An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager

Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
Examining the mental health of university students: A quantitative and qualitative approach to identifying prevalence, associations, stressors, and interventions
Affiliations.
- 1 Department of Dental Public Health and Behavioural Sciences, University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Dentistry, Kansas City, MO, USA.
- 2 Office of Research and Graduate Programs, University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Dentistry, Kansas City, MO, USA.
- PMID: 35380931
- DOI: 10.1080/07448481.2022.2057192
Objective To identify the prevalence of anxiety, depression, and suicidal ideation that would place university students at risk for mental health disorders. To explore the source of stressors and possible interventions that may benefit student mental health in a university setting.
Participants: University students (n = 483) who had been learning remotely due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: A mixed-methods cross-sectional survey was administered in 2020.
Results: Students were at an increased rate of depression, anxiety and suicidal ideation as compared to the general population. Female gender, lack of social support, living alone, being a first-generation college student and COVID-19 were significantly associated with mental health disorders. Stressors were identified and categorized into themes and interventions were recognized that may improve student well-being.
Conclusion: Students enrolled in university programs appear to experience significant amounts of anxiety, depression, and suicidal ideation. Additional mental health education, resources, and support is needed.
Keywords: Anxiety; COVID-19; college students; depression; suicidal ideation.
PubMed Disclaimer
Similar articles
- Investigating Mental Health of US College Students During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Cross-Sectional Survey Study. Wang X, Hegde S, Son C, Keller B, Smith A, Sasangohar F. Wang X, et al. J Med Internet Res. 2020 Sep 17;22(9):e22817. doi: 10.2196/22817. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 32897868 Free PMC article.
- Mental Health Symptoms of University Students 15 Months After the Onset of the COVID-19 Pandemic in France. Wathelet M, Horn M, Creupelandt C, Fovet T, Baubet T, Habran E, Martignène N, Vaiva G, D'Hondt F. Wathelet M, et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Dec 1;5(12):e2249342. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.49342. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 36580328 Free PMC article.
- Prevalence and associated factors of suicidal ideation and attempt among undergraduate medical students of Haramaya University, Ethiopia. A cross sectional study. Asfaw H, Yigzaw N, Yohannis Z, Fekadu G, Alemayehu Y. Asfaw H, et al. PLoS One. 2020 Aug 12;15(8):e0236398. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236398. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32785295 Free PMC article.
- Prevalence and associated factors of suicidal ideation among college students during the COVID-19 pandemic in China: a 3-wave repeated survey. Liang SW, Liu LL, Peng XD, Chen JB, Huang AD, Wang XY, Zhao JB, Fan F, Liu XC. Liang SW, et al. BMC Psychiatry. 2022 May 15;22(1):336. doi: 10.1186/s12888-022-03968-2. BMC Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35570282 Free PMC article.
- The Impact of COVID-Related Restrictions on the Mental Health of Students. Reuter PR. Reuter PR. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1458:35-50. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-61943-4_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39102188 Review.
- "You would think she would hug me": Micropractices of Care Between First-Generation College Students and Their Parents During Covid-19. Flores A, Mason KA. Flores A, et al. Cult Med Psychiatry. 2024 Mar;48(1):91-112. doi: 10.1007/s11013-023-09833-5. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Cult Med Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 37768495
- Search in MeSH
Related information
Linkout - more resources, full text sources.
- Taylor & Francis
- MedlinePlus Health Information
- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
- Open access
- Published: 20 September 2022
Factors that influence mental health of university and college students in the UK: a systematic review
- Fiona Campbell 1 ,
- Lindsay Blank 1 ,
- Anna Cantrell 1 ,
- Susan Baxter 1 ,
- Christopher Blackmore 1 ,
- Jan Dixon 1 &
- Elizabeth Goyder 1
BMC Public Health volume 22 , Article number: 1778 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
120k Accesses
72 Citations
98 Altmetric
Metrics details
Worsening mental health of students in higher education is a public policy concern and the impact of measures to reduce transmission of COVID-19 has heightened awareness of this issue. Preventing poor mental health and supporting positive mental wellbeing needs to be based on an evidence informed understanding what factors influence the mental health of students.
To identify factors associated with mental health of students in higher education.
We undertook a systematic review of observational studies that measured factors associated with student mental wellbeing and poor mental health. Extensive searches were undertaken across five databases. We included studies undertaken in the UK and published within the last decade (2010–2020). Due to heterogeneity of factors, and diversity of outcomes used to measure wellbeing and poor mental health the findings were analysed and described narratively.
We included 31 studies, most of which were cross sectional in design. Those factors most strongly and consistently associated with increased risk of developing poor mental health included students with experiences of trauma in childhood, those that identify as LGBTQ and students with autism. Factors that promote wellbeing include developing strong and supportive social networks. Students who are prepared and able to adjust to the changes that moving into higher education presents also experience better mental health. Some behaviours that are associated with poor mental health include lack of engagement both with learning and leisure activities and poor mental health literacy.
Improved knowledge of factors associated with poor mental health and also those that increase mental wellbeing can provide a foundation for designing strategies and specific interventions that can prevent poor mental health and ensuring targeted support is available for students at increased risk.
Peer Review reports
Poor mental health of students in further and higher education is an increasing concern for public health and policy [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ]. A 2020 Insight Network survey of students from 10 universities suggests that “1 in 5 students has a current mental health diagnosis” and that “almost half have experienced a serious psychological issue for which they felt they needed professional help”—an increase from 1 in 3 in the same survey conducted in 2018 [ 5 ]. A review of 105 Further Education (FE) colleges in England found that over a three-year period, 85% of colleges reported an increase in mental health difficulties [ 1 ]. Depression and anxiety were both prevalent and widespread in students; all colleges reported students experiencing depression and 99% reported students experiencing severe anxiety [ 5 , 6 ]. A UK cohort study found that levels of psychological distress increase on entering university [ 7 ], and recent evidence suggests that the prevalence of mental health problems among university students, including self-harm and suicide, is rising, [ 3 , 4 ] with increases in demand for services to support student mental health and reports of some universities finding a doubling of the number of students accessing support [ 8 ]. These common mental health difficulties clearly present considerable threat to the mental health and wellbeing of students but their impact also has educational, social and economic consequences such as academic underperformance and increased risk of dropping out of university [ 9 , 10 ].
Policy changes may have had an influence on the student experience, and on the levels of mental health problems seen in the student population; the biggest change has arguably been the move to widen higher education participation and to enable a more diverse demographic to access University education. The trend for widening participation has been continually rising since the late 1960s [ 11 ] but gained impetus in the 2000s through the work of the Higher Education Funding Council for England (HEFCE). Macaskill (2013) [ 12 ] suggests that the increased access to higher education will have resulted in more students attending university from minority groups and less affluent backgrounds, meaning that more students may be vulnerable to mental health problems, and these students may also experience greater challenges in making the transition to higher education.
Another significant change has been the introduction of tuition fees in 1998, which required students to self fund up to £1,000 per academic year. Since then, tuition fees have increased significantly for many students. With the abolition of maintenance grants, around 96% of government support for students now comes in the form of student loans [ 13 ]. It is estimated that in 2017, UK students were graduating with average debts of £50,000, and this figure was even higher for the poorest students [ 13 ]. There is a clear association between a student’s mental health and financial well-being [ 14 ], with “increased financial concern being consistently associated with worse health” [ 15 ].
The extent to which the increase in poor mental health is also being seen amongst non-students of a similar age is not well understood and warrants further study. However, the increase in poor mental health specifically within students in higher education highlights a need to understand what the risk factors are and what might be done within these settings to ensure young people are learning and developing and transitioning into adulthood in environments that promote mental wellbeing.
Commencing higher education represents a key transition point in a young person’s life. It is a stage often accompanied by significant change combined with high expectations of high expectations from students of what university life will be like, and also high expectations from themselves and others around their own academic performance. Relevant factors include moving away from home, learning to live independently, developing new social networks, adjusting to new ways of learning, and now also dealing with the additional greater financial burdens that students now face.
The recent global COVID-19 pandemic has had considerable impact on mental health across society, and there is concern that younger people (ages 18–25) have been particularly affected. Data from Canada [ 16 ] indicate that among survey respondents, “almost two-thirds (64%) of those aged 15 to 24 reported a negative impact on their mental health, while just over one-third (35%) of those aged 65 and older reported a negative impact on their mental health since physical distancing began” (ibid, p.4). This suggests that older adults are more prepared for the kind of social isolation which has been brought about through the response to COVID-19, whereas young adults have found this more difficult to cope with. UK data from the National Union of Students reports that for over half of UK students, their mental health is worse than before the pandemic [ 17 ]. Before COVID-19, students were already reporting increasing levels of mental health problems [ 2 ], but the COVID-19 pandemic has added a layer of “chronic and unpredictable” stress, creating the perfect conditions for a mental health crisis [ 18 ]. An example of this is the referrals (both urgent and routine) of young people with eating disorders for treatment in the NHS which almost doubled in number from 2019 to 2020 [ 19 ]. The travel restrictions enforced during the pandemic have also impacted on student mental health, particularly for international students who may have been unable to commence studies or go home to see friends and family during holidays [ 20 ].
With the increasing awareness and concern in the higher education sector and national bodies regarding student mental health has come increasing focus on how to respond. Various guidelines and best practice have been developed, e.g. ‘Degrees of Disturbance’ [ 21 ], ‘Good Practice Guide on Responding to Student Mental Health Issues: Duty of Care Responsibilities for Student Services in Higher Education’ [ 22 ] and the recent ‘The University Mental Health Charter’ [ 2 ]. Universities UK produced a Good Practice Guide in 2015 called “Student mental wellbeing in higher education” [ 23 ]. An increasing number of initiatives have emerged that are either student-led or jointly developed with students, and which reflect the increasing emphasis students and student bodies place on mental health and well-being and the increased demand for mental health support: Examples include: Nightline— www.nightline.ac.uk , Students Against Depression— www.studentsagainstdepression.org , Student Minds— www.studentminds.org.uk/student-minds-and-mental-wealth.html and The Alliance for Student-Led Wellbeing— www.alliancestudentwellbeing.weebly.com/ .
Although requests for professional support have increased substantially [ 24 ] only a third of students with mental health problems seek support from counselling services in the UK [ 12 ]. Many students encounter barriers to seeking help such as stigma or lack of awareness of services [ 25 ], and without formal support or intervention, there is a risk of deterioration. FE colleges and universities have identified the need to move beyond traditional forms of support and provide alternative, more accessible interventions aimed at improving mental health and well-being. Higher education institutions have a unique opportunity to identify, prevent, and treat mental health problems because they provide support in multiple aspects of students’ lives including academic studies, recreational activities, pastoral and counselling services, and residential accommodation.
In order to develop services that better meet the needs of students and design environments that are supportive of developing mental wellbeing it is necessary to explore and better understand the factors that lead to poor mental health in students.
Research objectives
The overall aim of this review was to identify, appraise and synthesise existing research evidence that explores the aetiology of poor mental health and mental wellbeing amongst students in tertiary level education. We aimed to gain a better understanding of the mechanisms that lead to poor mental health amongst tertiary level students and, in so doing, make evidence-based recommendations for policy, practice and future research priorities. Specific objectives in line with the project brief were to:
To co-produce with stakeholders a conceptual framework for exploring the factors associated with poorer mental health in students in tertiary settings. The factors may be both predictive, identifying students at risk, or causal, explaining why they are at risk. They may also be protective, promoting mental wellbeing.
To conduct a review drawing on qualitative studies, observational studies and surveys to explore the aetiology of poor mental health in students in university and college settings and identify factors which promote mental wellbeing amongst students.
To identify evidence-based recommendations for policy, service provision and future research that focus on prevention and early identification of poor mental health
Methodology
Identification of relevant evidence.
The following inclusion criteria were used to guide the development of the search strategy and the selection of studies.
We included students from a variety of further education settings (16 yrs + or 18 yrs + , including mature students, international students, distance learning students, students at specific transition points).
Universities and colleges in the UK. We were also interested in the context prior to the beginning of tertiary education, including factors during transition from home and secondary education or existing employment to tertiary education.
Any factor shown to be associated with mental health of students in tertiary level education. This included clinical indicators such as diagnosis and treatment and/or referral for depression and anxiety. Self-reported measures of wellbeing, happiness, stress, anxiety and depression were included. We did not include measures of academic achievement or engagement with learning as indicators of mental wellbeing.
Study design
We included cross-sectional and longitudinal studies that looked at factors associated with mental health outcomes in Table 5 .
Data extraction and quality appraisal
We extracted and tabulated key data from the included papers. Data extraction was undertaken by one reviewer, with a 10% sample checked for accuracy and consistency The quality of the included studies were evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale [ 26 ] and the findings of the quality appraisal used in weighting the strength of associations and also identifying gaps for future high quality research.
Involvement of stakeholders
We recruited students, ex-students and parents of students to a public involvement group which met on-line three times during the process of the review and following the completion of the review. During a workshop meeting we asked for members of the group to draw on their personal experiences to suggest factors which were not mentioned in the literature.
Methods of synthesis
We undertook a narrative synthesis [ 27 ] due to the heterogeneity in the exposures and outcomes that were measured across the studies. Data showing the direction of effects and the strength of the association (correlation coefficients) were recorded and tabulated to aid comparison between studies.
Search strategy
Searches were conducted in the following electronic databases: Medline, Applied Social Sciences Index and Abstracts (ASSIA), International Bibliography of Social Sciences (IBSS), Science,PsycINFO and Science and Social Sciences Ciatation Indexes. Additional searches of grey literature, and reference lists of included studies were also undertaken.
The search strategy combined a number of terms relating to students and mental health and risk factors. The search terms included both subject (MeSH) and free-text searches. The searches were limited to papers about humans in English, published from 2010 to June 2020. The flow of studies through the review process is summarised in Fig. 1 .
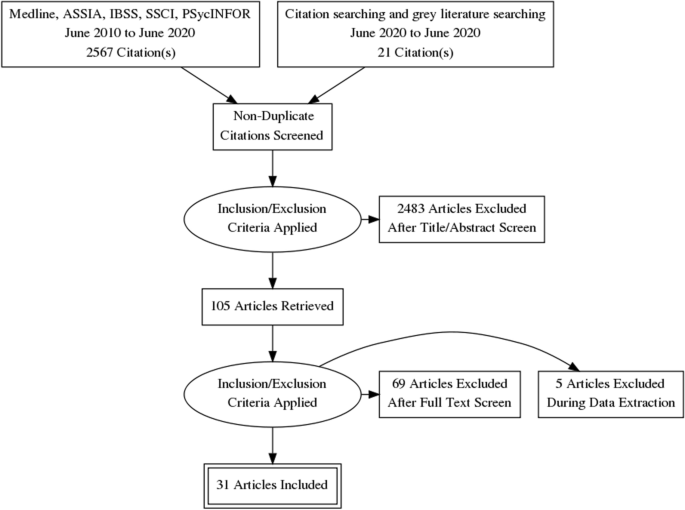
Flow diagram
The full search strategy for Medline is provided in Appendix 1 .
Thirty-one quantitative, observational studies (39 papers) met the inclusion criteria. The total number of students that participated in the quantitative studies was 17,476, with studies ranging in size from 57 to 3706. Eighteen studies recruited student participants from only one university; five studies (10 publications) [ 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 ] included seven or more universities. Six studies (7 publications) [ 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 ] only recruited first year students, while the majority of studies recruited students from a range of year groups. Five studies [ 39 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 ] recruited only, or mainly, psychology students which may impact on the generalisability of findings. A number of studies focused on students studying particular subjects including: nursing [ 46 ] medicine [ 47 ], business [ 48 ], sports science [ 49 ]. One study [ 50 ] recruited LGBTQ (lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, intersex, queer/questioning) students, and one [ 51 ] recruited students who had attended hospital having self-harmed. In 27 of the studies, there were more female than male participants. The mean age of the participants ranged from 19 to 28 years. Ethnicity was not reported in 19 of the studies. Where ethnicity was reported, the proportion that were ‘white British’ ranged from 71 – 90%. See Table 1 for a summary of the characteristics of the included studies and the participants.
Design and quality appraisal of the included studies
The majority of included studies ( n = 22) were cross-sectional surveys. Nine studies (10 publications) [ 35 , 36 , 39 , 41 , 43 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 62 ] were longitudinal in design, recording survey data at different time points to explore changes in the variables being measured. The duration of time that these studies covered ranged from 19 weeks to 12 years. Most of the studies ( n = 22) only recruited participants from a single university. The use of one university setting and the large number of studies that recruited only psychology students weakens the wider applicability of the included studies.
Quantitative variables
Included studies ( n = 31) measured a wide range of variables and explored their association with poor mental health and wellbeing. These included individual level factors: age, gender, sexual orientation, ethnicity and a range of psychological variables. They also included factors that related to mental health variables (family history, personal history and mental health literacy), pre-university factors (childhood trauma and parenting behaviour. University level factors including social isolation, adjustment and engagement with learning. Their association was measured against different measures of positive mental health and poor mental health.
Measurement of association and the strength of that association has some limitations in addressing our research question. It cannot prove causality, and nor can it capture fully the complexity of the inter-relationship and compounding aspect of the variables. For example, the stress of adjustment may be manageable, until it is combined with feeling isolated and out of place. Measurement itself may also be misleading, only capturing what is measureable, and may miss variables that are important but not known. We included both qualitative and PPI input to identify missed but important variables.
The wide range of variables and different outcomes, with few studies measuring the same variable and outcomes, prevented meta-analyses of findings which are therefore described narratively.
The variables described were categorised during the analyses into the following categories:
Vulnerabilities – factors that are associated with poor mental health
Individual level factors including; age, ethnicity, gender and a range of psychological variables were all measured against different mental health outcomes including depression, anxiety, paranoia, and suicidal behaviour, self-harm, coping and emotional intelligence.
Six studies [ 40 , 42 , 47 , 50 , 60 , 63 ] examined a student’s ages and association with mental health. There was inconsistency in the study findings, with studies finding that age (21 or older) was associated with fewer depressive symptoms, lower likelihood of suicide ideation and attempt, self-harm, and positively associated with better coping skills and mental wellbeing. This finding was not however consistent across studies and the association was weak. Theoretical models that seek to explain this mechanism have suggested that older age groups may cope better due to emotion-regulation strategies improving with age [ 67 ]. However, those over 30 experienced greater financial stress than those aged 17-19 in another study [ 63 ].
Sexual orientation
Four studies [ 33 , 40 , 64 , 68 ] examined the association between poor mental health and sexual orientation status. In all of the studies LGBTQ students were at significantly greater risk of mental health problems including depression [ 40 ], anxiety [ 40 ], suicidal behaviour [ 33 , 40 , 64 ], self harm [ 33 , 40 , 64 ], use of mental health services [ 33 ] and low levels of wellbeing [ 68 ]. The risk of mental health problems in these students compared with heterosexual students, ranged from OR 1.4 to 4.5. This elevated risk may reflect the greater levels of isolation and discrimination commonly experienced by minority groups.
Nine studies [ 33 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 42 , 47 , 50 , 60 , 63 ] examined whether gender was associated mental health variables. Two studies [ 33 , 47 ] found that being female was statistically significantly associated with use of mental health services, having a current mental health problem, suicide risk, self harm [ 33 ] and depression [ 47 ]. The results were not consistent, with another study [ 60 ] finding the association was not significant. Three studies [ 39 , 40 , 42 ] that considered mediating variables such as adaptability and coping found no difference or very weak associations.
Two studies [ 47 , 60 ] examined the extent to which ethnicity was associated with mental health One study [ 47 ] reported that the risks of depression were significantly greater for those who categorised themselves as non-white (OR 8.36 p = 0.004). Non-white ethnicity was also associated with poorer mental health in another cross-sectional study [ 63 ]. There was no significant difference in the McIntyre et al. (2018) study [ 60 ]. The small number of participants from ethnic minority groups represented across the studies means that this data is very limited.
Family factors
Six studies [ 33 , 40 , 42 , 50 , 60 ] explored the association of a concept that related to a student’s experiences in childhood and before going to university. Three studies [ 40 , 50 , 60 ] explored the impact of ACEs (Adverse Childhood Experiences) assessed using the same scale by Feletti (2009) [ 69 ] and another explored the impact of abuse in childhood [ 46 ]. Two studies examined the impact of attachment anxiety and avoidance [ 42 ], and parental acceptance [ 46 , 59 ]. The studies measured different mental health outcomes including; positive and negative affect, coping, suicide risk, suicide attempt, current mental health problem, use of mental health services, psychological adjustment, depression and anxiety.
The three studies that explored the impact of ACE’s all found a significant and positive relationship with poor mental health amongst university students. O’Neill et al. (2018) [ 50 ] in a longitudinal study ( n = 739) showed that there was in increased likelihood in self-harm and suicidal behaviours in those with either moderate or high levels of childhood adversities (OR:5.5 to 8.6) [ 50 ]. McIntyre et al. (2018) [ 60 ] ( n = 1135) also explored other dimensions of adversity including childhood trauma through multiple regression analysis with other predictive variables. They found that childhood trauma was significantly positively correlated with anxiety, depression and paranoia (ß = 0.18, 0.09, 0.18) though the association was not as strong as the correlation seen for loneliness (ß = 0.40) [ 60 ]. McLafferty et al. (2019) [ 40 ] explored the compounding impact of childhood adversity and negative parenting practices (over-control, overprotection and overindulgence) on poor mental health (depression OR 1.8, anxiety OR 2.1 suicidal behaviour OR 2.3, self-harm OR 2.0).
Gaan et al.’s (2019) survey of LGBTQ students ( n = 1567) found in a multivariate analyses that sexual abuse, other abuse from violence from someone close, and being female had the highest odds ratios for poor mental health and were significantly associated with all poor mental health outcomes [ 33 ].
While childhood trauma and past abuse poses a risk to mental health for all young people it may place additional stresses for students at university. Entry to university represents life stage where there is potential exposure to new and additional stressors, and the possibility that these students may become more isolated and find it more difficult to develop a sense of belonging. Students may be separated for the first time from protective friendships. However, the mechanisms that link childhood adversities and negative psychopathology, self-harm and suicidal behaviour are not clear [ 40 ]. McLafferty et al. (2019) also measured the ability to cope and these are not always impacted by childhood adversities [ 40 ]. They suggest that some children learn to cope and build resilience that may be beneficial.
McLafferty et al. (2019) [ 40 ] also studied parenting practices. Parental over-control and over-indulgence was also related to significantly poorer coping (OR -0.075 p < 0.05) and this was related to developing poorer coping scores (OR -0.21 p < 0.001) [ 40 ]. These parenting factors only became risk factors when stress levels were high for students at university. It should be noted that these studies used self-report, and responses regarding views of parenting may be subjective and open to interpretation. Lloyd et al.’s (2014) survey found significant positive correlations between perceived parental acceptance and students’ psychological adjustment, with paternal acceptance being the stronger predictor of adjustment.
Autistic students may display social communication and interaction deficits that can have negative emotional impacts. This may be particularly true during young adulthood, a period of increased social demands and expectations. Two studies [ 56 ] found that those with autism had a low but statistically significant association with poor social problem-solving skills and depression.
Mental health history
Three studies [ 47 , 51 , 68 ] investigated mental health variables and their impact on mental health of students in higher education. These included; a family history of mental illness and a personal history of mental illness.
Students with a family history or a personal history of mental illness appear to have a significantly greater risk of developing problems with mental health at university [ 47 ]. Mahadevan et al. (2010) [ 51 ] found that university students who self-harm have a significantly greater risk (OR 5.33) of having an eating disorder than a comparison group of young adults who self-harm but are not students.
Buffers – factors that are protective of mental wellbeing
Psychological factors.
Twelve studies [ 29 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 46 , 49 , 54 , 58 , 64 ] assessed the association of a range of psychological variables and different aspects of mental wellbeing and poor mental health. We categorised these into the following two categories: firstly, psychological variables measuring an individual’s response to change and stressors including adaptability, resilience, grit and emotional regulation [ 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 46 , 49 , 54 , 58 ] and secondly, those that measure self-esteem and body image [ 29 , 64 ].
The evidence from the eight included quantitative studies suggests that students with psychological strengths including; optimism, self-efficacy [ 70 ], resilience, grit [ 58 ], use of positive reappraisal [ 49 ], helpful coping strategies [ 42 ] and emotional intelligence [ 41 , 46 ] are more likely to experience greater mental wellbeing (see Table 2 for a description of the psychological variables measured). The positive association between these psychological strengths and mental well-being had a positive affect with associations ranging from r = 0.2–0.5 and OR1.27 [ 41 , 43 , 46 , 49 , 54 ] (low to moderate strength of association). The negative associations with depressive symptoms are also statistically significant but with a weaker association ( r = -0.2—0.3) [ 43 , 49 , 54 ].
Denovan (2017a) [ 43 ] in a longitudinal study found that the association between psychological strengths and positive mental wellbeing was not static and that not all the strengths remained statistically significant over time. The only factors that remained significant during the transition period were self-efficacy and optimism, remaining statistically significant as they started university and 6 months later.
Parental factors
Only one study [ 59 ] explored family factors associated with the development of psychological strengths that would equip young people as they managed the challenges and stressors encountered during the transition to higher education. Lloyd et al. (2014) [ 59 ] found that perceived maternal and paternal acceptance made significant and unique contributions to students’ psychological adjustment. Their research methods are limited by their reliance on retrospective measures and self-report measures of variables, and these results could be influenced by recall bias.
Two studies [ 29 , 64 ] considered the impact of how individuals view themselves on poor mental health. One study considered the impact of self-esteem and the association with non-accidental self-injury (NSSI) and suicide attempt amongst 734 university students. As rates of suicide and NSSI are higher amongst LGBT (lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender) students, the prevalence of low self-esteem was compared. There was a low but statistically significant association between low self-esteem and NSSI, though not for suicide attempt. A large survey, including participants from seven universities [ 42 ] compared depressive symptoms in students with marked body image concerns, reporting that the risk of depressive symptoms was greater (OR 2.93) than for those with lower levels of body image concerns.
Mental health literacy and help seeking behaviour
Two studies [ 48 , 68 ] investigated attitudes to mental illness, mental health literacy and help seeking for mental health problems.
University students who lack sufficient mental health literacy skills to be able to recognise problems or where there are attitudes that foster shame at admitting to having mental health problems can result in students not recognising problems and/or failing to seek professional help [ 48 , 68 ]. Gorcyznski et al. (2017) [ 68 ] found that women and those who had a history of previous mental health problems exhibited significantly higher levels of mental health literacy. Greater mental health literacy was associated with an increased likelihood that individuals would seek help for mental health problems. They found that many students find it hard to identify symptoms of mental health problems and that 42% of students are unaware of where to access available resources. Of those who expressed an intention to seek help for mental health problems, most expressed a preference for online resources, and seeking help from family and friends, rather than medical professionals such as GPs.
Kotera et al. (2019) [ 48 ] identified self-compassion as an explanatory variable, reducing social comparison, promoting self-acceptance and recognition that discomfort is an inevitable human experience. The study found a strong, significant correlation between self-compassion and mental health symptoms ( r = -0.6. p < 0.01).
There again appears to be a cycle of reinforcement, where poor mental health symptoms are felt to be a source of shame and become hidden, help is not sought, and further isolation ensues, leading to further deterioration in mental health. Factors that can interrupt the cycle are self-compassion, leading to more readiness to seek help (see Fig. 2 ).
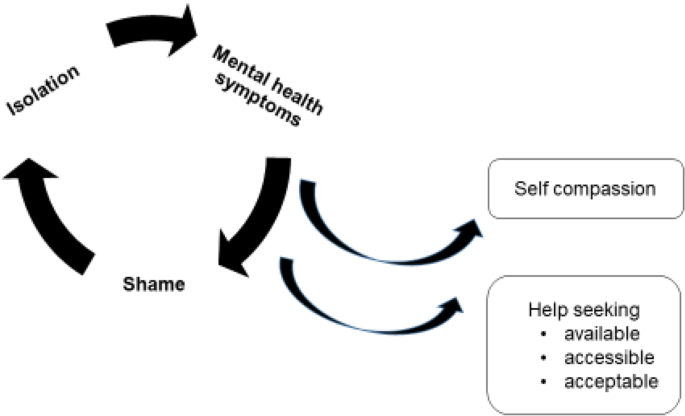
Poor mental health – cycles of reinforcement
Social networks
Nine studies [ 33 , 38 , 41 , 46 , 51 , 54 , 60 , 64 , 65 ] examined the concepts of loneliness and social support and its association with mental health in university students. One study also included students at other Higher Education Institutions [ 46 ]. Eight of the studies were surveys, and one was a retrospective case control study to examine the differences between university students and age-matched young people (non-university students) who attended hospital following deliberate self-harm [ 51 ].
Included studies demonstrated considerable variation in how they measured the concepts of social isolation, loneliness, social support and a sense of belonging. There were also differences in the types of outcomes measured to assess mental wellbeing and poor mental health. Grouping the studies within a broad category of ‘social factors’ therefore represents a limitation of this review given that different aspects of the phenomena may have been being measured. The tools used to measure these variables also differed. Only one scale (The UCLA loneliness scale) was used across multiple studies [ 41 , 60 , 65 ]. Diverse mental health outcomes were measured across the studies including positive affect, flourishing, self-harm, suicide risk, depression, anxiety and paranoia.
Three studies [ 41 , 60 , 62 ] measuring loneliness, two longitudinally [ 41 , 62 ], found a consistently positive association between loneliness and poor mental health in university students. Greater loneliness was linked to greater anxiety, stress, depression, poor general mental health, paranoia, alcohol abuse and eating disorder problems. The strength of the correlations ranged from 0–3-0.4 and were all statistically significant (see Tables 3 and 4 ). Loneliness was the strongest overall predictor of mental distress, of those measured. A strong identification with university friendship groups was most protective against distress relative to other social identities [ 60 ]. Whether poor mental health is the cause, or the result of loneliness was explored further in the studies. The results suggest that for general mental health, stress, depression and anxiety, loneliness induces or exacerbates symptoms of poor mental health over time [ 60 , 62 ]. The feedback cycle is evident, with loneliness leading to poor mental health which leads to withdrawal from social contacts and further exacerbation of loneliness.
Factors associated with protecting against loneliness by fostering supportive friendships and promoting mental wellbeing were also identified. Beliefs about the value of ‘leisure coping’, and attributes of resilience and emotional intelligence had a moderate, positive and significant association with developing mental wellbeing and were explored in three studies [ 46 , 54 , 66 ].
The transition to and first year at university represent critical times when friendships are developed. Thomas et al. (2020) [ 65 ] explored the factors that predict loneliness in the first year of university. A sense of community and higher levels of ‘social capital’ were significantly associated with lower levels of loneliness. ‘Social capital’ scales measure the development of emotionally supportive friendships and the ability to adjust to the disruption of old friendships as students transition to university. Students able to form close relationships within their first year at university are less likely to experience loneliness (r-0.09, r- 0.36, r- 0.34). One study [ 38 ] investigating the relationship between student experience and being the first in the family to attend university found that these students had lower ratings for peer group interactions.
Young adults at university and in higher education are facing multiple adjustments. Their ability to cope with these is influenced by many factors. Supportive friendships and a sense of belonging are factors that strengthen coping. Nightingale et al. (2012) undertook a longitudinal study to explore what factors were associated with university adjustment in a sample of first year students ( n = 331) [ 41 ]. They found that higher skills of emotion management and emotional self-efficacy were predictive of stable adjustment. These students also reported the lowest levels of loneliness and depression. This group had the skills to recognise their emotions and cope with stressors and were confident to access support. Students with poor emotion management and low levels of emotional self-efficacy may benefit from intervention to support the development of adaptive coping strategies and seeking support.
The positive and negative feedback loops
The relationship between the variables described appeared to work in positive and negative feedback loops with high levels of social capital easing the formation of a social network which acts as a critical buffer to stressors (see Fig. 3 ). Social networks and support give further strengthening and reinforcement, stimulating positive affect, engagement and flourishing. These, in turn, widen and deepen social networks for support and enhance a sense of wellbeing. Conversely young people who enter the transition to university/higher education with less social capital are less likely to identify with and locate a social network; isolation may follow, along with loneliness, anxiety, further withdrawal from contact with social networks and learning, and depression.
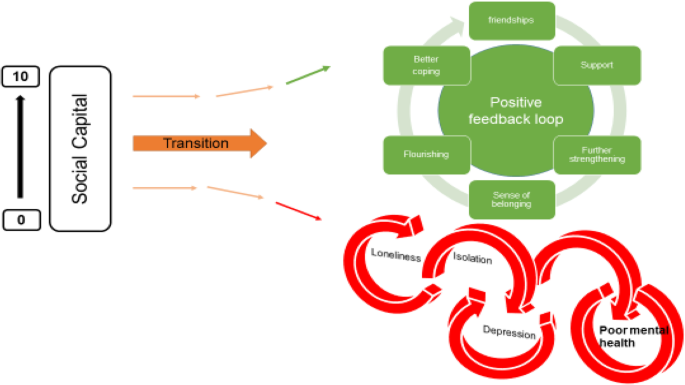
Triggers – factors that may act in combination with other factors to lead to poor mental health
Stress is seen as playing a key role in the development of poor mental health for students in higher education. Theoretical models and empirical studies have suggested that increases in stress are associated with decreases in student mental health [ 12 , 43 ]. Students at university experience the well-recognised stressors associated with academic study such as exams and course work. However, perhaps less well recognised are the processes of transition, requiring adapting to a new social and academic environment (Fisher 1994 cited by Denovan 2017a) [ 43 ]. Por et al. (2011) [ 46 ] in a small ( n = 130 prospective survey found a statistically significant correlation between higher levels of emotional intelligence and lower levels of perceived stress ( r = 0.40). Higher perceived stress was also associated with negative affect in two studies [ 43 , 46 ], and strongly negatively associated with positive affect (correlation -0.62) [ 54 ].
University variables
Eleven studies [ 35 , 39 , 47 , 51 , 52 , 54 , 60 , 63 , 65 , 83 , 84 ] explored university variables, and their association with mental health outcomes. The range of factors and their impact on mental health variables is limited, and there is little overlap. Knowledge gaps are shown by factors highlighted by our PPI group as potentially important but not identified in the literature (see Table 5 ). It should be noted that these may reflect the focus of our review, and our exclusion of intervention studies which may evaluate university factors.
High levels of perceived stress caused by exam and course work pressure was positively associated with poor mental health and lack of wellbeing [ 51 , 52 , 54 ]. Other potential stressors including financial anxieties and accommodation factors appeared to be less consistently associated with mental health outcomes [ 35 , 38 , 47 , 51 , 60 , 62 ]. Important mediators and buffers to these stressors are coping strategies and supportive networks (see conceptual model Appendix 2 ). One impact of financial pressures was that students who worked longer hours had less interaction with their peers, limiting the opportunities for these students to benefit from the protective effects of social support.
Red flags – behaviours associated with poor mental health and/or wellbeing
Engagement with learning and leisure activities.
Engagement with learning activities was strongly and positively associated with characteristics of adaptability [ 39 ] and also happiness and wellbeing [ 52 ] (see Fig. 4 ). Boulton et al. (2019) [ 52 ] undertook a longitudinal survey of undergraduate students at a campus-based university. They found that engagement and wellbeing varied during the term but were strongly correlated.
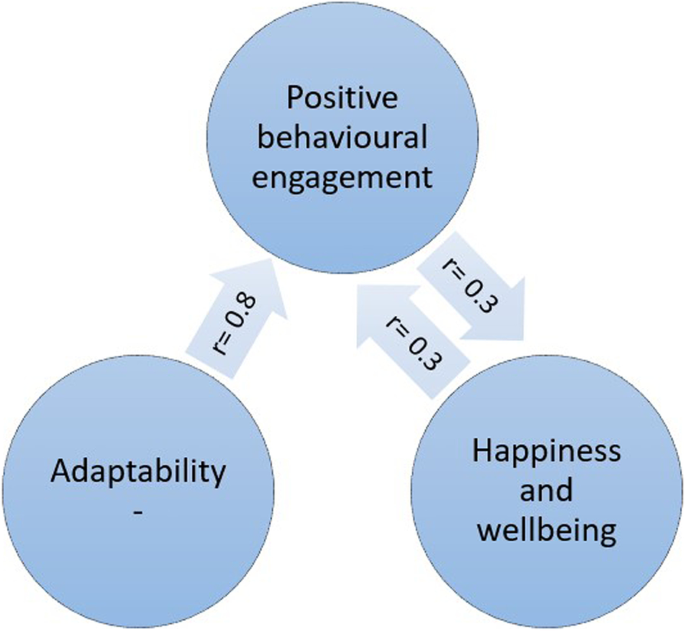
Engagement and wellbeing
Engagement occurred in a wide range of activities and behaviours. The authors suggest that the strong correlation between all forms of engagement with learning has possible instrumental value for the design of systems to monitor student engagement. Monitoring engagement might be used to identify changes in the behaviour of individuals to assist tutors in providing support and pastoral care. Students also were found to benefit from good induction activities provided by the university. Greater induction satisfaction was positively and strongly associated with a sense of community at university and with lower levels of loneliness [ 65 ].
The inte r- related nature of these variables is depicted in Fig. 4 . Greater adaptability is strongly associated with more positive engagement in learning and university life. More engagement is associated with higher mental wellbeing.
Denovan et al. (2017b) [ 54 ] explored leisure coping, its psychosocial functions and its relationship with mental wellbeing. An individual’s beliefs about the benefits of leisure activities to manage stress, facilitate the development of companionship and enhance mood were positively associated with flourishing and were negatively associated with perceived stress. Resilience was also measured. Resilience was strongly and positively associated with leisure coping beliefs and with indicators of mental wellbeing. The authors conclude that resilient individuals are more likely to use constructive means of coping (such as leisure coping) to proactively cultivate positive emotions which counteract the experience of stress and promote wellbeing. Leisure coping is predictive of positive affect which provides a strategy to reduce stress and sustain coping. The belief that friendships acquired through leisure provide social support is an example of leisure coping belief. Strong emotionally attached friendships that develop through participation in shared leisure pursuits are predictive of higher levels of well-being. Friendship bonds formed with fellow students at university are particularly important for maintaining mental health, and opportunities need to be developed and supported to ensure that meaningful social connections are made.
The ‘broaden-and-build theory’ (Fredickson 2004 [ 85 ] cited by [ 54 ]) may offer an explanation for the association seen between resilience, leisure coping and psychological wellbeing. The theory is based upon the role that positive and negative emotions have in shaping human adaptation. Positive emotions broaden thinking, enabling the individual to consider a range of ways of dealing with and adapting to their environment. Conversely, negative emotions narrow thinking and limit options for adapting. The former facilitates flourishing, facilitating future wellbeing. Resilient individuals are more likely to use constructive means of coping which generate positive emotion (Tugade & Fredrickson 2004 [ 86 ], cited by [ 54 ]). Positive emotions therefore lead to growth in coping resources, leading to greater well-being.
Health behaviours at university
Seven studies [ 29 , 31 , 38 , 45 , 51 , 54 , 66 ] examined how lifestyle behaviours might be linked with mental health outcomes. The studies looked at leisure activities [ 63 , 80 ], diet [ 29 ], alcohol use [ 29 , 31 , 38 , 51 ] and sleep [ 45 ].
Depressive symptoms were independently associated with problem drinking and possible alcohol dependence for both genders but were not associated with frequency of drinking and heavy episodic drinking. Students with higher levels of depressive symptoms reported significantly more problem drinking and possible alcohol dependence [ 31 ]. Mahadevan et al. (2010) [ 51 ] compared students and non-students seen in hospital for self-harm and found no difference in harmful use of alcohol and illicit drugs.
Poor sleep quality and increased consumption of unhealthy foods were also positively associated with depressive symptoms and perceived stress [ 29 ]. The correlation with dietary behaviours and poor mental health outcomes was low, but also confirmed by the negative correlation between less perceived stress and depressive symptoms and consumption of a healthier diet.
Physical activity and participation in leisure pursuits were both strongly correlated with mental wellbeing ( r = 0.4) [ 54 ], and negatively correlated with depressive symptoms and anxiety ( r = -0.6, -0.7) [ 66 ].
Thirty studies measuring the association between a wide range of factors and poor mental health and mental wellbeing in university and college students were identified and included in this review. Our purpose was to identify the factors that contribute to the growing prevalence of poor mental health amongst students in tertiary level education within the UK. We also aimed to identify factors that promote mental wellbeing and protect against deteriorating poor mental health.
Loneliness and social isolation were strongly associated with poor mental health and a sense of belonging and a strong support network were strongly associated with mental wellbeing and happiness. These associations were strongly positive in the eight studies that explored them and are consistent with other meta-analyses exploring the link between social support and mental health [ 87 ].
Another factor that appeared to be protective was older age when starting university. A wide range of personal traits and characteristics were also explored. Those associated with resilience, ability to adjust and better coping led to improved mental wellbeing. Better engagement appeared as an important mediator to potentially explain the relationship between these two variables. Engagement led to students being able to then tap into those features that are protective and promoting of mental wellbeing.
Other important risk factors for poor mental wellbeing that emerged were those students with existing or previous mental illness. Students on the autism spectrum and those with poor social problem-solving also were more likely to suffer from poor mental health. Negative self-image was also associated with poor mental health at university. Eating disorders were strongly associated with poor mental wellbeing and were found to be far more of a risk in students at university than in a comparative group of young people not in higher education. Other studies of university students also found that pre-existing poor mental health was a strong predictor of poor mental health in university students [ 88 ].
At a family level, the experience of childhood trauma and adverse experiences including, for example, neglect, household dysfunction or abuse, were strongly associated with poor mental health in young people at university. Students with a greater number of ‘adverse childhood experiences’ were at significantly greater risk of poor mental health than those students without experience of childhood trauma. This was also identified in a review of factors associated with depression and suicide related outcomes amongst university undergraduate students [ 88 ].
Our findings, in contrast to findings from other studies of university students, did not find that female gender associated with poor mental health and wellbeing, and it also found that being a mature student was protective of mental wellbeing.
Exam and course work pressure was associated with perceived stress and poor mental health. A lack of engagement with learning activities was also associated with poor mental health. A number of variables were not consistently shown to be associated with poor mental health including financial concerns and accommodation factors. Very little evidence related to university organisation or support structures was assessed in the evidence. One study found that a good induction programme had benefits for student mental wellbeing and may be a factor that enables students to become a part of a social network positive reinforcement cycle. Involvement in leisure activities was also found to be associated with improved coping strategies and better mental wellbeing. Students with poorer mental health tended to also eat in a less healthy manner, consume more harmful levels of alcohol, and experience poorer sleep.
This evidence review of the factors that influence mental health and wellbeing indicate areas where universities and higher education settings could develop and evaluate innovations in practice. These include:
Interventions before university to improve preparation of young people and their families for the transition to university.
Exploratory work to identify the acceptability and feasibility of identifying students at risk or who many be exhibiting indications of deteriorating mental health
Interventions that set out to foster a sense of belonging and identify
Creating environments that are helpful for building social networks
Improving mental health literacy and access to high quality support services
This review has a number of limitations. Most of the included studies were cross-sectional in design, with a small number being longitudinal ( n = 7), following students over a period of time to observe changes in the outcomes being measured. Two limitations of these sources of data is that they help to understand associations but do not reveal causality; secondly, we can only report the findings for those variables that were measured, and we therefore have to support causation in assuming these are the only factors that are related to mental health.
Furthermore, our approach has segregated and categorised variables in order to better understand the extent to which they impact mental health. This approach does not sufficiently explore or reveal the extent to which variables may compound one another, for example, feeling the stress of new ways of learning may not be a factor that influences mental health until it is combined with a sense of loneliness, anxiety about financial debt and a lack of parental support. We have used our PPI group and the development of vignettes of their experiences to seek to illustrate the compounding nature of the variables identified.
We limited our inclusion criteria to studies undertaken in the UK and published within the last decade (2009–2020), again meaning we may have limited our inclusion of relevant data. We also undertook single data extraction of data which may increase the risk of error in our data.
Understanding factors that influence students’ mental health and wellbeing offers the potential to find ways to identify strategies that enhance the students’ abilities to cope with the challenges of higher education. This review revealed a wide range of variables and the mechanisms that may explain how they impact upon mental wellbeing and increase the risk of poor mental health amongst students. It also identified a need for interventions that are implemented before young people make the transition to higher education. We both identified young people who are particularly vulnerable and the factors that arise that exacerbate poor mental health. We highlight that a sense of belonging and supportive networks are important buffers and that there are indicators including lack of engagement that may enable early intervention to provide targeted and appropriate support.
Availability of data and materials
Further details of the study and the findings can be provided on request to the lead author ([email protected]).
Association of Colleges. Association of Colleges’ survey on students with mental health conditions in further education. London: 2017.
Google Scholar
Hughes G, Spanner L. The University Mental Health Charter. Leeds: Student Minds; 2019.
Sivertsen B, Hysing M, Knapstad M, Harvey AG, Reneflot A, Lønning KJ, et al. Suicide attempts and non-suicidal self-harm among university students: prevalence study. BJPsych Open. 2019;5(2):e26.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Storrie K, Ahern K, Tuckett A. A systematic review: students with mental health problems—a growing problem. Int J Nurs Pract. 2010;16(1):1–6.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Pereira S, Reay K, Bottell J, Walker L, Dzikiti C, Platt C, Goodrham C. Student Mental Health Survey 2018: A large scale study into the prevalence of student mental illness within UK universities. 2019.
Bayram N, Bilgel N. The prevalence and socio-demographic correlations of depression, anxiety and stress among a group of university students. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2008;43(8):667–72.
Bewick B, Koutsopoulou G, Miles J, Slaa E, Barkham M. Changes in undergraduate students’ psychological well-being as they progress through university. Stud High Educ. 2010;35(6):633–45.
Article Google Scholar
Thorley C. Not By Degrees: Not by degrees: Improving student mental health in the UK’s universities. London: IPPR; 2017.
Eisenberg D, Golberstein E, Hunt JB. Mental health and academic success in college. BE J Econ Anal Pol. 2009;9(1):1–37.
Hysenbegasi A, Hass SL, Rowland CR. The impact of depression on the academic productivity of university students. J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2005;8(3):145.
PubMed Google Scholar
Chowdry H, Crawford C, Dearden L, Goodman A, Vignoles A. Widening participation in higher education: analysis using linked administrative data. J R Stat Soc A Stat Soc. 2013;176(2):431–57.
Macaskill A. The mental health of university students in the United Kingdom. Br J Guid Couns. 2013;41(4):426–41.
Belfield C, Britton J, van der Erve L. Higher Education finance reform: Raising the repayment threshold to£ 25,000 and freezing the fee cap at £ 9,250: Institute for Fiscal Studies Briefing note. London: Institute for Fiscal Studies; 2017. Available from https://ifs.org.uk/publications/9964 .
Benson-Egglenton J. The financial circumstances associated with high and low wellbeing in undergraduate students: a case study of an English Russell Group institution. J Furth High Educ. 2019;43(7):901–13.
Jessop DC, Herberts C, Solomon L. The impact of financial circumstances on student health. Br J Health Psychol. 2005;10(3):421–39.
(2020) SCSC. Canadians’ mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic. 2020.
(NUS) NUoS. Coronavirus Student Survey phase III November 2020. 2020.
Hellemans K, Abizaid A, Gabrys R, McQuaid R, Patterson Z. For university students, COVID-19 stress creates perfect conditions for mental health crises. The Conversation. 2020. Available from: https://theconversation.com/for-university-students-covid-19-stress-creates-perfect-conditions-for-mental-health-crises-149127 .
England N. Children and Young People with an Eating Disorder Waiting Times: NHS England; 2021 [Available from: https://www.england.nhs.uk/statistics/statistical-work-areas/cyped-waiting-times/
King JA, Cabarkapa S, Leow FH, Ng CH. Addressing international student mental health during COVID-19: an imperative overdue. Australas Psychiatry. 2020;28(4):469.
Rana R, Smith E, Walking J. Degrees of disturbance: the new agenda; the Impact of Increasing Levels of Psychological Disturbance Amongst Students in Higher Education. England: Association for University and College Counselling Rugby; 1999.
AMOSSHE. Responding to student mental health issues: 'Duty of Care' responsibilities for student services in higher education. https://www.amosshe.org.uk/resources/Documents/AMOSSHE_Duty_of_Care_2001.pdf [accessed 24.12.2020]. (2001).
Universities UK. Student mental wellbeing in higher education. Good practice guide. London: Universities UK; 2015.
Williams M, Coare P, Marvell R, Pollard E, Houghton A-M, Anderson J. 2015. Understanding provision for students with mental health problems and intensive support needs: Report to HEFCE by the Institute for Employment Studies (IES) and Researching Equity, Access and Partnership (REAP). Institute for Employment Studies.
Hunt J, Eisenberg D. Mental health problems and help-seeking behavior among college students. J Adolesc Health. 2010;46(1):3–10.
Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, Tugwell P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. In.: Oxford; 2000.
Campbell M, McKenzie JE, Sowden A, Katikireddi SV, Brennan SE, Ellis S, et al. Synthesis without meta-analysis (SWiM) in systematic reviews: reporting guideline. BMJ. 2020;368:l6890.
El Ansari W, Adetunji H, Oskrochi R. Food and mental health: relationship between food and perceived stress and depressive symptoms among university students in the United Kingdom. Cent Eur J Public Health. 2014a;22(2):90–7.
El Ansari W, Dibba E, Stock C. Body image concerns: levels, correlates and gender differences among students in the United Kingdom. Cent Eur J Public Health. 2014b;22(2):106–17.
Ansari EL, W, Oskrochi R, Stock C. Symptoms and health complaints and their association with perceived stress: Students from seven universities in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. J Public Health. 2013;21(5):413–25.
El Ansari W, Sebena R, Stock C. Do importance of religious faith and healthy lifestyle modify the relationships between depressive symptoms and four indicators of alcohol consumption? A survey of students across seven universities in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland. Subst Use Misuse. 2014c;49(3):211–20.
El Ansari W, Stock C. Is the health and wellbeing of university students associated with their academic performance? Cross sectional findings from the United Kingdom. International Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health [Electronic Resource]. 2010;7(2):509–27.
Gnan GH, Rahman Q, Ussher G, Baker D, West E, Rimes KA. General and LGBTQ-specific factors associated with mental health and suicide risk among LGBTQ students. J Youth Stud. 2019;22(10):1393–408.
Jackson SL, Dritschel B. Modeling the impact of social problem-solving deficits on depressive vulnerability in the broader autism phenotype. Res Aut Spectr Disord. 2016;21:128–38.
Richardson T, Elliott P, Roberts R. The impact of tuition fees amount on mental health over time in British students. J Public Health. 2015;37(3):412–8.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Richardson T, Mma Y, Jansen M, Elliott P, Roberts R. Financial difficulties and psychosis risk in British undergraduate students: a longitudinal analysis. J Public Ment Health. 2018;17(2):61–8.
Thomas L, Briggs P, Hart A, Kerrigan F. Understanding social media and identity work in young people transitioning to university. Comput Hum Behav. 2017;76:541–53.
Hixenbaugh P, Dewart H, Towell T. What enables students to succeed? An investigation of socio-demographic, health and student experience variables. Psychodyn Pract. 2012;18(3):285–301.
Holliman A, Martin A, Collie R. Adaptability, engagement, and degree completion: a longitudinal investigation of university students. Educ Psychol. 2018;38(6):785–99.
McLafferty M, Armour C, Bunting B, Ennis E, Lapsley C, Murray E, et al. Coping, stress, and negative childhood experiences: the link to psychopathology, self-harm, and suicidal behavior. Psychic J. 2019;8(3):293–306.
Nightingale S, Roberts S, Tariq V, Appleby Y, Barnes L, Harris R, et al. Trajectories of university adjustment in the United Kingdom: EMOTION management and emotional self-efficacy protect against initial poor adjustment. Learn Individ Differ. 2013;27:174–81.
Berry K, Kingswell S. An investigation of adult attachment and coping with exam-related stress. Br J Guid Couns. 2012;40(4):315.
Denovan A, Macaskill A. Stress and subjective well-being among first year UK undergraduate students. J Happiness Stud. 2017a;18(2):505–25.
Hassel S, Ridout N. An investigation of first-year students’ and lecturers’ expectations of university education. Front Psychol. 2018;8:2218.
Norbury R, Evans S. Time to think: subjective sleep quality, trait anxiety and university start time. Psychiatry Res. 2019;271:214–9.
Por J, Barriball L, Fitzpatrick J, Roberts J. Emotional intelligence: its relationship to stress, coping, well-being and professional performance in nursing students. Nurse Educ Today. 2011;31(8):855.
Honney K, Buszewicz M, Coppola W, Griffin M. Comparison of levels of depression in medical and non-medical students. Clin Teach. 2010;7(3):180–4.
Kotera Y, Conway E, Van Gordon W. Mental health of UK university business students: Relationship with shame, motivation and self-compassion. Journal of Education for Business. 2019;94(1):11–20.
Oliver EJ, Markland D, Hardy J. Interpretation of self-talk and post-lecture affective states of higher education students: a self-determination theory perspective. Br J Educ Psychol. 2010;80(Pt 2):307–23.
O’Neill S, McLafferty M, Ennis E, Lapsley C, Bjourson T, Armour C, et al. Socio-demographic, mental health and childhood adversity risk factors for self-harm and suicidal behaviour in College students in Northern Ireland. J Affect Disord. 2018;239:58–65.
Mahadevan S, Hawton K, Casey D. Deliberate self-harm in Oxford University students, 1993–2005: a descriptive and case-control study. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2010;45(2):211–9.
Boulton CA, Hughes E, Kent C, Smith JR, Williams HTP. Student engagement and wellbeing over time at a higher education institution. PLoS One [Electronic Resource]. 2019;14(11): e0225770.
Davies EL, Paltoglou AE. Public self-consciousness, pre-loading and drinking harms among university students. Subst Use Misuse. 2019;54(5):747–57.
Denovan A, Macaskill A. Stress, resilience and leisure coping among university students: Applying the broaden-and-build theory. Leisure Studies. 2017b;36(6):852–65.
El Ansari W, Vallentin-Holbech L, Stock C. Predictors of illicit drug/s use among university students in Northern Ireland, Wales and England. Glob J Health Sci. 2015;7(4):18–29.
Freeth M, Bullock T, Milne E. The distribution of and relationship between autistic traits and social anxiety in a UK student population. Autism. 2013;17(5):571–81.
Jessop DC, Reid M, Solomon L. Financial concern predicts deteriorations in mental and physical health among university students. Psychology Health. 2020;35(2):196–209.
Kannangara CS, Allen RE, Waugh G, Nahar N, Khan SZN, Rogerson S, Carson J. All that glitters is not grit: Three studies of grit in university students. Front Psychol. 2018;9:1539.
Lloyd J, Ward T, Young J. Do parental interpersonal power and prestige moderate the relationship between parental acceptance and psychological adjustment in U.K. Students? Cross-Cultural Research. The Journal of Comparative Social Science. 2014;48(3):326–35.
McIntyre JC, Worsley J, Corcoran R, Harrison Woods P, Bentall RP. Academic and non-academic predictors of student psychological distress: the role of social identity and loneliness. J Ment Health. 2018;27(3):230–9.
Ribchester C, Ross K, Rees EL. Examining the impact of pre-induction social networking on the student transition into higher education. Innov Educ Teach Int. 2014;51(4):355–65.
Richardson T, Elliott P, Roberts R. Relationship between loneliness and mental health in students. J Public Ment Health. 2017a;16(2):48–54.
Richardson T, Elliott P, Roberts R, Jansen M. A Longitudinal Study of Financial Difficulties and Mental Health in a National Sample of British Undergraduate Students. Community Ment Health J. 2017;53(3):344–52.
Taylor PJ, Dhingra K, Dickson JM, McDermott E. Psychological Correlates of Self-Harm within Gay, Lesbian and Bisexual UK University Students. Arch Suicide Res. 2020;24(sup1):41–56.
Thomas L, Orme E, Kerrigan F. Student loneliness: The role of social media through life transitions. Comput Educ. 2020;146:103754.
Tyson P, Wilson K, Crone D, Brailsford R, Laws K. Physical activity and mental health in a student population. J Ment Health. 2010;19(6):492–9.
Folkman S. The Oxford handbook of stress, health, and coping. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2011.
Gorczynski P, Sims-schouten W, Hill D, Wilson JC. Examining mental health literacy, help seeking behaviours, and mental health outcomes in UK university students. J Ment Health Train Educ Pract. 2017;12(2):111–20.
Felitti VJ. Adverse childhood experiences and adult health. Acad Pediatr. 2009;9(3):131–2.
Denovan A, Macaskill A. An interpretative phenomenological analysis of stress and coping in first year undergraduates. Br Educ Res J. 2013;39(6):1002–24.
Bandura A. Self-efficacy: The foundation of agency. Control of human behavior, mental processes, and consciousness: Essays in honor of the 60th birthday of August Flammer. 2000;16.
Martin AJ, Nejad H, Colmar S, Liem GAD. Adaptability: Conceptual and empirical perspectives on responses to change, novelty and uncertainty. J Psychol Couns Sch. 2012;22(1):58–81.
Lazarus RS, Folkman S. Stress, appraisal, and coping: Springer publishing company; 1984.
Gross JJ. Emotion regulation: Past, present, future. Cogn Emot. 1999;13(5):551–73.
Mayer JD, Salovey P, Caruso DR. TARGET ARTICLES:" Emotional Intelligence: Theory, Findings, and Implications". Psychol Inq. 2004;15(3):197–215.
Duckworth AL, Peterson C, Matthews MD, Kelly DR. Grit: perseverance and passion for long-term goals. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2007;92(6):1087.
Snyder CR, Ilardi SS, Cheavens J, Michael ST, Yamhure L, Sympson S. The role of hope in cognitive-behavior therapies. Cognit Ther Res. 2000;24(6):747–62.
Scheier MF, Carver CS, Bridges MW. Optimism, pessimism, and psychological well-being. 2001.
Seligman ME. Positive psychology in practice: Wiley; 2012.
Masten AS. Ordinary magic: Lessons from research on resilience in human development. Education Canada. 2009;49(3):28–32.
Rosenberg M, Schooler C, Schoenbach C, Rosenberg F. Global self-esteem and specific self-esteem: Different concepts, different outcomes. Am Sociol Rev. 1995:141–56.
Oliver EJ, Markland D, Hardy J. Interpretation of self-talk and post-lecture affective states of higher education students: A self-determination theory perspective. Br J Educ Psychol. 2010;80(2):307–23.
Hofmann W, Friese M, Strack F. Impulse and self-control from a dual-systems perspective. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2009;4(2):162–76.
Aceijas C, Waldhausl S, Lambert N, Cassar S, Bello-Corassa R. Determinants of health-related lifestyles among university students. Perspect Public Health. 2017;137(4):227–36.
Fredrickson BL. The broaden–and–build theory of positive emotions. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2004;359(1449):1367–77.
Tugade MM, Fredrickson BL, Feldman Barrett L. Psychological resilience and positive emotional granularity: Examining the benefits of positive emotions on coping and health. J Pers. 2004;72(6):1161–90.
Harandi TF, Taghinasab MM, Nayeri TD. The correlation of social support with mental health: A meta-analysis. Electron physician. 2017;9(9):5212.
Sheldon E, Simmonds-Buckley M, Bone C, Mascarenhas T, Chan N, Wincott M, Gleeson H, Sow K, Hind D, Barkham M. Prevalence and risk factors for mental health problems in university undergraduate students: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2021;287:282–92.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the input from our public advisory group which included current and former students, and family members of students who have struggled with their mental health. The group gave us their extremely valuable insights to assist our understanding of the evidence.
This project was supported by funding from the National Institute for Health Research as part of the NIHR Public Health Research Programme (fuding reference 127659 Public Health Review Team). The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NIHR or the Department of Health and Social Care.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK
Fiona Campbell, Lindsay Blank, Anna Cantrell, Susan Baxter, Christopher Blackmore, Jan Dixon & Elizabeth Goyder
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All of the included authors designed the project methods and prepared a protocol. A.C. designed the search strategy. F.C, L.B and C.B screened the identified citations and undertook data extraction. S.B. led the PPI involvement. JD participated as a member of the PPI group. F.C and L.B undertook the analysis. F.C. and L.B wrote the main manuscript text. All authors reviewed the manuscript. F.C designed Figs. 2 , 3 and 4 . The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Fiona Campbell .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable as this was secondary research.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
None of the authors have competing interests or other interests that might be perceived to influence the results and/or discussion reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1., additional file 2., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Campbell, F., Blank, L., Cantrell, A. et al. Factors that influence mental health of university and college students in the UK: a systematic review. BMC Public Health 22 , 1778 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-13943-x
Download citation
Received : 03 February 2022
Accepted : 25 July 2022
Published : 20 September 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-13943-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Student mental health
- Mental wellbeing
- Risk factors
- Rapid review
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Research Topics & Ideas: Mental Health
100+ Mental Health Research Topic Ideas To Fast-Track Your Project
If you’re just starting out exploring mental health topics for your dissertation, thesis or research project, you’ve come to the right place. In this post, we’ll help kickstart your research topic ideation process by providing a hearty list of mental health-related research topics and ideas.
PS – This is just the start…
We know it’s exciting to run through a list of research topics, but please keep in mind that this list is just a starting point . To develop a suitable education-related research topic, you’ll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap , and a viable plan of action to fill that gap.
If this sounds foreign to you, check out our free research topic webinar that explores how to find and refine a high-quality research topic, from scratch. Alternatively, if you’d like hands-on help, consider our 1-on-1 coaching service .
Overview: Mental Health Topic Ideas
- Mood disorders
- Anxiety disorders
- Psychotic disorders
- Personality disorders
- Obsessive-compulsive disorders
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Neurodevelopmental disorders
- Eating disorders
- Substance-related disorders

Mood Disorders
Research in mood disorders can help understand their causes and improve treatment methods. Here are a few ideas to get you started.
- The impact of genetics on the susceptibility to depression
- Efficacy of antidepressants vs. cognitive behavioural therapy
- The role of gut microbiota in mood regulation
- Cultural variations in the experience and diagnosis of bipolar disorder
- Seasonal Affective Disorder: Environmental factors and treatment
- The link between depression and chronic illnesses
- Exercise as an adjunct treatment for mood disorders
- Hormonal changes and mood swings in postpartum women
- Stigma around mood disorders in the workplace
- Suicidal tendencies among patients with severe mood disorders
Anxiety Disorders
Research topics in this category can potentially explore the triggers, coping mechanisms, or treatment efficacy for anxiety disorders.
- The relationship between social media and anxiety
- Exposure therapy effectiveness in treating phobias
- Generalised Anxiety Disorder in children: Early signs and interventions
- The role of mindfulness in treating anxiety
- Genetics and heritability of anxiety disorders
- The link between anxiety disorders and heart disease
- Anxiety prevalence in LGBTQ+ communities
- Caffeine consumption and its impact on anxiety levels
- The economic cost of untreated anxiety disorders
- Virtual Reality as a treatment method for anxiety disorders
Psychotic Disorders
Within this space, your research topic could potentially aim to investigate the underlying factors and treatment possibilities for psychotic disorders.
- Early signs and interventions in adolescent psychosis
- Brain imaging techniques for diagnosing psychotic disorders
- The efficacy of antipsychotic medication
- The role of family history in psychotic disorders
- Misdiagnosis and delayed treatment of psychotic disorders
- Co-morbidity of psychotic and mood disorders
- The relationship between substance abuse and psychotic disorders
- Art therapy as a treatment for schizophrenia
- Public perception and stigma around psychotic disorders
- Hospital vs. community-based care for psychotic disorders

Personality Disorders
Research topics within in this area could delve into the identification, management, and social implications of personality disorders.
- Long-term outcomes of borderline personality disorder
- Antisocial personality disorder and criminal behaviour
- The role of early life experiences in developing personality disorders
- Narcissistic personality disorder in corporate leaders
- Gender differences in personality disorders
- Diagnosis challenges for Cluster A personality disorders
- Emotional intelligence and its role in treating personality disorders
- Psychotherapy methods for treating personality disorders
- Personality disorders in the elderly population
- Stigma and misconceptions about personality disorders
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders
Within this space, research topics could focus on the causes, symptoms, or treatment of disorders like OCD and hoarding.
- OCD and its relationship with anxiety disorders
- Cognitive mechanisms behind hoarding behaviour
- Deep Brain Stimulation as a treatment for severe OCD
- The impact of OCD on academic performance in students
- Role of family and social networks in treating OCD
- Alternative treatments for hoarding disorder
- Childhood onset OCD: Diagnosis and treatment
- OCD and religious obsessions
- The impact of OCD on family dynamics
- Body Dysmorphic Disorder: Causes and treatment
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Research topics in this area could explore the triggers, symptoms, and treatments for PTSD. Here are some thought starters to get you moving.
- PTSD in military veterans: Coping mechanisms and treatment
- Childhood trauma and adult onset PTSD
- Eye Movement Desensitisation and Reprocessing (EMDR) efficacy
- Role of emotional support animals in treating PTSD
- Gender differences in PTSD occurrence and treatment
- Effectiveness of group therapy for PTSD patients
- PTSD and substance abuse: A dual diagnosis
- First responders and rates of PTSD
- Domestic violence as a cause of PTSD
- The neurobiology of PTSD

Neurodevelopmental Disorders
This category of mental health aims to better understand disorders like Autism and ADHD and their impact on day-to-day life.
- Early diagnosis and interventions for Autism Spectrum Disorder
- ADHD medication and its impact on academic performance
- Parental coping strategies for children with neurodevelopmental disorders
- Autism and gender: Diagnosis disparities
- The role of diet in managing ADHD symptoms
- Neurodevelopmental disorders in the criminal justice system
- Genetic factors influencing Autism
- ADHD and its relationship with sleep disorders
- Educational adaptations for children with neurodevelopmental disorders
- Neurodevelopmental disorders and stigma in schools
Eating Disorders
Research topics within this space can explore the psychological, social, and biological aspects of eating disorders.
- The role of social media in promoting eating disorders
- Family dynamics and their impact on anorexia
- Biological basis of binge-eating disorder
- Treatment outcomes for bulimia nervosa
- Eating disorders in athletes
- Media portrayal of body image and its impact
- Eating disorders and gender: Are men underdiagnosed?
- Cultural variations in eating disorders
- The relationship between obesity and eating disorders
- Eating disorders in the LGBTQ+ community
Substance-Related Disorders
Research topics in this category can focus on addiction mechanisms, treatment options, and social implications.
- Efficacy of rehabilitation centres for alcohol addiction
- The role of genetics in substance abuse
- Substance abuse and its impact on family dynamics
- Prescription drug abuse among the elderly
- Legalisation of marijuana and its impact on substance abuse rates
- Alcoholism and its relationship with liver diseases
- Opioid crisis: Causes and solutions
- Substance abuse education in schools: Is it effective?
- Harm reduction strategies for drug abuse
- Co-occurring mental health disorders in substance abusers

Choosing A Research Topic
These research topic ideas we’ve covered here serve as thought starters to help you explore different areas within mental health. They are intentionally very broad and open-ended. By engaging with the currently literature in your field of interest, you’ll be able to narrow down your focus to a specific research gap .
It’s important to consider a variety of factors when choosing a topic for your dissertation or thesis . Think about the relevance of the topic, its feasibility , and the resources available to you, including time, data, and academic guidance. Also, consider your own interest and expertise in the subject, as this will sustain you through the research process.
Always consult with your academic advisor to ensure that your chosen topic aligns with academic requirements and offers a meaningful contribution to the field. If you need help choosing a topic, consider our private coaching service.
Good morning everyone. This are very patent topics for research in neuroscience. Thank you for guidance
What if everything is important, original and intresting? as in Neuroscience. I find myself overwhelmd with tens of relveant areas and within each area many optional topics. I ask myself if importance (for example – able to treat people suffering) is more relevant than what intrest me, and on the other hand if what advance me further in my career should not also be a consideration?
This information is really helpful and have learnt alot
Phd research topics on implementation of mental health policy in Nigeria :the prospects, challenges and way forward.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- How it works

Useful Links
How much will your dissertation cost?
Have an expert academic write your dissertation paper!
Dissertation Services

Get unlimited topic ideas and a dissertation plan for just £45.00
Order topics and plan

Get 1 free topic in your area of study with aim and justification
Yes I want the free topic

Mental Health Dissertation Topics & Titles
Published by Carmen Troy at January 9th, 2023 , Revised On June 10, 2024
You probably found your way here looking for mental health topics for your final year research project. Look no further, we have drafted a list of issues, and their research aims to help you when you are brainstorming for dissertation or thesis topics on mental health.
PhD-qualified writers of our team have developed these topics, so you can trust to use these topics for drafting your dissertation.
You may also want to start your dissertation by requesting a brief research proposal or full dissertation service from our writers on any of these topics, which includes an introduction to the topic, research question , aim and objectives, literature review , and the proposed research methodology to be conducted. Let us know if you need any help in getting started.
Check our dissertation examples to understand how to structure your dissertation .
Also read: Psychology dissertation topics & nursing dissertation topics
List Of Trending Mental Health Research Topics & Ideas
- The Impact of Social Media on Body Image and Self Esteem in Youngsters.
- How Does Loneliness Link to Depression in People Above the Age of 70
- The Effects of Israeli-Palestinian Conflicts on the Mental Health of Children in Gaza
- The Impact of Posting Pictures From War on the Mental Health of Viewers
- The Effectiveness of Excercise Programs in Managing Symptoms of Depression
- Role of Cultural Competency in Providing Effective Mental Healthcare for Diverse Populations
- The Impact of Social Stigma on Help-Seeking Behaviours for Mental Health Concerns
- The Effectiveness of Art Therapy Interventions in Managing Symptoms of Post-traumatic Stress Disorder (Ptsd)
- How Group Therapy Interventions Impacts Promoting Social Connection and Reducing Loneliness
- Animal-Assisted Therapy Interventions in Reducing Symptoms of Anxiety and Depression
- Psychedelic-Assisted Psychotherapy in Treating Eating Disorders
Latest Mental Health Dissertation Topics
Review the step-by-step guide on how to write your dissertation here .
Topic 1: An assessment of the Influence of Parents' Divorce or Separation on Adolescent Children in terms of long-term psychological impact.
Research Aim: This study aims to investigate the level of traumas experienced by the children of divorced or separated parents. The principal aim of this study is to explore the long-term psychological impacts of parents’ divorce on the life of children regardless of their gender and age in terms of mental wellbeing, academic performance, and self-worth.
Topic 2: An investigation of the impact of Trauma and Health-related quality of life on the Mental health and Self-worth of a child.
Research Aim: This study aims to assess the long-term impacts of the trauma children face in their early years of life on their overall mental health. Also, numerous studies have emphasised improving the quality of life for children who tend to experience multiple traumas and take them along in adulthood. Therefore, this study also proposed the impacts of traumatic childhood experiences on self-worth, mental health, and vitality of implementing firm intervention before the child reaches adulthood.
Topic 3: Assessing the effect of Psychological training on males suffering from Post-Surgery Anxiety in the UK.
Research Aim: Postoperative problems may occur as a result of surgical stress. This study aims to examine different approaches to control post-surgical anxiety and improve patients’ lives in the short and long term, focusing on male patients in the UK. It will also give us an understanding of how psychological training and interventions affect anxiety in male patients and help them overcome this through a systematic review.
Topic 4: Investigating the Relationship between Mental illness and Suicides- A case study of UK's Young Adults.
Research Aim: This study aims to find the relationship between mental illness and suicides and risk factors in the UK. This study will specifically focus on young adults. It will examine different mental disorders and how they have led to suicide and will analyse further studies of people who have died by suicide and find evidence of the presence or absence of mental illness.
Topic 5: Examining the behaviour of Mental Health Nurses taking care of Schizophrenia Patients in the UK.
Research Aim: Negative behaviours and discrimination have been usually reported as a reason for the inconvenience in the treatment of mentally ill or schizophrenia patients, which negatively impacts the patient’s results. Healthcare professionals’ attitudes have been regarded as being more negative than the general public, which lowers the outlook for patients suffering from mental illness. This study will examine the behaviour of mental health nurses regarding schizophrenia patients in the UK and also focus on the characteristics associated with nurses’ attitudes.
COVID-19 Mental Health Research Topics
Topic1: impacts of the coronavirus on the mental health of various age groups.
Research Aim: This study will reveal the impacts of coronavirus on the mental health of various age groups
Topic 2: Mental health and psychological resilience during COVID-19
Research Aim: Social distancing has made people isolated and affected their mental health. This study will highlight various measures to overcome the stress and mental health of people during coronavirus.
Topic 3: The mental health of children and families during COVID-19
Research Aim: This study will address the challenging situations faced by children and families during lockdown due to COVID-19. It will also discuss various ways to overcome the fear of disease and stay positive.
Topic 4: Mental wellbeing of patients during the Coronavirus pandemic
Research Aim: This study will focus on the measures taken by the hospital management, government, and families to ensure patients’ mental well-being, especially COVID-19 patients.
Best Mental Health Topics for Your Dissertation
Topic 1: kids and their relatives with cancer: psychological challenges.
Research Aim: In cancer diagnoses and therapies, children often don’t know what happens. Many have psychosocial problems, including rage, terror, depression, disturbing sleep, inexpiable guilt, and panic. Therefore, this study is designed to identify and treat the child and its family members’ psychological issues.
Topic 2: Hematopoietic device reaction in ophthalmology patient’s radiation therapy
Research Aim: This research is based on the analysis of hematopoietic devices’ reactions to ophthalmology radiation.
Topic 3: Psychological effects of cyberbullying Vs. physical bullying: A counter study
Research Aim: This research will focus on the effects of cyberbullying and physical bullying and their consequences on the victim’s mental health. The most significant part is the counter effects on our society’s environment and human behaviour, particularly youth.
Topic 4: Whether or not predictive processing is a theory of perceptual consciousness?
Research Aim: This research aims to identify whether or not predictive processing is a theory of perceptual consciousness.
Topic 5: Importance of communication in a relationship
Research Aim: This research aims to address the importance of communication in relationships and the communication gap consequences.
Topic 6: Eating and personality disorders
Research Aim: This research aims to focus on eating and personality disorders
Topic 7: Analysis of teaching, assessment, and evaluation of students and learning differences
Research Aim: This research aims to analyse teaching methods, assessment, and evaluation systems of students and their learning differences
Topic 8: Social and psychological effects of virtual networks
Research Aim: This research aims to study the social and psychological effects of virtual networks
Topic 9: The role of media in provoking aggression
Research Aim: This research aims to address the role of media in provoking aggression among people
Mental Health Topics for Your Dissertation For Research
Topic 1: what is the impact of social media platforms on the mental wellbeing of adults.
Research Aim: the current study aims to investigate the impact social media platforms tend to have on adults’ mental well-being with a particular focus on the United Kingdom. While many studies have been carried out to gauge the impact of social media platforms on teenagers’ mental well-being, little to no research has been performed to investigate how the health of adults might be affected by the same and how social media platforms like Facebook impact them.
Topic 2: The contemporary practical management approach to treating personality disorders
Research Aim: This research will discuss the contemporary practical management approach for treating personality disorders in mental health patients. In the previous days, much of the personality disorder treatments were based on medicines and drugs. Therefore, this research will address contemporary and practical ways to manage how personality disorders affect the mental state of the individuals who have the disease.
Topic 3: How is Prozac being used in the modern-day to treat self-diagnosed depression?
Research Aim: In the current day and age, besides people suffering from clinical depression, many teens and adults have started to suffer from self-diagnosed depression. To treat their self-diagnosed depression, individuals take Prozac through all the wrong means, which harms their mental state even more. Therefore, the current study aims to shed light on how Prozac is being used in the modern age and the adverse effects of misinformed use on patients.
Topic 4: Are women more prone to suffer from mental disorders than men: A Comparative analysis
Research Aim: There have been several arguments regarding whether women are more likely to suffer from mental disorders than men. Much of the research carried out provides evidence that women are more prone to suffer from mental disorders. This research study aims to conduct a comparative analysis to determine whether it’s more likely for men or women to suffer from mental disorders and what role biological and societal factors play in determining the trend.
Topic 5: The impact of breakups on the mental health of men?
Research Aim: Several studies have been carried out to discuss how women are affected more by a breakup than men. However, little research material is available in support of the impact the end of a relationship can have on men’s mental health. Therefore, this research study will fill out the gap in research to determine the impact of a breakup on men’s mental health and stability.
Topic 6: A theoretical analysis of the Impact of emotional attachment on mental health?
Research Aim: This research aims to analyse the theories developed around emotional attachment to address how emotional attachment can harm individuals’ mental health across the globe. Several theories discuss the role that emotional attachment tends to play in the mind of a healthy being, and how emotional attachment can often negatively affect mental well-being.
Topic 7: How do social media friendships contribute to poor mental health?
Research Aim: This research idea aims to address how social media friendships and networking can often lead to a lack of self-acceptance, self-loathing, self-pity, self-comparison, and depression due to the different mindsets that are present in today’s world.
Topic 8: What role do parents play in ensuring the mental well-being of their children?
Research Aim: It is assumed that parents tend to stop playing a role in ensuring that the mental health and well-being of their children are being maintained after a certain age. Therefore, this study will aim to put forward the idea that even after the children pass the age of 18, activities and their relationship with their parents will always play a role in the way their mental health is being transformed.
Topic 9: A study on the mental health of soldiers returning from Iraq?
Research Aim: This topic idea puts forward the aim that the mental health of soldiers who return from war-struck areas is always a subject of interest, as each of the soldiers carries a mental burden. Therefore, it is vital to understand the soldiers’ mental health returning from Iraq, focusing on what causes their mental health to deteriorate during the war and suggestions of what to do or who to call if they do become unwell.
Topic 10: How the contemporary media practices in the UK are leading to mental health problems?
Research Aim: The media is known to have control and influence over people’s mindsets who are connected to it. Many of the contemporary media practices developed in the UK can negatively impact the mental well-being of individuals, which makes it necessary to analyse how they are contributing to the mental health problems among the UK population.
Topic 11: What is the impact of television advertising on the mental development of children in the UK?
Research Aim: This topic aims to address how television advertising can negatively impact children’s mental development in the United Kingdom, as it has been observed in many studies that television advertising is detrimental to the mental health of children.
Topic 12: How deteriorating mental health can have an Impact on physical health?
Research Aim: This research aims to address the side-effects of deteriorating mental health on the physical health of individuals in society, as it is believed that the majority of the physical ailments in the modern-day age are due to the deteriorating mental health of individuals. The study can address the treatments for many ailments in our society due to deteriorating mental health and well-being.
Topic 13: The relationship between unemployment and mental health
Research Aim: How unemployment relates to concepts, such as a declining economy or lack of social skills and education, has been frequently explored by many researchers in the past. However, not many have discussed the relationship between unemployment and the mental health of unemployed individuals. Therefore, this topic will help address the problems faced by individuals due to unemployment because of the mental blocks they are likely to develop and experience. In the future, it will lead to fewer people being depressed due to unemployment when further research is carried out.
Topic 14: The mental health problems of prisoners in the United Kingdom
Research Aim: While prisoners across the globe are criticised and studied for the negativity that goes on in their mindsets, one would rarely research the mental health problems they tend to develop when they become prisoners for committing any crime. It is often assumed that it is the life inside the prison walls that impacts the prisoners’ mental health in a way that leads to them committing more crimes. Therefore, this research topic has been developed to study prison’s impact on prisoners’ mental well-being in the United Kingdom to eventually decrease the number of crimes that occur due to the negative environment inside the prisons.
Topic 15: Mental well-being of industry workers in China
Research Aim: While many research studies have been carried out regarding the conditions that the workers in China tend to be exposed to, there is very little supporting evidence regarding the impact such working conditions have on the mindset and mental health of the workers. Therefore, this study aims to address the challenges faced by industry workers in China and the impact that such challenges can have on their mental well-being.
Topic 16: Is the provision of mental health care services in the United Kingdom effective?
Research Aim: Many people have made different assumptions regarding the mental health care services provided across the globe. However, it seems that little to no research has been carried out regarding the efficiency and effectiveness of the provision of mental health care services in the United Kingdom. Therefore, this study aims to put forward research into the mental health care services provided in well-developed countries like the United Kingdom to gauge the awareness and importance of mental health in the region.
Topic 17: What are the mental health problems that minorities in the United Kingdom face?
Research Aim: It is believed that minorities in the United Kingdom are likely to experience physical abuse, and societal abuse and are often exposed to discrimination and unfair acts at the workplace and in their social circle. The study investigates the range of mental problems faced by minorities in the UK, which need to be addressed to have equality, diversity, and harmony.
Topic 18: The impact the Coronavirus has had on the mental health of the Chinese people
Research Aim: The spread of the deadly Coronavirus has led to many deaths in the region of China, and many of those who have been suspected of the virus are being put in isolation and quarantine. Such conditions tend to hurt the mental health of those who have suffered from the disease and those who have watched people suffer from it. Therefore, the current study aims to address how the Coronavirus has impacted the mental health of the Chinese people.
Topic 19: How to create change in mental health organisations in China?
Research Aim: Research suggests little awareness about mental health in many Asian countries. As mental health problems are on the rise across the globe, it is necessary to change mental health organisations. Therefore, the study aims to discuss how to create change in mental health organisations in the Asian region using China’s example.
Topic 20: Addressing the mental health concerns of the Syrian refugees in the UK
Research Aim: This research project would address the concerns in terms of the refugees’ mental health and well-being, using an example of the Syrian refugees who had been allowed entry into the United Kingdom. This idea aims to put forward the negative effects that migration can have on refugees and how further research is required to combat such issues not just in the United Kingdom but worldwide.
How Can ResearchProspect Help?
ResearchProspect writers can send several custom topic ideas to your email address. Once you have chosen a topic that suits your needs and interests, you can order for our dissertation outline service which will include a brief introduction to the topic, research questions , literature review , methodology , expected results , and conclusion . The dissertation outline will enable you to review the quality of our work before placing the order for our full dissertation writing service!
Important Notes:
As a mental health student looking to get good grades, it is essential to develop new ideas and experiment on existing mental health theories – i.e., to add value and interest in the topic of your research.
Mental health is vast and interrelated to so many other academic disciplines like civil engineering , construction , project management , engineering management , healthcare , finance and accounting , artificial intelligence , tourism , physiotherapy , sociology , management , project management , and nursing . That is why it is imperative to create a project management dissertation topic that is articular, sound, and actually solves a practical problem that may be rampant in the field.
We can’t stress how important it is to develop a logical research topic based on your entire research. There are several significant downfalls to getting your topic wrong; your supervisor may not be interested in working on it, the topic has no academic creditability, the research may not make logical sense, and there is a possibility that the study is not viable.
This impacts your time and efforts in writing your dissertation as you may end up in a cycle of rejection at the initial stage of the dissertation. That is why we recommend reviewing existing research to develop a topic, taking advice from your supervisor, and even asking for help in this particular stage of your dissertation.
While developing a research topic, keeping our advice in mind will allow you to pick one of the best mental health dissertation topics that fulfill your requirement of writing a research paper and add to the body of knowledge.
Therefore, it is recommended that when finalising your dissertation topic, you read recently published literature to identify gaps in the research that you may help fill.
Remember- dissertation topics need to be unique, solve an identified problem, be logical, and be practically implemented. Please look at some of our sample mental health dissertation topics to get an idea for your own dissertation.
How to Structure Your Mental Health Dissertation
A well-structured dissertation can help students to achieve a high overall academic grade.
- A Title Page
- Acknowledgements
- Declaration
- Abstract: A summary of the research completed
- Table of Contents
- Introduction : This chapter includes the project rationale, research background, key research aims and objectives, and the research problems. An outline of the structure of a dissertation can also be added to this chapter.
- Literature Review : This chapter presents relevant theories and frameworks by analysing published and unpublished literature available on the chosen research topic to address research questions . The purpose is to highlight and discuss the selected research area’s relative weaknesses and strengths whilst identifying any research gaps. Break down the topic, and key terms that can positively impact your dissertation and your tutor.
- Methodology : The data collection and analysis methods and techniques employed by the researcher are presented in the Methodology chapter which usually includes research design , research philosophy, research limitations, code of conduct, ethical consideration, data collection methods, and data analysis strategy .
- Findings and Analysis : Findings of the research are analysed in detail under the Findings and Analysis chapter. All key findings/results are outlined in this chapter without interpreting the data or drawing any conclusions. It can be useful to include graphs, charts, and tables in this chapter to identify meaningful trends and relationships.
- Discussion and Conclusion : The researcher presents his interpretation of results in this chapter and states whether the research hypothesis has been verified or not. An essential aspect of this section of the paper is to draw a linkage between the results and evidence from the literature. Recommendations with regard to the implications of the findings and directions for the future may also be provided. Finally, a summary of the overall research, along with final judgments, opinions, and comments, must be included in the form of suggestions for improvement.
- References : This should be completed following your University’s requirements
- Bibliography
- Appendices : Any additional information, diagrams, and graphs used to complete the dissertation but not part of the dissertation should be included in the Appendices chapter. Essentially, the purpose is to expand the information/data.
About ResearchProspect Ltd
ResearchProspect is the world’s best academic writing service that provides help with Dissertation Proposal Writing , PhD Proposal Writing , Dissertation Writing , Dissertation Editing, and Improvement .
Our team of writers is highly qualified. They are experts in their respective fields. They have been working in the industry for a long, thus are aware of the issues and the trends of the industry they are working in.
Free Dissertation Topic
Phone Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Graduate PHD
Academic Subject
Area of Research
Frequently Asked Questions
How to find mental health dissertation topics.
To find mental health dissertation topics:
- Research recent mental health issues.
- Examine gaps in existing literature.
- Consider diverse populations or perspectives.
- Explore treatment approaches or therapies.
- Look into stigma and societal factors.
- Select a topic that resonates with you for in-depth study.
You May Also Like
Students will undoubtedly experience anxiety when working on their dissertations on educational management. It is a fact that a topic like this necessitates in-depth study, and the paper.
Are you looking for dissertation topics in the field of climate change? Research Prospect offers a wide range of topics that will help you write your dissertation.
Most people associate nurses with white dresses and nursing caps. However, nursing is much more diversified than that. The fact that nursing offers many specialties and career options is no longer surprising.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works

Student mental health is in crisis. Campuses are rethinking their approach
Amid massive increases in demand for care, psychologists are helping colleges and universities embrace a broader culture of well-being and better equipping faculty to support students in need
Vol. 53 No. 7 Print version: page 60
- Mental Health

By nearly every metric, student mental health is worsening. During the 2020–2021 school year, more than 60% of college students met the criteria for at least one mental health problem, according to the Healthy Minds Study, which collects data from 373 campuses nationwide ( Lipson, S. K., et al., Journal of Affective Disorders , Vol. 306, 2022 ). In another national survey, almost three quarters of students reported moderate or severe psychological distress ( National College Health Assessment , American College Health Association, 2021).
Even before the pandemic, schools were facing a surge in demand for care that far outpaced capacity, and it has become increasingly clear that the traditional counseling center model is ill-equipped to solve the problem.
“Counseling centers have seen extraordinary increases in demand over the past decade,” said Michael Gerard Mason, PhD, associate dean of African American Affairs at the University of Virginia (UVA) and a longtime college counselor. “[At UVA], our counseling staff has almost tripled in size, but even if we continue hiring, I don’t think we could ever staff our way out of this challenge.”
Some of the reasons for that increase are positive. Compared with past generations, more students on campus today have accessed mental health treatment before college, suggesting that higher education is now an option for a larger segment of society, said Micky Sharma, PsyD, who directs student life’s counseling and consultation service at The Ohio State University (OSU). Stigma around mental health issues also continues to drop, leading more people to seek help instead of suffering in silence.
But college students today are also juggling a dizzying array of challenges, from coursework, relationships, and adjustment to campus life to economic strain, social injustice, mass violence, and various forms of loss related to Covid -19.
As a result, school leaders are starting to think outside the box about how to help. Institutions across the country are embracing approaches such as group therapy, peer counseling, and telehealth. They’re also better equipping faculty and staff to spot—and support—students in distress, and rethinking how to respond when a crisis occurs. And many schools are finding ways to incorporate a broader culture of wellness into their policies, systems, and day-to-day campus life.
“This increase in demand has challenged institutions to think holistically and take a multifaceted approach to supporting students,” said Kevin Shollenberger, the vice provost for student health and well-being at Johns Hopkins University. “It really has to be everyone’s responsibility at the university to create a culture of well-being.”
Higher caseloads, creative solutions
The number of students seeking help at campus counseling centers increased almost 40% between 2009 and 2015 and continued to rise until the pandemic began, according to data from Penn State University’s Center for Collegiate Mental Health (CCMH), a research-practice network of more than 700 college and university counseling centers ( CCMH Annual Report , 2015 ).
That rising demand hasn’t been matched by a corresponding rise in funding, which has led to higher caseloads. Nationwide, the average annual caseload for a typical full-time college counselor is about 120 students, with some centers averaging more than 300 students per counselor ( CCMH Annual Report , 2021 ).
“We find that high-caseload centers tend to provide less care to students experiencing a wide range of problems, including those with safety concerns and critical issues—such as suicidality and trauma—that are often prioritized by institutions,” said psychologist Brett Scofield, PhD, executive director of CCMH.
To minimize students slipping through the cracks, schools are dedicating more resources to rapid access and assessment, where students can walk in for a same-day intake or single counseling session, rather than languishing on a waitlist for weeks or months. Following an evaluation, many schools employ a stepped-care model, where the students who are most in need receive the most intensive care.
Given the wide range of concerns students are facing, experts say this approach makes more sense than offering traditional therapy to everyone.
“Early on, it was just about more, more, more clinicians,” said counseling psychologist Carla McCowan, PhD, director of the counseling center at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. “In the past few years, more centers are thinking creatively about how to meet the demand. Not every student needs individual therapy, but many need opportunities to increase their resilience, build new skills, and connect with one another.”
Students who are struggling with academic demands, for instance, may benefit from workshops on stress, sleep, time management, and goal-setting. Those who are mourning the loss of a typical college experience because of the pandemic—or facing adjustment issues such as loneliness, low self-esteem, or interpersonal conflict—are good candidates for peer counseling. Meanwhile, students with more acute concerns, including disordered eating, trauma following a sexual assault, or depression, can still access one-on-one sessions with professional counselors.
As they move away from a sole reliance on individual therapy, schools are also working to shift the narrative about what mental health care on campus looks like. Scofield said it’s crucial to manage expectations among students and their families, ideally shortly after (or even before) enrollment. For example, most counseling centers won’t be able to offer unlimited weekly sessions throughout a student’s college career—and those who require that level of support will likely be better served with a referral to a community provider.
“We really want to encourage institutions to be transparent about the services they can realistically provide based on the current staffing levels at a counseling center,” Scofield said.
The first line of defense
Faculty may be hired to teach, but schools are also starting to rely on them as “first responders” who can help identify students in distress, said psychologist Hideko Sera, PsyD, director of the Office of Equity, Inclusion, and Belonging at Morehouse College, a historically Black men’s college in Atlanta. During the pandemic, that trend accelerated.
“Throughout the remote learning phase of the pandemic, faculty really became students’ main points of contact with the university,” said Bridgette Hard, PhD, an associate professor and director of undergraduate studies in psychology and neuroscience at Duke University. “It became more important than ever for faculty to be able to detect when a student might be struggling.”
Many felt ill-equipped to do so, though, with some wondering if it was even in their scope of practice to approach students about their mental health without specialized training, Mason said.
Schools are using several approaches to clarify expectations of faculty and give them tools to help. About 900 faculty and staff at the University of North Carolina have received training in Mental Health First Aid , which provides basic skills for supporting people with mental health and substance use issues. Other institutions are offering workshops and materials that teach faculty to “recognize, respond, and refer,” including Penn State’s Red Folder campaign .
Faculty are taught that a sudden change in behavior—including a drop in attendance, failure to submit assignments, or a disheveled appearance—may indicate that a student is struggling. Staff across campus, including athletic coaches and academic advisers, can also monitor students for signs of distress. (At Penn State, eating disorder referrals can even come from staff working in food service, said counseling psychologist Natalie Hernandez DePalma, PhD, senior director of the school’s counseling and psychological services.) Responding can be as simple as reaching out and asking if everything is going OK.
Referral options vary but may include directing a student to a wellness seminar or calling the counseling center to make an appointment, which can help students access services that they may be less likely to seek on their own, Hernandez DePalma said. Many schools also offer reporting systems, such as DukeReach at Duke University , that allow anyone on campus to express concern about a student if they are unsure how to respond. Trained care providers can then follow up with a welfare check or offer other forms of support.
“Faculty aren’t expected to be counselors, just to show a sense of care that they notice something might be going on, and to know where to refer students,” Shollenberger said.
At Johns Hopkins, he and his team have also worked with faculty on ways to discuss difficult world events during class after hearing from students that it felt jarring when major incidents such as George Floyd’s murder or the war in Ukraine went unacknowledged during class.
Many schools also support faculty by embedding counselors within academic units, where they are more visible to students and can develop cultural expertise (the needs of students studying engineering may differ somewhat from those in fine arts, for instance).
When it comes to course policy, even small changes can make a big difference for students, said Diana Brecher, PhD, a clinical psychologist and scholar-in-residence for positive psychology at Toronto Metropolitan University (TMU), formerly Ryerson University. For example, instructors might allow students a 7-day window to submit assignments, giving them agency to coordinate with other coursework and obligations. Setting deadlines in the late afternoon or early evening, as opposed to at midnight, can also help promote student wellness.
At Moraine Valley Community College (MVCC) near Chicago, Shelita Shaw, an assistant professor of communications, devised new class policies and assignments when she noticed students struggling with mental health and motivation. Those included mental health days, mindful journaling, and a trip with family and friends to a Chicago landmark, such as Millennium Park or Navy Pier—where many MVCC students had never been.
Faculty in the psychology department may have a unique opportunity to leverage insights from their own discipline to improve student well-being. Hard, who teaches introductory psychology at Duke, weaves in messages about how students can apply research insights on emotion regulation, learning and memory, and a positive “stress mindset” to their lives ( Crum, A. J., et al., Anxiety, Stress, & Coping , Vol. 30, No. 4, 2017 ).
Along with her colleague Deena Kara Shaffer, PhD, Brecher cocreated TMU’s Thriving in Action curriculum, which is delivered through a 10-week in-person workshop series and via a for-credit elective course. The material is also freely available for students to explore online . The for-credit course includes lectures on gratitude, attention, healthy habits, and other topics informed by psychological research that are intended to set students up for success in studying, relationships, and campus life.
“We try to embed a healthy approach to studying in the way we teach the class,” Brecher said. “For example, we shift activities every 20 minutes or so to help students sustain attention and stamina throughout the lesson.”
Creative approaches to support
Given the crucial role of social connection in maintaining and restoring mental health, many schools have invested in group therapy. Groups can help students work through challenges such as social anxiety, eating disorders, sexual assault, racial trauma, grief and loss, chronic illness, and more—with the support of professional counselors and peers. Some cater to specific populations, including those who tend to engage less with traditional counseling services. At Florida Gulf Coast University (FGCU), for example, the “Bold Eagles” support group welcomes men who are exploring their emotions and gender roles.
The widespread popularity of group therapy highlights the decrease in stigma around mental health services on college campuses, said Jon Brunner, PhD, the senior director of counseling and wellness services at FGCU. At smaller schools, creating peer support groups that feel anonymous may be more challenging, but providing clear guidelines about group participation, including confidentiality, can help put students at ease, Brunner said.
Less formal groups, sometimes called “counselor chats,” meet in public spaces around campus and can be especially helpful for reaching underserved groups—such as international students, first-generation college students, and students of color—who may be less likely to seek services at a counseling center. At Johns Hopkins, a thriving international student support group holds weekly meetings in a café next to the library. Counselors typically facilitate such meetings, often through partnerships with campus centers or groups that support specific populations, such as LGBTQ students or student athletes.
“It’s important for students to see counselors out and about, engaging with the campus community,” McCowan said. “Otherwise, you’re only seeing the students who are comfortable coming in the door.”
Peer counseling is another means of leveraging social connectedness to help students stay well. At UVA, Mason and his colleagues found that about 75% of students reached out to a peer first when they were in distress, while only about 11% contacted faculty, staff, or administrators.
“What we started to understand was that in many ways, the people who had the least capacity to provide a professional level of help were the ones most likely to provide it,” he said.
Project Rise , a peer counseling service created by and for Black students at UVA, was one antidote to this. Mason also helped launch a two-part course, “Hoos Helping Hoos,” (a nod to UVA’s unofficial nickname, the Wahoos) to train students across the university on empathy, mentoring, and active listening skills.
At Washington University in St. Louis, Uncle Joe’s Peer Counseling and Resource Center offers confidential one-on-one sessions, in person and over the phone, to help fellow students manage anxiety, depression, academic stress, and other campus-life issues. Their peer counselors each receive more than 100 hours of training, including everything from basic counseling skills to handling suicidality.
Uncle Joe’s codirectors, Colleen Avila and Ruchika Kamojjala, say the service is popular because it’s run by students and doesn’t require a long-term investment the way traditional psychotherapy does.
“We can form a connection, but it doesn’t have to feel like a commitment,” said Avila, a senior studying studio art and philosophy-neuroscience-psychology. “It’s completely anonymous, one time per issue, and it’s there whenever you feel like you need it.”
As part of the shift toward rapid access, many schools also offer “Let’s Talk” programs , which allow students to drop in for an informal one-on-one session with a counselor. Some also contract with telehealth platforms, such as WellTrack and SilverCloud, to ensure that services are available whenever students need them. A range of additional resources—including sleep seminars, stress management workshops, wellness coaching, and free subscriptions to Calm, Headspace, and other apps—are also becoming increasingly available to students.
Those approaches can address many student concerns, but institutions also need to be prepared to aid students during a mental health crisis, and some are rethinking how best to do so. Penn State offers a crisis line, available anytime, staffed with counselors ready to talk or deploy on an active rescue. Johns Hopkins is piloting a behavioral health crisis support program, similar to one used by the New York City Police Department, that dispatches trained crisis clinicians alongside public safety officers to conduct wellness checks.
A culture of wellness
With mental health resources no longer confined to the counseling center, schools need a way to connect students to a range of available services. At OSU, Sharma was part of a group of students, staff, and administrators who visited Apple Park in Cupertino, California, to develop the Ohio State: Wellness App .
Students can use the app to create their own “wellness plan” and access timely content, such as advice for managing stress during final exams. They can also connect with friends to share articles and set goals—for instance, challenging a friend to attend two yoga classes every week for a month. OSU’s apps had more than 240,000 users last year.
At Johns Hopkins, administrators are exploring how to adapt school policies and procedures to better support student wellness, Shollenberger said. For example, they adapted their leave policy—including how refunds, grades, and health insurance are handled—so that students can take time off with fewer barriers. The university also launched an educational campaign this fall to help international students navigate student health insurance plans after noticing below average use by that group.
Students are a key part of the effort to improve mental health care, including at the systemic level. At Morehouse College, Sera serves as the adviser for Chill , a student-led advocacy and allyship organization that includes members from Spelman College and Clark Atlanta University, two other HBCUs in the area. The group, which received training on federal advocacy from APA’s Advocacy Office earlier this year, aims to lobby public officials—including U.S. Senator Raphael Warnock, a Morehouse College alumnus—to increase mental health resources for students of color.
“This work is very aligned with the spirit of HBCUs, which are often the ones raising voices at the national level to advocate for the betterment of Black and Brown communities,” Sera said.
Despite the creative approaches that students, faculty, staff, and administrators are employing, students continue to struggle, and most of those doing this work agree that more support is still urgently needed.
“The work we do is important, but it can also be exhausting,” said Kamojjala, of Uncle Joe’s peer counseling, which operates on a volunteer basis. “Students just need more support, and this work won’t be sustainable in the long run if that doesn’t arrive.”
Further reading
Overwhelmed: The real campus mental-health crisis and new models for well-being The Chronicle of Higher Education, 2022
Mental health in college populations: A multidisciplinary review of what works, evidence gaps, and paths forward Abelson, S., et al., Higher Education: Handbook of Theory and Research, 2022
Student mental health status report: Struggles, stressors, supports Ezarik, M., Inside Higher Ed, 2022
Before heading to college, make a mental health checklist Caron, C., The New York Times, 2022
Related topics
- Mental health
- Stress effects on the body
Contact APA
You may also like.
150+ Trending Mental Health Research Topics For Students (2023)

Mental health is an important part of our well-being, encompassing our emotional, psychological, and social health. In the United States, the importance of addressing mental health has gained recognition, with growing concerns about stress, anxiety, and depression.
In this blog, we will guide you the meaning of mental health research topics with our 5 useful tips. Moreover, we give you a list of 150+ Mental Health Research Topics in 2023, including qualitative, interesting, and even controversial ones, you’ll find options that suit your interests. From the impact of social media to the intersection of Mental Health with political science and music therapy, we’ve got you covered.
Stay tuned for more on mental health research topics, and do not forget our bonus tips for selecting the best topics.
What Is Mental Health?
Table of Contents
Mental health is about how we feel and think inside our minds. It’s like taking care of our thoughts and emotions, just like we take care of our bodies. When our mental health is good, we usually feel happy and calm and can handle life’s challenges. But when our mental health is not so good, we might feel sad, anxious, or overwhelmed.
What Are Mental Health Research Topics?
Mental health research topics are subjects that scientists and experts study to learn more about our thoughts and emotions. These topics include things like understanding what causes mental health problems, finding better ways to help people who are struggling, and figuring out how to prevent these issues from happening. Researchers also examine how different treatments, like therapy or medication, can help improve mental health.
These research topics are important because they help us learn more about our minds and how to keep them healthy. By studying these topics, scientists can discover new ways to support people who are facing mental health challenges, making it easier for everyone to lead happier and more balanced lives.

5 Useful Tips For Choosing Mental Health Research Topics
Here are some useful tips for choosing mental health research topics:
1. Your research will be more focused and impactful.
2. You will be more likely to find funding and support.
3. You will be more likely to publish your research in peer-reviewed journals.
4. You will be more likely to make a huge contribution to the field of mental health research.
5. You will be more likely to enjoy your research experience.
Choosing the right mental health research topic is essential for success. By following the tips above, you can choose a topic that is focused, impactful, and relevant to your interests and expertise.
150+ Mental Health Research Topics In 2023
In this section, we will explore 150+ mental health research topics on different categories:
Mental Health Research Topics For College Students
College students often face unique mental health challenges. Here are 15 research topics for studying mental health in this demographic:
- The impact of academic stress on college students’ mental health.
- Exploring the relationship between sleep patterns and mental well-being among college students.
- Analyzing the effectiveness of campus mental health services.
- Investigating the prevalence of substance abuse and its effects on mental health in college students.
- The role of peer support groups in reducing anxiety and depression among college students.
- Examining the influence of social media usage on the mental health of college students.
- The correlation between mental stress and financial stress issues in college students.
- The value of practicing mindfulness and meditation for college students’ mental health.
- Getting a better idea of how different cultures affect college students’ mental health.
- Trying to figure out how mental health and physical movement affect college students.
- Investigating the stigma surrounding mental health issues in college environments.
- Analyzing the role of academic pressure in the onset of eating disorders among college students.
- The effectiveness of online mental health resources and apps for college students.
- Examining the mental health challenges faced by LGBTQ+ college students.
- The impact of COVID-19 and remote learning on the mental health of college students.
Mental Health Research Topics For High School Students
High school students also encounter unique mental health concerns. Here are 15 research topics for studying mental health in this age group:
- The effects of academic pressure on the mental health of high school students.
- Investigating the role of family dynamics in the emotional well-being of high school students.
- Analyzing the impact of bullying and cyberbullying on the mental health of teenagers.
- The relationship between social media use and body image issues in high school students.
- Examining the effectiveness of mental health education programs in high schools.
- Investigating the prevalence of self-harm and suicidal ideation among high school students.
- Analyzing the influence of peer relationships on the mental health of adolescents.
- The role of extracurricular activities in promoting positive mental health in high school students.
- Exploring the effects of substances abuse on the mental well-being of teenagers.
- Investigating the stigma surrounding mental health issues in high schools.
- The effects of COVID-19 and remote learning on the mental health of high school students.
- Examining the mental health challenges faced by immigrant and refugee high school students.
- Analyzing the relationship between sleep patterns and mental health in adolescents.
- The effectiveness of art and creative therapies in treating mental health issues in high school students.
- Investigating the role of teachers and school counselors in supporting students’ mental health.
Mental Health Research Topics For Nursing Students
Nursing students play a vital role in mental health care. Here are 15 research topics relevant to nursing students:
- The impact of nursing education on students’ mental health.
- Investigating the effectiveness of therapeutic communication in psychiatric nursing.
- Analyzing the role of psychiatric medications in mental health treatment.
- The importance of self-care practices for nursing students’ mental well-being.
- Exploring the challenges faced by nursing students in caring for patients with severe mental illness.
- Investigating the influence of nursing curricula on reducing mental health stigma.
- Analyzing the role of clinical placements in preparing nursing students for mental health nursing.
- The effects of peer support programs on nursing students’ mental health.
- Examining the prevalence of burnout and stress among nursing students.
- The importance of cultural skills in nursing care for different mental health patients.
- Investigating the impact of technology and telehealth on mental health nursing practices.
- Analyzing the ethical dilemmas faced by nursing students in mental health care.
- Exploring the use of simulation training in psychiatric nursing education.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness and stress management programs for nursing students.
- Finding out what nursing students think about the healing model in mental health care is the goal of this study.
Read More
- Frontend Project Ideas
- Business Intelligence Projects For Beginners
Psychology Culture, And Mental Health Research Topics
Psychology and culture intersect in complex ways. Here are 15 research topics in this area:
- Cross-cultural variations in the manifestation of mental disorders.
- The influence of cultural beliefs on help-seeking behaviors for mental health issues.
- Analyzing cultural factors in the diagnosis and treatment of depression.
- The effect of acculturation on the mental health of newcomers.
- Exploring cultural stigma surrounding mental illness in different societies.
- Investigating the role of traditional healing practices in mental health care.
- Cross-cultural perspectives on the concept of resilience in mental health.
- Analyzing cultural variations in the experience of anxiety disorders.
- The role of cultural competence in psychotherapy and counseling.
- Exploring indigenous perspectives on mental health and well-being.
- The impact of globalization on cultural attitudes toward mental health.
- Investigating the influence of religion and spirituality on mental health outcomes.
- Analyzing cultural differences in the perception and treatment of eating disorders.
- The role of cultural identity in coping with trauma and adversity.
- Cross-cultural perspectives on the use of psychotropic medications in mental health treatment.
Community Mental Health Research Topics
Community mental health research is crucial for improving public well-being. Here are 15 research topics in this field:
- Evaluating the effectiveness of community-based mental health programs.
- Investigating the role of peer support networks in community mental health.
- Analyzing the impact of housing instability on mental health in urban communities.
- Why early intervention programs are so important for avoiding serious mental illness.
- Exploring the use of telemedicine in delivering mental health services to underserved communities.
- Investigating the integration of mental health care into primary care settings.
- Analyzing the effectiveness of crisis intervention teams in community policing.
- The role of community art and creative programs in promoting mental well-being.
- Examining the mental health challenges faced by homeless populations.
- The impact of community outreach and education on reducing mental health stigma.
- Investigating the use of community gardens and green spaces for improving mental health.
- Analyzing the relationship between neighborhood characteristics and mental health disparities.
- Exploring the role of community leaders and advocates in mental health policy.
- The effectiveness of community-based substance abuse treatment programs.
- Finding out what part social determinants of health play in the mental health of a community.
Global Mental Health Research Topics
Mental health is a global issue with unique challenges. Here are 15 research topics in global mental health:
- Analyzing the burden of mental illness on global public health.
- Investigating the cultural variations in mental health stigma worldwide.
- The impact of arms conflict and displacement on mental well-being.
- Exploring the use of teletherapy for improving access to mental health care in low-resource settings.
- Analyzing the role of traditional healers in global mental health care.
- Investigating the mental health challenges faced by refugees and asylum seekers.
- The effectiveness of international mental health aid and interventions.
- Examining the mental health implications of weather change and natural disasters.
- Analyzing the global prevalence and treatment of common mental disorders.
- Exploring the intersection of infectious diseases (e.g., HIV/AIDS) and mental health.
- Mental Health in Urban Environments: Analyzing the unique challenges faced by individuals living in densely populated urban areas.
- Mental Health and Digital Technology: Exploring the impact of digital technology on mental well-being across cultures and age groups.
- Mental Health in Indigenous Communities: Investigating mental health disparities among indigenous populations and the role of cultural preservation.
- Mental Health in the Workplace: Examining workplace-related stressors and policies to support employees’ mental well-being globally.
- Youth Mental Health: Studying mental health challenges among children and adolescents, considering factors like education and family dynamics.
Qualitative Mental Health Research Topics
Qualitative research in mental health can provide rich insights into individuals’ experiences and perceptions. Here are 15 qualitative research topics in mental health:
- Exploring the lived experiences of individuals with schizophrenia.
- Qualitative analysis of the stigma associated with seeking mental health treatment.
- Understanding the coping mechanisms of parents with children diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder.
- Investigating the narratives of individuals recovering from addiction.
- Analyzing the cultural perceptions of depression and its treatment.
- Examining the subjective experiences of caregivers of dementia patients.
- Discussing the role of spirituality in the recovery process for people with mental illness.
- Qualitative assessment of the impact of mindfulness-based interventions on stress reduction.
- Investigating the narratives of survivors of suicide attempts.
- Understanding the experiences of LGBTQ+ individuals in mental health care.
- Analyzing the perceptions of veterans regarding post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) treatment.
- Exploring the subjective experiences of individuals with eating disorders.
- Qualitative assessment of the role of peer support groups in recovery from substance abuse.
- Investigating the stigma and barriers faced by individuals with bipolar disorder.
- Understanding the cultural variations in perceptions of anxiety disorders.
Interesting Mental Health Research Topics
Fascinating mental health topics can engage researchers and readers alike. Here are 15 intriguing research topics in mental health:
- The impact of virtual reality therapy on anxiety and phobias.
- Investigating the connection between creativity and mental well-being.
- Analyzing the role of pet therapy in reducing stress and anxiety.
- Exploring the effects of nature and green spaces on mental health.
- The relationship between personality types (e.g., introversion, extroversion) and mental health outcomes.
- Investigating the benefits of laughter therapy on mood and stress.
- Analyzing the effects of lucid dreaming on nightmares and trauma.
- Exploring the mental health benefits of volunteering and altruism.
- The impact of time-restricted eating on mood and cognitive function.
- Investigating the use of virtual support groups for individuals with social anxiety.
- Analyzing the relationship between music and memory in Alzheimer’s disease.
- Exploring the mental health effects of color psychology and interior design.
- The role of adventure therapy in enhancing self-esteem and resilience.
- Investigating the influence of childhood hobbies on adult mental well-being.
- Analyzing the connection between humor and emotional intelligence in mental health promotion.
Social Media On Mental Health Research Topics
Social media’s impact on mental health is a timely and relevant research area. Here are 15 research topics on this subject:
- Analyzing the relationship between social media use and feelings of loneliness.
- Investigating the effects of cyberbullying on adolescent mental health.
- The influence of social media comparison on body image dissatisfaction.
- Exploring the role of social media in the dissemination of mental health information.
- Analyzing the impact of social media detoxes on well-being.
- Investigating the link between excessive screen time and sleep disturbances.
- The effects of online support communities on mental health recovery.
- Exploring the role of influencer culture in shaping mental health perceptions.
- Analyzing the relationship between social media activism and mental well-being.
- Investigating the impact of “FOMO” (Fear of Missing Out) on anxiety levels.
- The role of social media in spreading wrong information about mental health.
- Exploring the effects of targeted advertising on mental health outcomes.
- Analyzing the relationship between online gaming and addictive behaviors.
- Investigating the influence of social media on political polarization and mental health.
- The role of social media in fostering a sense of community among marginalized groups with mental health issues.
Cool Mental Health Research Topics
Cool mental health topics can pique interest and lead to innovative research. Here are some cool research topics in mental health:
- Investigating the therapeutic potential of psychedelic substances for mental health treatment.
- Analyzing the impact of virtual reality gaming on managing stress and anxiety.
- Exploring the use of artificial intelligence and chatbots in mental health counseling.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness apps and wearable devices in promoting mental well-being.
- Investigating the role of gut microbiota in mood and mental health.
- Analyzing the use of neurofeedback technology for improving attention and focus in ADHD.
- Exploring the benefits of equine-assisted therapy for individuals with PTSD .
- The potential of psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy for treating depression.
- Investigating the use of art therapy and virtual art galleries for mental health support.
- Analyzing the impact of music and sound therapy on sleep quality and anxiety.
- Exploring the use of scent and aroma therapy in mood regulation.
- The role of biofeedback and wearable sensors in managing panic disorders.
- Investigating the mental health benefits of urban gardening and green rooftops.
- Analyzing the use of brain-computer interfaces in enhancing emotional regulation.
- Exploring the connection between outdoor adventure activities and resilience in mental health recovery.
| 1. Choose a research topic according to your interest ,expertise, and career goals. 2. Make sure the topic is feasible and can be completed within the given time and resources. 3. Choose a topic that will make a meaningful contribution to the mental health field. 4. Consider the ethical implications of your research and ensure that it protects the rights and well-being of 5. participants. 5. Select a topic that is original and innovative and not simply a rehash of existing research. |
Understanding what mental health is and exploring various mental health research topics is crucial in addressing the challenges individuals face today. Choosing the right topic involves considering your audience and interests, as highlighted in our five tips. With 150+ mental health research topics for 2023, we have provided options for college, high school, and nursing students and those interested in psychology, culture, and global perspectives.
Moreover, qualitative and intriguing topics offer diverse avenues for exploration while acknowledging the impact of social media on mental health is essential. Remember our bonus tips when selecting your mental health research topic – prioritize relevance and impact to make a meaningful contribution to this vital field.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
207 Mental Health Research Topics For Top Students

College and university students pursuing psychology studies must write research papers on mental health in their studies. It is not always an exciting moment for the students since getting quality mental health topics is tedious. However, this article presents expert ideas and writing tips for students in this field. Enjoy!
What Is Mental Health?
It is an integral component of health that deals with the feeling of well-being when one realizes his or her abilities, cope with the pressures of life, and productively work. Mental health also incorporates how humans interact with each other, emote, or think. It is a vital concern of any human life that cannot be neglected.
How To Write Mental Health Research Topics
One should approach the subject of mental health with utmost preciseness. If handled carelessly, cases such as depression, suicide or low self-esteem may occur. That is why students are advised to carefully choose mental health research paper topics for their paper with the mind reader.
To get mental health topics for research paper, you can use the following sources:
- The WHO website
- Websites of renowned psychology clinics
- News reports and headlines.
However, we have a list of writing ideas that you can use for your inspiration. Check them out!
Top Mental Disorders Research Topics
- Is the psychological treatment of mental disorders working for all?
- How do substance-use disorders impede the healing process?
- Discuss the effectiveness of the mental health Gap Action Programme (mhGAP)
- Are non-specialists in mental health able to manage severe mental disorders?
- The role of the WHO in curbing and treating mental disorders globally
- The contribution of coronavirus pandemic to mental disorders
- How does television contribute to mental disorders among teens?
- Does religion play a part in propagating mental disorders?
- How does peer pressure contribute to mental disorders among teens?
- The role of the guidance and counselling departments in helping victims of mental disorders
- How to develop integrated and responsive mental health to such disorders
- Discuss various strategies for promotion and prevention in mental health
- The role of information systems in mental disorders
Mental Illness Research Questions
- The role of antidepressant medicines in treating mental illnesses
- How taxation of alcoholic beverages and their restriction can help in curbing mental illnesses
- The impact of mental illnesses on the economic development of a country
- Efficient and cost-effective ways of treating mental illnesses
- Early childhood interventions to prevent future mental illnesses
- Why children from single-parent families are prone to mental illnesses
- Do opportunities for early learning have a role in curbing mental diseases?
- Life skills programmes that everyone should embrace to fight mental illnesses
- The role of nutrition and diet in causing mental illness
- How socio-economic empowerment of women can help promote mental health
- Practical social support for elderly populations to prevent mental illnesses
- How to help vulnerable groups against mental illnesses
- Evaluate the effectiveness of mental health promotional activities in schools
Hot Mental Health Topics For Research
- Do stress prevention programmes on TV work?
- The role of anti-discrimination laws and campaigns in promoting mental health
- Discuss specific psychological and personality factors leading to mental disorders
- How can biological factors lead to mental problems?
- How stressful work conditions can stir up mental health disorders
- Is physical ill-health a pivotal contributor to mental disorders today?
- Why sexual violence has led many to depression and suicide
- The role of life experiences in mental illnesses: A case of trauma
- How family history can lead to mental health problems
- Can people with mental health problems recover entirely?
- Why sleeping too much or minor can be an indicator of mental disorders.
- Why do people with mental health problems pull away from others?
- Discuss confusion as a sign of mental disorders
Research Topics For Mental Health Counseling
- Counselling strategies that help victims cope with the stresses of life
- Is getting professional counselling help becoming too expensive?
- Mental health counselling for bipolar disorders
- How psychological counselling affects victims of mental health disorders
- What issues are students free to share with their guiding and counselling masters?
- Why are relationship issues the most prevalent among teenagers?
- Does counselling help in the case of obsessive-compulsive disorders?
- Is counselling a cure to mental health problems?
- Why talking therapies are the most effective in dealing with mental disorders
- How does talking about your experiences help in dealing with the problem?
- Why most victims approach their counsellors feeling apprehensive and nervous
- How to make a patient feel comfortable during a counselling session
- Why counsellors should not push patients to talk about stuff they aren’t ready to share
Mental Health Law Research Topics
- Discuss the effectiveness of the Americans with Disabilities Act
- Does the Capacity to Consent to Treatment law push patients to the wall?
- Evaluate the effectiveness of mental health courts
- Does forcible medication lead to severe mental health problems?
- Discuss the institutionalization of mental health facilities
- Analyze the Consent to Clinical Research using mentally ill patients
- What rights do mentally sick patients have? Are they effective?
- Critically analyze proxy decision making for mental disorders
- Why some Psychiatric Advance directives are punitive
- Discuss the therapeutic jurisprudence of mental disorders
- How effective is legal guardianship in the case of mental disorders?
- Discuss psychology laws & licensing boards in the United States
- Evaluate state insanity defence laws
Controversial Research Paper Topics About Mental Health
- Do mentally ill patients have a right to choose whether to go to psychiatric centres or not?
- Should families take the elderly to mental health institutions?
- Does the doctor have the right to end the life of a terminally ill mental patient?
- The use of euthanasia among extreme cases of mental health
- Are mental disorders a result of curses and witchcraft?
- Do violent video games make children aggressive and uncontrollable?
- Should mental institutions be located outside the cities?
- How often should families visit their relatives who are mentally ill?
- Why the government should fully support the mentally ill
- Should mental health clinics use pictures of patients without their consent?
- Should families pay for the care of mentally ill relatives?
- Do mentally ill patients have the right to marry or get married?
- Who determines when to send a patient to a mental health facility?
Mental Health Topics For Discussion
- The role of drama and music in treating mental health problems
- Explore new ways of coping with mental health problems in the 21 st century
- How social media is contributing to various mental health problems
- Does Yoga and meditation help to treat mental health complications?
- Is the mental health curriculum for psychology students inclusive enough?
- Why solving problems as a family can help alleviate mental health disorders
- Why teachers can either maintain or disrupt the mental state of their students
- Should patients with mental health issues learn to live with their problems?
- Why socializing is difficult for patients with mental disorders
- Are our online psychology clinics effective in handling mental health issues?
- Discuss why people aged 18-25 are more prone to mental health problems
- Analyze the growing trend of social stigma in the United States
- Are all people with mental health disorders violent and dangerous?
Mental Health Of New Mothers Research Topics
- The role of mental disorders in mother-infant bonding
- How mental health issues could lead to delays in the emotional development of the infant
- The impact of COVID-19 physical distancing measures on postpartum women
- Why anxiety and depression are associated with preterm delivery
- The role of husbands in attending to wives’ postpartum care needs
- What is the effectiveness of screening for postpartum depression?
- The role of resilience in dealing with mental issues after delivery
- Why marginalized women are more prone to postpartum depression
- Why failure to bond leads to mental disorders among new mothers
- Discuss how low and middle-income countries contribute to perinatal depression
- How to prevent the recurrence of postpartum mental disorders in future
- The role of anti-depression drugs in dealing with depression among new mothers
- A case study of the various healthcare interventions for perinatal anxiety and mood disorders
What Are The Hot Topics For Mental Health Research Today
- Discuss why mental health problems may be a result of a character flaw
- The impact of damaging stereotypes in mental health
- Why are many people reluctant to speak about their mental health issues?
- Why the society tends to judge people with mental issues
- Does alcohol and wasting health help one deal with a mental problem?
- Discuss the role of bullying in causing mental health disorders among students
- Why open forums in school and communities can help in curbing mental disorders
- How to build healthy relationships that can help in solving mental health issues
- Discuss frustration and lack of understanding in relationships
- The role of a stable and supportive family in preventing mental disorders
- How parents can start mental health conversations with their children
- Analyze the responsibilities of the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE)
- The role of a positive mind in dealing with psychological problems
Good Research Topics On Refugees Mental Health
- Why do refugees find themselves under high levels of stress?
- Discuss the modalities of looking after the mental health of refugees
- Evaluate the importance of a cultural framework in helping refugees with mental illnesses
- How refugee camp administrators can help identify mental health disorders among refugees
- Discuss the implications of dangerous traditional practices
- The role of the UNHCR in assisting refugees with mental problems
- Post-traumatic Stress Disorder among refugees
- Dealing with hopelessness among refugees
- The prevalence of traumatic experiences in refugee camps
- Does cognitive-behavioural therapy work for refugees?
- Discuss the role of policy planning in dealing with refugee-mental health problems
- Are psychiatry and psychosomatic medicine effective in refugee camps?
- Practical groups and in‐group therapeutic settings for refugee camps
Adolescent Mental Health Research Topics
- Discuss why suicide is among the leading causes of death among adolescents
- The role of acting-out behaviour or substance use in mental issues among adolescents
- Mental effects of unsafe sexual behaviour among adolescents
- Psychopharmacologic agents and menstrual dysfunction in adolescents
- The role of confidentiality in preventive care visits
- Mental health disorders and impairment among adolescents
- Why adolescents not in school risk developing mental disorders
- Does a clinical model work for adolescents with mental illnesses?
- The role of self-worth and esteem in dealing with adolescent mental disorders
- How to develop positive relationships with peers
- Technology and mental ill-health among adolescents
- How to deal with stigma among adolescents
- Curriculum that supports young people to stay engaged and motivated
Research Topics For Mental Health And Government
- Evaluate mental health leadership and governance in the United States
- Advocacy and partnerships in dealing with mental health
- Discuss mental health and socio-cultural perspective
- Management and coordination of mental health policy frameworks
- Roles and responsibilities of governments in dealing with mental health
- Monitoring and evaluation of mental health policies
- What is the essence of a mental health commission?
- Benefits of mental well-being to the prosperity of a country
- Necessary reforms to the mental health systems
- Legal frameworks for dealing with substance use disorders
- How mental health can impede the development of a country
- The role of the government in dealing with decaying mental health institutions
- Inadequate legislation in dealing with mental health problems
Abnormal Psychology Topics
- What does it mean to display strange behaviour?
- Role of mental health professionals in dealing with abnormal psychology
- Discuss the concept of dysfunction in mental illness
- How does deviance relate to mental illness?
- Role of culture and social norms
- The cost of treating abnormal psychology in the US
- Using aversive treatment in abnormal psychology
- Importance of psychological debriefing
- Is addiction a mental disease?
- Use of memory-dampening drugs
- Coercive interrogations and psychology
Behavioural Health Issues In Mental Health
- Detachment from reality
- Inability to withstand daily problems
- Conduct disorder among children
- Role of therapy in behavioural disorders
- Eating and drinking habits and mental health
- Addictive behaviour patterns for teenagers in high school
- Discuss mental implications of gambling and sex addiction
- Impact of maladaptive behaviours on the society
- Extreme mood changes
- Confused thinking
- Role of friends in behavioural complications
- Spiritual leaders in helping deal with behavioural issues
- Suicidal thoughts
Latest Psychology Research Topics
- Discrimination and prejudice in a society
- Impact of negative social cognition
- Role of personal perceptions
- How attitudes affect mental well-being
- Effects of cults on cognitive behaviour
- Marketing and psychology
- How romance can distort normal cognitive functioning
- Why people with pro-social behaviour may be less affected
- Leadership and mental health
- Discuss how to deal with anti-social personality disorders
- Coping with phobias in school
- The role of group therapy
- Impact of dreams on one’s psychological behaviour
Professional Psychiatry Research Topics
- The part of false memories
- Media and stress disorders
- Impact of gender roles
- Role of parenting styles
- Age and psychology
- The biography of Harry Harlow
- Career paths in psychology
- Dissociative disorders
- Dealing with paranoia
- Delusions and their remedy
- A distorted perception of reality
- Rights of mental caregivers
- Dealing with a loss
- Handling a break-up
Consider using our expert research paper writing services for your mental health paper today. Satisfaction is guaranteed!

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
- Supporting Student Mental Health: Key…
Supporting Student Mental Health: Key Takeaways From School and District Staff
Date posted:.

Mental health concerns among youth remain prevalent following the COVID-19 pandemic. Percentages of youth experiencing symptoms of depression, anxiety or traumatic stress are particularly troublesome. In fact, the National Center for Education Statistics reported that almost 60% of public schools noted increases in youth requesting school-based mental health services last school year.
Given these rising mental health concerns, K-12 schools are an important setting to help address youth mental health needs. In particular, schools are well-suited to provide mental health prevention programs to support the well-being of all students, which are known as Tier I services, as well as to provide targeted interventions to those at risk, which are Tier II services.
Researchers from PolicyLab have worked closely with local school districts on several studies of Tier I and Tier II mental health programs and other initiatives. This connection provided an opportunity to build on these relationships to work together on the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) Tri-County School Mental Health Consortium (SMHC) . In SMHC, our team of CHOP researchers is partnering with the Chester, Delaware and Montgomery County Intermediate Units to support public schools’ Tier I and Tier II mental health efforts. In Pennsylvania, Intermediate Units are regional education agencies that provide a range of services to schools and districts.
During the first phase of this project, we wanted to learn from district and school leaders, teachers, and other student support staff who are on the front lines of supporting student mental health and well-being.
We surveyed school district leaders and conducted qualitative interviews with each of these groups of school professionals. Our goals were to learn about the current landscape of Tier I and Tier II mental health programming in this region. We also wanted to understand what programs are in place, what is going well, and what school and district staff see as key needs and priorities to help support students.
Through this phase of our research, we identified several key takeaways:
1. Regardless of their roles, school and district staff care deeply about student mental health and well-being.
Many educators we spoke with recognized that student mental health and well-being are closely linked with academic engagement. Although they shared that it can be challenging to support student mental health within the context of limited resources, competing demands, and schools' primary focus on academics, they also shared their dedication to doing so.
2. Schools and districts face continued challenges regarding unmet youth mental health needs.
Many of the school professionals we spoke with shared that they have seen increased mental health needs among students in recent years. Many educators expressed particular concern about anxiety among students. They frequently attributed this and related concerns to structural factors, including disruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic, stressors related to social media use, and academic demands.
One district leader emphasized the link between youth anxiety and increased school demands: “I think anxiety is probably at the top of the list, and I think there’s a variety of reasons. I think there’s a lot of pressure around students being exceptional all the time.”
3. Schools and districts are utilizing innovative and thoughtful approaches to support implementation of Tier I and Tier II programming .
School and district staff described approaches they use to garner buy-in from key parties in many roles, including students and caregivers. They also described the importance of using a “common language” within the school building and aligning programming to school and district structures and priorities.
4. Supporting youth mental health takes a team effort.
Educators spoke about the importance of partnerships: they highlighted the value of their partnerships with Intermediate Units and academic partners, and how much they benefit from collaborating with and learning from other schools and districts.
As one school principal shared, “I think communication is critical, and just the partnerships between the different agencies…and make sure that the stakeholders that need to be at that table talking about this are at the table.” Other educators highlighted the critical importance of being able to connect students to mental health resources in the community, including higher levels of care when necessary.
We were grateful to have the opportunity to learn from school and district staff, as these individuals have important perspectives about youth mental health needs and priorities for school-based programming.
Our learnings from this phase of the research highlight the importance of mental health prevention programming in schools, particularly given the level of mental health needs that school and district staff see during their day-to-day work. Our learnings also highlight the excellent work that schools and districts are already doing to support student mental health and well-being. We plan to disseminate these findings over the coming year, through presentations and publications aimed at both school and research audiences.
We hope that the next phase of the SMHC project , which includes learning collaboratives to inform and support Tier I and Tier II programs, can build upon these strengths to provide another layer of support for schools and districts in helping their students thrive.
Latest Blog Posts
Lgbtq+ youth need tailored eating disorder treatments.
Eating disorders are serious mental health conditions that have a profound impact on individuals’ physical and psychological health and well-being…
Improving Access to Vision Care for Youth in Foster Care: We Can’t Lose Sight of This Fundamental Back-to-School Need
Ads for children’s back-to-school supplies are everywhere this time of year. While the notebooks and backpacks featured in these ads are important,…

Unraveling Preterm Birth Disparities: How A Better Understanding of Data Enables Tailored Solutions
In the United States, where approximately 1 in 10 infants are born too early, preterm birth (generally defined as born before 37 weeks gestation) is…
Check out our new Publications View Publications
Adolescent Health & Well-Being
Behavioral health, population health sciences, health equity, family & community health.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BJPsych Open
- v.8(3); 2022 May

Key questions: research priorities for student mental health
Katie sampson.
Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology and Neurosciences, King's College London, UK
Michael Priestley
School of Education, Durham University, UK
Alyson L. Dodd
Department of Psychology, Northumbria University, UK
Emma Broglia
School of Psychology, University of Sheffield, UK
Dan Robotham
The McPin Foundation, UK
Katie Tyrrell
Research Directorate, University of Suffolk, UK
Marta Ortega Vega
Maudsley Learning, South London & Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust, UK
Nicola C. Byrom
Department of Psychology, Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology and Neurosciences, King's College London, UK
Associated Data
The fully anonymised data that support the findings of this study are available online from figshare at https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.15124908 .
The high prevalence of mental distress among university students is gaining academic, policy and public attention. As the volume of research into student mental health increases, it is important to involve students to ensure that the evidence produced can translate into meaningful improvements.
For the first time, we consult UK students about their research priorities on student mental health.
This priority setting exercise involved current UK university students who were asked to submit three research questions relating to student mental health. Responses were aggregated into themes through content analysis and considered in the context of existing research. Students were involved throughout the project, including inception, design, recruitment, analysis and dissemination.
UK university students ( N = 385) submitted 991 questions, categorised into seven themes: epidemiology, causes and risk factors, academic factors and work–life balance, sense of belonging, intervention and services, mental health literacy and consequences. Across themes, respondents highlighted the importance of understanding the experience of minority groups.
Conclusions
Students are interested in understanding the causes and consequences of poor mental health at university, across academic and social domains. They would like to improve staff and students’ knowledge about mental health, and have access to evidence-based support. Future research should take a broad lens to evaluate interventions; considering how services are designed and delivered, and investigating institutional and behavioural barriers to accessibility, including how this varies across different groups within the student population.
In the context of increasing prevalence of youth and young adult mental health problems, 1 , 2 including university students, 3 concern about mental health in the university setting is mounting and gaining media and public attention. 4 Increasing demand for services on campus has been observed internationally. 2 , 3 However, current approaches lack a solid evidence base, 5 , 6 and students have voiced concerns that existing services do not meet their needs. 7 In the UK, representatives of university leadership and students are urging the sector to adopt a whole-institution approach. 8 , 9 However, questions about how to achieve this remain unanswered. Eliciting student perspectives and experiences has been highlighted as an enabling strategy for the sector to develop effective and targeted initiatives attuned to diverse student needs and situated within a whole-university approach. 9 As research efforts mount, 10 it is important to involve students to ensure that work in this field translates into meaningful improvements attuned to students’ lived experiences. 11 This project set out to consult students in the UK on their priorities for future research into student mental health. Our aim is to ensure that the student voice is influential in shaping the direction of future research.
Lived experience involvement
The project was initiated through the UK Research and Innovation funded Student Mental Health Research Network (SMaRteN), with a steering group developed from the SMaRteN leadership team. The group recruited diverse stakeholders, including students (both with and without lived experience of mental health difficulties at university), clinical psychologists, tutors and academic researchers. Co-creation was central to this project. This is distinguished from student consultation and participation, by the active involvement of students as equal stakeholders, 12 reciprocally sharing knowledge and networks as part of a strengths and asset-based approach. 13 Students were operating in a ‘peer researcher’ context, and worked with academic researchers to design the methodology, recruit a diverse student sample, analyse data and write up the findings. Several student peer researchers are authors on this paper.
Participants
All procedures contributing to this work comply with the ethical standards of the relevant national and institutional committees on human experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008. All procedures involving human participants were approved by the university ethics board (approval number LRS-19/20-14288). All participants were provided with information about the study and the opportunity to contact the researchers to ask questions before providing informed consent through an online form.
Our sample included 385 UK university students, who responded to advertisements publicised by SMaRteN and the student mental health charity, Student Minds. Advertisements were circulated through newsletters, Facebook, Twitter and Instagram. We did not provide any monetary incentive for participation. Adverts and the study information sheet reminded participants that the survey would provide an opportunity to help shape the future of research in this area, with SMaRteN funding being allocated to address the top priority questions.
Our sample was primarily under 25 years old ( n = 285, 74%) and mostly comprised women ( n = 251, 65%). Our sample included UK domiciled ( n = 279, 72%) and international ( n = 106, 28%) students and was 72% White, 15% Asian and 6% Black. A substantial minority of respondents identified as a sexual or romantic minority ( n = 118, 31%) and/or reported having a disability ( n = 95, 25%). Students represented all years and levels of study (undergraduate, 66%; taught postgraduate, 17%; postgraduate research, 15%), and represented most subject areas (see Table 1 ).
Sample representation across academic areas, compared with UK representation, as reported in Higher Education Statistics Agency data
| Academic area | Our sample (%) | UK university students (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Medicine and dentistry | 9 | 3 |
| Subjects allied to medicine | 9 | 12 |
| Biological sciences | 22 | 10 |
| Veterinary science | − | <1 |
| Agriculture and related subjects | 1 | 1 |
| Physical sciences | 6 | 4 |
| Mathematical sciences | 3 | 2 |
| Computer science | 10 | 5 |
| Engineering and technology | 2 | 7 |
| Architecture, building and planning | − | 2 |
| Total sciences | 62 | 46 |
| Social studies | 12 | 10 |
| Law | 3 | 4 |
| Business and administrative studies | 3 | 15 |
| Mass communications and documentation | 5 | 2 |
| Languages | 5 | 4 |
| Historical and philosophical studies | 7 | 3 |
| Creative arts and design | 4 | 8 |
| Education | 4 | 6 |
| Total non-sciences | 38 | 54 |
Data collection was carried out via an online survey hosted on Qualtrics (Seattle, WA, USA; see https://www.qualtrics.com/uk/ ) between October 2019 and February 2020. The survey was designed to be as short and simple as possible to make participation as easy. Respondents submitted up to three questions in response to the prompt: ‘In terms of student mental health, what do you think are the priority issues for researchers to explore?’. There was no word limit for the respondents’ submissions. After submitting questions, respondents were asked to complete demographic details.
Data analysis
The objective of our analysis was to understand respondents’ recommendations for future research and categorise these to create a shortlist of research priorities. We sought to capture student recommendations without passing judgement regarding the value of the research topic or whether the question had already been addressed.
A team of 26 students were involved in analysing the data, supported by experienced researchers. The student team were recruited through SMaRteN from universities across the UK. Selection focused on bringing together a diverse team. SMaRteN hosted a 2-day workshop, covering expenses to bring students together for training and co-creation activities.
To facilitate reflexivity, 14 we followed an iterative approach, with themes developed and refined through consultation with all members of the team. This improves the reliability of analysis, minimising biases arising from individual researchers’ preconceptions. As respondents were invited to provide single sentence questions, without explaining their rationale, it was important not to overanalyse the data. In this context, content analysis was appropriate. As summarised in Fig. 1 , we followed four steps of content analysis, embedding the principles of co-creation in each step. 15

Content analysis process.
In stage 1, codes were generated inductively, working with the questions provided rather than bringing in any preconceived ideas of the research questions that might be important. This approach was adopted to ensure we think carefully about the questions students were asking, as opposed to trying to fit their questions into the existing research framework. This process was completed independently by members of the steering group, before in-depth discussion, through which a single list of codes was agreed. 14
At stage 2, students checked that all aspects of the content had been covered by revisiting the original questions, determining what should be included and excluded, and developing more detailed codes. 15 For example, although the initial list of codes had included ‘academic pressure’, student analysis here clarified that this should include all questions related academic grades, success, workload, deadline and course-specific challenges.
In stage 3, the lead researcher (N.C.B.) worked iteratively with small groups of students to create categories around the codes, with the goal of reducing the categories without losing the content of units. 16 Returning to the example of academic pressure, we identified parallels between the questions that had been grouped into this code and questions relating to the university extenuating/mitigating circumstances process. Students agreed it was hard to consider the impact of extenuating circumstances without considering these in the wider context of academic culture and assessment practice. Further, most questions relating to work–life balance focused on managing workload, and hence had clear relationship to the questions grouped under academic pressure. As such, we reduced the number of categories by grouping questions together into the category of ‘academic factors’. This process was continuously appraised to ensure categories were internally homogenous and externally heterogenous. 17 For instance, although the questions around academic pressure and extenuating circumstances align, questions relating to academics’ appreciation for the pressure students experienced aligned more clearly with other questions about mental health literacy and academics’ understanding of mental health. In the final stage, categories were checked, named and described.
Across the analysis, although we primarily followed a manifest analysis, describing respondents’ questions as they were presented, at times a more latent approach was necessary to interpret questions that were phrased less clearly. 13 For example, the question ‘What is the effect of workload on students’ mental health?’ can be simply described as asking about student workload, and thus grouped with other questions around workload and academic pressure. In contrast, we received a question reading ‘the amount of work?’. We chose to retain this question and place it within the category of ‘academic factors and work–life balance’. However, here we have assumed the respondent is referring to the work students have to do, rather than the amount of work universities might have to put in to improve student mental health.
In total, 991 questions were submitted and arranged into seven categories. In Table 2 , these categories are set out in descending order of frequency based on the number of questions asked in that category. We discuss each of these categories below.
Summary of key priorities in context of existing research
| Research priority (number of questions asked) | Current evidence | Direction for future research |
|---|---|---|
| Intervention and services ( = 224) | Short-term embedded counselling at university shows clinical efficacy. Limited evidence suggests non-clinical interventions may be effective | How effective and accessible are university mental health services for a diverse student population? How effective is a whole-university approach to mental health? What is the impact of collaboration between universities and the NHS [National Health Service]? Are non-clinical interventions, e.g. yoga and exercise, beneficial to the student population? |
| Academic factors and work–life balance ( = 121) | Student workload contributes to stress. Changes to university curricula and pedagogy can have beneficial consequences for student well-being | What are the consequences of making curricula and pedagogy changes, which are mindful of student mental health and well-being, across different types of degrees? |
| Mental health literacy ( = 114) | Programmes to improve mental health literacy may be effective in student populations. Academics are under increased pressure to support student mental health, but many find it challenging to understand their role and the best response | What approaches to mental health literacy programmes are most effective and accessible to students? How can academic staff be supported to recognise and help students with mental health difficulties? |
| Causes and risk factors ( = 107) | Multiple individual risk factors have been associated with poor mental health among students | Can we identify relative risk and protective factors associated with mental health difficulties? |
| Sense of belonging ( = 97) | Loneliness, which has negative consequences for mental health, is associated with transition to adulthood and away from the family home | In what way, and for what reasons, do students experience loneliness and how can it be prevented? How are students from minority groups affected by loneliness and structural exclusion? |
| Epidemiology ( = 68) | Prevalence estimates of mental health problems are 20–40%, and have been increasing in recent years | How does prevalence for mental health problems vary between students, considering institution, year of study, academic discipline and minority groups? |
| Consequences ( = 26) | Mental health affects education achievement at university | Do mental health difficulties among students have long-term implications for social and career development? |
Intervention and services
The efficacy of existing services (including counselling, workshops and drop-in services) was raised, including whether these services meet the needs of a diverse student population. Respondents suggested the potential effects of a broad range of specific and sometimes novel interventions, including physical activity, yoga, mindfulness, social activities and events, and sleeping pods on campus. Questions considered cost-efficacy as well as how to increase funding.
Respondents questioned the appropriate balance between preventative work and responsive treatment, and how university support services should be designed to meet needs ranging from well-being through to complex and enduring mental health problems: ‘How can the support for student well-being versus chronic/severe mental illness be differentiated and acknowledged as separate issues?’
Respondents identified a need to clarify where the boundaries of responsibility between the National Health Service (NHS) and university services should lie and how these services should be better integrated, especially with the split between home and term-time addresses: ‘What is the role of universities in treating, preventing, helping with mental health? Where do they fit in with the NHS, charities and family/social structures?’ Questions asked whether there is adequate provision of professional mental health support for students, whether this is suitably accessible and what steps can be taken to improve availability and accessibility.
Academic factors and work–life balance
Respondents queried how academic pressure, including challenging content, high workload and a pressure to succeed, contribute to mental health problems. This pressure also included how academic success affects self-worth and how to overcome feelings of shame or embarrassment when struggling academically. Pressure was raised in relation to postgraduate students, with a focus on the relationship between mental health, performance and output. Respondents asked what steps can be taken to help those studying at university to cope with pressure: ‘How can students’ resilience and coping be increased so they are best equipped to deal with HE [higher education] study?’
Participants questions indicated that methods of assessment at university may affect mental health and asked whether changes to assessment design could reduce negative effects. Respondents were interested in examinations versus coursework, as well as how deadlines affect stress. A few questions considered the accessibility and efficacy of university extenuating circumstances: ‘Are universities able/willing to make the more flexible adjustments needed for students with long-term mental health conditions to engage?’
University teaching, including module organisation and structure, number of contact hours and online versus in-person teaching, were raised as potentially affecting mental health. Teaching style changes between school and university were also flagged as possibly problematic: ‘I feel like a lot of people are struggling with the first year. How can we make the gap between uni and high school smaller?’ These questions were raised by students across academic disciplines. Healthcare students uniquely also questioned how placements affect mental health.
Respondents asked about the challenge of time management and maintaining balance in their lives. Questions considered how to balance academic work with a social life and part-time job, and postulated whether trying to achieve this places strain on relationships and well-being. Although there were comparatively few questions relating to balance, students involved in the analysis requested that this theme be highlighted because of its relevance and importance.
Mental health literacy
Questions included whether, and in what ways, a culture of increased awareness, education and conversation would affect student mental health: ‘How is the growing awareness of mental health impacting student's mental health?’ Students were concerned about to identify mental health problems in themselves and their peers, and asked for more knowledge about how to respond to and help someone struggling with mental health problems. The importance of providing support to those who are helping friends with mental health problems was also highlighted. Students wanted knowledge of self-help strategies, and questioned how best to manage and cope with their own mental health problems at university: ‘What steps can students take to minimise their risk of adverse mental health issues?’ This theme also included whether students know what support and advice is available at university, and how they can access it, including how comfortable people feel reaching out for support, the role of stigma and shame, and how to encourage help-seeking behaviour.
Academic staff also play a part in creating a culture around mental health, and so respondents were interested in their mental health literacy and suggested providing resources, training programmes or policy implementation to help staff recognise and support students with mental health problems. Some questions considered whether students feel they are treated as individuals or in a more depersonalised and anonymous manner, and what impact this has on student mental health: ‘Would students suffering with poor mental health be able to work better with more consideration from teachers?’
Causes and risk factors
Identifying potential risk and protective factors for poor mental health was highlighted: ‘Which students are most at risk of poor mental health/well-being and why? And most likely to have good mental health and why – protective factors?’ Respondents posed questions about underlying reasons, triggers or drivers for problems, with some assuming that university has a negative impact on mental health: ‘What is causing mental illness at university, and is it a systemic problem?’ Specific possible contributing factors included student finances, living arrangements, drug and alcohol use, unhealthy lifestyles and concerns for future career prospects. Questions about living arrangements considered the impact of living away from home, transitioning between home and term-time addresses, communal versus solitary living and how living in halls of residence affects mental health. Respondents queried how a sense of belonging and academic factors, including the challenge of finding a work–life balance, might contribute to mental health problems. These questions have not been included here because there was sufficient interest to create independent categories.
Sense of belonging
Respondents wanted to know whether all students feel valued, included and appreciated within their university community, and how to improve this: ‘How can students feel more ‘at home’ and comfortable in their universities?’ Loneliness and isolation were raised, particularly the reasons why students are lonely, how this affects mental health and what can be done to reduce it. Respondents questioned how to make meaningful connections, and why students may feel alone despite being surrounded by people. Respondents considered how student social life affects mental health, including the role of societies and sports groups as well as negative experiences such as peer pressure, elitism and bullying.
Questions considered these problems from the perspective of minority or vulnerable groups, with issues surrounding loneliness being raised specifically for international, mature and commuter students. Respondents queried whether the university environment is inclusive for neurodiverse, minority ethnic, LGBTQ+, working class and disabled students, and how a lack of representation may accentuate loneliness. Victimisation and discrimination, including racism and sexual assault, were identified as potentially contributing to mental health problems at university: ‘How safe do you feel on your campus? Specifically, relevant for minoritized groups, i.e. BAME, LGBTQ, non-neurotypical students, etc. and women’.
Epidemiology
Questions falling into this category considered the prevalence of mental health problems among university students, including identifying the most common conditions, how the incidence of these problems is changing in universities and how prevalence differs between students and non-students. Many questions revealed underlying presumptions that student mental health is declining, and that students are more vulnerable to mental health problems than their peers: ‘Why has the prevalence of mental health problems in university students increased?’ They also questioned when mental health problems develop, whether this is before or after coming to university and how the move to university changes peoples’ experiences.
Consequences
A small number of questions asked about the consequences of mental health problems at university, and particularly the impact on academic achievement and social life. Respondents asked about drop-out rates in relation to mental health, and consequences for career development. Respondents were interested in the prognosis for those who struggle with mental health problems at university, including rates of recovery.
The aim of this co-creation project was to identify the mental health research priorities of university students and enable the student voice to shape the direction of future research. Our study identified seven key areas for future research. Many themes overlapped, reflecting the interconnectedness of different facets of student life. As summarised in Table 2 , we have positioned the students’ priorities in the context of the existing research, which is often small scale and narrowly focused, with limited consideration of racial, ethnic and sexual minorities. The project was undertaken before the COVID-19 pandemic, which has resulted in substantial disruption to students’ lives and rapid changes to university practices, and highlights the long-term challenges facing student mental health. It is important that student priorities are considered as the higher education sector transitions to a post-pandemic world.
Although the data available suggest that short-term embedded counselling at university is clinically effective, 18 evaluation of the efficacy of university mental health services has been minimal. 19 There has been limited evaluation of interventions and services as part of a whole-university approach, 5 , 6 and to our knowledge, no published evaluation of the impact of collaboration between universities and the NHS. Although there has been some consideration of non-clinical interventions such as yoga and exercise, most studies are of poor quality, and it is not possible to rank which interventions work best, where and for whom. 6 Future studies must take a broader lens to evaluate interventions for students, especially how they are designed, delivered and made accessible, and should employ robust evaluation of service efficacy. In line with student priorities, it is vital that future research considers the efficacy of services for the diverse student population.
International research indicates that student workload is a major factor contributing to stress and can result in prolonged study times or drop-out. 20 , 21 However, despite growing research interest in a ‘whole of curriculum approach’, knowledge about how to support student mental health through curricula and pedagogy is lacking. Preliminary evidence from the USA demonstrated that a multidimensional curricula intervention involving reduction in contact time, a change in grading system, collaborative and practical learning initiatives, and an embedded resilience and mindfulness intervention, resulted in significant decreases in depressive and anxiety symptoms among medical students, with corresponding increases in quality of life, group cohesion, student satisfaction and examination scores. 22 This suggests that there is a promising way forward that could be adopted in the UK context across different types of degrees, in keeping with the many student questions on this topic.
Mental health literacy is defined as ‘knowledge and belief about mental disorders which aid their recognition, management or prevention’. 23 Within this, understanding how to look after your own mental health and support peers is fundamental. 24 Preliminary research has demonstrated potential efficacy and acceptability of peer support programmes 25 and programmes to improve student mental health literacy among students. 26 However, further research is needed to evaluate these more thoroughly and compare different approaches. Academics are under increased pressure to support student mental health, but many find it challenging to understand their role and the best response. 27 Research findings around mental health literacy are varied, with some studies identifying knowledge gaps 28 and others noting good levels of literacy among students and staff. 29 Exploring how staff and students can support themselves and others with mental health difficulties is an important priority for future research.
Research has only focused on whether a specific factor, in isolation, is relevant to mental health. For example, there is strong evidence of relationships between mental health problems and financial stress, 30 , 31 drug and alcohol consumption, 32 , 33 isolation and loneliness, 34 and sleep disruption 35 , 36 among students, as well as experiences of adverse events before and during university. 37 Although studies have increasingly explored the link between factors such as accommodation environments, 38 , 39 and physical activity 40 and student mental health, investigating general and comparative risk, protective and causal factors associated with mental health problems among students remains a high priority.
The repeated use of the word ‘loneliness’ within submitted questions was striking. There are strong links between loneliness and mental health problems, 41 and loneliness is particularly associated with the transition from adolescence to adulthood. 42 Loneliness appears to be accentuated by the significant upheaval in social networks that occurs when young adults leave the family home. 43 Research focusing on loneliness and student and postgraduate mental health is developing, 34 , 44 but studies to establish how student friendship groups form, how and why students experience loneliness at university and how student loneliness can be prevented should continue, particularly with student input. The COVID-19 pandemic caused further disruption to students’ social networks, with public concern for students missing the university experience. 45 , 46 It will be important for research exploring the impact of COVID-19 to recognise that challenges around sense of belonging on the university campus predate the pandemic.
A sense of belonging is unique to the individual. As recognised by the students in our study, it is vital for issue of belonging and loneliness to be investigated among minority groups. Although there is a substantive body of research on attainment gaps for students from minority ethnic backgrounds in UK higher education, 47 there are evidence gaps related to how structural exclusion affects mental health. 48
Existing evidence suggests 20–40% of university students are likely to meet criteria for mental health problems, and prevalence rates have been increasing over recent years. 2 , 3 Analysis of large population data-sets provides conflicting evidence about the relative prevalence of mental health problems between university students and peers not in higher education. 2 , 49 With notable exceptions, 50 , 51 there has been limited work within the UK identifying how mental health problems might vary across years of study, academic disciplines and universities, although this has been explored extensively within the USA. 21 Current data around the prevalence of mental health problems for minority student groups also remains limited.
In line with student priorities, future research must provide more precise estimates of the prevalence of student mental health problems, and identify how these vary across the student population. This will have important implications for service planning and provision. Given many students have pre-existing beliefs regarding prevalence and trends of mental health problems at university, clear communication of existing data and future findings is imperative.
In keeping with students’ concerns, research suggests mental health does affect educational achievement at university. 52 – 54 However longitudinal studies assessing long-term consequences across a wider breadth of domains, including social life and future career development, are lacking.
Strengths and limitations
Student involvement in every stage of the study increased the likelihood that the project would be responsive to students’ needs and research priorities. Our sample was broadly representative of the student population, although it overrepresented women, underrepresented undergraduate students and overrepresented students studying sciences, primarily because of a large representation of students studying medicine and dentistry, biological sciences (including psychology) and computer science (see Table 1 ). Given the widespread underrepresentation of men in research into student mental health, it will remain important for future research to develop specific strategies to consult and engage male students in research design. As a self-selective sample, it is important to recognise that the voices of students who care passionately about student mental health are likely to have been overrepresented in this project.
In conclusion, this project identifies seven key priorities for future research into student mental health from the perspective of UK university students. Students’ questions are mostly unmet in the existing literature, with less research into the mental health of racial, ethnic and sexual minority student communities. Research is needed in each of these seven areas, and Table 2 highlights key questions to be answered. However, three areas stand out as particularly important. ‘Interventions and services’ was the largest category of questions. This is also an area where there are research gaps. We do not need more research evaluating whether one-to-one clinical interventions are effective. Rather, research needs to assess the whole-university approach, understand the range of needs across a diverse student population and consider the broad student experience of services, from initial help-seeking through identifying appropriate support, triaging, waiting lists and using the service. In contrast to the attention students have given to academic factors, the research in this area is sparce. We need robust, large-scale evaluations of the impact of curricula and pedagogy on student mental health. Finally, there is a stark gap between student interest and research exploring sense of belonging. Future research must address the university social experience, to enhance our understanding of how this relates to student mental health and how it might be leveraged to improve mental health.
Our results have important implications for future funding to ensure research produces knowledge that is useful, relevant and meaningful to diverse student populations, as well as ensuring that knowledge can be translated into positive and practical changes within the higher education sector.
Data availability
Acknowledgements.
The research was supported by the project steering group and the SMaRteN student team, including Oskar Kaleta, Aleks Saunders, Connor Gayle, Kwan Lui Cheng, Joshua Melwani, Eadie Simons, Sania Deshpande, Lesley Turner, Elizabeth James, Isabel De Castro, Megan Lawrence, Kirellos Miseih, Paulina Pawlak, Samuel Chu, Andrea Prisecaru, Keerthi Ramesh, Wangjingyi Liao, Reihannah Mahmoud, Emily Wielezynski, Chloe Casey, Nuvera Mukaty, Anusha Ramji, Oliver Anderson, Anna Ambwene, Ka Wai Li, Elizabeta Farys and Kristyana Taneva.
Author contributions
K.S. contributed to data analysis and interpretation, including checking, naming and describing categories from students’ questions, and contributed to the write-up and editing of the final paper. M.P. contributed to the design/procedure as a student in the steering group, by recruiting students to submit key questions, through analysing/thematising submitted questions and in editing the manuscript. A.L.D. contributed to the initial design of the priority setting exercise, supported student recruitment and made critical revisions to several drafts of the manuscript. E.B. advised in her role on the SMaRteN leadership team and contributed to the preparation of this manuscript. T.W. contributed to the design of the priority setting exercise, advised on the analysis and contributed to the writing up of the manuscript. D.R. helped to develop and support the priority setting exercise, helped with analysis and suggested comments on the final paper. K.T. contributed to the conceptualisation and development of study materials, project administration and writing (reviewing and editing) of the manuscript. M.O.V. contributed as a steering group member for the research, reviewing initial responses and providing feedback on themes. N.C.B. is Principal Investigator, and therefore took the lead on designing and implementing the priority setting exercise, analysing data and writing the manuscript. All authors had access to the data, and K.S., M.P., D.R. and N.C.B. in particular can verify the underlying data. All authors approved the final manuscript.
This project was funded by the Economic and Social Research Council (grant number ES/S00324X/1) awarded to N.C.B., A.L.D., E.B., T.W. and D.R. The funder had no involvement in the design, implementation or dissemination of this study.
Declaration of interest
Stress and Your Health
Relaxation techniques for stress relief.
- Burnout: Symptoms and Tips on How to Deal
Journaling for Mental Health and Wellness
Stress relief guide, social support for stress relief, 12 ways to reduce stress with music, surviving tough times by building resilience.
- Online Therapy: Is it Right for You?
- Mental Health
- Health & Wellness
- Children & Family
- Relationships
Are you or someone you know in crisis?
- Bipolar Disorder
- Eating Disorders
- Grief & Loss
- Personality Disorders
- PTSD & Trauma
- Schizophrenia
- Therapy & Medication
- Exercise & Fitness
- Healthy Eating
- Well-being & Happiness
- Weight Loss
- Work & Career
- Illness & Disability
- Heart Health
- Learning Disabilities
- Family Caregiving
- Teen Issues
- Communication
- Emotional Intelligence
- Love & Friendship
- Domestic Abuse
- Healthy Aging
- Alzheimer’s Disease & Dementia
- End of Life
- Meet Our Team
What is stress?
Eustress vs. distress, how stress can make you sick, signs and symptoms of chronic stress, causes of stress.
- What's stressful for you?
How much stress is too much?
Improving your ability to handle stress, stress symptoms, signs, and causes.
Chronic stress can take a heavy toll on your mind, body, and behavior. But by identifying the stressors in your life, and distinguishing eustress from distress, you can reduce its harmful effects.

Stress is your body’s way of responding to any kind of demand or threat. When you sense danger—whether it’s real or imagined—the body’s defenses kick into high gear in a rapid, automatic process known as the “fight-or-flight” reaction or the “stress response.”
The stress response is the body’s way of protecting you. When working properly, it helps you stay focused, energetic, and alert. In emergency situations, stress can save your life—giving you extra strength to defend yourself, for example, or spurring you to slam on the brakes to avoid a car accident.
Stress can have other positive aspects, sometimes referred to as “eustress.” For example, it can help you rise to meet challenges such as keeping you on your toes during a presentation at work, sharpening your concentration when you’re attempting a game-winning free throw, or driving you to study for an exam when you’d rather be watching TV.
But while not all stress is bad for you, beyond a certain point, it stops being helpful and starts to cause major damage. Stress that feels overwhelming can have a negative impact on your health, mood, productivity, relationships, and your quality of life.
If you frequently find yourself feeling frazzled and overwhelmed, it’s time to take action to bring your nervous system back into balance. You can protect yourself—and improve how you think and feel—by learning how to recognize the signs and symptoms of chronic stress and taking steps to reduce its harmful effects.
How stress works: The stress response
When you feel threatened or in danger, your body’s stress or “fight or flight” response is automatically triggered. Your nervous system releases a flood of stress hormones, including adrenaline and cortisol, which rouse the body for emergency action.
Your heart pounds faster, muscles tighten, blood pressure rises, breath quickens, and your senses become sharper. These physical changes increase your strength and stamina, speed up your reaction time, and enhance your focus—preparing you to either fight or flee from the danger at hand.
Stress doesn’t always look stressful
Psychologist Connie Lillas uses a driving analogy to describe the three most common ways people respond when they’re overwhelmed by stress:
Foot on the gas . An angry, agitated, or “fight” stress response. You’re heated, keyed up, overly emotional, and unable to sit still.
Foot on the brake . A withdrawn, depressed, or “flight” stress response. You shut down, pull away, space out, and show very little energy or emotion.
Foot on both . A tense or “freeze” stress response. You become frozen under pressure and can’t do anything. You look paralyzed, but under the surface you’re extremely agitated.
Speak to a Licensed Therapist
BetterHelp is an online therapy service that matches you to licensed, accredited therapists who can help with depression, anxiety, relationships, and more. Take the assessment and get matched with a therapist in as little as 48 hours.
It can be helpful to think of stress as being on a spectrum. At one end, you have “eustress” or positive stress, the manageable levels of stress that can motivate you to meet challenges at work, school, or in your personal life. While eustress may take you out of your comfort zone, it can help you to meet the challenge of a job interview or first date, for example, or complete a project at school or work that means stretching yourself and learning new skills.
At the other end of the spectrum, you have “distress,” the stress that makes you feel overwhelmed. This negative stress can damage your mood and outlook, disrupt your sleep, and trigger health issues such as depression and anxiety. Distress occurs when you feel you’re under more stress than you can handle, whether it’s from feeling too busy at work, not having enough money, or suffering an illness or bereavement.
Everyone experiences stress differently
Your individual perception of stress can also affect whether you experience positive eustress or negative distress in a situation. For example, if an impending work deadline leaves you feeling worried, exhausted, and overwhelmed by, you’ll likely experience distress. On the other hand, if you the same impending deadline makes you feel excited about the positive affect it could have on your career, then stress you experience is more likely to be eustress, motivating and helpful.
Similarly, something that’s stressful for one person may not faze someone else; they may even enjoy it. While some of us are terrified of getting up in front of people to speak, for example, others live for the spotlight. And while you may enjoy helping to care for your elderly parents, your siblings may find the demands of caretaking overwhelming and stressful.
Your nervous system isn’t very good at distinguishing between emotional and physical threats. If you’re super stressed over an argument with a friend, a work deadline, or a mountain of bills, your body can react just as strongly as if you’re facing a true life-or-death situation. And the more your emergency stress system is activated, the easier it becomes to trigger, making it harder to shut off.
If you tend to get stressed out frequently, like many of us in today’s demanding world, your body may exist in a heightened state of stress most of the time. And that can lead to serious health problems. Chronic stress disrupts nearly every system in your body. It can suppress your immune system, upset your digestive and reproductive systems, increase the risk of heart attack and stroke, and speed up the aging process. It can even rewire the brain, leaving you more vulnerable to anxiety, depression, and other mental health problems.
Health problems caused or exacerbated by stress include:
- Depression and anxiety.
- Pain of any kind.
- Sleep problems, such as insomnia.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Digestive problems.
- Skin conditions, such as eczema, stress rash, or hives.
- Heart disease and high blood pressure.
- Weight problems.
- Reproductive issues.
- Thinking and memory problems.
When you’re stressed out, the hormones produced by your body in a stressful situation can trigger a variety of physical and emotional responses.
- You may feel sick or dizzy, anxious, worried, or nervous, or become tense, angry, short-tempered, or even despairing.
- Physically, you may react by sweating excessively, experiencing muscle aches, chest pains, blurred eyesight, or itchy skin.
But many symptoms of stress can be less immediately noticeable. That’s because the most dangerous thing about stress is how easily it can creep up on you. In fact, many of us simply get used to it. After a while, feeling constantly stressed can start to feel familiar, even normal. You don’t notice how much it’s affecting you, even as it takes a heavy toll on your health and well-being.
That’s why it’s important to be aware of the common symptoms of excessive stress. These include:
Cognitive symptoms:
- Memory problems.
- Inability to concentrate.
- Poor judgment.
- Seeing only the negative.
- Anxious or racing thoughts.
- Constant worrying.
Emotional symptoms:
- Depression or general unhappiness.
- Anxiety and agitation.
- Moodiness, irritability, or anger.
- Feeling overwhelmed.
- Loneliness and isolation.
- Other mental or emotional health problems.
Physical symptoms:
- Aches and pains.
- Diarrhea or constipation.
- Nausea, dizziness.
- Chest pain, rapid heart rate.
- Loss of sex drive.
- Frequent colds or flu.
Behavioral symptoms:
- Eating more or less.
- Sleeping too much or too little.
- Withdrawing from others.
- Procrastinating or neglecting responsibilities.
- Using alcohol, cigarettes, or drugs to relax.
- Nervous habits (e.g. nail biting, pacing).
Is it stress or anxiety?
Stress and anxiety are closely connected. They share many similar symptoms, such as muscle tension, moodiness, and sleep, concentration, and digestive problems. In fact, overwhelming stress can even lead to anxiety and panic attacks.
However, stress is often caused by a specific trigger or “stressor,” such as work pressure, a break-up, or financial problems. Once the circumstances change, the stress usually starts to ease up.
An anxiety disorder, on the other hand, doesn’t necessarily have a specific trigger and the feelings of unease often remain even when the circumstances have changed and the stressor is resolved.
Read: Anxiety Disorders and Anxiety Attacks .
The situations and pressures that cause stress are known as stressors. We usually think of stressors as being negative, such as an exhausting work schedule or a rocky relationship. However, anything that puts high demands on you can be stressful. This includes positive events such as getting married, buying a house, going to college, or receiving a promotion.
Of course, not all stress is caused by external factors. Stress can also be internal or self-generated, when you worry excessively about something that may or may not happen, or have irrational, pessimistic thoughts about life.
Finally, what causes stress depends, at least in part, on your perception of it. Something that’s stressful to you may not faze someone else; they may even enjoy it. While some of us are terrified of getting up in front of people to perform or speak, for example, others live for the spotlight. Where one person thrives under pressure and performs best in the face of a tight deadline, another will shut down when work demands escalate. And while you may enjoy helping to care for your elderly parents, your siblings may find the demands of caretaking overwhelming and stressful.
Common external causes of stress include:
- Major life changes.
- Work or school problems.
- Relationship difficulties.
- Financial troubles.
- Being too busy.
- Children and family.
Common internal causes of stress include:
- Pessimism, a negative outlook on life.
- Inability to accept uncertainty.
- Rigid thinking, lack of flexibility.
- Negative self-talk.
- Unrealistic expectations/perfectionism.
- All-or-nothing attitude.
Top 10 stressful life events
According to the widely validated Holmes and Rahe Stress Scale, these are the top ten stressful life events for adults that can contribute to illness:
- Death of a spouse
- Marriage separation
- Imprisonment
- Death of a close family member
- Injury or illness
- Marriage reconciliation
What’s stressful for you?
Whatever event or situation is stressing you out, there are ways of coping with the problem and regaining your balance. Some of life’s most common sources of stress include:
Stress at work
While some workplace stress is normal, excessive stress can interfere with your productivity and performance, impact your physical and emotional health, and affect your relationships and home life. It can even determine the difference between success and failure on the job. Whatever your ambitions or work demands, there are steps you can take to protect yourself from the damaging effects of stress, improve your job satisfaction, and bolster your well-being in and out of the workplace.
Job loss and unemployment stress
Losing a job is one of life’s most stressful experiences. It’s normal to feel angry, hurt, or depressed, grieve for all that you’ve lost, or feel anxious about what the future holds. Job loss and unemployment involves a lot of change all at once, which can rock your sense of purpose and self-esteem. While the stress can seem overwhelming, there are many steps you can take to come out of this difficult period stronger, more resilient, and with a renewed sense of purpose.
Financial stress
Many of us, from all over the world and from all walks of life, are having to deal with financial stress and uncertainty at this difficult time. Whether your problems stem from a loss of work, escalating debt, unexpected expenses, or a combination of factors, financial worry is one of the most common stressors in modern life. But there are ways to get through these tough economic times, ease stress and anxiety, and regain control of your finances.
No matter how much you’ve been looking forward to it, retiring from work can bring stress as well as benefits. Escaping the daily grind and a long commute can seem like a great relief at first. But after a few months you may miss the sense of identity, meaning, and purpose that came with work, the structure it gave your days, and the social aspect of having co-workers. To help you through the stress of retirement , there are healthy ways to make adjustments and deal with this major life change.
Caregiver stress
The demands of caregiving can be overwhelming, especially if you feel that you’re in over your head or have little control over the situation. If the stress of caregiving is left unchecked, it can take a toll on your health, relationships, and state of mind — eventually leading to burnout. However, there are plenty of things you can do to rein in the stress of caregiving and regain a sense of balance, joy, and hope in your life.
Grief and loss
Coping with the loss of someone or something you love is one of life’s biggest stressors. Often, the pain and stress of loss can feel overwhelming . You may experience all kinds of difficult and unexpected emotions, from shock or anger to disbelief, guilt, and profound sadness. While there is no right or wrong way to grieve, there are healthy ways to cope with the pain that, in time, can ease your sadness and help you come to terms with your loss, find new meaning, and move on with your life.
Because of the widespread damage stress can cause, it’s important to know your own limit. But just how much stress is “too much” differs from person to person. Some people seem to be able to roll with life’s punches, while others tend to crumble in the face of small obstacles or frustrations. Some people even thrive on the excitement of a high-stress lifestyle.
Factors that influence your stress tolerance level include:
Your support network . A strong network of supportive friends and family members is an enormous buffer against stress. When you have people you can count on, life’s pressures don’t seem as overwhelming. On the flip side, the lonelier and more isolated you are, the greater your risk of succumbing to stress.
Your sense of control . If you have confidence in yourself and your ability to influence events and persevere through challenges, it’s easier to take stress in stride. On the other hand, if you believe that you have little control over your life—that you’re at the mercy of your environment and circumstances—stress is more likely to knock you off course.
Your attitude and outlook . The way you look at life and its inevitable challenges makes a huge difference in your ability to handle stress. If you’re generally hopeful and optimistic, you’ll be less vulnerable. Stress-hardy people tend to embrace challenges, have a stronger sense of humor, believe in a higher purpose, and accept change as an inevitable part of life.
Your ability to deal with your emotions . If you don’t know how to calm and soothe yourself when you’re feeling sad, angry, or troubled, you’re more likely to become stressed and agitated. Having the ability to identify and deal appropriately with your emotions can increase your tolerance to stress and help you bounce back from adversity.
Your knowledge and preparation . The more you know about a stressful situation, including how long it will last and what to expect, the easier it is to cope. For example, if you go into surgery with a realistic picture of what to expect post-op, a painful recovery will be less stressful than if you were expecting to bounce back immediately.
How well do you handle stress in your life?
Ask yourself which of these statements apply to you:
- I have people I confide in when I’m feeling under pressure who make me feel better.
- I feel comfortable expressing how I feel when something is bothering me.
- In general, I feel in control of my life and confident in my ability to handle what comes my way.
- I find reasons to laugh and feel grateful, even when going through difficulties.
- No matter how busy I am, I make it a priority to sleep, exercise, and eat right.
- I’m able to calm myself down when I start to feel overwhelmed.
Each “yes” answer represents an important stress coping skill. Each “no” represents an area to work on to better deal with stress and become more resilient.
Improving how well you handle stress means building your resilience. The more resilient you are, the better you’re able to not just tolerate stress, but also cope with uncertainty and adversity, and rebound from setbacks in life.
Resilience isn’t a quality that you’re either born with or not. Rather, it’s something that you can learn to build over time.
Building resilience can help you to:
- Stay focused and productive in stressful circumstances.
- Improve how well you communicate under pressure.
- Feel more confident when facing hardships, setbacks, or uncertainty.
- Maintain control of your emotions when you’re stressed out—even strong ones like anger or despair.
[Read: Surviving Tough Times by Building Resilience]
Tips to relieve stress and build resilience
Get moving . Upping your activity level is one tactic you can employ right now to help relieve stress and start to feel better. Regular exercise can lift your mood and serve as a distraction from worries, allowing you to break out of the cycle of negative thoughts that feed stress. Rhythmic exercises such as walking, running, swimming, and dancing are particularly effective, especially if you exercise mindfully (focusing your attention on the physical sensations you experience as you move).
Connect to others . The simple act of talking face-to-face with another human can trigger hormones that relieve stress when you’re feeling agitated or insecure. Even just a brief exchange of kind words or a friendly look from another human being can help calm and soothe your nervous system. So, spend time with people who improve your mood and don’t let your responsibilities keep you from having a social life. If you don’t have any close relationships, or your relationships are the source of your stress, make it a priority to build stronger and more satisfying connections .
Engage your senses . Another fast way to relieve stress is by engaging one or more of your senses —sight, sound, taste, smell, touch, or movement. The key is to find the sensory input that works for you. Does listening to an uplifting song make you feel calm? Or smelling ground coffee? Or maybe petting an animal works quickly to make you feel centered? Everyone responds to sensory input a little differently, so experiment to find what works best for you.
Learn to relax . You can’t completely eliminate stress from your life, but you can control how much it affects you. Relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing activate the body’s relaxation response, a state of restfulness that is the polar opposite of the stress response. When practiced regularly, these activities can reduce your everyday stress levels and boost feelings of joy and serenity. They also increase your ability to stay calm and collected under pressure.
Eat a healthy diet . The food you eat can improve or worsen your mood and affect your ability to cope with life’s stressors. Eating a diet full of processed and convenience food, refined carbohydrates, and sugary snacks can worsen symptoms of stress, while a diet rich in fresh fruit and vegetables, high-quality protein, and omega-3 fatty acids, can help you better cope with life’s ups and downs.
Get your rest . Feeling tired can increase stress by causing you to think irrationally. At the same time, chronic stress can disrupt your sleep. Whether you’re having trouble falling asleep or staying asleep at night, there are plenty of ways to improve your sleep so you feel less stressed and more productive and emotionally balanced.
[Read: Stress Management]
More Information
- Stress Management - Enhance your well-being by reducing stress and building resilience. (Harvard Medical School Special Health Report)
- Understanding the Stress Response - Learn what happens in your body when you’re stressed, and how chronic activation of this survival mechanism impairs health. (Harvard Health)
- Stress Effects on the Body - An interactive guide to how stress affects the physical health of your body. (American Psychological Association)
- Stress and Your Health - Learn how stress affects women’s health. (Office on Women’s Health)
- Trauma- and Stressor-Related Disorders. (2013). In Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders . American Psychiatric Association. Link
- Yaribeygi, Habib, Yunes Panahi, Hedayat Sahraei, Thomas P. Johnston, and Amirhossein Sahebkar. “The Impact of Stress on Body Function: A Review.” EXCLI Journal 16 (July 21, 2017): 1057–72. Link
- Schneiderman, Neil, Gail Ironson, and Scott D. Siegel. “STRESS AND HEALTH: Psychological, Behavioral, and Biological Determinants.” Annual Review of Clinical Psychology 1 (2005): 607–28. Link
- McEwen, Bruce, and Robert Sapolsky. “Stress and Your Health.” The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 91, no. 2 (February 1, 2006): E2. Link
- https://www.apa.org. “Health Care, Mass Shootings, 2020 Presidential Election Causing Americans Significant Stress, New Stress in AmericaTM Survey Finds.” Accessed November 10, 2021. Link
- Loprinzi, Paul D., and Emily Frith. “Protective and Therapeutic Effects of Exercise on Stress-Induced Memory Impairment.” The Journal of Physiological Sciences: JPS 69, no. 1 (January 2019): 1–12. Link
- Nabi, Hermann, Mika Kivimäki, G. David Batty, Martin J. Shipley, Annie Britton, Eric J. Brunner, Jussi Vahtera, Cédric Lemogne, Alexis Elbaz, and Archana Singh-Manoux. “Increased Risk of Coronary Heart Disease among Individuals Reporting Adverse Impact of Stress on Their Health: The Whitehall II Prospective Cohort Study.” European Heart Journal 34, no. 34 (September 7, 2013): 2697–2705. Link
- Parks, Elizabeth P., Shiriki Kumanyika, Reneé H. Moore, Nicolas Stettler, Brian H. Wrotniak, and Anne Kazak. “Influence of Stress in Parents on Child Obesity and Related Behaviors.” Pediatrics 130, no. 5 (November 2012): e1096–1104. Link
- Sara, Jaskanwal D., Megha Prasad, Mackram F. Eleid, Ming Zhang, R. Jay Widmer, and Amir Lerman. “Association Between Work‐Related Stress and Coronary Heart Disease: A Review of Prospective Studies Through the Job Strain, Effort‐Reward Balance, and Organizational Justice Models.” Journal of the American Heart Association: Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Disease 7, no. 9 (April 27, 2018): e008073. Link
- Pascoe, Michaela C., Sarah E. Hetrick, and Alexandra G. Parker. “The Impact of Stress on Students in Secondary School and Higher Education.” International Journal of Adolescence and Youth 25, no. 1 (December 31, 2020): 104–12. Link
- Saleh, Dalia, Nathalie Camart, Fouad Sbeira, and Lucia Romo. “Can We Learn to Manage Stress? A Randomized Controlled Trial Carried out on University Students.” PLOS ONE 13, no. 9 (September 5, 2018): e0200997. Link
- Bisht, Kanchan, Kaushik Sharma, and Marie-Ève Tremblay. “Chronic Stress as a Risk Factor for Alzheimer’s Disease: Roles of Microglia-Mediated Synaptic Remodeling, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress.” Neurobiology of Stress 9 (November 1, 2018): 9–21. Link
- Mariotti, Agnese. “The Effects of Chronic Stress on Health: New Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of Brain–Body Communication.” Future Science OA 1, no. 3 (November 1, 2015). Link
- Wang, Xingmin, Lin Cai, Jing Qian, and Jiaxi Peng. “Social Support Moderates Stress Effects on Depression.” International Journal of Mental Health Systems 8, no. 1 (November 13, 2014): 41. Link
- Salmon, P. “Effects of Physical Exercise on Anxiety, Depression, and Sensitivity to Stress: A Unifying Theory.” Clinical Psychology Review 21, no. 1 (February 2001): 33–61. Link
- Branson, V., Dry, M. J., Palmer, E., & Turnbull, D. (2019). The Adolescent Distress-Eustress Scale: Development and Validation. SAGE Open , 9(3), 215824401986580. Link
- Pluut, H., Curșeu, P. L., & Fodor, O. C. (2022). Development and Validation of a Short Measure of Emotional, Physical, and Behavioral Markers of Eustress and Distress (MEDS). Healthcare , 10(2), 339. Link
More in Stress
How stress management helps fight disease

The power of the relaxation response to reduce stress and boost mood

Burnout Symptoms and Coping Tips
Techniques for dealing with overwhelming stress

Tips and prompts to journal

Quick tips for when you’re short on time

Using close relationships to manage stress and improve well-being

Fill your life with music that reduces daily stress

Tips for overcoming adversity

Professional therapy, done online
BetterHelp makes starting therapy easy. Take the assessment and get matched with a professional, licensed therapist.
Help us help others
Millions of readers rely on HelpGuide.org for free, evidence-based resources to understand and navigate mental health challenges. Please donate today to help us save, support, and change lives.
- Student Success
- Health & Wellness
Survey: College Students Impacted by Anti-LGBTQ+ Policies
A new analysis from the Trevor Project found connections between students who reported their institution had policies that didn’t support LGBTQ+ students and poor mental health as well as negative experiences at their school.
By Ashley Mowreader
You have / 5 articles left. Sign up for a free account or log in.
Young people in the LGBTQ+ community who attend schools with anti-LGBTQ+ practices are more likely to attend class less frequently or report mental health concerns.
Anderson Arboleda/iStock/Getty Images Plus
Anti-LGBTQ+ school policies, in addition to harming students’ feelings of belonging at their institution, may also have consequences for students’ mental health, according to new research from the Trevor Project.
Using survey data, researchers found LGBTQ+ students who reported experiencing anti-LGBTQ+ practices or policies were more likely to report feeling anxious, depressed or suicidal, compared to their peers who did not experience anti-LGBTQ+ practices at their institution.
The findings point to a need for continued support for LGBTQ+ students in schools and how inclusive policies support mental health and well-being.
Most Popular
- Open-access expansion threatens academic publishing industry
- Researchers find exam answers for half their modules on Chegg
Methodology: The report draws on data from the Trevor Project’s 2024 U.S. National Survey of the Mental Health of LGBTQ+ Young People , which included 18,663 young people between the ages of 13 and 24.
Around 78 percent of respondents were enrolled in school at the time of the survey administration in fall 2023.
To identify if students’ schools had anti-LGBTQ+ policies, students were asked if they had experienced any of the following from list of policies or practices, which included those that prevented someone “from using your chosen name and pronouns,” “disciplined for public affection that is not disciplined if it does not involve LGBTQ students” or “prevented from discussing or writing about LGBTQ topics in extracurricular activities.” Students who responded yes to at least one practice were included.
State of play: Just under 30 percent of young people said they were enrolled at a school with at least one anti-LGBTQ+ policy. Among respondents ages 18 to 24, 16 percent said they were at an institution with at least one anti-LGBTQ+ policy.
Transgender and nonbinary youth were more likely to say their institution had at least one anti-LGBTQ+ policy compared to those who are cisgender, which could point to a higher awareness of the barriers present for these students or policies that target these learners, according to the report.
Students enrolled at institutions that have at least one anti-LGBTQ+ policy were more likely to say they were attending school “sometimes” (44 percent), compared to their peers who reported attending a school with no anti-LGBTQ+ policies (38 percent), showing a correlation between anti-LGBTQ+ policies and attendance. Previous research found that LGBTQ+ learners with a high rate of anti-LGBTQ+ victimization report higher rates of truancy, compared to their LGBTQ+ peers who do not.
“Our finding may reflect the impact of anti-LGBTQ+ policies, with LGBTQ+ students having fewer protections against victimization, feeling less comfortable at school, and attending less often, or experiencing higher rates of discipline from school administration due to their LGBTQ+ identity,” the report authors wrote.
Students’ perception of anti-LGBTQ+ policies at their college or university varied by their institution type. Half of students in a dual- or concurrent-enrollment program said their institution had at least one anti-LGBTQ+ policy, too, but whether students were referring to their high school, the college or both is unclear.
Thirty percent of students enrolled in community colleges said their institution had at least one anti-LGBTQ+ policy, and 47 percent of students at technical school said their institution had at least one anti-LGBTQ+ policy. Among four-year and graduate school students, one-quarter said their institution had such a policy.
Editors’ Picks
Academic publishers threatened by open-access expansion.
- New Sweet Briar Policy Bars Transgender Students
- Supreme Court Keeps Debt-Relief Plan Blocked for Now
Across all young people, those at religiously affiliated institutions were more likely to report anti-LGBTQ+ practices (64 percent).
So what? LGBTQ+ students enrolled at schools with these kinds of practices were more likely to say they experienced verbal harassment due to their identity, physical attacks, unwanted sexual contact, discipline for fighting back against bullies or they left school entirely due to anti-LGBTQ+ mistreatment, compared to their peers who did not report anti-LGBTQ+ policies.
Campus infrastructure was also less likely to be inclusive to LGBTQ+ students if students reported anti-LGBTQ practices. Compared to their peers, students were less likely to have access to a Gay-Straight Alliance (49 percent versus 68 percent) or gender-neutral bathrooms (30 percent versus 48 percent).
Attending a school with anti-LGBTQ+ policies was associated with worse mental health and higher suicide risk among LGBTQ+ young people, as well. Those attending schools with noninclusive policies had higher rates of anxiety, recent depression, seriously considering suicide in the past year or attempting suicide in the past year. Poor mental health responses also grew with the number of anti-LGBTQ+ policies students said were present at their schools.
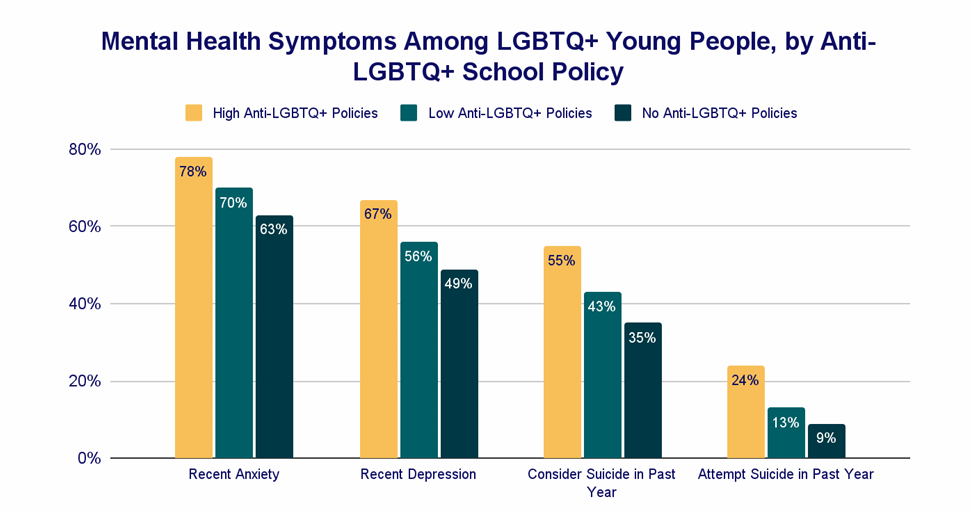
Students who attended schools with more reported anti-LGBTQ+ policies were more likely to demonstrate symptoms of poor mental health.
The Trevor Project
Report authors suggest these findings have implications for people who work with young people to advocate for LGBTQ+ students in their educational settings. “LGBTQ+ students deserve the right to feel safe in school, to openly discuss their LGBTQ+ identity with peers and adults without fear of being outed to potentially unsupportive families, and to see themselves reflected in school curricula,” they wrote.
Do you have a wellness tip that might help others encourage student success? Tell us about it.

Critics say a directive to make federally funded research immediately free to the public could violate authors’ copyr
Share This Article
More from health & wellness.

Student Wellness Tip: Add Syllabus Policy on Mental Health Days
College students want their professors to have formal policies on mental health days.

Student Wellness Tip: Supporting Spiritual Wellness
For students looking for meaning in their lives, colleges and universities can encourage purposeful living.

Survey: Cost of Course Materials Impacts Student Success
New data from Bay View Analytics found the price of textbooks and other class materials has negatively impacted many
- Become a Member
- Sign up for Newsletters
- Learning & Assessment
- Diversity & Equity
- Career Development
- Labor & Unionization
- Shared Governance
- Academic Freedom
- Books & Publishing
- Financial Aid
- Residential Life
- Free Speech
- Physical & Mental Health
- Race & Ethnicity
- Sex & Gender
- Socioeconomics
- Traditional-Age
- Adult & Post-Traditional
- Teaching & Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Publishing
- Data Analytics
- Administrative Tech
- Alternative Credentials
- Financial Health
- Cost-Cutting
- Revenue Strategies
- Academic Programs
- Physical Campuses
- Mergers & Collaboration
- Fundraising
- Research Universities
- Regional Public Universities
- Community Colleges
- Private Nonprofit Colleges
- Minority-Serving Institutions
- Religious Colleges
- Women's Colleges
- Specialized Colleges
- For-Profit Colleges
- Executive Leadership
- Trustees & Regents
- State Oversight
- Accreditation
- Politics & Elections
- Supreme Court
- Student Aid Policy
- Science & Research Policy
- State Policy
- Colleges & Localities
- Employee Satisfaction
- Remote & Flexible Work
- Staff Issues
- Study Abroad
- International Students in U.S.
- U.S. Colleges in the World
- Intellectual Affairs
- Seeking a Faculty Job
- Advancing in the Faculty
- Seeking an Administrative Job
- Advancing as an Administrator
- Beyond Transfer
- Call to Action
- Confessions of a Community College Dean
- Higher Ed Gamma
- Higher Ed Policy
- Just Explain It to Me!
- Just Visiting
- Law, Policy—and IT?
- Leadership & StratEDgy
- Leadership in Higher Education
- Learning Innovation
- Online: Trending Now
- Resident Scholar
- University of Venus
- Student Voice
- Academic Life
- The College Experience
- Life After College
- Academic Minute
- Weekly Wisdom
- Reports & Data
- Quick Takes
- Advertising & Marketing
- Consulting Services
- Data & Insights
- Hiring & Jobs
- Event Partnerships
4 /5 Articles remaining this month.
Sign up for a free account or log in.
- Sign Up, It’s FREE
- marquette.edu //
- Contacts //
- A-Z Index //
- Give to Marquette
Marquette.edu // College of Education // Graduate Studies // Counselor Education and Counseling Psychology //
Forms for Practica and Internships
Practicum/internship forms.
- Background check consent and release
- Curriculum vitae/Resume model
- Sample practicum/internship cover letter
- Liability insurance requirement form
- Overview of Online CMHC Program Practicum/Internship Process
Master's Practicum/Internship Handbook
- Handbook for Master's Practicum and Internship
- ONLINE Program Practicum and Internship Handbook
Clinical Mental Health Counseling Practicum/Internship Forms
- Practicum/Internship Supervisor Information Sheet
- Practicum/Internship Hours Log
Clinical Mental Health Counseling Practicum Forms
- Supervision Agreement for Practicum
- Supervisor Evaluation form for practicum
- Practicum Site Evaluation
Clinical Mental Health Counseling Internship Forms
- Supervision Agreement for Internship
- Supervisor Evaluation form for internship
- Internship Site Evaluation
- Supplemental Group Supervisor Evaluation form
School Counseling Practicum/Internship Forms
- School counseling internship requirements
- Supervision agreement form: Practicum
- Supervision agreement form: Internship
- Supervisor evaluation: Elementary Practicum
- Supervisor evaluation: Elementary Internship
- Supervisor evaluation: Middle school Practicum
- Supervisor evaluation: Middle school Internship
- Supervisor evaluation: High school Practicum
- Supervisor evaluation: High school Internship
- Practicum site evaluation
- Internship site evaluation
- Practicum and Internship hours log sheet
- School counseling internship performance assessment handout
Counseling Psychology Ph.D. Practicum Handbook and Forms
- Doctoral practicum handbook (COPS 8965)
- Doctoral practicum application form
- Supervision agreement form (COPS 8965)
- Mid-semester field placement student evaluation form
- Practicum/field placement student evaluation form (completed by supervisor)
- Practicum hours worksheets
- Practicum site evaluation form
- Practicum/field placement supervisor evaluation form (completed by student)
- Practicum hours documentation definitions
- Instructions on how to use new Excel spreadsheets
- Practicum sites chart
- Practicum Assessment Site Info
- Integrative Psychological Reports Rubric

Quick Links
- Resources for Current Students
- Resources for Admitted Students
- Our Commitment to Diversity
- Ph.D. in Counseling Psychology
- Ph.D. Program Outcome and Disclosure
- Master of Science in Clinical Mental Health Counseling
- Online Master of Science in Clinical Mental Health Counseling
- Master of Arts in School Counseling
- Master's Degrees Program and Student Outcomes
- Faculty Expertise
- Faculty and Staff Directory
- Research Centers and Clinics
PROBLEM WITH THIS WEBPAGE?
Report an accessibility problem
To report another problem, please contact [email protected] .
Marquette University Schroeder Health and Education Complex Milwaukee, WI 53233 Phone: (800) 222-6544
- Campus contacts
- Search marquette.edu
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Privacy Policy Legal Disclaimer Non-Discrimination Policy Accessible Technology
© 2024 Marquette University

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
found mental health concerns can cause a student to have difficulty in school. with poor academic performance, even chronic absenteeism, and disciplinary. concerns. Weist (2005) notes that in the prior two decades, "school mental health. programs have increased due to the recognition of the crisis in children's mental.
This manuscript summarizes areas of school mental health (SMH) research relevant to the interplay between students' academic and social-emotional outcomes.
COVID-19 and Student Mental Health. Empirical studies reported a high prevalence of college mental health issues during the early phase of COVID-19 around the world (Cao et al., 2020; Chang et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2020, Rajkumar, 2020; Saddik et al., 2020).In the U.S. a few, but a growing number of empirical surveys and studies were conducted to assess college students' mental health ...
Abstract. The purpose of this study is to map the literature on mental health and well-being of university students using metadata extracted from 5,561 journal articles indexed in the Web of Science database for the period 1975-2020. More specifically, this study uses bibliometric procedures to describe and visually represent the available ...
This qualitative study explores the lived experience of mental distress within college. student identity. The purposes of this study is to: (1) address a gap in extant literature on mental. health as an aspect of college identity from students' own voice, (2) add to literature that.
American Student report, which published in fall 2022. That report outlined the contours of the crisis American students faced during the pandemic and offered a path to recovery for all students—which must include building a new and better approach to public education that ensures an educational crisis of this magnitude cannot happen again.
Introduction. Mental health issues are the leading impediment to academic success. Mental illness can affect students' motivation, concentration, and social interactions—crucial factors for students to succeed in higher education [].The 2019 Annual Report of the Center for Collegiate Mental Health [] reported that anxiety continues to be the most common problem (62.7% of 82,685 respondents ...
Baltimore, Maryland July 2017 Abstract. ent demands f. r mental health services in institutions of higher education have growndr. matically. College students are at higher risk of developi. g mental illnesses such as. epression, anxiety disorders, and alcohol and drug abuse. A stude. t's psychologic.
Introduction. A report from World Health Organization (WHO) reveals that in the world, one in every four individuals will suffer from mental health problems at some point in their lives and that 450 million people worldwide have a mental health problem (WHO, Citation 2001).In 2015, the global prevalence of common mental illnesses such as depression and anxiety disorders are estimated at 5.5% ...
ObjectiveTo identify the prevalence of anxiety, depression, and suicidal ideation that would place university students at risk for mental health disorders.To explore the source of stressors and possible interventions that may benefit student mental health in a university setting. Participants: University students (n = 483) who had been learning remotely due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Poor mental health of students in further and higher education is an increasing concern for public health and policy [1,2,3,4].A 2020 Insight Network survey of students from 10 universities suggests that "1 in 5 students has a current mental health diagnosis" and that "almost half have experienced a serious psychological issue for which they felt they needed professional help"—an ...
mental health problems the risk of increased childhood behaviors was higher if the mother had mental health problems compared to only the father having mental health problems. Further research is needed to know if the mother's mental health has more of an impact because it has effects on the developing fetus.
implications for practice and future research. Keywords: college students, mental health, stigma, help-seeking behavior . iv ... Student mental health is an increasingly important issue in higher education as college students present on campuses with more serious issues and needs for services (Gallagher, 2012; ...
Here are a few ideas to get you started. The impact of genetics on the susceptibility to depression. Efficacy of antidepressants vs. cognitive behavioural therapy. The role of gut microbiota in mood regulation. Cultural variations in the experience and diagnosis of bipolar disorder.
Likewise, research from Deepa and Priya (2020), social media has an impact on students' mental health problems, especially depression and anxiety. Researchers have also conducted research on final ...
As a mental health student looking to get good grades, it is essential to develop new ideas and experiment on existing mental health theories - i.e., to add value and interest in the topic of your research. Mental health is vast and interrelated to so many other academic disciplines like civil engineering, construction, project management ...
The number of students seeking help at campus counseling centers increased almost 40% between 2009 and 2015 and continued to rise until the pandemic began, according to data from Penn State University's Center for Collegiate Mental Health (CCMH), a research-practice network of more than 700 college and university counseling centers (CCMH Annual Report, 2015).
Abstract. Mental Health has been one of the topics which is being neglected and given less focus since the past days. In this 21 st century where there is so many educated groups of people around ...
Here are 15 research topics for studying mental health in this demographic: The impact of academic stress on college students' mental health. Exploring the relationship between sleep patterns and mental well-being among college students. Analyzing the effectiveness of campus mental health services.
Conduct disorder among children. Role of therapy in behavioural disorders. Eating and drinking habits and mental health. Addictive behaviour patterns for teenagers in high school. Discuss mental implications of gambling and sex addiction. Impact of maladaptive behaviours on the society. Extreme mood changes.
Of the resilient students, 83.9% perceived their health as good. Our assessment tool can reliably distinguish between students who are in reasonably good mental health or can be considered resilient, and those who are at increased risk and need further attention and targeted support during their studies.
The contents of the National Center on Safe Supportive Learning Environments Web site were assembled under contracts from the U.S. Department of Education, Office of Safe and Supportive Schools to the American Institutes for Research (AIR), Contract Number 91990021A0020.
Other educators highlighted the critical importance of being able to connect students to mental health resources in the community, including higher levels of care when necessary.We were grateful to have the opportunity to learn from school and district staff, as these individuals have important perspectives about youth mental health needs and ...
Supporting student mental health and well-being has become a priority for schools. This was the case even prior to the increased signs of child and youth mental health adversity in and after the ...
Campus leaders at Ohio State University are using state funding to bolster resources and services for graduate and professional students on campus and remotely. As student mental health needs have grown, more institutional leaders are investing dollars into supporting preventative and interventional measures to aid in student well-being. Ohio's House Bill 33 allocated $2.5 million to Ohio ...
College students want their professors to have formal policies on mental health days. Here are some examples of syllabus language faculty members can use. A 2024 Student Voice survey by Inside Higher Ed, conducted by Generation Lab, found one in five students believes if institutions encourage faculty members to build student mental health day policies into their syllabi, it would be helpful ...
Research has only focused on whether a specific factor, in isolation, is relevant to mental health. For example, there is strong evidence of relationships between mental health problems and financial stress, 30, 31 drug and alcohol consumption, 32, 33 isolation and loneliness, 34 and sleep disruption 35, 36 among students, as well as ...
It can suppress your immune system, upset your digestive and reproductive systems, increase the risk of heart attack and stroke, and speed up the aging process. It can even rewire the brain, leaving you more vulnerable to anxiety, depression, and other mental health problems. Health problems caused or exacerbated by stress include:
Methodology: The report draws on data from the Trevor Project's 2024 U.S. National Survey of the Mental Health of LGBTQ+ Young People, which included 18,663 young people between the ages of 13 and 24. Around 78 percent of respondents were enrolled in school at the time of the survey administration in fall 2023. To identify if students' schools had anti-LGBTQ+ policies, students were asked ...
Resources for Current Students; Resources for Admitted Students; Our Commitment to Diversity; Ph.D. in Counseling Psychology; Ph.D. Program Outcome and Disclosure; Master of Science in Clinical Mental Health Counseling; Online Master of Science in Clinical Mental Health Counseling; Master of Arts in School Counseling; Master's Degrees Program ...