The Site is down as we are performing important server maintenance, during which time the server will be unavailable for approximately 24 hours. Please hold off on any critical actions until we are finished. As always your feedback is appreciated.

- Study Packages
- NCERT Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Online Test

- Questions Bank
- Test Series
- Ncert Solutions
- Solved Papers
- Current Affairs
- JEE Main & Advanced
- Pre-Primary
- MP State Exams
- UP State Exams
- Rajasthan State Exams
- Jharkhand State Exams
- Chhattisgarh State Exams
- Bihar State Exams
- Haryana State Exams
- Gujarat State Exams
- MH State Exams
- Himachal State Exams
- Delhi State Exams
- Uttarakhand State Exams
- Punjab State Exams
- J&K State Exams

9th Class Science Tissues Question Bank
Done case based mcqs - tissues total questions - 30.

A) Contains undifferentiated cells done clear
B) They exhibit the property of food storage done clear
C) The meristem has a quality of self-renewal done clear
D) They have a single, large and prominent nucleus done clear
A) I Only done clear
B) II and IV done clear
C) III and IV done clear
D) VI and III done clear
question_answer 3) Refer to the diagram given in the question and identify the different meristems labelled as P, Q and R.
question_answer 4) Select the incorrect match.
A) Meristematic tissue - Growth tissue done clear
B) Apical meristem - Growing tips of stem and roots done clear
C) Lateral meristem - Plant elongation done clear
D) Intercalary meristem - Leaf base or internodes done clear
question_answer 5) Identify the incorrect statement from the following
A) Cells keep dividing in the meristematic zone done clear
B) Meristem produces new cells which are similar in appearance initially, but change later done clear
C) Meristematic tissues lack vacuoles done clear
D) Lateral meristem acts as pro-meristem. done clear
A) chloroplast done clear
B) chlorophyll done clear
C) cutin done clear
D) lignin done clear
question_answer 7) Which of the following is not a function performed by epidermis?
A) Protection against mechanical injury done clear
B) Protection against insects done clear
C) Protection against waterless done clear
D) Regulation of gaseous exchange done clear
A) I and IV done clear
B) II and III done clear
C) I and II done clear
D) III and IV done clear
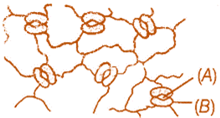
question_answer 10) Epidermal tissue system consists of
A) epidermal cells done clear
B) stomata done clear
C) roots done clear
D) AII of these done clear
A) simple done clear
B) complex done clear
C) free done clear
D) detached done clear
question_answer 12) Which of the following best describes Trachieds?
A) They are dead cells done clear
B) They are elongated and have pits done clear
C) Both [a] and [b] done clear
D) None of the above done clear
question_answer 13) Look at the diagram given below and identify A, B, X and Y from the options given below.
question_answer 14) Sieve tubes are devoid of...... but contain ......
A) cytoplasm; nucleus done clear
B) nucleus; cytoplasm done clear
C) companion cells; nucleus done clear
D) nucleus; tracheids done clear
question_answer 15) Which of the following is the correct sequence of transportation of food in plants?
A) Mesophyll cells \[\to \] Tracheids \[\to \] Vessels \[\to \] Plant parts done clear
B) Mesophyll cells \[\to \] Xylem vessels \[\to \] Sieve tubes \[\to \] Plant parts done clear
C) Epidermal cells \[\to \] Mesophyll cells \[\to \] Sieve tube \[\to \] Plant parts done clear
D) Mesophyll cells \[\to \] Sieve tubes \[\to \] Plant parts done clear
A) There are more dead supportive tissues in plants and more living tissues in animals done clear
B) There are more dead supportive tissues in animals and more living tissues in plants done clear
C) Organisation of plant tissues is quite complex when compared to animals done clear
question_answer 17) The diagram given in the passage depicts
A) connective tissue done clear
B) ciliated columnar epithelium done clear
C) simple squamous epithelium done clear
D) columnar epithelium done clear
question_answer 18) Which among the following is not an animal tissue?
A) Epithelial tissue done clear
B) Blood done clear
C) Glandular epithelium done clear
D) Epidermal tissue done clear
question_answer 19) In which of the following places, can we not find ciliated columnar epithelium?
A) Mouth done clear
B) Respiratory tract done clear
C) Kidney tubules done clear
D) Oviduct done clear
question_answer 20) Which among the following is a function of columnar epithelial tissues possessing cilia?
A) It helps in absorption, excretion and secretion of materials. done clear
B) Helps in forward movement of mucus done clear
C) Protects cells from injury done clear
D) It fills space inside organs done clear
A) Only I done clear
B) Only II done clear
C) Both I and II done clear
question_answer 22) Epidermal cells of roots bear long hair like parts that increase
A) transpiration rate done clear
B) photosynthesis rate done clear
C) total absorptive surface area done clear
D) AII of the above done clear
question_answer 23) Choose the pair that is correctly matched.
A) Ciliated epithelium-Inner lining of salivary duct done clear
B) Glandular epithelium-Moist surface of buccal cavity done clear
C) Cuboidal epithelium-Ducts of salivary gland done clear
D) Stratified epithelium-Oesophagus done clear
question_answer 24) ........ is not a simple permanent tissue.
A) Sclerenchyma done clear
B) Collenchyma done clear
C) Parenchyma done clear
D) Xylem done clear
question_answer 25) Which of the following is/are responsible for storage and mechanical support?
A) Parenchyma done clear
B) Xylem done clear
C) Collenchyma done clear
D) Both [a] and [c] done clear
A) Skeletal done clear
B) Smooth done clear
C) Cardiac done clear
D) Both [b] and [c] done clear
question_answer 27) Smooth muscles are also known as visceral muscles as they have the capacity to increase in size and bulk, whenever needed. Based on the information provided in the table, identify which of the following cannot be a function of these muscles?
A) Contraction of blood vessels done clear
B) Movement of food in alimentary canal done clear
C) Movement of body and skeleton done clear
D) Relaxation of blood vessels done clear
question_answer 28) Which of the following will be called multinucleated?
A) Skeletal muscles done clear
B) Cardiac muscles done clear
C) Smooth muscles done clear
D) Both [a] and [b] done clear
question_answer 29) Which of the following is/are voluntary muscles?
A) Smooth muscles done clear
C) Striated muscles done clear
question_answer 30) Select the statement that is true for cardiac muscles.
A) They are unstriated muscles done clear
B) Cells of these muscles are long cylindrical and multinucleate done clear
C) Cells of these muscles are long, cylindrical and uninucleate done clear
D) They are short and branched done clear
Study Package

Case Based MCQs - Tissues
Related question.

Reset Password.
OTP has been sent to your mobile number and is valid for one hour
Mobile Number Verified
Your mobile number is verified.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues

CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter-6 Important Questions - Free PDF Download
There are some very important questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 that students need to know about if they want to ensure that their results for their final exams are good enough. Vedantu provides the Class 9 Science Chapter 6 important questions in PDF format, so that students can easily prepare for their examinations. Students can download the important questions PDF for free from Vedantu and practice them to get good marks in the exams. Not to mention that a few extra questions for class 9 science chapter 6 will also give them some additional knowledge for sure.
Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions ,they can download Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions 2023-24 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions for other chapters:

Study Important Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues
Very Short Answer Questions: (1 Marks)
1. Where is apical meristem found?
Ans: The apical meristem is found in the growing tips of stems and roots in plants.
2. Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Ans: Sclerenchyma tissue.
3. What are the constituents of phloem?
Ans: The constituents of phloem are: sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma, phloem fibres(bast).
4. Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
Ans: Muscle/muscular tissue.
5. Vertical growth in plants takes place by –
(a) Lateral meristem
(b) apical meristem
(c) Intercalary meristem
(d) none of the above
Ans: (b) apical meristem
6. Which of these components of blood fight infection?
(c) Platelets
(d) serum
Ans: (b) WBC
7. In desert plants, rate of water loss gets reduced due to presence of :
(a) cuticle
(b) stomata
(d) suberin
Ans: (a) cuticle
8. Cartilage is not found in
(d) larynx
Ans: (c) kidney
9. Which of these types of cells is most likely to divide?
(a) Epidermis
(b) Parenchyma
(c) Meristem
Ans: (c) Meristem
10. Companion cells are associated with –
(a) Sieve tubes
(b) Sclerenchyma
(c) Vessels
(d) Parenchyma
Ans: (a) Sieve tubes
11. Which tissue has chloroplast in cells?
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Chlorenchyma
(c) Sclerenchyma
(d) Aerenchyma
Ans: (b) Chlorenchyma
12. Intestine absorbs due digested food materials. What type of epithelial are responsible for that?
(a) Stratified squamous epithelium
(b) columnar epithelium
(c) pseudostratified epithelium
(d) Cuboidal epithelium
Ans: (b) columnar epithelium
13. The meristematic tissue is found
(a) In flowers
(b) At the tip of the leaves
(c) Below the epidermis of stem
(d) At root tip
Ans: (d) At root tip
14. Movement of passage of food in the intestine is caused by the contraction of
(a) cardiac muscles
(b) unstriated muscles
(c) striated muscles
(d) Nerve tissue
Ans: (b) unstriated muscles
15. A long tubular outgrowth of a nerve cell which conducts impulses away from the cell body is termed as
(d) dendrite
Ans: (d) dendrite
16. You have been provided with narrow thick – walled living cells, elongated in shape and possessing thickening of cellulose and pectin these cells belong to:
(b) collenchyma
(c) sclerenchyma
Ans: (b) collenchyma
17. Which one of the following is the correct definition of the tissues?
(a) Group of dissimilar cells which perform similar function
(b) Group of similar cells which perform similar functions.
(c) group of similar cells which perform specific functions
(d) Group of dissimilar cells which perform different functions.
Ans: (a) Group of dissimilar cells which perform similar function
18. A long tree has several branches. The tissue that helps in the sideways conduction of water in the branches is:
(a) collenchyma
(b) xylem parenchyma
(c) parenchyma
(d) xylem vessels
Ans: (d) xylem vessels
19. White blood corpuscles:
(a)help in blood clotting
(b)help in transport of oxygen
(c)are enucleated
(d) protect the body from diseases
Ans: (d) protect the body from diseases
20. A person met with an accident in which two long bones of hand were dislocated. Which among the following may be possible reason?
(a) tendon break
(b) break of skeletal muscles
(c) ligament break
(d) Areolar tissue breaks
Ans: (b) ligament break
Short Answer Questions: (2 Marks)
1. What is a tissue?
Ans: It is a group of cells similar in origin and arrangement, they are specialized to perform a particular function. Tissue the cluster of cells in a manner to give the highest of possible efficiency of the required function. Examples of tissues are blood, phloem and muscle .
2. What are the constituents of phloem?
Ans: The five constituents of phloem are sieve cells, sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres
3. Name types of simple tissues.
Ans: Three types simple tissues are:
I. Parenchyma
II. Collenchyma
III. Sclerenchyma
4. What does a neuron look like?
Ans: A neuron comprises a cell body from which long thin hair-like parts(arise). Then the neuron has a single long part(axon) and many short, branched parts(dendrites).
5. How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Ans: Xylem tissue consist of four types of elements:
I. Tracheids
II. vessels
III. Xylem fibres
IV. Xylem parenchyma
6. How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Ans: Difference between simple tissues and complex tissues in plants is given below:
7. Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall.
Ans: Difference between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall is given below:
8. What are the functions of the stomata?
Ans: The functions of stomata are:
I. Gaseous exchange with the atmosphere.
II. Transpiration (formation of water vapours for the removal of excess water)
9. What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Ans: Cardiac muscles are the muscles of heart that pumps blood to all parts of body and it shows rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life without any fatigue. The cells of heart muscles are branched, cylindrical and uninucleate.
10. Name the following:
a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
Ans: Epithelial tissue
b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
Ans: Tendon
c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
Ans: Phloem
d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
Ans: Adipose tissue
e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
f) Tissue presents in the brain.
Ans: Nerve tissue
11. Identify the type of tissue in the following: skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
Ans: the type of tissues of the given is listed below:.
12. Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Ans: Parenchymatous tissue is present in the soft plant parts including leaf mesophyll , young stem, root, leaves, vascular bundles, flowers and fruits of plants.
13. What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Ans: Epidermis is a protective layer to all the plant parts. It will provide protection against water loss, Control the process of gas exchange, Epidermis secretes a waxy, water-resistant layer.
14. How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Ans: In the plant a strip of secondary meristem located in the cortex forms layers of cells that are dead and arranged in a compact manner without intercellular spaces which is cork. They have deposition of suberin in their walls which is very hard and impermeable hence protects plants from unfavorable conditions and microbial attack etc.
15. What are meristematic and permanent tissue?
Meristematic Tissue: dividing tissue is the reason for growth of plants occurs only in specific regions this is also known as meristematic tissue. Apical, lateral and intercalary are the classification of the meristematic tissues.
Permanent Tissue: The cells formed by meristematic tissue later lose the ability to divide as a result permanent tissue is formed. The process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and a function is called differentiation; this also leads to the development of permanent tissues.
16. What is the function of Tendon and ligament?
Ligaments: They connect one bone to another bone and another type of connective tissue. They are strong, elastic, consisting of yellow fibers.
Tendon: They connect muscle to bone and another type of connective tissue. They are tough, non – elastic, consisting of white fibres.
17. Draw a well labeled diagram of neuron
18. Differentiate the following activities on the basis of voluntary or involuntary:
a) Jumping of frog
Ans: Voluntary
b) Pumping of the heart
Ans: Involuntary
c) writing with hand
d) Moving of chocolate in stomach
19. Name the following:
a) Tissue that stores fats in our body.
b) Tissue presents in the brain
Ans: Nervous tissue
c) Connective tissue with fluid matrix.
d) Tissue that connects muscles to bones in humans.
Ans: Tendons
20. Write the difference between cartilage and bone.
Ans: Difference between cartilage and bone is listed below:
21. Which components of xylem are living and which ones are dead?
Ans: Xylem is composed of four elements:
Tracheid: Dead
Vessels: Dead
Xylem parenchyma: Living
Xylem fibres: Dead
22. Define due process of differentiation.
Ans: Dividing tissue is the reason for growth of plants occurs only in specific regions this is also known as meristematic tissue. The cells formed by meristematic tissue later lose the ability to divide as a result permanent tissue is formed. The process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and a function is called differentiation.
23. Define tissue. What is the utility of tissue in multicellular organisms?
Ans: Group of similar cells performing similar functions are called tissue. Millions of cells will be there in multicellular organisms. Specific functions are carried out by different groups of cells.
24. Mention characteristics of permanent tissues.
Ans: Characteristics of permanent tissues are:
Cells are large, comparatively thick walls and well developed .
Cytoplasm is present as a layer along the cell wall.
Bigger nucleus , vacuole is present in the cell.
There is lack of the power for the cell division in permanent tissue
25. Mention the functions of nervous tissue.
Ans: Function of nervous tissues are:
They conduct nerve impulses from one part of the body to another part.
The nervous tissues in the body are specialised for being stimulated and then pass on the stimulus very quickly from one place to another.
26. Animals of colder regions and fishes of cold water have thick layers of subcutaneous fat. Explain, why?
Ans: Thick layer of subcutaneous fat acts as an insulator. It retains heat in animals of colder regions and fishes of cold-water and thus maintains the body temperature. The heat loss will be less when the layer of subcutaneous fat is thicker.
27. Name the two main types of plant tissues.
Ans: Plant tissues are mainly divided into two types they are:
Meristematic tissue
Permanent tissue
28. Water hyacinth floats on the water surface. Explain.
Ans: Water hyacinth floats on the surface of water due to presence of aerenchyma. It is a special form of parenchyma, which contains air cavities. It provides buoyancy because of the air trapped inside which helps water hyacinth in floating because of the air trapped inside.
29. Name the two types of vascular tissues.
Ans: Types of vascular tissues are
Xylem: It conduct water and minerals from roots to the parts of the plant
Phloem: It conduct food from leaves to all parts of plant
30. How many types of elements are present in the phloem?
Ans: There are four types of elements are present in the phloem they are:
Sieve tube: Helps in conduction of food material
Companion cells: It helps sieve tube in conduction of food material
Phloem parenchyma: storage
Phloem fibres: It provides mechanical support.
Short Answer Questions: (3 Marks)
1. What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms?
Ans: Millions of cells will be there in multicellular organisms. Specific functions are carried out by different groups of cells. There is a clear-cut division of labour in multicellular organisms i.e., different parts of the body of a multicellular organism perform specific functions. For example, the brain controls all other parts of the body, the heart pumps blood to all parts of the body, kidneys remove waste materials from the body, sense organs collect information from external sources and transfer to the brain etc. All these functions would never be possible without formation of tissues in multicellular organisms.
2. Give three features of cardiac muscles.
I. Cardiac muscles are involuntary i.e.; they don’t work under our will.
II. Cells of cardiac muscles are cylindrical, branched, striated and uninucleate.
III. It shows rhythmic contraction and relaxation.
3. What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Ans: Areolar tissue is a connecting tissue found between skin and muscles, around our blood vessels and nerve cells and also in the bone marrow. Its functions are,
I. To fill the space inside organs.
II. To support internal organs.
III. To help in repair tissues
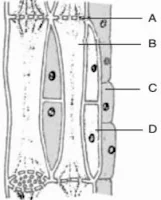
4. Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
Ans: The difference is shown as below,
5. Differentiate between striated, untreated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
Ans: difference between striated, untreated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body is given below :, 6. complete the table:.
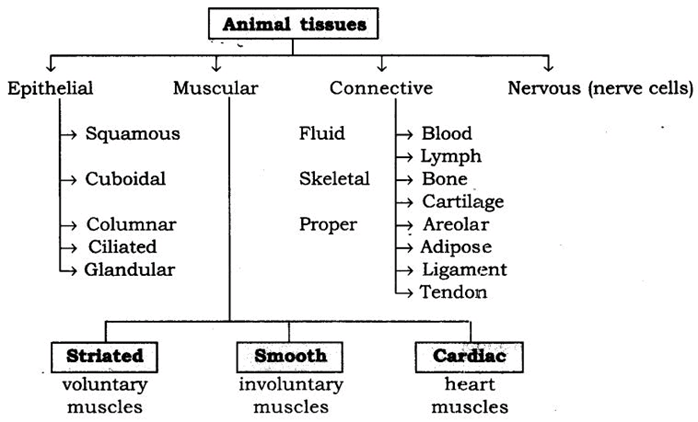
7. How many types of tissues are found in animals? Name the different types.
Ans: In animal four types of tissues are found:
Epithelium or Epithelial tissue (covering tissue): It forms outer protective covering all over the body.
Connective tissue (supporting tissue): It binds cells of other tissues in the body and give them rigidity and support.
Muscular tissue (contractile tissue): It helps the movement of the body by contraction and relaxation.
Nervous tissue: Its receiver stimulates and transmit the messages
8. Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles. Give one example of each
Ans: difference between voluntary and involuntary muscles are given below:.
9. What are the major functions of blood?
Ans: Blood is a type of connective tissue, and its functions are:
Blood flow can transport oxygen, food, hormones and waste material from one part of the body to the other part of the body
Blood carries oxygen and food to all cells. It also collects wastes from all parts of the body and carries them to the liver and kidney for disposal purposes.
Regulates temperature by distributing heat within the body
WBC’S protect due body from disease and helps in wound healing
Platelets help in blood clotting
10. Write about the functions of,
a) Epidermis
Ans: Epidermis, its main function is protection. It forms a waterproof coating, which reduces loss of water.
Ans: Cork: It is protective in function. It prevents desiccation, by preventing loss of water from the plant body. It prevents infection and mechanical injury
c) Stomata.
Ans: Stomata:These are the small opening which helps in exchange of gases
11. Differentiate between parenchyma and collenchyma
Ans: difference between parenchyma and collenchyma is given below:.
12. Mention the characteristics features of connective tissue .
Ans: Characteristics of connective tissue:
The cells are loosely spaced and are embedded in a non – living intercellular matrix
The intercellular matrix may be like jelly, fluid, dense or rigid.
Depending on the connective tissues functions the nature of the matrix varies.
13. How does cardiac muscle differ from both voluntary and involuntary muscles in both structure and function?
Ans: Cardiac muscles are the muscles of the heart that pumps blood to all parts of the body and it shows rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life without any fatigue. The cells of heart muscles are branched, cylindrical and uninucleate.
Cardiac Muscles are involuntary
More akin in structure and only found in heart.
They function throughout the life
14. Write differences between blood and lymph.
Ans : difference between blood and lymph is listed below:.
15. Give reasons for:
a) Intercellular spaces are absent in sclerenchyma tissues.
Ans: Sclerenchyma cells are closely packed Hence intercellular spaces are absent. Its tissues are dead simple permanent tissues.
b) Meristematic cells have a prominent muscle and dense cytoplasm but they lack muscles
Ans: Meristematic cells have continuously dividing cells. Cells of meristem are not differentiated. It continuously divides and forms new cells which increase length and girth of the plant body.
c) We get crunchy and granular feeling, when we chew pear fruit.
Ans: due to presence of stone cells or grit cells, known as sclereids
16. Why is epidermis important for the plants?
Ans: Epidermis is the Outer protective covering of plants:
Epidermis is covered with a waterproof coating or layer called cuticle which can reduce water loss.
It also helps in the exchange of gases by the small pores called stomata.
17. Describe different types of meristems.
Ans: Based on their location in the plant body, meristems are of three types.
a) Apical meristems – Occurs at the growing tips of roots and shoots and brings about an increase in length of the plant
b) Lateral meristems – It occurs on the sides almost parallel to the long axis of the root, stem and its branches. Brings about an increase in the width or girth of the stem or root.
c) Intercalary meristems – located near to the node. Cells are very active, and have dense cytoplasm and thin cellulose. lack of vacuoles in intercalary meristems.
18. If you are provided with three slides, each containing one types muscles fibres, how will you identify them?
Ans: If we are provided with three slides, each containing one types muscles fibres, we can identify them by following points:
a) Skeletal muscles or voluntary muscles show alternate light and dark bands under microscope.
b) Unstriated muscles or involuntary muscles show no light or dark bands, multinucleate.
c) Cardiac muscles fibres show light and dark bands, fibres are interconnected with one or two nuclei.

19. If a potted plant is covered with a glass jar, water vapours appear on the wall of the glass jar. Explain why?
Ans: This is because of the process called transpiration. Plants always lose water from the surface of leaves. Water reaches leaves by xylem vessels, where evaporation takes place by stomata. Gaseous exchange and also removal of excess water are performed by the Stomata present in the leaves.
20. Identify the following tissue and mention their function.
A) Parenchyma: stores food , it sometimes contains chlorophyll so performs photosynthesis, after that it is called chlorenchyma, in aquatic plants parenchyma to help them float because of large air cavities.
B) Collenchyma: It provides mechanical strength and allows bending of various parts of a plant without breaking.
C) Sclerenchyma: Provides strength to the plant parts, makes the plant hard and stiff.
21. Differentiate between meristematic and permanent tissue.
Ans: difference between meristematic and permanent tissue is given below:.
With the help of important questions for Tissues Class 9 chapter , students can revise the chapter for their exam in a better way. They can prepare their notes by referring to these important questions and answers, hence get some time for revision as well. These important questions for class 9 science tissues can be downloaded from Vedantu mobile app and official website. Also, the CBSE Class 9 tissues important questions will help them to understand the proper answer-writing technique for this chapter.
With these questions, students will be able to learn basics such as what tissues are and what is their application in living organisms.
The students also get to know about the plant tissues and animal tissues along with some other details such as meristematic tissues and permanent tissues with the help of the Class 9 Science chapter Tissue important questions.
The students can also know about different types of muscles.
Important Questions For Class 9 Chapter 6 Science
Explain why water vapor appears on the leaves of a potted plant when it is covered with a jar of glass.
Explain the difference between voluntary and involuntary muscles. Provide examples for each.
What structure is responsible for the protection of plant bodies against parasite invasion.
Explain the importance of the epidermis for the plants.
Differentiate between meristematic and permanent tissues in plants.
These questions provide some deep insights into the chapter for the students who need to know what the topic is all about. Also, the important questions for tissues class 9 play a very important role when it comes to giving some information to the students about certain entrance examinations as biology is a very common subject in these and to download the questions would really be a great idea in such cases. All they have to do is pay attention to their classes and make sure that they practice the class 9th science chapter 6 important questions more and more to gain better knowledge and information.
Why Choose Us to Get Extra Questions of Tissues Class 9
One of the main reasons why students need to choose Vedantu’s class 9 science ch 6 important questions is that we have the best materials for studying. Students that need some help in clearing their doubts can rely on these questions to gain a better understanding of the chapter.
We also have a team of expert teachers and professors who have personally selected these important questions for class 9 science chapter 6 . So, these questions will be very authentic and reliable. Not to mention that all of these questions are created according to the CBSE syllabus as well as the NCERT guidelines. The scope of scoring marks for students becomes a lot higher due to this fact.
We certainly aspire to provide the best help available with the class 9 science chapter 6 important questions. For students that need some help in scoring some good marks in their examinations for the finals, there is no doubt that taking the help of extra questions for class 9 science chapter 6 will really be a very good idea as they might find exactly what they are looking for and much more. Download the class 9 science chapter 6 questions from us right away.
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 9

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues
Q1. What is the Role of the Epidermis in Plants?
The epidermis is a single layer of cells that covers the leaves, flowers, stems, roots, etc. It acts as a boundary between the plant and the external environment. The role of the epidermis in plants is to provide protection to the various parts of the plants. Moreover, it can absorb water from the soil, from the roots and allows the exchange of gases through stomata.
Q2. What is the Main Difference Between Tendons and Ligaments?
The main difference between tendons and ligaments is that tendons connect muscles to bones while ligaments connect one bone to another. Tendons are tough, non-elastic and contain white fibres. Ligaments are strong, non-elastic and consist of yellow fibres.
Q3. Which Website Caters to Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues?
Preparing for exams can be overwhelming for students at times. Vedantu, India’s leading online educational platform, caters to various types of study materials to make the learning process easy and effective. Among such materials, one of the most useful is chapter-wise important questions. Vedantu provides the free PDF of Important Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues. The questions are selected by subject matter experts. The online repository for important questions is prepared considering the exam pattern and curriculum. Students can also avail the answers to these questions. The answers are also provided by subject experts and include all the important information.
Q4. What are the Tissues? What are the Simple and Complex Tissues?
The group of cells similar in origin and structure can be defined as a tissue. These cells are specialised to perform a particular function. For instance, muscle cells in our body form muscle tissues that bring about body movement or specific functions. Tissues can be broadly classified as Simple Tissues and Complex Tissues.
Simple Tissues: It is made up of only one type of cell. All the cells of such tissues work as individual units to perform a particular function. Example: parenchyma, collenchyma, etc.
Complex Tissues: It is made up of more than one type of cells. These cells work together as a single unit to perform a particular function. Example: Xylem, Phloem, etc.
Q5. What is the importance of tissue according to Chapter 6 of Class 9 Science?
Tissues refer to a group of blood cells that work together to perform certain jobs in the body. Tissues are important to the body as they provide a level of organization in all living organisms. Apart from this, tissues help to protect the body organs for any damage or injury. It even connects body parts to other bones in the body. Tissues also provide nutrition to the body. One of the major importance of tissues is that it helps to fight many infections.
Q6. Where can I download NCERT Solutions for Chapter 6 of Class 9 Science?
Vedantu provides you with an opportunity to download NCERT Solutions for Chapter 6 of Class 9 Science PDF for free. There are many important questions and answers available in NCERT Solutions that will help you ace your exams. These important questions have been taken from all the important topics and concepts of the chapter. These solutions are available at free of cost on Vedantu(vedantu.com) and mobile app. Most of these questions are a part of the NCERT Textbook, hence you will be able to understand the chapter better. There are in-text questions and exercise questions that are available in NCERT Solutions.
Q7. What is the function of stomata?
Stomata is known as the pores that are available in the cells of leaves. The outermost layer available in the cells is known as the epidermis. This epidermis is very porous in nature, and these pores are known as Stomata. Stomata are very important to keep the plants alive. One of the main functions of stomata refers to the exchange of gases in and out of plants. Apart from this, the stomata even helps in the process of transpiration.
Q8. What does a neuron look like?
Neuron helps to pass informational messages throughout the body. A neuron refers to a nerve cell. This nerve cell consists of a cell body that contains cytoplasm and a nucleus and a thin hair-like structure that emerges from it. Every neuron consists of an elongated part known as an axon. It also contains small and short branch-like structures known as dendrites. A single neuron can grow up to a meter long and not more than that.
Q9. How can I study Chapter 6 Tissues of Class 9 Science?
While you're preparing for your exams, you need to stick to the syllabus. To study for Chapter 6 Tissues of Class 9 Science, you must pay attention to all the important questions. You should solve practice papers, sample papers, and previous year's question papers. By doing this you will get an idea of all the important questions. In most sample papers there are some questions which are repeated. Looking at this, you will be able to figure out what the important questions are.
CBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions
Cbse study materials.

Class 9 Science Case Study Questions PDF Download
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 9th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Class 9 Science Case Study Questions play a crucial role in the field of science education as they provide real-life scenarios for students to analyze, apply their knowledge, and develop problem-solving skills. This article aims to present a comprehensive collection of case study questions for Class 9 Science , covering various topics and concepts.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

CBSE Class 9 Science Exam will have a set of questions based on case studies in the form of MCQs. The CBSE Class 9 Science Question Bank on Case Studies, provided in this article, can be very helpful to understand the new format of questions. Share this link with your friends.
If you want to want to prepare all the tough, tricky & difficult questions for your upcoming exams, this is where you should hang out. CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 will provide you with detailed, latest, comprehensive & confidence-inspiring solutions to the maximum number of Case Study Questions covering all the topics from your NCERT Text Books !
Table of Contents
CBSE Class 9th SCIENCE Chapterwise Case Study Question & Solution
Case study questions provide students with real-life scenarios that require critical thinking and application of scientific concepts. They help students understand the practical application of scientific principles and develop problem-solving skills in various scientific disciplines.
Chapterwise Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science
Inboard exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning. Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. For Science subjects, there would be 5 case-based sub-part questions, wherein a student has to attempt 4 sub-part questions.
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure?
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Structure of Atom
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Tissues
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Gravitation
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Work and Energy
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Sound
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Why do we Fall ill
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 14 Natural Resources
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources
The above Case studies for Class 9 Science will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 9 Science Case Studies have been developed by experienced teachers of schools.studyrate.in for the benefit of Class 10 students.
Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions
Benefits of Case Studies in Science Education
Case studies offer several advantages over traditional teaching methods. Here are some key benefits:
- Real-World Application : Case studies present authentic scenarios, enabling students to understand how scientific concepts are applied in real-life situations.
- Critical Thinking : Analyzing case studies requires students to think critically, make connections, and apply scientific knowledge to solve problems.
- Interdisciplinary Approach : Case studies often involve multiple scientific disciplines, fostering an interdisciplinary understanding of complex issues.
- Engagement and Active Learning : Case studies actively engage students in the learning process, promoting active participation, discussion, and collaboration.
- Skill Development : Case studies develop essential skills such as analytical thinking, problem-solving, and effective communication of scientific concepts.
Importance of Practicing Case Study Questions
Practicing case study questions is crucial for Class 9 Science students to enhance their understanding and application of scientific concepts. Here’s why it is important:
- Application of Knowledge : Case studies allow students to apply their theoretical knowledge to practical situations, bridging the gap between theory and real-world scenarios.
- Developing Analytical Skills : Analyzing case studies improves students’ ability to identify relevant information, make connections, and draw logical conclusions.
- Problem-Solving Skills : Case studies present complex problems that require students to think critically and develop effective problem-solving strategies.
- Enhanced Exam Performance : Practicing case study questions familiarizes students with the format and types of questions they may encounter in exams, leading to improved performance.
Subjects Covered in the Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science
The case study questions for Class 9 Science cover the following subjects:
- Motion and Forces
- Light and Reflection
- Electricity
- Matter and Its Properties
- Atoms and Molecules
- Structure of the Atom
- Chemical Reactions
- Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Diversity in Living Organisms
- Natural Resources
Tips for Approaching Case Study Questions
To tackle case study questions effectively, consider the following tips:
- Read Carefully : Pay close attention to the details provided in the case study, as they hold crucial information for solving the problem.
- Analyze Methodically : Break down the problem into smaller components and analyze each part systematically.
- Apply Relevant Concepts : Identify the scientific principles relevant to the case study and apply them appropriately.
- Consider Multiple Perspectives : Explore different angles and viewpoints while proposing solutions, taking into account various scientific factors.
- Provide Justifications : Support your answers with scientific explanations and logical reasoning to strengthen your responses.
The Class 9 Science Case Study Questions provided in this article serve as a valuable resource for students seeking to enhance their scientific knowledge and problem-solving skills. By practicing these case studies, students can develop a deeper understanding of scientific concepts and their practical applications. Embrace this opportunity to engage with real-world scenarios and strengthen your scientific acumen.
Q1: Are the Class 9 Science Case Study Questions aligned with the official curriculum?
Yes, the Class 9 Science Case Study Questions presented in this article are aligned with the official curriculum. They cover relevant topics and concepts that students need to study for their exams.
Q2: Can practicing case study questions alone guarantee success in Class 9 Science exams?
Practicing case study questions is an important part of exam preparation, but it should be complemented with a thorough understanding of the subject matter. It is advisable to study the concepts in detail, refer to textbooks, and engage in other learning activities to achieve success in exams.
Q3: Where I Can get Class 9 Science Case Study Questions ?
You can practice Class 9 Science Case Study Questions on schools.studyrate.in for free.
You Might Also Like
Class 9 maths case study questions of chapter 13 surface areas and volumes, class 9 maths case study questions chapter 14 statistics, class 9 maths case study questions of chapter 15 probability pdf download, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE Expert

Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science PDF Download
Download PDF Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 9 Exams Exam 2023-24. With the help of our well-trained and experienced faculty, we provide solved examples and detailed explanations for the recently added Class 9 Science case study questions .

Case study questions are based on real or hypothetical scenarios that require students to analyze, evaluate, and apply scientific concepts to solve problems or make informed decisions. They often present a detailed context, providing students with the opportunity to demonstrate their understanding of the subject matter beyond basic recall.
Table of Contents
Class 9 Science: Case Study Questions
The inclusion of case study questions in Class 9 science CBSE is a great way to engage students in critical thinking and problem-solving. By working through real-world scenarios, Class 9 Science students will be better prepared to tackle challenges they may face in their future studies and careers. Class 9 Science Case study questions also promote higher-order thinking skills, such as analysis and synthesis. In addition, case study questions can help to foster creativity and innovation in students. As per the recent pattern of the Class 9 Science examination, a few questions based on case studies/passages will be included in the CBSE Class 9 Science Paper. There will be a paragraph presented, followed by questions based on it.
Chapterwise Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure?
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Structure of Atom
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Tissues
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Gravitation
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Work and Energy
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Sound
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Why do we Fall ill
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 14 Natural Resources
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources
You can find a wide range of solved case studies on cbseexperts, covering various topics and concepts. Class 9 Science case studies are designed to help you understand the application of various concepts in real-life situations.
Class 9 Science Syllabus
Unit I: Matter-Nature and Behaviour
Definition of matter; solid, liquid, and gas; characteristics – shape, volume, density; change of statementing (absorption of heat), freezing, evaporation (cooling by evaporation), condensation, sublimation.
Nature of matter: Elements, compounds, and mixtures. Heterogeneous and homogenous mixtures, colloids, and suspensions. Physical and chemical changes (excluding separating the components of a mixture).
Particle nature and their basic units: Atoms and molecules, Law of Chemical Combination, Chemical formula of common compounds, Atomic and molecular masses.
Structure of atoms: Electrons, protons and neutrons, Valency, Atomic Number and Mass Number, Isotopes and Isobars.
Unit II: Organization in the Living World
Cell – Basic Unit of life: Cell as a basic unit of life; prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, multicellular organisms; cell membrane and cell wall, cell organelles and cell inclusions; chloroplast, mitochondria, vacuoles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus; nucleus, chromosomes – basic structure, number.
Tissues, Organs, Organ System, Organism: Structure and functions of animal and plant tissues (only four types of tissues in animals; Meristematic and Permanent tissues in plants).
Unit III: Motio n, Force, and Work
Motion: Distance and displacement, velocity; uniform and non-uniform motion along a straight line; acceleration, distance-time and velocity-time graphs for uniform motion and uniformly accelerated motion, elementary idea of uniform circular motion.
Force and Newton’s laws: Force and Motion, Newton’s Laws of Motion, Action and Reaction forces, Inertia of a body, Inertia and mass, Momentum, Force and Acceleration.
Gravitation: Gravitation; Universal Law of Gravitation, Force of Gravitation of the earth (gravity), Acceleration due to Gravity; Mass and Weight; Free fall. Floatation: Thrust and Pressure. Archimedes’ Principle; Buoyancy.
Work, Energy and Power: Work done by a Force, Energy, power; Kinetic and Potential energy; Law of conservation of energy (excluding commercial unit of Energy).
Sound: Nature of sound and its propagation in various media, speed of sound, range of hearing in humans; ultrasound; reflection of sound; echo.
Unit IV: Food Production
Plant and animal breeding and selection for quality improvement and management; Use of fertilizers and manures; Protection from pests and diseases; Organic farming.
Books for Class 9 Science Exams

Benefits of Case Study Questions
- Enhancing Analytical Skills : Case study questions challenge students to analyze complex scenarios, identify relevant information, and derive meaningful insights. By engaging with these questions, students develop critical analytical skills that are essential for scientific thinking and problem-solving.
- Promoting Critical Thinking : Case study questions encourage students to think critically and evaluate different perspectives. They require students to reason, make logical deductions, and justify their answers with supporting evidence. This process helps in honing their critical thinking abilities, enabling them to approach problems from multiple angles.
- Encouraging Practical Application of Concepts : By presenting real-world or hypothetical situations, case study questions promote the application of scientific concepts in practical scenarios. This application-based approach fosters a deeper understanding of the subject matter and helps students see the relevance of what they learn in the classroom to everyday life.
Case study questions of Class 9 Science provide students with an opportunity to apply their knowledge, enhance analytical skills, and think critically. By understanding the format, benefits, and effective strategies for answering case study questions, students can excel in this form of assessment. While challenges may arise, practicing time management, improving information extraction skills, and enhancing observation abilities will enable students to overcome these obstacles and perform well. Embracing case study questions as a valuable learning tool can contribute to a holistic understanding of scientific concepts and foster problem-solving abilities.
1. What is the purpose of case study questions in Class 9 Science?
Case study questions serve the purpose of evaluating a student’s understanding of scientific concepts, their ability to apply knowledge in real-life situations, and their analytical and critical thinking skills.
2. How can case study questions help improve analytical skills?
Case study questions require students to analyze complex scenarios, identify relevant information, and derive meaningful insights. Regular practice with such questions can significantly enhance analytical skills.
3. Are case study questions difficult to answer?
Case study questions can be challenging due to their comprehensive nature and the need for critical thinking. However, with practice and effective strategies, students can develop the skills necessary to answer them effectively.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science - Pdf PDF Download
Cbse case study questions for class 9 science.
Case based questions for Class 9 Science involve exploring a real-world situation through scientific analysis and inquiry. These questions allow students to make connections between science concepts and the world around them, as well as develop critical thinking skills. For example, a case study may involve challenging a student to determine the cause of an illness in a local population by researching the disease, its symptoms, and the local environment. Through this exercise, students learn how to identify a problem, break it down into parts, and come up with a solution that is supported by evidence. This type of question helps students to understand how science is at the centre of solving real-world problems.
Chapter Wise Case Based Questions for Class 9 Science
Chapter-wise case-based questions for Class 9 Science are a set of questions based on specific chapters or topics covered in the science textbook. These questions are designed to help students apply their understanding of scientific concepts to real-world situations and events.
The CBSE Class 9 Case Based Questions can be accessed from Chapetrwise Links provided below:
Chapter 1: Matter In Our Surroundings
Chapter 2: is matter around us pure.
- Case Based Questions: Is Matter Around Us Pure?
Chapter 3: Atoms And Molecules
- Case Based Questions: Atoms And Molecules
Chapter 4: Structure Of The Atom
- Case Based Questions: Structure Of The Atom
Chapter 5: The Fundamental Unit Of Life
- Case Based Questions: The Fundamental Unit Of Life- 1
- Case Based Questions: The Fundamental Unit Of Life- 2
Chapter 6: Tissues
- Case Based Questions: Tissues- 1
- Case Based Questions: Tissues- 2
Chapter 7: Motion
- Case Based Questions: Motion-1
- Case Based Questions: Motion- 2
Chapter 8: Force And Laws Of Motion
- Case Based Questions: Force And Laws Of Motion
Chapter 9: Gravitation
- Case Based Questions: Gravitation
Chapter 10: Work And Energy
- Case Based Questions: Work And Energy- 1
- Case Based Questions: Work And Energy- 2
Chapter 11: Diversity In Living Organisms
Chapter 12: sound, chapter 13: natural resources, chapter 14: improvement in food resource, chapter 15: why do we fall ill.
- Case Based Questions: Why Do We Fall Ill?
Weightage of Case Based Questions in Class 9 Science
Why are Case Study Questions important in Science Class 9?
- Enhance critical thinking: Case study questions require students to analyze a real-life scenario and think critically to identify the problem and come up with possible solutions. This enhances their critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Apply theoretical concepts: Case study questions allow students to apply theoretical concepts that they have learned in the classroom to real-life situations. This helps them to understand the practical application of the concepts and reinforces their learning.
- Develop decision-making skills: Case study questions challenge students to make decisions based on the information provided in the scenario. This helps them to develop their decision-making skills and learn how to make informed decisions.
- Improve communication skills: Case study questions often require students to present their findings and recommendations in written or oral form. This helps them to improve their communication skills and learn how to present their ideas effectively.
- Enhance teamwork skills: Case study questions can also be done in groups, which helps students to develop teamwork skills and learn how to work collaboratively to solve problems.
In summary, case study questions are important in Class 9 because they enhance critical thinking, apply theoretical concepts, develop decision-making skills, improve communication skills, and enhance teamwork skills. They provide a practical and engaging way for students to learn and apply their knowledge and skills to real-life situations.
Class 9 Science Curriculum at Glance
The Class 9 Science curriculum in India covers a wide range of topics and concepts. Here is a brief overview of the Science curriculum at a glance:
- Physics: The Physics section includes topics such as motion, force, work and energy, sound, and light.
- Chemistry: The Chemistry section includes topics such as matter, atoms and molecules, structure of the atom, and chemical reactions.
- Biology: The Biology section includes topics such as cell structure and functions, tissues, diversity in living organisms, natural resources, and environmental management.
- Practical Work: The Science curriculum also includes practical work, where students perform experiments to observe and understand scientific phenomena.
The Class 9 Science curriculum is designed to provide a strong foundation in science and prepare students for higher education in the field. The curriculum is structured to develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills, and to promote the application of scientific concepts in real-life situations. The curriculum is also designed to help students prepare for competitive exams and develop a strong scientific base for future academic and professional pursuits.
Students can also access Case Based Questions of all subjects of CBSE Class 9
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Maths
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Social Science
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 English
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Hindi
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Sanskrit
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Case Based Questions for Class 9 Science
Are case-based questions on the class 9 science exam.
Yes, case-based questions are often included in science exams at the class 9 level as they test students' ability to apply their scientific knowledge and skills to real-world situations.
How are case-based questions different from traditional science questions?
Traditional science questions typically focus on testing students' knowledge of specific facts, concepts, and theories. Case-based questions, on the other hand, require students to use their knowledge and understanding to analyze and interpret real-world situations and make informed decisions.
How can students prepare for case-based questions in science?
To prepare for case-based questions in science, students should practice analyzing data and interpreting scientific experiments. They should also work on developing their critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Top Courses for Class 9
Faqs on cbse case study questions for class 9 science - pdf, important questions, cbse case study questions for class 9 science - pdf, sample paper, previous year questions with solutions, practice quizzes, past year papers, objective type questions, shortcuts and tricks, video lectures, semester notes, mock tests for examination, study material, viva questions, extra questions.

CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science - Pdf Free PDF Download
Importance of cbse case study questions for class 9 science - pdf, cbse case study questions for class 9 science - pdf notes, cbse case study questions for class 9 science - pdf class 9, study cbse case study questions for class 9 science - pdf on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country.
- NCERT SOLUTIONS
- CHAPTER NOTES
- PRIVACY POLICY

- RD SHARMA SOLUTIONS
- IIT JEE SOLVED QUESTIONS
Class 9 Science Tissues

About STUDYGUIDE360 STUDYGUIDE360 is a student centric educational web portal which provides quality test papers and study materials for the students preparing for CBSE or targeting various entrance exams. During past few years, a number of surveys on students were made to better understand their problems regarding their studies and their basic requirement.
LIKE US ON FACEBOOK
Contact form.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 6: Tissues
- No videos or articles available in this lesson
- Meristematic tissue Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Simple and Complex Permanent tissue Get 5 of 6 questions to level up!
- Squamous epithelium (Opens a modal)
- Ciliated epithelium (Opens a modal)
- Glandular epithelium (Opens a modal)
- Epithelial tissue Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Connective tissue Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Muscular tissue and neural tissue Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!

Extra Questions for Class 9th: Ch 6 Tissues Science
Extra questions for class 9th: ch 6 tissues (science) important questions answer included.
Contact Form
Extra Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
Extra questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues with answers is given below. Our subject expert prepared these solutions as per the latest NCERT textbook. These questions will be helpful to revise the all topics and concepts. CBSE Class 9 extra questions are the most simple and conceptual questions that are prepared by subject experts for the students to study well for the final exams. By solving these extra questions, students can be very efficient in their exam preparations.
Tissues Class 9 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Very short answer questions.
1: Name the tissues responsible for the movement of the body. Answer: Muscle tissue and nervous tissue
2: How does neuron look like? Answer: A neuron is the unit cell of nervous tissue. It is a thread-like structure with cell body and axon.
3: Name the types of simple tissues. Answer: (a) Parenchyma (b) Collenchyma (c) Sclerenchyma
4: Name the types of complex tissues. Answer: Xylem and phloem.
5: Where is apical meristem found? . Answer: It is present at the growing tips of stem and root, it increases the length of the stem and roots.
6: Which tissue make up the husk of coconut? Answer: Sclerenchyma.
7: What are the constituents of phloem? Answer: Phloem constitutes the sieve tubes, companion cell, phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres.
8: Define aerenchyma. Answer: When the cells have air-filled large cavities of parenchyma, it is called aerenchyma. Aerenchyma helps aquatic plants in floating.
9: What is the utility of tissues in multicellular organisms? Answer: It helps in growth, organisation of different organs and performing functions.
10: Name the two types of tissues. Answer: Plant tissues and animal tissues.
11: Name the two types of plant tissue. Answer: Meristematic tissue and permanent tissue.
12: What is differentiation? Answer: The process of taking up a permanent shape, size and function by cells is called differentiation.
13: Name the three types of meristematic tissues. Answer: The three types are: (a) Apical tissue—tips of root and shoot (b) Lateral tissue—sides of stem (c) Intercalary tissue—at nodes
14: Where is apical tissue found? Answer: Present at the tips of roots and stems.
15: Tissues present at the lateral surface of the stem are called apical tissues. Put (T) if true and put (F) if false. Rewrite the answer if (F). Answer: (F). Tissues present at the lateral surface of the stem are called lateral tissue.
16: Which tissues are present at the nodes of the plants? Answer: Intercalary tissue.
17: What are the various types of blood cells? Answer: There are three types: (a) RBC’s (b) WBC’s and (c) Platelets.
18: What are tracheids? Answer: They are elongated cells with tapering ends.
19: What are guard cells? Answer: Each stomata is bounded by a pair of specialised kidney-shaped epidermal cells called guard cells.
20: Epithelial tissue is the simplest tissue. Write (F) for false or (T) for true. Answer: (T).
21: What are the functions of cuboidal epithelium? Answer: It helps in absorption, excretion, secretion, it also provides mechanical support.
Short Answer Type Questions
1: Give four differences between bone and cartilage. Answer:
2: Give the functions of bone.
Answer: The functions of bone are: (i) It provides shape to the body. (ii) It provides skeletal support to the body. (iii) It anchors the muscles. (iv) It protects the vital body organs like brain, lungs, etc. 3: Give the functions of cartilage. . Answer: (i) It provides support and flexibility to the body parts. (ii) It smoothens surface at joints.
4: Fill in the blanks: (i) Water and minerals are conducted by _________ (ii) In higher plants food is conducted by _________ (iii) Blood is a __________ tissue. (iv) Bone consists of __________ cells. (v) Cartilage consists of __________ cells. (vi) Fibres are absent in __________ type of connective tissue.
Answer: (i) Xylem (ii) Phloem (iii) Connective (iv) Osteocyte (v) Chondrocyte (vi) Blood
5: What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Answer: Functions are: (i) It helps in repair of tissues after an injury. (ii) It also helps in combating foreign toxins. (iii) It fixes skin to underlying muscles. 6: Give difference between xylem and phloem. Answer:
7: What are fibres? Answer: Fibres consist of very long, narrow and thick cells. Example, jute fibre.
8: Name the tissues for the following: (a) Stores fat in animal body. (b) Divides and re-divides to grow in plants. (c) Tissue that joins hone to hone. (d) Covers the external surface of animal body.
Answer: (a) Adipose tissue (b) Meristematic tissue . (c) Ligament (d) Epithelial tissue.
9: What is stomata? Answer: Stomata are small pores present on the surface of a leaf which helps in the exchange of gases and in transpiration.
10: Why does epidermal tissue have no intercellular space?
Answer: The epidermal (layer) tissue forms a protective outer covering for the plants and it protects the internal parts of the plant. It aid in the protection against loss of water, mechanical injury and invasion by parasitic fungi. For this protective role to play the continuation of cells is necessary, hence it does not have intercellular space.
11: Name and give the function of each cell of xylem:
Answer: Xylem consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres. Tracheids and vessels—Allows the transport of water and minerals. Xylem parenchyma—Stores food and helps in the sideways conduction of water. Xylem fibres—Are supportive in function.
12: What is the function and location of stratified squamous epithelium? Answer: Stratified squamous epithelium is present in the skin. The layers of cells are arranged to prevent wear and tear.
13: Give difference between ligament and tendon. Answer:
14: Give difference between striated muscles and unstriated muscles. Answer:
15: State the difference between bone and blood. Answer:
16: Name all different types of tissues present in animal.
Answer: There are four main types of tissues present in animal. ‘ (a) Epithelial tissue present on the outer and inner lining of the body. (b) Muscular tissue are made up of muscles, help in movement. (c) Connective tissue connects the different organs in the body. (d) Nervous tissue consists of nerve cells and are present in the nervous system.
17: Why is blood called connective tissue?
Answer: The blood is composed of cells and plasma. Plasma is a fluid and cells like red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets are present in it. All these cells are connected due to plasma. It also transports food, water to different parts of the body and connects them.
18: Name three types of muscle tissues and give function of each.
Answer: Three types of muscle tissues are: (a) Striated muscle (b) Smooth muscle (c) Cardiac muscle
(a) Striated muscle: These muscles show alternate light and dark bands or striations. They are involuntary and present in skeletal tissues, help in movement of body and bones.
(b) Smooth muscle: These are involuntary muscles, control the movement of food in alimentary canal, contraction and relaxation of blood vessels. Present in iris, uterus etc.
(c) Cardiac muscle: These muscles are present in heart, help in the rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout the life.
19: State the difference between simple tissues of plants. Answer: The simple tissues of plants are: (i) Parenchyma (v) Collenchyma (iii) Sclerenchyma
20: With the help of diagram show the difference between striated muscle fibre, smooth muscle fibre and cardiac muscle fibre. Answer:
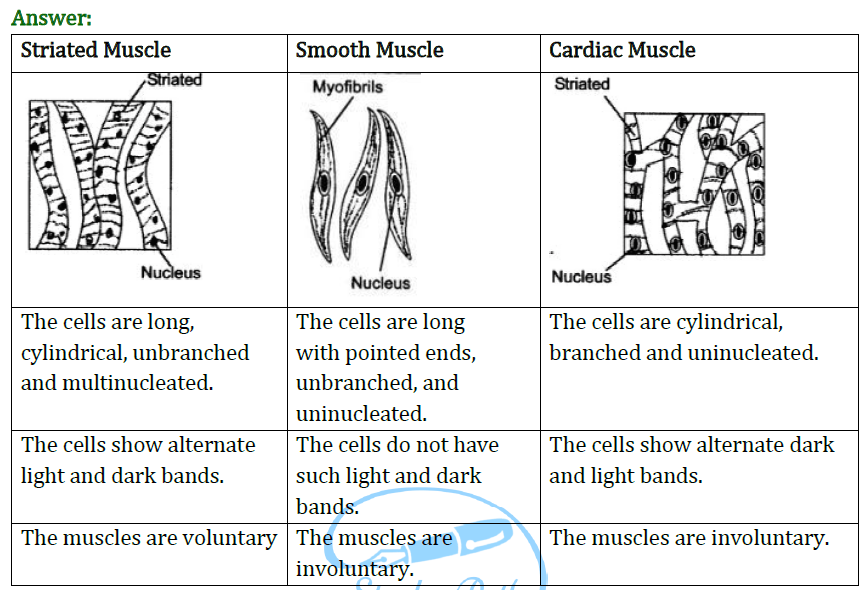
21: Name different types of meristematic tissue and draw diagram to show their location.
Answer: The 3 different types of meristematic tissue are: (a) Apical meristem—Function: growth in length. (b) Lateral meristem—Function: growth in thickness. (c) Intercalary meristem—Function: growth in internodes.
22: Explain the structure, function and location of nervous tissue.
Answer: Structure: Nervous tissue consists of cells called nerve cells joined end to end (neurons). A neuron (nerve cell) consists of a cell body with nucleus and cytoplasm. From these cell body a long thin hair-like parts arise called axon and many short branched parts called dendrites. Location: Nervous tissue are present in brain, spinal cord and nerves. Function: Nervous tissue receives the stimuli and transmit the stimulus rapidly from one place to another within the body. The nerve impulse allows us to move our muscles and respond to any stimuli.
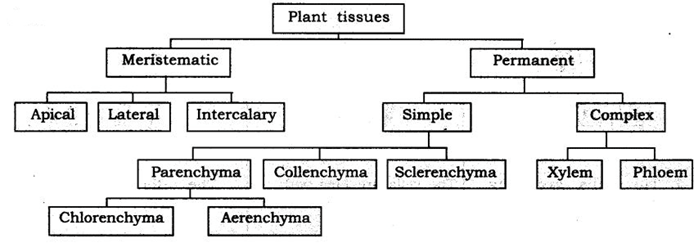
23: Give the flow chart of plant tissues. Answer:
Long Answer Type Questions
1: Write a note on plant tissues.
Answer: Plant tissues consist of two main types of tissue.
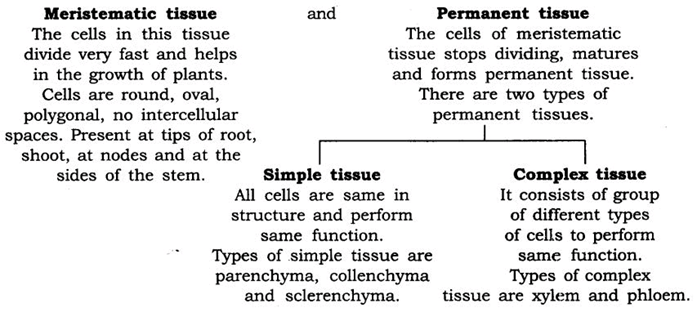
Parenchyma: Present in soft parts of the plant.
Collenchyma: Provides mechanical support to plant present in stalks. Sclerenchyma: They provide strength and flexibility to the plants.
Xylem: Conduct water in plants from root to shoot. Consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres.
Phloem: Conduct food to all parts of plant. Consist of sieve tubes, companion cell, phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres.
2: Show the types of animal tissues using flow chart. Answer:
3: What is connective tissue? Explain its types.
Answer: The connective tissue consists of different types of cells, all of them perform same function.
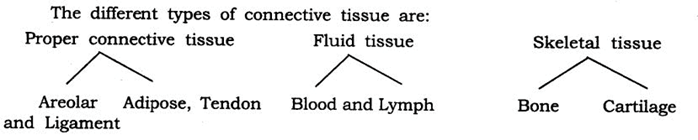
Areolar connective tissue: It is found between the skin and muscles, around blood vessels and nerves and in the bone marrow. Areolar tissue fills the space inside the organs. It supports internal organs and helps in repair of tissues.
Adipose tissue: Adipose tissue stores fat, found below the skin and between internal organs. The cells of this tissue are filled with fat globules. It acts as insulator due to fat storage.
Blood: It has a fluid called plasma, in plasma are present red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Blood flows all over the body and helps in the transport of gases, digested food, hormones and waste material to different parts of the body.
Lymph: Lymph carries digested fat and lot of white blood cells in the plasma. Bone: It forms the framework that supports the body. It supports the different parts of our body. It is strong and non-flexible tissue.
Cartilage: It is present in nose, ear, trachea and larynx. It smoothens bone surfaces at joints.
Tendon: It connects bone and muscles. These tissues are fibrous, flexible and with lot of strength.
Ligament: It connects bone to ‘bone. It is elastic, has lot of strength.
4: Describe ‘epidermis’ in plants.
Answer: Epidermis forms the entire outermost layer of the plant. It is made up of single cell layer. It protects all the internal parts of the plant. On aerial parts, epidermis secretes waxy, water-resistant layer on their outer surface. This helps in protection against loss of water, mechanical injury and invasion of parasitic fungi.
In leaves, epidermis consists of small pores called stomata. These pores help in the transpiration and exchange of gases, like oxygen and carbon dioxide for plants. In roots, epidermis have long hair-like parts that provide greater surface for water absorption. In desert plants, epidermis has a thick waxy coating of cutting which acts as a water proofing agent.
5: Explain the “complex tissue” of plants.
Answer: Complex tissues are made up of more than one type of cells. All these cells co-ordinate to perform common function. These are—xylem and phloem. Both are conducting tissues and form a vascular bundle.
Xylem consists of—tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres. Most of these cells are dead. Tracheids and vessels helps in water transportation, parenchyma stores food and helps in the sideways conduction of water and fibres are mainly supportive in function. Phloem is made up of four types of elements—sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres and phloem parenchyma. It helps in the transportation of food in both the directions, i.e. from leaves to roots and to other parts of the plant.
Value Based Questions
1: A group of students completed the project of finding the botanical names of all the trees present in the school campus. They prepared metal plates with names carved on it, to fix it on the plant trunks. Shreya was concerned that if the metal plate is fixed into tree many cells of the tree may get damaged. But the group members explained her that the outer layer of trunk does not have living cells and there won’t be any damage to the tree. (a) What type of cells are present on the outer layer of the bark/tree trunk? (b) How does the cork act as a protective tissue? (c) What value of the group is seen in the above cast?
Answer: (a) On the outer layer of the tree trunk/bark all thick layer of dead cells is present which acts as protective tissue. (b) In cork, all cells are dead without intercellular spaces, the walls of the cells have deposition of suberin. (c) The students in a group show team effort, peer learning and cooperative.
2: A paralytic patient was unable to walk. ‘The family member of the patient took the outmost care of the patient. (a) Name two tissues responsible for the movement of a body. (b) Name the tissues present in brain and spine. (c) What value of the family members is seen in the above case?
Answer: (a) The two tissues responsible for movement of the body are muscular tissue and nervous tissue. (b) The tissues present in brain and spine are nervous tissues. (c) The family members showed the value of being caring, responsible, dutiful and kind.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Category: Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement In Food Resources
Case study questions for class 9 science chapter 14 natural resources, case study questions for class 9 science chapter 12 sound, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 9 force and laws of motion, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 8 motion, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 7 diversity in living organisms, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 6 tissues, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 2 is matter around us pure, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 5 the fundamental unit of life, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 13 why do we fall ill, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 11 work and energy, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 10 gravitation, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 4 structure of atom, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 3 atoms and molecules.
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
CASE 4. Blood is a type of connective tissue. The cells of connective tissue are loosely spaced and embedded in an intercellular matrix. The matrix may be jelly like, fluid, dense or rigid. The nature of matrix differs in concordance with the function of the particular connective tissue.
Case Study 1: Meristematic tissue takes up a specific role and loses the ability to divide. As a result, they form permanent tissue. This process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and function is called differentiation. Differentiation leads to the development of various types of permanent tissues.
Case Study/Passage Based Questions: Question 1: Read the following and answer any four questions below from (i) to (v): Bone is a solid, hard porous tissue. It forms the natural skeleton and gives the body its basic structure and also supports the body. Its matrix is impregnated with phosphates and carbonates of calcium and magnesium … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions ...
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: Meristematic tissue takes up a specific role and loses the ability to divide. As a result, they form permanent tissue. This process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and function is called differentiation. Differentiation leads to the development of various types of permanent tissues.
Class 9 science case study question 1. Gases are highly compressible as compared to solids and liquids. The liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) cylinder that we get in our home for cooking or the oxygen supplied to hospitals in cylinders is compressed gas. Compressed natural gas (CNG) is used as fuel these days in vehicles.
By Dr. Ananya Dixit Ma'am. Delve deeper into the realm of tissues in Chapter 6 of Class 9 Biology through case-based questions. These questions present real-...
question_answer 26) Read the passage given below and answer the questions from [26] to [30]. Muscular tissue possesses elongated cells, called muscle fibres. The tissue contains special type of proteins which help in muscle movement. Different types of muscular tissues are given in tabular form below.
To study for Chapter 6 Tissues of Class 9 Science, you must pay attention to all the important questions. You should solve practice papers, sample papers, and previous year's question papers. By doing this you will get an idea of all the important questions. In most sample papers there are some questions which are repeated.
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - CBSE Free PDF Download. The NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues is the best study material through which students can refer and prepare their notes for their CBSE exam. These NCERT Solutions are available chapter-wise, and students can also find answers to all the questions ...
MORE QUESTIONS SOLVED. NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Questions. Choose the correct option: 1. The cells of cork are dead and have a chemical in their walls that makes them impervious to gases and water. The chemical is. (a) lignin (b) suberin. (c) cutin (d) wax. 2.
In these solutions, we have answered all the intext and exercise questions provided in NCERT class 9 science textbook. Class 9 NCERT Solutions Science Chapter 6 provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum. Students can easily download these solutions in PDF format for free from our app.
This article aims to present a comprehensive collection of case study questions for Class 9 Science, covering various topics and concepts. Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th. CBSE Class 9 Science Exam will have a set of questions based on case studies in ...
by experts. Download PDF Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 9 Exams Exam 2023-24. With the help of our well-trained and experienced faculty, we provide solved examples and detailed explanations for the recently added Class 9 Science case study questions. Case study questions are based on real or ...
Chapter 6 Tissues Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions. These NCERT Solutions for Class 9 will improve application skills and clear your confusions. It will help the students in learning complex topics and problems in an easy way. These NCERT Solutions are prepared as per the accordance of latest CBSE guidelines so you can score maximum marks.
Case based questions for Class 9 Science involve exploring a real-world situation through scientific analysis and inquiry. These questions allow students to make connections between science concepts and the world around them, as well as develop critical thinking skills. For example, a case study may involve challenging a student to determine ...
Class 9 Science Tissues. 1. The cells of cork are dead and have a chemical in their walls that makes them impervious to gases and water. The chemical is. 2. The flexibility in plants is due to a tissue called, 3. The tissue present in the lining of kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands is. 4.
Unit 6 Tissues. Unit 7 Motion. Unit 8 Force and Laws of motion. Unit 9 Gravitation. Unit 10 Work and Energy. Unit 11 Sound. Unit 12 Improvement in food resources. Course challenge. Test your knowledge of the skills in this course.
Important Questions CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues cover the key highlights of the Chapter 6 of the NCERT Science textbook. These questions are used by students to prepare well for the final exams. Students can learn the textbooks thoroughly, and then they can try solving these questions as a way to not only gauge their preparation ...
Important Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues. Get important questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues with PDF. Our subject expert prepared these important questions and answers as per the latest NCERT textbook. These important questions will be helpful to revise the important topics and concepts.
Q6. Name the following tissues: (i) The connective tissue found between the skin and muscles. (ii) The tissue which connects two bones. (iii) The epithelial tissue which forms the lining of the kidney tubules. (iv) The tissue which is present in the veins of leaves. Answer.
Very Short Answer Questions. 1: Name the tissues responsible for the movement of the body. Answer: Muscle tissue and nervous tissue. 2: How does neuron look like? Answer: A neuron is the unit cell of nervous tissue. It is a thread-like structure with cell body and axon. 3: Name the types of simple tissues.
July 30, 2022 July 30, 2022 Physics Gurukul 1 Comment on Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement In Food Resources. Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement In Food Resources. ... Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues. March 29, ...
Question 9. Describe the types of connective tissues along with their functions. Answer: There are five types of connective tissues: (i) Areolar connective tissue: It is a loose and cellular connective tissue. It joins skin to muscles, fills spaces inside organs, and is found around muscles, blood vessels and nerves.