

Grant Proposals (or Give me the money!)
What this handout is about.
This handout will help you write and revise grant proposals for research funding in all academic disciplines (sciences, social sciences, humanities, and the arts). It’s targeted primarily to graduate students and faculty, although it will also be helpful to undergraduate students who are seeking funding for research (e.g. for a senior thesis).
The grant writing process
A grant proposal or application is a document or set of documents that is submitted to an organization with the explicit intent of securing funding for a research project. Grant writing varies widely across the disciplines, and research intended for epistemological purposes (philosophy or the arts) rests on very different assumptions than research intended for practical applications (medicine or social policy research). Nonetheless, this handout attempts to provide a general introduction to grant writing across the disciplines.
Before you begin writing your proposal, you need to know what kind of research you will be doing and why. You may have a topic or experiment in mind, but taking the time to define what your ultimate purpose is can be essential to convincing others to fund that project. Although some scholars in the humanities and arts may not have thought about their projects in terms of research design, hypotheses, research questions, or results, reviewers and funding agencies expect you to frame your project in these terms. You may also find that thinking about your project in these terms reveals new aspects of it to you.
Writing successful grant applications is a long process that begins with an idea. Although many people think of grant writing as a linear process (from idea to proposal to award), it is a circular process. Many people start by defining their research question or questions. What knowledge or information will be gained as a direct result of your project? Why is undertaking your research important in a broader sense? You will need to explicitly communicate this purpose to the committee reviewing your application. This is easier when you know what you plan to achieve before you begin the writing process.
Diagram 1 below provides an overview of the grant writing process and may help you plan your proposal development.
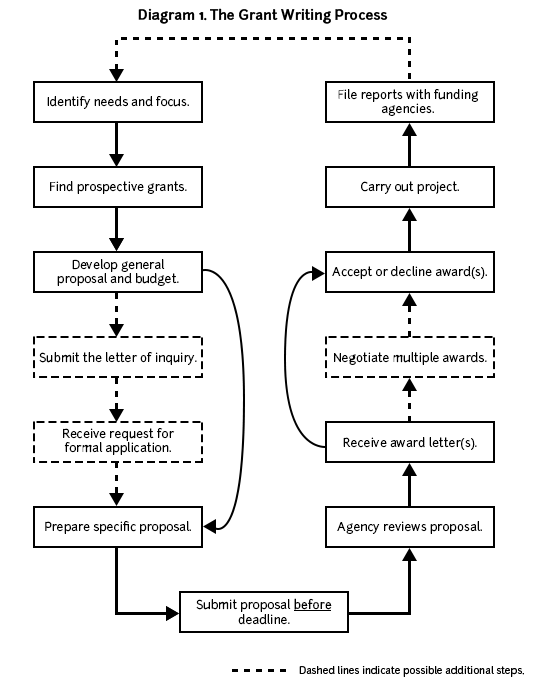
Applicants must write grant proposals, submit them, receive notice of acceptance or rejection, and then revise their proposals. Unsuccessful grant applicants must revise and resubmit their proposals during the next funding cycle. Successful grant applications and the resulting research lead to ideas for further research and new grant proposals.
Cultivating an ongoing, positive relationship with funding agencies may lead to additional grants down the road. Thus, make sure you file progress reports and final reports in a timely and professional manner. Although some successful grant applicants may fear that funding agencies will reject future proposals because they’ve already received “enough” funding, the truth is that money follows money. Individuals or projects awarded grants in the past are more competitive and thus more likely to receive funding in the future.
Some general tips
- Begin early.
- Apply early and often.
- Don’t forget to include a cover letter with your application.
- Answer all questions. (Pre-empt all unstated questions.)
- If rejected, revise your proposal and apply again.
- Give them what they want. Follow the application guidelines exactly.
- Be explicit and specific.
- Be realistic in designing the project.
- Make explicit the connections between your research questions and objectives, your objectives and methods, your methods and results, and your results and dissemination plan.
- Follow the application guidelines exactly. (We have repeated this tip because it is very, very important.)
Before you start writing
Identify your needs and focus.
First, identify your needs. Answering the following questions may help you:
- Are you undertaking preliminary or pilot research in order to develop a full-blown research agenda?
- Are you seeking funding for dissertation research? Pre-dissertation research? Postdoctoral research? Archival research? Experimental research? Fieldwork?
- Are you seeking a stipend so that you can write a dissertation or book? Polish a manuscript?
- Do you want a fellowship in residence at an institution that will offer some programmatic support or other resources to enhance your project?
- Do you want funding for a large research project that will last for several years and involve multiple staff members?
Next, think about the focus of your research/project. Answering the following questions may help you narrow it down:
- What is the topic? Why is this topic important?
- What are the research questions that you’re trying to answer? What relevance do your research questions have?
- What are your hypotheses?
- What are your research methods?
- Why is your research/project important? What is its significance?
- Do you plan on using quantitative methods? Qualitative methods? Both?
- Will you be undertaking experimental research? Clinical research?
Once you have identified your needs and focus, you can begin looking for prospective grants and funding agencies.
Finding prospective grants and funding agencies
Whether your proposal receives funding will rely in large part on whether your purpose and goals closely match the priorities of granting agencies. Locating possible grantors is a time consuming task, but in the long run it will yield the greatest benefits. Even if you have the most appealing research proposal in the world, if you don’t send it to the right institutions, then you’re unlikely to receive funding.
There are many sources of information about granting agencies and grant programs. Most universities and many schools within universities have Offices of Research, whose primary purpose is to support faculty and students in grant-seeking endeavors. These offices usually have libraries or resource centers to help people find prospective grants.
At UNC, the Research at Carolina office coordinates research support.
The Funding Information Portal offers a collection of databases and proposal development guidance.
The UNC School of Medicine and School of Public Health each have their own Office of Research.
Writing your proposal
The majority of grant programs recruit academic reviewers with knowledge of the disciplines and/or program areas of the grant. Thus, when writing your grant proposals, assume that you are addressing a colleague who is knowledgeable in the general area, but who does not necessarily know the details about your research questions.
Remember that most readers are lazy and will not respond well to a poorly organized, poorly written, or confusing proposal. Be sure to give readers what they want. Follow all the guidelines for the particular grant you are applying for. This may require you to reframe your project in a different light or language. Reframing your project to fit a specific grant’s requirements is a legitimate and necessary part of the process unless it will fundamentally change your project’s goals or outcomes.
Final decisions about which proposals are funded often come down to whether the proposal convinces the reviewer that the research project is well planned and feasible and whether the investigators are well qualified to execute it. Throughout the proposal, be as explicit as possible. Predict the questions that the reviewer may have and answer them. Przeworski and Salomon (1995) note that reviewers read with three questions in mind:
- What are we going to learn as a result of the proposed project that we do not know now? (goals, aims, and outcomes)
- Why is it worth knowing? (significance)
- How will we know that the conclusions are valid? (criteria for success) (2)
Be sure to answer these questions in your proposal. Keep in mind that reviewers may not read every word of your proposal. Your reviewer may only read the abstract, the sections on research design and methodology, the vitae, and the budget. Make these sections as clear and straightforward as possible.
The way you write your grant will tell the reviewers a lot about you (Reif-Lehrer 82). From reading your proposal, the reviewers will form an idea of who you are as a scholar, a researcher, and a person. They will decide whether you are creative, logical, analytical, up-to-date in the relevant literature of the field, and, most importantly, capable of executing the proposed project. Allow your discipline and its conventions to determine the general style of your writing, but allow your own voice and personality to come through. Be sure to clarify your project’s theoretical orientation.
Develop a general proposal and budget
Because most proposal writers seek funding from several different agencies or granting programs, it is a good idea to begin by developing a general grant proposal and budget. This general proposal is sometimes called a “white paper.” Your general proposal should explain your project to a general academic audience. Before you submit proposals to different grant programs, you will tailor a specific proposal to their guidelines and priorities.
Organizing your proposal
Although each funding agency will have its own (usually very specific) requirements, there are several elements of a proposal that are fairly standard, and they often come in the following order:
- Introduction (statement of the problem, purpose of research or goals, and significance of research)
Literature review
- Project narrative (methods, procedures, objectives, outcomes or deliverables, evaluation, and dissemination)
- Budget and budget justification
Format the proposal so that it is easy to read. Use headings to break the proposal up into sections. If it is long, include a table of contents with page numbers.
The title page usually includes a brief yet explicit title for the research project, the names of the principal investigator(s), the institutional affiliation of the applicants (the department and university), name and address of the granting agency, project dates, amount of funding requested, and signatures of university personnel authorizing the proposal (when necessary). Most funding agencies have specific requirements for the title page; make sure to follow them.
The abstract provides readers with their first impression of your project. To remind themselves of your proposal, readers may glance at your abstract when making their final recommendations, so it may also serve as their last impression of your project. The abstract should explain the key elements of your research project in the future tense. Most abstracts state: (1) the general purpose, (2) specific goals, (3) research design, (4) methods, and (5) significance (contribution and rationale). Be as explicit as possible in your abstract. Use statements such as, “The objective of this study is to …”
Introduction
The introduction should cover the key elements of your proposal, including a statement of the problem, the purpose of research, research goals or objectives, and significance of the research. The statement of problem should provide a background and rationale for the project and establish the need and relevance of the research. How is your project different from previous research on the same topic? Will you be using new methodologies or covering new theoretical territory? The research goals or objectives should identify the anticipated outcomes of the research and should match up to the needs identified in the statement of problem. List only the principle goal(s) or objective(s) of your research and save sub-objectives for the project narrative.
Many proposals require a literature review. Reviewers want to know whether you’ve done the necessary preliminary research to undertake your project. Literature reviews should be selective and critical, not exhaustive. Reviewers want to see your evaluation of pertinent works. For more information, see our handout on literature reviews .
Project narrative
The project narrative provides the meat of your proposal and may require several subsections. The project narrative should supply all the details of the project, including a detailed statement of problem, research objectives or goals, hypotheses, methods, procedures, outcomes or deliverables, and evaluation and dissemination of the research.
For the project narrative, pre-empt and/or answer all of the reviewers’ questions. Don’t leave them wondering about anything. For example, if you propose to conduct unstructured interviews with open-ended questions, be sure you’ve explained why this methodology is best suited to the specific research questions in your proposal. Or, if you’re using item response theory rather than classical test theory to verify the validity of your survey instrument, explain the advantages of this innovative methodology. Or, if you need to travel to Valdez, Alaska to access historical archives at the Valdez Museum, make it clear what documents you hope to find and why they are relevant to your historical novel on the ’98ers in the Alaskan Gold Rush.
Clearly and explicitly state the connections between your research objectives, research questions, hypotheses, methodologies, and outcomes. As the requirements for a strong project narrative vary widely by discipline, consult a discipline-specific guide to grant writing for some additional advice.
Explain staffing requirements in detail and make sure that staffing makes sense. Be very explicit about the skill sets of the personnel already in place (you will probably include their Curriculum Vitae as part of the proposal). Explain the necessary skill sets and functions of personnel you will recruit. To minimize expenses, phase out personnel who are not relevant to later phases of a project.
The budget spells out project costs and usually consists of a spreadsheet or table with the budget detailed as line items and a budget narrative (also known as a budget justification) that explains the various expenses. Even when proposal guidelines do not specifically mention a narrative, be sure to include a one or two page explanation of the budget. To see a sample budget, turn to Example #1 at the end of this handout.
Consider including an exhaustive budget for your project, even if it exceeds the normal grant size of a particular funding organization. Simply make it clear that you are seeking additional funding from other sources. This technique will make it easier for you to combine awards down the road should you have the good fortune of receiving multiple grants.
Make sure that all budget items meet the funding agency’s requirements. For example, all U.S. government agencies have strict requirements for airline travel. Be sure the cost of the airline travel in your budget meets their requirements. If a line item falls outside an agency’s requirements (e.g. some organizations will not cover equipment purchases or other capital expenses), explain in the budget justification that other grant sources will pay for the item.
Many universities require that indirect costs (overhead) be added to grants that they administer. Check with the appropriate offices to find out what the standard (or required) rates are for overhead. Pass a draft budget by the university officer in charge of grant administration for assistance with indirect costs and costs not directly associated with research (e.g. facilities use charges).
Furthermore, make sure you factor in the estimated taxes applicable for your case. Depending on the categories of expenses and your particular circumstances (whether you are a foreign national, for example), estimated tax rates may differ. You can consult respective departmental staff or university services, as well as professional tax assistants. For information on taxes on scholarships and fellowships, see https://cashier.unc.edu/student-tax-information/scholarships-fellowships/ .
Explain the timeframe for the research project in some detail. When will you begin and complete each step? It may be helpful to reviewers if you present a visual version of your timeline. For less complicated research, a table summarizing the timeline for the project will help reviewers understand and evaluate the planning and feasibility. See Example #2 at the end of this handout.
For multi-year research proposals with numerous procedures and a large staff, a time line diagram can help clarify the feasibility and planning of the study. See Example #3 at the end of this handout.
Revising your proposal
Strong grant proposals take a long time to develop. Start the process early and leave time to get feedback from several readers on different drafts. Seek out a variety of readers, both specialists in your research area and non-specialist colleagues. You may also want to request assistance from knowledgeable readers on specific areas of your proposal. For example, you may want to schedule a meeting with a statistician to help revise your methodology section. Don’t hesitate to seek out specialized assistance from the relevant research offices on your campus. At UNC, the Odum Institute provides a variety of services to graduate students and faculty in the social sciences.
In your revision and editing, ask your readers to give careful consideration to whether you’ve made explicit the connections between your research objectives and methodology. Here are some example questions:
- Have you presented a compelling case?
- Have you made your hypotheses explicit?
- Does your project seem feasible? Is it overly ambitious? Does it have other weaknesses?
- Have you stated the means that grantors can use to evaluate the success of your project after you’ve executed it?
If a granting agency lists particular criteria used for rating and evaluating proposals, be sure to share these with your own reviewers.
Example #1. Sample Budget
Jet travel $6,100 This estimate is based on the commercial high season rate for jet economy travel on Sabena Belgian Airlines. No U.S. carriers fly to Kigali, Rwanda. Sabena has student fare tickets available which will be significantly less expensive (approximately $2,000).
Maintenance allowance $22,788 Based on the Fulbright-Hays Maintenance Allowances published in the grant application guide.
Research assistant/translator $4,800 The research assistant/translator will be a native (and primary) speaker of Kinya-rwanda with at least a four-year university degree. They will accompany the primary investigator during life history interviews to provide assistance in comprehension. In addition, they will provide commentary, explanations, and observations to facilitate the primary investigator’s participant observation. During the first phase of the project in Kigali, the research assistant will work forty hours a week and occasional overtime as needed. During phases two and three in rural Rwanda, the assistant will stay with the investigator overnight in the field when necessary. The salary of $400 per month is based on the average pay rate for individuals with similar qualifications working for international NGO’s in Rwanda.
Transportation within country, phase one $1,200 The primary investigator and research assistant will need regular transportation within Kigali by bus and taxi. The average taxi fare in Kigali is $6-8 and bus fare is $.15. This figure is based on an average of $10 per day in transportation costs during the first project phase.
Transportation within country, phases two and three $12,000 Project personnel will also require regular transportation between rural field sites. If it is not possible to remain overnight, daily trips will be necessary. The average rental rate for a 4×4 vehicle in Rwanda is $130 per day. This estimate is based on an average of $50 per day in transportation costs for the second and third project phases. These costs could be reduced if an arrangement could be made with either a government ministry or international aid agency for transportation assistance.
Email $720 The rate for email service from RwandaTel (the only service provider in Rwanda) is $60 per month. Email access is vital for receiving news reports on Rwanda and the region as well as for staying in contact with dissertation committee members and advisors in the United States.
Audiocassette tapes $400 Audiocassette tapes will be necessary for recording life history interviews, musical performances, community events, story telling, and other pertinent data.
Photographic & slide film $100 Photographic and slide film will be necessary to document visual data such as landscape, environment, marriages, funerals, community events, etc.
Laptop computer $2,895 A laptop computer will be necessary for recording observations, thoughts, and analysis during research project. Price listed is a special offer to UNC students through the Carolina Computing Initiative.
NUD*IST 4.0 software $373.00 NUD*IST, “Nonnumerical, Unstructured Data, Indexing, Searching, and Theorizing,” is necessary for cataloging, indexing, and managing field notes both during and following the field research phase. The program will assist in cataloging themes that emerge during the life history interviews.
Administrative fee $100 Fee set by Fulbright-Hays for the sponsoring institution.
Example #2: Project Timeline in Table Format
Example #3: project timeline in chart format.

Some closing advice
Some of us may feel ashamed or embarrassed about asking for money or promoting ourselves. Often, these feelings have more to do with our own insecurities than with problems in the tone or style of our writing. If you’re having trouble because of these types of hang-ups, the most important thing to keep in mind is that it never hurts to ask. If you never ask for the money, they’ll never give you the money. Besides, the worst thing they can do is say no.
UNC resources for proposal writing
Research at Carolina http://research.unc.edu
The Odum Institute for Research in the Social Sciences https://odum.unc.edu/
UNC Medical School Office of Research https://www.med.unc.edu/oor
UNC School of Public Health Office of Research http://www.sph.unc.edu/research/
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Holloway, Brian R. 2003. Proposal Writing Across the Disciplines. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Levine, S. Joseph. “Guide for Writing a Funding Proposal.” http://www.learnerassociates.net/proposal/ .
Locke, Lawrence F., Waneen Wyrick Spirduso, and Stephen J. Silverman. 2014. Proposals That Work . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Przeworski, Adam, and Frank Salomon. 2012. “Some Candid Suggestions on the Art of Writing Proposals.” Social Science Research Council. https://s3.amazonaws.com/ssrc-cdn2/art-of-writing-proposals-dsd-e-56b50ef814f12.pdf .
Reif-Lehrer, Liane. 1989. Writing a Successful Grant Application . Boston: Jones and Bartlett Publishers.
Wiggins, Beverly. 2002. “Funding and Proposal Writing for Social Science Faculty and Graduate Student Research.” Chapel Hill: Howard W. Odum Institute for Research in Social Science. 2 Feb. 2004. http://www2.irss.unc.edu/irss/shortcourses/wigginshandouts/granthandout.pdf.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 20 December 2019
Secrets to writing a winning grant
- Emily Sohn 0
Emily Sohn is a freelance journalist in Minneapolis, Minnesota.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
When Kylie Ball begins a grant-writing workshop, she often alludes to the funding successes and failures that she has experienced in her career. “I say, ‘I’ve attracted more than $25 million in grant funding and have had more than 60 competitive grants funded. But I’ve also had probably twice as many rejected.’ A lot of early-career researchers often find those rejections really tough to take. But I actually think you learn so much from the rejected grants.”
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Nature 577 , 133-135 (2020)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-019-03914-5
Related Articles

- Communication

Londoners see what a scientist looks like up close in 50 photographs
Career News 18 APR 24
Deadly diseases and inflatable suits: how I found my niche in virology research
Spotlight 17 APR 24

How young people benefit from Swiss apprenticeships

Canadian science gets biggest boost to PhD and postdoc pay in 20 years
News 17 APR 24

How India can become a science powerhouse
Editorial 16 APR 24

NASA admits plan to bring Mars rocks to Earth won’t work — and seeks fresh ideas
News 15 APR 24

‘Shrugging off failure is hard’: the $400-million grant setback that shaped the Smithsonian lead scientist’s career
Career Column 15 APR 24

How I harnessed media engagement to supercharge my research career
Career Column 09 APR 24

Tweeting your research paper boosts engagement but not citations
News 27 MAR 24
Postdoctoral Position
We are seeking highly motivated and skilled candidates for postdoctoral fellow positions
Boston, Massachusetts (US)
Boston Children's Hospital (BCH)
Qiushi Chair Professor
Distinguished scholars with notable achievements and extensive international influence.
Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Zhejiang University
ZJU 100 Young Professor
Promising young scholars who can independently establish and develop a research direction.
Head of the Thrust of Robotics and Autonomous Systems
Reporting to the Dean of Systems Hub, the Head of ROAS is an executive assuming overall responsibility for the academic, student, human resources...
Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)
Head of Biology, Bio-island
Head of Biology to lead the discovery biology group.
BeiGene Ltd.
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a grant proposal: a step-by-step guide

What is a grant proposal?
Why should you write a grant proposal, format of a grant proposal, how to write a grant proposal, step 1: decide what funding opportunity to apply for, and research the grant application process, step 2: plan and research your project, preliminary research for your grant proposal, questions to ask yourself as you plan your grant proposal, developing your grant proposal, step 3: write the first draft of your grant proposal, step 4: get feedback, and revise your grant proposal accordingly, step 5: prepare to submit your grant proposal, what happens after submitting the grant proposal, final thoughts, other useful sources for writing grant proposals, frequently asked questions about writing grant proposals, related articles.
You have a vision for a future research project, and want to share that idea with the world.
To achieve your vision, you need funding from a sponsoring organization, and consequently, you need to write a grant proposal.
Although visualizing your future research through grant writing is exciting, it can also feel daunting. How do you start writing a grant proposal? How do you increase your chances of success in winning a grant?
But, writing a proposal is not as hard as you think. That’s because the grant-writing process can be broken down into actionable steps.
This guide provides a step-by-step approach to grant-writing that includes researching the application process, planning your research project, and writing the proposal. It is written from extensive research into grant-writing, and our experiences of writing proposals as graduate students, postdocs, and faculty in the sciences.
A grant proposal is a document or collection of documents that outlines the strategy for a future research project and is submitted to a sponsoring organization with the specific goal of getting funding to support the research. For example, grants for large projects with multiple researchers may be used to purchase lab equipment, provide stipends for graduate and undergraduate researchers, fund conference travel, and support the salaries of research personnel.
As a graduate student, you might apply for a PhD scholarship, or postdoctoral fellowship, and may need to write a proposal as part of your application. As a faculty member of a university, you may need to provide evidence of having submitted grant applications to obtain a permanent position or promotion.
Reasons for writing a grant proposal include:
- To obtain financial support for graduate or postdoctoral studies;
- To travel to a field site, or to travel to meet with collaborators;
- To conduct preliminary research for a larger project;
- To obtain a visiting position at another institution;
- To support undergraduate student research as a faculty member;
- To obtain funding for a large collaborative project, which may be needed to retain employment at a university.
The experience of writing a proposal can be helpful, even if you fail to obtain funding. Benefits include:
- Improvement of your research and writing skills
- Enhancement of academic employment prospects, as fellowships and grants awarded and applied for can be listed on your academic CV
- Raising your profile as an independent academic researcher because writing proposals can help you become known to leaders in your field.
All sponsoring agencies have specific requirements for the format of a grant proposal. For example, for a PhD scholarship or postdoctoral fellowship, you may be required to include a description of your project, an academic CV, and letters of support from mentors or collaborators.
For a large research project with many collaborators, the collection of documents that need to be submitted may be extensive. Examples of documents that might be required include a cover letter, a project summary, a detailed description of the proposed research, a budget, a document justifying the budget, and the CVs of all research personnel.
Before writing your proposal, be sure to note the list of required documents.
Writing a grant proposal can be broken down into three major activities: researching the project (reading background materials, note-taking, preliminary work, etc.), writing the proposal (creating an outline, writing the first draft, revisions, formatting), and administrative tasks for the project (emails, phone calls, meetings, writing CVs and other supporting documents, etc.).
Below, we provide a step-by-step guide to writing a grant proposal:
- Decide what funding opportunity to apply for, and research the grant application process
- Plan and research your project
- Write the first draft of your grant proposal
- Get feedback, and revise your grant proposal accordingly
- Prepare to submit your grant proposal

- Start early. Begin by searching for funding opportunities and determining requirements. Some sponsoring organizations prioritize fundamental research, whereas others support applied research. Be sure your project fits the mission statement of the granting organization. Look at recently funded proposals and/or sample proposals on the agency website, if available. The Research or Grants Office at your institution may be able to help with finding grant opportunities.
- Make a spreadsheet of grant opportunities, with a link to the call for proposals page, the mission and aims of the agency, and the deadline for submission. Use the information that you have compiled in your spreadsheet to decide what to apply for.
- Once you have made your decision, carefully read the instructions in the call for proposals. Make a list of all the documents you need to apply, and note the formatting requirements and page limits. Know exactly what the funding agency requires of submitted proposals.
- Reach out to support staff at your university (for example, at your Research or Grants Office), potential mentors, or collaborators. For example, internal deadlines for submitting external grants are often earlier than the submission date. Make sure to learn about your institution’s internal processes, and obtain contact information for the relevant support staff.
- Applying for a grant or fellowship involves administrative work. Start preparing your CV and begin collecting supporting documents from collaborators, such as letters of support. If the application to the sponsoring agency is electronic, schedule time to set up an account, log into the system, download necessary forms and paperwork, etc. Don’t leave all of the administrative tasks until the end.
- Map out the important deadlines on your calendar. These might include video calls with collaborators, a date for the first draft to be complete, internal submission deadlines, and the funding agency deadline.
- Schedule time on your calendar for research, writing, and administrative tasks associated with the project. It’s wise to group similar tasks and block out time for them (a process known as ” time batching ”). Break down bigger tasks into smaller ones.

Now that you know what you are applying for, you can think about matching your proposed research to the aims of the agency. The work you propose needs to be innovative, specific, realizable, timely, and worthy of the sponsoring organization’s attention.
- Develop an awareness of the important problems and open questions in your field. Attend conferences and seminar talks and follow all of your field’s major journals.
- Read widely and deeply. Journal review articles are a helpful place to start. Reading papers from related but different subfields can generate ideas. Taking detailed notes as you read will help you recall the important findings and connect disparate concepts.
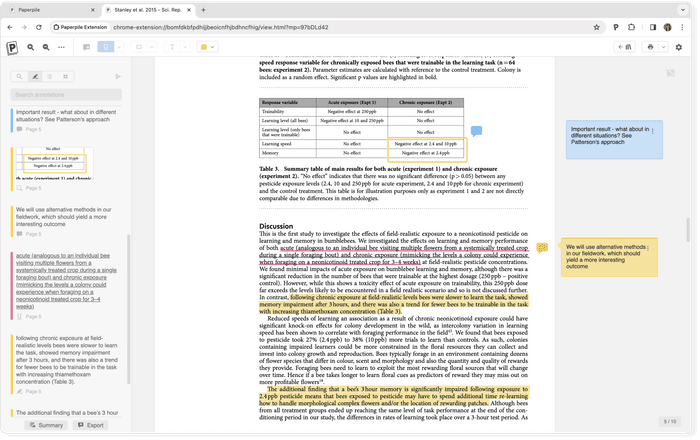
- Writing a grant proposal is a creative and imaginative endeavor. Write down all of your ideas. Freewriting is a practice where you write down all that comes to mind without filtering your ideas for feasibility or stopping to edit mistakes. By continuously writing your thoughts without judgment, the practice can help overcome procrastination and writer’s block. It can also unleash your creativity, and generate new ideas and associations. Mind mapping is another technique for brainstorming and generating connections between ideas.
- Establish a regular writing practice. Schedule time just for writing, and turn off all distractions during your focused work time. You can use your writing process to refine your thoughts and ideas.
- Use a reference manager to build a library of sources for your project. You can use a reference management tool to collect papers , store and organize references , and highlight and annotate PDFs . Establish a system for organizing your ideas by tagging papers with labels and using folders to store similar references.
To facilitate intelligent thinking and shape the overall direction of your project, try answering the following questions:
- What are the questions that the project will address? Am I excited and curious about their answers?
- Why are these questions important?
- What are the goals of the project? Are they SMART (Specific, Measurable, Actionable, Relevant, and Timely)?
- What is novel about my project? What is the gap in current knowledge?
- What methods will I use, and how feasible is my approach?
- Can the work be done over the proposed period, and with the budget I am requesting?
- Do I have relevant experience? For example, have I completed similar work funded by previous grants or written papers on my proposed topic?
- What pilot research or prior work can I use, or do I need to complete preliminary research before writing the proposal?
- Will the outcomes of my work be consequential? Will the granting agency be interested in the results?
- What solutions to open problems in my field will this project offer? Are there broader implications of my work?
- Who will the project involve? Do I need mentors, collaborators, or students to contribute to the proposed work? If so, what roles will they have?
- Who will read the proposal? For example, experts in the field will require details of methods, statistical analyses, etc., whereas non-experts may be more concerned with the big picture.
- What do I want the reviewers to feel, and take away from reading my proposal?
- What weaknesses does my proposed research have? What objections might reviewers raise, and how can I address them?
- Can I visualize a timeline for my project?
Create an actionable plan for your research project using the answers to these questions.
- Now is the time to collect preliminary data, conduct experiments, or do a preliminary study to motivate your research, and demonstrate that your proposed project is realistic.
- Use your plan to write a detailed outline of the proposal. An outline helps you to write a proposal that has a logical format and ensures your thought process is rational. It also provides a structure to support your writing.
- Follow the granting agency’s guidelines for titles, sections, and subsections to inform your outline.
At this stage, you should have identified the aims of your project, what questions your work will answer, and how they are relevant to the sponsoring agency’s call for proposals. Be able to explain the originality, importance, and achievability of your proposed work.

Now that you have done your research, you are ready to begin writing your proposal and start filling in the details of your outline. Build on the writing routine you have already started. Here are some tips:
- Follow the guidelines of the funding organization.
- Keep the proposal reviewers in mind as you write. Your audience may be a combination of specialists in your field and non-specialists. Make sure to address the novelty of your work, its significance, and its feasibility.
- Write clearly, concisely, and avoid repetition. Use topic sentences for each paragraph to emphasize key ideas. Concluding sentences of each paragraph should develop, clarify, or summarize the support for the declaration in the topic sentence. To make your writing engaging, vary sentence length.
- Avoid jargon, where possible. Follow sentences that have complex technical information with a summary in plain language.
- Don’t review all information on the topic, but include enough background information to convince reviewers that you are knowledgeable about it. Include preliminary data to convince reviewers you can do the work. Cite all relevant work.
- Make sure not to be overly ambitious. Don’t propose to do so much that reviewers doubt your ability to complete the project. Rather, a project with clear, narrowly-defined goals may prove favorable to reviewers.
- Accurately represent the scope of your project; don’t exaggerate its impacts. Avoid bias. Be forthright about the limitations of your research.
- Ensure to address potential objections and concerns that reviewers may have with the proposed work. Show that you have carefully thought about the project by explaining your rationale.
- Use diagrams and figures effectively. Make sure they are not too small or contain too much information or details.
After writing your first draft, read it carefully to gain an overview of the logic of your argument. Answer the following questions:
- Is your proposal concise, explicit, and specific?
- Have you included all necessary assumptions, data points, and evidence in your proposal?
- Do you need to make structural changes like moving or deleting paragraphs or including additional tables or figures to strengthen your rationale?
- Have you answered most of the questions posed in Step 2 above in your proposal?
- Follow the length requirements in the proposal guidelines. Don't feel compelled to include everything you know!
- Use formatting techniques to make your proposal easy on the eye. Follow rules for font, layout, margins, citation styles , etc. Avoid walls of text. Use bolding and italicizing to emphasize points.
- Comply with all style, organization, and reference list guidelines to make it easy to reviewers to quickly understand your argument. If you don’t, it’s at best a chore for the reviewers to read because it doesn’t make the most convincing case for you and your work. At worst, your proposal may be rejected by the sponsoring agency without review.
- Using a reference management tool like Paperpile will make citation creation and formatting in your grant proposal quick, easy and accurate.

Now take time away from your proposal, for at least a week or more. Ask trusted mentors or collaborators to read it, and give them adequate time to give critical feedback.
- At this stage, you can return to any remaining administrative work while you wait for feedback on the proposal, such as finalizing your budget or updating your CV.
- Revise the proposal based on the feedback you receive.
- Don’t be discouraged by critiques of your proposal or take them personally. Receiving and incorporating feedback with humility is essential to grow as a grant writer.

Now you are almost ready to submit. This is exciting! At this stage, you need to block out time to complete all final checks.
- Allow time for proofreading and final editing. Spelling and grammar mistakes can raise questions regarding the rigor of your research and leave a poor impression of your proposal on reviewers. Ensure that a unified narrative is threaded throughout all documents in the application.
- Finalize your documents by following a checklist. Make sure all documents are in place in the application, and all formatting and organizational requirements are met.
- Follow all internal and external procedures. Have login information for granting agency and institution portals to hand. Double-check any internal procedures required by your institution (applications for large grants often have a deadline for sign-off by your institution’s Research or Grants Office that is earlier than the funding agency deadline).
- To avoid technical issues with electronic portals, submit your proposal as early as you can.
- Breathe a sigh of relief when all the work is done, and take time to celebrate submitting the proposal! This is already a big achievement.
Now you wait! If the news is positive, congratulations!
But if your proposal is rejected, take heart in the fact that the process of writing it has been useful for your professional growth, and for developing your ideas.
Bear in mind that because grants are often highly competitive, acceptance rates for proposals are usually low. It is very typical to not be successful on the first try and to have to apply for the same grant multiple times.
Here are some tips to increase your chances of success on your next attempt:
- Remember that grant writing is often not a linear process. It is typical to have to use the reviews to revise and resubmit your proposal.
- Carefully read the reviews and incorporate the feedback into the next iteration of your proposal. Use the feedback to improve and refine your ideas.
- Don’t ignore the comments received from reviewers—be sure to address their objections in your next proposal. You may decide to include a section with a response to the reviewers, to show the sponsoring agency that you have carefully considered their comments.
- If you did not receive reviewer feedback, you can usually request it.
You learn about your field and grow intellectually from writing a proposal. The process of researching, writing, and revising a proposal refines your ideas and may create new directions for future projects. Professional opportunities exist for researchers who are willing to persevere with submitting grant applications.
➡️ Secrets to writing a winning grant
➡️ How to gain a competitive edge in grant writing
➡️ Ten simple rules for writing a postdoctoral fellowship
A grant proposal should include all the documents listed as required by the sponsoring organization. Check what documents the granting agency needs before you start writing the proposal.
Granting agencies have strict formatting requirements, with strict page limits and/or word counts. Check the maximum length required by the granting agency. It is okay for the proposal to be shorter than the maximum length.
Expect to spend many hours, even weeks, researching and writing a grant proposal. Consequently, it is important to start early! Block time in your calendar for research, writing, and administration tasks. Allow extra time at the end of the grant-writing process to edit, proofread, and meet presentation guidelines.
The most important part of a grant proposal is the description of the project. Make sure that the research you propose in your project narrative is new, important, and viable, and that it meets the goals of the sponsoring organization.
A grant proposal typically consists of a set of documents. Funding agencies have specific requirements for the formatting and organization of each document. Make sure to follow their guidelines exactly.
How to Write a Successful Grant Proposal
Research budgets are getting tighter. Funding agencies are enforcing stricter guidelines and restrictions. All the while, few researchers receive formal training on how to write effective grant applications. Here we improve your career prospects as a researcher by writing better grant proposals.
Updated on May 26, 2022

Research budgets have become more stressed, while funding agencies enforce strict guidelines and restrictions. At the same time, few researchers receive formal training on how to write effective grant applications. Writing better grant proposals will hugely improve your career prospects as a researcher.
Grant writing is especially challenging if you're an early-career researcher and/or English isn't your first language. However, it's not rocket science (unless it's a grant for researching rocket science). You can get what you want if you know how to get it.
Here we outline the key components of a successful grant proposal to help you navigate the intricacies of the application process, including:
- Searching for and identifying grant opportunities
- Writing and reviewing a grant proposal
- What to do after you submit your proposal
What's a grant proposal and why do you need one?
A grant proposal or application is a document (or set of documents) addressed to an organization or funding agency to get funding for a research project.
Grant proposals differ widely across the scientific disciplines, but there are general tips that work universally.
A successful grant proposal can be a key to achieving your research goals by getting money. But writing a grant application also offers many indirect benefits, such as:
- If you're a researcher on a fixed-term contract, getting funding can extend your contract.
- You can use a successful grant proposal to take on a temporary position with another research group or institution.
- Receiving a research grant can mean that an expert review panel views your research ideas as better than others.
Conducting pre-proposal research
The efforts you put in before you send your proposal can improve your chances of acceptance a great deal. You'll hone in on what you really need and you'll see ways of successfully getting it. Think ahead and you'll benefit.
Tough competition
Competition for grants has never been tougher.
Look at the European Commission's Horizon 2020 program. Horizon is the EU's most extensive research and innovation program. Nearly 80 billion euros (~US$84 billion)in funding was set aside in 2014–2020.
A Nature article shows that EU Horizon 2020 reported a 14% success rate for its first 100 calls for proposals—submissions to some categories had lower success rates.
Don't play the short game, think longer-term
Considering those odds, it's critical to start the process early. Give yourself at least 4–6 months to put your proposal together.
To increase your chances of success, before you begin drafting your grant proposal, you need to develop a SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and anchored within a Timeframe) plan for what you want to do and why you want to do it.
View samples of successful grant proposals
Look at what's worked (and what hasn't) and you'll save yourself time repeating other people's mistakes. Look for previous proposals you can get from your:
- University library
- Trusted peers
- Supervisor or mentor
- Past or prospective funding body
- Online sites and databases
For example, on Open Grants, you can read 250+ grant proposals , both successful and unsuccessful, for free.
Focus on samples of successful proposals in your discipline or applications that have obtained the grant you're applying for. But don't overlook the failures. Read them critically and think how you can do better.
Identifying a grant opportunity and pitching your proposal
Just like choosing the right school, scientific niche, and journal to publish your research, you're seeking the right grant for your future work.
Search grant databases
The easiest way to find grant opportunities is via a database. Although some require a subscription, they can do in seconds what could take days of Googling. This is also a much easier way to organize and keep track of grant opportunities.
Pivot , Scientifyresearch , and ResearchConnect are free, structured databases providing global funding information. They also guide you on how to navigate their interface and use filters (scientific field, submission deadline, allocated budget, etc.) to refine your results.
Evaluate requirements in the solicitation
Finding the right funding body takes more than researching available grants. It takes a critical eye.
If you're unclear about what they're looking for, then writing that grant application may not be worth your time. And knowing that will save you time.
Once you decide to apply for funding, read the grant guidelines carefully. Stick to the suggested structure (e.g., subheadings), format (e.g., font), and language (terminology used).
While reading the instructions, make a list of everything needed for submission, and who on your side will be responsible for gathering this information.
Understand the sponsor's scoring system
Find out how the grant will be evaluated. This will ensure your proposal is tailored to the assessment criteria. For example, the UK Research and Innovation scoring matrix is based on
- Scientific quality and impact
- Scientific leadership
- Justification of resources
- Other: ethical and governance issues
The deadline is also a critical factor, not just in terms of being on time. If it's in three weeks, it might not be worth your time trying to prepare a proposal. As noted above, it's more realistic to think in months rather than weeks. You'll save yourself wasted time, not to mention stress.
Identify the funder's mission
Granting agencies don't exist solely to give out money. Their priorities vary based on their foundations' missions. Research the organization to see if its mission statement closely aligns with your project and target your request to their mission.
Among others, the Economic and Social Research Council funding priorities now include understanding the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on individuals, groups, and institutions in society. So, a medical researcher studying the impact of COVID-19 on neonatal mortality is better off targeting a different funder.
For example, the UK's National Institute for Health and Care Research focuses on health and social care research.
Make friends with the program manager
Directly contact the granting source if you've read the grant instructions and you're still not sure if your project is eligible. Making a human connection is generally a good thing, unless they specifically indicate they don't want to be contacted. In this regard, it's quite like a job application and networking.
They'll have a dedicated grants officer (maybe called a program manager or director) helping applicants like you. Beyond clearing up what's eligible and what's not, developing a relationship with them can help build their confidence in you and your work.
Note that the role of the program manager varies greatly among granting agencies. The U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), for example, encourages young researchers to contact program managers. It offers step-by-step instructions on whom you should contact and how .
In some smaller foundations, however, program officers are very busy and might discourage you from getting in touch. To figure this out, you need to research the sponsor's culture on a case-by-case basis.
Make friends with your research support office
Writing a grant proposal doesn't have to be a solo journey. Your institution will likely have a research support office/department (also called a sponsored research office).
These valuable folks can give administrative help with the grant submission process. They'll be able to help fill out relevant forms and double-check that the proposal meets the granting agency's guidelines.
Writing the main body of your grant proposal
All the agencies, people, and processes of grant writing are crucial. But the fundamental part of any grant application remains the written proposal itself.
To get your grant, you need to make a strong case for the importance of your research, particularly regarding community benefit and social impact.
Prove your research will solve real-world problems
Many researchers don't put much thought into the real-world relevance of their work. Yet, most funders want to finance proposals that promise to solve society's biggest challenges.
Before you draft your proposal, you need to consider how your research will confer value to society.
You want to be able to argue that it might save lives or money, improve people's well-being, or have another tangible impact.
Team up with project partners
Involving suitable research collaborators can also increase your chance of success.
If you're conducting cancer research, you could liaise with hospital clinicians or an association against a particular type of cancer. You could team up with a museum or heritage foundation if you're a history researcher. This will help translate your research into practice.
You don't have to go far to find collaborators. Start from your peers and direct contacts or links that your institution or research group might have.
Networking with fellow researchers or industry representatives in your field in conferences and seminars will also help you identify suitable grant collaborators. You can also look for them when you go through previously funded research projects.
Involve peers from relevant disciplines
Interdisciplinary research is seen as innovative because insights from each field contribute to the others. This extends the impact across different scientific specialties and across society.
For example, if you're a social psychologist studying drivers' perceptions of speeding risks. Involving researchers in transport studies, engineering, and related disciplines, not to mention community organizations and law enforcement, will make your proposal look more robust. And it'll actually be more robust.
Adopt research storytelling
Grant proposals can all start to sound the same for those who read and assess them. They're like job applications. As the applicant, you need to set yourself apart and inspire the reader.
You can do this by marketing yourself and your science in an engaging story. Spend less time formulating complex research questions and more time stressing how your research will benefit society. Providing an effective solution will give the reviewers positive emotions. It's like storytelling.
Getting some science communication training will help with this. Try using free science-storytelling tools, like Message Box . This easy-to-use solution lets you convey the information in your head about your work in ways that resonate with your audience. Start by reading real Message Boxes .
Set realistic research questions
A common mix-up among first-time applicants is that promising lots of work will make your proposal look better. It might be tempting to argue that you can solve these big, challenging problems in a single project. But, realistically, that's not often feasible.
For a 2–3-year project, have no more than four research questions. Even after you have proposed these, you'll have just enough space to provide a literature review, a research plan, and a list of expected impacts for each question.
Gather supplementary documents
The proposal itself is the core document, but it's the product of many supporting documents.
Describe the research environment
Other than your expertise, the funders will also want to confirm if you (or your research team) have the capacity to deliver the proposed project successfully.
Do you have access to the necessary facilities to complete the project? This might include access to a university library, to laboratory resources and equipment, or to your study population.
Your proposal needs to prove that you have everything required to start and complete the proposed research project successfully (within time and budget). You cannot be too thorough here.
Create biosketches for the research team
Most funding agencies and institutions ask for a biographical sketch (biosketch): a simplified version of the research team members' CVs. Biosketches stress team members' expertise and experience related to the research project.
Agencies like the National Institutes of Health ( NIH ) and the National Science Foundation both use standard biosketch formats that are regularly updated. They even provide tools to help you create your biosketch and format it according to NIH requirements.
We can't reprint them here, but you can view NIH sample biosketches here .
However, foundations and industry sponsors also set specific requirements for your CV/Biosketches. Follow these precisely.
Create a project timeline
Explain the timeframe for the research project in some detail. When will you begin and complete each step? Presenting a visual version of your timeline makes it easier to understand.
For complex multi-year research proposals, a timeline diagram can clarify the study's feasibility and planning (see below).
Here's a sample timeline to give you a general idea.

Gather supporting documentation
The supporting documents you'll need entirely depend on the sponsors' requirements. Most often, these include a cover letter, letters of support, and CVs.
Write the executive summary
The executive summary (abstract) outlines the most critical elements of your proposal in a condensed form. For longer proposals, you may be able to use a whole page. For others, you'll have to stick to just one paragraph. Either way, tell the reviewers:
- What's the goal of your project, the need you're addressing, and/or the real-world problem you're solving?
- What are your project's projected outcomes and broader impact, and how will you achieve them?
- How will you evaluate your project's success?
- Who are you, and why do you deserve this funding?
Let the mission and funding proprieties of the granting agency inform your abstract. Although the summary is the first part of your proposal, it's best to write it at the end. In the same way, it's best to write your manuscript abstract after writing your manuscript. That's the point where you have all your details, your entire story. Now you just have to write it out in a concise and accessible way.
Develop a grant budget
The funder will want to know precisely how you plan to spend their money. They want to ensure that your research project's cost-effective and that you've considered the actual costs of running your project.
In their calls for proposals, agencies provide information on the number of grants expected to be funded and the estimated size of each grant award. This information should inform the creation of your budget.
Meet with the grant office to talk through expenses
As mentioned, most institutions have grant administrators who can work with you to create the budgets and complete any budget forms required by the funder. If you're awarded the grant, they are most likely to manage these budgets.
In preparing a grant budget, there are three main considerations:
- Policies and requirements of the funding agency
- Policies of your institution
- Costs related to each project task
Knowing these rules before developing a grant application will save you time. The grant office can help you understand them, plus translate your project's goal and objectives into money.
Identify categories
Budgets are typically formatted in tables and figures. They contain three components:
- Direct costs
- Facilities and administrative costs
- Institutional commitments
The latter describes your institution's agreement to share the expenses of a research project with the funding body.
Each component is divided into separate categories.
For example, direct costs refer to expenses linked to the performance of specific activities and the resources needed to deliver the project. These often comprise:
- Personnel: research project team members' salaries
- External consultants: e.g., you might need an expert adviser to do a cost-benefit analysis for your project
- Equipment: furniture or laboratory equipment
- Travel expenses: transportation, accommodation, and/or daily subsistence costs
Create and justify a budget
On top of providing a line-by-line budget, you'll need to justify each expense. This involves a brief explanation for each line item in your budget. When writing this, follow the order in which budget items are presented.
In computing your budget, be as realistic as possible.
If your proposed budget is under the grant limit, think bigger. Think about how your research plans could be better, such as by choosing a bigger population sample or conducting more experiments.
If your estimated budget is over the available limit, you may be proposing too much. Think about removing a research question or staff involved.
The following is a sample 12-month research project budget (in which the university and sponsor share project expenses):
Budget Period: 10/15/2022 to 10/14/2023

Create a budget timeline
You've established your project's specific aims. Now it's time to create a timeline of key activities and specify when each activity will be completed. This is key to the construction of a sound budget.
Imagine you're proposing a two-year study. You plan to enroll 80 research participants over 12 months (around six people monthly). You'll interview each one for 1 hour in their home.
In year one, you'll need to budget for recruiting and interviewing study participants and traveling to their houses. In year two, though, the project won't involve such activities. Instead, the budget might reflect data entry, analyses, and report generation.
Get down to specifics. Explain yourself clearly. Show your plan.
Finalize, review, and polish your proposal
Think like the reviewer (just like you need to think like a journal editor when you submit a manuscript, or a job interviewer when you're trying to get hired).
Suppose you're tired and hungry. You've got multiple applications to read in a short period. How can you make it as easy as possible for the reviewers?
Avoid jargon
No matter how innovative your ideas are, sloppy or unfocused writing can hide them.
Use clear, concise, and accessible language. Flow clearly from one idea to the next. Use a “plain” word instead of a “smart-sounding” one.
Compare these pairs of sentences:
Bad: I propose dissecting the wartime mnemonic practices of externally displaced Afghan populations.
Better: I would like to see how Afghan refugees remember and talk about the war in their country.
Bad: I aim to explore the heterogeneity of forest ecosystems in spatial and temporal recovery following numerous turbulences.
Better: I hope to see what occurs when a forest grows back after being logged, burned, and cultivated.
Avoiding scientific jargon will help you tell your story from the heart, in words that many more people can understand. Take that type of thinking into your manuscript writing, and you'll increase your research impact.
Use reader-friendly formatting
Along with omitting jargon, formatting also increases readability.
White space, bold headings, standard fonts, and illustrations all make proposals easier to read. Widening margins and reducing the font size to 9-point (or less!) to squeeze in more text may add detail. But it also makes your document harder to read.
Organize ideas with numbered lists. Lists are easier to scan and encourage succinctness. Preface the lists with phrases like, “This project's three main goals are:” or “This work will involve four stages:”
Make sure your English is grammatically correct and readable
Spelling errors, bad grammar, unnatural word choice, exceeding the word limit... these issues can make the reader doubt how rigorous your research is. They might also wonder how careful you'll be with their money.
English errors can result from both a lack of English skills and from hurried writing.
Apart from the usual advice about getting a professional edit or proofread , and using a grammar tool , allow plenty of time. If you wait until the last day, week, or even month to prepare your grant, you're almost guaranteed to make language mistakes.
Even if you're a good writer, you'll probably miss a chance to write something more clearly, remove jargon and idioms, and have a consistent, professional tone.
Once your proposal's clearly written and you've edited it until it seems “perfect,” set it aside for a week. Yes, you're in a hurry, but you'll benefit from this break.
Then go back to it and edit/proofread/revise. Better yet, do it twice.
Get lots of feedback
Peer review is key to all research funding applications.
Even if you follow the advice outlined above, there might still be unclear bits of your proposal (at least to some). To strengthen your proposal, get other people to read it. Don't limit yourself to colleagues from your field. They'll probably be familiar with research jargon and methods.
- Former grant recipients
- The funding agency you're applying to
- Trusted peers in your field
They'll all help you learn more about what successful grant proposals look like in your career stage.
The more feedback you receive, and from a greater variety of people, the better. Arrange early on when and which person will look at your proposal and revise the proposal after each set of feedback.
Life after grant submission
There's no guarantee of funding, no matter how strong your application is. In fact, rejection is common because of the tough competition (see above).
Even renowned scientists aren't always successful.
The Nature article cited above notes that on the day molecular biologist Dr. Carol Greider was awarded the 2009 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, she learned her recently submitted grant proposal got the thumbs down. Wonder how that grant funder felt when they read the news the next day!
So, even if your proposal ends up not getting funded, the process of planning and writing is valuable, to say the least. Why? Because…
- You'll generate new ideas.
- You'll expand your horizons by talking to peers or involving project partners.
- You may even decide there's a better way to do your study or another research question that's important for you.
Grant writing can be frustrating and tiring, especially if you're an early-career researcher and not used to it.
Take your time to learn from past rejections and negative feedback. It will increase your chances of nailing your next grant proposal.
Final thoughts
Need help with your grant proposal? We can create a concise and polished proposal according to the funder's requirements while communicating the impact of your proposed research project. Learn more about our grant services .
Additional resources
- Ardehali, H. (2014). How to Write a Successful Grant Application and Research Paper. Circulation Research, 114(8), 1231–1234.
- Brownson, R. C., Colditz, G. A., Dobbins, M., Emmons, K. M., Kerner, J. F., Padek, M., Proctor, E. K., & Stange, K. C. (2015). Concocting that Magic Elixir: Successful Grant Application Writing in Dissemination and Implementation Research . Clinical and Translational Science, 8(6), 710–716.
- Chung, K. C., & Shauver, M. J. (2008). Fundamental Principles of Writing a Successful Grant Proposal . The Journal of Hand Surgery, 33(4), 566–572.
- MacKellar, P. H. (2011). Writing Successful Technology Grant Proposals: A LITA Guide. New York: Neal-Schuman Publishers, Inc.
- Pequegnat, W., Stover, E., & Boyce, C. A. (1995). How to Write a Successful Research Grant Application: A Guide for Social and Behavioral Scientists. New York: Plenum Press.
- Porter, R. (2005). What Do Grant Reviewers Really Want, Anyway? (PDF)
- Przeworski, A., & Salomon, F. (2012). Some Candid Suggestions on the Art of Writing Proposals . Revised for the Drugs, Security and Democracy Fellowship Program by SSRC staff (PDF)
- Ries, J. B., & Leukefeld, C. (1994). Applying for Research Funding: Getting Started and Getting Funded (1st ed.). California, London: SAGE Publications, Inc.
- Squitieri, L., & Chung, K. C. (2014). Funding Research in the Twenty-First Century . Hand Clinics, 30(3), 367–376.
- Wisdom, J. P, Riley, H, Myers, N. (2015). Recommendations for Writing Successful Grant Proposals , Academic Medicine: 90(12), 1720-1725.

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"

How to Write a Successful Grant Proposal

Introduction
What is a research project grant, why should you seek grant funding, how do i get a research grant, how to write a grant proposal, navigating the peer review process, ethical considerations and compliance in grant writing.
Grant writing can be a formidable aspect of the research process, particularly for new scholars and professionals. A grant not only secures the necessary financial support but also opens doors to career opportunities and other collaborations. This article will look at the process of writing effective grant proposals, providing you with the essential tools and insights needed to transform your innovative ideas into funded projects. We will explore each step of the process in detail from identifying the right funding agency for your research to creating a solid grant proposal.

A research project grant is a financial award provided by a funding organization like a governmental organization, private foundation, or corporation to support scientific, academic, or professional research. These grants are pivotal in advancing knowledge across various disciplines and are often essential for researchers to pursue innovative projects, conduct experiments, or explore new theories.
Unlike loans, research project grants are typically non-repayable funds. They are awarded based on the merit of the proposed project and its alignment with the funding body's objectives. The granting agency assesses this merit through a competitive process, where proposals are reviewed and selected based on criteria such as relevance, potential impact, feasibility, and the researcher's expertise.
Grants can vary significantly in size and scope. Some are small, designed to support preliminary data collection or pilot studies , while others are substantial, funding entire research projects over several years. The nature of the grant often dictates the level of detail required in the proposal, the expected outcomes, and the reporting requirements.
To be successful, a grant proposal must clearly articulate the research question or problem , the methodology to be employed, the expected outcomes, and how these outcomes will contribute to the field. It should also include a detailed budget, outlining how the grant funds will be utilized. This budget must be both realistic and justifiable, as it plays a crucial role in the funding decision.
Research project grants are not just about financial support; they also offer validation and recognition of the researcher's work. Securing a grant is often seen as a mark of prestige and can significantly impact a researcher's career, facilitating further opportunities for research and collaboration.
The process of obtaining a research grant is highly competitive. Researchers seeking funding must not only demonstrate the scientific merit and innovation of their proposal but also align their project with the priorities and objectives of the funding body. Understanding these elements is key to developing a successful grant application.
In summary, research project grants are essential instruments in the advancement of knowledge and innovation. They provide the necessary resources for researchers to explore uncharted territories in their respective fields, contributing significantly to the development of new theories, technologies, and solutions for global challenges.
Grant funding is an integral part of the research landscape, offering a range of benefits that extend beyond mere financial assistance. This section explores the key reasons for pursuing grant funding, highlighting its diverse impacts.
Financial support for research
The primary reason to seek grant funding is to obtain financial support for research. Research endeavors, particularly in areas like science and technology, often incur significant expenses for equipment, materials, and personnel. Grant funding relieves these financial burdens, allowing researchers to concentrate on their work without the stress of limited budgets. It ensures the availability of necessary resources, including sophisticated lab equipment and software , and provides for the payment of research assistants and collaborators. Moreover, consistent grant funding can sustain long-term research projects, ensuring they continue uninterrupted.
Advancing career opportunities
Beyond financial aid, grants are crucial for advancing a researcher's career. They bring recognition and credibility within the academic and professional realms, which is vital for career development. Receiving a grant is a mark of prestige, indicating that peers in the field have reviewed and endorsed the value of the research. Furthermore, grant projects often foster collaborations with other researchers, institutions, or industries, broadening one's professional network and opening doors to new opportunities.
Contribution to societal progress
Grants are instrumental in driving societal progress and innovation. They enable research that tackles complex issues and pushes the boundaries of knowledge, having far-reaching implications. Many grants focus on research aimed at solving global challenges like environmental issues and health crises. Additionally, they support the development of new discoveries, technologies, and methodologies, playing a critical role in the advancement of various fields and industries.
Educational impact
The impact of grant funding extends into the educational sphere as well. It offers avenues for training and skill development, benefiting not just principal researchers but also students and upcoming scholars. Research projects provide practical experience, essential for nurturing the next generation of researchers. They also contribute to the dissemination of knowledge, with many grants requiring the publication and sharing of findings, thereby enriching the wider educational landscape.
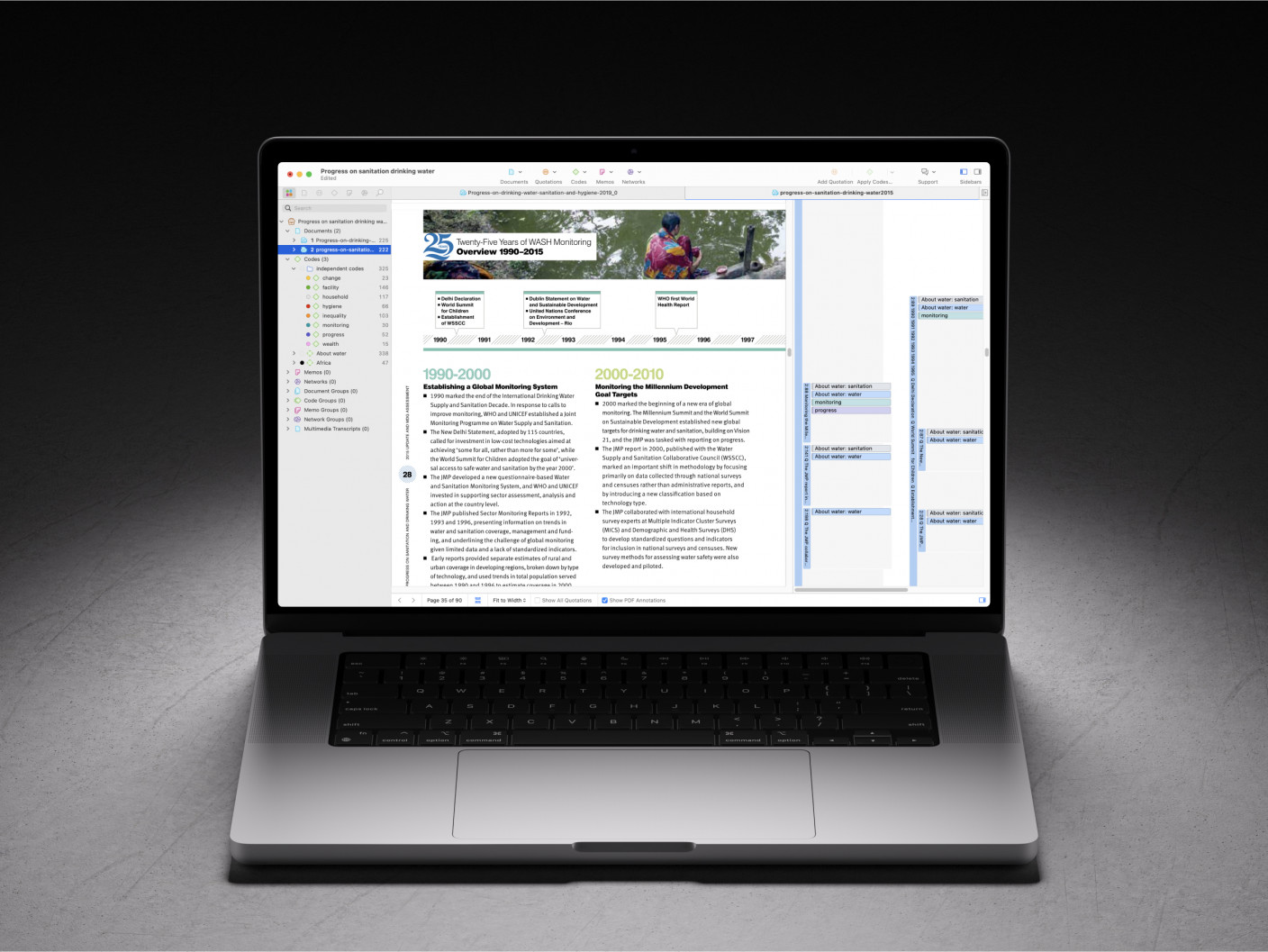
Organize and analyze your research with ATLAS.ti
An intuitive interface helps you make sense of your qualitative research. Start with a free trial today.
Securing a research grant involves a series of intricate steps, each pivotal to the success of the application. This section outlines the major tasks involved in obtaining a research grant.
Understanding grant requirements and guidelines
The first and foremost step before a researcher can write grant proposals is gaining a deep understanding of the grant's requirements and guidelines. This stage is foundational to crafting a successful application. It involves extensive research into the granting body's mission and goals, ensuring your project aligns with their objectives. This research includes studying the agency's focus, examining previously funded projects, and understanding their strategic interests. Tailoring your proposal to meet these interests is crucial.
The guidelines provided by the funding agency are a treasure trove of information, detailing everything from submission deadlines and funding limits to eligibility criteria and required documentation. A thorough review of these guidelines is critical to ensure compliance and completeness. Each guideline, whether it pertains to the format of the application, the scope of the research, or the nature of the required documentation, is a vital piece in the puzzle of grant application.
Engagement with the granting agency for clarification is a proactive step that should not be overlooked. Misinterpretation of guidelines can lead to errors that might jeopardize the chances of your application being successful. Many agencies are open to answering queries and clarifying doubts, making it a wise decision to reach out to them if any aspect of the guideline seems ambiguous or unclear.
Finding prospective grants and funding agencies
The next pivotal task in the grant application process is identifying the right grants and funding agencies that align with the proposed research. This step is as much about research as it is about strategy. Utilizing online databases and resources is a practical approach to begin this search. These platforms list available grants, offering filters by field, grant size, eligibility, and other criteria, enabling you to pinpoint opportunities that align best with your research goals.
However, online resources are just one part of the equation. Networking within your field plays a significant role in uncovering suitable grants. Engaging with peers, attending conferences, seminars, and workshops opens up avenues for learning about upcoming or lesser-known funding opportunities. These interactions often provide insider knowledge on what funding bodies are looking for in research proposals and can offer guidance on how to approach your application.
Consultation with institutional support staff, such as grant officers or research administrators, adds another layer of insight into the process. These professionals have experience and expertise in grant writing and can assist in identifying grants that match your research objectives. They can also provide invaluable guidance on the intricacies of the application process.
Preparing a compelling grant proposal
Crafting a compelling grant proposal is the cornerstone of your application. This document is your opportunity to showcase the significance and feasibility of your research project. It should be clear, concise, and persuasive, articulating your research objectives, methodology, expected outcomes, and the project's alignment with the funding organization's goals.
Developing a clear and comprehensive research plan is the heart of your proposal. It should detail the objectives of your research, the methods you will use, the expected outcomes, and how these outcomes contribute to the field. Clarity and specificity in this section are paramount to convey the potential impact and feasibility of your research.
A well-thought-out and realistic budget is a crucial component of the proposal. It should justify the funding request, covering all necessary expenses such as personnel costs, equipment, travel, and operational costs. This budget must be both defensible and aligned with the scope of the project, demonstrating efficient and effective use of funds.
Highlighting your qualifications and experience positions you as a capable and suitable candidate to conduct the research. This includes detailing relevant experience, past successes in similar projects, and any unique skills or resources you bring to the table. It's also important to illustrate how your background and expertise align with the objectives of the grant.
Before final submission, seeking feedback from mentors, colleagues, or professionals in the field is a wise step. Constructive feedback can significantly refine your proposal, addressing potential weaknesses and strengthening your arguments. This peer review process can provide a fresh perspective and enhance the overall quality of your application, increasing its chances of success.
Writing a grant proposal is a critical skill for researchers and academics. It involves presenting your research idea in a compelling and organized manner to convince funding agencies of its value and feasibility. This part of the guide will provide insights into the structure and content of a successful grant proposal, discussing its format, ideal length, and the significance of planning in the proposal writing process.
What is the format of a grant proposal?
The format of a grant proposal can vary depending on the funding agency’s guidelines, but there is a generally accepted structure that most proposals follow. This structure typically includes several key components: an abstract or executive summary, introduction, literature review, research design and methods, budget, and conclusion.
The abstract or executive summary is a concise overview of the proposal, summarizing the research question , methodology , and anticipated outcomes. It's crucial as it's often the first (and sometimes the only) part read by reviewers.
The introduction sets the stage for your proposal, providing background information on the research problem and its significance. It should capture the reader's interest and establish the context of your study.
Following the introduction, a literature review is presented, demonstrating your understanding of the existing research and how your project will contribute to or differ from this body of work.
The research design and methods section is where you detail your research plan. This includes the methodology, data collection and analysis plans, and any other pertinent information about how you will conduct your research.
The budget section outlines the financial requirements for your project. It should be detailed and justify each expense, ensuring that the costs align with the project's scope and objectives.
The conclusion summarizes the proposal, reiterating the significance and expected impact of your research. It's an opportunity to reinforce the importance of your project and leave a lasting impression on the reviewer.
How many pages should a grant proposal be?
The length of a research proposal varies depending on the funding agency’s requirements. Typically, proposals range from 5 to 20 pages. It's essential to adhere strictly to the page limit set by the funding body. A concise, well-structured proposal demonstrates your ability to communicate complex ideas effectively and efficiently. Every section of the proposal should be succinct yet comprehensive, providing all necessary information without superfluous details.
The importance of planning in research grant proposal writing
Effective planning is crucial in putting together a full grant proposal. It involves understanding the scope of your research, the requirements of the funding body, and the timeline for the proposal submission.
Start by mapping out each section of the proposal, ensuring you understand what is required in each part. This planning stage should involve extensive research, thoughtful consideration of your methodology, and a detailed budget plan.
Good planning also involves time management. Allocate sufficient time for each section, including time for revisions and feedback from colleagues or mentors. A rushed proposal is often evident to reviewers and can undermine the quality of your application.
Additionally, planning should extend to understanding the review process. Knowing who your audience is and what they are looking for in a proposal can help tailor your content to meet their expectations. This involves researching the funding agency's priorities and ensuring your proposal aligns with their objectives.
Navigating the peer review process is a critical aspect of submitting a grant proposal. This process, often shrouded in mystery for first-time applicants, plays a pivotal role in determining whether a proposal is funded. Understanding what happens during peer review and how to effectively respond to it can significantly increase the chances of success.
When a grant proposal is submitted, it typically undergoes a peer review process, where it is scrutinized by experts in the field. These reviewers, often experienced researchers or academics, assess the proposal based on various criteria such as the significance and originality of the research question , the feasibility and appropriateness of the methodology , the potential impact of the research, and the qualifications of the applicant. Understanding these criteria is crucial as it guides applicants on what aspects to emphasize in their proposals.
The peer review process usually starts with an initial screening to check if the proposal meets the basic submission criteria set by the funding body. Proposals that pass this screening are then evaluated more thoroughly. Reviewers often provide scores or ratings based on the evaluation criteria, and these scores significantly influence the funding decision. It's important to note that the review process can be highly competitive, with only a small percentage of proposals receiving funding.
One common reason for the rejection of grant proposals is a lack of clarity or detail in the research plan. Reviewers need to be convinced of the feasibility and significance of the research. Proposals that are vague, overly ambitious without sufficient justification, or lacking in methodological rigor are less likely to be successful. Therefore, it is essential for applicants to be clear, concise, and thorough in their proposals, ensuring that every aspect of their research plan is well-articulated and justified.
Receiving feedback or comments from reviewers is a crucial part of the peer review process. This feedback, whether leading to funding or not, is invaluable. It provides insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the proposal from the perspective of experts in the field. Successful applicants often use this feedback to refine and improve their proposals for future submissions. It is important to approach this feedback constructively, using it as a learning opportunity to enhance the quality of your research proposal.
For proposals that are not funded, it is common to revise and resubmit them during subsequent funding cycles. In such cases, addressing the reviewers' comments and concerns in the revised proposal is crucial. This shows that the applicant has taken the feedback seriously and has made efforts to enhance their research plan accordingly. It is also advisable to include a cover letter with the resubmitted proposal, outlining how the reviewers' comments have been addressed.
In some cases, applicants may disagree with the feedback or find certain comments unclear. In such situations, it is appropriate to seek clarification from the funding agency or, if allowed, provide a polite and concise rebuttal in the resubmission. However, this should be done carefully and respectfully, ensuring that the response is constructive and focused on clarifying misunderstandings or providing additional information.
Ethical considerations and compliance play a crucial role in grant writing and are integral to the integrity and success of any research project. This section explores the ethical landscape of grant writing, highlighting the importance of honesty, transparency, and adherence to regulations throughout the process.
At the heart of ethical grant writing is the commitment to honesty and integrity. This encompasses accurately representing one's qualifications, the potential impact of the research, and the need for funding. Fabrication, falsification, or plagiarism in any part of the grant proposal is not only unethical but can also lead to severe professional consequences. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that all information and data provided in the proposal are accurate and verifiable.
Transparency in the budgeting process is another critical ethical consideration. It involves providing a clear and detailed account of how the funds will be used. Overestimating costs or including unjustifiable expenses in the budget can undermine the credibility of the proposal. Funders expect a realistic and well-justified budget that aligns with the scope and needs of the research project.
Another key aspect of ethical grant writing is respecting confidentiality and privacy . This is particularly pertinent in research involving human subjects, sensitive data, or proprietary information. Researchers must ensure that their proposals comply with ethical standards and regulatory requirements regarding data protection and confidentiality. This includes obtaining necessary permissions and approvals, such as Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval for research involving human subjects.
Conflicts of interest must also be addressed transparently in grant writing. Researchers are required to disclose any potential conflicts that might impact their research. This includes financial interests, personal relationships, or professional affiliations that could be perceived as influencing the research outcomes. Proper management of these conflicts is essential to maintain the integrity of the research process.

Turn to ATLAS.ti for conducting quality research
Powerful data analysis tools are at your fingertips, starting with a free trial.

Step-By-Step Guide to Writing a Grant Proposal
Writing a grant proposal is incredibly time-consuming.
No joke. It's one of the most complicated documents you could write in your entire life.
There are different requirements, expectations, and formats—not to mention all the prep work you need to do, like market research and clarifying your project timeline.
Depending on the type of company or organization you represent and which grants you’re applying for, your grant could run anywhere from a dozen to a hundred pages. It’s a lot of work, and we’re here to help.
In this guide to grant proposals, we offer writing steps and examples, as well as resources and templates to help you start applying for funding right away.


Types of grant proposals
Grant proposals typically fall into one of these main categories:
Research grant proposals - Research grant proposals are usually sent by university professors or private research organizations in order to fund research into medical, technological, engineering, and other advancements.
Nonprofit grant proposals - Nonprofits send grant proposals to philanthropic organizations and government agencies to acquire funds for community development, health, education, and similar projects.
Technology grant proposals - Grant proposals can also be sent by technology companies (software, hardware, solar, recycling, environmental, manufacturing, health, and other types of tech companies). These proposals are often sent to large government organizations looking for solutions to current and future problems, as well as VC firms looking to invest in smart startups.
Small business grant proposals - Local governments often give grant awards to small businesses to help them kickstart, market, or expand.
Arts grants - Grants allow artists that would otherwise lack the financial resources to devote extended periods of time to their art. They might need to complete an installation that can be enjoyed by the community as part of the grant.
Grant RFP proposals - There can also be a request for proposals (RFP) for just about anything. From multinational organizations like the UN to family philanthropic grants, you can find RFPs for a variety of projects.
How to prep before you write
Before you can sit down to write your grant proposal, you’ll need to have a deep understanding of:
Existing scientific literature (for research grants) or relevant reports and statistics
Market and competitor landscape
Current available solutions and technologies (and why they’re not good enough)
Expected positive impact of your project
The methods and strategies you’ll employ to complete your project
Project phases and timelines
Project budget (broken down into expense categories)
With these things all buttoned down, you’ll have a much easier time writing the sections that cover those details, as well as the sections that highlight their meaning and importance (such as your statement of need and objectives).
Create a document where you can play around. Take notes, write down ideas, link out to your research, jot down different potential budgets, etc.
Then, when you’re ready to write, create a fresh document for your actual grant proposal and start pulling from your notes as needed.
How to write a grant proposal (ideal format)
Now, let’s get writing.
The ideal outline for a grant proposal is:
Cover Letter
Executive summary, table of contents, statement of need, project description, methods and strategies, execution plan and timeline, evaluation and expected impact, organization bio and qualifications.
If you’re not writing a super formal grant proposal, you might be able to cut or combine some of these sections. When in doubt, check with the funding agency to learn their expectations for your proposal. They might have an RFP or other guidelines that specify the exact outline they want you to follow.
Note: In business proposals, the cover letter and executive summary are the same, and those phrases are used interchangeably. But for grant proposals, the cover letter is a short and simple letter, while the executive summary offers a description of key aspects of the proposal.
In your cover letter, you'll write a formal introduction that explains why you are sending the proposal and briefly introduces the project.
What to include :
The title of the RFP you are responding to (if any)
The name of your proposed project (if any)
Your business or nonprofit organization name
A description of your business or organization, 1-2 sentences
Why you are submitting the proposal, in 1-2 sentences
What you plan to do with the funds, in 2-4 sentences
Dear [Name], The Rockville Community Garden is responding to the city of Rockville’s request for proposals for nonprofit community improvement projects. The Rockville Community Garden is a space for relaxation, healthy eating, exercise, and coming together. We are submitting a proposal to request funding for Summer at the Garden. Every summer, parents are tasked with finding childcare for their children, and we have received countless requests to host a summer camp. We're requesting funding to cover tuition for 100 low-income children ages 5 to 12. The funds will make our summer camp accessible to those who need it most. Thank you for your consideration, [Signature] [Title]
The executive summary of a grant proposal goes into far more detail than the cover letter. Here, you’ll give
Statement of Need overview, in 2 - 5 sentences
Company Bio and Qualifications, in 2 - 5 sentences
Objectives, in 2 - 5 sentences
Evaluation and Expected Impact, in 2 - 5 sentences
Roman architecture stands the test of time until it doesn’t. Roman building techniques can last thousands of years but will crumble to dust instantaneously when earthquakes strike. Meanwhile, our own building techniques of reinforced concrete and steel last only a couple of centuries. Ancient Architecture Research firm is dedicated to modernizing roman building techniques to create new structures that are earthquake safe and sustainable. Our principle investigators hold PhDs from renowned architecture universities and have published in numerous journals. Our objectives for the research grant are to create a prototype structure using Roman building techniques and test it on a shake table to simulate an earthquake. The prototype will pave the way for our application for an amendment to the California building code to permit unreinforced masonry construction. With the success of the prototype, we will prove the safety and viability of this technique. This project will have an enormous potential impact on several crises plaguing the state of California now and in the future: disaster relief, affordable housing, homelessness, and climate migration. Unreinforced masonry construction can be taught and learned by amateur builders, allowing volunteers to quickly deploy temporary or permanent structures.
Next up, you need your Table of Contents! Make sure it matches the names of each of your following sections exactly. After you’ve written, edited, and finalized your grant proposal, you should then enter accurate page numbers to your TOC.
Next up is the statement of need. This is where you sell why you’re submitting your grant request and why it matters.
A description of who will benefit from your proposal
Market and competitive analysis
Statistics that paint a picture of the problem you’re solving
Scientific research into how the problem is expected to worsen in the future
Reasons why your small business deserves funding (founder story, BIPOC founder, female founder, etc.)
While women hold 30% of entry-level jobs in tech, they only make up 10% of C-suite positions. The Female Leadership Initiative seeks to develop women tech leaders for the benefit of all genders. Female leaders have been proven to positively impact work-life balance, fairer pay, creativity, innovation, teamwork, and mentorship.
In this section, you’ll describe the basics of your research project, art project, or small business plan. This section can be kept fairly short (1 - 3 paragraphs), because you’ll be clarifying the details in the next 5 paragraphs.
The name of your project (if any)
Who will benefit from your project
How your project will get done
Where your project will take place
Who will do the project
The Fair Labor Project will seek to engage farm workers in the fields to identify poor working conditions and give back to those who ensure food security in our communities. Trained Spanish-speaking volunteers will visit local farms and speak with workers about their pay and work conditions, helping to uncover any instances of abuse or unfair pay. Volunteers will also pass out new work gloves and canned food. Volunteers will also place orders for work boots and ensure that boots are later delivered to workers that need them.
You should also write out clear goals and objectives for your grant proposal. No matter the type of agency, funding sources always want to see that there is a purpose behind your work.
Measurable objectives tied directly to your proposed project
Why these objectives matter
We seek to boost volunteer turnout for our voter registration efforts by 400%, allowing us to reach an additional 25,000 potential voters and five additional neighborhoods.
Now it’s time to clarify how you’ll implement your project. For science and technology grants, this section is especially important. You might do a full literature review of current methods and which you plan to use, change, and adapt. Artists might instead describe their materials or process, while small business grant writers can likely skip this section.
The names of the methods and strategies you will use
Accurate attribution for these methods and strategies
A literature review featuring the effectiveness of these methods and strategies
Why you are choosing these methods and strategies over others
What other methods and strategies were explored and why they were ultimately not chosen
“We plan to develop our mobile app using React Native. This framework is widely regarded as the future of mobile development because of the shared codebase that allows developers to focus on features rather than create everything from scratch. With a high workload capacity, react native also provides user scalability, which is essential for our plan to offer the app for free to residents and visitors of Sunny County.”
You’ll also need to cover how you plan to implement your proposal. Check the RFP or type or grant application guidelines for any special requirements.
Project phases
The reasoning behind these phases
Project deliverables
Collaborators
In our experience and based on the literature,11,31-33 program sustainability can be improved through training and technical assistance. Therefore, systematic methods are needed to empirically develop and test sustainability training to improve institutionalization of evidence-based programs. This will be accomplished in three phases. In Phase 1, (yr. 1, months 1-6) we will refine and finalize our Program Sustainability Action Planning Model and Training Curricula. As part of this refinement, we will incorporate experiential learning methods3-6 and define learning objectives. The Program Sustainability Action Planning Training will include action planning workshops, development of action plans with measurable objectives to foster institutional changes, and technical assistance. We will also deliver our workshops in Phase 1 (yrs. 1 and 2, months 6-15) to 12 state TC programs. Phase 2 (yrs. 1, 2, and 3) uses a quasi-experimental effectiveness trial to assess the Program Sustainability Action Planning Training in 24 states (12 intervention, 12 comparison). Evaluation of our training program is based on the theory of change that allows for study on how a change (intervention) has influenced the design, implementation, and institutionalization of a program.7,8,11,28 We will collect data on programmatic and organizational factors that have been established as predictors of sustainability9,11 using state level programmatic record abstraction and the Program Sustainability Assessment Tool (PSAT)43 to assess level of institutionalization across intervention and comparison states at three time points. Data will be used to establish the efficacy of the Program Sustainability Action Planning Model and Training Curricula. In Phase 3 (yr. 4, months 36-48), we will adapt our training based on results and disseminate Program Sustainability Action Planning Model and Training materials. - From Establishing The Program Sustainability Action Planning Training Model
A budget table with various expense categories
An explanation of what each category entails
Expenses broken down by month or year (if this fits your proposal)
Here’s an example budget table with expense categories:
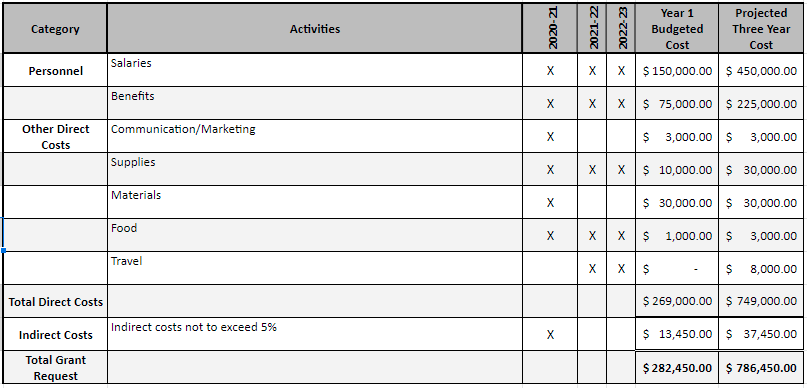
You can then include a brief description of each category and the expenses you expect within them.
A great grant proposal should clarify how you will measure positive outcomes and impact.
Details on the expected impact of your project
Who will benefit from your project and how
Your plan for evaluating project success
How you will measure project success
We will measure the success of the project by monitoring the school district’s math scores. We are expecting an 8% increase in state testing scores from the fall to the spring across grades 1 through 3.
And lastly, finish up your grant proposal with a bio of your organization, your company, or yourself.
Company name
The names of people on your team
Professional bios for everyone on your team
Your educational background
Any relevant awards, qualifications, or certifications
Jane Doe received her masters in fine arts specializing in ceramics from Alfred University. She has received the Kala Fellowship and the Eliza Moore Fellowship for Artistic Excellence.
Successful grant proposal examples
Want to write winning grant applications?
We’ve rounded up examples of successful, awarded grants to help you learn from the best.
Check out these real examples across science, art, humanities, agriculture, and more:
Funded arts and research grants from the University of Northern Colorado
Samples of awarded proposals from the Women’s Impact Network
National Cancer Institute examples of funded grants
Institute of Museum and Library Services sample applications
Specialty Crop Block Grant Program awarded grants examples
Grant application and funding resources
To help you get started writing and sending grant proposals, we’ve found some great application resources.
Research grants:
United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) grants
William T. Grant Foundation grants on reducing inequality
Russel Sage Foundation research grants
Nonprofit grants:
Walmart’s Local Community Grants
Bank of America’s Grant Funding for Nonprofits
Canada GrantWatch’s database of nonprofit grants
Technology grants:
Google Impact Challenges
UN Sustainable Development Goals Fund
US Department of Energy Funding
Small business grants:
US Chamber of Commerce Small Business grants
Canada Small Business Benefits Finder
US Small Business Administration (SBA) grants
Arts grants :
National Endowment for the Arts grants
Art Prof Artist Grants
Canada Council for the Arts grants
Get started with our proposal writing templates
The best way to start any proposal is with a template. A template informs your writing, while drastically speeding up the time it takes to design an attractive proposal.
All of our 75+ proposal templates can easily be adapted for any purpose, including grants or requests for funding. Try our project proposal template and make it your own by adding your executive summary, statement of need, project description, execution plan, budget, and company bio.
Start a free trial to check out all of our proposal software features , including reusable content snippets, e-signatures, viewing and signing analytics, and more.

How to Create Business Proposals Faster
November 14, 2017

Ready to make every deal a closed deal?
Get started with a free Proposify 14-day trial. No credit card required. Just more closed deals.
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write a Grant Proposal for Research

Writing and submitting a grant proposal is not a task enjoyed by most people. However, if you’re a researcher, writing a grant proposal is something that you will probably need to undertake many times. And that is why, questions like how to write a grant proposal for research are commonly asked in the field of academia.
Research grant proposals are critical for showcasing your work and convincing funders to back your research project. While obtaining grants brings prestige to the researcher and the institution, in some fields such as medicine, academic success depends on the number of grants and amount of funding received 1 . So, how can you write a persuasive research grant proposal that will impress funders and enable you to grow your career?
Table of Contents
The importance of planning in research grant proposal writing, how to write a research grant proposal: detailed steps, frequently asked questions (faqs).
As with most major projects, the key to writing a successful research grant proposal is planning. This includes an effective plan for not only writing the grant but also a strong plan for the research itself. Planning is extremely important for writing a successful research grant proposal because your final submission needs to be a complete and consistent story of your proposed work. Imagine trying to draft a novel linearly from start to finish without knowing the ending beforehand. Writing a successful research grant proposal requires that you attend to every detail, which means you need a plan.
Remember, you are telling a story through your written grant application . Therefore, every part of the grant proposal must work together, with nothing extra to distract the reader. This requires detailed planning.
The core of a research grant proposal is the research plan. A poorly planned study will not impress the funders. In addition to clearly showing the reader what your proposed study will look like, you will also want to emphasize the positive impact the study results will have on the field and on society at large. Planning time will also need to be spent in identifying a suitable funding source and ensuring that their mission aligns with your research. The story you tell when writing your research grant proposal needs to be a story that interests them.
- Identify an idea: It all starts with an idea. What are you trying to find out with your study? A good place to start is by identifying your research question 2,3 . Can you explicitly state the impact of the results and who might benefit? What makes your study different or novel? How will you conduct your research? In addition, make sure you identify your needs. What are you asking the funders for? Money for equipment, supplies, staffing? Will your research continue long term or will it consist of a single experiment? All of this will be important when you start searching for a suitable funder.
- Find a matching funding source: Once you have your research plan, it’s time to look for suitable funders. Spend the time to identify all available grants that may be a fit for your study. Look beyond the obvious and the popular 5 . There may be more potential funders out there than you think.
- Research the funder and topic: Once you have identified a suitable funder, spend a lot of time on their website. Read about their mission and history, and find out what they have been funding recently. Examine the Call for Proposals very carefully. Consider calling the program officer for the grant of interest 4 . They will answer any questions you have and may provide feedback on your topic or review your proposal draft.
- Write the technical section: This will be the most difficult step for many researchers in the process of writing a research grant proposal. While you may have a handle on the nuts and bolts of the study, communicating it clearly and concisely to those reviewing your proposal is more difficult. Like with any writing, don’t make it difficult for the readers to understand. Remember, you are trying to sell this idea to them.
Remember to be confident and definitive when discussing the need for this study. It’s always a good idea to read and study successful samples of grant proposals from the organization to get an idea of what they want to see.
- Review the call for proposals again : Go through the instructions very carefully. Make sure all the formatting is correct and all the required details are included in each section. You don’t want to give the reviewers any easy excuses for rejecting your submission.

- Submit your proposal: Make sure you follow the submission instructions exactly. Submit your proposal early so you can avoid the stress of having technical difficulties the day the research grant proposal is due.
- Learn from rejections and repeat: Keep in mind that most grant proposals are not funded, and even the most successful researchers get rejected . However, you can learn a lot from examples of unsuccessful proposals. Examine the feedback provided by the readers and use it the next time you write a research grant proposal.
- Zlowodzki M., Jönsson A., Kregor P.J., Bhandari M. How to write a grant proposal. Indian J Orthop . 2007, 41, 23-6. doi: 10.4103/0019-5413.30521.
- The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Grant proposals (or give me the money!). https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/grant-proposals-or-give-me-the-money/ [Accessed August 10, 2022].
- Elsevier Author Services. Writing a successful grant application – step by step. https://scientific-publishing.webshop.elsevier.com/research-process/writing-successful-grant-application-step-by-step/ [Accessed August 10, 2022].
- Santoro, H. The daunting but vital world of grant writing. Monitor on Psychology, 2021, 52. https://www.apa.org/monitor/2021/11/career-grant-writing . [Accessed August 10, 2022].
Write a convincing research proposal with Paperpal’s AI writing assistant
A research grant proposal is a comprehensive document that outlines your project or program, explains its significance, and requests funding. It typically includes sections such as an executive summary, introduction, project description, budget, and evaluation plan. On the other hand, a grant letter is a shorter document that serves as an initial contact with a potential funder. It is typically a letter of inquiry or a letter of intent that provides a brief overview of your project, highlights its relevance, and expresses your interest in seeking funding. A grant letter is often used to gauge the funder’s interest before submitting a full grant proposal.
The length of a grant proposal can vary depending on the specific guidelines provided by the funding organization. It is important to carefully review the application instructions or guidelines to determine the preferred length. In general, grant proposals can range from a few pages to several dozen pages. However, most funders specify a preferred page limit. Commonly, grant proposals may be around 10 to 20 pages, excluding supporting documents such as budgets, appendices, or letters of support. It’s essential to follow the funder’s guidelines regarding page limits and formatting requirements.
To make your grant proposal stand out, consider the following tips: a. Thoroughly research the funder: Understand the goals, priorities, and preferences of the funding organization. Tailor your proposal to align with their mission and objectives. b. Clearly articulate the problem or need: Clearly describe the issue your project aims to address and explain its significance. Provide compelling evidence and data to support your claims. c. Develop a well-structured and logical proposal: Organize your proposal into sections that flow logically, including an engaging executive summary, a detailed project plan, a realistic budget, and a comprehensive evaluation strategy. d. Highlight your project’s innovation and impact: Emphasize the unique aspects of your project or program. Demonstrate how it fills a gap in existing services or approaches. Clearly articulate the potential positive outcomes and impact your project will have. e. Provide evidence of your capabilities: Showcase your organization’s track record, expertise, and experience in successfully implementing similar projects. Highlight the qualifications of your team members and partnerships that strengthen your proposal. f. Write with clarity and conciseness: Use clear, concise, and persuasive language. Avoid jargon and technical terms that may confuse the reader. Ensure your proposal is well-organized and free from errors.
Yes, seeking feedback on your grant proposal before submission is highly recommended. Feedback from colleagues, mentors, or individuals with experience in grant writing can provide valuable insights and help improve the quality of your proposal. They can offer suggestions on clarity, organization, persuasiveness, and adherence to the funder’s guidelines. Constructive criticism can help you identify areas that may need further development or revision.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- How to Respond to Peer Reviewer Comments [Do’s and Dont’s for Authors]
- How to Write a Cover Letter for Journal Submission
- Manuscript Withdrawal: Reasons, Consequences, and How to Withdraw Submitted Manuscripts
- 4 Key Writing Styles and Examples of Academic Writing
9 Tips to Improve Readability and Language in Your Research Paper
Duplicate publications: how to avoid overlapping publications in research, you may also like, what is academic writing: tips for students, what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content, how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., how to write an essay introduction (with examples)..., should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., what are the benefits of generative ai for....

Writing Successful Research Grant Proposals
Spencer staff have put together a guide with helpful information on writing a successful field-initiated research grant proposal.

Browse Our Resources and Tools

Writing Proposals That Engage Research With Youth, Families, and CBOs

Proposal Review Process Infographic

Research-Practice Partnerships Writing Guide
Site-wide links
- Skip to content
- Search RIT Search
- VP for Research
- Human Subjects Research Office
- Intellectual Property Management Office
- Research Computing
- Research Relations Office
- Venture Creations Incubator
- Simone Center for Entrepreneurship
- Sponsored Programs Accounting

You are here
Writing a successful proposal.
- Tips for Success
- Following Sponsor Guidelines
- RIT Profile & Important Numbers (EIN, DUNS, etc)
- Human Subjects Protection Statement
- Proposal Writing Short Course (The Foundation Center)
- Basic Elements of Grants Writing (Corporation for Public Broadcasting)
Getting Started: The Concept Paper
The most universal advice on writing a successful grant proposal is to present a well written, focused solution to a problem in a logical progression. This is much easier said than done, and finding the focus is often the most difficult piece of the puzzle. To find this focus, we suggest writing a "concept paper." A concept paper summarizes in two to three pages the entire project from beginning to end. The point is to take all of the ideas in your head and put them down on paper as concisely as possible. Writing a concept paper is a good exercise in defining your priorities and mission, and can be a useful tool in obtaining valuable feedback before "diving into" the full proposal.
Organize your concept paper with three sections, which are discussed in more detail below:
- A Mission Statement that explains what it is your are trying to do in fifty words or less.
- A Statement of Need that explains what the need is that you are trying to address.
- A Project Narrative that explains what the proposed activities are going to be.
Putting it Together: Writing the Proposal
Following is a suggested format for grant proposals. Many grant competitions have their own prescribed format which may require you to modify the suggestions offered here accordingly .
Generally, there are seven major sections of a proposal:
- Table of Contents
- Mission Statement
- Statement of Need
- Project Rationale Incorporating Literature Review
- Goals and Objectives
- Proposed Activities
- Facilities and Resources
- Dissemination
- Sustainability
- Bibliography
- Letters of Support/Endorsement
- Relevant Publications (if allowed)
I. Table of Contents
After you write your proposal, create a table of contents.
II. Mission Statement
In 50 words or less, what is the mission of your project? This helps you clarify the project's primary goal. Most importantly, this allows the reader to have an immediate understanding of what you are proposing right from the start without having to search for what you are trying to do embedded in the narrative of the proposal. Following is an example of a mission statement from a successful grant proposal:
"Our mission is to establish a self-sustaining, continuing education program to retrain middle managers in the hospitality industry in Croatia with the ultimate goal of making the Croatian hospitality industry more competitive in a global free-market system."
III. Abstract
The well-written abstract is the single most important part of the proposal. Often, initial proposal review, or "first cuts", are based on the abstract alone. The abstract should not be the last part of the proposal that is written. Deadline pressures prior to submission of the proposal are often intense. The writing of this crucial aspect of the proposal should be given the time and consideration it deserves. The abstract should be written early in the proposal preparation process, and modified as needed as the proposal develops. The abstract be understandable to a scientifically or technically literate lay reader, and it should be suitable for publication. The abstract should be written in the third person. It should include objectives, methods to be employed, and the potential impact of the project.
IV. Statement of Need
This is where you present the problem you are trying to solve. Our advice is as follows:
- Stick to one problem.
- Avoid circular logic in your thinking and in the development of your statement of need. Circular logic decrees that the lack of a solution is the problem. Requesting scholarship funds as a solution to the lack of scholarship funds is an example of circular logic. A more convincing argument is based on a problem with a much larger scope. For example, women are greatly underrepresented in engineering-related fields and scholarship funds will enable more women to pursue engineering as a career choice.
- Use a logical progression in your statement of need starting as globally as possible. You will need to prove that you have an understanding of the problem and the latest research on the problem. For example, if you are proposing a computer lab to serve a minority population your statement of need should focus on the "digital divide." Hence, your statement of need will start with a discussion of the digital divide in the United States, then it will focus on the digital divide in Rochester (in this case), then it will focus further on the digital divide in the specific community you are proposing to work with.
- Close with a discussion of what else is being done, and lead into the project narrative with a brief discussion of how your idea is better or different. To do this, you will need to cite that latest body of research and specific projects that are currently happening and how yours is different and better. Preparation is essential, and you are encouraged to pick up the phone and call people who are working on similar projects, call program officers at agencies, and gather as much information as possible. This is an area where the Sponsored Research Services office can offer guidance, advice, and assistance.
V. Project Rationale Incorporating Literature Review
Any successful grant application must incorporate a strong theoretical basis that is grounded with an extensive discussion of the literature. The rationale for the project comes from what the literature says works, does not work, is missing, needs to be looked at differently, or however you choose to broach this extensive discussion. This is how the proposal demonstrates that the individual making application is incorporating the latest research into the project.
VI. Project Narrative
A project narrative has six main sections. Check the funding agency announcement for a specific outline; some agencies require a different organization of the proposal narrative.
- Goals and Objectives . What are the major goal(s) and objectives of the project? Describe the expected outcomes of this project and how success will be measured in the project (and reference the evaluations section below).
- Proposed Activities . What are the activities that are going to happen during the period of this grant? What are you are proposing to do? What timeframe are you accomplishing this during the project?
- Facilities, Resources, and Project Management . What facilities and resources are available? How is the project going to be managed? Who will provide leadership and management for the project, and who are the people involved in implementing the project? What credentials make this project team unbeatable?
- shortening time-to-degree
- broadening career opportunities
- assessment of the graduate trainees' performance
- impact of the research experience on the career plans of undergraduates
- placement of graduate students and postdoctoral fellows upon completion of the program
- the participation of women and members of underrepresented groups
The absence of a good evaluation plan may result in the rejection of a proposal with an otherwise innovative idea and well-described goals and objectives.
- Serve as a content expert for science/education web sites
- Establish mutual links to suitable science/education sites
- Peer-reviewed journals
- Newsletters
- Fliers/Pamphlets
- Interim Working Papers
- Books or Manuals
- Nontraditional journals, such as trade journals
- Poster Displays
- Audio-Visual Materials (CD ROM, Videotape, etc.)
- Press Releases
- Conferences with industry specifically for dissemination
- Teleconferences or videoconferences
- Course Materials
- Distance Learning Courses
- Workshops that provide hands-on experience
- Mentorships to undergraduate students, high school students, teachers
- Summer institutes for students and educators
- Visit local classrooms as guest speaker
- Assist teachers in developing curricula related to your field
- Provide professional development or research orientation for staff
- NETAC (Northeast Technical Assistance Center, located at NTID)
- PEPNet (Postsecondary Education Programs Network) - see their website at www.pepnet.org
- Public lecture series
- Public open-house of research facilities
- Host a public science day
- Exhibits at the Student Alumni Union or Wallace Memorial Library
- Serve as a content expert for a museum exhibit
- Contribute articles to museum publications
- Sustainability . It is important for the potential sponsor to know that the project will not simply end once the grant funds are gone. The best way to do this is it ensure that this is a project that the institution is committed to as a part of the bigger picture and that it will be supported beyond the funding period. It is also important to build in and discuss a plan for growth of the project. Grant funding should be used as seed funding for follow-on funding. The proposed management plan can indicate to the sponsor that not only sustainability, but growth of the project is going to occur. Multi-year grants are usually awarded contingent upon the successful progress of the project. Sponsors often require interim technical reports upon which the decision to continue the grant is based. Others, such as the National Institutes of Health, require the submission of non-competing continuation proposals. Specific guidelines, similar to those of the initial proposal submission, must be followed. Some agencies require site visits in order to assess the progress of the project. Principal investigators should review the continuation criteria as soon as the initial award is made, so as to properly prepare for this important part of the grant cycle.
VII. Attachments
- Bibliography . As mentioned, this needs to be a well-researched project, and a bibliography is an essential component of good, scientific inquiry. If the format is not dictated, any reasonable format will suffice as long as it is consistent.
- Resume . Credentials of the project management will be taken into consideration in every proposal. Check the guidelines to see if there are limits as to pages for a resume or biographical sketch.
- Letters of Support/Endorsement . If the proposed project is a partnership, letters of support from the listed partners are required. In any situation, letters of support from carefully selected individuals and/or organizations may be in order. For example, on a recent proposal to host a conference targeting secondary school teachers, we enclosed letters of support from school districts and the teachers' unions.
- Relevant Publications (if allowed). The funding announcement or guidelines will explain if you can attach relevant publications (such as a paper you wrote last year that further provides the rationale for your project). If you are uncertain about attaching anything further to your proposal, check with SRS .
Successful Grant Proposal Examples: The Ultimate List for 2024
Reviewed by:
September 13, 2021
Last Updated:
January 29, 2024
Table of Contents
Writing grant proposals can be a stressful process for many organizations. However, it's also an exciting time for your nonprofit to secure the funds needed to deliver or expand your services.
In this article, we'll dig into successful grant proposal examples to show how you can start winning grant funding for your organization.
By the time you finish reading this, you'll understand the characteristics of successful proposals, examples of grant proposals in a variety of program areas, and know exactly where you can find more sample grant proposals for nonprofit organizations .
Ready? Let's dig in!
.png)
Why Should You Find Successful Grant Proposal Examples?

Whether you are a seasoned grant writer or are preparing your first proposal ever, grant writing can be an intimidating endeavor. Grant writing is like any skill in that if you apply yourself, practice, and practice some more, you are sure to increase your ability to write compelling proposals.
Successful grant proposals not only convey the great idea you have for your organization but convince others to get excited about the future you envision. Many follow similar structures and developing a process that works best for your writing style can help make the task of preparing proposals much easier.
In addition to showing what to and not to do, finding successful grant proposals can help you see significant trends and structures that can help you develop your grant writing capabilities.
What Characteristics Make a Grant Proposal Successful?

"Grant writing is science, but it's not rocket science." - Meredith Noble
There's a lot that goes into creating a successful grant proposal. If you're feeling overwhelmed, Meredith Noble, grant writing expert, shares a straightforward step-by-step process to win funding.
1. Successful grant proposals have a clear focus.
Your first step when searching for funds is to clearly understand why you need those funds and what they will accomplish. Funders want to invest in programs they believe will be successful and impactful.
In your proposals, you want to instill confidence in your organization's commitment to the issue, dedication to the communities you serve, and capacity to fulfill the proposed grant activities.
Some questions that you may want to consider include:
- Are you looking for funds to establish a new program, launch a pilot project, or expand an existing program?
- Will your proposed program be finished in a year, or will it take multiple years to achieve your goal?
- Who is involved in your program, and who will benefit from its success?
- What problem will the proposed program address, and how is that solution unique?
- What are the specific, tangible goals that you hope to accomplish with the potential grant award?
Click to find the best grants for your nonprofit from 12,000+ active opportunities.
Search 150+ subcategories
2. Successful grant proposals are supported with relevant data.
Before starting your grant proposal, you want to take the time to do your research and make sure that your action plan is realistic and well-supported with data. By presenting yourself as capable and knowledgeable with reliable data, a thorough action plan, and a clear understanding of the subject matter.
It can also be beneficial to include data that your organization has collected to show program impacts and staff successes. Conduct regular analysis of program activities, grant deliverables, and collect success stories from clients and community members.
Some tips for when you collect your grant research :
- Make sure that you gather data from reputable sources. For example, at government sites such as Data.Census.gov , the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics for demographic data, or the U.S. Small Business, Explore Census Data Administration for industry analyses.

- Include diverse data. There may be some statistics where the numbers are enough to grab the reader's attention; other times, it may be helpful to have illustrations, graphs, or maps.
- In addition to quantitative data, qualitative data such as a story from an impacted community member may be extremely compelling.
- Make sure that the data you include is relevant. Throwing random numbers or statistics into the proposal does not make it impressive. All of the included data should directly support the main point of your proposal.
- You may find it useful to log important notes around what data you want to include in your grant proposal using a grant tracking tool such as Instrumentl .
By the way, check out our post on grant statistics after you finish this one!
3. Successful grant proposals are well-organized
Make sure to pay close attention to all of the requirements that a potential funder includes in their grant details and/or request for proposals (RFP). Your submission and all accompanying attachments, which may also include any graphs and illustrations, should adhere precisely to these guidelines.
Frequently the RFP or grant description will include directions for dividing and organizing your proposal. If, however, it does not, it is still best practice to break your proposal into clear sections with concise headings. You can include a table of contents with page numbers as well.
Standard grant proposal sections include:
- Proposal Summary: Also called the Executive Summary, this is a very brief statement (1-3 paragraphs) that explains your proposal and specifically states the amount of funding requested.
- Project Narrative: The bulk of your proposal, the Project Narrative, will do most of the work introducing your organization, the program, and describing your project. - Organization History: Who you are, what you do, where and how you do it. - Statement of the Problem: Background information on the problem and how it will be solved through the grant. - Project Description: Detailed explanation of the program you intend to implement with the grant, including a detailed timeline.
- Budget and Budget Justification: A breakdown of the project resources into specific budget categories, the amount allocated to each category, and appropriate reasons for that breakdown.
4. Successful grant proposals are tailored to the funder.
In addition to finding the basic details on the funding opportunity and application guidelines, you should also look into the funder, their giving priorities, and history.
Funders are much more likely to select your organization among others if they clearly understand and empathize with your cause and recognize the impact your work has in the community.
For more details on establishing meaningful relationships with funders, check out our article on How to Approach and Build Grant Funder Relationships .
The first step in determining whether a funding opportunity is a good fit, do some research to ensure your organization's programs and financial needs meet the funder’s interests and resources.
A few questions to ask include:
- What are the organization’s values, written mission, and goals?
- How is what you want to do aligned with the overall mission of this agency?
- Do their giving priorities match with the vision of your proposed program?
- Will this grant cover the entire cost of your program, or will you need to find additional funds?
- Does the grant timeline meet the budget needs of your organization?
- Are there other considerations that might be useful for us to know in preparing your application?
5. Successful grant proposals are proofread!
If you have been in the grant writing game for any extended period of time, chances are that you’ve dealt with tight deadlines. Nonprofit staff often have a lot on their plates, and if you happen to find an attractive funding opportunity when there’s only a handful of days before its deadline, it may be difficult to walk away.
It is crucial to plan an appropriate amount of time to review and proofread your proposal. Grammar mistakes can make or break your submission and they are easy to fix.
General strategies for editing your proposal include:
- Use one of the many available grammar-checking software such as Grammarly or GrammarCheck.me . These online tools are often free to use and can help you quickly and accurately review your work.
- Ask other members of your team to peer-review the proposal. It is especially important to have staff working on or who are directly impacted by the program proposed to ensure everyone is on the same page. Additionally, these staff members have the most information about the program's implementation and can catch inconsistency or unrealistic promises in the proposal.
- It is also helpful to ask someone unfamiliar with your program and the subject matter discussed in the proposal. Sometimes the grant reviewer may not have the same level of knowledge you or your staff have about the subject matter, and so you want to ensure you stay away from overly-specific jargon and undefined acronyms.
- Read through it (again!). A final read-through, maybe out loud, after all the edits have been made, can help you catch overlooked mistakes or inconsistencies in the proposal.
If you're looking to start building your own nonprofit financial statement and nonprofit membership application, get started quickly by using our Nonprofit Financial Statement Template and Nonprofit Membership Application Template . The template is made in Canva, an an easy-to-use creative design tool. You can jump right in, change colors, add your logo, and adjust the copy so it fits your brand.Why start from scratch when you can use one of our templates?
The Ultimate List of Grant Proposal Examples

As stated early on in the article, every grant proposal is unique. We have curated a list of sample grants for various types of projects or nonprofit organizations. This list is in no way exhaustive, but several examples cover common program designs and focus areas that receive philanthropic support through grants.
Research Grant Proposal Samples
Finding a grant opportunity to fund research can be a challenge. These types of grants are typically intensive and require in-depth expertise, a proposed research design, explanation of methodology, project timelines, and evidence of the principal investigator(s) qualifications.
The following are examples of grant proposals in support of research projects or studies.
Harvard University - Proposal to the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (2009) :
Researchers at Harvard University proposed to research the “growth of policies in the United States around the use of genomic science in medicine and racial identity.”
For grants focused on research, it is important to ensure that the proposal can be understood by different kinds of stakeholders. While the research may be very specific and require some expertise to understand, the purpose and need for the research undertaken should be able to be understood by anyone.
For example, being cognizant of jargon and when it is and isn’t appropriate to use is incredibly important when developing a research grant proposal.
This proposal to the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, while very detailed and specific, still lays out the intent of the proposal in laymans terms and includes the appropriate amount of detail while ensuring that a broader audience can read and understand the request and purpose of the study.
Northwestern University - Annotated Grant Proposal Sample (2016)
For individuals or organizations who are interested in developing a great grant proposal in support of a research project, Northwestern University has a catalog of grant proposal samples with annotations denoting notable strengths and weaknesses of the application.
Linked above is one such example, a grant proposal in support of a project titled “Understanding the Stability of Barium-Containing Ceramic Glazes”. Review Northwestern University’s catalog of sample proposals here for additional guidance and inspiration.
Clinical Trial Grant Proposal Sample
Clinical trials are important research projects that test medical, behavioral, or surgical inventions to prove or disprove hypotheses about their efficacy. These trials are an important component of scientific and medical advancement. Oftentimes, hospitals or research institutions require robust funding from grants to initiate a trial of this kind.
While clinical trials are highly specific and require a great deal of expert input to develop, reviewing a grant proposal sample can help you prepare should your nonprofit organization decide to pursue a funding opportunity of this kind.
University of Alabama at Birmingham, Center for Clinical and Translational Science – NIH Grant R Series Samples :
If your nonprofit organization is seeking funding for a clinical trial, a great place to begin for tools and resources is the University of Alabama’s Center for Clinical and Translational Science.
The Center’s website has several sample proposals submitted to the National Institutes of Health. For professionals hoping to submit a grant proposal in support of a clinical trial, you may find one among these excellent examples that aligns closely with your work and can guide the grant development process.
Community Garden Grant Proposal Sample
Community gardens are idyllic cornerstones of their neighborhoods, cultivating lush, green spaces where residents can build a thriving community. Some community gardens are run by nonprofits such as land trusts or are born out of special projects initiated by nonprofit organizations.
Either way, to ensure the sustainability of local community gardens, gardeners and community garden managers may need to apply for funding through grant opportunities. Below is just one grant proposal sample in support of a community garden that may help you develop your own winning community garden grant application.
Stockton University – Community Garden 2020 Proposal :
This grant proposal submitted on behalf of Stockton University does an excellent job of illustrating the success of their community garden project and justifies the need for funding to sustain the momentum of the project going forward.
This proposal is also visually compelling and well-designed, incorporating photos and color schemes that directly evoke the image of a flourishing community garden. Ensuring your proposal document is easy to read and incorporates a strong layout and design can sometimes make or break an otherwise strong proposal that is being judged in a competitive pool of applicants. Strong design elements can set your proposal apart and make it shine!
Government Grant Proposal Samples
Government grants are some of the most complex and challenging funding opportunities that a person can come across. Funding from government entities is allocated from tax-payer dollars, and as such the government employs strict requirements and rigorous oversight over the grantmaking process.
Having a successful template or sample in hand can help position you for success when you need help applying for a government grant.
National Endowment for the Humanities - Challenge Grant Proposal Narrative Sample :
Developing a grant narrative is a challenge regardless of the opportunity. Government grants, which require very specific detail, can pose an even greater challenge than most opportunities. Linked here is a successfully funded project of the Alexandria Archive Institute, Inc . through a grant from the National Endowment for the Humanities (NEH).
This project is a great example of how to develop a grant narrative that successfully addresses the stringent requirements associated with grant proposals. Note how each section is laid out, the double spacing, citations, and other key elements that are required in a government proposal to adhere to specific standards.
Even though this is a great example, also be aware that every government agency is different and while this proposal was a successful application for the NEH, other agencies may have different requirements including specific narrative sections, attachments and work plans, among other key items.

Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) – City of Pleasantville Clean School Bus, Clean Snow Removal Trucks and Clean Bulldozers Project Proposal Sample :
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) offers an example grant for potential grantees to review. This sample proposal envisions a project by a local municipality to procure buses, snow removal trucks, and bulldozers that produce less emissions thereby decreasing air pollution in the region. This sample proposal is a great guide for developing a compelling narrative and weaving in evidence-based data and information to support throughout.
Conference Grant Proposal Sample
Conferences are an important aspect of a nonprofit or educational institution's operations. Conferences can help bring together like minded individuals across sectors to find solutions and sharpen their skills, and they can facilitate the formation of powerful coalitions and advocacy groups.
Identifying funding for conferences can be difficult, and requires a thoughtful, strategic approach to achieve success. Following a template or grant proposal sample can help guide you through the application process and strengthen your chances of submitting a successful application.
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality – American Urological Associations Quality Improvement Summit :
This sample proposal provides an extensive template to follow for writing a successful conference grant proposal. The proposal follows an easily understood, structured narrative, and includes a detailed budget and key personnel profiles that will help anyone applying for grant support strengthen their chances of developing a high-quality application.
Dance Grant Proposal Sample
There are countless arts and cultural nonprofit organizations in the United States. According to Americans for the Arts , there are over 113,000 organizations (nonprofit or otherwise) devoted to promoting arts and culture in communities throughout the country—including dance.
Whether a theater that focuses on dance performance or a studio that teaches beginners how to appreciate the art form, there are a variety of dance-focused nonprofits that exist. Identifying strong grant proposal samples for dance-focused organizations or projects can be helpful as you work to help your dance program grow and gain revenue.
Mass Cultural Council – Dance/Theater Project Grant Sample :
This is an example proposal for an interactive dance/theatrical puppet project that focuses on engaging families. While this example captures a very unique and specific project, it also provides a good example of how to craft a case statement , write a strong project description, and develop a detailed project budget.
Daycare Grant Proposal Sample
In the United States, daycares are a vital component of childhood development, but unfortunately many families are unable to access them due to cost or accessibility. Studies show that in 2020 alone, over 57% of working families spent more than $10,000 on childcare while 51% U.S. residents live in regions classified as “childcare deserts”.
Given this, nonprofit daycares are vital to supporting future generations and providing accessible and affordable childcare for parents throughout the country. Many nonprofit daycares rely on generous funding through grants. Nonprofit day care professionals can use all the help they can get to submit winning proposals and sustain their daycare’s operations.
Relying on a high-quality grant proposal sample or template can be a huge help when working on a grant application or writing a proposal in support of a daycare.
AWE - Digital Learning Solutions – Grant Proposal Template :
While not a straightforward grant proposal sample, this grant template provides detailed guidance and helpful examples of how to respond to common questions and how to craft essential elements of a grant proposal focused on childcare and childhood development.
For example, the template provides easy to understand steps and bulleted lists for every key component of the grant proposal including a case statement, organizational capacity and information, project sustainability, project budget, and project evaluation.

Literacy Grant Proposal Sample
Promoting literacy is a very common mission for nonprofit organizations throughout the U.S. and the world. Literacy projects and programs are typically provided by educational institutions or education focused nonprofits.
In fact, according to the Urban Institute , Education focused nonprofits made up 17.2% of all public charities. With numbers like these, it can be helpful to gain insights from a grant proposal sample that will help you win grants and grow your organization.
Suburban Council of International Literacy (Reading) Association “Simply Reading” – Grant Proposal Sample :
This sample proposal to the Suburban Council of International Literacy (Reading) Association (SCIRA) is a great example of a strongly developed narrative that makes a powerful case for how fostering a love for reading among young students can result in improved educational outcomes. This helpful guide provides a framework for drafting a high-quality grant narrative while also giving examples of other key proposal elements such as a project budget.
Successful Educational Grant Proposals
Educational programming can be highly diverse in its delivery. Check out these examples of successful grant proposals for education to help you get started winning funds for your next educational program.
Kurzweil Educational Systems : In addition to this being a successful grant proposal, this example also includes detailed explanations of each section and provides useful guidelines that can help you frame your proposal.
Salem Education Foundation : This foundation has posted a sample application of a school seeking funding for increasing youth enrichment opportunities for their annual grant.
This is a great example for funding opportunities that ask specific questions about your organization and the proposed project instead of requesting a general proposal or narrative.

Successful Youth Grant Proposals
These examples of grant proposals for youth programs can help you tap into one of the largest categories of charitable dollars.
Family Service Association (FSA): This example of a grant proposal that is well-written and comprehensive. It is for a community block grant focused on youth development to expand services and cover staff salaries.
The Boys and Girls Club of America (BGCA): This is a sample produced by the national office of the BGCA to assist local branches in securing funds for youth programming and expanding services.
Successful Health-Related Grant Proposals
There is a large amount of funding for health-related initiatives, from healthcare grants to individuals, operational support for organizations or clinicians, and supporting researchers advancing the field. These sample grants give a bit of insight into this diverse sphere.
Centerville Community Center : Follow this link to read a grant to support community-based programming to raise awareness of cardiovascular disease prevention. This proposal does a great job of breaking down the project description, proposed activities, tracking measures, and timeline.
Prevention Plus Wellness : This is a sample grant proposal for nonprofit organizations to assist those looking to secure funds to address substance use and wellness programming for youth and young adults.

National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease (NIAID): The NIAID has released several examples of proposal applications and scientific research grant proposal samples that successfully secured funding for scientific research related to healthcare.
Other Successful Grant Proposals
Of the over 1.6 million nonprofit organizations in the United States , your funding requests may fall out of the three general categories described above. We have included additional grants that may help meet your diverse needs.
Kennett Area Senior Center : Submitted to a local community foundation, this proposal requests funding between the range of $1,000 to $10,000 to provide critical services and assistance to local seniors.
In addition to being very detailed in describing the program details it also carefully describes the problem to be addressed.
Region 2 Arts Council: This comprehensive grant proposal requests funds to support an artist to continue expanding their skills and professional experience. This is a useful example for individual grants or scholarships for professional or scholastic opportunities in supported fields.
St. Stephen’s Episcopal Church: This is an excellent example of a faith-based organization’s proposal to secure funds for a capital project to repair their building. The framing of this proposal and the language in the narrative can be used to help shape proposal letters to individual donors and to foundations, which can be especially useful for faith-based organizations or other groups looking to secure funds.
Get access to weekly advice and grant writing templates

10k+ grant writers have already subscribed
Tips to Get More Successful Grant Proposal Examples

If you are interested in finding more grant proposal examples, especially those directly related to your organization's priorities and service area, you can look at a few places.
1st: Foundation Websites
Sometimes a foundation will include past proposal submissions publicly on the website. These are especially useful if you are seeking grants from the organization. You can see exactly what kind of proposals they found compelling enough to fund and see if there are any trends in their structure or language.
2nd: Online Tools and Workshops
Sites like the Community Tool Box or Non-Profit Guides offer free online resources for organizations working to support healthier communities and support social change. They provide helpful advice for new nonprofits and provide a whole suite of sample grants to help you start winning grants step by step.
You may also be able to ask other members of the Instrumentl community for their past successful grant proposals by attending our next live workshop. Hundreds of grant proposals attend these every few weeks. To RSVP, go here .
3rd: Collect your own!
As you start submitting grants, you are also creating a collection of sample grants tailored to your subject area. Every response offers an invaluable learning opportunity that can help you strengthen your grant writing skills.
Perhaps there are similarities among proposals that do exceptionally well. If a submission is rejected, ask for feedback or a score breakdown. Then, you may be able to see what areas need improvement for the future. Read our post on grant writing best practices for more on how to evaluate your past proposals.
Wrapping Things Up: Successful Grant Proposal Examples

Grant writing is a skill that anyone can learn. And as you begin to build your skills and prepare to write your next proposal, let these examples of successful grant proposals act as a guide to successful grant writing. Don’t however mistake a useful example as the ultimate guide to winning a grant for your organization.
Make sure to keep your unique mission, vision, and voice in the proposal!
Are you ready to get started?
Try Instrumentl free for 14-days now to start finding funders that fit your organization’s needs. Our unique matching algorithm will only show you active open grant opportunities that your nonprofit can apply for so you can start winning more grant funding.
Instrumentl's Tracker makes saving all your grant proposals to one place easy and encourages more collaboration across your team. To get started, click the button below.
Instrumentl team
Instrumentl is the all-in-one grant management tool for nonprofits and consultants who want to find and win more grants without the stress of juggling grant work through disparate tools and sticky notes.
Become a Stronger Grant Writer in Just 5 Minutes
Share this article, related posts, 5 tips for using ai to write grants: 4 experts putting it to the test.
These days, it feels like Artificial Intelligence (AI) is everywhere. We spoke to four industry experts to learn how they are—or are not—using AI to support their grant-seeking efforts.
How to Make Your Letter of Inquiry Stand Out To Funders
Learn how to write compelling Letters of Inquiry (LOIs) with practical advice from grant experts. Discover essential tips from recorded events with Arnisha Johnson and Margit Brazda Poirier to increase your chances of success in securing funding for your nonprofit.
These Grant Writers Raised Millions: Tactics They Swear By To Win Over Funders
Unlock the secrets to becoming a game-changing grants professional with insights from industry experts who have secured millions in funding. Learn from their years of experience.
Try Instrumentl
The best tool for finding & organizing grants
128 reviews | High Performer status on g2.com

Jump to navigation
Search form

Tips for Developing a Training Grant Proposal
Training grants tips.jpg.

Research Development Services (RDS)
—TUCSON, AZ—
Follow these steps, and you'll be well on your way to developing a successful training grant proposal!
- Utilize the RDS Training Grants Resources website
- Heed the following advice from current training grant principal investigators:
"Go for training grants in areas you're passionate about. Writing these things is truly a labor of love. Make sure it's a need you feel comfortable filling whether or not you're an expert in that area." — Michael Johnson , Associate Professor of Immunobiology and and PI for NSF-funded National Summer Undergraduate Research Project (NSURP) "Be sure to put together a community of people as excited as you are about the project, and don't just focus on the science but also think about people who will reinforce connections and keep things running in the day-in, day-out tasks." — Heather Ingram , Program Manager for NSF-funded Building Resources for Interdisciplinary Training in Genomic and Ecosystem Sciences (BRIDGES) "I'd recommend finding a co-PI. My co-PI and I are very different people, but we work well together. It's amazing how, when one of us has a hyper-crazy schedule, the other can fill in." — Scott Saleska , Professor of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and PI for NSF-funded Building Resources for Interdisciplinary Training in Genomic and Ecosystem Sciences (BRIDGES) "Talk to the agency about the grants you're interested in. NIH is surprisingly approachable, and talking with them goes a long way to hone your ideas into something they'll actually fund." — Felicia Goodrum , Professor of Immunobiology and PI of Infection and Inflammation as Drivers of Aging (IIDA) , funded by NIH National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) "Talk to at least three people on campus who have training grants; they're all listed on the new website. Then, come talk to us at the Office of Diversity and Inclusion in the graduate college. One of our university's strengths that interests funding agencies is its support of diverse students. We're still a work in progress, but we do much better than most of the top 30 public schools. We can give you information to emphasize that in your proposal."— Frans Tax , Molecular and Cellular Biology Professor and PI for NIH-funded Initiative for Maximizing Student Development (IMSD) "Make sure real-life, hands-on work is an essential part of the training." — Kevin Fitzsimmons , Researcher and Professor of Environmental Science and PI for USDA-funded Preparing Hispanic and other Underrepresented Students in Fisheries and Aquaculture Read " Principal investigators share the unique significance and challenges of training grants " for more from UArizona training grant PIs.
Subscribe to the UArizona Impact in Action newsletter to receive featured stories and event info to connect you with UArizona's research, innovation, entrepreneurial ventures, and societal impacts.
Subscribe now
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PMC10250258

How to write a successful grant application: guidance provided by the European Society of Clinical Pharmacy
Anita e. weidmann.
1 Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Innsbruck University, Innsbruck, Austria
Cathal A. Cadogan
2 School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland
Daniela Fialová
3 Department of Social and Clinical Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy in Hradec Králové, Charles University, Hradec Králové, Czech Republic
4 Department of Geriatrics and Gerontology, 1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic
Ankie Hazen
5 Julius Centre for Health Sciences and Primary Care, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Martin Henman
6 Trinity College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland
Monika Lutters
7 Kantonsspital Aarau, Aarau, Switzerland
Betul Okuyan
8 Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Marmara University, Istanbul, Turkey
Vibhu Paudyal
9 University of Birmingham, Birmingham, United Kingdom
Francesca Wirth
10 Department of Pharmacy, University of Malta, Msida, Malta
Considering a rejection rate of 80–90%, the preparation of a research grant is often considered a daunting task since it is resource intensive and there is no guarantee of success, even for seasoned researchers. This commentary provides a summary of the key points a researcher needs to consider when writing a research grant proposal, outlining: (1) how to conceptualise the research idea; (2) how to find the right funding call; (3) the importance of planning; (4) how to write; (5) what to write, and (6) key questions for reflection during preparation. It attempts to explain the difficulties associated with finding calls in clinical pharmacy and advanced pharmacy practice, and how to overcome them. The commentary aims to assist all pharmacy practice and health services research colleagues new to the grant application process, as well as experienced researchers striving to improve their grant review scores. The guidance in this paper is part of ESCP’s commitment to stimulate “ innovative and high-quality research in all areas of clinical pharmacy ”.
Writing research grants is a central part of any good quality research. Once a detailed research proposal has been submitted, it is subjected to an expert peer review process. Such reviews are designed to reach a funding decision, with feedback provided to improve the study for this and any future submissions. Depending on the length of the proposal, complexity of the research and experience of the research team, a proposal can take between six to twelve months to write [ 1 ]. Ample time must be given to the writing of hypothesis/research aim, budgeting, discussion with colleagues and several rounds of feedback [ 2 ]. The draft research proposal should always be completed well before the deadline to allow for last minute delays. An application which is not fully developed should not be submitted since it will most likely be rejected [ 3 ].
Despite the large effort that goes into each grant application, success rates are low. Application success rates for Horizon 2020 were < 15% [ 4 ] and < 20% for the National Institute of Health (NIH) [ 5 – 8 ]. With these statistics in mind, it is evident that often repeated submissions are required before securing funding. Due to a paucity of specific clinical pharmacy grant awarding bodies, writing a grant application for a clinical pharmacy or pharmacy practice research project often involves multidisciplinary collaborations with other healthcare professions and focus on a specific patient population or condition. There is no guarantee of success when trying to secure funding for research. Even the most seasoned researchers will have applications rejected. The key is to never give up. This commentary provides useful pointers for the planning and execution of grant writing.
Conceptualising your research idea
Before writing a research grant proposal/application, consider what the research should achieve in the short, medium, and long term, and how the research goals will serve patients, science and society [ 9 , 10 ]. Practical implications of research, policy impact or positive impact on society and active patient/public involvement are highly valued by many research agencies as research should not be conducted “only for research”, serving the researchers’ interests. EU health policy and action strategies (CORDIS database) and other national strategies, such as national mental health strategy for grants within mental disorders, should be considered, as well as dissemination strategies, project deliverables, outcomes and lay public invitations to participate. The Science Community COMPASS has developed a useful “Message Box Tool” that can help in the identification of benefits and solutions, as well as the all-important “So What?” of the research [ 11 ]. Clearly determine what the lead researcher’s personal and professional strengths, expertise and past experiences are, and carefully select the research team to close these gaps [ 12 – 14 ].
How to find the right funding call
When trying to identify the right type of grant according to the research ambitions, one should be mindful that several types of grants exist, including small project grants (for equipment, imaging costs), personal fellowships (for salary costs, sometimes including project costs), project grants (for a combination of salary and project costs), programme grants (for comprehensive project costs and salary for several staff members), start-up grants and travel grants [ 15 ]. Types of grants include EU grants (e.g. Horizon, Norway Grant), commercial grants (e.g. healthcare agencies and insurance companies), New Health Program grants ideal for new, reimbursed clinical pharmacy service projects and national grants (e.g. FWF (Austria), ARRS (Slovenia), NKFIH (Hungary), NCN (Poland), FWO (Belgium), HRZZ (Croatia), GAČR (Czech Republic), SNSF (Switzerland), SSF (Sweden). It is worth remembering that early career researchers, normally within ten years of finishing a PhD, have a particular sub-category within most grants.
Many national agencies only have one “Pharmacy” category. This results in clinical pharmacy and advanced clinical pharmacy practice projects competing with pharmaceutical chemistry, pharmaceutical biology and pharmacy technology submissions, thereby reducing the success rate as these research areas can often be very advanced in most EU countries compared to clinical and advanced pharmacy practice. A second possible submission category is “Public Health”. Several essential factors can impact the grant selection, such as research field, budget capacity, leading researcher’s experience and bilateral grants. Examples of successful clinical pharmacy funded research studies can be found in the published literature [ 16 – 20 ].
Plan, plan, plan
One key element of successful grant writing is the ability to plan and organise time. In order to develop a realistic work plan and achieve milestones, it is imperative to note deadlines and to be well-informed about the details of what is required. The development of a table or Gantt Chart that notes milestones, outcomes and deliverables is useful [ 21 ].
All funders are quite specific about what they will and will not fund. Research your potential funders well in advance. It is vital to pay attention to the aims, ambitions and guidelines of the grant awarding bodies and focus your proposal accordingly. Submitting an application which does not adhere to the guidelines may lead to very early rejection. It is helpful to prepare the grant application in such a way that the reviewers can easily find the information they are looking for [ 15 , 22 ]. This includes checking the reviewers’ reports and adding “bolded” sentences into the application to allow immediate emphasis. Reviewers’ reports are often available on the agencies’ websites. It is extremely useful to read previously submitted and funded or rejected proposals to further help in the identification of what is required in each application. Most funding agencies publish a funded project list, and the ‘Centre for Open Science (COS) Database of Funded Research’ enables tracking of funding histories from leading agencies around the world [ 23 ]. Another useful recommendation is to talk to colleagues who have been successful when applying to that particular funder. Funding agency grant officers can provide advice on the suitability of the proposal and the application process.
It is important to pay particular attention to deadlines for the grant proposal and ensure that sufficient time is allocated for completion of all parts of the application, particularly those that are not fully within one’s own control, for example, gathering any required signatures/approvals. Funders will generally not review an application submitted beyond the deadline.
Lastly, it is important to obtain insight into the decision process of grants. Research applications are sent to several reviewers, who are either volunteers or receive a small compensation to judge the application on previously determined criteria. While the judging criteria may vary from funder to funder, the key considerations are:
- Is there a clear statement of the research aim(s)/research question(s)/research objective(s)?
- Is the proposed research “state-of-the-art” in its field and has all relevant literature been reviewed?
- Is the method likely to yield valid, reliable, trustworthy data to answer question 1.?
- If the answer to the second question is ’yes’, then what is the impact of financing this study on patient care, professional practice, society etc.?
- Is there sufficient confidence that the research team will deliver this study on time with expected quality outputs and on budget?
- Does the study provide value for money?
How to write
The key to good grant proposal writing is to be concise yet engaging. The use of colour and modern web-based tools such as #hashtags, webpage links, and links to YouTube presentations are becoming increasingly popular to improve the interest of a submission and facilitate a swift decision-making process. Ensure use of the exact section headings provided in the guidance, and use the keywords provided in the funding call documentation to reflect alignment with the funding bodies’ key interests. Attention to detail cannot be overstated; the quality and accuracy of the research proposal reflect the quality and accuracy of the research [ 24 ]. Try to adopt a clear, succinct, and simple writing style, making the grant easy to read. Having a clear focus can help to boost a grant to the top of a reviewer’s pile [ 25 , 26 ]. A clearly stated scientific question, hypothesis, and rationale are imperative. The reviewer should not have to work to understand the project [ 27 ]. Allow for plenty of time to incorporate feedback from trusted individuals with the appropriate expertise and consider having reviews for readability by non-experts.
What to write
Abstract, lay summary and background/rationale.
Take sufficient time to draft the scientific abstract and summary for the lay public. These should clearly state the long-term goal of the research, the aim and specific testable objectives, as well as the potential impact of the work. The research aim is a broad statement of research intent that sets out what the project hopes to achieve at the end. Research objectives are specific statements that define measurable outcomes of the project [ 28 , 29 ].
The lay summary is important for non-subject experts to quickly grasp the purpose and aims of the research. This is important in light of the increased emphasis on patient and public involvement in the design of the research. The abstract is often given little attention by the applicants, yet is essential. If reviewers have many applications to read, they may form a quick judgement when reading the abstract. The background should develop the argument for the study. It should flow and highlight the relevant literature and policy or society needs statements which support the argument, but at the same time must be balanced. It should focus on the need for the study at the local, national and international level, highlighting the knowledge gap the study addresses and what the proposed research adds. Ensure this section is well-referenced. The innovation section addresses the ‘‘So what?’’ question and should clearly explain how this research is important to develop an understanding in this field of practice and its potential impact. Will it change practice, or will it change the understanding of the disease process or its treatment? Will it generate new avenues for future scientific study? [ 30 ].
Hypothesis/aims and objectives
For the hypothesis, state the core idea of the grant in one or two sentences. It should be concise, and lead to testable specific aims. This section is fundamental; if it is unclear or poorly written, the reviewers may stop reading and reject the application. Do not attempt to make the aims overly complex. Well-written aims should be simply stated. Criteria such as PICO (population, intervention, comparison, outcomes) [ 31 ], and FINER (feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, relevant) [ 32 ], provide useful frameworks to help in writing aim(s), research question(s), objective(s) and hypotheses. Pay attention to the distinction between aim(s), research question(s), objective(s) and hypotheses. While it is tempting to want to claim that enormously complex problems can be solved in a single project, do not overreach. It is important to be realistic [ 25 ].
Experimental design, methods and expertise
The methodology is one of the most important parts of getting a grant proposal accepted. The reviewing board should be convinced that the relevant methodology is well within the research teams’ expertise. Any evidence of potential success, such as preliminary results or pilot studies strengthen the application significantly [ 33 ]. The methodology must relate directly to the aim. Structuring this section into specific activities/ set of activities that address each research question or objective should be considered. This clarifies how each question/ objective will be addressed. Each work-package should clearly define the title of the research question/objective to be addressed, the activities to be carried out including milestones and deliverables, and the overall duration of the proposed work-package. Deliverables should be presented in table format for ease of review. Each subsequent work-package should start once the previous one has been completed to provide a clear picture of timelines, milestones and deliverables which reflect stakeholder involvement and overall organisation of the proposed project. Using relevant EQUATOR Network reporting guidelines enhances the quality of detail included in the design [ 34 ]. Key elements of this methodology are detailed in Table 1 .
Summary of the key elements of the experimental design, methods and expertise
Proposed budget
The budget should be designed based on the needs of the project and the funding agency’s policies and instructions. Each aspect of the budget must be sufficiently justified to ensure accountability to the grant awarding body [ 35 ]. Costing and justification of the time of those involved, any equipment, consumables, travel, payment for participants, dissemination costs and other relevant costs are required. The funders will be looking for value for money and not necessarily a low-cost study. Ensure that the total budget is within the allocated funding frame.
Provide a breakdown of the key work packages and tasks to be completed, as well as an indication of the anticipated duration. Include a Gantt chart (A table detailing the most general project content milestones and activities) to demonstrate that all aspects of the proposal have been well thought through [ 21 ].
Critical appraisal, limitations, and impact of the proposed research
It is important to detail any strengths and limitations of the proposed project. Omitting these will present the reviewing board with sufficient grounds to reject the proposal [ 36 ]. Provide a clear statement about the short and long-term impact of the research [ 37 , 38 ]. The reviewers will pay particular attention to the differences the study can make and how potential impact aligns with the funding bodies goals as well as national policies. This statement is essential to make an informed decision whether or not to support the application. Useful diagrams summarise the different levels of impact [ 39 ].
Table 2 provides a summary of the key elements of project grants and key questions to ask oneself.
Summary of the key elements of project grants and key questions to ask oneself.
(Adapted from [ 5 ]: Koppelmann GH, Holloway JW. Successful grant writing. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2012; 13:63–66.)
Although the grant writing process is time-consuming and complex, support is widely available at each stage. It is important to involve colleagues and collaborators to improve the proposal as much as possible and invest time in the detailed planning and execution. Even if the grant is not awarded, do not be disheartened. Use the feedback for improvement and exercise resilience and persistence in pursuing your research ambition.
The guidance in this paper is part of ESCP’s commitment to stimulate “innovative and high-quality research in all areas of clinical pharmacy”. In a previous ESCP survey, it was found that few opportunities for collaboration (especially for grant applications) was one of the key barriers for members towards conducting research [ 40 ]. ESCP promotes networking, which is essential for multi-centre grant applications, both among ESCP members and with other organisations as it recognises the need for “multi-centre research in all areas of clinical pharmacy both within countries and between countries or differing healthcare delivery systems”. ESCP is planning to relaunch its own research grant which was paused during the pandemic, and it is also planning to provide ESCP members with information about the research grants offered by other organizations. ESCP is exploring partnering with other organisations to develop research proposals in areas of common interest and, in the near future, it will ask its members about their research priorities. Taken together, these initiatives will inform ESCP’s research strategy and help it to formulate policies to address the challenges its members face.
Acknowledgements
Research works of Assoc. Prof. Fialová were also supported by the institutional program Cooperation of the Faculty of Pharmacy, Charles University.
Open access funding provided by University of Innsbruck and Medical University of Innsbruck. This work was conducted without external funding.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Report on “Writing successful project proposals – 2024”

photo: Mandy Kong
The CHESS workshop “From idea to project: Writing successful project proposals” was held on 9. – 10. April 2024. A total of 16 participants joined the workshop, coming from the universities of Bergen and Tromsø, and NORCE Climate and Environment.
The main objective of the workshop was to enable early-career climate scientists to successfully apply for external funding for their research, by gaining competences to plan, write, and submit a successful research project proposal. Participants gained knowledge about the different components of a project proposal, and about the most relevant funding sources for early career climate scientists. They obtained skills to present a project idea shortly and concisely (pitching), to develop the different components of a project description, to plan and structure the project description, and to draft a project budget. The newly generated knowledge and skills should enable the participants to independently write a project proposal, and to identify relevant funding opportunities.

photo: Nina Hecej
The workshop included lectures, group work and plenary discussion. At the beginning of the workshop, six participants pitched their project ideas. All participants then selected three of these ideas to be developed step by step into draft proposals in group work during the workshop. Results from each group work were presented in plenary, and the other groups provided peer feedback. Background knowledge about the respective proposal sections and instructions to develop them during group work were given by the instructors in plenary lectures.
Several measures were taken to enable a smooth workflow during group work: The group developed the work tasks using an online document with templates and instructions which was also used for plenary presentation. To facilitate active participation of all group members, they took specific roles such as note keeper, presenter, and time-keeper which they swapped for each group work session. One instructor joined the group work to answer questions and to moderate the work if necessary. New to this year’s workshop was the practice of peer reviewing. After being given instructions on how to give constructive feedback, each group got to discuss the work presented by another group and then provide their consensus feedback to that group. The instructors also provided feedback.

The three participants whose ideas were chosen for development into draft proposals, confirmed that their ideas were developed substantially during the workshop, and felt confident to submit them as full research project proposals within the coming year. The participants who presented a pitch which was not selected felt confident to apply the skills obtained during the workshop to develop their own project ideas. The other participants felt as well that they had obtained the skills and competence necessary to develop research ideas into proposals. The feedback from the participants was very positive, both during, directly after the workshop and in the workshop evaluation.
Text: Friederike Hoffmann, Nadine Goris and Mahaut de Vareilles
Post navigation

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Abstract. The abstract is a summary of your research proposal. It should be around 150 to 200 words and summarize your aims, the gap in literature, the methods you plan to use, and how long you might take. 2. Literature Review. The literature review is a review of the literature related to your field.
Writing successful grant applications is a long process that begins with an idea. Although many people think of grant writing as a linear process (from idea to proposal to award), it is a circular process. Many people start by defining their research question or questions.
4 Tips for Writing a Persuasive Grant Proposal; Writing Effective Grant Applications; 7 Tips for Writing an Effective Grant Proposal; The best-kept secrets to winning grants; The Best Grant Writing Books for Beginner Grant Writers; Research Grant Proposal Funding: How I got $1 Million; Final thoughts. The bottom line - applying for grants is ...
Create your grant proposal. Create, send and eSign your grant proposals. Receive automatic follow-up reminders to keep the conversation going. Start a free trial. Step 1. Write a strong cover letter. Your cover letter is the perfect opportunity to capture the funder's attention and get your foot in the door.
Writing is hard, and experienced grant writers recommend devoting plenty of time to the task. Smythe recommends setting aside a week for each page of a proposal, noting that some applications ...
Step 2: Plan and research your project. Preliminary research for your grant proposal. Questions to ask yourself as you plan your grant proposal. Developing your grant proposal. Step 3: Write the first draft of your grant proposal. Step 4: Get feedback, and revise your grant proposal accordingly.
Give yourself at least 4-6 months to put your proposal together. To increase your chances of success, before you begin drafting your grant proposal, you need to develop a SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and anchored within a Timeframe) plan for what you want to do and why you want to do it.
Writing a grant proposal is not something to be undertaken alone. Even the most seasoned of researchers will need advice, guidance and constructive criticism from trusted and experienced colleagues when developing new grant proposals. For many junior researchers, a supervisor will be the appropriate person to provide this support.
To be successful, a grant proposal must clearly articulate the research question or problem, the methodology to be employed, the expected outcomes, and how these outcomes will contribute to the field. It should also include a detailed budget, outlining how the grant funds will be utilized. This budget must be both realistic and justifiable, as ...
The executive summary of a grant proposal goes into far more detail than the cover letter. Here, you'll give. What to include: Statement of Need overview, in 2 - 5 sentences. Company Bio and Qualifications, in 2 - 5 sentences. Objectives, in 2 - 5 sentences. Evaluation and Expected Impact, in 2 - 5 sentences.
Unfortunately, grant writing is generally considered very difficult, more so than the actual research. In this post, we will discuss how to write a grant proposal. 10 characteristics of an effective scientific research grant proposal. Aims to advance science and benefit human knowledge, society, or the environment; Has focused and measurable aims
Abstract. This article aims to provide a step-by-step overview of the process of applying for research funding and will be most relevant to either a new academic joining a group or a young clinician wanting to establish their own research. The article covers the steps involved in preparing, writing and submitting an application.
Developing a grant application can feel daunting at first, but with practice and good support, becomes easier with experience. 1. Get Visible - The Sooner, the Better! It's a good idea to start building up your profile within academia early on. Make use of all the resources available to you to showcase yourself, your research, and your ...
Writing a successful research grant proposal requires that you attend to every detail, which means you need a plan. Remember, you are telling a story through your written grant application. Therefore, every part of the grant proposal must work together, with nothing extra to distract the reader. This requires detailed planning. The core of a ...
a successful grant proposal and presents specific examples for new business ventures Outcome: Readers will understand the necessary steps in writing a successful grant proposal. Introduction For many people, applying for a grant is a mysterious process. You may have the feeling that those who are successful and
SpencerFoundation. Writing Successful Research Grant Proposals. Resources. Spencer staff have put together a guide with helpful information on writing a successful field-initiated research grant proposal. View / Download (PDF) Browse Our Resources and Tools. Resources. 07/11/2023. Writing Proposals That Engage Research With Youth, Families, and ...
How to Write a Successful Grant. Writing a grant application is a demanding process, especially in the current environment of historically low funding levels. 1 The current funding rate of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute is 10%, compared with ≈30% funding rate in 2001. When preparing a grant application, the 5 criteria that reviewers will use to score the grant (ie ...
Getting Started: The Concept Paper. The most universal advice on writing a successful grant proposal is to present a well written, focused solution to a problem in a logical progression. This is much easier said than done, and finding the focus is often the most difficult piece of the puzzle. To find this focus, we suggest writing a "concept ...
Writing a grant proposal is not something to be undertaken alone. Even someone with prior experience in developing grant proposals will need advice, guidance and constructive criticism from trusted and experienced colleagues. For many junior researchers, a supervisor will be the appropriate person to provide this support.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use" Title page
This sample proposal provides an extensive template to follow for writing a successful conference grant proposal. The proposal follows an easily understood, structured narrative, and includes a detailed budget and key personnel profiles that will help anyone applying for grant support strengthen their chances of developing a high-quality ...
For multi-centric grants different organizations may have different roles and responsibilities. 9. Be prepared as time from call for proposal to last date may only be 1-2 weeks. 10. Have a maximum of three to four research objectives in the grant application. 11. Detail the preliminary work like that of a publication.
Friday. Research Development Services (RDS) —TUCSON, AZ—. Follow these steps, and you'll be well on your way to developing a successful training grant proposal! Utilize the RDS Training Grants Resources website. Heed the following advice from current training grant principal investigators: "Go for training grants in areas you're passionate ...
Conceptualising your research idea. Before writing a research grant proposal/application, consider what the research should achieve in the short, medium, and long term, and how the research goals will serve patients, science and society [9, 10].Practical implications of research, policy impact or positive impact on society and active patient/public involvement are highly valued by many ...
The CHESS workshop "From idea to project: Writing successful project proposals" was held on 9. - 10. April 2024. A total of 16 participants joined the workshop, coming from the universities of Bergen and Tromsø, and NORCE Climate and Environment. The main objective of the workshop was to enable early-career climate scientists to ...