

How to Write a Purpose Statement (Templates, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on September 30, 2023 — 15 minutes to read
- Key Elements of a Purpose Statement Part 1
- How to Write a Purpose Statement Step-by-Step Part 2
- Identifying Your Goals Part 3
- Defining Your Audience Part 4
- Outlining Your Methods Part 5
- Stating the Expected Outcomes Part 6
- Purpose Statement Example for a Research Paper Part 7
- Purpose Statement Example For Personal Goals Part 8
- Purpose Statement Example For Business Objectives Part 9
- Purpose Statement Example For an Essay Part 10
- Purpose Statement Example For a Proposal Part 11
- Purpose Statement Example For a Report Part 12
- Purpose Statement Example For a Project Part 13
- Purpose Statement Templates Part 14
A purpose statement is a vital component of any project, as it sets the tone for the entire piece of work. It tells the reader what the project is about, why it’s important, and what the writer hopes to achieve.
Part 1 Key Elements of a Purpose Statement
When writing a purpose statement, there are several key elements that you should keep in mind. These elements will help you to create a clear, concise, and effective statement that accurately reflects your goals and objectives.
1. The Problem or Opportunity
The first element of a purpose statement is the problem or opportunity that you are addressing. This should be a clear and specific description of the issue that you are trying to solve or the opportunity that you are pursuing.
2. The Target Audience
The second element is the target audience for your purpose statement. This should be a clear and specific description of the group of people who will benefit from your work.
3. The Solution
The third element is the solution that you are proposing. This should be a clear and specific description of the action that you will take to address the problem or pursue the opportunity.
4. The Benefits
The fourth element is the benefits that your solution will provide. This should be a clear and specific description of the positive outcomes that your work will achieve.
5. The Action Plan
The fifth element is the action plan that you will follow to implement your solution. This should be a clear and specific description of the steps that you will take to achieve your goals.
Part 2 How to Write a Purpose Statement Step-by-Step
Writing a purpose statement is an essential part of any research project. It helps to clarify the purpose of your study and provides direction for your research. Here are some steps to follow when writing a purpose statement:
- Start with a clear research question: The first step in writing a purpose statement is to have a clear research question. This question should be specific and focused on the topic you want to research.
- Identify the scope of your study: Once you have a clear research question, you need to identify the scope of your study. This involves determining what you will and will not include in your research.
- Define your research objectives: Your research objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. They should also be aligned with your research question and the scope of your study.
- Determine your research design: Your research design will depend on the nature of your research question and the scope of your study. You may choose to use a qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods approach.
- Write your purpose statement: Your purpose statement should be a clear and concise statement that summarizes the purpose of your study. It should include your research question, the scope of your study, your research objectives, and your research design.
Research question: What are the effects of social media on teenage mental health?
Scope of study: This study will focus on teenagers aged 13-18 in the United States.
Research objectives: To determine the prevalence of social media use among teenagers, to identify the types of social media used by teenagers, to explore the relationship between social media use and mental health, and to provide recommendations for parents, educators, and mental health professionals.
Research design: This study will use a mixed-methods approach, including a survey and interviews with teenagers and mental health professionals.
Purpose statement: The purpose of this study is to examine the effects of social media on teenage mental health among teenagers aged 13-18 in the United States. The study will use a mixed-methods approach, including a survey and interviews with teenagers and mental health professionals. The research objectives are to determine the prevalence of social media use among teenagers, to identify the types of social media used by teenagers, to explore the relationship between social media use and mental health, and to provide recommendations for parents, educators, and mental health professionals.
Part 3 Section 1: Identifying Your Goals
Before you start writing your purpose statement, it’s important to identify your goals. To do this, ask yourself the following questions:
- What do I want to achieve?
- What problem do I want to solve?
- What impact do I want to make?
Once you have a clear idea of your goals, you can start crafting your purpose statement. Your purpose statement should be a clear and concise statement that outlines the purpose of your work.
For example, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a business, your statement might look something like this:
“Our purpose is to provide high-quality products and services that improve the lives of our customers and contribute to the growth and success of our company.”
If you’re writing a purpose statement for a non-profit organization, your statement might look something like this:
“Our purpose is to improve the lives of underserved communities by providing access to education, healthcare, and other essential services.”
Remember, your purpose statement should be specific, measurable, and achievable. It should also be aligned with your values and goals, and it should inspire and motivate you to take action.
Part 4 Section 2: Defining Your Audience
Once you have established the purpose of your statement, it’s important to consider who your audience is. The audience for your purpose statement will depend on the context in which it will be used. For example, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a research paper, your audience will likely be your professor or academic peers. If you’re writing a purpose statement for a business proposal, your audience may be potential investors or clients.
Defining your audience is important because it will help you tailor your purpose statement to the specific needs and interests of your readers. You want to make sure that your statement is clear, concise, and relevant to your audience.
To define your audience, consider the following questions:
- Who will be reading your purpose statement?
- What is their level of knowledge or expertise on the topic?
- What are their needs and interests?
- What do they hope to gain from reading your purpose statement?
Once you have a clear understanding of your audience, you can begin to craft your purpose statement with their needs and interests in mind. This will help ensure that your statement is effective in communicating your goals and objectives to your readers.
For example, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a research paper on the effects of climate change on agriculture, your audience may be fellow researchers in the field of environmental science. In this case, you would want to make sure that your purpose statement is written in a way that is clear and concise, using technical language that is familiar to your audience.
Or, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a business proposal to potential investors, your audience may be less familiar with the technical aspects of your project. In this case, you would want to make sure that your purpose statement is written in a way that is easy to understand, using clear and concise language that highlights the benefits of your proposal.
The key to defining your audience is to put yourself in their shoes and consider what they need and want from your purpose statement.
Part 5 Section 3: Outlining Your Methods
After you have identified the purpose of your statement, it is time to outline your methods. This section should describe how you plan to achieve your goal and the steps you will take to get there. Here are a few tips to help you outline your methods effectively:
- Start with a general overview: Begin by providing a brief overview of the methods you plan to use. This will give your readers a sense of what to expect in the following paragraphs.
- Break down your methods: Break your methods down into smaller, more manageable steps. This will make it easier for you to stay organized and for your readers to follow along.
- Use bullet points: Bullet points can help you organize your ideas and make your methods easier to read. Use them to list the steps you will take to achieve your goal.
- Be specific: Make sure you are specific about the methods you plan to use. This will help your readers understand exactly what you are doing and why.
- Provide examples: Use examples to illustrate your methods. This will make it easier for your readers to understand what you are trying to accomplish.
Part 6 Section 4: Stating the Expected Outcomes
After defining the problem and the purpose of your research, it’s time to state the expected outcomes. This is where you describe what you hope to achieve by conducting your research. The expected outcomes should be specific and measurable, so you can determine if you have achieved your goals.
It’s important to be realistic when stating your expected outcomes. Don’t make exaggerated or false claims, and don’t promise something that you can’t deliver. Your expected outcomes should be based on your research question and the purpose of your study.
Here are some examples of expected outcomes:
- To identify the factors that contribute to employee turnover in the company.
- To develop a new marketing strategy that will increase sales by 20% within the next year.
- To evaluate the effectiveness of a new training program for improving customer service.
- To determine the impact of social media on consumer behavior.
When stating your expected outcomes, make sure they align with your research question and purpose statement. This will help you stay focused on your goals and ensure that your research is relevant and meaningful.
In addition to stating your expected outcomes, you should also describe how you will measure them. This could involve collecting data through surveys, interviews, or experiments, or analyzing existing data from sources such as government reports or industry publications.
Part 7 Purpose Statement Example for a Research Paper
If you are writing a research paper, your purpose statement should clearly state the objective of your study. Here is an example of a purpose statement for a research paper:
The purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of social media on the mental health of teenagers in the United States.
This purpose statement clearly states the objective of the study and provides a specific focus for the research.
Part 8 Purpose Statement Example For Personal Goals
When writing a purpose statement for your personal goals, it’s important to clearly define what you want to achieve and why. Here’s a template that can help you get started:
“I want to [goal] so that [reason]. I will achieve this by [action].”
Example: “I want to lose 10 pounds so that I can feel more confident in my body. I will achieve this by going to the gym three times a week and cutting out sugary snacks.”
Remember to be specific and realistic when setting your goals and actions, and to regularly review and adjust your purpose statement as needed.
Part 9 Purpose Statement Example For Business Objectives
If you’re writing a purpose statement for a business objective, this template can help you get started:
[Objective] [Action verb] [Target audience] [Outcome or benefit]
Here’s an example using this template:
Increase online sales by creating a more user-friendly website for millennial shoppers.
This purpose statement is clear and concise. It identifies the objective (increase online sales), the action verb (creating), the target audience (millennial shoppers), and the outcome or benefit (a more user-friendly website).
Part 10 Purpose Statement Example For an Essay
“The purpose of this essay is to examine the causes and consequences of climate change, with a focus on the role of human activities, and to propose solutions that can mitigate its impact on the environment and future generations.”
This purpose statement clearly states the subject of the essay (climate change), what aspects will be explored (causes, consequences, human activities), and the intended outcome (proposing solutions). It provides a clear roadmap for the reader and sets the direction for the essay.
Part 11 Purpose Statement Example For a Proposal
“The purpose of this proposal is to secure funding and support for the establishment of a community garden in [Location], aimed at promoting sustainable urban agriculture, fostering community engagement, and improving local access to fresh, healthy produce.”
Why this purpose statement is effective:
- The subject of the proposal is clear: the establishment of a community garden.
- The specific goals of the project are outlined: promoting sustainable urban agriculture, fostering community engagement, and improving local access to fresh produce.
- The overall objective of the proposal is evident: securing funding and support.
Part 12 Purpose Statement Example For a Report
“The purpose of this report is to analyze current market trends in the electric vehicle (EV) industry, assess consumer preferences and buying behaviors, and provide strategic recommendations to guide [Company Name] in entering this growing market segment.”
- The subject of the report is provided: market trends in the electric vehicle industry.
- The specific goals of the report are analysis of market trends, assessment of consumer preferences, and strategic recommendations.
- The overall objective of the report is clear: providing guidance for the company’s entry into the EV market.
Part 13 Purpose Statement Example For a Project
“The purpose of this project is to design and implement a new employee wellness program that promotes physical and mental wellbeing in the workplace.”
This purpose statement clearly outlines the objective of the project, which is to create a new employee wellness program. The program is designed to promote physical and mental wellbeing in the workplace, which is a key concern for many employers. By implementing this program, the company aims to improve employee health, reduce absenteeism, and increase productivity. The purpose statement is concise and specific, providing a clear direction for the project team to follow. It highlights the importance of the project and its potential benefits for the company and its employees.
Part 14 Purpose Statement Templates
When writing a purpose statement, it can be helpful to use a template to ensure that you cover all the necessary components:
Template 1: To [action] [target audience] in order to [outcome]
This template is a straightforward way to outline your purpose statement. Simply fill in the blanks with the appropriate information:
- The purpose of […] is
- To [action]: What action do you want to take?
- [Target audience]: Who is your target audience?
- In order to [outcome]: What outcome do you hope to achieve?
For example:
- The purpose of our marketing campaign is to increase brand awareness among young adults in urban areas, in order to drive sales and revenue growth.
- The purpose of our employee training program is to improve customer service skills among our frontline staff, in order to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- The purpose of our new product launch is to expand our market share in the healthcare industry, by offering a unique solution to the needs of elderly patients with chronic conditions.
Template 2: This [project/product] is designed to [action] [target audience] by [method] in order to [outcome].
This template is useful for purpose statements that involve a specific project or product. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate information:
- This [project/product]: What is your project or product?
- Is designed to [action]: What action do you want to take?
- By [method]: What method will you use to achieve your goal?
- This app is designed to provide personalized nutrition advice to athletes by analyzing their training data in order to optimize performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key elements of a purpose statement.
A purpose statement should clearly communicate the main goal or objective of your writing. It should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your work. The key elements of a purpose statement include the topic or subject matter, the intended audience, and the overall goal or objective of your writing.
How can a purpose statement benefit your writing?
A purpose statement can help you stay focused and on track when writing. It can also help you to avoid going off-topic or getting bogged down in unnecessary details. By clearly identifying the main goal or objective of your writing, a purpose statement can help you to stay organized and ensure that your writing is effective and impactful.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when writing a purpose statement?
One common mistake is being too vague or general in your purpose statement. Another mistake is making your purpose statement too long or complex, which can make it difficult to understand. Additionally, it’s important to avoid including unnecessary information or details that are not directly relevant to your main goal or objective.
How can you tailor your purpose statement to your audience?
When writing a purpose statement, it’s important to consider your audience and their needs. You should tailor your purpose statement to your audience by using language and terminology that they will understand. You should also consider their level of knowledge or expertise on the subject matter and adjust your purpose statement accordingly.
What are some effective templates for writing a purpose statement?
There are many effective templates for writing a purpose statement, but one common approach is to use the following structure: “The purpose of this writing is to [insert goal or objective] for [insert audience] regarding [insert topic or subject matter].”
Can you provide examples of successful purpose statements?
- “The purpose of this report is to provide an analysis of the current market trends and make recommendations for future growth strategies for our company.”
- “The purpose of this essay is to explore the impact of social media on modern communication and its implications for society.”
- “The purpose of this proposal is to secure funding for a new community center that will provide educational and recreational opportunities for local residents.”
- How to Write a Personal Mission Statement (20 Examples)
- How to Write a Letter of Employment (Templates, Examples)
- How to Ask for a Letter of Recommendation [Examples]
- Individual Development Plan [Examples & Templates]
- How to Write a Two-Week Notice [Effective Examples]
- Job Application Email (Templates, Examples)
Understanding Your Purpose
The first question for any writer should be, "Why am I writing?" "What is my goal or my purpose for writing?" For many writing contexts, your immediate purpose may be to complete an assignment or get a good grade. But the long-range purpose of writing is to communicate to a particular audience. In order to communicate successfully to your audience, understanding your purpose for writing will make you a better writer.
A Definition of Purpose
Purpose is the reason why you are writing . You may write a grocery list in order to remember what you need to buy. You may write a laboratory report in order to carefully describe a chemistry experiment. You may write an argumentative essay in order to persuade someone to change the parking rules on campus. You may write a letter to a friend to express your excitement about her new job.
Notice that selecting the form for your writing (list, report, essay, letter) is one of your choices that helps you achieve your purpose. You also have choices about style, organization, kinds of evidence that help you achieve your purpose
Focusing on your purpose as you begin writing helps you know what form to choose, how to focus and organize your writing, what kinds of evidence to cite, how formal or informal your style should be, and how much you should write.
Types of Purpose
Don Zimmerman, Journalism and Technical Communication Department I look at most scientific and technical writing as being either informational or instructional in purpose. A third category is documentation for legal purposes. Most writing can be organized in one of these three ways. For example, an informational purpose is frequently used to make decisions. Memos, in most circles, carry key information.
When we communicate with other people, we are usually guided by some purpose, goal, or aim. We may want to express our feelings. We may want simply to explore an idea or perhaps entertain or amuse our listeners or readers. We may wish to inform people or explain an idea. We may wish to argue for or against an idea in order to persuade others to believe or act in a certain way. We make special kinds of arguments when we are evaluating or problem solving . Finally, we may wish to mediate or negotiate a solution in a tense or difficult situation.
Remember, however, that often writers combine purposes in a single piece of writing. Thus, we may, in a business report, begin by informing readers of the economic facts before we try to persuade them to take a certain course of action.
In expressive writing, the writer's purpose or goal is to put thoughts and feelings on the page. Expressive writing is personal writing. We are often just writing for ourselves or for close friends. Usually, expressive writing is informal, not intended for outside readers. Journal writing, for example, is usually expressive writing.
However, we may write expressively for other readers when we write poetry (although not all poetry is expressive writing). We may write expressively in a letter, or we may include some expressive sentences in a formal essay intended for other readers.
Entertaining
As a purpose or goal of writing, entertaining is often used with some other purpose--to explain, argue, or inform in a humorous way. Sometimes, however, entertaining others with humor is our main goal. Entertaining may take the form of a brief joke, a newspaper column, a television script or an Internet home page tidbit, but its goal is to relax our reader and share some story of human foibles or surprising actions.
Writing to inform is one of the most common purposes for writing. Most journalistic writing fits this purpose. A journalist uncovers the facts about some incident and then reports those facts, as objectively as possible, to his or her readers. Of course, some bias or point-of-view is always present, but the purpose of informational or reportorial writing is to convey information as accurately and objectively as possible. Other examples of writing to inform include laboratory reports, economic reports, and business reports.
Writing to explain, or expository writing, is the most common of the writing purposes. The writer's purpose is to gather facts and information, combine them with his or her own knowledge and experience, and clarify for some audience who or what something is , how it happened or should happen, and/or why something happened .
Explaining the whos, whats, hows, whys, and wherefores requires that the writer analyze the subject (divide it into its important parts) and show the relationship of those parts. Thus, writing to explain relies heavily on definition, process analysis, cause/effect analysis, and synthesis.
Explaining versus Informing : So how does explaining differ from informing? Explaining goes one step beyond informing or reporting. A reporter merely reports what his or her sources say or the data indicate. An expository writer adds his or her particular understanding, interpretation, or thesis to that information. An expository writer says this is the best or most accurate definition of literacy, or the right way to make lasagne, or the most relevant causes of an accident.
An arguing essay attempts to convince its audience to believe or act in a certain way. Written arguments have several key features:
- A debatable claim or thesis . The issue must have some reasonable arguments on both (or several) sides.
- A focus on one or more of the four types of claims : Claim of fact , claim of cause and effect , claim of value , and/or claim of policy (problem solving).
- A fair representation of opposing arguments combined with arguments against the opposition and for the overall claim.
- An argument based on evidence presented in a reasonable tone . Although appeals to character and to emotion may be used, the primary appeal should be to the reader's logic and reason.
Although the terms argument and persuasion are often used interchangeably, the terms do have slightly different meanings. Argument is a special kind of persuasion that follows certain ground rules. Those rules are that opposing positions will be presented accurately and fairly, and that appeals to logic and reason will be the primary means of persuasion. Persuasive writing may, if it wishes, ignore those rules and try any strategy that might work. Advertisements are a good example of persuasive writing. They usually don't fairly represent the competing product, and they appeal to image, to emotion, to character, or to anything except logic and the facts--unless those facts are in the product's favor.
Writing to evaluate a person, product, thing, or policy is a frequent purpose for writing. An evaluation is really a specific kind of argument: it argues for the merits of the subject and presents evidence to support the claim. A claim of value --the thesis in an evaluation--must be supported by criteria (the appropriate standards of judgment) and supporting evidence (the facts, statistics, examples, or testimonials).
Writers often use a three-column log to set up criteria for their subject, collect relevant evidence, and reach judgments that support an overall claim of value. Writing a three-column log is an excellent way to organize an evaluative essay. First, think about your possible criteria. Remember: criteria are the standards of judgment (the ideal case) against which you will measure your particular subject. Choose criteria which your readers will find valid, fair, and appropriate . Then, collect evidence for each of your selected criteria. Consider the following example of a restaurant evaluation:
Overall claim of value : This Chinese restaurant provides a high quality dining experience.
Problem Solving
Problem solving is a special kind of arguing essay: the writer's purpose is to persuade his audience to adopt a solution to a particular problem. Often called "policy" essays because they recommend the readers adopt a policy to resolve a problem, problem-solving essays have two main components: a description of a serious problem and an argument for specific recommendations that will solve the problem .
The thesis of a problem-solving essay becomes a claim of policy : If the audience follows the suggested recommendations, the problem will be reduced or eliminated. The essay must support the policy claim by persuading readers that the recommendations are feasible, cost-effective, efficient, relevant to the situation, and better than other possible alternative solutions.
Traditional argument , like a debate, is confrontational. The argument often becomes a kind of "war" in which the writer attempts to "defeat" the arguments of the opposition.
Non-traditional kinds of argument use a variety of strategies to reduce the confrontation and threat in order to open up the debate.
- Mediated argument follows a plan used successfully in labor negotiations to bring opposing parties to agreement. The writer of a mediated argument provides a middle position that helps negotiate the differences of the opposing positions.
- Rogerian argumen t also wishes to reduce confrontation by encouraging mutual understanding and working toward common ground and a compromise solution.
- Feminist argument tries to avoid the patriarchal conventions in traditional argument by emphasizing personal communication, exploration, and true understanding.
Combining Purposes
Often, writers use multiple purposes in a single piece of writing. An essay about illiteracy in America may begin by expressing your feelings on the topic. Then it may report the current facts about illiteracy. Finally, it may argue for a solution that might correct some of the social conditions that cause illiteracy. The ultimate purpose of the paper is to argue for the solution, but the writer uses these other purposes along the way.
Similarly, a scientific paper about gene therapy may begin by reporting the current state of gene therapy research. It may then explain how a gene therapy works in a medical situation. Finally, it may argue that we need to increase funding for primary research into gene therapy.
Purposes and Strategies
A purpose is the aim or goal of the writer or the written product; a strategy is a means of achieving that purpose. For example, our purpose may be to explain something, but we may use definitions, examples, descriptions, and analysis in order to make our explanation clearer. A variety of strategies are available for writers to help them find ways to achieve their purpose(s).
Writers often use definition for key terms of ideas in their essays. A formal definition , the basis of most dictionary definitions, has three parts: the term to be defined, the class to which the term belongs, and the features that distinguish this term from other terms in the class.
Look at your own topic. Would definition help you analyze and explain your subject?
Illustration and Example
Examples and illustrations are a basic kind of evidence and support in expository and argumentative writing.
In her essay about anorexia nervosa, student writer Nancie Brosseau uses several examples to develop a paragraph:
Another problem, lying, occurred most often when my parents tried to force me to eat. Because I was at the gym until around eight o'clock every night, I told my mother not to save me dinner. I would come home and make a sandwich and feed it to my dog. I lied to my parents every day about eating lunch at school. For example, I would bring a sack lunch and sell it to someone and use the money to buy diet pills. I always told my parents that I ate my own lunch.
Look at your own topic. What examples and illustrations would help explain your subject?
Classification
Classification is a form of analyzing a subject into types. We might classify automobiles by types: Trucks, Sport Utilities, Sedans, Sport Cars. We can (and do) classify college classes by type: Science, Social Science, Humanities, Business, Agriculture, etc.
Look at your own topic. Would classification help you analyze and explain your subject?
Comparison and Contrast
Comparison and contrast can be used to organize an essay. Consider whether either of the following two outlines would help you organize your comparison essay.
Block Comparison of A and B
- Intro and Thesis
- Description of A
- Description of B (and how B is similar to/different from A)
Alternating Comparison of A and B
- Aspect One: Comparison/contrast of A and B
- Aspect Two: Comparison/contrast of A and B
- Aspect Three: Comparison/contrast of A and B
Look at your own topic. Would comparison/contrast help you organize and explain your subject?
Analysis is simply dividing some whole into its parts. A library has distinct parts: stacks, electronic catalog, reserve desk, government documents section, interlibrary loan desk, etc. If you are writing about a library, you may need to know all the parts that exist in that library.
Look at your own topic. Would analysis of the parts help you understand and explain your subject?
Description
Although we usually think of description as visual, we may also use other senses--hearing, touch, feeling, smell-- in our attempt to describe something for our readers.
Notice how student writer Stephen White uses multiple senses to describe Anasazi Indian ruins at Mesa Verde:
I awoke this morning with a sense of unexplainable anticipation gnawing away at the back of my mind, that this chilly, leaden day at Mesa Verde would bring something new . . . . They are a haunting sight, these broken houses, clustered together down in the gloom of the canyon. The silence is broken only by the rush of the wind in the trees and the trickling of a tiny stream of melting snow springing from ledge to ledge. This small, abandoned village of tiny houses seems almost as the Indians left it, reduced by the passage of nearly a thousand years to piles of rubble through which protrude broken red adobe walls surrounding ghostly jet black openings, undisturbed by modern man.
Look at your own topic. Would description help you explain your subject?
Process Analysis
Process analysis is analyzing the chronological steps in any operation. A recipe contains process analysis. First, sift the flour. Next, mix the eggs, milk, and oil. Then fold in the flour with the eggs, milk and oil. Then add baking soda, salt and spices. Finally, pour the pancake batter onto the griddle.
Look at your own topic. Would process analysis help you analyze and explain your subject?
Narration is possibly the most effective strategy essay writers can use. Readers are quickly caught up in reading any story, no matter how short it is. Writers of exposition and argument should consider where a short narrative might enliven their essay. Typically, this narrative can relate some of your own experiences with the subject of your essay. Look at your own topic. Where might a short narrative help you explain your subject?
Cause/Effect Analysis
In cause and effect analysis, you map out possible causes and effects. Two patterns for doing cause/effect analysis are as follows:
Several causes leading to single effect: Cause 1 + Cause 2 + Cause 3 . . . => Effect
One cause leading to multiple effects: Cause => Effect 1 + Effect 2 + Effect 3 ...
Look at your own topic. Would cause/effect analysis help you understand and explain your subject?
How Audience and Focus Affect Purpose
All readers have expectations. They assume what they read will meet their expectations. As a writer, your job is to make sure those expectations are met, while at the same time, fulfilling the purpose of your writing.
Once you have determined what type of purpose best conveys your motivations, you will then need to examine how this will affect your readers. Perhaps you are explaining your topic when you really should be convincing readers to see your point. Writers and readers may approach a topic with conflicting purposes. Your job, as a writer, is to make sure both are being met.
Purpose and Audience
Often your audience will help you determine your purpose. The beliefs they hold will tell you whether or not they agree with what you have to say. Suppose, for example, you are writing to persuade readers against Internet censorship. Your purpose will differ depending on the audience who will read your writing.
Audience One: Internet Users
If your audience is computer users who surf the net daily, you could appear foolish trying to persuade them to react against Internet censorship. It's likely they are already against such a movement. Instead, they might expect more information on the topic.
Audience Two: Parents
If your audience is parents who don't want their small children surfing the net, you'll need to convince them that censorship is not the solution to the problem. You should persuade this audience to consider other options.
Purpose and Focus
Your focus (otherwise known as thesis, claim, main idea, or problem statement) is a reflection of your purpose. If these two do not agree, you will not accomplish what you set out to do. Consider the following examples below:
Focus One: Informing
Suppose your purpose is to inform readers about relationships between Type A personalities and heart attacks. Your focus could then be: Type A personalities do not have an abnormally high risk of suffering heart attacks.
Focus Two: Persuading
Suppose your purpose is to persuade readers not to quarantine AIDS victims. Your focus could then be: Children afflicted with AIDS should not be prevented from attending school.
Writer and Reader Goals
Kate Kiefer, English Department Readers and writers both have goals when they engage in reading and writing. Writers typically define their goals in several categories-to inform, persuade, entertain, explore. When writers and readers have mutually fulfilling goals-to inform and to look for information-then writing and reading are most efficient. At times, these goals overlap one another. Many readers of science essays are looking for science information when they often get science philosophy. This mismatch of goals tends to leave readers frustrated, and if they communicate that frustration to the writer, then the writer feels misunderstood or unsuccessful.
Donna Lecourt, English Department Whatever reality you are writing within, whatever you chose to write about, implies a certain audience as well as your purpose for writing. You decide you have something to write about, or something you care about, then purpose determines audience.
Writer Versus Reader Purposes
Steve Reid, English Department A general definition of purpose relates to motivation. For instance, "I'm angry, and that's why I'm writing this." Purposes, in academic writing, are intentions the writer hopes to accomplish with a particular audience. Often, readers discover their own purpose within a text. While the writer may have intended one thing, the text actually does another, according to its readers.
Purpose and Writing Assignments
Instructors often state the purpose of a writing assignment on the assignment sheet. By carefully examining what it is you are asked to do, you can determine what your writing's purpose is.
Most assignment sheets ask you to perform a specific task. Key words listed on the assignment can help you determine why you are writing. If your instructor has not provided an assignment sheet, consider asking what the purpose of the assignment is.
Read over your assignment sheet. Make a note of words asking you to follow a specific task. For example, words such as:
These words require you to write about a topic in a specific way. Once you know the purpose of your writing, you can begin planning what information is necessary for that purpose.
Example Assignment
Imagine you are an administrator for the school district. In light of the Columbus controversy, you have been assigned to write a set of guidelines for teaching about Columbus in the district's elementary and junior high schools. These guidelines will explain official policy to parents and teachers in teaching children about Columbus and the significance of his voyages. They will also draw on arguments made on both sides of the controversy, as well as historical facts on which both sides agree.
The purpose of this assignment is to explain the official policy about teaching Columbus' voyages to parents and teachers.
Steve Reid, English Department Keywords in writing assignments give teachers and students direction about why we are writing. For instance, many assignments ask students to "describe" something. The word "describe" specifically indicated the writer is supposed to describe something visually. This is very general. Often, assignments are looking for something more specific. Maybe there is an argument the instructor intends be formulated. Maybe there is an implied thesis, but often teachers use general words such as "Write about" or "Describe" something, when they should use more specific words like, "Define" or "Explain" or "Argue" or "Persuade."
Purpose and Thesis
Writers choose from a variety of purposes for writing. They may write to express their thoughts in a personal letter, to explain concepts in a physics class, to explore ideas in a philosophy class, or to argue a point in a political science class.
Once they have their purpose in mind (and an audience for whom they are writing), writers may more clearly formulate their thesis. The thesis , claim , or main idea of an essay is related to the purpose. It is the sentence or sentences that fulfill the purpose and that state the exact point of the essay.
For example, if a writer wants to argue that high schools should strengthen foreign language training, her thesis sentence might be as follows:
"Because Americans are so culturally isolated, we need a national policy that supports increased foreign language instruction in elementary and secondary schools."
How Thesis is Related to Purpose
The following examples illustrate how subject, purpose and thesis are related. The subject is the most general statement of the topic. The purpose narrows the focus by indicating whether the writer wishes to express or explore ideas or actually explain or argue about the topic. The thesis sentence, claim, or main idea narrows the focus even farther. It is the sentence or sentences which focuses the topic for the writer and the reader.
Citation Information
Stephen Reid and Dawn Kowalski. (1994-2024). Understanding Your Purpose. The WAC Clearinghouse. Colorado State University. Available at https://wac.colostate.edu/repository/writing/guides/.
Copyright Information
Copyright © 1994-2024 Colorado State University and/or this site's authors, developers, and contributors . Some material displayed on this site is used with permission.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Thesis Statements
Basics of thesis statements.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper. Specific means the thesis deals with a narrow and focused topic, appropriate to the paper's length. Arguable means that a scholar in your field could disagree (or perhaps already has!).
Strong thesis statements address specific intellectual questions, have clear positions, and use a structure that reflects the overall structure of the paper. Read on to learn more about constructing a strong thesis statement.
Being Specific
This thesis statement has no specific argument:
Needs Improvement: In this essay, I will examine two scholarly articles to find similarities and differences.
This statement is concise, but it is neither specific nor arguable—a reader might wonder, "Which scholarly articles? What is the topic of this paper? What field is the author writing in?" Additionally, the purpose of the paper—to "examine…to find similarities and differences" is not of a scholarly level. Identifying similarities and differences is a good first step, but strong academic argument goes further, analyzing what those similarities and differences might mean or imply.
Better: In this essay, I will argue that Bowler's (2003) autocratic management style, when coupled with Smith's (2007) theory of social cognition, can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover.
The new revision here is still concise, as well as specific and arguable. We can see that it is specific because the writer is mentioning (a) concrete ideas and (b) exact authors. We can also gather the field (business) and the topic (management and employee turnover). The statement is arguable because the student goes beyond merely comparing; he or she draws conclusions from that comparison ("can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover").
Making a Unique Argument
This thesis draft repeats the language of the writing prompt without making a unique argument:
Needs Improvement: The purpose of this essay is to monitor, assess, and evaluate an educational program for its strengths and weaknesses. Then, I will provide suggestions for improvement.
You can see here that the student has simply stated the paper's assignment, without articulating specifically how he or she will address it. The student can correct this error simply by phrasing the thesis statement as a specific answer to the assignment prompt.
Better: Through a series of student interviews, I found that Kennedy High School's antibullying program was ineffective. In order to address issues of conflict between students, I argue that Kennedy High School should embrace policies outlined by the California Department of Education (2010).
Words like "ineffective" and "argue" show here that the student has clearly thought through the assignment and analyzed the material; he or she is putting forth a specific and debatable position. The concrete information ("student interviews," "antibullying") further prepares the reader for the body of the paper and demonstrates how the student has addressed the assignment prompt without just restating that language.
Creating a Debate
This thesis statement includes only obvious fact or plot summary instead of argument:
Needs Improvement: Leadership is an important quality in nurse educators.
A good strategy to determine if your thesis statement is too broad (and therefore, not arguable) is to ask yourself, "Would a scholar in my field disagree with this point?" Here, we can see easily that no scholar is likely to argue that leadership is an unimportant quality in nurse educators. The student needs to come up with a more arguable claim, and probably a narrower one; remember that a short paper needs a more focused topic than a dissertation.
Better: Roderick's (2009) theory of participatory leadership is particularly appropriate to nurse educators working within the emergency medicine field, where students benefit most from collegial and kinesthetic learning.
Here, the student has identified a particular type of leadership ("participatory leadership"), narrowing the topic, and has made an arguable claim (this type of leadership is "appropriate" to a specific type of nurse educator). Conceivably, a scholar in the nursing field might disagree with this approach. The student's paper can now proceed, providing specific pieces of evidence to support the arguable central claim.
Choosing the Right Words
This thesis statement uses large or scholarly-sounding words that have no real substance:
Needs Improvement: Scholars should work to seize metacognitive outcomes by harnessing discipline-based networks to empower collaborative infrastructures.
There are many words in this sentence that may be buzzwords in the student's field or key terms taken from other texts, but together they do not communicate a clear, specific meaning. Sometimes students think scholarly writing means constructing complex sentences using special language, but actually it's usually a stronger choice to write clear, simple sentences. When in doubt, remember that your ideas should be complex, not your sentence structure.
Better: Ecologists should work to educate the U.S. public on conservation methods by making use of local and national green organizations to create a widespread communication plan.
Notice in the revision that the field is now clear (ecology), and the language has been made much more field-specific ("conservation methods," "green organizations"), so the reader is able to see concretely the ideas the student is communicating.
Leaving Room for Discussion
This thesis statement is not capable of development or advancement in the paper:
Needs Improvement: There are always alternatives to illegal drug use.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go. What further points can be made? If there are "always alternatives" to the problem the student is identifying, then why bother developing a paper around that claim? Ideally, a thesis statement should be complex enough to explore over the length of the entire paper.
Better: The most effective treatment plan for methamphetamine addiction may be a combination of pharmacological and cognitive therapy, as argued by Baker (2008), Smith (2009), and Xavier (2011).
In the revised thesis, you can see the student make a specific, debatable claim that has the potential to generate several pages' worth of discussion. When drafting a thesis statement, think about the questions your thesis statement will generate: What follow-up inquiries might a reader have? In the first example, there are almost no additional questions implied, but the revised example allows for a good deal more exploration.
Thesis Mad Libs
If you are having trouble getting started, try using the models below to generate a rough model of a thesis statement! These models are intended for drafting purposes only and should not appear in your final work.
- In this essay, I argue ____, using ______ to assert _____.
- While scholars have often argued ______, I argue______, because_______.
- Through an analysis of ______, I argue ______, which is important because_______.
Words to Avoid and to Embrace
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize , and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing.
Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question , and interrogate . These more analytical words may help you begin strongly, by articulating a specific, critical, scholarly position.
Read Kayla's blog post for tips on taking a stand in a well-crafted thesis statement.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Introductions
- Next Page: Conclusions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- Identifying a Purpose
- Mohamed Taymour Writing and Communication Center
- Writing Tips and Resources
All writing has a purpose. You may need to argue to prove that something is true or that a solution will work. You may need to analyze to understand why something is the way it is, and you may need to summarize to demonstrate another person's point of view or your findings from an experiment.
Usually, writing has more than one purpose. Academic writing often has the following purposes:
- To demonstrate knowledge and comprehension of a topic.
- To apply that knowledge to solving a problem or understanding an event.
Identifying your purpose will help you focus your writing to accomplishing that purpose and only that purpose. Thus, your writing will stay on target.
Sometimes the assignment provided to you by your instructor will have keywords in it to help you identify your purpose. For example, "compare," "contrast," "explain" and "evaluate" usually indicate that an analysis is needed. Words like "support," "defend," "devise,"and "justify" usually require an argument. Words like "state," "describe," "define," or "identify" usually call for a summary of some kind.
Analysis breaks a whole into its separate parts in order to examine the parts to give meaning to the whole. To analyze something is to break it down into smaller parts and reconstruct it.
Whether we are analyzing the layout in our local supermarket or the writings of Samuel Huntington, we follow the same processes of deconstruction and reconstruction when we analyze.
Analysis DOES NOT just describe, summarize, or interpret. Although critical analysis is different from argument, analysis is used to support argument.
The subject for analysis can be anything: a text, a place, a person, a policy, an event, etc. Start by identifying the purpose of the whole thing. For example, if analyzing a text, what is the theme of the text? If analyzing a place, what is the purpose of this place? If anlayzing a person, what is this person's significant purpose?
Prepare questions before reading, visiting, or viewing the subject to be analyzed. Typical questions include:
- What are the parts of this whole?
- What are the benefits of the parts to accomplishing the purpose of the whole?
- What are the problems of the parts to accomplishing the purpose of the whole?
For example, if analyzing an academic integrity policy at a university, you might ask the following questions:
- What are the parts/requirements of this policy?
- What are the benefits of these parts/requirements to accomplishing academic integrity?
- What are the problems of the parts/requirements to accomplishing academic integrity?
Research! Use the gathered information to answer your questions about the subject. Indicate if the whole has accomplished its purpose, and explain how well the individual parts work together to help the whole accomplish this purpose. You might suggest reasons why the parts do not work well and offer suggestions for improvement.
For example, if analyzing an academic integrity policy at a university, you might answer your questions in this way:
- What are the parts/requirements of this policy? The policy has specific requirements for students and faculty (name them).
- What are the benefits of these parts/requirements to accomplishing academic integrity? Most of the requirements help ensure that students do not plagiarize (show how).
- What are the problems of the parts/requirements to accomplishing academic integrity? Some of the requirements are not strict enough to keep students from plagiarizing (show how).
Argument essays deal with controversial and debatable topics, for which there are two or more sides. In an argument essay your purpose is to convince or persuade a specific audience of a particular claim or viewpoint and support that with logic and evidence. Arguments are different from reports, whose purpose is to state information and facts, and are different from descriptive essays, whose purpose is to describe a particular object, situation and so on because they make controversial claims.
More on Arguments
Most writing is shaped by a set of conventions that inform the structure and content of what you write. These are also limited by a specific length (word count or number of pages) required.
- Rhetorical analyses
- Counterarguments
- Response papers
- Reflection papers
- Personal statements and CVs
- Executive summaries
- Undergraduate research papers
- Theses and dissertations
- Literature reviews
Developing a Thesis Statement
Many papers you write require developing a thesis statement. In this section you’ll learn what a thesis statement is and how to write one.
Keep in mind that not all papers require thesis statements . If in doubt, please consult your instructor for assistance.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement . . .
- Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic.
- Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper.
- Is focused and specific enough to be “proven” within the boundaries of your paper.
- Is generally located near the end of the introduction ; sometimes, in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or in an entire paragraph.
- Identifies the relationships between the pieces of evidence that you are using to support your argument.
Not all papers require thesis statements! Ask your instructor if you’re in doubt whether you need one.
Identify a topic
Your topic is the subject about which you will write. Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic; or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper.
Consider what your assignment asks you to do
Inform yourself about your topic, focus on one aspect of your topic, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts, generate a topic from an assignment.
Below are some possible topics based on sample assignments.
Sample assignment 1
Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II.
Identified topic
Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis
This topic avoids generalities such as “Spain” and “World War II,” addressing instead on Franco’s role (a specific aspect of “Spain”) and the diplomatic relations between the Allies and Axis (a specific aspect of World War II).
Sample assignment 2
Analyze one of Homer’s epic similes in the Iliad.
The relationship between the portrayal of warfare and the epic simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64.
This topic focuses on a single simile and relates it to a single aspect of the Iliad ( warfare being a major theme in that work).
Developing a Thesis Statement–Additional information
Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic, or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper. You’ll want to read your assignment carefully, looking for key terms that you can use to focus your topic.
Sample assignment: Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II Key terms: analyze, Spain’s neutrality, World War II
After you’ve identified the key words in your topic, the next step is to read about them in several sources, or generate as much information as possible through an analysis of your topic. Obviously, the more material or knowledge you have, the more possibilities will be available for a strong argument. For the sample assignment above, you’ll want to look at books and articles on World War II in general, and Spain’s neutrality in particular.
As you consider your options, you must decide to focus on one aspect of your topic. This means that you cannot include everything you’ve learned about your topic, nor should you go off in several directions. If you end up covering too many different aspects of a topic, your paper will sprawl and be unconvincing in its argument, and it most likely will not fulfull the assignment requirements.
For the sample assignment above, both Spain’s neutrality and World War II are topics far too broad to explore in a paper. You may instead decide to focus on Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis , which narrows down what aspects of Spain’s neutrality and World War II you want to discuss, as well as establishes a specific link between those two aspects.
Before you go too far, however, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts. Try to avoid topics that already have too much written about them (i.e., “eating disorders and body image among adolescent women”) or that simply are not important (i.e. “why I like ice cream”). These topics may lead to a thesis that is either dry fact or a weird claim that cannot be supported. A good thesis falls somewhere between the two extremes. To arrive at this point, ask yourself what is new, interesting, contestable, or controversial about your topic.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times . Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Derive a main point from topic
Once you have a topic, you will have to decide what the main point of your paper will be. This point, the “controlling idea,” becomes the core of your argument (thesis statement) and it is the unifying idea to which you will relate all your sub-theses. You can then turn this “controlling idea” into a purpose statement about what you intend to do in your paper.
Look for patterns in your evidence
Compose a purpose statement.
Consult the examples below for suggestions on how to look for patterns in your evidence and construct a purpose statement.
- Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis
- Franco turned to the Allies when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from the Axis
Possible conclusion:
Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: Franco’s desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power.
Purpose statement
This paper will analyze Franco’s diplomacy during World War II to see how it contributed to Spain’s neutrality.
- The simile compares Simoisius to a tree, which is a peaceful, natural image.
- The tree in the simile is chopped down to make wheels for a chariot, which is an object used in warfare.
At first, the simile seems to take the reader away from the world of warfare, but we end up back in that world by the end.
This paper will analyze the way the simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64 moves in and out of the world of warfare.
Derive purpose statement from topic
To find out what your “controlling idea” is, you have to examine and evaluate your evidence . As you consider your evidence, you may notice patterns emerging, data repeated in more than one source, or facts that favor one view more than another. These patterns or data may then lead you to some conclusions about your topic and suggest that you can successfully argue for one idea better than another.
For instance, you might find out that Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis, but when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from them, he turned to the Allies. As you read more about Franco’s decisions, you may conclude that Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: his desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power. Based on this conclusion, you can then write a trial thesis statement to help you decide what material belongs in your paper.
Sometimes you won’t be able to find a focus or identify your “spin” or specific argument immediately. Like some writers, you might begin with a purpose statement just to get yourself going. A purpose statement is one or more sentences that announce your topic and indicate the structure of the paper but do not state the conclusions you have drawn . Thus, you might begin with something like this:
- This paper will look at modern language to see if it reflects male dominance or female oppression.
- I plan to analyze anger and derision in offensive language to see if they represent a challenge of society’s authority.
At some point, you can turn a purpose statement into a thesis statement. As you think and write about your topic, you can restrict, clarify, and refine your argument, crafting your thesis statement to reflect your thinking.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Compose a draft thesis statement
If you are writing a paper that will have an argumentative thesis and are having trouble getting started, the techniques in the table below may help you develop a temporary or “working” thesis statement.
Begin with a purpose statement that you will later turn into a thesis statement.
Assignment: Discuss the history of the Reform Party and explain its influence on the 1990 presidential and Congressional election.
Purpose Statement: This paper briefly sketches the history of the grassroots, conservative, Perot-led Reform Party and analyzes how it influenced the economic and social ideologies of the two mainstream parties.
Question-to-Assertion
If your assignment asks a specific question(s), turn the question(s) into an assertion and give reasons why it is true or reasons for your opinion.
Assignment : What do Aylmer and Rappaccini have to be proud of? Why aren’t they satisfied with these things? How does pride, as demonstrated in “The Birthmark” and “Rappaccini’s Daughter,” lead to unexpected problems?
Beginning thesis statement: Alymer and Rappaccinni are proud of their great knowledge; however, they are also very greedy and are driven to use their knowledge to alter some aspect of nature as a test of their ability. Evil results when they try to “play God.”
Write a sentence that summarizes the main idea of the essay you plan to write.
Main idea: The reason some toys succeed in the market is that they appeal to the consumers’ sense of the ridiculous and their basic desire to laugh at themselves.
Make a list of the ideas that you want to include; consider the ideas and try to group them.
- nature = peaceful
- war matériel = violent (competes with 1?)
- need for time and space to mourn the dead
- war is inescapable (competes with 3?)
Use a formula to arrive at a working thesis statement (you will revise this later).
- although most readers of _______ have argued that _______, closer examination shows that _______.
- _______ uses _______ and _____ to prove that ________.
- phenomenon x is a result of the combination of __________, __________, and _________.
What to keep in mind as you draft an initial thesis statement
Beginning statements obtained through the methods illustrated above can serve as a framework for planning or drafting your paper, but remember they’re not yet the specific, argumentative thesis you want for the final version of your paper. In fact, in its first stages, a thesis statement usually is ill-formed or rough and serves only as a planning tool.
As you write, you may discover evidence that does not fit your temporary or “working” thesis. Or you may reach deeper insights about your topic as you do more research, and you will find that your thesis statement has to be more complicated to match the evidence that you want to use.
You must be willing to reject or omit some evidence in order to keep your paper cohesive and your reader focused. Or you may have to revise your thesis to match the evidence and insights that you want to discuss. Read your draft carefully, noting the conclusions you have drawn and the major ideas which support or prove those conclusions. These will be the elements of your final thesis statement.
Sometimes you will not be able to identify these elements in your early drafts, but as you consider how your argument is developing and how your evidence supports your main idea, ask yourself, “ What is the main point that I want to prove/discuss? ” and “ How will I convince the reader that this is true? ” When you can answer these questions, then you can begin to refine the thesis statement.
Refine and polish the thesis statement
To get to your final thesis, you’ll need to refine your draft thesis so that it’s specific and arguable.
- Ask if your draft thesis addresses the assignment
- Question each part of your draft thesis
- Clarify vague phrases and assertions
- Investigate alternatives to your draft thesis
Consult the example below for suggestions on how to refine your draft thesis statement.
Sample Assignment
Choose an activity and define it as a symbol of American culture. Your essay should cause the reader to think critically about the society which produces and enjoys that activity.
- Ask The phenomenon of drive-in facilities is an interesting symbol of american culture, and these facilities demonstrate significant characteristics of our society.This statement does not fulfill the assignment because it does not require the reader to think critically about society.
Drive-ins are an interesting symbol of American culture because they represent Americans’ significant creativity and business ingenuity.
Among the types of drive-in facilities familiar during the twentieth century, drive-in movie theaters best represent American creativity, not merely because they were the forerunner of later drive-ins and drive-throughs, but because of their impact on our culture: they changed our relationship to the automobile, changed the way people experienced movies, and changed movie-going into a family activity.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast-food establishments, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize America’s economic ingenuity, they also have affected our personal standards.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast- food restaurants, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize (1) Americans’ business ingenuity, they also have contributed (2) to an increasing homogenization of our culture, (3) a willingness to depersonalize relationships with others, and (4) a tendency to sacrifice quality for convenience.
This statement is now specific and fulfills all parts of the assignment. This version, like any good thesis, is not self-evident; its points, 1-4, will have to be proven with evidence in the body of the paper. The numbers in this statement indicate the order in which the points will be presented. Depending on the length of the paper, there could be one paragraph for each numbered item or there could be blocks of paragraph for even pages for each one.
Complete the final thesis statement
The bottom line.
As you move through the process of crafting a thesis, you’ll need to remember four things:
- Context matters! Think about your course materials and lectures. Try to relate your thesis to the ideas your instructor is discussing.
- As you go through the process described in this section, always keep your assignment in mind . You will be more successful when your thesis (and paper) responds to the assignment than if it argues a semi-related idea.
- Your thesis statement should be precise, focused, and contestable ; it should predict the sub-theses or blocks of information that you will use to prove your argument.
- Make sure that you keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Change your thesis as your paper evolves, because you do not want your thesis to promise more than your paper actually delivers.
In the beginning, the thesis statement was a tool to help you sharpen your focus, limit material and establish the paper’s purpose. When your paper is finished, however, the thesis statement becomes a tool for your reader. It tells the reader what you have learned about your topic and what evidence led you to your conclusion. It keeps the reader on track–well able to understand and appreciate your argument.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
7 Essay Types and Their Purposes

Have you ever struggled with the purpose of an essay?
For some, it may be a question of “what’s the point of all this essay writing?”
For others, the word purpose is synonymous with type , and they simply need to determine what kind of essay to write in order to achieve their goal (or ace an assignment).
In either case, we hope to help you today.
What Is the Purpose of an Essay in Education?
Does it seem like every time you turn around, someone’s asking (okay, telling) you to write an essay?
That’s because there is a very good reason. Essay writing is an integral part of education that serves several purposes that may surprise you.
First, essay writing helps improve your spelling, grammar, and punctuation. However, those benefits are more on the superficial side. Necessary, yes, but writing an essay provides far more value than that.
Look at the many benefits you stand to gain:
- Writing in essay format teaches you how to communicate more effectively.
- You’ll learn to organize your thoughts and fine-tune your reasoning.
- Essay writing teaches you valuable research skills as you find and filter facts to support your viewpoint.
- As you learn to express yourself better, you’ll become more concise and precise in your language.
You are essentially practicing the ability to explain yourself clearly and articulate your thoughts. This will serve you well as you interact with future partners, bosses, and others.

ENTER THE GIVEAWAY!
The right topic is critical to the success of any essay. Enter to win a copy of our newest resource:
170 Good Argument Topics for High School Essays & Debate
Points to Consider as You Craft Your Purpose Statement
Now that we’ve discussed the purpose of essay writing, let’s transition into learning more about the purpose of each individual essay.
It’s important to know your essay’s purpose before ever putting pen to paper.
Once you’ve decided on an objective for each essay, you’ll want to let your reader know your intent right away.
To do that, you need to learn how to state the purpose of an essay effectively. This is called, appropriately enough, a “purpose statement.”
Unlike a thesis statement, which lays out your topic and arguments in your introduction, a purpose statement is more about how you intend to do that.
Are you defending a stance in hopes of convincing someone to take action? Tell your reader that’s what you plan to do.
Are you hoping to teach people how to implement an idea or produce something? State upfront that the purpose of this essay is instructional.
A purpose statement includes defining the scope of the paper, along with sharing the focus of the essay and the direction in which you plan to take it.
Let me pause here and say something that may sound odd:
Your purpose statement doesn’t necessarily have to be used in your essay. It may, especially if it doubles as your thesis statement, but defining your essay’s purpose is more for your own direction.
Clearly defining what you are doing and why will help you craft a coherent essay that achieves its goal.
7 Types of Essays: Their Purposes and Examples
After clarifying the purpose of your essay, you’ll want to choose an essay genre to achieve your intention effectively—if it hasn’t be chosen for you, that is.
(If you aren’t sure what to write about, get help with choosing a topic here .)
There are several essay types that help communicate different ideas, so it’s helpful to know which type lends itself to the best outcome.
To help you decide, we’ve laid out seven common essay types and their purposes:
One reason to write an essay is to teach your reader new or changing information on a topic.
The purpose of an informative essay could be to provide a deeper understanding of a well-known subject, but it can also introduce the reader to an unfamiliar topic.
This would be a type of educational essay —one meant to use facts and data to inform your audience. This is not an essay designed to persuade the reader or evoke emotion.
Another form of an educational essay is one designed to teach a process or simplify a difficult subject.
One function of an expository essay , as it’s also known, is to explain a topic, so it’s important for you to be familiarize yourself with the topic first before digging into the writing.
You can’t clarify what you don’t know.
Sometimes an essay is written in response to someone else’s ideas. Depending on the topic, this can be an academic essay or less formal analysis of some sort (like a personal reaction).
In either case, the purpose of a response essay is to share your own perspective with the reader.
The ideas you’re responding to can come from a body of work, a literary analysis, a news story, or a statement from a public figure. It can even be in response to a commonly held opinion or belief.
In a response essay, you’ll begin by providing an overview of the subject to which you’re replying. You would then continue this type of essay by providing your opinion backed by research and facts.
4. Persuade
The purpose of persuasive writing is to use logic to convince someone to react one way or another.
You may include a specific call to action, such as exhorting the reader to petition their local government for positive change.
Crafting a persuasive essay is similar to preparing for a debate but without the opposing party. It typically involves a strong opinion that is so well researched and backed by facts that it influences the reader to change their own opinion.
5. Entertain
While most people think of formal, academic papers when they hear the word “essay,” you can also write an essay solely to entertain your reader.
Essays designed to entertain, such as narratives, aim to elicit some sort of emotional response from the reader. The purpose of descriptive text in this type of essay is to bring forth a clear picture in the reader’s mind.
Careful choice of words is critical in this type of essay. You will use them to trigger some form of emotion in the heart of your reader.
6. Contrast
I’m sure you’ve seen or heard of an essay type called “Compare and Contrast.”
This is a common type of essay in which the writer discusses the differences or similarities between separate ideas or topics.
For example, you may be asked to compare two works of literature. On the other hand, the purpose of your essay may be to shed light on the pros and cons of two choices, such as attending college vs. heading straight into a career.
If it’s a contrast piece, you will want to note less obvious differences between your two topics. For example, everyone knows that college costs money while working pays money.
But what are the more subtle differences that the reader may not have considered? It’s your job to clearly identify those distinctions.
In a review essay, the writer summarizes and critically evaluates a body of work, usually a novel, poem, or film.
The review essay uses the writer’s own perspective of the work to talk at length about its strengths and weaknesses.
Once you solidify the purpose of an essay, your first two steps are clear:
First, you will craft either a purpose statement for your own clarification or a thesis statement to use in the introduction, which should present your essay’s topic in an intriguing way.
Then, you’ll choose an appropriate vehicle to convey that message effectively by choosing an essay type that serves your purpose well.
(Once you know what type of essay you’ll be writing, discover how to start an essay effectively .)
If you need help polishing your essay writing, don’t miss the incredible tales and tips found in Philosophy Adventure :

Teach Your Students to Write Skillfully
As they explore the history of ideas!
About The Author
Jordan Mitchell

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.2: Purpose, Audience, Tone, and Content
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 6705

- Kathryn Crowther et al.
- Georgia Perimeter College via GALILEO Open Learning Materials
Imagine reading one long block of text, with each idea blurring into the next. Even if you are reading a thrilling novel or an interesting news article, you will likely lose interest in what the author has to say very quickly. During the writing process, it is helpful to position yourself as a reader. Ask yourself whether you can focus easily on each point you make. Keep in mind that three main elements shape the content of each essay:
- Purpose : The reason the writer composes the essay.
- Audience : The individual or group whom the writer intends to address.
- Tone : The attitude the writer conveys about the essay’s subject.
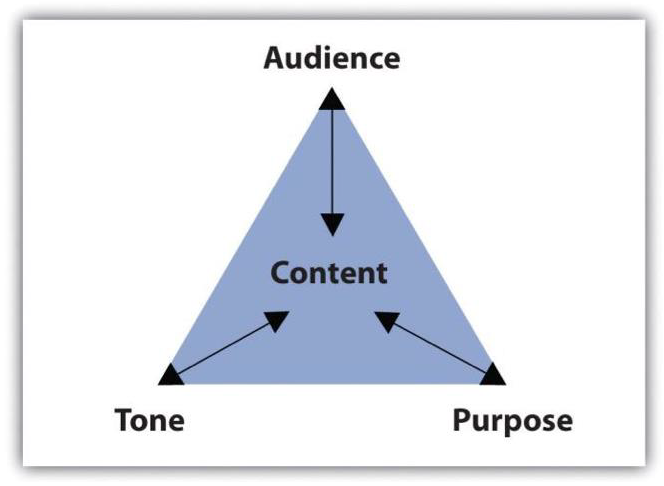
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)
The assignment’s purpose, audience, and tone dictate what each paragraph of the essay covers and how the paragraph supports the main point—the thesis.
Identifying Common Academic Purposes
The purpose for a piece of writing identifies the reason you write it by, basically, answering the question “Why?” For example, why write a play? To entertain a packed theater. Why write instructions to the babysitter? To inform him or her of your schedule and rules. Why write a letter to your congressman? To persuade him to address your community’s needs.
In academic settings, the reasons for writing typically fulfill four main purposes:
- to summarize
- to synthesize
- to evaluate
A summary shrinks a large amount of information into only the essentials, using your own words; although shorter than the original piece of writing, a summary should still communicate all the key points and key support of the original document.
An analysis , on the other hand, separates complex materials into their different parts and studies how the parts relate to one another. In the sciences, for example, the analysis of simple table salt would require a deconstruction of its parts—the elements sodium (Na) and chloride (Cl). Then, scientists would study how the two elements interact to create the compound NaCl, or sodium chloride: simple table salt.
In an academic analysis , instead of deconstructing compounds, the essay takes apart a primary source (an essay, a book, an article, etc.) point by point. It communicates the main points of the document by examining individual points and identifying how the points relate to one another.
The third type of writing— synthesis —combines two or more items to create an entirely new item. Take, for example, the electronic musical instrument aptly named the synthesizer. It looks like a simple keyboard but displays a dashboard of switches, buttons, and levers. With the flip of a few switches, a musician may combine the distinct sounds of a piano, a flute, or a guitar—or any other combination of instruments—to create a new sound. The purpose of an academic synthesis is to blend individual documents into a new document by considering the main points from one or more pieces of writing and linking the main points together to create a new point, one not replicated in either document.
Finally, an evaluation judges the value of something and determines its worth. Evaluations in everyday life are often not only dictated by set standards but also influenced by opinion and prior knowledge such as a supervisor’s evaluation of an employee in a particular job. Academic evaluations, likewise, communicate your opinion and its justifications about a particular document or a topic of discussion. They are influenced by your reading of the document as well as your prior knowledge and experience with the topic or issue. Evaluations typically require more critical thinking and a combination of summary, analysis, and synthesis skills.
You will encounter these four purposes not only as you read for your classes but also as you read for work or pleasure, and, because reading and writing work together, your writing skills will improve as you read. Remember that the purpose for writing will guide you through each part of your paper, helping you make decisions about content and style.
When reviewing directions for assignments, look for the verbs that ask you to summarize, analyze, synthesize, or evaluate. Instructors often use these words to clearly indicate the assignment’s purpose. These words will cue you on how to complete the assignment because you will know its exact purpose.
Read the following paragraphs about four films and then identify the purpose of each paragraph: to summarize, to analyze, to synthesize, or to evaluate.
- This film could easily have been cut down to less than two hours. By the final scene, I noticed that most of my fellow moviegoers were snoozing in their seats and were barely paying attention to what was happening on screen. Although the director sticks diligently to the book, he tries too hard to cram in all the action, which is just too ambitious for such a detail-oriented story. If you want my advice, read the book and give the movie a miss.
- During the opening scene, we learn that the character Laura is adopted and that she has spent the past three years desperately trying to track down her real parents. Having exhausted all the usual options—adoption agencies, online searches, family trees, and so on—she is on the verge of giving up when she meets a stranger on a bus. The chance encounter leads to a complicated chain of events that ultimately result in Laura getting her lifelong wish. But is it really what she wants? Throughout the rest of the film, Laura discovers that sometimes the past is best left where it belongs.
- To create the feeling of being gripped in a vice, the director, May Lee, uses a variety of elements to gradually increase the tension. The creepy, haunting melody that subtly enhances the earlier scenes becomes ever more insistent, rising to a disturbing crescendo toward the end of the movie. The desperation of the actors, combined with the claustrophobic atmosphere and tight camera angles create a realistic firestorm, from which there is little hope of escape. Walking out of the theater at the end feels like staggering out of a Roman dungeon.
- The scene in which Campbell and his fellow prisoners assist the guards in shutting down the riot immediately strikes the viewer as unrealistic. Based on the recent reports on prison riots in both Detroit and California, it seems highly unlikely that a posse of hardened criminals will intentionally help their captors at the risk of inciting future revenge from other inmates. Instead, both news reports and psychological studies indicate that prisoners who do not actively participate in a riot will go back to their cells and avoid conflict altogether. Examples of this lack of attention to detail occur throughout the film, making it almost unbearable to watch.
Collaboration : Share with a classmate and compare your answers.
Group activity : Working in a group of four or five, assign each group member the task of collecting one document each. These documents might include magazine or newspaper articles, workplace documents, academic essays, chapters from a reference book, film or book reviews, or any other type of writing. As a group, read through each document and discuss the author’s purpose for writing. Use the information you have learned in this chapter to decide whether the main purpose is to summarize, analyze, synthesize, or evaluate. Write a brief report on the purpose of each document, using supporting evidence from the text.
Consider the essay most recently assigned to you. Identify the most effective academic purpose for the assignment.
My assignment: ____________________________________________
My purpose: ____________________________________________

Writing at Work
Thinking about the purpose of writing a report in the workplace can help focus and structure the document. A summary should provide colleagues with a factual overview of your findings without going into too much specific detail. In contrast, an evaluation should include your personal opinion, along with supporting evidence, research, or examples to back it up. To help determine a purpose for writing, listen for words such as summarize, analyze, synthesize, or evaluate when your boss asks you to complete a report.
Identifying the Audience
Imagine you must give a presentation to a group of executives in an office. Weeks before the big day, you spend time creating and rehearsing the presentation. You must make important, careful decisions not only about the content but also about your delivery. Will the presentation require technology to project figures and charts? Should the presentation define important words, or will the executives already know the terms? Should you wear your suit and dress shirt? The answers to these questions will help you develop an appropriate relationship with your audience, making them more receptive to your message.
Now imagine you must explain the same business concepts from your presentation to a group of high school students. Those important questions you previously answered may now require different answers. The figures and charts may be too sophisticated, and the terms will certainly require definitions. You may even reconsider your outfit and sport a more casual look. Because the audience has shifted, your presentation and delivery will shift as well to create a new relationship with the new audience.
In these two situations, the audience—the individuals who will watch and listen to the presentation—plays a role in the development of presentation. As you prepare the presentation, you visualize the audience to anticipate their expectations and reactions. What you imagine affects the information you choose to present and how you will present it. Then, during the presentation, you meet the audience in person and discover immediately how well you perform.
Although the audience for writing assignments—your readers—may not appear in person, they play an equally vital role. Even in everyday writing activities, you identify your readers’ characteristics, interests, and expectations before making decisions about what you write. In fact, thinking about audience has become so common that you may not even detect the audience-driven decisions.
For example, you update your status on a social networking site with the awareness of who will digitally follow the post. If you want to brag about a good grade, you may write the post to please family members. If you want to describe a funny moment, you may write with your friends’ senses of humor in mind. Even at work, you send emails with an awareness of an unintended receiver who could intercept the message.
In other words, being aware of “invisible” readers is a skill you most likely already possess and one you rely on every day. Consider the following paragraphs. Which one would the author send to her parents? Which one would she send to her best friend?
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\):
Last Saturday, I volunteered at a local hospital. The visit was fun and rewarding. I even learned how to do cardiopulmonary resuscitation, or CPR. Unfortunately, I think caught a cold from one of the patients. This week, I will rest in bed and drink plenty of clear fluids. I hope I am well by next Saturday to volunteer again.
OMG! You won’t believe this! My advisor forced me to do my community service hours at this hospital all weekend! We learned CPR but we did it on dummies, not even real peeps. And some kid sneezed on me and got me sick! I was so bored and sniffling all weekend; I hope I don’t have to go back next week. I def do NOT want to miss the basketball tournament!
Most likely, you matched each paragraph to its intended audience with little hesitation. Because each paragraph reveals the author’s relationship with the intended readers, you can identify the audience fairly quickly. When writing your own essays, you must engage with your audience to build an appropriate relationship given your subject. Imagining your readers during each stage of the writing process will help you make decisions about your writing. Ultimately, the people you visualize will affect what and how you write.
While giving a speech, you may articulate an inspiring or critical message, but if you left your hair a mess and laced up mismatched shoes, your audience would not take you seriously. They may be too distracted by your appearance to listen to your words. Similarly, grammar and sentence structure serve as the appearance of a piece of writing. Polishing your work using correct grammar will impress your readers and allow them to focus on what you have to say.
Because focusing on audience will enhance your writing, your process, and your finished product, you must consider the specific traits of your audience members. Use your imagination to anticipate the readers’ demographics, education, prior knowledge, and expectations.
- Demographics : These measure important data about a group of people, such as their age range, their ethnicity, their religious beliefs, or their gender. Certain topics and assignments will require these kinds of considerations about your audience. For other topics and assignments, these measurements may not influence your writing in the end. Regardless, it is important to consider demographics when you begin to think about your purpose for writing.
- Education : Education considers the audience’s level of schooling. If audience members have earned a doctorate degree, for example, you may need to elevate your style and use more formal language. Or, if audience members are still in college, you could write in a more relaxed style. An audience member’s major or emphasis may also dictate your writing.
- Prior knowledge : This refers to what the audience already knows about your topic. If your readers have studied certain topics, they may already know some terms and concepts related to the topic. You may decide whether to define terms and explain concepts based on your audience’s prior knowledge. Although you cannot peer inside the brains of your readers to discover their knowledge, you can make reasonable assumptions. For instance, a nursing major would presumably know more about health-related topics than a business major would.
- Expectations : These indicate what readers will look for while reading your assignment. Readers may expect consistencies in the assignment’s appearance, such as correct grammar and traditional formatting like double-spaced lines and legible font. Readers may also have content-based expectations given the assignment’s purpose and organization. In an essay titled “The Economics of Enlightenment: The Effects of Rising Tuition,” for example, audience members may expect to read about the economic repercussions of college tuition costs.
On your own sheet of paper, generate a list of characteristics under each category for each audience. This list will help you later when you read about tone and content.
- Demographics ____________________________________________
- Education ____________________________________________
- Prior knowledge ____________________________________________
- Expectations ____________________________________________
- Collaboration : Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
At some point during your career, you may be asked to write a report or to complete a presentation. Imagine that you have been asked to report on the issue of health and safety in the workplace. Using the information in this section complete an analysis of your intended audience—your fellow office workers. Consider how demographics, education, prior knowledge, and expectations will influence your report and explain how you will tailor it to your audience accordingly.
Collaboration : Pair with a classmate and compare your answers.
Selecting an Appropriate Tone
Tone identifies a speaker’s attitude toward a subject or another person. You may pick up a person’s tone of voice fairly easily in conversation. A friend who tells you about her weekend may speak excitedly about a fun skiing trip. An instructor who means business may speak in a low, slow voice to emphasize her serious mood. Or, a coworker who needs to let off some steam after a long meeting may crack a sarcastic joke.
Just as speakers transmit emotion through voice, writers can transmit a range of attitudes and emotions through prose--from excited and humorous to somber and critical. These emotions create connections among the audience, the author, and the subject, ultimately building a relationship between the audience and the text. To stimulate these connections, writers intimate their attitudes and feelings with useful devices, such as sentence structure, word choice, punctuation, and formal or informal language. Keep in mind that the writer’s attitude should always appropriately match the audience and the purpose.
Read the following paragraph and consider the writer’s tone. How would you describe the writer’s attitude toward wildlife conservation?
Many species of plants and animals are disappearing right before our eyes. If we don’t act fast, it might be too late to save them. Human activities, including pollution, deforestation, hunting, and overpopulation, are devastating the natural environment. Without our help, many species will not survive long enough for our children to see them in the wild. Take the tiger, for example. Today, tigers occupy just seven percent of their historical range, and many local populations are already extinct. Hunted for their beautiful pelts and other body parts, the tiger population has plummeted from one hundred thousand in 1920 to just a few thousand. Contact your local wildlife conservation society today to find out how you can stop this terrible destruction.
Think about the assignment, purpose, and audience that you selected in previous exercises. Now, identify the tone you would use in the assignment.
My audience: ____________________________________________
My tone: ____________________________________________
Choosing Appropriate, Interesting Content
Content refers to all the written substance in a document. After selecting an audience and a purpose, you must choose what information will make it to the page. Content may consist of examples, statistics, facts, anecdotes, testimonies, and observations, but no matter the type, the information must be appropriate and interesting for the audience and purpose. An essay written for third graders that summarizes the legislative process, for example, would have to contain succinct and simple content.
Content is also shaped by tone. When the tone matches the content, the audience will be more engaged, and you will build a stronger relationship with your readers. Consider that audience of third graders. You would choose simple content that the audience will easily understand, and you would express that content through an enthusiastic tone. The same considerations apply to all audiences and purposes.
Match the content of the following listed examples to the appropriate audience and purpose. On your own sheet of paper, write the correct letter in the blank next to the word “content.”
- Whereas economist Holmes contends that the financial crisis is far from over, the presidential advisor Jones points out that it is vital to catch the first wave of opportunity to increase market share. We can use elements of both experts’ visions. Let me explain how.
- In 2000, foreign money flowed into the United States, contributing to easy credit conditions. People bought larger houses than they could afford, eventually defaulting on their loans as interest rates rose.
- The Emergency Economic Stabilization Act, known by most of us as the humongous government bailout, caused mixed reactions. Although supported by many political leaders, the statute provoked outrage among grassroots groups. In their opinion, the government was actually rewarding banks for their appalling behavior.
Audience : An instructor
Purpose: To analyze the reasons behind the 2007 financial crisis
Content: ____________________________________________
Audience : Classmates
Purpose: To summarize the effects of the $700 billion government bailout
Audience : An employer
Purpose: To synthesize two articles on preparing businesses for economic recovery
Using the assignment, purpose, audience, and tone from Exercise 7, generate a list of content ideas. Remember that content consists of examples, statistics, facts, anecdotes, testimonies, and observations.
My content ideas: ____________________________________________
key takeaways
- The content of each paragraph in the essay is shaped by purpose, audience, and tone.
- The four common academic purposes are to summarize , to analyze , to synthesize , and to evaluate .
- Identifying the audience’s demographics, education, prior knowledge, and expectations will affect how and what you write.
- Devices such as sentence structure, word choice, punctuation, and formal or informal language communicate tone and create a relationship between the writer and his or her audience.
- Content may consist of examples, statistics, facts, anecdotes, testimonies, and observations . All content must be appropriate and interesting for the audience, purpose and tone.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
6.1 Purpose, Audience, Tone, and Content
Learning objectives.
- Identify the four common academic purposes.
- Identify audience, tone, and content.
- Apply purpose, audience, tone, and content to a specific assignment.
Imagine reading one long block of text, with each idea blurring into the next. Even if you are reading a thrilling novel or an interesting news article, you will likely lose interest in what the author has to say very quickly. During the writing process, it is helpful to position yourself as a reader. Ask yourself whether you can focus easily on each point you make. One technique that effective writers use is to begin a fresh paragraph for each new idea they introduce.
Paragraphs separate ideas into logical, manageable chunks. One paragraph focuses on only one main idea and presents coherent sentences to support that one point. Because all the sentences in one paragraph support the same point, a paragraph may stand on its own. To create longer assignments and to discuss more than one point, writers group together paragraphs.
Three elements shape the content of each paragraph:
- Purpose . The reason the writer composes the paragraph.
- Tone . The attitude the writer conveys about the paragraph’s subject.
- Audience . The individual or group whom the writer intends to address.
Figure 6.1 Purpose, Audience, Tone, and Content Triangle
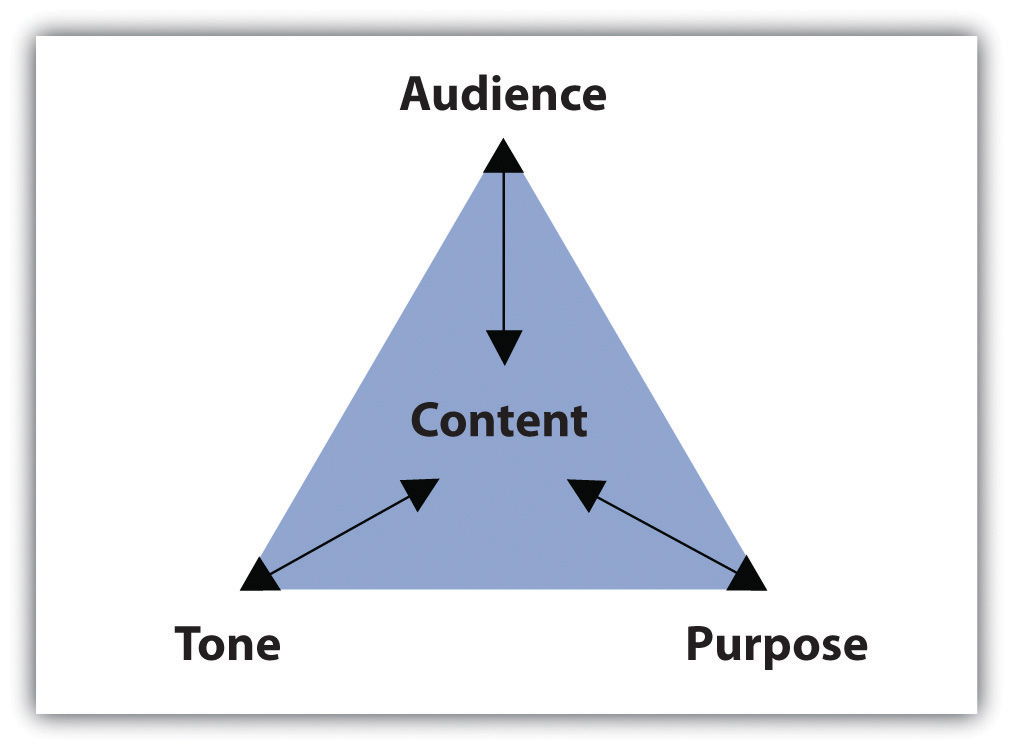
The assignment’s purpose, audience, and tone dictate what the paragraph covers and how it will support one main point. This section covers how purpose, audience, and tone affect reading and writing paragraphs.
Identifying Common Academic Purposes
The purpose for a piece of writing identifies the reason you write a particular document. Basically, the purpose of a piece of writing answers the question “Why?” For example, why write a play? To entertain a packed theater. Why write instructions to the babysitter? To inform him or her of your schedule and rules. Why write a letter to your congressman? To persuade him to address your community’s needs.
In academic settings, the reasons for writing fulfill four main purposes: to summarize, to analyze, to synthesize, and to evaluate. You will encounter these four purposes not only as you read for your classes but also as you read for work or pleasure. Because reading and writing work together, your writing skills will improve as you read. To learn more about reading in the writing process, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .
Eventually, your instructors will ask you to complete assignments specifically designed to meet one of the four purposes. As you will see, the purpose for writing will guide you through each part of the paper, helping you make decisions about content and style. For now, identifying these purposes by reading paragraphs will prepare you to write individual paragraphs and to build longer assignments.
Summary Paragraphs
A summary shrinks a large amount of information into only the essentials. You probably summarize events, books, and movies daily. Think about the last blockbuster movie you saw or the last novel you read. Chances are, at some point in a casual conversation with a friend, coworker, or classmate, you compressed all the action in a two-hour film or in a two-hundred-page book into a brief description of the major plot movements. While in conversation, you probably described the major highlights, or the main points in just a few sentences, using your own vocabulary and manner of speaking.
Similarly, a summary paragraph condenses a long piece of writing into a smaller paragraph by extracting only the vital information. A summary uses only the writer’s own words. Like the summary’s purpose in daily conversation, the purpose of an academic summary paragraph is to maintain all the essential information from a longer document. Although shorter than the original piece of writing, a summary should still communicate all the key points and key support. In other words, summary paragraphs should be succinct and to the point.

A summary of the report should present all the main points and supporting details in brief. Read the following summary of the report written by a student:

Notice how the summary retains the key points made by the writers of the original report but omits most of the statistical data. Summaries need not contain all the specific facts and figures in the original document; they provide only an overview of the essential information.
Analysis Paragraphs
An analysis separates complex materials in their different parts and studies how the parts relate to one another. The analysis of simple table salt, for example, would require a deconstruction of its parts—the elements sodium (Na) and chloride (Cl). Then, scientists would study how the two elements interact to create the compound NaCl, or sodium chloride, which is also called simple table salt.
Analysis is not limited to the sciences, of course. An analysis paragraph in academic writing fulfills the same purpose. Instead of deconstructing compounds, academic analysis paragraphs typically deconstruct documents. An analysis takes apart a primary source (an essay, a book, an article, etc.) point by point. It communicates the main points of the document by examining individual points and identifying how the points relate to one another.
Take a look at a student’s analysis of the journal report.

Notice how the analysis does not simply repeat information from the original report, but considers how the points within the report relate to one another. By doing this, the student uncovers a discrepancy between the points that are backed up by statistics and those that require additional information. Analyzing a document involves a close examination of each of the individual parts and how they work together.
Synthesis Paragraphs
A synthesis combines two or more items to create an entirely new item. Consider the electronic musical instrument aptly named the synthesizer. It looks like a simple keyboard but displays a dashboard of switches, buttons, and levers. With the flip of a few switches, a musician may combine the distinct sounds of a piano, a flute, or a guitar—or any other combination of instruments—to create a new sound. The purpose of the synthesizer is to blend together the notes from individual instruments to form new, unique notes.
The purpose of an academic synthesis is to blend individual documents into a new document. An academic synthesis paragraph considers the main points from one or more pieces of writing and links the main points together to create a new point, one not replicated in either document.
Take a look at a student’s synthesis of several sources about underage drinking.

Notice how the synthesis paragraphs consider each source and use information from each to create a new thesis. A good synthesis does not repeat information; the writer uses a variety of sources to create a new idea.
Evaluation Paragraphs
An evaluation judges the value of something and determines its worth. Evaluations in everyday experiences are often not only dictated by set standards but also influenced by opinion and prior knowledge. For example, at work, a supervisor may complete an employee evaluation by judging his subordinate’s performance based on the company’s goals. If the company focuses on improving communication, the supervisor will rate the employee’s customer service according to a standard scale. However, the evaluation still depends on the supervisor’s opinion and prior experience with the employee. The purpose of the evaluation is to determine how well the employee performs at his or her job.
An academic evaluation communicates your opinion, and its justifications, about a document or a topic of discussion. Evaluations are influenced by your reading of the document, your prior knowledge, and your prior experience with the topic or issue. Because an evaluation incorporates your point of view and reasons for your point of view, it typically requires more critical thinking and a combination of summary, analysis, and synthesis skills. Thus evaluation paragraphs often follow summary, analysis, and synthesis paragraphs. Read a student’s evaluation paragraph.

Notice how the paragraph incorporates the student’s personal judgment within the evaluation. Evaluating a document requires prior knowledge that is often based on additional research.
When reviewing directions for assignments, look for the verbs summarize , analyze , synthesize , or evaluate . Instructors often use these words to clearly indicate the assignment’s purpose. These words will cue you on how to complete the assignment because you will know its exact purpose.
Read the following paragraphs about four films and then identify the purpose of each paragraph.
- This film could easily have been cut down to less than two hours. By the final scene, I noticed that most of my fellow moviegoers were snoozing in their seats and were barely paying attention to what was happening on screen. Although the director sticks diligently to the book, he tries too hard to cram in all the action, which is just too ambitious for such a detail-oriented story. If you want my advice, read the book and give the movie a miss.
- During the opening scene, we learn that the character Laura is adopted and that she has spent the past three years desperately trying to track down her real parents. Having exhausted all the usual options—adoption agencies, online searches, family trees, and so on—she is on the verge of giving up when she meets a stranger on a bus. The chance encounter leads to a complicated chain of events that ultimately result in Laura getting her lifelong wish. But is it really what she wants? Throughout the rest of the film, Laura discovers that sometimes the past is best left where it belongs.
- To create the feeling of being gripped in a vice, the director, May Lee, uses a variety of elements to gradually increase the tension. The creepy, haunting melody that subtly enhances the earlier scenes becomes ever more insistent, rising to a disturbing crescendo toward the end of the movie. The desperation of the actors, combined with the claustrophobic atmosphere and tight camera angles create a realistic firestorm, from which there is little hope of escape. Walking out of the theater at the end feels like staggering out of a Roman dungeon.
- The scene in which Campbell and his fellow prisoners assist the guards in shutting down the riot immediately strikes the viewer as unrealistic. Based on the recent reports on prison riots in both Detroit and California, it seems highly unlikely that a posse of hardened criminals will intentionally help their captors at the risk of inciting future revenge from other inmates. Instead, both news reports and psychological studies indicate that prisoners who do not actively participate in a riot will go back to their cells and avoid conflict altogether. Examples of this lack of attention to detail occur throughout the film, making it almost unbearable to watch.
Collaboration
Share with a classmate and compare your answers.
Writing at Work
Thinking about the purpose of writing a report in the workplace can help focus and structure the document. A summary should provide colleagues with a factual overview of your findings without going into too much specific detail. In contrast, an evaluation should include your personal opinion, along with supporting evidence, research, or examples to back it up. Listen for words such as summarize , analyze , synthesize , or evaluate when your boss asks you to complete a report to help determine a purpose for writing.
Consider the essay most recently assigned to you. Identify the most effective academic purpose for the assignment.
My assignment: ____________________________________________
My purpose: ____________________________________________
Identifying the Audience
Imagine you must give a presentation to a group of executives in an office. Weeks before the big day, you spend time creating and rehearsing the presentation. You must make important, careful decisions not only about the content but also about your delivery. Will the presentation require technology to project figures and charts? Should the presentation define important words, or will the executives already know the terms? Should you wear your suit and dress shirt? The answers to these questions will help you develop an appropriate relationship with your audience, making them more receptive to your message.
Now imagine you must explain the same business concepts from your presentation to a group of high school students. Those important questions you previously answered may now require different answers. The figures and charts may be too sophisticated, and the terms will certainly require definitions. You may even reconsider your outfit and sport a more casual look. Because the audience has shifted, your presentation and delivery will shift as well to create a new relationship with the new audience.
In these two situations, the audience—the individuals who will watch and listen to the presentation—plays a role in the development of presentation. As you prepare the presentation, you visualize the audience to anticipate their expectations and reactions. What you imagine affects the information you choose to present and how you will present it. Then, during the presentation, you meet the audience in person and discover immediately how well you perform.
Although the audience for writing assignments—your readers—may not appear in person, they play an equally vital role. Even in everyday writing activities, you identify your readers’ characteristics, interests, and expectations before making decisions about what you write. In fact, thinking about audience has become so common that you may not even detect the audience-driven decisions.
For example, you update your status on a social networking site with the awareness of who will digitally follow the post. If you want to brag about a good grade, you may write the post to please family members. If you want to describe a funny moment, you may write with your friends’ senses of humor in mind. Even at work, you send e-mails with an awareness of an unintended receiver who could intercept the message.
In other words, being aware of “invisible” readers is a skill you most likely already possess and one you rely on every day. Consider the following paragraphs. Which one would the author send to her parents? Which one would she send to her best friend?
Last Saturday, I volunteered at a local hospital. The visit was fun and rewarding. I even learned how to do cardiopulmonary resuscitation, or CPR. Unfortunately, I think caught a cold from one of the patients. This week, I will rest in bed and drink plenty of clear fluids. I hope I am well by next Saturday to volunteer again.
OMG! You won’t believe this! My advisor forced me to do my community service hours at this hospital all weekend! We learned CPR but we did it on dummies, not even real peeps. And some kid sneezed on me and got me sick! I was so bored and sniffling all weekend; I hope I don’t have to go back next week. I def do NOT want to miss the basketball tournament!
Most likely, you matched each paragraph to its intended audience with little hesitation. Because each paragraph reveals the author’s relationship with her intended readers, you can identify the audience fairly quickly. When writing your own paragraphs, you must engage with your audience to build an appropriate relationship given your subject. Imagining your readers during each stage of the writing process will help you make decisions about your writing. Ultimately, the people you visualize will affect what and how you write.
While giving a speech, you may articulate an inspiring or critical message, but if you left your hair a mess and laced up mismatched shoes, your audience would not take you seriously. They may be too distracted by your appearance to listen to your words.
Similarly, grammar and sentence structure serve as the appearance of a piece of writing. Polishing your work using correct grammar will impress your readers and allow them to focus on what you have to say.
Because focusing on audience will enhance your writing, your process, and your finished product, you must consider the specific traits of your audience members. Use your imagination to anticipate the readers’ demographics, education, prior knowledge, and expectations.
- Demographics. These measure important data about a group of people, such as their age range, their ethnicity, their religious beliefs, or their gender. Certain topics and assignments will require these kinds of considerations about your audience. For other topics and assignments, these measurements may not influence your writing in the end. Regardless, it is important to consider demographics when you begin to think about your purpose for writing.
- Education. Education considers the audience’s level of schooling. If audience members have earned a doctorate degree, for example, you may need to elevate your style and use more formal language. Or, if audience members are still in college, you could write in a more relaxed style. An audience member’s major or emphasis may also dictate your writing.
- Prior knowledge. This refers to what the audience already knows about your topic. If your readers have studied certain topics, they may already know some terms and concepts related to the topic. You may decide whether to define terms and explain concepts based on your audience’s prior knowledge. Although you cannot peer inside the brains of your readers to discover their knowledge, you can make reasonable assumptions. For instance, a nursing major would presumably know more about health-related topics than a business major would.
- Expectations. These indicate what readers will look for while reading your assignment. Readers may expect consistencies in the assignment’s appearance, such as correct grammar and traditional formatting like double-spaced lines and legible font. Readers may also have content-based expectations given the assignment’s purpose and organization. In an essay titled “The Economics of Enlightenment: The Effects of Rising Tuition,” for example, audience members may expect to read about the economic repercussions of college tuition costs.
On your own sheet of paper, generate a list of characteristics under each category for each audience. This list will help you later when you read about tone and content.
1. Your classmates
- Demographics ____________________________________________
- Education ____________________________________________
- Prior knowledge ____________________________________________
- Expectations ____________________________________________
2. Your instructor
3. The head of your academic department
4. Now think about your next writing assignment. Identify the purpose (you may use the same purpose listed in Note 6.12 “Exercise 2” ), and then identify the audience. Create a list of characteristics under each category.
My audience: ____________________________________________
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
Keep in mind that as your topic shifts in the writing process, your audience may also shift. For more information about the writing process, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .
Also, remember that decisions about style depend on audience, purpose, and content. Identifying your audience’s demographics, education, prior knowledge, and expectations will affect how you write, but purpose and content play an equally important role. The next subsection covers how to select an appropriate tone to match the audience and purpose.
Selecting an Appropriate Tone
Tone identifies a speaker’s attitude toward a subject or another person. You may pick up a person’s tone of voice fairly easily in conversation. A friend who tells you about her weekend may speak excitedly about a fun skiing trip. An instructor who means business may speak in a low, slow voice to emphasize her serious mood. Or, a coworker who needs to let off some steam after a long meeting may crack a sarcastic joke.
Just as speakers transmit emotion through voice, writers can transmit through writing a range of attitudes, from excited and humorous to somber and critical. These emotions create connections among the audience, the author, and the subject, ultimately building a relationship between the audience and the text. To stimulate these connections, writers intimate their attitudes and feelings with useful devices, such as sentence structure, word choice, punctuation, and formal or informal language. Keep in mind that the writer’s attitude should always appropriately match the audience and the purpose.
Read the following paragraph and consider the writer’s tone. How would you describe the writer’s attitude toward wildlife conservation?
Many species of plants and animals are disappearing right before our eyes. If we don’t act fast, it might be too late to save them. Human activities, including pollution, deforestation, hunting, and overpopulation, are devastating the natural environment. Without our help, many species will not survive long enough for our children to see them in the wild. Take the tiger, for example. Today, tigers occupy just 7 percent of their historical range, and many local populations are already extinct. Hunted for their beautiful pelt and other body parts, the tiger population has plummeted from one hundred thousand in 1920 to just a few thousand. Contact your local wildlife conservation society today to find out how you can stop this terrible destruction.
Think about the assignment and purpose you selected in Note 6.12 “Exercise 2” , and the audience you selected in Note 6.16 “Exercise 3” . Now, identify the tone you would use in the assignment.
My tone: ____________________________________________
Choosing Appropriate, Interesting Content
Content refers to all the written substance in a document. After selecting an audience and a purpose, you must choose what information will make it to the page. Content may consist of examples, statistics, facts, anecdotes, testimonies, and observations, but no matter the type, the information must be appropriate and interesting for the audience and purpose. An essay written for third graders that summarizes the legislative process, for example, would have to contain succinct and simple content.
Content is also shaped by tone. When the tone matches the content, the audience will be more engaged, and you will build a stronger relationship with your readers. Consider that audience of third graders. You would choose simple content that the audience will easily understand, and you would express that content through an enthusiastic tone. The same considerations apply to all audiences and purposes.
Match the content in the box to the appropriate audience and purpose. On your own sheet of paper, write the correct letter next to the number.
- Whereas economist Holmes contends that the financial crisis is far from over, the presidential advisor Jones points out that it is vital to catch the first wave of opportunity to increase market share. We can use elements of both experts’ visions. Let me explain how.
- In 2000, foreign money flowed into the United States, contributing to easy credit conditions. People bought larger houses than they could afford, eventually defaulting on their loans as interest rates rose.
- The Emergency Economic Stabilization Act, known by most of us as the humungous government bailout, caused mixed reactions. Although supported by many political leaders, the statute provoked outrage among grassroots groups. In their opinion, the government was actually rewarding banks for their appalling behavior.
Audience: An instructor
Purpose: To analyze the reasons behind the 2007 financial crisis
Content: ____________________________________________
Audience: Classmates
Purpose: To summarize the effects of the $700 billion government bailout
Audience: An employer
Purpose: To synthesize two articles on preparing businesses for economic recovery
Using the assignment, purpose, audience, and tone from Note 6.18 “Exercise 4” , generate a list of content ideas. Remember that content consists of examples, statistics, facts, anecdotes, testimonies, and observations.
My content ideas: ____________________________________________
Key Takeaways
- Paragraphs separate ideas into logical, manageable chunks of information.
- The content of each paragraph and document is shaped by purpose, audience, and tone.
- The four common academic purposes are to summarize, to analyze, to synthesize, and to evaluate.
- Identifying the audience’s demographics, education, prior knowledge, and expectations will affect how and what you write.
- Devices such as sentence structure, word choice, punctuation, and formal or informal language communicate tone and create a relationship between the writer and his or her audience.
- Content may consist of examples, statistics, facts, anecdotes, testimonies, and observations. All content must be appropriate and interesting for the audience, purpose and tone.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
II. Getting Started
2.3 Purpose, Audience, Tone, and Content
Kathryn Crowther; Lauren Curtright; Nancy Gilbert; Barbara Hall; Tracienne Ravita; Kirk Swenson; and Terri Pantuso
Now that you have determined the assignment parameters , it’s time to begin drafting. While doing so, it is important to remain focused on your topic and thesis in order to guide your reader through the essay. Imagine reading one long block of text with each idea blurring into the next. Even if you are reading a thrilling novel or an interesting news article, you will likely lose interest in what the author has to say very quickly. During the writing process, it is helpful to position yourself as a reader. Ask yourself whether you can focus easily on each point you make. Keep in mind that three main elements shape the content of each essay (see Figure 2.3.1). [1]
- Purpose: The reason the writer composes the essay.
- Audience: The individual or group whom the writer intends to address.
- Tone: The attitude the writer conveys about the essay’s subject.
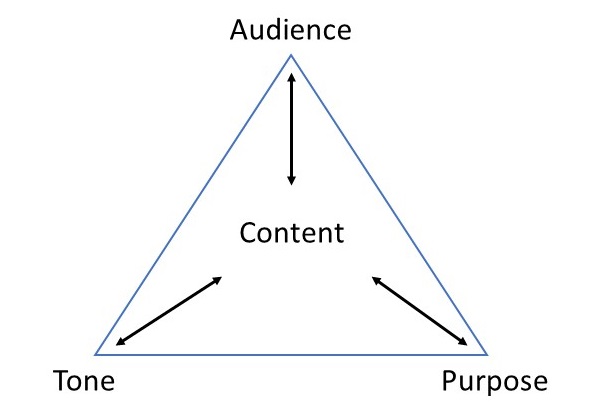
The assignment’s purpose, audience, and tone dictate what each paragraph of the essay covers and how the paragraph supports the main point or thesis.
Identifying Common Academic Purposes
The purpose for a piece of writing identifies the reason you write it by, basically, answering the question “Why?” For example, why write a play? To entertain a packed theater. Why write instructions to the babysitter? To inform him or her of your schedule and rules. Why write a letter to your congressman? To persuade him to address your community’s needs.
In academic settings, the reasons for writing typically fulfill four main purposes:
- to classify
- to synthesize
- to evaluate
A classification shrinks a large amount of information into only the essentials , using your own words; although shorter than the original piece of writing, a classification should still communicate all the key points and key support of the original document without quoting the original text. Keep in mind that classification moves beyond simple summary to be informative .
An analysis , on the other hand, separates complex materials into their different parts and studies how the parts relate to one another. In the sciences, for example, the analysis of simple table salt would require a deconstruction of its parts—the elements sodium (Na) and chloride (Cl). Then, scientists would study how the two elements interact to create the compound NaCl, or sodium chloride: simple table salt.
In an academic analysis , instead of deconstructing compounds, the essay takes apart a primary source (an essay, a book, an article, etc.) point by point. It communicates the main points of the document by examining individual points and identifying how the points relate to one another.
The third type of writing— synthesis —combines two or more items to create an entirely new item. Take, for example, the electronic musical instrument aptly named the synthesizer. It looks like a simple keyboard but displays a dashboard of switches, buttons, and levers. With the flip of a few switches, a musician may combine the distinct sounds of a piano, a flute, or a guitar—or any other combination of instruments—to create a new sound. The purpose of an academic synthesis is to blend individual documents into a new document by considering the main points from one or more pieces of writing and linking the main points together to create a new point, one not replicated in either document.
Finally, an evaluation judges the value of something and determines its worth. Evaluations in everyday life are often not only dictated by set standards but also influenced by opinion and prior knowledge such as a supervisor’s evaluation of an employee in a particular job. Academic evaluations, likewise, communicate your opinion and its justifications about a particular document or a topic of discussion. They are influenced by your reading of the document as well as your prior knowledge and experience with the topic or issue. Evaluations typically require more critical thinking and a combination of classifying , analysis , and synthesis skills.
You will encounter these four purposes not only as you read for your classes but also as you read for work or pleasure and, because reading and writing work together, your writing skills will improve as you read. Remember that the purpose for writing will guide you through each part of your paper, helping you make decisions about content and style .
When reviewing directions for assignments, look for the verbs that ask you to classify, analyze, synthesize, or evaluate. Instructors often use these words to clearly indicate the assignment’s purpose. These words will cue you on how to complete the assignment because you will know its exact purpose.
Identifying the Audience
Imagine you must give a presentation to a group of executives in an office. Weeks before the big day, you spend time creating and rehearsing the presentation. You must make important, careful decisions not only about the content but also about your delivery. Will the presentation require technology to project figures and charts? Should the presentation define important words, or will the executives already know the terms? Should you wear your suit and dress shirt? The answers to these questions will help you develop an appropriate relationship with your audience, making them more receptive to your message.
Now imagine you must explain the same business concepts from your presentation to a group of high school students. Those important questions you previously answered may now require different answers. The figures and charts may be too sophisticated, and the terms will certainly require definitions. You may even reconsider your outfit and sport a more casual look. Because the audience has shifted, your presentation and delivery will shift as well to create a new relationship with the new audience.
In these two situations, the audience —the individuals who will watch and listen to the presentation—plays a role in the development of presentation. As you prepare the presentation, you visualize the audience to anticipate their expectations and reactions. What you imagine affects the information you choose to present and how you will present it. Then, during the presentation, you meet the audience in person and discover immediately how well you perform.
Although the audience for writing assignments—your readers—may not appear in person, they play an equally vital role. Even in everyday writing activities, you identify your readers’ characteristics, interests, and expectations before making decisions about what you write. In fact, thinking about the audience has become so common that you may not even detect the audience-driven decisions. For example, you update your status on a social networking site with the awareness of who will digitally follow the post. If you want to brag about a good grade, you may write the post to please family members. If you want to describe a funny moment, you may write with your friends’ senses of humor in mind. Even at work, you send emails with an awareness of an unintended receiver who could intercept the message.
In other words, being aware of “invisible” readers is a skill you most likely already possess and one you rely on every day. Consider the following paragraphs. Which one would the author send to her parents? Which one would she send to her best friend?
Last Saturday, I volunteered at a local hospital. The visit was fun and rewarding. I even learned how to do cardiopulmonary resuscitation, or CPR. Unfortunately, I think I caught a cold from one of the patients. This week, I will rest in bed and drink plenty of clear fluids. I hope I am well by next Saturday to volunteer again.
OMG! You won’t believe this! My advisor forced me to do my community service hours at this hospital all weekend! We learned CPR but we did it on dummies, not even real peeps. And some kid sneezed on me and got me sick! I was so bored and sniffling all weekend; I hope I don’t have to go back next week. I def do NOT want to miss the basketball tournament!
Most likely, you matched each paragraph to its intended audience with little hesitation. Because each paragraph reveals the author’s relationship with the intended readers, you can identify the audience fairly quickly. When writing your own essays, you must engage with your audience to build an appropriate relationship given your subject.
Imagining your readers during each stage of the writing process will help you make decisions about your writing. Ultimately, the people you visualize will affect what and how you write.
While giving a speech, you may articulate an inspiring or critical message, but if you left your hair a mess and laced up mismatched shoes, your audience might not take you seriously. They may be too distracted by your appearance to listen to your words.
Similarly, grammar and sentence structure serve as the appearance of a piece of writing. Polishing your work using correct grammar will impress your readers and allow them to focus on what you have to say.
Because focusing on your intended audience will enhance your writing, your process, and your finished product, you must consider the specific traits of your audience members. Use your imagination to anticipate the readers’ demographics, education, prior knowledge, and expectations.
Demographics
These measure important data about a group of people such as their age range, their ethnicity, their religious beliefs, or their gender. Certain topics and assignments will require these kinds of considerations about your audience. For other topics and assignments, these measurements may not influence your writing in the end. Regardless, it is important to consider demographics when you begin to think about your purpose for writing.
Education considers the audience’s level of schooling. If audience members have earned a doctorate degree, for example, you may need to elevate your style and use more formal language. Or, if audience members are still in college, you could write in a more relaxed style. An audience member’s major or emphasis may also dictate your writing.
Prior Knowledge
This refers to what the audience already knows about your topic. If your readers have studied certain topics, they may already know some terms and concepts related to the topic. You may decide whether to define terms and explain concepts based on your audience’s prior knowledge. Although you cannot peer inside the brains of your readers to discover their knowledge, you can make reasonable assumptions . For instance, a nursing major would presumably know more about health-related topics than a business major would.
Expectations
These indicate what readers will look for while reading your assignment. Readers may expect consistencies in the assignment’s appearance such as correct grammar and traditional formatting like double-spaced lines and legible font. Readers may also have content-based expectations given the assignment’s purpose and organization. In an essay titled “The Economics of Enlightenment: The Effects of Rising Tuition,” for example, audience members may expect to read about the economic repercussions of college tuition costs.
Selecting an Appropriate Tone
Tone identifies a speaker’s attitude toward a subject or another person. You may pick up a person’s tone of voice fairly easily in conversation. A friend who tells you about her weekend may speak excitedly about a fun skiing trip. An instructor who means business may speak in a low, slow voice to emphasize her serious mood. Or, a coworker who needs to let off some steam after a long meeting may crack a sarcastic joke.
Just as speakers transmit emotion through voice, writers can transmit a range of attitudes and emotions through prose –from excited and humorous to somber and critical. These emotions create connections among the audience, the author, and the subject, ultimately building a relationship between the audience and the text. To stimulate these connections, writers convey their attitudes and feelings with useful devices such as sentence structure, word choice, punctuation, and formal or informal language. Keep in mind that the writer’s attitude should always appropriately match the audience and the purpose.
Read the following paragraph and consider the writer’s tone. How would you describe the writer’s attitude toward wildlife conservation?
“Many species of plants and animals are disappearing right before our eyes. If we don’t act fast, it might be too late to save them. Human activities, including pollution, deforestation, hunting, and overpopulation, are devastating the natural environment. Without our help, many species will not survive long enough for our children to see them in the wild. Take the tiger, for example. Today, tigers occupy just seven percent of their historical range, and many local populations are already extinct. Hunted for their beautiful pelts and other body parts, the tiger population has plummeted from one hundred thousand in 1920 to just a few thousand. Contact your local wildlife conservation society today to find out how you can stop this terrible destruction.”
Choosing Appropriate, Interesting Content
Content refers to all the written substance in a document. After selecting an audience and a purpose, you must choose what information will make it to the page. Content may consist of examples, statistics, facts, anecdotes , testimonies , and observations, but no matter the type, the information must be appropriate and interesting for the audience and purpose. An essay written for third graders that summarizes the legislative process, for example, would have to contain succinct and simple content.
Content is also shaped by tone . When the tone matches the content, the audience will be more engaged, and you will build a stronger relationship with your readers. When applied to that audience of third graders, you would choose simple content that the audience would easily understand, and you would express that content through an enthusiastic tone.
The same considerations apply to all audiences and purposes.
This section contains material from:
Crowther, Kathryn, Lauren Curtright, Nancy Gilbert, Barbara Hall, Tracienne Ravita, and Kirk Swenson. Successful College Composition . 2nd edition. Book 8. Georgia: English Open Textbooks, 2016. http://oer.galileo.usg.edu/english-textbooks/8 . Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License .
- “The Rhetorical Triangle” was derived by Brandi Gomez from an image in: Kathryn Crowther et al., Successful College Composition, 2nd ed. Book 8. (Georgia: English Open Textbooks, 2016), https://oer.galileo.usg.edu/english-textbooks/8/ . Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . ↵
The bounds, limits, or confines of something.
A statement, usually one sentence, that summarizes an argument that will later be explained, expanded upon, and developed in a longer essay or research paper. In undergraduate writing, a thesis statement is often found in the introductory paragraph of an essay. The plural of thesis is theses .
The essence of something; those things that compose the foundational elements of a thing; the basics.
A brief and concise statement or series of statements that outlines the main point(s) of a longer work. To summarize is to create a brief and concise statement or series of statements that outlines the main point(s) of a longer work.
To give or relay information; explanatory.
The fusion, combination, or integration of two or more ideas or objects that create new ideas or objects.
To copy, duplicate, or reproduce.
To organize or arrange.
The process of critically examining, investigating, or interpreting a specific topic or subject matter in order to come to an original conclusion.
The subject matter; the information contained within a text; the configuration of ideas that make up an argument.
The choices that a writer makes in order to make their argument or express their ideas; putting different elements of writing together in order to present an argument. Style refers to the way an argument is framed, written, and presented.
To interrupt, stop, or prevent someone or something from coming to pass or getting from one place to the other.
Clear or lucid speech; the expression of an idea in a coherent or logical manner; the communication of a concept in a way that is easily understandable to an audience.
The person or group of people who view and analyze the work of a writer, researcher, or other content creator.
Qualities, features, or attributes relating to something, particularly personal characteristics.
Taking something for granted; an expected result; to be predisposed towards a certain outcome.
Consequences; the impact, usually negative, of an action or event.
Writing that is produced in sentence form; the opposite of poetry, verse, or song. Some of the most common types of prose include research papers, essays, articles, novels, and short stories.
A short account or telling of an incident or story, either personal or historical; anecdotal evidence is frequently found in the form of a personal experience rather than objective data or widespread occurrence.
Verbal or written proof from an individual; the statement made by a witness that is understood to be truth. Testimony can be a formal process, such as a testimony made in official court proceedings, or an informal process, such as claiming that a company’s product or service works.
To express an idea in as few words as possible; concise, brief, or to the point.
The feeling or attitude of the writer which can be inferred by the reader, usually conveyed through vocabulary, word choice, and phrasing; associated with emotion.
2.3 Purpose, Audience, Tone, and Content Copyright © 2022 by Kathryn Crowther; Lauren Curtright; Nancy Gilbert; Barbara Hall; Tracienne Ravita; Kirk Swenson; and Terri Pantuso is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to write an introduction paragraph in 3 steps.
General Education

It’s the roadmap to your essay, it’s the forecast for your argument, it’s...your introduction paragraph, and writing one can feel pretty intimidating. The introduction paragraph is a part of just about every kind of academic writing , from persuasive essays to research papers. But that doesn’t mean writing one is easy!
If trying to write an intro paragraph makes you feel like a Muggle trying to do magic, trust us: you aren’t alone. But there are some tips and tricks that can make the process easier—and that’s where we come in.
In this article, we’re going to explain how to write a captivating intro paragraph by covering the following info:
- A discussion of what an introduction paragraph is and its purpose in an essay
- An overview of the most effective introduction paragraph format, with explanations of the three main parts of an intro paragraph
- An analysis of real intro paragraph examples, with a discussion of what works and what doesn’t
- A list of four top tips on how to write an introduction paragraph
Are you ready? Let’s begin!

What Is an Introduction Paragraph?
An introduction paragraph is the first paragraph of an essay , paper, or other type of academic writing. Argumentative essays , book reports, research papers, and even personal essays are common types of writing that require an introduction paragraph. Whether you’re writing a research paper for a science course or an argumentative essay for English class , you’re going to have to write an intro paragraph.
So what’s the purpose of an intro paragraph? As a reader’s first impression of your essay, the intro paragraph should introduce the topic of your paper.
Your introduction will also state any claims, questions, or issues that your paper will focus on. This is commonly known as your paper’s thesis . This condenses the overall point of your paper into one or two short sentences that your reader can come back and reference later.
But intro paragraphs need to do a bit more than just introduce your topic. An intro paragraph is also supposed to grab your reader’s attention. The intro paragraph is your chance to provide just enough info and intrigue to make your reader say, “Hey, this topic sounds interesting. I think I’ll keep reading this essay!” That can help your essay stand out from the crowd.
In most cases, an intro paragraph will be relatively short. A good intro will be clear, brief, purposeful, and focused. While there are some exceptions to this rule, it’s common for intro paragraphs to consist of three to five sentences .
Effectively introducing your essay’s topic, purpose, and getting your reader invested in your essay sounds like a lot to ask from one little paragraph, huh? In the next section, we’ll demystify the intro paragraph format by breaking it down into its core parts . When you learn how to approach each part of an intro, writing one won’t seem so scary!

Once you figure out the three parts of an intro paragraph, writing one will be a piece of cake!
The 3 Main Parts of an Intro Paragraph
In general, an intro paragraph is going to have three main parts: a hook, context, and a thesis statement . Each of these pieces of the intro plays a key role in acquainting the reader with the topic and purpose of your essay.
Below, we’ll explain how to start an introduction paragraph by writing an effective hook, providing context, and crafting a thesis statement. When you put these elements together, you’ll have an intro paragraph that does a great job of making a great first impression on your audience!
Intro Paragraph Part 1: The Hook
When it comes to how to start an introduction paragraph, o ne of the most common approaches is to start with something called a hook.
What does hook mean here, though? Think of it this way: it’s like when you start a new Netflix series: you look up a few hours (and a few episodes) later and you say, “Whoa. I guess I must be hooked on this show!”
That’s how the hook is supposed to work in an intro paragrap h: it should get your reader interested enough that they don’t want to press the proverbial “pause” button while they’re reading it . In other words, a hook is designed to grab your reader’s attention and keep them reading your essay!
This means that the hook comes first in the intro paragraph format—it’ll be the opening sentence of your intro.
It’s important to realize that there are many different ways to write a good hook. But generally speaking, hooks must include these two things: what your topic is, and the angle you’re taking on that topic in your essay.
One approach to writing a hook that works is starting with a general, but interesting, statement on your topic. In this type of hook, you’re trying to provide a broad introduction to your topic and your angle on the topic in an engaging way .
For example, if you’re writing an essay about the role of the government in the American healthcare system, your hook might look something like this:
There's a growing movement to require that the federal government provide affordable, effective healthcare for all Americans.
This hook introduces the essay topic in a broad way (government and healthcare) by presenting a general statement on the topic. But the assumption presented in the hook can also be seen as controversial, which gets readers interested in learning more about what the writer—and the essay—has to say.
In other words, the statement above fulfills the goals of a good hook: it’s intriguing and provides a general introduction to the essay topic.
Intro Paragraph Part 2: Context
Once you’ve provided an attention-grabbing hook, you’ll want to give more context about your essay topic. Context refers to additional details that reveal the specific focus of your paper. So, whereas the hook provides a general introduction to your topic, context starts helping readers understand what exactly you’re going to be writing about
You can include anywhere from one to several sentences of context in your intro, depending on your teacher’s expectations, the length of your paper, and complexity of your topic. In these context-providing sentences, you want to begin narrowing the focus of your intro. You can do this by describing a specific issue or question about your topic that you’ll address in your essay. It also helps readers start to understand why the topic you’re writing about matters and why they should read about it.
So, what counts as context for an intro paragraph? Context can be any important details or descriptions that provide background on existing perspectives, common cultural attitudes, or a specific situation or controversy relating to your essay topic. The context you include should acquaint your reader with the issues, questions, or events that motivated you to write an essay on your topic...and that your reader should know in order to understand your thesis.
For instance, if you’re writing an essay analyzing the consequences of sexism in Hollywood, the context you include after your hook might make reference to the #metoo and #timesup movements that have generated public support for victims of sexual harassment.
The key takeaway here is that context establishes why you’re addressing your topic and what makes it important. It also sets you up for success on the final piece of an intro paragraph: the thesis statement.
Elle Woods' statement offers a specific point of view on the topic of murder...which means it could serve as a pretty decent thesis statement!
Intro Paragraph Part 3: The Thesis
The final key part of how to write an intro paragraph is the thesis statement. The thesis statement is the backbone of your introduction: it conveys your argument or point of view on your topic in a clear, concise, and compelling way . The thesis is usually the last sentence of your intro paragraph.
Whether it’s making a claim, outlining key points, or stating a hypothesis, your thesis statement will tell your reader exactly what idea(s) are going to be addressed in your essay. A good thesis statement will be clear, straightforward, and highlight the overall point you’re trying to make.
Some instructors also ask students to include an essay map as part of their thesis. An essay map is a section that outlines the major topics a paper will address. So for instance, say you’re writing a paper that argues for the importance of public transport in rural communities. Your thesis and essay map might look like this:
Having public transport in rural communities helps people improve their economic situation by giving them reliable transportation to their job, reducing the amount of money they spend on gas, and providing new and unionized work .
The underlined section is the essay map because it touches on the three big things the writer will talk about later. It literally maps out the rest of the essay!
So let’s review: Your thesis takes the idea you’ve introduced in your hook and context and wraps it up. Think of it like a television episode: the hook sets the scene by presenting a general statement and/or interesting idea that sucks you in. The context advances the plot by describing the topic in more detail and helping readers understand why the topic is important. And finally, the thesis statement provides the climax by telling the reader what you have to say about the topic.
The thesis statement is the most important part of the intro. Without it, your reader won’t know what the purpose of your essay is! And for a piece of writing to be effective, it needs to have a clear purpose. Your thesis statement conveys that purpose , so it’s important to put careful thought into writing a clear and compelling thesis statement.

How To Write an Introduction Paragraph: Example and Analysis
Now that we’ve provided an intro paragraph outline and have explained the three key parts of an intro paragraph, let’s take a look at an intro paragraph in action.
To show you how an intro paragraph works, we’ve included a sample introduction paragraph below, followed by an analysis of its strengths and weaknesses.
Example of Introduction Paragraph
While college students in the U.S. are struggling with how to pay for college, there is another surprising demographic that’s affected by the pressure to pay for college: families and parents. In the face of tuition price tags that total more than $100,000 (as a low estimate), families must make difficult decisions about how to save for their children’s college education. Charting a feasible path to saving for college is further complicated by the FAFSA’s estimates for an “Expected Family Contribution”—an amount of money that is rarely feasible for most American families. Due to these challenging financial circumstances and cultural pressure to give one’s children the best possible chance of success in adulthood, many families are going into serious debt to pay for their children’s college education. The U.S. government should move toward bearing more of the financial burden of college education.
Example of Introduction Paragraph: Analysis
Before we dive into analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of this example intro paragraph, let’s establish the essay topic. The sample intro indicates that t he essay topic will focus on one specific issue: who should cover the cost of college education in the U.S., and why. Both the hook and the context help us identify the topic, while the thesis in the last sentence tells us why this topic matters to the writer—they think the U.S. Government needs to help finance college education. This is also the writer’s argument, which they’ll cover in the body of their essay.
Now that we’ve identified the essay topic presented in the sample intro, let’s dig into some analysis. To pin down its strengths and weaknesses, we’re going to use the following three questions to guide our example of introduction paragraph analysis:
- Does this intro provide an attention-grabbing opening sentence that conveys the essay topic?
- Does this intro provide relevant, engaging context about the essay topic?
- Does this intro provide a thesis statement that establishes the writer’s point of view on the topic and what specific aspects of the issue the essay will address?
Now, let’s use the questions above to analyze the strengths and weaknesses of this sample intro paragraph.
Does the Intro Have a Good Hook?
First, the intro starts out with an attention-grabbing hook . The writer starts by presenting an assumption (that the U.S. federal government bears most of the financial burden of college education), which makes the topic relatable to a wide audience of readers. Also note that the hook relates to the general topic of the essay, which is the high cost of college education.
The hook then takes a surprising turn by presenting a counterclaim : that American families, rather than students, feel the true burden of paying for college. Some readers will have a strong emotional reaction to this provocative counterclaim, which will make them want to keep reading! As such, this intro provides an effective opening sentence that conveys the essay topic.
Does the Intro Give Context?
T he second, third, and fourth sentences of the intro provide contextual details that reveal the specific focus of the writer’s paper . Remember: the context helps readers start to zoom in on what the paper will focus on, and what aspect of the general topic (college costs) will be discussed later on.
The context in this intro reveals the intent and direction of the paper by explaining why the issue of families financing college is important. In other words, the context helps readers understand why this issue matters , and what aspects of this issue will be addressed in the paper.
To provide effective context, the writer refers to issues (the exorbitant cost of college and high levels of family debt) that have received a lot of recent scholarly and media attention. These sentences of context also elaborate on the interesting perspective included in the hook: that American families are most affected by college costs.
Does the Intro Have a Thesis?
Finally, this intro provides a thesis statement that conveys the writer’s point of view on the issue of financing college education. This writer believes that the U.S. government should do more to pay for students’ college educations.
However, the thesis statement doesn’t give us any details about why the writer has made this claim or why this will help American families . There isn’t an essay map that helps readers understand what points the writer will make in the essay.
To revise this thesis statement so that it establishes the specific aspects of the topic that the essay will address, the writer could add the following to the beginning of the thesis statement:
The U.S. government should take on more of the financial burden of college education because other countries have shown this can improve education rates while reducing levels of familial poverty.
Check out the new section in bold. Not only does it clarify that the writer is talking about the pressure put on families, it touches on the big topics the writer will address in the paper: improving education rates and reduction of poverty. So not only do we have a clearer argumentative statement in this thesis, we also have an essay map!
So, let’s recap our analysis. This sample intro paragraph does an effective job of providing an engaging hook and relatable, interesting context, but the thesis statement needs some work ! As you write your own intro paragraphs, you might consider using the questions above to evaluate and revise your work. Doing this will help ensure you’ve covered all of your bases and written an intro that your readers will find interesting!

4 Tips for How To Write an Introduction Paragraph
Now that we’ve gone over an example of introduction paragraph analysis, let’s talk about how to write an introduction paragraph of your own. Keep reading for four tips for writing a successful intro paragraph for any essay.
Tip 1: Analyze Your Essay Prompt
If you’re having trouble with how to start an introduction paragraph, analyze your essay prompt! Most teachers give you some kind of assignment sheet, formal instructions, or prompt to set the expectations for an essay they’ve assigned, right? Those instructions can help guide you as you write your intro paragraph!
Because they’ll be reading and responding to your essay, you want to make sure you meet your teacher’s expectations for an intro paragraph . For instance, if they’ve provided specific instructions about how long the intro should be or where the thesis statement should be located, be sure to follow them!
The type of paper you’re writing can give you clues as to how to approach your intro as well. If you’re writing a research paper, your professor might expect you to provide a research question or state a hypothesis in your intro. If you’re writing an argumentative essay, you’ll need to make sure your intro overviews the context surrounding your argument and your thesis statement includes a clear, defensible claim.
Using the parameters set out by your instructor and assignment sheet can put some easy-to-follow boundaries in place for things like your intro’s length, structure, and content. Following these guidelines can free you up to focus on other aspects of your intro... like coming up with an exciting hook and conveying your point of view on your topic!
Tip 2: Narrow Your Topic
You can’t write an intro paragraph without first identifying your topic. To make your intro as effective as possible, you need to define the parameters of your topic clearly—and you need to be specific.
For example, let’s say you want to write about college football. “NCAA football” is too broad of a topic for a paper. There is a lot to talk about in terms of college football! It would be tough to write an intro paragraph that’s focused, purposeful, and engaging on this topic. In fact, if you did try to address this whole topic, you’d probably end up writing a book!
Instead, you should narrow broad topics to identify a specific question, claim, or issue pertaining to some aspect of NCAA football for your intro to be effective. So, for instance, you could frame your topic as, “How can college professors better support NCAA football players in academics?” This focused topic pertaining to NCAA football would give you a more manageable angle to discuss in your paper.
So before you think about writing your intro, ask yourself: Is my essay topic specific, focused, and logical? Does it convey an issue or question that I can explore over the course of several pages? Once you’ve established a good topic, you’ll have the foundation you need to write an effective intro paragraph .

Once you've figured out your topic, it's time to hit the books!
Tip 3: Do Your Research
This tip is tightly intertwined with the one above, and it’s crucial to writing a good intro: do your research! And, guess what? This tip applies to all papers—even ones that aren’t technically research papers.
Here’s why you need to do some research: getting the lay of the land on what others have said about your topic—whether that’s scholars and researchers or the mass media— will help you narrow your topic, write an engaging hook, and provide relatable context.
You don't want to sit down to write your intro without a solid understanding of the different perspectives on your topic. Whether those are the perspectives of experts or the general public, these points of view will help you write your intro in a way that is intriguing and compelling for your audience of readers.
Tip 4: Write Multiple Drafts
Some say to write your intro first; others say write it last. The truth is, there isn’t a right or wrong time to write your intro—but you do need to have enough time to write multiple drafts .
Oftentimes, your professor will ask you to write multiple drafts of your paper, which gives you a built-in way to make sure you revise your intro. Another approach you could take is to write out a rough draft of your intro before you begin writing your essay, then revise it multiple times as you draft out your paper.
Here’s why this approach can work: as you write your paper, you’ll probably come up with new insights on your topic that you didn’t have right from the start. You can use these “light bulb” moments to reevaluate your intro and make revisions that keep it in line with your developing essay draft.
Once you’ve written your entire essay, consider going back and revising your intro again . You can ask yourself these questions as you evaluate your intro:
- Is my hook still relevant to the way I’ve approached the topic in my essay?
- Do I provide enough appropriate context to introduce my essay?
- Now that my essay is written, does my thesis statement still accurately reflect the point of view that I present in my essay?
Using these questions as a guide and putting your intro through multiple revisions will help ensure that you’ve written the best intro for the final draft of your essay. Also, revising your writing is always a good thing to do—and this applies to your intro, too!

What's Next?
Your college essays also need great intro paragraphs. Here’s a guide that focuses on how to write the perfect intro for your admissions essays.
Of course, the intro is just one part of your college essay . This article will teach you how to write a college essay that makes admissions counselors sit up and take notice.
Are you trying to write an analytical essay? Our step-by-step guide can help you knock it out of the park.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Greater Good Science Center • Magazine • In Action • In Education
Mind & Body Articles & More
How patience can help you find your purpose, a two-year study suggests practicing patience may be critical to finding and pursuing purpose..
What am I going to do with my life? What really matters to me? How will I leave my mark?
These questions can fill us with hope, inspiration, and direction when we have some sense of what the answers may be. If we don’t, they can fill us with confusion, frustration, and irritation.
Leading a life of purpose, or making an enduring commitment to contributing to the broader world in personally meaningful ways, is associated with a range of benefits, including better physical health, enhanced psychological well-being, superior academic achievement, and enriched social connections. Despite these advantages, leading a life of purpose is rare, as researcher William Damon describes in his 2009 book, The Path to Purpose : As many as two out of three young adults struggle to articulate a clear purpose for their lives.

Before young people can identify a purpose, they need to engage in a process of self-exploration. Searching for a purpose in life is not often studied, but when it has been, scholars have found it to be a source of stress and anxiety, especially when it feels like everyone else has it all figured out. (Rest assured, others are likely still working it out, too!)
Members of my Adolescent Moral Development Lab and I became interested in how we could help young adults navigate the potentially distressing process of searching for a purpose in life. With the generous support of a grant from the Templeton Religion Trust, we conducted a two-year study, and our emerging findings suggest practicing patience may be a critical and often overlooked element of a productive and fulfilling search for purpose.
How patience and purpose go hand in hand
Patience is the ability to stay actively engaged in working toward a goal without becoming frustrated. Patiently pursuing purpose does not mean sitting by and waiting for inspiration to strike. Instead, it means engaging in the personal reflection and intentional conversations that help us figure out how we want to contribute to the broader world without feeling rushed or hurried. Accepting that the search is a long-term endeavor can help us cultivate our purpose in a more efficient and growth-supporting way.
Practicing patience may facilitate the search for purpose, and this is important because our research also suggests that searching for purpose is not a one-and-done kind of activity. It is unlikely to be the case that we search for a purpose once and then spend the rest of our lives pursuing that single purpose. Instead, we tend to pursue multiple purposes across our lifetimes. Purposes wax and wane with the other things going on in our lives.
For instance, we may find purpose in parenting, but that purpose may transform when we launch our adult children and reinvest in personally meaningful work-related aims. Others of us may find purpose in work, and upon retirement those purposes may recede as we find new ways of contributing to our communities. For young adults, purposes are likely to evolve as they navigate the many transitions associated with this stage of life (e.g., moving from high school into college and from college into the working world). Moves like these are often accompanied by evolutions in our purposes in life.
The point is that the search for purpose is an ongoing activity. Even when we know how we want to leave our mark, we are still likely to search for new ways of making progress toward our personally meaningful aims or for new ways of contributing to the broader world.
Given that the search for purpose is likely to represent a long-term, possibly even a lifelong, activity, it is worthwhile to understand how we can engage in the self-exploration process in the most productive and rewarding way possible. Emerging findings from our study suggest patience may help optimize the search process in at least five ways.
Practicing patience allows us to stand back and take in the full picture of the aim we are after. We can become so focused on figuring out what it is we want to accomplish that we lose the forest for the trees. Taking a broad perspective on the purpose development process may yield insights into progress made to date, and recognizing and even celebrating this progress can fuel our ongoing efforts. Allowing ourselves time to take in the bigger picture may reveal more efficient routes for making progress toward our purpose.
Patience may bolster resilience. Patient individuals take setbacks in stride; they continue making forward progress despite them. Rather than being derailed by challenges in the pursuit of purpose, patient individuals view hardships as inevitable and surmountable. Practicing patience is an important way of cultivating the resilience required to both search for and pursue a purpose in life, as Anne Colby suggests in her 2020 paper, “Purpose as a Unifying Goal for Higher Education.”
Practicing patience may encourage a more thoughtful approach to pursuing meaningful aims. Rather than moving forward in haste, patient individuals move ahead with intention and deliberation, and this may support more sustainable progress in the search for purpose. Compared to others, patient individuals may be more likely to take time to develop relationships with mentors and like-minded peers who can facilitate their progress toward purpose. Slowing down to connect with others along our path to purpose can help us make progress in figuring out how we want to leave our mark (and these relationships may also support our pursuit of purpose, once we have determined what it entails).
Patience in the pursuit of larger aims may foster personal growth. In addition to encouraging resilience and social connections, practicing patience builds self-regulation, self-discipline, and deferred-gratification skills. Developing these strengths of character is likely to benefit individuals in many life domains, including in future periods of self-exploration and subsequent purpose cultivation efforts.
Finally, patient individuals may be more likely than impatient individuals to enjoy the search. Patience enables us to savor the process of figuring out what matters most and how we want to meaningfully contribute to the broader world. It allows us time to celebrate the small successes and be present in the purpose cultivation process. The mindfulness that can accompany a patient pursuit of purpose is likely to enhance our well-being during the search process and in our lives more generally.
In each of these ways, patience may represent a critical component of a healthy and productive search for purpose.
The bottom line: Whether searching for our own purpose in life or supporting someone in their search, remember to practice patience. When we find ourselves becoming agitated and frustrated by the feeling that everyone else has it all figured out, we should remind ourselves to slow down. Take heart in knowing that the process requires time. Focus on the big picture, recall that setbacks are inevitable and surmountable, connect with others who can support your search, take stock of gains, and find the joy in the process, if you can. Before you know it, you might just have figured out how you want to use your skills and talents to contribute in meaningful ways to the world beyond yourself. To read the published manuscripts from which these findings were drawn, please visit Kendall Cotton Bronk’s website . Upon publication, articles from this study will be posted there.
About the Author

Kendall Cotton Bronk
Kendall Cotton Bronk, Ph.D. , is an associate professor of psychology at the Claremont Graduate University in the Division of Behavioral and Social Sciences, where she studies the things that give young people’s lives purpose. Dr. Bronk teamed up with the Greater Good Science Center and social impact firm ProSocial, with support from the John Templeton Foundation, to translate research on purpose into an online toolkit called The Purpose Challenge , which youth can use to explore their own purpose in life.
You May Also Enjoy

This article — and everything on this site — is funded by readers like you.
Become a subscribing member today. Help us continue to bring “the science of a meaningful life” to you and to millions around the globe.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Race Is Central to Identity for Black Americans and Affects How They Connect With Each Other
Many learn about ancestors, u.s. black history from family, table of contents.
- The importance of being Black for connections with other Black people
- The importance of Blackness for knowing family history and U.S. Black history
- Younger Black people are less likely to speak to relatives about ancestors
- Black Americans differ by party on measures of identity and connection
- The importance of race, ancestry and place to personal identity
- The importance of gender and sexuality to personal identity
- Black Americans and connectedness to other Black people
- Intra-racial connections locally, nationally and globally
- How Black Americans learn about their family history
- Most Black adults say their ancestors were enslaved, but some are not sure
- Most Black adults are at least somewhat informed about U.S. Black history
- For many Black adults, where they live shapes how they think about themselves
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology

Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to understand the rich diversity of Black people in the United States and their views of Black identity. This in-depth, robust survey explores differences among Black Americans in views of identity such as between U.S.-born Black people and Black immigrants; Black people living in different regions of the country; and between Black people of different ethnicities, political party affiliations, ages and income levels. The analysis is the latest in the Center’s series of in-depth surveys of public opinion among Black Americans (read the first, “ Faith Among Black Americans ”).
The online survey of 3,912 Black U.S. adults was conducted Oct. 4-17, 2021. The survey includes 1,025 Black adults on Pew Research Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP) and 2,887 Black adults on Ipsos’ KnowledgePanel. Respondents on both panels are recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses.
Recruiting panelists by phone or mail ensures that nearly all U.S. Black adults have a chance of selection. This gives us confidence that any sample can represent the whole population (see our Methods 101 explainer on random sampling). Here are the questions used for the survey of Black adults , along with its responses and methodology .
The terms “Black Americans” , “Black people” and “Black adults” are used interchangeably throughout this report to refer to U.S. adults who self-identify as Black, either alone or in combination with other races or Hispanic identity.
Throughout this report, “Black, non-Hispanic” respondents are those who identify as single-race Black and say they have no Hispanic background. “Black Hispanic” respondents are those who identify as Black and say they have Hispanic background. We use the terms “Black Hispanic” and “Hispanic Black” interchangeably. “Multiracial” respondents are those who indicate two or more racial backgrounds (one of which is Black) and say they are not Hispanic.
Respondents were asked a question about how important being Black was to how they think about themselves. In this report, we use the terms “being Black” and “Blackness” interchangeably when referencing responses to this question.
In this report, “immigrant” refers to people who were not U.S. citizens at birth – in other words, those born outside the U.S., Puerto Rico or other U.S. territories to parents who were not U.S. citizens. We use the terms “immigrant” and “foreign-born” interchangeably.
Throughout this report, “Democrat and Democratic leaners” refers to respondents who say in they identify politically with the Democratic Party or are independent but lean toward the Democratic Party. “ Republican and Republican leaners” refers to respondents who identify politically with the Republican Party or are independent but lean toward the Republican Party.
To create the upper-, middle- and lower-income tiers, respondents’ 2020 family incomes were adjusted for differences in purchasing power by geographic region and household size. Respondents were then placed into income tiers: “Middle income” is defined as two-thirds to double the median annual income for the entire survey sample. “Lower income” falls below that range, and “upper income” lies above it. For more information about how the income tiers were created, read the methodology .
No matter where they are from, who they are, their economic circumstances or educational backgrounds, significant majorities of Black Americans say being Black is extremely or very important to how they think about themselves, with about three-quarters (76%) overall saying so.
A significant share of Black Americans also say that when something happens to Black people in their local communities, across the nation or around the globe, it affects what happens in their own lives, highlighting a sense of connectedness. Black Americans say this even as they have diverse experiences and come from an array of backgrounds.
Even so, Black adults who say being Black is important to their sense of self are more likely than other Black adults to feel connected to other groups of Black people. They are also more likely to feel that what happens to Black people inside and outside the United States affects what happens in their own lives. These findings emerge from an extensive new survey of Black U.S. adults conducted by Pew Research Center.
A majority of non-Hispanic Black Americans (78%) say being Black is very or extremely important to how they think about themselves. This racial group is the largest among Black adults , accounting for 87% of the adult population, according to 2019 Census Bureau estimates. But among other Black Americans, roughly six-in-ten multiracial (57%) and Hispanic (58%) Black adults say this.
Black Americans also differ in key ways in their views about the importance of being Black to personal identity. While majorities of all age groups of Black people say being Black shapes how they think about themselves, younger Black Americans are less likely to say this – Black adults ages 50 and older are more likely than Black adults ages 18 to 29 to say that being Black is very or extremely important to how they think of themselves. Specifically, 76% of Black adults ages 30 to 49, 80% of those 50 to 64 and 83% of those 65 and older hold this view, while only 63% of those under 30 do.
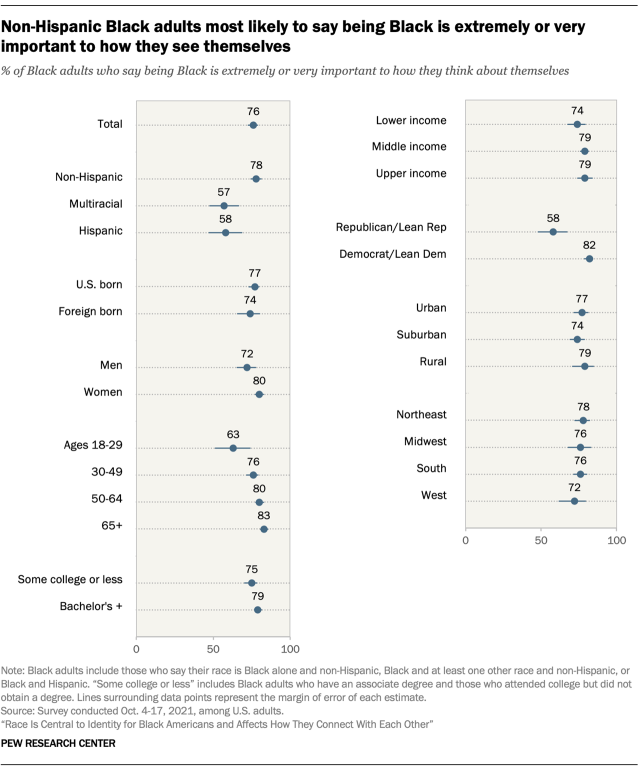
Black adults who identify with or lean toward the Democratic Party are more likely than those who identify with or lean toward the Republican Party to say being Black is important to how they see themselves – 86% vs. 58%. And Black women (80%) are more likely than Black men (72%) to say being Black is important to how they see themselves.
Still, some subgroups of Black Americans are about as likely as others to say that being Black is very or extremely important to how they think about themselves. For example, U.S.-born and immigrant Black adults are about as likely to say being Black is important to how they see their identity. However, not all Black Americans feel the same about the importance of being Black to their identity – 14% say it is only somewhat important to how they see themselves while 9% say it has little or no impact on their personal identity, reflecting the diversity of views about identity among Black Americans.
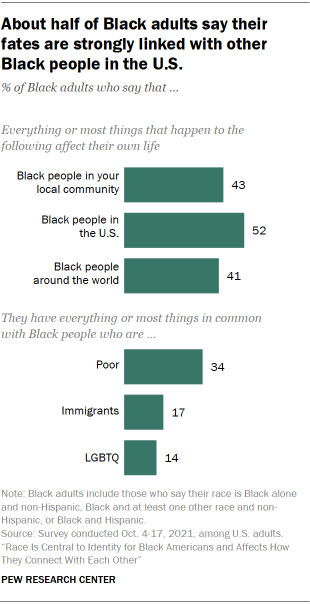
Beyond the personal importance of Blackness – that is, the importance of being Black to personal identity – many Black Americans feel connected to each other. About five-in-ten (52%) say everything or most things that happen to Black people in the United States affect what happens in their own lives, with another 30% saying some things that happen nationally to Black people have a personal impact. And 43% say all or most things that happen to Black people in their local community affect what happens in their own lives, while another 35% say only some things in their lives are affected by these events. About four-in-ten Black adults in the U.S. (41%) say they feel their fates are strongly linked to Black people around the world, with 36% indicating that some things that happen to Black people around the world affect what happens in their own lives.
The survey also asked respondents how much they have in common with different groups of Black Americans. Some 17% of Black adults say they have everything or most things in common with Black people who are immigrants. But this sense of commonality differs sharply by nativity: 14% of U.S.-born Black adults say they have everything or most things in common with Black immigrants, while 43% of Black immigrants say the same. Conversely, only about one-in-four Black immigrants (26%) say they have everything or most things in common with U.S.-born Black people, a share that rises to 56% among U.S.-born Black people themselves.
About one-third of Black Americans (34%) say they have everything or most things in common with Black people who are poor, though smaller shares say the same about Black people who are wealthy (12%). Relatively few Black Americans (14%) say they have everything or most things in common with Black people who identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender or queer (LGBTQ). However, a larger share of Black Americans (25%) say they have at least some things in common with Black people who identify as LGBTQ. All these findings highlight the diversity of the U.S. Black population and how much Black people feel connected to each other.
These are among the key findings from a recent Pew Research Center survey of 3,912 Black Americans conducted online Oct. 4-17, 2021. This report is the latest in a series of Pew Research Center studies focused on describing the rich diversity of Black people in the United States.
The nation’s Black population stood at 47 million in 2020 , making up 14% of the U.S. population – up from 13% in 2000. While the vast majority of Black Americans say their racial background is Black alone (88% in 2020), growing numbers are also multiracial or Hispanic. Most were born in the U.S. and trace their roots back several generations in the country, but a growing share are immigrants (12%) or the U.S.-born children of immigrant parents (9%). Geographically, while 56% of Black Americans live in the nation’s South , the national Black population has also dispersed widely across the country.
It is this diversity – among U.S.-born Black people and Black immigrants; between Black people who live in different regions; and across different ethnicities, party affiliations, ages and income levels – that this report explores. The survey also provides a robust opportunity to examine the importance of race to Black Americans’ sense of self and their connections to other Black people.
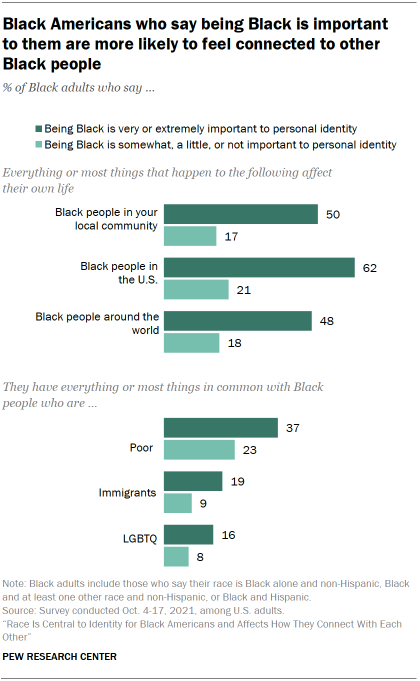
The importance of being Black to personal identity is a significant factor in how connected Black Americans feel toward each other. Those who say that being Black is a very or extremely important part of their personal identity are more likely than those for whom Blackness is relatively less important to express a sense of common fate with Black people in their local communities (50% vs. 17%), in the United States overall (62% vs. 21%), and even around the world (48% vs. 18%).
They are also more likely to say that they have everything or most things in common with Black people who are poor (37% vs. 23%) and Black immigrants (19% vs. 9%). Even so, fewer than half of Black Americans, no matter how important Blackness is to their personal identity, say they have everything or most things in common with Black people who are poor, immigrants or LGBTQ.
The new survey also explores Black Americans’ knowledge about their family histories and the history of Black people in the United States, with the importance of Blackness linked to greater knowledge.
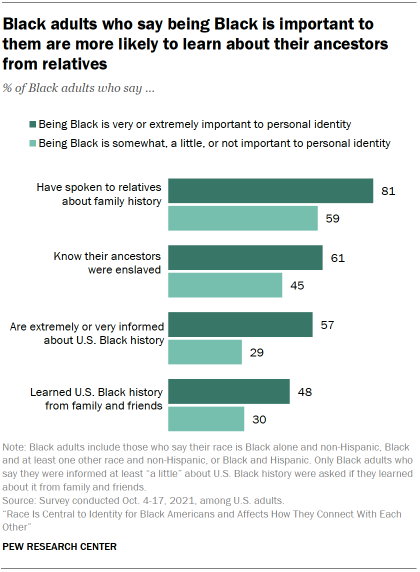
Nearly six-in-ten Black adults (57%) say their ancestors were enslaved either in the U.S. or another country, with nearly all who say so (52% of the Black adults surveyed) saying it was in the U.S., either in whole or in part. Black adults who say that being Black is a very or extremely important part of how they see themselves (61%) are more likely than those for whom being Black is less important (45%) to say that their ancestors were enslaved. In fact, Black adults for whom Blackness is very or extremely important (31%) are less likely than their counterparts (42%) to say that they are not sure if their ancestors were enslaved at all.
When it comes to learning more about their family histories, Black adults for whom Blackness is very or extremely important (81%) are more likely than those for whom Blackness is less important (59%) to have spoken to their relatives. They are about as likely to have researched their family’s history online (36% and 30%, respectively) and to have used a mail-in DNA service such as AncestryDNA or 23andMe (15% and 16%) to learn more about their ancestry.
The importance of Blackness also figures prominently into how informed Black Americans feel about U.S. Black history. Black adults who say Blackness is a significant part of their personal identity are more likely than those for whom Blackness is less important to say that they feel very or extremely informed about U.S. Black history (57% vs. 29%). Overall, about half of Black Americans say they feel very or extremely informed about the history of Black people in the United States.
Among Black adults who feel at least a little informed about U.S. Black history, the sources of their knowledge also differ by the importance of Blackness to personal identity. Nearly half of Black adults for whom Blackness is very or extremely important (48%) say they learned about Black history from their families and friends, making them more likely to say so than Black adults for whom Blackness is less important (30%). Similarly, those who say being Black is important to their identity are more likely than those who did not say this to have learned about Black history from nearly every source they were asked about, be it media (33% vs. 22%), the internet (30% vs. 18%) or college, if they attended (26% vs. 14%). The only source for which both groups were about equally likely to say they learned about Black history was their K-12 schools (24% and 21%, respectively).
Overall, among Black Americans who feel at least a little informed about U.S. Black history, 43% say they learned about it from their relatives and friends, 30% say they learned about it from the media, 27% from the internet, and 24% from college (if they attended) and 23% from K-12 school.
Black adults under 30 years old differ significantly from older Black adults in their views on the importance of Blackness to their personal identity. However, Black adults also differ by age in how they pursue knowledge of family history, how informed they feel about U.S. Black history, and their sense of connectedness to other Black people.
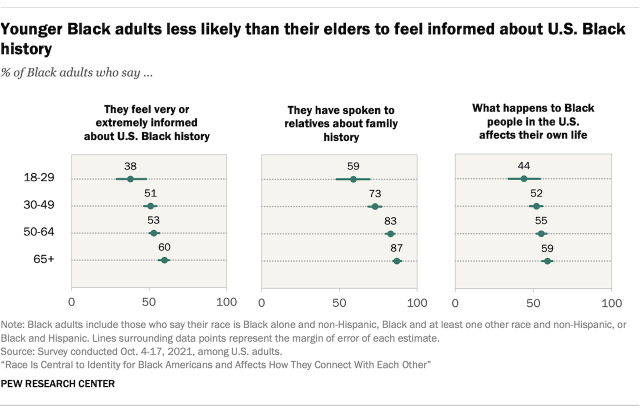
Black adults under 30 (50%) are less likely than those 65 and older (64%) to say their ancestors were enslaved. In fact, 40% of Black adults under 30 say that they are not sure whether their ancestors were enslaved. Black adults in the youngest age group (59%) are less likely than the oldest (87%) to have spoken to their relatives about family history or to have used a mail-in DNA service to learn about their ancestors (11% vs. 21%). They are only slightly less likely to have conducted research on their families online (26% vs. 39%).
Black adults under 30 have the lowest share who say they feel very or extremely informed about the history of Black people in the United States (40%), compared with 60% of Black adults 65 and older and about half each of Black adults 50 to 64 (53%) and 30 to 49 (51%). In fact, Black adults under 30 are more likely than those 50 and older to say they feel a little or not at all informed about Black history. While Black adults are generally most likely to cite family and friends as their source for learning about Black history, the share under 30 (38%) who also cite the internet as a source of information is higher than the shares ages 50 to 64 (22%) and 65 and older (14%) who say this.
These age differences persist in the sense of connectedness that Black Americans have with other Black people. Black adults under 30 are less likely than those 65 and older to say that everything or most things that happen to Black people in the United States will affect their own lives. This youngest group is also less likely than the oldest to have this sense of common fate with Black people in their local community. One exception to this pattern occurs when Black adults were asked how much they had in common with Black people who identify as LGBTQ. Black adults under 30 (21%) were considerably more likely than those 65 and older (10%) to say they have everything or most things in common with Black people who identify as LGBTQ.
Black Democrats and Republicans differ on how important Blackness is to their personal identities. However, there are also partisan gaps when it comes to their connectedness to other Black people. 1
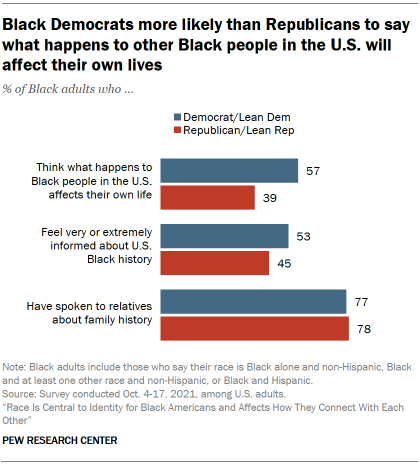
Black Democrats and those who lean to the Democratic Party are more likely than Black Republicans and Republican leaners to say that everything or most things that happen to Black people in the United States (57% vs. 39%) and their local communities (46% vs. 30%) affect what happens in their own lives. However, Black Republicans (24%) are more likely than Black Democrats (14%) to say that they have everything or most things in common with Black people who are LGBTQ. They are also more likely than Black Democrats to say they have everything or most things in common with Black people who are wealthy (25% vs. 11%).
When it comes to knowledge of family and racial histories, Black Democrats and Republicans do not differ. Democrats (59%) are just as likely as Republicans (54%) to know that their ancestors were enslaved. Nearly 80% of Black adults from both partisan coalitions say they have spoken to their relatives about their family history. Similar shares have also researched their family histories online and used mail-in DNA services.
Black Democrats are also not significantly more likely than Black Republicans to say they feel very or extremely informed about U.S. Black history (53% vs. 45%). And among those who feel at least a little informed about U.S. Black history, Democrats and Republicans are about equally likely to say they learned it from family and friends (45% vs. 38%).
Place is a key part of Black Americans’ personal identities
The majority of Black adults who live in the United States were born there, but an increasing portion of the population is comprised of immigrants. Of those immigrants, nearly 90% were born in the Caribbean or Africa . Regardless of their region of birth, 58% of Black adults say the country they were born in is very or extremely important to how they think about themselves. A smaller share say the same about the places where they grew up (46%).
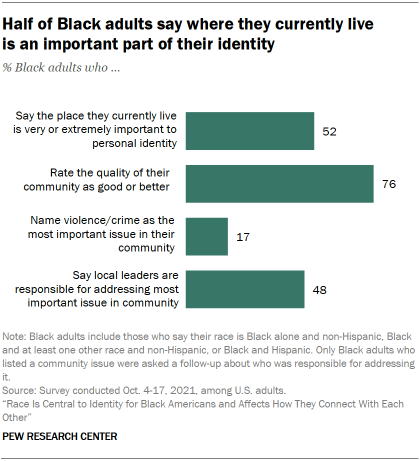
Black adults also feel strongly about their current communities. About half of Black adults (52%) say that where they currently live is very or extremely important to how they think about themselves. And when it comes to the quality of their neighborhoods, 76% of Black adults rate them as at least good places to live, including 41% who say the quality of their community is very good or excellent.
Still, Black adults say there are concerning issues in the communities they live in. When asked in an open-ended question to list the issue that was most important in their neighborhoods, nearly one-in-five Black adults listed issues related to violence or crime (17%). Smaller shares listed other points of concern such as economic issues like poverty and homelessness (11%), housing (7%), COVID-19 and public health (6%), or infrastructure issues such as the availability of public transportation and the conditions of roads (5%).
While nearly one-in-five Black Americans (17%) say that individual people like themselves should be responsible for solving these problems, they are most likely to say that local community leaders should address these issues (48%). Smaller shares say the U.S. Congress (12%), the U.S. president (8%) or civil rights organizations (2%) bear responsibility.
- According to the survey, 80% of Black adults say they identify with or lean toward the Democratic Party, 10% say the same of the Republican Party and 10% did not answer the question or indicated that they did not affiliate with either party. Among Black registered voters, the survey finds 85% identify with or lean toward the Democratic Party, 10% identify with or lean toward the Republican Party and 5% did not answer the question or indicated that they did not affiliate with either party. ↩
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Black Americans
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Racial & Ethnic Identity
- Rural, Urban and Suburban Communities
A look at Black-owned businesses in the U.S.
8 facts about black americans and the news, black americans’ views on success in the u.s., among black adults, those with higher incomes are most likely to say they are happy, fewer than half of black americans say the news often covers the issues that are important to them, most popular, report materials.
- American Trends Panel Wave 97
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
Earth Day: What is it, when is it and why is it important?

Earth Day takes place on 22 April each year. Image: UNSPLASH/Markus Spiske
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Lindsey Ricker
Hanh nguyen.

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Climate Crisis is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, climate crisis.
Listen to the article
This article was last updated on 11 April 2024. It was originally published on 19 April 2022.
- Earth Day takes place every year on 22 April and is one of the biggest environmental protest movements on the planet.
- The theme of Earth Day this year is 'Planet vs. Plastics' - campaigners are calling for a 60% reduction in the production of plastics by 2040.
- The World Economic Forum's Global Risks Report 2024 finds that environmental risks make up half of the top 10 risks over the next 10 years.
“Good evening, a unique day in American history is ending. A day set aside for a nationwide outpouring of mankind seeking its own survival.”
Those were the words of US TV presenter Walter Cronkite as he described the aftermath of the first Earth Day back in 1970.
Here’s what you need to know about Earth Day in 2024.
What is Earth Day and what is the theme in 2024?
Earth Day is an international day devoted to our planet. It draws attention to the environment and promotes conservation and sustainability. Each year on 22 April, around 1 billion people around the world take action to raise awareness of the climate crisis and bring about behavioural change to protect the environment.
Participation in Earth Day can take many forms, including small home or classroom projects like planting a herb garden or picking up litter. People also volunteer to plant trees, join other ecological initiatives or take part in street protests about climate change and environmental degradation.
Official Earth Day campaigns and projects aim to increase environmental literacy and bring together like-minded people or groups to address issues such as deforestation, biodiversity loss and other challenges .
The global theme for this year's Earth Day is ' Planet vs. Plastics ', which recognizes the threat plastics pose to human health and with campaigners demanding a 60% reduction in the production of plastics by 2040.
From 23 to 29 April 2024, governments and NGOs from around the world will gather in Ottawa to continue negotiating the terms of the United Nations Global Plastic Treaty .
How did Earth Day begin?
Millions of people took to the streets of US cities and towns on 22 April 1970 in mass protests over the damage being done to the planet and its resources. Amid the demonstrations, protesters brought New York City’s usually bustling Fifth Avenue to a halt, while students in Boston held a “die-in” at Logan Airport. The environmental impact of the post-war consumer boom was beginning to be felt at that time. Oil spills, factory pollution and other ecological threats were on the rise, with little if any legislation in place to prevent them.

The protests brought together people from all walks of American life – accounting for about 10% of the US population – to demonstrate and voice their demands for sustainable change. The Earth Day website calls it the birth of the modern environmental movement.
What led to the street protests in 1970?
Concerned about increasing levels of unchecked environmental destruction, Junior Senator Gaylord Nelson of Wisconsin suggested a series of “teach-ins” on university campuses across the US in 1969 to raise awareness of environmental threats. Nelson was joined by Congressman Pete McCloskey and activist Denis Hayes to organize the teach-ins, but the group soon recognized an opportunity to broaden the event’s appeal beyond student populations.
The newly named Earth Day protest events attracted national media attention and support from around 20 million Americans across age and political spectrums, occupations and income groups.
What did the protests achieve?
The Earth Day demonstrations left an indelible mark on US policy. By the end of 1970, the US Environmental Protection Agency came into being and a stream of laws followed to help protect the environment . These included the National Environmental Education Act, the Occupational Safety and Health Act and the Clean Air Act. Further legislation was soon introduced to protect water quality and endangered species, and to control the use of harmful chemicals and pesticides.
When did Earth Day go global?
Earth Day went beyond the US in 1990. Around 200 million people from 141 countries joined efforts to boost recycling around the world that year, paving the way for the 1992 United Nations Conference on Environment and Development in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Climate change poses an urgent threat demanding decisive action. Communities around the world are already experiencing increased climate impacts, from droughts to floods to rising seas. The World Economic Forum's Global Risks Report continues to rank these environmental threats at the top of the list.
To limit global temperature rise to well below 2°C and as close as possible to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, it is essential that businesses, policy-makers, and civil society advance comprehensive near- and long-term climate actions in line with the goals of the Paris Agreement on climate change.
The World Economic Forum's Climate Initiative supports the scaling and acceleration of global climate action through public and private-sector collaboration. The Initiative works across several workstreams to develop and implement inclusive and ambitious solutions.
This includes the Alliance of CEO Climate Leaders, a global network of business leaders from various industries developing cost-effective solutions to transitioning to a low-carbon, climate-resilient economy. CEOs use their position and influence with policy-makers and corporate partners to accelerate the transition and realize the economic benefits of delivering a safer climate.
Contact us to get involved.
This “Earth Summit”, as it became known, led to the formation of the UN Convention on Climate Change and the UN Convention on Biological Diversity , along with the Commission on Sustainable Development to monitor and report on the implementation of Earth Summit agreements.
And as citizens were increasingly concerned with corporate impacts on the natural environment, big and small businesses started to feel the pressure to consider sustainability in their practice.
Have you read?
Is climate inaction a human rights violation, how earth observation from space helps advance climate change research, why is earth day important today.
As the millennium loomed, the Earth Day movement turned its attention to the growing reality of the impending climate crisis with a clear message for world leaders and business: urgent action is needed to address global warming.
It’s a message that is even more relevant today. The latest report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change states that without further immediate action to curb greenhouse gas emissions, the world is on course for temperatures 3.2°C above pre-industrial levels by 2100. This level of warming would be catastrophic for the planet and all life on it, including humans.
The year 2023 was the hottest ever recorded .
The World Economic Forum's Global Risks Report 2024 finds that environmental risks make up half of the top 10 risks over the next 10 years, with extreme weather events, critical change to Earth's systems, biodiversity loss and ecosystem collapse being the top three.

Nature is our biggest ally in fighting the climate crisis and has slowed global warming by absorbing 54% of human-related carbon dioxide emissions over the past 10 years. Yet, we are losing animals, marine species, plants, and insects at an unprecedented rate, not seen in 10 million years . Threats from human activity for food production and ocean use, infrastructure, energy and mining endanger around 80% of all threatened or near-threatened species .
Earth Day has become a leading light in the fight to combat climate change and nature loss. As we celebrate its 54th anniversary, we must make use of this truly global movement to act, as citizens and governments, as consumers and businesses, and as individuals and communities. Our survival could well depend on it.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Climate Crisis .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Reducing barriers to maritime fuel projects is key to decarbonizing shipping
Mette Asmussen and Takahiro Furusaki
April 18, 2024

Private climate finance: 4 things to consider
Laia Barbarà and Ameya Hadap
April 17, 2024

Governments want to make green good for business locally, without stalling economic progress globally
John Letzing

Why protecting the ocean floor matters for climate change
William Austin

This explorer and conservationist is training citizen scientists to save the planet
Rebecca Geldard

The EU is banning single-use plastics by 2030
Earth Day 2024: Planet Vs. Plastic
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Born in 1970, Earth Day has evolved into one of the largest civic events of all time. When we observe the 54 th Earth Day on April 22, the health and safety of the planet couldn’t be timelier, especially when it comes to dealing with the proliferation of plastic.
Over the past 60 years, around eight billion tons of plastic has been produced, according to a recent study in the journal Science Advances — 90.5 per cent of which has not been recycled . As a result, this year’s Earth Day theme— “Planet vs. Plastic”— demands a 60% reduction in the production of all plastics by 2040.
Just how big of a challenge is this? What type of numbers are we talking about? Here’s some perspective:
- In 1950, the world produced just two million tons of plastic. We now produce over 450 million tons .
- Half of all plastics ever manufactured have been made in the last 15 years.
- P roduction is expected to double by 2050.
- More than one million plastic water bottles are sold every minute.
- Every year, about 11 million tons of plastic waste escapes into the ocean.
- Only 9% of plastics ever produced has been recycled.
- Plastics often contain additives that can extend the life of products, with some estimates ranging to at least 400 years to break down.
Plastic is literally everywhere
An advertisement from the American Plastics Council in a 1997 edition of the New Yorker suggested that plastic wrappers and containers were the “sixth food group” that were there to keep contaminates out of our food.
Close up shot of microplastics on a hand.
In a twisted type of irony, Microplastics are now in almost everything and everywhere. Even in in much of the food we eat and water we drink! Microplastics are tiny particles of plastic (from ½ inch to microscopic) is synthetic that never disappears. As Stephen Jamieson recently explained in a Future of Supply Chain podcast, “We're ingesting a credit card size worth of plastic every single week as humans, and the real health impacts of that, we don't truly know and don't truly understand.”
What is the world doing about it?
In the Podcast, Stephen discussed the upcoming fourth session of the United Nations Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee he is attending in Ottawa, Canada from 23rd to the 29th of April. The goal is to develop an international legally binding instrument on plastic pollution, including in the marine environment, that will, as Stephen stated, “by early next year, actually ratify a new treaty at the United Nations to eliminate plastic pollution by 2040”.
What can businesses do about it?
Think about optimizing your entire supply chain for sustainability, rather than just individual functions.
For example, you may be pulling certain levers in your design processes, or manufacturing plants, only to realize that the sustainability gains in that process are offset by much a much larger negative impact on logistics or at the end of life of a product.
Perform Life Cycle Assessments on your products
A Life Cycle Assessment is a method for the compilation and evaluation of the inputs, outputs and the potential environmental impacts of a product throughout its life cycle (ISO standard 14040).
In simple terms, it’s a way by which you can understand the sustainability footprint of a product throughout it’s full lifecycle, from “cradle to grave.”
By enabling product footprints periodically across the entire product lifecycle, you can gain insights on the environmental impacts of your products across the entire lifecycle for disclosure and internal product and process optimization.
Design with end of life in mind
As Earthday.org says, “We need to invest in innovative technologies and materials to build a plastic-free world”.
And this starts with how we design products and packaging material in the goods we manufacture and deliver. The sooner we phase out all single use plastics, the better. We need responsible design and production solutions that facilitate a product and package redesign that enables companies to engage in the circular economy and reduces waste without sacrificing quality.
Enforce compliance at each step of the product lifecycle
If you look at most companies’ website for their mission statement or purpose, sustainability is front and center. And supply chain sits right in the middle, both as a major contributor to the problem, and a major opportunity to improve.
But you can’t manage regulatory and sustainability requirements, track registrations and substance volumes, classify products, and create compliance documents, as well as package, transport, and store hazardous materials properly with accurate labeling you won’t be able to measure how you are performing.
This takes a stepwise approach to:
Record: The first step is to gather all necessary ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) data along the entire value chain. This data cannot be found easily in one single system. Currently this is a highly manual and therefore time consuming effort compounded by data quality challenges.
Report: There are more than 600 ESG frameworks/standards out there and they are being constantly developed further (Take the evolving plastics taxes across Europe for example). The requirements for companies are constantly changing. A high effort is required to keep up with the current requirements to report along the respective regulatory & voluntary frameworks.
Act: In many companies sustainability action is already happening but in many cases this this is still partly disjoint from the strategy or not yet covering all business processes
What can we as individuals do about it?
The reality is that everybody has a role to play in the “Planet vs. Plastics battle, and the sustainability of the planet in general.
Little things like using reusable bottles and straws and bringing reusable bags to the store are great first step.
You can also go to earthday.org to learn more about the battle between planet vs. plastics, and find an event near you where you can help clean up the planet.
Let’s make every day Earth Day, to protect this beautiful rock we live on for future generations.
To learn more, listen to The Future of Supply Chain Podcast – Earth vs. Planet .
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

Understanding Your Purpose
The first question for any writer should be, "Why am I writing?" "What is my goal or my purpose for writing?" For many writing contexts, your immediate purpose may be to complete an assignment or get a good grade. But the long-range purpose of writing is to communicate to a particular audience. In order to communicate successfully to your audience, understanding your purpose for writing will make you a better writer.
A Definition of Purpose
Purpose is the reason why you are writing . You may write a grocery list in order to remember what you need to buy. You may write a laboratory report in order to carefully describe a chemistry experiment. You may write an argumentative essay in order to persuade someone to change the parking rules on campus. You may write a letter to a friend to express your excitement about her new job.
Notice that selecting the form for your writing (list, report, essay, letter) is one of your choices that helps you achieve your purpose. You also have choices about style, organization, kinds of evidence that help you achieve your purpose
Focusing on your purpose as you begin writing helps you know what form to choose, how to focus and organize your writing, what kinds of evidence to cite, how formal or informal your style should be, and how much you should write.
Types of Purpose
Don Zimmerman, Journalism and Technical Communication Department I look at most scientific and technical writing as being either informational or instructional in purpose. A third category is documentation for legal purposes. Most writing can be organized in one of these three ways. For example, an informational purpose is frequently used to make decisions. Memos, in most circles, carry key information.
When we communicate with other people, we are usually guided by some purpose, goal, or aim. We may want to express our feelings. We may want simply to explore an idea or perhaps entertain or amuse our listeners or readers. We may wish to inform people or explain an idea. We may wish to argue for or against an idea in order to persuade others to believe or act in a certain way. We make special kinds of arguments when we are evaluating or problem solving . Finally, we may wish to mediate or negotiate a solution in a tense or difficult situation.
Remember, however, that often writers combine purposes in a single piece of writing. Thus, we may, in a business report, begin by informing readers of the economic facts before we try to persuade them to take a certain course of action.
In expressive writing, the writer's purpose or goal is to put thoughts and feelings on the page. Expressive writing is personal writing. We are often just writing for ourselves or for close friends. Usually, expressive writing is informal, not intended for outside readers. Journal writing, for example, is usually expressive writing.
However, we may write expressively for other readers when we write poetry (although not all poetry is expressive writing). We may write expressively in a letter, or we may include some expressive sentences in a formal essay intended for other readers.
Entertaining
As a purpose or goal of writing, entertaining is often used with some other purpose--to explain, argue, or inform in a humorous way. Sometimes, however, entertaining others with humor is our main goal. Entertaining may take the form of a brief joke, a newspaper column, a television script or an Internet home page tidbit, but its goal is to relax our reader and share some story of human foibles or surprising actions.
Writing to inform is one of the most common purposes for writing. Most journalistic writing fits this purpose. A journalist uncovers the facts about some incident and then reports those facts, as objectively as possible, to his or her readers. Of course, some bias or point-of-view is always present, but the purpose of informational or reportorial writing is to convey information as accurately and objectively as possible. Other examples of writing to inform include laboratory reports, economic reports, and business reports.
Writing to explain, or expository writing, is the most common of the writing purposes. The writer's purpose is to gather facts and information, combine them with his or her own knowledge and experience, and clarify for some audience who or what something is , how it happened or should happen, and/or why something happened .
Explaining the whos, whats, hows, whys, and wherefores requires that the writer analyze the subject (divide it into its important parts) and show the relationship of those parts. Thus, writing to explain relies heavily on definition, process analysis, cause/effect analysis, and synthesis.
Explaining versus Informing : So how does explaining differ from informing? Explaining goes one step beyond informing or reporting. A reporter merely reports what his or her sources say or the data indicate. An expository writer adds his or her particular understanding, interpretation, or thesis to that information. An expository writer says this is the best or most accurate definition of literacy, or the right way to make lasagne, or the most relevant causes of an accident.
An arguing essay attempts to convince its audience to believe or act in a certain way. Written arguments have several key features:
- A debatable claim or thesis . The issue must have some reasonable arguments on both (or several) sides.
- A focus on one or more of the four types of claims : Claim of fact , claim of cause and effect , claim of value , and/or claim of policy (problem solving).
- A fair representation of opposing arguments combined with arguments against the opposition and for the overall claim.
- An argument based on evidence presented in a reasonable tone . Although appeals to character and to emotion may be used, the primary appeal should be to the reader's logic and reason.
Although the terms argument and persuasion are often used interchangeably, the terms do have slightly different meanings. Argument is a special kind of persuasion that follows certain ground rules. Those rules are that opposing positions will be presented accurately and fairly, and that appeals to logic and reason will be the primary means of persuasion. Persuasive writing may, if it wishes, ignore those rules and try any strategy that might work. Advertisements are a good example of persuasive writing. They usually don't fairly represent the competing product, and they appeal to image, to emotion, to character, or to anything except logic and the facts--unless those facts are in the product's favor.
Writing to evaluate a person, product, thing, or policy is a frequent purpose for writing. An evaluation is really a specific kind of argument: it argues for the merits of the subject and presents evidence to support the claim. A claim of value --the thesis in an evaluation--must be supported by criteria (the appropriate standards of judgment) and supporting evidence (the facts, statistics, examples, or testimonials).
Writers often use a three-column log to set up criteria for their subject, collect relevant evidence, and reach judgments that support an overall claim of value. Writing a three-column log is an excellent way to organize an evaluative essay. First, think about your possible criteria. Remember: criteria are the standards of judgment (the ideal case) against which you will measure your particular subject. Choose criteria which your readers will find valid, fair, and appropriate . Then, collect evidence for each of your selected criteria. Consider the following example of a restaurant evaluation:
Overall claim of value : This Chinese restaurant provides a high quality dining experience.
Problem Solving
Problem solving is a special kind of arguing essay: the writer's purpose is to persuade his audience to adopt a solution to a particular problem. Often called "policy" essays because they recommend the readers adopt a policy to resolve a problem, problem-solving essays have two main components: a description of a serious problem and an argument for specific recommendations that will solve the problem .
The thesis of a problem-solving essay becomes a claim of policy : If the audience follows the suggested recommendations, the problem will be reduced or eliminated. The essay must support the policy claim by persuading readers that the recommendations are feasible, cost-effective, efficient, relevant to the situation, and better than other possible alternative solutions.
Traditional argument , like a debate, is confrontational. The argument often becomes a kind of "war" in which the writer attempts to "defeat" the arguments of the opposition.
Non-traditional kinds of argument use a variety of strategies to reduce the confrontation and threat in order to open up the debate.
- Mediated argument follows a plan used successfully in labor negotiations to bring opposing parties to agreement. The writer of a mediated argument provides a middle position that helps negotiate the differences of the opposing positions.
- Rogerian argumen t also wishes to reduce confrontation by encouraging mutual understanding and working toward common ground and a compromise solution.
- Feminist argument tries to avoid the patriarchal conventions in traditional argument by emphasizing personal communication, exploration, and true understanding.
Combining Purposes
Often, writers use multiple purposes in a single piece of writing. An essay about illiteracy in America may begin by expressing your feelings on the topic. Then it may report the current facts about illiteracy. Finally, it may argue for a solution that might correct some of the social conditions that cause illiteracy. The ultimate purpose of the paper is to argue for the solution, but the writer uses these other purposes along the way.
Similarly, a scientific paper about gene therapy may begin by reporting the current state of gene therapy research. It may then explain how a gene therapy works in a medical situation. Finally, it may argue that we need to increase funding for primary research into gene therapy.
Purposes and Strategies
A purpose is the aim or goal of the writer or the written product; a strategy is a means of achieving that purpose. For example, our purpose may be to explain something, but we may use definitions, examples, descriptions, and analysis in order to make our explanation clearer. A variety of strategies are available for writers to help them find ways to achieve their purpose(s).
Writers often use definition for key terms of ideas in their essays. A formal definition , the basis of most dictionary definitions, has three parts: the term to be defined, the class to which the term belongs, and the features that distinguish this term from other terms in the class.
Look at your own topic. Would definition help you analyze and explain your subject?
Illustration and Example
Examples and illustrations are a basic kind of evidence and support in expository and argumentative writing.
In her essay about anorexia nervosa, student writer Nancie Brosseau uses several examples to develop a paragraph:
Another problem, lying, occurred most often when my parents tried to force me to eat. Because I was at the gym until around eight o'clock every night, I told my mother not to save me dinner. I would come home and make a sandwich and feed it to my dog. I lied to my parents every day about eating lunch at school. For example, I would bring a sack lunch and sell it to someone and use the money to buy diet pills. I always told my parents that I ate my own lunch.
Look at your own topic. What examples and illustrations would help explain your subject?
Classification
Classification is a form of analyzing a subject into types. We might classify automobiles by types: Trucks, Sport Utilities, Sedans, Sport Cars. We can (and do) classify college classes by type: Science, Social Science, Humanities, Business, Agriculture, etc.
Look at your own topic. Would classification help you analyze and explain your subject?
Comparison and Contrast
Comparison and contrast can be used to organize an essay. Consider whether either of the following two outlines would help you organize your comparison essay.
Block Comparison of A and B
- Intro and Thesis
- Description of A
- Description of B (and how B is similar to/different from A)
Alternating Comparison of A and B
- Aspect One: Comparison/contrast of A and B
- Aspect Two: Comparison/contrast of A and B
- Aspect Three: Comparison/contrast of A and B
Look at your own topic. Would comparison/contrast help you organize and explain your subject?
Analysis is simply dividing some whole into its parts. A library has distinct parts: stacks, electronic catalog, reserve desk, government documents section, interlibrary loan desk, etc. If you are writing about a library, you may need to know all the parts that exist in that library.
Look at your own topic. Would analysis of the parts help you understand and explain your subject?
Description
Although we usually think of description as visual, we may also use other senses--hearing, touch, feeling, smell-- in our attempt to describe something for our readers.
Notice how student writer Stephen White uses multiple senses to describe Anasazi Indian ruins at Mesa Verde:
I awoke this morning with a sense of unexplainable anticipation gnawing away at the back of my mind, that this chilly, leaden day at Mesa Verde would bring something new . . . . They are a haunting sight, these broken houses, clustered together down in the gloom of the canyon. The silence is broken only by the rush of the wind in the trees and the trickling of a tiny stream of melting snow springing from ledge to ledge. This small, abandoned village of tiny houses seems almost as the Indians left it, reduced by the passage of nearly a thousand years to piles of rubble through which protrude broken red adobe walls surrounding ghostly jet black openings, undisturbed by modern man.
Look at your own topic. Would description help you explain your subject?
Process Analysis
Process analysis is analyzing the chronological steps in any operation. A recipe contains process analysis. First, sift the flour. Next, mix the eggs, milk, and oil. Then fold in the flour with the eggs, milk and oil. Then add baking soda, salt and spices. Finally, pour the pancake batter onto the griddle.
Look at your own topic. Would process analysis help you analyze and explain your subject?
Narration is possibly the most effective strategy essay writers can use. Readers are quickly caught up in reading any story, no matter how short it is. Writers of exposition and argument should consider where a short narrative might enliven their essay. Typically, this narrative can relate some of your own experiences with the subject of your essay. Look at your own topic. Where might a short narrative help you explain your subject?
Cause/Effect Analysis
In cause and effect analysis, you map out possible causes and effects. Two patterns for doing cause/effect analysis are as follows:
Several causes leading to single effect: Cause 1 + Cause 2 + Cause 3 . . . => Effect
One cause leading to multiple effects: Cause => Effect 1 + Effect 2 + Effect 3 ...
Look at your own topic. Would cause/effect analysis help you understand and explain your subject?
How Audience and Focus Affect Purpose
All readers have expectations. They assume what they read will meet their expectations. As a writer, your job is to make sure those expectations are met, while at the same time, fulfilling the purpose of your writing.
Once you have determined what type of purpose best conveys your motivations, you will then need to examine how this will affect your readers. Perhaps you are explaining your topic when you really should be convincing readers to see your point. Writers and readers may approach a topic with conflicting purposes. Your job, as a writer, is to make sure both are being met.
Purpose and Audience
Often your audience will help you determine your purpose. The beliefs they hold will tell you whether or not they agree with what you have to say. Suppose, for example, you are writing to persuade readers against Internet censorship. Your purpose will differ depending on the audience who will read your writing.
Audience One: Internet Users
If your audience is computer users who surf the net daily, you could appear foolish trying to persuade them to react against Internet censorship. It's likely they are already against such a movement. Instead, they might expect more information on the topic.
Audience Two: Parents
If your audience is parents who don't want their small children surfing the net, you'll need to convince them that censorship is not the solution to the problem. You should persuade this audience to consider other options.
Purpose and Focus
Your focus (otherwise known as thesis, claim, main idea, or problem statement) is a reflection of your purpose. If these two do not agree, you will not accomplish what you set out to do. Consider the following examples below:
Focus One: Informing
Suppose your purpose is to inform readers about relationships between Type A personalities and heart attacks. Your focus could then be: Type A personalities do not have an abnormally high risk of suffering heart attacks.
Focus Two: Persuading
Suppose your purpose is to persuade readers not to quarantine AIDS victims. Your focus could then be: Children afflicted with AIDS should not be prevented from attending school.
Writer and Reader Goals
Kate Kiefer, English Department Readers and writers both have goals when they engage in reading and writing. Writers typically define their goals in several categories-to inform, persuade, entertain, explore. When writers and readers have mutually fulfilling goals-to inform and to look for information-then writing and reading are most efficient. At times, these goals overlap one another. Many readers of science essays are looking for science information when they often get science philosophy. This mismatch of goals tends to leave readers frustrated, and if they communicate that frustration to the writer, then the writer feels misunderstood or unsuccessful.
Donna Lecourt, English Department Whatever reality you are writing within, whatever you chose to write about, implies a certain audience as well as your purpose for writing. You decide you have something to write about, or something you care about, then purpose determines audience.
Writer Versus Reader Purposes
Steve Reid, English Department A general definition of purpose relates to motivation. For instance, "I'm angry, and that's why I'm writing this." Purposes, in academic writing, are intentions the writer hopes to accomplish with a particular audience. Often, readers discover their own purpose within a text. While the writer may have intended one thing, the text actually does another, according to its readers.
Purpose and Writing Assignments
Instructors often state the purpose of a writing assignment on the assignment sheet. By carefully examining what it is you are asked to do, you can determine what your writing's purpose is.
Most assignment sheets ask you to perform a specific task. Key words listed on the assignment can help you determine why you are writing. If your instructor has not provided an assignment sheet, consider asking what the purpose of the assignment is.
Read over your assignment sheet. Make a note of words asking you to follow a specific task. For example, words such as:
These words require you to write about a topic in a specific way. Once you know the purpose of your writing, you can begin planning what information is necessary for that purpose.
Example Assignment
Imagine you are an administrator for the school district. In light of the Columbus controversy, you have been assigned to write a set of guidelines for teaching about Columbus in the district's elementary and junior high schools. These guidelines will explain official policy to parents and teachers in teaching children about Columbus and the significance of his voyages. They will also draw on arguments made on both sides of the controversy, as well as historical facts on which both sides agree.
The purpose of this assignment is to explain the official policy about teaching Columbus' voyages to parents and teachers.
Steve Reid, English Department Keywords in writing assignments give teachers and students direction about why we are writing. For instance, many assignments ask students to "describe" something. The word "describe" specifically indicated the writer is supposed to describe something visually. This is very general. Often, assignments are looking for something more specific. Maybe there is an argument the instructor intends be formulated. Maybe there is an implied thesis, but often teachers use general words such as "Write about" or "Describe" something, when they should use more specific words like, "Define" or "Explain" or "Argue" or "Persuade."
Purpose and Thesis
Writers choose from a variety of purposes for writing. They may write to express their thoughts in a personal letter, to explain concepts in a physics class, to explore ideas in a philosophy class, or to argue a point in a political science class.
Once they have their purpose in mind (and an audience for whom they are writing), writers may more clearly formulate their thesis. The thesis , claim , or main idea of an essay is related to the purpose. It is the sentence or sentences that fulfill the purpose and that state the exact point of the essay.
For example, if a writer wants to argue that high schools should strengthen foreign language training, her thesis sentence might be as follows:
"Because Americans are so culturally isolated, we need a national policy that supports increased foreign language instruction in elementary and secondary schools."
How Thesis is Related to Purpose
The following examples illustrate how subject, purpose and thesis are related. The subject is the most general statement of the topic. The purpose narrows the focus by indicating whether the writer wishes to express or explore ideas or actually explain or argue about the topic. The thesis sentence, claim, or main idea narrows the focus even farther. It is the sentence or sentences which focuses the topic for the writer and the reader.
Reid, Stephen, & Dawn Kowalski. (1995). Understanding Your Purpose. Writing@CSU . https://writing.colostate.edu/guides/guide.cfm?guideid=94

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Purpose statements. A purpose statement announces the purpose, scope, and direction of the paper. It tells the reader what to expect in a paper and what the specific focus will be. Common beginnings include: "This paper examines . . .," "The aim of this paper is to . . .," and "The purpose of this essay is to . . ."
The first element of a purpose statement is the problem or opportunity that you are addressing. This should be a clear and specific description of the issue that you are trying to solve or the opportunity that you are pursuing. 2. The Target Audience. The second element is the target audience for your purpose statement.
Purpose is the reason why you are writing. You may write a grocery list in order to remember what you need to buy. You may write a laboratory report in order to carefully describe a chemistry experiment. You may write an argumentative essay in order to persuade someone to change the parking rules on campus.
What is the purpose of an essay? Every good essay is an argument incorporating proof, evidence, the opinions of critics and experts, logic, reasoning, and problem-solving solutions in order to convince the reader of something. Think of the essay as a conversation you are having with someone. If you are telling someone a story, you need context.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper.
A€purpose is the€aim or goal€of the writer or the written product; a strategy is a€means€of ... Writers often use definition for key terms of ideas in their essays. A€formal definition, the basis of most dictionary definitions, has three parts: the term to be defined, the class to which the term
In an argument essay your purpose is to convince or persuade a specific audience of a particular claim or viewpoint and support that with logic and evidence. Arguments are different from reports, whose purpose is to state information and facts, and are different from descriptive essays, whose purpose is to describe a particular object ...
The essay writing process consists of three main stages: Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline. Writing: Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion. Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling ...
The content of each paragraph in the essay is shaped by purpose, audience, and tone. The four common academic purposes are to summarize, to analyze, to synthesize, and to evaluate. Identifying the audience's demographics, education, prior knowledge, and expectations will affect how and what you write. Devices such as sentence structure, word ...
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
The purpose of descriptive text in this type of essay is to bring forth a clear picture in the reader's mind. Careful choice of words is critical in this type of essay. You will use them to trigger some form of emotion in the heart of your reader. 6. Contrast.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement, a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas. The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ...
Keep in mind that three main elements shape the content of each essay: Purpose: The reason the writer composes the essay. Audience: The individual or group whom the writer intends to address. Tone: The attitude the writer conveys about the essay's subject. Figure 1.2.1 1.2. 1.
Analysis is not limited to the sciences, of course. An analysis paragraph in academic writing fulfills the same purpose. Instead of deconstructing compounds, academic analysis paragraphs typically deconstruct documents. An analysis takes apart a primary source (an essay, a book, an article, etc.) point by point.
Keep in mind that three main elements shape the content of each essay (see Figure 2.3.1). [1] Purpose: The reason the writer composes the essay. Audience: The individual or group whom the writer intends to address. Tone: The attitude the writer conveys about the essay's subject.
The 3 Main Parts of an Intro Paragraph. In general, an intro paragraph is going to have three main parts: a hook, context, and a thesis statement. Each of these pieces of the intro plays a key role in acquainting the reader with the topic and purpose of your essay. Below, we'll explain how to start an introduction paragraph by writing an ...
The purpose of an essay is the writer's reason for writing the piece. Does the writer want to inform the readers of something? Does the writer want to tell a story to entertain readers? Perhaps ...
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
Practicing patience is an important way of cultivating the resilience required to both search for and pursue a purpose in life, as Anne Colby suggests in her 2020 paper, "Purpose as a Unifying Goal for Higher Education.". Practicing patience may encourage a more thoughtful approach to pursuing meaningful aims.
The terms "Black Americans", "Black people" and "Black adults" are used interchangeably throughout this report to refer to U.S. adults who self-identify as Black, either alone or in combination with other races or Hispanic identity.. Throughout this report, "Black, non-Hispanic" respondents are those who identify as single-race Black and say they have no Hispanic background.
It was originally published on 19 April 2022. Earth Day takes place every year on 22 April and is one of the biggest environmental protest movements on the planet. The theme of Earth Day this year is 'Planet vs. Plastics' - campaigners are calling for a 60% reduction in the production of plastics by 2040. The World Economic Forum's Global Risks ...
Over the past 60 years, around eight billion tons of plastic has been produced, according to a recent study in the journal Science Advances — 90.5 per cent of which has not been recycled. As a ...
Purpose is the reason why you are writing. You may write a grocery list in order to remember what you need to buy. You may write a laboratory report in order to carefully describe a chemistry experiment. You may write an argumentative essay in order to persuade someone to change the parking rules on campus.
Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Amdt1.3.6.1 Lemon's Purpose Prong. Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof; or abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press; or the right of the people peaceably to assemble, and to petition the Government for a redress of grievances. The Supreme Court's 1971 decision in ...
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates. In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills. Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative: you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence ...
Iran says Saturday night's bombardment of Israel is a response to the 1 April air strike on an Iranian consulate building in the Syrian capital Damascus, which killed senior Iranian commanders ...