
Headings identify the content within sections of a paper.
Make your headings descriptive and concise. Headings that are well formatted and clearly worded aid both visual and nonvisual readers of all abilities.

Levels of heading
There are five levels of heading in APA Style. Level 1 is the highest or main level of heading, Level 2 is a subheading of Level 1, Level 3 is a subheading of Level 2, and so on through Levels 4 and 5.
The number of headings to use in a paper depends on the length and complexity of the work.
- If only one level of heading is needed, use Level 1.
- If two levels of heading are needed, use Levels 1 and 2.
- If three levels of heading are needed, use Levels 1, 2, and 3 (and so on).
Use only the number of headings necessary to differentiate distinct sections in your paper; short student papers may not require any headings. Furthermore, avoid these common errors related to headings:
- Avoid having only one subsection heading within a section, just like in an outline.
- Do not label headings with numbers or letters.
- Double-space headings; do not switch to single spacing within headings.
- Do not add blank lines above or below headings, even if a heading falls at the end of a page.
Headings are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Sections 2.26 and 2.27 and the Concise Guide Sections 1.25 and 1.26
Related handouts
- Heading Levels Template: Student Paper (PDF, 257KB)
- Heading Levels Template: Professional Paper (PDF, 213KB)
Format of headings
The following table demonstrates how to format headings in APA Style.
|
|
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
Text begins as a new paragraph.
|
| 2 |
Text begins as a new paragraph.
|
| 3 |
Text begins as a new paragraph.
|
| 4 | Text begins on the same line and continues as a regular paragraph.
|
| 5 | Text begins on the same line and continues as a regular paragraph.
|
Note. In title case, most words are capitalized .
Headings in the introduction
Because the first paragraphs of a paper are understood to be introductory, the heading “Introduction” is not needed. Do not begin a paper with an “Introduction” heading; the paper title at the top of the first page of text acts as a de facto Level 1 heading.
It is possible (but not required) to use headings within the introduction. For subsections within the introduction, use Level 2 headings for the first level of subsection, Level 3 for subsections of any Level 2 headings, and so on. After the introduction (regardless of whether it includes headings), use a Level 1 heading for the next main section of the paper (e.g., Method).
Creating accessible headings
Writers who use APA Style may use the automatic headings function of their word-processing program to create headings. This not only simplifies the task of formatting headings but also ensures that headings are coded appropriately in any electronic version of the paper, which aids readers who use navigation tools and assistive technologies such as screen readers.
Here are some tips on how to create headings in some common word-processing programs:
- If you use Academic Writer to write your APA Style papers, the headings menu in the Writing Center will format headings for you in 7th edition APA Style.
- Follow these headings directions from Microsoft to customize the heading formats for your future use.
- To apply Level 4 and 5 headings (which are inline headings, meaning the heading appears on the same line as paragraph text), first type the heading and a few words of the text that follows. Then highlight the text that you want to be your heading and select the appropriate heading level from the Styles menu. Only the highlighted text will be formatted as the Level 4 or 5 heading.

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
How to Format A College Essay: 15 Expert Tips
College Essays

When you're applying to college, even small decisions can feel high-stakes. This is especially true for the college essay, which often feels like the most personal part of the application. You may agonize over your college application essay format: the font, the margins, even the file format. Or maybe you're agonizing over how to organize your thoughts overall. Should you use a narrative structure? Five paragraphs?
In this comprehensive guide, we'll go over the ins and outs of how to format a college essay on both the micro and macro levels. We'll discuss minor formatting issues like headings and fonts, then discuss broad formatting concerns like whether or not to use a five-paragraph essay, and if you should use a college essay template.
How to Format a College Essay: Font, Margins, Etc.
Some of your formatting concerns will depend on whether you will be cutting and pasting your essay into a text box on an online application form or attaching a formatted document. If you aren't sure which you'll need to do, check the application instructions. Note that the Common Application does currently require you to copy and paste your essay into a text box.
Most schools also allow you to send in a paper application, which theoretically gives you increased control over your essay formatting. However, I generally don't advise sending in a paper application (unless you have no other option) for a couple of reasons:
Most schools state that they prefer to receive online applications. While it typically won't affect your chances of admission, it is wise to comply with institutional preferences in the college application process where possible. It tends to make the whole process go much more smoothly.
Paper applications can get lost in the mail. Certainly there can also be problems with online applications, but you'll be aware of the problem much sooner than if your paper application gets diverted somehow and then mailed back to you. By contrast, online applications let you be confident that your materials were received.
Regardless of how you will end up submitting your essay, you should draft it in a word processor. This will help you keep track of word count, let you use spell check, and so on.
Next, I'll go over some of the concerns you might have about the correct college essay application format, whether you're copying and pasting into a text box or attaching a document, plus a few tips that apply either way.
Formatting Guidelines That Apply No Matter How You End Up Submitting the Essay:
Unless it's specifically requested, you don't need a title. It will just eat into your word count.
Avoid cutesy, overly colloquial formatting choices like ALL CAPS or ~unnecessary symbols~ or, heaven forbid, emoji and #hashtags. Your college essay should be professional, and anything too cutesy or casual will come off as immature.

Mmm, delicious essay...I mean sandwich.
Why College Essay Templates Are a Bad Idea
You might see college essay templates online that offer guidelines on how to structure your essay and what to say in each paragraph. I strongly advise against using a template. It will make your essay sound canned and bland—two of the worst things a college essay can be. It's much better to think about what you want to say, and then talk through how to best structure it with someone else and/or make your own practice outlines before you sit down to write.
You can also find tons of successful sample essays online. Looking at these to get an idea of different styles and topics is fine, but again, I don't advise closely patterning your essay after a sample essay. You will do the best if your essay really reflects your own original voice and the experiences that are most meaningful to you.
College Application Essay Format: Key Takeaways
There are two levels of formatting you might be worried about: the micro (fonts, headings, margins, etc) and the macro (the overall structure of your essay).
Tips for the micro level of your college application essay format:
- Always draft your essay in a word processing software, even if you'll be copy-and-pasting it over into a text box.
- If you are copy-and-pasting it into a text box, make sure your formatting transfers properly, your paragraphs are clearly delineated, and your essay isn't cut off.
- If you are attaching a document, make sure your font is easily readable, your margins are standard 1-inch, your essay is 1.5 or double-spaced, and your file format is compatible with the application specs.
- There's no need for a title unless otherwise specified—it will just eat into your word count.
Tips for the macro level of your college application essay format :
- There is no super-secret college essay format that will guarantee success.
- In terms of structure, it's most important that you have an introduction that makes it clear where you're going and a conclusion that wraps up with a main point. For the middle of your essay, you have lots of freedom, just so long as it flows logically!
- I advise against using an essay template, as it will make your essay sound stilted and unoriginal.
Plus, if you use a college essay template, how will you get rid of these medieval weirdos?
What's Next?
Still feeling lost? Check out our total guide to the personal statement , or see our step-by-step guide to writing the perfect essay .
If you're not sure where to start, consider these tips for attention-grabbing first sentences to college essays!
And be sure to avoid these 10 college essay mistakes .

Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Ellen has extensive education mentorship experience and is deeply committed to helping students succeed in all areas of life. She received a BA from Harvard in Folklore and Mythology and is currently pursuing graduate studies at Columbia University.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Format and Structure Your College Essay
←What Is a College Application Theme and How Do You Come Up With One?
How to Write a Personal Statement That Wows Colleges→

Does your Common App essay actually stand out?
Your essay can be the difference between an acceptance and rejection — it allows you to stand out from the rest of applicants with similar profiles. Get a free peer review or review other students’ essays right now to understand the strength of your essay.
Submit or Review an Essay — for free!
College essays are an entirely new type of writing for high school seniors. For that reason, many students are confused about proper formatting and essay structure. Should you double-space or single-space? Do you need a title? What kind of narrative style is best-suited for your topic?
In this post, we’ll be going over proper college essay format, traditional and unconventional essay structures (plus sample essays!), and which structure might work best for you.
General College Essay Formatting Guidelines
How you format your essay will depend on whether you’re submitting in a text box, or attaching a document. We’ll go over the different best practices for both, but regardless of how you’re submitting, here are some general formatting tips:
- There’s no need for a title; it takes up unnecessary space and eats into your word count
- Stay within the word count as much as possible (+/- 10% of the upper limit). For further discussion on college essay length, see our post How Long Should Your College Essay Be?
- Indent or double space to separate paragraphs clearly
If you’re submitting in a text box:
- Avoid italics and bold, since formatting often doesn’t transfer over in text boxes
- Be careful with essays meant to be a certain shape (like a balloon); text boxes will likely not respect that formatting. Beyond that, this technique can also seem gimmicky, so proceed with caution
- Make sure that paragraphs are clearly separated, as text boxes can also undo indents and double spacing
If you’re attaching a document:
- Use a standard font and size like Times New Roman, 12 point
- Make your lines 1.5-spaced or double-spaced
- Use 1-inch margins
- Save as a PDF since it can’t be edited. This also prevents any formatting issues that come with Microsoft Word, since older versions are sometimes incompatible with the newer formatting
- Number each page with your last name in the header or footer (like “Smith 1”)
- Pay extra attention to any word limits, as you won’t be cut off automatically, unlike with most text boxes
Conventional College Essay Structures
Now that we’ve gone over the logistical aspects of your essay, let’s talk about how you should structure your writing. There are three traditional college essay structures. They are:
- In-the-moment narrative
- Narrative told over an extended period of time
- Series of anecdotes, or montage
Let’s go over what each one is exactly, and take a look at some real essays using these structures.
1. In-the-moment narrative
This is where you tell the story one moment at a time, sharing the events as they occur. In the moment narrative is a powerful essay format, as your reader experiences the events, your thoughts, and your emotions with you . This structure is ideal for a specific experience involving extensive internal dialogue, emotions, and reflections.
Here’s an example:
The morning of the Model United Nation conference, I walked into Committee feeling confident about my research. We were simulating the Nuremberg Trials – a series of post-World War II proceedings for war crimes – and my portfolio was of the Soviet Judge Major General Iona Nikitchenko. Until that day, the infamous Nazi regime had only been a chapter in my history textbook; however, the conference’s unveiling of each defendant’s crimes brought those horrors to life. The previous night, I had organized my research, proofread my position paper and gone over Judge Nikitchenko’s pertinent statements. I aimed to find the perfect balance between his stance and my own.
As I walked into committee anticipating a battle of wits, my director abruptly called out to me. “I’m afraid we’ve received a late confirmation from another delegate who will be representing Judge Nikitchenko. You, on the other hand, are now the defense attorney, Otto Stahmer.” Everyone around me buzzed around the room in excitement, coordinating with their allies and developing strategies against their enemies, oblivious to the bomb that had just dropped on me. I felt frozen in my tracks, and it seemed that only rage against the careless delegate who had confirmed her presence so late could pull me out of my trance. After having spent a month painstakingly crafting my verdicts and gathering evidence against the Nazis, I now needed to reverse my stance only three hours before the first session.
Gradually, anger gave way to utter panic. My research was fundamental to my performance, and without it, I knew I could add little to the Trials. But confident in my ability, my director optimistically recommended constructing an impromptu defense. Nervously, I began my research anew. Despite feeling hopeless, as I read through the prosecution’s arguments, I uncovered substantial loopholes. I noticed a lack of conclusive evidence against the defendants and certain inconsistencies in testimonies. My discovery energized me, inspiring me to revisit the historical overview in my conference “Background Guide” and to search the web for other relevant articles. Some Nazi prisoners had been treated as “guilty” before their court dates. While I had brushed this information under the carpet while developing my position as a judge, it now became the focus of my defense. I began scratching out a new argument, centered on the premise that the allied countries had violated the fundamental rule that, a defendant was “not guilty” until proven otherwise.
At the end of the three hours, I felt better prepared. The first session began, and with bravado, I raised my placard to speak. Microphone in hand, I turned to face my audience. “Greetings delegates. I, Otto Stahmer would like to…….” I suddenly blanked. Utter dread permeated my body as I tried to recall my thoughts in vain. “Defence Attorney, Stahmer we’ll come back to you,” my Committee Director broke the silence as I tottered back to my seat, flushed with embarrassment. Despite my shame, I was undeterred. I needed to vindicate my director’s faith in me. I pulled out my notes, refocused, and began outlining my arguments in a more clear and direct manner. Thereafter, I spoke articulately, confidently putting forth my points. I was overjoyed when Secretariat members congratulated me on my fine performance.
Going into the conference, I believed that preparation was the key to success. I wouldn’t say I disagree with that statement now, but I believe adaptability is equally important. My ability to problem-solve in the face of an unforeseen challenge proved advantageous in the art of diplomacy. Not only did this experience transform me into a confident and eloquent delegate at that conference, but it also helped me become a more flexible and creative thinker in a variety of other capacities. Now that I know I can adapt under pressure, I look forward to engaging in activities that will push me to be even quicker on my feet.
This essay is an excellent example of in-the-moment narration. The student openly shares their internal state with us — we feel their anger and panic upon the reversal of roles. We empathize with their emotions of “utter dread” and embarrassment when they’re unable to speak.
For in-the-moment essays, overloading on descriptions is a common mistake students make. This writer provides just the right amount of background and details to help us understand the situation, however, and balances out the actual event with reflection on the significance of this experience.
One main area of improvement is that the writer sometimes makes explicit statements that could be better illustrated through their thoughts, actions, and feelings. For instance, they say they “spoke articulately” after recovering from their initial inability to speak, and they also claim that adaptability has helped them in other situations. This is not as engaging as actual examples that convey the same meaning. Still, this essay overall is a strong example of in-the-moment narration, and gives us a relatable look into the writer’s life and personality.
2. Narrative told over an extended period of time
In this essay structure, you share a story that takes place across several different experiences. This narrative style is well-suited for any story arc with multiple parts. If you want to highlight your development over time, you might consider this structure.
When I was younger, I was adamant that no two foods on my plate touch. As a result, I often used a second plate to prevent such an atrocity. In many ways, I learned to separate different things this way from my older brothers, Nate and Rob. Growing up, I idolized both of them. Nate was a performer, and I insisted on arriving early to his shows to secure front row seats, refusing to budge during intermission for fear of missing anything. Rob was a three-sport athlete, and I attended his games religiously, waving worn-out foam cougar paws and cheering until my voice was hoarse. My brothers were my role models. However, while each was talented, neither was interested in the other’s passion. To me, they represented two contrasting ideals of what I could become: artist or athlete. I believed I had to choose.
And for a long time, I chose athlete. I played soccer, basketball, and lacrosse and viewed myself exclusively as an athlete, believing the arts were not for me. I conveniently overlooked that since the age of five, I had been composing stories for my family for Christmas, gifts that were as much for me as them, as I loved writing. So when in tenth grade, I had the option of taking a creative writing class, I was faced with a question: could I be an athlete and a writer? After much debate, I enrolled in the class, feeling both apprehensive and excited. When I arrived on the first day of school, my teacher, Ms. Jenkins, asked us to write down our expectations for the class. After a few minutes, eraser shavings stubbornly sunbathing on my now-smudged paper, I finally wrote, “I do not expect to become a published writer from this class. I just want this to be a place where I can write freely.”
Although the purpose of the class never changed for me, on the third “submission day,” – our time to submit writing to upcoming contests and literary magazines – I faced a predicament. For the first two submission days, I had passed the time editing earlier pieces, eventually (pretty quickly) resorting to screen snake when hopelessness made the words look like hieroglyphics. I must not have been as subtle as I thought, as on the third of these days, Ms. Jenkins approached me. After shifting from excuse to excuse as to why I did not submit my writing, I finally recognized the real reason I had withheld my work: I was scared. I did not want to be different, and I did not want to challenge not only others’ perceptions of me, but also my own. I yielded to Ms. Jenkin’s pleas and sent one of my pieces to an upcoming contest.
By the time the letter came, I had already forgotten about the contest. When the flimsy white envelope arrived in the mail, I was shocked and ecstatic to learn that I had received 2nd place in a nationwide writing competition. The next morning, however, I discovered Ms. Jenkins would make an announcement to the whole school exposing me as a poet. I decided to own this identity and embrace my friends’ jokes and playful digs, and over time, they have learned to accept and respect this part of me. I have since seen more boys at my school identifying themselves as writers or artists.
I no longer see myself as an athlete and a poet independently, but rather I see these two aspects forming a single inseparable identity – me. Despite their apparent differences, these two disciplines are quite similar, as each requires creativity and devotion. I am still a poet when I am lacing up my cleats for soccer practice and still an athlete when I am building metaphors in the back of my mind – and I have realized ice cream and gummy bears taste pretty good together.
The timeline of this essay spans from the writer’s childhood all the way to sophomore year, but we only see key moments along this journey. First, we get context for why the writer thought he had to choose one identity: his older brothers had very distinct interests. Then, we learn about the student’s 10th grade creative writing class, writing contest, and results of the contest. Finally, the essay covers the writers’ embarrassment of his identity as a poet, to gradual acceptance and pride in that identity.
This essay is a great example of a narrative told over an extended period of time. It’s highly personal and reflective, as the piece shares the writer’s conflicting feelings, and takes care to get to the root of those feelings. Furthermore, the overarching story is that of a personal transformation and development, so it’s well-suited to this essay structure.
3. Series of anecdotes, or montage
This essay structure allows you to focus on the most important experiences of a single storyline, or it lets you feature multiple (not necessarily related) stories that highlight your personality. Montage is a structure where you piece together separate scenes to form a whole story. This technique is most commonly associated with film. Just envision your favorite movie—it likely is a montage of various scenes that may not even be chronological.
Night had robbed the academy of its daytime colors, yet there was comfort in the dim lights that cast shadows of our advances against the bare studio walls. Silhouettes of roundhouse kicks, spin crescent kicks, uppercuts and the occasional butterfly kick danced while we sparred. She approached me, eyes narrowed with the trace of a smirk challenging me. “Ready spar!” Her arm began an upward trajectory targeting my shoulder, a common first move. I sidestepped — only to almost collide with another flying fist. Pivoting my right foot, I snapped my left leg, aiming my heel at her midsection. The center judge raised one finger.
There was no time to celebrate, not in the traditional sense at least. Master Pollard gave a brief command greeted with a unanimous “Yes, sir” and the thud of 20 hands dropping-down-and-giving-him-30, while the “winners” celebrated their victory with laps as usual.
Three years ago, seven-thirty in the evening meant I was a warrior. It meant standing up straighter, pushing a little harder, “Yes, sir” and “Yes, ma’am”, celebrating birthdays by breaking boards, never pointing your toes, and familiarity. Three years later, seven-thirty in the morning meant I was nervous.
The room is uncomfortably large. The sprung floor soaks up the checkerboard of sunlight piercing through the colonial windows. The mirrored walls further illuminate the studio and I feel the light scrutinizing my sorry attempts at a pas de bourrée , while capturing the organic fluidity of the dancers around me. “ Chassé en croix, grand battement, pique, pirouette.” I follow the graceful limbs of the woman in front of me, her legs floating ribbons, as she executes what seems to be a perfect ronds de jambes. Each movement remains a negotiation. With admirable patience, Ms. Tan casts me a sympathetic glance.
There is no time to wallow in the misery that is my right foot. Taekwondo calls for dorsiflexion; pointed toes are synonymous with broken toes. My thoughts drag me into a flashback of the usual response to this painful mistake: “You might as well grab a tutu and head to the ballet studio next door.” Well, here I am Master Pollard, unfortunately still following your orders to never point my toes, but no longer feeling the satisfaction that comes with being a third degree black belt with 5 years of experience quite literally under her belt. It’s like being a white belt again — just in a leotard and ballet slippers.
But the appetite for new beginnings that brought me here doesn’t falter. It is only reinforced by the classical rendition of “Dancing Queen” that floods the room and the ghost of familiarity that reassures me that this new beginning does not and will not erase the past. After years spent at the top, it’s hard to start over. But surrendering what you are only leads you to what you may become. In Taekwondo, we started each class reciting the tenets: honor, courtesy, integrity, perseverance, self-control, courage, humility, and knowledge, and I have never felt that I embodied those traits more so than when I started ballet.
The thing about change is that it eventually stops making things so different. After nine different schools, four different countries, three different continents, fluency in Tamil, Norwegian, and English, there are more blurred lines than there are clear fragments. My life has not been a tactfully executed, gold medal-worthy Taekwondo form with each movement defined, nor has it been a series of frappés performed by a prima ballerina with each extension identical and precise, but thankfully it has been like the dynamics of a spinning back kick, fluid, and like my chances of landing a pirouette, unpredictable.
This essay takes a few different anecdotes and weaves them into a coherent narrative about the writer’s penchant for novel experiences. We’re plunged into her universe, in the middle of her Taekwondo spar, three years before the present day. She then transitions into a scene in a ballet studio, present day. By switching from past tense to present tense, the writer clearly demarcates this shift in time.
The parallel use of the spoken phrase “Point” in the essay ties these two experiences together. The writer also employs a flashback to Master Pollard’s remark about “grabbing a tutu” and her habit of dorsiflexing her toes, which further cements the connection between these anecdotes.
While some of the descriptions are a little wordy, the piece is well-executed overall, and is a stellar example of the montage structure. The two anecdotes are seamlessly intertwined, and they both clearly illustrate the student’s determination, dedication, reflectiveness, and adaptability. The writer also concludes the essay with a larger reflection on her life, many moves, and multiple languages.
Unconventional College Essay Structures
Unconventional essay structures are any that don’t fit into the categories above. These tend to be higher risk, as it’s easier to turn off the admissions officer, but they’re also higher reward if executed correctly.
There are endless possibilities for unconventional structures, but most fall under one of two categories:
1. Playing with essay format
Instead of choosing a traditional narrative format, you might take a more creative route to showcase your interests, writing your essay:
- As a movie script
- With a creative visual format (such as creating a visual pattern with the spaces between your sentences forming a picture)
- As a two-sided Lincoln-Douglas debate
- As a legal brief
- Using song lyrics
2. Linguistic techniques
You could also play with the actual language and sentence structure of your essay, writing it:
- In iambic pentameter
- Partially in your mother tongue
- In code or a programming language
These linguistic techniques are often hybrid, where you write some of the essay with the linguistic variation, then write more of an explanation in English.
Under no circumstances should you feel pressured to use an unconventional structure. Trying to force something unconventional will only hurt your chances. That being said, if a creative structure comes naturally to you, suits your personality, and works with the content of your essay — go for that structure!
←What is a College Application Theme and How Do You Come Up With One?
Want help with your college essays to improve your admissions chances? Sign up for your free CollegeVine account and get access to our essay guides and courses. You can also get your essay peer-reviewed and improve your own writing skills by reviewing other students’ essays.
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

- Essay Editor
College Assignment Heading: A Simple Guide for Formatting

Crafting an effective college assignment heading is key to making a strong first impression on professors. The title serves as the face of your paper and reflects your focus on precision and adherence to academic standards. Curious about how to create a proper title? This guide provides clear instructions on creating an impressive college paper heading, guiding you to comprehend what a header in writing is, and the appropriate way to format it. By applying these tips and guidelines, be confident your prep aligns with the required scholarly standards.
Basic Rules for an Assignment Header
A well-organized college assignment heading is crucial for clearly identifying your assignment and presenting it professionally. Adhering to the basic rules will help you craft a carefully designed title:
- Include Crucial Information: A typical heading generally features the student and teacher’s name and surname, the due date, and the current course name. Clearly display and align the project’s title to the document’s left margin.
- Use the Correct Font and Size: Standard academic papers require a legible font like Times New Roman or sometimes Arial and 12-point size. Avoid choosing decorative fonts that may undermine the professional quality of your composition.
- Follow Proper Spacing Guidelines: Your prep’s heading needs to be double-spaced, and coherent with the remainder of the writing. This maintains uniformity and readability within the document.
- Add Page Numbers (if indicated): Some teachers might ask for page numbers to be positioned in the header section. So, format them as per the given instructions.
A well-crafted essay title guarantees your assignment recognition for clarity and compliance with academic standards, paving the way for successful submission.
How to Head an Assignment?
Understanding what is a heading in an essay and grasping how to head a paper correctly are foundational skills in scholarly writing. A proper essay header normally contains the instructor’s and student’s details, the course code or title, the current date, and the prep’s title. Most colleges follow APA, MLA, or Chicago-style guidelines, so familiarize yourself with these standards. Your header needs to be aligned correctly and placed where it doesn’t interfere with your work’s content. Adhering to these guidelines ensures your college paper heading is both succinct and polished.
Formatting Rules for a Heading
Following these guidelines guarantees your heading format meets academic expectations:
- Ensure Consistent Alignment: Align all components of your header close to the left margin, maintaining uniformity in the paper.
- Use Double-Spacing: Keep double-spacing between the lines of your prep’s heading.
- Avoid Unnecessary Information: Keep the college heading concise, avoiding any extra text or embellishments.
- Capitalization and Punctuation: Properly capitalize and punctuate your essay heading consistent with style guidelines, ensuring consistency across the prep.
- Consistency: Use identical size, font, and style for all components in your header.
Adhering to these rules will give your composition a polished look. This simplifies it for the lecturer to move through your composition.
Why Is a Good College Assignment Heading Important?
A skillfully designed paper heading gives your assignment a sophisticated look and helps to clearly organize the essentials for your readers. It signals to your lecturer that you have carefully followed educational standards and put thought into every aspect of your project. In addition, a proper heading for an essay guarantees that all relevant data is easily accessible. That’s specifically useful in larger classes where preps are handled by multiple lecturers or TAs. By concentrating on a succinct and accurate essay heading, you set a strong foundation for the rest of your home tasks.
Tips for Refining Your College Paper Heading
Refining your college paper heading is vital to guarantee it meets academic criteria and effectively represents your paper. By carefully focusing on the particulars, you can elevate the expertise and coherence of your home assignment. See some practical tips to consider:
- Review institutional guidelines: Always verify your institution's detailed formatting instructions or templates to ensure adherence.
- Keep it simple: Steer clear of irrelevant information in your heading; a clean, straightforward format is best.
- Maintain consistency: Make sure that the font, size, and alignment are uniform across your header.
- Double-check accuracy: Verify that all components in your title, comprising your name and surname, course name, and submission date, are correct.
- Align with your prep's style: Confirm the header complements the overall tone and style of your written work.
By applying these suggestions, you can develop an assignment title that fulfills academic standards and improves the overall appearance of your prep.
Recap
A well-formatted college paper heading is a minor but vital part of academic composition. From understanding what a title is to mastering how to head a text, focusing on these details can make a notable difference in the overall presentation of your composition. Always stick to the fundamental formatting standards and each time confirm that you follow the heading format specified by your educational institution's guidelines. To further enhance your writing, consider utilizing our tools at AI Essay Detector and College Essay Generator to help you create outstanding essays with ease.
Related articles
Can plagiarism be detected on pdf.
Plagiarism has been a challenge for a long time in writing. It's easy to find information online, which might make some people use it without saying where it came from. But plagiarism isn't just taking someone else's words. Sometimes, we might do it by accident or even use our own old work without mentioning it. When people plagiarize, they can get into serious trouble. They might lose others' trust or even face legal problems. Luckily, we now have tools to detect plagiarism. But what about PDF ...
What Is Self-Plagiarism & How To Avoid It
Have you ever thought about whether using your own work again could be seen as copying? It might seem strange, but self-plagiarism is a real issue in school and work writing. Let's look at what this means and learn how to avoid self-plagiarism so your work stays original and ethical. What is self-plagiarism? Self-plagiarism, also called auto-plagiarism or duplicate plagiarism, happens when a writer uses parts of their old work without saying where it came from. This isn't just about copying w ...
Paraphrasing vs Plagiarism: Do They Really Differ?
Academic assignments require much knowledge and skill. One of the most important points is rendering and interpreting material one has ever studied. A person should avoid presenting word-for-word plagiarism but express his or her thoughts and ideas as much as possible. However, every fine research is certain to be based on the previous issues, data given, or concepts suggested. And here it's high time to differentiate plagiarism and paraphrasing, to realize its peculiarities and cases of usage. ...
How To Write Essays Faster Using AI?
Creating various topical texts is an obligatory assignment during studies. For a majority of students, it seems like a real headache. It is quite difficult to write a smooth and complex work, meeting all the professors' requirements. However, thanks to modern technologies there appeared a good way of getting a decent project – using AI to write essays. We'd like to acquaint you with Aithor, an effective tool of this kind, able to perform fine and elaborated texts, and, of course, inspiration, i ...
How to Write a Dialogue in an Essay: Useful Tips
A correct usage of dialogues in essays may seem quite difficult at first sight. Still there are special issues, for instance, narrative or descriptive papers, where this literary technique will be a good helper in depicting anyone's character. How to add dialogues to the work? How to format them correctly? Let's discuss all relevant matters to master putting conversation episodes into academic essays. Essay Dialogue: Definition & Purpose A dialogue is a literary technique for presenting a con ...
Top 10 Use Cases for AI Writers
Writing is changing a lot because of AI. But don't worry — AI won't take human writers' jobs. It's a tool that can make our work easier and help us write better. When we use AI along with our own skills, we can create good content faster and better. AI can help with many parts of writing, from coming up with ideas to fixing the final version. Let's look at the top 10 ways how to use AI for content creation and how it can make your writing better. What Is AI Content Writing? AI content writin ...
What is Citation and Why Should You Cite the Sources When Writing Content
When we write something for school, work, or just for fun, we often use ideas and facts from other places. This makes us ask: what is a citation in writing? Let's find out what this means and why it's really important when we write. What is Citation? Citation in research refers to the practice of telling your readers where you got your information, ideas, or exact words from. It's like showing them the path to the original information you used in your writing. When you cite something, you us ...
Plagiarism: 7 Types in Detail
Your professor says that it is necessary to avoid plagiarism when writing a research paper, essay, or any project based on the works of other people, so to say, any reference source. But what does plagiarism mean? What types of it exist? And how to formulate the material to get rid of potential bad consequences while rendering original texts? Today we try to answer these very questions. Plagiarism: Aspect in Brief Plagiarism is considered to be a serious breach, able to spoil your successful ...
Ultimate Guide to Writing Your College Essay
Tips for writing an effective college essay.
College admissions essays are an important part of your college application and gives you the chance to show colleges and universities your character and experiences. This guide will give you tips to write an effective college essay.
Want free help with your college essay?
UPchieve connects you with knowledgeable and friendly college advisors—online, 24/7, and completely free. Get 1:1 help brainstorming topics, outlining your essay, revising a draft, or editing grammar.
Writing a strong college admissions essay
Learn about the elements of a solid admissions essay.
Avoiding common admissions essay mistakes
Learn some of the most common mistakes made on college essays
Brainstorming tips for your college essay
Stuck on what to write your college essay about? Here are some exercises to help you get started.
How formal should the tone of your college essay be?
Learn how formal your college essay should be and get tips on how to bring out your natural voice.
Taking your college essay to the next level
Hear an admissions expert discuss the appropriate level of depth necessary in your college essay.
Student Stories
Student Story: Admissions essay about a formative experience
Get the perspective of a current college student on how he approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about personal identity
Get the perspective of a current college student on how she approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about community impact
Student story: admissions essay about a past mistake, how to write a college application essay, tips for writing an effective application essay, sample college essay 1 with feedback, sample college essay 2 with feedback.
This content is licensed by Khan Academy and is available for free at www.khanacademy.org.

A step-by-step guide for creating and formatting APA Style student papers
The start of the semester is the perfect time to learn how to create and format APA Style student papers. This article walks through the formatting steps needed to create an APA Style student paper, starting with a basic setup that applies to the entire paper (margins, font, line spacing, paragraph alignment and indentation, and page headers). It then covers formatting for the major sections of a student paper: the title page, the text, tables and figures, and the reference list. Finally, it concludes by describing how to organize student papers and ways to improve their quality and presentation.
The guidelines for student paper setup are described and shown using annotated diagrams in the Student Paper Setup Guide (PDF, 3.40MB) and the A Step-by-Step Guide to APA Style Student Papers webinar . Chapter 1 of the Concise Guide to APA Style and Chapter 2 of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association describe the elements, format, and organization for student papers. Tables and figures are covered in Chapter 7 of both books. Information on paper format and tables and figures and a full sample student paper are also available on the APA Style website.
Basic setup
The guidelines for basic setup apply to the entire paper. Perform these steps when you first open your document, and then you do not have to worry about them again while writing your paper. Because these are general aspects of paper formatting, they apply to all APA Style papers, student or professional. Students should always check with their assigning instructor or institution for specific guidelines for their papers, which may be different than or in addition to APA Style guidelines.
Seventh edition APA Style was designed with modern word-processing programs in mind. Most default settings in programs such as Academic Writer, Microsoft Word, and Google Docs already comply with APA Style. This means that, for most paper elements, you do not have to make any changes to the default settings of your word-processing program. However, you may need to make a few adjustments before you begin writing.
Use 1-in. margins on all sides of the page (top, bottom, left, and right). This is usually how papers are automatically set.
Use a legible font. The default font of your word-processing program is acceptable. Many sans serif and serif fonts can be used in APA Style, including 11-point Calibri, 11-point Arial, 12-point Times New Roman, and 11-point Georgia. You can also use other fonts described on the font page of the website.
Line spacing
Double-space the entire paper including the title page, block quotations, and the reference list. This is something you usually must set using the paragraph function of your word-processing program. But once you do, you will not have to change the spacing for the entirety of your paper–just double-space everything. Do not add blank lines before or after headings. Do not add extra spacing between paragraphs. For paper sections with different line spacing, see the line spacing page.
Paragraph alignment and indentation
Align all paragraphs of text in the body of your paper to the left margin. Leave the right margin ragged. Do not use full justification. Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5-in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. For paper sections with different alignment and indentation, see the paragraph alignment and indentation page.
Page numbers
Put a page number in the top right of every page header , including the title page, starting with page number 1. Use the automatic page-numbering function of your word-processing program to insert the page number in the top right corner; do not type the page numbers manually. The page number is the same font and font size as the text of your paper. Student papers do not require a running head on any page, unless specifically requested by the instructor.
Title page setup
Title page elements.
APA Style has two title page formats: student and professional (for details, see title page setup ). Unless instructed otherwise, students should use the student title page format and include the following elements, in the order listed, on the title page:
- Paper title.
- Name of each author (also known as the byline).
- Affiliation for each author.
- Course number and name.
- Instructor name.
- Assignment due date.
- Page number 1 in the top right corner of the page header.
The format for the byline depends on whether the paper has one author, two authors, or three or more authors.
- When the paper has one author, write the name on its own line (e.g., Jasmine C. Hernandez).
- When the paper has two authors, write the names on the same line and separate them with the word “and” (e.g., Upton J. Wang and Natalia Dominguez).
- When the paper has three or more authors, separate the names with commas and include “and” before the final author’s name (e.g., Malia Mohamed, Jaylen T. Brown, and Nia L. Ball).
Students have an academic affiliation, which identities where they studied when the paper was written. Because students working together on a paper are usually in the same class, they will have one shared affiliation. The affiliation consists of the name of the department and the name of the college or university, separated by a comma (e.g., Department of Psychology, George Mason University). The department is that of the course to which the paper is being submitted, which may be different than the department of the student’s major. Do not include the location unless it is part of the institution’s name.
Write the course number and name and the instructor name as shown on institutional materials (e.g., the syllabus). The course number and name are often separated by a colon (e.g., PST-4510: History and Systems Psychology). Write the assignment due date in the month, date, and year format used in your country (e.g., Sept. 10, 2020).
Title page line spacing
Double-space the whole title page. Place the paper title three or four lines down from the top of the page. Add an extra double-spaced blank like between the paper title and the byline. Then, list the other title page elements on separate lines, without extra lines in between.
Title page alignment
Center all title page elements (except the right-aligned page number in the header).
Title page font
Write the title page using the same font and font size as the rest of your paper. Bold the paper title. Use standard font (i.e., no bold, no italics) for all other title page elements.
Text elements
Repeat the paper title at the top of the first page of text. Begin the paper with an introduction to provide background on the topic, cite related studies, and contextualize the paper. Use descriptive headings to identify other sections as needed (e.g., Method, Results, Discussion for quantitative research papers). Sections and headings vary depending on the paper type and its complexity. Text can include tables and figures, block quotations, headings, and footnotes.
Text line spacing
Double-space all text, including headings and section labels, paragraphs of text, and block quotations.
Text alignment
Center the paper title on the first line of the text. Indent the first line of all paragraphs 0.5-in.
Left-align the text. Leave the right margin ragged.
Block quotation alignment
Indent the whole block quotation 0.5-in. from the left margin. Double-space the block quotation, the same as other body text. Find more information on the quotations page.
Use the same font throughout the entire paper. Write body text in standard (nonbold, nonitalic) font. Bold only headings and section labels. Use italics sparingly, for instance, to highlight a key term on first use (for more information, see the italics page).
Headings format
For detailed guidance on formatting headings, including headings in the introduction of a paper, see the headings page and the headings in sample papers .
- Alignment: Center Level 1 headings. Left-align Level 2 and Level 3 headings. Indent Level 4 and Level 5 headings like a regular paragraph.
- Font: Boldface all headings. Also italicize Level 3 and Level 5 headings. Create heading styles using your word-processing program (built into AcademicWriter, available for Word via the sample papers on the APA Style website).
Tables and figures setup
Tables and figures are only included in student papers if needed for the assignment. Tables and figures share the same elements and layout. See the website for sample tables and sample figures .
Table elements
Tables include the following four elements:
- Body (rows and columns)
- Note (optional if needed to explain elements in the table)
Figure elements
Figures include the following four elements:
- Image (chart, graph, etc.)
- Note (optional if needed to explain elements in the figure)
Table line spacing
Double-space the table number and title. Single-, 1.5-, or double-space the table body (adjust as needed for readability). Double-space the table note.
Figure line spacing
Double-space the figure number and title. The default settings for spacing in figure images is usually acceptable (but adjust the spacing as needed for readability). Double-space the figure note.
Table alignment
Left-align the table number and title. Center column headings. Left-align the table itself and left-align the leftmost (stub) column. Center data in the table body if it is short or left-align the data if it is long. Left-align the table note.
Figure alignment
Left-align the figure number and title. Left-align the whole figure image. The default alignment of the program in which you created your figure is usually acceptable for axis titles and data labels. Left-align the figure note.
Bold the table number. Italicize the table title. Use the same font and font size in the table body as the text of your paper. Italicize the word “Note” at the start of the table note. Write the note in the same font and font size as the text of your paper.
Figure font
Bold the figure number. Italicize the figure title. Use a sans serif font (e.g., Calibri, Arial) in the figure image in a size between 8 to 14 points. Italicize the word “Note” at the start of the figure note. Write the note in the same font and font size as the text of your paper.
Placement of tables and figures
There are two options for the placement of tables and figures in an APA Style paper. The first option is to place all tables and figures on separate pages after the reference list. The second option is to embed each table and figure within the text after its first callout. This guide describes options for the placement of tables and figures embedded in the text. If your instructor requires tables and figures to be placed at the end of the paper, see the table and figure guidelines and the sample professional paper .
Call out (mention) the table or figure in the text before embedding it (e.g., write “see Figure 1” or “Table 1 presents”). You can place the table or figure after the callout either at the bottom of the page, at the top of the next page, or by itself on the next page. Avoid placing tables and figures in the middle of the page.
Embedding at the bottom of the page
Include a callout to the table or figure in the text before that table or figure. Add a blank double-spaced line between the text and the table or figure at the bottom of the page.
Embedding at the top of the page
Include a callout to the table in the text on the previous page before that table or figure. The table or figure then appears at the top of the next page. Add a blank double-spaced line between the end of the table or figure and the text that follows.
Embedding on its own page
Embed long tables or large figures on their own page if needed. The text continues on the next page.
Reference list setup
Reference list elements.
The reference list consists of the “References” section label and the alphabetical list of references. View reference examples on the APA Style website. Consult Chapter 10 in both the Concise Guide and Publication Manual for even more examples.
Reference list line spacing
Start the reference list at the top of a new page after the text. Double-space the entire reference list (both within and between entries).
Reference list alignment
Center the “References” label. Apply a hanging indent of 0.5-in. to all reference list entries. Create the hanging indent using your word-processing program; do not manually hit the enter and tab keys.
Reference list font
Bold the “References” label at the top of the first page of references. Use italics within reference list entries on either the title (e.g., webpages, books, reports) or on the source (e.g., journal articles, edited book chapters).
Final checks
Check page order.
- Start each section on a new page.
- Arrange pages in the following order:
- Title page (page 1).
- Text (starts on page 2).
- Reference list (starts on a new page after the text).
Check headings
- Check that headings accurately reflect the content in each section.
- Start each main section with a Level 1 heading.
- Use Level 2 headings for subsections of the introduction.
- Use the same level of heading for sections of equal importance.
- Avoid having only one subsection within a section (have two or more, or none).
Check assignment instructions
- Remember that instructors’ guidelines supersede APA Style.
- Students should check their assignment guidelines or rubric for specific content to include in their papers and to make sure they are meeting assignment requirements.
Tips for better writing
- Ask for feedback on your paper from a classmate, writing center tutor, or instructor.
- Budget time to implement suggestions.
- Use spell-check and grammar-check to identify potential errors, and then manually check those flagged.
- Proofread the paper by reading it slowly and carefully aloud to yourself.
- Consult your university writing center if you need extra help.
About the author

Undergraduate student resources
Academic Editing and Proofreading
- Tips to Self-Edit Your Dissertation
- Guide to Essay Editing: Methods, Tips, & Examples
- Journal Article Proofreading: Process, Cost, & Checklist
- The A–Z of Dissertation Editing: Standard Rates & Involved Steps
- Research Paper Editing | Guide to a Perfect Research Paper
- Dissertation Proofreading | Definition & Standard Rates
- Thesis Proofreading | Definition, Importance & Standard Pricing
- Research Paper Proofreading | Definition, Significance & Standard Rates
- Essay Proofreading | Options, Cost & Checklist
- Top 10 Paper Editing Services of 2024 (Costs & Features)
- Top 10 Essay Checkers in 2024 (Free & Paid)
- Top 10 AI Proofreaders to Perfect Your Writing in 2024
- Top 10 English Correctors to Perfect Your Text in 2024
- Top 10 Essay Editing Services of 2024
- 10 Advanced AI Text Editors to Transform Writing in 2024
Academic Research
- Research Paper Outline: Templates & Examples
- How to Write a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Write a Lab Report: Examples from Academic Editors
- Research Methodology Guide: Writing Tips, Types, & Examples
- The 10 Best Essential Resources for Academic Research
- 100+ Useful ChatGPT Prompts for Thesis Writing in 2024
- Best ChatGPT Prompts for Academic Writing (100+ Prompts!)
- Sampling Methods Guide: Types, Strategies, and Examples
- Independent vs. Dependent Variables | Meaning & Examples
Academic Writing & Publishing
- Difference Between Paper Editing and Peer Review
- What are the different types of peer review?
- How to deal with rejection from a journal?
- Editing and Proofreading Academic Papers: A Short Guide
- How to Carry Out Secondary Research
- The Results Section of a Dissertation
- Checklist: Is my Article Ready for Submitting to Journals?
- Types of Research Articles to Boost Your Research Profile
- 8 Types of Peer Review Processes You Should Know
- The Ethics of Academic Research
- How does LaTeX based proofreading work?
- How to Improve Your Scientific Writing: A Short Guide
- Chicago Title, Cover Page & Body | Paper Format Guidelines
- How to Write a Thesis Statement: Examples & Tips
- Chicago Style Citation: Quick Guide & Examples
- The A-Z Of Publishing Your Article in A Journal
- What is Journal Article Editing? 3 Reasons You Need It
- 5 Powerful Personal Statement Examples (Template Included)
- Complete Guide to MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Book in APA Style | Format & Examples
- How to Start a Research Paper | Step-by-step Guide
- APA Citations Made Easy with Our Concise Guide for 2024
- A Step-by-Step Guide to APA Formatting Style (7th Edition)
- Top 10 Online Dissertation Editing Services of 2024
- Academic Writing in 2024: 5 Key Dos & Don’ts + Examples
- What Are the Standard Book Sizes for Publishing Your Book?
- MLA Works Cited Page: Quick Tips & Examples
- 2024’s Top 10 Thesis Statement Generators (Free Included!)
- Top 10 Title Page Generators for Students in 2024
- What Is an Open Access Journal? 10 Myths Busted!
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources: Definition, Types & Examples
- How To Write a College Admissions Essay That Stands Out
- How to Write a Dissertation & Thesis Conclusion (+ Examples)
- APA Journal Citation: 7 Types, In-Text Rules, & Examples
- What Is Predatory Publishing and How to Avoid It!
- What Is Plagiarism? Meaning, Types & Examples
- How to Write a Strong Dissertation & Thesis Introduction
- How to Cite a Book in MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Website in MLA Format | 9th Edition Rules
- 10 Best AI Conclusion Generators (Features & Pricing)
- Top 10 Academic Editing Services of 2024 [with Pricing]
- 100+ Writing Prompts for College Students (10+ Categories!)
- Additional Resources
- Plagiarism: How to avoid it in your thesis?
- Final Submission Checklist | Dissertation & Thesis
- 7 Useful MS Word Formatting Tips for Dissertation Writing
- How to Write a MEAL Paragraph: Writing Plan Explained in Detail
- Em Dash vs. En Dash vs. Hyphen: When to Use Which
- The 10 Best Citation Generators in 2024 | Free & Paid Plans!
- 2024’s Top 10 Self-Help Books for Better Living
- The 10 Best Free Character and Word Counters of 2024
- Know Everything About How to Make an Audiobook
- Citation and Referencing
- Citing References: APA, MLA, and Chicago
- How to Cite Sources in the MLA Format
- MLA Citation Examples: Cite Essays, Websites, Movies & More
- Citations and References: What Are They and Why They Matter
- APA Headings & Subheadings | Formatting Guidelines & Examples
- Formatting an APA Reference Page | Template & Examples
- Research Paper Format: APA, MLA, & Chicago Style
- How to Create an MLA Title Page | Format, Steps, & Examples
- How to Create an MLA Header | Format Guidelines & Examples
- MLA Annotated Bibliography | Guidelines and Examples
- APA Website Citation (7th Edition) Guide | Format & Examples
- APA Citation Examples: The Bible, TED Talk, PPT & More
- APA Header Format: 5 Steps & Running Head Examples
- APA Title Page Format Simplified | Examples + Free Template
- How to Write an Abstract in MLA Format: Tips & Examples
- 10 Best Free Plagiarism Checkers of 2024 [100% Free Tools]
- 5 Reasons to Cite Your Sources Properly | Avoid Plagiarism!
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Writing a Dissertation Proposal
- The Acknowledgments Section of a Dissertation
- The Table of Contents Page of a Dissertation
- The Introduction Chapter of a Dissertation
- The Literature Review of a Dissertation
- The Only Dissertation Toolkit You’ll Ever Need!
- 5 Thesis Writing Tips for Master Procrastinators
- How to Write a Dissertation | 5 Tips from Academic Editors
- The 5 Things to Look for in a Dissertation Editing Service
- Top 10 Dissertation Editing & Proofreading Services
- Why is it important to add references to your thesis?
- Thesis Editing | Definition, Scope & Standard Rates
- Expert Formatting Tips on MS Word for Dissertations
- A 7-Step Guide on How to Choose a Dissertation Topic
- 350 Best Dissertation Topic Ideas for All Streams in 2024
- A Guide on How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- Dissertation Defense: What to Expect and How to Prepare
- Creating a Dissertation Title Page (Examples & Templates)
- Essay Writing Guide
- Essential Research Tips for Essay Writing
- What Is a Mind Map? Free Mind Map Templates & Examples
- How to Write an Essay Outline: 5 Examples & Free Template
How to Write an Essay Header: MLA and APA Essay Headers
- What Is an Essay? Structure, Parts, and Types
- How to Write an Essay in 8 Simple Steps (Examples Included)
- 8 Types of Essays | Quick Summary with Examples
- Expository Essays | Step-by-Step Manual with Examples
- Narrative Essay | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay (Examples Included)
- Guide to a Perfect Descriptive Essay [Examples & Outline Included]
- How to Start an Essay: 4 Introduction Paragraph Examples
- How to Write a Conclusion for an Essay (Examples Included!)
- How to Write an Impactful Personal Statement (Examples Included)
- Literary Analysis Essay: 5 Steps to a Perfect Assignment
- Compare and Contrast Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
- Top AI Essay Writers in 2024: 10 Must-Haves
- 100 Best College Essay Topics & How to Pick the Perfect One!
- College Essay Format: Tips, Examples, and Free Template
- Structure of an Essay: 5 Tips to Write an Outstanding Essay
- 10 Best AI Essay Outline Generators of 2024
- The Best Essay Graders of 2024 That You Can Use for Free!
- Top 10 Free Essay Writing Tools for Students in 2024
Still have questions? Leave a comment
Add Comment

Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!
Examples: Edited Papers
Need editing and proofreading services.
- Tags: Essay , Essay Editing
A header for an essay is an important part of APA or MLA formatting guidelines . In this article, we’ll find out the purpose of an essay header, how to format it, and the APA and MLA essay header variations.
A properly formatted header helps your professor quickly and easily identify your essay. In APA format , the essay header also carries a gist of your larger topic, providing the reader with basic information about your essay in one glance.
Let’s take a more detailed look at how to write a header for an essay.
Ensure top-notch essay formatting! Get started
What is a header in an essay?
A header for an essay is a line of text typically included at the top of the page. The content of the header depends on your essay header format. The MLA essay header includes your last name whereas the APA essay header includes a shortened title of your essay.
The use of a header is especially important in longer essays, as it helps professors navigate the document with ease. The page number helps them locate specific information quickly and the author’s name helps them associate each essay with the student who wrote it.
MLA essay header
The Modern Language Association (MLA), often used in literature and humanities essays, requires a specific type of header. It consists of your last name, followed by a space and then the page number. Thus, the MLA essay header helps the instructor easily associate your work with you amidst a sea of other assignments.
The header for an MLA format essay is typically placed in the top right-hand corner of each page of the document. The information is right-aligned, double-spaced, and is usually preceded by a 0.5-inch margin.
Here’s an essay header example to help you understand:
It is important to note that the MLA essay header is not the same as a title page. The title page is a separate page that includes the essay title, your name, the course title, and the date of submission. The MLA format essay header is simply a standardized way to format page numbers and your personal information within the document itself.
APA essay header
The American Psychological Association (APA) usually requires a header to be included in both student and professional essays. The APA essay header includes an abbreviated title of the essay along with the page number.
The title should be in all capital letters and should not be more than 50 characters long. It should be included on the top left corner of the page. The page number should be included opposite the title, in the top right corner of the page.
Take a look at this essay header example:
It is important to note that running head in an APA essay header is optional for students but compulsory for professionals. While the header must be present in both types of APA essays, the elements differ.
How to write a header for an essay
1. To activate the header for an essay, double-right-click on the top of the page.
If you need additional help with headers and other formatting guidelines, you can also consider working with a professional essay editing service .
Want to keep reading? Here are the newest articles we’ve worked on:
- How to Write an Essay in 8 Simple Steps
- Learn About What is an Essay and Parts of an Essay
- How to Write an Essay Outline

Frequently Asked Questions
Are the header and title exactly the same, should i use my full name in the mla header, what are running apa headers.
Found this article helpful?
Leave a Comment: Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Your vs. You’re: When to Use Your and You’re
Your organization needs a technical editor: here’s why, your guide to the best ebook readers in 2024, writing for the web: 7 expert tips for web content writing.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get carefully curated resources about writing, editing, and publishing in the comfort of your inbox.
How to Copyright Your Book?
If you’ve thought about copyrighting your book, you’re on the right path.
© 2024 All rights reserved
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self Publishing Guide
- Pre-Publishing Steps
- Fiction Writing Tips
- Traditional Publishing
- Academic Writing and Publishing
- Partner with us
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Job Applicant
- Cover letter
- Resource Center
- Case studies
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
College Application Essay Format Rules
The college application essay has become the most important part of applying to college. In this article, we will go over the best college essay format for getting into top schools, including how to structure the elements of a college admissions essay: margins, font, paragraphs, spacing, headers, and organization.
We will focus on commonly asked questions about the best college essay structure. Finally, we will go over essay formatting tips and examples.
Table of Contents
- General college essay formatting rules
- How to format a college admissions essay
- Sections of a college admissions essay
- College application essay format examples
General College Essay Format Rules
Before talking about how to format your college admission essays, we need to talk about general college essay formatting rules.
Pay attention to word count
It has been well-established that the most important rule of college application essays is to not go over the specific Application Essay word limit . The word limit for the Common Application essay is typically 500-650 words.
Not only may it be impossible to go over the word count (in the case of the Common Application essay , which uses text fields), but admissions officers often use software that will throw out any essay that breaks this rule. Following directions is a key indicator of being a successful student.
Refocusing on the essay prompt and eliminating unnecessary adverbs, filler words, and prepositional phrases will help improve your essay.
On the other hand, it is advisable to use almost every available word. The college essay application field is very competitive, so leaving extra words on the table puts you at a disadvantage. Include an example or anecdote near the end of your essay to meet the total word count.
Do not write a wall of text: use paragraphs
Here is a brutal truth: College admissions counselors only read the application essays that help them make a decision . Otherwise, they will not read the essay at all. The problem is that you do not know whether the rest of your application (transcripts, academic record, awards, etc.) will be competitive enough to get you accepted.
A very simple writing rule for your application essay (and for essay editing of any type) is to make your writing readable by adding line breaks and separate paragraphs.
Line breaks do not count toward word count, so they are a very easy way to organize your essay structure, ideas, and topics. Remember, college counselors, if you’re lucky, will spend 30 sec to 1 minute reading your essay. Give them every opportunity to understand your writing.
Do not include an essay title
Unless specifically required, do not use a title for your personal statement or essay. This is a waste of your word limit and is redundant since the essay prompt itself serves as the title.
Never use overly casual, colloquial, or text message-based formatting like this:
THIS IS A REALLY IMPORTANT POINT!. #collegeapplication #collegeessay.
Under no circumstances should you use emojis, all caps, symbols, hashtags, or slang in a college essay. Although technology, texting, and social media are continuing to transform how we use modern language (what a great topic for a college application essay!), admissions officers will view the use of these casual formatting elements as immature and inappropriate for such an important document.
How To Format A College Application Essay
There are many tips for writing college admissions essays . How you upload your college application essay depends on whether you will be cutting and pasting your essay into a text box in an online application form or attaching a formatted document.
Save and upload your college essay in the proper format
Check the application instructions if you’re not sure what you need to do. Currently, the Common Application requires you to copy and paste your essay into a text box.
There are three main formats when it comes to submitting your college essay or personal statement:
If submitting your application essay in a text box
For the Common Application, there is no need to attach a document since there is a dedicated input field. You still want to write your essay in a word processor or Google doc. Just make sure once you copy-paste your essay into the text box that your line breaks (paragraphs), indents, and formatting is retained.
- Formatting like bold , underline, and italics are often lost when copy-pasting into a text box.
- Double-check that you are under the word limit. Word counts may be different within the text box .
- Make sure that paragraphs and spacing are maintained; text input fields often undo indents and double-spacing .
- If possible, make sure the font is standardized. Text input boxes usually allow just one font .
If submitting your application essay as a document
When attaching a document, you must do more than just double-check the format of your admissions essay. You need to be proactive and make sure the structure is logical and will be attractive to readers.
Microsoft Word (.DOC) format
If you are submitting your application essay as a file upload, then you will likely submit a .doc or .docx file. The downside is that MS Word files are editable, and there are sometimes conflicts between different MS Word versions (2010 vs 2016 vs Office365). The upside is that Word can be opened by almost any text program.
This is a safe choice if maintaining the visual elements of your essay is important. Saving your essay as a PDF prevents any formatting issues that come with Microsoft Word, since older versions are sometimes incompatible with the newer formatting.
Although PDF viewing programs are commonly available, many older readers and Internet users (who will be your admissions officers) may not be ready to view PDFs.
- Use 1-inch margins . This is the default setting for Microsoft Word. However, students from Asia using programs like Hangul Word Processor will need to double-check.
- Use a standard serif font. These include Times New Roman, Courier, and Garamond. A serif font adds professionalism to your essay.
- Use standard 12-font size.
- Use 1.5- or double-spacing. Your application essay should be readable. Double spaces are not an issue as the essay should already fit on one page.
- Add a Header with your First Name, Last Name, university, and other required information.
- Clearly separate your paragraphs. By default, just press ‘ENTER’ twice.
Sections Of A College Admissions Essay
University admissions protocols usually allow you to choose the format and style of your writing. Despite this, the general format of “Introduction-Body-Conclusion” is the most common structure. This is a common format you can use and adjust to your specific writing style.
College Application Essay Introduction
Typically, your first paragraph should introduce you or the topic that you will discuss. You must have a killer opener if you want the admissions committees to pay attention.
Essays that use rhetorical tools, factual statements, dialog, etc. are encouraged. There is room to be creative since many application essays specifically focus on past learning experiences.
College Application Essay Body
Clearly answering the essay prompt is the most important part of the essay body. Keep reading over the prompt and making sure everything in the body supports it.
Since personal statement essays are designed to show you are as a person and student, the essay body is also where you talk about your experiences and identity.
Make sure you include the following life experiences and how they relate to the essay prompt. Be sure to double-check that they relate back to the essay prompt. A college admissions essay is NOT an autobiography:
Personal challenges
- How did you overcome them?
- How or how much do past challenges define your current outlook or worldview?
- What did you learn about yourself when you failed?
Personal achievements and successes
- What people helped you along the way?
- What did you learn about the nature of success
Lessons learned
- In general, did your experiences inform your choice of university or major?
Personal beliefs
- Politics, philosophy, and religion may be included here, but be careful when discussing sensitive personal or political topics.
- Academic goals
- Personal goals
- Professional goals
- How will attending the university help you achieve these goals?
College Application Essay Conclusion
The conclusion section is a call to action directly aimed at the admissions officers. You must demonstrate why you are a great fit for the university, which means you should refer to specific programs, majors, or professors that guided or inspired you.
In this “why this school” part of the essay, you can also explain why the university is a great fit for your goals. Be straightforward and truthful, but express your interest in the school boldly.

College Application Essay Format Examples
Here are several formatting examples of successful college admission essays, along with comments from the essay editor.
Note: Actual sample essays edited by Wordvice professional editors . Personal info has been redacted for privacy. This is not a college essay template.
College Admission Essay Example 1
This essay asks the student to write about how normal life experiences can have huge effects on personal growth:
Common App Essay Prompt: Thoughtful Rides
The Florida turnpike is a very redundant and plain expressway; we do not have the scenic luxury of mountains, forests, or even deserts stretching endlessly into the distance. Instead, we are blessed with repetitive fields of grazing cows and countless billboards advertising local businesses. I have been subjected to these monotonous views three times a week, driving two hours every other day to Sunrise and back to my house in Miami, Florida—all to practice for my competitive soccer team in hopes of receiving a scholarship to play soccer at the next level.
The Introduction sets up a clear, visceral memory and communicates a key extracurricular activity.
When I first began these mini road trips, I would jam out to my country playlist and sing along with my favorite artists, and the trek would seem relatively short. However, after listening to “Beautiful Crazy” by Luke Combs for the 48th time in a week, the song became as repetitive as the landscape I was driving through. Changing genres did not help much either; everything I played seemed to morph into the same brain-numbing sound. Eventually, I decided to do what many peers in my generation fail to do: turn off the distractions, enjoy the silence, and immerse myself in my own thoughts. In the end, this seemingly simple decision led to a lot of personal growth and tranquility in my life.
The first part of the Body connects the student’s past experience with the essay prompt: personal growth and challenging assumptions.
Although I did not fully realize it at the time, these rides were the perfect opportunity to reflect on myself and the people around me. I quickly began noticing the different personalities surrounding me in the flow of traffic, and this simple act of noticing reminded me that I was not the only human on this planet that mattered. I was just as unimportant as the woman sitting in the car next to mine. Conversely, I also came to appreciate how a gesture as simple as letting another driver merge into your lane can impact a stranger’s day. Maybe the other driver is late for a work interview or rushing to the hospital because their newborn is running a high fever and by allowing them to advance in the row of cars, you made their day just a little less stressful. I realized that if I could improve someone else’s day from my car, I could definitely be a kinder person and take other people’s situations into consideration—because you never know if someone is having one of the worst days of their lives and their interaction with you could provide the motivation they need to keep going on .
This part uses two examples to support the writer’s answer to the essay prompt. It ends the paragraph with a clear statement.
Realizing I was not the only being in the universe that mattered was not the only insight I attained during these drives. Over and over, I asked myself why I had chosen to change soccer clubs, leaving Pinecrest, the team I had played on for 8 years with my best friends and that was only a 10-minute drive from my house, to play for a completely unfamiliar team that required significantly more travel. Eventually, I came to understand that I truly enjoy challenging myself and pushing past complacency . One of my main goals in life is to play and experience college soccer—that, and to eventually pursue a career as a doctor. Ultimately, leaving my comfort zone in Pinecrest, where mediocrity was celebrated, to join a team in Sunrise, where championships were expected and college offers were abundant, was a very positive decision in my life.
This part clearly tells how the experience shaped the writer as a person. The student’s personality can be directly attributed to this memory. It also importantly states personal and academic goals.
Even if I do not end up playing college soccer, I know now that I will never back down from any challenge in my life; I am committed to pushing myself past my comfort zone. These car rides have given me insight into how strong I truly am and how much impact I can have on other people’s lives.
The Conclusion restates the overall lesson learned.
College Admission Essay Example 2
The next essay asks the reader to use leadership roles or extracurricular activities and describe the experience, contribution, and what the student learned about themselves.
As I release the air from the blood-pressure monitor’s valve, I carefully track the gauge, listening for the faint “lub-dub” of Winnie’s heart. Checking off the “hypertensive” box on his medical chart when reading 150/95, I then escort Winnie to the blood sugar station. This was the typical procedure of a volunteer at the UConn Migrant Farm Worker Clinic. Our traveling medical clinic operated at night, visiting various Connecticut farms to provide healthcare for migrant workers. Filling out charts, taking blood pressure, and recording BMI were all standard procedures, but the relationships I built with farmers such as Winnie impacted me the most.
This Introduction is very impactful. It highlights the student’s professional expertise as a healthcare worker and her impact on marginalized communities. It also is written in the present tense to add impact.
While the clinic was canceled this year due to COVID-19, I still wanted to do something for them. During a PPE-drive meeting this July, Winnie recounted his family history. I noticed his eyebrows furrow with anxiety as he spoke about his family’s safety in Tierra Blanca, Mexico. I realized that Winnie lacked substantial information about his hometown, and fear-mongering headlines did nothing to assuage his fears. After days of searching, I discovered that his hometown, Guanajuato, reported fewer cases of COVID-19 in comparison with surrounding towns. I then created a color-coded map of his town, showing rates across the different districts. Winnie’s eyes softened, marveling at the map I made for him this August. I didn’t need to explain what he saw: Guanajuato, his home state, was pale yellow, the color I chose to mark the lowest level of cases. By making this map, I didn’t intend to give him new hope; I wanted to show him where hope was.
The student continues to tell the powerful story of one of her patients. This humbles and empowers the student, motivating her in the next paragraph.
This interaction fueled my commitment to search for hope in my journey of becoming a public health official. Working in public health policy, I hope to tackle complex world problems, such as economic and social barriers to healthcare and find creative methods of improving outcomes in queer and Latinx communities. I want to study the present and potential future intervention strategies in minority communities for addressing language barriers to information including language on posters and gendered language, and for instituting social and support services for community youth. These stepping stones will hopefully prepare me for conducting professional research for the Medical Organization for Latino Advancement. I aspire to be an active proponent of healthcare access and equity for marginalized groups, including queer communities. I first learned about the importance of recognizing minority identities in healthcare through my bisexual sister, Sophie, and her nonbinary friend, Gilligan. During discussions with her friends, I realized the importance of validating diverse gender expressions in all facets of my life.
Here, the past experience is directly connected to future academic and professional goals, which themselves are motivated by a desire to increase access among communities as well as personal family experiences. This is a strong case for why personal identity is so important.
My experiences with Winnie and my sister have empowered me to be creative, thoughtful, and brave while challenging the assumptions currently embedded in the “visual vocabulary” of both the art and science fields. I envision myself deconstructing hegemonic ideas of masculinity and femininity and surmounting the limitations of traditional perceptions of male and female bodies as it relates to existing healthcare practices. Through these subtle changes, I aim to make a large impact.
The Conclusion positions the student as an impactful leader and visionary. This is a powerful case for the admissions board to consider.
If you want to read more college admissions essay examples, check out our articles about successful college personal statements and the 2021-2022 Common App prompts and example essays .
Wordvice offers a full suite of proofreading and editing services . If you are a student applying to college and are having trouble with the best college admissions essay format, check out our application essay editing services (including personal statement editing ) and find out how much online proofreading costs .
Finally, don’t forget to receive common app essay editing and professional admissions editing for any other admissions documents for college, university, and post-doctoral programs.
Our Services
College Admissions Counseling
UK University Admissions Counseling
EU University Admissions Counseling
College Athletic Recruitment
Crimson Rise: College Prep for Middle Schoolers
Indigo Research: Online Research Opportunities for High Schoolers
Delta Institute: Work Experience Programs For High Schoolers
Graduate School Admissions Counseling
Private Boarding & Day School Admissions
Essay Review
Financial Aid & Merit Scholarships
Our Leaders and Counselors
Our Student Success
Crimson Student Alumni
Our Results
Our Reviews
Our Scholarships
Careers at Crimson
University Profiles
US College Admissions Calculator
GPA Calculator
Practice Standardized Tests
SAT Practice Test
ACT Practice Tests
Personal Essay Topic Generator
eBooks and Infographics
Crimson YouTube Channel
Summer Apply - Best Summer Programs
Top of the Class Podcast
ACCEPTED! Book by Jamie Beaton
Crimson Global Academy
+1 (646) 419-3178
Go back to all articles
How To Format & Structure Your College Application Essay
/f/64062/1200x630/0e6a407858/college-essay-format.jpg)
Part I: What Is a College Essay?
Part II: College Essay Formats
Choosing the Best Format
Part III: Structure
Part IV: Revising With a Rubric
Part V: Nuts & Bolts Formatting
This blog post provides a comprehensive guide to college essay formats and structures, covering the purpose of the essay in admissions, the differences between personal narratives and personal essays, and a variety of both common and creative essay structures. It also includes a concise rubric for evaluating essays and practical tips on formatting and submitting your final draft. Whether you’re just starting your essay or refining your final version, your essay is a crucial application component. The principles and insights in this post will position you to write the kind of essays submitted by top applicants.
Crafting a compelling college essay is a critical part of the admissions process, but it can also be one of the most daunting. Understanding the different formats and structures available can help you tell your story in a way that resonates with admissions officers.
Whether you're writing a personal narrative , personal essay , or a reflective essay , this guide will walk you through the key elements to consider, offering practical tips and creative strategies to help your essay stand out.
First, it's important to understand that the essays you write in high school differ from what you have to write in your college application essays . Whether you’re writing the Common App Essay , Supplemental Essays, or UCAS Personal Statement , it's crucial that you prepare ahead of time to do your absolute best. Read ahead for guidelines on how to format and structure a college application essay and what mistakes to avoid.
Interested in learning more? Attend one of our free events
How to get into top stem schools like stanford & mit.
Tuesday, September 10, 2024 12:00 AM CUT
Hear from a Former Princeton Admissions Officer about what it takes to get into ultra-competitive STEM programs at the country's best universities!
REGISTER NOW
Part I. What Is a College Essay?
A college essay introduces you to your prospective college or university.
It’s common for these essays to have a prescribed length between 200 and 600 words .
The college essay is a pillar of most applications because it offers a glimpse into who you are as a person and helps admissions officers gauge your potential fit in a college community.
Your choice of format and structure will also be guided by the specific prompt you’re writing to and how you approach the prompt, based on your own unique personal circumstances and the college context.
The Format Is Not Familiar to Many Students; But It's Not Counter-intuitive Either
Many students have little experience or formal teaching for this kind of writing format, and have had little opportunity to experiment with it and get feedback.
Shifting gears away from what many US students learn about writing a 5-Paragraph Essay or any similar form of expository essay, let's put the college essay writing format into a more familiar perspective.
Imagine you’ve decided to (or been asked to) write a brief memoir of your life.
Or, imagine you’re asked to develop and write a thoughtful personal reflection about a favorite activity, book, or influential event in your life.
Do these examples make writing a college essay feel a bit more approachable? I hope so!
We all have a story to tell that can help strangers know us better.
We all have a capacity for sharing our reflections on formative and memorable personal experiences or big life questions or concepts.
And when we do that, we’re sharing in much the same way we share in a college essay.
Navigating College Essays Prompts
For some students, the prompt can be both helpful and intimidating:
- It narrows the focus of your essay, providing some clear direction, but also setting an expectation about what the reader wants to learn about you.
- It often leaves you lots of latitude for interpreting it how you want to.
- It leaves you to choose, develop, and share the most relevant personal thoughts and experiences.
- It can offer quite a bit of latitude for how you format and structure the final essay.
Here is an example of an actual college essay prompt from Yale :
Reflect on your membership in a community to which you feel connected. Why is this community meaningful to you? You may define community however you like.
Prompts Typically Probe Your Personal Experiences and Thoughts
This kind of essay isn’t about information and facts, or your resume! You're going to need to write about yourself, through the lens of your own feelings, thoughts, perceptions, and experiences. This can involve some uncomfortable honesty, candor, and vulnerability, and a level of subjectivity that's foreign to most academic writing you're used to!
To drive this point home, note that the words you/your appear five times in the prompt from Yale!
Also, the prompt even tells you that “community” can be defined however you like . That's nice freedom... BUT, you're left with the challenge of making a coherent essay out of your thoughts and reflections.
Decoding College Essay Prompts
While the general purpose of a college essay is to introduce yourself to admissions officers or help school leaders gauge your "fit" with their school, you’ll want to decode the essay prompt for more nuanced clarity on the purpose of your essay.
For most college essay prompts, “decoding” is very straightforward, but it’s still important:
- Helping you think about the purpose of your essay in more specific terms
- Guiding your editorial choices, in terms of what you want to share, highlight, and emphasize
Use the specific admissions context to guide decoding.
Using the example above, it’s clear Yale wants to get a sense of how you’ll thrive in a very social learning environment: from interactions with a study group, to collaborating in a school club, orchestra, or athletic team, or thriving in the the larger campus community…
One can go a step further, putting the prompt (and the essay you’ll write) into a larger context . Yale no doubt understands its role in preparing students for future leadership. High-level, innovative leadership requires a well-honed ability to navigate complex community and public/private interactions, collaborations, and even rivalries.
In the end, your essay will focus on what’s real and authentic for you personally, but decoding the prompt in its larger admissions context can help you decide what content is most relevant.
Key Takeaways for Writing to College Essay Prompts:
- Understand what prompts are: A prompt provides a question or statement that highlights something the admissions officers want you to reveal about yourself, but also allows for a fair amount of subjectivity and personal voice, style, and creativity.
- Decode the prompt and brainstorm relevant content: Think about the underlying purpose and context for the prompt and essay — make sure the content is responsive, but also personalized, being genuine and authentic.
- Leverage the prompt as a catalyst to say something important, insightful, and compelling about your personality, character, and/or aspirations, values, and commitments.

What’s the Difference Between a College Essay and a Personal Statement ?
Good question!
In some contexts, or when used loosely, the two terms may periodically be used interchangeably.
But in most contexts, personal statements are different from college essays , even if both are used for admissions.
1. Personal Statement
- A personal statement is common when you apply for a scholarship, or a school wants you to clarify your interest and motivation for applying to a specific major. And personal statements are prevalent in the UK admissions process.
- It tends to be more factual and less personal than a college essay (a bit more like a resume).
If you use the UCAS platform to apply to a UK school, you’ll be asked to write a clear and concise “personal statement” under 4,000 characters that includes the following type of personal information:
- Personal skills and achievements
- Work experience and future plans
- Positions of responsibility held, or have held, both in and out of school
- Details of jobs, placements, work experience, or voluntary work, particularly if it's relevant to the course
- How the applicant has prepared for their chosen area of study
- Why they enjoy and are good at the subject
- A good level of academic terminology and experience
As you can see, a personal statement is autobiographical but in a more matter of fact way , making it less subjective and less intimate in terms of sharing about identity, nuanced thoughts, and formative personal experiences.
A personal statement requires time and effort, but the task is more straightforward, based on resume-type information, qualifications, and academic or professional goals.
A college essay has a prescribed focus, but it’s also asking you to share values, reflections, and ideas, and speak to your personality, attributes, and aspirations. This makes your approach more open-ended, and it’s a big departure from more practical forms of business communication or academic writing.
Part II: The Format of a College Essay
In this section will delve more deeply into the general format of a college essay, with a closer look at the two most relevant formats for this kind of writing task:
- Personal Essay & Reflective Essay
- Personal Narrative
A college essay will typically have the overall format (structure, voice, and perspective) of a personal essay/reflective essay OR personal narrative .
Features of a Personal Essay Format
A personal essay is a reflective piece of writing that explores a specific theme or topic from the author's life. Rather than following a story arc, a personal essay delves into events, influences, personality traits, or beliefs and reflections related to a larger personal theme.
Features of a Personal or Reflective Essay Format:
- Topical Structure : Organized around a central theme or topic, rather than following a chronological narrative. The essay often explores different facets of the theme through various examples or reflections.
- Analytical Approach : Focuses on analyzing and reflecting on personal experiences, thoughts, or ideas. The writing is introspective and seeks to draw broader insights or conclusions from personal events.
- Logical Flow : Maintains a clear, logical progression of ideas, often following the structure of an introduction, body, and conclusion. Each paragraph or section builds on the previous one to support the essay's main theme or argument.
- Reflective Tone : Emphasizes the writer's internal thought process and personal growth. The tone is often contemplative, exploring how specific experiences or ideas have shaped the writer's perspective.
- Less Dialogue, More Reflection : Unlike a narrative, a personal essay rarely includes dialogue or detailed storytelling. Instead, it focuses on the writer's reflections, insights, and the connections they make between their experiences and the essay's theme.
- Unified Theme : The essay revolves around a single, cohesive theme or message. All examples and reflections are tied back to this central idea, creating a sense of unity and purpose throughout the essay.
- Purposeful Conclusion : Ends with a thoughtful conclusion that ties together the reflections and insights, often leaving the reader with a lasting impression or a broader understanding of the theme.
A reflective essay format is similar to a personal essay format, but making a distinction may be helpful.
Some college essay prompts will ask students to share their introspective views of a big idea or concept. This aligns with a reflective essay format , for most circumstances.
With less focus on life events and experiences than a personal essay, a reflective essay focuses on a writer's inner thoughts : this format is ideally suited for sharing thoughts and ideas, revealing how you make mental connections between influences, experiences, and thoughts, and spotlighting evolving ideas and perspectives that shape your identity or academic interests.
Features of a Personal Narrative Format
A personal narrative is a story about a specific experience or event from the author's life, focusing on a particular moment or series of events and the emotions and lessons associated with it.
Features of a Personal Narrative Format:
- Storytelling Elements : Utilizes writing techniques and elements commonly found in novels and short stories, such as character development, plot, and setting.
- Descriptive Details : Includes vivid descriptions that evoke the setting, characters, and atmosphere, helping the reader visualize and connect with the story.
- Dialogue and Inner Thoughts : May incorporate dialogue and inner thoughts to reveal character emotions, intentions, and relationships, making the narrative more dynamic and engaging.
- Chronological Order : Often unfolds in chronological order, recounting events as they happened. This can be over an extended period or within a single moment, depending on the story's focus.
- Sensory Details : Enriches the narrative with sensory details — sights, sounds, smells, tastes, and textures — that immerse the reader in the experience.
- Suspense and Conflict : Includes elements of suspense, conflict, or intrigue that engage the reader and drive the narrative forward, often creating anticipation for the reader about a resolution or revelation.
- Focused on a Specific Event or Experience : Centers around a particular event or moment in the author’s life, exploring the emotions, lessons, and impacts associated with it.
Depending on the prompt and the content and themes that you most want to recount and share, a college essay may use one of the formats above exclusively, but oftentimes a college essay will be made more effective by integrating features from one or more of these college essay formats.
A Note on the Unconventional “Third-Person” Personal Essay
There can always be creative exceptions to what’s most common…
One such example is using the third-person voice instead of the first-person voice.
While personal essays are typically written in the first person, some applicants choose to take an unconventional approach by writing about themselves from an external perspective.
This method involves observing oneself as if under a microscope, adopting a tone that is intentionally dispassionate, objective, and impersonal — even though the essay is deeply personal. In this style, the writer may even refer to themselves in the third person (using "he," "she," or sometimes their own name) instead of the usual first person ("I").
This approach can offer a unique angle and a distinctive narrative voice, though it requires some artistry to maintain clarity and a strong connection with the reader.
Choosing a Dominant Format: Personal Essay vs. Personal Narrative
When choosing the best format for a college essay, you’ll want to start with brainstorming and ideation.
Your final choice of format and perspective will depend on the prompt in particular, and how you envision responding to the prompt.
What kind of information is the prompt asking you to share about yourself?
- If a prompt asks an applicant to delve into their “life story” so to speak, most writers will find a narrative format a natural choice.
- If a prompt asks the applicant to share their thoughts about a core value or concept shaping their academic goals and interests, the writer will probably find a reflective essay format is best.
- Another writer, however, may have a gripping life experience, or set of experiences, that shaped a core value in their life, so they may want to share these experiences using narrative features within a larger essay structure.
As you can see, both narrative features and analytical essay features can be effective for a college essay.
When deciding which formats are best for your essay, you’ll want to consider both the prompt itself and the kind of content you want to share based on your personal circumstances.
Showing, Not Telling
Whether you choose a narrative or essay format, the purpose of a college essay is to introduce yourself in a very personal way, including expressing some personal, intellectual, and emotional honesty, authenticity, and vulnerability, rather than just listing autobiographical data, as on a resume.
Doing this effectively can also make an essay more memorable, leaving a stronger impact on the reader (which is a challenge when top schools have so many applicants).
Showing, not telling is an effective strategy to create a stronger bond between writer and reader, and to cultivate empathy and intimacy.
Tips and Techniques for Showing, Not Telling
- Use Anecdotes : Share personal stories that reveal key aspects of your personality, character, or perspectives in a narrative style.
- Use an Authentic First-Person Voice : Write in a way that allows the reader to hear your unique voice and thoughts, rather than adopting an academic tone.
- Cultivate Empathy : Aim to make the reader feel as if they are walking in your shoes, getting to know you as they would a character in a novel.
- Show Authenticity and Vulnerability : Include your thought process, doubts, and the evolution of your beliefs or values, reflecting personal growth and individuality.
- Incorporate Introspection : Enrich your narrative with insights into your inner thoughts, impressions, and changing understandings.
- Embrace Subjectivity : Share candid, fun, and interesting details about yourself using your authentic voice.
- Use Vivid Descriptions : Depict scenes, people, or settings with sensory details, dialogue, and inner thoughts to show rather than tell.
Key Takeaways for the College Essay Format
- Understanding the Context : The "college essay" here refers to the personal essays you write for college applications, not the academic essays you'll write in college classes.
- Format Flexibility : This type of essay is not a 5-paragraph academic or expository essay. It typically takes the form of a personal essay or personal narrative.
- Choosing the Right Format : Select a format—personal essay or personal narrative—that best suits the prompt and the story or message you want to convey. Align your format with the content you wish to highlight.
- Showing vs. Telling : Focus on "showing" through vivid descriptions, anecdotes, and introspection. However, a more reflective essay may emphasize ideas and concepts over storytelling.
Key Do’s and Don’ts
- Use an Authentic Voice : Let your true personality and perspective shine through.
- Engage the Reader : Share insights that reveal compelling personal qualities or traits.
- Show, Don’t Tell : Use vivid descriptions, candid reflections, and personal stories to illustrate your points.
- Be Introspective : Reflect on your experiences and share your thought process, showing authenticity and vulnerability.
- Make a Positive Impression : Highlight your strengths while being honest and humble.
- Always Get Outside Input: Always have a trusted peer and trusted adult, a skilled admissions counselor if possible, give you input before you spend too much time on an essay or submit a final version of an essay.
- Don't Overshare: You want to help schools know you, and you want to make a memorable impression, but a college application is not an arena for sharing overly personal or overly sensitive details about your life. Be sincere and genuine but remain discreet and professional overall.
- Avoid Boasting : Refrain from listing achievements or writing a resume in essay form.
- Don’t Repeat Application Information : Avoid discussing grades or activities already covered in other parts of your application. Use your essay to add depth and insight beyond the facts.
We’ve done a deep dive into the format, perspective, and kinds of writing elements to use in a college essay. But when it comes time to put it together — to outline, compose, and organize — you’ll often find you really don’t have a lot of room in a college essay. this makes it imperative to work within a well defined structure that fits your prompt and the content you're sharing.
In Part III, below, you'll learn crucial tips for structuring an essay so it's memorable and makes its mark on readers. You'll also discover just how many kinds of creative structures you can choose from!
Red Flags To Avoid On Your College Essay
Top 5 Common App Personal Essay Red Flags
Part III: The Structure of a College Essay
First, let’s take a look at how to structure the beginning, middle, and end of a college essay to make it as effective as possible.
Start Your Essay With a Strong Hook
You’ll want an effective hook to give your essay a strong start, and set the stage for making a bigger impact on your reader, helping your essay, and application, stand out!
A creative and imaginative hook is one that announces a larger, unifying theme and also creates some form of invitation or tension, drawing the reader in, so almost without realizing it, they need to read the next part and can't wait to find out more…
One caution here: don’t create a “hook” because you think it’s necessary to show you’re a “good writer.” That’s not really the point.
- The hook should be one hundred percent authentic to what you’re revealing or introducing about yourself
- The hook should bring to the foreground a compelling theme, question, doubt, emotion, or conflict (to be explored and potentially also resolved later in the essay or narrative)
- The hook gets the college essay off to a strong start, so the reader forgets the pile of essays on their desk, being drawn into your story, or your dilemma, or your thoughts…
- Instead of thinking about an “introduction” to your essay, as in a 5-Paragraph Essay, imagine you’re skipping the introduction— the preliminaries — altogether. Go straight to the heart of the matter instead. This is like grabbing the reader by the shirt, or like shooting a gun to start a race!
Create intrigue, suspense, or curiosity…
Since a hook can take so many forms and needs to be so integral to your essay, there’s no fixed recipe to offer.
That said, one way to gauge the power of a hook is by the measure of intrigue, emotion, and curiosity it sparks in the reader .
Here are examples for inspiration:
When I read Frederick Douglass’ account of learning how to read while enslaved, there was one detail that I couldn’t forget, one I’ve been thinking about in my own life over and over again…
My brother died when I was only thirteen and while I look whole on the outside, I sometimes think if people really could see me it would be like I was missing a leg or confined to a wheelchair, it’s just that it’s not physical, but the loss doesn't go away and makes me feel different. And it's become part of who I am.
My stepfather doesn’t believe college is worth it and doesn’t approve of my decision to go to college, let alone go to a really selective one. One week in my junior year the conflict took a turn for the worse, but what happened eventually helped me understand why my motivation to study political science is different from the interest others have in fixing laws and making the country better.
As you can see, each hook has most or all of these features:
- Spotlights a dominant question, emotion, or conflict
- Leaves something crucial unsaid (for the time being), sparking intrigue, suspense, and curiosity
- Announces a central theme , such as an idea or concept shaping my worldview; a key insight into my own sense of self and identity; a compelling conflict that ended up shaping my academic interests...
- Cultivates intimacy and a bond with the reader , immediately conveying honesty, authenticity, and a dose of vulnerability.
With an effective hook your essay comes out of the gate like a racehorse, beginning with the very first sentence! Most likely your reader won’t put down your essay to go to the concession stand either. Instead, they'll keep reading and really start to care about your story and your educational aspirations and future!
The Middle Phase: A Body of Ideas, Experiences, Impressions…
The middle phase is all the stuff you need to share to add depth and conviction to your writing and core themes, while also maintaining the reader’s engagement. It will also help you personalize your essay, as you share inner thoughts or recount real personal experiences.
Here are some strategies you may find helpful as you develop your ideas for this section of your essay.
Note: you may need to ignore what's not relevant or less relevant based on the structure, content, or approach you're using.
1. Develop Your Narrative or Argument
- Build on the Introduction : Expand on the themes, ideas, or experiences introduced at the beginning. This helps create a sense of continuity and deepens the reader's understanding of your perspective.
- Include Specific Examples : Use concrete examples, anecdotes, or details to illustrate your points. Specificity adds credibility and helps the reader connect with your experiences on a personal level.
- Show, Don’t Just Tell : Use descriptive language and sensory details to create vivid images that allow the reader to experience the story alongside you. This technique makes your writing more engaging and impactful.
2. Maintain a Clear Structure
- Use a Well-defined and Well-aligned Structure : Be clear on the structure you’re using and how it aligns with your content. You have lots of structures to choose from (as you’ll see in a moment), so don’t get stuck thinking about your college essay like it’s a 5-Paragraph Essay; it’s not. Clear organization helps the reader follow your train of thought, but some essays will be great with more creative, less linear structures, to create strong sensory impressions or elicit emotional responses from the reader.
- Develop Key Themes : Reinforce your main themes or ideas throughout the middle section. Repeated references to these themes emphasize their importance and help create a unified narrative.
3. Show Growth and Reflection
- Explore Personal Growth : Use the middle section to delve into how your experiences have shaped you. Reflect on challenges you’ve faced, lessons you’ve learned, and how you’ve changed over time.
- Analyze the Significance : Go beyond describing events; analyze their significance. Explain why certain moments were important to you and how they contributed to your development or perspective.
4. Engage the Reader Emotionally
- Tap into Emotions : Share your thoughts and feelings authentically to build an emotional connection with the reader. Whether through moments of joy, fear, determination, or introspection, emotional depth makes your narrative more compelling.
- Create Tension or Conflict : Introduce challenges, conflicts, or turning points in your story. These elements add drama and keep the reader invested in how you navigate or resolve these situations.
5. Balance Introspection and Action
- Interweave Action with Reflection : Combine narrative action (what happened) with reflective passages (what you thought or felt about it). This balance keeps the story dynamic while allowing for introspection and analysis.
- Avoid Overloading with Reflection : While reflection is important, too much can slow down the narrative. Ensure that your essay maintains momentum by interspersing reflective moments with storytelling.
6. Develop a Unique Voice
- Maintain Consistent Voice and Tone : Ensure that your voice and tone remain consistent throughout the middle section. This consistency helps maintain the reader’s connection to you as the narrator.
- Be Authentic : Write in a way that feels true to who you are. Authenticity resonates with readers and can make your story more relatable and believable.
Making a Strong Finish
There are actually many effective ways to conclude a college essay that are compact but also likely to help make your essay more memorable and give your central theme stronger resonance.
Whether you choose to focus on a resolution (or lack of resolution), or you want to craft a conclusion with a strong future-facing insight, it’s up to you. As author and editor-in-chief, you'll decide what kind of ending works best, but here are ideas to give you a head start:
Circle Back to the Introduction :
Revisit an image, theme, or idea from the opening of your essay. This creates a sense of cohesion and closure, giving the reader a feeling of completeness. For example, if you started with a specific memory or metaphor, bringing it back in the conclusion can effectively tie your story together.
Reflect on Growth or Change :
End with a reflection on how the experiences or ideas discussed in the essay have shaped you. Highlight the personal growth, lessons learned, or changes in perspective. This helps demonstrate self-awareness and the ability to learn from experiences—qualities valued by admissions committees.
Look Forward :
Use the conclusion to connect your past experiences or reflections to your future goals. This shows that you’ve not only learned from your experiences but are also motivated and focused on what comes next. For example, you can mention how the skills or insights gained will help you succeed in college or contribute to your chosen field.
Leave a Lasting Impression :
End with a strong, memorable statement or image that resonates with the reader. This could be a powerful sentence that encapsulates your main theme or a vivid image that leaves the reader thinking. Avoid clichés and aim for something unique to your experience.
Pose a Thoughtful Question :
Conclude by posing a question that invites the reader to think more deeply about the themes of your essay. This can be a rhetorical question that leaves the reader pondering your insights or the broader implications of your experiences.
End with a Call to Action (for Yourself) :
Consider concluding with a personal resolution or commitment related to what you’ve discussed in your essay. This shows forward-thinking and a proactive attitude. For instance, you might write about how you plan to apply what you’ve learned in college or in your future endeavors.
Keep it Concise and Focused :
The conclusion should be succinct and avoid introducing new ideas or topics. Focus on reinforcing the main themes of your essay and leave the reader with a clear understanding of your message.
Use an Appropriate Tone :
Ensure that your conclusion matches the tone of the rest of the essay. If your essay is reflective and serious, the conclusion should maintain that tone. If your essay has a lighter, more optimistic tone, your conclusion should also reflect that.
Creative Essay Structures
While most college essays follow the dominant format of a personal narrative, personal essay, or reflective essay, there are many creative ways you can structure elements from each format .
These structures are not, most of them, used for academic writing, so it’s new territory for many young scholars. On the bright side, consider it an opportunity to use a creative structure to convey something fresh and unique about your personality.
Tip: Only use a structure when it aligns effectively with content you're presenting in your essay.
The Personal Background Structure
This structure focuses on the people, places, and transitions that shaped your upbringing.
- Focus on Key Influences : The essay revolves around significant people, places, or transitions in your life, offering insights into how these elements shaped your identity and perspective.
- Flexible Structure : You can choose a topical essay structure to explore different aspects of your background or a personal narrative structure that follows a chronological sequence, depending on what best suits your story.
- Vivid Descriptions : Use concise, vivid descriptions to bring people and places to life, employing the "show, don't tell" technique to engage the reader and create a strong sense of place and character.
- Unified Theme : Select elements of your personal story that connect to a central theme you wish to highlight. This unifying theme gives your essay coherence and amplifies its impact, ensuring that each part of your background contributes to the overall message.
This structure is effective when it ties together various aspects of your background to illustrate a cohesive narrative about your personal development.
The Pivotal or Memorable Anecdote Structure
This structure centers around a specific event or experience that was highly formative and memorable for you.
- Personal Impact : The essay recounts a significant event, offering insights into how it unfolded, how you experienced it, and how it impacted or shaped you in a meaningful way. The narrative is focused and tied to a clear theme.
- Engaging Storytelling : It uses narrative and cinematic techniques, such as vivid sensory descriptions, to bring the experience to life for the reader. This helps cultivate empathy and creates a sense of intimacy.
- Avoiding Clichés : Steer clear of recounting dramatic events that, while memorable, may not lead to deep, nuanced reflections. Instead, focus on experiences that truly contributed to your personal growth, offering unique and thoughtful insights.
This structure is effective when the anecdote is not only memorable but also reveals significant personal growth and understanding.
The "What Doesn’t Kill You Makes You Stronger" Structure
This structure is all about overcoming adversity , often framed as a three-act drama:
- ACT 1: The Challenge : Start by presenting a provocative question, dilemma, conflict, or challenge in your life. This sets the stage for the reader and introduces the struggle or hardship that serves as the essay’s focal point.
- ACT 2: The Transformation : This act delves into the process of inner transformation, growth, or reflection. It explores how you navigated the challenges, the steps you took to address them, and how these experiences shaped important personal attributes. This is where you bring the reader through your journey, revealing the depth and nature of the adversity and your response to it.
- ACT 3: Moving Beyond and Gaining Wisdom : Conclude by showing how you overcame the adversity and what you learned from the experience. Highlight the wisdom gained, how it informs your future aspirations, and how it has contributed to a more mature self or perspective on life.
- Key Considerations : The "overcoming adversity" narrative is timeless, but it requires careful handling. To avoid clichés and ensure your story resonates, focus on authenticity and nuance. Be sincere and offer a detailed, intimate, and honest account of your journey. Show how the experience reshaped you in a meaningful and compelling way.
Vignette or Montage Structure
Think of this structure like a nonlinear mix of short video clips or a photo montage. It mirrors the disjointedness of our memories, where seemingly unrelated moments, anecdotes, or events come together to form a cohesive theme in your life.
Each vignette stands alone, not connected by chronology or topic, but when combined, they create an impressionistic and layered narrative.
The key to this structure is ensuring that each vignette is tied to a common theme , allowing the separate pieces to coalesce into a meaningful whole. This structure may help a writer foreground attributes such as creativity and imagination.
The Thinker: Reflective Structure
This structure blends recounting past experiences or influences — such as an event, a book, or a trip — with reflections on their significance from a present-day perspective.
- Focus on Present Beliefs : The essay centers on a current conviction, value, commitment, or belief, showing how it has been shaped by past experiences.
- Intellectual Exploration : It offers a deeper intellectual or philosophical exploration, revealing how extended reflection has helped you build connections between different experiences and ideas.
- Add Nuance and Depth : Enhance this structure by incorporating honesty and vulnerability, sharing how you navigated a life dilemma or philosophical doubt. This adds depth to your reflections and highlights your growth.
This structure is effective when you want to demonstrate how your past has influenced your present beliefs , showcasing your capacity for deep thought and introspection.
Additional Creative Structures to Choose From
There are a whole host of creative structures that may appeal to your creative side or prove to be a good fit for a particular prompt and how you want to respond to it.
Circular Structure :
The essay begins and ends with a similar idea, image, or event, creating a sense of closure and emphasizing the cyclical nature of the experience or the lesson learned.
Braided Structure :
Multiple storylines or themes are interwoven throughout the essay, with each thread contributing to the overall message or insight. The threads may converge or contrast with each other by the end.
Parallel Narrative Structure :
Two or more narratives are told side by side, either contrasting or complementing each other. This structure is often used to highlight connections between different experiences or themes.
Question-and-Answer Structure :
The essay is framed around a central question or a series of questions that the author seeks to answer through their reflections and experiences. This structure often lends itself to a conversational tone.
Frame Story Structure :
The essay begins with an introductory narrative (the “frame”) that sets the stage for the main story or stories within it. The frame is revisited at the end to provide closure or reflection.
Fragmented Structure :
The narrative is broken into non-linear segments or fragments, jumping between different times or events. This structure often reflects the complexity or disjointed nature of memory and experience.
List Structure :
The essay is organized as a list, with each item on the list representing a different memory, thought, or aspect of the central theme. This structure allows for flexibility and creativity in presentation.
You can use these structures alone or combined, depending on your particular story and the specific prompt, purpose, and context for your essay!
3 Tips on How to Structure Your College Application Essay
Common App Essay Guide Part 2: Structure
Part IV. Revising and Polishing College Essays With a Rubric
The rubric below uses a 3-point scale to evaluate key components of a college admissions essay. Use to gauge your progress when you get into the work of revising your essay drafts.
The "Content and Ideas" category can also be used as a guide while developing content for the initial draft and outline.
Content and Ideas
3 (Excellent) : The essay presents a compelling and original story or theme, offering deep insights into the applicant's personality, experiences, and values. It effectively addresses the prompt and demonstrates the applicant's readiness important aspects of college life and learning.
2 (Satisfactory) : The essay provides a clear and relevant narrative or reflection with some insights, but may lack depth or originality in certain areas. It addresses the prompt adequately but may not fully showcase the applicant’s potential.
1 (Needs Improvement) : The essay lacks focus or depth and may not clearly address the prompt. The content may feel generic, overly personal, or unsuitable for an admissions essay.
Organization and Structure
3 (Excellent) : The essay is well-organized with a strong hook and a clear, logical flow. The structure complements the content and purpose, making the essay engaging and easy to follow.
2 (Satisfactory) : The essay has a basic structure that is generally clear but may have some organizational issues. The flow is adequate, though it could be improved to enhance engagement.
1 (Needs Improvement) : The essay lacks clear organization, making it difficult to follow. The structure may be disjointed, with a weak hook and unclear transitions between ideas.
Wording, Voice, and Tone
3 (Excellent) : The essay has a strong, authentic voice that reflects the applicant’s personality. The tone is consistent, engaging, and appropriate for the content, helping to create a connection with the reader.
2 (Satisfactory) : The essay’s voice is clear but may lack some authenticity or consistency. The tone is generally appropriate but may not fully engage the reader or complement the content.
1 (Needs Improvement) : The essay’s voice is weak or inconsistent, and the tone may feel detached or inappropriate. It does not effectively convey the applicant’s personality or engage the reader.
Grammar, Punctuation, and Mechanics
3 (Excellent) : The essay is free from grammatical, punctuation, and spelling errors, demonstrating careful editing. The mechanics support the essay’s structure, voice, and tone.
2 (Satisfactory) : The essay has a few minor errors but they do not significantly detract from the overall quality. The mechanics are generally sound but may need some polishing.
1 (Needs Improvement) : The essay contains multiple errors that affect readability and clarity. The mechanics need significant improvement to support the essay effectively.
Adherence to Guidelines
3 (Excellent) : The essay adheres fully to length and formatting guidelines and is completely relevant to the prompt and purpose.
2 (Satisfactory) : The essay meets most guidelines but may slightly exceed length or have minor formatting issues. It is generally relevant but may not fully align with the prompt.
1 (Needs Improvement) : The essay fails to adhere to length or formatting guidelines and may not be fully relevant to the prompt or purpose.

Part V. College Essay Formatting & Submission: The Nuts and Bolts Stuff
The main focus of your college essay is the content. The format and structure should make the essay easy to read to maintain this focus.
A title to your college essay is generally not required and takes from your word count. It can also confine your essay to a single meaning, so if you decide to use titles, use them with care. Keep your font double-spaced with a line space between the paragraphs to keep the essay easy on the eyes.
When the word count is not given, staying around 600 words is a safe bet. While it’s important to share about yourself in your essay, oversharing could make you stand out from your competition — in the worst way possible!
Uploading Your Essay
If you are copying and pasting your essay into a text box, here are some necessary actions to take to ensure your essay will be received as intended.
- Make sure that your essay is transferred over completely and without transfer errors . Formatting on a different program initially and then using the copy/paste function could cut your essay off, change your word count, alter the paragraph structure, and overall change the initial way you meant your essay to be read.
- The smaller details, such as bold and italics, may not be possible depending on the platform . As the point of the essay is the text, not including bold/italics only makes for a more straightforward read — it might just be a blessing in disguise!
When attaching a document, you’ll need to be more precise with your formatting, but here are a few rules of thumb to follow:
- 1” margin is the standard, and difficult to go wrong with.
- An easy-to-read font, such as Times New Roman and Arial, is the way to go . The last thing you want is for the admissions officers to have difficulty reading your essay due to a complicated font.
- Download your college essay in an accepted format according to the submissions site.
These are just general guidelines... Always review all explicit instructions and requirements for layout, submission, and length for each particular school and essay.
Final Thoughts
The college essay format can feel like uncharted territory for many young scholars, presenting unique challenges and often becoming a stumbling block in the application process. However, you should find this resource abundantly helpful as you navigate the writing process. By understanding the distinct elements of the college essay format and thoughtfully applying the tips and insights we've just shared, you can apply strategies used by top applicants to top schools. Remember, the college essay is an opportunity to showcase your authentic voice and personal experiences in a way that sets you apart.
If you’re looking for additional guidance, consider signing up for a free consultation with a Crimson admissions advisor. They can provide personalized feedback, connect you with essay writing mentors, and help you refine your essay to make a lasting impression.
What Makes Crimson Different
About the Author
/f/64062/412x444/0a1d13023e/2021_keith_nickolaus-author.jpg)
Keith Nickolaus
Keith Nickolaus is a former educator with a passion for languages, literature, and lifelong learning. After obtaining a B.A. from UC Santa Cruz and exploring university life in Paris, Keith earned his Ph.D. in Comparative Literature from UC Berkeley, and then worked for 16 years in K12 education before setting up shop as a freelance writer.
More Articles
How to answer upenn's 2024/25 supplemental essays: tips & insights.
/f/64062/800x451/fd960bb163/upenn-supplemental-essays.jpg)
Ace Your NYU Supplemental Essay: Expert Advice From a Former Admissions Officer
/f/64062/800x451/2ea207e4ba/nyu-law.jpg)
How To Answer Northwestern Supplemental Essays in 2024-2025
/f/64062/800x450/481dfd6c99/northwestern-blog.jpg)

How to Head a College Paper

How to Remove a Course From Your College Transcript
College is a new experience for students in many ways. From the freedom of scheduling classes at your convenience to finding your way around a new campus, the changes are evident immediately. Even the way you head your research papers may be different from what you have used in high school. There are a few simple rules to follow when heading a college paper. Once you get the format down, it will become second nature and you'll find yourself doing it automatically.
Paper Style
You can use MLA style for most papers you turn including homework assignments. When using this style on a written paper, do not skip lines in between the four lines of the initial heading. Your heading on subsequent pages should consist of your last name followed by the page number in a right justified format. Other paper formats you might use in college can include American Psychological Association (APA) and Chicago Style.
Heading and Margins
Place your heading in the upper left-hand corner of the page. To make sure your typed paper is easy to read on a visual level, use a 12-point font and recognizable font style. While the Times New Roman font is often chosen, Arial, Modern, Lucina and Palermo are also acceptable because they are not script-style fonts. This follows Modern Language Association (MLA) formatting which is the accepted standard for college papers.
First and Last Name
Place your first and last names on the first line. Double space each line of the heading. All lines of the heading are left justified at the left margin.
Professor's Name
Place your professor's name on the next line. Use his first and last name preceded by Professor. For example, "Professor John Doe" goes on this line.
Course Name
Place the name of your course on the next line. For example, you could use "English 101."
Place the date on the final line. To follow MLA formatting, the date should appear as the day in numeral format, the month in written format and the year. For example, "5 January 2011" is appropriate.
Title of Paper
Double space after the last line of your heading, and center the title of your paper on the next line. Use Title Case style to type the title. For example, "A History of Life During the Tudor Period."
First Paragraph
Double space after the heading and begin your paper using a 1-inch indent to begin the first paragraph.
Related Articles
How to write a paper in mba style.

How to Write a Lab Report Title

How to Find a Course Reference Number

Styles & Tones Used in Research Essays

Do You Italicize Latin in MLA-Format Papers?

APA-Style Citation of a Case Complaint

How to Write a Letter to First Lady Michelle Obama

How to Notate a Field Trip As a Reference for a Bibliography
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: MLA Formatting and Style Guide
- The MLA Style Center: Formatting a Research Paper
- Olympus: MLA Format For Essays and Research Papers
Amie Taylor has been a writer since 2000. Book reviews, gardening and outdoor lawn equipment repair articles and short fiction account for a handful of her published works. Taylor gained her gardening and outdoor equipment repair experience from working in the landscaping and lawn-care business she and her husband own and operate.
Calculate for all schools
Your chance of acceptance, your chancing factors, extracurriculars, how to format a college essay header.
Hi guys, I'm writing my college essays and I was wondering what the proper header format is for a college essay? Should I include my name, date, class, or anything else? Thanks in advance!
Hi there! When it comes to formatting a college essay header, simplicity is key. Most colleges prefer the following format:
- In the top left corner of the first page, include your full name, followed by a space, and then your high school (or the abbreviation of your high school name).
- On the line below your high school's name, type the course title (if applicable) or the purpose of the essay (for example, "Personal Statement" or "X School Supplement").
- Add one more space, and then type the date of submission.
It should look something like this:
City High School
Personal Statement
December 1, 2023
For the body of the essay, use 12-point font, double-spacing, and 1-inch margins. Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri are common font choices. Don't forget to proofread and check for any specific formatting requirements provided by the colleges you're applying to.
Keep in mind that for schools that use the Common App you won't need to format your essay like this; you just copy and paste your essay into the provided text boxes. Good luck with your essays!
About CollegeVine’s Expert FAQ
CollegeVine’s Q&A seeks to offer informed perspectives on commonly asked admissions questions. Every answer is refined and validated by our team of admissions experts to ensure it resonates with trusted knowledge in the field.
Generate accurate MLA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- MLA format for academic papers and essays
MLA Format | Complete Guidelines & Free Template
Published on December 11, 2019 by Raimo Streefkerk . Revised on May 6, 2024 by Jack Caulfield.
The MLA Handbook provides guidelines for creating MLA citations and formatting academic papers. This includes advice on structuring parenthetical citations, the Works Cited page, and tables and figures. This quick guide will help you set up your MLA format paper in no time.
Cite your MLA source
Start by applying these MLA format guidelines to your document:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Set 1 inch page margins
- Use double line spacing
- Include a ½” indent for new paragraphs
- Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page
- Center the paper’s title
- Use title case capitalization for headings
- Cite your sources with MLA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a Works Cited page at the end
Alternatively, you can automatically apply the formatting with our MLA docx or Google Docs template.
Table of contents
How to set up mla format in google docs, header and title, running head, works cited page, creating mla style citations, headings and subheadings, tables and figures, frequently asked questions about mla format.
The header in MLA format is left-aligned on the first page of your paper. It includes
- Your full name
- Your instructor’s or supervisor’s name
- The course name or number
- The due date of the assignment
After the MLA header, press ENTER once and type your paper title. Center the title and don’t forget to apply title-case capitalization. Read our article on writing strong titles that are informative, striking and appropriate.
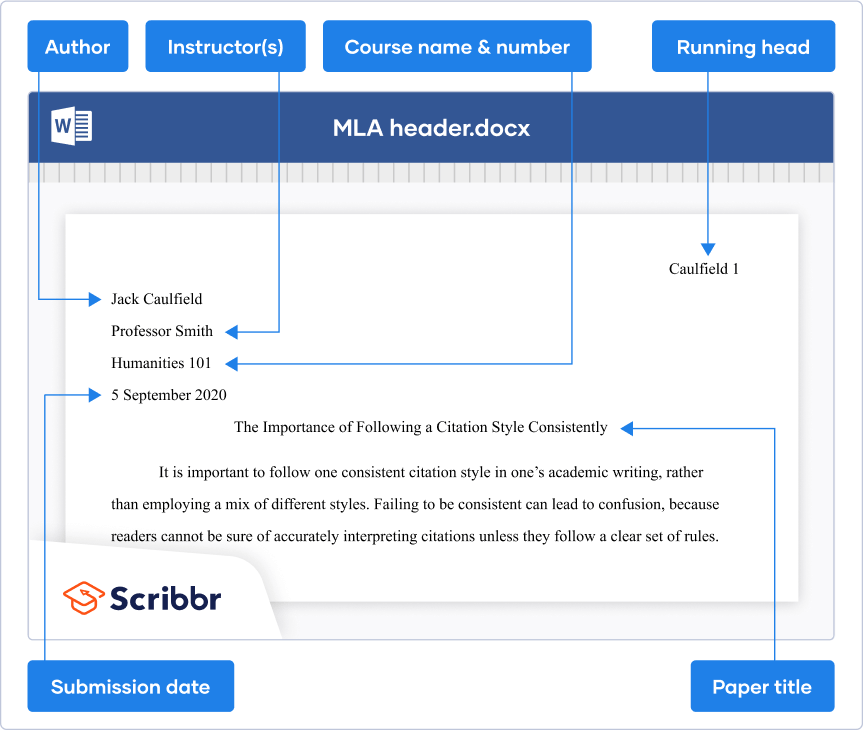
For a paper with multiple authors, it’s better to use a separate title page instead.
At the top of every page, including the first page, you need to include your last name and the page number. This is called the “running head.” Follow these steps to set up the MLA running head in your Word or Google Docs document:
- Double-click at the top of a page
- Type your last name
- Insert automatic page numbering
- Align the content to the right
The running head should look like this:
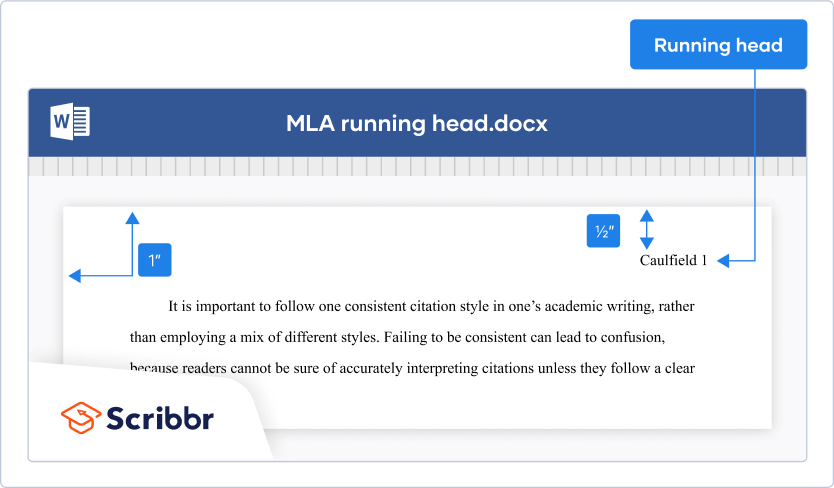
The Works Cited list is included on a separate page at the end of your paper. You list all the sources you referenced in your paper in alphabetical order. Don’t include sources that weren’t cited in the paper, except potentially in an MLA annotated bibliography assignment.
Place the title “Works Cited” in the center at the top of the page. After the title, press ENTER once and insert your MLA references.
If a reference entry is longer than one line, each line after the first should be indented ½ inch (called a hanging indent ). All entries are double spaced, just like the rest of the text.
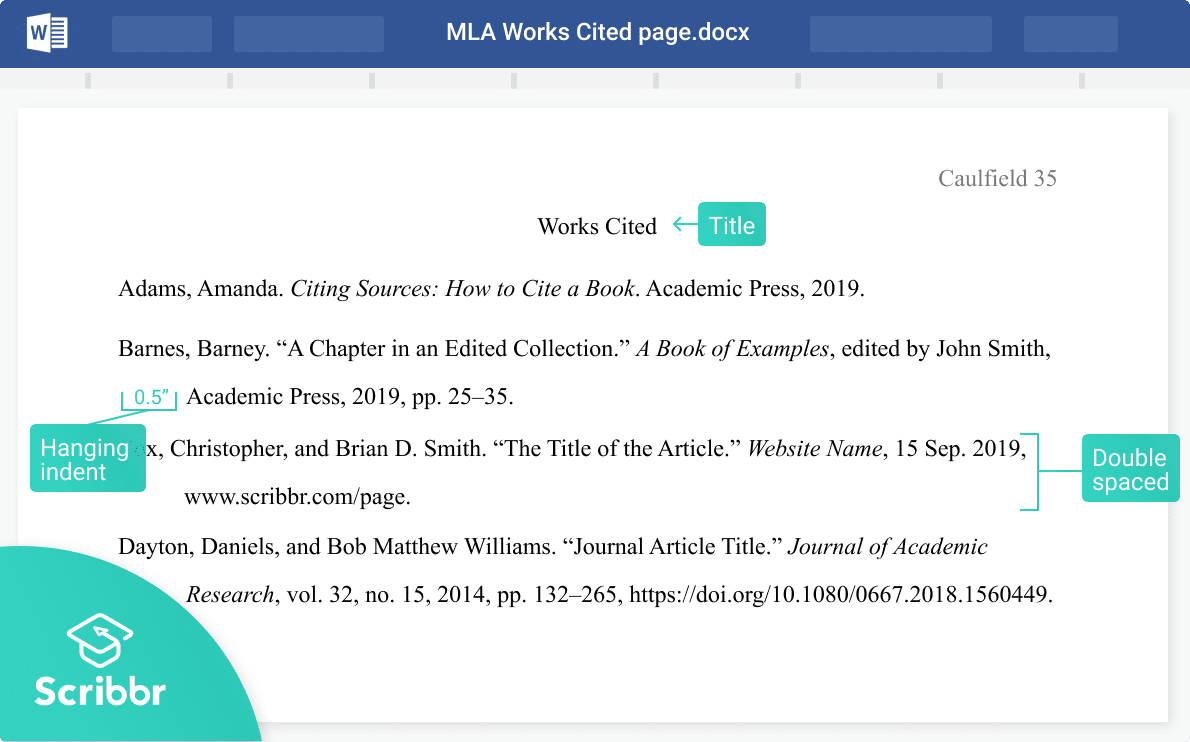
Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
Prefer to cite your sources manually? Use the interactive example below to see what the Works Cited entry and MLA in-text citation look like for different source types.
Headings and subheadings are not mandatory, but they can help you organize and structure your paper, especially in longer assignments.
MLA has only a few formatting requirements for headings. They should
- Be written in title case
- Be left-aligned
- Not end in a period
We recommend keeping the font and size the same as the body text and applying title case capitalization. In general, boldface indicates greater prominence, while italics are appropriate for subordinate headings.
Chapter Title
Section Heading
Tip: Both Google Docs and Microsoft Word allow you to create heading levels that help you to keep your headings consistent.
Tables and other illustrations (referred to as “figures”) should be placed as close to the relevant part of text as possible. MLA also provides guidelines for presenting them.
MLA format for tables
Tables are labeled and numbered, along with a descriptive title. The label and title are placed above the table on separate lines; the label and number appear in bold.
A caption providing information about the source appears below the table; you don’t need one if the table is your own work.
Below this, any explanatory notes appear, marked on the relevant part of the table with a superscript letter. The first line of each note is indented; your word processor should apply this formatting automatically.
Just like in the rest of the paper, the text is double spaced and you should use title case capitalization for the title (but not for the caption or notes).
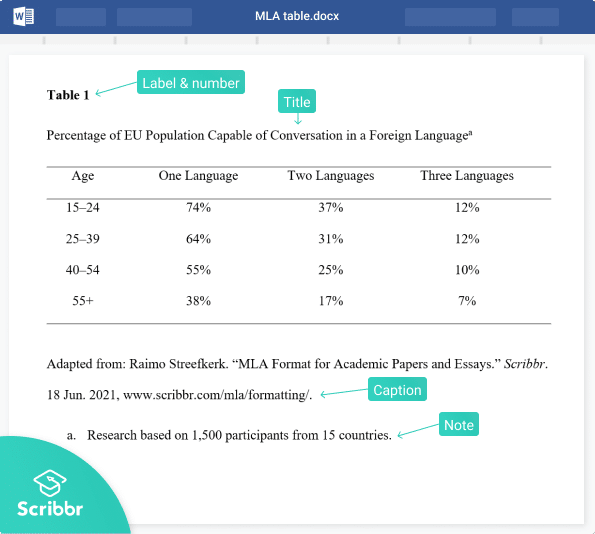
MLA format for figures
Figures (any image included in your paper that isn’t a table) are also labeled and numbered, but here, this is integrated into the caption below the image. The caption in this case is also centered.
The label “Figure” is abbreviated to “Fig.” and followed by the figure number and a period. The rest of the caption gives either full source information, or (as in the example here) just basic descriptive information about the image (author, title, publication year).

Source information in table and figure captions
If the caption of your table or figure includes full source information and that source is not otherwise cited in the text, you don’t need to include it in your Works Cited list.
Give full source information in a caption in the same format as you would in the Works Cited list, but without inverting the author name (i.e. John Smith, not Smith, John).
MLA recommends using 12-point Times New Roman , since it’s easy to read and installed on every computer. Other standard fonts such as Arial or Georgia are also acceptable. If in doubt, check with your supervisor which font you should be using.
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA style are as follows:
- Apply double line spacing
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch
The fastest and most accurate way to create MLA citations is by using Scribbr’s MLA Citation Generator .
Search by book title, page URL, or journal DOI to automatically generate flawless citations, or cite manually using the simple citation forms.
The MLA Handbook is currently in its 9th edition , published in 2021.
This quick guide to MLA style explains the latest guidelines for citing sources and formatting papers according to MLA.
Usually, no title page is needed in an MLA paper . A header is generally included at the top of the first page instead. The exceptions are when:
- Your instructor requires one, or
- Your paper is a group project
In those cases, you should use a title page instead of a header, listing the same information but on a separate page.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Streefkerk, R. (2024, May 06). MLA Format | Complete Guidelines & Free Template. Scribbr. Retrieved September 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/mla/formatting/
Is this article helpful?
Raimo Streefkerk
Other students also liked, creating an mla header, block quoting in mla style, how to format your mla works cited page, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Again, we'd recommend sticking with standard fonts and sizes—Times New Roman, 12-point is a standard workhorse. You can probably go with 1.5 or double spacing. Standard margins. Basically, show them you're ready to write in college by using the formatting you'll normally use in college.
At the outset, make a plan for how you will deal with matters of capitalization, formatting and sequencing of headings. Headings at the same level should be formatted the same. For instance, "Section 2.2" should get the same treatment as "Section 4.1". They should also have parallel structure.
Headings and subheadings provide structure to a document. They signal what each section. is about and allow for easy navigation of the document. APA headings have five possible levels. Each heading level is formatted differently. Note: Title case simply means that you should capitalize the first word, words with four or more letters, and all ...
There are five levels of heading in APA Style. Level 1 is the highest or main level of heading, Level 2 is a subheading of Level 1, Level 3 is a subheading of Level 2, and so on through Levels 4 and 5. The number of headings to use in a paper depends on the length and complexity of the work. If only one level of heading is needed, use Level 1.
Clearly delineate your paragraphs. A single tab at the beginning is fine. Use a font that's easy to read, like Times, Arial, Calibri, Cambria, etc. Avoid fonts like Papyrus and Curlz. And use 12 pt font. You may want to include a college essay heading with a page number and your application ID.
1. In-the-moment narrative. This is where you tell the story one moment at a time, sharing the events as they occur. In the moment narrative is a powerful essay format, as your reader experiences the events, your thoughts, and your emotions with you. This structure is ideal for a specific experience involving extensive internal dialogue ...
There are no set rules for how to structure a college application essay, but you should carefully plan and outline to make sure your essay flows smoothly and logically. Typical structural choices include. a series of vignettes with a common theme. a single story that demonstrates your positive qualities. Although many structures can work, there ...
Avoid Unnecessary Information: Keep the college heading concise, avoiding any extra text or embellishments. Capitalization and Punctuation: Properly capitalize and punctuate your essay heading consistent with style guidelines, ensuring consistency across the prep. Consistency: Use identical size, font, and style for all components in your header.
Sample College Essay 2 with Feedback. This content is licensed by Khan Academy and is available for free at www.khanacademy.org. College essays are an important part of your college application and give you the chance to show colleges and universities your personality. This guide will give you tips on how to write an effective college essay.
This article walks through the formatting steps needed to create an APA Style student paper, starting with a basic setup that applies to the entire paper (margins, font, line spacing, paragraph alignment and indentation, and page headers). It then covers formatting for the major sections of a student paper: the title page, the text, tables and ...
4. Hover over "Top of Page" and select "Plain Number 3". 5. For the MLA header, enter your last name along with the page number, both right-aligned. For the APA header, input the abbreviated version of the title in all capital letters and press the "Tab" key. MLA essay header example. APA essay header example.
For many, getting started is the hardest part of anything. And that's understandable. First, because it turns whatever you're doing into a reality, which raises the stakes. Second, because where you start can easily dictate the quality of where you end up. College essays have their own special brand of DTDT.
The college application essay has become the most important part of applying to college. In this article, we will go over the best college essay format for getting into top schools, including how to structure the elements of a college admissions essay: margins, font, paragraphs, spacing, headers, and organization.. We will focus on commonly asked questions about the best college essay structure.
Step 2: Pick one of the things you wrote down, flip your paper over, and write it at the top of your paper, like this: This is your thread, or a potential thread. Step 3: Underneath what you wrote down, name 5-6 values you could connect to this. These will serve as the beads of your essay.
Revised on March 5, 2024. The first page of your MLA format paper starts with a four-line left-aligned header containing: Your full name. Your instructor's name. The course name and number. The date of submission. After the header, the title of the paper is centred on a new line, in title case. The header and title do not take any special ...
1. Be authentic. One of the most essential parts of how to format a college application essay is to be authentic. The college wants to know who you are, and they will be reading dozens of essays a day. The best way to make yours stand out is to just be yourself instead of focusing on what you think they want to hear.
Key Takeaways for the College Essay Format. Understanding the Context: The "college essay" here refers to the personal essays you write for college applications, not the academic essays you'll write in college classes. Format Flexibility: This type of essay is not a 5-paragraph academic or expository essay. It typically takes the form of a ...
Making an all-state team → outstanding achievement. Making an all-state team → counting the cost of saying "no" to other interests. Making a friend out of an enemy → finding common ground, forgiveness. Making a friend out of an enemy → confront toxic thinking and behavior in yourself.
Use your essays to empower your chances of acceptance, merit money, and scholarships.". This college essay tip is by Dr. Rebecca Joseph, professor at California State University and founder of All College Application Essays, develops tools for making the college essay process faster and easier. 15. Get personal.
Double space after the last line of your heading, and center the title of your paper on the next line. Use Title Case style to type the title. For example, "A History of Life During the Tudor Period." First Paragraph. Double space after the heading and begin your paper using a 1-inch indent to begin the first paragraph.
Certainly! The proper heading format for a college essay is pretty straightforward. Here's a quick guide to help you out: 1. Align your text to the left. Most college essays use a standard left-aligned format, as it's easy to read and universally accepted. 2. Use a legible, 12-point font. Times New Roman, Arial, and Calibri are some common, easy-to-read options.
Hi there! When it comes to formatting a college essay header, simplicity is key. Most colleges prefer the following format: - In the top left corner of the first page, include your full name, followed by a space, and then your high school (or the abbreviation of your high school name). - On the line below your high school's name, type the course title (if applicable) or the purpose of the ...
Cite your MLA source. Start by applying these MLA format guidelines to your document: Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman. Set 1 inch page margins. Use double line spacing. Include a ½" indent for new paragraphs. Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page. Center the paper's title.