We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Template Lists
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business

8 Best Business Plan Software for 2024
By Krystle Wong , Jan 01, 2024

Gone are the days of staring at blank pages and struggling to structure a business plan effectively. With user-friendly interfaces and a wide range of business plan templates catering to various industries, creating business plans that are polished, professional and data-driven can now be done in a fraction of the time.
For startups, business plan software guides them through the crucial early stages with comprehensive business plan templates and financial modeling tools. Established businesses on the other hand benefit from the software’s collaborative features, enabling seamless teamwork as they pivot, innovate and pursue new growth opportunities.
In this article, let’s delve into exploring the seven best business plan software for 2024. Whether you’re an aspiring entrepreneur with a groundbreaking idea or a seasoned business owner ready to elevate your enterprise to new heights, these software solutions have all you need to create a solid business plan.
Click to jump ahead:
What is a business plan software?
- 7 Best business plan software for 2024
Factors to consider when choosing a business plan software
7 steps to create your own business plan, business plan software faq, key takeaway.
A Business plan software is a specialized digital tool designed to assist entrepreneurs, startups and established businesses in creating, organizing and presenting comprehensive business plans.
Business plan software significantly reduces the time and effort required to create a comprehensive business plan . The availability of business plan templates, financial modeling tools and automated features streamlines the process of business planning and eliminates the need for starting from scratch.
Some advanced business planning software even integrates market research capabilities. This feature provides users with access to market trends, industry benchmarks and relevant data. Access to such data helps users make informed decisions and demonstrate a thorough understanding of their target market.
8 Best business plan software for 2024
1. venngage.

Venngage specializes in transforming traditional business plans into captivating visual stories. Visuals can communicate complex information effectively, ensuring your ideas stand out and resonate with your audience.
When it comes to business planning, conveying your ideas with impact is just as important as the content itself. In this digital age, visual storytelling has emerged as a powerful way to captivate audiences and leave a lasting impression. That’s where Venngage steps in.
With a rich library of templates, Venngage offers a variety of themes and styles to suit different industries and business types. Customize your business plans with our user-friendly drag-and-drop tools by adding your brand elements, customizing colors, fonts and visuals to make your business plan truly unique. Check out our library of sample business plans to get started today.
However, while Venngage excels in visual storytelling, it might not be the go-to tool for in-depth financial forecasts and analysis. Users seeking extensive financial modeling might want to complement Venngage with a comprehensive business planning tool.
Pricing options:
Create your first 5 designs with Venngage for free and upgrade to a premium or business plan for $10/month per user and $24/month per user respectively to enjoy premium features. For larger teams who need extra support, controls and security, the enterprise plan starts from $499/month for 10+ seats.
Can I collaborate with team members using this business plan software?
Yes, absolutely! Venngage offers collaborative features that allow you to work seamlessly with multiple team members when creating business plans. You can invite team members to join your Venngage account and they can contribute to the design process in real time.
Can I export my business plan to different file formats?
Upgrade to a premium or business plan on Venngage to export your professional business plan to different file formats. After designing your business plan, you can choose to export it as a high-quality PDF document, which is ideal for sharing and printing. Additionally, Venngage allows you to export your business plan as an image file (PNG or JPG), making it easy to use in presentations or on your website.
Is this business plan software suitable for startups or established businesses?
Venngage is great for entrepreneurs and businesses looking to enhance their business plans with visually engaging infographics and visual assets.
Instead of sharing a lengthy, 50-page document that may bore your audience and fail to effectively convey your message — present your business plan with infographics. Here’s how you can create a business plan infographic that will wow your readers and showcase your business at its best.
2. LivePlan

Source: Screenshot from LivePlan
In the realm of business planning software, LivePlan stands out as a reliable and user-friendly tool. With a focus on seamless financial forecasting and budgeting capabilities, LivePlan streamlines the planning process, helping businesses transform their visions into reality.
The software’s financial forecasting tools provide users with the ability to project revenue, expenses and cash flow accurately. This financial insight is invaluable for making informed decisions and setting realistic goals.
For hassle-free data integration, the business plan software offers seamless integration with accounting software . This feature allows users to import financial data effortlessly, saving time and reducing manual data entry.
While LivePlan excels in financial planning and user-friendliness, some users may find the customization options for design and layout to be limited. For businesses seeking highly tailored visual aesthetics, LivePlan’s template-based approach might be less ideal.
The standard plan is available at $20/month for monthly billing and $15/month for annual billing. For businesses seeking extensive financial tools to support their operations and growth, the Premium plan costs $20 for the first month and $40/month (monthly billing) or $30/month (annual billing) for subsequent months.
LivePlan facilitates seamless collaboration among users within your account, allowing multiple individuals to work on the same plan concurrently. To prevent conflicting edits, LivePlan restricts access to specific sections, allowing only one user to edit at a time while others observe the locked section.
You can export your business plan by using the print to PDF feature. This generates your plan content in a standard file format compatible with Adobe Reader and other free reader programs. Alternatively, you can export your plan to Microsoft Word (2007 or later).
A great tool for small businesses, startups and entrepreneurs looking for easy-to-use software with solid financial planning tools.
3. Upmetrics
Upmetrics is an AI-powered business planning software that helps businesses of all sizes and industries write their business plan.
With Upmetrics AI Assistant, you can write your plan faster, get answers to any business-related queries, and prepare financial forecasts in no time.
Besides, the subscription includes access to 400+ sample business plans, various informative guides, and video tutorials to keep your business plan writing process on track.
Additionally, it has collaborative features, so that everyone on the team can share their insights. Not just that, the software provides you with an AI pitch deck generator, so you can make a stellar pitch.
As an AI business plan builder , Upmetrics is suitable for entrepreneurs, startups, and small businesses to write their plans at any stage. Although it has various cover page designs and immense customization options, it might still lack visual appeal.
Pricing plan options
- Starter plan – $7 monthly
- Premium plan – $14 monthly
Yes, you can collaborate with your team members while using Upmetrics. It offers collaboration tools that allow you to work effortlessly with your team on the business plan. You can invite team members to collaborate, assign tasks, and track the progress together.
You can download your business plan as a PDF or directly as a document in Word. Besides, you can share the business plan directly to any email, and they will get the viewer access to the plan.
Upmetrics is a versatile business planning software suitable for startups and established businesses. But its financial planning features, step-by-step guidance, and AI Assistant make it more useful for startups writing business plans for the first time.
4. BizPlan by Startups.com

Source: Screenshot from BizPlan
If you’re a startup aiming to raise investments, BizPlan is the one for you. As a universal professional business plan builder, BizPlan offers the added advantage of seamless integration with all the tools within the Startups.com network.
Designed with startups in mind, BizPlan’s step-by-step approach allows you to break down the entire scope of work into manageable steps and the built-in Progress Tracker tool keeps you on track towards success.
Once you subscribe, BizPlan opens the door to utilizing all the tools offered by Startups.com, making it a one-stop shop for your entrepreneurial needs. Whether it’s lifetime access to the service, connectivity to Findable to attract financial investments, a wealth of online educational programs or the ability to connect multiple owners to a single account, BizPlan delivers comprehensive support.
While the business plan software offers an array of benefits, it’s essential to consider the possible downsides. The absence of a free version and a mobile app, along with a lack of industry-specific templates for business plans may be worth considering before making your decision
Pricing plan options:
- Monthly plan ($29 per month)
- Annual plan ($20.75 per month or $249/year)
- Lifetime access (one-time fee of $349)
Bizplan encourages collaboration with partners, team members, advisors and subject matter experts by allowing threaded comments throughout the entire plan. It provides control over who can access sensitive financial data and enables convenient cloud-based access from anywhere.
Bizplan provides multiple options for sharing your business plan with others. You can generate an online version of your plan, which can be set as private by default or made publicly accessible through a unique shareable URL. Additionally, Bizplan offers the option to create a custom-branded PDF of your business plan.
BizPlan is great for entrepreneurs and small businesses who value a vast collection of resources and need support in financial analysis.

Source: Screenshot from Enloop
Enloop emerges as one of the best business plan tools for startups, catering to entrepreneurs who crave a streamlined planning process. With the ability to automatically generate basic text for each section of your plan, Enloop saves time and effort in crafting your business vision.
A highlight of the business plan tool is its automatic generation of financial projections, offering accurate insights based on your entered data. This powerful feature empowers entrepreneurs to make informed decisions and project future outcomes with confidence.
For those with a penchant for strategic thinking, Enloop’s “what-if” scenario analysis becomes an invaluable tool. It allows users to explore various business strategies and assess their potential impact on plan outcomes, enabling sound decision-making.
Enloop doesn’t stop at generating numbers; it goes a step further by providing a business plan grading system. This insightful feature assesses plan quality, giving users valuable feedback to refine and enhance their business plans.
However, it’s essential to consider the software’s limitations as customization and design options are relatively limited. Additionally, the basic version of Enloop might not meet the needs of all users, as it lacks certain advanced features.
- Seven day free trial (no credit card required)
- Detailed plan ($19.95/month or $11/month when billed annually)
- Performance plan ($39.95/month or $24/month when billed annually)
Enloop’s online business plan writing app lets you invite and collaborate with anyone on your business plans using the ‘Invite & Share’ feature.
Enloop allows you to download your business plan in PDF format whenever you’re ready. The plans remain accessible in your paid account, encouraging regular updates to keep track of your business’s health and have an up-to-date plan ready for financing needs.
Suitable for entrepreneurs seeking a tool that simplifies financial forecasting and scenario analysis.
6. PlanGuru

Source: Screenshot from PlanGuru
PlanGuru’s standout feature lies in its ability to forecast all three financial statements – income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statement so that users can make data-driven decisions.
Creating detailed analyses becomes a breeze with PlanGuru’s general ledger import utilities, allowing seamless historical data import. The software facilitates budget vs actual reporting and enables building rolling forecasts with just a few clicks each month.
Unlimited budgeting flexibility is another advantage offered by the business plan builder. Users can craft simple high-level small business budgets or delve into intricate multi-department operating budgets with ease.
With scenario analysis capabilities, PlanGuru empowers users to interpret the financial impact of specific events accurately. This feature enables making critical investments and strategic decisions with confidence, knowing thorough due diligence has been performed.
Given its sophisticated features, PlanGuru may be more suitable for financial professionals and analysts looking for in-depth financial analysis and budgeting tools. Users not familiar with financial modeling may face a steeper learning curve when utilizing Enloop’s robust capabilities.
- Single entity ($99/month or $75/month when billed annually)
- Multi-department consolidations ($299/month or $225/month when billed annually)
You can add up to 3 users with the multi-department consolidation plan. Additionally, all plans allow you to add on $29/month (billed monthly) or $25/month (billed annually) for each extra user.
What other apps does PlanGuru integrate with?
The cloud-based platform is also accessible as a Windows-based desktop version, giving you the freedom to choose the format that suits you best. Additionally, PlanGuru seamlessly integrates with MS Excel, QuickBooks Online and Xero, providing further flexibility and convenience in using the software.
The cloud-based version is suitable for SMBs or nonprofits budgeting for a single entity while the multi-department consolidations plan is for companies with multiple departments needing consolidated budgets.
7. Business Sorter

Source: Screenshot from Business Sorter
With Business Sorter’s card sort system, crafting the foundation of your plan becomes a breeze. Featuring 273 cards covering various business situations, the business plan generator offers flexibility, allowing users to customize their plan by adding their cards or modifying existing ones, tailoring the plan to their specific needs.
The platform also provides the convenience of viewing your plan on any device, including smartphones, which not many business plan apps have. Additionally, guidance is at hand with Business Sorter as the software provides valuable tips and advice for every key step, empowering users to implement their business strategy with confidence.
While Business Sorter excels in its interactive features, it may not offer as extensive financial analysis tools as other business plan software. For businesses requiring advanced financial modeling capabilities, Business Sorter might not fully meet their requirements.
- For small teams with up to 3 users ($10/month or $80/year)
- For medium teams with up to 10 users ($30/month or $240/year)
- For large teams with up to 30 users ($80/month or $640/year)
- For enterprises with unlimited users (custom pricing)
Your business plan can be edited by only one user at a time. When a user opens a plan, it automatically locks to prevent any data loss and remains locked until the user finishes their work and exits the plan.
You can print each business plan directly from the plan summaries on your dashboard.
Suitable for both entrepreneurs and businesses looking for an interactive and visually appealing planning approach.
9. AchieveIt

Source: Screenshot from AchieveIt
AchieveIt stands as a versatile software for business plans, designed to simplify the planning process for businesses of all sizes and planning methods. With AchieveIt, you can easily build plans, ensuring alignment and engagement among your employees and optimizing plans for seamless execution.
Regardless of your preferred planning method, AchieveIt empowers you to construct plans effortlessly, providing a flexible solution for any planning use case. The software ensures your plans are well-aligned with your organization’s objectives, engaging all team members for successful plan execution.
The business plan tool provides robust tracking and reporting features, allowing businesses to monitor the progress of their plans and measure performance against set goals. Users can create customized dashboards to visualize key performance metrics, making it easier to identify trends and insights.
That said, In comparison to most business plan software, AchieveIt’s pricing might be relatively higher with its extensive features. On top of that, for users new to strategic planning software, AchieveIt may present a learning curve during the initial adoption phase.
The business plan software packages for AchieveIt varies based on factors like organization size, required functionality and the number of users. AchieveIt being an enterprise-level software offers custom pricing to cater to the specific needs of each business. For accurate pricing details, it’s best to contact their sales or customer support team.
AchieveIt allows team members, stakeholders and advisors to have shared access to the platform, providing them with visibility into the latest updates and progress on the plans. Users can assign tasks to team members and track their progress within the platform.
Can AchieveIt integrate with existing systems?
AchieveIt’s Data Integration API lets you import key metric data from existing systems, saving time and reducing errors by eliminating the need for data entry in multiple places.
AchieveIt is best suited for medium to large-sized businesses and organizations that require a comprehensive and collaborative strategic planning platform. It caters to teams and enterprises seeking to improve their planning processes, track performance and drive organizational alignment to achieve business objectives effectively.
No idea what your business plan should look like? Check out these business plan examples for inspiration.
When searching for the best business planning software, you may be wondering — what features should I look for in business plan software? You want to make sure it meets your specific requirements and streamlines the planning process effectively. Here are the top six factors to consider:
Ease of use
The software should have a user-friendly interface that simplifies the process of creating a business plan. Look for intuitive navigation, clear instruction and a layout that makes it easy to input and organize your information.
Features and business plan templates
Check the range of features and business plan templates the software offers. Look for a diverse selection of business plan templates catering to various industries and business types. The software should provide essential sections like executive summaries, market analysis, financial projections and more.
Financial modeling tools
Your business plan software should allow you to input financial data and generate accurate and comprehensive financial projections. These business plan creation tools are vital for assessing the financial viability of your business.
Collaboration and sharing
If you’ll be working with a team or seeking feedback from others, consider software that enables real-time collaboration and easy sharing. The ability to work together seamlessly can enhance productivity and improve the quality of your business plan.
Built for fast-moving teams that need to be on the same page, Venngage’s real-time collaboration enables you to polish your design with your team in real time, leave comments on each other’s work,and save your designs in one shared folder. With your Venngage Business account, you can easily invite and manage your team members to collaborate on a design, all in real time.
Security and data protection
Since a business plan contains sensitive information, prioritize software that prioritizes security. Ensure that the software uses encryption and data protection measures to keep your data safe from unauthorized access.
Exporting and sharing options
Check the software’s export options. You’ll likely want to share your business plan with others, so ensure it can be exported in popular formats like PDF or PowerPoint.
Are you an entrepreneur starting a new business or expanding your existing business? This guide on how to create a small business plan might come in handy for you.

Creating business plans can be a crucial step in setting your entrepreneurial vision on the right track. To help you through the process, here are 7 steps to guide you in crafting a comprehensive business plan:
Step 1: Executive summary
Start with an attention-grabbing executive summary. This section provides an overview of your business. In your executive summary, make sure to highlight your mission, goals, products or services, target market and the unique value you offer. Keep it concise, yet compelling.

Step 2: Company description
Give a detailed description of your company. Explain your business’s history, its legal structure (e.g. sole proprietorship, LLC, corporation) and the reasons why your business will succeed in the market.

Step 3: Market analysis
Conduct thorough market research to understand your industry, target market and competition. Identify your ideal customers, their needs and preferences. Analyze your competitors and highlight your competitive advantages.
Step 4: Products and Services
Describe your products or services in depth. Explain their features, benefits and how they meet the needs of your target customers. Emphasize what sets your offerings apart from the competition.

Step 5: Marketing and sales strategy
Outline your marketing and sales strategies to reach your target audience. Explain your promotional activities, pricing strategies, distribution channels and sales tactics. Detail how you plan to acquire and retain customers.
Step 6: Financial projections
Project your financial performance over the next three to five years. Include estimated revenue, expenses and cash flow. Detail your startup costs and funding requirements if applicable. Be realistic and supported by market research.
Step 7: Implementation plan
Create a detailed roadmap for executing your business plan. Set specific goals and milestones. Break down tasks and assign responsibilities. Include timelines and a plan for measuring progress.

A great tip here is to start with a well-structured outline. This guide on how to create a business plan outline will help you in creating your blueprint to easily identify your business’ resource needs, including finances, personnel and equipment.
Is my business data safe with business plan software?
Most reputable business plan software providers prioritize data security and employ encryption and other measures to keep your business data safe from unauthorized access.
What are the benefits of using business planning tools?
Business planning tools offer time efficiency, professional presentation, error reduction, collaborative features and accessibility, making it easier to create a comprehensive business plan that impresses investors and stakeholders.
Do I need any specific skills or expertise to use business plan software?
No, many business plan software solutions are designed to be user-friendly, requiring no specific skills or expertise. They often come with templates and step-by-step guidance to assist you through the planning process.
In the dynamic landscape of 2024, businesses are on the lookout for innovative tools to stay ahead of the curve and drive their growth. These 7 business plan software picks for 2024 offer a wide range of features, from user-friendly interfaces and real-time collaboration to sophisticated financial analysis tools and customizable dashboards.
Whether you’re looking for user-friendly platform business planning tools that aligns with your business planning processes or a business plan writing software that allows you to tailor the business plan according to your industry, goals and unique requirements — I’m quite certain I’ve got them all covered.
The value of these business plan software options lies not only in their efficiency but also in their ability to save time and reduce errors. By integrating with existing systems through Data Integration APIs, users can seamlessly import key metric data, eliminating redundant data entry and streamlining the process.
If you’re still unsure about which is the right business plan software for your business, you can always take advantage of free trials or video tutorials and demos offered by software providers. Testing the platform firsthand will give you a practical understanding of its usability and suitability for your business.
- Contact sales
Start free trial
How to Write a Business Requirements Document (BRD)

It’s easy to get lost in the weeds when you’re managing a project. There are day-to-day operations that the project manager obsesses over, but they also need to see the big picture. That’s why a business requirements document is so important.
To prove this point, let’s define what a business requirements document (BRD) is and what its components are. Plus, we’ll give you tips on how to write a better one before showing how project management software can make the process even more efficient.
What Is a Business Requirements Document?
A business requirements document offers an overview of what a business does and why it needs the project deliverable to be undertaken. It outlines the business solutions for project requirements that are necessary for the project to deliver value and becomes the foundation of the project’s life cycle.
The business requirements document highlights what the end result of the project should be. When a change request is introduced to the project, the business requirements document must be revised to reflect this change.
The main purpose of a BRD is to show what the system will look like from a business perspective. It includes both the business solution and the technical solution to the project. The business requirements document helps answer the question of what is needed for the business. It also answers how the project will be delivered and contains a prioritized list of features and business requirements that the delivered software, product or service must provide.
Think of the business requirements document as the defined steps you should follow to reach a result that serves both the customers and stakeholders for the delivered product, system or service. The project team is involved in this process to help determine how to implement the delivery of the project and fulfill what the business needs. Stakeholders are also involved and must agree on the plan before it’s implemented.
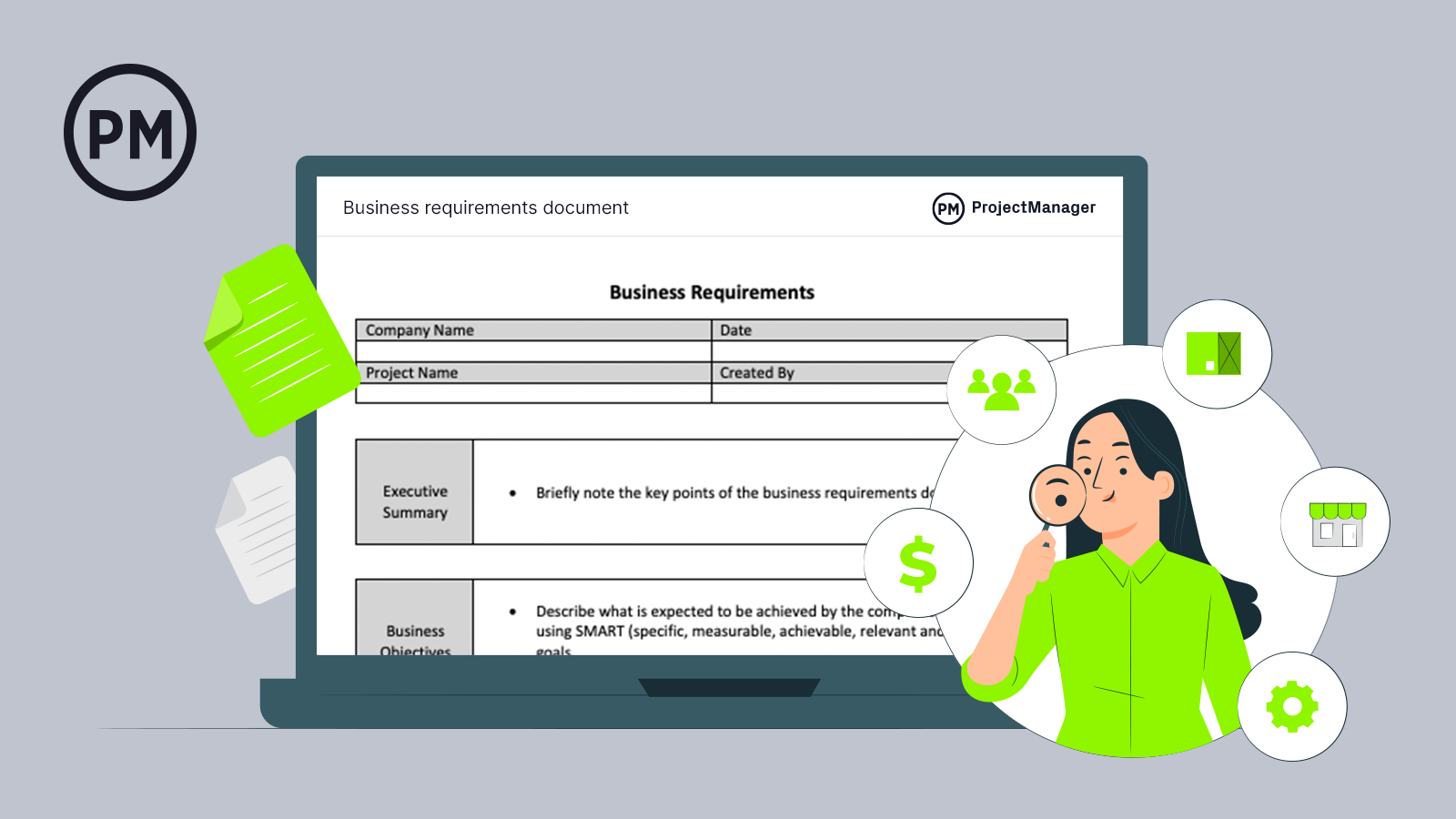
Get your free
Business Requirements Document Template
Use this free Business Requirements Document Template for Word to manage your projects better.
Business Requirements vs. Functional Requirements
It’s common to confuse business requirements with functional requirements. They’re both requirements, but they serve different purposes. To review, business requirements explain the final results of a business goal in the project and why the organization should initiate that project.
A business requirement isn’t about offering or proposing a solution, only defining the task at hand. This includes defining the short and long-term goals, the company vision and the scope of the business problem.
On the other hand, the functional requirement is about how a system needs to operate in order to achieve its business goal. It proposes subjective solutions based on the organization’s strengths and limitations as well as being technically focused. A functional requirement is also presented with a use case.
It’s not always easy to tell the difference between a business requirement and a functional requirement. Project activities can be both a business requirement and a functional requirement or even neither.
To accomplish this, you’ll need project management software that can organize tasks and connect the entire project team. ProjectManager is online project management software that delivers real-time data across multiple project views that lets everyone work how they want. Our interactive Gantt chart can be shared with teams and stakeholders as tasks are organized on a timeline. You can link dependent tasks, add milestones and filter for the critical path. Then, set a baseline and track your business requirements document in real time over the life cycle of the project. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
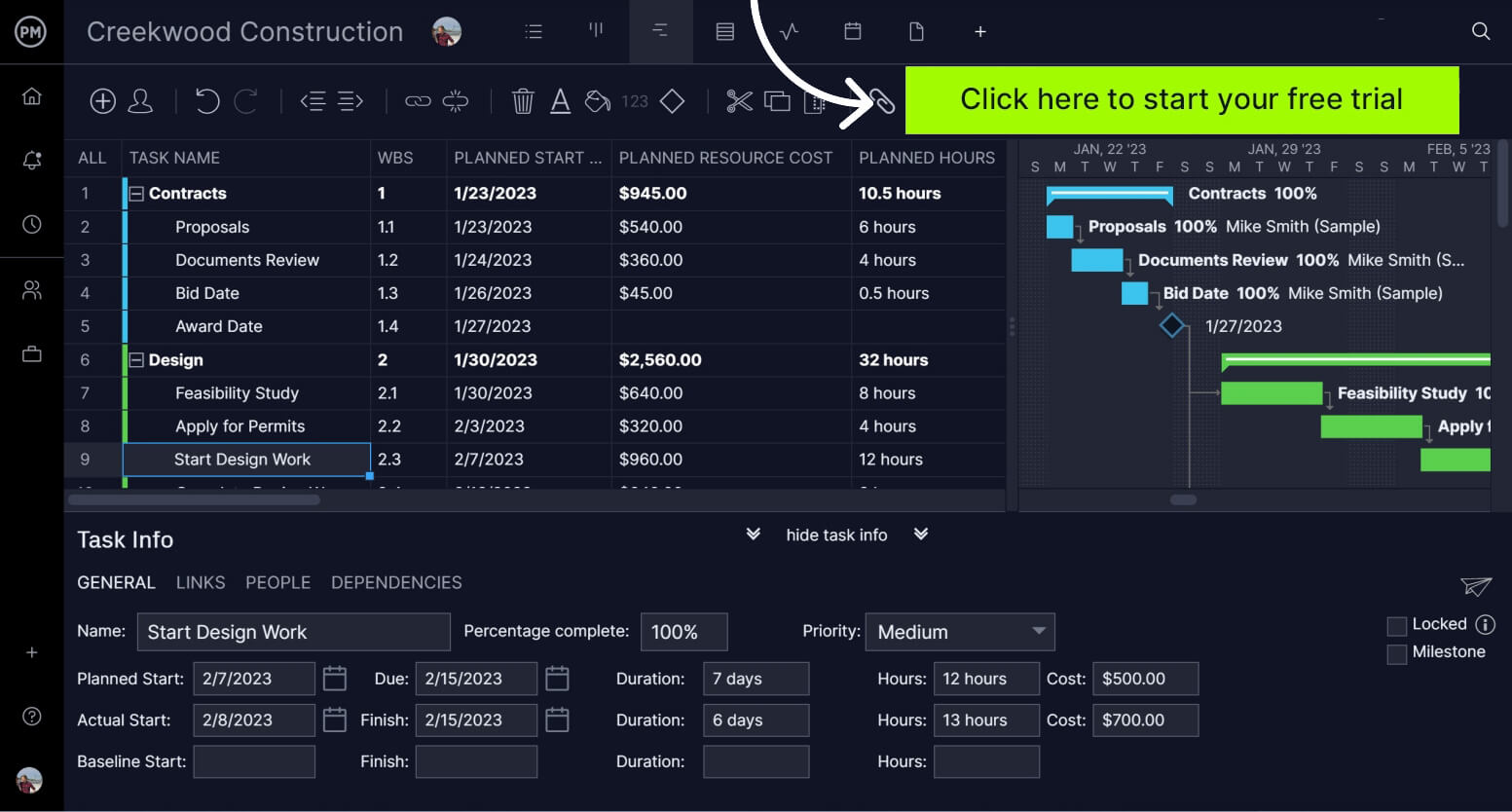
What Should Be Included in a BRD?
Why should you create a business requirements document? It reduces the chances that your project will fail due to misalignment with business requirements and connects the organization’s business goals with the project. It brings stakeholders and the team together and saves costs that accrue due to change requests, training, etc.
You’ll want to create a business requirement document, and even though it’s an involved process, it can be broken down into seven key steps. They are as followed.
1. Executive Summary
To begin, you’ll need to create an executive summary that provides an overview of the organization and the challenges facing the business. You’ll explain the issues and what the organization is trying to achieve to ensure everyone is on the same page. This section should be short, like an elevator pitch, summarizing the rest of the business requirements document.
2. Project Objectives
After summarizing the issue you plan to address in the project, you’ll want to clearly define the project’s objective . This helps define the project phases, creates a way to identify solutions for the requirements of the business and the customer, gains consensus from stakeholders and the project team and describes how you arrived at the objectives.
3. Project Scope
The project scope should define in detail what is covered in the project and what would make it run out of scope. This creates a clear boundary for the project and allows stakeholders and teams to agree on the business goals and high-level outcomes. Note what problems are being addressed, the boundaries for implementing the project and the expected return on investment (ROI).
4. Business Requirements
Here you’ll want to list the business requirements or critical activities that must be completed to meet the organization’s objectives. These business requirements should meet both stakeholder and customer needs. This can include a process that must be completed, a piece of data that is needed for the process or a business rule that governs that process and data.
Related: Free Requirements Gathering Template for Word
5. Key Stakeholders
Now you’ll want to identify and list the key stakeholders in the project. Once you have that list, assign roles and responsibilities to each. These might be people outside of your department so you should define their role in the success of the project. This information needs to be distributed in order for everyone to know what’s expected of them in the project. You can even use this section to assign tasks.
6. Project Constraints
At this point, you’ll want to explore the project constraints . Define the limitations of the project and share those with the project team so they know of any obstacles earlier than later. In order for them to clear those hurdles, you’ll want to provide any necessary training or allocate resources to help the project stay on track.
7. Cost-Benefit Analysis
You’ll also want to do a cost-benefit analysis to determine if the costs associated with the project are worth the benefits you’ll get. This requires first determining the associated costs of the project, such as upfront development costs, unexpected costs, future operating costs and tangible and intangible costs. You’ll also need to figure out what benefits derive from the project.
3 Key Tips to Write a Business Requirements Document
As noted, the best way to begin writing a business requirements document is to meet with your stakeholders and team to get a clear picture of their expectations. But that’s only the start. There are many other best practices for writing a BRD. Here are a few.
1. Start With Thorough Requirements Gathering
Requirements gathering is the process of identifying all requirements necessary for the project. That means everything from the start of the project to the end of the project. You’ll want to address the length of the project, who will be involved and what risks are possible.
2. Differentiate Between Business Requirements and Functional Requirements
Remember, business requirements are what needs to be done, such as the project goals, and why that’s important for the organization. Functional requirements are how the processes, be they a system or person, need to work in order to achieve the project goals.
3. Use a Stakeholder Matrix
An important aspect of any business requirements document is identifying stakeholders . In fact, this should be done early in the process and a stakeholder matrix can help you analyze those stakeholders. It helps you understand the needs and expectations of your stakeholder in terms of their power or influence and the level of interest in your project.
ProjectManager Helps You Track Business Requirements
Once you have your business requirements document, the real work begins. There are many project management software tools that can help you plan and measure your project. ProjectManager is unique in that it adds real-time tracking to make sure your business requirements are being met.
Monitor Project With Real-Time Dashboards
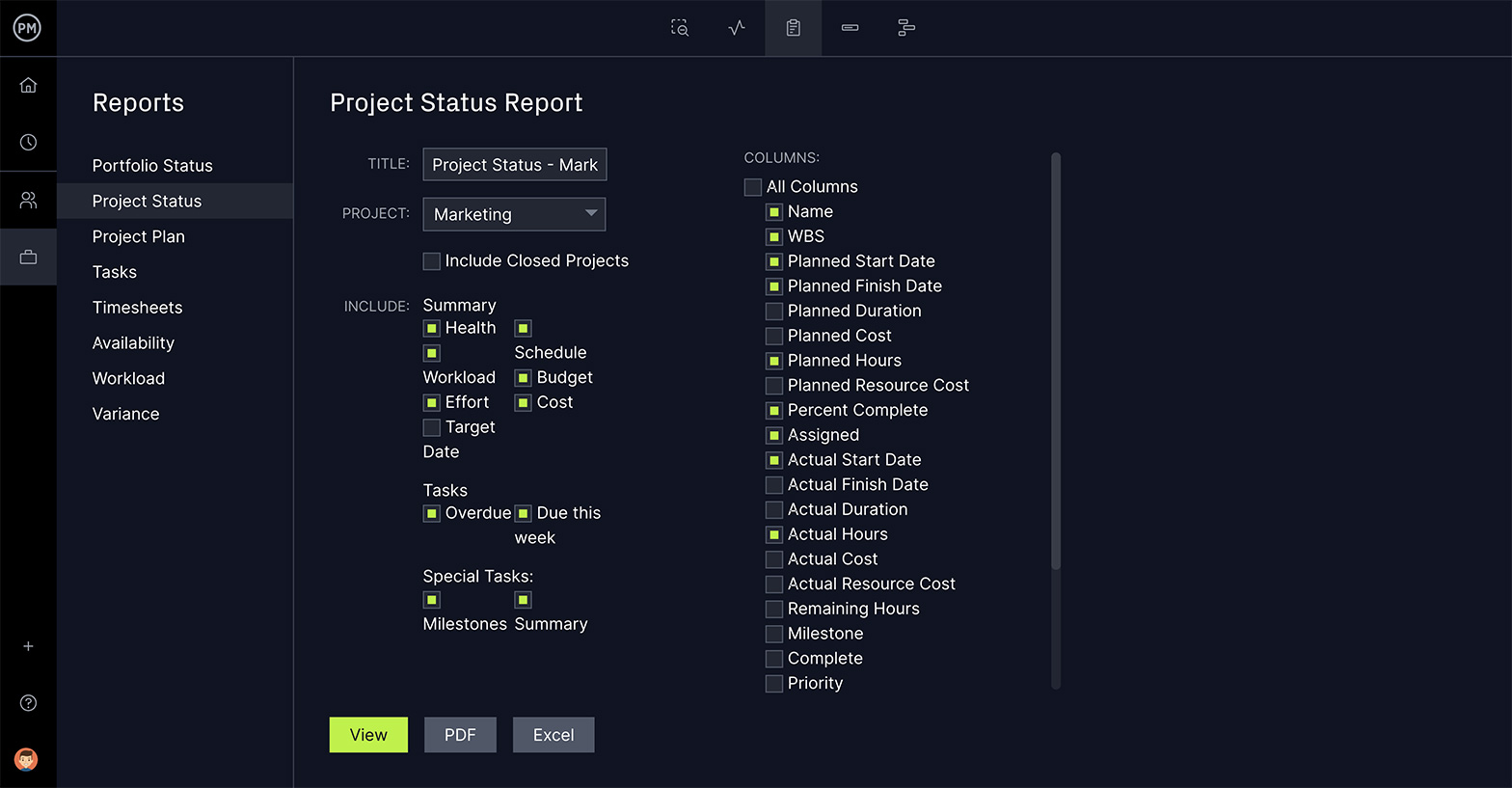
When you make your plan on our interactive Gantt charts , the last thing is to set the baseline. Now you can track project variance across many of our features. Keeping projects on time and under budget is critical to meeting the business requirements of your stakeholders. To get a high-level view of the project, simply toggle to the dashboard where you can view six project metrics. Get live data on costs to tasks, and workload to health, all in easy-to-read graphs and charts. Unlike other tools that offer dashboards, you don’t have to waste time setting ours up. It’s plug-and-play.
Share Progress Reports With Stakeholders
Being able to view your progress and performance in real time is important for stakeholders and project managers. We have customizable reports that can be generated with a keystroke. As stakeholders don’t need all of the details, filters make it easy to focus on only the data they need to see. Then, easily share the report as a PDF or print it out, whichever delivery method your stakeholders prefer. We have reports on status and portfolio status, time, cost, timesheets and more. It’s a great way for project managers to dig into the data and keep stakeholders updated.
ProjectManager is award-winning project management software that helps you plan, schedule and track your project in real time. Use our tool to make sure you’re meeting all the business requirements in your BRD. Our collaborative platform makes it easy to connect with teams to help them work more productively and stakeholders to keep them up-to-date. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.
Home > Business > Business Startup
- 5 Best Business Plan Software and Tools in 2023 for Your Small Business

Data as of 3 /13/23 . Offers and availability may vary by location and are subject to change.

We are committed to sharing unbiased reviews. Some of the links on our site are from our partners who compensate us. Read our editorial guidelines and advertising disclosure .
A business plan can do a lot for your business. It can help you secure investors or other funding. It can give your company direction. It can keep your finances healthy. But, if we’re being honest, it can also be a pain to write.
Luckily, you don’t have to start from scratch or go it alone. Business plan software and services can help you craft a professional business plan, like our top choice LivePlan , which provides templates, guidance, and more.
You’ve got quite a few choices for business plan help, so we’re here to help you narrow things down. Let’s talk about the best business plan tools out there.
- LivePlan : Best overall
- BizPlanBuilder : Most user-friendly
- Wise Business Plans : Best professional service
- Business Sorter : Best for internal plans
- GoSmallBiz.com : Most extra features
- Honorable mentions
Business plan software 101
The takeaway, business plan software faq, compare the best business plan software.
By signing up I agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
LivePlan: Best overall business plan software
Data as of 3 /13/23 . Offers and availability may vary by location and are subject to change. *With annual billing
LivePlan has been our favorite business plan software for a while now, despite the stiff competition.
There’s a lot to like about LivePlan. It has pretty much all the features you could want from your business plan software. LivePlan gives you step-by-step instructions for writing your plan, helps you create financial reports, lets you compare your business’s actual financials to your plan’s goals, and much more. And if you ever need inspiration, it includes hundreds of sample business plans that can guide your writing.
LivePlan software pricing
But the best part? You get all that (and more) at a very competitive price. (You can choose from annual, six-month, or monthly billing.) While LivePlan isn’t quite the cheapest business plan builder out there, it’s not too far off either. And if comes with a 60-day money back guarantee. So there’s no risk in trying LivePlan out for yourself.
With a great balance of features and cost, LivePlan offers the best business plan solution for most businesses.
BizPlanBuilder: Most user-friendly
Need something easy to use? BizPlanBuilder fits the bill.
BizPlanBuilder doesn’t have a flashy, modern user interface―but it does have a very clear, intuitive one. You’ll be able to see your plan’s overall structure at a glance, so you can quickly navigate from your title page to your market trend section to that paragraph on your core values. And as you write, you’ll use a text editor that looks a whole lot like the word processing programs you’re already familiar with.
BizPlanBuilder software pricing
Data effective 3/13/23. At publishing time, amounts, rates, and requirements are current but are subject to change. Offers may not be available in all areas.
BizPlanBuilder also offers lots of helpful guidance for actually writing your plan. It gives you pre-written text, in which you just have to fill in relevant details. It offers explanations for what information you need to include in each section of your plan and way. It even gives you helpful tips from experts, so you’ll have all the information you need to plan like a pro.
So if you want planning software with almost no learning curve, you’ll like BizPlanBuilder.
Wise Business Plans: Best professional service
- Custom quote
Unlike all the other companies on this list, Wise Business Plans doesn’t offer software. Instead, it offers professional business plan writing services―meaning someone does all the hard work for you.
Now, you might think that sounds expensive―and you’re probably right (you have to request a custom quote for your plan). But there’s a lot to be said for expertise, and Wise Business Plans has plenty of that. Your business plan will get written by an experienced writer (with an MBA, no less). They’ll get information from you, do their own research, and then write your plan. You get one free revision, and you can always pay for more.
Wise Business Plans service pricing
Your end result will be a polished, entirely original business plan. (You can even get printed copies.) And best of all, you won’t have to spend your precious time working on the plan yourself. Wise Business Plans takes care of all the hard parts, and makes your business look good while doing it. Sounds like a service worth paying for, right?
Put simply, if you want the most professional business plan possible, we recommend using Wise Business Plans’s writing service.
Business Sorter: Best for internal plans
Many businesses need plans to show to people outside the company (to get financing, for example). But what if you just need a plan for internal use? In that case, we suggest Business Sorter.
Business Sorter uses a unique card-based method to help you craft the perfect business plan. (You can watch a demo video to see how it works.) You’ll plan some of the usual things, like finances and marketing. But Business Sorter also lets you make plans for specific teams and team members. It also emphasizes more internal matters, like operations, that might get overlooked in a business plan for outsiders.
Business Sorter software pricing
After you’ve made your business plan, Business Sorter also helps you stay accountable to it. You can create tasks, give them deadlines, and assign them to team members―giving you basic project management tools to make sure your business plans become business actions. (Oh, and did we mention that Business Sorter has the lowest starting prices of any software on this list?)
It all adds up to a business plan software that works great for internal planning.
GoSmallBiz: Most extra features
Want to get way more than just business planning software? Then you probably want GoSmallBiz.
See, GoSmallBiz offers business plan software as part of its service―but it’s just one part of a much bigger whole. You also get everything from discounts on legal services to a website builder to a CRM (customer relationship manager) to business document templates. And more. In other words, you get just about everything you need to get your startup off the ground.
GoSmallBiz software pricing
Don’t worry though―you still get all the business planning help you need. GoSmallBiz gives you business plan templates, step-by-step instructions, and the ability to create financial projections. And if you get stuck, GoSmallBiz will put you in touch with experts who can offer advice.
If you want business planning and much, much more, give GoSmallBiz a try.
- PlanGuru : Best financial forecasting
- EnLoop : Cheapest tool for startups
We recommend the software above for most business planning needs. Some businesses, though, might be interested in these more specialized planning software.
Honorable mention software pricing
Planguru: best financial forecasting features.

PlanGuru is pretty pricey compared to our other picks, but you might find its forecasting features worth paying for. It has more forecasting methods than other software (over 20) plus it lets you forecast up to 10 years.
EnLoop: Cheapest tool for startups

EnLoop doesn’t have our favorite features or interface, but it does have really, really low pricing plus a seven-day free trial. It's the most affordable software for startup business planning and still provides all the essential features like financial analysis, team collaboration, charting, and more.
Data as of 3 /13/23 . Offers and availability may vary by location and are subject to change. * With annual billing
Several of our previous favorite planning software, including BusinessPlanPro and StratPad, seem to have gone out of business.
A business plan is a written, living document that tells the story of your business and what you plan to do with it. It serves as the source of truth for you—the business owner—as well as potential partners, employees, and investors, but it also serves as a roadmap of what you want your business to be.
Why you need a business plan
While some small-business owners don’t see the point of creating a formal business plan, it can have some concrete benefits for your business. For example, one 2016 study found that business owners with written plans are more successful than those that don’t. 1
Still too vague? Then let’s get specific.
If you ever seek business funding (from, say, banks, angel investors , or venture capitalists ), you’ll have to prove that your business deserves the money you want. A formal business plan―complete with financial data and projections―gives you a professional document you can use to make your case. (In fact, most potential investors will expect you to have a business plan ready.)
Even if you’re not seeking funding right now, a business plan can help your business. A formal plan can guide your business’s direction and decision making. It can keep your business accountable (by, for example, seeing if your business meets the financial projections you included). And a formal plan offers a great way to make sure your team stays on the same page.
What to include in your business plan
Not all business plans are created equal. To make a really useful business plan, you’ll want to include a number of elements:
- Basic information about your business
- Your products/services
- Market and industry analysis
- What makes your business competitive
- Strategies and upcoming plans
- Your team (and your team’s background)
- Current financial status
- Financial and market projections
- Executive summary
Of course, you can include more or fewer elements―whatever makes sense for your business. Just make sure your business plan is comprehensive (but not overwhelming).
How business plan software can help
With so many elements to include, business plan creation can take a while. Business plan software tries to speed things up.
Most business plan software will include prompts for each section. In some cases, you can just fill in your business’s specific information, and the software will write the text for you. In other cases, the software will give you specific guidance and examples, helping you write the text yourself.
Plus, business plan software can help you stay organized. You’ll usually get intuitive menus that let you quickly flip through sections. So rather than endlessly scrolling through a long document in a word processor, you can quickly find your way around your plan. Some software even lets you drag and drop sections to reorganize your plan.
Sounds way easier than just staring at a blank page and trying to start from scratch, right?
Choosing business plan software
To find the right business plan builder for your business, you’ll want to compare features. For example, would you rather write your own text, getting prompts and advice from your software? Or would you rather go with a fill-in-the-blank method?
Likewise, think about the elements you need. If your plan will have a heavy focus on finances, you’ll want to choose business plan software with robust financial projection features. If you care more about market and competitor analysis, look for software that can help with that research.
You may also want to find business plan software that integrates with your business accounting software . Some plan builders will import data from Xero, QuickBooks, etc. to quickly generate your financial data and projections.
And of course, you’ll want to compare prices. After all, you always want to end up with software that fits your business budget.
The right business plan software can make your life easier. With LivePlan ’s wide breadth of features and online learning tools, you can’t go wrong. Plus, BizPlanBuilder 's one-time pricing makes it easy to invest while Business Sorter has a low starting cost. And if you're business is looking to grow, GoSmallBiz and Wise Business Plans will scale with you.
But of course, different companies have different needs. So shop around until you find the software that’s best for you and your business.
Now that you've got a business plan, take a look at our checklist for starting a small business. It can help you make sure you have everything else you need to get your startup off to a good start!
Related content
- 7 Steps to Build a Successful Project Management Sales Plan
- Best Project Management Software and Tools in 2023
- 4 Cost Management Techniques for Small Businesses
Creating a business plan can take anywhere from a couple hours to several weeks. Your timeline will depend on things like the elements you choose to include, whether you use software or hire a writing service, and how much research goes into your plan.
That said, much of the business plan software out there brags that it can help you create a fairly detailed plan in a few hours. So if you’re going the software route, that can help you set your expectations.
If you want to get the most out of your business plan, you should update it on a regular basis―at least annually. That way, you can continually refer to it to inform your company’s strategies and direction.
At the very least, you should update your business plan before you start looking for a new round of funding (whether that’s with investors or lenders).
Thanks to business plan software, you can easily write your own business plan rather than pay someone to do it for you. And in most cases, software will cost you less than a professional business plan service.
There are some times you might want to go with a service though. If time is tight, you might find that it’s worth the cost of a service. Or if you’ve got big investor meetings on the horizon, you might want the expertise and polish that a professional service can offer.
Ultimately, you’ll have to decide for yourself whether business plan software or a business plan service will work better for your company.
Methodology
We ranked business plan software and tools based on features, pricing and plans, and connections to project management and other services. The value of each plan and service, along with what it offers, was a big consideration in our rankings, and we looked to see if what was offered was useful to small businesses or just extra. The final thing we looked at was the ease of use of the software to see if it's too complex for small businesses.
At Business.org, our research is meant to offer general product and service recommendations. We don't guarantee that our suggestions will work best for each individual or business, so consider your unique needs when choosing products and services.
Sources 1. Harvard Business Review, “ Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed .” Accessed March 13, 2023.

5202 W Douglas Corrigan Way Salt Lake City, UT 84116
Accounting & Payroll
Point of Sale
Payment Processing
Inventory Management
Human Resources
Other Services
Best Small Business Loans
Best Inventory Management Software
Best Small Business Accounting Software
Best Payroll Software
Best Mobile Credit Card Readers
Best POS Systems
Best Tax Software
Stay updated on the latest products and services anytime anywhere.
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Disclaimer: The information featured in this article is based on our best estimates of pricing, package details, contract stipulations, and service available at the time of writing. All information is subject to change. Pricing will vary based on various factors, including, but not limited to, the customer’s location, package chosen, added features and equipment, the purchaser’s credit score, etc. For the most accurate information, please ask your customer service representative. Clarify all fees and contract details before signing a contract or finalizing your purchase.
Our mission is to help consumers make informed purchase decisions. While we strive to keep our reviews as unbiased as possible, we do receive affiliate compensation through some of our links. This can affect which services appear on our site and where we rank them. Our affiliate compensation allows us to maintain an ad-free website and provide a free service to our readers. For more information, please see our Privacy Policy Page . |
© Business.org 2023 All Rights Reserved.
What stage is your business at?
Tell us and we’ll match you with a special LivePlan discount:
New Business Idea
Startup Phase
Established Business
Enter your email address to unlock it.
Please enter a valid email address
We care about your privacy. See our Privacy Policy .
Customer Support

The World's Leading Cloud-Based Business Plan Software
- Fill-in-the-blanks simplicity
- Real sample business plans to inspire you
- Works in all web browsers
See how it works

Start planning for $20 per month
Rated 4.8 out of 5
Trusted by 1 million+
entrepreneurs like you
Rated 4.9 out of 5
“LivePlan earns the top spot on our list of best business plan software—and for good reason. LivePlan's slick and interactive service provides a step-by-step business plan approach, a rich collection of cloud-based features, and online learning tools.”

Brooke Hayes Software Reviewer, Business.org
Here's How LivePlan Makes it Surprisingly Simple to Write a Convincing Business Plan

You get a step-by-step process to follow
- Ways to write a pitch that grabs investors' attention
- What to include in your marketing plan
- Every other essential piece of your business plan
“LivePlan saved me a lot of time because the software does so much of the work for you. All you have to do is answer questions and plug in numbers.”
Brian Sung, Eugene, OR Owner of Tailored Coffee
All the financials are calculated for you
LivePlan tells you exactly what kind of financial information you need to enter and then it does all the calculations automatically using built-in formulas. So you end up with razor-accurate financial statements that include all the tables that a lender or investor expects to see.

“Most people are intimidated by the financials, but LivePlan made planning simple, saved me so much time and just knowing that the calculations are correct makes this tool worth every penny!”

Brandie Slaton, Merced, CA Noelle Notals LLC
If you ever get stuck, we'll help you out
Most LivePlan users are able to breeze through their first business plan. But if you ever have a question, there are 3 ways to get advice:
- Call a LivePlan expert at 1-888-498-6136
- Start a chat with our advocacy team. Click here to try it .
- Or refer to more than 550 sample plans and tutorial videos built into LivePlan
See how we support our customers
Get Started Risk Free

“LivePlan was user friendly, supportive and provided meaningful guidance all while remaining very flexible.”

Freja Nelson, Oregon Freja Foods
Get a Polished Business Plan That Will Impress Lenders
Once your plan is done, you can:
- Customize the look of your plan using 10 beautiful document themes
- Download your plan as a PDF or Word doc so you share it easily
- Print out your plan to get a clean, professional document
See inside a completed plan »

Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with LivePlan
35-day money back guarantee. Start planning for $20 per month.
“LivePlan is incredibly simple and easy to use. The financial sales forecasting tool is very intuitive and makes writing a business plan more fun.”

Helga Douglas Owner, Svala
LivePlan Also Gives You Tools to Help Your New Business Succeed
Access Essential Business & Legal Form Templates
Search our library of hundreds of legal forms that cover credit applications, contractor agreements, employee contracts and more.
Get Insights That Will Help Your Company Grow
Are you charging enough? Will you meet your revenue goals? LivePlan's forecasting tool can answer these type of questions at a glance.
See How You Stack Up Against Competitors
Plug in your industry and where you're located, and LivePlan will tell you how you're doing compared to businesses just like yours.
You Might Be Surprised By What New Business Owners Have Achieved with LivePlan
E'a williams, be fit tri wellness, chicago, il.
“Once the investor saw the plan, he believed in it. The interface was fresh and lively. The program gave wonderful examples of what should be in the different sections. I was able to take bits and pieces of those examples, but when I finished each section it sounded like I had written it. “I could just plug in information without having to do any of the math. That saved a lot of work. It made it very easy to get the business plan done. Once the investor saw my business plan on LivePlan, he immediately got back to me and said, ‘I'm in.’”
Mandie O'Neill
Lucky dog daycare, eugene or.
“LivePlan made an overwhelming task easy. LivePlan is incredibly easy to use. LivePlan's web-based nature allows me to log in anywhere (for me it was with my Mac Book Pro or iPad). At times writing a business plan can be a overwhelming task, especially when it comes to formatting and layout. LivePlan has made it easy to focus on putting your business ideas and goals on paper instead of fussing with all the other pesky stuff. I really liked how each section is defined and gives examples of what a quality business plan should look like.”

Rachid Tajiouti
Olive oil usa, llc, new york, ny.
“I've raised $3M so far with LivePlan! I needed to write a business plan for my investors. I was going nuts trying to create charts and properly format them. Then a friend recommended LivePlan! The financials were so easy to use and I liked knowing the calculations were all correct. It helped me create a precise plan to confidently share with investors, and I've raised $3M so far!”
Our customers give LivePlan 5 out of 5 stars
Software is professional and user-friendly. Highly recommend to any Entrepreneur. Would not be where I am today without LivePlan.
Mar. 15, 2024
I've been using LivePlan to help me write top-tier business plans over the last 2 years. A prominent business plan writing company referred me to this site to help me produce the best business plans, to collaboratively support their clients. I've consistently had the best customer service, whether by email or live chat. Rapid responses that are helpful and this is one of the "hand-down" best platforms if you're looking for high-quality products and services - and AMAZING customer service. The price of the plan subscription is a tiny drop in the ocean compared to the results I've had with business plans created through LivePlan. Thank you for the products and services here that help me present well
Feb. 29, 2024
I've used Liveplan for two projects and I have been happy with both experiences. I've needed support twice and both experiences were quickly resolved using the chat function. I'd highly recommend Liveplan to anyone wanting to get serious about new projects. They have great customer support, and it can be a vital tool to anyone wanting to build something from the ground up.
Feb. 20, 2024
I needed a business plan for a government grant and the platform helped me tremendously. It was super organized with all the touchpoints I had to fill and the AI for improving the texts was also amazing. I did a finance plan a well and I had no clue beforehand in how to do it and that was excellent and everything I needed to submit a full case! I finished my plan and submitted it. I will definitely use it again for when i need another business plan. Thank you
Feb. 3, 2024
Extremely user friendly. I appreciated how intuitive it was and useful when I got stuck or when wanting to rephrase sections - AI was a true support for me then
Sep. 26, 2023
LivePlan helps put your ideas and beliefs on paper in a professional & organized manner. It guides you through planning, organizing, and monitoring your plan.
Sep. 2, 2023
I didn't only get value for the money paid but also got the best customer service experience as well. And of course, I'm sticking to LivePlan forever.
IsefConsult
Aug. 14, 2023
Using LivePlan since March 2015, I've created precise financial plans and business strategies for ventures of all sizes. It's the perfect tool for rapid evaluation, eliminating the risk of spreadsheet errors.
Jul. 7, 2023
It's a great Financial planning software. It can also sync with Xero and Quickbooks.
Jun. 17, 2023
If you are looking to create a Business Plan then don't waste any time, buy LivePlan as it will make your life so much easier and save you days of work!
Jun. 28, 2022
A great tool for entrepreneurs with non-finance backgrounds. We all have business ideas but long-term planning is a challenge. LivePlan makes it simple and easy.
Jun. 24, 2022
I had put off writing a plan because I dreaded the research and didn't really know what I was doing. Because of you, I now have a comprehensive, professional-looking business plan.
May 24, 2022
Overall experience with LivePlan is awesome. Very informative and easy to read. Plans come with templates and other examples you can use to build your plan.
Deonta from Texas
May 11, 2022
The best part for me is the feeling of confidence it gave me. It really made me feel like my goals and even dreams were actually possible to reach.
Mar. 29, 2022
LivePlan was a lifesaver when starting our business! It helped us make a business plan and financial projections to show others, and everyone was blown away.
The Silver Fern Shop
Jan. 27, 2022
University Cycle Works
7 Best Business Plan Software for Startups in 2024

- Resources for Planning a Business
- Best Business Plan Software
Last Updated: January 23, 2024 By TRUiC Team
Launching a new startup is an exciting yet challenging endeavor. Crafting a comprehensive business plan is a critical first step for any founder to outline their vision, objectives, and strategy. It acts as a roadmap to help guide important decisions and next steps as a company grows.
With so many options available, finding the right business planning tool can be daunting. The best software should be affordable, user-friendly, and offer a robust set of features to aid in financial modeling, strategic planning, and more.
In this review, we'll explore some of the top business plan software solutions designed specifically for entrepreneurs. We'll compare capabilities, ease of use, templates and resources, integrations, pricing, and more. Whether you’re looking to create an investor-ready plan or simply organize your strategy, choosing the right tool can help you get started on the right foot.
Best Business Plan Software for Startups: LivePlan
Top Business Plan Software Solutions
In this review, we'll look at seven of the best business plan software platforms — discussing their pros, cons, features, pricing, and more — so you can decide which one is right for your startup.
Best Business Plan Software for Startups 2024:
- LivePlan - Best Overall
- Bizplan - Easiest to Use
- Enloop - Best Automation Features
- PlanGuru - Best Financial Forecasting
- IdeaBuddy - Best for Idea Validation
- iPlanner - Best for Nonprofits
- Wise Business Plans - Best Professional Services
The following tools all have their own great features. Based on its affordable pricing and usability, LivePlan is our top business plan software choice for startups.
Try LivePlan today or continue reading to explore your options!
Best Business Plan Software: LivePlan
LivePlan is the overall best business plan tool, offering a large number of features at an affordable price.
Visit LivePlan
1. LivePlan - $15/month to $30/month
We love LivePlan overall because it offers great value at an affordable cost. The software lets you quickly create a business plan from anywhere in the world using what is arguably the best business plan software available on the market. It does everything better than its competition and costs way less.
What’s more, the online “cloud-based” platform is easy to use and you are under no contract or obligation to keep paying for the service. Even better, if you decide to stop service for whatever reason, Palo Alto Software, the makers of LivePlan, will keep your account active and data preserved for at least a year should you decide to reactivate your account later.
- Create an unlimited number of business plans
- A forecast feature for those less mathematically inclined. Plug in data, and it will generate charts, graphs, figures, and even the profit and loss, balance sheet, and cash flow statements
- 500+ business plan templates spanning all major industries
- Real-time financial data tracking
- Performance dashboards track sales and budgeting
- Create one-page pitch plans for potential investors
- Milestone scheduling feature — Some people will use it when working with others on their plan; it will let you assign milestones to people.
- Low-cost annual plans
- Affordable pay-as-you-go plans
- No cancellation fees
- Data saved for 12-months, even after cancellation
- Clean, modern platform
- Cloud-based; works on any business machine (Linus, Windows, Mac)
- Integrates with Quickbooks and Xero to import your data easily
- Knowledgeable customer support to get help with your plan
- No valuation capabilities
- Templates built on Palo Alto Software’s earlier software Business Plan Pro require some modifications to be used on LivePlan
Insider Information
Talking to the nice people at LivePlan we learned some inside information that we wanted to share with our readers.
Here's what we learned:
- LivePlan has been used by contestants on ABC's hit show "Shark Tank" to win over angel investors to help them get their ideas and businesses funded.
- Accountants use LivePlan as an added-value service to sell to their clients.
- Businesses continue using LivePlan because of a feature called “Dashboard” which lets you manually enter your actuals or pull actuals from Quickbooks online to do comparative forecasting and analysis.
- LivePlan helps with business continuity planning (BCP).
- LivePlan executives use LivePlan to make important business decisions.
- "Dashboard" does profit and loss, cash flow, and balance sheet reports and lets you compare and contrast your actuals from your forecasts to be able to show to investors.
- LivePlan lets you create business plans in 1/5th the time it takes using templates.
Customer Reviews
LivePlan receives great feedback from customers. LivePlan reviews average 4.5 stars out of 5 on GetApp. LivePlan is an easy company for us to recommend for the best business plan software.

2. Bizplan - $29/month, $249/year, $349 lifetime
Bizplan rates high on our list because they offer a lifetime plan that gets you "forever access" to their business plan software. As an added bonus, you also receive free access to Startup Courses and LaunchRock, a landing page builder.
- Easy, "fill-in-the-blanks" plan builder
- Publish your business plan online
- Unlimited business plans
- Bizplan takes care of the financials
- Cloud-based (use any browser on any computer)
- Options to add more graphics and photos
- Low-cost yearly plans
- Create unlimited business plans
- Xero to import your data easily
- Excellent and responsive customer support (email/chat/phone)
- Free access to Startup.com and LaunchRock.com
- Discount at Fundable.com (connect with lenders and investors)
- Can't export in Word
- Doesn't currently integrate with QuickBooks
- No free trial
- No third-party app integrations
Talking with BizPlan insiders, we learned that the premise behind BizPlan is to help startups easily create professional business plans to give them a leg-up with lenders and investors.
Here's what else we learned:
- BizPlan's does all your financial calculations for you.
- BizPlan strives to be an all-in-one solution for Startups needing funding.
- BizPlan is constantly making improvements to its software.
BizPlan receives great feedback from customers. BizPlan reviews average 4.4 stars out of 5 on GetApp. Still a relatively new option, BizPlan already has over 30,000 satisfied customers. As their platform grows, we wouldn’t be surprised to see them integrate even more valuable features. Keep a close eye on this one.

3. Enloop - Free to $39.95/month
If you’re looking to try before you buy, Enloop is a strong choice as one of the only business planning software tools with a free trial.
- User-friendly platform
- Compare your financials against your industry's performance
- Bank ready financial statements (Profit and Loss, Balance Sheet, Cash flow)
- Lets multiple team members work on a business plan
- 36-Month detailed financial reports
- Sync date and text into your business plan
- Real-time performance rating
- Generated business plan Pass/Fail report
- Multiple currency formatting
- Seven-day free trial (no credit card required)
- Advanced financial ratios
- Financial projections
- Video tutorials to help you with the writing process
- No phone or chat support, just a "contact us" form.
- Three business plan limit per account
- Doesn't integrate with QuickBooks or Xero
- No financial forecasts beyond 36-months
- No 30-day money-back guarantee
We learned that the premise behind Enloop is to make business planning easier for entrepreneurs. Enloop achieves this by making software simple to navigate through and takes risks off the table with their no credit card needed seven-day free trial. Their business plan creation software offers financial forecasting features for up to 36 months.
- Enloop utilizes 16 financial ratios to get your business ready for investors.
- Enloop offers some sample business plans that are easy to modify.
- Enloop's performance score increases as you create your detailed plan.
- A new business or small businesses benefit the most from Enloop's solutions.
Enloop receives fair feedback from customers. Enloop's reviews average 3 stars out of 5 on PCMag. Enloop's main complaint is its lack of instructional text for writing mission statements and other key sections. What they rank high on is their efficiency and the speed at which the software lets you write a business plan.
Even beyond the free version, Enloop Basic is just $9.95/month ($6/month when paid annually), so they’re one of the least expensive tools for writing a business plan.

4. PlanGuru - $99/month to $299/month
PlanGuru is a good option if you’re looking for considerably more robust software that offers quite a bit more. The most notable feature we like is the valuation tool, only present on the desktop version of the software. PlanGuru lets you calculate the valuation of your business using three different methods. No other business plan software offers this that we know of.
PlanGuru also offers budgeting, forecasting, and performance tools to help you put together a business plan. In the main, PlanGuru allows you to get a custom-tailored three financial statement budget model up and running out of QuickBooks or Xero in a matter of minutes. PlanGuru's business plan writing software takes you through a setup process where it asks you questions such as:
- What's the first month of your fiscal year?
- How many historical years do you want to import?
And, once you answer these questions, PlanGuru then generates a model for you that you can then populate with your historical data if you have it. Then you can go through PlanGuru's 20+ projection methods.
Some financial data projection methods include:
- Expenses, like payroll, etc.
- Balance sheet items, like accounts receivable, accounts payable, crude expenses, prepaid expenses, loans, etc.
These are only a few of the features the business plan software offers. Here are some more.
- Budgeting/Forecasting Software
- Analytics Service for Financial Performance & KPIs
- Valuation calculations (desktop software only)
- Desktop and cloud-based options
- Free 14-day trial and 30-day money-back guarantee
- Great customer support and knowledgeable sales staff
- Lower-cost yearly plans offered
- Advanced financial calculations
- Business valuation calculations
- No contracts
- Integrates with QuickBooks and Xero
- Costlier than LivePlan and most other business plan software options
- Additional cost per user can add up quickly
The great thing about PlanGuru is that the only thing you have to worry about is the income statement and balance sheet projections because the cash flow statement is automatically generated.
Then once you have the cash flow statement, income statement, and balance sheet in place, you can then lock down the budget.
- PlanGuru's desktop version has three different types of valuation methods that calculate the worth of your business.
- PlanGuru has some really nice reporting tools that pull together your financial statements into table formats, say, for the bank, line-by-line.
- PlanGuru also has some nice charts, graphs, scorecards, and some easily digestible reports that can help you visualize how your company is performing.
- Exports to Excel, PDF, and Word documents --and, there's even a tool that lets you create customized reports.
- You can print your plan off too to show partners, lenders, and investors.
- PlanGuru now offers a cloud-based version of its software, though it will take some time to catch up to the rich features offered by the current desktop software version.
- With PlanGuru you also get free updates, bug fixes, and new releases as they become available.
Important Note: These tools are important because investors may want to see not only historical performance but also projections.

5. IdeaBuddy - Free to $35/month
IdeaBuddy makes our list because of what's behind their approach. IdeaBuddy focuses on helping entrepreneurs develop their idea first, then share it, and then refine it into a plan. If you have a business idea and don't know what to do next, IdeaBuddy could be what you're looking for in a business plan software.
- Single-page business plan pitch (Idea plan)
- Clean modern design platform combined with great financial tools
- Marketing plan for selling and promoting your products
- Market overview plan where you create targeted customer profiles, identify your competition and calculate the market potential
- Business plan creation that includes forecasting performance and cash flow projections
- A proprietary algorithm calculates a final score for your idea providing recommendations for improvement after you complete "Story Mode"
- Idea Journal, that is an internal business plan for you to show potential investors
- A lifetime plan costs only $178
- Great for developing ideas
- Great for doing market research
- Pay-as-you-go plans offered
- Email-only customer service
- Software lag time issues
- Fewer software options than most other small business options
IdeaBuddy has some great features that are fantastic from idea conceptualization down to cost projections and the laying out of steps to take to start a business. We would have liked, however, to been given more KPIs that would notify us of tasks, help with idea validation, and help us measure other objectives to better monitor the health of our business. Another thing lacking was the design of the finished plan--it contained some noticeable structural issues.
IdeaBuddy has received some outstanding customer reviews on GetApp. IdeaBuddy has earned a 4.6-star rating out of 5 possible stars.

6. iPlanner - Starts at $55/year
iPlanner is a comprehensive business plan software that has been aiding entrepreneurs since 2007, providing a robust framework for developing business plans, models, and financial forecasts online.
- Unlimited Team Members & Collaboration
- A La Carte Pricing Model vs Packages
- Discounts for Serial Entrepreneurs & Business Coaches
- Solid amount of industry knowledge and experience.
- They've got two trademarked business planning services, Startup Framework™ and Strategy Designer™
- All of their business planning packages allow you to have unlimited collaborators and assign people three different roles: Project Owners, Advisors, and Viewers.
- Their Startup Framework software has a business modeling section where you can design a business model canvas and strategize as much as you need before diving into your plan.
- Doesn't have a month-to-month option for either of their services. Their Strategy Designer is payable only annually, while their Startup Framework is available for 3-month, 6-month, or 12-month payments.
- They don't offer refunds
- Their website is pretty old school and tough to navigate.
- Unlike other business planning software, iPlanner doesn't offer a free version or trial. However, you can take a tour of their Startup Framework software or view a demo of the Strategy Designer to get a feel for them.
iPlanner's Business Planning Software
If a simple framework is all you're looking for, iPlanner can help you out. They don't have many bells and whistles, but at these price points, they offer a good value for nonprofits and corporations.

7. Wise Business Plans - Pricing by Request
Wise business plans website is a little confusing to navigate, and pricing is by request only, which can get frustrating. They do have a lot of options for different kinds of business plans for various types of business types, which makes them versatile. They also have business building and funding options as well. And, if you wish to establish business credit, they offer net-30 accounts that get reported to Equifax business.
- Claim to be the only business plan company to write for Fortune 100 and 500 companies
- Business formation services
- Business license searches
- EIN services
- Digital marketing services
- Business website design and branding
- Has a lot of helpful information
- Helpful options for forming your business
- Options to help after you start your business
- Helps small businesses establish business credit
- Not an actual business plan software
- Expensive by comparison
- Website is difficult to navigate
- Pricing is by request only
- Limited products and features
- Turnaround is one month
- Requires some work on your end

Business Plan Software Pros and Cons
- By using business plan software providers, you’ll be able to create a solid outline for your business. Although some of the options above are better than others, each will walk you through from start to finish.
- No matter how you look at it, business plan software is cost-effective. As long as you actually use the tool, you’ll generate significantly more value than you’re spending on monthly subscription fees.
- If you spend the time to create a solid plan, you’re much more likely to hold yourself accountable. Think of planning software like an accountability buddy for entrepreneurship.
- Your business plan tool will help set realistic financial goals, and most can also keep your bottom line in check by integrating your accounting software.
- Business planning software enables you to collaborate with partners, mentors and investors.
- Some of the business plan tools don’t offer support and can have slightly buggy features. That said, if you’re serious about writing a solid plan, go with a tool that’s constantly updated and well made.
- Although some business plan tools have a collaboration feature, none of them can review it when you’re done. All business planning tools lack a human touch.
How to Choose the Right Business Plan Software
With the array of business planning tools available, it can be daunting to select the right one for your needs. Here are some tips for choosing a business plan software solution:
- Consider your skill level – Opt for software like a wizard-guided template if you are less experienced in writing plans. Choose more advanced software with greater flexibility once you know what you are doing. Look for drag-and-drop tools to easily organize sections.
- Determine your budget – Prices range from free to several hundred dollars. Know how much you can spend before shopping.
- Compare features – Look for software with the specific tools you need, like financial projections, sample text, customizable templates, and more.
- Evaluate the financial tool capabilities – The software should provide extensive financial tools like forecasting, modeling, projections, and dashboards to streamline financial planning.
- Check reviews and ratings – Get feedback from other users about their experience with the software. High reviews indicate easier, more user-friendly software.
Which Is the Best Business Plan Software?
You know the unique requirements of your startup better than we do. These are all quality services that offer business planning software tools for entrepreneurs like you. Feel free to read over our full reviews if you’d like to know more about any of them or even visit the websites directly.
In general, we do prefer LivePlan because they have a huge library of business plan templates, and we love their convenient dashboard. They're the planning software that is most likely to help you via customer support, continue updating their tool, and figure out ways to make your business experience better. Enjoy!
What is the purpose of a business plan?
The purpose of a business plan is to provide a structured outline and roadmap for a business's goals, strategies, and operations. It serves as a guide for decision-making, resource allocation, and management.
Furthermore, it can be a crucial tool for attracting investors, securing loans, and ensuring that all stakeholders have a clear understanding of the business's direction and objectives.
What does business plan software do?
Business plan software assists entrepreneurs and businesses in creating, organizing, and refining their business plans. It provides tools, templates, and guidance to streamline the planning process.
Features often include financial forecasting, market analysis, visual aids like charts and graphs, collaboration capabilities, and even integration with other business tools. This software aims to simplify the task of creating a thorough and professional business plan.
How do you write a business plan?
To write a business plan, start by writing an executive summary that provides an overview of your business idea, products/services, market opportunity, and projected growth. Outline your company description, industry analysis, target customers, competitive advantage, marketing and sales plans, operations, management team, and financial projections.
How long should a business plan be?
The length can vary based on the complexity of the business, its stage, and its intended audience. In general, it might range from 15-50 pages. However, the key is to ensure that the plan is comprehensive yet concise.
For many situations, especially when seeking investment, a more detailed one is preferable. Yet, for internal purposes or for businesses at very early stages, a shorter, more concise plan might suffice.
Are there business plan templates on Word?
Yes, Microsoft Word has business plan templates you can download and customize. The templates provide section headings, instructions, sample text, and tables to input your specific business information.
What is Palo Alto Software?
Palo Alto Software is a company that's been around since the late 1980s. They created business management software for startups and existing businesses. The software has since been updated and rebranded as LivePlan and today happens to be one of the most sought-after business plan software available in the marketplace.
Individual Business Plan Reviews
Featured articles.

What Is a Business Plan?

Lean Startup Business Plan Guide

How to Write a Business Plan
Requirements Management 101: Processes, Plans, and Best Practices
By Joe Weller | July 22, 2022
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Learn the essentials of requirements management, including the different types and how to write a management plan. We share the most effective methods and free templates to get you started.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a requirements management plan, requirements activities , a sample requirement management plan template , and a comprehensive starter kit .
What Is a Requirement?
A requirement is a single component that is necessary to complete a deliverable. All requirements represent a need, and every product or service includes several requirements.
The internationally recognized business analysis standard, Business Analysis Book of Knowledge (BABOK® Guide) , Version 2.0 , defines a requirement as follows:
- A condition or capability needed by a stakeholder to solve a problem or achieve an objective.
- A condition or capability that must be met or possessed by a solution or solution component to satisfy a contract, standard, specification, or other formally imposed documents.
- A documented representation of a condition or capability as in (1) or (2).
An assigned team identifies, gathers, and analyzes a project’s requirements to ensure the project is in line with business goals.
Types of Requirements
There are three primary types of requirements — business requirements, stakeholder requirements, and solution requirements — some of which contain functional and non-functional sub-requirements. Temporary or transitional requirements help to implement process changes.
Learn more about each requirement type below:
- Business Requirements : Business requirements state the problem and the business objectives at a high level, and they help inform how the proposed project will solve the business problem. The team defines the requirements in a business requirements document (BRD) .A business requirement might be a process, data necessary for the process, or a business rule influencing that process or data. These requirements align the project goals with the business objects. For example, if the company needs to upgrade its IT ticketing software system, the business requirement might state, “Install, implement, train, and migrate existing data into the new system to reduce lost tickets and employee frustration, which is the highest contributor to employee retention issues. Plus, increase efficiency by properly categorizing ticketing priorities to address IT requests based on an urgency.” Project documents, such as a project charter or stakeholder analysis , typically include business requirements.
- Stakeholder Requirements: Also called user requirements or user needs , these requirements detail the activities and elements that users require to interact with the system. First, stakeholders define and share what they expect from the given solution. Then the team describes these in a requirements specification document , citing use cases or user stories . The requirement will vary depending on the stakeholder. For example, a customer’s requirement might be, “As a person with a visual impairment, I need the screen text to have a large font size for words to be readable on my device,” whereas an operation’s requirement might be, “The application must maintain internal document security with a password-protected lock for every external download.”
- Solution Requirements: These requirements reconcile the necessary product characteristics with business and stakeholder needs. There are two types of solution requirements: functional and non-functional.
- Functional Requirements: These requirements include tasks a user needs to accomplish their goal within the working system. They describe what features or functions the product needs to be usable, and further distill these functions into specific categories, such as authentication, authorization, transactions, reporting, or compliance. For example, the functional requirement might read, “The user receives an automated text after the customer service call confirming the refund transaction was processed.” Development teams identify technical requirements as part of the functional requirements. The business analysis or systems analyst prepares a technical requirements document , also called a product requirements document . This document ensures that the product the developers build meets customer needs. Other business documents might help you discover and detail the functional requirements, such as a work breakdown structure (WBS) , software requirements specifications , or a functional specifications document . They might also be presented visually in models, diagrams, or prototypes.
- Nonfunctional Requirements: Nonfunctional requirements are the general properties that define the system’s performance. They are also called quality attributes . For example, a nonfunctional requirement might read, “Each website page needs to load in under 3 seconds,” or “During peak hours, the website must operate smoothly with up to 100,000 users.”
- Transition Requirements: These are the temporary requirements necessary during the implementation of the new system. They are also called implementation requirements . For example, a transition requirement might read, “The user must be properly trained with the updated features and functions.”
Requirements exist throughout the business in the following areas, from the highest-level strategy to the day-to-day operations:
What Is Meant by Requirements Management?
Requirements management is the formalized process used to meet customer and stakeholder needs. First, managers and analysts list the needs in a requirements management plan (RMP) document. Then they track and validate each requirement’s progress.
Effective requirements management planning visualizes, organizes, and communicates a proposed project’s requirements. Typically, a business analyst develops the document, sometimes referred to as a business analysis plan . However, if the company has limited resources, a project or product manager is responsible for collecting, analyzing, refining, and prioritizing the requirements.

Gerard Blokdyk, founder and CEO of The Art of Service , describes requirements management as the way to ensure “your organization assists project members with analysis and evaluation and with the preparation of recommendations for requirements of system improvements, optimization, development, and maintenance efforts.”
Requirements management is most common in system engineering, but is also part of other disciplines, such as business analysis and project management. Blodijk identifies requirements management in “information systems architecture, networking, telecommunications, automation, communications protocols, electronic analysis, software, lifecycle management, software development methodologies, modeling and simulation, and disaster recovery.”
What Does Requirements Management Involve?
Requirements management involves five activities: collection, analysis, definition, prioritization, and validation. A business analyst leads the team in planning, tracking, and controlling the requirements. Once validated, a requirement might need maintenance or enhancement.
As the analyst develops and executes the RMP, each requirement goes through the following activities:
- Collection: Gather the proposed needs from customers, stakeholders, and internal departments.
- Analysis: Review the proposed requirements and determine if they align with the business objectives and product goals.
- Definition: Formally document and categorize each requirement. Define “complete” for each requirement.
- Prioritization: Order requirement execution based on the project schedule, release plan, or sprint.
- Validation: Track each requirement’s progress through completion and test it to make sure the product meets the client’s needs.
- Maintenance: Schedule ongoing improvements or upkeep.
You can find more detailed examples of what occurs during each activity below.
Once obtained, it is helpful to itemize the requirement’s actions and deliverables on a checklist template, as in the example below.
Who Is Responsible for Requirements Management?
A project manager or business analyst is responsible for requirements management. They lead a team that gathers the requirements from stakeholders and subject matter experts, and they own all stages of the process, including developing the requirements management plan.
The primary owner is the business analyst, but teams might also include the following roles and responsibilities:
Every member of the requirements team is responsible for communicating updates and requirements changes. Additionally, the RMP document includes sections for details about the following activities, which both support the team’s effectiveness:
- Baselining: The team documents baselines as a comparison tool between all or a subset of requirements over a select period. It is used as a common language when communicating changes. This baseline is not a one-time event but a snapshot of a moment. The team develops a baseline strategy by determining baselining guidelines, including the frequency, content, and revisions.
- Change Control: This RMP section defines how the team communicates, manages, and controls requirement changes. It identifies the process owners on the change control board and the authorization levels when making changes.
What Is Requirements Management Planning?
Requirements management planning is a repeatable process during which the project team defines the approach and techniques they will use to carry out all requirements-related activities. It occurs during the development stage of the requirements management process.
During this planning phase, the project manager works with stakeholders and subject matter experts to identify all requirements necessary in the RMP. They use this information to help manage the project scope. Additionally, the designated planners document their approach for identifying stakeholders, collecting artifacts, employing management tools, monitoring requirement progress, controlling changes, and reporting.
What Is in a Requirements Management Plan?
A requirements management plan documents the project team’s approach to collecting, monitoring, and controlling each requirement. It is a reference document that details all approaches and procedures the team will use to execute the requirement management activities.
Though there is no standard format for an RMP, each document should record the processes and details involved in the following areas:
- General Information: Lists the project information and stakeholder roles.
- Process: Details the collection, analysis, definition, prioritization, validation, and maintenance approach.
- Type: Categorizes, names, describes, and defines each requirement. These might also specify sub-categories within the stakeholder, business, and solution requirements, such as delivery, project, quality, or portfolio.
- Mapping: Visually models the theoretical requirements to the business objects. This section may have a Requirements Matrix Map (RMM) to display the process, such as a flowchart.
- Conventions: Explains the document formats (optional).
- Owner: Lists each requirement’s responsible party.
- Prioritization: Uses criteria to evaluate and determine which requirements to include in an upcoming release or project. This section might rank each with a requirements prioritization matrix .
- Traceability: Tracks the requirement throughout the product development cycle.
- Versioning: Records requirement plan changes and maintains the change history.
- Baselining: Captures the stakeholder agreed-upon specifications for a specific product release. Controls any changes to the set specifications.
- Communication Strategy: Structures the communication plan, including defining the flow of information, such as what information gets shared, who receives it, and when.
- Management Tools: Lists additional instruments necessary to monitor and control the project, such as status tracing information or activity references, including requirements change management (RCM).
What Are Requirement Management Activities?
Requirements management activities occur in an ordered process cycle, including gathering, analyzing, defining, and prioritizing each requirement, and ending with requirement validation and maintenance.
Below, we’ve defined each activity in more detail.
Gathering Requirements
During this phase, the team talks with stakeholders to determine the requirements, using any of the following methods:
- Interviews: During one-on-one or focus group sessions, a facilitator pinpoints the product needs by asking who, what, where, when, why, and how questions.
Here are some example questions:
- Who will use this product or feature?
- What does the end result look like?
- Where does the process start?
- When will this feature be used?
- How does this product meet the business objectives?
These questions help the interviewees talk about the product vision and cover all its needs. The team might involve the end user in the product’s design and development, called a joint application development (JAD) method.
- Document Review: Draw information from any existing documents pertinent to the project, such as a request for proposal . The team also creates documents, such as questionnaires or surveys, if they do not already exist.
- Observations: Team members follow ideal users and study their needs to see how they currently use a product. This also helps determine what features are necessary to improve the product.
- Brainstorming: These sessions develop use cases and walk through them together to identify how a user will experience and interact with the product.
- Interface Analysis: This method determines the requirements necessary for interfacing between the solution and the application. It helps ensure the requirements interact effectively.
Analyze Requirements:
The business analyst employs techniques and software tools to visualize the data through business process models . They understand the sequence of events with open-source Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) software and create charts, such as flowcharts , Gantt charts , and gap analysis using business process model templates . The business analyst also conducts an impact analysis to identify any implications of the proposed changes. They might walk through a use case to realize the end user’s experience with the proposed requirements.
Define Requirements:
The business analyst describes each requirement using the characteristics of a well-defined requirement, as explained below:
- Unique: Identifies only one requirement and does not conflict with other requirements.
- Specific: Is relevant and current.
- Consistent: The descriptors are not in conflict with other requirement descriptors.
- Necessary: It is essential for delivery.
- Understandable: Written in clear, unambiguous language.
- Accurate: Identified data and capabilities accurately within a specified percentage.
- Testable and Verifiable: Contains verifiable characteristics validated through inspections and analyses.
- Feasible: Stays within business costs and technical capabilities.
- Traceable: Can be tracked at each stage, from the identification to the delivered product.
- Prioritized: In software, identifies which requirements to include in a release. Reduces risk by completing the essential requirements first.
Prioritize Requirements:
The analyst works with stakeholders to order the importance based on the customer needs and the project constraints . The analyst must use people management skills to ensure stakeholders come to a consensus while meeting the strategic business goal.
Business analysts can ask the following questions, based on the BABOK® 3.0, to help order the requirements:
- How will the requirement benefit or provide an advantage to the business (i.e., functionality, quality, business goals)?
- What is the opportunity cost if the requirement is not implemented? Consider financial costs, penalties, or customer losses.
- Which resources are necessary to implement the requirement?
- Can the requirement deliver the expected value?
- What is the risk of implementation?
- What are the dependencies? Which requirements must be completed before starting this one?
- When will the requirement expire? Is it time sensitive?
- Will the requirement be easy to maintain once implemented? Will it remain stable?
- Do the requirements meet regulations?
Validate and Maintain Requirements:
The team performs checks and tests based on the definition to identify errors, confirm the requirement meets the customer needs, and identify any issues early in the development process.
Santosh Kumar Reddy Peddireddy and Sri Ram Nidamanuri classify six validation techniques in their study, “ Requirements Validation Techniques and Factors Influencing Them .” Companies might use one or multiple techniques during the validation process:
- Requirement Inspections: A formal requirements review process calls for systemic peer review. The team checks for correctness, completeness, verifiability, feasibility, clarity, and consistency. Testing activities generate a list of the detected issues and actions the team will take for each problem.
- Prototyping: The team clarifies ambiguous requirements and system designs early in development by building mockups. They may quickly create an inexpensive prototype, called rapid or throw-away, or an evolutionary prototype that is updated with each issue improvement.
- Viewpoint-Oriented Requirement Validation: The team analyzes two competing viewpoints to identify gaps between the two viewpoints. They then reconcile the viewpoints into a single solution.
- Testing Based: Using the verifications created in the definition stage, the team designs and conducts tests to reveal errors. Testing occurs early in the development process to reduce costs by identifying defects, incompleteness, and low quality. A good test is effective, timely, efficient, and manageable.
- Model Based: Testers trained to develop diagrams from use cases check that the use case descriptions meet user needs.
- Feature-Oriented Requirement Validation: Feature validations are either structural or functional, and they note the feature itself and its specified behaviors during validation.
The team lists any observable issues from the validation tests and creates a maintenance schedule list. After the team executes the listed activities, they might find that some requirements could need multiple versions.
How to Write a Requirements Management Plan
You write a requirements management plan at the same time as the project plan. The team discusses and documents all process-related activities for managing, tracking, and reporting the requirements, as well as strategizes the communication and change management.
Once the plan is completed, you’ll have answers to the following questions:
- Who is the end user for the product or service?
- Who is responsible for each requirements management activity?
- What is our approach to identifying, defining, and prioritizing requirements?
- What is our change management process? How will we communicate changes?
- How will we track, test, and monitor each requirement?
- How will we determine which requirements to include?
The analyst collects and records the information into the requirements management plan, sequenced below. The RMP combines several documents into one location. Attach it to the project plan for larger projects.
- Using a requirements management plan template, write the project’s general information, purpose, scope, and stakeholders. Refer to the project charter to find the information.
- Outline the tentative schedule and any document conventions.
- Determine the process the team will use to prepare the RMP. You might need to schedule meetings with the team to discuss the best methods.
- Specify the necessary methods or processes for each requirement activity (gather, analyze, define, prioritize, validate, trace, track, report, and maintain).
- Detail how you will share the information in a communication plan.
- Outline the procedure for requesting changes in a change management plan.
- Determine the authorization levels necessary for any change approvals.
- Attach additional supporting documents that clarify how you will gather, manage, analyze, define, and track the requirements, such as in a work breakdown structure, gap analysis, BPMN, or dashboard, or by using definition criteria.
- Review the document. Confirm the document specifies all procedures for the product or project. Double-check your organizational planning and activities by answering the following questions, provided by Blokdyk:
- Are software tools used to improve efficiency in roadmaps, requirements management, and business planning?
- Look at identifying resource requirements management planning. Does the team have bandwidth to take on the outlined commitments, and will the document help you to make more informed decisions about the activities?
- Does the RMP define how changes will be identified?
- Does the RMP indicate that each requirement will be uniquely identified?
- Does the software group use the allocated requirements as a basis for software plans, work products, and activities?
Once you complete the requirements management plan, share it with stakeholders. That said, don’t assume stakeholders will read the plan. Instead, meet with each group to baseline and agree on the requirements before approval.
Then put the plan into action. Establish and update traceability metrics to monitor each requirement. Follow through on the change management procedures outlined in the plan for any change requests. Document and report any compliance issues.
Requirements Management Plan Example
Download Requirement Management Plan Example Template Microsoft Word | Google Docs
Use this requirements management plan example to get an idea of the data you need for an effective plan. It outlines the format for each activity and provides a framework to organize all necessary documents before presenting it for approval.
What Is the Requirements Management Process?
A requirements management process includes four major activities: planning, development, verification, and change management. The sub-processes within each activity involve gathering, defining, documenting, and testing. Change management tracks and controls the requirements once implemented.
Here is more info on each stage of the process:
- Requirements Planning: The team creates their approach to developing and executing the plan, which is reviewed and approved by stakeholders and sponsors. The team uses the information from this stage as the primary input to all other requirements processes.
- Requirements Development: The team takes action on the approved plan by gathering, defining, and analyzing the requirements.
- Requirements Verification: The team performs acceptance testing and validation to track and measure how the requirements are satisfied.
- Requirement Change Management (RCM): This technique manages the change control system implementation and the changes. It identifies the change control board as the deciding body for procedures and change requests.
Requirements Management Metrics
Requirement management metrics monitor how each requirement adds value. The team internally decides which metrics best monitor the project progress. The metrics ensure the end product satisfies the original vision.
Here are common metrics that teams use:
- Size: Document the number of requirements within a single project. Then compare the actual requirements completed from the estimated between iterations.
- Traceability: Link the functional requirements to the product (i.e., between design and code). You should also track the percentage of traced requirements.
- Quality: Use inspection data to calculate the product’s efficiency and effectiveness.
- Stability: Track the number of change requests over the number that have been resolved to identify the relative stability of the requirement.
- Status: Monitor the completion percentage of each requirement. Common statuses are proposed, approved, implemented, verified, deferred, deleted, or rejected. This metric helps developers and managers communicate, especially for developers working on multiple requirements.
- Change: Record the number of change requests.
Requirements Management Starter Kit
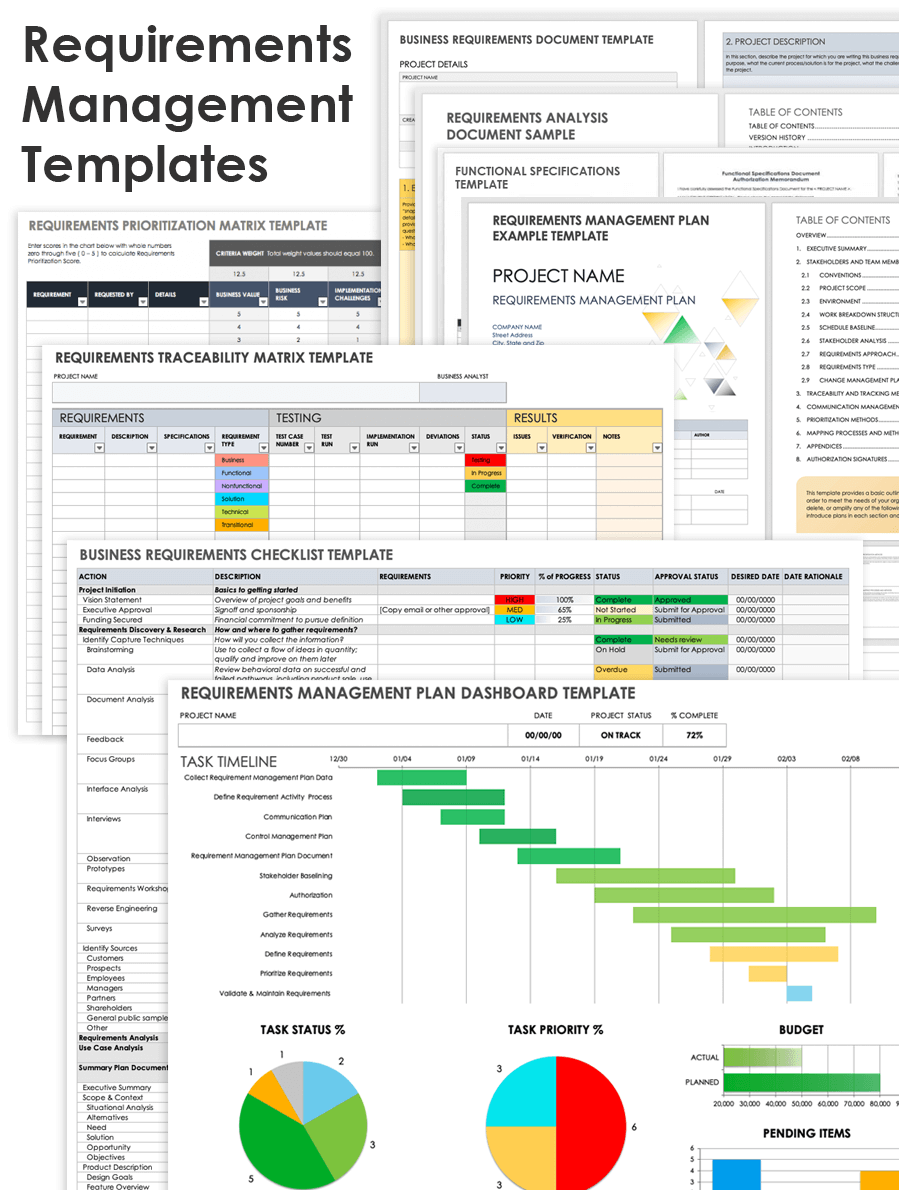
Download Requirements Management Starter Kit
Use this starter kit to handle the planning, documentation, analysis, and maintenance needs of requirements management. These essential templates will help you take care of the data and information demands of requirements management and communicate effectively.
In this kit, you’ll find:
- A requirements management plan template for Microsoft Word to use alongside a project plan so that you can thoroughly document your approach and processes.
- A requirements plan dashboard template for Excel to visualize and track the document’s completion progress.
- A business requirements document (BRD) template for Microsoft Word to define your project components and critical business needs.
- A r equirements checklist template for Excel to account for and track each requirement’s status.
- A requirements analysis template for Microsoft Word to document the project purpose, business drivers, and versioning.
- A requirements prioritization matrix template for Excel to evaluate and prioritize requirements, features, or use cases.
- A functional specifications template for Microsoft Word to detail what the product or feature(s) will do for the user. Alternatively, view our roundup of functional specifications templates or technical specification templates .
- A r equirements traceability matrix template for Excel to ensure each requirement meets customer needs.
Need more templates to boost your requirement management activities? View our extended collection of free, customizable project requirements templates .
Why Is Requirements Management Important?
Requirements management is important because it ensures the end product meets customer needs. Requirements management integrates business goals with the team’s deliverables, and it boosts team productivity by reinforcing strong communication and clear procedures.
For every project, program, or portfolio, stakeholders must agree on what is essential. However, miscommunication is one of the most common influencers of failed projects. Requirements management reduces the risk of project failure by creating a communication channel among stakeholders. This process creates a shared understanding of expectations and general protocols to help the team reach a consensus.
Additionally, by defining the requirements at the project’s start, the project is less likely to incur cost overruns and mistakes.
Especially in Agile development methodology, Blokdyk advises, “Have a best practice in place for incorporating requirements management, risk management, system architecture definition, and testing or documentation.”
Benefits of Requirements Management
Requirements management empowers a team to deliver the product and allows stakeholders to express their expectations. It also improves the organization’s strategy and operations to create the most business value and maximizes business value by optimizing limited resources.
Ultimately, the process structure builds communication within the team and with stakeholders. The design helps the team understand stakeholder needs, envision the final product, organize their efforts, and control the process with fewer unexpected roadblocks. This helps the business in the following ways:
- Lowers costs by reducing risks such as reworking, defects, and scope creep
- Improves quality and stakeholder satisfaction by maximizing time and communication
- Delivers the product faster by reducing the time required
- Avoids work duplication by reusing definitions
- Builds a cohesive team by clearly defining roles and responsibilities
Requirements Management Best Practices
Best practices for requirements management include providing upfront communication, clearly defining requirements, and adhering to the requirements management plan. In addition, analysts must work to engage and educate stakeholders and team members.
In Understanding the Sources of Information Systems Project Failure , John McManus and Trevor Harper-Wood identify poor requirement definition as a leading factor contributing to 35 percent of project failures. In addition to clearly defining your project requirements, adhere to the following best practices:
- Proactively communicate and encourage feedback from team members.
- Include requirements management throughout the business’s strategic objectives and as a part of operations.
- Confirm that all project team members understand the importance of following the RMP and actively managing requirements.
- Do not change the baseline requirements once completed without going through a change process and approval.
- Have a clear change management plan.
- Avoid surprises by planning requirements upfront and communicating roles, timelines, and responsibilities. Make sure your requirements are well defined.
- Link each requirement to a test to assess its ongoing performance.
- Engage stakeholders and managers in the RM process from the beginning.
- Implement the RMP at the project’s start, and refer to it throughout its lifecycle.
- Use requirement management software tools to expedite processes, communication roadblocks, and schedules.
Blokdyk also adds the following best practices:
- Rate the quality of requirements management at your supplier organization.
- Ensure that systems engineers do the requirements management work.
- Keep the tools synchronized when you maintain multiple tools in the same lifecycle domain for requirements management.
What Is Digital Requirements Management?
Digital requirements management refers to a centralized collection platform. It is the hub where the team tracks, analyzes, and manages the requirements online securely. Teams use software to support real-time collaboration.
Digital solutions benefit the company by doing the following:
- Reusing the same requirement in several locations without redefining it
- Working in real time to identify the requirement state, reducing errors
- Sharing information between documents within the system
- Collaborating live from any location
- Automatically recording each requirement’s history
- Tracking the time, date, and user for each change
- Building a database of history for audits
- Organizing data according to the team’s communication style
- Sorting requirements by categories, such as type, priority, risk, and status
- Consistently keeping track of the status
What Is Requirement Lifecycle Management?
Requirement lifecycle management is an official knowledge area in the BABOK®. It describes the tasks a business analyst performs to manage and maintain requirements, including tracing, maintaining, prioritizing, assessing changes, and approving the requirements from start to finish.
A business analyst (BA) leads an Agile project management process , documenting artifacts and advancing each stage. The BA is responsible for creating an environment that encourages analysis from all teams, as well as aligning the stakeholders, design team, and management to the requirement’s business objectives.
The input categories in requirements lifecycle management are requirements, designs, and proposed changes. The analyst conducts the following five activities for these inputs:
- Trace Requirements: The analyst creates traces between the design and requirements, then determines which requirements are relevant to the design initiative and sets up how they will be evaluated.
- Maintain Requirements: The analyst supports the requirement’s accuracy and consistency throughout the process, as well as examines and facilitates the requirements reuse.
- Prioritize Requirements: Next, assess the business value and risk, and then rank the requirements in order of urgency in the context of each initiative.
- Assess Requirements Change: Review newly suggested requirements or changes to existing ones to determine if they are essential to the project.
- Approve Requirements: The analyst communicates with stakeholders and prepares requirements for approval.
Once completed, the analyst will have the following outputs:
- Completed requirements from the task cycle
- Completed designs from the task cycle
- Design and requirement change assessments
Enterprise Requirements Management
Large corporations use enterprise requirements management to organize projects between hundreds of employees. Companies this size must use RM software and modeling tools. These tools help cross-functional teams trace, develop, and execute the RMP in real time.
An enterprise requires an architecture , or structured framework, for a team to manage the dynamic requirement changes. They have the resources and budget to implement top-level management software. Typically, the enterprise has a business architect who develops the company’s model and maintains the software. This digital platform helps business teams maintain momentum in recording and tracing data. Plus, it supports the team’s communication, agility, and momentum in a fast-paced environment.
The future of requirements management revolves around improving and enhancing current practices. Companies will increasingly adopt automation tools to optimize their processes and systems as technology advances. As a result, artificial intelligence (AI) will be a major player.
Companies continuously seek to improve their systems and processes, and requirements management is no different. Generally, companies look to advance the requirements data management through the following activities:
- Consolidating requirements and models
- Automating processes
- Reducing requirements
- Aligning current and future IT initiatives
- Updating RM platforms
- Integrating advanced remote work procedures
- Evaluating new technology
- Developing future-oriented IT architecture strategies
As Blokdyk recommends, “Safeguard that your strategy is collaborating with your engineering and product peers to analyze enterprise business context (business strategy and trends), as well as change requirements in other enterprise architecture viewpoints to derive the technology architecture future state.”
Forward-looking businesses are also experimenting with AI to enhance their existing data management systems.

Kavita Ganesan, the Founder of Opinosis Analytics and author of The Business Case for AI: A Leader's Guide to AI Strategies, Best Practices & Real-World Applications , sees the use case for AI to prioritize and structure the data, particularly text data.
“Specifically, with the use of Natural Language Processing, a branch of study within AI, you can extract the most common set of requirements from all requirements and problems submitted,” she says. “You can then organize these requirements by type (e.g., user interface, speed, display, etc.) and summarize the requirements so that it becomes easy for teams to plan around those requirements.”
In the future, she notes that AI can align the requirements with the company’s product visions and augment the requirements gathering process with real-time requirements input analysis. But it requires the correct data, specifically historical data, to make AI-powered solutions possible.
Implement Requirements Management with Real-Time Work Management with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business

Your 2024 Guide to Writing a Software Requirements Specification – SRS Document
Any application starts with an idea, and mobile app development begins with a Software Requirements Specification – SRS document. You might have a truly brilliant and unique digital product idea, but the journey to the implementation phase ultimately defines whether your application will succeed or fail. The SRS document is a vital part of this journey.
Approaching development without documentation and a clear plan leads to a chaotic implementation process, costly reworks, delays, or even a failed project. In fact, inadequate or incomplete requirements are the most common reason for project failure and a cause of nearly 50% of product defects. However, the good news is you can avoid all these issues and lay the groundwork for a successful outcome by creating accurate and understandable SRS documentation.
200+ companies from 25 countries outsourced software development to Relevant
We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software. Let's talk about how we can help you.
In this guide, we explore the essentials of this document, why it’s a cornerstone for any software project in 2024, and what makes up an effective SRS in software engineering. Moreover, we’ll share an SRS document example and our expertise on how to write your own to make it a practical guide for stakeholders and all participants involved in the project development.
Table of Contents
What is SRS, and Why is This Document Important?
Let’s start with the SRS meaning. Software requirements specification is a technical document describing your project’s functionality, features, design, limitations, and goals. Simply put, an SRS outlines how an application should operate and how the product development team should build it. While you as a client may use it to define your project expectations and deliverables, your development company will use it to assess the amount of work, define the technology stack , and estimate the project cost.
The main goal of the this report is to clarify all potentially vague aspects of development and communicate to the team:
- How the app should be built
- How it should work (preferably, it should include use cases)
- The app’s purpose, features, and behavior
Just as a statement of work (SOW) , this document is crucial, especially when you outsource software development . An SRS document serves as a project roadmap for you and your dedicated team, leaving little room for confusion and misunderstandings. As a single source of truth that everyone can refer to, the requirement document sheds light on product specifications and deadlines, ensuring a shared understanding and alignment.
Moreover, it’s next to impossible to develop an app exactly what you expect without an SRS. Think we’re exaggerating? Now consider how software engineers will know which features to build, UX designers match the design to use cases, and QA specialists test the app. That’s why writing down clear software requirements guarantees your development team will build the product matching your needs. What’s more, an SRS is helpful for:
What Does an SRS Include?
Software requirements specification is a blueprint for the development team, providing all the information they need to build the tool according to your requirements. But it also should outline your product’s purpose, describing what the application is supposed to do and how it should perform.
An SRS can vary in format and length depending on how complex the project is and the selected development methodology. However, there are essential elements every good SRS document must contain:
- Purpose of the digital product is a clear and concise statement that defines the intent of the solution. This statement should address your needs, outlining what the app will achieve once completed.
- Description of the product provides a high-level overview of the future tool, including intended users, the type of environment it will operate in, and any other relevant information that could impact the software development process .
- Functionality of the product describes the features, capabilities, and limitations or constraints that might affect the tool’s performance.
- Performance of the product should include requirements related to its performance in a production environment: speed, efficiency, reliability, and scalability.
- Non-functional requirements address such factors as security, compatibility, and maintainability.
- External interfaces include information about how the application will interact with other systems it must connect to. So, here communication protocols and data formats are described. Also, it outlines details of the screen layout, logic interface, hardware interface, and design.
- Design constraints or environmental limitations that may impact the development process or the software’s functionality.
- Assumptions and dependencies note the presuppositions made during the SRS document formulation and any external or third-party dependencies critical for project planning and risk assessment.
- Quality attributes define the standards for usability, reliability, and accessibility you expect in terms of the software’s quality.
- Security protocols explain the security requirements to protect the software against unauthorized access and ensure data privacy.
- Acceptance criteria specify the must-do list for the software to be considered finished and ready to go live, including all the tests the software needs to pass and the goals it must achieve.
The Difference Between Functional Requirements Document and Non-functional Requirements
To understand the difference, think of it this way: functional requirements are like the meat and potatoes of a meal, while non-functional are like the seasoning.
Functional requirements document is essential to the system’s core function, describing the features and fundamental behavior, just as meat and potatoes are the core elements of a meal. Without them, the system won’t work as intended, just as a meal won’t be satisfying without the main course. For example, when you register and sign in to a system, it sends you a welcome email.
On the other hand, non-functional requirements enhance the user experience and make the system more delightful to use, just as the seasoning makes a meal more enjoyable to eat. They specify the general characteristics impacting user experience.
Coming back to an example of the registration confirmation, a welcome email sent within five seconds after signing in would be a non-functional requirement.
So while functional requirements are crucial to the system’s operation, non-functional are equally important to the user’s needs and expectations. A system that is slow, unreliable, or difficult to use will significantly impact the user’s decision to use it.
How to Write a Software Requirement Specification Document
The creation of an SRS should be one of the first things to do when you plan to develop a new project. Writing it may seem daunting, but it’s essential to building successful software. Moreover, you can always use a software requirement specification example to simplify the task. The more elaborate and detailed your SRS is, the fewer chances for the development team to take the wrong turns.
To make the process of writing an SRS more efficient and manageable, we recommend you follow a structure that starts with a skeleton and general info on the project. Then it will be easier for you to flesh out the details to create a comprehensive draft. Here’s a six-step guide to creating an SRS document in 2024:
Step 1. Create an Outline
The first step is to create an outline that will act as a framework for the document and your guide through the writing process. You can either create your outline or use an SRS document template as a basis. Anyway, the outline should contain the following important elements:
- Intended use and target audience
- Product scope
- Definitions
- Business requirements
- Product limitations and constraints
- Assumptions and dependencies
- External interface
- Non-functional
- Supporting information
Step 2. Define What the Purpose of Your Software is
In fact, this section is a summary of the SRS document. It allows you to write a clear picture of what you want your product to do and how you want it to function. So, here you should include a detailed description of the intended users, how they will interact with the product, and the value your product will deliver. Answering the following question will help you to write the purpose:
- What problems does your product solve?
- Who are the intended users?
- Why is your product important?
Building on the basic summary of SRS, it’s a good idea to also think about how your product fits into the bigger picture. Look at what makes your product stand out from the rest and how it might change the game in its market. It will help you sharpen its purpose and value proposition.
Step 3. Give an Overview
Here’s the section where you clarify your idea and explain why it can be appealing to users. Describe all features and functions and define how they will fit the user’s needs. Also, mention whether the product is new or a replacement for the old one, is it a stand-alone app or an add-on to an existing system? Additionally, you can highlight any assumptions about the product’s functionality. And don’t forget to mention what makes your product special or different from others, and make sure to share these unique points clearly.
Step 4. Describe Functional and Non-functional Requirements
Often, clients don’t have a clear idea about the intended functionality at the start of the project. In this case, Relevant cooperates closely with you to understand the demands and assigns business analysts to assist with it.
Whether you write it internally or with the help of external experts, you should detail all the requirements associated with your app. For your dedicated development team to understand it properly, describe this information adequately. It would help them if you include use cases here as well since they can vividly illustrate how a user will interact with your system.
Did you know that performing a technical feasibility study as part of the requirement-gathering phase can significantly enhance the project’s success rate? Relevant business analysts, along with our technical experts, assess your project against current technological trends, potential integration points, and existing solutions. In such a way, the software will be technologically viable and forward-looking.
Step 5. Add Supplemental Details
If you have something else to add, any alternative ideas or proposals, references, or any other additional information that could help developers finish the job, write them down in this section of the software requirements specification. You may have suggestions on technologies you want to use, ideas for design patterns, or examples of case studies that have tackled similar challenges. Here, you can also define priorities for certain features and highlight areas where your development team has room for flexibility and creativity. Get this: the more details you specify, the better the software will meet your expectations.
Step 6. Get Approval
Now it’s time to have stakeholders review the SRS report carefully and leave comments or additions if there are any. After edits, give them to read the document again, and if everything is correct from their perspective, they’ll approve it and accept it as a plan of action. Here, it’s important to include every change in the latest SRS version and inform your development team right away to ensure everyone is on the same page. After that, you’re ready to move toward app or web development .
How to Write Software Use Cases in an SRS
Use cases help you ensure that the users have a smooth and robust experience using your product. To write use cases, you should put yourself in the shoes of your intended audience and get a better understanding of how they will interact with your program. By doing so, you’ll be able to identify potential issues early on and ensure your product meets the users’ expectations and needs.
To begin, describe your product’s targeted users. Who are they, and what tasks will they need to perform with your software? Then, focus on one of these users and break down their interaction into use cases. Each use case will represent a specific interaction the user has with your solution.
Now depict the sequence of events that will take place for each use case. This will let you map out the user’s actions and how your software should respond. Then expand each use case with alternative actions and probable system responses to ensure that you’ve covered all possible scenarios.
Finally, repeat these steps for each user type. Thus, you’ll create a comprehensive set of software use cases that accurately represent how your application will be actually used. By following these steps, you’ll create software that truly delights your users.
What are the Characteristics of a Great SRS in Software Engineering?
We provide some features of a good quality SRS so you can ensure your technical requirements document is good enough to serve as a guide for your professional development team.
An SRS requires clear and easy-to-read content using agreed terminology so that all members of the product development process can easily understand it. Very handy are visuals like diagrams, models, or schemes as they can explain some points straight away.
Unless the software requirements are measurable, it will be hard to know whether you are going in the right direction and whether the team is completing the milestones. Project managers have to understand how to assess the project progress and validate and verify the end product against the specifications. So, make your requirements measurable.
The SRS document must contain all the features you want to build with enough detail for your development team to complete the project: software requirements, assumptions, dependencies, and prerequisites. The stakeholders should check whether every part of it is described or if any details are missing.
When writing the specifications, you should take into account the budget, timeframe, and tech realities of the current environment.
Note that an SRS is a living document that may be updated and refined throughout the development process, so it’s important to keep it flexible and adjustable.
It’s also vital to make the document available to all development team members so they can refer to it whenever necessary. The indicator of clear requirements would be no questions for clarification or demands for more details from the team.
The software requirements in the document shouldn’t contradict each other. Also, the format of the whole SRS should be consistent, and ensure you use the same terminology throughout the paper.
No Implementation Constraints
Although the software requirements specification requires detailed information, we don’t recommend you make it overly specific, impose technological or architectural solutions, or specify a design methodology, as it may restrict development.
SRS documentation should accurately depict the product’s functionality, specifications, and instructions so that the team members have no additional questions while using it. So, make sure every requirement has only one possible interpretation by avoiding subjective suggestions, ambiguity, and loopholes.
By adhering to these characteristics, you can create an SRS document that meets the needs of all stakeholders and provides a comprehensive and clear plan of action for your development team.
A Software Requirements Specification Example
Below, we provide a condensed SRS document example for a mobile shopping app, “FashionStyle”.
Introduction
This document outlines the development plan for “FashionStyle”, a mobile app that will allow users to browse and purchase clothes from different brands. This plan is intended for software engineers, designers, and investors of the project.
Overall Description
In the age of e-commerce, users are constantly seeking convenient ways to shop. However, with so many brands and products available online, it can be overwhelming for customers to find what they want. “FashionStyle” aims to solve this problem by offering a platform where consumers can easily find and buy fashion items from a variety of brands.
The target customers are primarily fashion-conscious individuals who prefer to shop online. They are likely to be tech-savvy and comfortable using mobile apps to make purchases.
Functionality
- Users should be able to create an account with email or social media.
- Users should be able to browse and search for clothes based on brand, category, color, and price range.
- Users should be able to view product details, such as descriptions, images, and reviews.
- Users should be able to add products to a cart and checkout securely.
- Users should be able to receive push notifications about new arrivals, sales, and promotions.
The app will be built using React Native , a cross-platform framework that will allow for both IOS and Android app development. The app will connect to a REST API created with Node.js and MongoDB to store and retrieve information.
Development Responsibilities
The development team for “FashionStyle” will be responsible for programming the app, designing the user interface, and testing the app for quality assurance.
User Class and Characteristics
There will be two types of users for “FashionStyle”: customers and admins. Customers will be able to use all the app’s features, while admins will have access to additional features such as managing product listings and discounts.
System Features and Requirements
- Users should be able to view product details, such as descriptions, images, and review
- Users should be able to add products to a cart and checkout securely
Internal Interfaces
User interfaces.
- Back-end software: Node.js
- Database software: MongoDB
- Front-end software: React Native
Hardware Interfaces
- IOS and Android mobile devices
Non-functional Requirements
Performance.
- The app should load and be ready to use within 5 seconds.
- The app should react to user interaction within 2 seconds.
- The database should be optimized to ensure fast query performance.
- The app should ensure secure transactions and protect user data through encryption and other security measures.
- The REST API’s keys should be stored securely.
Quality Attributes
Availability: The app should have a goal of 99.9% availability to ensure customers can shop anytime.
Correctness: The app should accurately display product information and ensure secure transactions.
Maintainability: The app should be continuously integrated so that features, updates, and bug fixes can be deployed rapidly without downtime.
Usability: The interface should be intuitive and easy to navigate, allowing users to shop and make purchases without confusion.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing an SRS Document
Don’t let your software requirements specification become a confusing mess! While there is no right way to write the requirement document, we will highlight the most common mistakes to avoid to help you ensure that your requirements are crystal clear.
First, be careful not to be ambiguous in your language . Remember, a software requirements specification aims to prevent misunderstandings, so ensure your requirements can’t be misinterpreted. Provide a clear description for every functionality, and avoid using words with multiple meanings.
Second, avoid overcomplicating your document . Standardizing the language of your document is not that big of a deal. Simply avoid using jargon and define terms before using them. Also, it would help to use references, such as “as shown in” or “in accordance with”.
Third, don’t over-specify your requirements . The document is not intended to become a complete description of the system for developers and architects. Stick to the essentials and avoid providing too many extra details. This can make the document less readable and vaguer.
Finally, if you struggle with structure and formatting, use a software requirements specification example to achieve clarity. If you’re unsure how to handle parts of the software requirements specification template, contact Relevant. We’ll help you write a comprehensive specification document for your project and ensure your requirements are communicated effectively. Don’t let a poorly written specification document derail your project – take the time or assistance to get it right the first time.
The success of any software project relies heavily on the availability of a well-written Software Requirements Specification document. It’s a critical component that serves as a roadmap for developers and stakeholders, outlining what the software should do, its technical details, and user needs.
Although creating a comprehensive SRS takes time and effort initially, it will pay off later with a robust app that meets both your and your users’ expectations. Moreover, following our expert tips, you can create an effective and detailed specification document.
At Relevant, we recognize the importance of SRS in software engineering and have helped over 200 companies build successful products with the help of software requirements specification. We can draft your requirement document either as a part of a full-cycle project or as a part of a stand-alone discovery phase . We’ll help you get high-quality SRS and stay relevant with the best development practices.
An SRS is a document providing a detailed description of the requirements and technical specifications of the software. It also guides software engineers on how to build the app to meet the client’s expectations. The software requirements specification document gives all the stakeholders and the development team a complete understanding of your entire project. An SRS provides a single source of information that everyone related to the project will follow.
– Every good SRS document should include the following crucial elements: – The purpose of the project – General description – Functional requirements – Non-functional requirements – Constraints and limitations – Assumptions
Typically, a business analyst or the project manager is responsible for writing an SRS, which beyond system features and functional and non-functional requirements, should describe the business’ understanding of the end user’s needs.
Success cases
projects delivered remotely
of a team senior and middle engineers
employee turnover rate
customer satisfaction score

Our core services:
Do you want a price estimate for your project, hand-selected developers to fit your needs at scale.
- 200+ projects delivered remotely
- 7 years of software development expertise
- 92% of a team – senior and middle engineers
- World-class code quality delivered by Agile approach
Contact us to get the following:
- Price estimation
- Time to delivery
- Recommendation on tech stack
Get a quote

Privacy Overview

Do you know that we helped 200+ companies build web/mobile apps and scale dev teams?
Let's talk about your engineering needs.

Small Business Trends
How to create a business plan: examples & free template.
This is the ultimate guide to creating a comprehensive and effective plan to start a business . In today’s dynamic business landscape, having a well-crafted business plan is an important first step to securing funding, attracting partners, and navigating the challenges of entrepreneurship.
This guide has been designed to help you create a winning plan that stands out in the ever-evolving marketplace. U sing real-world examples and a free downloadable template, it will walk you through each step of the process.
Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or launching your very first startup, the guide will give you the insights, tools, and confidence you need to create a solid foundation for your business.
Table of Contents
How to Write a Business Plan
Embarking on the journey of creating a successful business requires a solid foundation, and a well-crafted business plan is the cornerstone. Here is the process of writing a comprehensive business plan and the main parts of a winning business plan . From setting objectives to conducting market research, this guide will have everything you need.
Executive Summary

The Executive Summary serves as the gateway to your business plan, offering a snapshot of your venture’s core aspects. This section should captivate and inform, succinctly summarizing the essence of your plan.
It’s crucial to include a clear mission statement, a brief description of your primary products or services, an overview of your target market, and key financial projections or achievements.
Think of it as an elevator pitch in written form: it should be compelling enough to engage potential investors or stakeholders and provide them with a clear understanding of what your business is about, its goals, and why it’s a promising investment.
Example: EcoTech is a technology company specializing in eco-friendly and sustainable products designed to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. Our mission is to create innovative solutions that contribute to a cleaner, greener environment.
Our target market includes environmentally conscious consumers and businesses seeking to reduce their carbon footprint. We project a 200% increase in revenue within the first three years of operation.
Overview and Business Objectives

In the Overview and Business Objectives section, outline your business’s core goals and the strategic approaches you plan to use to achieve them. This section should set forth clear, specific objectives that are attainable and time-bound, providing a roadmap for your business’s growth and success.
It’s important to detail how these objectives align with your company’s overall mission and vision. Discuss the milestones you aim to achieve and the timeframe you’ve set for these accomplishments.
This part of the plan demonstrates to investors and stakeholders your vision for growth and the practical steps you’ll take to get there.
Example: EcoTech’s primary objective is to become a market leader in sustainable technology products within the next five years. Our key objectives include:
- Introducing three new products within the first two years of operation.
- Achieving annual revenue growth of 30%.
- Expanding our customer base to over 10,000 clients by the end of the third year.
Company Description

The Company Description section is your opportunity to delve into the details of your business. Provide a comprehensive overview that includes your company’s history, its mission statement, and its vision for the future.
Highlight your unique selling proposition (USP) – what makes your business stand out in the market. Explain the problems your company solves and how it benefits your customers.
Include information about the company’s founders, their expertise, and why they are suited to lead the business to success. This section should paint a vivid picture of your business, its values, and its place in the industry.
Example: EcoTech is committed to developing cutting-edge sustainable technology products that benefit both the environment and our customers. Our unique combination of innovative solutions and eco-friendly design sets us apart from the competition. We envision a future where technology and sustainability go hand in hand, leading to a greener planet.
Define Your Target Market

Defining Your Target Market is critical for tailoring your business strategy effectively. This section should describe your ideal customer base in detail, including demographic information (such as age, gender, income level, and location) and psychographic data (like interests, values, and lifestyle).
Elucidate on the specific needs or pain points of your target audience and how your product or service addresses these. This information will help you know your target market and develop targeted marketing strategies.
Example: Our target market comprises environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking for innovative solutions to reduce their carbon footprint. Our ideal customers are those who prioritize sustainability and are willing to invest in eco-friendly products.
Market Analysis

The Market Analysis section requires thorough research and a keen understanding of the industry. It involves examining the current trends within your industry, understanding the needs and preferences of your customers, and analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.
This analysis will enable you to spot market opportunities and anticipate potential challenges. Include data and statistics to back up your claims, and use graphs or charts to illustrate market trends.
This section should demonstrate that you have a deep understanding of the market in which you operate and that your business is well-positioned to capitalize on its opportunities.
Example: The market for eco-friendly technology products has experienced significant growth in recent years, with an estimated annual growth rate of 10%. As consumers become increasingly aware of environmental issues, the demand for sustainable solutions continues to rise.
Our research indicates a gap in the market for high-quality, innovative eco-friendly technology products that cater to both individual and business clients.
SWOT Analysis

A SWOT analysis in your business plan offers a comprehensive examination of your company’s internal and external factors. By assessing Strengths, you showcase what your business does best and where your capabilities lie.
Weaknesses involve an honest introspection of areas where your business may be lacking or could improve. Opportunities can be external factors that your business could capitalize on, such as market gaps or emerging trends.
Threats include external challenges your business may face, like competition or market changes. This analysis is crucial for strategic planning, as it helps in recognizing and leveraging your strengths, addressing weaknesses, seizing opportunities, and preparing for potential threats.
Including a SWOT analysis demonstrates to stakeholders that you have a balanced and realistic understanding of your business in its operational context.
- Innovative and eco-friendly product offerings.
- Strong commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility.
- Skilled and experienced team with expertise in technology and sustainability.
Weaknesses:
- Limited brand recognition compared to established competitors.
- Reliance on third-party manufacturers for product development.
Opportunities:
- Growing consumer interest in sustainable products.
- Partnerships with environmentally-focused organizations and influencers.
- Expansion into international markets.
- Intense competition from established technology companies.
- Regulatory changes could impact the sustainable technology market.
Competitive Analysis

In this section, you’ll analyze your competitors in-depth, examining their products, services, market positioning, and pricing strategies. Understanding your competition allows you to identify gaps in the market and tailor your offerings to outperform them.
By conducting a thorough competitive analysis, you can gain insights into your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, enabling you to develop strategies to differentiate your business and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Example: Key competitors include:
GreenTech: A well-known brand offering eco-friendly technology products, but with a narrower focus on energy-saving devices.
EarthSolutions: A direct competitor specializing in sustainable technology, but with a limited product range and higher prices.
By offering a diverse product portfolio, competitive pricing, and continuous innovation, we believe we can capture a significant share of the growing sustainable technology market.
Organization and Management Team

Provide an overview of your company’s organizational structure, including key roles and responsibilities. Introduce your management team, highlighting their expertise and experience to demonstrate that your team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
Showcasing your team’s background, skills, and accomplishments instills confidence in investors and other stakeholders, proving that your business has the leadership and talent necessary to achieve its objectives and manage growth effectively.
Example: EcoTech’s organizational structure comprises the following key roles: CEO, CTO, CFO, Sales Director, Marketing Director, and R&D Manager. Our management team has extensive experience in technology, sustainability, and business development, ensuring that we are well-equipped to execute our business plan successfully.
Products and Services Offered

Describe the products or services your business offers, focusing on their unique features and benefits. Explain how your offerings solve customer pain points and why they will choose your products or services over the competition.
This section should emphasize the value you provide to customers, demonstrating that your business has a deep understanding of customer needs and is well-positioned to deliver innovative solutions that address those needs and set your company apart from competitors.
Example: EcoTech offers a range of eco-friendly technology products, including energy-efficient lighting solutions, solar chargers, and smart home devices that optimize energy usage. Our products are designed to help customers reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Marketing and Sales Strategy

In this section, articulate your comprehensive strategy for reaching your target market and driving sales. Detail the specific marketing channels you plan to use, such as social media, email marketing, SEO, or traditional advertising.
Describe the nature of your advertising campaigns and promotional activities, explaining how they will capture the attention of your target audience and convey the value of your products or services. Outline your sales strategy, including your sales process, team structure, and sales targets.
Discuss how these marketing and sales efforts will work together to attract and retain customers, generate leads, and ultimately contribute to achieving your business’s revenue goals.
This section is critical to convey to investors and stakeholders that you have a well-thought-out approach to market your business effectively and drive sales growth.
Example: Our marketing strategy includes digital advertising, content marketing, social media promotion, and influencer partnerships. We will also attend trade shows and conferences to showcase our products and connect with potential clients. Our sales strategy involves both direct sales and partnerships with retail stores, as well as online sales through our website and e-commerce platforms.

Logistics and Operations Plan

The Logistics and Operations Plan is a critical component that outlines the inner workings of your business. It encompasses the management of your supply chain, detailing how you acquire raw materials and manage vendor relationships.
Inventory control is another crucial aspect, where you explain strategies for inventory management to ensure efficiency and reduce wastage. The section should also describe your production processes, emphasizing scalability and adaptability to meet changing market demands.
Quality control measures are essential to maintain product standards and customer satisfaction. This plan assures investors and stakeholders of your operational competency and readiness to meet business demands.
Highlighting your commitment to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction underlines your business’s capability to maintain smooth, effective operations even as it scales.
Example: EcoTech partners with reliable third-party manufacturers to produce our eco-friendly technology products. Our operations involve maintaining strong relationships with suppliers, ensuring quality control, and managing inventory.
We also prioritize efficient distribution through various channels, including online platforms and retail partners, to deliver products to our customers in a timely manner.
Financial Projections Plan

In the Financial Projections Plan, lay out a clear and realistic financial future for your business. This should include detailed projections for revenue, costs, and profitability over the next three to five years.
Ground these projections in solid assumptions based on your market analysis, industry benchmarks, and realistic growth scenarios. Break down revenue streams and include an analysis of the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and potential investments.
This section should also discuss your break-even analysis, cash flow projections, and any assumptions about external funding requirements.
By presenting a thorough and data-backed financial forecast, you instill confidence in potential investors and lenders, showcasing your business’s potential for profitability and financial stability.
This forward-looking financial plan is crucial for demonstrating that you have a firm grasp of the financial nuances of your business and are prepared to manage its financial health effectively.
Example: Over the next three years, we expect to see significant growth in revenue, driven by new product launches and market expansion. Our financial projections include:
- Year 1: $1.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $200,000.
- Year 2: $3 million in revenue, with a net profit of $500,000.
- Year 3: $4.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $1 million.
These projections are based on realistic market analysis, growth rates, and product pricing.
Income Statement

The income statement , also known as the profit and loss statement, provides a summary of your company’s revenues and expenses over a specified period. It helps you track your business’s financial performance and identify trends, ensuring you stay on track to achieve your financial goals.
Regularly reviewing and analyzing your income statement allows you to monitor the health of your business, evaluate the effectiveness of your strategies, and make data-driven decisions to optimize profitability and growth.
Example: The income statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
- Revenue: $1,500,000
- Cost of Goods Sold: $800,000
- Gross Profit: $700,000
- Operating Expenses: $450,000
- Net Income: $250,000
This statement highlights our company’s profitability and overall financial health during the first year of operation.
Cash Flow Statement

A cash flow statement is a crucial part of a financial business plan that shows the inflows and outflows of cash within your business. It helps you monitor your company’s liquidity, ensuring you have enough cash on hand to cover operating expenses, pay debts, and invest in growth opportunities.
By including a cash flow statement in your business plan, you demonstrate your ability to manage your company’s finances effectively.
Example: The cash flow statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
Operating Activities:
- Depreciation: $10,000
- Changes in Working Capital: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Operating Activities: $210,000
Investing Activities:
- Capital Expenditures: -$100,000
- Net Cash from Investing Activities: -$100,000
Financing Activities:
- Proceeds from Loans: $150,000
- Loan Repayments: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Financing Activities: $100,000
- Net Increase in Cash: $210,000
This statement demonstrates EcoTech’s ability to generate positive cash flow from operations, maintain sufficient liquidity, and invest in growth opportunities.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan

1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively.
2. Conduct thorough research: Before writing your business plan, gather as much information as possible about your industry, competitors, and target market. Use reliable sources and industry reports to inform your analysis and make data-driven decisions.
3. Set realistic goals: Your business plan should outline achievable objectives that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Setting realistic goals demonstrates your understanding of the market and increases the likelihood of success.
4. Focus on your unique selling proposition (USP): Clearly articulate what sets your business apart from the competition. Emphasize your USP throughout your business plan to showcase your company’s value and potential for success.
5. Be flexible and adaptable: A business plan is a living document that should evolve as your business grows and changes. Be prepared to update and revise your plan as you gather new information and learn from your experiences.
6. Use visuals to enhance understanding: Include charts, graphs, and other visuals to help convey complex data and ideas. Visuals can make your business plan more engaging and easier to digest, especially for those who prefer visual learning.
7. Seek feedback from trusted sources: Share your business plan with mentors, industry experts, or colleagues and ask for their feedback. Their insights can help you identify areas for improvement and strengthen your plan before presenting it to potential investors or partners.
FREE Business Plan Template
To help you get started on your business plan, we have created a template that includes all the essential components discussed in the “How to Write a Business Plan” section. This easy-to-use template will guide you through each step of the process, ensuring you don’t miss any critical details.
The template is divided into the following sections:
- Mission statement
- Business Overview
- Key products or services
- Target market
- Financial highlights
- Company goals
- Strategies to achieve goals
- Measurable, time-bound objectives
- Company History
- Mission and vision
- Unique selling proposition
- Demographics
- Psychographics
- Pain points
- Industry trends
- Customer needs
- Competitor strengths and weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Competitor products and services
- Market positioning
- Pricing strategies
- Organizational structure
- Key roles and responsibilities
- Management team backgrounds
- Product or service features
- Competitive advantages
- Marketing channels
- Advertising campaigns
- Promotional activities
- Sales strategies
- Supply chain management
- Inventory control
- Production processes
- Quality control measures
- Projected revenue
- Assumptions
- Cash inflows
- Cash outflows
- Net cash flow
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a strategic document that outlines an organization’s goals, objectives, and the steps required to achieve them. It serves as a roadmap as you start a business , guiding the company’s direction and growth while identifying potential obstacles and opportunities.
Typically, a business plan covers areas such as market analysis, financial projections, marketing strategies, and organizational structure. It not only helps in securing funding from investors and lenders but also provides clarity and focus to the management team.
A well-crafted business plan is a very important part of your business startup checklist because it fosters informed decision-making and long-term success.

Why You Should Write a Business Plan
Understanding the importance of a business plan in today’s competitive environment is crucial for entrepreneurs and business owners. Here are five compelling reasons to write a business plan:
- Attract Investors and Secure Funding : A well-written business plan demonstrates your venture’s potential and profitability, making it easier to attract investors and secure the necessary funding for growth and development. It provides a detailed overview of your business model, target market, financial projections, and growth strategies, instilling confidence in potential investors and lenders that your company is a worthy investment.
- Clarify Business Objectives and Strategies : Crafting a business plan forces you to think critically about your goals and the strategies you’ll employ to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for success. This process helps you refine your vision and prioritize the most critical objectives, ensuring that your efforts are focused on achieving the desired results.
- Identify Potential Risks and Opportunities : Analyzing the market, competition, and industry trends within your business plan helps identify potential risks and uncover untapped opportunities for growth and expansion. This insight enables you to develop proactive strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities, positioning your business for long-term success.
- Improve Decision-Making : A business plan serves as a reference point so you can make informed decisions that align with your company’s overall objectives and long-term vision. By consistently referring to your plan and adjusting it as needed, you can ensure that your business remains on track and adapts to changes in the market, industry, or internal operations.
- Foster Team Alignment and Communication : A shared business plan helps ensure that all team members are on the same page, promoting clear communication, collaboration, and a unified approach to achieving the company’s goals. By involving your team in the planning process and regularly reviewing the plan together, you can foster a sense of ownership, commitment, and accountability that drives success.
What are the Different Types of Business Plans?
In today’s fast-paced business world, having a well-structured roadmap is more important than ever. A traditional business plan provides a comprehensive overview of your company’s goals and strategies, helping you make informed decisions and achieve long-term success. There are various types of business plans, each designed to suit different needs and purposes. Let’s explore the main types:
- Startup Business Plan: Tailored for new ventures, a startup business plan outlines the company’s mission, objectives, target market, competition, marketing strategies, and financial projections. It helps entrepreneurs clarify their vision, secure funding from investors, and create a roadmap for their business’s future. Additionally, this plan identifies potential challenges and opportunities, which are crucial for making informed decisions and adapting to changing market conditions.
- Internal Business Plan: This type of plan is intended for internal use, focusing on strategies, milestones, deadlines, and resource allocation. It serves as a management tool for guiding the company’s growth, evaluating its progress, and ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall vision. The internal business plan also helps identify areas of improvement, fosters collaboration among team members, and provides a reference point for measuring performance.
- Strategic Business Plan: A strategic business plan outlines long-term goals and the steps to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for the company’s direction. It typically includes a SWOT analysis, market research, and competitive analysis. This plan allows businesses to align their resources with their objectives, anticipate changes in the market, and develop contingency plans. By focusing on the big picture, a strategic business plan fosters long-term success and stability.
- Feasibility Business Plan: This plan is designed to assess the viability of a business idea, examining factors such as market demand, competition, and financial projections. It is often used to decide whether or not to pursue a particular venture. By conducting a thorough feasibility analysis, entrepreneurs can avoid investing time and resources into an unviable business concept. This plan also helps refine the business idea, identify potential obstacles, and determine the necessary resources for success.
- Growth Business Plan: Also known as an expansion plan, a growth business plan focuses on strategies for scaling up an existing business. It includes market analysis, new product or service offerings, and financial projections to support expansion plans. This type of plan is essential for businesses looking to enter new markets, increase their customer base, or launch new products or services. By outlining clear growth strategies, the plan helps ensure that expansion efforts are well-coordinated and sustainable.
- Operational Business Plan: This type of plan outlines the company’s day-to-day operations, detailing the processes, procedures, and organizational structure. It is an essential tool for managing resources, streamlining workflows, and ensuring smooth operations. The operational business plan also helps identify inefficiencies, implement best practices, and establish a strong foundation for future growth. By providing a clear understanding of daily operations, this plan enables businesses to optimize their resources and enhance productivity.
- Lean Business Plan: A lean business plan is a simplified, agile version of a traditional plan, focusing on key elements such as value proposition, customer segments, revenue streams, and cost structure. It is perfect for startups looking for a flexible, adaptable planning approach. The lean business plan allows for rapid iteration and continuous improvement, enabling businesses to pivot and adapt to changing market conditions. This streamlined approach is particularly beneficial for businesses in fast-paced or uncertain industries.
- One-Page Business Plan: As the name suggests, a one-page business plan is a concise summary of your company’s key objectives, strategies, and milestones. It serves as a quick reference guide and is ideal for pitching to potential investors or partners. This plan helps keep teams focused on essential goals and priorities, fosters clear communication, and provides a snapshot of the company’s progress. While not as comprehensive as other plans, a one-page business plan is an effective tool for maintaining clarity and direction.
- Nonprofit Business Plan: Specifically designed for nonprofit organizations, this plan outlines the mission, goals, target audience, fundraising strategies, and budget allocation. It helps secure grants and donations while ensuring the organization stays on track with its objectives. The nonprofit business plan also helps attract volunteers, board members, and community support. By demonstrating the organization’s impact and plans for the future, this plan is essential for maintaining transparency, accountability, and long-term sustainability within the nonprofit sector.
- Franchise Business Plan: For entrepreneurs seeking to open a franchise, this type of plan focuses on the franchisor’s requirements, as well as the franchisee’s goals, strategies, and financial projections. It is crucial for securing a franchise agreement and ensuring the business’s success within the franchise system. This plan outlines the franchisee’s commitment to brand standards, marketing efforts, and operational procedures, while also addressing local market conditions and opportunities. By creating a solid franchise business plan, entrepreneurs can demonstrate their ability to effectively manage and grow their franchise, increasing the likelihood of a successful partnership with the franchisor.
Using Business Plan Software

Creating a comprehensive business plan can be intimidating, but business plan software can streamline the process and help you produce a professional document. These tools offer a number of benefits, including guided step-by-step instructions, financial projections, and industry-specific templates. Here are the top 5 business plan software options available to help you craft a great business plan.
1. LivePlan
LivePlan is a popular choice for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features. It offers over 500 sample plans, financial forecasting tools, and the ability to track your progress against key performance indicators. With LivePlan, you can create visually appealing, professional business plans that will impress investors and stakeholders.
2. Upmetrics
Upmetrics provides a simple and intuitive platform for creating a well-structured business plan. It features customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, and collaboration capabilities, allowing you to work with team members and advisors. Upmetrics also offers a library of resources to guide you through the business planning process.
Bizplan is designed to simplify the business planning process with a drag-and-drop builder and modular sections. It offers financial forecasting tools, progress tracking, and a visually appealing interface. With Bizplan, you can create a business plan that is both easy to understand and visually engaging.
Enloop is a robust business plan software that automatically generates a tailored plan based on your inputs. It provides industry-specific templates, financial forecasting, and a unique performance score that updates as you make changes to your plan. Enloop also offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget.
5. Tarkenton GoSmallBiz
Developed by NFL Hall of Famer Fran Tarkenton, GoSmallBiz is tailored for small businesses and startups. It features a guided business plan builder, customizable templates, and financial projection tools. GoSmallBiz also offers additional resources, such as CRM tools and legal document templates, to support your business beyond the planning stage.
Business Plan FAQs
What is a good business plan.
A good business plan is a well-researched, clear, and concise document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, target market, competitive advantages, and financial projections. It should be adaptable to change and provide a roadmap for achieving success.
What are the 3 main purposes of a business plan?
The three main purposes of a business plan are to guide the company’s strategy, attract investment, and evaluate performance against objectives. Here’s a closer look at each of these:
- It outlines the company’s purpose and core values to ensure that all activities align with its mission and vision.
- It provides an in-depth analysis of the market, including trends, customer needs, and competition, helping the company tailor its products and services to meet market demands.
- It defines the company’s marketing and sales strategies, guiding how the company will attract and retain customers.
- It describes the company’s organizational structure and management team, outlining roles and responsibilities to ensure effective operation and leadership.
- It sets measurable, time-bound objectives, allowing the company to plan its activities effectively and make strategic decisions to achieve these goals.
- It provides a comprehensive overview of the company and its business model, demonstrating its uniqueness and potential for success.
- It presents the company’s financial projections, showing its potential for profitability and return on investment.
- It demonstrates the company’s understanding of the market, including its target customers and competition, convincing investors that the company is capable of gaining a significant market share.
- It showcases the management team’s expertise and experience, instilling confidence in investors that the team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
- It establishes clear, measurable objectives that serve as performance benchmarks.
- It provides a basis for regular performance reviews, allowing the company to monitor its progress and identify areas for improvement.
- It enables the company to assess the effectiveness of its strategies and make adjustments as needed to achieve its objectives.
- It helps the company identify potential risks and challenges, enabling it to develop contingency plans and manage risks effectively.
- It provides a mechanism for evaluating the company’s financial performance, including revenue, expenses, profitability, and cash flow.
Can I write a business plan by myself?
Yes, you can write a business plan by yourself, but it can be helpful to consult with mentors, colleagues, or industry experts to gather feedback and insights. There are also many creative business plan templates and business plan examples available online, including those above.
We also have examples for specific industries, including a using food truck business plan , salon business plan , farm business plan , daycare business plan , and restaurant business plan .
Is it possible to create a one-page business plan?
Yes, a one-page business plan is a condensed version that highlights the most essential elements, including the company’s mission, target market, unique selling proposition, and financial goals.
How long should a business plan be?
A typical business plan ranges from 20 to 50 pages, but the length may vary depending on the complexity and needs of the business.
What is a business plan outline?
A business plan outline is a structured framework that organizes the content of a business plan into sections, such as the executive summary, company description, market analysis, and financial projections.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
The five most common business plan mistakes include inadequate research, unrealistic financial projections, lack of focus on the unique selling proposition, poor organization and structure, and failure to update the plan as circumstances change.
What questions should be asked in a business plan?
A business plan should address questions such as: What problem does the business solve? Who is the specific target market ? What is the unique selling proposition? What are the company’s objectives? How will it achieve those objectives?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan focuses on the overall vision, goals, and tactics of a company, while a strategic plan outlines the specific strategies, action steps, and performance measures necessary to achieve the company’s objectives.
How is business planning for a nonprofit different?
Nonprofit business planning focuses on the organization’s mission, social impact, and resource management, rather than profit generation. The financial section typically includes funding sources, expenses, and projected budgets for programs and operations.
Image: Envato Elements

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
© Copyright 2003 - 2024, Small Business Trends LLC. All rights reserved. "Small Business Trends" is a registered trademark.
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Discover how today’s most successful IT leaders stand out from the rest. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Read the report .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Project management |
- Everything you need to know about requi ...
Everything you need to know about requirements management

Requirements management helps you ensure your final project deliverable meets the needs of stakeholders. Simply put—a requirement is something stakeholders want or need, and requirements management helps you fulfill that need. Read on to learn how requirements management works, then do it yourself with six simple steps.
It’s Friday night and you’re about to order pizza. You’ve got the phone in one hand and a list of requests from your friends in the other. But first, you need to sort through everyone’s preferences and decide what type of pizza to order. Pepperoni? Cheese? Vegetarian?
Ordering pizza is starting to feel eerily like managing requirements for your latest product launch. Just like the above situation, requirements management is all about listening to your stakeholders and understanding how to best cater to their needs.
What is requirements management?
Requirements management is most often used by development teams working on software products and features, but can also be applied more generally to project management . For example, a requirement could be a feature that allows customers to successfully use your product, or an aspect of your product that will help cross-functional partners achieve their business goals .
Before you start working on a product, you need to agree on the exact requirements so you can make sure you’re giving stakeholders what they need. Requirements management helps you document and prioritize requirements, keep track of changes, and stay aligned with stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle. It also helps you manage changing requirements and ensure your project stays within scope.
What is a requirement?
A requirement is a component you need to implement in order to complete a feature or product. In other words, it’s something your product needs to have or do to meet your stakeholders’ needs. Software products can have hundreds of requirements. But regardless of how many requirements your product has, all of them should be:
Necessary: You need this requirement in order to achieve your business or product goals.
Specific: The requirement is detailed and has a clear purpose.
Understandable: The requirement is clearly written and easy to comprehend.
Accurate: The requirement has enough accurate information about the challenge or need this requirement is addressing. That means instead of just describing what needs to be done, you should also clarify why the requirement is important.
Feasible: You should research the requirement to make sure you can implement it with your current tech stack and code infrastructure.
Testable: You should be able to test the requirement through user testing, A/B testing, or another method.
Here’s an example. Imagine you’re creating an app, and one of your requirements is that the entire app needs to be translated into English, Chinese, Japanese, and French—because those languages align with your main business markets.
This requirement is necessary in order to launch your app in your company’s main markets and achieve business objectives.
It’s specific because you outline which languages you need and that the entire app needs to be translated.
It’s understandable because it doesn’t go into technical details—rather, it’s written in a way your team members and cross functional stakeholders can understand.
It’s accurate because you’ve clearly outlined why the requirement is important—because English, Chinese, Japanese, and French align with your company’s primary markets.
It’s feasible because you’ve already built prototypes and test cases in other languages, so you know localization is possible and will perform as expected.
It’s testable because you have a system in place to test and confirm the accuracy of each translated version.
Why is requirements management important?
To create a great product, you need requirements management. Here’s why:
Ship the right features. The requirements management process helps define what your users need by understanding how they interact with the product. This helps you align your deliverables first and foremost with the essential needs of your customers.
Align with business goals. As you document and prioritize requirements, make sure each of them aligns with your overarching business goals. For example, a requirement to translate your app into 12 languages would support a business goal to expand into international markets. If a requirement doesn’t support business goals, that probably means you should invest resources elsewhere—or have a really good reason why the requirement is important.
Prevent scope creep . Defined requirements function as a project scope —they set boundaries and define exactly what goals and deliverables you’ll be working towards. Defining requirements in advance helps you identify potential roadblocks and push back when stakeholders try to add on additional requirements.
Avoid roadblocks. Creating a product is complex—there’s software development, design, and testing—not to mention complex code stacks and engineering systems. Requirements management helps you plan how to develop a product within the constraints of your code stack and keep track of what you need to accomplish at every stage of the product development process .
Who is responsible for requirements management?
The person responsible for requirements management depends on your individual project or team. That said, product owners or product managers typically manage requirements for development teams. These two roles are similar, except product owners are a standard role on Scrum teams while product managers are a more universal role—regardless of whether your team uses an Agile methodology . If you’re working on a more general project instead of developing a product, the project manager is responsible for requirements management.
Requirements management requires cross-functional collaboration between your team and project stakeholders. You need to collect feedback from stakeholders, work with them to understand each requirement, and help your team plan how to address each need. That means the person who manages requirements for your project should have strong collaboration skills and excel at cross-functional communication, because they’ll be at the center of it all.
What are the different types of requirements?
There are three main types of requirements: business requirements, user requirements, and systems requirements. It’s important to define the different types of requirements before work kicks off—because this often determines the stakeholders you need to collaborate with.
Here’s an overview of the different types of requirements:
Business requirements
Business requirements are the overarching business goals or metrics your product serves. They aren’t necessarily something the product needs to do, but rather things your business needs to do to satisfy both internal and external stakeholders.
For example, imagine you work for an online retail business and your sales team uses a content management system to create and update product pages on your website. To accommodate growing inventory, your product team is building improved search functionality within your CMS. This project aligns with the following business requirement: Scale product inventory by 50% in Q1.
User requirements
User requirements define what users need from your product and how they’ll interact with it. They describe a pain point or an action the customer wants to accomplish, plus how the product should alleviate that pain point or help the customer achieve their desired action.
Agile teams typically format user requirements as user stories , which are informal explanations of a software feature written from the perspective of an end user. User stories follow this format: “As a [persona], I want to [software goal], so that [result].”
Let’s return to the CMS example we outlined above. Here’s an example user story written from the perspective of the end user—in this case, a sales associate who uses the CMS to perform their job duties.
“As a sales associate, I want to easily search for and find specific product listings in our CMS so I can update and manage our growing online inventory.”
Systems requirements
Systems requirements define what the product will do. Think of it this way—while user requirements outline the “why” and “what” of product features from a user’s perspective, systems requirements define the “how” of building that feature from the engineering team’s perspective.
Systems requirements are often broken down into functional requirements and non-functional requirements. Functional requirements define what the product will do, while non-functional requirements define how well the product performs its functions. That means non-functional requirements typically have to do with security, performance, and reliability.
For example, here’s how an engineering team might break down the above CMS user requirement into systems requirements:
Functional requirements
Each product listing stores the following information: product type, date created, author, URL, and publish status.
New products can’t be created unless authors select a product type from a dropdown menu.
The search bar includes an option to apply the following additional filters: product type, date created, author, URL, and publish status.
Multiple filters can be selected at once.
Non-functional requirements
Search results are returned in less than five seconds.
Search results are 100% accurate.
6 steps of the requirements management process
Requirements management doesn’t have to feel overwhelming. If you create a standardized process for your team, you can follow the same steps every time instead of worrying about which stakeholders to loop in when.
To get you started, we’ve simplified the process into six steps. Then once you try things out and learn what works for your team, you can tailor your requirements management process accordingly.
1. Collect requirements
Before you can define your project requirements, you first need to collect what those requirements are going to be. At this stage, collecting requirements doesn’t mean they will be built into your project—rather, this is a chance for you to connect with stakeholders and customers to learn more about their needs.
There are a few different approaches to this—you can meet with stakeholders in person to let them know about the product or feature you’re creating, then ask what they need or want from your project in order to help customers or achieve business goals. During this time, you can develop requirements with the stakeholder’s help to get a full understanding of what they need. You can also communicate with stakeholders asynchronously to cut down on meeting time. And if you need to understand requirements from end users, you may need to conduct user testing or reach out to your user research team.
During these conversations, make sure you’re managing expectations with stakeholders so they know the requirements they request won’t necessarily be built into your product. Ultimately, it’s up to you and your team to prioritize and select which requirements are most important to pursue.
2. Analyze requirements
Now it’s time to sort through all of that feedback and decide which requirements align with your product and business goals . Ultimately, every requirement should contribute to an overarching business goal—like increasing revenue, expanding into new markets, or improving customer satisfaction.
3. Define requirements
Now that you’ve analyzed requirements and picked the ones that align with your goals, it’s time to clearly define the requirements to make sure your team has all the information they need. This helps you outline all of the components your development team needs to accomplish in order to complete the product or feature.
One way to do this is to create user stories for each requirement in order to articulate what users need and how they’ll interact with your product. Then you can break down those user requirements into more specific systems requirements. As you go, you may need to collect additional information from stakeholders to ensure you have enough context to complete each requirement.
4. Document requirements
There isn’t one set way to document and track requirements. Your product team may historically have used a software requirements specification (SRS), product requirements document (PRD), or requirements traceability matrix (RTM).
But to ensure your team has real-time insight into all of your project requirements, try using a project management tool like Asana. That means no more outdated spreadsheets for requirements—instead, both your team and stakeholders can see the most up-to-date descriptions of each requirement. You can also track the status of each requirement as you work on your project, and even set up automations to alert stakeholders when progress is made.
You can also integrate Asana with more specialized apps and requirements management tools like Jira and GitHub . This is especially useful if you work with stakeholders who don’t have permissions to access developer tools.
5. Prioritize requirements
Now that you have your set of requirements written down, work with your team to prioritize and plan how you’ll tackle them. This prioritization allows you to tackle the most important tasks first, especially if they’re blocking any other tasks down the line.
If your team uses Agile, add the requirements to your product backlog and then host a sprint planning session to decide which tasks to include in your next sprint. If you don’t work in sprints, that’s ok—you can create a project timeline to lay out when each requirement should be completed and whether there are any dependencies .
6. Make a plan for changes
Requirements management isn’t just about planning requirements before your project kicks off—it’s also about navigating changing requirements during the course of your project. That means you should plan how to incorporate additional tasks that will impact your project scope.
One option is to create a change control process . This provides a way for stakeholders to submit new requirements that will impact your project scope, plus dictates who should approve or deny those requests. A change control process also helps you document and keep track of how requirements change during the course of your project—so you can measure the impacts of change later on.
Tools to streamline requirements management
Requirements management has a lot of moving parts, but it doesn’t have to feel out of control. With the right tools, you can set up a repeatable process that lays out exactly who to talk to, when to do it, and how to document and organize requirements throughout the project lifecycle.
If you track requirements in Asana , you can create a standardized template to help you manage requirements for every project. That means instead of starting the process from scratch each time, you can reuse a predefined workflow—plus rest easy knowing that you’re not forgetting any critical pieces.
Related resources

How Asana uses work management to optimize resource planning
Understanding dependencies in project management
Program manager vs. project manager: Key differences to know
Critical path method: How to use CPM for project management
8 Business Plan Templates You Can Get for Free
8 min. read
Updated April 10, 2024
A business plan template can be an excellent tool to simplify the creation of your business plan.
The pre-set structure helps you organize ideas, covers all critical business information, and saves you time and effort on formatting.
The only issue? There are SO many free business plan templates out there.
So, which ones are actually worth using?
To help remove the guesswork, I’ve rounded up some of the best business plan templates you can access right now.
These are listed in no particular order, and each has its benefits and drawbacks.
What to look for in a business plan template
Not all business plan templates are created equal. As you weigh your options and decide which template(s) you’ll use, be sure to review them with the following criteria in mind:
- Easy to edit: A template should save you time. That won’t be the case if you have to fuss around figuring out how to edit the document, or even worse, it doesn’t allow you to edit at all.
- Contains the right sections: A good template should cover all essential sections of a business plan , including the executive summary, product/service description, market/competitive analysis, marketing and sales plan, operations, milestones, and financial projections.
- Provides guidance: You should be able to trust that the information in a template is accurate. That means the organization or person who created the template is highly credible, known for producing useful resources, and ideally has some entrepreneurial experience.
- Software compatibility: Lastly, you want any template to be compatible with the software platforms you use. More than likely, this means it’s available in Microsoft Word, Google Docs, or PDF format at a minimum.
1. Bplans — A plan with expert guidance

Since you’re already on Bplans, I have to first mention the templates that we have available.
Our traditional and one-page templates were created by entrepreneurs and business owners with over 80 years of collective planning experience. We revisit and update them annually to ensure they are approachable, thorough, and aligned with our team’s evolving best practices.
The templates, available in Word, PDF, or Google Doc formats, include in-depth guidance on what to include in each section, expert tips, and links to additional resources.
Plus, we have over 550 real-world sample business plans you can use for guidance when filling out your template.
Download: Traditional lender-ready business plan template or a simple one-page plan template .
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
2. SBA — Introduction to business plans

The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) offers two different business plan templates along with a short planning guide.
While not incredibly in-depth, it’s enough to help you understand how traditional and lean plans are structured and what information needs to be covered. The templates themselves are more like examples, providing you with a finished product to reference as you write your plan.
The key benefit of using these templates is that they were created by the SBA. While they may provide less guidance, you can be assured that the information and structure meet their expectations.
Explore: The SBA’s planning guide and free templates
3. SCORE — Planning workbook

SCORE’s template is more like a workbook. It includes exercises after each section to help you get your ideas down and turn them into a structured plan.
The market research worksheets are especially useful. They provide a clear framework for identifying your target market and analyzing competitors from multiple angles. Plus, they give you an easy way to document all the information you’re collecting.
You will likely have to remove the exercises in this template to make it investor-ready. But it can be worth it if you’re struggling to get past a blank page and want a more interactive planning method.
Download: SCORE’s business plan template
4. PandaDoc — A template with fillable forms

PandaDoc’s library offers a variety of industry-specific business plan templates that feature a modern design flair and concise instructions.
These templates are designed for sharing. They include fillable fields and sections for non-disclosure agreements, which may be necessary when sending a plan to investors.
But the real benefit is their compatibility with PandaDoc’s platform. Yes, they are free, but if you’re a PandaDoc subscriber, you’ll have far more customization options.
Out of all their templates, the standard business plan template is the most in-depth. The rest, while still useful, go a bit lighter on guidance in favor of tailoring the plan to a specific industry.
Explore: PandaDoc’s business plan template library
5. Canva — Pitch with your plan

Canva is a great option for building a visually stunning business plan that can be used as a pitch tool. It offers a diverse array of templates built by their in-house team and the larger creative community, meaning the number of options constantly grows.
You will need to verify that the information in the template you choose matches the standard structure of a traditional business plan.
You should do this with any template, but it’s especially important with any tool that accepts community submissions. While they are likely reviewed and approved, there may still be errors.
Remember, you can only edit these templates within Canva. Luckily, you only need a free subscription, and you may just miss out on some of the visual assets being used.
To get the most value, it may be best to create a more traditional planning document and transfer that information into Canva.
Explore: Canva’s business plan gallery
6. ClickUp — The collaborative template

Out of all the project management tools that offer free business plan templates, ClickUp’s is the most approachable.
Rather than throwing you into all the features and expecting you to figure it out—ClickUp provides a thorough startup guide with resource links, images, and videos explaining how to write a plan using the tool.
There’s also a completed sample plan (structured like an expanded one-page plan) for you to reference and see how the more traditional document can connect to the product management features. You can set goals, target dates, leave comments, and even assign tasks to someone else on your team.
These features are limited to the ClickUp platform and will not be useful for everyone. They will likely get in the way of writing a plan you can easily share with lenders or investors.
But this is a great option if you’re looking for a template that makes internal collaboration more fluid and keeps all your information in one place.
Sign Up: Get a free trial of ClickUp and explore their template library
7. Smartsheet — A wide variety of templates

I’m including Smartsheet’s library of templates on this list because of the sheer number of options they provide.
They have a simple business plan template, a one-page plan, a fill-in-the-blank template, a plan outline, a plan grading rubric, and even an Excel-built project plan. All are perfectly usable and vary in visual style, depth of instructions, and the available format.
Honestly, the only drawback (which is also the core benefit) is that the amount of templates can be overwhelming. If you’re already uncertain which plan option is right for you, the lengthy list they provide may not provide much clarity.
At the same time, it can be a great resource if you want a one-stop shop to view multiple plan types.
Explore: Smartsheet’s business plan template library
8. ReferralRock affiliate marketing business plan

I’m adding ReferralRock’s template to this list due to its specificity.
It’s not your standard business plan template. The plan is tailored with specific sections and guidance around launching an affiliate marketing business.
Most of the template is dedicated to defining how to choose affiliates, set commissions, create legal agreements, and track performance.
So, if you plan on starting an affiliate marketing business or program, this template will provide more specific guidance. Just know that you will likely need to reference additional resources when writing the non-industry sections of your plan.
Download: ReferralRock affiliate marketing business plan template
Does it matter what business plan template you use?
The short answer is no. As long as the structure is correct, it saves you time, and it helps you write your business plan , then any template will work.
What it ultimately comes down to, is what sort of value you hope to get from the template.
- Do you need more guidance?
- A simple way to structure your plan?
- An option that works with a specific tool?
- A way to make your plan more visually interesting?
Hopefully, this list has helped you hone in on an option that meets one (or several) of these needs. Still, it may be worth downloading a few of these templates to determine the right fit.
And really, what matters most is that you spend time writing a business plan . It will help you avoid early mistakes, determine if you have a viable business, and fully consider what it will take to get up and running.
If you need additional guidance, check out our library of planning resources . We cover everything from plan formats , to how to write a business plan, and even how to use it as a management tool .
If you don’t want to waste time researching other templates, you can download our one-page or traditional business plan template and jump right into the planning process.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Kody Wirth is a content writer and SEO specialist for Palo Alto Software—the creator's of Bplans and LivePlan. He has 3+ years experience covering small business topics and runs a part-time content writing service in his spare time.
.png?format=auto)
Table of Contents
- Qualities of a good template
- ReferralRock
- Does the template matter?
Related Articles

12 Min. Read
Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes

10 Min. Read
14 Reasons Why You Need a Business Plan

Use This Simple Business Plan Outline to Organize Your Plan

5 Min. Read
Business Plan Vs Strategic Plan Vs Operational Plan—Differences Explained
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
A guide to requirements management software
When developing projects, stakeholder expectations are very hard to manage. Aligning expectations with project goals is critical for success as a product manager. The good news is that when you run requirements gathering correctly, the process becomes much smoother.

In the requirements gathering phase, teams need to keep track of user needs, and expectations. Requirements management software can become a powerful tool to capture, analyze, and meet these expectations throughout the project lifecycle.
Let’s dive deep into the nuances of RM software and how teams can make the best use of them to streamline the process.
What is requirements management software?
A requirements management software is a tool designed to facilitate the process of handling project requirements from gathering ideas to project completion. Think of it as a central point for collecting, documenting, analyzing, and tracking stakeholder expectations.
It provides a structure to the process from the very beginning and ensures that every project element is aligned with defined objectives. This minimizes the communication gap and scope creep, enhancing overall efficiency.
It helps with:
- Capturing requirements from various stakeholders
- Documenting, organizing, and recording requirements for easy access
- Analyzing the requirements for feasibility and impact
- Tracking changes to requirements throughout the project
Key features of requirements management software
A requirements management software has a range of features designed to address the complex nature of a project lifecycle by addressing the challenges of each aspect:
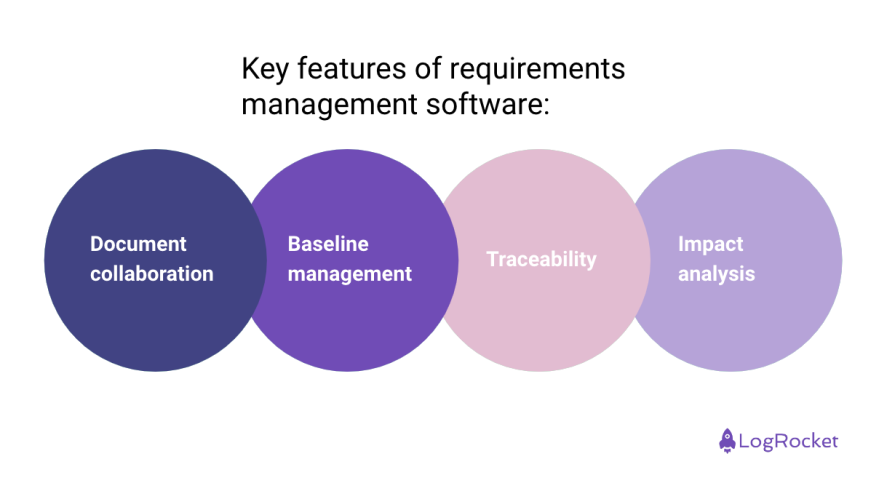
Document collaboration
This feature facilitates a workspace where team members can work on documents in a collective manner. It helps to gather feedback from all stakeholders making sure all ideas are taken into consideration. These tools can include version control and change tracking, acting as a single source of truth for all teams involved.
Baseline management
Baseline management provides an overview of project requirements and their evolution during the entire lifecycle. It acts as a reference point to gauge progress and manage changes. Project teams can reference specific versions of requirement documents when discussing project milestones.
Traceability
Traceability in RM software is essential for systematic linkage between a requirement and its deliverable. This can include, design documents, test cases, and plans of deployment. Such transparent connectivity promotes a sense of accountability, ensuring the final delivery tackles every set objective.
Impact analysis
Gauging impact at any given stage of a project lifecycle is a challenge. Impact analysis tools help teams evaluate the consequences of each change. It also helps to understand how a change in one area of a project affects a different area. This applies to project scope, budget, timelines, and resource allocation.
These features form the base of a well-rounded requirement management software. With RM software, you can navigate the dynamic process of project development with confidence in each phase.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
The importance of visuals in RM tools
To enhance usability and user engagement, the use of visual elements in these tools cannot be overstated. Elements like charts, graphs, and visual dashboards transform complex data into simple visuals. These visuals eventually take the shape of actionable insights for the teams involved.
This aids the teams with understanding:
- Project requirements
- Dependencies
- Pinpointing issues
- Identifying trends
- Creating reports
The overall purpose of visual cues is to help teams make data-driven decisions more efficiently. It ultimately results in improved project outcomes. This is made possible with the ease of use and intuitive user experience of RM tools.
Usability and user experience of requirements management software
If RM tools are easy to use, they will make a difference. Teams should be able to interact with the software in a manner that is both intuitive and still gets the job done. A steep learning curve will be a major issue in such a fast-paced environment. It also takes away the focus from the actual tasks at hand, thus minimizing productivity and maximizing errors.
The integration of RM tools with third-party applications is also important as it ensures their introduction to the product team’s workflow, with zero disturbance.
RM software integration capabilities
The project management ecosystem is large and always evolving. RM tools need to have up-to-date integration options for third-party applications. They should seamlessly blend in with the rest of the tools used for project management, testing assistants, and development kits.
This connectivity ensures the free flow of data between systems, reducing manual work, and errors. For instance, the integration of requirement management tools with version control like Git allows the linkage of requirements with code commits. As a result, you gain traceability from idea to final implementation.
Pricing and cost considerations for requirements management software
Cost consideration is always a challenge for organizations. RM software provides a lot of value for your product team, but it can also impact the budget of an organization.
More great articles from LogRocket:
- How to implement issue management to improve your product
- 8 ways to reduce cycle time and build a better product
- What is a PERT chart and how to make one
- Discover how to use behavioral analytics to create a great product experience
- Explore six tried and true product management frameworks you should know
- Advisory boards aren’t just for executives. Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
The solution is to choose the correct pricing model based on your organizational needs and workflow. There are:
- Subscription-based plans with monthly/annual fees
- Perpetual licenses where a one-time payment is required
- Size-based plans where the price relates to organization size
The critical factors when making a choice should be integration capabilities, range of features, and alignment with organizational needs. For most teams, a subscription-based plan is the best option. There’s also a key distinction between cloud-based and license-based software, which can be an overlooked factor when making a choice.
Cloud-based vs. license-based software
SaaS applications (cloud-based) are becoming more mainstream in all domains. The main benefit is that the maintenance responsibility is taken by the service provider. On the other hand, license-based software (on-premise) is maintained and updated on the organization’s servers. Both options have pros and cons.
Benefits of cloud-based software
- Accessibility — Cloud-based RM tools offer the convenience of access from any location. The only requirement is a stable internet connection. This is really helpful for organizations that facilitate remote work Scalability — Cloud-based apps are scalable and ever-evolving. They cater to project growth and resource allocation becomes easier with it
- Maintenance and updates — With constant updates and regular maintenance checks, SaaS applications reduce the workload on organizations
The negatives of the cloud-based RM tools mostly arise due to data privacy concerns and less flexibility offered for certain projects.
Benefits of license-based software
- Control over data — On-premise installation gives you complete control over your data. This added layer of security gives more freedom to organizations in addressing compliance requirements in a direct manner
- Customization — License-based software can be customized to fit specific organizational processes. The integration and usage are modified based on different projects. Many organizations prefer this tailored approach
License-based RM tools are more secure but the maintenance cost becomes too much for many organizations.
Selecting the right RM tool for your team
The choice of a requirement management tool varies from team to team. Making a choice based on certain key factors is the optimal route as it gives weight to the workflow-related factors. For any organization, it is important to:
- Assess project complexity — Choosing a tool that can handle the majority of the complexities of your project might be a good starting point
- Consider team dynamics — Look for features that support your team’s size, their skill level, and geographical distribution
- Evaluate integration capabilities — Ensure the tool integrates well with other software your team uses, on a day-to-day basis
- Flexibility and scalability — The tool should adapt to evolving project requirements and team needs
- Usability and support — Give priority to tools that are user-friendly and offer reliable support services. The dependency on RM software can become a problem in such cases
By considering the outlined factors, you can select a tool that aids the project lifecycle in each step.
Key insights
Requirements management tools are foundational to transforming project concepts into successful realities. They bridge the gap between stakeholder expectations and deliverables, in every single phase.
Introducing RM software into your team’s workflow can have its own set of challenges. But if done correctly, the benefits are long-term and pivotal for project success. They help streamline workflows, enhance team collaboration, and boost productivity, leading to project success and ultimately the advancement of the organization.
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #collaboration and communication
- #tools and resources

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.
Leader Spotlight: Empowering analytics and business intelligence teams, with Akash Gupta
Akash Gupta discusses the importance of empowering analytics and business intelligence teams to find “golden nuggets” of insights.

What are product lines? Types, examples, and strategies
Product lines are more than just a collection of products. They are a reflection of a company’s strategic vision and market positioning.

Leader Spotlight: The impact of macroeconomic trends on product roles, with Lori Edwards
Lori Edwards, Director of Product at Niche, discusses challenges with the transition from an individual contributor to a people manager.
Techniques for building rapport in professional settings
Effective rapport fosters trust, facilitates communication, and creates a foundation for successful collaboration and conflict resolution.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
SoftwareDominos

Business Requirements: An Essential Guide to Definition and Application in IT Projects
1. What Are Business Requirements?
Business requirements describe the changes that must be implemented in specific business areas to enhance product or service production and improve the organisation’s value proposition . More specifically, a business requirement defines the technology adopted, the integration methods applied between the users and the systems, and how this integration will impact user experience.
The agenda for this series of articles is the following:
Business Requirements in Software Engineering
Business Requirements Document (BRD)
Business Requirements Document: 7 Easy Steps for Writing a Great BRD
Stakeholder Analysis and Management
Overview of Stakeholder Analysis and Management
Cost of Change
Cost of Change — The Hidden Driver Behind Our Software Delivery Choices
2. Where Do Business Requirements Come From?
The quote below is from Professor Murray Gell-Mann’s brilliant book “The Quark and the Jaguar – Adventures in the Simple and the Complex”, which describes the interplay between technology and medicine, a vital field of human science .
The experts can be consulted again, of course, and the internal model [ of the computer program aiding the doctors’ diagnosis of hospital patients ] redesigned to take account of the successes and failures of the computer diagnoses. In that case, the extended system consisting of the computer, the model designers, and the experts can be regarded as a complex adaptive system, an artificial one “with humans in the loop”.
— Murray Gell-Mann, The Quark and the Jaguar – Adventures in the Simple and the Complex
Technology has entered most human endeavours, with experts disagreeing on how much of it is good vs bad. However, most will agree that technology will continue to be perfected while businesses strive to integrate it into their production processes .
Imagine you are running a business in an environment with plenty of competition. To survive, you use technology to enhance your offering or become more efficient in producing it. You might also use technology to create a business need that was never there in the first place. These integration requirements broadly define your business requirements .
Soon enough, your competitors will leverage those same technologies, just as you did, to improve their products or deliveries. Now, you must find newer ways or better technology just to stay in the game. This dance between business and technology is a recurring pattern familiar to most, especially in software.

The cycle between one innovation and the next, one version of the product and its successor, looks something like this:
This article will examine the business requirements creation processes from definition to gathering, documentation, review, validation, and acceptance. We also explain the purpose and methods of stakeholder analysis and management .
By the end of this article, we hope you will better understand the subtle concepts behind creating, documenting, and handling adequate business requirements.
3. Business Requirements in Software Engineering
In various industries, including IT and manufacturing, “ business requirements ” refer to a comprehensive set of specifications and functionalities that a system or product must possess to meet the objectives and needs of a business.
These requirements are a foundation for designing, developing, and implementing solutions to address specific business challenges or opportunities. The definition of business requirements can vary slightly across industries, but the fundamental concept remains the same. Let’s see how business requirements can differ for two critical industries: Information Technology and manufacturing.
- Information Technology (IT)
- Manufacturing
4. Business Requirements Development

Developing business requirements typically involves collaboration between business analysts, stakeholders, and subject matter experts, regardless of the industry. This collaboration aims to capture the business’s specific needs, constraints, and expectations, providing a clear roadmap for the subsequent development or production phases.
It is important to note that effective communication and documentation of business requirements are crucial for project success . Ambiguous or incomplete requirements can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and suboptimal outcomes.
To alleviate the risk of developing incorrect business requirements, businesses often employ standardized methodologies and documentation formats, such as use cases, user stories , or requirement specifications, to ensure clarity and precision in conveying business requirements to the relevant teams.
Agile Software Development — First Principles and Foundational Elements
4. Business in the Digital Age
4.1 complex it solutions for highly sophisticated businesses.
The complexity of business requirements in IT projects has experienced exponential growth due to pressures from increasingly sophisticated client preferences, novel technologies, and fierce competition.

Consider, for example, the case of financial payments. In the mid-80s, most payment transactions occurred inside bank branches, and only the most prominent banks offered services on ATM or POS machines. Today, we live almost exclusively in cashless societies that exist on electronic fund transfers (EFT), where an average consumer can pay with plastic cards, mobile phones, watches, cheques, web links, and mobile applications. These taken-for-granted technologies might have sounded more sci-fi than real only a decade or two ago.
Hundreds of applications are simultaneously involved in enabling and supporting these payment methods, working together seamlessly, while their success rests prominently on a clear definition and implementation of business requirements.
4.2 Project Failure and Unclear Requirements
Many instances of IT project failure can be traced back to unclear requirements, poor understanding of the business case, and scope creep (ref. 6 reasons why your IT project will fail and Top 10 Reasons Why Projects Fail ).
Overshooting the budget, missing deadlines and software deliveries of little or no business value to customers are typical outcomes of failed projects.
IT projects are notoriously difficult to manage. A survey published in HBR found that the average IT project overran its budget by 27%. Moreover, at least one in six IT projects turns into a “black swan” with a cost overrun of 200% and a schedule overrun of 70%. In other words, while most IT projects will fall short of their budget targets, a few might overshoot the targets so much as to cause catastrophic organization-wide problems. KMart’s massive $1.2B failed IT modernization project, for instance, was a big contributor to its bankruptcy.
Numerous other reasons contribute to project failures, such as size (the bigger they are, the more likely they are to fail), inconsistent practices , lack of talent and support from leadership , and cultural blockers .
The challenges that requirement definition brings probably compound these factors as full knowledge of business requirements at the beginning of the project is not possible for reasons we elaborate on later.
4.3 Kano’s Model of Customer Satisfaction
In the customer satisfaction model proposed by Noriaki Kano, there are three levels of customer requirements.
The Critical Importance of Software Project Management
5. Defining Business Requirements
In the remainder of this article, we will discuss business requirements specifically in the context of IT solutions; otherwise, the ideas will be a bit vaguer than they need to be.
5.1 Business Requirements and Solution Design
A collection of business requirements determines a project’s goals and constraints , feeding into the solution design . You will undoubtedly remember seeing the words shall and should in a business requirements document (BRD) .
In IT specifications, the words shall and should have a special meaning. Shall is often used to define a hard constraint that developers must implement. On the other hand, should denote a desirable but not compulsory requirement.
Any successful solution design must satisfy all hard constraints and whatever can be achieved from the list of desirable ones.

We must remember that solution design is an optimization exercise where tradeoffs are made between budget, deadlines, performance, and feature richness. To better understand how this optimization exercise unfolds, we need to explain three concepts from Systems Engineering :
- Design Space :
- Objective Space :
- Mapping the design to the objective space :
Part 1: Solution Design — Introduction and First Principles
5.2 Business Requirements Quality
The quality of the requirements and their definitions can be divided into two levels:
- On the individual level, every requirement should be verifiable, clear (unambiguous), and feasible.
- As a whole , the set of requirements should not contain redundancies or conflicting constraints (otherwise, the technical feasibility of the solution would be jeopardized) and should be complete.
6. Business Requirement Challenges
6.1 addressable challenges.
Defining business requirements that can be set in stone is not feasible for technical and other reasons. Here is a list of the most prominent:
- A vague understanding of the business case prevents writing precise requirements initially, and you will only have more clarity as you get to know the problem more. This issue occurs when inexperienced Business Analysts (BA) define requirements without being proficient in the business/technical aspects of the problem.
- Volatility : Requirements originate from various stakeholders, and the lengthier the schedule, the more likely it would be to observe a change in business requirements. A typical example would be new regulations that regulatory agencies constantly publish and mandate.
- Conflicting requirements : These may go undetected at the start of the project if the requirements review process is not diligent and rigorous enough and stakeholder analysis is not completed.
- Technical infeasibility: When working with novel or emerging technologies, some features’ integration problems or technical infeasibility might only be discovered after development has started. This problem does not exist for old problems with tried and tested solutions.
- Scope creep is another issue . Stakeholders typically create additional requirements after the project scope has been signed off.
All of the issues presented above can be managed and controlled with the proper procedures:
6.2 Inherent Challenges
A more fundamental obstacle exists, however, that prevents the requirement definition from being fully elucidated at project initiation. This problem is innate, cannot be quickly addressed, and has to do with defining low-level requirements.
You typically have high-level requirements from which solution architects would create a high-level design at project inception.
The high-level solution does not cover critical design decisions, such as the technologies used , as these would primarily come during the low-level solution design phase.
Your design choices will require further input from the stakeholders, and a constant dialogue must be maintained.
From an article published on pmi.org discussing the top reasons for IT project failures, we the following:
Include the customer at the beginning of the project and continually involve the customer as things change so that the required adjustments can be made together.
— Include the customer at the beginning of the project and continually involve the customer as things change so that the required adjustments can be made together.
To illustrate the idea, consider the choice you have to make when selecting a database vendor.
On a high level, you know you need a storage mechanism to persist application data , but at this stage, this storage mechanism could be a file, a relational, or a NoSQL database.
You can have specific requirements for this mechanism, including high availability and replication to a different geographical location. These two requirements are solution-agnostic as there might be various ways to satisfy them.
Assuming a relational database is the way to go, you must select a provider. You can go for open-source software to avoid licensing fees, or you could choose to collaborate with a well-known brand. You must make further decisions regarding deployment methods, license size, hardware procurement, and support options.
These are business decisions involving the client, the project manager , and the procurement and supplier management departments.
Hence, your low-level persistence requirements could not be defined before settling on a specific mechanism.
6.3 Handling Requirement Definition Challenges
Two broad categories encompass the many solutions proposed for handling big projects with complex requirements. These categories are lightweight (Extreme Programming , Agile, and DevOps ) and heavyweight project delivery methodologies ( Waterfall and the Hybrid Model).
The methods they employ for dealing with business requirements ambiguity are pretty different.
The success of Waterfall-based project management is predicated on complete requirement clarity as early as the beginning of the design phase of the SDLC .
Massive analysis and design efforts are carried out before implementation to achieve the desired clarity requirement. The trade-off is a high cost of change .
In contrast, Agile acknowledges this approach’s fallibility in light of the inherent challenges in obtaining complete visibility of business requirements and proposes an iterative method instead.
The iterative approach does not try to find the shortest path towards project closure but focuses instead on smaller and more frequent releases , and the trade-off here is the timeframe for scope.
It is interesting to note that Agile and Waterfall are imperfect , and project suitability should be assessed before adopting one or the other. In most cases, a Hybrid model will do just fine unless you can implement DevOps, which is the best we have today.
Understanding the SDLC in Software Engineering: A Comprehensive Guide
7. Types of Requirements
Six types of requirements can be defined:
- Functional requirements . These take the form of an actor completing an action on a specific object. The actor is a system component, the action is a function it provides, and the object is the recipient of that action. For example, ” the user management interface shall allow clients to change their passwords”.
- Performance requirements . These requirements act as qualifiers for functional requirements. For example, “the IT system must support 1000 Transactions per Second on weekends with response times averaging 1 second and 95% of response times less than 5 seconds”.
- Constraints are mandatory requirements that are typically applied to the solution components. They cannot be traded off for cost, timeline, or performance. For example, the solution must not cost more than $0.5M.
- Integration requirements determine which third-party systems the solution interfaces with.
- Environmental requirements determine the conditions under which the solution would run. For example, how well-trained support or operations staff must be, which languages the user interface must support, and which OS systems will be used.
- Non-functional requirements . These are covered by the ISO 25010 software quality standard, such as compatibility, reliability, and security.
Part 4: Solution Design Documents — What You Need to Know
A BRD outlines the business requirements for a software application or system, while a Functional Specification Document (FSD) outlines the technical requirements for implementing the solution. The FSD is typically based on the BRD and provides a more detailed description of how the solution will be built.
Creating a BRD requires collaboration between business stakeholders, subject matter experts, and the development team. Each group brings a unique perspective to the project and can help ensure the requirements are comprehensive and accurate.
The length of a BRD will depend on the complexity of the project and the level of detail required. A typical BRD may range from 10 to 50 pages, but no set length exists.
Yes, a BRD can be revised as needed based on feedback and changes in the project scope. It is important to keep all stakeholders informed of any changes to the BRD.
If the BRD is not clear or complete, it can lead to misunderstandings and delays in the project. Ensuring the BRD is comprehensive and accurate to minimize these risks is important.
9. Conclusion
Even considering the most conservative estimates, the percentage of failed IT projects is still staggering. A recent article published on financesonline.com states that 22% of all IT projects surveyed did not reach their goals, while 12% were deemed failures.
Of the various reasons given, “inaccurate requirement gathering” made it to third place, with 35% citing it as one of the reasons behind the failure of their projects.
Other equally consequential reasons could have some element of stakeholder mismanagement inferred:
Hence, substantial gains can be made simply by improving the requirement gathering, definition, documentation, and validation processes.
Operational Excellence is predicated on the flawless execution of every SDLC stage, starting with requirement definition. We hope that you find this article valuable in that regard.
Principles of Operational Excellence in Software Development
10. References
- Environmental Scanning–The Impact of the Stakeholder Concept — Aubrey Mendelow
- Toward a Theory of Stakeholder Identification and Salience: Defining the Principle of Who and What Really Counts — Ronald K. Mitchell, Bradley R. Agle, and Donna J. Wood
- A great lecture on Requirement Definition (geared for Systems Engineering) can be found on the MIT Open Couse YouTube channel.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Small Business Tools
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
- Sample Business Plans
- IT, Staffing & Customer Service
Software Company Business Plan
High margins, low startup costs, global reach, and a recurring revenue model make starting a software company a lucrative and rewarding profession.
Need help writing a business plan for your software company? You’re at the right place. Our software company business plan template will help you get started.

Free Business Plan Template
Download our free business plan template now and pave the way to success. Let’s turn your vision into an actionable strategy!
- Fill in the blanks – Outline
- Financial Tables
How to Write A Software Company Business Plan?
Writing a software company business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan:
1. Executive Summary
An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan. However, it is written after the entire business plan is ready and summarizes each section of your plan.
Here are a few key components to include in your executive summary:
Introduce your Business:
Start your executive summary by briefly introducing your business to your readers.
Market Opportunity:
Products and services:.
Highlight the software company services you offer your clients. The USPs and differentiators you offer are always a plus.
Marketing & Sales Strategies:
Financial highlights:, call to action:.
Ensure your executive summary is clear, concise, easy to understand, and jargon-free.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

2. Business Overview
The business overview section of your business plan offers detailed information about your company. The details you add will depend on how important they are to your business. Yet, business name, location, business history, and future goals are some of the foundational elements you must consider adding to this section:
Business Description:
Describe your business in this section by providing all the basic information:
Describe what kind of software company you run and the name of it. You may specialize in one of the following software company businesses:
- Enterprise software companies
- SaaS companies
- Mobile app development companies
- Web development companies
- Cybersecurity companies
- HealthTech companies
- Describe the legal structure of your software company, whether it is a sole proprietorship, LLC, partnership, or others.
- Explain where your business is located and why you selected the place.
Mission Statement:
Business history:.
If you’re an established software company, briefly describe your business history, like—when it was founded, how it evolved over time, etc.
Future Goals
This section should provide a thorough understanding of your business, its history, and its future plans. Keep this section engaging, precise, and to the point.
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section of your business plan should offer a thorough understanding of the industry with the target market, competitors, and growth opportunities. You should include the following components in this section.
Target market:
Start this section by describing your target market. Define your ideal customer and explain what types of services they prefer. Creating a buyer persona will help you easily define your target market to your readers.
Market size and growth potential:
Describe your market size and growth potential and whether you will target a niche or a much broader market.
Competitive Analysis:
Market trends:.
Analyze emerging trends in the industry, such as technology disruptions, changes in customer behavior or preferences, etc. Explain how your business will cope with all the trends.
Regulatory Environment:
Here are a few tips for writing the market analysis section of your internet software company business plan:
- Conduct market research, industry reports, and surveys to gather data.
- Provide specific and detailed information whenever possible.
- Illustrate your points with charts and graphs.
- Write your business plan keeping your target audience in mind.
4. Products And Services
The product and services section should describe the specific services and products that will be offered to customers. To write this section should include the following:
Describe your products & services:
Mention the software company products or services your business will offer. This list may include:
- Custom Software Development
- Commercial Off-the-Shelf (COTS) Software
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Software Development Tools
- Software Consulting
- Software Maintenance and Support
- Software Testing and Quality Assurance
- Training and Documentation
Industry focus:
Quality measures, additional services.
In short, this section of your software company plan must be informative, precise, and client-focused. By providing a clear and compelling description of your offerings, you can help potential investors and readers understand the value of your business.
5. Sales And Marketing Strategies
Writing the sales and marketing strategies section means a list of strategies you will use to attract and retain your clients. Here are some key elements to include in your sales & marketing plan:
Unique Selling Proposition (USP):
Define your business’s USPs depending on the market you serve, the equipment you use, and the unique services you provide. Identifying USPs will help you plan your marketing strategies.
Pricing Strategy:
Marketing strategies:, sales strategies:, customer retention:.
Overall, this section of your software company business plan should focus on customer acquisition and retention.
Have a specific, realistic, and data-driven approach while planning sales and marketing strategies for your software company, and be prepared to adapt or make strategic changes in your strategies based on feedback and results.
6. Operations Plan
The operations plan section of your business plan should outline the processes and procedures involved in your business operations, such as staffing requirements and operational processes. Here are a few components to add to your operations plan:
Staffing & Training:
Operational process:, software & tools:.
Include the list of software & tools required for a software company, such as cloud services & infrastructure, project management tools, Version Control Systems, collaboration & communication tools, etc.
Adding these components to your operations plan will help you lay out your business operations, which will eventually help you manage your business effectively.
7. Management Team
The management team section provides an overview of your software company’s management team. This section should provide a detailed description of each manager’s experience and qualifications, as well as their responsibilities and roles.
Founders/CEO:
Key managers:.
Introduce your management and key members of your team, and explain their roles and responsibilities.
Organizational structure:
Compensation plan:, advisors/consultants:.
Mentioning advisors or consultants in your business plans adds credibility to your business idea.
This section should describe the key personnel for your software company services, highlighting how you have the perfect team to succeed.
8. Financial Plan
Your financial plan section should provide a summary of your business’s financial projections for the first few years. Here are some key elements to include in your financial plan:
Profit & loss statement:
Cash flow statement:, balance sheet:, break-even point:.
Determine and mention your business’s break-even point—the point at which your business costs and revenue will be equal.
Financing Needs:
Be realistic with your financial projections, and make sure you offer relevant information and evidence to support your estimates.
9. Appendix
The appendix section of your plan should include any additional information supporting your business plan’s main content, such as market research, legal documentation, financial statements, and other relevant information.
- Add a table of contents for the appendix section to help readers easily find specific information or sections.
- In addition to your financial statements, provide additional financial documents like tax returns, a list of assets within the business, credit history, and more. These statements must be the latest and offer financial projections for at least the first three or five years of business operations.
- Provide data derived from market research, including stats about the industry, user demographics, and industry trends.
- Include any legal documents such as permits, licenses, and contracts.
- Include any additional documentation related to your business plan, such as product brochures, marketing materials, operational procedures, etc.
Use clear headings and labels for each section of the appendix so that readers can easily find the necessary information.
Remember, the appendix section of your software company business plan should only include relevant and important information supporting your plan’s main content.
This sample software company business plan will provide an idea for writing a successful software company plan, including all the essential components of your business.
After this, if you still need clarification about writing an investment-ready business plan to impress your audience, download our software company business plan pdf .
Related Posts
IT Consulting Business Plan
SaaS Business Plan
Cover Page Design for Business Plan
How to Prepare Business Plan Outline
Sample Business Plan Example
A Simple Business Plan Guide
Frequently asked questions, why do you need a software company business plan.
A business plan is an essential tool for anyone looking to start or run a successful software company business. It helps to get clarity in your business, secures funding, and identifies potential challenges while starting and growing your business.
Overall, a well-written plan can help you make informed decisions, which can contribute to the long-term success of your software company.
How to get funding for your software company?
There are several ways to get funding for your software company, but self-funding is one of the most efficient and speedy funding options. Other options for funding are
- Bank loan – You may apply for a loan in government or private banks.
- Small Business Administration (SBA) loan – SBA loans and schemes are available at affordable interest rates, so check the eligibility criteria before applying for it.
- Crowdfunding – The process of supporting a project or business by getting a lot of people to invest in your business, usually online.
- Angel investors – Getting funds from angel investors is one of the most sought startup options.
Apart from all these options, there are small business grants available, check for the same in your location and you can apply for it.
Where to find business plan writers for your software company?
There are many business plan writers available, but no one knows your business and ideas better than you, so we recommend you write your software company business plan and outline your vision as you have in your mind.
What is the easiest way to write your software company business plan?
A lot of research is necessary for writing a business plan, but you can write your plan most efficiently with the help of any software company business plan example and edit it as per your need. You can also quickly finish your plan in just a few hours or less with the help of our business plan software .
How do I write a good market analysis in a software company business plan?
Market analysis is one of the key components of your business plan that requires deep research and a thorough understanding of your industry. We can categorize the process of writing a good market analysis section into the following steps:
- Stating the objective of your market analysis—e.g., investor funding.
- Industry study—market size, growth potential, market trends, etc.
- Identifying target market—based on user behavior and demographics.
- Analyzing direct and indirect competitors.
- Calculating market share—understanding TAM, SAM, and SOM.
- Knowing regulations and restrictions
- Organizing data and writing the first draft.
Writing a marketing analysis section can be overwhelming, but using ChatGPT for market research can make things easier.
How detailed should the financial projections be in my software company business plan?
The level of detail of the financial projections of your software company may vary considering various business aspects like direct and indirect competition, pricing, and operational efficiency. However, your financial projections must be comprehensive enough to demonstrate a complete view of your financial performance.
Generally, the statements included in a business plan offer financial projections for at least the first three or five years of business operations.
What key components should a software company business plan include?
The following are the key components your software company business plan must include:
- Executive summary
- Business Overview
- Market Analysis
- Products and services
- Sales and marketing strategies
- Operations plan
- Management team
- Financial plan
Can a good software company business plan help me secure funding?
Indeed. A well-crafted software company will help your investors better understand your business domain, market trends, strategies, business financials, and growth potential—helping them make better financial decisions.
So, if you have a profitable and investable business, a comprehensive business plan can certainly help you secure your business funding.
What's the importance of a marketing strategy in a software company business plan?
Marketing strategy is a key component of your software company business plan. Whether it is about achieving certain business goals or helping your investors understand your plan to maximize their return on investment—an impactful marketing strategy is the way to do it!
Here are a few pointers to help you understand the importance of having an impactful marketing strategy:
- It provides your business an edge over your competitors.
- It helps investors better understand your business and growth potential.
- It helps you develop products with the best profit potential.
- It helps you set accurate pricing for your products or services.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .

How to Start a Software Development Business
Software is ubiquitous in today’s world, and many people and organizations can no longer function without the programs they rely on. These programs, of course, must be created, distributed and maintained. That’s the work of software development companies.
The software development industry is both big and strong. According to IBISWorld , the software publishing industry has an annual revenue of $238 billion and a growth rate of 3.9 percent per year. In total, the industry employs more than a half-million people.
Learn how to start your own Software Development Business and whether it is the right fit for you.
Ready to form your LLC? Check out the Top LLC Formation Services .

Start a software development business by following these 10 steps:
- Plan your Software Development Business
- Form your Software Development Business into a Legal Entity
- Register your Software Development Business for Taxes
- Open a Business Bank Account & Credit Card
- Set up Accounting for your Software Development Business
- Get the Necessary Permits & Licenses for your Software Development Business
- Get Software Development Business Insurance
- Define your Software Development Business Brand
- Create your Software Development Business Website
- Set up your Business Phone System
We have put together this simple guide to starting your software development business. These steps will ensure that your new business is well planned out, registered properly and legally compliant.
Exploring your options? Check out other small business ideas .
STEP 1: Plan your business
A clear plan is essential for success as an entrepreneur. It will help you map out the specifics of your business and discover some unknowns. A few important topics to consider are:
What will you name your business?
- What are the startup and ongoing costs?
- Who is your target market?
How much can you charge customers?
Luckily we have done a lot of this research for you.
Choosing the right name is important and challenging. If you don’t already have a name in mind, visit our How to Name a Business guide or get help brainstorming a name with our Software Development Business Name Generator
If you operate a sole proprietorship , you might want to operate under a business name other than your own name. Visit our DBA guide to learn more.
When registering a business name , we recommend researching your business name by checking:
- Your state's business records
- Federal and state trademark records
- Social media platforms
- Web domain availability .
It's very important to secure your domain name before someone else does.
Want some help naming your software development business?
Business name generator, what are the costs involved in opening a software development business.
The costs associated with opening a software development company can range from very little (i.e. less than $1,000) to extremely high sums (i.e. venture capital funds). The money invested in a business typically goes toward:
- website hosting expenses and data storage fees
- specialized programs that a project requires
- copyright, trademark and patent fees
- additional employees or contract workers
The variance in startup costs is primarily due to the number of employees and contract workers brought onto the project. Workers speed up the development timeline, but also increase costs.
Paul Jarvis’ company OfCourseBooks is a good example of how a successful business can be started for very little. Jarvis and his team spent $1,125 in startup costs. The funds paid for a website, specialized fonts, stock photography, legal fees, the first month’s operating expenses and a couple other miscellaneous items.
John Sung Kim took a different approach with his company, getting a $40,000 initial investment before developing a call center software program.
What are the ongoing expenses for a software development business?
The ongoing expenses for a software development company also vary. OfCourseBooks costs $45 per month to maintain. A program like Microsoft Dynamics 365 require many more servers and a lot more personnel to maintain, and therefore, has much higher operating expenses.
Who is the target market?
The target market for a software development company can be almost anyone, but it must be well-defined. Business owners need a clear understanding of a need that people or businesses have, and how a program addresses that specific need.
How does a software development business make money?
Software development companies have traditionally charged customers on a per-license basis, but many companies are transitioning to a software-as-a-service (SaaS) structure instead. In SaaS arrangements, customers pay an ongoing fee in order to use the developing company’s program. Some level of support is usually included in this fee.
A few outlying software development companies don’t charge license or subscription fees. Instead, these companies typically either build advertisements into their programs or offer training that does have a fee associated with it.
There is a great range in how much computer programs cost. Simple apps are frequently free or just a few dollars. Complex enterprise solutions can cost tens of thousands of dollars. For example, Angry Birds originally cost $0.99 to $2.99 and is now free. Microsoft Dynamics 365 can be $190 per user / per month.
How much profit can a software development business make?
While not every business reaches this level, the profit potential for a software development business can be enormous. John Sung Kim stayed with Five9 until its revenue reached $10 million. An IPO on the NASDAQ valued the company at $350 million.
Even much more modest companies have substantial profits. For instance, OfCourseBooks brought in a little over $11,000 in profit before even launching a program.
How can you make your business more profitable?
Software development companies can increase their profits by providing additional services to clients. Expedited support, extra training and program customizations might be offered at an extra cost.
Want a more guided approach? Access TRUiC's free Small Business Startup Guide - a step-by-step course for turning your business idea into reality. Get started today!
STEP 2: Form a legal entity
The most common business structure types are the sole proprietorship , partnership , limited liability company (LLC) , and corporation .
Establishing a legal business entity such as an LLC or corporation protects you from being held personally liable if your software development business is sued.
Form Your LLC
Read our Guide to Form Your Own LLC
Have a Professional Service Form your LLC for You
Two such reliable services:
You can form an LLC yourself and pay only the minimal state LLC costs or hire one of the Best LLC Services for a small, additional fee.
Recommended: You will need to elect a registered agent for your LLC. LLC formation packages usually include a free year of registered agent services . You can choose to hire a registered agent or act as your own.
STEP 3: Register for taxes
You will need to register for a variety of state and federal taxes before you can open for business.
In order to register for taxes you will need to apply for an EIN. It's really easy and free!
You can acquire your EIN through the IRS website . If you would like to learn more about EINs, read our article, What is an EIN?
There are specific state taxes that might apply to your business. Learn more about state sales tax and franchise taxes in our state sales tax guides.
STEP 4: Open a business bank account & credit card
Using dedicated business banking and credit accounts is essential for personal asset protection.
When your personal and business accounts are mixed, your personal assets (your home, car, and other valuables) are at risk in the event your business is sued. In business law, this is referred to as piercing your corporate veil .
Open a business bank account
Besides being a requirement when applying for business loans, opening a business bank account:
- Separates your personal assets from your company's assets, which is necessary for personal asset protection.
- Makes accounting and tax filing easier.
Recommended: Read our Best Banks for Small Business review to find the best national bank or credit union.
Get a business credit card
Getting a business credit card helps you:
- Separate personal and business expenses by putting your business' expenses all in one place.
- Build your company's credit history , which can be useful to raise money later on.
Recommended: Apply for an easy approval business credit card from BILL and build your business credit quickly.
STEP 5: Set up business accounting
Recording your various expenses and sources of income is critical to understanding the financial performance of your business. Keeping accurate and detailed accounts also greatly simplifies your annual tax filing.
Make LLC accounting easy with our LLC Expenses Cheat Sheet.
STEP 6: Obtain necessary permits and licenses
Failure to acquire necessary permits and licenses can result in hefty fines, or even cause your business to be shut down.
State & Local Business Licensing Requirements
Certain state permits and licenses may be needed to operate a software development business. Learn more about licensing requirements in your state by visiting SBA’s reference to state licenses and permits .
Most businesses are required to collect sales tax on the goods or services they provide. To learn more about how sales tax will affect your business, read our article, Sales Tax for Small Businesses .
Certificate of Occupancy
A software development business is generally run out of an office. Businesses operating out of a physical location typically require a Certificate of Occupancy (CO). A CO confirms that all building codes, zoning laws and government regulations have been met.
- If you plan to lease a location :
- It is generally the landlord’s responsibility to obtain a CO.
- Before leasing, confirm that your landlord has or can obtain a valid CO that is applicable to a software development business.
- After a major renovation, a new CO often needs to be issued. If your place of business will be renovated before opening, it is recommended to include language in your lease agreement stating that lease payments will not commence until a valid CO is issued.
- If you plan to purchase or build a location :
- You will be responsible for obtaining a valid CO from a local government authority.
- Review all building codes and zoning requirements for your business’ location to ensure your software development business will be in compliance and able to obtain a CO.
STEP 7: Get business insurance
Just as with licenses and permits, your business needs insurance in order to operate safely and lawfully. Business Insurance protects your company’s financial wellbeing in the event of a covered loss.
There are several types of insurance policies created for different types of businesses with different risks. If you’re unsure of the types of risks that your business may face, begin with General Liability Insurance . This is the most common coverage that small businesses need, so it’s a great place to start for your business.
Another notable insurance policy that many businesses need is Workers’ Compensation Insurance . If your business will have employees, it’s a good chance that your state will require you to carry Workers' Compensation Coverage.
FInd out what types of insurance your Software Development Business needs and how much it will cost you by reading our guide Business Insurance for Software Development Business.
STEP 8: Define your brand
Your brand is what your company stands for, as well as how your business is perceived by the public. A strong brand will help your business stand out from competitors.
If you aren't feeling confident about designing your small business logo, then check out our Design Guides for Beginners , we'll give you helpful tips and advice for creating the best unique logo for your business.
Recommended : Get a logo using Truic's free logo Generator no email or sign up required, or use a Premium Logo Maker .
If you already have a logo, you can also add it to a QR code with our Free QR Code Generator . Choose from 13 QR code types to create a code for your business cards and publications, or to help spread awareness for your new website.
How to promote & market a software development business
Most software development companies market their programs online, through websites and other platforms. What other platforms are most appropriate for a particular business to use depends on what programs that business creates. A business that makes spell checkers for legal documents won’t want to market in the same place as a video game.
How to keep customers coming back
A software company’s programs must work well, or else customers will switch to more user-friendly and error-free programs. For this reason, the testing and debugging phase of development shouldn’t be rushed.
STEP 9: Create your business website
After defining your brand and creating your logo the next step is to create a website for your business .
While creating a website is an essential step, some may fear that it’s out of their reach because they don’t have any website-building experience. While this may have been a reasonable fear back in 2015, web technology has seen huge advancements in the past few years that makes the lives of small business owners much simpler.
Here are the main reasons why you shouldn’t delay building your website:
- All legitimate businesses have websites - full stop. The size or industry of your business does not matter when it comes to getting your business online.
- Social media accounts like Facebook pages or LinkedIn business profiles are not a replacement for a business website that you own.
- Website builder tools like the GoDaddy Website Builder have made creating a basic website extremely simple. You don’t need to hire a web developer or designer to create a website that you can be proud of.
Recommended : Get started today using our recommended website builder or check out our review of the Best Website Builders .
Other popular website builders are: WordPress , WIX , Weebly , Squarespace , and Shopify .
STEP 10: Set up your business phone system
Getting a phone set up for your business is one of the best ways to help keep your personal life and business life separate and private. That’s not the only benefit; it also helps you make your business more automated, gives your business legitimacy, and makes it easier for potential customers to find and contact you.
There are many services available to entrepreneurs who want to set up a business phone system. We’ve reviewed the top companies and rated them based on price, features, and ease of use. Check out our review of the Best Business Phone Systems 2023 to find the best phone service for your small business.
Recommended Business Phone Service: Phone.com
Phone.com is our top choice for small business phone numbers because of all the features it offers for small businesses and it's fair pricing.
Is this Business Right For You?
While many different types of people work within the software development industry, business founders tend to be people who bridge the gap between logic and creativity. Writing programs, of course, requires a strong command of logic. Having the vision for a software program that’ll be useful, however, requires creativity.
Want to know if you are cut out to be an entrepreneur?
Take our Entrepreneurship Quiz to find out!
Entrepreneurship Quiz
What happens during a typical day at a software development business?
Much of the work that goes on at a software development company is done on a computer. Business owners spend time writing code, testing and debugging programs, marketing their programs and providing support to customers.
What are some skills and experiences that will help you build a successful software development business?
Business owners must themselves know how to code in at least one programming language, and competency in several languages is highly advisable. This technical knowledge is necessary to code and debug programs. Business owners also need it so they can discuss issues with other programmers or developers working on the company’s projects.
People who don’t have sufficient coding knowledge can study different languages through both in-person and online courses. Many community colleges and four-year colleges have computer science programs, and local software developers may offer private tutoring. Regent University , Saint Leo University , Southern New Hampshire University and many other schools offer online degree programs in Computer Science.
What is the growth potential for a software development business?
A software development company can be a small, one-person business, or it can grow into an international corporation. Gorges is a local development company in Ithaca, NY, and Logos is a good example of a niche-specific company. Microsoft and Apple are two of the largest software developers in the world, although their work isn’t limited to only making programs.
TRUiC's YouTube Channel
For fun informative videos about starting a business visit the TRUiC YouTube Channel or subscribe to view later.
Take the Next Step
Find a business mentor.
One of the greatest resources an entrepreneur can have is quality mentorship. As you start planning your business, connect with a free business resource near you to get the help you need.
Having a support network in place to turn to during tough times is a major factor of success for new business owners.
Learn from other business owners
Want to learn more about starting a business from entrepreneurs themselves? Visit Startup Savant’s startup founder series to gain entrepreneurial insights, lessons, and advice from founders themselves.
Resources to Help Women in Business
There are many resources out there specifically for women entrepreneurs. We’ve gathered necessary and useful information to help you succeed both professionally and personally:
If you’re a woman looking for some guidance in entrepreneurship, check out this great new series Women in Business created by the women of our partner Startup Savant.
What are some insider tips for jump starting a software development business?
Many successful software development companies have raised support on Kickstarter before launching. Jarvis used this strategy to raise over $12,000 before launching OfCourseBooks. Pillars of Eternity , a computer-based role-playing game (RPG) raised almost $4 million on Kickstarter.
How and when to build a team
Whether a software development company hires people depends on the business’ owners expertise, program’s complexity, business’ budget and required timeline.
Business owners who do hire employees frequently bring on computer programmers, computer developers, designers and marketers. All of these people can be hired as traditional employees or on a contract basis. Sometimes, salespeople are brought on board . They may be given a salary, a commission or both.
Useful Links
Industry opportunities.
- Software & Information Industry Association
Real World Examples
- Cylon Technologies
Further Reading
- Advice on Starting Your Own Software Company
- Software Development Business Models: What to Choose for Your Business?
Have a Question? Leave a Comment!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Best Business Plan Software of 2024. Wrike: Best overall. Smartsheet: Best for goal management. LivePlan: Best for financial forecasting. Aha!: Best for roadmapping. Bizplan: Best for ...
3. Upmetrics. Upmetrics is an AI-powered business planning software that helps businesses of all sizes and industries write their business plan. With Upmetrics AI Assistant, you can write your plan faster, get answers to any business-related queries, and prepare financial forecasts in no time.
1. LivePlan. Best overall business plan software. If you want template-rich, modern-feeling business plan software, then LivePlan may be the right pick for you. LivePlan excels with their user ...
These business requirements should meet both stakeholder and customer needs. This can include a process that must be completed, a piece of data that is needed for the process or a business rule that governs that process and data. Related: Free Requirements Gathering Template for Word. 5. Key Stakeholders.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
5 Best Business Plan Software and Tools in 2023 for Your Small Business. Entrepreneurs who write formal business plans are 16% more likely to achieve success than entrepreneurs who don't. 1 This software can help. Data as of 3/13/23. Offers and availability may vary by location and are subject to change.
4. IdeaBuddy. Ideabuddy is an innovative business plan software helping new-age entrepreneurs turn their ideas into successful business plans. Customizable templates, industry-based guides, and streamlined idea and business plan creation make it one of the most user-friendly applications on the list.
"LivePlan earns the top spot on our list of best business plan software—and for good reason. LivePlan's slick and interactive service provides a step-by-step business plan approach, a rich collection of cloud-based features, and online learning tools." Brooke Hayes Software Reviewer, Business.org
Best Business Plan Software: LivePlan. LivePlan is the overall best business plan tool, offering a large number of features at an affordable price. Visit LivePlan. 1. LivePlan - $15/month to $30/month. We love LivePlan overall because it offers great value at an affordable cost.
A software requirement specifications (SRS) document lists the requirements, expectations, design, and standards for a future project. These include the high-level business requirements dictating the goal of the project, end-user requirements and needs, and the product's functionality in technical terms. To put it simply, an SRS provides a ...
Learn more about each requirement type below: Business Requirements: Business requirements state the problem and the business objectives at a high level, and they help inform how the proposed project will solve the business problem. The team defines the requirements in a business requirements document (BRD).A business requirement might be a process, data necessary for the process, or a ...
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
January 21st, 2024 5 min read. Summary. A business requirements document (BRD) is a report detailing everything a new project requires for success. There are seven key components of a BRD template, which serve to provide clarity and context for stakeholders. In this piece, learn how a BRD template can increase your chances for project success.
Here's a six-step guide to creating an SRS document in 2024: Step 1. Create an Outline. The first step is to create an outline that will act as a framework for the document and your guide through the writing process. You can either create your outline or use an SRS document template as a basis.
Franchise Business Plan: Focuses on the franchisor's requirements, as well as the franchisee's goals, strategies, and financial projections. Franchise Agreement, Brand Standards, Marketing Efforts, Operational Procedures, Financial Projections. ... Enloop is a robust business plan software that automatically generates a tailored plan based on ...
Requirements management is a way to ensure your final project deliverables meet customers' and internal stakeholders' needs. In this case, a requirement is something stakeholders need or want from your product. Stakeholders can be internal (like cross-functional partners) or external (like customers or clients).
The rest, while still useful, go a bit lighter on guidance in favor of tailoring the plan to a specific industry. Explore: PandaDoc's business plan template library. 5. Canva — Pitch with your plan. Canva is a great option for building a visually stunning business plan that can be used as a pitch tool.
A requirements management software is a tool designed to facilitate the process of handling project requirements from gathering ideas to project completion. Think of it as a central point for collecting, documenting, analyzing, and tracking stakeholder expectations. It provides a structure to the process from the very beginning and ensures that ...
A software requirements specification (SRS) is a document that describes what the software will do and how it will be expected to perform. It also describes the functionality the product needs to fulfill the needs of all stakeholders (business, users). You can think of an SRS as a blueprint or roadmap for the software you're going to build.
Information Technology (IT) Business requirements are explicit statements that outline the features, capabilities, and characteristics a software application or system must exhibit to satisfy the business needs. These needs can encompass many aspects, including functionality, performance, security, and user experience.
Writing a software company business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan: 1. Executive Summary. An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan. However, it is written after the entire business plan is ready ...
Whether you want to launch a side gig, a solo operation or a small business, you need a simple business plan template to guide you. Forbes Advisor offers you a comprehensive and easy-to-follow ...
STEP 4: Open a business bank account & credit card. Using dedicated business banking and credit accounts is essential for personal asset protection. When your personal and business accounts are mixed, your personal assets (your home, car, and other valuables) are at risk in the event your business is sued.
CAPM requirements. You'll need to have the following to sit for the CAPM exam: Secondary degree, defined as a high school diploma, GED, associate degree, or the global equivalent. 23 hours of project management education, completed before the time of the exam, or 1,500 hours of experience.