- Artificial Intelligence
- Generative AI
- Business Operations
- Cloud Computing
- Data Center
- Data Management
- Emerging Technology
- Enterprise Applications
- IT Leadership
- Digital Transformation
- IT Strategy
- IT Management
- Diversity and Inclusion
- IT Operations
- Project Management
- Software Development
- Vendors and Providers
- Enterprise Buyer’s Guides
- United States
- Middle East
- España (Spain)
- Italia (Italy)
- Netherlands
- United Kingdom
- New Zealand
- Data Analytics & AI
- Newsletters
- Foundry Careers
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Copyright Notice
- Member Preferences
- About AdChoices
- Your California Privacy Rights

Our Network
- Computerworld
- Network World

3 Case studies demonstrate the power of modern enterprise content management
Customers in insurance, banking, and healthcare find benefits in replacing aging content management tools with modern systems..

From insurance to banking to healthcare, organizations of all stripes are upgrading their aging content management systems with modern, advanced systems that introduce new capabilities, flexibility, and cloud-based scalability. In this post, we’ll touch on three such case studies.
Global insurance company
A large insurance company adopted a cloud-based document management system to enable paperless operations around the world and simplify regulatory compliance. The organization had some tactical document management systems, but they were siloed and based on slow, outdated technology. Plus, all files were stored in U.S. data centers, creating obstacles for a globally dispersed user base.
After adopting Alfresco Content Services and Alfresco Governance Services running on Amazon Web Services (AWS), the insurer fully digitized its operations. The IT team worked closely with business users to build a solution “in which paper wasn’t part of the process,” the company’s SVP and CIO said.
The solution provides electronic file and records management capabilities that integrate seamlessly with the company’s core insurance applications, automating everything from document retrieval to records management . The solution is saving the company $21 million over five years thanks to massive reductions in paper, printing, and storage costs.
Large community bank
When a 28-branch community bank decided to sunset its document storage system, it needed a solution that would work with its cloud-based core banking system.
After identifying dozens of company requirements, the organization selected OnBase running on the Hyland Cloud. With support from Hyland Professional Services, the bank migrated 2.5 million documents, representing the past 15 years of business documents, to OnBase. Soon after, the bank added WorkView , Hyland’s low-code application builder, to create solutions and address new challenges with speed and agility.
“With WorkView, you can build workable solutions with almost no code at all. It’s enabled us like a force multiplier. We can accomplish so much with a small team,” said the bank’s enterprise process manager.
Among the benefits, the solution helped the bank’s lending department retire its manual, paper-based workflow in favor of more automated processing using OnBase workflows. The results have been significant: a mortgage loan process now takes less than 20 minutes to complete each day, down from two hours.
What’s more, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the bank was able to bring on remote, temporary workers to handle an onslaught of Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) applications.
“All the documents needed were visible in OnBase without relying on paper to complete the work,” said the bank’s senior vice president and director of operations and process improvements. “We couldn’t have managed the loan volume without OnBase in the cloud.”
Large pharmacy and healthcare firm
A large American retail pharmacy and healthcare company was looking to upgrade its aging knowledge management systems. Its executive leadership team directed the business to select a knowledge management platform with a modern, open-source approach that would reduce the company’s dependence on IBM, Oracle, and other proprietary solutions.
The company opted for Hyland’s Nuxeo Platform , an open-source and highly scalable platform that enables the provider’s customer care representatives to quickly access their customers’ current coverage details. It also gives the company the flexibility to introduce new solutions in the future without worrying about being constrained by proprietary technology.
Ultimately, the healthcare firm used Nuxeo to replace two aging platforms:
- A mission-critical solution, previously based on IBM File Net, that’s used by more than 20,000 customer care agents to serve clients daily.
- A content management solution based on Oracle Stellent for managing policies, procedures, and other business content.
Now, the company is confident its agents will be up to date on the latest information they need to do their jobs effectively, from patient details to urgent notices about drug recalls.
“We’re confident the Nuxeo Platform will enable us to inform our reps ASAP,” said a healthcare company rep. “This is critical not only for our business, but also for the well-being of the millions of people who use [our] services.”
To learn more, visit Hyland .
Related content
The evolving state of enterprise content management: how ai changes the game, the secret to effective enterprise content management: building from a sound base, how intelligent document processing automates content-intensive processes, 5 benefits intelligent document processing brings to content management, from our editors straight to your inbox, show me more, salesforce: latest news and insights.

Salesforce mulls consumption pricing for AI agents

Navigate AI market uncertainty by bringing AI to your data

CIO Leadership Live Australia with Nazih Battal, Chief Information and Technology Officer at Rashays

Mike Aiello, CTO at Secureworks, joins CIO Leadership Live from Foundry's CIO100 event NEW

CIO Leadership Live Australia with Andrew Dome, Chief Digital Information Officer at Uniting

Kubecost helps firms monitor, optimize their Kubernetes and cloud spend

Mike Aiello, CTO at Secureworks, joins CIO Leadership Live from Foundry's CIO100 event

Sponsored Links
- The future of identity is here. Unlock brand growth with Merkury
- Everyone’s moving to the cloud. Are they realizing expected value?
- The cloud shouldn’t be complicated. Unlock its potential with SAS.
- Everybody's ready for AI except your data. Unlock the power of AI with Informatica
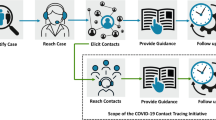
Lessons Learned from the Launch and Implementation of the COVID-19 Contact Tracing Program in New York City: a Qualitative Study
- Original Article
- Published: 29 August 2024
Cite this article

- Margaret M. Paul ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3281-6234 1 ,
- Lorraine Kwok 2 ,
- Rachel E. Massar 2 ,
- Michelle Chau 2 ,
- Rita Larson 2 ,
- Stefanie Bendik 2 ,
- Lorna E. Thorpe 2 ,
- Anna Bershteyn 2 ,
- Nadia Islam 2 &
- Carolyn A. Berry 2
On June 1, 2020, NYC Health + Hospitals, in partnership with the NYC Department of Health and Mental Hygiene, other city agencies, and a large network of community partners, launched the New York City Test & Trace (T2) COVID-19 response program to identify and isolate cases, reduce transmission through contact tracing, and provide support to residents during isolation or quarantine periods. In this paper, we describe lessons learned with respect to planning and implementation of case notification and contact tracing. Our findings are based on extensive document review and analysis of 74 key informant interviews with T2 leadership and frontline staff, cases, and contacts conducted between January and September 2022. Interviews elicited respondent background, history of program development, program leadership and structure, goals of the program, program evolution, staffing, data systems, elements of community engagement, trust with community, program reach, timeliness, equity, general barriers and challenges, general facilitators and best practices, and recommendations/improvement for the program. Facilitators and barriers revealed in the interviews primarily revolved around hiring and managing staff, data and technology, and quality of interactions with the public. Based on these facilitators and barriers, we identify suggestions to support effective planning and response for future case notification and contact tracing programs, including recommendations for planning during latent periods, case management and data systems, and processes for outreach to cases and contacts.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Evaluation of the implementation of a community health worker-led COVID-19 contact tracing intervention in Chiapas, Mexico, from March 2020 to December 2021
Lessons learned from implementing a surge capacity support program for COVID-19 contact management in Ontario
Evaluation of the New York City COVID-19 case investigation and contact tracing program: a cascade of care analysis
Explore related subjects.
- Artificial Intelligence
Thompson CN, Baumgartner J, Pichardo C, et al. COVID-19 Outbreak - New York City, February 29-June 1, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep . 2020;69(46):1725–9.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Paul MM, Conderino S, Massar R, et al. Evaluation of New York City’s Test & Trace Program for the SARS0-COV-2 Pandemic: Lessons Learned to Advance Reach, Equity, and Timeliness . A Report from the NYU Grossman School of Medicine Department of Population Health; 2023
Madad S, Cagliuso NV, Chokshi DA, Allen M, Newton-Dame R, Singer J. NYC Health + Hospitals’ Rapid Responses To COVID-19 Were Built On A Foundation Of Emergency Management, Incident Command, And Analytics . Health Affairs Blog. 2020
Thomas Craig KJ, Rizvi R, Willis VC, Kassler WJ, Jackson GP. Effectiveness of contact tracing for viral disease mitigation and suppression: Evidence-based review. JMIR Public Health Surveill . 2021;7(10):e32468.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Blaney K, Foerster S, Baumgartner J, et al. COVID-19 case investigation and contact tracing in New York City, June 1, 2020, to October 31, 2021. JAMA Netw Open . 2022;5(11):e2239661.
Conderino S, Thorpe L, Islam N, et al. Evaluation of the New York City COVID-19 case investigation and contact tracing program: a cascade of care analysis. BMC Public Health. under review
Harper-Hardy P, Ruebush E, Allen M, Carlin M, Plescia M, Blumenstock JS. COVID-19 case investigation and contact tracing programs and practice: snapshots from the field. J Public Health Manag Pract . 2022;28(4):353–7.
Gale RC, Wu J, Erhardt T, et al. Comparison of rapid vs in-depth qualitative analytic methods from a process evaluation of academic detailing in the Veterans Health Administration. Implement Sci . 2019;14(1):1–12.
Article Google Scholar
Pratt B, Parker M, Bull S. Equitable design and use of digital surveillance technologies during COVID-19: norms and concerns. J Empir Res Hum Res Ethics . 2022;17(5):573–86.
Ruebush E, Fraser MR, Poulin A, Allen M, Lane JT, Blumenstock JS. COVID-19 case investigation and contact tracing: early lessons learned and future opportunities. J Public Health Manag Pract. 2021;27 Suppl 1, COVID-19 and Public Health: Looking Back, Moving Forward:S87-S97
Woodward A, Rivers C. Building case investigation and contact tracing programs in US state and local health departments: a conceptual framework. Disaster Med Public Health Prep . 2023;17:e540.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Eliaz A, Blair AH, Chen YH, et al. Evaluating the impact of language concordance on Coronavirus Disease 2019 contact tracing outcomes among Spanish-speaking adults in San Francisco between June and November 2020. Open Forum Infect Dis . 2022;9(1):ofab612
Download references
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NYC Health + Hospitals (1007645); L.T). The funder had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Robert D. and Patricia E. Kern Center for the Science of Health Care Delivery, Mayo Clinic, 5777 E Mayo Blvd, Phoenix, AZ, 85054, USA
Margaret M. Paul
Department of Population Health, NYU Grossman School of Medicine, 180 Madison Avenue, New York, NY, 10016, USA
Lorraine Kwok, Rachel E. Massar, Michelle Chau, Rita Larson, Stefanie Bendik, Lorna E. Thorpe, Anna Bershteyn, Nadia Islam & Carolyn A. Berry
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Margaret M. Paul .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
(PDF 10.1 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Paul, M.M., Kwok, L., Massar, R.E. et al. Lessons Learned from the Launch and Implementation of the COVID-19 Contact Tracing Program in New York City: a Qualitative Study. J Urban Health (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11524-024-00898-0
Download citation
Accepted : 09 July 2024
Published : 29 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11524-024-00898-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Implementation evaluation
- Contact tracing
- COVID-19 prevention and control
- Public health emergency preparedness
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

- Project Management
Home » Free Resources » »
What is Quality Management? A Complete Guide
- Written by Contributing Writer
- Updated on August 27, 2024

The importance of quality cannot be overstated when it comes to businesses, their success and their longevity. When there is quality, it translates to value for customers, streamlined processes, and continual growth.
We often hear the term “quality control” in the context of how a business produces goods or services to the satisfaction of its customers consistently. However, there’s a larger concept at play, which covers quality control and other quality-related strategies. It’s called quality management.
So, what is quality management?
If you’re a project manager or aspiring to be one, you’ll want to understand how quality management works. This article comprehensively examines what it is, how it works, the methods, and everything you need to know about quality management.
We’ll also discuss how you can better understand quality and other project management concepts through a Lean Six Sigma course .
Quality Management: Definition & Examples
In short, it involves management tasks and roles focused on defining and executing quality policies through strategies like quality planning, assurance, and control.
Let’s understand this through an example.
Consider running a bakery on your street. Sales are good, but you notice some areas for enhancement. The nearby shop has fresher flour, and your oven isn’t heating evenly. You decide to upgrade. You monitor the results and plan further refinements.
In essence, this illustrates quality management (QM). It’s the act of assessing and refining quality throughout an organization. It is the act of combining quality assurance (QA) with process enhancement.
QM sets objectives, identifies shortcomings, and makes necessary adjustments. In short, it’s the strategy to improve operations and bridge experience gaps.
Also Read: What Is Lean Management, and Why Is It Worth Mastering?
History of Quality Management in a Nutshell
Quality Management started with Walter Shewhart at Bell Laboratories in the early 20th century. He introduced statistical quality control (SQC), focusing on process improvement over the end product.
During World War II, the U.S. applied SQC for military production. However, post-war civilian manufacturers lagged in adopting these improvements. Then, engineers Deming and Juran traveled to war-torn Japan. Their approach emphasized ‘Total Quality,’ a holistic approach to improvement. Their efforts transformed Japan into a manufacturing titan.
By the 1980s, recognizing Japan’s success and shortcomings, the U.S. adopted Total Quality Management (TQM). 1987, the ISO 9000 standard was introduced, becoming a global quality benchmark.
As the 21st century rolled in, with globalization and technology at the forefront, approaches like Motorola’s Six Sigma emerged, emphasizing near-perfect outputs.
Today, quality management isn’t limited to manufacturing; it’s a universal pursuit, spanning sectors from healthcare to cutting-edge technologies like Blockchain.
What is Quality Management: Four Stages
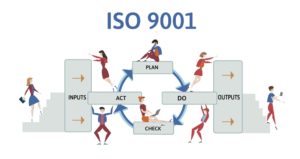
The four Quality Management (QM) stages are often described as part of the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, also known as the Deming Cycle or Shewhart Cycle.
Here’s a brief overview:
This is the initial stage where you identify an opportunity and plan for change. This involves setting objectives, defining processes to meet the objectives, and determining the resources needed.
In this stage, you implement the plan on a small scale, ideally in a controlled environment. This is where the changes are tested, and data is collected for the next step.
Here, you assess your test results, comparing them against the expected outcomes to determine any differences. You’ll analyze the data collected during the “Do” phase to understand whether the change has led to improvements.
You take corrective action Based on the “Check” phase results. If the implemented change leads to the desired improvement, you can scale up the implementation. If not, you must revisit the “Plan” phase to identify new or refined solutions.
This cycle keeps repeating, always aiming to make things better. When one cycle finishes, it helps set up the next, ensuring we’re always checking and improving our methods for the best results.
Also Read: What Is Process Mapping & How to Create It?
Most Popular Quality Management Methods
Four essential quality management methods stand out. Each offers unique benefits and challenges; the best fit depends on a company’s structure, needs, and goals.
Standardized Systems
Set by the government, these standards, like ISO certifications, are mandatory for certain products (e.g., baby car seats). Some firms adopt these standards voluntarily to enhance their reputation or align with their vision.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
This aims to boost quality throughout a company. It assesses the firm’s overarching quality goals and then evaluates every process and factor affecting quality for improvement.
A detailed, data-centered approach, Six Sigma focuses on defining, measuring, analyzing, enhancing, and maintaining quality. Predominantly used by large manufacturers, it necessitates thorough training. For deeper insights, consider enrolling in a boot camp.
Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI)
As the name suggests, the enhancement never stops. Recognizing perfection is a journey, CQI prioritizes people over processes, using the Plan, Do, Check, Act framework to improve quality.
What are the Main Quality Management Principles?
Quality management revolves around several guiding principles. Adopted by the International Standard for Quality Management, these principles enable organizations to refine their processes for optimal results:
Prioritizing Customers
Every organization’s main goal should be to understand and surpass the needs and expectations of its customers. By recognizing and fulfilling both current and future customer needs, businesses ensure customer loyalty, leading to increased revenue. Effective and efficient processes enhance quality, satisfying more customers.
Importance of Leadership
The success of any organization is directly linked to its leadership. Effective leaders foster unity, setting clear goals that engage employees and stakeholders. A positive organizational culture helps employees achieve their potential and work towards company goals. Engaging employees in goal-setting often leads to heightened productivity and commitment.
Engaging Employees
Active employee involvement is crucial. All staff should be empowered to contribute value regardless of their employment status or role. Constant skill improvement and consistent performance should be promoted. Empowerment, decision-making involvement, and recognition motivate employees, ensuring they feel valued and responsible for their contributions.
Adopting a Process-Centric Mindset
Organizational performance hinges on efficient and effective processes. Recognizing that superior processes lead to consistency, efficiency, and ongoing improvement is vital. Organizations thrive when they can effectively manage inputs and the processes that yield outputs.
Commitment to Ongoing Improvement
An enduring focus on improvement can transform organizations, enhancing flexibility, performance, and adaptability. A proactive stance on creating and evolving processes is crucial to stay competitive.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Grounding decisions in analyzed and validated data offers a clearer understanding of the market dynamics. Such a factual approach ensures businesses can execute strategies that yield desired outcomes while providing a basis for past decisions. It aids in understanding the interconnected nature of actions and their consequences.
Building Strong Relationships
Effective relationship management, especially with suppliers and stakeholders, is paramount. Recognizing that various parties can influence an organization’s trajectory ensures better supply chain management. By cultivating and maintaining these relationships, businesses enhance their chances of long-term success and collaboration.
Also Read: What Is Lean Six Sigma? A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Methodology
What is a Quality Management System (QMS)?
Let us look at how the principles of quality management are implemented through the QMS or Quality Management System.
A Quality Management System (QMS) ensures that products are made to meet quality standards. It monitors products from start to finish, ensuring they align with industry and regulatory norms.
QMS can be manual or software-driven and comprises two main parts: quality assurance and quality control.
While quality assurance focuses on inspecting processes during production, quality control evaluates the end products using customer feedback and on-site inspections. Quality assurance maintains consistent quality during production, and quality control verifies the final product’s quality.
The Importance of Quality Management Systems in Business
Why do businesses need QMS? Here is a breakdown of what it means to the business processes:
Product Oversight
The QMS constantly monitors products, beginning with acquiring raw materials and continuing to ship finished goods. It’s vigilant about tracking the quantity of products made and promptly identifying faulty ones.
Vendor Product Evaluation
This aspect of the QMS ensures that products sourced from vendors align with predetermined quality benchmarks. Vendor products can be quickly identified and returned if they fall short of these standards.
Scheduled Evaluations
Regular assessments are scheduled for staff, products, and equipment, ensuring ongoing quality compliance.
Error Tracking and Rectification
One vital feature of a QMS is its ability to spot and record current errors within the system. Beyond identifying them, it establishes strategies to both rectify present issues and devise mechanisms to prevent similar problems in the future.
Supplier Performance Assessment
A QMS employs key performance indicators (KPIs) to evaluate suppliers’ efficiency and reliability critically.
Policy and Procedure Updates
An effective QMS stays updated with any changes to company policies and procedures.
Moreover, it provides detailed and actionable reports on all facets of the quality management process.
Things to Remember When Choosing a Quality Management System
When choosing a QMS, numerous options can be overwhelming. Here’s a condensed guide to making an informed decision.
Industry Experience
It’s essential to check if the QMS provider has experience in your sector. They should have worked with similar businesses and be conversant with your specific quality requirements. Moreover, they should offer reliable references and display deep industry knowledge in software, installation, and training.
Functionality Needs
Determine if the software aligns with your business requirements. Key functionalities to consider include:
- Meeting industry-specific quality compliance standards
- Integration capabilities with other systems
- Tracking non-conformities and offering a comprehensive audit trail
- Features like Correct and Preventative Action (CAPA) management to address root causes
- AQL and RQL sampling throughout processes
- Efficient document control to log all quality endeavors
- Display of KPIs for supplier performance evaluation
- Flexibility to gather data from various sources, including mobile devices or the web
Real-time visibility into quality events is crucial. A robust QMS provides insights across the enterprise, allowing proactive issue resolution. It should offer the ability to monitor vendors and employees for compliance and training needs.
Master Quality Management for Better Project Outcomes
Quality management is paramount in every industry. For project managers, it’s critical to ensure streamlined processes that lead to the desired level of quality and performance.
If you want formal training in quality management, enrolling in a professional Lean Six Sigma certification can be a great starting point.
You might also like to read:
Six Sigma Principles: A Comprehensive Guide to Implementing and Optimizing Your Processes
Six Sigma vs. Lean Six Sigma: Which Methodology Is Right for Your Business?
What is Lean Methodology?
Six Sigma in Healthcare: Concept, Benefits and Examples
The Top 24 Lean Six Sigma Interview Questions for 2023
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Recommended Articles

Career Tips: How to Handle Project Failures?
Understanding why projects fail is the key to preventing future setbacks. Learn how to handle project failures and turn them into valuable learning experiences.

Ensuring Project Success: What is the Critical Path Method in Project Management?
The critical path method in project management helps identify tasks that affect a project’s timeline. Learn its basics and how to apply it to keep complex projects on track.

What is a Stakeholder in Project Management?
Understand the role of stakeholders in project management. This guide explains who they are, why they matter, and how to manage them for successful project delivery.

WBS in Project Management: What It Is and How You Use It?
Discover the significance of Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) in project management on the UMass Amherst Boot Camps blog. Learn what WBS is and how it can streamline your project planning and execution process.

Project Management Qualifications: Here’s What You Need to Know
This article provides an in-depth look at project management qualifications, including what it entails, eligibility, requirements, a solid career path, and why certification is a good idea.

How to Ace the PMP Exam in 2024-25? A Comprehensive Guide
Looking for help with PMP exam preparation? Our comprehensive guide is the ultimate resource for your PMP exam-related tips and strategies.
Lean Six Sigma Certification
Learning Format
Online Bootcamp
Program benefits.
- Green and Black Belt exam training material included
- Aligned with IASSC-Lean Six Sigma
- Masterclasses from top faculty of UMass Amherst
- UMass Amherst Alumni Association membership
- Publications
- News and Events
- Education and Outreach
Software Engineering Institute
Sei digital library, latest publications, embracing ai: unlocking scalability and transformation through generative text, imagery, and synthetic audio, august 28, 2024 • webcast, by tyler brooks , shannon gallagher , dominic a. ross.
In this webcast, Tyler Brooks, Shannon Gallagher, and Dominic Ross aim to demystify AI and illustrate its transformative power in achieving scalability, adapting to changing landscapes, and driving digital innovation.
Counter AI: What Is It and What Can You Do About It?
August 27, 2024 • white paper, by nathan m. vanhoudnos , carol j. smith , matt churilla , shing-hon lau , lauren mcilvenny , greg touhill.
This paper describes counter artificial intelligence (AI) and provides recommendations on what can be done about it.
Using Quality Attribute Scenarios for ML Model Test Case Generation
August 27, 2024 • conference paper, by rachel brower-sinning , grace lewis , sebastián echeverría , ipek ozkaya.
This paper presents an approach based on quality attribute (QA) scenarios to elicit and define system- and model-relevant test cases for ML models.
3 API Security Risks (and How to Protect Against Them)
August 27, 2024 • podcast, by mckinley sconiers-hasan.
McKinley Sconiers-Hasan discusses three API risks and how to address them through the lens of zero trust.
Lessons Learned in Coordinated Disclosure for Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Systems
August 20, 2024 • white paper, by allen d. householder , vijay s. sarvepalli , jeff havrilla , matt churilla , lena pons , shing-hon lau , nathan m. vanhoudnos , andrew kompanek , lauren mcilvenny.
In this paper, the authors describe lessons learned from coordinating AI and ML vulnerabilities at the SEI's CERT/CC.
On the Design, Development, and Testing of Modern APIs
July 30, 2024 • white paper, by alejandro gomez , alex vesey.
This white paper discusses the design, desired qualities, development, testing, support, and security of modern application programming interfaces (APIs).
Evaluating Large Language Models for Cybersecurity Tasks: Challenges and Best Practices
July 26, 2024 • podcast, by jeff gennari , samuel j. perl.
Jeff Gennari and Sam Perl discuss applications for LLMs in cybersecurity, potential challenges, and recommendations for evaluating LLMs.
Capability-based Planning for Early-Stage Software Development
July 24, 2024 • podcast, by anandi hira , bill nichols.
This SEI podcast introduces capability-based planning (CBP) and its use and application in software acquisition.
A Model Problem for Assurance Research: An Autonomous Humanitarian Mission Scenario
July 23, 2024 • technical note, by gabriel moreno , anton hristozov , john e. robert , mark h. klein.
This report describes a model problem to support research in large-scale assurance.
Safeguarding Against Recent Vulnerabilities Related to Rust
June 28, 2024 • podcast, by david svoboda.
David Svoboda discusses two vulnerabilities related to Rust, their sources, and how to mitigate them.
MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Management Case Studies » Case Study: Quality Management System at Coca Cola Company
Case Study: Quality Management System at Coca Cola Company
Coca Cola’s history can be traced back to a man called Asa Candler, who bought a specific formula from a pharmacist named Smith Pemberton. Two years later, Asa founded his business and started production of soft drinks based on the formula he had bought. From then, the company grew to become the biggest producers of soft drinks with more than five hundred brands sold and consumed in more than two hundred nations worldwide.
Although the company is said to be the biggest bottler of soft drinks, they do not bottle much. Instead, Coca Cola Company manufactures a syrup concentrate, which is bought by bottlers all over the world. This distribution system ensures the soft drink is bottled by these smaller firms according to the company’s standards and guidelines. Although this franchised method of distribution is the primary method of distribution, the mother company has a key bottler in America, Coca Cola Refreshments.
Coca Cola started diversifying its products during the First World War when ‘Fanta’ was introduced. During World War 1, the heads of Coca Cola in Nazi Germany decided to establish a new soft drink into the market. During the ongoing war, America’s promotion in Germany was not acceptable. Therefore, he decided to use a new name and ‘Fanta’ was born. The creation was successful and production continued even after the war. ‘Sprite’ followed soon after.
In the 1990’s, health concerns among consumers of soft drinks forced their manufactures to consider altering the energy content of these products. ‘Minute Maid’ Juices, ‘PowerAde’ sports drinks, and a few flavored teas variants were Coca Cola’s initial reactions to this new interest. Although most of these new products were well received, some did not perform as well. An example of such was Coca Cola classic, dubbed C2.

The Quality Management System at Coca Cola
It is very important that each product that Coca Cola produces is of a high quality standard to ensure that each product is exactly the same. This is important as the company wants to meet with customer requirements and expectations. With the brand having such a global presence, it is vital that these checks are continually consistent. The standardized bottle of Coca Cola has elements that need to be checked whilst on the production line to make sure that a high quality is being met. The most common checks include ingredients, packaging and distribution. Much of the testing being taken place is during the production process, as machines and a small team of employees monitor progress. It is the responsibility of all of Coca Colas staff to check quality from hygiene operators to product and packaging quality. This shows that these constant checks require staff to be on the lookout for problems and take responsibility for this, to ensure maintained quality.
Coca-cola uses both Quality Control (QC) and Quality Assurance (QA) throughout its production process. QC mainly focuses on the production line itself, whereas QA focuses on its entire operations process and related functions, addressing potential problems very quickly. In QC and QA, state of the art computers check all aspects of the production process, maintaining consistency and quality by checking the consistency of the formula, the creation of the bottle (blowing), fill levels of each bottle, labeling of each bottle, overall increasing the speed of production and quality checks, which ensures that product demands are met. QC and QA helps reduce the risk of defective products reaching a customer; problems are found and resolved in the production process, for example, bottles that are considered to be defective are placed in a waiting area for inspection. QA also focuses on the quality of supplied goods to Coca-cola, for example sugar, which is supplied by Tate and Lyle. Coca-cola informs that they have never had a problem with their suppliers. QA can also involve the training of staff ensuring that employees understand how to operate machinery. Coca-Cola ensures that all members of staff receive training prior to their employment, so that employees can operate machinery efficiently. Machinery is also under constant maintenance, which requires highly skilled engineers to fix problems, and help Coca-cola maintain high outputs.
Every bottle is also checked that it is at the correct fill level and has the correct label. This is done by a computer which every bottle passes through during the production process. Any faulty products are taken off the main production line. Should the quality control measures find any errors, the production line is frozen up to the last good check that was made. The Coca Cola bottling plant also checks the utilization level of each production line using a scorecard system. This shows the percentage of the line that is being utilized and allows managers to increase the production levels of a line if necessary.
The Production Process
Before production starts on the line cleaning quality tasks are performed to rinse internal pipelines, machines and equipment. This is often performed during a switch over of lines for example, changing Coke to Diet Coke to ensure that the taste is the same. This quality check is performed for both hygiene purposes and product quality. When these checks are performed the production process can begin.
Coca Cola uses a database system called Questar which enables them to perform checks on the line. For example, all materials are coded and each line is issued with a bill of materials before the process starts. This ensures that the correct materials are put on the line. This is a check that is designed to eliminate problems on the production line and is audited regularly. Without this system, product quality wouldn’t be assessed at this high level. Other quality checks on the line include packaging and carbonation which is monitored by an operator who notes down the values to ensure they are meeting standards.
The successfulness of this system can be measured by assessing the consistency of the product quality. Coca Cola say that ‘Our Company’s Global Product Quality Index rating has consistently reached averages near 94 since 2007, with a 94.3 in 2010, while our Company Global Package Quality Index has steadily increased since 2007 to a 92.6 rating in 2010, our highest value to date’. This is an obvious indication this quality system is working well throughout the organisation. This increase of the index shows that the consistency of the products is being recognized by consumers.
Related posts:
- Case Study: The Coca-Cola Company Struggles with Ethical Crisis
- Case Study: Analysis of the Ethical Behavior of Coca Cola
- Case Study of Burger King: Achieving Competitive Advantage through Quality Management
- SWOT Analysis of Coca Cola
- Case Study: Marketing Strategy of Walt Disney Company
- Case Study of Papa John’s: Quality as a Core Business Strategy
- Case Study: Johnson & Johnson Company Analysis
- Case Study: Inventory Management Practices at Walmart
- Case Study: Analysis of Performance Management at British Petroleum
- Total Quality Management And Continuous Quality Improvement
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

4 A CASE STUDY ON QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM IN CONSTRUCTION PROJECT
Related documents.

Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer
- Preferences

Quality Assurance System of SaintPetersburg State University - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

Quality Assurance System of SaintPetersburg State University
... in accordance with the government educational standards ... educational activities of spbsu. academic policy department. educatonal affair department ... – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- Dr. Stanislav Tkachenko
- School of International Relations
- St.Petersburg State University
- evaluation,
- accreditation,
- internal and external audit
- of university activities.
- Works out the university standards of QA for Ba/Ma
- Assesses efficiency of quality management system at the university
- Prepares the university quality management system for the external international non-government audit
- Government Educational Standards Data Performance Internal Control
- Students Educational Affair
- Students Extracurricula Activity
- Maintenance and Curriculum Design etc
- State accreditation in accordance with the Government Educational Standards
- Independent accreditation including international accreditation in accordance with non-government standards (ex ISO 9000 series, Standards and Guidelines for Quality Assurance in the European Higher Education Area (2005, ENQA).
- Vice-Rector for Education is responsible for the establishment, organization and operation of the QA system, for the management of students affairs (include foreign students affairs) and educational policy and implementation of standards at the University.
- for the quality management system of the faculty programs of studies(B.A., M.A., and Specialist Programs)
- For the faculty students curricula and extracurricular activities
- For the effective utilization of institutional budget, which consists of state funding and additional financial sources
- Government Educational Standards Data Performance Internal Control at the faculty level
- The University's Academic Board is an elected representative body performing general governance of the University. The University Rector and Vice-Rectors are members of the Board, with the Rector holding the chairperson's position. Other Board members are elected from a list of candidates put forward by the University units. Election takes place at a University Conference, its participants representing teaching and research staff and other categories of University employees and students. The Board's term of office is 5 years.
- Reform of the Academic Board of St.Petersburg State University
- The Academic Board takes decisions on all organizational issues dealing with areas of education, research, informatization, institutional development, personnel development, finances, economic activities and international relations.
- Other issues within the Board's responsibility include
- Hearing and discussion of annual reports by the Rector
- Discussing and establishing principles of financial distribution between the faculties, research institutes and other University units
- Establishing the University structure introducing structural changes adopting regulations on the structural units
- Convening the University Conference for (i) introducing changes and additions into the University Statutes (ii) electing the Rector (iii) electing the Board members (iv) endorsing internal rules of procedure
- Adopting an annual thematic plan of University research works and hearing a report on scientific activities of the University
- Endorsing the University logo, regalia etc.
- Awarding the title "Doctor honoris causa of St. Petersburg State University"
- Putting forward the names of candidates for honorary titles and state awards of the Russian Federation
- Awarding prizes to University employees for scientific and pedagogical merits.
- The Academic Board forms the Senate. The Senate is the Board's instrument, accountable to the latter in all its activities, which include
- Hearing and considering reports by heads of general University departments and offices of central administration
- Controlling the implementation of the Academic Board's decisions
- Considering issues of the practical management of the University coordinating work of the faculties and other structural units
- Considering draft documents of inter-university co-operation
- Preparing proposals for discussion at Academic Board's sittings.
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.

- Tech Insights
- Careers Insights
- Careers @ Zenkins
- Careers Portal
- Custom Software Development
- Web Application Development
- Mobile App Development
- SaaS Product Development
- Enterprise Software Development
- Software Testing and Quality Assurance
- Cloud Integration
- API Development and Integration
- DevOps and CI/CD
- UI/UX Design
- AI and ML Integration
- IoT Software Development
- Digital Transformation
- IT Staff Augmentation
- Data Engineering
- Product Engineering
- IT Consulting
- Platform And Infrastructure
- Manufacturing
- Professional Services
- Transportation & Logistics
- Telecommunications
- Construction
- Travel & Hospitality
- Industry 4.0
- Capital Markets
- Consumer Goods & Distribution
- Communications, Media & Information Services
- Energy, Resources & Utilities
- Life Sciences
- Public Services
- Frontend Development
- Backend Development
- Full-Stack Development
- Cloud & DevOps
- UI/UX & Design
- Quality Assurance & Testing
- Enterprise Solutions
- Specialized Roles
- ASP.NET Developers
- Blazor Developers
- C# Developers
- WPF Developers
- WinForms Developers
- VB.NET Developers
- Angular Developers
- React.js Developers
- Vue.js Developers
- HTML CSS Developers
- .NET Developers
- .NET Core Developers
- Azure Developers
- SQL Server Developers
- SharePoint Developers
- Entity Framework Developers
- WCF Developers
- Umbraco CMS Developers
- Full-Stack Developers
- MEAN Stack Developers
- MERN Stack Developers
- Xamarin Developers
- MAUI Developers
- UWP Developers
- Azure DevOps Engineers
- Microsoft Azure Engineers
- Microsoft Cloud Engineers
- Azure Solutions Architects
- Azure Security Engineers
- Azure Data Engineers
- Data Engineers (Microsoft Stack)
- Data Analysts (Microsoft Stack)
- Power BI Consultants
- Machine Learning Engineers (Microsoft Stack)
- AI Developers
- UI/UX Developers
- XAML Developers
- QA Engineers
- Automation Testers
- TestComplete Engineers
- MS Dynamics 365 Developers
- BizTalk Developers
- ServiceNow Developers
- Office 365 Developers
- Microsoft 365 Developers
- RPA Developers (Microsoft Power Automate)
- Azure AI Engineers
- Azure IoT Developers
- .NET Frameworks
- Programming Languages
- Front-End Technologies
- Data & Analytics
- AI & Machine Learning
- API & Integration
- .NET Framework
- ASP.NET Core
- ASP.NET MVC
- ASP.NET Web API
- Entity Framework (EF Core)
- WCF (Windows Communication Foundation)
- WPF (Windows Presentation Foundation)
- WinForms (Windows Forms)
- VB.NET (Visual Basic .NET)
- Microsoft Azure
- Azure DevOps
- Azure Functions
- Azure Logic Apps
- Azure App Services
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Azure Active Directory (AAD)
- Azure Cosmos DB
- Azure SQL Database
- Azure Virtual Machines
- Azure Service Bus
- Azure Key Vault
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- AWS EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)
- AWS S3 (Simple Storage Service)
- AWS RDS (Relational Database Service)
- AWS DynamoDB
- AWS CloudFormation
- AWS ECS (Elastic Container Service)
- AWS EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service)
- AWS IAM (Identity and Access Management)
- AWS API Gateway
- AWS Route 53
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- GCP Compute Engine
- GCP App Engine
- GCP Cloud Functions
- GCP Cloud Storage
- GCP BigQuery
- GCP Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
- GCP Cloud Pub/Sub
- GCP Cloud SQL
- GCP Cloud Spanner
- GCP Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- GCP Cloud Run
- JavaScript (ES6+)
- Blazor WebAssembly
- Razor Pages
- SSRS (SQL Server Reporting Services)
- SSIS (SQL Server Integration Services)
- SSAS (SQL Server Analysis Services)
- Azure Synapse Analytics
- Azure Data Lake
- Azure Data Factory
- Apache Hadoop
- Apache Spark
- Apache Kafka
- QlikView/Qlik Sense
- D3.js (Data-Driven Documents)
- Azure Machine Learning
- Azure Cognitive Services
- Azure Bot Service
- RESTful Services
- Azure API Management
- Customized Products
- Case Studies
- Manufacturing Execution System
- Enterprise Resource Planning System
- Deviation Management System
- Customized Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) System
- Customized Work Permit System
- Product Lifecycle Management System Case Study
- Research Project Management Software: A Case Study
- Employee Training Management Software: A Case Study
- Nonprofit Donor Management Software: A Case Study
- Environmental Sustainability Management Software: A Case Study
Quality Management Software: A Case Study
- Post author: Maryliya M J
- Post published: January 19, 2024
- Reading time: 11 mins read

Table of Contents
Quality management plays a critical role in ensuring organizations meet and exceed customer expectations while maintaining operational excellence. To achieve this, many businesses are turning to quality management software solutions. This article presents a case study that explores the implementation and impact of quality management software in an organization. It delves into the challenges faced in quality management, the process of selecting and integrating the software, as well as the benefits and lessons learned from its implementation.
Introduction to Quality Management Software
Quality management is an essential aspect of any organization, ensuring that products or services meet or exceed customer expectations. In today’s fast-paced and competitive business landscape, the need for effective quality management has become even more crucial. Enter quality management software, a powerful tool that can streamline and optimize quality management processes.
Understanding Quality Management
Quality management refers to the systematic processes, procedures, and activities an organization implements to achieve and maintain excellence in its products or services. It involves various aspects, such as quality planning, quality control, quality assurance, and continuous improvement. By focusing on quality management, organizations can enhance customer satisfaction, reduce costs, increase efficiency, and foster a culture of excellence.
Importance of Quality Management Software
Quality management software plays a vital role in enabling organizations to effectively manage and control their quality processes. It provides a centralized platform for capturing, analyzing, and monitoring quality-related data and activities. With quality management software, organizations can automate and streamline various tasks, such as document control, non-conformance management, corrective actions, audits, and supplier management. This software helps in standardizing processes, ensuring compliance with regulations and industry standards, and facilitating continuous improvement initiatives. By leveraging quality management software, organizations can enhance their overall quality management efforts and achieve desired business outcomes.
About the Client
Our client, a manufacturing company, encountered challenges in maintaining product quality standards and effectively tracking defects. Recognizing the critical importance of systematic quality control processes, they sought a Quality Management Software ( QMS ) to enhance their quality assurance procedures. The primary goal was to implement a comprehensive QMS that ensures adherence to quality standards, streamlines quality inspections, and enables efficient tracking of defects.

Project Overview
The project aimed to develop a robust .NET-based QMS to address the client’s challenges. The primary objectives included implementing modules for quality inspections, defect tracking, and corrective action management.
The Challenges
- Maintaining Quality Standards: Inconsistent adherence to quality standards was affecting the overall product quality.
- Defect Tracking Difficulties: Difficulty in tracking defects and implementing timely corrective actions.
- Lack of Systematic Processes: Absence of a systematic quality control process led to operational inefficiencies and increased defects.
The Solution
Our team of experienced developers and project managers collaborated to design and implement a comprehensive .NET-based Quality Management Software. The solution included modules for quality inspections, defect tracking, and corrective action management to ensure systematic adherence to quality standards.

Key Features of the QMS
- Quality Inspections: The QMS facilitated systematic quality inspections to ensure product quality standards were met.
- Defect Tracking: Comprehensive tools for tracking defects and identifying root causes for timely corrective actions.
- Corrective Action Management: The software provided a structured approach to corrective action management, addressing issues promptly.
- Adherence to Quality Standards: Ensured consistent adherence to quality standards through standardized processes.
The Outcome
The QMS was successfully deployed, resulting in significant improvements in product quality and defect tracking. Systematic quality inspections, defect tracking capabilities, and structured corrective action management contributed to a more streamlined and efficient quality control process.
Our team’s expertise in developing a tailored Quality Management Software using .NET technologies effectively addressed the client’s challenges. The implementation of quality inspections, defect tracking modules, and corrective action management contributed to a more rigorous and effective quality assurance process.
By leveraging the software’s capabilities across various departments, organizations can achieve greater operational efficiency, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced overall performance. However, it is crucial to thoroughly assess the integration requirements and ensure proper training and support are provided to users.
In conclusion, the case study highlights the immense value of quality management software in organizations. By addressing the challenges faced in quality management and implementing an effective software solution, businesses can experience improved efficiency, enhanced quality control, and significant cost reductions.
Are you struggling with maintaining quality standards and defect tracking? Contact us today to explore how our expertise in QMS development can transform your quality control processes and enhance product quality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. what is quality management software.
Quality management software is a technological solution designed to assist organizations in effectively managing and improving their quality control processes. It typically includes features such as document control, corrective and preventive actions, audit management, risk assessment, and performance tracking, enabling companies to streamline their quality management practices.
2. How can qMS benefit my organization?
Implementing quality management software can bring numerous benefits to an organization. It enhances operational efficiency, facilitates compliance with industry standards and regulations, reduces the risk of product defects, and improves customer satisfaction by ensuring consistent quality. Additionally, it provides real-time visibility into quality metrics, enabling data-driven decision-making and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
3. Are there specific industries or sectors that can benefit from quality management software?
QMS can benefit organizations across various industries and sectors. It is particularly valuable for industries with stringent quality requirements, such as manufacturing, healthcare, pharmaceuticals, aerospace, and automotive. However, any organization that values quality, consistency, and process optimization can reap the benefits of implementing quality management software.
4. What are some key considerations for successful implementation of quality management software?
Successful implementation of QMS requires careful planning and execution. Some key considerations include clearly defining quality objectives, involving stakeholders throughout the implementation process, choosing a software solution that aligns with the organization’s needs, providing adequate training to employees, and regularly evaluating and refining quality management processes to ensure ongoing improvement.
You Might Also Like

Streamlining Insurance Operations: How IT Staff Augmentation Services Revolutionized Our Client’s Business

Conference Room Booking System: A Case Study

Retail Point of Sale Software: A Case Study
Book a free consultation.
Tailored Solutions, Expert Advice, and Project Estimates Await.
Expect a Prompt Call from one of our Account Managers.
- Elite IT Professionals
- Time Zone Aligned
- Experienced Team
At Zenkins, we bring together a curated network of elite IT professionals ready to elevate your projects to new heights. From seasoned developers to innovative designers, our handpicked talent pool is here to turn your visions into reality. Experience unparalleled expertise, reliability, and dedication to excellence with our team of Elite IT Professionals.
At Zenkins, we understand the importance of global collaboration. That’s why our team is strategically aligned across time zones, ensuring seamless communication and productivity no matter where you are. From brainstorming sessions to project updates, our time zone-aligned approach guarantees that deadlines are met and progress never stalls. Experience the convenience of working with a team that’s always in sync.
At Zenkins, we pride ourselves on our experienced team of professionals who bring years of industry knowledge and skill to every project. From seasoned developers to seasoned project managers, our team has the expertise to tackle even the most complex challenges. With a proven track record of success, we deliver results that exceed expectations.
+91 70690 18504
[email protected]
Zenkins is a leading software development company based in India, specializing in SAAS Product Development, Digital Transformation, and Product Engineering. With a dedicated team of professionals and a commitment to excellence, we deliver innovative solutions that drive business growth and success. Partner with Zenkins for all your software development needs and experience the difference firsthand.
- Methodologies
- Technologies
- Our Services
- IT Staffing Services
- Software Outsourcing
- .NET Development
- Careers @Zenkins
- Current Openings
- Technology Insights

Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Get 50% off your first project with us!
Join our community of satisfied customers and experience the power of our software team today. Contact now and get 50% off your first software project/ product. Don’t miss out on this exclusive offer!
(267) 808-6227
Case Study: Optimizing a Quality Management System (QMS)
Prosit gathered a team together with seven employees. The QMS was brought up and a list of priorities was created to get a grasp on what to tackle. One by one, the team went down the list creating flow charts where they were missing, updated employee information records, and validated processes that were being done versus what the process forms were stating.
If anything needed to be changed it was attacked and action items were created. The team met on a weekly basis for two months. This was all in preparation for an internal and external audit that was to be conducted in 2020.
Current status, this company now has validated most of their documents and effectively cleaned up the QMS system. However, this has created more action items and areas to be improved which Prosit is actively working on with the team. In the near future, the system will fully reflect what is being done on the shop floor accurately.
Additionally, the improvement team will use these learned skills to conduct more events similar to this one, if the need arises.
Please contact Prosit to see how we can assist your company with your lean enterprise and consulting needs.
EJ Lydon has extensive experience in Operations and Manufacturing management. He now passionately provides Advanced Process and Strategic consulting services to small to medium sized companies, focusing on Lean Manufacturing methodologies with roots in the Toyota Production System.
Privacy Policy | Sitemap
WE'RE HIRING! JOIN OUR TEAM
Case Study: Quality Management System

A biopharmaceutical company specializing in the development of gene therapies had an impressive late-stage clinical program progressing several drug candidates towards commercial approval. However, the existing quality system would need to be revamped to handle the potential marketing of multiple approved biologic and drug products.
The company needed to help develop a more robust quality system to fit the commercial needs of this growing organization. It also needed a resource partner that could develop project plans, supply temporary experienced, top-level consultants to address the additional workload and manage the resources and deliverables to ensure the development and implementation of the new quality management system.
The additional demands of commercial expansion taxed the bandwidth and expertise of the company’s quality system, quality assurance and quality control teams.
Moreover, the expansion of the quality system would require significant investment in time and resources including process mapping and development, documentation creation, systems integration and improvements, training and other critical activities. The company would also need time to find, recruit and onboard permanent employees for newly identified positions.
How We Helped
The client and Black Diamond Networks collaborated on a comprehensive strategy to identify the compliance gaps and associated risks, understand the needs of the organization and build out the quality system. Black Diamond developed the project plans, identified and addressed the resource gaps, managed the resources and milestones, and ensured the execution of the project.
We also sourced contract-to-hire and consulting personnel to bridge the gap until permanent hires could be transitioned in the new roles created by the changes to the quality system. In total, we supplied over 20 professional resources with the experience, expertise and drive to ensure the success of the project.
Successful Results
Black Diamond Networks aided in the design, development and implementation of an improved quality system covering preclinical, clinical and commercial operations. This successful project created a lasting impact through improved processes, more compliant procedures, stronger documentation and better trained and prepared personnel.
Working with Black Diamond
How do we do it?
Our staffing model is wired for speed and precision, thanks to a cultivated community of experts in life sciences, engineering, and technology.
In fact, we have almost 1000 contractors with cell and gene therapy and tissue engineering experience in our network.
These highly-skilled candidates are already fully vetted and Black Diamond approved.
Typical roles we fill for our cell and gene therapy clients
- Clinical Development Scientists
- CMC Experts
- Regulatory Professionals
- Analytical Development Scientists
- Process Engineers
- Manufacturing Engineers
- Project Managers
- QA/QC Specialists
- MS&T/MSAT Specialists
Black Diamond Networks actively supports our clients across the cell and gene therapy sector by providing the hard to find talent needed throughout the entire process, from design and development to commercialization.
Clients in the life sciences industry turn to us, time and time again, thanks to the quality of our candidates and the speed we can fill their most specialized roles.
We understand that each company and project is unique, which is why we have a flexible staffing model, from traditional staff augmentation to complete project solutions, so you get the support you need, where you need it.
Need project support?
We’re supporting clients on a variety of scales – by overseeing and staffing multi-site projects to sourcing individual subject matter experts. How can we help you? Let’s discuss.
You May Also Like
Employee Spotlight: Brandon Klier
Employee Spotlight: Sami Samali
Biotechnology Recruiters and Headhunters: Experts in Biotech Staffing
Employee Spotlight: Jillian Getchell
Employee Spotlight: DaniJo Neuman
Employee Spotlight: Daniel Challoner
Need to fill a position?
If you need technical staffing support, contact us today or call 800-681-4734
" * " indicates required fields
23 Main St Suite 3 Andover, MA 01810
Powered by Getfused | Privacy Policy | Sitemap

Sign up to receive our latest insights
Powered by Getfused | Privacy Policy
Quality Management System for Managing Construction Projects: A Case Study in Engineers India Ltd.
The IUP Journal of Operations Management, Vol. XVIII, No. 2, May 2019, pp. 25-55
Posted: 4 Aug 2020
D.K. Choudhury
Gitarattan International Business School
Date Written: 2019
Any construction project comprises a set of components, and the successful completion of a project depends on the quality of work done by each of these components. The quality of construction project mainly depends on the quality of materials and the quality of workmanship. Therefore, the selection of vendor and contractor plays an important role in the quality management system in constructing a project. Two research methodologies — the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) and physical system theory — have been used. In this research work, a case has been demonstrated as to how AHP could be used for selection of quality vendor and quality contractor. The Physical System Theory (PST) has been used to develop an inspection system model for inspection of quality both at vendor’s end and at construction project site. In the light of Quality Management System (QMS), a case study was conducted in Engineers India Ltd. (EIL), who are one of the renowned project management consultants in the country, to find out how EIL takes care of the above-mentioned factors, along with others, to support their QMS in construction project management.
Suggested Citation: Suggested Citation
D.K. Choudhury (Contact Author)
Gitarattan international business school ( email ).
PSP 2A & 2B Complex - II, Madhuban Chowk Sector – 14, Rohini, Delhi 110085 India
Do you have a job opening that you would like to promote on SSRN?
Paper statistics, related ejournals, civil engineering ejournal.
Subscribe to this fee journal for more curated articles on this topic
Case Study: Pharmaceutical Quality Management System
- April 26, 2022
- Case Study , Salesforce Consulting , Salesforce Development
- case study , Health and Life Sciences , Pharma , Pharmaceutical , Quality Management System , Salesforce

Embracing challenges is our thing at Red Argyle. What energizes us are Salesforce development projects that are globally impactful.
When a global pharmaceutical company needed a unified and scalable quality management system to help get medicines to market, in true Red Argyle fashion, we said, “Let’s get started!”
Download the case study here .
Challenge: Potential Confusion and Inefficiency
Salesforce scalability was the top priority – and an ultimate challenge.
From the first claim that a molecule has therapeutic benefit, through its global marketing, teams and vendor partners rely on Salesforce as an essential quality management system to track work and comply with regulations.
Although the organization’s Salesforce footprint is large, each team – stationed worldwide – had a different way of managing oversight. As a result, each team performed similar tasks and processes differently, and all, with one exception, performed this work manually on paper. The inconsistency created a potential for confusion and inefficiency.
Solution: Customizable and Flexible Salesforce Platform
The Red Argyle team developed a customizable and flexible Salesforce platform that enabled each group in the pharma company (10 units in total) to manage their quality processes in a unified way globally.
One of the most complex undertakings to date for Red Argyle, the project encompassed:
- Initial discovery, architecture, and prototype
- Building the first production version, plus feature enhancements and development
- Project clean-up, deep documentation, and hand-off to the client team
- Industry compliance validation of the solution
- Assistance with scaling and additional team onboards
Our Approach
Our team of Argylers went into the project well-prepared; this included prep meetings, consuming documentation, and researching known challenges. Discovery was delivered quickly, with a total time from the sales process to the completed discovery of about two months . Red Argyle’s subject matter expertise enabled a successful knowledge transfer at the end of the engagement.
The scope of the Salesforce project included:
- Creation of screen flows to enhance the users’ experience and efficiency; for example, automatic field population.
- Integration of MuleSoft with seven other apps.
- Establishment of specified security customization-enabled permissions.
- Major classes of features were defined, named, and documented, along with their sub-features. (Because of this, the client can continue building and adding to each feature.)
A Validated Solution
In the highly regulated world of healthcare, the developed Salesforce tool had to go through validation. The Red Argyle team defined and ensured security and compliance with documentation, rigorous testing and procedures, and risk assessment .
Fast Turnaround
The project was delivered using the Agile methodology and ceremonies throughout its lifecycle. The relationship with the organization was collaborative, fostering rapid feedback, backlog grooming, demos, and agreement on features.
According to the client, a project of this size and scope typically takes up to four years to complete. Some never get off the ground because they’re obsolete when they finally launch. The project was finished in 18 months – beating the historic project length by 266%.
Results: Unified Teams and Data
The Red Argyle team developed a customizable and flexible Salesforce platform that enabled each group to manage their quality processes in a unified way globally .
Increased Visibility and Efficient Vendor Management
Before this project, employees had difficulty viewing work across different projects and stages and their suppliers’ work. Now, they have a global solution that gives them visibility across groups and medicines; they can easily monitor vendors involved in research and marketing.
Orchestrated Tasks
One of the most significant benefits of Salesforce is its ability to unify teams and data. Our team of Argylers ensured Salesforce was configured to help people do the right kind of work at the right time, creating a master schedule that managers can follow. As a result, they know which paperwork to submit by which deadline, how to schedule on-site meetings, and they quickly understand who’s on or off-plan. No more calendar wrangling!
Safety and Compliance Reporting
By building a Salesforce platform that’s consistent across teams and meets their specific needs, the pharma teams have saved time on reporting.
- Handwritten, 20-page documents are created instantly and automatically. Paperwork writes itself based on the data populated in the system.
- All tasks are in logs in the correct format for easy compliance reporting and information sharing.
Salesforce Solution Set Up to Be Successful for Many Years
With extensive documentation and in-depth onboarding and training, the client’s development team of in-house and off-shore third-party resources was set up for success to assume ownership and maintenance of the quality management system. This type of support during transition ensures continued success for many years. The investment in this Salesforce solution will pay significant dividends .
Make the most out of Salesforce
The above pharma company was referred to Red Argyle because of our proven success in the enterprise space and navigating unique challenges at scale. We’re happy to help you, too (we love a good Salesforce challenge!). Contact us to start a conversation.

Related Blog Posts

Argyler Spotlight: Selena Garzio, Staff UX

Building Accessible Salesforce Apps: Part 5 – Salesforce Accessibility Across All Devices and Connections

Building Accessible Salesforce Apps: Part 4 – Designing for Dexterity
Salesforce Cybersecurity
Get the tools you need to confidently plot a plan to secure your organization.
- 243 Gorham Street
- Canandaigua, NY 14424
- [email protected]
- 585.412.2153
© 2022 All rights reserved

Case Study: Quality System Optimization
- March 4, 2020
At QualityHub, we have experience in quality systems for several types of companies and situations. Here are nine examples of quality system case studies to give you some background on that experience.
CAPA System Overhaul
When QualityHub is brought on to do CAPA system revisions, it is often more reactive than proactive. However, one particular client — a major international pharmaceutical and medical device company — noticed shortcomings and wanted to take a more proactive approach to their CAPA system.
Discover how QualityHub worked alongside one client to transform their CAPA system into what the FDA called “one of the best systems they had ever seen.” Read the full case study here .
Compliance Master Plan
Qualityhub assisted an international device company with its existing compliance master plan. working with the project manager and qa director we were able to develop a newer version of the document that was more understandable and more detailed. using our ex-fda expertise we determined more emphasis was needed on accountability and responsibilities. we were able to improve the document to more closely hold persons responsible..
We also guided the company to use measurable data for the milestones, thus focusing on the metrics that were needed to demonstrate the success of the milestones via objective evidence. Since numerous project teams were involved in implementation, we worked with the project manager, who held the project team leaders responsible for providing key details in the document.
Based on our guidance and requirements, the teams provided us with improved responsibilities information and information on the objective evidence they would use to demonstrate the accomplishment of the milestones.
Investigation Analysis and Training
QualityHub worked with a major international drug/device corporation to help improve its internal investigation processes and skills. Internal reviews and FDA inspections pointed out weaknesses in that area. We performed a gap analysis by reviewing samples of investigations from divisions across the organization.
Working with company representatives, QualityHub developed a full-day training program on conducting investigations. The course materials were licensed to several thousand users, who became the corporation’s trainers worldwide (using “train-the-trainers”).
QualityHub participated in training the first two levels of trainers and certified the initial cadre. The company trainers presented the training to sites worldwide and initiated other improvements in their investigation programs.
To determine if the program was successful, we performed a second gap analysis of their investigations about six months later and at one-year post-deployment. These gap analyses showed great improvements.
Warning Letter Intervention
QualityHub was contacted by a strategic consulting partner to assist with a drug manufacturer who had recently received an FDA warning letter. Working with the partner company, we assisted in developing the overall compliance plan and writing the FDA update submissions.
The compliance plan included major improvements in the validation program, investigations/CAPA, change control and management controls. Utilizing several specialized contractor consultants and company personnel, we were able to implement a new quality system—and work on culture change initiatives—to ready the company for the inevitable FDA inspection.
CAPA Program Development
QualityHub was contacted by a drug company to assist in the development of a new CAPA program. Working with the company we reviewed their current program and guided them in the development of a new CAPA program. QualityHub also briefed local management and provided training to all applicable personnel on the new system. We also provided some guidance on the role of automation systems for their CAPA information.
Corporate Survey/Gap Analysis – Complaint Handling
QualityHub was contacted by a drug/device company to provide the main office with an analysis of practices company-wide. We visited numerous sites in Europe and the U.S. and provided a report of our findings. Process maps were developed and information was gathered on the strengths and weaknesses of the program. This information will be used for future process improvements as well as organizational analysis.
Corporate Survey/Gap Analysis – MDR and Complaint Handling
QualityHub was contacted by a major international device company to perform an analysis of complaint handling practices company-wide and worldwide. We visited over 20 sites to gather information about their complaint handling and MDR practices. The analysis included an extensive sampling of complaints—both non-MDR reported and MDR reported.
The project included an extensive data-gathering activity using pre-planned sampling plans, questions and analysis tools. Reports were prepared, which the company used to improve its complaint and MDR practices worldwide. We also consulted on their new and improved complaint and MDR procedures.
FDA Preparation Training
QualityHub helped numerous medical device companies in the U.S., Asia and Europe, prepare and handle FDA inspections. Overwhelmingly, the clients reported that our assistance was very helpful in handling the FDA inspections, and also in minimizing the number of FDA 483s the sites received at the conclusion of the inspections. The reduction of FDA 483s resulted in no warning letters for nearly all of these companies.
FDA Inspection Preparation and Back-Room support
We helped a European company plan for handling an FDA inspection. This included pre-inspection gap assessments, SME interviews and SME training, as well as management training and site preparation for the inspection.
During the actual inspection, we helped the back room in orchestrating the documents and SMEs that presented during the inspection. The company passed the inspection with flying colors .
Looking for more information on quality management systems ?
Quality system consulting.

- 976 Lake Baldwin Lane Suite 204 Orlando, FL 32814 USA
- (407) 896-3386
- Quality System Auditing
- Staff Augmentation
- EU MDR Regulatory Compliance
- Quality System Training
- FDA Regulatory Compliance Consulting
- FDA Premarket Planning & Product Development
- Risk Management
- Quality Management Systems Consulting
Stay Connected | Now it’s even easier to stay connected to the leader in FDA quality system compliance. Sign up to be part of the QualityHub community.
- Enter Email
Gillette’s Total Quality Management System Case Study
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Gillette gets employees to take on the new system, involving teams in the tqm process, the working culture.
Gillette began its global operations in 1905 when it opened a manufacturing plant in Germany. This global strategy and success saw the firm extending its operation to Latin America. Argentina was a potential market after tariffs and business policies were revised. Having operated under unfavorable regime, the firm perceived future competition and decided to create competitive advantages.
Key figures in the firm such as Carlos Rotundo and Jorge Micozzi suggested better quality as the solution to the market issues. The management had to change the organizational culture which was not strategic for the future market circumstances. Rotundo had already began creating a new organizational culture when Micozzin came up with the idea of total quality management (TQM) that made Gillette Argentina the most successful affiliate in Latin America.
Due to the great success of Gillette’s TQM system, this research was commenced to do a case study on “quality at Gillette Argentina”. The paper begins by evaluating the ways in which the firm got its employees to take on the new TQM system. It proceeds to discuss the importance of getting the teams involved in TQM process as well as identifying the ways in which the teams improved the process.
The paper also explains the meaning of the phrase “Beyond the hanging fruits, the most important outcome of this effort was a different way of working with sales” and highlights how Gillette changed the way it looks at its customers. Finally, there is a description of the working culture before and after the implementation of TQM as well as the economic benefits of the system.
In a firm where decision making is solely the responsibility of leaders such that the employees have to act as the subjects to them, it is likely that the employees would not readily accept the adoption of total quality management (TQM). This is because TQM requires them to take elevated roles, become self-dependent and consider themselves as the owners of the firm.
It is apparent that Gillette had earlier managed its activities in a manner that left the managerial roles such as decision making and steering initiatives exclusively to the leaders. Therefore, the effort to adopt TQM compelled leaders to take measures that would prepare the employees better for the change. These measures involved several initiatives especially triggered by several key figures in the firm.
The very first initiative Gillette took was to hire the Organizational Dynamics Inc (ODI) as a consulting and training firm. The firm became the key source of information and motivation for the Gillette Latin America management. It can be argued that the source of a successful organizational change begins with leaders who in turn transfer it to employees.
This means that the employees would rarely have accepted an initiative that their leaders did not support appropriately. The consulting firm played a central role in preaching the benefits of TQM to the leaders. Indeed, the firm reinforced the idea Rotundo had already started to instill in Argentina. Organizational Dynamics Inc. developed the quality initiative and recommended the creation of a quality structure.
Secondly, Gillette offered training to the employees as a way of preparing them for TQM system. One of the landmark training was FADE that prepared employees for quality action teams. The specialized training involved four phases of problem solving: focus, analyze, develop and execute.
The focus phase was concerned with the development of a problem statement; the analyze phase dealt with the use of data to understand the magnitude of the problem; the develop phase involved the determination of a solution and implementation plan; and the execute phase was about implementing the plan and measuring its impact. In addition to FADE training, the employees received training in seven basic quality tools as well as brainstorming, force field analysis and cost benefit analysis.
Furthermore, training was extended to management and leadership levels. The Argentine directors, managers and other officials were trained by ODI as trainers of the rest of the organization. The teams were allocated facilitators who received training on leadership development.
Team leaders were trained in areas relating to group dynamics, effective meetings, leadership skills and group conflicts (Donnellon & Engelkemeyer, 1999). As a matter of fact, training was the backbone of the TQM process. Most of the members who got training became experts in their respective areas and eventually steered the process towards success.
Another way that Gillette used to prepared employees for the TQM process was through workshops. Through the leadership of Walker, workshops were conducted with all employees to inform them about the changes that would take place. The staff got information about the new working style and culture to be attained through TQM.
Team sponsors were identified and their roles explained to the staff. They were to support the teams in any way needed including helping them to attain their objectives with recognition of their empowerment. Other workshops that Walker would offer involved problem-solving and statistical analysis, and at the same time inspiring everyone.
Finally, Gillette endeavored to meet the challenges of quality that the employees faced. Initially, Rotundo responded quickly to the employee complaints about the contract approach by delegating responsibility to investigate them to Victor Walker. The newly hired quality manager emerged to be a successful preparer of the team members and organizer of TQM process.
Through his stewardship, teams were guided in their TQM process by sponsors and ODI methodology. In addition, a steering committee was formed in an effort to respond to quality challenges.
The council systematically supported the employees towards TQM process and formed the backbone in the creation of a new working culture. Through such support, the employees were assured of the leaders’ commitment to the process and ultimately embarked on the mission whole-heartedly.
Team involvement was paramount for the success of Gillette TQM process. The initiative was adopted by the firm in an effort to enhance overall performance and position better in the Argentine market. As Jorge Micozzi observed, the market was opening and thus the firm perceived the entry of new competitors from United States and Europe (Donnellon & Engelkemeyer, 1999).
In that respect, team involvement was important to create a competitive advantage. This would allow for creativity and emergence of new ideas as the team members presented diverse suggestions. There was need to improve decisions and processes ahead of competition trough team work. Therefore, the new competitive advantage was to assist Gillette to compete and keep their market share.
Team involvement was important in consolidating individual interests with the interest of the company as a whole. Before the implementation of TQM, the employees pursued their interests with no chance for a broader perspective on the organizational goals and objectives. This working culture was not particularly strategic for the creation of customer value through quality services. Therefore, team involvement was a way of changing this individualistic culture as well as the focus of the workforce towards goal attainment.
Organizational Dynamics Inc which was hired to develop the quality initiative recommended the creation of teams. With the success history of the firm in Mexico, it was very important for Gillette to abide with this recommendation.
Team involvement was the only way to achieve the quality structure suggested by ODI. In addition, the basis of TQM being total participation, customer focus, systematic support and continuous improvement relied completely on team involvement for success.
Team involvement was important in enriching business ideas within Gillette. It can be argued that when employees are offered the chance to contribute to decision-making process, more and better ideas are achieved. Indeed, individuals are challenged to bring new ideas and suggestions when they are members of a team.
The individualistic working culture which existed prior to implementation of TQM process was a huge obstacle to the generation of new ideas. Decisions were entirely made by the top leaders who had little knowledge about the challenges at the operation level. Therefore, team involvement as Walker observed was a way of creating a conduit through which ideas would flow up and down the hierarchical structure.
The other importance of involving teams was to eliminate departmental barriers that the previous system had created. As a manufacturing firm, Gillette had denied employees the necessary interaction between departments. Rarely could the design team interact with the production team or the assembly team which gave in to low quality products and wastage of materials.
As much as the implementation of TQM process was to succeeds, so was the effort to involve teams. This involvement of diverse teams gave the need to understand what other departments did and how they were related to each other. Therefore, for the success of the TQM processes, interaction and coordination among departments was very crucial.
Team involvement in the TQM process was also important in improving customer satisfaction. Although it was more relevant to the sales team, it permeated through all other teams. The sales team had the direct contact with the customer and when involved in the TQM process could offer the needed feedbacks to the rest.
The other teams chipped in when responding to these feedbacks especially those which related to product offered. The involvement of these teams enabled Gillette to meet customer expectations and ultimately increase their satisfaction. Moreover, the increased strength and commitment of the sales team made the customers to feel more satisfied when transacting with the team members.
The TQM process at Gillette was greatly improved by teamwork. It enabled the management to identify and meet challenges of quality. Team involvement increased employee participation in which they launched their complaints. For instance, the assignment of Victor Walker who emerged to be the cornerstone in the processes was triggered by complaints from the employees (Donnellon & Engelkemeyer, 1999). In addition, team involvement allowed the steering committee to turn to TQM problems that barred the success of such programs.
Team involvement also allowed for the creation of the necessary working culture. As the team members increased their participation, new ideas emerged and departmental coordination became a reality. The roles of team leaders and members were defined and the members focused more on the organizational goals and objectives. Autonomy and efficiency increased such that each employee became a significant contributor to the success of the process.
Team involvement in the TQM actually speeded up the implementation. The firm was able to make quick, but effective decisions on how to go about implementing the components of the process. The process that had earlier faced challenges picked up as the teams increased their participation. Micozzi offers the success example of the administrative building (Donnellon & Engelkemeyer, 1999).
The building was designed and built in ten months by nine teams. Therefore, it can be argued that team involvement was the key factor that contributed to the success of TQM process within such a short time.
“Beyond the hanging fruits, the most important outcome of this effort was a different way of working with sales”
This statement was coined by Rotundo when he moved to interface sales with cross-functional teams after succeeding in managing inventories. According to him, customer focus was more important than anything in Gillette. After all, the manufacturing operations undertaken by the firm were determined by its capacity to make sustainable sales.
He likened other achievements of the effort to hanging fruits pointing sales focus as the most important attainment. The sales focus Rotundo had in mind was that of changing the way Gillette looked at its customers. This change was that which responded to the needs of the customers despite their nature or demands. It was a change that the firm could make while looking at things from the perspective of a customer and responding to customer demands without question.
Actually, the quality effort had to be focused on the enhancement of customer satisfaction. According to Daft, Murphy and Willmott (2010), customer is the most crucial stakeholder of an organization as he defines the reason for its existence and eventual success. Other achievements could be important, but lie far below the capacity to drive sales (hanging fruits).
As Rotundo highlights, this driving force could only be achieved by changing the way the firm worked with sales. The fact that customer needs could be clearly understood, the quality management program necessary would automatically be defined. The changed perspective about the customer would actually allow the customer needs to act as the roadmap towards continuous improvement of the quality management practices. Therefore, in spite of the achievement made by quality effort, the influence it could have on sales was paramount.
In response to the call made by Rotundo, Gillette completely changed the way it looked at its customers. First, customer satisfaction became the main purpose of TQM process as Micozzi noted (Donnellon & Engelkemeyer, 1999).
The teams were encouraged to align their goals with the corporate goals in order to drive sales. Starting from the design department to production department to sales department, all teams were involved in TQM process with a focus on their contribution towards customer satisfaction. In fact, the continuous improvement component of the TQM process involved responses to the changing needs of the customers. This is confirmed in the various team projects undertaken in the implementation of the process.
Gillette Argentina also changed the way it looked at the customers by having a special focus on the sales department. The sales teams were encouraged to be more proficient in working together and increase their efficiency to make customers more satisfied. The emphasis on customer needs was real and made the sales team more compelling.
As the local sales manager observed, the emphasis on sales department made people to like working with the team as they learned about the entire firm, gaining a global perspective (Donnellon & Engelkemeyer, 1999). Nonetheless, Gillette conducted continuous survey on customer satisfaction to ensure that the teams were delivering the expected results.
Immediately the teams were formed, the firm conducted customer surveys and customer critiques were assigned to each group. The success was clear-cut in these surveys suggesting the complete change of the firm’s way of looking at the customer.
Initially, Gillette’s organizational culture was characterized by individualism in which there were leaders and subjects to lead. Apparently, the employees got orders from above and had to act upon them without question. Decisions were solely made by the management without any input from the lower ranks.
Each department was assigned to specifically defined roles that were only approved by the management. There were few linkages to other departments with no interaction between departmental employees. Coordination between the departments was the role of managers whereby they advised rather than discussing on the work-related issues.
The employees focused on completing tasks rather than meeting goals and objectives. It can be argued that customer focus was not a crucial factor when working in the company. Workers pursued their interest and the interest of the company had little relevance when performing the assigned tasks.
Even before the implementation of TQM process, Carlos Rotundo had attempted to change the existing working culture. He introduced a quality-focused culture that supported team work with special emphasis on sales. The culture assigned many of the responsibilities to team leaders, but did not give individual employees much autonomy. Clearly, leaders made many of the decisions without any contribution coming from team members.
Each team pursued a specific task that was defined by the customer’s critique identified in the customer survey. Also, the management was responsible for most of the decisions that were beyond teams’ jurisdiction. Departmental interaction was not supported by this culture which ended prematurely after the introduction of TQM process.
The working culture that emerged from the adoption of TQM process was characterized by team work. Each activity that was accomplished in the firm including product design, development, production and offering was the cumulative efforts of individual teams. The team formation involved both the employees and the management. As a result, decision-making at department level as well as corporate level involved all team members.
The culture allowed each employee to contribute to any undertaking of the firm regardless of the source department. The ultimate goal in the new culture was customer satisfaction and all teams endeavored to achieve this goal.
Therefore, working to achieve this goal was the “sign post” of teams’ activities and leaders were not there to give orders but to discuss issues with members. In fact, Rotundo acknowledged that the new culture did not allow for orders, but consensus whereby the management listened to others’ problems and worked jointly to solve them.
The new culture was a supportive culture where tasks were shared among teams as well as team members. Individual employees became more responsible and industrious as they perceived assistance from other members. There was new confidence in their decisions and satisfaction in the tasks completed, especially when they were acknowledged with gifts.
The support formed a platform for knowledge creation and acquisition by the employees due to the focus on identifying problems and solving them. The cooperative working culture gave way to efficiency in the services offered to customers. Employees were willing more than ever to launch their complaints which allowed the managing team to act upon them on time. Thus, the working culture gave room for continuous improvement of the TQM process and eventually improvement on services offered to customers.
The TQM process implemented by Gillette had great tangible and intangible benefits. Perhaps, the economic benefits that came about due to improved performance and wastage elimination are most important. The high performance resulted from increased customer satisfaction which by 1994, the firm topped the list with 8 on a ten-point scale.
The higher economic performance could also have stemmed from the creativity and innovativeness of the firm as the team members acquired new knowledge and ideas. It can be argued that the larger part of the firm’s performance revolved around the capacity to bring new products to the market. The creative culture established by TQM process was clearly described in the rapid growth of financial determinants.
Some of the economic benefits include growth in sales, higher profits, POE decrease, inventory turns increase, and ROA increase. Between 1993 and 1998, sales grew by 19 percent while average profits increased by 22 percent. Period operating expense (POE) decreased by 40 percent while inventory turns increased from 4.8 to 8.7 in that period.
Return on assets (ROA) rose by 60 percent between the years. Profitability attributed to TQM was forecasted at $17.8 million by the turn of the millennium. Another economic benefit directly related to TQM was the expansion of the firm’s facilities. Clearly, the development of the new professional and administrative building was an outcome of the TQM process. The firm was also able to decrease material wastage and increase employee output per unit cost of the labor input.
As competition threat continued to intensify in the Argentine market, Gillette embarked on a TQM system to counter the competition. The challenge the firm faced of getting the employees to take on the system was solved by extensive training, workshops, consultation and proper response to the quality challenges perceived.
Teams were formed and involved in the process for various significances including: to create competitive advantage, to consolidate individual interests with the interest of the company, to act on the recommendations made by ODI, to enrich business ideas within firm, to eliminate departmental barriers, and to improve customer satisfaction.
This involvement allowed for the creation of the necessary working culture and speeded up the implementation of TQM. A different way of working sales that Rotundo had suggested led to the firm changing the way it looked at its customer by having a special focus on the sales, making customer satisfaction the main purpose of TQM process and conducting continuous survey on customer satisfaction. The working culture which changed from individualistic culture to team-working culture benefited the firm economically.
Daft, R., Murphy, J. & Willmott, H. (2010). Organization Theory and Design . Florence, KY: Cengage Learning EMEA.
Donnellon, A. & Engelkemeyer, S. (1999). Quality at Gillette Argentina . Web.
- Vehicle Supporting Processes
- Decision Making Processes for Flexible Work Arrangements
- Procter and Gamble Company's Innovation Strategies
- Marketing Principles and Practice
- Procter & Gamble Company Analysis
- Importance and Role of Management
- Need for Effective Networking for Consultants
- Deloitte Company Recruitment Process for Graduate Program
- Talent Management at Norvatis
- How The Demands On Management Are Different In Running A Resort Operation Than A Full Service Hotel Operation
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, April 4). Gillette’s Total Quality Management System. https://ivypanda.com/essays/tqm-case-study/
"Gillette’s Total Quality Management System." IvyPanda , 4 Apr. 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/tqm-case-study/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Gillette’s Total Quality Management System'. 4 April.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Gillette’s Total Quality Management System." April 4, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/tqm-case-study/.
1. IvyPanda . "Gillette’s Total Quality Management System." April 4, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/tqm-case-study/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Gillette’s Total Quality Management System." April 4, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/tqm-case-study/.
- Manufacturing Trends
- Supply Chain
- Customer Success

QMS Success Stories: Case Studies of How Companies Effectively Implemented QMS

Customer satisfaction, more often than not, begins with effective management. However, it is not as easy as it sounds. Although there are various tools and methods aimed at quality management and improvement, only a handful of them have proven to be substantially effectual. To understand how, here are two case studies on companies in various industries that have successfully implemented QMS into their systems and optimized it.
HFI is a Columbus, Ohio-based automotive interior supplier, committed to a value-driven business climate and high-quality products. Before implementing QMS, they relied on separate individually ran quality management systems that significantly hindered connectivity and productivity, especially after they began expanding and assimilating more facilities into their company. Because of this:
- Production slowed due to connectivity problems.
- Human resources were ineffectively distributed across all the departments and production areas.
- Corruption became an imminent system risk.
- Specialized knowledge was required to operate even some of the most basic databases.
- Human participation was required even when processing and completing electronic approvals.
- Documents became hard to locate, process, and share.
After operating their fourth facility began, it was critical to leverage an effective system that would not only boost efficiency, but also facilitate progressive company growth. So they turned to QAD for help, and consequently adopted a more effective system that:
- Was configured according to their respective goals and needs.
- Was structured according to phases that began with small, controlled groups before ultimately breaking out to other production elements.
- Was designed to address the hesitation, confusion, and concerns among employees, especially in regards to big transitions.
- Was integrated into their regular operations to standardize all company departments and levels.
By turning to quality management software from QAD, HFI was able to boost productivity and launch three more facilities in a span of just two years- subsequently doubling their number of new projects on an annual basis. Since then, their new quality management system has provided them with:
- A structured system for launching new facilities more efficiently.
- Effectual systems that collectively operate to boost efficiency and quality.
- Smooth operations that significantly improve customer satisfaction.
- Increased visibility and access to all the processes within the company.
- Improved utilization of human resources.
Vishay Dale Inc.
Vishay Dale Incorporated is a world renowned manufacturer of electronic, engineering, and tech components, most of which were initially only supplied to military and government industries. Currently, they serve a broad range of industries, including solar power systems, automobiles, tablets, and smartphones.
Even though they are an established company, Vishay still experienced many challenges, which included:
- The risk of misplacing, changing, damaging, or losing critical internal documents.
- Lack of sufficient resources and manpower to seamlessly execute a quality management system that would facilitate a TQM resource for automotive customers.
- Delays in implementation and completion of approvals and changes.
- Difficulties in auditing and storing their paper documents.
To mitigate these issues, the company knew that it had to leverage a solution that would seamlessly facilitate quick, accurate changes within the company without compromising on their leadership position in the automotive industry. They eventually settled on a QMS solution from QAD, which was able to help them:
- Get rid of paper-based systems, consequently granting them additional space for productivity.
- Streamline auditing operations through straightforward click searches that provide relevant document information.
- Create a system that significantly minimized time and efforts required to approve and execute engineering changes.
- Increased process speeds by improving data handling.
- Develop more than 500,000 entries linking all related documents, to ease the search-and-locate process.
- Transfer more than 65,000 documents.
In addition to dramatically improving their audit and change operations, Vishay has grown to become a lead supplier for the automotive industry. Thanks to their growth-tweaked quality management system software , they can now enjoy:
- Approval processes that don’t require restarts in case faults discovered by the lead engineer.
- Changes that can be swiftly and easily executed.
- Revisions that are made quickly and accurately.
- Approvals or rejections made and delivered in real time.
- A system that can autonomously operate.
- A minimal volume of paper documents.
Other companies have been able to achieve similar results. With such visible results, it can be confirmed that Quality Management Systems are not just a tool optimized for quality improvement, but one that also boosts overall efficiency and growth.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR

CSA and CSV: Streamlining Life Sciences Software Validation

6 Steps to Increasing Profit Through Workforce Engagement

EV Diffusion in Mainstream Markets
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.

QAD Transform: 5 Reasons to Visit Chicago
- Business & Money
- Management & Leadership
Sorry, there was a problem.

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player

Quality Management Systems - a Selective Presentation of Case-studies Showcasing Its Evolution Hardcover – March 21, 2018
- Print length 206 pages
- Language English
- Publisher IntechOpen
- Publication date March 21, 2018
- Dimensions 7 x 0.68 x 10 inches
- ISBN-10 9535139193
- ISBN-13 978-9535139195
- See all details
Product details
- Publisher : IntechOpen (March 21, 2018)
- Language : English
- Hardcover : 206 pages
- ISBN-10 : 9535139193
- ISBN-13 : 978-9535139195
- Item Weight : 1.17 pounds
- Dimensions : 7 x 0.68 x 10 inches
Customer reviews
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 5 star 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 4 star 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 3 star 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 2 star 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 1 star 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
No customer reviews
- About Amazon
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell products on Amazon
- Sell on Amazon Business
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Become an Affiliate
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Host an Amazon Hub
- › See More Make Money with Us
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Amazon and COVID-19
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
There's a sea change underway that makes enterprise content management systems more useful and accurate while embracing automation and AI capabilities. By Paul Desmond Aug 21, 2024 4 mins
Findings from a study characterizing various US-based case investigation and contact tracing programs indicate that programs were highly ... hiring and managing staff; (2) data and technology; and (3) quality of interactions with the public; within each area, we discuss key facilitators and barriers. ... a case management system selected by T2 ...
Various studies have effectively captured spatiotemporal correlations in air quality, meteorological, and emission data. Sequence-to-sequence models with attention mechanisms (Jia, Cao, and Yang Citation 2021 ; Wang et al. Citation 2020 ) and the SpatioTemporal (ST)-Transformer (Yu et al. Citation 2023 ) have shown particular promise in ...
What is a Quality Management System (QMS)? Let us look at how the principles of quality management are implemented through the QMS or Quality Management System. A Quality Management System (QMS) ensures that products are made to meet quality standards. It monitors products from start to finish, ensuring they align with industry and regulatory ...
The SEI Digital Library provides access to more than 6,000 documents from three decades of research into best practices in software engineering. These documents include technical reports, presentations, webcasts, podcasts and other materials searchable by user-supplied keywords and organized by topic, publication type, publication year, and author.
Case Study: Quality Management System at Coca Cola Company. Abey Francis. Coca Cola's history can be traced back to a man called Asa Candler, who bought a specific formula from a pharmacist named Smith Pemberton. Two years later, Asa founded his business and started production of soft drinks based on the formula he had bought.
A Case Study on Quality Management System in Construction Project 51 PROCESS CONTROL All parties indicate that the output of the elements of quality planning and resources management are the input for the process control such as work programme, cost programme etc. The constraints and mechanism are relatively similar with the ITP as an extra ...
products and processes continually.Our dual-certified Quality Management System meets the ISO 9001:2015 requirements and the even stricter AS9100:D standards, as required by the Aerospace in. ustry and the Department of Defense. This proven level of process control, with integrated layered quality gates, provides confidence that our products ...
The Principles of Quality Management System Quality Management System (QMS) is the interaction of people, processes and documentation to meet both customers‟ stated and implied needs (Mohammed, A. H. 2006 and Abdullah, M. N. 2006). Figure 1.0: Approaches to conformance in Quality Management
T oyota Quality System case study. Introduction. T oyota from the early 1960s alongside their supplier network consolidated the way in which. they were able to refine their production system ...
A Pharmaceutical & Chemical Manufacturing Case Study. An international multi-plant company bogged down by labor-intensive manual processes implements the AssurX platform to streamline Adverse Event/ Defect Handling, CAPA, Complaint Management, Supplier Quality and Audit Management—saving more than 10,500 personnel hours per year.
for the quality management system of the faculty programs of studies(B.A., M.A., and Specialist Programs) For the faculty students curricula and extracurricular activities ; For the effective utilization of institutional budget, which consists of state funding and additional financial sources ; Government Educational Standards Data Performance
Quality management software plays a vital role in enabling organizations to effectively manage and control their quality processes. It provides a centralized platform for capturing, analyzing, and monitoring quality-related data and activities. With quality management software, organizations can automate and streamline various tasks, such as ...
Case Study: Optimizing a Quality Management System (QMS) One of Prosit's regular clients needed more assistance involving their Quality Management System (QMS). There were documents that were outdated, references incorrect, job descriptions were too vague, and employees listed that were no longer with the company. ...
Case Study: Quality Management System. A biopharmaceutical company specializing in the development of gene therapies had an impressive late-stage clinical program progressing several drug candidates towards commercial approval. However, the existing quality system would need to be revamped to handle the potential marketing of multiple approved ...
In the light of Quality Management System (QMS), a case study was conducted in Engineers India Ltd. (EIL), who are one of the renowned project management consultants in the country, to find out how EIL takes care of the above-mentioned factors, along with others, to support their QMS in construction project management. ...
A Case Study: Implementation of Quality Management System ISO 9001:2008 in Education Institute, www.iosrjournals.org 87 | Page Education provides the base for socio-economic development. An education system of poor quality may be one of the most important reasons why poor countries do not grow.
Case study utilizes recognized quality risk management tools. Case study is appropriately simple and succinct to assure clear understanding. Case study provides areas for decreased and increased response actions. 7. Case study avoids excessive redundancy in subject and tools as compared to other planned models. 8.
Подробная информация об аэропорте Kronshtadt Airfield: Коды, расположение, тип - S, технические ...
For the past 15 years, there has been a growing body of literature relating to the ISO 9000 quality management system. Many studies have been conducted on the implementation of ISO 9000 in small ...
When a global pharmaceutical company needed a unified and scalable quality management system to help get medicines to market, in true Red Argyle fashion, we said, "Let's get started!" Download the case study here. Challenge: Potential Confusion and Inefficiency. Salesforce scalability was the top priority - and an ultimate challenge.
Here are nine examples of quality system case studies to give you some background on that experience. CAPA System Overhaul. ... Looking for more information on quality management systems? Quality System Consulting View Services 976 Lake Baldwin Lane Suite 204 Orlando, FL 32814 USA (407) 896-3386; Facebook Twitter Linkedin.
Due to the great success of Gillette's TQM system, this research was commenced to do a case study on "quality at Gillette Argentina". The paper begins by evaluating the ways in which the firm got its employees to take on the new TQM system. It proceeds to discuss the importance of getting the teams involved in TQM process as well as ...
With such visible results, it can be confirmed that Quality Management Systems are not just a tool optimized for quality improvement, but one that also boosts overall efficiency and growth. Two contrasting case studies on companies in various industries that successfully implemented and optimized Quality Management Software into their systems.
Quality management systems form an integral part of modern corporations. Acknowledging current socio-economic and environmental challenges, quality standards ought to be dynamic and flexible so as to cater for different markets and requirements. This book portrays a collection of international papers addressing current research and practice ...
Гаражи для частных катеров и лодок в Ломоносове. Поделись своим мнением на карте интересных мест. Фотографии и истории.Адрес: Россия, Санкт-Петербург, город Ломоносов, Транспортный переулок, 10.
1 фотография. 2 комментария. Парк-Отель Кантри в Санкт-петербурге. Парк-Отель «Кантри» расположен в здании старинной усадьбы на побережье. Воплощенная идея загородного отдыха - уютный отель, шум волн за окнами и ...