interesting, and thought-provoking, they're hooked. If it's fiction, students can dissect plot, theme, and characters. If it's nonfiction, they can plunge into a subject that fascinates them or learn a lot about something they've never heard of before. Here's a list of surefire selections for students in sixth, seventh, and eighth grades. For even more ideas, check out 50 Books All Kids Should Read Before They're 12 .

Anne Frank: The Diary of a Young Girl
Inspiring wartime journal reveals teen's inner life.

The Apothecary, Book 1
Cold War kids use magic to save world in brilliant novel.

Everything Sad Is Untrue: (A True Story)
Young refugee's story is told in memories, myths, fables.

Goodbye Stranger
Bittersweet, lovely story of friendship and social media.

Genesis Begins Again
Teen learns to love herself in uplifting tale of misfits.

Hold on tight for an intense tale of survival.

A Long Walk to Water
Touching take on Lost Boys of Sudan, based on true story.

One Crazy Summer
A gem, with strong girl characters, '60s black history.

Poverty, being unhoused explored in hopeful tale.

The Port Chicago 50: Disaster, Mutiny, and the Fight for Civil Rights
Little-known disaster gets overdue, in-depth treatment.

The Red Badge of Courage
Compelling Civil War novel questions morality of battle.

Uglies: Uglies Quartet, Book 1
Thoughtful sci-fi about the price of beauty.

Interned girl, Native boy find common ground in moving tale.

All-American Muslim Girl
Captivating coming-of-age tale explores identity, racism.

American Ace
Moving, fast-paced novel-in-verse; great for teen boys.

Bomb: The Race to Build -- and Steal -- the World's Most Dangerous Weapon
Complex, suspenseful story of developing The Bomb.

The Boys Who Challenged Hitler: Knud Pedersen and the Churchill Club
Thrilling true story of teenagers who stood up to the Nazis.

Enchanted Air: Two Cultures, Two Wings
Poignant memoir-in-verse recalls Cuban American's childhood.

Long Way Down
Gripping, unnerving story of teen boy contemplating revenge.

My Name Is Not Easy
Fascinating story of Alaskan kids growing up in the 1960s.
Other great lists from our editors
- Coming-of-Age Books
- Books to Help Your Kid Survive Middle School
- How to Raise a Reader
- Help Your Kids Find Books with Diverse Characters
- How Comics Helped My Kid Love Reading
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Arts and Entertainment
A Beginner's Guide to Writing a Book Report (with Examples)
Last Updated: March 13, 2024 Fact Checked
- Researching
- Drafting the Report
- Reviewing & Revising
Sample Book Reports & Summaries
Expert q&a.
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams and by wikiHow staff writer, Raven Minyard, BA . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,410,678 times.
A book report is a short essay that summarizes and analyzes a work of fiction or nonfiction. Writing a book report may not seem fun at first, but it gives you a great chance to fully understand a work and its author. In this article, we’ll teach you everything you need to know about how to write a book report, from choosing a book and outlining to drafting and editing your final paper.
Things You Should Know
- Read the entire book and take notes on important themes, characters, and events. Use your notes to create an outline with evidence that supports your analysis.
- Include the title and author in your intro, then summarize the plot, main characters, and setting of the book.
- Analyze the author’s writing style, as well as the main themes and arguments of the book. Include quotes and examples to support your statements.
Researching Your Book Report

- For example, find out if your teacher wants you to include citations, such as page numbers from the book, in your report.
- Ask your teacher how much of your paper to devote to summary versus analysis. Most book reports are direct summaries with objective analysis rather than your personal opinions. In contrast, a book review or commentary is more opinion-driven.
- Some popular books for book reports include To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee, Animal Farm by George Orwell, and The Hunger Games by Suzanne Collins. Choose a book at your grade level.

- Author: Who wrote the book? Do you know any other works by this author?
- Genre: Is the book fiction or nonfiction? If it’s fiction, is it historical, fantasy, horror, etc.? If it’s nonfiction, is it a biography, memoir, science, etc.?
- Audience: Who would find this book appealing? Is it intended for a specific age range or gender? Do you typically enjoy books like this?
- Title: Does the title catch your interest? Does it fit well with the book’s content?
- Book Cover/Illustrations: What does the book cover convey and does it accurately represent the book? How do you feel when you look at it? If the book has illustrations, what are they and do they hold your interest?

- Take breaks while reading to keep your attention sharp. Try to find a pace that is comfortable for you. If you get distracted after 15 minutes, read in 15-minute intervals. If you can go an hour, read for an hour at a time.
- Give yourself enough time to read the entire book. It’s very difficult to write a book report if you’ve just skimmed over everything. Don’t procrastinate!
- Don’t trust online book summaries. You can’t guarantee that they are accurate or true to the text.

- For example, look for a sentence that clearly describes a main setting in the book, such as “The castle was gloomy and made out of large black stones.”
Outlining Your Book Report

- Introduction: Introduce the title, author, and publication information. Include a brief overview of the book’s genre and main theme, and state your purpose for writing the report.
- Summary: Concisely summarize the plot or central idea, highlighting main events, characters, and conflicts. Focus on important aspects while avoiding spoilers.
- Analysis and Evaluation: Evaluate the author’s writing style and use of literary devices, like foreshadowing, metaphors, imagery, etc. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the book and use quotes and examples from the text.
- Themes and Messages: Identify the book’s main themes or messages and how they develop through the course of the book. Provide specific quotes and examples.
- Character Analysis: Analyze the main characters in the book, their development, and their relationships. Explain their motivations, personalities, and significance to the story. Provide examples and quotes to support your analysis.
- Personal Reflection: Depending on your teacher’s instructions, you might share your personal opinions and discuss what you liked and disliked about the book. Reflect on how the book relates to broader themes or issues.
- Conclusion: Summarize your main points and conclude with your final thoughts or reflections on the book.
- Bibliography: If required, include a works cited page or bibliography listing all the sources you used to write your book report.
- Outlining takes time, but it saves you more time once you reach the editing stage.
- Some people prefer to outline with pen and paper, while others just type up a list on the computer. Choose the method that works best for you.

- Be careful not to overuse quotes. If it seems like every other line is a quote, try to dial back. Aim to include a maximum of one quotation per paragraph. Quotes and examples should still take a backseat to your summary.

- For example, you’ll likely need to focus primarily on discussing the most important characters or the characters that appear most frequently in the text.
- When you are finished with your outline, go back through it to see if it makes sense. If the paragraphs don’t flow into one another, move them around or add/delete new ones until they do.
- Also, check to see if your outline covers all of the major elements of the book, such as the plot, characters, and setting.
Writing Your Book Report

- For example, a sentence summary might state, “This book is about the main character’s journey to Africa and what she learns on her travels.”
- Don’t take up too much space with your introduction. In general, an introduction should be 3-6 sentences long, though in rare cases, they may be longer or shorter.

- Use vivid language when you can and include plenty of details. For example, you might write, “The farm was surrounded by rolling hills.”

- For instance, if the main character moves to Africa, you might describe what happens before the move, how the move goes, and how they settle in once they arrive.

- For example, you might write that the main character is “a middle-aged woman who enjoys the finer things in life, such as designer clothes.” Then, connect this description to the plot summary by describing how her views change after her travels, if they do.
- Expect to introduce the characters in the same sentences and paragraphs as the plot introduction.

- You might write, “The author argues that travel gives you a new perspective. That is why her main characters all seem happier and more grounded after visiting new places.”
- For fiction, determine if the author is using the story to pass along a certain moral or lesson. For example, a book about an underdog athlete could encourage readers to take chances to pursue their dreams.

- For example, an author who uses lots of slang terms is probably going for a hip, approachable style.

- Some teachers require, or strongly suggest, that you include the author’s name and the book title in your concluding paragraph.
- When writing a conclusion , don’t introduce any new thoughts. Any important points should be made in your body paragraphs. Save the space for your recap.

Reviewing and Revising Your Book Report

- Before you submit your paper, make sure that you’ve spelled the author’s name and any character names correctly.
- Don’t trust your computer’s spell check to catch all the errors for you. Spell check can be helpful, but it isn’t perfect and can make mistakes.

- If you’re nervous about asking, try saying something like “It would be great if you could go over my book report and make sure that it reads smoothly.”
- Remember, no one’s first draft is perfect, so don’t get upset if someone suggests you do something differently. They want to help make your report the best it can be, so don’t take constructive criticism personally.

- For example, double-check that you are using the correct font, font size, and margins.
- Once you've finished proofreading, revising, and checking that you've addressed all the requirements, you're ready to submit your book report!

- Even though your book report is your own work, avoid using “I” too much. It can make your writing feel choppy. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- It might be tempting to watch the movie or read the online notes instead of reading the book. Resist this urge! Your teacher will be able to tell the difference. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
Tips from our Readers
- Calm down and walk around if you get too frustrated while writing. If you write a book report while angry, you're more likely to misspell things!
- Choose a unique book. Harry Potter or Percy Jackson is an absolute no. Everyone chooses those. Try something different!
- Write when anything comes to mind! You don't want to lose your ideas!

- Give yourself plenty of time to write your report. Don’t wait until the last minute or you may feel rushed. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- Stealing or using another person’s work is considered plagiarism and academic dishonesty. Make sure that the work you submit is all your own. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.aresearchguide.com/write-book-report.html
- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 24 July 2020.
- ↑ https://grammark.org/how-to-write-a-book-report/
- ↑ https://library.valleycollege.edu/elements_of_book_report.pdf
- ↑ https://takelessons.com/blog/steps-to-writing-a-book-report
- ↑ https://www.infoplease.com/homework-help/homework-center-writing-book-report
- ↑ https://liberalarts.oregonstate.edu/wlf/what-setting
- ↑ https://www.tcc.edu/wp-content/uploads/archive/writing-center-handouts/essay-types-plot-summary.pdf
- ↑ https://www.cornerstone.edu/blog-post/six-steps-to-really-edit-your-paper/
About This Article

To write a book report, start by introducing the author and the name of the book and then briefly summarizing the story. Next, discuss the main themes and point out what you think the author is trying to suggest to the reader. Finally, write about the author’s style of writing, paying particular attention to word choice and the overall tone of the book. For tips on editing and polishing your paper before turning it in, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Louise Pena
May 17, 2016
Did this article help you?
Ashley Egerage
Nov 13, 2017
Aug 20, 2016
Charlotte Arney
Mar 10, 2023
Nov 16, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter

How to Write a Book Report
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Book Report Fundamentals
Preparing to write, an overview of the book report format, how to write the main body of a book report, how to write a conclusion to a book report, reading comprehension and book reports, book report resources for teachers .
Book reports remain a key educational assessment tool from elementary school through college. Sitting down to close read and critique texts for their content and form is a lifelong skill, one that benefits all of us well beyond our school years. With the help of this guide, you’ll develop your reading comprehension and note-taking skills. You’ll also find resources to guide you through the process of writing a book report, step-by-step, from choosing a book and reading actively to revising your work. Resources for teachers are also included, from creative assignment ideas to sample rubrics.
Book reports follow general rules for composition, yet are distinct from other types of writing assignments. Central to book reports are plot summaries, analyses of characters and themes, and concluding opinions. This format differs from an argumentative essay or critical research paper, in which impartiality and objectivity is encouraged. Differences also exist between book reports and book reviews, who do not share the same intent and audience. Here, you’ll learn the basics of what a book report is and is not.
What Is a Book Report?
"Book Report" ( ThoughtCo )
This article, written by a professor emeritus of rhetoric and English, describes the defining characteristics of book reports and offers observations on how they are composed.
"Writing a Book Report" (Purdue OWL)
Purdue’s Online Writing Lab outlines the steps in writing a book report, from keeping track of major characters as you read to providing adequate summary material.
"How to Write a Book Report" ( Your Dictionary )
This article provides another helpful guide to writing a book report, offering suggestions on taking notes and writing an outline before drafting.
"How to Write a Successful Book Report" ( ThoughtCo )
Another post from ThoughtCo., this article highlights the ten steps for book report success. It was written by an academic advisor and college enrollment counselor.
What’s the Difference Between a Book Report and an Essay?
"Differences Between a Book Report & Essay Writing" ( Classroom)
In this article from the education resource Classroom, you'll learn the differences and similarities between book reports and essay writing.
"Differences Between a Book Report and Essay Writing" (SeattlePi.com)
In this post from a Seattle newspaper's website, memoirist Christopher Cascio highlights how book report and essay writing differ.
"The Difference Between Essays and Reports" (Solent Online Learning)
This PDF from Southampton Solent University includes a chart demonstrating the differences between essays and reports. Though it is geared toward university students, it will help students of all levels understand the differing purposes of reports and analytical essays.
What’s the Difference Between a Book Report and a Book Review?
"How to Write a Book Review and a Book Report" (Concordia Univ.)
The library at Concordia University offers this helpful guide to writing book report and book reviews. It defines differences between the two, then presents components that both forms share.
"Book Reviews" (Univ. of North Carolina)
The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill’s writing guide shows the step-by-step process of writing book reviews, offering a contrast to the composition of book reports.
Active reading and thoughtful preparation before you begin your book report are necessary components of crafting a successful piece of writing. Here, you’ll find tips and resources to help you learn how to select the right book, decide which format is best for your report, and outline your main points.
Selecting and Finding a Book
"30 Best Books for Elementary Readers" (Education.com)
This article from Education.com lists 30 engaging books for students from kindergarten through fifth grade. It was written by Esme Raji Codell, a teacher, author, and children's literature specialist.
"How to Choose a Good Book for a Report (Middle School)" (WikiHow)
This WikiHow article offers suggestions for middle schoolers on how to choose the right book for a report, from getting started early on the search process to making sure you understand the assignment's requirements.
"Best Book-Report Books for Middle Schoolers" (Common Sense Media)
Common Sense Media has compiled this list of 25 of the best books for middle school book reports. For younger students, the article suggests you check out the site's "50 Books All Kids Should Read Before They're 12."
"50 Books to Read in High School" (Lexington Public Library)
The Lexington, Kentucky Public Library has prepared this list to inspire high school students to choose the right book. It includes both classics and more modern favorites.
The Online Computer Library Center's catalogue helps you locate books in libraries near you, having itemized the collections of 72,000 libraries in 170 countries.
Formats of Book Reports
"Format for Writing a Book Report" ( Your Dictionary )
Here, Your Dictionary supplies guidelines for the basic book report format. It describes what you'll want to include in the heading, and what information to include in the introductory paragraph. Be sure to check these guidelines against your teacher's requirements.
"The Good Old Book Report" (Scholastic)
Nancy Barile’s blog post for Scholastic lists the questions students from middle through high school should address in their book reports.
How to Write an Outline
"Writer’s Web: Creating Outlines" (Univ. of Richmond)
The University of Richmond’s Writing Center shows how you can make use of micro and macro outlines to organize your argument.
"Why and How to Create a Useful Outline" (Purdue OWL)
Purdue’s Online Writing Lab demonstrates how outlines can help you organize your report, then teaches you how to create outlines.
"Creating an Outline" (EasyBib)
EasyBib, a website that generates bibliographies, offers sample outlines and tips for creating your own. The article encourages you to think about transitions and grouping your notes.
"How to Write an Outline: 4 Ways to Organize Your Thoughts" (Grammarly)
This blog post from a professional writer explains the advantages of using an outline, and presents different ways to gather your thoughts before writing.
In this section, you’ll find resources that offer an overview of how to write a book report, including first steps in preparing the introduction. A good book report's introduction hooks the reader with strong opening sentences and provides a preview of where the report is going.
"Step-by-Step Outline for a Book Report" ( Classroom )
This article from Classroom furnishes students with a guide to the stages of writing a book report, from writing the rough draft to revising.
"Your Roadmap to a Better Book Report" ( Time4Writing )
Time4Writing offers tips for outlining your book report, and describes all of the information that the introduction, body, and conclusion should include.
"How to Start a Book Report" ( ThoughtCo)
This ThoughtCo. post, another by academic advisor and college enrollment counselor Grace Fleming, demonstrates how to write a pithy introduction to your book report.
"How to Write an Introduction for a Book Report" ( Classroom )
This brief but helpful post from Classroom details what makes a good book report introduction, down to the level of individual sentences.
The body paragraphs of your book report accomplish several goals: they describe the plot, delve more deeply into the characters and themes that make the book unique, and include quotations and examples from the book. Below are some resources to help you succeed in summarizing and analyzing your chosen text.
Plot Summary and Description
"How Do You Write a Plot Summary?" ( Reference )
This short article presents the goals of writing a plot summary, and suggests a word limit. It emphasizes that you should stick to the main points and avoid including too many specific details, such as what a particular character wears.
"How to Write a Plot for a Book Report" ( The Pen & The Pad )
In this article from a resource website for writers, Patricia Harrelson outlines what information to include in a plot summary for a book report.
"How to Write a Book Summary" (WikiHow)
Using Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone as an example, this WikiHow article demonstrates how to write a plot summary one step at a time.
Analyzing Characters and Themes
"How to Write a Character Analysis Book Report" ( The Pen & The Pad )
Kristine Tucker shows how to write a book report focusing on character. You can take her suggestions as they are, or consider incorporating them into the more traditional book report format.
"How to Write a Character Analysis" (YouTube)
The SixMinuteScholar Channel utilizes analysis of the film Finding Nemo to show you how to delve deeply into character, prioritizing inference over judgment.
"How to Define Theme" ( The Editor's Blog )
Fiction editor Beth Hill contributes an extended definition of theme. She also provides examples of common themes, such as "life is fragile."
"How to Find the Theme of a Book or Short Story" ( ThoughtCo )
This blog post from ThoughtCo. clarifies the definition of theme in relation to symbolism, plot, and moral. It also offers examples of themes in literature, such as love, death, and good vs. evil.
Selecting and Integrating Quotations
"How to Choose and Use Quotations" (Santa Barbara City College)
This guide from a college writing center will help you choose which quotations to use in your book report, and how to blend quotations with your own words.
"Guidelines for Incorporating Quotes" (Ashford Univ.)
This PDF from Ashford University's Writing Center introduces the ICE method for incorporating quotations: introduce, cite, explain.
"Quote Integration" (YouTube)
This video from The Write Way YouTube channel illustrates how to integrate quotations into writing, and also explains how to cite those quotations.
"Using Literary Quotations" (Univ. of Wisconsin-Madison)
This guide from the University of Wisconsin-Madison’s Writing Center helps you emphasize your analysis of a quotation, and explains how to incorporate quotations into your text.
Conclusions to any type of paper are notoriously tricky to write. Here, you’ll learn some creative ways to tie up loose ends in your report and express your own opinion of the book you read. This open space for sharing opinions that are not grounded in critical research is an element that often distinguishes book reports from other types of writing.
"How to Write a Conclusion for a Book Report" ( Classroom )
This brief article from the education resource Classroom illustrates the essential points you should make in a book report conclusion.
"Conclusions" (Univ. of North Carolina)
The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill’s Writing Center lays out strategies for writing effective conclusions. Though the article is geared toward analytical essay conclusions, the tips offered here will also help you write a strong book report.
"Ending the Essay: Conclusions" (Harvard College Writing Center)
Pat Bellanca’s article for Harvard University’s Writing Center presents ways to conclude essays, along with tips. Again, these are suggestions for concluding analytical essays that can also be used to tie up a book report's loose ends.
Reading closely and in an engaged manner is the strong foundation upon which all good book reports are built. The resources below will give you a picture of what active reading looks like, and offer strategies to assess and improve your reading comprehension. Further, you’ll learn how to take notes—or “annotate” your text—making it easier to find important information as you write.
How to Be an Active Reader
"Active Reading Strategies: Remember and Analyze What You Read" (Princeton Univ.)
Princeton University’s McGraw Center for Teaching and Learning recommends ten strategies for active reading, and includes sample diagrams.
"Active Reading" (Open Univ.)
The Open University offers these techniques for reading actively alongside video examples. The author emphasizes that you should read for comprehension—not simply to finish the book as quickly as possible.
"7 Active Reading Strategies for Students" ( ThoughtCo )
In this post, Grace Fleming outlines seven methods for active reading. Her suggestions include identifying unfamiliar words and finding the main idea.
"5 Active Reading Strategies for Textbook Assignments" (YouTube)
Thomas Frank’s seven-minute video demonstrates how you can retain the most important information from long and dense reading material.
Assessing Your Reading Comprehension
"Macmillan Readers Level Test" (MacMillan)
Take this online, interactive test from a publishing company to find out your reading level. You'll be asked a number of questions related to grammar and vocabulary.
"Reading Comprehension Practice Test" (ACCUPLACER)
ACCUPLACER is a placement test from The College Board. This 20-question practice test will help you see what information you retain after reading short passages.
"Reading Comprehension" ( English Maven )
The English Maven site has aggregated exercises and tests at various reading levels so you can quiz your reading comprehension skills.
How to Improve Your Reading Comprehension
"5 Tips for Improving Reading Comprehension" ( ThoughtCo )
ThoughtCo. recommends five tips to increase your reading comprehension ability, including reading with tools such as highlighters, and developing new vocabulary.
"How to Improve Reading Comprehension: 8 Expert Tips" (PrepScholar)
This blog post from PrepScholar provides ideas for improving your reading comprehension, from expanding your vocabulary to discussing texts with friends.
CrashCourse video: "Reading Assignments" (YouTube)
This CrashCourse video equips you with tools to read more effectively. It will help you determine how much material you need to read, and what strategies you can use to absorb what you read.
"Improving Reading Comprehension" ( Education Corner )
From a pre-reading survey through post-reading review, Education Corner walks you through steps to improve reading comprehension.
Methods of In-text Annotation
"The Writing Process: Annotating a Text" (Hunter College)
This article from Hunter College’s Rockowitz Writing Center outlines how to take notes on a text and provides samples of annotation.
"How To Annotate Text While Reading" (YouTube)
This video from the SchoolHabits YouTube channel presents eleven annotation techniques you can use for better reading comprehension.
"5 Ways To Annotate Your Books" ( Book Riot )
This article from the Book Riot blog highlights five efficient annotation methods that will save you time and protect your books from becoming cluttered with unnecessary markings.
"How Do You Annotate Your Books?" ( Epic Reads )
This post from Epic Reads highlights how different annotation methods work for different people, and showcases classic methods from sticky notes to keeping a reading notebook.
Students at every grade level can benefit from writing book reports, which sharpen critical reading skills. Here, we've aggregated sources to help you plan book report assignments and develop rubrics for written and oral book reports. You’ll also find alternative book report assessment ideas that move beyond the traditional formats.
Teaching Elementary School Students How to Write Book Reports
"Book Reports" ( Unique Teaching Resources )
These reading templates courtesy of Unique Teaching Resources make great visual aids for elementary school students writing their first book reports.
"Elementary Level Book Report Template" ( Teach Beside Me )
This printable book report template from a teacher-turned-homeschooler is simple, classic, and effective. It asks basic questions, such as "who are the main characters?" and "how did you feel about the main characters?"
"Book Reports" ( ABC Teach )
ABC Teach ’s resource directory includes printables for book reports on various subjects at different grade levels, such as a middle school biography book report form and a "retelling a story" elementary book report template.
"Reading Worksheets" ( Busy Teacher's Cafe )
This page from Busy Teachers’ Cafe contains book report templates alongside reading comprehension and other language arts worksheets.
Teaching Middle School and High School Students How to Write Book Reports
"How to Write a Book Report: Middle and High School Level" ( Fact Monster)
Fact Monster ’s Homework Center discusses each section of a book report, and explains how to evaluate and analyze books based on genre for students in middle and high school.
"Middle School Outline Template for Book Report" (Trinity Catholic School)
This PDF outline template breaks the book report down into manageable sections for seventh and eighth graders by asking for specific information in each paragraph.
"Forms for Writing a Book Report for High School" ( Classroom )
In this article for Classroom, Elizabeth Thomas describes what content high schoolers should focus on when writing their book reports.
"Forms for Writing a Book Report for High School" ( The Pen & The Pad )
Kori Morgan outlines techniques for adapting the book report assignment to the high school level in this post for The Pen & The Pad .
"High School Book Lists and Report Guidelines" (Highland Hall Waldorf School)
These sample report formats, grading paradigms, and tips are collected by Highland Hall Waldorf School. Attached are book lists by high school grade level.
Sample Rubrics
"Book Review Rubric Editable" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This free resource from Teachers Pay Teachers allows you to edit your book report rubric to the specifications of your assignment and the grade level you teach.
"Book Review Rubric" (Winton Woods)
This PDF rubric from a city school district includes directions to take the assignment long-term, with follow-up exercises through school quarters.
"Multimedia Book Report Rubric" ( Midlink Magazine )
Perfect for oral book reports, this PDF rubric from North Carolina State University's Midlink Magazine will help you evaluate your students’ spoken presentations.
Creative Book Report Assignments
"25 Book Report Alternatives" (Scholastic)
This article from the Scholastic website lists creative alternatives to the standard book report for pre-kindergarteners through high schoolers.
"Fresh Ideas for Creative Book Reports" ( Education World )
Education World offers nearly 50 alternative book report ideas in this article, from a book report sandwich to a character trait diagram.
"A Dozen Ways to Make Amazingly Creative Book Reports" ( We Are Teachers )
This post from We Are Teachers puts the spotlight on integrating visual arts into literary study through multimedia book report ideas.
"More Ideas Than You’ll Ever Use for Book Reports" (Teachnet.com)
This list from Teachnet.com includes over 300 ideas for book report assignments, from "interviewing" a character to preparing a travel brochure to the location in which the book is set.
"Fifty Alternatives to the Book Report" (National Council of Teachers of English)
In this PDF resource from the NCTE's English Journal, Diana Mitchell offers assignment ideas ranging from character astrology signs to a character alphabet.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1890 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 39,819 quotes across 1890 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!

Book Report Writing
Book Report Writing Guide - Outline, Format, & Topics
15 min read

People also read
Guide to Crafting an Outstanding Book Report Outline
Creative and Excellent Book Report Ideas for Students
Writing a book report can be a challenging task for students at all levels of education. Many struggle to strike the right balance between providing a concise summary and offering insightful analysis.
The pressure to submit a well-structured report often leaves students feeling overwhelmed and uncertain about where to begin. Unlike a book review that is longer and more detailed, the purpose of writing a book report is to summarize what happened in the story.
In this blog, we will learn the book report writing, providing you with step-by-step instructions and creative ideas. Whether you're a reader or just starting your literary journey, this guide will help you write book reports that shine.
So, let's dive in!
- 1. What is a Book Report?
- 2. How to Write a Book Report Outline?
- 3. How to Write a Book Report?
- 4. Book Report Formatting
- 5. Book Report vs. Book Review - How Do they Differ from Each Other?
- 6. Book Report Templates for Different Grades
- 7. How to Write a Book Report for High School?
- 8. How to Write a Book Report for College Level?
- 9. Book Report Examples
- 10. Book Report Ideas
What is a Book Report?
A book report is a written summary and analysis of a book's content, designed to provide readers with insights into the book's key elements. It's a valuable exercise for students, offering a chance to look deeper into a book's characters, and overall impact. Why are book reports important? They serve as a way to not only showcase your reading comprehension but also your critical thinking skills. They help you reflect on the book's strengths and weaknesses, and they can be a great tool to start a discussion.
How to Write a Book Report Outline?
Before you start writing a book report, it's crucial to create a well-organized outline. A book report outline serves as the roadmap for your report, ensuring that you cover all essential aspects. Here's how to create an effective book report outline:
How to Write a Book Report?
Writing an effective book report is not just about summarizing a story; it's a chance to showcase your analytical skills.
Let’s go through the process of creating a compelling book report that will impress your instructor.
How to Start a Book Report
To start a book report follow the steps below:
- Pick the Perfect Book Selecting the right book for your report is the first crucial step. If you have the freedom to choose, opt for a book that aligns with your interests. Engaging with a book you're passionate about makes the entire process more enjoyable.
- Dive into the Pages Reading the book thoroughly is non-negotiable. While summaries and online resources can be helpful, they can't replace the depth of understanding gained from reading the actual text. Take notes as you read to capture key moments and insights.
- Document Key Insights Keeping a physical notebook for jotting down important points and insights is a tried-and-true method. This tangible record allows for quick reference when you're ready to write your report.
- Collect Powerful Quotes Quotes from the book can be the secret sauce that adds weight to your report. Choose quotes that align with your report's themes and ideas. These quotes will serve as evidence to support your analysis and perspective.
- Craft Your Report Outline An book report outline serves as your roadmap for creating a structured and coherent report. Ensure it includes all the vital elements, from basic book information to your in-depth analysis. An organized outline keeps your writing on track.
Writing Your Book Report
Now that you've completed the preliminary steps, it's time to put pen to paper (or fingers to keyboard). Follow these guidelines for an exceptional book report:
- Introduction: Open with a captivating introduction that introduces the book, its author, and your main thesis. This initial "hook" draws readers in and sparks their interest.
- Plot Summary: Concisely summarize the book's plot, including key events, main characters, and the overall narrative. Offer enough information for understanding without revealing major spoilers.
- Analysis: The core of your report, where you dissect the book's themes, characters, writing style, and any symbolism. Back your insights with book quotes and examples, revealing the author's intentions and how they achieved them.
- Conclusion: Summarize your main points, restate your thesis, and share your overall evaluation of the book. End with a thought-provoking statement or recommendation to leave readers engaged and curious.
Book Report Formatting
When it comes to formatting a book report, simplicity and clarity are key. Here's a straightforward guide on the essential formatting elements:
Book Report vs. Book Review - How Do they Differ from Each Other?
The table below highlights how is a book report different from a book review :
What are the SImilarities between Book Report and Book Review?
Here are the things that are added in both a book report and a book review.
- Bibliographic details
- Background of the author
- The recommended audience for the book
- The main subject of the book or work
- Summary of the work and the only difference is that in the review, a critical analysis is also added
Due to the similarities, many students think that both of these are the same. It is wrong and could cost you your grade.
How to Write a Nonfiction Book Report?
Writing a nonfiction book report may seem daunting, but with a few simple steps, you can craft an informative report. Here's a streamlined guide:
- Read Actively: Carefully read the chosen nonfiction book, highlighting key information. For instance, if you're reporting on a biography, mark significant life events and their impact.
- Introduction: Begin with the author's name, the book's publication year, and why the author wrote the book. Create an engaging opening sentence, such as "In 'The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks,' Rebecca Skloot delves into the fascinating world of medical ethics."
- Focused Body: Structure the body into three paragraphs, each addressing crucial aspects. For instance, in a report on a science book, one paragraph could cover the book's key scientific discoveries.
- Concluding Thoughts: Share your personal opinion, if applicable. Would you recommend the book? Mention reasons, like "I highly recommend 'Sapiens' by Yuval Noah Harari for its thought-provoking insights into human history."
Writing a nonfiction book report requires adhering to facts but can still be enjoyable with a strategic approach.
How to Write a Book Report without Reading the Book?
Short on time to read the entire book? Here are quick steps to create a book report:
- Consult Summary Websites: Visit websites providing book summaries and analyses. For instance, SparkNotes or CliffsNotes offer concise overviews.
- Focus on Key Details: Select 2-3 crucial aspects of the book, like major themes or character development. Discuss these in-depth.
- Consider a Writing Service: Utilize professional writing services when time is tight. They can craft a well-structured report based on provided information.
- Offer a Unique Perspective: Differentiate your report by approaching it from a unique angle. For example, explore a theme or character relationship that hasn't been extensively covered by peers.
While challenging, writing a book report without reading the book is possible with these strategies.

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Book Report Templates for Different Grades
Students studying at different levels have different skills and ability levels. Here is how they can write book reports for their respective academic levels.
How to Write a Book Report for an Elementary School?
The following are some book report templates that you can use for your primary or elementary school.

How to Write a Book Report for Middle School
Here are the book report worksheets that you can use to write your middle school book report.

How to Write a Book Report for High School?
Writing a high school book report includes the following steps:
- Read the book thoroughly and with purpose.
- Make an outline before writing the report as a pre-writing step.
- Follow the guidelines and the given format to create the title page for your report.
- Add basic details in the introduction of your book report.
- Analyze the major and minor characters of the story and the role they play in the progress of the story.
- Analyze the major and significant plot, events, and themes. Describe the story and arguments and focus on important details.
- Conclude by adding a summary of the main elements, characters, symbols, and themes.
How to Write a Book Report for College Level?
Follow this college book report template to format and write your report effectively:
- Understand the Assignment: Familiarize yourself with the assignment and book details to ensure proper adherence.
- Read Thoroughly: Read the book attentively, noting essential details about the plot, characters, and themes.
- Introduction: Craft an informative introduction with bibliographic details.
- Summary: Summarize key aspects like setting, events, atmosphere, narrative style, and the overall plot.
- Plot: Cover the entire story, highlighting essential details, plot twists, and conflicts.
- Conclusion: Summarize the story and assess its strengths and weaknesses. Unlike a review, a book report provides a straightforward summary.
Book Report Examples
Book Report of Charlie and the Chocolate Factory
Book Report of Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Book Report Ideas
Basic ideas include presenting your narrative and analysis in simple written form, while more creative ideas include a fun element. Some notable books to choose from for your book report writing assignment are mentioned below:
- "To Kill a Mockingbird" by Harper Lee
- "1984" by George Orwell
- "The Great Gatsby" by F. Scott Fitzgerald
- "Pride and Prejudice" by Jane Austen
- "The Catcher in the Rye" by J.D. Salinger
- "The Lord of the Rings" by J.R.R. Tolkien
- "Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone" by J.K. Rowling
- "The Hunger Games" by Suzanne Collins
- "The Diary of Anne Frank" by Anne Frank
- "The Hobbit" by J.R.R. Tolkien
Need more ideas? Check out our book report ideas blog to get inspiration!
To Sum it Up! Crafting a good book report involves striking the right balance between introducing the book, summarizing its key themes, and avoiding spoilers. It's a delicate art, but with the right guidance you can grasp this skill effortlessly.
Need expert assistance with writing your book report? MyPerfectWords.com is here to help you out!
If you're asking yourself, "Can someone write my essay for me ?"Our professional writers have the answer. We can write a custom book report according to your personalized requirements and instructions. Get a high-quality book report to help you earn the best grades on your assignment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the parts of a book report.
A book report often contains different sections that describe the setting, main characters, and key themes of the story. A common type is an expository one which details what happened in detail or discusses how people feel about it.
Is a report a summary?
No, a summary is more detailed than a book report. A book report is usually based on a short summary of the book, while a standalone summary is more detailed and could have headings, subheadings, and supporting quotes.
How many paragraphs should be included in a book report?
The book report is a typical assignment in middle and high school, usually with one introduction, three body, and one conclusion paragraph.
The number of paragraphs could vary depending on the academic level, with an expert or professional book report having more than three body paragraphs.
How long is a book report?
It should not exceed two double-spaced pages, be between 600 and 800 words in length. Your book report is a written reflection on the content of a novel or work of nonfiction.
How do you end a book report?
Sum up your thesis statement and remind the readers of the important points, one final time. Do not add any new ideas or themes here and try to leave a lasting impression on the reader.

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

- Try for free
How to Write a Book Report (+ Book Report Example)
Download for free, specific tips for writing effective book reports..
Write better book reports using the tips, examples, and outlines presented here. This resource covers three types of effective book reports: plot summaries, character analyses, and theme analyses. It also features a specific book report example for students.
How to write a book report (+ book report example)
Whether you're a student looking to show your comprehension of a novel, or simply a book lover wanting to share your thoughts, writing a book report can be a rewarding experience. This guide, filled with tips, tricks, and a book report example, will help you craft a report that effectively communicates your understanding and analysis of your chosen book.
Looking for a printable resource on book reports? See our Printable Book Report Outlines and Examples
What is a book report?
Book reports can take on many different forms. Writing a book review helps you practice giving your opinion about different aspects of a book, such as an author's use of description or dialogue.
You can write book reports of any type, from fiction to non-fiction research papers, or essay writing; however, there are a few basic elements you need to include to convey why the book you read was interesting when writing a good book report.

Types of book reports
Three types of effective book reports are plot summaries, character analyses, and theme analyses. Each type focuses on different aspects of the book and requires a unique approach. These three types of book reports will help you demonstrate your understanding of the book in different ways.
Plot summary
When you are writing a plot summary for your book report you don't want to simply summarize the story. You need to explain what your opinion is of the story and why you feel the plot is so compelling, unrealistic, or sappy. It is the way you analyze the plot that will make this a good report. Make sure that you use plenty of examples from the book to support your opinions.
Try starting the report with a sentence similar to the following:
The plot of I Married a Sea Captain , by Monica Hubbard, is interesting because it gives the reader a realistic sense of what it was like to be the wife of a whaling captain and live on Nantucket during the 19th century.
Character analysis
If you choose to write a character analysis, you can explore the physical and personality traits of different characters and the way their actions affect the plot of the book.
- Explore the way a character dresses and what impression that leaves with the reader.
- What positive characteristics does the character possess?
- Does the character have a "fatal flaw" that gets him/her into trouble frequently?
- Try taking examples of dialogue and analyzing the way a character speaks. Discuss the words he/she chooses and the way his/her words affect other characters.
- Finally, tie all of your observations together by explaining the way the characters make the plot move forward.
In the novel Charlotte's Web , by E. B. White, Templeton the rat may seem like an unnecessary character but his constant quest for food moves the plot forward in many ways.
Theme analyses
Exploring the themes (or big ideas that run throughout the story) in a book can be a great way to write a book report because picking a theme that you care about can make the report easier to write. Try bringing some of your thoughts and feelings as a reader into the report as a way to show the power of a theme. Before you discuss your own thoughts, however, be sure to establish what the theme is and how it appears in the story.
- Explain exactly what theme you will be exploring in your book report.
- Use as many examples and quotations from the book as possible to prove that the theme is important to the story.
- Make sure that you talk about each example or quotation you've included. Make a direct connection between the theme and the example from the book.
- After you have established the theme and thoroughly examined the way it affects the book, include a few sentences about the impact the theme had upon you and why it made the book more or less enjoyable to read.
In the novel Roll of Thunder Hear My Cry , by Mildred Taylor, the theme of racial prejudice is a major catalyst in the story.
How to write a book report

1. Thoroughly read the book
Immerse yourself in the book, taking the time to read it in its entirety. As you read, jot down notes on important aspects such as key points, themes, and character developments.
2. Identify the main elements of the book
Scrutinize the book's primary components, including its main themes, characters, setting, and plot. These elements will form the basis of your report.
3. Formulate a thesis statement
Compose a thesis statement that encapsulates your personal perspective about the book. This should be a concise statement that will guide your analysis and give your report a clear focus.
4. Create a detailed outline
Plan the structure of your book report. This outline should include an introduction, body paragraphs each focusing on a different aspect of the book, and a conclusion.
5. Craft the introduction
The introduction should provide basic information such as the book's title and author, and present your thesis statement. It should engage the reader and make them interested in your analysis.
6. Write the body of the report
In the body of your report, discuss in detail the book's main elements that you identified in step 3. Use specific examples from the text to support your analysis and to prove your thesis statement.
7. Write a strong conclusion
Your conclusion should summarize your analysis, reaffirm your thesis, and provide a closing thought or reflection on the overall book.
8. Review and edit your report
After writing, take the time to revise your report for clarity and coherence. Check for and correct any grammar or spelling errors. Ensure that your report clearly communicates your understanding and analysis of the book.
9. Include citations
If you have used direct quotes or specific ideas from the book, make sure to include proper citations . This is crucial in academic writing and helps avoid plagiarism.
10. Proofread
Finally, proofread your work. Look for any missed errors and make sure that the report is the best it can be before submitting it.

Book report example
Below is a book report example on the novel To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee.
In To Kill a Mockingbird , Harper Lee presents a thoughtful exploration of racial prejudice, morality, and the loss of innocence. Set in the small, fictional town of Maycomb, Alabama, during the Great Depression, the book centers around the Finch family - young Scout, her older brother Jem, and their widowed father, Atticus. Scout's character provides a fresh perspective as she narrates her experiences and observations of the unjust racial prejudice in her town. Her honesty and curiosity, coupled with her father's teachings, allow her to grow from innocence to a more profound understanding of her society's inequalities. The plot revolves around Atticus Finch, a respected lawyer, defending a black man, Tom Robinson, unjustly accused of raping a white woman. As the trial progresses, it becomes clear that Robinson is innocent, and the accusation was a product of racial prejudice. Despite compelling evidence in Robinson's favor, he is convicted, symbolizing the power of bias over truth. The theme of racial prejudice is a significant part of the book. Lee uses the trial and its unjust outcome to critique the racial prejudice prevalent in society. For example, despite Atticus's solid defense, the jury's racial bias leads them to find Robinson guilty. This instance highlights how deeply ingrained prejudice can subvert justice. The book also explores the theme of the loss of innocence. Scout and Jem's experiences with prejudice and injustice lead to their loss of innocence and a better understanding of the world's complexities. For example, Scout's realization of her town's unfair treatment of Robinson demonstrates her loss of innocence and her understanding of societal biases. Overall, To Kill a Mockingbird is a compelling exploration of the harsh realities of prejudice and the loss of innocence. Harper Lee's intricate characters and vivid storytelling have made this book a classic.
The above is an excellent book report example for several reasons. First, it provides a clear, concise summary of the plot without giving away the entire story. Second, it analyzes the main characters, their roles, and their impacts on the story. Third, it discusses the major themes of the book - racial prejudice and loss of innocence - and supports these themes with evidence from the text. Finally, it presents a personal perspective on the book's impact and overall message, demonstrating a deep understanding of the book's significance.
Book report checklist
Always include the following elements in any book report:
- The type of book report you are writing
- The book's title
- The author of the book
- The time when the story takes place
- The location where the story takes place
- The names and a brief description of each of the characters you will be discussing
- Many quotations and examples from the book to support your opinions
- A thesis statement
- The point of view of the narrator
- Summary of the book
- The main points or themes discussed in the work of fiction or non-fiction
- The first paragraph (introductory paragraph), body paragraphs, and final paragraph
- The writing styles of the author
- A critical analysis of the fiction or non-fiction book
Don't forget!
No matter what type of book report you decide to write, ensure it includes basic information about the main characters, and make sure that your writing is clear and expressive so that it’s easy for audiences in middle school, high school, college-level, or any grade level to understand. Also, include examples from the book to support your opinions. Afterward, conduct thorough proofreading to complete the writing process. Book reports may seem disconnected from your other schoolwork, but they help you learn to summarize, compare and contrast, make predictions and connections, and consider different perspectives & skills you'll need throughout your life.
Looking for more writing resources? You can find them in our creative writing center .
Featured Middle School Resources
Related Resources

- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Book Report

- 5-minute read
- 5th September 2021
A book report is an essay that summarizes the main ideas presented by the author. But how do you write a good book report? Our top tips include:
- Check the assignment instructions so you know what you need to do.
- Read the book , making notes as you go.
- Plan your book report and create an essay outline .
- Write up your report , using examples and quotes to support your points.
- Revise and proofread your work to eliminate errors.
In the rest of this post, we look at how to write a book report in more detail.
1. Check the Assignment Instructions
Book reports come in many different types, so the first thing you should do if you’re asked to write one is check the assignment instructions carefully. Key aspects of the essay instructions to pay attention to include:
- The required length of the book report (and any maximum word count ).
- Whether you will be assigned a book to write about or whether you will be asked to pick one yourself (either from a list supplied by the tutor or based on a set of requirements, such as a book about a set topic).
- What aspects of the book to write about (e.g., will it just be a summary of the book’s content, or will you also need to offer some critical analysis?).
- Any requirements for structuring and formatting your report (e.g., whether to break the essay up into sections with headings and subheadings).
If anything about the instructions is unclear, check it with your tutor.
2. Read the Book and Make Notes
Next, you’ll need to read the book you’re writing about in full, not just skim through or read a synopsis! This means you’ll need to leave enough time before the deadline to read the text thoroughly (and write up your report).
When you are reading, moreover, make sure to take notes on:
- Basic bibliographic details, including the title, author name(s), year of publication, publisher, and number of pages.
- How the book is structured (e.g., whether it uses chapters).
- The overall plot or argument, plus key ideas and/or plot points from each part.
- For works of fiction, important characters and themes.
- Significant quotations or examples you might want to use in your report.
Where possible, make sure to note down page numbers as well. This will make it easier to find the relevant parts again when you’re reviewing your notes.
3. Outline Your Book Report
How you structure your report will ultimately depend on the length (e.g., a short, 500-word report is unlikely to use separate sections and headings, while a longer one will need these to help break up the text and guide the reader) and the assignment instructions, so make sure to review these carefully.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
However, common elements of a book report include:
- An introductory paragraph or section with basic book details (e.g., the title, author(s), genre, publisher, publication date, and intended audience).
- Information about the author’s background and, where relevant, credentials.
- An overview of the book’s plot (fiction and narrative non-fiction), or its main idea (other non-fiction), sometimes with a section-by-section breakdown.
- Information on characters, setting, and themes (fiction and narrative non-fiction), or key ideas and concepts set out by the author (other non-fiction).
- Where required, critical analysis or evaluation of the book.
When planning your book report, then, use your notes and the assignment instructions to outline your essay, breaking it down into clearly defined sections and noting what you will include in each one.
4. Write Up Your Book Report
When it comes to writing up your report, helpful tips include:
- Imagine the reader will be unfamiliar with the book and try to ensure your report covers all the information they’d need to know what it is about.
- Use clear, concise language to make your report easy to follow. Look out for wordiness and repetition, and don’t be tempted to pad out your report with irrelevant details just to increase the word count!
- Use examples and quotations to support your points (but don’t rely too heavily on quotations; keep in mind that the report should be in your own words).
- Follow the formatting instructions set out in your style guide or the assignment instructions (e.g., for fonts, margins, and presenting quotations).
If you use quotations in your report, moreover, make sure to include page numbers! This will help the reader find the passages you’ve quoted.
5. Revise and Proofread Your Work
When you have the first draft of your book report, if you have time, take a short break (e.g., overnight) before re-reading it. This will help you view it objectively. Then, when you do re-read it, look out for ways you could improve it, such as:
- Typos and other errors that need correcting.
- Issues with clarity or places where the writing could be more concise (reading your work aloud can make it easier to spot clunky sentences).
- Passages that would benefit from being supported with a quote or example.
It’s also a good idea to re-read the assignment instructions one last time before submitting your work, which will help you spot any issues you missed.
Finally, if you’d like some extra help checking your writing, you can have it proofread by a professional . Submit a free sample document today to find out more.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
4-minute read
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
3-minute read
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....
The 7 Best Market Research Tools in 2024
Market research is the backbone of successful marketing strategies. To gain a competitive edge, businesses...
Google Patents: Tutorial and Guide
Google Patents is a valuable resource for anyone who wants to learn more about patents, whether...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
🐇 Books for Your Little Bunny's Easter Basket → 🐇

How to Write a Killer Book Report
By melissa taylor.
Book reports (also called book reviews or critiques) check for a student’s reading comprehension skills and ability to express his or her thoughts about the book in writing.
Depending on the grade level and the teacher’s specific assignment, a book report can be from one to five or more paragraphs. But no matter the length, book reports need to include these essential elements:
Book Report Checklist
_____ title and author.
Always include the book’s title and the author’s name. If you’re writing an essay, this goes in the first sentence or first paragraph.
_____ Summary
Fiction : Summaries can be challenging. So here’s how to pare down everything that happened in the book.
Remember doing story maps? If your book is fiction, start with a story map to jot down the story elements: setting; beginning, middle, and end (or problem and resolution); and main characters. You can find story map examples here . Take the information from the story map and combine it into sentences to form a concise summary.
Fiction summary example: A blond girl entered a house in the woods where she broke furniture, ate cereal, and took a nap. When the bear homeowners returned, the little girl ran away.
Another way to summarize is to use the “ somebody-wanted-but-so-then ” method . For each word (i.e. somebod y), write the story element. For example: Somebody = the aliens, wanted = underpants, but = mom came outside to get laundry, so then = they zoomed back to space. Put this all together and you have a short and sweet summary: The aliens wanted underpants but the mom came outside to get the laundry so they zoomed back to space .
Nonfiction: If your book is nonfiction, instead of a story map, start with a graphic organizer or thinking map to organize the most important information. Use this information to write your summary.
Nonfiction summary example: Each strata of the rainforest is home to diverse animals, from the upper canopy to the lower forest floor.
Adapt the “ somebody-wanted-but-so-then ” method for nonfiction using this formula: “ something-happened-and-then ”. Here’s an example: The hurricane destroyed the small village and made it difficult for residents to get clean water and shelter.
Reminder: Don’t put in any of those oh-so-interesting details in your summary. We don’t need to know that the main character stubbed her toe or her favorite band is The Rolling Stones. Only include the most important information.
_____ Analysis
Your teacher wants to know what you thought about the book and why. Depending on your grade level, she’ll want either your most basic thoughts ( What made it good or not good and why?) or a more complex analysis ( What was the book’s theme?) .
Here are questions to consider when you write your analysis: (Remember to always justify your reasons with an explanation. In other words, always answer WHY after you state your thoughts.)
- Did you like this book?
- Could you relate to something in the character’s life?
- Did the book teach you anything?
- What made the book difficult or interesting?
- What surprised you and why?
- What do you know now that you didn’t know before?
- Would you read another book by this author?
- What motivated the main character?
- How did the main character change throughout the story?
- Talk about author’s craft. What about the writing was notable?
- What was the symbolism in the book?
- What wisdom did older characters impart to younger ones?
_____ Examples from the Text
Most teachers require citations, or specific examples, to support analysis, especially after a close reading . You’ll have two choices: paraphrase the part in the book in your own words or quote directly from the text.
When using a direct quote, elementary students are required to put quotation marks around the passage as well as indicate the page where the quote is found. Example: “ But wherever these friends of mine are — that’s my home. ” (480)
For middle and high school students, teachers require MLA or APA style citations. MLA citations are (last name page number) while APA citations are (last name, publication year). For more specifics, visit this helpful tutorial .
Book reports are important for a student’s academic success. An Anchor Common Core Standard for Reading confirms this , saying that students should be able to: “Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text.”
If you or your kiddos need a bit of book report inspiration, and a laugh or two along the way, check out this classic “Peanuts” video .
- pinterest-p
- Homework Help
- Essay Examples
- Citation Generator
Writing Guides
- Essay Title Generator
- Essay Outline Generator
- Flashcard Generator
- Plagiarism Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
Writing Guides / How to Write the Perfect Book Report (4 easy steps)
How to Write the Perfect Book Report (4 easy steps)

Introduction
Writing the perfect book report shouldn’t be as daunting as it sounds. With the right help, you can do it in no time at all. In just four easy steps we’ll show you how. First, let’s lay the groundwork and cover some basics—like, what is a book report? What’s the difference between a book report and a book review? And what kind of template or outline would you use? We’ll give you all that and more. Let’s get going!
What is a Book Report
In one sense, the best way to understand a book report is to understand what it is not. A book report is not a critical analysis. It is not an exhaustive examination. It is not an evaluation or a synthesis of scholarly research regarding the book’s merits or intentions. A book report is quite literally a report of what the book is—i.e., an objective report. Like any report, you are sticking to the facts.
So, what facts? Facts like: the title, the author, the year of publication, the genre, the plot, the characters, and the themes. The book report is basically a summary of everything about the book. It describes the book from an objective point of view, as impartially as possible.
Difference between a Book Report and a Book Review
It’s easy to confuse a book report for a book review. After all, they sound similar. But they are really quite different.
A book report is informational. A book review is critical.
A book report focuses on summarizing the book’s plot. It may describe the characters, the setting, the author’s style of writing, where the book fits within a particular genre, what the author does in the book that resonates with or departs from what he has done in the past. In other words, the book report tells the facts. One can imagine the reader being a jury, and the book report is the lawyer telling the jury everything the book has done. Subjective arguments or criticisms are not admissible. Just the facts, and nothing but the facts.
A book review is much more than a book report. The review analyzes, criticizes, reflects on and evaluates the merits of the book. It can apply any theoretical perspective it wants to draw out an argument or present the book in a different light. The review is more subjective in that sense; it is not about reporting the facts but rather about interpreting them. The review is just that—an interpretation of the book. It can discuss the strengths and/or weaknesses of the book. The report, however, is a presentation of the facts of the book. It does not weigh them or judge them; it merely presents them without commentary.
Now, with that said, it is important to remember that a book report does allow one the space to offer one’s own personal response to the book. This is usually added at the end of the report and should only be a small section in relation to the rest of the review. The personal reflection is not the main point of the book report. It is rather a kind of add-on where the report opens itself up a bit to allow some review to get in. Not much—just a little. Otherwise, the report risks turning into a review—and that is not what should happen!
Book Report Template
A book report template is simply a standard approach to composing your report. Here is an example of what that might look like, using To Kill a Mockingbird .
Title: To Kill a Mockingbird Author: Harper Lee Published: 1960 Genre: Southern Gothic, Bildungsroman (Coming-of-Age), Courtroom Drama
To Kill a Mockingbird is set in the town of Maycomb, Alabama, during the Great Depression. The story is narrated by Scout Finch, a young girl, and follows her and her brother Jem as they confront issues of morality, honor, justice/injustice, racism, fear, and prejudice in their own community. Their father, Atticus Finch, is for all intents and purposes a noble man who represents the moral backbone of the story: he is an honest lawyer who is appointed to defend Tom Robinson, a Black man falsely accused of raping a white woman, Mayella Ewell. The trial exposes some of the flaws of the people of the town. Finch does a stand-up job of defending the innocent Tom, but in spite of the clear evidence showing Tom’s innocence, he is still convicted. Some justice is done, however, in the end, as the true nature of Tom’s accuser is revealed—unfortunately it is a bloody ending. Meanwhile, Scout and Jem also wrestle with their fascination and fear of their reclusive neighbor, Boo Radley, who ultimately becomes an unexpected protector and savior of the children.
- Scout Finch: The young, spirited narrator of the story.
- Jem Finch: Scout’s older brother, who shares in her adventures.
- Atticus Finch: Their father, a lawyer with a strong sense of justice and what is right.
- Tom Robinson: The black man unjustly accused of rape.
- Boo Radley: The mysterious and reclusive neighbor.
- Mayella Ewell: The white woman who falsely accuses Tom Robinson.
- Bob Ewell: Mayella’s racist and abusive father.
The novel focuses on themes of growing up, morality, racism, justice, and the mystery of human nature. It could be called the original anti-cancel culture novel, as it deals ultimately with questions of empathy and understanding.
Writing Style
Harper Lee uses a first-person narrative style: the story is seen and told through the eyes of the young girl Scout. This perspective gives the story a layer of innocence, authenticity, novelty, and sincerity. It also opens the door for mature reflections on serious social issues thanks to insights given by Scout’s wise father Atticus. The Southern Gothic genre is evident in the setting and the exploration of social issues, the suspense, the violence, and the threatening issues underlying the plot.
Personal Reflection
I found this book to be a very good and a very powerful exploration of morality and justice, full of suspense and examples of good character. Atticus Finch stands out as a just man doing good work and teaching good lessons. The other characters are also well-developed, and the narrative style is effective in bringing together all the different genres. The novel basically asks readers to reflect on their own lives and try to live to a high standard.
In conclusion, To Kill a Mockingbird is a modern classic and a novel that is as surprising and relevant today as it was some sixty years ago when it was first published. As the saying goes, the more things change, the more they stay the same. The fact that this novel still feels powerful even though generations have passed indicates that the issues it touches on are still very much in play today. Plus, Harper Lee’s masterful prose, plotting, insight, and characters make this a must-read novel for all adolescent and adult readers.
View 120,000+ High Quality Essay Examples
Learn-by-example to improve your academic writing
Book Report Outline
A basic book report outline can also help you with your composition. Let’s look at an example using the book 1984 by George Orwell.
I. Introduction
a. Identify the author, the book, the year of publication, and the plot.
b. Identify the genre: political/social satire; dystopian fiction
c. Identify the main themes: totalitarianism and loss of free will.
d. Identify the concepts: War is Peace; newspeak; doublethink.
e. State the thesis—i.e., the main point of the review.
II. Summary
a. Setting
i. Oceania
ii. Inside and Outside the Party
b. Main Characters
i. Winston Smith—hero who questions the Party line and dares to oppose it, only to be crushed into subservience in the end
ii. O’Brien—the seemingly well-meaning high-ranking Party member who lures the rebel lovers Winston and Julia back into the Party line
iii. Julia—Winston’s love interest
iv. Big Brother—the totalitarian government that spies on all, twists the meaning of words, and rewrites history to its purposes
v. Emmanuel Goldstein—the mythical enemy of Oceania whose existence is used to justify the Party’s authoritarianism and totalitarianism
i. Winston begins to doubt the Party line
ii. He breaks with Party orthodoxy
iii. He finds a kindred spirit in Julia and they begin a romance
iv. The discovery a world outside the controls of Big Brother—a world where nature, authenticity, beauty, and harmony still exist
v. Winston and Julia are betrayed by O’Brien and tortured into submission
vii. Winston
III. Themes
a. Totalitarianism—Big Brother represents the totalitarianism of the novel
b. Loss of free will—Winston breaks free from Big Brother, but comes up empty in the end because he has nothing stronger than the Party with which to combat O’Brien
IV. Concepts
a. War is Peace—a motto of the Party and an example of how Big Brother subverts common sense by promoting falsehood as truth
b. Newspeak—the Party’s language, which denies reality by lying about what words mean
c. Doublethink—when the Party’s indoctrination is so successful that one can hold two simultaneously contradictory thoughts in one’s head without trouble
V. Personal Reflection
a. Great book—a bit difficult to read at times—but very solid in terms of concepts that reflect the modern world
b. Too close to reality in some ways
VI. Conclusion
a. Reiterate the main points
b. What is the legacy of the book?
c. Do you recommend it?

How to Write a Book Report (4 steps)
Before you start writing the book report, you need to read the book carefully and attentively. As you read, take notes on important details such as the main characters, setting, key events, and any significant themes or symbols. Pay attention to your own reactions to the book and any questions that you may have as you read. This preparatory step is essential as it provides the foundation for your book report. You will use the notes you take during this step to write the report.
Once you have finished reading the book and have taken thorough notes, it is time to start organizing your thoughts. Create an outline to structure your report like the one in the example above. Make sure you over all the necessary components. A typical book report includes information about the book: summary of the plot, main characters, themes, writing style, genre, author, and so on. The facts! The best way to organize them is to create an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. In the introduction, state your purpose. In the body, stick to the main points—summary, characters, themes, etc. In the conclusion, restate the purpose in new words and give your own personal recommendation.
Time to write the report! With your notes and outline in hand, start writing. Follow the structure of your outline, so that every section flows logically to the next. Use clear and concise language; use transitional sentences; avoid slang and casual language; and remember to be as objective as possible—no personal opinions or interpretations. Save that for the personal reflection at the end. It is also good practice to give specific examples from the book to support your report.
Edit and revise. This is one of the most important steps, and unfortunately it is one that a lot of people avoid. Just because you have written a first draft does not mean you are done. Now you have to make sure it is devoid of mistakes. Read over it twice, checking grammar, punctuation, style, and accuracy. Make sure everything you have written is on topic and valid. Correct any mistakes. If you’re unsure, get a second opinion from someone who can help.
Book Report Example
Title: Fahrenheit 451 Author: Ray Bradbury Published: 1953 Genre: Dystopian Fiction; Science-Fiction
Fahrenheit 451 is a mid-20 th century science-fiction dystopian novel written by Ray Bradbury. The setting is a future society where books are banned and “firemen” don’t put out fires—they start them. Their job is to burn unlawful hoarding of books. The reason? The old ways, wisdom, and knowledge of the Old World is deemed dangerous by the powers that be. In other words, the world is upside down; common sense is uncommon, and truth is oppressed. The hero of the book is Guy Montag. Like Winston Smith in Orwell’s 1984, Montag begins to question the orthodoxy of the regime in power. Then he steps out of line. The result is a total change in life direction. This book report will summarize the plot, identify the characters and themes of the novel, and provide a recommendation.
The novel opens with Guy Montag happily burning books as part of his job as a fireman. However, his contentment is disrupted when he meets his new neighbor, Clarisse McClellan, a young woman who opens his eyes to the beauty of nature. She opens a door for Montag that he did not know existed.
Guy becomes disillusioned with his work and begins to collect books and hide them in his home. His wife, Mildred, is obsessed with interactive television and is indifferent to Montag’s concerns. Montag contacts a former English professor named Faber for help in understanding the books he has collected.
Montag’s life unravels when his wife reports him, and he is forced to burn his own house down. In a fit of rage, he also kills his boss, Captain Beatty, with a flamethrower. Montag becomes a fugitive, on the run from the regime’s Mechanical Hound and the authorities.
In the end, Montag escapes the oppressive city and finds a group of friends who are like him: they are led by a man named Granger. They welcome him, and he learns about their plan to preserve books by memorizing their contents. The novel closes with Montag looking forward to a better future where the Old World wisdom and art is honored and restored.
Themes, Genre, and Style
One of the themes of the book is censorship; but if one looks more closely one sees that dehumanization is actually the bigger theme. The book is about what it means to be disconnected from society, to live vicariously through TV, and to be so denatured that the natural world seems abhorrent. The novel criticizes the isolating effects of technology, as shown by Mildred’s obsession with her TV screens.
Bradbury uses an easy-to-read literary style within the science-fiction dystopian genre to paint a concerning view of the here and now. The book reads as a warning about where society is heading if it continues to censor anyone who clings to the old ways in the face of the “progress” pushed by the regime.
Fahrenheit 451 is a modern classic—a great book that I whole-heartedly recommend. It is a terrific reminder of what we have and what we can lose if we fail to take care of our literary heritage. It is not just the knowledge, beauty, wisdom and art of these books that might be lost; it is also our own humanity.
There! At last, you should have a really good idea of how to write the perfect book report. If you follow these recommendations, that work you may have been putting off might now just be able to basically write itself. Trust us, we’ve been doing this for years! Stick to our steps, and you won’t have any further difficulties when it comes to your next book report. Happy writing…
Take the first step to becoming a better academic writer.
Writing tools.
- How to write a research proposal 2021 guide
- Guide to citing in MLA
- Guide to citing in APA format
- Chicago style citation guide
- Harvard referencing and citing guide
- How to complete an informative essay outline

How to Write a Synthesis Essay: Tips and Techniques

Why Using Chat-GPT for Writing Your College Essays is Not Smart

The Importance of an Outline in Writing a Rhetorical Analysis Essay

A Guide to Choosing the Perfect Compare and Contrast Essay Topic
BibGuru Blog
Be more productive in school
- Citation Styles
How to write a book report

A book report is one of the first types of essays you probably learned to write in elementary school. But no matter how many book reports you turn in over the course of your student life, they can still inspire some anxiety and some confusion about the best way to write a book report, especially as you reach the high school and college level.
The good news is that the basics you learned in the early grades will serve you in good stead, since the book report format remains mostly the same. The very same structure and tools you used to dissect Charlotte’s Web and Superfudge will work just as well for Animal Farm and The Handmaid’s Tale . What changes is the depth and breadth of your analysis as a high school and college student.
So, If you are wondering how to start a book report for a college class assignment, here are some of the key pieces of information you need to know.
What is a book report?
Let’s start off with some definitions. In the most general terms, a book report is a summary of a written text, often a fiction novel, but can also include other genres such as memoir and creative non-fiction. It includes an analysis of the different elements and authorial choices that comprise the work, such as tone, theme, perspective, diction, dialogue, etc.
While the analysis should be reasoned and objective, it should also include your opinion and assessment of the impact and overall success of the author’s choices on the final work.
Book reports usually fall into one of the following types:
Plot summary
This type of book report isn’t just a re-telling of the story, it’s a comment on your overall impression of the plot — whether you thought it was engaging or maudlin or vapid, for example — backed up by direct quotes from the text to support your opinion.
Example of a plot summary thesis statement: The plot of Herman Melville’s short story, “Bartleby the Scrivener,” offers a poignant portrait of how depression robs a person of all motivation and momentum in life.
Character analysis
A character analysis zeroes in on a particular character (their characterization and actions) and their impact on the unfolding of the plot and its eventual outcome.
Example of a character analysis thesis statement: In J.D. Salinger’s novel, The Catcher in the Rye , the character of Phoebe, Holden’s bright and precocious younger sister, is a catalyst for rekindling his hope in humanity and reconsidering the choices he’s made in his life.
Theme analysis
A theme analysis looks at the overarching concepts, or themes, that run through a book and that give the text meaning and direction. Themes tend to be broad in nature, such as love, the importance of family, the impact of childhood, etc.
Example of a theme analysis thesis statement: Banana Yoshimoto’s novella, Kitchen , explores the theme of death and how everyone sooner or later has to come to terms with the mortality of the people they love as well as their own.
How to start a book report
The very first step in writing a stellar book report that earns a top grade is actually reading the book. This may seem obvious, but many students make the assignment much harder on themselves by not putting in the time up front to do a thorough and complete reading of the book they’re going to be writing their report on. So resist the urge to skim the text or to rely on the Cliff’s notes version. A nuanced analysis requires a deep grasp of the text, and there is no substitute for focused, firsthand reading.
It’s a lot easier to stick with a book that you enjoy reading! If you have the chance to choose the book you’ll be writing a report on, take some time to select a book that appeals to you, considering the genre, time period, writing style, and plot.
It can be helpful to start thinking about your book report while you are still making your way through your initial reading of the text. Mark down passages that provide key turning points in the action, descriptive passages that establish time and place, and any other passages that stand out to you in terms of their word choice and use of language. This makes it much easier to go back later and start collecting the evidence you’ll need to support your argument and analysis.
Once you finish reading the book from cover to cover, you’ll likely find that your mind is swirling with thoughts, impressions, and burgeoning analyses. At this stage, trying to distill all of these half-formed thoughts into one cohesive report may seem like a daunting task. One way to make this task more approachable is to start by collecting and listing the objective facts about the book. The following list covers the basic elements that should be included in every book report you write, no matter what topic or specific type of book report you’re writing:
- The book’s title and author
- The historical context of the book (when it was written)
- The time(s) during which the story is set
- The location(s) where the story takes place
- A summary of the main characters and action of the story
- Quotes from the book that will function as evidence to support your analysis
With all of the basics in hand, you can start to write your book report in earnest. Just like most other essay types, a well-written book report follows a basic structure that makes it easy for your reader to follow your thoughts and make sense of your argument.
A typical book report will open with an introduction that briefly summarizes the book and culminates with a thesis statement that advances an opinion or viewpoint about it. This is followed by body paragraphs that provide detailed points to flesh out and support that opinion in greater detail, including direct quotes from the text as supporting evidence. The report finishes with a conclusion that summarizes the main points and leaves the reader with an understanding of the book, its aims, and whether or not you feel the book (and its author) was successful in doing what it set out to do. Ideally, the conclusion will also make a statement about how the book fits into the larger literary world.
A book report template you can use for any book report
If you find yourself stuck on how to start a book report, here’s a handy book report template you can use to get things off the ground. Simply use this structure and start filling it in with the specifics of the book you are writing your report on. Feel free to expand upon this book report template, adding more sections as appropriate.
Introduction
Write three to five sentences introducing the book and author as well as important contextual information about the book, such as the publication year and the overall critical reception at the time. Finish the paragraph with your thesis statement.

Body paragraphs
Include at least three body paragraphs that offer detailed information and analysis to support your thesis statement. Each paragraph should contain one idea, backed up with direct quotes from the text alongside your critical analysis.
Write three to five sentences that restate your thesis and summarize the evidence you’ve presented in support of it. Relate your findings to a larger context about the book’s place within both the literary world and the world at large.
Frequently Asked Questions about book reports
A book report follows the format of most papers you write - it will have an introduction, a body and a conclusion. Depending on the type of book report, you will fill these parts with the required information.
These are the basic parts that should be included in every book report you write, no matter what topic or specific type of book report you’re writing:
- The historical context of the book and time(s) during which the story is set
The book report is, among other things, also a summary of the plot, main characters, and ideas and arguments of the author. Your book report should help readers decide whether they want to read the book or not.
How many pages a book report should have depends on your assignment. It can be a half page, but it can also have many pages. Make sure to carefully read through your assignment and ask your professor if you are unsure .
A book report is a summary of a written text. A good book report includes an analysis of the different elements and authorial choices that comprise the work, such as tone, theme, perspective, diction, dialogue, etc. A good book report helps the reader decide whether they want to read the book or not.

Make your life easier with our productivity and writing resources.
For students and teachers.
10 Steps to Writing a Successful Book Report
- Writing Essays
- Writing Research Papers
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
A book report should contain the basic elements, but a good book report will address a specific question or point of view and back up this topic with specific examples, in the form of symbols and themes. These steps will help you identify and incorporate those important elements in a process that takes three to four days.
How To Write a Book Report
- Have an objective in mind, if possible. Your objective is the main point you want to argue or the question you plan to answer. Sometimes your teacher will offer a question for you to answer as part of your assignment, which makes this step easy. If you have to come up with your own focal point for your paper, you may have to wait and develop the objective while reading and reflecting on the book.
- Keep supplies on hand when you read. This is very important. Keep sticky-note flags, pen, and paper nearby as you read. Don't try to take "mental notes." It just doesn't work.
- Read the book. As you read, keep an eye out for clues that the author has provided in the form of symbolism. These will indicate some important point that supports the overall theme. For instance, a spot of blood on the floor, a quick glance, a nervous habit, an impulsive action--these are worth noting.
- Use your sticky flags to mark pages. When you run into any clues, mark the page by placing the sticky note at the beginning of the relevant line. Mark everything that piques your interest, even if you don't understand their relevance.
- Note possible themes or patterns that emerge. As you read and record emotional flags or signs, you will begin to see a point or a pattern. On a notepad, write down possible themes or issues. If your assignment is to answer a question, you will record how symbols address that question.
- Label your sticky flags. If you see a symbol repeated several times, you should indicate this somehow on the sticky flags, for easy reference later. For instance, if blood shows up in several scenes, write a "b" on the relevant flags for blood. This may become your major book theme, so you'll want to navigate between the relevant pages easily.
- Develop a rough outline. By the time you finish reading the book , you will have recorded several possible themes or approaches to your objective. Review your notes and try to determine which view or claim you can back up with good examples (symbols). You may need to play with a few sample outlines to pick the best approach.
- Develop paragraph ideas. Each paragraph should have a topic sentence and a sentence that transitions to the next paragraph. Try writing these first, then filling out the paragraphs with your examples (symbols). Don't forget to include the basics for every book report in your first paragraph or two.
- Review, re-arrange, repeat. At first, your paragraphs are going to look like ugly ducklings. They will be clunky, awkward, and unattractive in their early stages. Read them over, re-arrange and replace sentences that don't quite fit. Then review and repeat until the paragraphs flow.
- Re-visit your introductory paragraph. The introductory paragraph will make the critical first impression of your paper. It should be great. Be sure it is well-written, interesting, and it contains a strong thesis sentence .
The objective: Sometimes it is possible to have a clear objective in mind before you start . Sometimes, it is not. If you have to come up with your own thesis, don't stress about a clear objective in the beginning. It will come later.
Recording emotional flags: Emotional flags are merely points in the book that bring about emotion. Sometimes, the smaller the better. For example, for an assignment for The Red Badge of Courage , the teacher might ask students to address whether they believe Henry, the main character, is a hero. In this book, Henry sees lots of blood (emotional symbol) and death (emotional symbol) and this causes him to run away from the battle at first (emotional response). He is ashamed (emotion).
Book report basics: In your first paragraph or two, you should include the book setting, time period, characters, and your thesis statement (objective).
Re-visiting the introductory paragraph: The introductory paragraph should be the last paragraph you complete. It should be mistake-free and interesting. It should also contain a clear thesis. Don't write a thesis early on in the process and forget about it. Your point of view or argument may change completely as you re-arrange your paragraph sentences. Always check your thesis sentence last.
- How to Write a Great Book Report
- How to Write a Response Paper
- The Ultimate Guide to the 5-Paragraph Essay
- 6 Steps to Writing the Perfect Personal Essay
- Tips for Writing an Art History Paper
- How to Develop a Research Paper Timeline
- The Introductory Paragraph: Start Your Paper Off Right
- How to Write a Research Paper That Earns an A
- How to Write and Format an MBA Essay
- How to Write a Great Process Essay
- How to Understand a Difficult Reading Passage
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- How to Remember What You Read
- How to Write a Paper at the Last Minute
- Write an Attention-Grabbing Opening Sentence for an Essay
- What Is Expository Writing?
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Book Bracket Template. For March and Beyond!
42 Creative Book Report Ideas for Students
Inspire your students to share their love of books.

Responding to what you read is an important literacy skill. Reading about other people’s experiences and perspectives helps kids learn about the world. And although students don’t need to dive deeply into every single book they read, occasionally digging into characters, settings, and themes can help them learn to look beyond the prose. Here are 42 creative book report ideas designed to make reading more meaningful.
1. Concrete Found Poem

This clever activity is basically a shape poem made up of words, phrases, and whole sentences found in the books students read. The words come together to create an image that represents something from the story.
2. Graphic Novel
Have students rewrite the book they are reading, or a chapter of their book, as a graphic novel. Set parameters for the assignment such as including six scenes from the story, three characters, details about the setting, etc. And, of course, include detailed illustrations to accompany the story.
3. Book Snaps
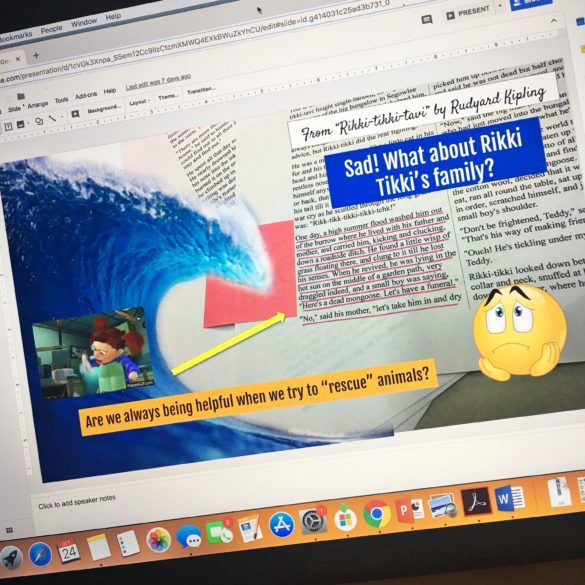
Book Snaps are a way for students to visually show how they are reacting to, processing, and/or connecting with a text. First, students snap a picture of a page in the book they are reading. Then, they add comments, images, highlights, and more.
4. Diary Entry
Have your students place themselves in the shoes of one of the characters from their book and write a first-person diary entry of a critical moment from the story. Ask them to choose a moment in the story where the character has plenty of interaction and emotion to share in a diary entry.
5. Character To-Do List

This fun activity is an off-the-beaten-path way to dive deep into character analysis. Get inside the head of the main character in a book and write a to-do list that they might write. Use actual information from the text, but also make inferences into what that character may wish to accomplish.
6. Mint Tin Book Report

There are so many super-creative, open-ended projects you can use mint tins for. This teacher blogger describes the process of creating book reports using them. There’s even a free template for cards that fit inside.
7. Fictional Yearbook Entries
Ask your students to create a yearbook based on the characters and setting in the book. What do they look like? Cut out magazine pictures to give a good visual image for their school picture. What kind of superlative might they get? Best looking? Class clown? What clubs would they be in or lead? Did they win any awards? It should be obvious from their small yearbooks whether your students dug deep into the characters in their books. They may also learn that who we are as individuals is reflected in what we choose to do with our lives.
8. Book Report Cake

This project would be perfect for a book tasting in your classroom! Each student presents their book report in the shape of food. See the sandwich and pizza options above and check out this blog for more delicious ideas.
9. Current Events Comparison
Have students locate three to five current events articles a character in their book might be interested in. After they’ve found the articles, have them explain why the character would find them interesting and how they relate to the book. Learning about how current events affect time, place, and people is critical to helping develop opinions about what we read and experience in life.
10. Sandwich Book Report

Yum! You’ll notice a lot of our creative book report ideas revolve around food. In this oldie but goodie, each layer of this book report sandwich covers a different element of the book—characters, setting, conflict, etc. A fun adaptation of this project is the book report cheeseburger.
11. Book Alphabet
Choose 15 to 20 alphabet books to help give your students examples of how they work around themes. Then ask your students to create their own Book Alphabet based on the book they read. What artifacts, vocabulary words, and names reflect the important parts of the book? After they find a word to represent each letter, have them write one sentence that explains where the word fits in.
12. Peekaboo Book Report

Using cardboard lap books (or small science report boards), students include details about their book’s main characters, plot, setting, conflict, resolution, etc. Then they draw a head and arms on card stock and attach them to the board from behind to make it look like the main character is peeking over the report.
13. T-Shirt Book Report

Another fun and creative idea: Create a wearable book report with a plain white tee. Come up with your own using Sharpie pens and acrylic paint. Get step-by-step directions .
14. Book Jacket
Have students create a new book jacket for their story. Include an attractive illustrated cover, a summary, a short biography of the author, and a few reviews from readers.
15. Watercolor Rainbow Book Report
This is great for biography research projects. Students cut out a photocopied image of their subject and glue it in the middle. Then, they draw lines from the image to the edges of the paper, like rays of sunshine, and fill in each section with information about the person. As a book report template, the center image could be a copy of the book cover, and each section expands on key information such as character names, theme(s), conflict, resolution, etc.
16. Act the Part
Have students dress up as their favorite character from the book and present an oral book report. If their favorite character is not the main character, retell the story from their point of view.
17. Pizza Box Book Report

If you’re looking for creative book report ideas that use upcycled materials, try this one using a pizza box. It works well for both nonfiction and fiction book reports. The top lid provides a picture of the book cover. Each wedge of the pizza pie tells part of the story.
18. Bookmark
Have students create a custom illustrated bookmark that includes drawings and words from either their favorite chapter or the entire book.
19. Book Reports in a Bag

Looking for book report ideas that really encourage creative thinking? With book reports in a bag, students read a book and write a summary. Then, they decorate a paper grocery bag with a scene from the book, place five items that represent something from the book inside the bag, and present the bag to the class.
20. Reading Lists for Characters
Ask your students to think about a character in their book. What kinds of books might that character like to read? Take them to the library to choose five books the character might have on their to-be-read list. Have them list the books and explain what each book might mean to the character. Post the to-be-read lists for others to see and choose from—there’s nothing like trying out a book character’s style when developing your own identity.
21. File Folder Book Report

Also called a lap book, this easy-to-make book report hits on all the major elements of a book study and gives students a chance to show what they know in a colorful way.
22. Collage
Create a collage using pictures and words that represent different parts of the book. Use old magazines or print pictures from the Internet.
23. Book Report Triorama

Who doesn’t love a multidimensional book report? This image shows a 3D model, but Elisha Ann provides a lesson to show students how to glue four triangles together to make a 4D model.
24. Timeline
Have students create a timeline of the main events from their book. Be sure to include character names and details for each event. Use 8 x 11 sheets of paper taped together or a long portion of bulletin board paper.
25. Clothes Hanger Book Report Mobile

This creative project doesn’t require a fancy or expensive supply list. Students just need an ordinary clothes hanger, strings, and paper. The body of the hanger is used to identify the book, and the cards on the strings dangling below are filled with key elements of the book, like characters, setting, and a summary.
26. Public Service Announcement
If a student has read a book about a cause that affects people, animals, or the environment, teach them about public service announcements . Once they understand what a PSA is, have them research the issue or cause that stood out in the book. Then give them a template for a storyboard so they can create their own PSA. Some students might want to take it a step further and create a video based on their storyboard. Consider sharing their storyboard or video with an organization that supports the cause or issue.
27. Dodecahedron Book Report

Creative book report ideas think outside the box. In this case, it’s a ball! SO much information can be covered on the 12 panels , and it allows students to take a deep dive in a creative way.
28. Character Cards
Make trading cards (like baseball cards) for a few characters from the book. On the front side, draw the character. On the back side, make a list of their character traits and include a quote or two.
29. Book Report Booklets

This clever book report is made from ordinary paper bags. Stack the paper bags on top of each other, fold them in half, and staple the closed-off ends of the bags together. Students can write, draw, and decorate on the paper bag pages. They can also record information on writing or drawing paper and glue the paper onto the pages. The open ends of the bags can be used as pockets to insert photos, cut-outs, postcards, or other flat items that help them tell their story.
30. Letter to the Author
Write a letter to the author of the book. Tell them three things you really liked about the story. Ask three questions about the plot, characters, or anything else you’re curious about.
31. Book Report Charm Bracelet

What a “charming” way to write a book report! Each illustrated bracelet charm captures a character, an event in the plot, setting, or other detail.
32. Fact Sheet
Have students create a list of 10 facts that they learned from reading the book. Have them write the facts in complete sentences, and be sure that each fact is something that they didn’t know before they read the book.
33. Cereal Box TV Book Report

This book report project is a low-tech version of a television made from a cereal box and two paper towel rolls. Students create the viewing screen cut-out at the top, then insert a scroll of paper with writing and illustrations inside the box. When the cardboard roll is rotated, the story unfolds.
34. Be a Character Therapist
Therapists work to uncover their clients’ fears based on their words and actions. When we read books, we must learn to use a character’s actions and dialogue to infer their fears. Many plots revolve around a character’s fear and the work it takes to overcome that fear. Ask students to identify a character’s fear and find 8 to 10 scenes that prove this fear exists. Then have them write about ways the character overcame the fear (or didn’t) in the story. What might the character have done differently?
35. Mind Maps
Mind maps can be a great way to synthesize what students have learned from reading a book. Plus, there are so many ways to approach them. Begin by writing a central idea in the middle of the page. For example, general information, characters, plot, etc. Then branch out from the center with ideas, thoughts, and connections to material from the book.
36. Foldables

From Rainbows Within Reach , this clever idea would be a great introduction to writing book reports. Adapt the flap categories for students at different levels. Adjust the number of categories (or flaps) per the needs of your students.
37. Board games
This is a great project if you want your students to develop a little more insight into what they’re reading. Have them think about the elements of their favorite board games and how they can be adapted to fit this assignment. For more, here are step-by-step directions .
38. Comic strips
If you’re looking for creative book report ideas for students who like graphic novels, try comic strips. Include an illustrated cover with the title and author. The pages of the book should retell the story using dialogue and descriptions of the setting and characters. Of course, no comic book would be complete without copious illustrations and thought bubbles.
39. Timeline
Create a timeline using a long roll of butcher paper, a poster board, or index cards taped together. For each event on the timeline, write a brief description of what happens. Add pictures, clip art, word art, and symbols to make the timeline more lively and colorful.
40. Cereal Box
Recycle a cereal box and create a book report Wheaties-style. Decorate all sides of the box with information about the book’s characters, setting, plot, summary, etc.
41. Wanted Poster

Make a “wanted” poster for one of the book’s main characters. Indicate whether they are wanted dead or alive. Include a picture of the character and a description of what the character is “wanted” for, three examples of the character showing this trait, and a detailed account of where the character was last seen.
42. Movie Version
If the book your students have read has been made into a movie, have them write a report about how the versions are alike and different. If the book has not been made into a movie, have them write a report telling how they would make it into a movie, using specific details from the book.
What creative book report ideas did we miss? Come share in our We Are Teachers HELPLINE group on Facebook.
Plus, check out the most popular kids’ books in every grade..

You Might Also Like

26 Read Across America Day Activities To Celebrate Literacy
National Read Across America week is March 2-6, 2024 Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

- Discussions
- Reading Challenge
- Kindle Notes & Highlights
- Favorite genres
- Friends’ recommendations
- Account settings
Best for Book Reports: Teens
A book’s total score is based on multiple factors, including the number of people who have voted for it and how highly those voters ranked the book.
People Who Voted On This List (6)

Post a comment » Comments
Related news.

- Create New List
- Lists I Created
- Lists I've Voted On
- Lists I've Liked
Anyone can add books to this list.
Saving My Votes
Friends votes, how to vote.
To vote on existing books from the list, beside each book there is a link vote for this book clicking it will add that book to your votes.
To vote on books not in the list or books you couldn't find in the list, you can click on the tab add books to this list and then choose from your books, or simply search.
Welcome back. Just a moment while we sign you in to your Goodreads account.
How to Write a Book Report in 4 Easy Steps
by Yen Cabag | 2 comments

Book reports are a common requirement for students, all the way from elementary school to university. Knowing how to write them will help you finish your assignment a lot faster, and also give you a better chance of wowing your instructors.
Book reports don’t have to be intimidating. Look at them as a way of expressing your thoughts and opinions about the books you read. Also, research shows that writing about what you read is an effective way of cementing the information in your mind, as opposed to simply reading it.
What Is a Book Report?
A book report is a written output that describes the contents of a book. Teachers often require a book report as a way of encouraging students to actually read the assigned materials. Reports also help the students to formulate their own opinions and reactions to what they read.
How Many Paragraphs is a Book Report?
The length of a book report does not guarantee the quality of the writing. Typically, though, you will have a clear introductory paragraph and a conclusion; the body paragraphs can range in number depending on how many themes you wish to explore. It will also depend greatly on the type of book report you choose to write.
3 Types of Book Reports
To write a great book report, you must first understand the different types of book reports. Sometimes your instructor may specify which type they want you to write, but if they don’t, you can choose the one that you feel most comfortable writing:
1. Plot Summary
The plot summary involves writing a summary of the book, but it doesn’t stop there: after you summarize the plot , you will also add your own thoughts and opinions. Some questions to ask yourself include:
- What did you think of the plot? Was it compelling? Unrealistic? Thought-provoking?
- Which factors helped you form that opinion? You may cite specific examples or scenes from the book.
- How did the story end? What did you think of story’s resolution?
- How would you have written things differently?
An example of an opening line for a plot summary is:
The plot of Roll of Thunder, Hear My Cry by Mildred Taylor was compelling because it gave a very clear picture of how racial injustice looked in practical terms during the Great Depression in Mississippi.
2. Theme Analysis
Sometimes, a book you read may contain certain themes that stand out to you. When that happens, a theme analysis is a great way to structure your book report.
Remember that the theme analysis will need to include an exploration of the theme presented in the book before you start sharing your own opinions. You can do this by showing examples of how the author expressed that theme.
Some questions to think about include:
- What theme does the story focus on? How does the author emphasize this?
- Which specific scenes cement that theme in the story?
- Is there any dialogue that helps emphasize this theme?
- How does the author portray the theme?
- What did you think about the theme and the way the author portrayed it? Do you agree with their opinions? Why or why not?
An example of an opening line for a book report with the theme analysis structure would be:
The novel Watership Down by Richard Adams powerfully portrayed the theme of leadership: Hazel’s humble but effective leadership was greatly contrasted with the tyrannical and controlling style of Captain Woundwort of the Efrafa warren.
3. Character Analysis
A character analysis is another interesting way of approaching a book report. You focus on a character (or characters) in the story, and how their decisions and behaviors affect the events in the plot.
Some questions to help you analyze characters include:
- How does the character act? What impressions did you have of them?
- What positive traits do they have? Negative traits?
- What are their main motivations and desires? What about fears or wrong beliefs?
- Does he talk in a specific way that sets him apart from other characters? If so, consider giving an example, and detailing how that impacts the character development.
- How does this character affect the main storyline?
For example, you might open a book report using character analysis with a line like this:
In the novel Gone with the Wind by Margaret Mitchell, the main character is Scarlett O’Hara, but it was the character Melanie Wilkes who really stood out: her steadfastness and belief in the good of everyone is what finally won over even the hardhearted Scarlett.
Note: Never copy summaries or book reports directly from the internet! Your teacher will likely check your work through a submissions platform that compares your writing to what’s already out there online. For more tips, check out our post on how to avoid plagiarism .
How to Write a Great Book Report
Whichever type of book report you choose to write, here are some tips to help you write in a clearer and more engaging way.

1. Choose a book you are interested in.
Some book reports may be based on an assigned book, but more often, instructors might ask you to choose your own book. They may or may not assign a genre, such as biography, classic literature, or nonfiction.
If you can choose which book to write your report on, now’s your chance to find one that you will be interested in. Some questions that can help you find a book include:
- What topics are you already interested in? Are you interested in a specific time in history, such as World War II or the Great Depression? Are you interested in a specific theme, such as racial discrimination, slavery, or poverty?
- Which genres are you already familiar with? Historical fiction? Family sagas? Nonfiction?
- Do you have authors that you are already familiar with and would love to read more from? For example, if you have read a children’s book by Mark Twain, such as Tom Sawyer, a high school level book report might be on his book Recollections of Joan of Arc .
- How much time do you have between now and when the book is due? You need to be realistic about how much time you have to read the book, and then write a thoughtful analysis.
2. Make sure you READ the book you’re writing about!
You may be tempted to search online for a book summary and try to write a whole book report based on those findings. (This is less likely to happen if you choose a book you’re actually interested in!)
While you might be able to scrape by with a summary, we highly discourage that tactic for at least two reasons: First, actually reading the book will benefit you by expanding your worldview. Second, you can only write a thorough, quality book report if you have truly read the book yourself.
In order to make sure you read the whole book, it’s important to plan ahead. The following tips might help:
- Start as soon as possible once you’re given the assignment. As soon as you pick your book,, factor in at least two weeks for writing and wrapping up your report. Divide the number of pages by the remaining days: that will be the number of pages you will have to read per day.
- Practice narration. Charlotte Mason, a British educator-reformer in the 1800s, recommended narration as the best tool for assimilating information. Read a few pages and then write a short narration of what you read. This will help you understand the story and also give you material for writing your book report.
- Take notes. If you don’t want to write too much in way of a narration, writing down bullet points or annotating the book will be faster, and it will also give you information to use in your report.
- Start writing little bits of the report along the way. You don’t have to finish the whole book before you start writing your report! You can schedule some time once a week to write portions of your book report. You might write it as though you were writing a journal, expressing your opinions about different scenes. This is especially helpful if you are writing a character or theme analysis.
3. Outline your book report.
Even before you are more than halfway through the book, you can start to make your outline. This might change after you finish the book, but if you already have a general idea of your report’s structure, it might even help you pay more attention as you read.
Try this format for your outline:
- Introduction
- Summary of Book
- Book Details: Characters
- Book Details: Plot
- Evaluation and Conclusion
4. Write the contents of your book report.
Once you’ve prepared your outline, you can start to write your report. You can use headings to organize your thoughts better. (This is where your written narrations or bullet point notes will come in handy!)
If you already wrote portions of the report as you were reading it, this is the time to organize them into a coherent piece. These tips should help you:
- Organize your ideas. You can write a good book report by identifying and analyzing major themes. Organize your ideas around these themes and write about each idea. If any new themes emerge (which often happens when you’re doing this kind of analysis), add them with a new header instead of mixing them with an existing thought.
- Focus on content. Don’t worry about the word count, but instead focus on getting your thoughts down on paper. The book report will be more valuable as you express the analysis that you underwent as you read the book.
- Be clear and concise. Being clear doesn’t require lots of words; just stick to the theme in each paragraph and avoid taking rabbit trails or using unnecessary words. Keep this in mind when you edit your work later on, as well.
- Add headings where necessary. When you find yourself writing several paragraphs under the same header, consider adding a new heading to make your ideas more clear.
Ace Your Book Report
With these steps, writing a book report can be a breeze. Remember, a book report is not just about grades, but what you learn along the journey, so don’t miss out on that experience by taking short-cuts.
And even if school is a distant memory for you, taking the time to reflect on what you’ve read can help you process information and key themes, as well as make you more prepared for your next book club meeting!
Did you find this post helpful? Let us know in the comments below!
If you enjoyed this post, then you might also like:
- Theme in Literature: Definition and Examples
- How to Write a Research Paper: The Complete Guide for Students
- How to Write a Biography: 8 Steps for a Captivating Story
- How to Annotate a Book: What to Look For and How to Take Notes
Yen Cabag is the Blog Writer of TCK Publishing. She is also a homeschooling mom, family coach, and speaker for the Charlotte Mason method, an educational philosophy that places great emphasis on classic literature and the masterpieces in art and music. She has also written several books, both fiction and nonfiction. Her passion is to see the next generation of children become lovers of reading and learning in the midst of short attention spans.
hi i need some tips on book report 3 tips
Hi Elana, do you have any questions about the tips in the post?

Learn More About
- Fiction (223)
- Nonfiction (71)
- Blogging (46)
- Book Promotion (28)
- How to Get Reviews (9)
- Audiobooks (17)
- Book Design (11)
- Ebook Publishing (13)
- Hybrid Publishing (8)
- Print Publishing (9)
- Self Publishing (70)
- Traditional Publishing (53)
- How to Find an Editor (11)
- Fitness (4)
- Mindfulness and Meditation (7)
- Miscellaneous (114)
- New Releases (17)
- Career Development (73)
- Online Courses (46)
- Productivity (45)
- Personal Finance (21)
- Podcast (179)
- Poetry Awards Contest (2)
- Publishing News (8)
- Readers Choice Awards (5)
- Reading Tips (145)
- Software (17)
- Technology (15)
- Contests (4)
- Grammar (58)
- Word Choice (63)
- Writing a Book (62)
- Writing Fiction (195)
- Writing Nonfiction (68)
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Book Report

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This resource discusses book reports and how to write them.
Book reports are informative reports that discuss a book from an objective stance. They are similar to book reviews but focus more on a summary of the work than an evaluation of it. Book reports commonly describe what happens in a work; their focus is primarily on giving an account of the major plot, characters, thesis, and/or main idea of the work. Most often, book reports are a K-12 assignment and range from 250 to 500 words.
Book reviews are most often a college assignment, but they also appear in many professional works: magazines, newspapers, and academic journals. If you are looking to write a book review instead of a book report, please see the OWL resource, Writing a Book Review .
Before You Read
Before you begin to read, consider what types of things you will need to write your book report. First, you will need to get some basic information from the book:
- Publisher location, name of publisher, year published
- Number of Pages
You can either begin your report with some sort of citation, or you can incorporate some of these items into the report itself.
Next, try to answer the following questions to get you started thinking about the book:
- Author: Who is the author? Have you read any other works by this author?
- Genre: What type of book is this: fiction, nonfiction, biography, etc.? What types of people would like to read this kind of book? Do you typically read these kinds of books? Do you like them?
- Title: What does the title do for you? Does it spark your interest? Does it fit well with the text of the book?
- Pictures/Book Jacket/Cover/Printing: What does the book jacket or book cover say? Is it accurate? Were you excited to read this book because of it? Are there pictures? What kinds are there? Are they interesting?
As You Read
While reading a work of fiction, keep track of the major characters. You can also do the same with biographies. When reading nonfiction works, however, look for the main ideas and be ready to talk about them.
- Characters: Who are the main characters? What happens to them? Did you like them? Were there good and bad characters?
- Main Ideas: What is the main idea of the book? What happens? What did you learn that you did not know before?
- Quotes: What parts did you like best? Are there parts that you could quote to make your report more enjoyable?
When You Are Ready to Write
Announce the book and author. Then, summarize what you have learned from the book. Explain what happens in the book, and discuss the elements you liked, did not like, would have changed, or if you would recommend this book to others and why. Consider the following items as well:
- Principles/characters: What elements did you like best? Which characters did you like best and why? How does the author unfold the story or the main idea of the book?
- Organize: Make sure that most of your paper summarizes the work. Then you may analyze the characters or themes of the work.
- Your Evaluation: Choose one or a few points to discuss about the book. What worked well for you? How does this work compare with others by the same author or other books in the same genre? What major themes, motifs, or terms does the book introduce, and how effective are they? Did the book appeal to you on an emotional or logical way?
- Recommend: Would you recommend this book to others? Why? What would you tell them before they read it? What would you talk about after you read it?
Revising/Final Copy
Do a quick double check of your paper:
- Double-check the spelling of the author name(s), character names, special terms, and publisher.
- Check the punctuation and grammar slowly.
- Make sure you provide enough summary so that your reader or instructor can tell you read the book.
- Consider adding some interesting quotes from the reading.
- Ghost Writing
- Proofreading
- Book Promotion
- e-Book Writing
- Blog Writing
- Website Content Writing
- Article Writing
- Book Video Trailer
- Author Website
- Case Studies
- Testimonials
- +1 628 227 3315
- Book a Call
- Get a Quote
Sign Up Now & Let’s Get Started
How to write a book report: 9 simple steps.
- January 8, 2024
Table of Contents:
Step 1: choose the book, step 2: read the book carefully, step 3: take notes, step 4: understand the assignment guidelines, step 5: outline., step 6: write a draft, step 7: analyze and evaluate, step 8: conclude thoughtfully, step 9: submit or share, conclusion:, book report.
Press The Play Button On The Audio To Listen Complete Article!
When writing a book report, you want to do more than just list the characters’ names, describe the plot, and summarize the action. You want to give a thoughtful analysis of each of these aspects and provide a context for your ideas by explaining how your experience reading the book affected your reaction to it.
But what if you’ve never written a book report before? What if you’ve only read one or two and gotten an F on them? How can you write a great book report?
That’s why we put together this guide: by following our 9 simple steps, you’ll be able to learn how to write a book report that will wow both your teacher and yourself!
To learn how to write a report, you must first pick up a book.
When choosing a book, many options are available, especially from American book writers . Look for authors who have made significant contributions to literature and have a writing style that resonates with you.
Consider the genre and subject matter that you find intriguing. Whether it’s a classic novel, a thought-provoking non-fiction work, or a contemporary bestseller, ensure it fits your assignment or personal reading goals.
An important aspect to consider is your comprehension level. It’s essential to choose a book that you can understand and engage with fully. If the language or complexity of the book is too challenging, it might hinder your enjoyment and comprehension. To avoid this, you can read reviews or sample chapters to understand the writing style and difficulty level.
Additionally, think about how the chosen book aligns with your interests. Reading something that genuinely captivates you will make the journey more enjoyable. It will also encourage you to delve deeper, analyze different aspects, and gain a more profound understanding of the book’s themes and messages.
When reading the book, it’s crucial to approach it with careful attention and focus. As you delve into the pages, make note of the essential elements, such as the plot, characters, and themes. Doing this step will help you learn how to write a book report.
Take time to understand the details of the story and how they interconnect. Pay attention to any notable quotes or passages that resonate with you.
It’s also important to consider the author’s writing style and the book’s overall tone. Some authors have a poetic or descriptive style, while others may have a more straightforward and concise approach. Understanding the writing style can enhance your appreciation for the book and help you analyze how effectively the author communicates their ideas.
Experienced book publishers play a vital role in the selection and publication of books. They have a keen eye for quality writing and can identify books that have the potential to engage readers. Taking note of the experiences and recommendations of trusted publishers can be a helpful guide in selecting well-crafted and engaging books.
As you read, take notes in the margins and use a highlighter to mark important passages. This will help you to remember what you found interesting or relevant.
It’s also helpful to write down any questions while reading. These can be used as prompts for an introductory paragraph or section of your report.
When writing a report, it’s important to be concise. You don’t want to just list the facts and figures–you want your reader to understand what they mean and how they relate to one another.
This is where your notes will come in handy. You can use them to ensure that the information you include is relevant, clear, and concise. You might start by briefly outlining what you want to include in each section of your report.
Understanding the guidelines and expectations of a book report assignment is crucial in learning how to write a book report and create insightful analysis.
For an academic task or personal project, familiarizing yourself with the specific requirements set by your instructor or the parameters of your project is essential. Pay attention to details such as the desired report length, formatting guidelines, and the depth of analysis expected.
In addition to adhering to assignment guidelines, employing a structured approach enhances the quality of your book report. Creating an outline delineating sections like introduction, summary, analysis, and conclusion helps organize your thoughts and ensures a coherent presentation of your ideas.
As you’re reading, it’s easy to get lost in the details of a book and forget its overall structure. Before writing it out, you must think about how your paper will be organized.
Your outline should include:
- A summary of what happened in each chapter (or section). This is especially helpful if there are many characters or locations in your story; having this information written down will help keep them straight as you write about them later.
- A list of important facts from each section/chapter that support your thesis statement (the main idea behind your essay). For example, if my thesis is “This book was very confusing,” then I would want examples from throughout the book where things were confusing to use as evidence when defending this point later in my essay.
In this step, you will write a draft of your book report. You may want to use some sticky notes or index cards to help organize your thoughts. But try not to get too caught up in formatting at this point. The most important thing is that you’ve got all the information on paper, making it easy for others to read and understand.
If possible, get feedback from someone else who has also read the book. Perhaps another student who took this class with you or even one of their parents! Ask them if they agree with how much detail went into each section of your report. Also, ask them if there were any areas where more explanation would benefit readers.
Once you have finished reading the book, it’s time to dive into a deeper analysis and evaluation. Start by identifying the book’s strengths and weaknesses. Consider aspects such as character development, writing style, themes, and the overall message conveyed by the author.
This evaluation will help you understand the book better and allow you to form your own opinions and interpretations.
For instance, if you read one of the best psychological horror books , analyze how effectively the author builds suspense and delivers psychological chills. Explore how the characters are developed and whether their psychological struggles are portrayed convincingly. Evaluate the writing style and how it adds to the atmosphere of fear and unease.
Be sure to offer personal insights and opinions. Discuss what resonated with you, what surprised you, or what you found particularly effective. Share any connections you drew between the book and your own experiences or beliefs.
Concluding a book report requires a thoughtful reflection on the main points discussed throughout the report. There is a simple way to learn how to wrap a book ; Consider it a way to encapsulate your thoughts and impressions after engaging with the book.
Start by summarizing the main points you raised throughout the report. Highlight key elements such as the plot, characters, themes, and writing style that stood out to you. This summary allows the reader to recollect the important aspects of the book you discussed.
Next, reflect on the book’s impact and relevance. Did the book leave a lasting impression on you? Did it challenge your perspectives or offer new insights? Consider how the book fits into the larger literary landscape.
Lastly, share your recommendation. Would you recommend this book to others? Explain your reasoning behind your recommendation. Discuss who might enjoy the book and why it could benefit different readers.
By concluding thoughtfully, you provide a satisfying end to your book report while leaving the reader with a clear understanding of your thoughts and recommendations. Remember to combine your main points and insights to create a cohesive and impactful ending.
Sharing your insights on a book report can be as rewarding as the reading process itself. After completing the analysis and crafting a comprehensive report, the final step is crucial—submitting or sharing your work. This step aligns with the purpose of your assignment, whether it’s for academic evaluation or sharing valuable perspectives.
When submitting your book report, ensure adherence to any specific guidelines your instructor or institution provides. Format the document according to the required structure, including title pages, citations (if applicable), and additional components.
On the other hand, if you’re sharing your thoughts and recommendations informally, consider the audience. Whether it’s peers, friends, or fellow book enthusiasts, engagingly conveys your key takeaways. Highlight the aspects that resonated with you, discuss the character’s themes, and provide insightful critiques.
Remember, the essence of sharing your book report lies in enthusiasm and confidence. Embrace the opportunity to showcase your analytical skills and understanding of the book, inspiring others to explore the same literary journey. Ultimately, enjoy the process and be proud of the effort you’ve dedicated to the report!
Writing a book report is a great way to get your name and show off your writing skills. It’s also a great way to improve your reading comprehension skills, as you must read the book closely and analyze it to write a good report.
If you’re ready to get started with your book report, use these 9 steps as a guide!
By following these nine steps and considering the additional tips, you’ll be able to craft a comprehensive and insightful book report that effectively communicates your understanding and analysis of the book.
limited Time offer
50% off on all services.
REDEEM YOUR COUPON: ABW50
Are You Prepared to Share Your Story with the World?
Proceed To The Next Phase Of Your Publishing Adventure And Transform Your Manuscript Into A Published Book.
Recommended Blogs
Icebreaker book by hannah grace: summary and review, what is ghostwriting and how does ghostwriting work, how to find the publisher of book, leaving so soon.
SIGN UP NOW TO ACTIVATE YOUR 50% OFF COUPON NOW!
Discuss With Our Content Strategist Toll Free +1 628 227 3315
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance

Elementary Assessments
7 Creative Book Report Ideas For First-Grade Students
Instead of giving your first graders a boring quiz or test, why not assess how much they comprehend a book by assigning a book report?
While there are lots of ideas that you can come up with for projects, we’ve done the work of putting together some of the best book report ideas for first grade students.
Not only are these book report ideas for first grade fun and creative, but they require little preparation.
Assisting adults won’t feel like they are the ones doing all the work.
What’s more, these first grade book project ideas engage students in a meaningful way since they are hands-on activities.
Some also integrate art, sparking creativity.
Even your most reluctant first graders will be excited to show what they know!
So during your literacy unit, incorporate one or more of these book report ideas for first grade students.
Book Report Ideas For First Grade
Following you will find the best creative book report and project ideas for 1st-grade students.
Complete a One-Page Book Report.
This is a simple first-grade book report idea that incorporates story elements.
Students will complete a one-page report that includes the setting, characters, problem, and solution.
Also include a space for students to draw an illustration that represents an important idea from the book.
Provide students with the one-page book report outline, or have them record the information in their readers’ notebooks.
Summarize the Book.
For this simple book report idea, students will write a summary that tells why they chose the particular book.
Additionally, they will write 2-4 sentences that share the main idea of the story.
Related Content:
11 More Book Report Ideas Students and Teachers Love
Create a Brown Paper Bag Puppet.
This is arguably one of the most popular book report ideas for first grade students. It integrates arts and crafts which in turn stretches creativity.
Since the main learning objective of this activity is character analysis, first graders will choose a favorite character from the book.
They will then transform that character into a brown paper bag puppet. (See step-by-step instructions for making a brown paper bag puppet .)
After creating the puppet, students will draft a short script (3-5 lines ideally) that includes any significant phrases the character said in the book OR any phrases that the character would say (a great way to seamlessly incorporate the literacy skill of inferencing).
Finally, one by one, students will perform their puppets in front of the class.
Each will recite his or her script while moving the puppet with a hand.
Compose An Acrostic Poem.
First graders tend to be somewhat familiar with acrostic poems, so these types of poems make for good book reports.
To do the activity, students will choose a significant word from their book and then compose an acrostic poem using the word.
Examples of words they may want to select include the author’s name, a character’s name, a setting, a symbol, a special phrase, etc.
Consider completing an acrostic poem as a whole class before having students do their own.
11+ Free Printable Book Report Templates
Write About the 5 Ws.
For easy book report ideas for first grade students, try this project.
Using a nonfiction book, students will answer the 5 Ws and H. If needed, provide academic support by giving students full questions.
- Who? (e.g. Who is the main character? )
- What? ( What is the main idea of the story? )
- When? ( When does the story take place? )
- Where? ( Where does the story take place? )
- Why? ( Why do you think the author wrote this book? )
- How? ( How does this book keep the reader entertained ? OR How is the book similar to another book that you read recently? )
Consider completing this activity as a whole class (modeling to students using an anchor chart) before sending them to complete their own 5Ws + H book report.
State Facts and Opinions.
It’s never too early to teach students about facts and opinions.
Using a fiction or nonfiction book, students will write three facts and three opinions about the book after reading it.
It is often helpful to first review with students examples of facts and opinions.
Also, to support first graders, provide them with fact and opinion sentence starters such as…
Facts Sentence Starters
- I know that…
- It is clear that…
- I can see that the book has…
- It is certain that…
Opinion Sentence Starters
- In my opinion,…
- What I feel…
Place Five Items In a Bag.
This is a very powerful reading project idea that promotes critical thinking.
Because this activity is a bit challenging for first graders, it fits well towards the end of the school year and/or with advanced learners.
After reading a book, encourage your first graders to brainstorm five artifacts that could represent the most important ideas from the book.
The idea is not for families to have to purchase anything but to collect five artifacts from around their homes or the classroom that would serve the purpose.
Students may also use drawings or other types of images as artifacts.
Once they have brainstormed the five artifacts, provide each student with a small brown paper bag.
Students will place their artifacts in their individual bags.
Then, taking turns, they will present their bags in front of the class.
They will pull out one item at a time, explaining to classmates why that particular artifact was chosen to represent their book.
Final Thoughts On Book Report Ideas For First Grade
Assessment doesn’t have to be boring.
Tap into students’ varied learning styles plus add some variety to your teaching routine by utilizing these fun book report ideas for first grade students.
These activities are sure to motivate even the most resistant students to put forth their best efforts.

24 Book Review Questions to Ask Before Writing a Review
By: Author Laura
Posted on Published: 23rd February 2021 - Last updated: 29th February 2024
Categories Book Blogging , Books
Trying to write a book review but don’t know where to start? Don’t worry, these book review questions for a book report will help you on your way!

Writing a book review or book report can feel overwhelming for one of two reasons. Either you have too much to say or nothing to say at all.
In either case, having some structure to your review and a roadmap of questions to answer can be helpful in focussing your thoughts so you can write a useful book review.
These book review questions are designed to get your brain thinking about some of the key issues and interesting points about your book in question.
You certainly don’t have to answer all of them and you don’t need to follow the order I have listed the book report questions below.
RELATED: How to Write a Good Review of a Bad Book
Book Review Questions: General Information
Before you delve into sharing your own opinions, you should share some general information about the book.
This can be to do with its plot, its genre, the setting and whether there is anything readers should be aware of before delving in.
These are good questions to ask about a book as a basic starting point and where you should always begin.
What is the book about?
What genre does this book fit into?
In what time and place is the book set?
Who is the intended audience of the book?
Is the book appropriate for that audience?
Should this book come with any content warnings?
Book Review Questions: Stylistic Points
An author could craft the most fascinating story in the world but if they can’t convey that story with an interesting or logical style then a book may well just fall flat.
Consider whether the author of the book you are reviewing has a particularly interesting style and what is it about their style that shaped the book and your opinion of it.
What style is the book written in?
What point of view is the book written from?
Does the author use any interesting techniques?
Book Review Questions: The Characters
Really compelling characters, whether you love them or hate them, can make a book really stand out. If they don’t feel real then a book can crumble pretty quickly.
Make sure to include some information about the main character (or characters) but there’s no need to mention every single person, there simply isn’t space!
Who are the key characters in the book?
Did the characters feel real?
Are the characters likeable?
Which character did you find most compelling?
Could you relate to the key characters?
Book Review Questions: Your Opinions
Of course, any good book review should contain what you, the reviewer, actually thought about it! These book review questions to ask yourself are some of the most important.
Did you discover a new favourite book or is this one you wish you had never picked up in the first place?
Try to share a balanced view so reader’s of your review can come to their own conclusions about whether this book is worth reading for them. Some points that you might not have liked might be another reader’s favourite trope!
What did you like about the book?
What did you dislike about the book?
What could have been improved?
How did the book make you feel?
How does the book compare to other similar books?
Book Review Questions: Conclusion
Make sure to wrap up your book review with some final reflections about who should read this book, what you learnt from it and what other books it is similar to.
If a reader sees that a book is similar to one they have already read and loved then that’s a great indication that they’ll love this one too.
Would you recommend this book?
What did you learn from reading this?
What sort of reader would like this book?
What other books did this one remind you of?
What star rating would you give this book?
That concludes my list of book questions to ask yourself kick your brain in gear and get you thinking about all the most interesting points of the book you’ve just read.
Do you have any more relevant book review questions to add to the list?
Let me know in the comments below!
Follow me on Instagram and Goodreads for regular book updates!
If you liked this post, check out these: How to Write a Negative Book Review How to Start a Book Blog 36 Easy Book Blog Post Ideas

Editor of What’s Hot?
Saturday 10th of December 2022
Book report question: What made this book unique from other books you have read?
Thursday 25th of February 2021
This is so so useful.
Tuesday 23rd of February 2021
Very key points here. That first part, where I talk about the synopsis, the intended audience, the genre, that is my biggest struggle.

Join Discovery, the new community for book lovers
Trust book recommendations from real people, not robots 🤓
Blog – Posted on Thursday, Nov 11
The only book review templates you'll ever need.

Whether you’re trying to become a book reviewer , writing a book report for school, or analyzing a book, it’s nice to follow a book review template to make sure that your thoughts are clearly presented.
A quality template provides guidance to keep your mind sharp and your thoughts organized so that you can write the best book review possible. On Reedsy Discovery , we read and share a lot of book reviews, which helps us develop quite a clear idea what makes up a good one. With that in mind, we’ve put together some trustworthy book review templates that you can download, along with a quick run-through of all the parts that make up an outstanding review — all in this post!
Pro-tip : But wait! How are you sure if you should become a book reviewer in the first place? If you're on the fence, or curious about your match with a book reviewing career, take our quick quiz:
Should you become a book reviewer?
Find out the answer. Takes 30 seconds!
Book review templates for every type of review
With the rapid growth of the book community on Instagram, Youtube, and even TikTok, the world of book commentary has evolved far beyond your classic review. There are now many ways you can structure a book review. Some popular formats include:
- Book reports — often done for school assignments;
- Commentary articles — think in-depth reviews in magazines and newspapers;
- Book blog reviews — short personal essays about the book; and
- Instagram reviews — one or two-paragraph reviews captioned under a nice photo.
But while the text in all these review styles can be organized in different ways, there are certain boxes that all good book reviews tick. So, instead of giving you various templates to use for different occasions, we’ve condensed it down to just two book review templates (one for fiction and one for nonfiction) that can guide your thoughts and help you nail just about any review.

⭐ Download our free fiction book review template
⭐ Download our free nonfiction book review template
All you need to do is answer the questions in the template regarding the book you’re reading and you’ve got the content of your review covered. Once that’s done, you can easily put this content into its appropriate format.
Now, if you’re curious about what constitutes a good book review template, we’ll explain it in the following section!
Elements of a book review template
Say you want to build your own book review template, or you want to customize our templates — here are the elements you’ll want to consider.
We’ve divided our breakdown of the elements into two categories: the essentials and the fun additions that’ll add some color to your book reviews.
What are the three main parts of a book review?
We covered this in detail (with the help of some stellar examples) in our post on how to write a book review , but basically, these are the three crucial elements you should know:
The summary covers the premise of the book and its main theme, so readers are able to understand what you’re referring to in the rest of your review. This means that, if a person hasn’t read the book, they can go through the summary to get a quick idea of what it’s about. (As such, there should be no spoilers!)
The analysis is where, if it’s a fiction book, you talk more about the book, its plot, theme, and characters. If it’s nonfiction, you have to consider whether the book effectively achieves what it set out to do.
The recommendation is where your personal opinion comes in the strongest, and you give a verdict as to who you think might enjoy this book.
You can choose to be brief or detailed, depending on the kind of review you’re writing, but you should always aim to cover these three points. If you’re needing some inspiration, check out these 17 book review examples as seen in magazines, blogs, and review communities like Reedsy Discovery for a little variation.
Which review community should you join?
Find out which review community is best for your style. Takes 30 seconds!
Which additional details can you include?
Once you’ve nailed down the basics, you can jazz things up a little and add some personal flavor to your book review by considering some of these elements:
- A star-rating (the default is five stars but you can create your own scales);
- A bullet-point pros and cons list;
- Your favorite quotation from the book;
- Commentary on the format you read (i.e., ebook, print, or audiobook);
- Fun facts about the book or author;
- Other titles you think are similar.
This is where you can really be creative and tailor your review to suit your purpose and audience. A formal review written for a magazine, for instance, will likely benefit from contextual information about the author and the book, along with some comment on how that might have affected the reading (or even writing) process.
Meanwhile, if you’re reviewing a book on social media, you might find bullet points more effective at capturing the fleeting attention of Internet users. You can also make videos, take creative pictures, or even add your own illustrations for more personal touches. The floor is yours at this point, so go ahead and take the spotlight!
That said, we hope that our templates can provide you with a strong foundation for even your most adventurous reviews. And if you’re interested in writing editorial reviews for up-and-coming indie titles, register as a reviewer on Reedsy Discovery !
Continue reading
More posts from across the blog.
The 10 Best H.P. Lovecraft Books for New Readers
The horror canon simply wouldn’t be the same without H.P. Lovecraft — the writer best known for creating Cthulhu, a winged Kraken-like creature, along with an entire mythos of similarly monstrous “Old Ones.” And though Lovecraft’s terrifying tales have been captivating read...
How to Find Kindle Unlimited Audiobooks (And 20 of Our Favorites)
We all love reading, but with more people working from home than ever before and screen time at all time high, giving your eyes a break is extra important — and that’s where audiobooks come in.
20 Latinx Authors With Books That Belong on Your TBR List
Latinx authors have been on the forefront of literary development for decades. From magical realist novels to heartfelt poetry, here are 20 Latinx masterpieces you can't miss out on.
Heard about Reedsy Discovery?
Trust real people, not robots, to give you book recommendations.
Or sign up with an
Or sign up with your social account
- Submit your book
- Reviewer directory

Writing a book review?
Use our free book review template to make sure you don't leave anything out.

10 creative ideas for homeschool book reports
by Kim Kautzer | May 10, 2021 | Books and Reading
Do your kids roll their eyes at the thought of having to write another boring book report? If so, they’ll jump for joy at the chance to try these creative ideas for book reports in your homeschool. There’s something for everyone, including your:
- Letter writer
- Game creator
- Imaginative child
So ditch the traditional book report! Instead of squashing your children’s love of books, invite them to extend the reading experience by wrapping it up with a delightful book-themed activity.
Which one will they choose first?
1. Design a Game
Make a game based a book you recently read. It can be a board game, card game, guessing game, or other idea. Write step-by-step directions and rules that are easy to follow. Gather any extra supplies needed to play the game, and then try it out with a friend or family member.
2. Plan a Birthday Gift
Imagine that you’ve been invited to a birthday party for one of the book’s characters, and you want to bring the perfect gift ! Consider the character’s personality, likes, and dislikes before deciding on a gift he or she would really love and use. Create a greeting card to go along with your gift. In the greeting, explain to your friend from the book why you chose this gift.
3. Walk in a Character’s Shoes
In a good novel, the main character must make some hard choices. Think about a book you read recently. Write 5-10 questions that will give this character a chance to talk about the choices they faced. Then, answer the questions as if you were the character . As you write your answers, talk about the events, thoughts, and feelings that surrounded your choices and discuss the impact of your decision(s).

4. Prepare a Lesson
Do you love history? Nature? Boating? Knitting? Basketball? Read a nonfiction book about a topic that interests you. Now, pretend that you get to be the teacher and create a lesson that will teach something you learned from the book. Your lesson can explain a concept or idea, teach some facts, or explain how to do something. Write the information in a logical order. Finally, present your lesson to a sibling, friend, or parent.
5. Create a Brochure
Does your novel take place in a different city, state, country, or planet? Think about the sites in the story that would be educational, fun, or exciting to visit. Whether the story setting is real or imaginary, design a travel brochure to entice visitors. Include maps, drawings, photos, text, bulleted lists, and attention-grabbing section titles. For content ideas, try this list of Things to Include in a Travel Brochure . It may also be helpful to look at some real travel brochures.
6. List Character Traits
What makes a book’s protagonist, or hero, likeable? What makes the antagonist, or “bad guy,” unlikeable? Write down the names of four or more characters from your book and list each one’s traits . (Remember that likeable characters can sometimes be jealous, angry, or selfish. Likewise, “bad guys” can sometimes demonstrate positive character qualities.)
7. Jump into a Book!
Pretend you’re going to join the characters in your book for a week. Make a list of all the things you’ll need to pack . Plan carefully, because you won’t be able to go home for (or buy) anything you forgot!
8. Make a Diorama
Creative ideas for book reports include projects like dioramas, which are short on writing and long on fun.
A diorama is a miniature 3-dimensional scene that recreates a setting . It can feature models of buildings, plants, animals, or people set against a background. A diorama can use photos and paper, or it can include 3-dimensional materials such as Styrofoam, plastic figurines, or natural items such as twigs, shells, or pebbles.
Make a diorama in a shoebox to represent a scene or main event from your book. Then write a vivid description of the scene OR explain what happened at this scene during one of the main events of the book.
9. Write to the Author
Write a letter to the author of a book you recently read.
- Mention this book, plus any others that you have read by this author.
- Tell the author three things about the book you just read (something you did or didn’t like; your opinions about the characters, setting, and plot; why you did or didn’t like the way the story ended; an idea for a sequel; etc.)
- Ask the author 2-3 questions. These can either be personal questions (favorite childhood memory, number of brothers or sisters, favorite book, favorite place to visit) or they can be about the process of writing this book.
10. Make a Timeline and Map
After reading a biography or historical-fiction novel , make a timeline to show the main events of the story. Use drawings, clipart, or magazine cutouts to illustrate events along the timeline. Then draw a map showing the location(s) where the story took place.

Looking for more ways to engage your kids with books? Writing About Books: Book Reports and Beyond offers loads of ideas that get kids talking and writing about the books they’re reading , from the earliest picture books to high-school level novels. It also includes printable reading logs for all ages, book-themed journal prompts, and loads of additional creative ideas for book reports. Sprinkle them into your weekly reading and writing lessons and watch your children make more meaningful connections with the books they read .
Let’s Stay Connected!
Subscribe to our newsletter.

- Gift Guides
- Reluctant or Struggling Writers
- Special Needs Writers
- Brainstorming Help
- Editing & Grading Help
- Encouragement for Moms
- Writing Games & Activities
- Writing for All Subjects
- Essays & Research Papers
- College Prep Writing
- Grammar & Spelling
- Writing Prompts
Recent Posts
- An exciting announcement!
- 10 Stumbling Blocks to Writing in Your Homeschool
- Help kids with learning challenges succeed at homeschool writing
- How to correct writing lessons without criticizing your child
- Craft and Criticism
- Fiction and Poetry
- News and Culture
- Lit Hub Radio
- Reading Lists

- Literary Criticism
- Craft and Advice
- In Conversation
- On Translation
- Short Story
- From the Novel
- Bookstores and Libraries
- Film and TV
- Art and Photography
- Freeman’s
- The Virtual Book Channel
- Behind the Mic
- Beyond the Page
- The Cosmic Library
- The Critic and Her Publics
- Emergence Magazine
- Fiction/Non/Fiction
- First Draft: A Dialogue on Writing
- Future Fables
- The History of Literature
- I’m a Writer But
- Just the Right Book
- Lit Century
- The Literary Life with Mitchell Kaplan
- New Books Network
- Tor Presents: Voyage Into Genre
- Windham-Campbell Prizes Podcast
- Write-minded
- The Best of the Decade
- Best Reviewed Books
- BookMarks Daily Giveaway
- The Daily Thrill
- CrimeReads Daily Giveaway

30 New Books Critics Think You Should Read Right Now
Nbcc board members review this year’s nbcc award finalists.
Every year, in the weeks leading up to the National Book Critics Circle Awards, the NBCC board members take the time to review and appreciate the thirty finalists , recognized in Autobiography, Biography, Criticism, Fiction, Nonfiction, and Poetry. Needless to say, these thirty books make a pretty good reading list.
This year’s National Book Critics Circle Awards will be held at the New School in New York City on March 21. In the meantime, see what the NBCC’s board members have to say about all of the finalists below:
AUTOBIOGRAPHY

Susan Kiyo Ito, I Would Meet You Anywhere: A Memoir (Mad Creek Books, an imprint of The Ohio State University Press)
Susan Ito’s heart-rending and courageous memoir holds a secret at its core. At nineteen, as a transracial adoptee raised by nisei parents, she sleuths out the identity of her Japanese-American birth mother, defying laws that keep adoption records sealed. Their fraught first meeting is the beginning of decades of emotional ebbs and flows, as Ito’s biological mother cuts off contact with her repeatedly to maintain anonymity and avoid naming the man who fathered her. What sustains Ito: Marriage, motherhood, advocating for adoptees, and writing her own story. I Would Meet You Anywhere illuminates the complexities of identity, family, and belonging.

David Masumoto, with artwork by Patricia Wakida, Secret Harvest: A Hidden Story of Separation and the Resilience of a Family Farm (Red Hen Press)
Secret Harvests limns the compounded tragedy of the Japanese internment for one family, when a cognitively disabled member, herself disabled via the racism of inadequate medical care–was separated and “lost” to the family during World War II. David Mas Masumoto uncovers the smallest thread of the story and achieves the seemingly impossible feat of reconnecting the lost family member whose story had been lost to racism but also family shame. In stark, stunning prose combined with Patricia Wakida’s evocative woodcut prints, Secret Harvests manages to take absence and turn it into presence, illuminating the hard-won resilience and joys as well as the darker corners of the author’s family history—and that of our nation as well.

Ahmed Naji, translated by Katharine Halls, Rotten Evidence: Reading and Writing in an Egyptian Prison (McSweeney’s)
Ahmed Naji’s eloquent, and at times searingly funny, memoir of his time spent in an Egyptian prison, Rotten Evidence , reveals the importance of literature as a form of self-liberation. Naji was convicted of “violating public modesty” after an excerpt from his novel Using Life was published in a journal in Egypt. Naji recounts his experiences in detail, from the mundane daily indignities of incarceration to the camaraderie that develops between prisoners. The memoir is also an erudite literary text as Naji expounds on works of Egyptian literature, the Arabic language itself, and the limits imposed by successions of authoritarian governments. Katharine Halls’s lively translation captures Naji’s distinctive voice, by turns intellectual, enraged, sardonic; Naji comes across as someone who remarkably can always crack wise about his bully jailers and the ignorance of his government’s censors.

Safiya Sinclair, How to Say Babylon: A Memoir (Simon & Schuster)
How to Say Babylon , Safiya Sinclair’s lyric memoir, is intimate, unforgettable and a shining example of why poets should write prose. The Eden of Sinclair’s Jamaican childhood is irrevocably altered under her father’s strict Rastafarian upbringing which first constrains, and then threatens, her life. Her poetic soul is matched by her resilience and perseverance and is the foundation of her courageous expressions of individuality and agency. Sinclair expertly weaves moments both harrowing and idyllic in a way that is candid, yet still generous to even those who have harmed her, which speaks both of her sensitivity and strength, and makes this memoir singular, universal and transporting.

Matthew Zapruder, Story of a Poem: A Memoir (Unnamed Press)
Matthew Zapruder’s Story of a Poem pursues two questions simultaneously: what makes a poem work, and what makes a life matter. If those questions seem to belong to different realms of meaning, it is the quiet brilliance of this book to convince you of their interdependence. The story is of the creation and revision of several poems—messy, developing drafts included—and the equally messy process of understanding a child whose autism diagnosis wrenches the author’s first draft of parenthood into a new shape—all while the air outside darkens with wildfire smoke. It is rare to see the competing calls to creativity and care explored so literally, and with such urgency and tenderness, as they are here.

Jonathan Eig, King: A Life (Farrar, Straus and Giroux)
In his sweeping biography of Martin Luther King Jr. Jonathan Eig recovers the civil rights leader from “the gray mist of hagiography.” Eig traces the arc of “Little Mike,” son of a Georgia sharecropper, to national prominence as an eloquent advocate for Black rights, as well as a crusader against the Vietnam War and poverty, all the way to Memphis and the Lorraine Motel balcony. Building on more than 200 interviews and recently released FBI files, Eig recently made national news by debunking a famous quotation about Malcolm X attributed to King, tracking fissures in the civil rights movement, and revealing King’s womanizing. With the velocity of a thriller, Eig evokes King in all his complexity, an imperfect but extraordinary man.

Gregg Hecimovich, The Life and Times of Hannah Crafts: The True Story of the Bondwoman’s Narrative (Ecco)
The Bondwoman’s Narrative , written in the mid-nineteenth century and believed to be the first novel by a Black woman, caused a sensation when it was authenticated and published by Henry Louis Gates Jr. in 2002. Until now, however, the author’s identity remained a mystery. In this compelling new biography, Hecimovich combs through public records, handwritten diaries, almanacs, wills, and slave inventories and invites readers into his search, even the dead ends, to reveal Crafts as the former Hannah Bond, a child traumatically separated from her enslaved mother, who learned to read and write before escaping to the North and completing the book. Hecimovich convincingly demonstrates that Crafts’ writing was influenced by popular literature, in particular Dickens’ Bleak House , yet stands, sui generis , as what he calls “one of the most powerful imaginative records we have of slavery.”

Yunte Huang, Daughter of the Dragon: Anna May Wong’s Rendezvous with American History (Liveright)
Daughter of the Dragon provides a riveting glimpse into the life of the beguiling actress Anna May Wong, one of Old Hollywood’s most recognizable faces. The book is the triumphant capstone to an ambitious trilogy: here, as in previous installments on Charlie Chan and the original Siamese twins (both NBCC finalists), Huang shines his spotlight upon a single, iconic figure in order to reveal a bigger picture. This dramatic account of Wong’s ascent to silver screen stardom—and subsequent descent into alcoholism and oblivion—thoughtfully illuminates the crucial role played by Asian Americans in the spectacle of modern culture.

Rachel Shteir, Betty Friedan (Yale University Press)
In Betty Friedan , Rachel Shteir investigates the life, work and complex legacy of the trailblazing feminist. While Friedan remains respected for her contributions to early second wave feminism, her resistance to intersectional feminist work leaves her out of sync with contemporary feminist activism. The first biography of Friedan in a generation, drawing on extensive research and interviews with Friedan’s contemporaries, Shteir examines the ways in which Friedan’s early years growing up Jewish in the midwest and living in the shadow of her mother’s thwarted education, shaped her ambition, career trajectory and personal life. The determination that led Friedan to become a forceful national leader also closed her off from compromise and evolution. In this timely, important biography, Shtier makes the case that her impact remained crucial to social change in 20th century America.

Jonny Steinberg, Winnie & Nelson: A Portrait of a Marriage (Knopf)
Jonny Steinberg’s deeply insightful, painstakingly researched Winnie and Nelson: A Portrait of a Marriage unmasks the Mandelas, sliding past their public mythos, and the simpler romantic narrative they told each other, to reveal the emotional labyrinth beneath. Steadily, through newly recovered material about the couple’s conversations – gathered by eavesdropping Afrikaner prison guards – Steinberg reveals how incarceration, torture, infidelity, and time itself, changed both husband and wife and their political stances. We’re left with a strong sense of the horrors they endured during apartheid, and the tenderness that remained between them at the end, even after they had inflictied pain on one another, and enduried so much cruelty and torture. With its exploration of two radically different approaches to apartheid, this beautiful biography speaks movingly to present-day struggles for racial justice.

Nicholas Dames, The Chapter: A Segmented History from Antiquity to the Twenty-First Century (Princeton University Press)
1.) One of the most thrilling things a book of criticism can do is answer a question that you didn’t know you had. 2.) The question in The Chapter is particularly delicious, because you likely accept chaptering as a matter of course, without asking why books are split up. 3.) Nicholas Dames roams wonderfully from the Gospels to, in a particular highlight, George Eliot. He explores time, transitions, and the literal manufacturing of books. 4.) Dames is also a clear, lucid writer. 5.) The critical cliché in this case is true: after reading The Chapter , you will never quite read anything else the same way.

Myriam Gurba, Creep: Accusations and Confessions (Avid Reader Press)
Creep is the very rare book of essays that could easily read as a single full-length study. Across her works to date ( Mean , Dahlia Season ) Myriam Gurba has developed a control over tone that lets her combine all of Creep’s elements—the creeping presence of Richard Ramirez, the itching fear of lice, anti-Mexican racism everywhere, cold Joan Didion beside the hot Los Angeles strawberries, Gurba teaching her high school students that that rape is about geography, not sex—into a coherent portrait in local sensibility. Creep is a tricky book that reads easy.

Naomi Klein, Doppelganger: A Trip into the Mirror World (Farrar, Straus and Giroux)
Naomi Klein has long challenged readers to look at the way we live from a slightly skewed angle in hopes of ultimately making the world more just. In this masterwork of storytelling, reporting, criticism, and analysis, she uses the idea of the twin, or the fun house version of our own world, to explore how truth works—or doesn’t—in today’s political and cultural climate. “It’s tough to live in a moment when so many truths that had been sold as settled suddenly become wobbly,” she writes. In this time of uncertainty we’re lucky to have her be one of our guiding voices.

Grace E. Lavery, Pleasure and Efficacy: Of Pen Names, Cover Versions, and Other Trans Techniques (Princeton University Press)
Pleasure and Efficacy provides a groundbreaking study of the idea of gender transition in the modern era. Grace E. Lavery, a literary scholar and prominent activist, marshals a kaleidoscopic array of examples—from pseudonyms to psychoanalysis to The Silence of the Lambs —in support of her claim that sex change is possible. By turns playful and polemical, Lavery unpacks complex theoretical texts with an efficacy that is as astonishing to behold as it is pleasurable to read: a bold affirmation of the trans condition.

Tina Post, Deadpan: The Aesthetics of Black Inexpression (NYU Press)
Deeply researched and refreshingly lucid, Tina Post’s Deadpan arrives as one of the most original and affecting aesthetic surveys in recent memory. Long consigned to the realm of play-it-straight humor, the book recontextualizes the act of withholding to taxonimize its origins and uses—specifically the tact it assumes when intersecting with blackness. Refusing to differentiate between “embodied blackness (or blackness as performed by black people) and symbolic blackness (or blackness in the cultural imaginary),” the author instead maps the many tributaries connecting the one to the other, illuminating how specimenization, perceived threat, gradients, and the tension between excess and absence evolve and get repurposed by black and white artists alike.
Teju Cole, Tremor (Random House)
In Cole’s triumphant return to fiction, the critic, novelist, and photographer finds new possibilities for autofiction. The book is dense with digressions on art and colonialism from Tunde, the Harvard-photography-professor narrator (one chapter takes the form of a lecture implicating an audience of museum patrons in the legacy of cultural appropriation). But it’s more than a vehicle for ideas. Rather, the story is about what these ideas mean for Tunde as he considers his own degrees of privilege and the exploitative nature of photography while reckoning with memories of growing up in Nigeria and of an old friend whose occasional presence adds to Tremor ’s elegiac and haunting quality.

Daniel Mason, North Woods (Random House)
A house surrounded by an apple orchard in Western Massachusetts provides the setting for Daniel Mason’s ghostly masterpiece. Told in vivid overlapping stories, spanning from the Puritan colonial era to the future, the novel lays bare the poisonous American obsession with property and its deleterious effect on ecological succession. Beauty, humor, and violence surface in the lives of the house’s colorful inhabitants over the years: spinster sisters, ambitious farmers, a painter harboring a secret desire, and a troubled young man, among others. The bold accordion-like structure of North Woods (letters, songs, and poetry are mixed with conventional narration) traces an erosion of humanity even as its players yearn for a better future.

Lorrie Moore, I Am Homeless if This Is Not My Home (Knopf)
Lorrie Moore’s I Am Homeless If This Is Not My Home is hilarious and beautifully written, which is no surprise coming from Moore, whose short stories and novels have delighted readers since 1985’s Self-Help . The surprise is in the absolute boldness of this novel—a zombie road trip is interspersed with letters from an innkeeper written just after the Civil War. Even more astounding is the beating heart of the work—amid the chaos and contortion of the plot, this is a tender and poignant examination of grief, loss, and memory. It’s a wonderfully elusive book from a master of form, packing multitudes into just under 200 pages.

Marie NDiaye, translated by Jordan Stump, Vengeance Is Mine (Knopf)
At the heart of Marie NDiaye’s hypnotic and ingenious literary thriller is a sensational legal case: Maître Susane is hired to represent a wealthy man’s wife, who has been accused of murdering the couple’s three children. Susane, who has never tried a murder case and is of a working-class background, believes she met Principaux, her client’s husband, decades earlier when she was ten years old. NDiaye, who began publishing her slippery and original fictions three decades ago at 17, entwines subtle mysteries with depictions of harrowing violence. Elliptical and lyrical, Vengeance Is Mine amounts to a disquieting exhumation of the past and its tight, invisible hold on the present.

Justin Torres, Blackouts (Farrar, Straus and Giroux)
Justin Torres radically experiments with the biographical fiction genre to stunning effect. Structured like an exquisite nesting doll of stories, the novel follows the arrival of the young exhausted narrator at the Palace, a convalescent home where he has come to help Juan finish his erasure project involving Sex Variants , a real-life 1941 collection of anonymous interviews with gay and lesbian people. Contributions by queer journalist Jan Gay were uncredited, and Juan and the narrator work together to highlight this unjustly forgotten legacy, as Juan prods the narrator for details of his own clouded past. Blackouts is a tour de force of desire and reclamation.

R oxana Asgarian, We Were Once A Family (Farrar, Straus and Giroux)
Asgarian draws on her background as a Houston court reporter for her astonishing debut. The book is a meticulous, harrowing, and deeply empathetic investigation of the story behind the deaths of a married white Portland, Ore., lesbian couple and their six Black Texas-born adopted children from a cliffside car crash in Mendocino County, Calif., that was ruled a murder-suicide. Asgarian provides a blistering indictment of the Houston family court, child protection agencies, and adoption agencies that wrest children such as the victims away from their birth families, and of the media’s focus, in looking for answers to explain the crime, on the psychology of the adoptive mothers rather than the structural conditions impacting the children’s birth families.

Kerry Howley, Bottoms Up and the Devil Laughs (Knopf)
You might not expect to be moved by a book whose title refers to a conspiracy theory about how Monster Energy Drinks are actually vehicles for Satan. But Bottoms Up and the Devil Laughs is a clear-eyed and nuanced accounting of the ways in which our modern security state reduces human beings into little more than unending terabytes of data. Kerry Howley interprets such data in a way that is distinctly human and deeply generous; she distills small, telling details from a larger story about conspiracy theorists and whistleblowers and everyone in between, while still allowing her narrative to meander and digress in surprising and revelatory ways.

Dina Nayeri, Who Gets Believed? (Catapult Books)
In Who Gets Believed? , Dina Nayeri ( The Ungrateful Refugee ) collates data from real situations where the stakes of personal credibility are high and their outcomes apparently arbitrary. She connects a refugee whose story is rejected on absurd grounds to her own skepticism, as a Christian child refugee in the United States, of the thrashing antics of the girls around her in church. Nayeri exploits her heterogenous life experience (a management consultancy interlude is among the book’s oblique surprises) to compose a work something like philosophy, one that forces old conceptual questions back into conversation with their crucial roles in daily life.

Jeff Sharlet, The Undertow (W. W. Norton)
In “The Undertow: Scenes From a Slow Civil War,” journalist and author Jeff Sharlet takes readers on a chillingly urgent tour of Donald Trump’s America. Sharlet gives us much more than soundbites as he immerses himself in Trump rallies, a men’s rights conference and a prosperity Gospel megachurch, and as he talks in depth with conspiracy theorists, white nationalists and acolytes of Ashli Babbitt, the woman shot on Jan. 6, 2021, as she tried to break into the U.S. Capitol, “transformed” after her death, Sharlet writes, into “yet another flag, like a new tarot card in the deck of fascism.”

Christina Sharpe, Ordinary Notes (Farrar, Straus and Giroux)
From the glimmering mosaic of Christina Sharpe’s Ordinary Notes emerges a luminous vision of a mind and life, “ordinary” only in the sense that it contains the matter of her daily reckonings, the memories of an extraordinary mother, the “antiblack notes” that have impinged on her and all Americans’ experience of life, and the lovely counter-notes—the lessons, the art, the courageous voicings—that create a new understanding of the world: “All of our renewed power to refuse the concentric senses of the ruinous.”

Saskia Hamilton, All Souls (Graywolf Press)
In the exquisite and profoundly affecting All Souls , completed just before her death, Saskia Hamilton wonders if writing can be “a form of practice or of preparation for death” and answers with a meditation on all the things that mattered deeply to her: family, memory, art, and literature. What she creates is something surpassingly rare, a kind of auto-elegy that is all the more moving for being devoid of sentimentality and self-pity, a vision of a brilliant mind mulling over the shards of what she knows, trying to see into and past death, not to vanquish it but to capture life, “caught in the far gone far alone glance / of mortality.”

Kim Hyesoon, translated by Don Mee Choi, Phantom Pain Wings (New Directions)
With stunning originality and audacity, Kim Hyesoon creates an alternative imaginative universe that reflects a consciousness battered by and overcoming life’s agonies: the aftereffects of war and dictatorship, the oppressions of a patriarchal society, the death of a father. In Don Mee Choi’s powerful translation of Phantom Pain Wings , the presence of the multi-faceted creature called “bird”—nemesis, inner daemon, doppelganger, muse—reverberates outward until, as with all great poetry, it assumes the fragile, mortal proportions of art itself: “I thought about bird flying freely in the ruins / bird that will fall if I don’t keep writing.”

Romeo Oriogun, The Gathering of Bastards (University of Nebraska Press)
“Perhaps exile is us running through history // I have not to give, even my body is empty of a country.” So begins Romeo Oriogun’s breathtaking The Gathering of Bastards , a multitemporal saga of migration charted against journeys of queerness and subsequent exile. Nigerian-born Oriogun’s poems are rooted between boundaries, engaging with war and dictatorship while employing a lyricism that instills a sense of magical possibility. Despite repeated losses, Oriogun pens an expansive dream of freedom: “Having known that there is no home apart from terror, / I lend my voice to our survival. I demand a wild life.” Through the wild lives of these poems, Oriogun offers readers a profound communion.

Robyn Schiff, Information Desk (Penguin Books)
With a sweep that encompasses the intelligence, eroticism, and callousness of the Western art canon, Robyn Schiff’s Information Desk presents a mundane setting for the epic: the eponymous desk at the Metropolitan Museum of Art, where the poet worked in her youth. Yet for all its cataloguing of the indignities of the role, Schiff’s epic poem refuses to stay grounded, taking readers on a whorl through art history, her personal relationships, and the behavior of parasitic wasps. What unites these topics is the symbiotic relationship the subjects have with their muses (or hosts). Like the book itself, these relationships are sometimes beautiful, oftentimes brutal, and alluring in their observation that not all monuments are erected on equal footing.

Charif Shanahan, Trace Evidence (Tin House)
“Dear one: I was trying to enter my own life, I felt outside my own life. I was / Looking, trying to find a door.” In the searching intimacies of Trace Evidence, Charif Shanahan uncovers his own hard-earned definitions of identity amidst the dislocations of a life at the margins–postcolonial, queer, biracial–in order to inhabit life on his own terms. A near-fatal accident in Morocco, the home country of his mother, becomes the focal point for gorgeously frank and delicate lyrics that both query and implore: “Is it possible my function is to hold / All the intricate, interstitial pain / And articulate clarity? / Tie a boat to my wrist, I sprout wings.”

Literary Hub
Previous article, next article.

- RSS - Posts
Created by Grove Atlantic and Electric Literature
Sign Up For Our Newsletters
How to Pitch Lit Hub
Advertisers: Contact Us
Privacy Policy
Support Lit Hub - Become A Member
Become a Lit Hub Supporting Member : Because Books Matter
For the past decade, Literary Hub has brought you the best of the book world for free—no paywall. But our future relies on you. In return for a donation, you’ll get an ad-free reading experience , exclusive editors’ picks, book giveaways, and our coveted Joan Didion Lit Hub tote bag . Most importantly, you’ll keep independent book coverage alive and thriving on the internet.

Become a member for as low as $5/month

A book about books, for book sort of people
I f you’re a book sort of a person, you are really going to enjoy this book, which is a book about books, by a book sort of a person for book sort of people: Nicholas Royle is fast becoming the bibliophile’s bibliophile, the general readers’ Nicholas Basbanes. (Basbanes is the author of the as-yet-unsurpassed A Gentle Madness: Bibliophiles, Bibliomanes, and the Eternal Passion for Books, published in 1995, and a must-read for all book collectors, would-be-collectors, or indeed anyone weary with the collectors in their lives. If you think you’re bad, read Basbanes.)
In 2021 Royle published White Spines: Confessions of a Book Collector, about his quest to collect all of the handsome white-spined Picadors published between 1972 and 2000. Shadow Lines might have well subtitled More Confessions of a Book Collector. It begins: “I said to my publisher that I wanted to do a follow-up to White Spines. He said, Sure, go ahead, but make sure it doesn’t feel too much like a follow-up.” It feels exactly like a follow-up, but not in a bad way.
Royle admits that he was considering whether to just stick with his whole white spine shtick and write a book about his hunt for the white-spined King Penguins published between 1981 and 1987, and the white-spined Sceptre paperbacks published between 1986 and 1994 – because, of course, he collects them too. Instead, Shadow Lines is about books in general. It’s about reading while walking, and the Penguin Modern Stories series of anthologies, and the Thomas the Tank engine illustrator C Reginald Dalby, and the bookish work of the artist Mike Nelson, and about books in films, and unread books, and books in dreams, and overheard conversations in bookshops. It is essentially a collection of good old-fashioned, rambling, bookish reminiscences.
But it’s mostly about the “inclusions” that Royle finds in various second-hand books. The title derives from Royle’s eccentric habit of seeking out those books in second-hand bookshops distinguished by what he calls “shadow lines”, the tell-tale mark at the top edge of a book that indicates someone has left something inside – a bus ticket, a postcard, a drawing, anything. While the rest of us might toss away such dreck, Royle cherishes his finds, and indeed does his utmost to reunite them with their original owners, or at least to discover their identity. As you can imagine, this results in some charming and rather peculiar encounters.
If Royle finds a phone number in a book, for example, he promptly calls it, including the number for a “Guardroom”, found in his copy of Standard Arabic, purchased at the Oxfam Bookshop in Herne Hill, alongside a number of inclusions, comprising a map of Cairo, some pages of cryptic notes and instructions, and a list of names which included “the nom de guerre of one of Osama Bin Laden’s twelve bodyguards”. He rings the number, of course: the conversation does not last long.
Even if his sleuthing doesn’t lead him very far, Royle at least googles the names of any previous owners inscribed on a book’s flyleaf or inside cover. Thus, when he buys a second-hand copy of Italo Calvino’s Cosmicomics, and discovers that it once belonged to a Bernard Filson, he does his due diligence: “A retired stockbroker, Bernard Filson sailed his yacht around the world, before returning to this family’s holiday home in the Cumbrian village of Boot and subsequently making Boot his permanent home. Singing in a local choir, taking art classes and becoming a church warden […] In 2007, he was involved in a serious four-vehicle accident on the A595 and died at the scene, leaving a son, two daughters, a brother and a granddaughter.” Bernard is now immortalised on the pages of Shadow Lines.
“My search for inclusions,” explains Royle, “for names of former owners, for phone numbers and email addresses, is not only a fishing expedition but also a reaching-out.” That reaching-out is also sometimes a case of bumping-into. Shadow Lines contains many tales of Royle’s encounters while out reading and walking. Strolling around south Manchester one day, reading Alberto Moravia’s The Voyeur, he wanders past several members of the South Manchester Muslim Walking Group and gets into conversation about books with a woman called Amina: they now follow each other on Instagram.
Among the many detours in the book, Royle recalls having been taught English at Manchester Grammar School by Peter Anthony Scott Farquhar, the man who was murdered by his lover, Ben Field, the tragic story recently dramatised on television as The Sixth Commandment . Shadow Lines very much celebrates the world of books – but it also serves as a poignant reminder of the shadow that eventually falls upon us all.
Shadow Lines is published by Salt at £10.99. To order your copy for £9.99, call 0844 871 1514 or visit Telegraph Books
Sign up to the Front Page newsletter for free: Your essential guide to the day's agenda from The Telegraph - direct to your inbox seven days a week.

More From Forbes
The 25 top historical fiction books of all time, top historical fiction novels, the best historical fiction romance novels, the best young adult historical fiction novels.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Clark Gable reading the novel "Gone With the Wind" by Margaret Mitchell. One of his greatest roles ... [+] was that of Rhett Butler in the MGM film adaption of the book.
For history enthusiasts, historical fiction serves as a cornerstone that vividly resurrects the ways of life from bygone eras. The genre, often characterized by its immersive storytelling and attention to detail, has produced some best-selling literary works that span decades. While this genre has historically been dismissed as trite, there is now a surge in its popularity, and whether their storylines explore the World War II era or other important historical epochs, readers have remained intrigued.
To celebrate this genre, here is a curated list of some of the most remarkable historical fiction novels ever.
25. Gone with the Wind By Margaret Mitchell
Margaret Mitchell created a cultural masterpiece when she penned Gone with the Wind . The historical fictional novel was published in 1936 and set against the backdrop of Clayton County and Atlanta, Georgia amid the tumultuous American Civil War. The book is not only a popular part of American literature, it was one of the leading novels to comfortably acknowledge the heaviness of complex issues like social class, race, war, gender and slavery in a way that stuck in the minds of consumers. To achieve this, Mitchell introduced readers to Scarlett O'Hara, whose character evolves as she navigates multiple changes and difficulties within the story. Scarlett is considered one of literature's most memorable and complex heroines, and Gone with the Wind is a monumental piece of literary art in American history . The work earned Mitchell a Pulitzer Prize for Fiction in 1937. Lovers of history, culture and classics can find this book on Simon & Schuster ’s website.
24. Homegoing By Yaa Gyasi
Yaa Gyasi’s Homegoing is a thematic masterpiece published in 2016 that explores difficult topics like slavery, freedom and strength. Gyasi blurs the boundaries of time and space by adapting a multigenerational narrative into the dark and burdensome legacy of slavery. The many characters in Gyasi’s Homegoing are multi-dimensional, making the story even more intriguing. Although Homegoing is Gyasi's debut book, it immediately cemented her role among her peers as a writer with the chops to approach intersecting characters, plots and places with seamless expertise. This book is a good read for anyone who is curious about slavery and the historical implications of it. The novel earned Gyasi an Audie Award for Literary Fiction & Classics and a PEN/Hemingway Award at the PEN Awards. The book is available for purchase at Penguin Random House .
23. Beloved By Toni Morrison
Toni Morrison is revered as one of the 21st century's most respected writers and intellectuals, and Beloved is one of her most decorated pieces of work. In Beloved , Morrison tells the gut-wrenching story of Sethe, a freed woman who escapes her haunting days as a slave in Kentucky to live in Cincinnati , Ohio with her children. Although Sethe and her children are free, she is still haunted by the memories of her time as a slave. Her worst fears come true when her former slave master seeks her out, finds her and attempts to place her back into slavery. In a fit of panic, Sethe kills one of her children in the hopes of saving them from going back into the agony of slavery. Beloved touches on painful cultural touchstones that have helped to shape conversations on race, trauma and grit. Beloved was published in 1987, and won a Pulitzer Prize in 1988. It can be purchased at Penguin Random House .
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024.
"Beloved" author Toni Morrison receives the Presidential Medal of Freedom from President Barack ... [+] Obama in the East Room of the White House on May 29, 2012.
22. Things Fall Apart By Chinua Achebe
Nigeria’s Chinua Achebe has a distinct style of writing that is poetic yet profoundly impactful. In his 1958 novel Things Fall Apart , Achebe delves into the intricate nature of Nigerian society in the pre-colonial era, employing Okonkwo, the protagonist, as a guide. Achebe is not only a master at his craft, he is able to explain emblems of Nigerian traditions in ways that are both fascinating and compelling. The book explores the dichotomy of Okonkwo’s two worlds and his journey from being one of his village’s most respected men, to being exiled for accidentally murdering someone. Achebe takes readers on a journey from Nigeria in the pre-colonial era, through how the way of life in Nigeria’s Igboland undertook a seismic shift after colonialism took off in the late 19th century. Achebe manages the duality of both eras well without losing the reader. This book is a go-to for curious minds of other cultures and traditions. Things Fall Apart is available at Penguin Random House .
21. A Midwife’s Tale By Laurel Thatcher Ulrich
Pulitzer Prize winner A Midwife's Tale strays away from the typical depiction of historical books. Instead, the book, released in 1990, immerses readers in a compelling true story drawn directly from the diary of an extraordinary woman, Martha Ballard. Martha, who is an eighteenth-century Maine midwife, gives readers cryptic details of her daily life and the scandals in her neighborhood, most of which would be befitting headlines for juicy gossip tabloids in modern times. The diary, which spans 27 years, was reimagined by Laurel Thatcher Ulrich, who carefully re-packaged the story without sacrificing its core essence. The book also won a Bancroft Prize, and the Joan Kelly Memorial Prize in Women's History, among others. This book is a good fit for people who are intrigued by true stories that have been re-imagined. It can be purchased at Penguin Random House .
20. Les Misérables By Victor Hugo
Victor Hugo's magnum opus, Les Misérables, is considered a literary titan, and was so monumental that it was later adapted into a stage musical and a film. Hugo’s core objective with Les Misérables was to show the timeless and multifaceted elements of the human experience. Published in 1862, the epic novel delves into the complex web of themes, including social class, wealth, poeverty morality and injustice. Set against the tumultuous backdrop of post-revolutionary France in the early 19th century, Les Misérables follows troubled protagonist Jean Valjean, a former convict who seeks redemption after serving an extended prison sentence for a desperate minor theft. Through Jean, Hugo validates the marginalized members of society forced into lives of petty crime, not because they are morally incompetent, but because they are in dire circumstances. The powerful French classic can be purchased on Simon & Schuster’ s website.
There are several widely acclaimed historical fiction romance novels that have garnered a lot of praise for their aptness, well-researched historical settings and rich romantic storylines. Many of these books have gone on to be timeless classics in literature . Here are some of the best historical fiction romance novels of all time.
19. Pride and Prejudice By Jane Austen
Set in rural England at the turn of the 19th century, Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice is an iconic English classic, celebrated for its wit, social commentary and exploration of love and social class in the Regency era. Austen introduces readers to a spirited set of characters in the Bennet family, which consists of five fascinating sisters with a range of interests and personalities. Austen hones in on Elizabeth, the novel's heroine, a quick-witted and independent young woman who meets Fitzwilliam Darcy, a wealthy yet initially aloof gentleman who eventually strikes a romantic relationship with Elizabeth. Like its name denotes, the book explores societal expectations and the intersection of personal prejudices, which can show up in romantic relationships regardless of the era. Pride and Prejudice is currently available for purchase at Dover Publications .
Actor Ashley Green reads from Jane Austen's "Pride and Prejudice" at the Jane Austen Centre in Bath, ... [+] England during the 2013 celebration of the 200th anniversary of the book's publication.
18. Outlander By Diana Gabaldon
Diana Gabaldon's 1991 series, Outlander, offers the mysterious story of Claire Beauchamp, a 20th-century British combat nurse who becomes an accidental time traveler when she finds herself transported back to 18th-century Scotland. Claire’s journey soon becomes an odyssey of romance, mystery and adventure when she crosses paths with a charming Scottsman, Jamie Fraser. Gabaldon’s effective storytelling prowess, characterized by meticulous historical attention to detail and engaging narrative, worked like a charm on readers, and the book has now sold over 50 million copies worldwide. The Outlander series is available to purchase on Penguin Random House .
17. Persuasion By Jane Austen
Jane Austen’s Persuasion marks the pinnacle of her legacy as a writer who is acutely aware of prose and has the skills to direct a story. The book was released posthumously in 1817 alongside Northanger Abbey in a four-volume set. The storyline hinges on Anne Elliot's love affair with Captain Frederick Wentworth, with whom she rekindles a relationship eight years after her family convinced her not to marry him. After Captain Wentworth achieves significant social status, he is deemed an acceptable suitor for Anne. As only Austen knows how to do best, she underscores the themes of social class, love, jealousy and how all of these realities can exist within society’s rigid expectations. The vintage classic is available on the Penguin Random House website.
16. The Grand Sophy By Georgette Heyer
Georgette Heyer created The Grand Sophy by tapping into the English Regency era, where society had very stiff expectations. Like most of Heyer’s work, The Grand Sophy has a riveting component to it: the ability to whisk readers away to a different world, where manners were as rigid as corsets and societal norms dictated every move. Heyer’s skillful storytelling follows the story of Sophy Stanton-Lacy, a strong-willed and unconventional young woman, and Charles Rivenhall, a wealthy heir. The two have different worldviews, but fall in love eventually. The Grand Sophy, which was published in 1950 , is a classic tale of love's rebellion against societal expectations. It is available on its official publisher website, Sourcebooks .
15. The Verdun Affair By Nick Dybek
Some of the most powerful war stories also have interweaving themes of romance and human sorrow. In The Verdun Affair , Dybek ushers his readers into the aftermath of Europe’s World War I by following the story of Chicago natives Tom and Sarah Hagen, two Americans struggling to wrap their minds around the devastation of the war, but gradually developing an illicit affair. Dybek’s directorial approach to the book uncovers overarching topics of morality, love, loss and the haunting impact of war on humanity. For fans of historical fiction, this 2018-published book is undoubtedly a page-turner. Simon & Schuster currently carries the book.
14. Seduce Me at Sunrise By Lisa Kleypas
Set in the evocative landscape of 19th-century England, Lisa Kleypa’s Seduce Me at Sunrise is a fictional commentary on forbidden love, passion, longing and emotional depth. At the heart of the story are Win Hathaway and Kev Merripen, whose lives become entwined in an unexpected web that defies the conventional ideas of their environment. Win, a wealthy heiress, and Kev, a Romani man with a checkered past, have diametrically opposed lives which influence the love they are trying to navigate against the conventions of their time. Seduce Me at Sunrise was published in the fall of 2008 and is available on Macmillan Publishers .
13. The Nightingale By Kristin Hannah
Kristin Hannah’s The Nightingale is a historical exploration of northwestern France during World War II. The popular book dives into the story of Vianne Mauriac and Isabelle Rossignol, two daring sisters who take divergent paths in response to German’s invasion of France. Determined to fight for a just cause, the two sisters actively joined the French Resistance, embodying the spirit of defiance against the Nazi regime. This powerful move helped them to protect Jewish children and lead a revolution. The book was published in 2017 and is currently available to buy on the Macmillan Publishers website.
12. Beneath a Scarlet Sky By Mark T. Sullivan
Based on the remarkable true story of an unsung hero, Beneath a Scarlet Sky is a powerful epic that showcases the extraordinary courage and resilience of Pino Lella, a spirited Italian young man trying to navigate life as a teenager. His life takes a sharp turn when his family home in Milan is blown up by Nazis. This sets him on a trajectory to take the war more seriously and do something meaningful about it. As the plot unfolds, he falls in love with Anna, a woman six years older than him. This complicates things a bit. Beneath a Scarlet Sky was inspired by a true story and highlights themes of courage, love and grit. It was published in 2017 by Lake Union Publishing , where it is currently being sold.
11. City of Thieves By David Benioff
In City of Thieves , David Benioff offers readers a gripping coming-of-age story set against the backdrop of the Nazis’ siege of Leningrad. Benioff zeros in on Lev Beniov, the book’s main character and an ordinary guy whose life swiftly becomes extraordinary overnight when he gets arrested for stealing. While behind bars, he meets Kolya, who adds an unexpected twist to their fates, and instead of facing the firing squad, they're hit with a seemingly mundane, yet significant challenge — getting a dozen eggs for a high-ranking Soviet colonel’s daughter’s wedding cake. Due to siege-driven food shortages, their quest for eggs turns into a dangerous escapade through chaotic streets and enemy territory. The book was published in 2008 by Penguin Radom House where it is currently available for sale.
Authors of young adult historical fiction novels are tasked with the responsibility offering a diverse range themes that are both engaging and compelling. These books are perfect for young readers who are intrigued by history and fiction.
10. The Fountains of Silence By Ruta Sepetys
Set in post-World War II Spain, Ruta Sepetys delves into the hidden history of General Francisco Franco’s regime with her 2019 book The Fountains of Silence . Sepetys tells the story through the lens of Daniel, an 18-year-old American photojournalist, and Ana, a Spanish hotel maid. Against the backdrop of a country grappling with its dark political past, the novel explores forbidden love, political intrigue and the enduring impact of war on a broader society. Sepetys’ meticulous research and powerful storytelling bring to life a chapter of history that often remains hidden. Penguin Random House currently carries the book.
9. Code Talker: A Novel About the Navajo Marines of World War Two By Joseph Bruchac
In his 2005 novel, Joseph Bruchac sheds light on a lesser-known aspect of World War II — the invaluable contribution of the Navajo Code Talkers. The historical novel provides an angular insight on the war, focusing on the Navajo Nation’s important role in developing an unbreakable code based on their native language. Through 16-year-old Ned Begay's perspective, readers get a front-row seat into the resilience and determination of the Navajo people during this precarious period in history. The book lauds Ned’s bravery well, but also highlights the challenges that Native Americans who were serving in the U.S. military encountered. Bruchac approaches these issues with sensitivity, addressing themes of identity, patriotism and the clash between tradition and the demands of war. Code Talker is currently available on Penguin Random House .
8. The Girl with the Red Balloon By Katherine Locke
Katherine Locke’s novel, The Girl with the Red Balloon , skillfully transports readers to post-World War II East Berlin, where historical fiction collides with a hint of realism. Published in 2017, the book tells the story of 16-year-old Ellie Baum, who time-travels with a magical red balloon to 1988 East Berlin, where she embarks on an unexpected journey, unearthing a mysterious tale that stretches across the vast boundaries of 20th-century Europe. Locke’s acute blend of historical accuracy with a creative element provides readers with a whimsical lens through which to explore the aftermath of war. The story is rich with historical nuances, capturing the atmosphere of a city still struggling to come to terms with the scars of conflict, divided by political ideologies and the tragic impact of wartime experiences. This book is currently being sold on Albert Whitman & Co .
7. The Boy in the Striped Pajamas By John Boyne
Through the innocent eyes of eight-year-old Bruno, who is The Boy in the Striped Pajamas, Boyne invites readers into a world where the dark realities of the Holocaust are filtered through the lens of childhood naiveté. Unaware of the grim circumstances around him, Bruno forms a genuine bond with Shmuel, a Jewish boy separated from him by the cruel confines of the camp. This unlikely friendship becomes a focal point, revealing the stark contrast between the innocence of childhood and the profound tragedy of historical events. The Boy in the Striped Pajamas was published in 2006. David Fickling Books currently carries the teen fiction book.
6. All the Light We Cannot See By Anthony Doerr
Anthony Doerr’s Pulitzer Prize-winning All the Light We Cannot See is a masterpiece of historical fiction, immersing readers in the exploration of the resilience of the human mind and revisiting World War II’s impact. Doerr invites readers to observe the disparate yet interconnected stories of two protagonists: a blind French girl, Marie-Laure, and a young German boy, Werner. The 2014-published novel underscores the complexities of war, unraveling the ways in which conflict shapes the lives of individuals on opposing sides. Marie-Laure’s journey, marked by her blindness and the refuge of a miniature model of her city, and Werner’s trajectory, powered by his impressive talent for radio technology, converge in unexpected ways. All the Light We Cannot See is available on Simon & Schuster ’s website.
5. Iqbal By Francesco D'Adamo
Francesco D'Adamo’s Iqbal is a gripping true story inspired by the real-life story of Iqbal Masih, as told through the voice of Fatima, a young Pakistani girl whose life is forever altered by Iqbal’s extraordinary courage. The book tells a story of children who are forced to work in a carpet factory, under grueling conditions, to repay their parents’ debt. It is Iqbal who not only exposes the grim reality of their situation, but also becomes a source of hope and strength for the other children, igniting a spark of collective defiance against the oppressive chains that keep them. Iqbal, a 13-year-old boy, successfully becomes a leader of hope, helping other children navigate their grim reality and push for their freedom. Iqbal was first published in 2001 and is available at Simon & Schuster .
4. Rose Under Fire By Elizabeth Wein
Elizabeth Wein’s book Rose Under Fire follows the story of Rose, an American pilot whose fate takes an swift turn when she becomes a prisoner of war in Nazi Germany's arduous Ravensbrück concentration camp. Wein’s words guide young readers through the harsh realities of life within the confines of the concentration camp, showing the abject conditions that Rose and her fellow prisoners face. Like many outstanding authors, Wein shows that even in the depth of despair, beautiful human connections can be formed in the darkest corners of pain and adversity. The book was published in 2001. Rose Under Fire is now available at Hachette Book Group .
3. Orphan Monster Spy By Matt Killeen
Matt Killeen's thrilling depiction of World War II is an espionage novel that follows the courageous story of Sarah, a Jewish teenager turned British spy infiltrating a Nazi elite boarding school. The book is a thriller in and of itself, and is rife with themes of danger, courage and identity complexities in the face of extreme adversity. The hours of research that Killeen pours into this are evident because he explores the gripping challenges of each character, plot and setting with acute attention to historical accuracy and emotional depth, offering readers the compelling and thought-provoking offering that is Orphan Monster. Killeen released the book in 2018 and it is now available at Penguin Random House .
2. I Must Betray You By Ruta Sepetys
Too often, writers find themselves having to dig into the ancestral history of an era and time to strike storytelling gold. If anyone is equal to this task, it is Ruta Sepetys, who makes this list for the second time with her 2022 release I Must Betray You. Like other notable pieces of work she has created , Sepetys guides readers through a harrowing 1980s of Communist Romania, ruled by Nicolae Ceaușescu; an era defined by intimidation, fear and secrecy. The protagonist, 17-year-old Cristian Florescu, is an ambitious young man who has big plans for his future — plans that are stifled by the mounting hostility in his country. Determined to stand up to oppression and demand change for other citizens, Florescu weighs the odds and comes to a gut-wrenching, yet brave conclusion in this incredible story. The book is available at Penguin Random House .
1. The War That Saved My Life By Kimberly Brubaker Bradley
Kimberly Brubaker Bradley’s 2015 novel takes a different approach to wartime storytelling by inviting readers to a poignant exploration of wartime England. Bradley guides readers through the story with Ada, a young girl with a deformed foot whose mother keeps her confined to their one-bedroom home all her life. Eventually, when little brother Jamie is sent to London to escape the war, Ada uses the opportunity to escape too, only to find herself in the English countryside. The book intricately weaves themes of resilience, self-discovery and the power of love as Ada learns to overcome her physical and emotional scars. Bradley's portrayal of the impact of war on the lives of children adds a touching layer to this emotionally charged story. The War That Saved My Life is also available at Penguin Random House .
Bottom Line
Gripping storylines require a careful analysis of history in a way that makes readers care. The authors of these stories have struck that fine balance by highlighting the relevant themes while honing in on elements of history. While these stories may be fiction, they all contain relics of lived and learned human experiences.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
The CEO’s secret to successful leadership: CEO Excellence revisited
In March 2022, McKinsey senior partners Carolyn Dewar, Scott Keller, and Vikram Malhotra launched CEO Excellence: The Six Mindsets That Distinguish the Best Leaders from the Rest (Scribner/Simon & Schuster, March 2022), a New York Times and a Wall Street Journal best-selling book that revealed the characteristics of the world’s most successful leaders. The authors studied nearly 8,000 CEOs across the globe and across various sectors to determine what set these leaders apart from the rest. Through detailed interviews with 67 successful CEOs, they uncovered the mindsets, approaches, and practices that informed their leadership styles and delivered powerful results.
Since 2022, CEO Excellence has gone on to sell more than 161,000 copies and is being translated into 14 languages. To commemorate the second anniversary of this international business bestseller, McKinsey Global Publishing leader Raju Narisetti sat down with Dewar, Keller, and Malhotra once again. In this retrospective, the authors revisit their journey of writing the book and reflect on its global impact. They also offer more practical insights for CEOs and aspiring leaders who are eager to excel in an increasingly challenging operating environment. An edited version of the first installment of this three-part conversation follows. Be sure to check back next week for the second part of the discussion, which will focus on the authors’ personal reflections and on their latest research.
Defining successful leadership
Remind our audience: Why did the three of you set out to write this book?
Scott Keller: We tell a little story at the beginning of the book about when it dawned on us that we should write it. But beneath that story are three things that we recognized. One is that this is a very important role. All the research conducted by some of our colleagues for a book called Strategy Beyond the Hockey Stick , which came before ours, suggested that high-performing CEOs and the high-performing companies they led dramatically outperformed the others.
If you are a company that has stayed in the top quintile of performance for more than ten years, you have 30 times the value creation for your stakeholders than the next three quintiles combined. They call it “the power curve.” That’s a lot of extra value created.
Second, there’s a lot of research on the CEO effect. The CEO effect essentially looks at, “How much do the actions a CEO takes affect company performance?” The research suggests that, over the past 50 years, the importance of what the CEO does for a company’s performance has increased twofold.
There are 70 million people who work for the top 2,000 companies in the world. It touches an incredible amount of souls and lives. When you think about the ethical, social, and environmental impact of big companies, you start to say, “That’s really important.” That’s a big deal. Then, you say, “Well, how are we doing as leaders in the role of the CEO?” And then you get to the statistics that say, “Two in five CEOs within 18 months of taking the role are struggling. One in three, after three years, are asked to leave.”

There’s some data that suggests that 60 percent of CEOs feel like they’re making it up as they go, because the role is one you can’t really prepare for. It’s one you’ve never had before. The third realization is this: “What is out there to help CEOs excel in this really important role?”
Sure, there are biographies from CEOs, and they’re well written. But they’re typically exciting because of a combination of personality, business context, and unique situation. They’re hard to generalize.
Then there’s work done by academics, which tends to be very descriptive. There’s work done by headhunters, which tends to be very trait-based: What traits do you need to have to become a CEO? But there are very few handbooks that ask, “How do I do the role well?” Those were the things that made us say, “Look, it’s an important role. It’s really hard. There’s not a lot of help out there. Why not McKinsey, and why not us to help fill that void?” To fill that void, we said, “We’re going to do two things.” First, we want to really clarify, “What is the role of a CEO?,” because we couldn’t go to a source and get the answer to that. Second, and most importantly, we want to answer, “What is it that separates the best from the rest?”
First, we want to really clarify, ‘What is the role of a CEO?,’ because we couldn’t go to a source and get the answer to that. Second, and most importantly, we want to answer, ‘What is it that separates the best from the rest?’ Scott Keller
To do that, we had to first identify, “Who are the best?” We had our own methodology for that, which was rigorous, and it took into account a number of factors, not just financial performance, but social, ethical, and environmental impact.
We wanted a group that had been tenured—so they had to “eat their own cooking,” so to speak—and that had been in the role for a long time. We wanted those who had won the approval of their shareholders and stakeholders. We also wanted a very diverse group. So our methodology was adjusted to make sure we had geographic, ethnic, racial, and gender diversity.
We ended up with 200 CEOs who we felt represented the best CEOs of this century to date. We then said, “Let’s get a statistically valid sample of them, interview them, and try to understand what separates the best from the rest.”
What did we actually find? Well, if you say to us, “What is the role of a CEO?,” we’re now crystal clear on what that is. We would say the irreducible core of the role consists of six things you will need to do:
- set the direction
- align your organization on that direction
- mobilize your leaders to deliver on that direction
- work with your board
- connect with a group of stakeholders
- manage your personal effectiveness
Whether you’re a great CEO or not, these are the six roles of a CEO. Six feels like a lot, but it’s a big job, and it’s a hard job, as we just described. I think all of our CEOs looked at that list and said, “You know what? That’s a good taxonomy.”
Then we had to answer the question, “What separates the best from the rest?” We started asking a lot of questions about what these CEOs did. There weren’t a lot of patterns that emerged. We then adjusted our approach using a technique called laddering. In operations, the technique is essentially the equivalent of what they call the “five whys.”
In operations, if a machine stops working, you say, “Why?” Well, the engine burnt out. Why? Because it overheated. Why? Because it didn’t get enough ventilation. Why? Because it was too close to the wall. Now we know the root cause, and we don’t just change the motor. We actually move the machine away from the wall. When applied to leadership, the laddering technique takes you from actions and behaviors to just how people think about the world and about their mindsets.
When we began that form of inquiry, we started to see concrete patterns of, “Ah, this is how this group of excellent CEOs thinks about direction setting. This is how they think about aligning the organization.” The power of mindsets is pretty profound.
To articulate the six mindsets that separate the best from the rest, you need to say, “What is it about direction setting? How do these leaders approach it? What do they think about it that causes them to act? What predisposes them to act in a certain way?”
Imagine you get handed the keys to drive an organization that’s worth $30 billion and has 20,000 employees. It would be easy to have a mindset that says, “OK, discretion is the better part of valor here. Do no harm is the first thing that I need to think about,” and to be relatively conservative.
Our CEOs did not have that mindset. They had the opposite mindset, which was, “Be bold. Fortune favors the bold.” They were consistently considering, “How do we take the next step, that change in performance?” We describe a lot of what they did that comes out of that. But “Be bold” was the mindset that really separated the best from the rest.
On the topic of aligning your organization, we often link to the Einstein quote of not everything that counts can be counted. I think people get that. When you think about organization, culture, talent, and more, people often think of that Einstein quote.
It matters, but it’s hard to count. We call it soft. Our CEOs didn’t think about it that way. The CEOs we interviewed said, “We’re going to put the same level of rigor and discipline into the ‘soft’ stuff that we put into all of our financial and operational work.”
They found ways to do that, because they had the mindset that said, “We will put rigor and discipline into the soft stuff.” Very powerful.
As for mobilizing leaders—the team and leaders that are close to you—the CEOs considered dynamics. They thought less about the mechanics of, “What do we meet on, with whom, and when,” and a lot more about, “What is the psychology of our team?” It was about dynamics, not mechanics. Are people showing up as what I would call thermostats, not thermometers?
It’s easy to show up and report what’s going on, in the way a thermometer would. But to actually do things that change the outcome is what you want in your leaders. Are people showing up as “we” versus “me”? They think about the psychology on a number of dimensions and work on that psychology. That’s more about where they put their time rather than the mechanics of how to run the team.
A lot of CEOs see their board as, “My job in relation to my board is to help them do their fiduciary duties.” Our CEOs? “My job as CEO is to help the board help the business.” Regarding stakeholders, it was less about thinking of the actions in relation to stakeholders and more about the motivations.
It begins with the why. Reed Hastings [cofounder and chairman of Netflix] gave a great, simple example of this. He said, “When I talk to the media, I know they want to be truth tellers. That’s why they got into the job. But they also have to be entertainers, because that’s how they get cut-through on their stories.
“So when I talk to the media, I understand their why. I understand what they’re solving for. And I give ‘em a bit of both. And I then get cut-through on what I want, which is the message to get through for Netflix.” So starting with why versus starting with what, who, when, or where is very important when it comes to stakeholders.
Finally, in terms of personal effectiveness, you are accountable for everything. It would be easy to have the mindset that says, “I need to do anything that needs to be done around here.” Our CEOs did not have that mindset toward their role.
They said, “I need to do what only I can do as the CEO and with the capabilities I have.” They were very focused on areas where they would get involved and delve more deeply, rather than letting themselves get spread thin in a way that adds very little value to other leaders and to the company. So that’s the answer as far as the six roles of the CEO and the mindsets that separate the best from the rest.
The book was the first time you put it all together: the audience is CEOs and aspiring CEOs. What was the response?
Carolyn Dewar: The response has been tremendous. It really has. Maybe even surprisingly so to us, to our colleagues, and to others, in terms of people’s openness and willingness to learn and share.
There could be a myth out there that, “Well, they’re CEOs. They must all be perfect already. They already know what they’re doing.” This opened the conversation that these are hard jobs. There’s volatility in the world right now, too.
It’s OK if we don’t all have all the perfect answers. There are some truths based on the data, on some insights, and on some patterns in terms of what mindsets work well. But I found that people were really excited to engage in questions like, “What does that mean for me? How do I learn? What does that look like?” I found this to be true even for—and perhaps less surprisingly so—folks who aspired to the role, who are trying to look ahead and say, “What do I need to do?”

This is the case for new CEOs in the role who are going up a very quick learning curve and trying to juggle all kinds of things. It’s even the case for those who’ve been in the role for a long time. When we played it back to the 67 high performers we interviewed, for example, Satya Nadella [Microsoft CEO and executive chairman] and Jamie Dimon [Chase CEO), all these folks who’ve been in the role for many, many years, they saw something in it, too.
Seeing it written out that way, even the six elements of the role, there was recognition that prompted, “Wow, I’ve never seen it laid out that way. And now that I see it that way, I understand why I’m so tired, why this job is so hard, why it’s so important.”
There was a broad recognition that the insights resonated and that they were true, but then there was a real hunger to engage and have hundreds of one-on-one conversations asking, “What does this mean? How do I think it through? How can I apply this in the day-to-day?”
There was a broad recognition that the insights resonated and that they were true, but then there was a real hunger to engage. Carolyn Dewar
The part that has made me most excited is actually seeing all of the versions that people have created. Tons of folks have shared in real time or have sent us photos of the crib sheets that they’ve created—or the worksheets, or the thing that they’re now using as a bookmark.
The idea that there are these CEOs around the world who are now using this book in their back pocket as a practical tool really makes you realize that you are never too seasoned in the role to learn. That message has really resonated.
I guess there’s a reason why the book shows up in a Netflix documentary.
Vik, you’ve spent a lifetime listening to CEOs and then talking to them. What was the response?
Vik Malhotra: One thing of the many things that surprised me was that I thought we were writing the book for either current or aspiring CEOs. It really has turned out to be a book about leadership.
There are a lot of people in an organization who have the aspiration to be a leader . It may not just be the CEO. It could also be the business unit head or a CXO [chief experience officer]. They’re eager to learn the leadership lessons here, too. They may realize that they may not end up having to do everything these great CEOs do. But there are plenty of learnings in there, particularly if you run through the list of dimensions. This is certainly true when it comes to setting the direction, aligning the organization, mobilizing through leaders, and managing the effectiveness of your own personal operating model.
Those four dimensions resonate with anyone who has an aspiration to be a leader. You get into more CEO-like territory when you start working with the board or begin dealing with a broader range of stakeholders.
I was very inspired by the fact that at least two-thirds of the book resonated with anyone who wanted to be a leader. They were grasping for lessons, frameworks, and ideas. They loved the stories. So when someone like Ajay Banga [president of World Bank Group] says, “You know, I boiled my vision down to two words, which is kill cash,” they say, “Oh, my God. It can be that simple,” right?

Of course, there are lots of cascading elements that come off it. But they understood the boldness. It’s one thing for a consultant to tell leaders, “Be bold.” It’s another thing when they actually see practical examples of people who’ve done it. They see the success play out, market cap, company growth, and societal impact.
There’s a large group of people out there who just want to be leaders, but not necessarily CEOs. Yet they got a lot out of this book. Then there was the next group, who were the aspiring CEOs. It might be a step or two away, sometime in the next three to five years.
It’s one thing for a consultant to tell leaders, ‘Be bold.’ It’s another thing when they actually see practical examples of people who’ve done it. Vik Malhotra
There were brand-new CEOs as well. They were hungry for a framework for thinking about their role. They were hungry to learn actions they might take: “Here are some things I can do about being bolder in my direction tomorrow,” or “Here are things that I can do in terms of shaping one element of my culture better,” or “Here are some actions I can take on talent.”
I’d say the more tenured CEOs were a mixed bag. There were clearly people who got the joke that, “If you’re going to be a CEO for nine years, there are probably three S-curves here.” They were eager to learn in terms of, “OK, if I’m approaching my three-year point, what does it mean to be bold, given what I’ve done relative to the go-forward picture?”
But there were others who were actually quite comfortable in their skin. They felt like they understood the role. That was OK, too. I haven’t quite done the math yet on whether their companies ended up in a better spot than the others. One day, we’ll do that. Once in the role for a while, some CEOs are very inquisitive, but there are others who are less so.
Scott Keller: Could I add two quick things on that topic? There are over 1,000 reviews now on Amazon, and a 4.7 rating, which is more than we could ever dream of. This reinforces the applicability far beyond senior executives.
There are over 1,000 reviews now on Amazon, and a 4.7 rating, which is more than we could ever dream of. This reinforces the applicability far beyond senior executives. Scott Keller
Raju Narisetti: Astonishing.
Scott Keller: But those 1,000 reviews aren’t from CEOs. They’re written by people from all walks of life, all geographies and profiles. We’ve also been asked to be guest lecturers at business schools: at Wharton, Stanford, and Harvard.
Carolyn Dewar: And INSEAD.
Scott Keller: And INSEAD. It has been interesting to see how hungry these students are to learn from this, as well. I would just reinforce that. The second thing I would say is, in my experience, at least, there are a couple of very senior CEOs who received the book from multiple places and were encouraged to reach out to us.
I would then go and talk to them, and say, “You received the book from four different people. You received it from a couple of people on your board and a couple people on your team. What’d you think of it?”
They would say, “Oh, it’s great. Beautiful articulation of the role.” When I asked, “Did you get any insights from it?” they would say, “Well, it just reinforced all that I’m doing.”
The self-serving bias is real. Tenured CEOs have a self-serving bias. We then said, “Well, why do you think four people handed it to you? What was on their mind? What did they think you could learn?”
“Oh, I don’t really think anything.” For a few of those CEOs, we’ve had them participate in the 360° review process. In the back of the book, there’s a way to do that. It was a real eye-opener for them to say, “Wow, actually, I thought I was great on aligning the organization, but you’re telling me I’m far from great.”
That was very helpful when they took that extra step to understand, “Well, I know how I view myself in relation to all this. But how do others view me?” That’s actually part of our ongoing research. One of our next steps is to create a very simple way to get that type of feedback on a regular basis for a CEO. So being a good CEO means understanding how people perceive you vis-à-vis how you perceive yourself on the six elements of the role.
Talk about the global response. Was it different from what you thought it might be?
Vik Malhotra: I would say that, first, there’s been a broad embrace globally. All three of us have been traveling, speaking to our colleagues, speaking to clients, all around the world: Japan, India, Germany, the UK, Latin America.
While these timeless lessons clearly apply, regardless of context, and geography, and the like, there are some important differences in certain countries. I don’t think you change how you think about being a leader, but you have to factor these differences in.
While these timeless lessons apply, regardless of context, and geography, there are some important differences in certain countries. I don’t think you change how you think about being a leader, but you have to factor these differences in. Vik Malhotra
The biggest difference that struck me was, if you go to India or you go to many parts of Latin America, family-owned businesses are at the big level. This is very much written [in the book] from a corporate lens. I have personally had to think through, if I’m talking to you and you’re the CEO of a family-owned business, how I could slightly adjust the narrative around how you can be bold in that context.
What does it take to be bold in that context? How do you shape culture? How do you actually understand that the stakeholders there may not have the same motivation about shareholder return? They may be more worried about dividend flow to the family. So you have to adjust to that. As we went global, being able to adjust the narrative was an interesting learning. The other difference in the US and globally is seen in the way in which start-ups and founder-owned businesses are run.
Carolyn Dewar: I live in the Bay Area. I get this question all the time.
Vik Malhotra: And there’s a version of this for founder-led companies because they have different dynamics that you need to factor in. I don’t think we change the narrative too broadly. But you’ve got to factor in what they’re worried about.
Carolyn Dewar: Yes, and there is potentially a private CEO or portfolio company CEO.
Vik Malhotra: Yes.
Scott Keller: Yes, and I would add government organizations.
Raju Narisetti: That’s right.
Scott Keller: Not-for-profits have their own flavors, as well.
Carolyn Dewar: Yes.
Scott Keller: It all applies, but there’s definitely tailoring in terms of ownership structure and leadership history for founder-led organizations.
Based on the time you spent with CEOs, what’s been different in the last two, three years?
Vik Malhotra: In the grander context of things, there are a few things that are different. Decision making is a whole lot faster than it’s ever been. There is a need for you as a leader, a CEO and a leader, to make decisions, often with imperfect data, in weeks, days, even hours. Relatively speaking, 20 years ago, you didn’t have that same—
Scott Keller: That speed.
Vik Malhotra: You didn’t have that same pace of decision making. The speed of decision making is very different. The push on important trends that we’re facing didn’t exist—sustainability, DE&I [diversity, equity, and inclusion]. Those are new things that people have to factor in.
The one element that actually feels a little different and maybe less timeless is the engagement of the external stakeholders. I think if you go back 20 years ago, maybe that was 10 percent of their responsibility.
Today, it’s not unusual for it to be 30, 40, 50 percent of some CEOs’ responsibilities, particularly when you factor in the customers, regulators, analysts, trade unions—the world at large. So there are some real changes in today’s world relative to history.
I still think the timeless messages all apply. But as a leader, you likely do have to move more quickly. You have to be cognizant of the many more stakeholders than perhaps there have been historically. And you certainly have to be cognizant of some very important long-term trends that are, in the grander scheme of things, relatively new.
Scott Keller: I’ll pick up on one of the strands there, Vik. When we wrote the book, it was in the peak of the pandemic and everything going on there, the George Floyd murder, the Capitol riots, and there was kind of a strong push saying, “CEOs need to get out there, and talk about all these issues, and be really frontward facing.”
I feel pretty good about when we talked about what we put in the book and said, “Look, there is a time to speak out, absolutely—if it affects your business and your business values, if it’s a place you can make a difference, if you can actually understand where your stakeholders stand and make an informed decision.”
There is a time to speak out, absolutely—if it affects your business and your business values, if it’s a place you can make a difference, if you can actually understand where your stakeholders stand and make an informed decision. Scott Keller
We tried to get a real middle-of-the-line, “You are going to have to speak out. This is going to be important, but you shouldn’t be out there opining on everything under the sun. It’s probably not your role, nor are you well informed enough or able to necessarily do that in the right sort of ways.” I feel good that we got that—right. But it’s been fascinating to see the swings—to witness those varying conversations. The second thing I’d say is, in a world that has gone from a blog-length thing that was considered short to a short Twitter headline and now a TikTok post, there’s now a higher premium on the ability to cut through with elegant simplicity.
Now CEOs have a company direction that they need to convey to 50,000 people around the world. How can they do that in six words or less in a way that’s emotive and powerful and gives all the information someone needs?
For example, having that conversation not just around the vision of the company but answering the question, “What’s the employee value proposition? What’s the proposition for customers, what we’re delivering for shareholders?” It was psychologist George Shultz who said that understanding goes from being simple to complex to elegantly simple.
On the far side of complexity is elegant simplicity. It becomes such a big tool for CEOs now to get cut through at scale. I love Piyush Gupta, what he did with DBS [Group], which is a Singapore-based bank that was the worst bank in Singapore when he took over, objectively speaking. And now, in most polls and measures, it’s the best bank in the world.
“We are a technology company that makes banking joyful.” That’s what you need to know about DBS. Six words: technology company that makes banking joyful. “Technology company” tells you a ton about where they’re investing assets, about how they think about product development, about running the place generally, the speed of decision making, and more.
“Making banking joyful” tells you a ton about what their customer experience is meant to be like and all of the investment they’ll put into it, what they expect of their colleagues and employees. There’s just so much richness in those six words that CEOs are able to get to the elegantly simple messaging around the things that matter. It might even be the bold moves.
“Here’s the five bold moves we’re making that are going to make the biggest difference.” They’re all crisp. There’s a real premium on that, and there will continue to be a premium on having more acuteness as we move forward—because the way that media and people digest information has changed. That’s my take on something that I feel has changed.
Carolyn Dewar is a senior partner in McKinsey’s Bay Area office, Scott Keller is a senior partner in the Southern California office, and Vik Malhotra is a senior partner in the New York office. Raju Narisetti is the leader of McKinsey Global Publishing and is based in McKinsey’s New York office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Actions the best CEOs are taking in 2023

Staying ahead: How the best CEOs continually improve performance

Stepping up: Becoming a high-potential CEO candidate
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. wants to get on the ballot in all 50 states. It won't be easy

Ashley Lopez

Independent presidential candidate Robert F. Kennedy Jr. speaks during a campaign rally in Phoenix on Dec. 20, 2023. Both Kennedy's campaign and a super PAC supporting him are working to get the conspiracy theorist on state ballots around the country. Rebecca Noble/Getty Images hide caption
Independent presidential candidate Robert F. Kennedy Jr. speaks during a campaign rally in Phoenix on Dec. 20, 2023. Both Kennedy's campaign and a super PAC supporting him are working to get the conspiracy theorist on state ballots around the country.
With many Americans unhappy at the prospect of a rematch between President Biden and former President Donald Trump, voters may be more open than usual to third-party and independent candidates come fall.
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. — who has a famous political last name and is a longtime leader of the anti-vaccine movement and a promoter of various conspiracy theories — is among the candidates hoping to appeal to voters looking for alternatives to Biden and Trump.
The effect Kennedy's independent candidacy could have on the general election remains an open question. Both Republican and Democratic leaders have called Kennedy's presidential run a potential spoiler campaign.

Untangling Disinformation
Rfk jr. is building a presidential campaign around conspiracy theories.
But first, he actually needs to get on ballots, a complicated and expensive state-by-state undertaking.
"I think it's sometimes overlooked the number of things you need," said Michael Arno, who runs a petition signature gathering company and has worked on ballot access for various independent candidates and the No Labels effort . "If you're going to run against the two major political parties, you have to operate like you're one of the two major political parties."
Millions of dollars for signature gathering
Amaryllis Kennedy, the campaign's director and the candidate's daughter in-law, told NPR that despite the support polls say he has , "he cannot win unless he is on the ballot."
"And unlike President Biden and former President Trump, he still has to collect over a million signatures despite all of that support in order to be on the ballot," she said. "So, it's a large part of our focus right now."
So far, the campaign reports to have enough signatures to appear on the presidential ballot in Hawaii, Nevada, New Hampshire and Utah. A super PAC supporting Kennedy has claimed to secure enough signatures for Kennedy to appear on the ballot in Arizona, Georgia, South Carolina and Michigan.
The campaign has said it estimates it will take about $15 million to obtain the roughly 1 million signatures needed to appear on ballots in all 50 states.
Because campaigns generally can't gather enough signatures with volunteers alone, they often hire signature gatherers to meet state-set deadlines. And the price of signature gatherers has been climbing in recent years.

The price of a ballot signature is way up, and experts worry it's encouraging fraud
"You have got to pay for signature collectors," Arno said. "And you may well have a great volunteer network, but you're going to have to have paid signature gatherers."
But Amaryllis Kennedy said the campaign is hoping to mostly rely on its network of volunteers.
"We are building some really groundbreaking digital tools to harness hundreds of thousands of volunteers and supporters and encourage each of them to go out and collect 10 or 12 or 16 signatures," she said.
Kennedy said the campaign does have some paid signature gatherers on staff for backup, as well as trainers for volunteers. She said the campaign wants to lean on paid gatherers as little as possible though.
"Our hope is that we won't need as many paid petitioners as we had expected," she said.
Get ready for lawsuits
Another big expense for independent campaigns trying to get on the ballot is legal fees.
These candidates often challenge state ballot access laws — as well as deal with lawsuits filed by the country's major political parties.
"So you've got to have several lawyers on retainer," Arno said. "The more the better, to be honest."
Richard Winger, a ballot access expert who publishes a monthly newsletter called Ballot Access News, said it's almost impossible to avoid lawsuits in this process.
"Even going back 100 years, nobody who got on the ballot in all the states ever did it without suing, except only one," Winger said. "In 1992, Ross Perot got himself on the ballot without a single lawsuit. But he's the only one."
The Kennedy campaign has already sued Utah and Idaho over their ballot access rules. At least one of those cases has been successful, so far.
The campaign's director said they are even factoring in lawsuits in deciding when to turn in petitions. Kennedy said they are "holding the signatures until the 11th hour," as a way to work around "challenge deadlines" in some states.
"The earlier you submit the signatures, the longer anybody who wants to pose a nuisance challenge is to drain your coffers with court expenses," she said.

A view of a Kennedy 2024 board, sticker and button during a campaign rally in Phoenix on Dec. 20, 2023. Rebecca Noble/Getty Images hide caption
Different states, different rules
Different states also have significantly different rules for getting on the ballot as an independent. Some states have high signature quotas and shorter timelines, which make getting on the ballot substantially more difficult.
But Winger thinks the difficulty of navigating state laws often gets overblown.
"The ballot access laws for president are much more lenient than they are for other offices," he said. "That's because state legislators really don't care that much who gets on the ballot for president. But they care intensely about who gets on the ballot for legislature. Ballot access for other offices is terrible. But for president, only six states are really monstrously hard."
Winger said those states are California, Texas, Florida, New York, Indiana and Arizona.
Arno sees ballot access rules for presidential candidates as a bit more challenging.
"Some of them are very easy," he said. "Some of them are more complex — or some of them are just downright created to make it almost impossible to get on the ballot."
Some states require signature gatherers to be registered voters in that state, which can be tricky for campaigns using a ballot petition company. Most paid signature gatherers work across the country and often aren't from the state they are working in.
Certain populous states have high signature thresholds. California , for example, requires independent candidates to gather 219,403 signatures by August, which is around the time most states have their signature gathering deadlines.
And some states have their deadlines even sooner. In Texas , independent candidates have from March 5 to May 13 to gather "113,151 signatures of registered voters who did not vote in the presidential primary of either party."
As a way to work around some tougher requirements for independent candidates, Kennedy is planning to run as a candidate from his own minor party in California, Texas and elsewhere .
Kennedy's campaign manager said some of the rules feel like unnecessary hurdles.
"Every state has different technical requirements, you know, paper size, whether or not it needs to be notarized, pen color, whether or not they have to be printed on the front and the back," she said. "And all of those technical requirements are reasons that you can discount thousands of voter signatures even once you do collect them."
Kennedy said she believes the purpose of all these rules is "to drain independent candidates of funds that they could otherwise be using to share their message" with voters.
"And I think that has a really chilling and damaging effect on our democracy," she said.

Here's what matters to voters — and what could change their minds if it's Biden-Trump
Big help from a super pac. is it legal.
The campaign, however, is getting quite a bit of help navigating all these requirements. An outside super PAC — which can raise unlimited sums of money — is supporting Kennedy's ballot access effort.
American Values 2024 has committed to getting Kennedy on the ballot in more than 10 states, including Texas and New York.
Tony Lyons — the super PAC's co-founder and president of Skyhorse Publishing, a small publisher known for giving book deals to authors like conspiracy theorist Alex Jones, as well as RFK Jr. — told NPR that getting Kennedy on the ballot is a "precondition to any other work" that his super PAC wants to do.
"We've raised somewhere in the $25 to $30 million range and we have allocated up to $15 million to get Bobby Kennedy on the ballot in 12 states," Lyons said. He said about $9 million or $10 million will be spent on paid signature gatherers — and the rest of $5 million to $6 million set aside for legal challenges.
Already, there's a complaint from the Democratic National Committee challenging the very fact that a super PAC is helping Kennedy get on the ballot. In their complaint to the Federal Election Commission, DNC officials said the campaign and super PAC are violating federal campaign finance laws because this kind of work amounts to illegal coordination.
Lyons said the FEC complaint is a "political game" aimed at hurting both the super PAC and the campaign. He said Democrats are also going to use super PAC money to influence the election.
"They've gotten something like 15 times the amount of money in their super PACs than all the super PACs that support Bobby Kennedy combined have raised," Lyons said.
But Ciara Torres-Spelliscy, a fellow at the Brennan Center for Justice and professor at Stetson University College of Law, said she thinks this complaint has some merit.
"The problem with a super PAC helping a candidate obtain ballot access is almost by definition, you would have to be coordinating between the candidate and the super PAC, which is not allowed," she said. "And what I mean by that is most of the states, when they require signature gathering, they are requiring the candidate to have gathered those signatures."
The FEC has a poor enforcement history, however. It has three Democratic appointees and three Republican appointees, and, Torres-Spelliscy said, they need four commissioners for the FEC "to do almost anything." She said this is why often the FEC just deadlocks 3-3.
"So you have political actors who know this," Torres-Spelliscy said. "And while a functioning FEC probably should be policing this line of true independence for super PACs, they have not had a good history of this in the last 14 years.
"It's always hard to know what the next round of thwarting the campaign finance system is going to look like."
- voting stories

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
My Name Is Not Easy. age 12+. Fascinating story of Alaskan kids growing up in the 1960s. By: Debby Dahl Edwardson (2011) See full review. Common Sense Media editors help you choose The Best Book-Report Books for Middle Schoolers. Find fiction, nonfiction, and memoirs perfect for engaging kids.
The Maze Runner (The Maze Runner, #1) by. James Dashner (Goodreads Author) (shelved 10 times as book-reports) avg rating 4.05 — 1,521,018 ratings — published 2009. Want to Read. Rate this book. 1 of 5 stars 2 of 5 stars 3 of 5 stars 4 of 5 stars 5 of 5 stars. Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows (Harry Potter, #7)
Include the title and author in your intro, then summarize the plot, main characters, and setting of the book. Analyze the author's writing style, as well as the main themes and arguments of the book. Include quotes and examples to support your statements. Part 1.
A good book report's introduction hooks the reader with strong opening sentences and provides a preview of where the report is going. "Step-by-Step Outline for a Book Report" ( Classroom ) This article from Classroom furnishes students with a guide to the stages of writing a book report, from writing the rough draft to revising.
Here are quick steps to create a book report: Consult Summary Websites: Visit websites providing book summaries and analyses. For instance, SparkNotes or CliffsNotes offer concise overviews. Focus on Key Details: Select 2-3 crucial aspects of the book, like major themes or character development. Discuss these in-depth.
Identify the main elements of the book. Scrutinize the book's primary components, including its main themes, characters, setting, and plot. These elements will form the basis of your report. 3. Formulate a thesis statement. Compose a thesis statement that encapsulates your personal perspective about the book.
The start of your book report provides an opportunity to make a solid introduction to the material and your own personal assessment of the work. You should try to write a strong introductory paragraph that grabs your reader's attention. Somewhere in your first paragraph, you should also state the book's title and the author's name.
3. Organize your notes and create an outline. Gather your notes and arrange them into categories. Once you've completed this, write an outline and organize the categories to become the paragraphs of your book report. Jot down bullet points on what each paragraph will include and what part of the book can support it.
2. Read the Book and Make Notes. Next, you'll need to read the book you're writing about in full, not just skim through or read a synopsis! This means you'll need to leave enough time before the deadline to read the text thoroughly (and write up your report). When you are reading, moreover, make sure to take notes on:
For each word (i.e. somebod y), write the story element. For example: Somebody = the aliens, wanted = underpants, but = mom came outside to get laundry, so then = they zoomed back to space. Put this all together and you have a short and sweet summary: The aliens wanted underpants but the mom came outside to get the laundry so they zoomed back ...
The book report is basically a summary of everything about the book. It describes the book from an objective point of view, as impartially as possible. Difference between a Book Report and a Book Review. It's easy to confuse a book report for a book review. After all, they sound similar. But they are really quite different.
The following list covers the basic elements that should be included in every book report you write, no matter what topic or specific type of book report you're writing: The book's title and author. The historical context of the book (when it was written) The time (s) during which the story is set. The location (s) where the story takes place.
A book report should contain the basic elements, but a good book report will address a specific question or point of view and back up this topic with specific examples, in the form of symbols and themes. These steps will help you identify and incorporate those important elements in a process that takes three to four days.
And although students don't need to dive deeply into every single book they read, occasionally digging into characters, settings, and themes can help them learn to look beyond the prose. Here are 42 creative book report ideas designed to make reading more meaningful. 1. Concrete Found Poem.
Showing 1-50 of 309. The Pearl (Paperback) by. John Steinbeck. (shelved 5 times as book-report-books) avg rating 3.53 — 236,968 ratings — published 1947. Want to Read. Rate this book. 1 of 5 stars 2 of 5 stars 3 of 5 stars 4 of 5 stars 5 of 5 stars.
1 of 5 stars 2 of 5 stars 3 of 5 stars 4 of 5 stars 5 of 5 stars. 2. Eragon (The Inheritance Cycle, #1) by. Christopher Paolini (Goodreads Author) 3.95 avg rating — 1,768,995 ratings. score: 396 , and 4 people voted. Want to Read.
Start as soon as possible once you're given the assignment. As soon as you pick your book,, factor in at least two weeks for writing and wrapping up your report. Divide the number of pages by the remaining days: that will be the number of pages you will have to read per day. Practice narration.
Book reports commonly describe what happens in a work; their focus is primarily on giving an account of the major plot, characters, thesis, and/or main idea of the work. Most often, book reports are a K-12 assignment and range from 250 to 500 words. Book reviews are most often a college assignment, but they also appear in many professional ...
Develop the body: You can follow your outline or a book report template to write the body of your report. Discuss each element (plot, characters, themes, etc.) in separate paragraphs or sections. Conclude your report: Summarize your main points and offer your final thoughts and evaluation of the book. Review and revise: Finally, review and ...
Step 1: Choose the Book. To learn how to write a report, you must first pick up a book. When choosing a book, many options are available, especially from American book writers. Look for authors who have made significant contributions to literature and have a writing style that resonates with you. Consider the genre and subject matter that you ...
Complete a One-Page Book Report. This is a simple first-grade book report idea that incorporates story elements. Students will complete a one-page report that includes the setting, characters, problem, and solution. Also include a space for students to draw an illustration that represents an important idea from the book.
Book Review Questions: General Information. Before you delve into sharing your own opinions, you should share some general information about the book. This can be to do with its plot, its genre, the setting and whether there is anything readers should be aware of before delving in. These are good questions to ask about a book as a basic ...
Blog - Posted on Thursday, Nov 11 The Only Book Review Templates You'll Ever Need Whether you're trying to become a book reviewer, writing a book report for school, or analyzing a book, it's nice to follow a book review template to make sure that your thoughts are clearly presented.. A quality template provides guidance to keep your mind sharp and your thoughts organized so that you can ...
8. Make a Diorama. Creative ideas for book reports include projects like dioramas, which are short on writing and long on fun. A diorama is a miniature 3-dimensional scene that recreates a setting. It can feature models of buildings, plants, animals, or people set against a background.
1.) One of the most thrilling things a book of criticism can do is answer a question that you didn't know you had. 2.) The question in The Chapter is particularly delicious, because you likely accept chaptering as a matter of course, without asking why books are split up. 3.) Nicholas Dames roams wonderfully from the Gospels to, in a ...
The title derives from Royle's eccentric habit of seeking out those books in second-hand bookshops distinguished by what he calls "shadow lines", the tell-tale mark at the top edge of a book ...
The book also won a Bancroft Prize, and the Joan Kelly Memorial Prize in Women's History, among others. This book is a good fit for people who are intrigued by true stories that have been re-imagined.
Attempts to restrict library books continued to accelerate last year, according to a report released Thursday from the American Library Association. Overall, the number of individual titles ...
In March 2022, McKinsey senior partners Carolyn Dewar, Scott Keller, and Vikram Malhotra launched CEO Excellence: The Six Mindsets That Distinguish the Best Leaders from the Rest (Scribner/Simon & Schuster, March 2022), a New York Times and a Wall Street Journal best-selling book that revealed the characteristics of the world's most successful leaders.
To run for president as an independent candidate, conspiracy theorist Robert F. Kennedy Jr. needs to get on ballots, a complicated and expensive state-by-state undertaking.